Patents
Literature
92 results about "Label switch router" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
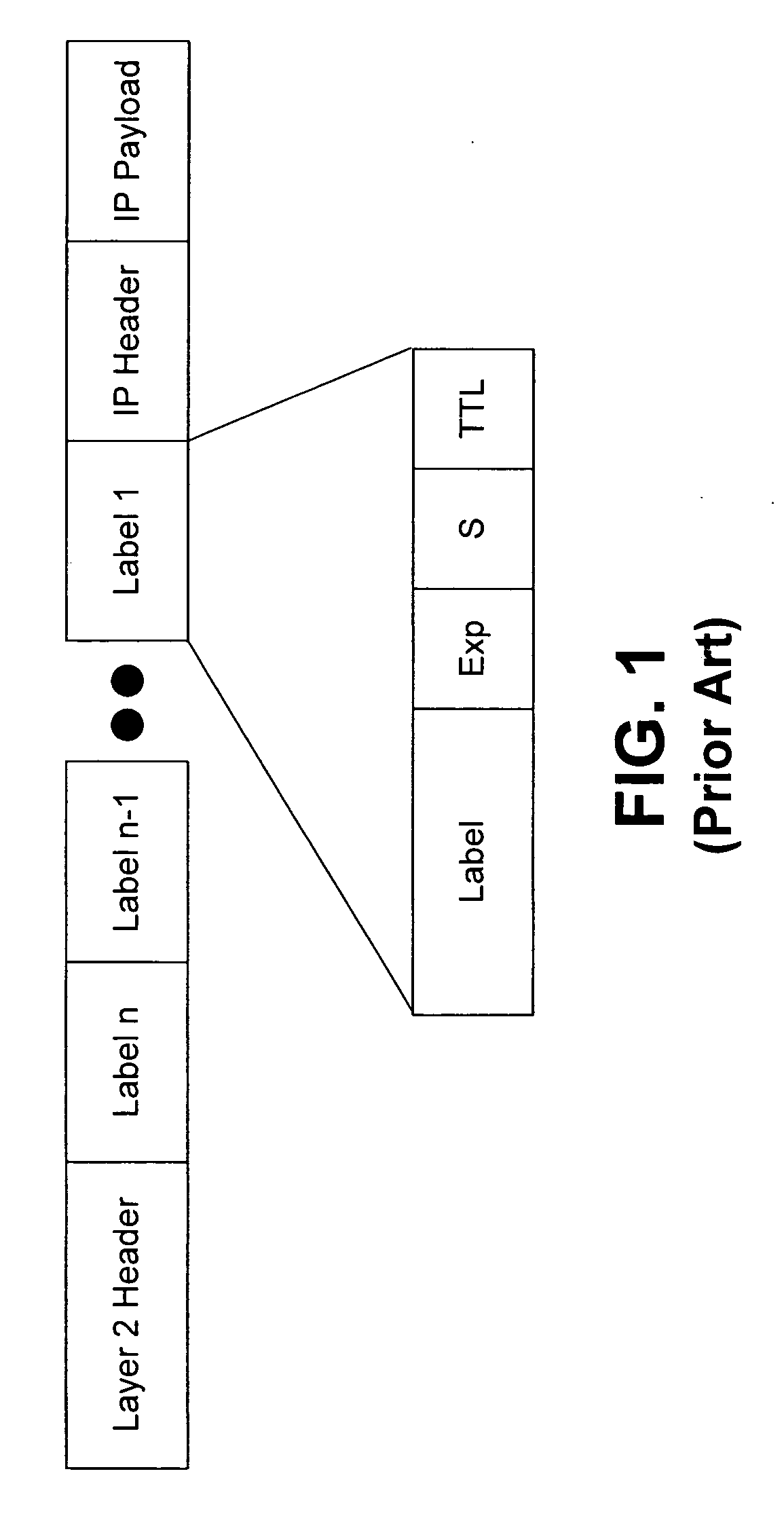
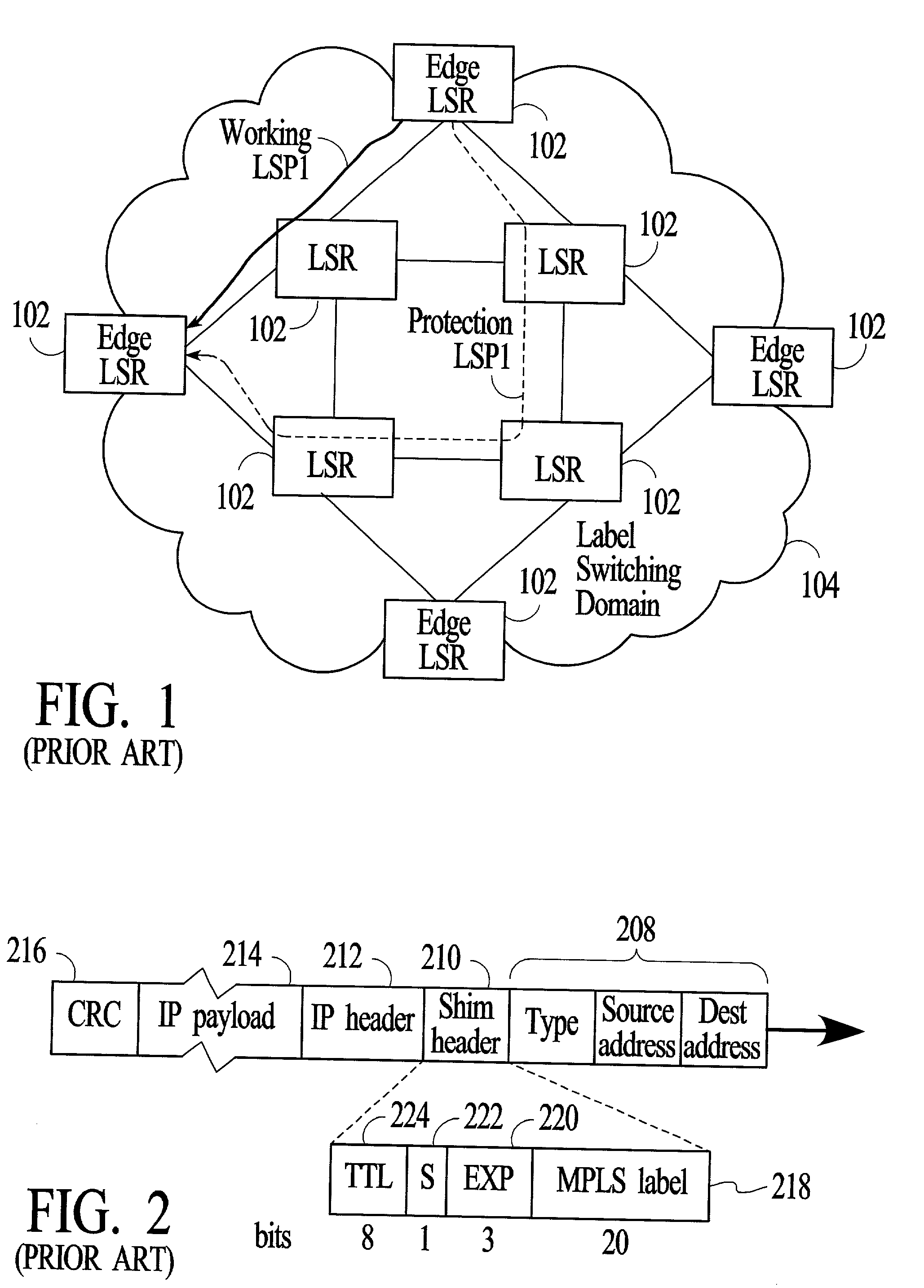
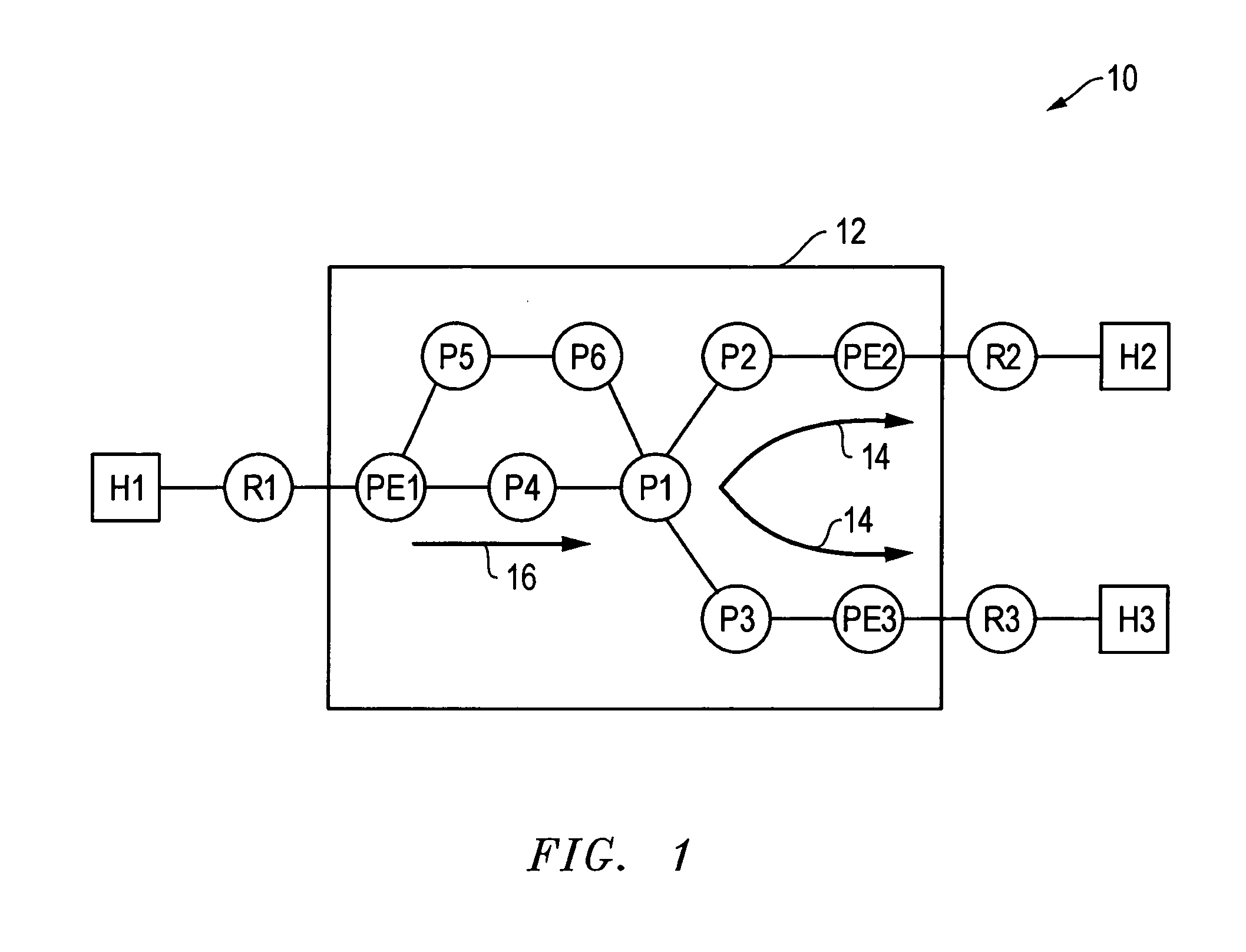
Label switch router. An MPLS router that performs routing based only on the label is called a label switch router (LSR) or transit router. This is a type of router located in the middle of an MPLS network. It is responsible for switching the labels used to route packets.
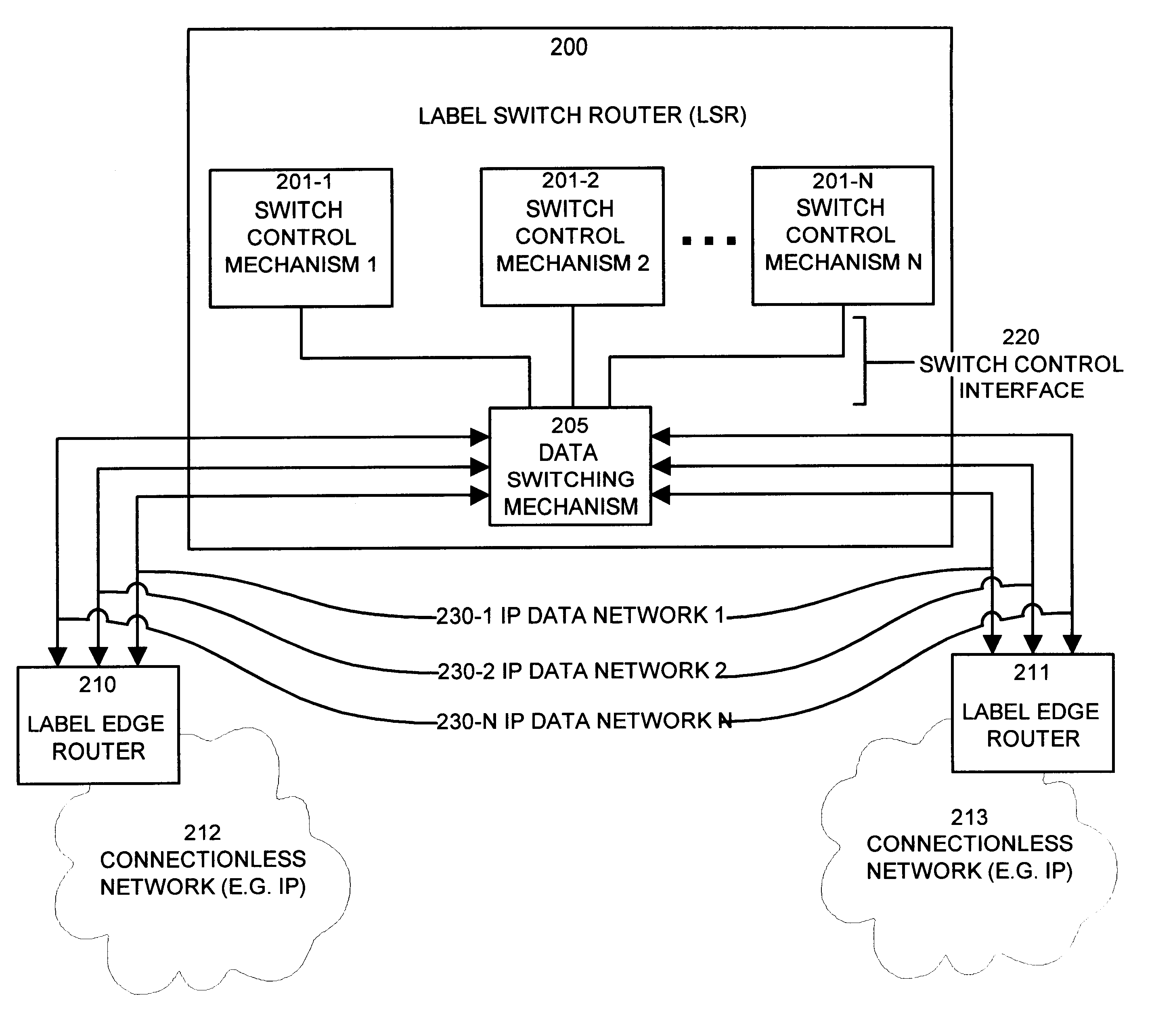
Apparatus and methods providing redundant routing in a switched network device
InactiveUS6628649B1Improve fault toleranceHigh degreeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationData transmissionData loss
The invention provides unique architectures and techniques for routing redundancy in a data switch configured to use label switching. Multiple label switch controllers (LSCs) each operate concurrently but independently of each other to provide routes through a data switching mechanism. Preferred embodiments provide a plurality of LSCs offering MPLS capabilities coupled to a single switch, such as an ATM switch. The similarly configured LSCs each can concurrently support a route for data (e.g., labeled ATM cells) within the data switching mechanism in parallel, thereby providing the ability to support redundant and multiple parallel data networks. The configuration is called a label switch router (LSR). A fully-meshed embodiment allows selected routes to share bandwidth on ports, while a fully parallel embodiment provides separate ports for selected routes. Since each LSC provides parallel routes with the other LSCs in an LSR, a communications between an LSR and a label edge router (LER) can use multipath routing to concurrently distribute data equally across the parallel routes for each destination. Alternatively, unipath routing techniques can select one route for use for each destination from the available routes concurrently offered by each LSC. In the event of a failure of one of the LSCs, multipath routing implementations can exclude transmission of data onto the failed network, while continuing to use the other parallel networks supported by non-failed LSCs in a concurrent manner. Alternatively, if a failure occurs with unipath routing, a new route offered by another LSC can be selected for data transfers. In either case, the LSC that fails does not need to provide state or connection information to the LSCs that operate subsequently to the failure, since they are already configured in parallel to support the same route. Upon an LSC failure, switch resources such as bandwidth that were used by the failed LSC are made available to the remaining non-failed LSCs. The design allows failures are handled gracefully without diminished network capacity or data loss resulting in a highly reliable routing capability provided within connection-based or circuit-switched networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
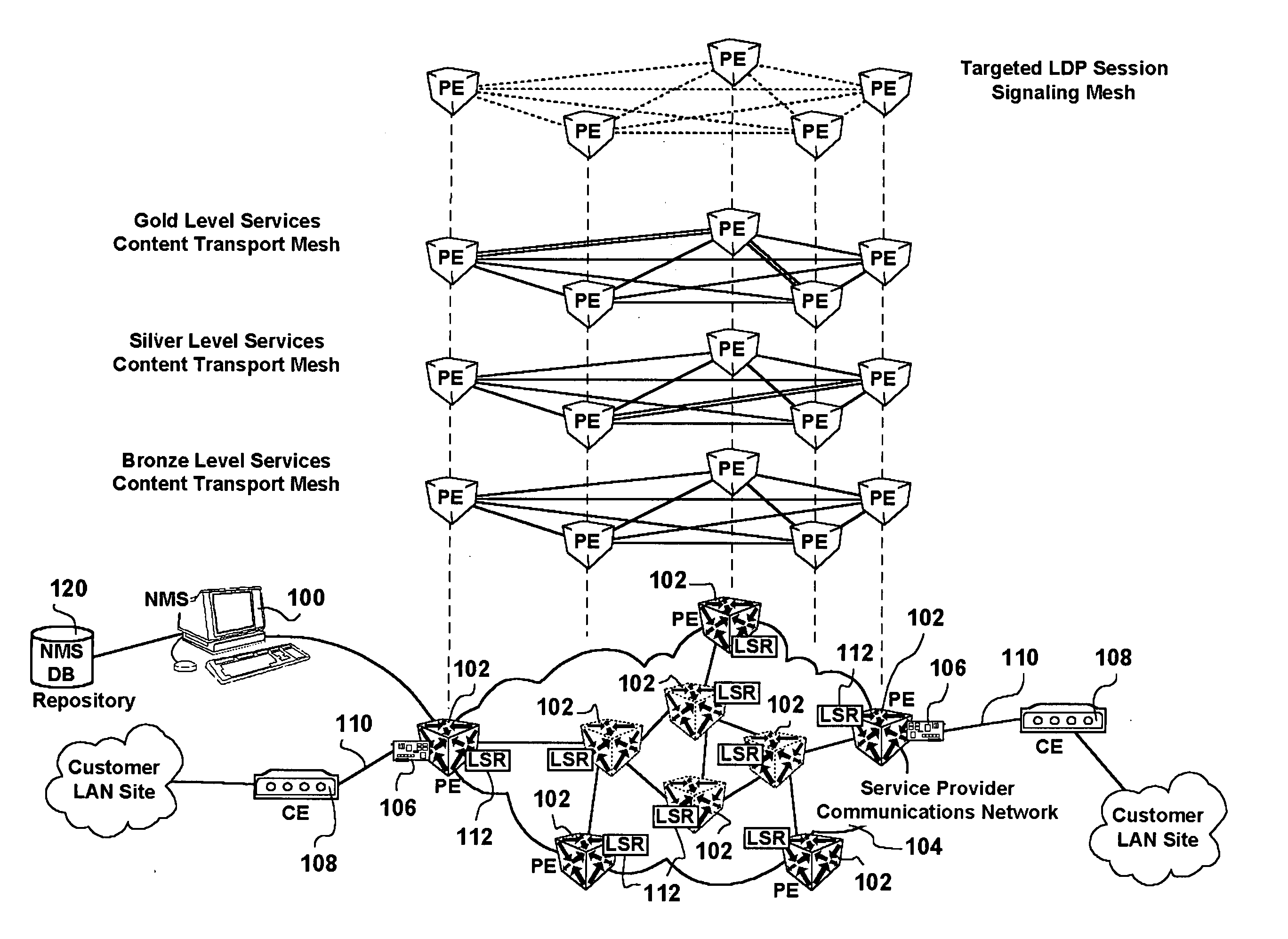
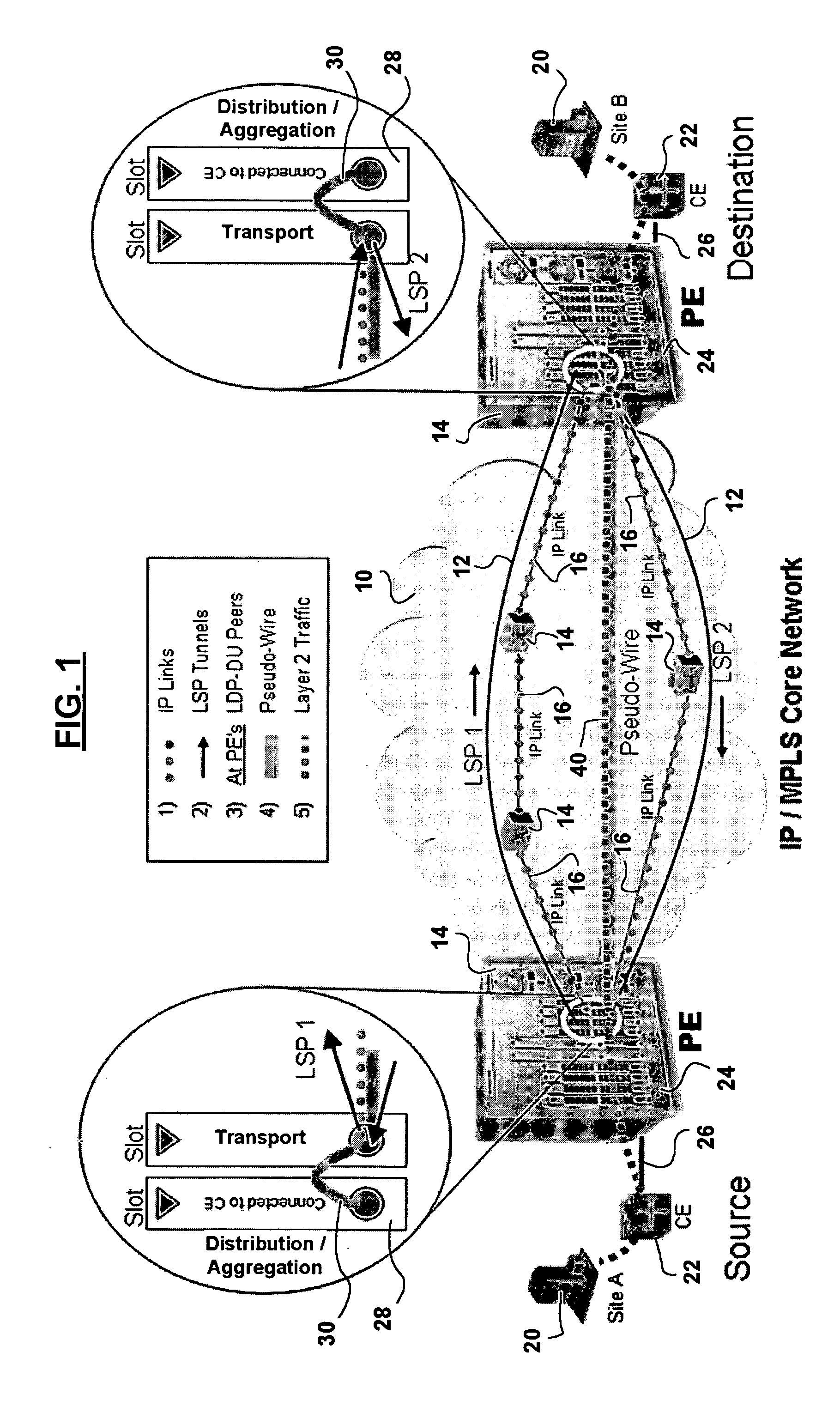
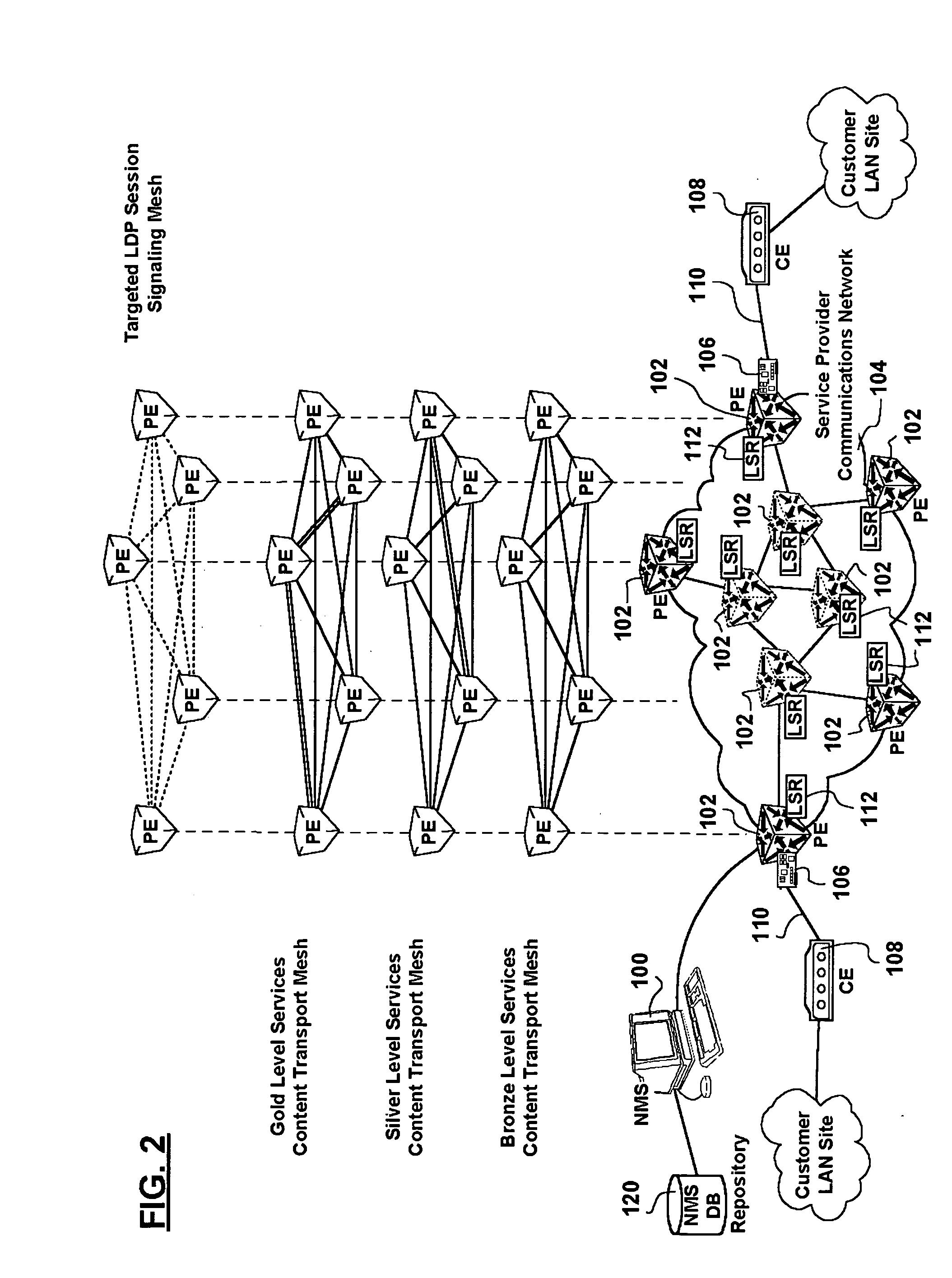
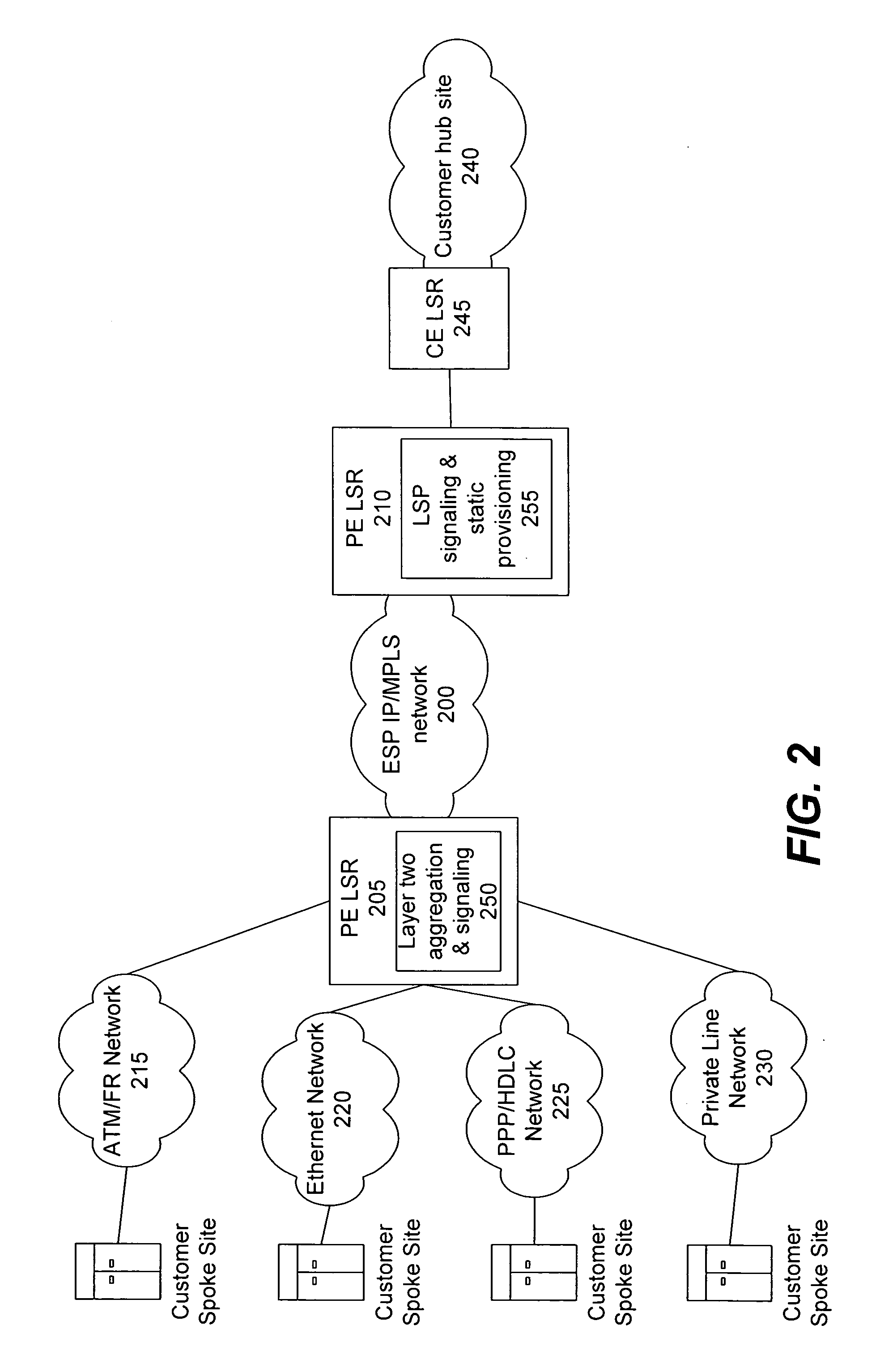
