Webpage malicious JavaScript code recognition and anti-obfuscation method based on hybrid analysis
A JS code and malicious technology, applied in the software and computer fields, can solve problems such as poor readability, unknown code attacks, no longer applicable detection of malicious JS code, etc., and achieve the effect of small operating overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
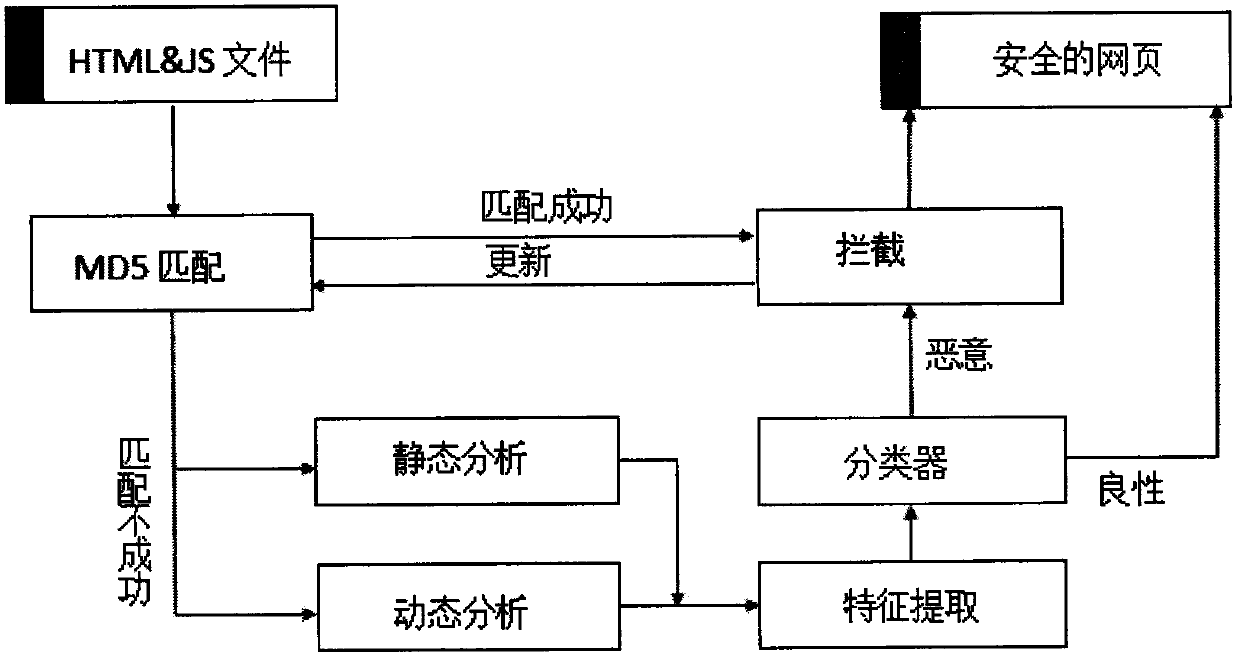
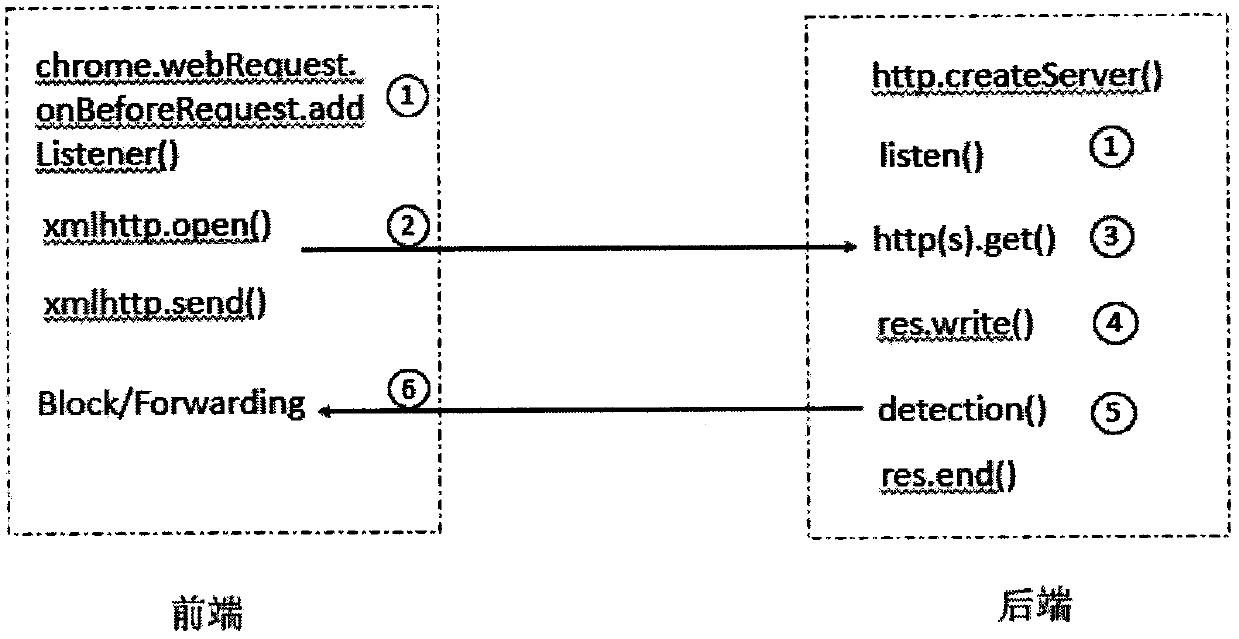
[0012] The present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
[0013] 1) First collect a large number of website source files containing malicious JS and a large number of benign web pages that do not contain malicious JS, and extract all JS scripts embedded in HTML documents and JS codes stored in JS files as a data set.
[0014] 2) Perform program analysis and feature recognition on the data set extracted in step 1), construct an abstract syntax tree in the semantic analysis stage, and perform semantic level analysis.
[0015] 3) Perform dynamic instrumentation of JS code, monitor runtime status, extract execution path and other runtime features. Combining semantic features and execution features into feature vectors.
[0016] 4) Using a classification model based on the random forest algorithm, a malicious JS detection system is formed by training a high-precision classifier model.
[0017] 5) On the basis of the dynamic instrumentation analysis in step 3), by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com