Reassignment and reconciliation for multi-dimensional sales territories
a multi-dimensional and sales territory technology, applied in the field of multi-dimensional modeling, can solve the problems of inefficient application, difficult to comprehend the level of interdependent rules in a typical sequential algorithm for defining territories, and undesirable use of rule-based algorithms in this way, so as to facilitate efficient and reliable gap and/or overlap processing, and minimize or eliminate the need for ordinal processing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiments
Realignment and Reconciliation Embodiments
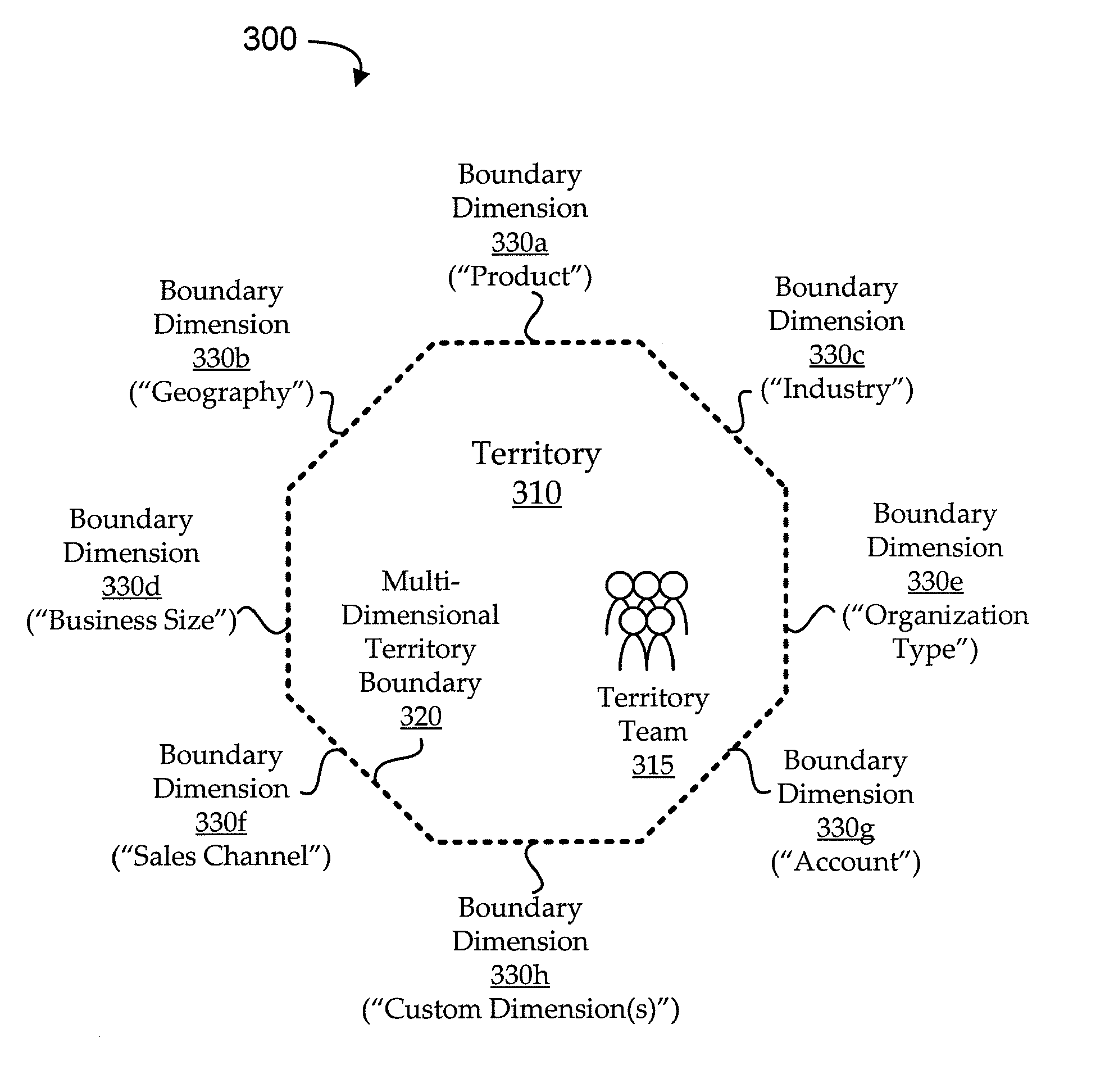
As described above, embodiments use multi-dimensional modeling to define territories in such a way as to account for applicable territory criteria as sets with logical boundaries, rather than as a defined rule-based architecture. For example, territory criteria are modeled as hierarchical dimensions that form boundaries to a territory hypercube. The multi-dimensional model is converted into a de-normalized definition configured, for example, to capture the multi-dimensional nature of the sales territory definitions while flattening hierarchical trees and minimizing or eliminating the need for ordinal processing of the data.
In some embodiments, the de-normalized territory definitions are used to optimize identification of territory regions where reassignment of opportunities is appropriate and / or to reassign opportunities in those regions. Some of these functions are referred to herein as “realignment” and / or “reconciliation” of sales territo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com