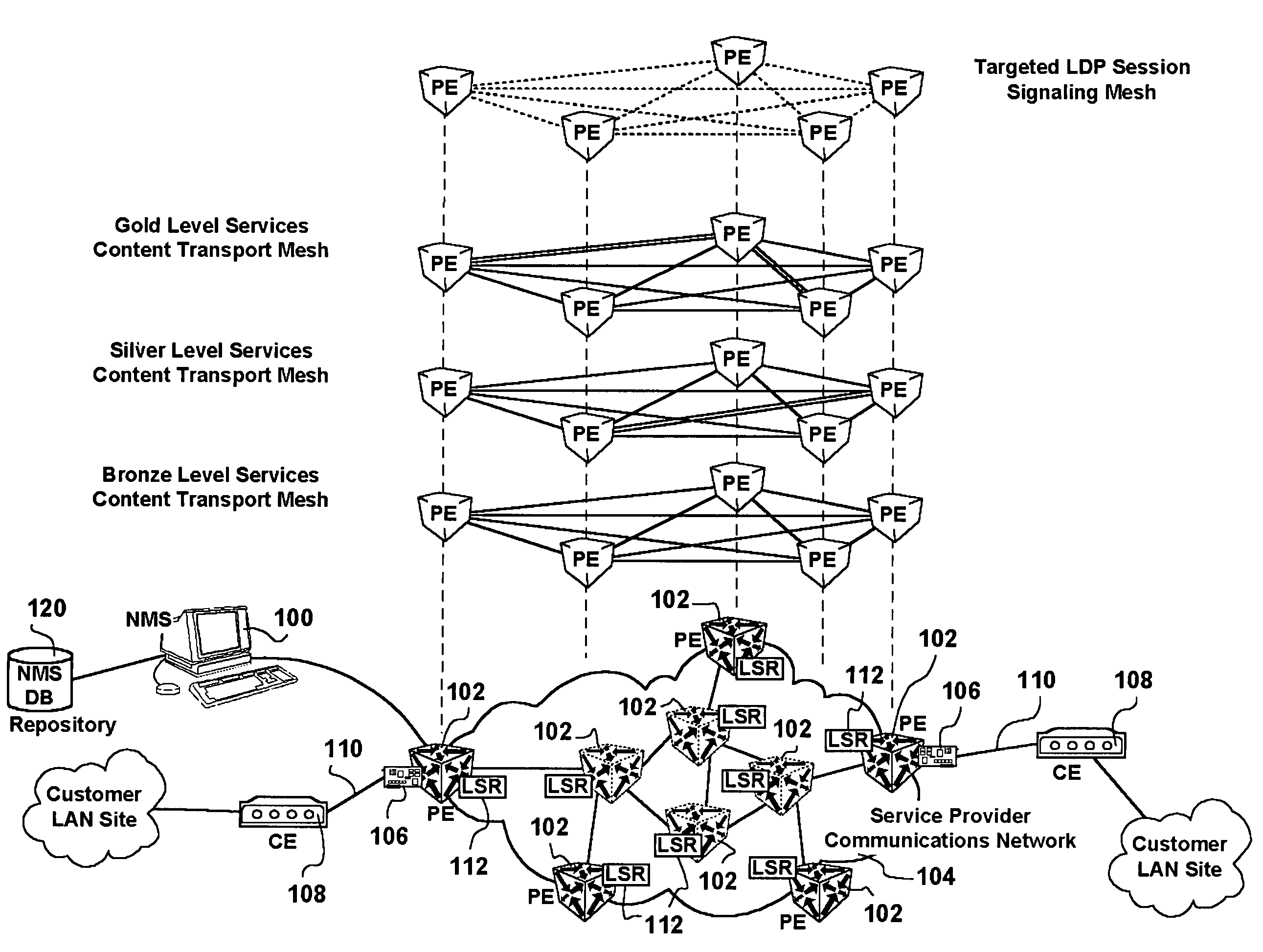
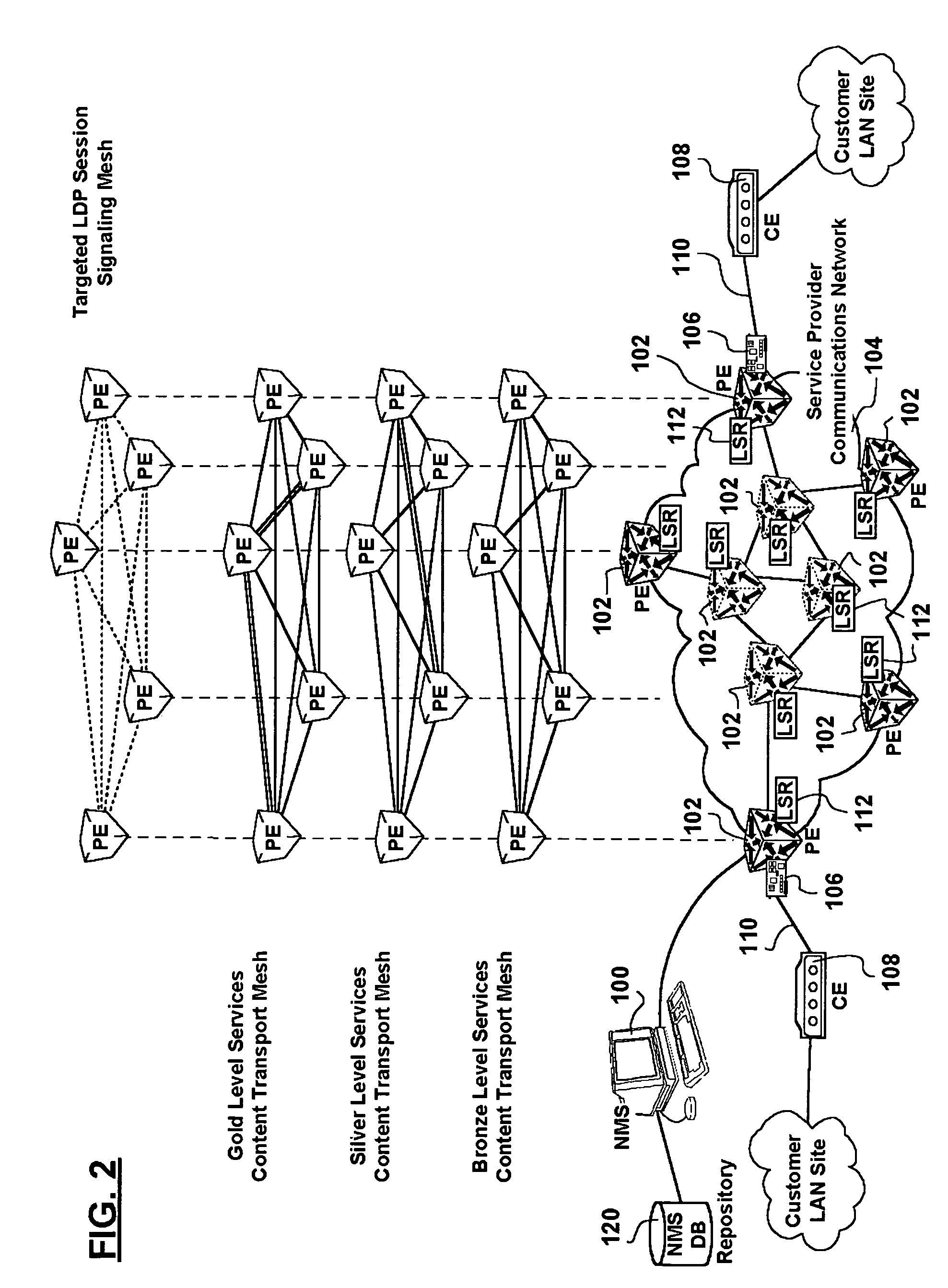
Full mesh LSP and full mesh T-LDP provisioning between provider edge routers in support of Layer-2 and Layer-3 Virtual Private Network services
ActiveUS20050213513A1Increased operation management personnel productivityReduce probabilityError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceService provision
A network management system, and a method of, centrally provisioning a full transport LSP mesh and a full targeted LDP signaling session mesh in support of VPN services provisioning are provided. A network management system repository tracks Provider Edge nodes (PE) having label switch router functionality, transport LSP meshes and targeted LDP session meshes. The method includes selecting PE nodes for inclusion in a node group, identifying PE node pairs, and issuing commands to paired PE nodes to commission managed transport LSPs and targeted LDP signaling sessions. The advantages are derived from the full mesh LSP content transport provisioning and targeted LDP signaling session provisioning effected in a centralized network management context enabling service providers to: assure network resiliency, assure service quality, and provide accounting, in respect of Layer-2 and Layer-3 VPN services irrespective of client side deployed infrastructure while leveraging installed infrastructure in the service provider communications network core. Additional advantages are derived from increased operations management personnel productivity while reducing the probability of human error compared to manual provisioning thereof enabling wide availability of VPN services.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
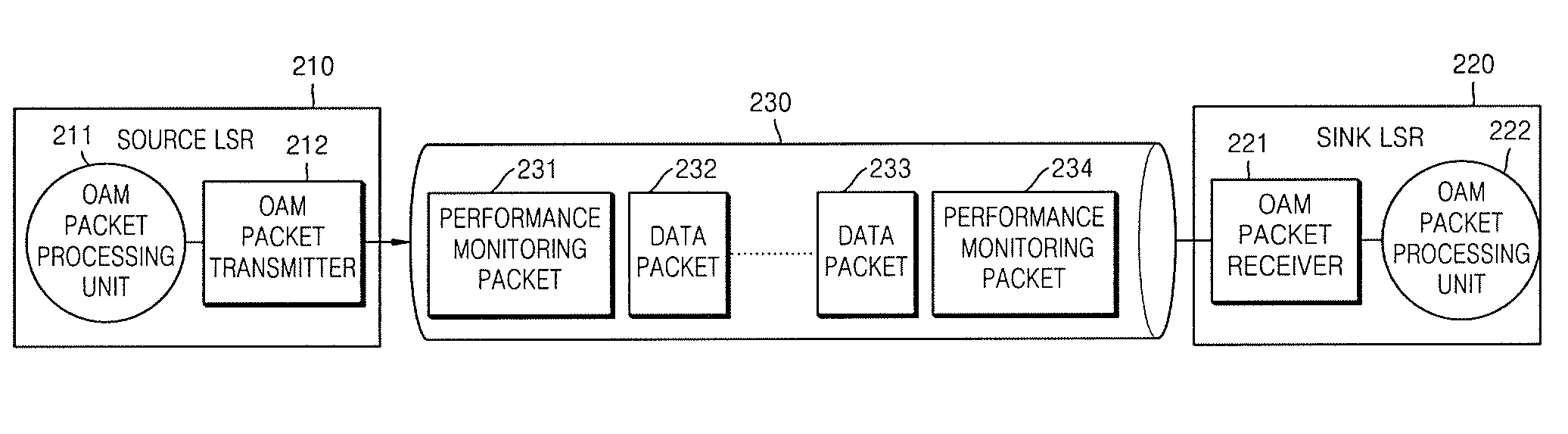
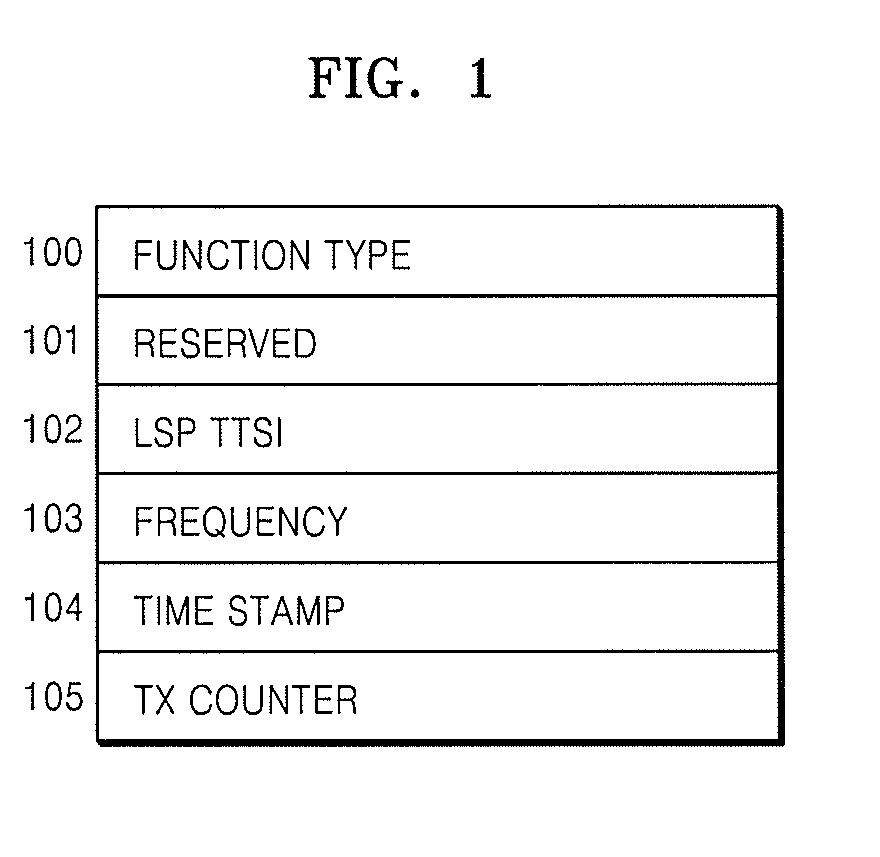
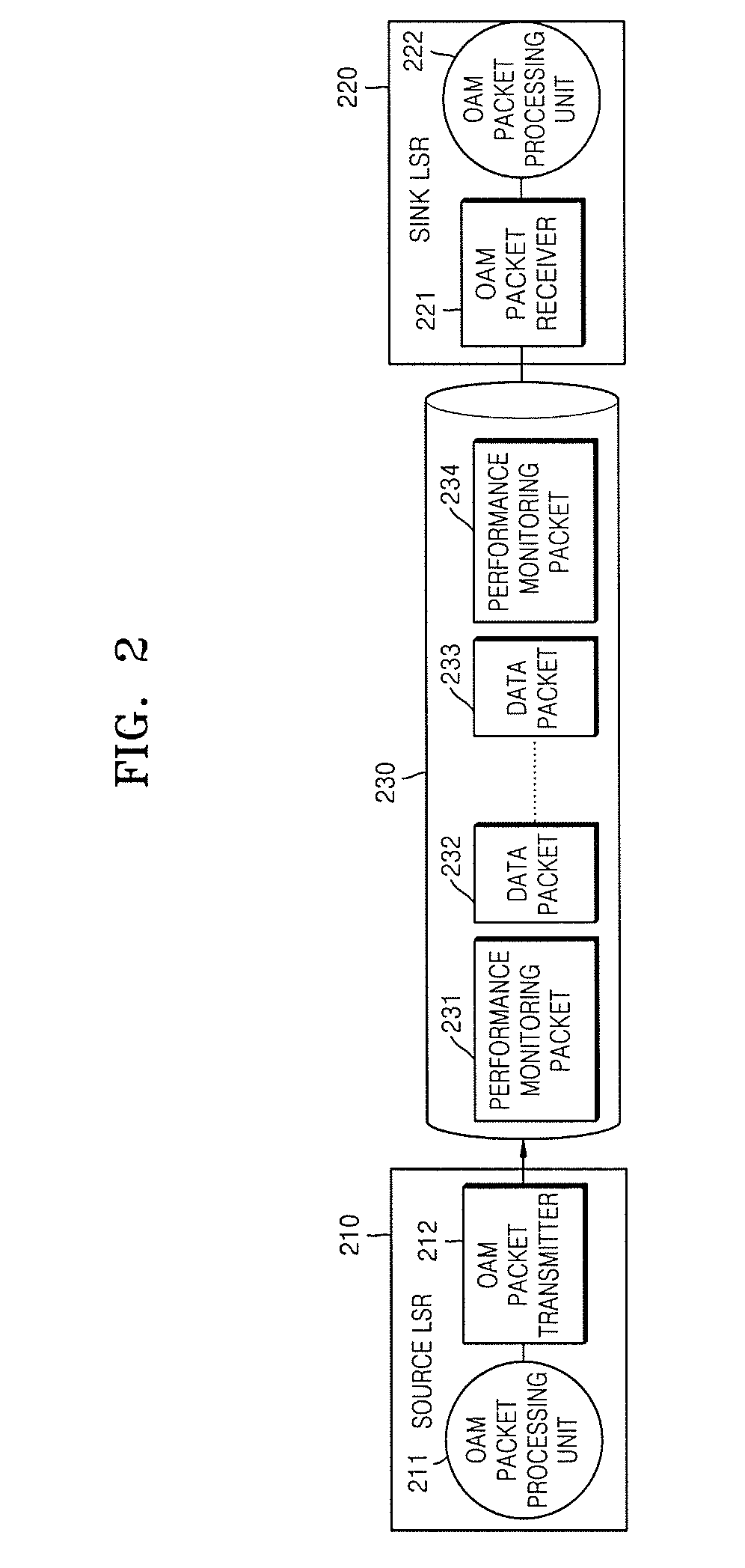
Method and apparatus for measuring label switch path performance parameters using performance monitoring operation and management packet in multi-protocol label switching network
InactiveUS20080031146A1Measurement performanceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket lossMulti protocol
Provided is a method and apparatus for measuring performance parameters of a Label Switch Path (LSP) using an Operation & Maintenance (OAM) performance monitoring packet in a Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) network, and more particularly, a method and apparatus for measuring packet loss, packet transfer delay, and jitter of an LSP set between two Label Switch Routers (LSRs) using an MPLS OAM packet. Accordingly, the present invention can overcome the limitation that existing MPLS OAM technology is dedicated to only identify malfunction of an LSP, and by also adding parameters (packet loss ratio, packet transfer delay and jitter related to SLA to a payload of an MPLS OAM packet as new required fields, provides a performance measurement method capable of measuring SLA performance parameters based on the newly added fields.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Dynamic update of a multicast tree
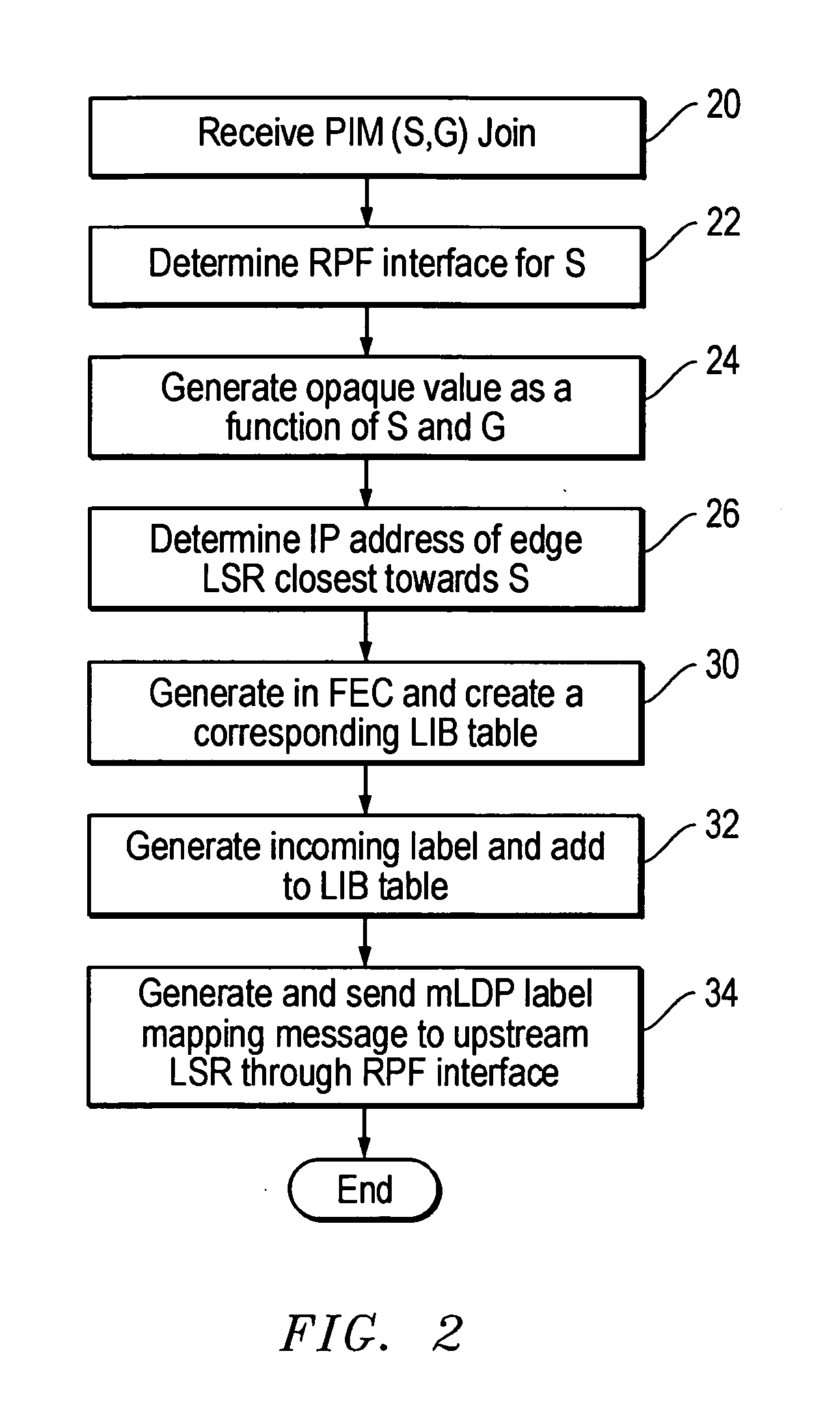
In an example embodiment, a multicast tree is accessed. The multicast tree defines one or more destination label switch routers and paths from a source label switch router to the destination label switch routers. Multicast addresses are then transmitted to the destination label switch routers. In an example embodiment, upon receipt of the multicast addresses, a request to update the multicast tree is transmitted. The request includes the identifier of the label switch router that originated the request.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus for using a verification probe in an LDP MPLS network
An ingress multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) label switched router (LSR) forwards a set of packets associated with a first set of forwarding equivalence classes (FECs) along a label switched path (LSP) to an egress MPLS LSR. Logic in the ingress MPLS LSR produces an operation and maintenance (OAM) connectivity verification probe message encoding the first set of FECs, and forwards the OAM connectivity verification probe message along the LSP to the egress MPLS LSR. Logic in the egress MPLS LSR produces an encoding of a second set of FECs. Logic in the egress MPLS LSR compares the encoding of the first set of FECs in the connectivity verification probe message to the encoding of the second set of FECs, and produces an indication if the comparison indicates that the first set of FECs is not a subset of the second set of FECs.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
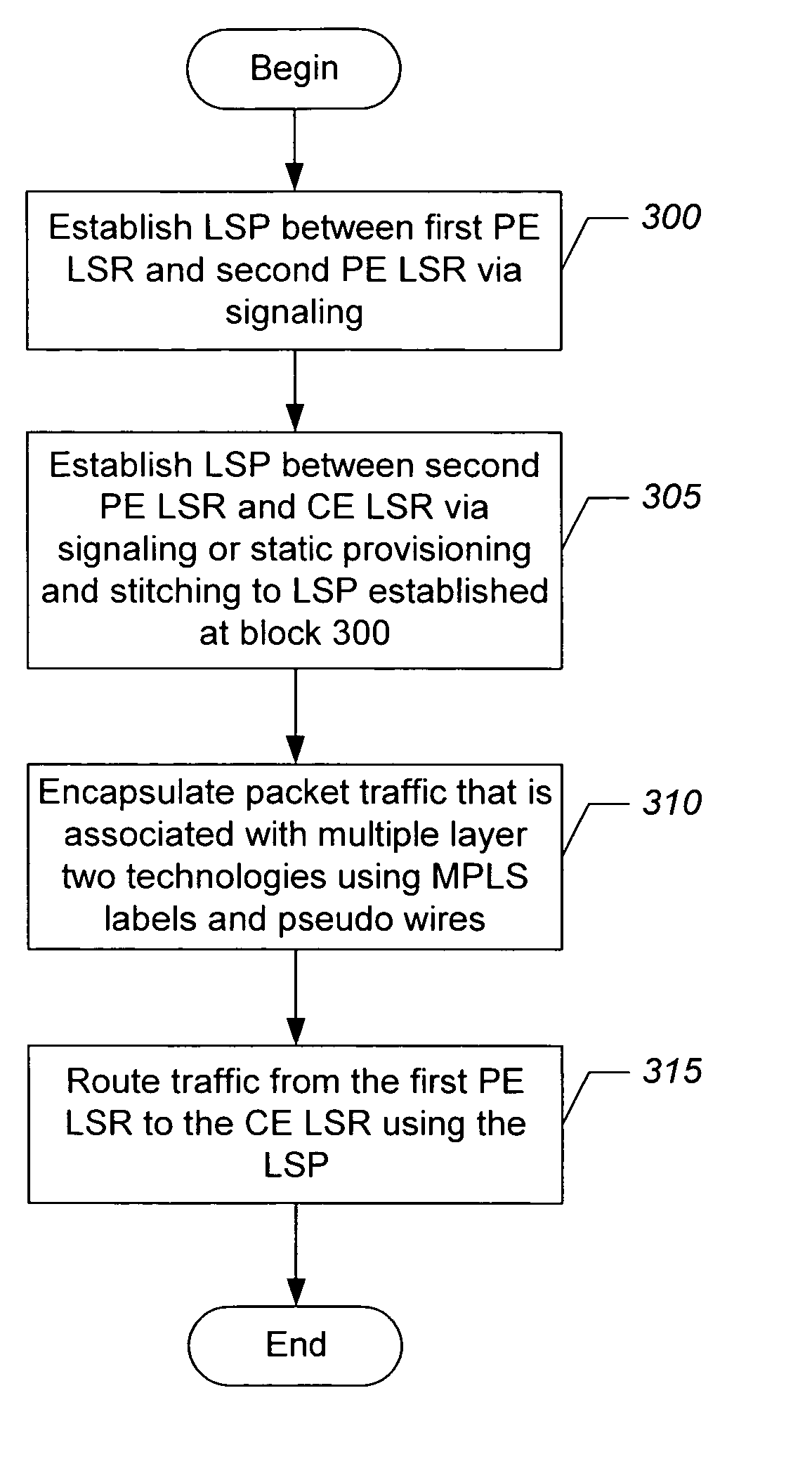
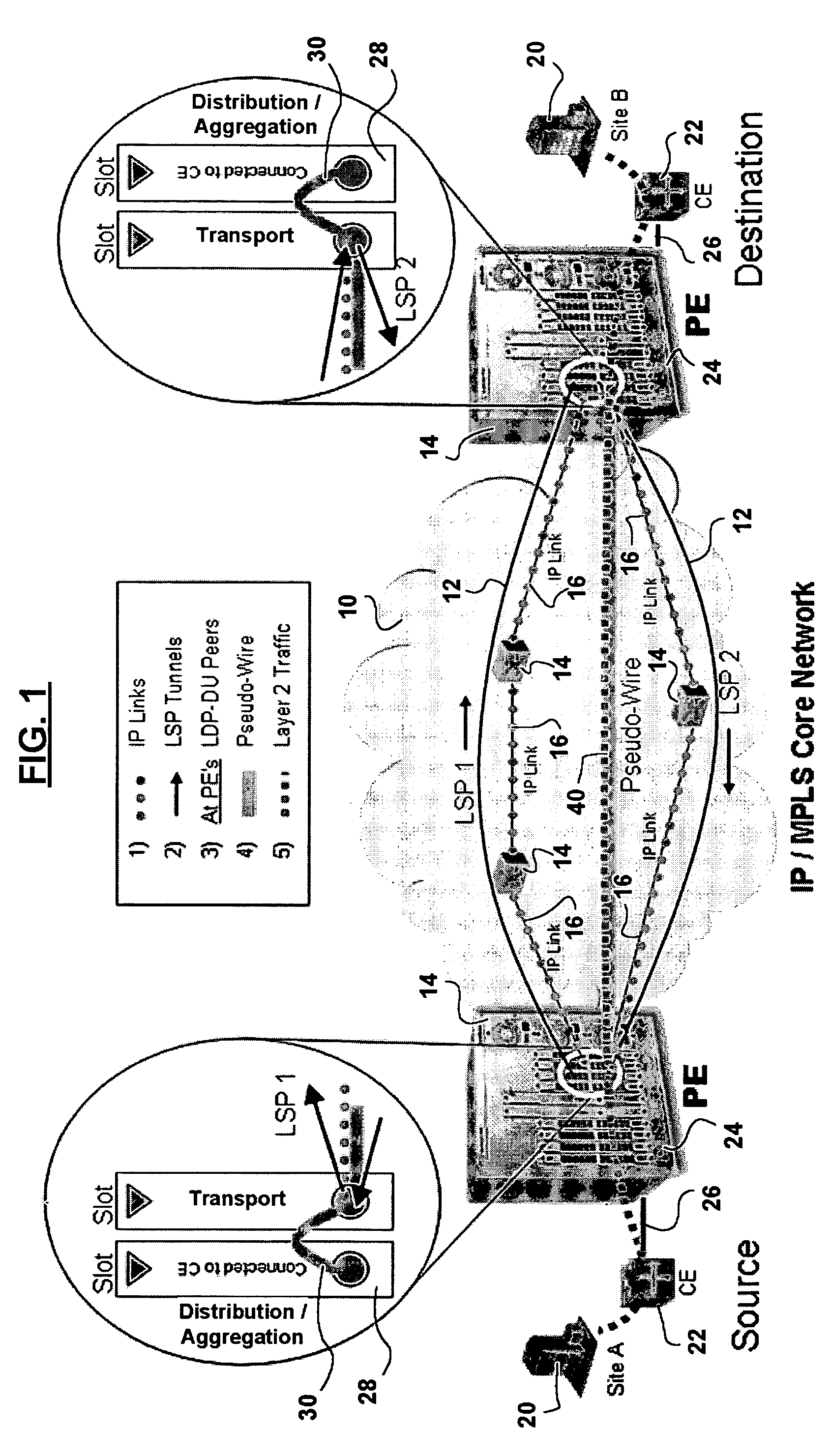
Methods, systems, and computer program products for encapsulating packet traffic associated with multiple layer two technologies
InactiveUS20050141504A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData packLabel switch router
A multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) network is operated by establishing a label switched path (LSP) that connects a first provider edge (PE) label switched router (LSR) a second PE LSR, and a customer edge (CE) LSR. The packet traffic that is associated with a plurality of different layer two technologies is encapsulated with an MPLS label. The encapsulated traffic is securely routed from the first PE LSR through the second PE LSR to the CE LSR using the LSP.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Method for using a verification probe in an LDP MPLS network
InactiveUS7283563B1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsForwarding equivalence classMulti protocol
An ingress multi-protocol label switching (MPLS) label switched router (LSR) forwards a set of packets associated with a first set of forwarding equivalence classes (FECs) along a label switched path (LSP) to an egress MPLS LSR. Logic in the ingress MPLS LSR produces an operation and maintenance (OAM) connectivity verification probe message encoding the first set of FECs, and forwards the OAM connectivity verification probe message along the LSP to the egress MPLS LSR. Logic in the egress MPLS LSR produces an encoding of a second set of FECs. Logic in the egress MPLS LSR compares the encoding of the first set of FECs in the connectivity verification probe message to the encoding of the second set of FECs, and produces an indication if the comparison indicates that the first set of FECs is not a subset of the second set of FECs.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Full mesh LSP and full mesh T-LDP provisioning between provider edge routers in support of Layer-2 and Layer-3 virtual private network services
ActiveUS7436782B2Reduce probabilityImprove productivityData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceService provision
A network management system, and a method of, centrally provisioning a full transport LSP mesh and a full targeted LDP signaling session mesh in support of VPN services provisioning are provided. A network management system repository tracks Provider Edge nodes (PE) having label switch router functionality, transport LSP meshes and targeted LDP session meshes. The method includes selecting PE nodes for inclusion in a node group, identifying PE node pairs, and issuing commands to paired PE nodes to commission managed transport LSPs and targeted LDP signaling sessions. The advantages are derived from the full mesh LSP content transport provisioning and targeted LDP signaling session provisioning effected in a centralized network management context enabling service providers to: assure network resiliency, assure service quality, and provide accounting, in respect of Layer-2 and Layer-3 VPN services irrespective of client side deployed infrastructure while leveraging installed infrastructure in the service provider communications network core. Additional advantages are derived from increased operations management personnel productivity while reducing the probability of human error compared to manual provisioning thereof enabling wide availability of VPN services.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Label switching system
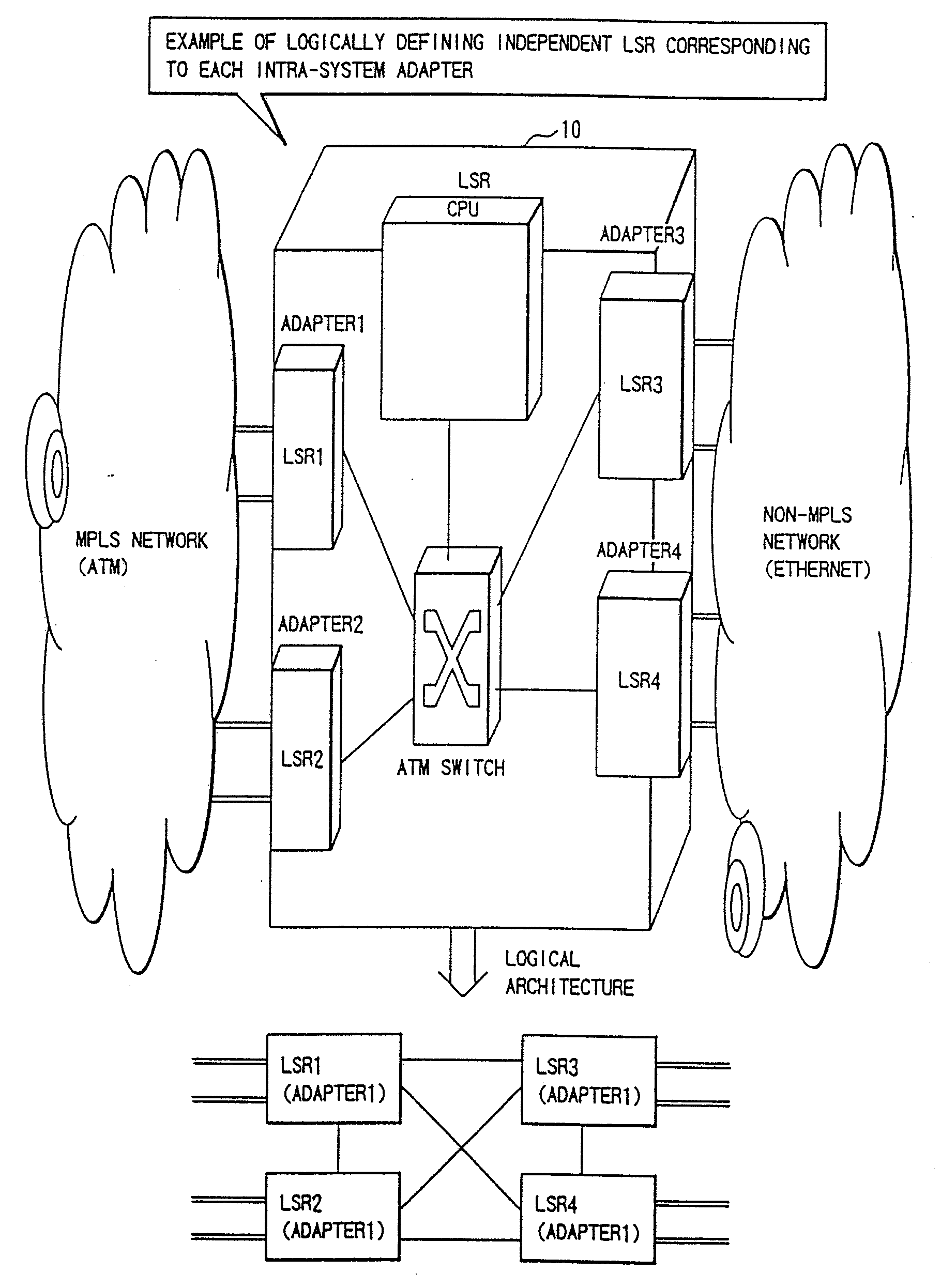
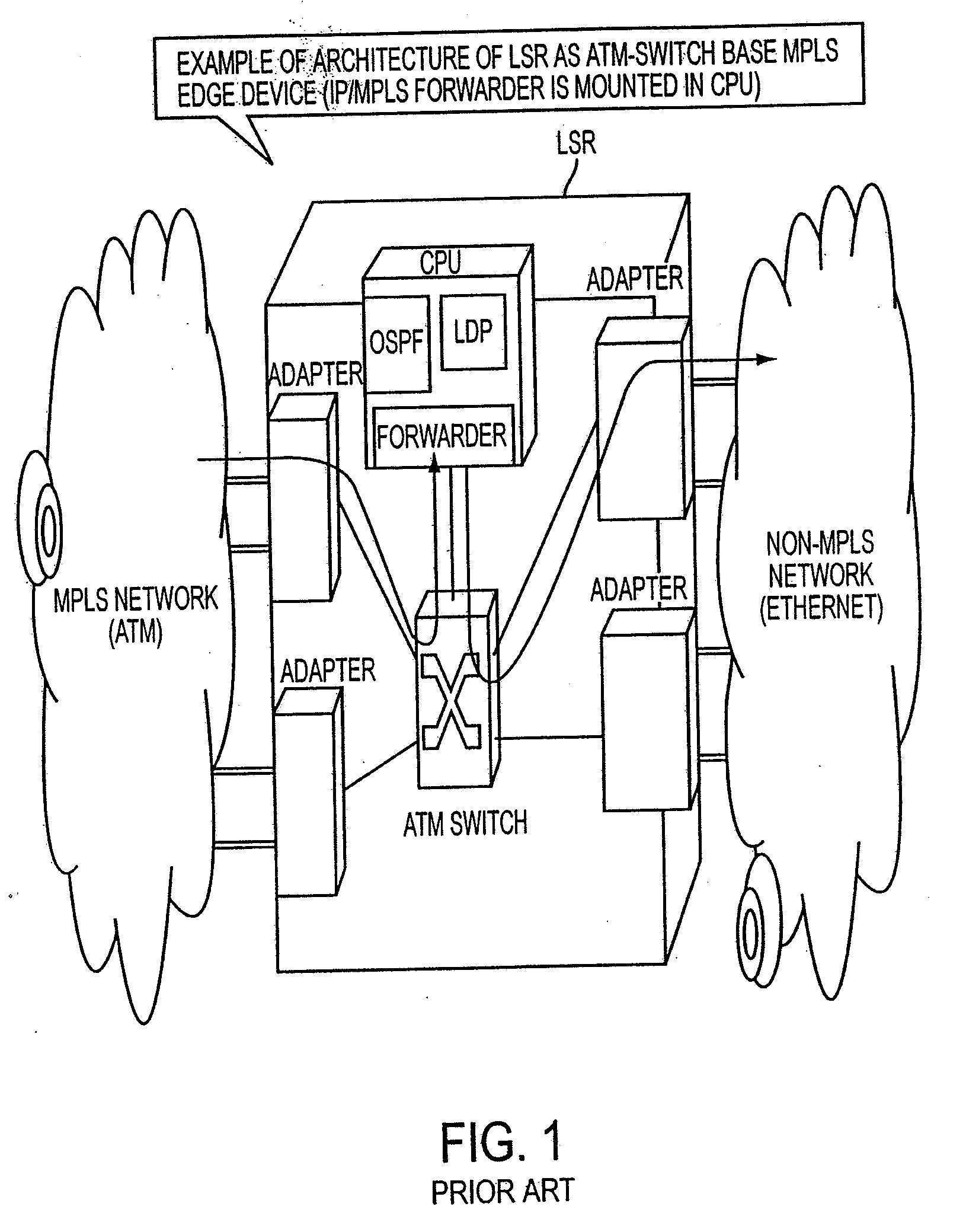
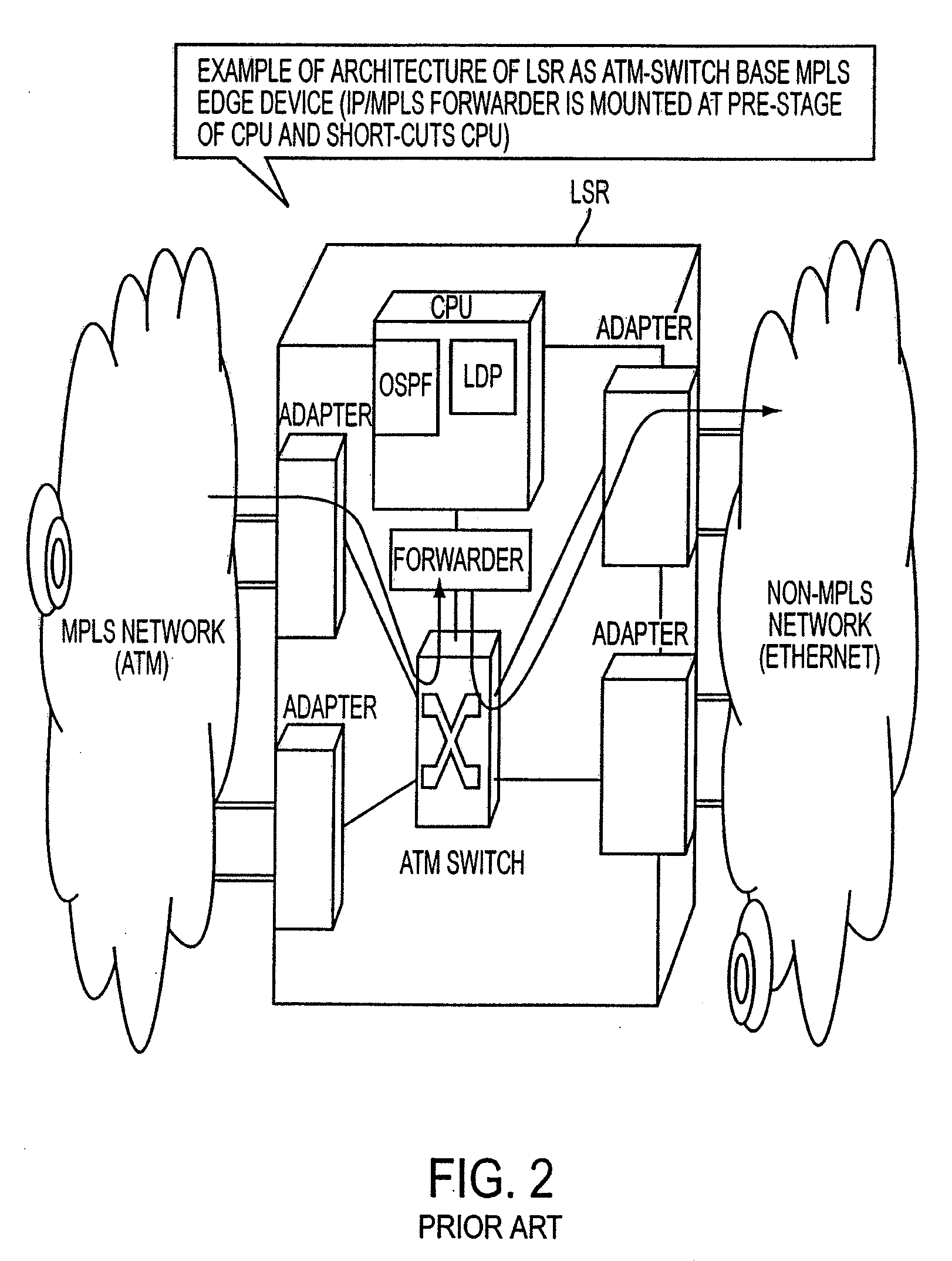
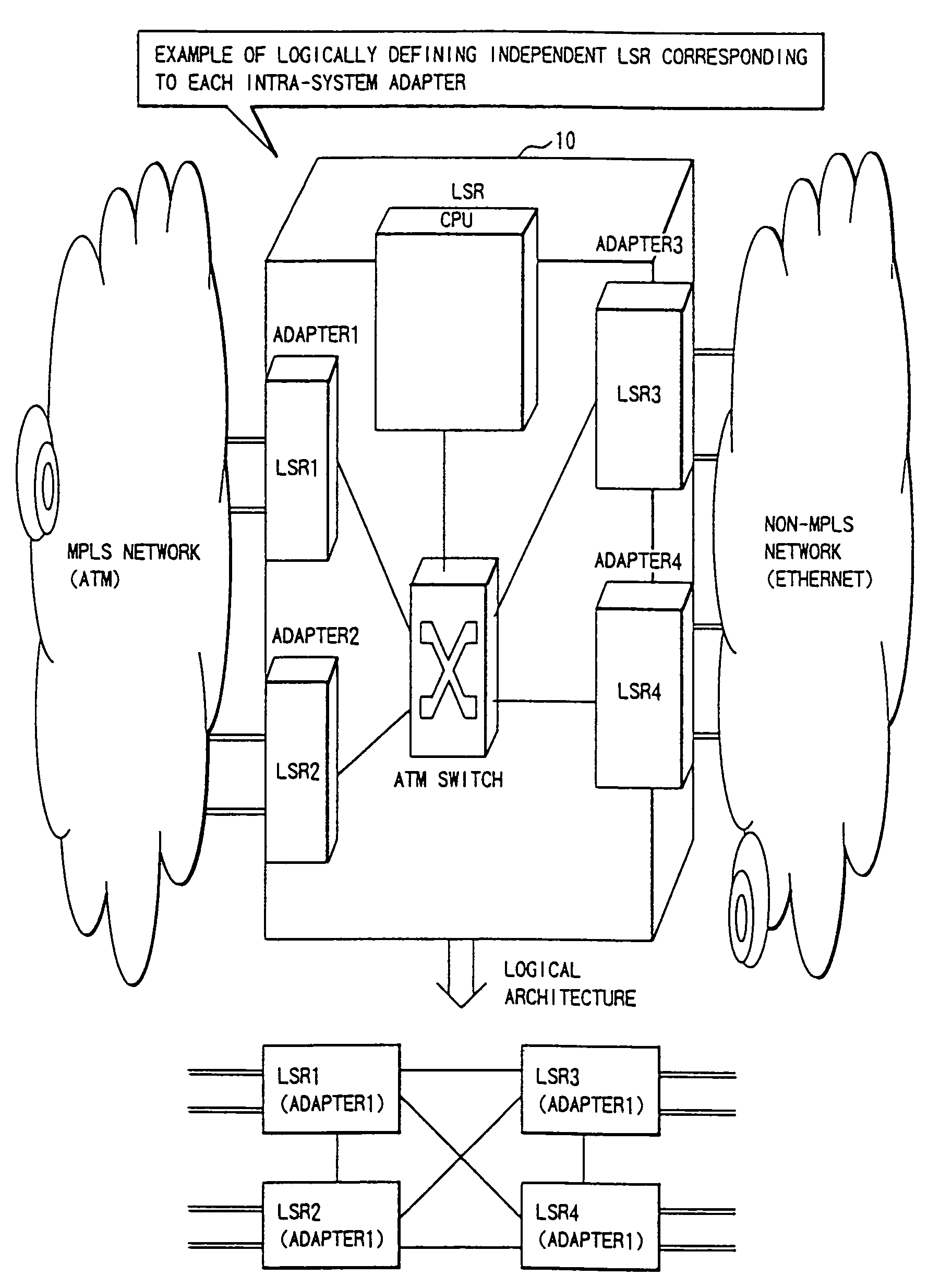
InactiveUS20080253379A1Easy to installNetworks interconnectionNetwork connectionsGranularityComputer science
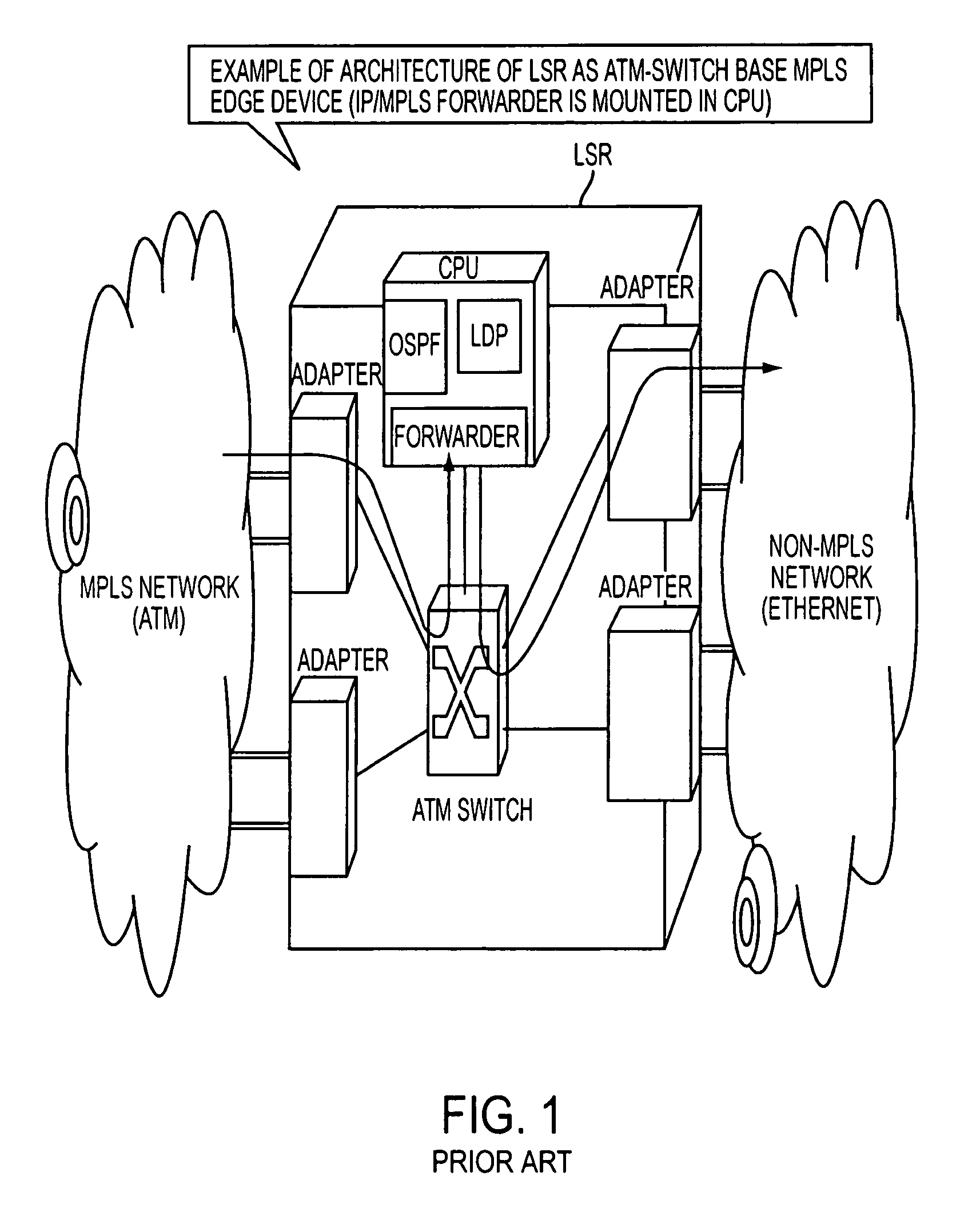
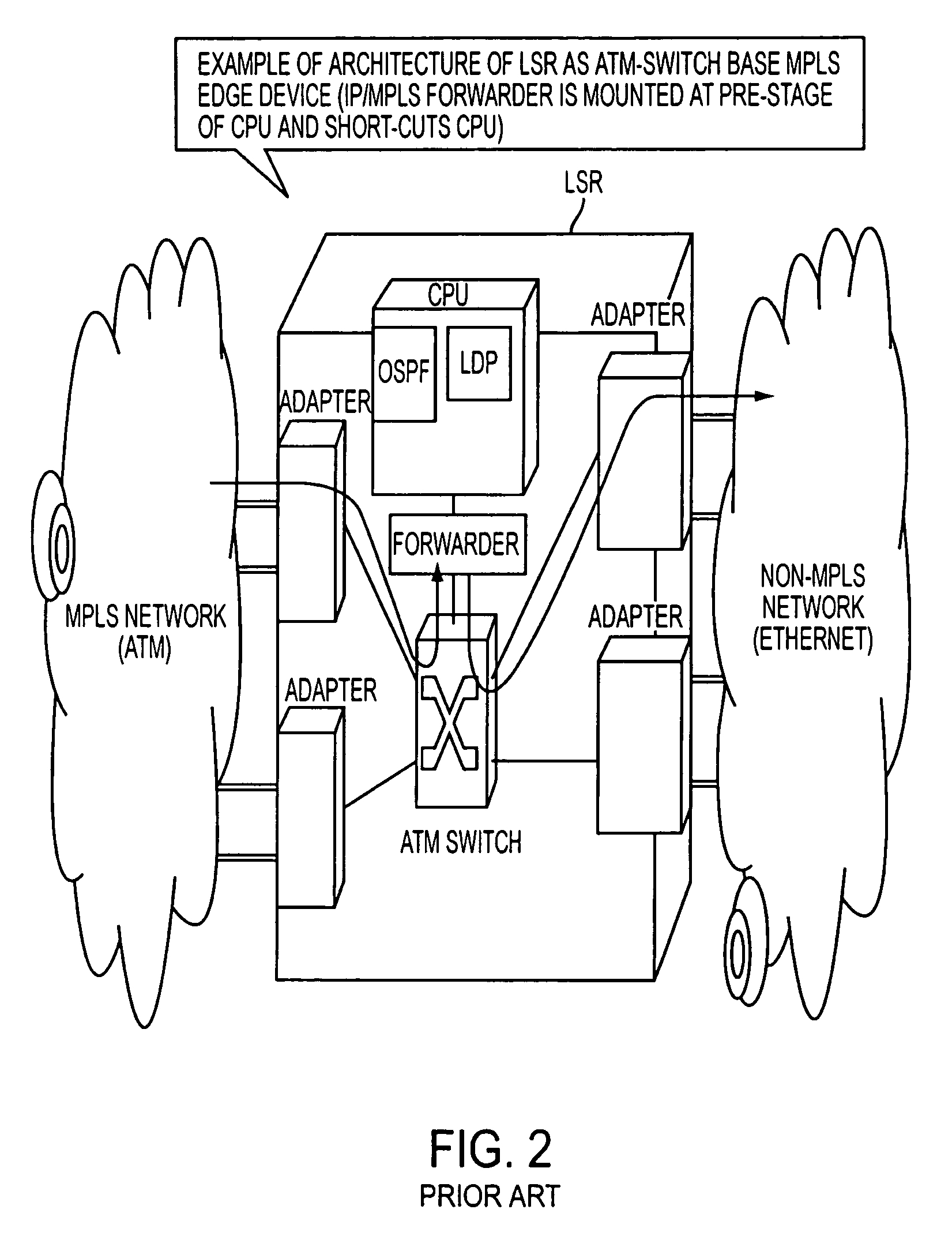
A packet router in a label switching system includes a logical router configuring module for logically dividing a label switching router (LSR) into a plurality of LSRs each having a label switching function, and a module for specifying, when setting a label switched path on the basis of an explicit route specified, a port or a port group of an egress node. With this construction, a label switching architecture in an ATM network for actualizing MPLS (label switching) can be mapped to an ATM-Switch base system architecture, and a granularity of function (Constraint Base Routing) of specifying a variety of routes provided by MPLS can be attained.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Label switching system
InactiveUS7336648B1Easy to installExpand the scope of useError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsGranularityLabel switch router
A packet router in a label switching system includes a logical router configuring module for logically dividing a label switching router (LSR) into a plurality of LSRs each having a label switching function, and a module for specifying, when setting a label switched path on the basis of an explicit route specified, a port or a port group of an egress node. With this construction, a label switching architecture in an ATM network for actualizing MPLS (label switching) can be mapped to an ATM-Switch base system architecture, and a granularity or function (Constraint Base Routing) of specifying a variety of routes provided by MPLS can be attained.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
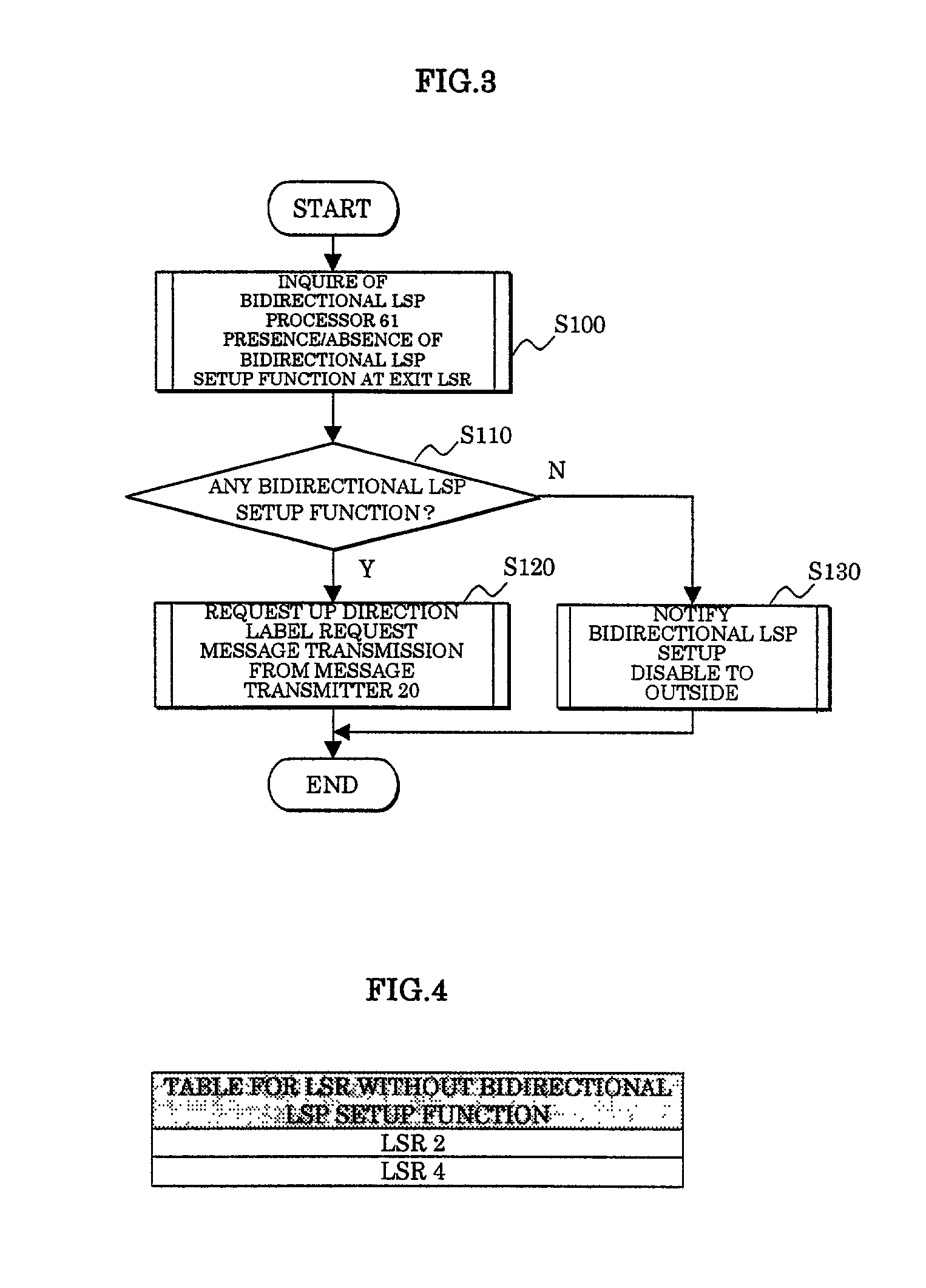
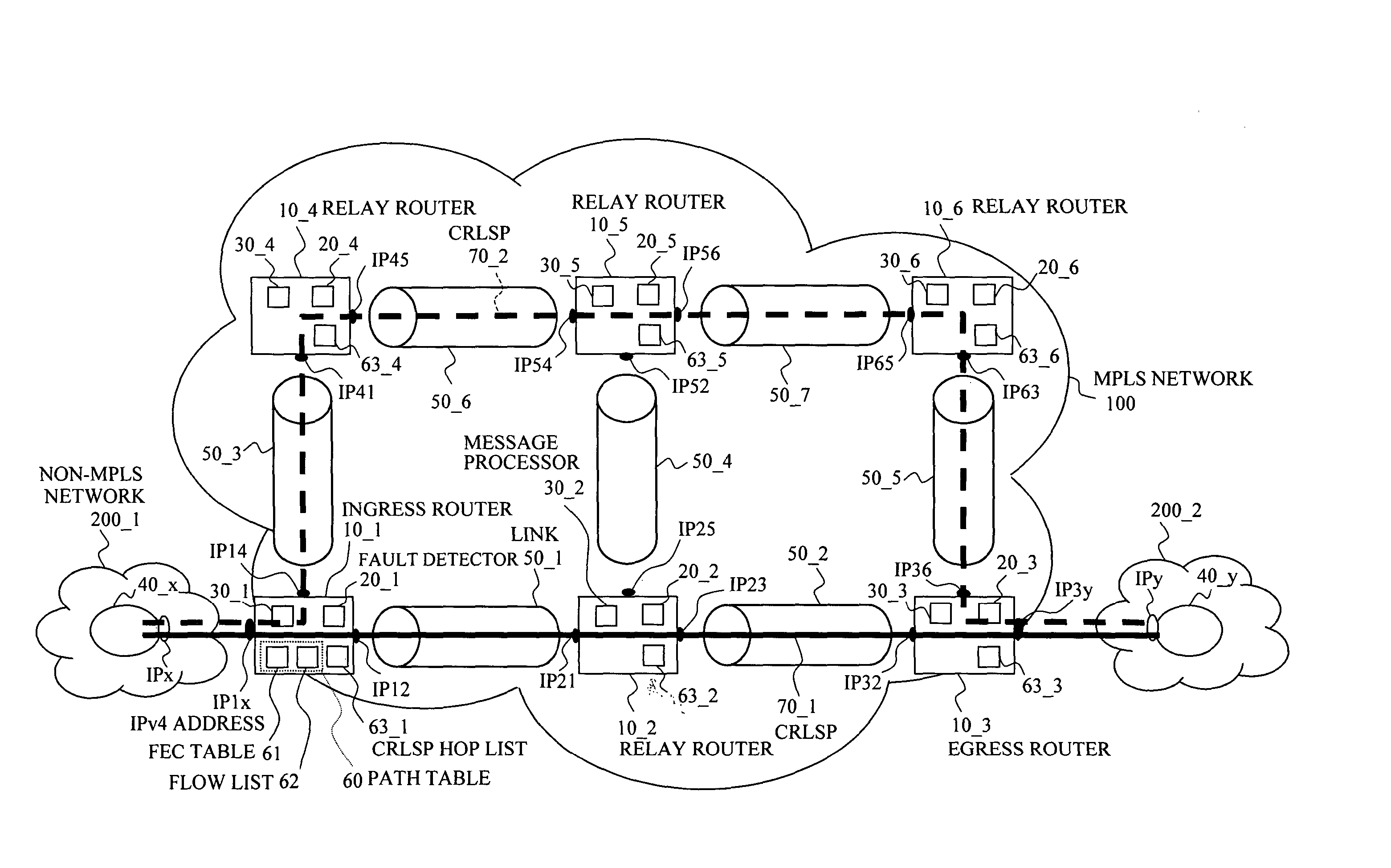
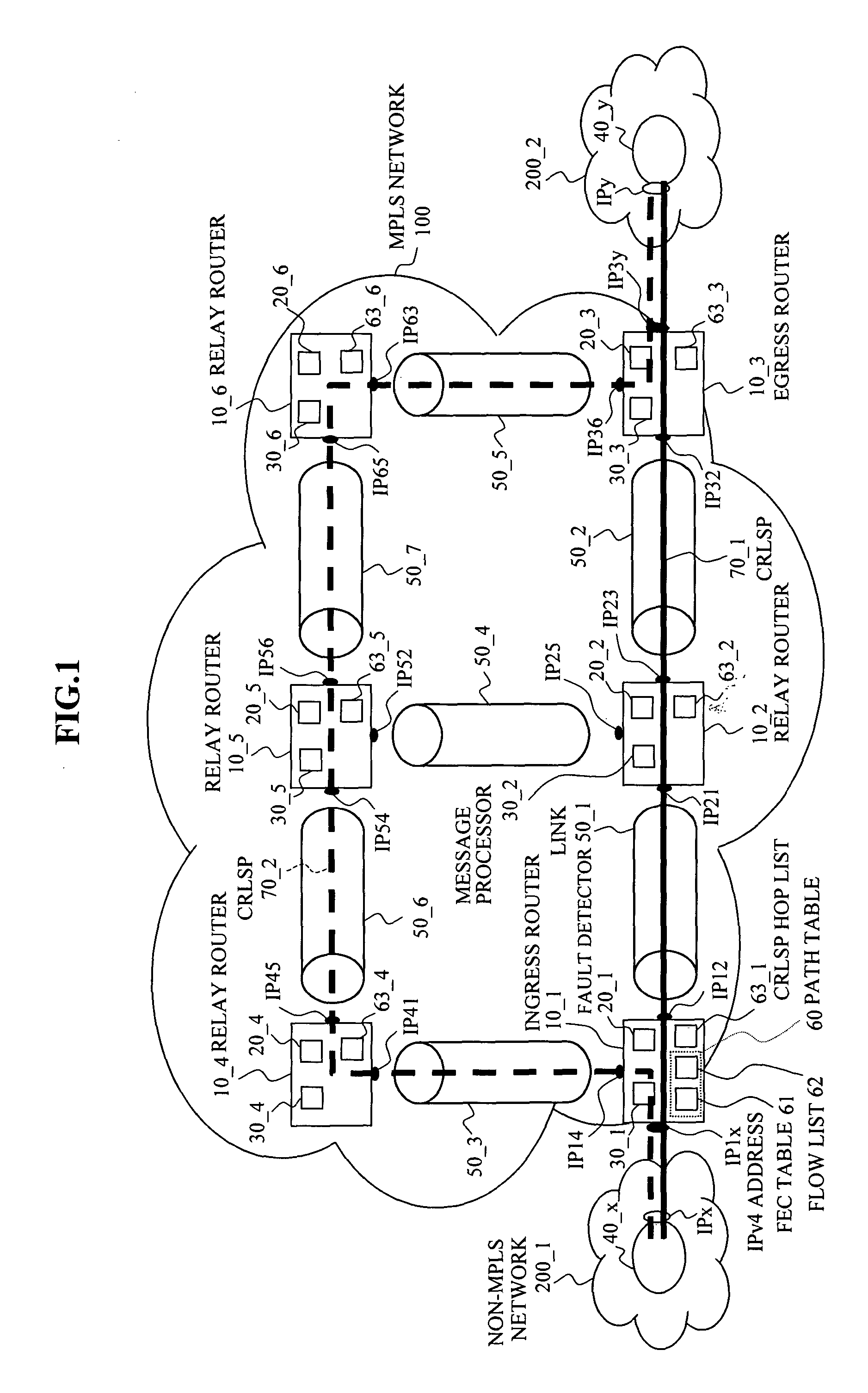
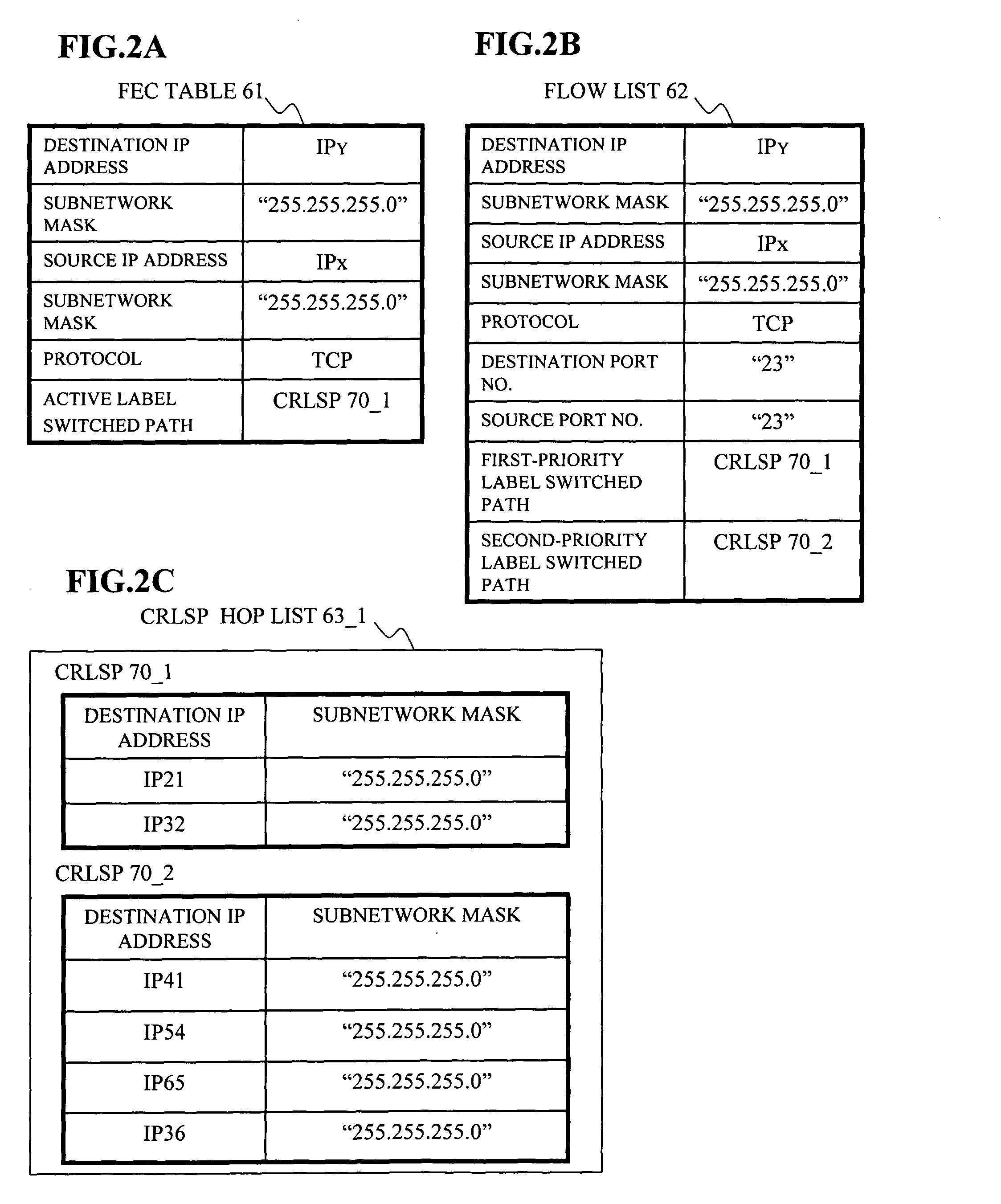
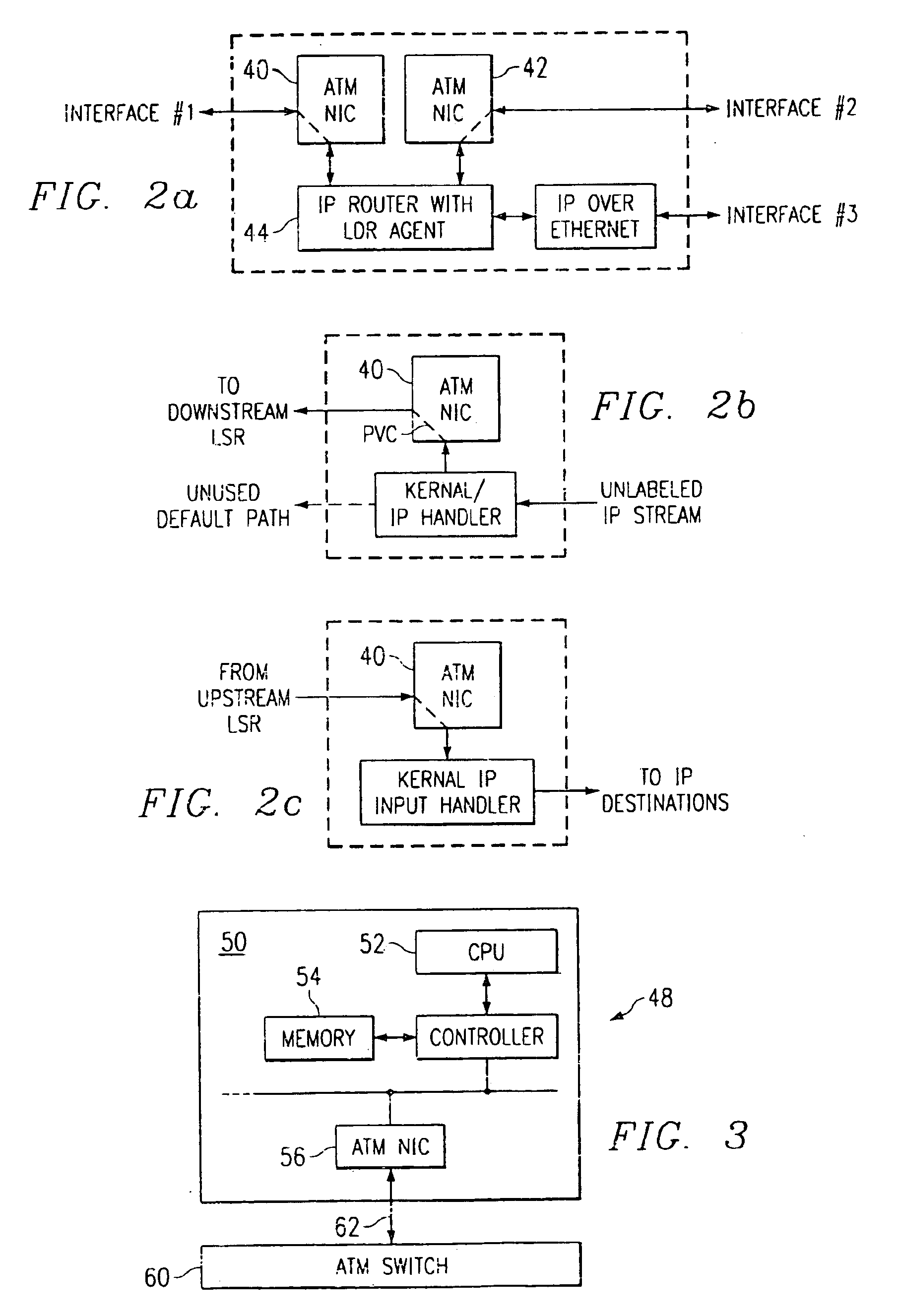
Label switching router
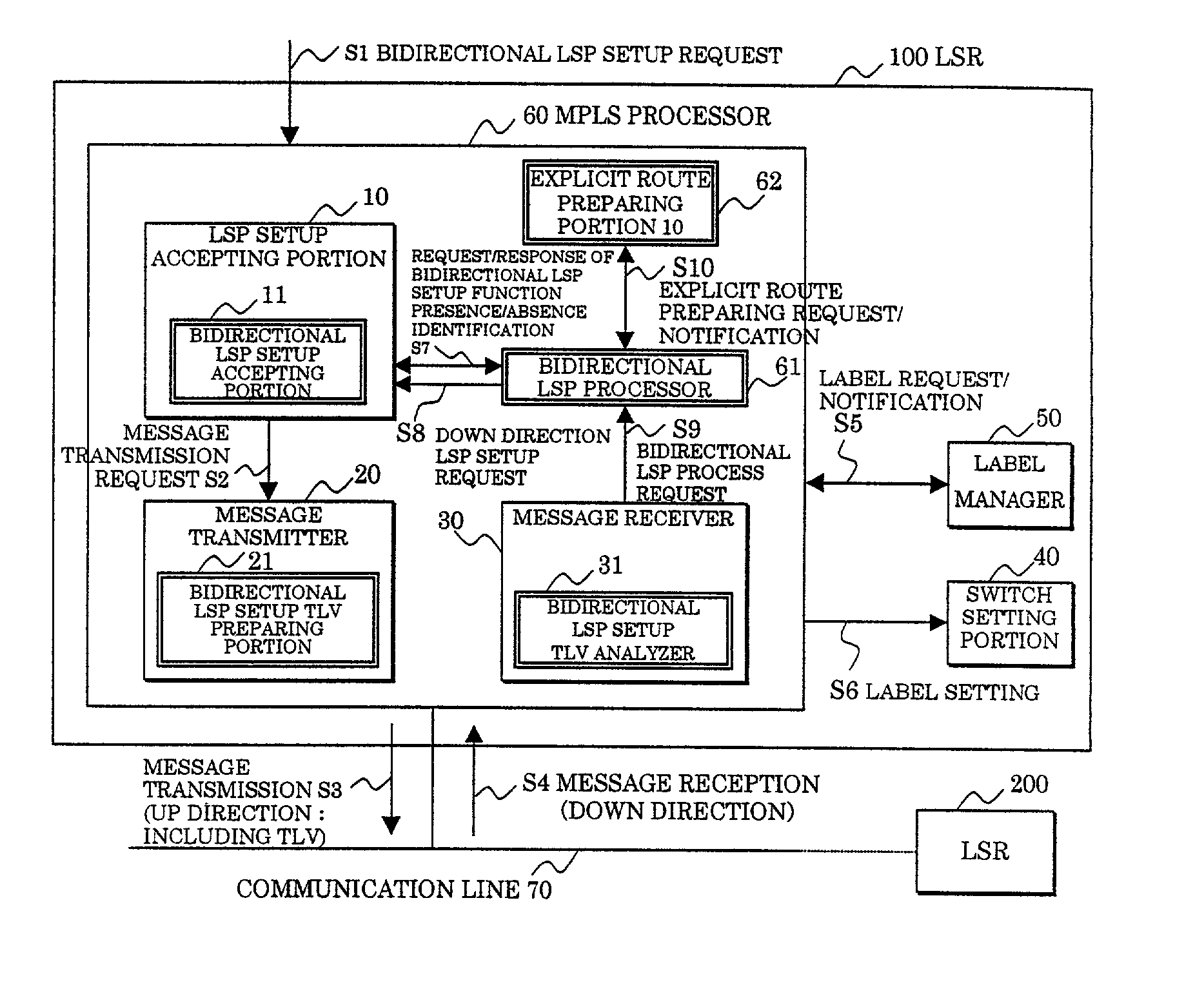
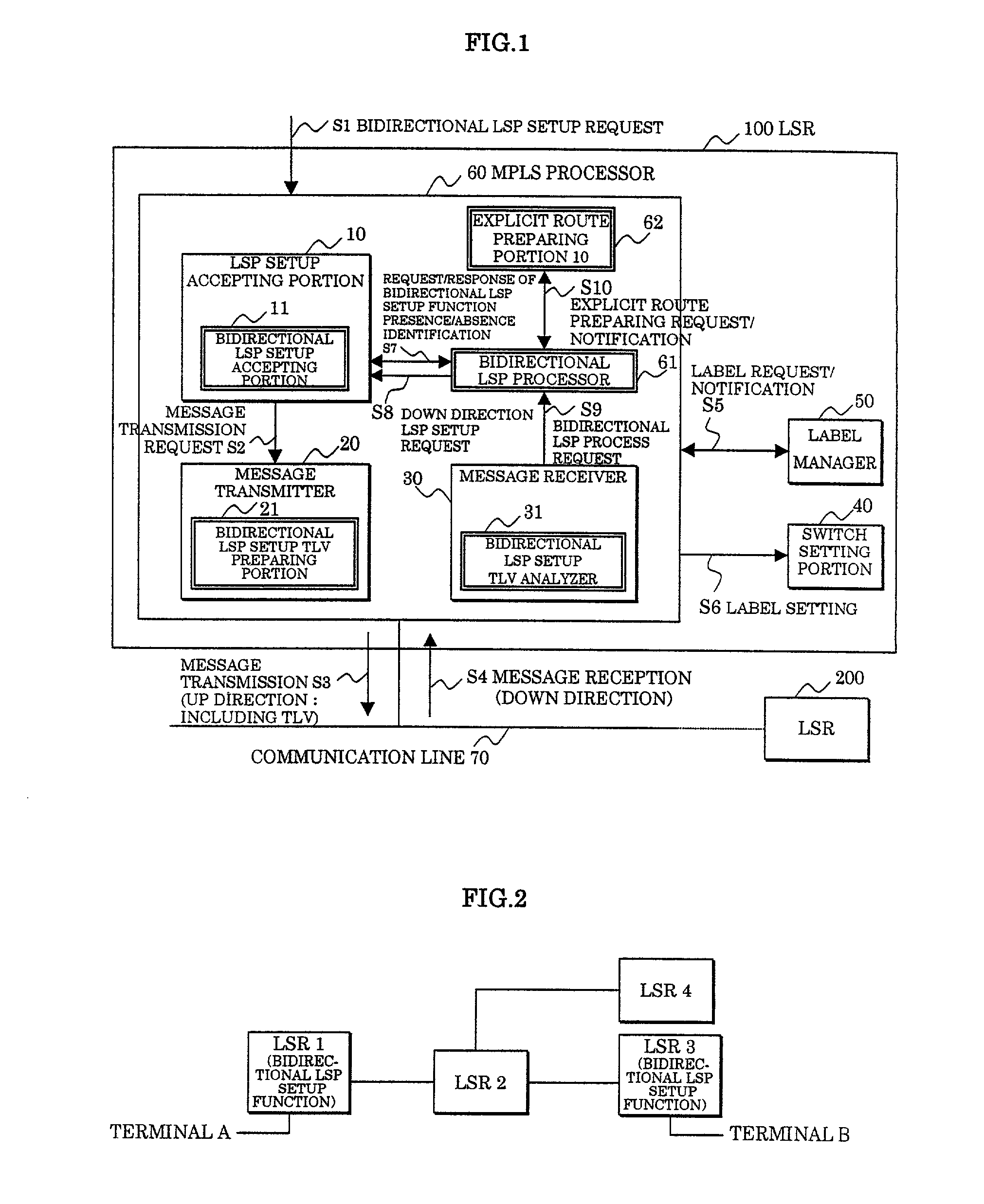
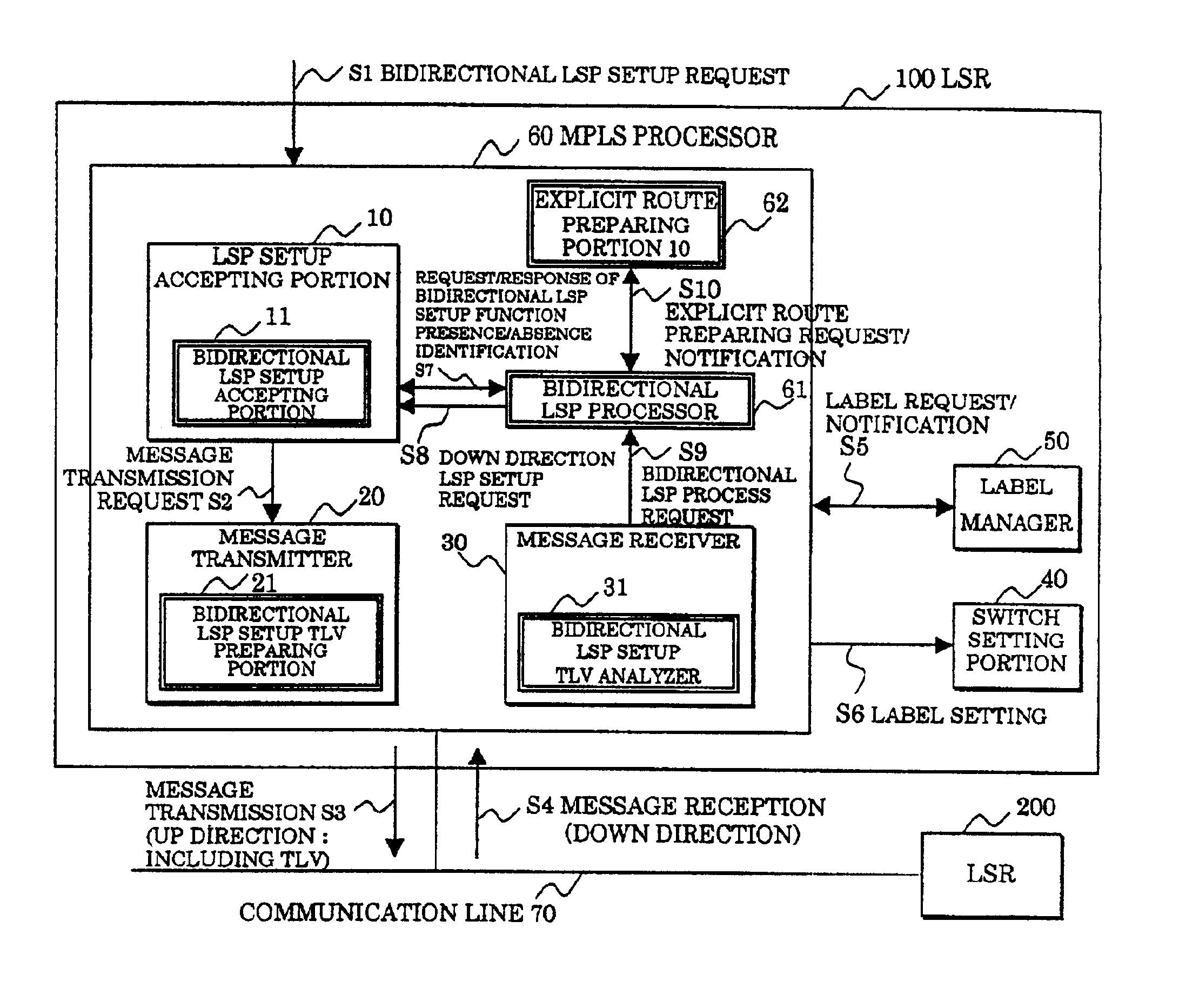
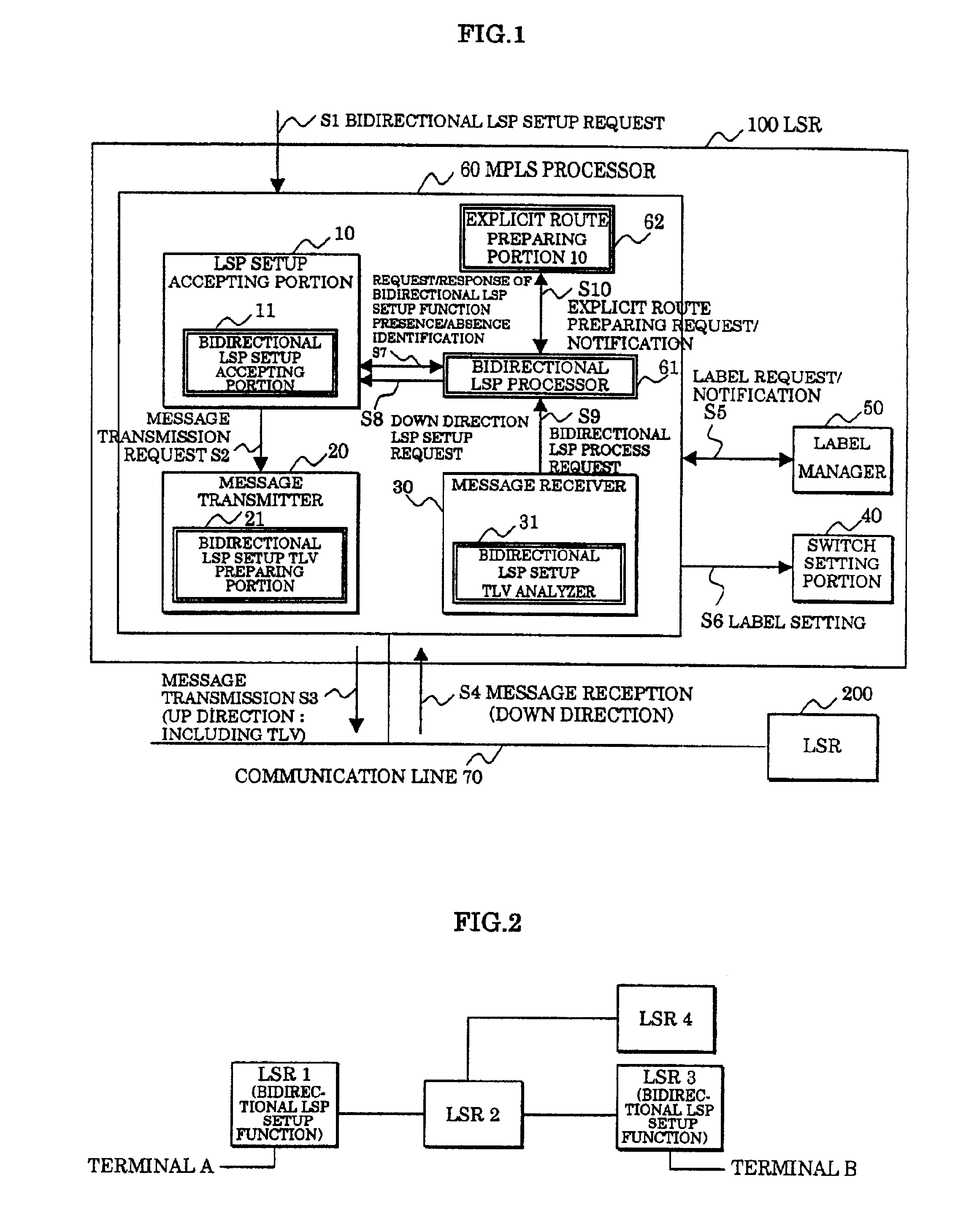
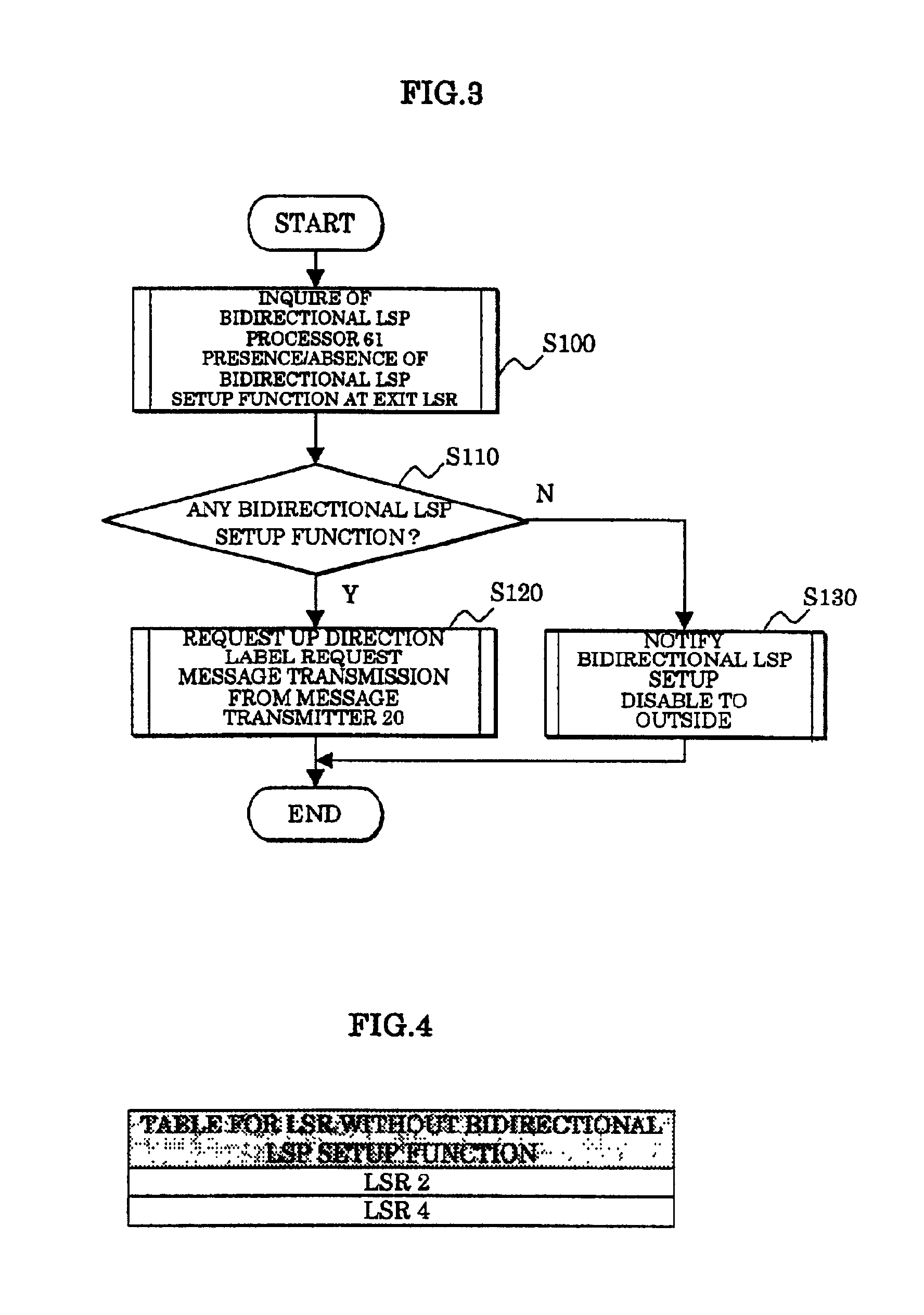
In a label switching router placed at one end of an LSP set by using CRLDP, a bidirectional LSP setup TLV preparing portion prepares a bidirectional LSP setup TLV included in a bidirectional setup label request message transmitted in an up direction to a label switching router placed at the other end of the LSP based on an external bidirectional LSP setup request accepted by a bidirectional LSP setup accepting portion, a bidirectional LSP setup TLV analyzer analyzes the bidirectional LSP setup TLV in the message when the message is received from the label switching router at the other end, a bidirectional LSP processor performs an LSP setup request in a down direction as opposed to the up direction based on the analyzed result by the bidirectional LSP setup TLV analyzer, and an explicit route preparing portion prepares an explicit route on which a router to be relayed in the down direction is prescribed, based on an explicit route preparing request from the bidirectional LSP processor and notifies the prepared route to the bidirectional LSP processor.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
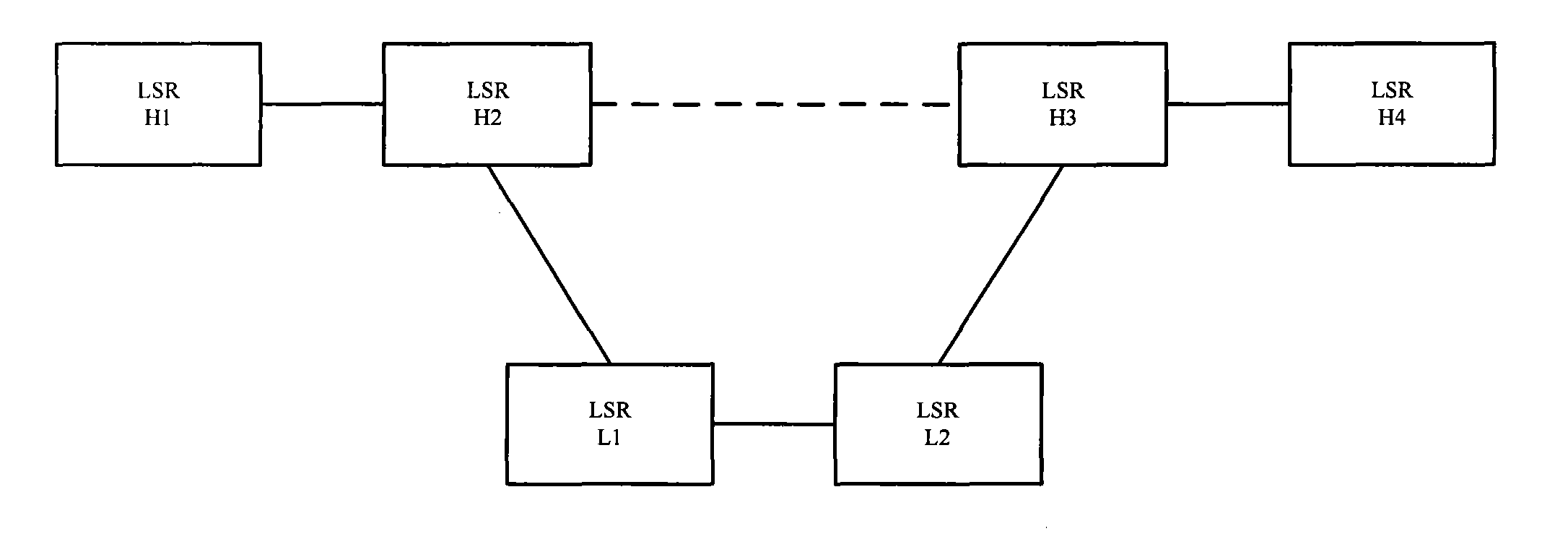
Label switching router and path switchover control method thereof
InactiveUS20040071080A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPath switchingComputer science
In a label switching router and a path switchover method thereof when a path fault occurs, a relay label switching router registers a hop destination indicated in a received message in a path hop list, forwards the message to a next hop destination without deleting the hop destination, and notifies an identifier of a path in which a fault has recovered to an ingress label switching router based on the path hop list, an egress label switching router registers the hop destination indicated in the received message in a path hop list, and notifies an identifier of a path in which a fault has recovered to the ingress label switching router based on the path hop list, and the ingress label switching router regards, when detecting a recovery of a path higher in priority than an active path or when receiving a recovery notification, the recovered path as an active path.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
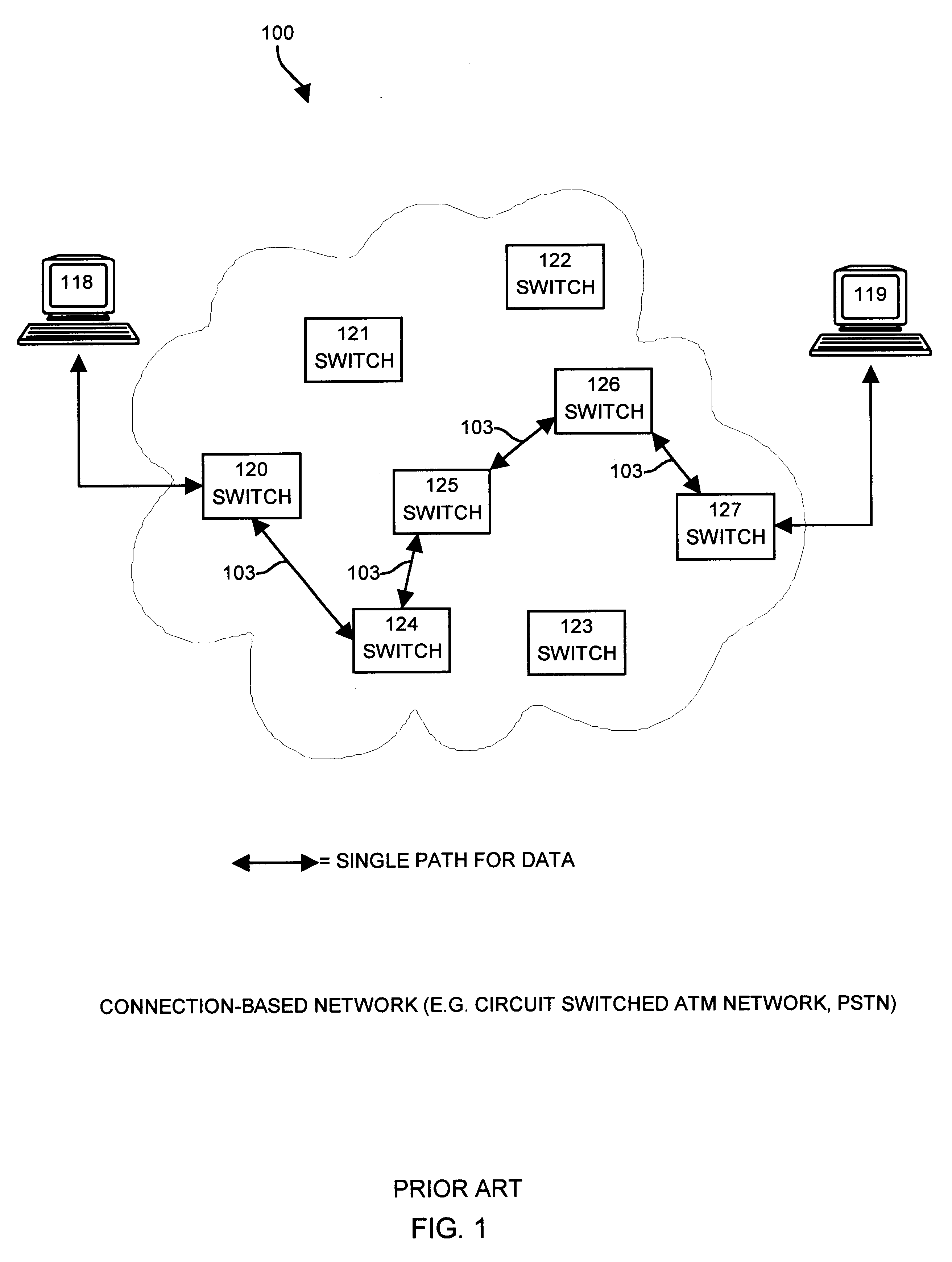
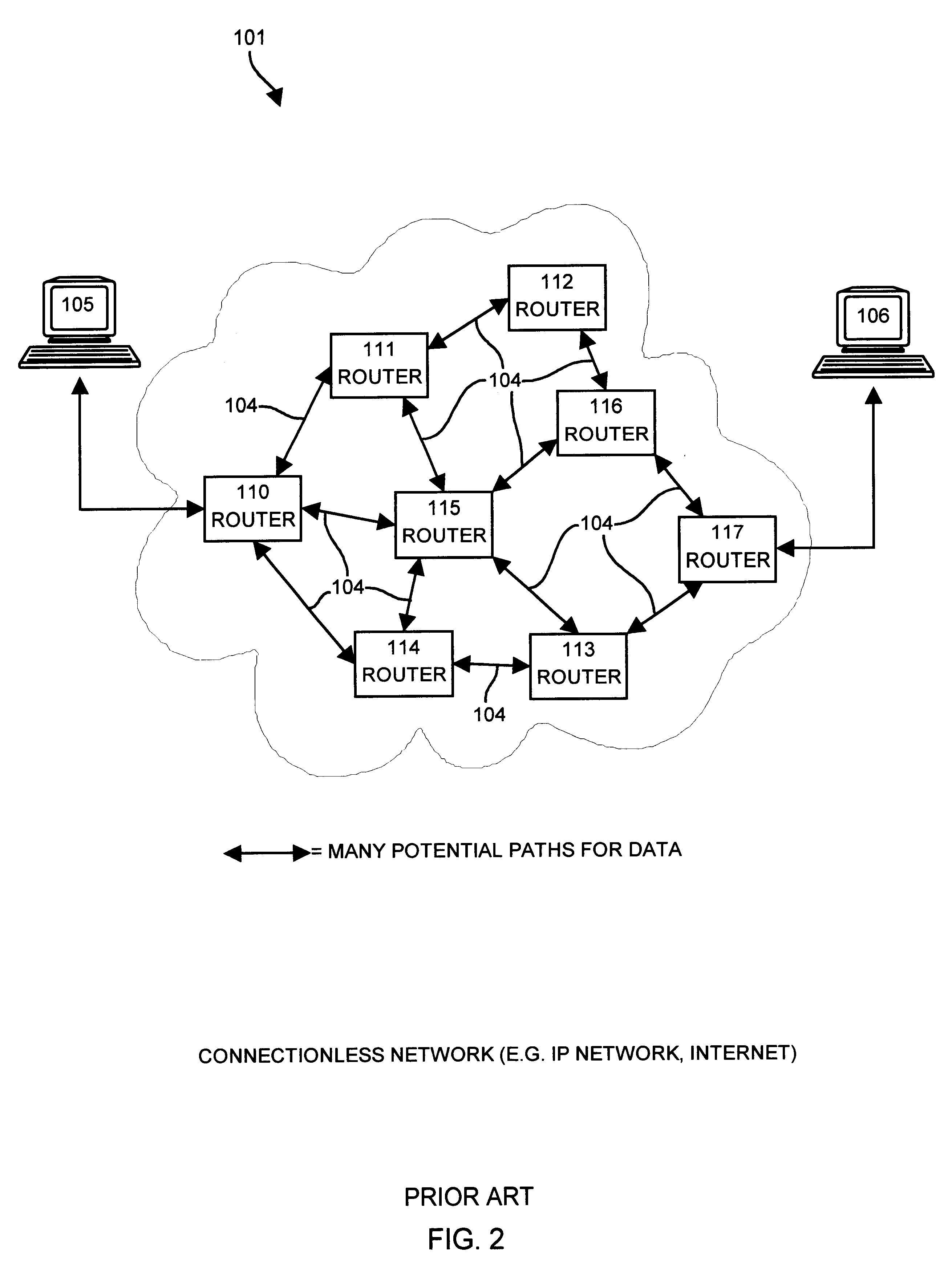
Multiprotocol label switching routers
InactiveUS6885677B1Equipment is cheapMinimize complexityTime-division multiplexData switching networksMultiprotocol Label SwitchingGeneral purpose computer
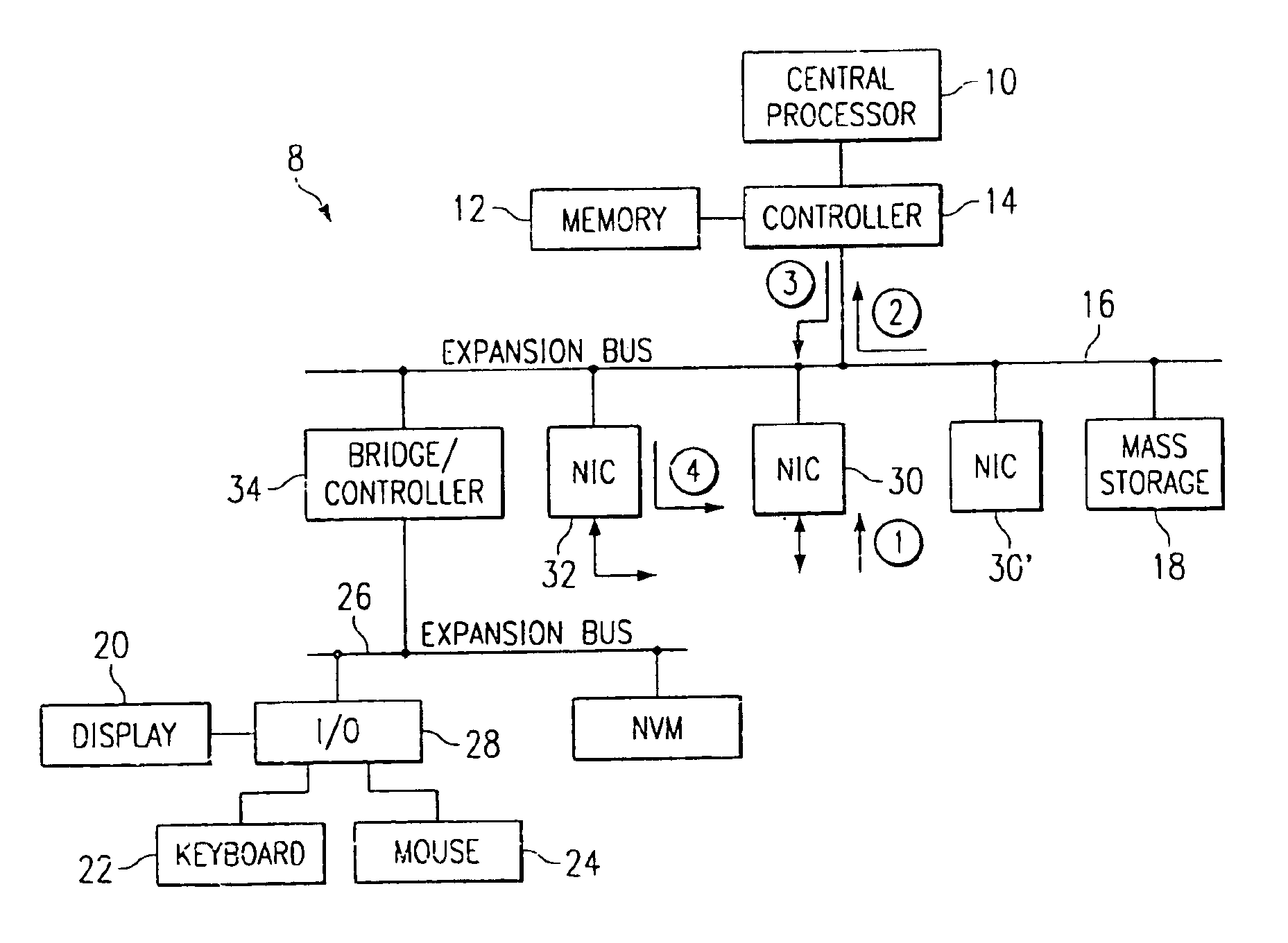
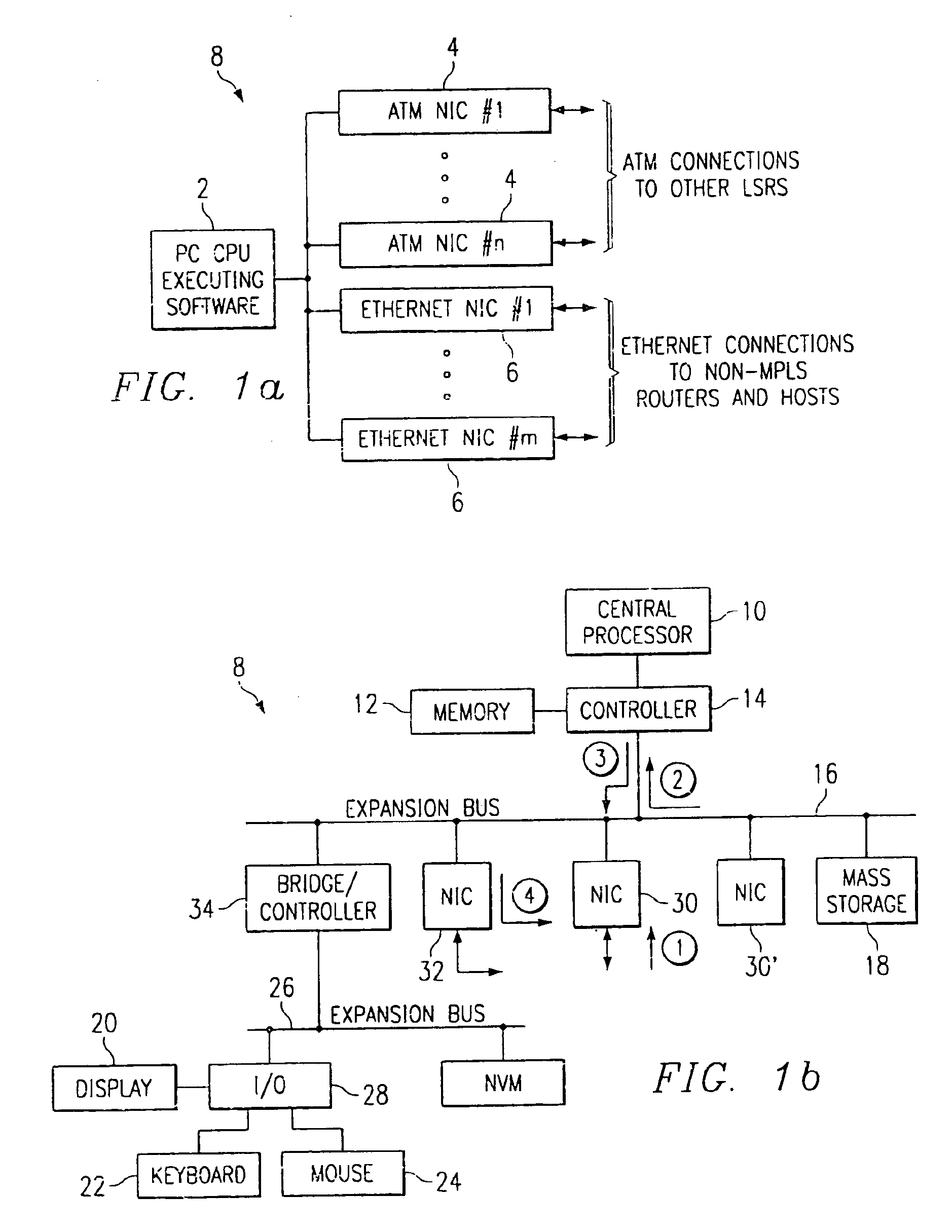
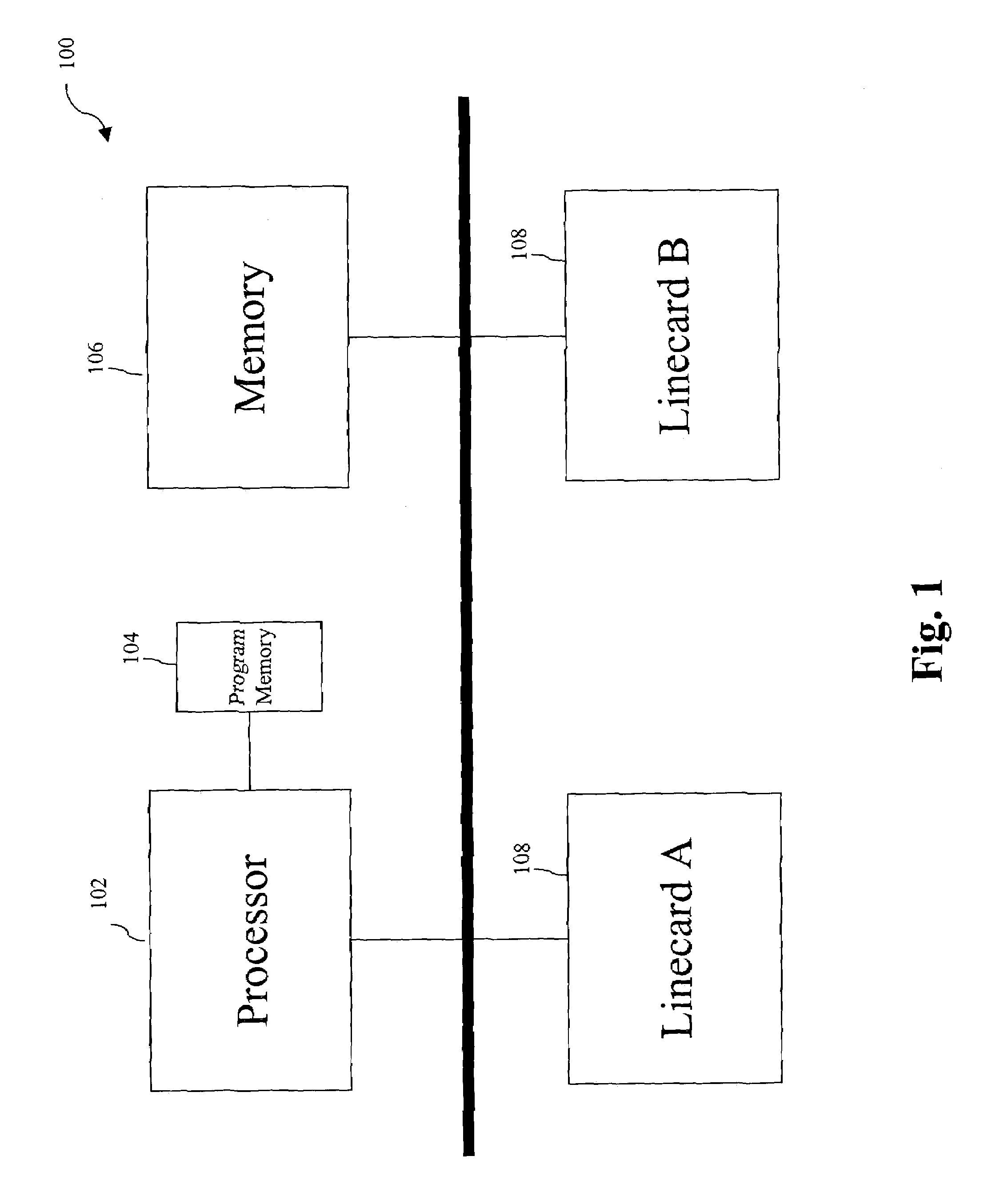
In one aspect, a method of using a general purpose computer 8 as an MPLS-enabled label switched router includes executing software on the general purpose computer 8 that allows it to communicate with other label switched routers using label distribution protocol. The general purpose computer 8 includes a central processor 10, a memory 12, network interface cards 30 and 32 and also typically includes local I / O such as a keyboard 22, a mouse 24 and a display device 20 for communicating with a local user.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
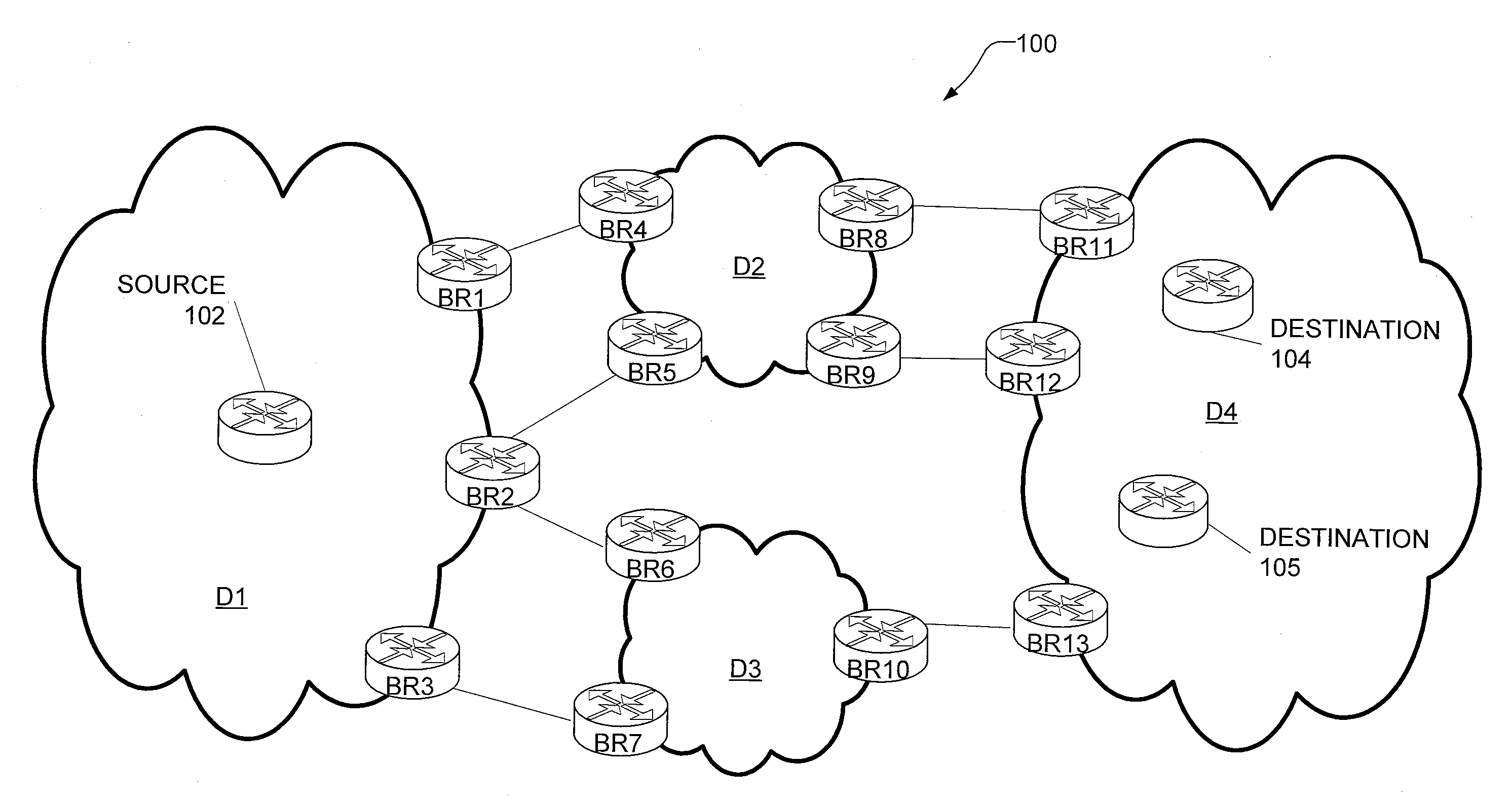
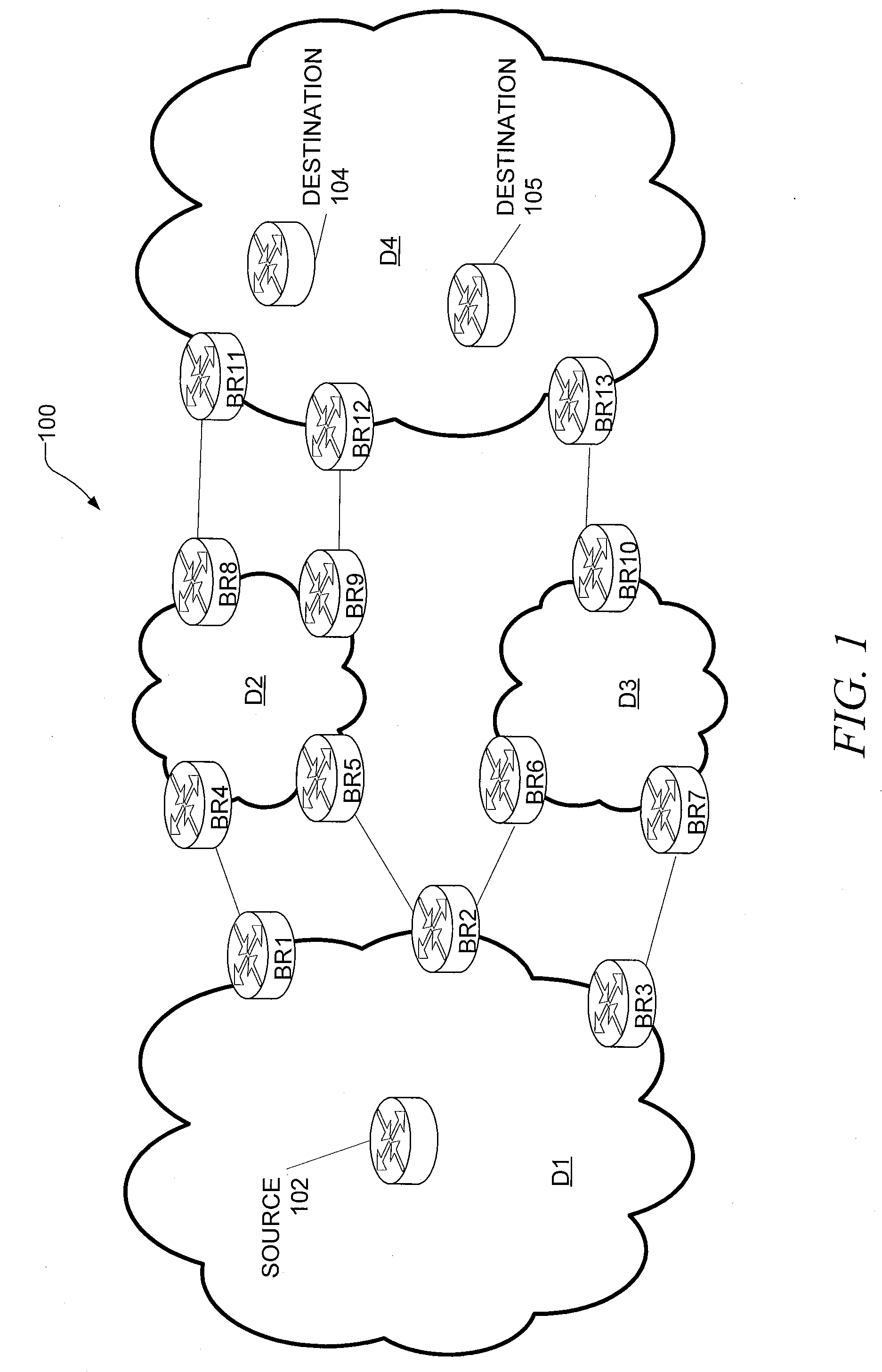
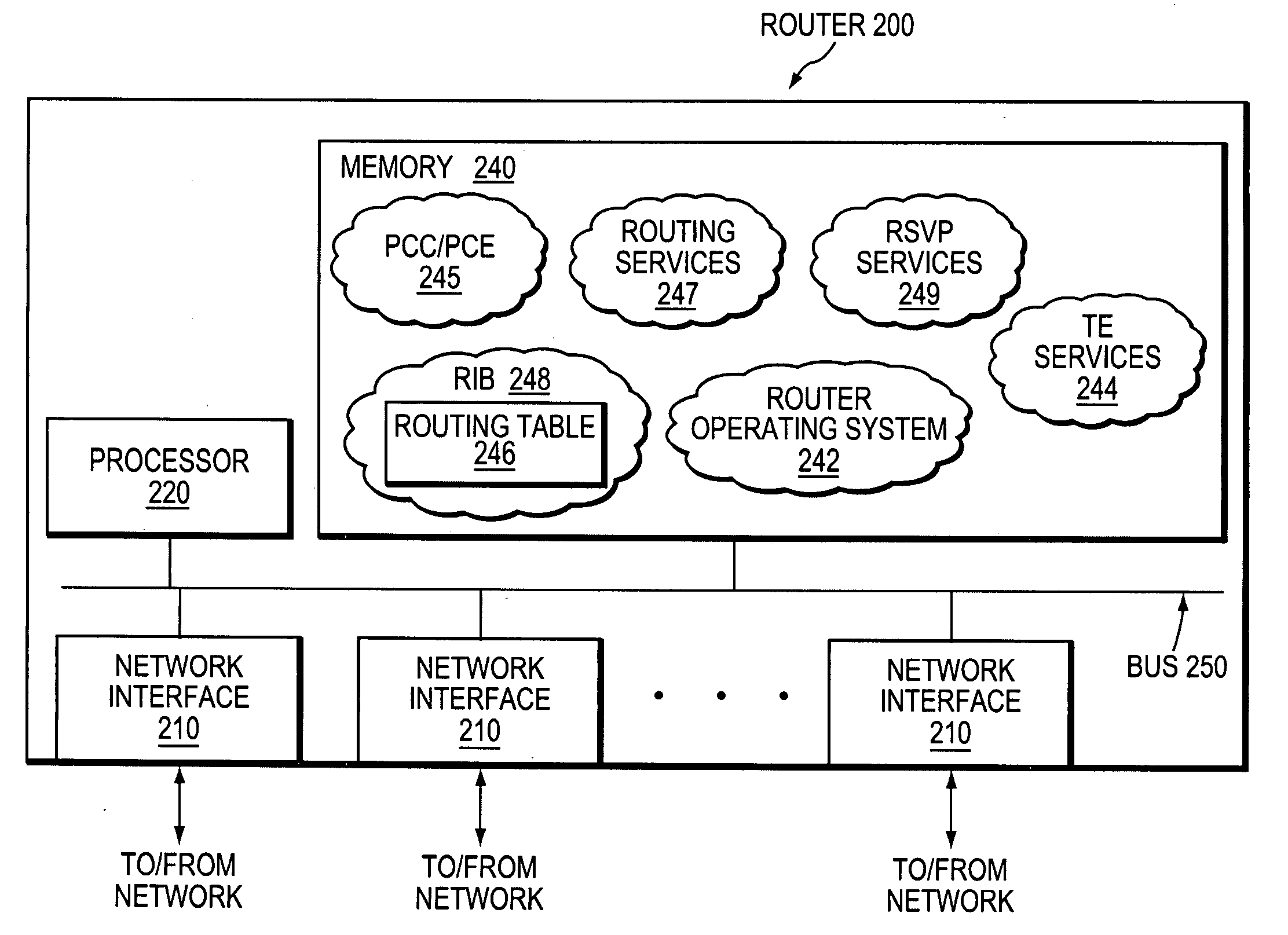
Inter-domain optimization trigger in PCE-based environment
ActiveUS20060176820A1Improve efficiencyOptimization pathError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPath computation elementDistributed computing
A technique triggers optimization of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) that spans multiple domains of a computer network from a head-end node of a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain. The technique is based on the detection of an event in the remote domain (“event domain”) that could create a more optimal TE-LSP, such as, e.g., restoration of a network element or increased available bandwidth. Specifically, a path computation element (PCE) in the event domain learns of the event and notifies other PCEs of the event through an event notification. These PCEs then flood an event notification to label switched routers (LSRs) in their respective domain. Upon receiving the notification, if an LSR has one or more TE-LSPs (or pending TE-LSPs), it responds to the PCE with an optimization request for the TE-LSPs. The PCE determines whether a particular TE-LSP may benefit from optimization based on the event domain (i.e., whether the TE-LSP uses the event domain), and processes the request accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for sharing backup path in MPLS network, label switching router for setting up backup in MPLS network, and system therefor
A method for sharing a backup path in a MultiProtocol Label Switching (MPLS) network, a label switching router (LSR) for setting a backup path in an MPLS network, a system for setting a backup path in an MPLS network, and a recording medium therefor are provided. The method includes the steps of acquiring link configuration information of links included in a working path when the working path is set between a source node and a destination node, and allocating bands for a backup path using the link configuration information when the backup path is set between the source node and the destination node. In the method, an optimal band is allocated to each of links included in a backup path by calculating a band using information, which is obtained during setting of a working path, about at least one other working path sharing links with the working path when the backup path is set, thereby efficiently managing network resources without wasting them.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
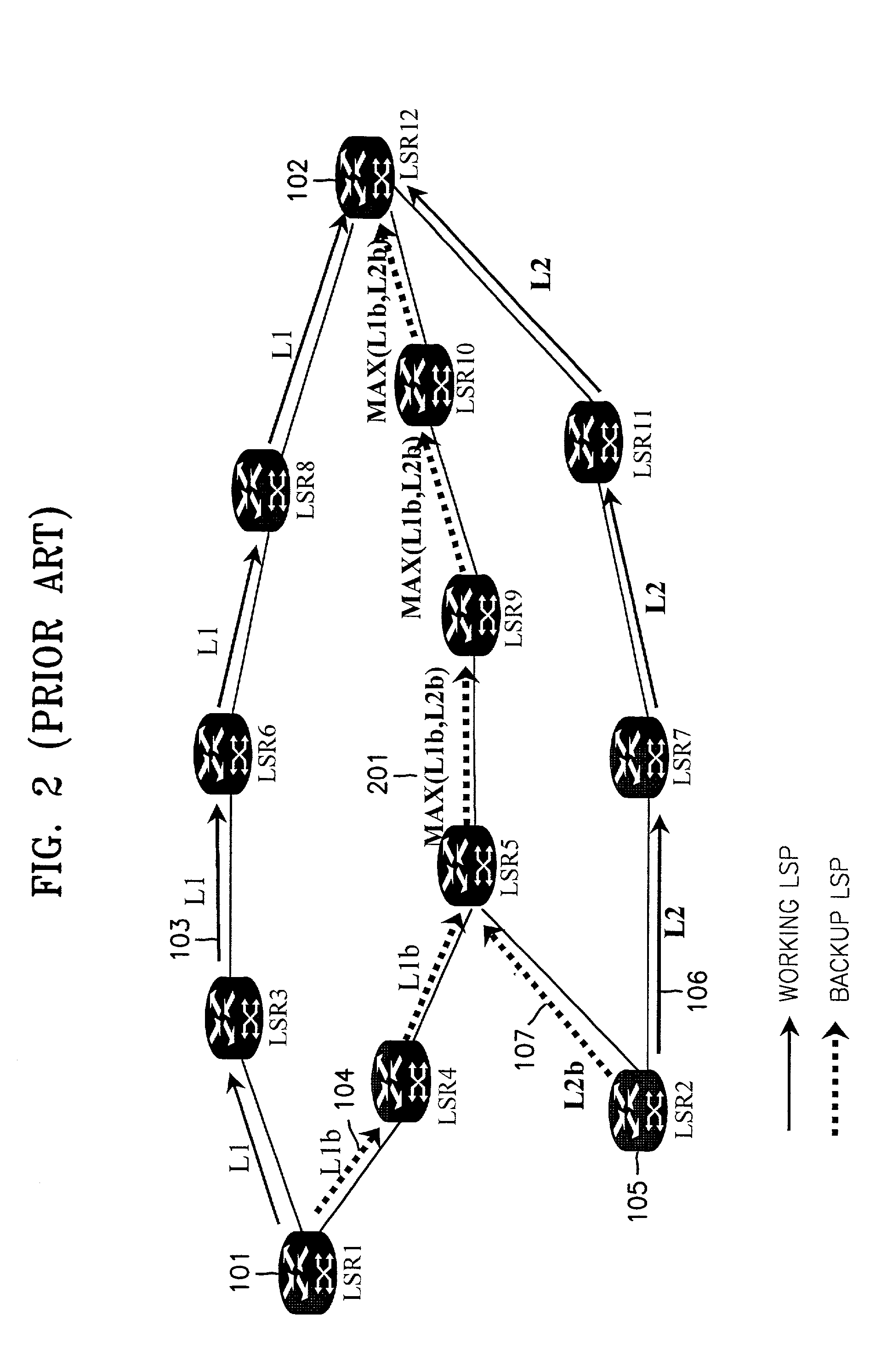
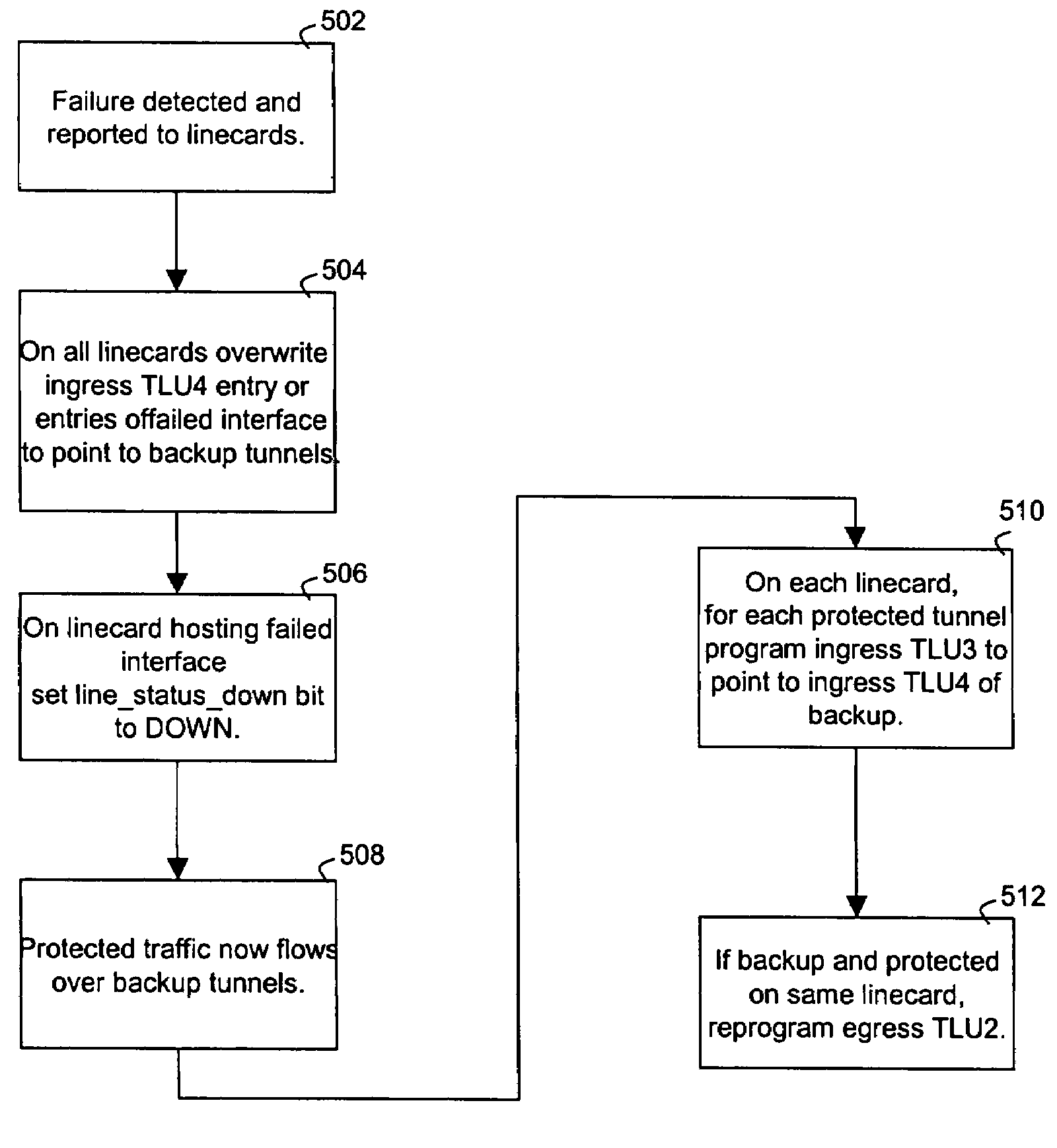
Scalable MPLS fast reroute switchover with reduced complexity
ActiveUS7370119B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationForwarding equivalence classDistributed computing
A Fast Reroute implementation suitable for use in a label switched router. Reroute from protected tunnels to backup tunnels may be achieved in constant time irrespective of the numbers of protected forwarding equivalence classes and protected tunnels.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Message processing method and label switching router
ActiveCN104980350AEasy maintenanceEasy to manageNetworks interconnectionMulti protocolMessage processing
The present invention provides a message processing method and a label switching router, so as to solve the problem that a current egress label switching router (LSR) can not learn about the LSRs passed by an IP message forwarded in a multi protocol label switching (MPLS) network. The method is applicable to the MPLS network of segment routing (SR) and includes the following steps: an ingress LSR of a label switching path (LSP) tunnel receives an interior gateway protocol (IGP) based notification message transmitted by an egress LSR of the LSP tunnel, wherein the notification message is used to notify the ingress LSR that the egress LSR has the capability of identifying a label history stack; after the notification message is received, an MPLS label stack is inserted into the IP message which enters into the LSP tunnel and an MPLS message is created, wherein, from the top to the bottom of the stack, the MPLS label stack includes: multiple segments, a label history identifier and a label history stack, wherein multiple segments are used to identify the LSRs passed in turn when the MPLS message is forwarded in the LSP tunnel, the label history identifier is used to identify the label history stack included in the MPLS message, and the label history stack includes multiple segments; the MPLS message is transmitted to the egress LSR through the LSP tunnel.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Label exchange route setting method, system and equipment of virtual special network channel
ActiveCN101090355AImprove build speedGuaranteed forwarding performanceNetworks interconnectionIp addressMPLS VPN
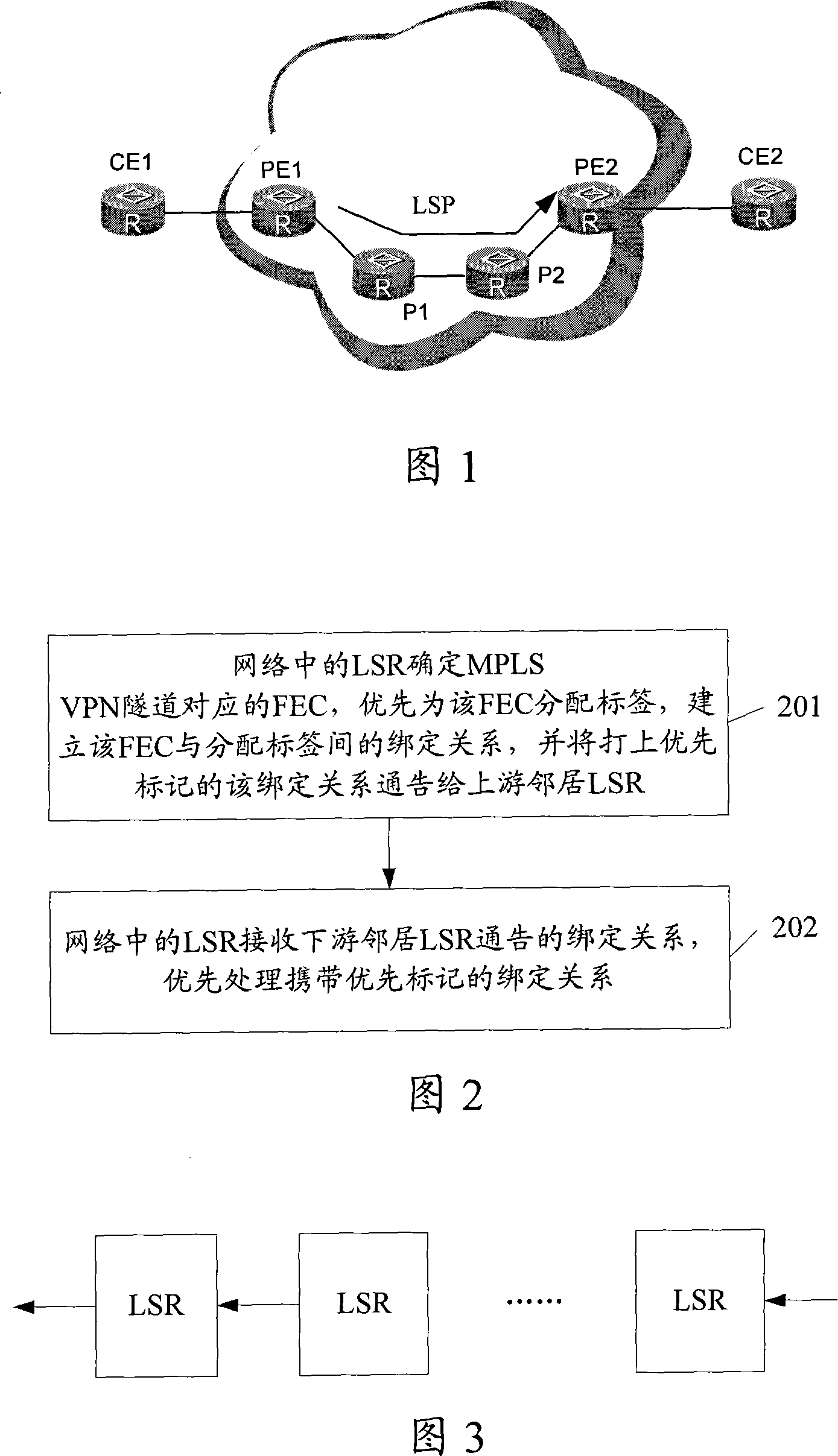
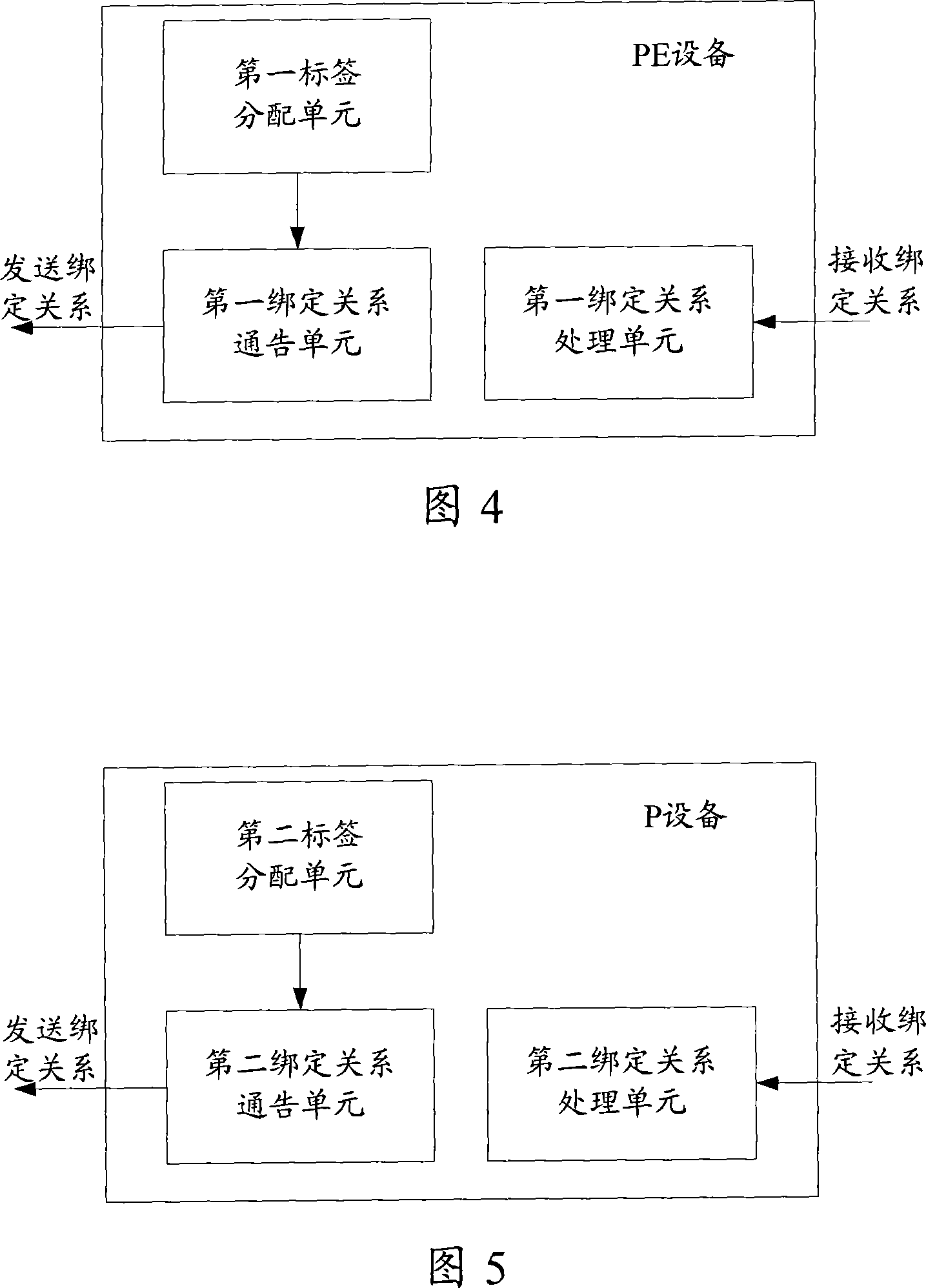
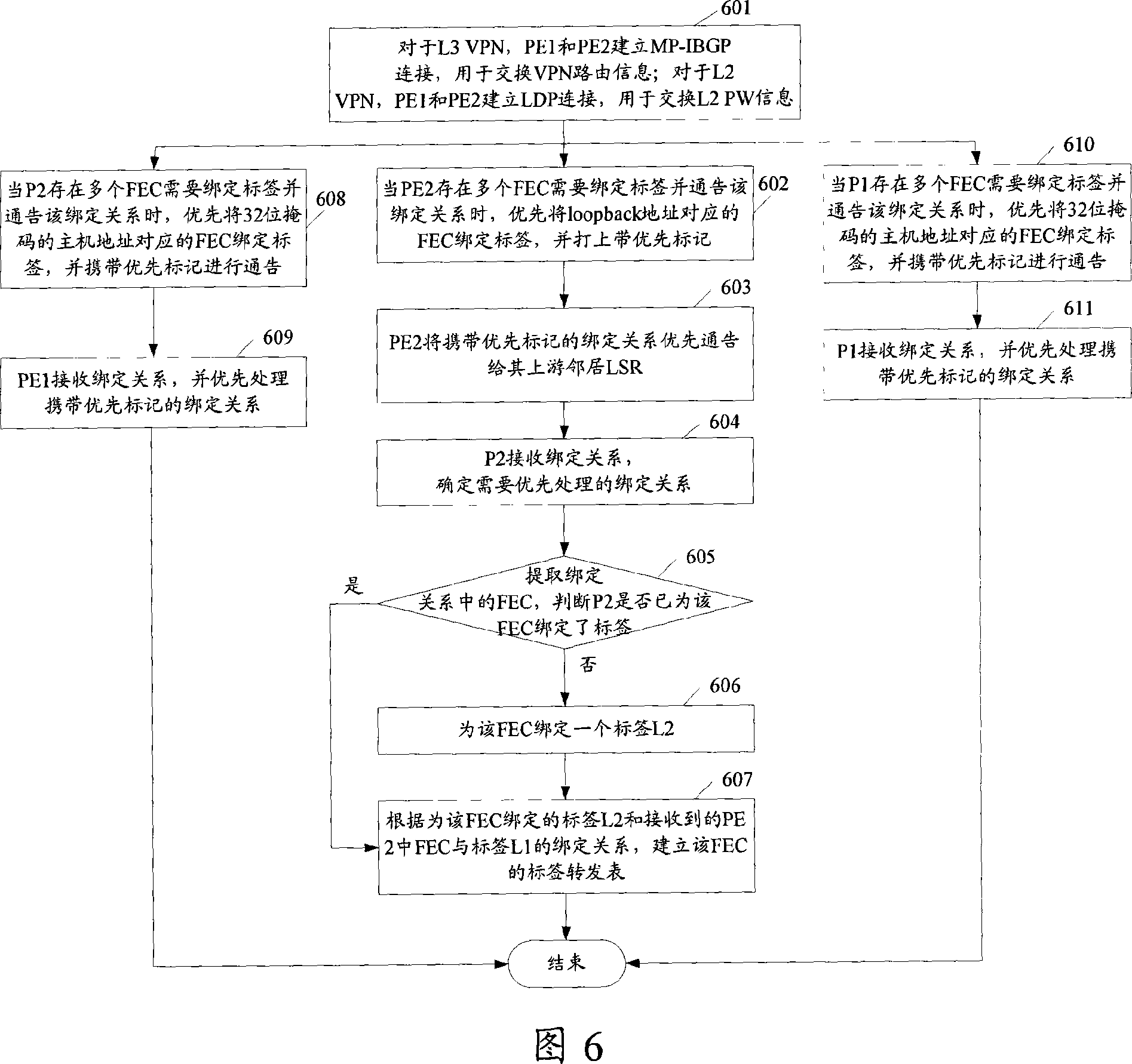
This invention discloses a method for setting up label switch path of MIPLS VPN tunnel including: a label switch router LSR in a network determines the forward equivalence FEC corresponding to the destination IP address of the MPLS VPN tunnel to distribute label to it firstly and set up a binding relation between the FEC and the distributed label and notifies the binding relation with the prior label to its upper reach LSR, which receives the binding relation notified by the lower reach LSR to process the binding relation with the prior label priorly. This invention also discloses a LSP set-up system and a device of the MPLS VPN tunnel.
Owner:XINHUASAN INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Distributed multi-protocol label switching router and managing labels therein
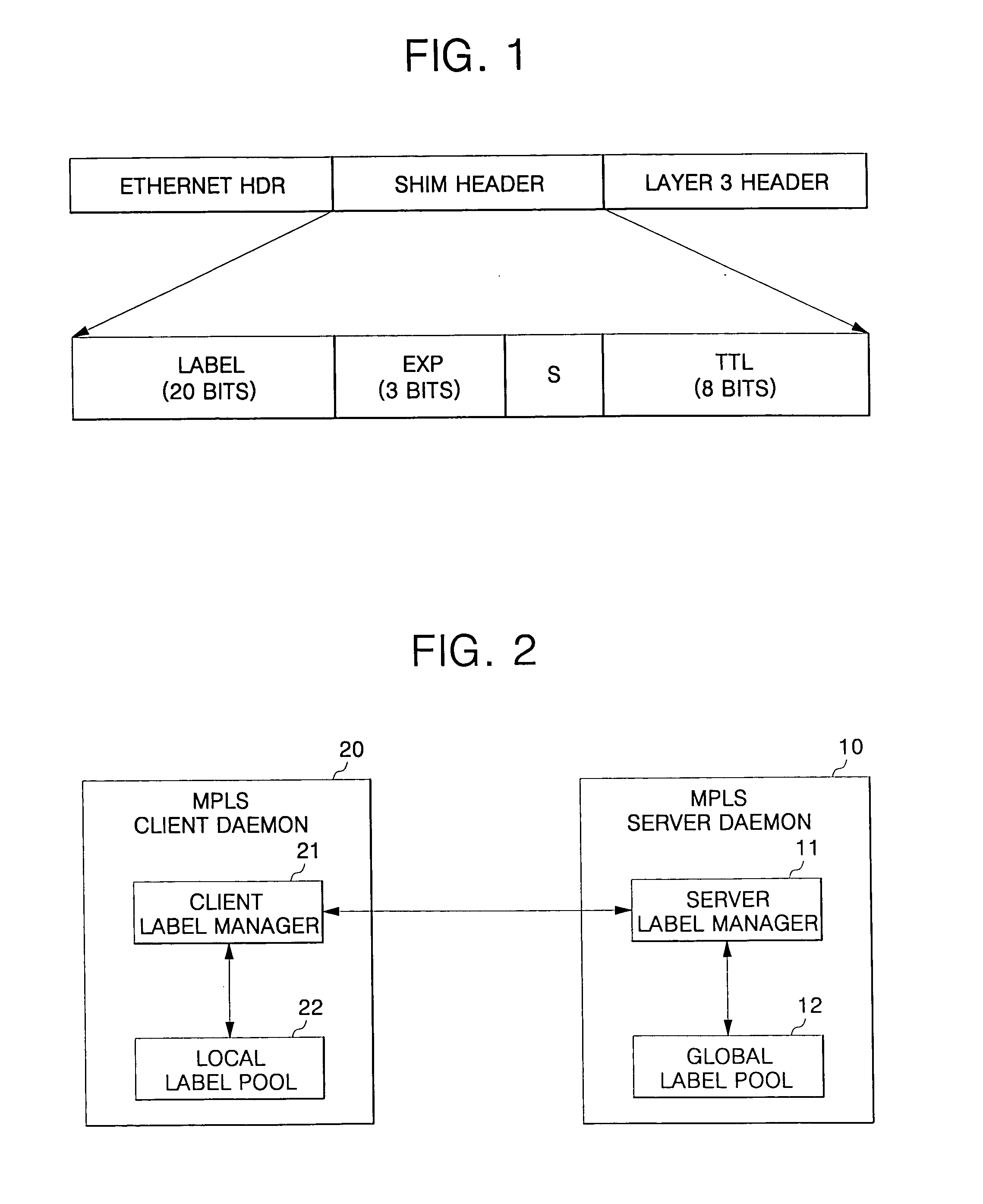
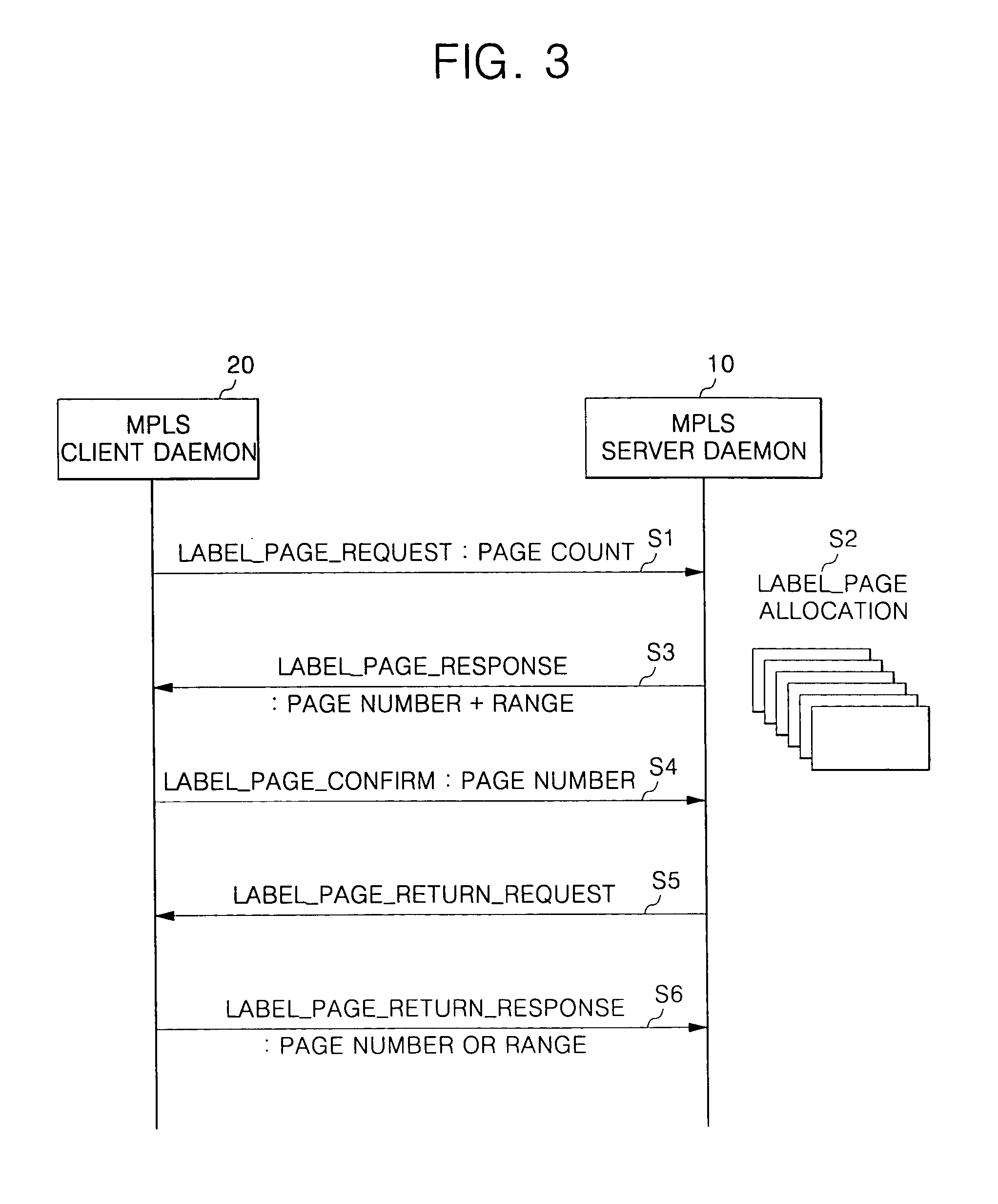
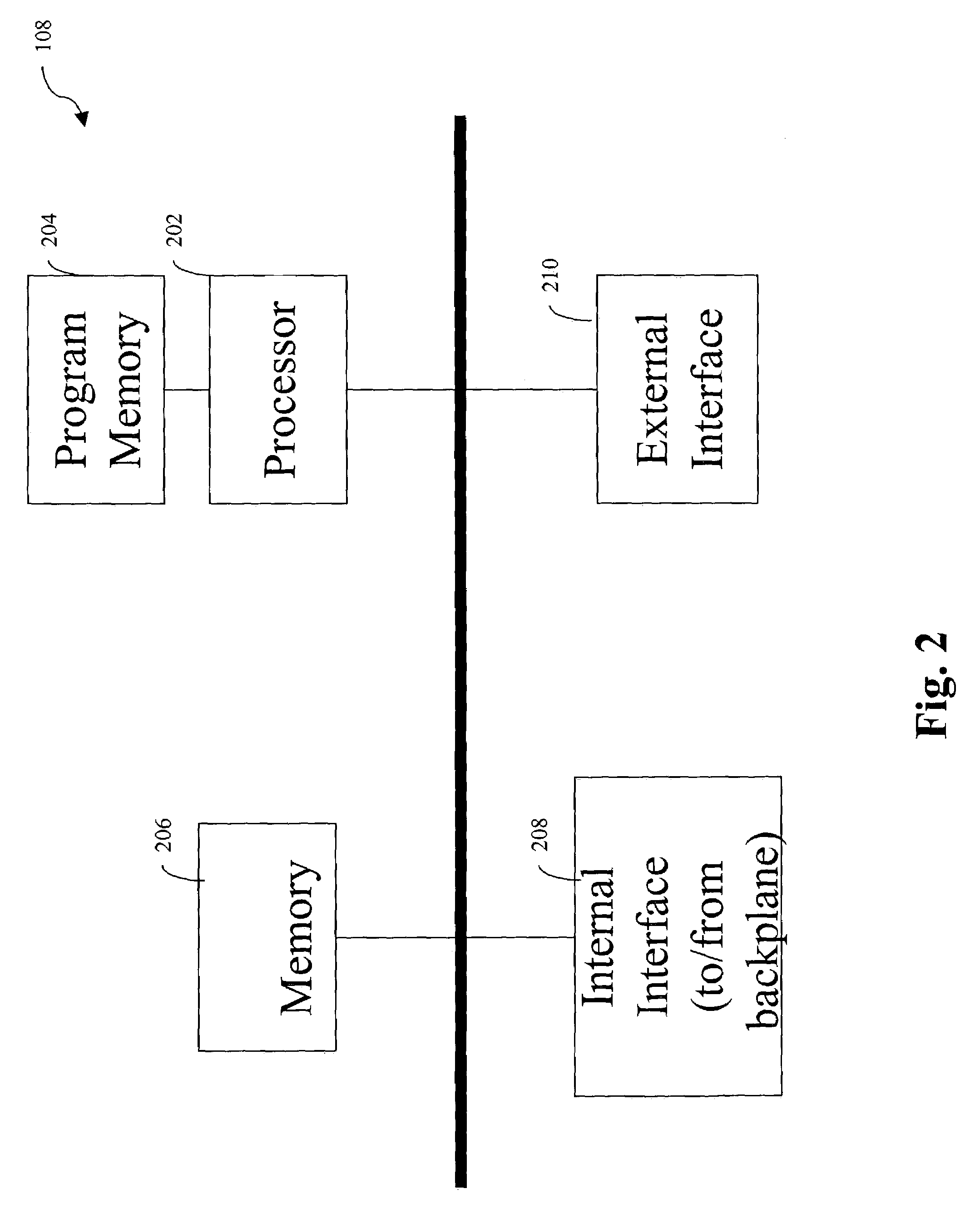
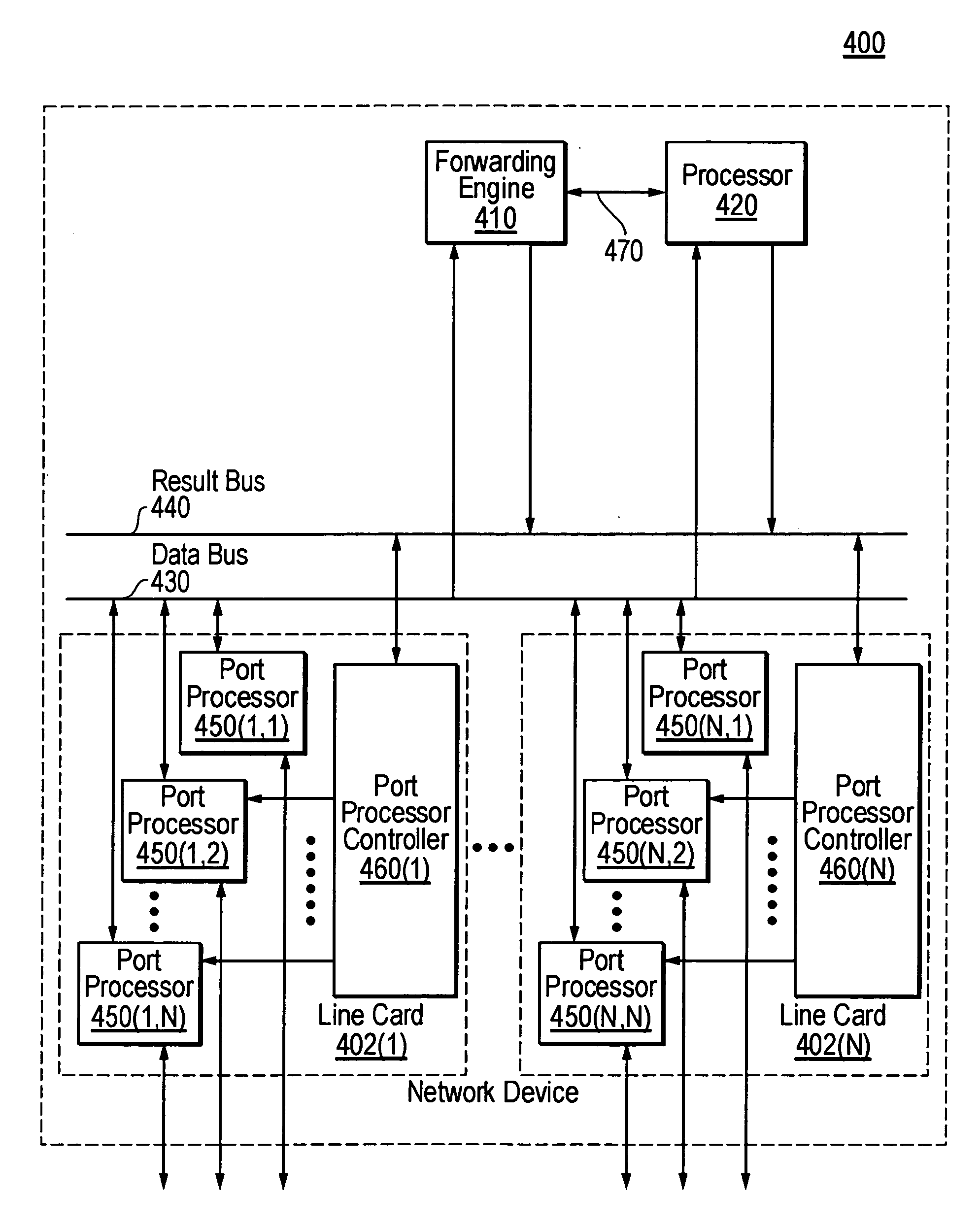
InactiveUS20050198375A1Efficient managementDoor/window protective devicesDigital computer detailsLine cardMulti protocol
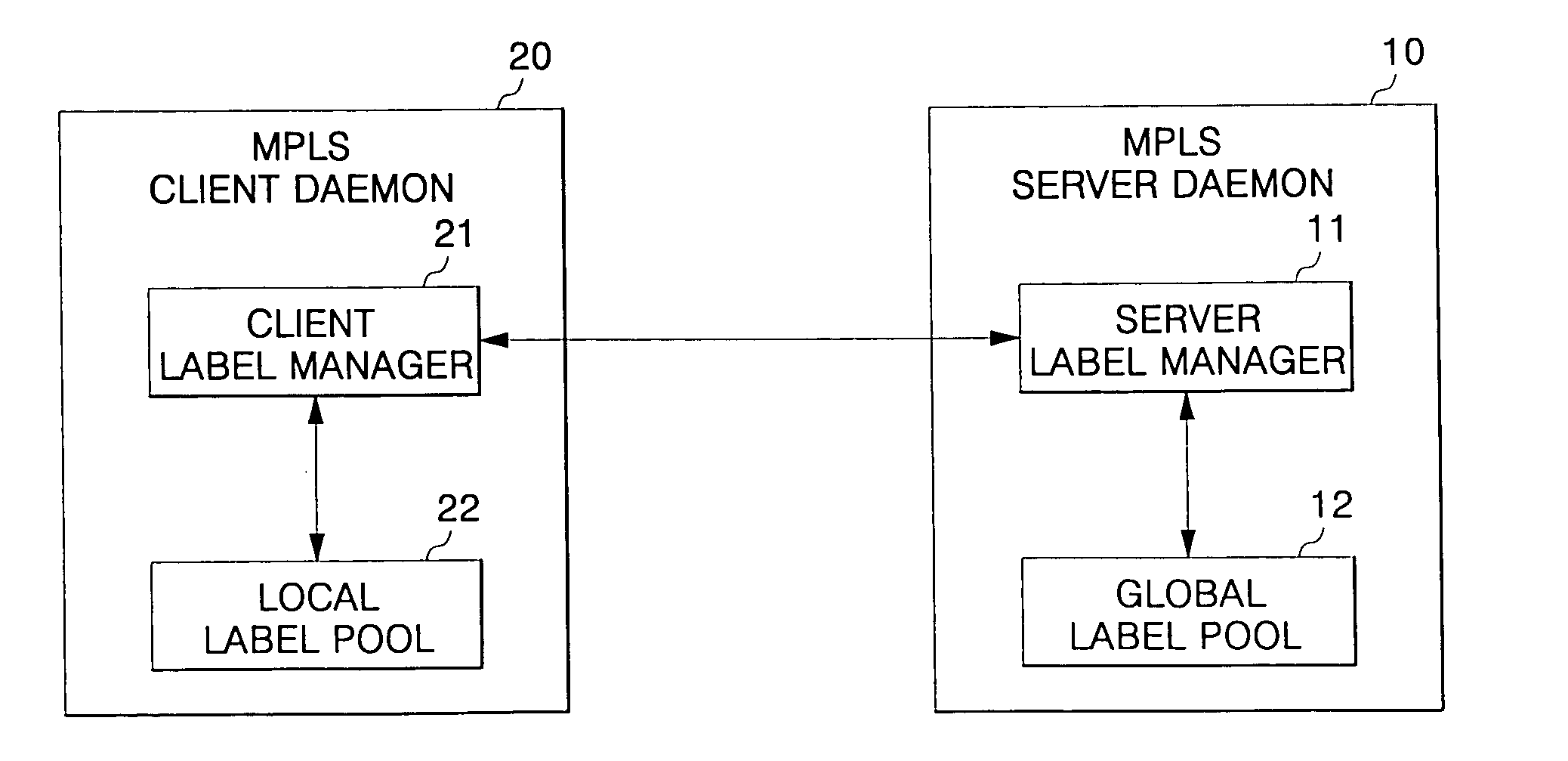
A distributed multi-protocol label switching router determines whether at least one extra label exists in a local label pool having information on allocated labels stored therein and requests allocation of the labels in preset units in a switching control card in response to a determination that no extra labels exists in response to a label allocation request to establish at least one label switched path in a subscriber line card. The labels are allocated at a label pool have information on all labels capable of being allocated in a distributed multi-protocol label switching router stored in preset units therein in response to the label allocation request of the subscriber line card in the switching control card, and the information of the allocated labels is transmitted to the subscriber line card. A label pool in the subscriber line card is updated according to information of the allocated labels transmitted from the switching control card, and the labels are allocated in the updated label pool in response to the label allocation request in the subscriber line card.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
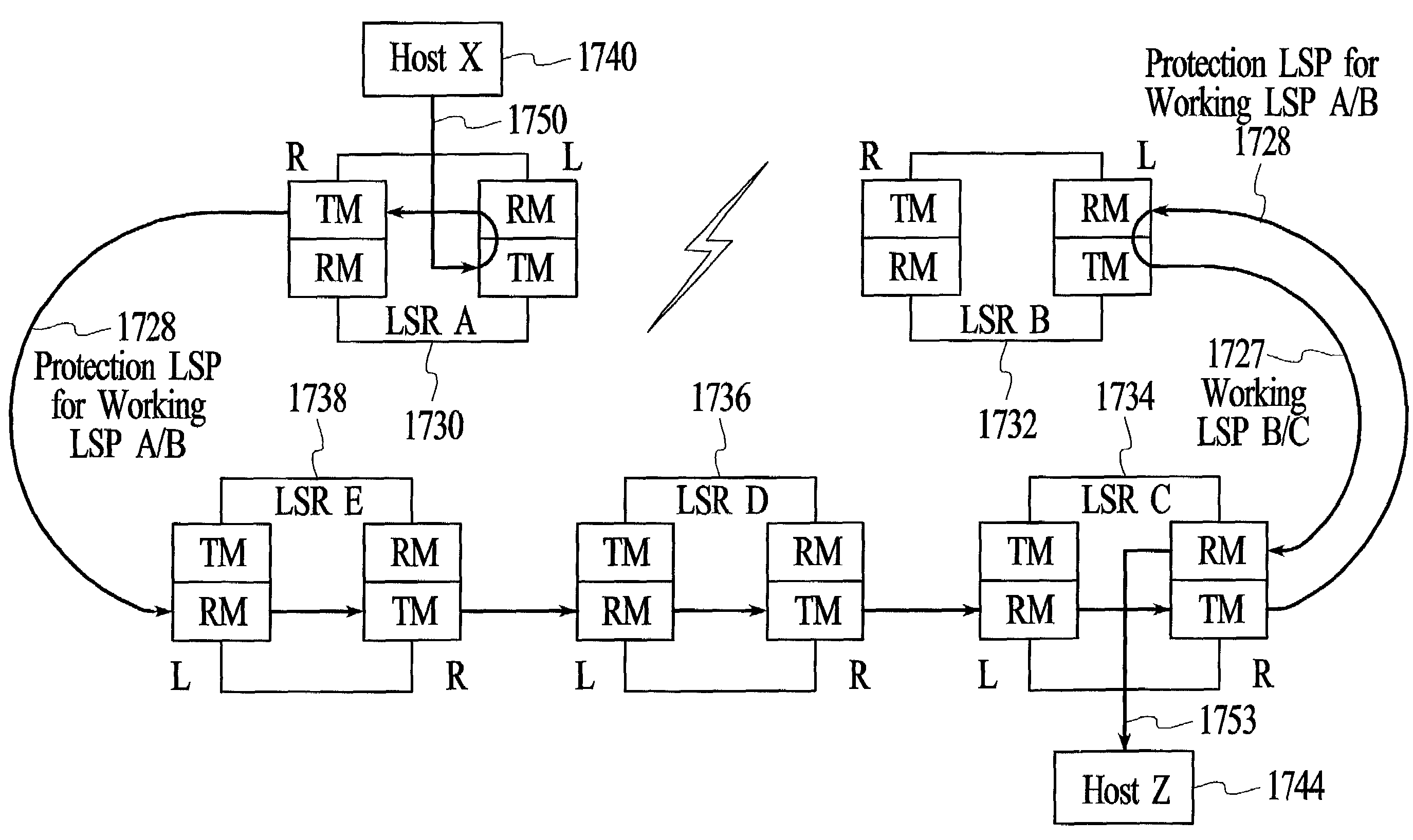
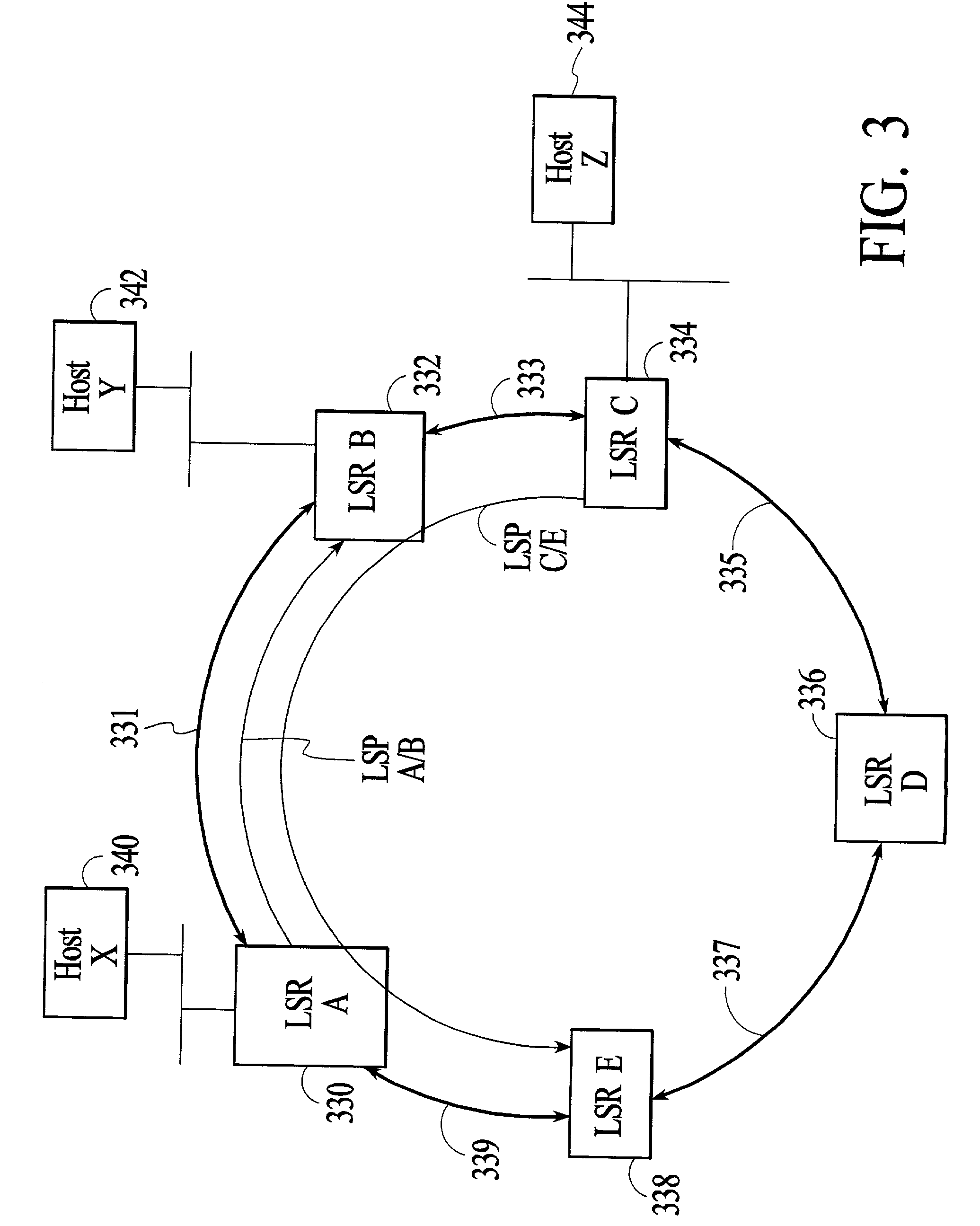
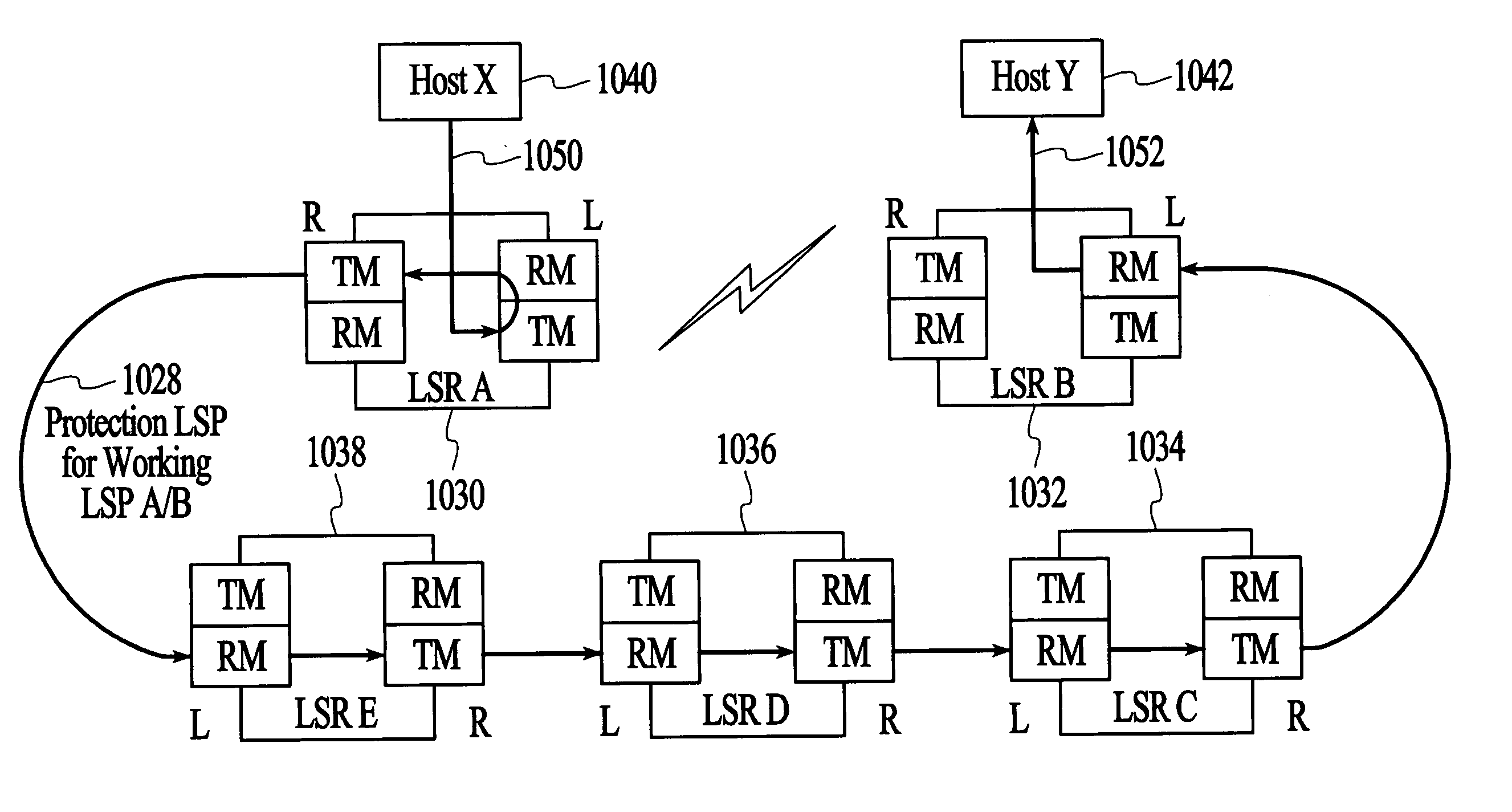
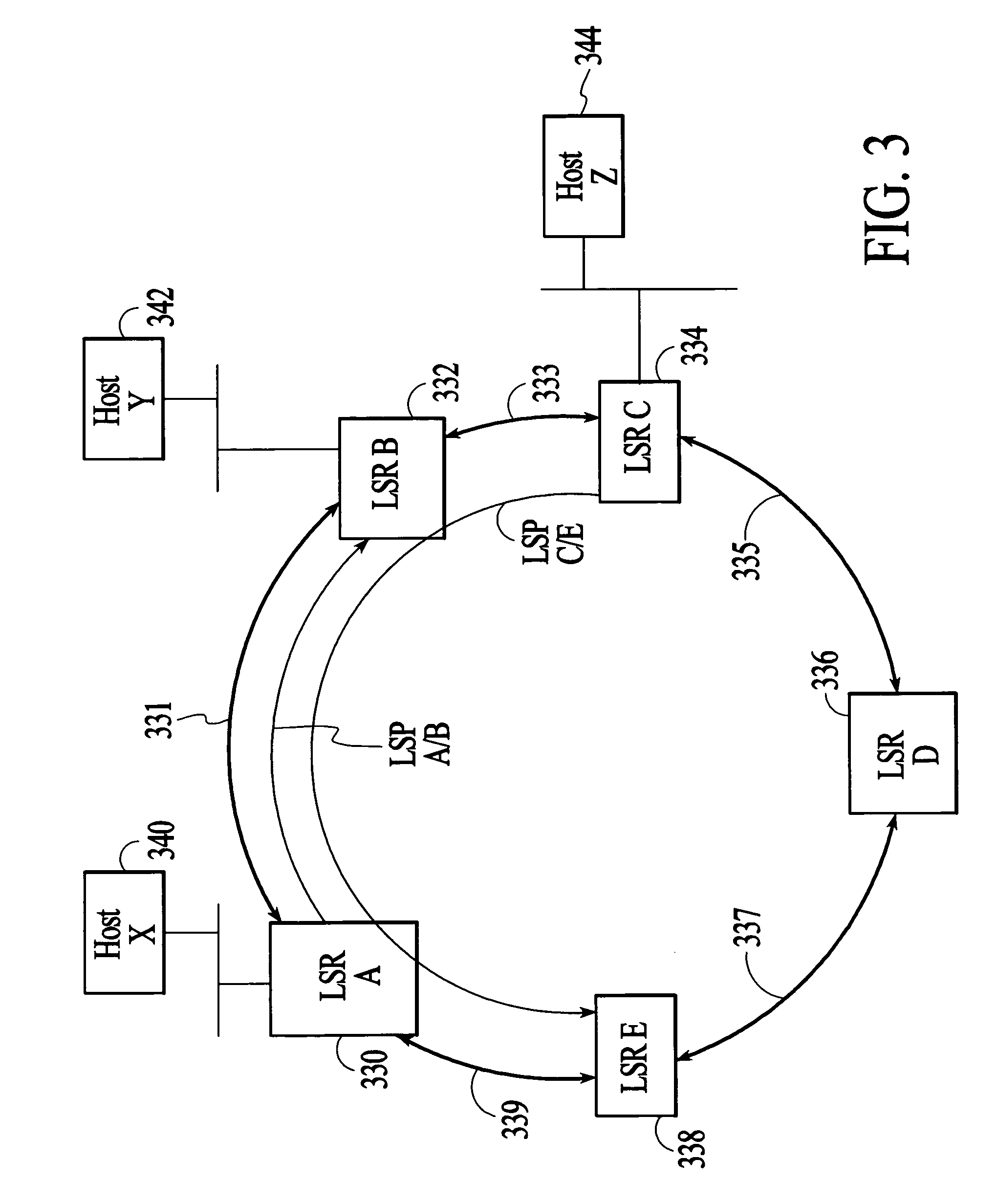
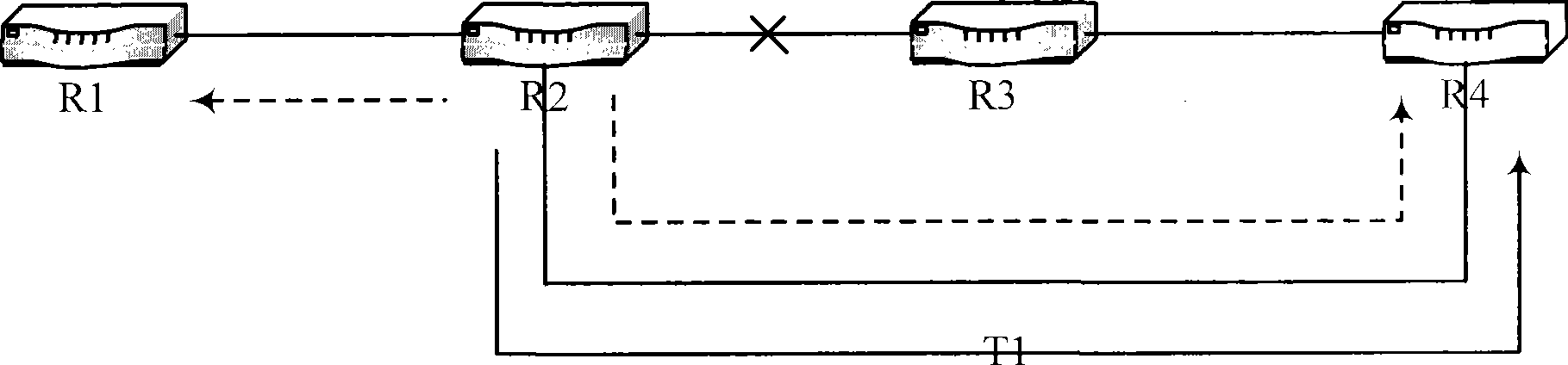
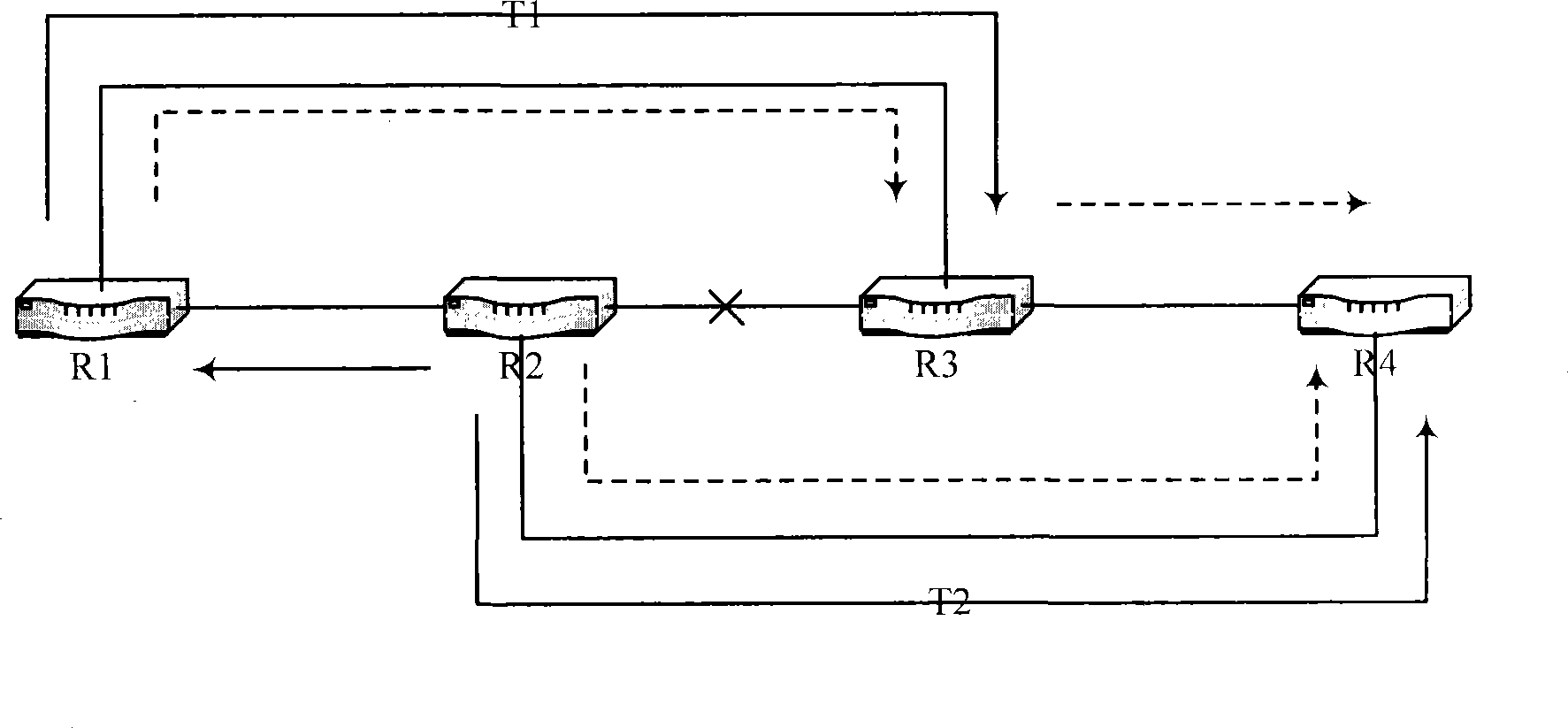
Method and system for providing failure protection in a ring network that utilizes label switching
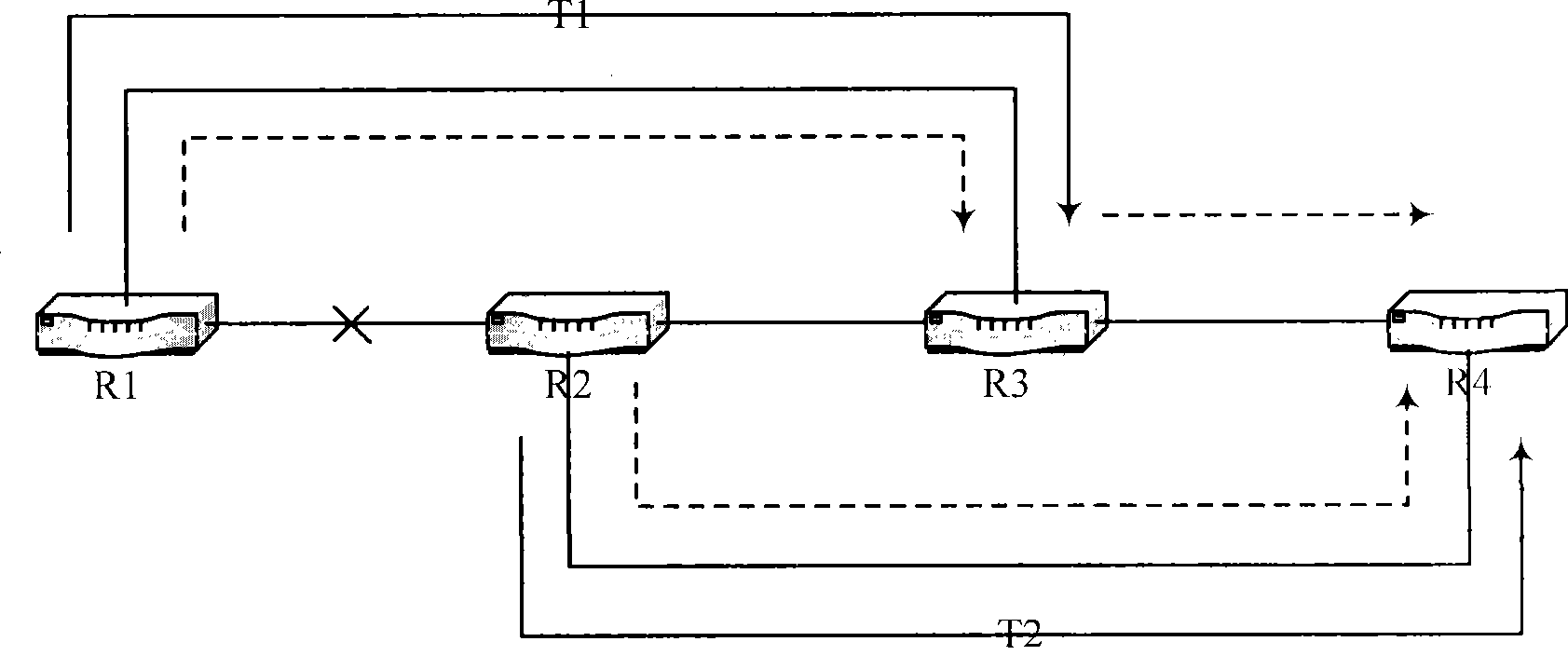
A working label switched path (LSP) between neighbor label switched routers (LSRs) in a ring network that utilizes label switching is protected by an LSP that connects the neighbor LSRs of the working LSP in an opposite direction to the working LSP. If the working LSP fails, then packets are switched to the protection LSP. Switched packets traverse the protection LSP until they reach the neighbor LSR that they would have reached had the packets traversed the working LSP. Time-to-live (TTL) values of packets that traverse the protection LSP are adjusted to account for the number of hops on the protection LSP so that the TTL values of the packets are the same after traversing the protection LSP as they would have been had they traversed the working LSP. After traversing the protection LSP packets can be switched back to the working LSP or switched to a next hop LSP.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
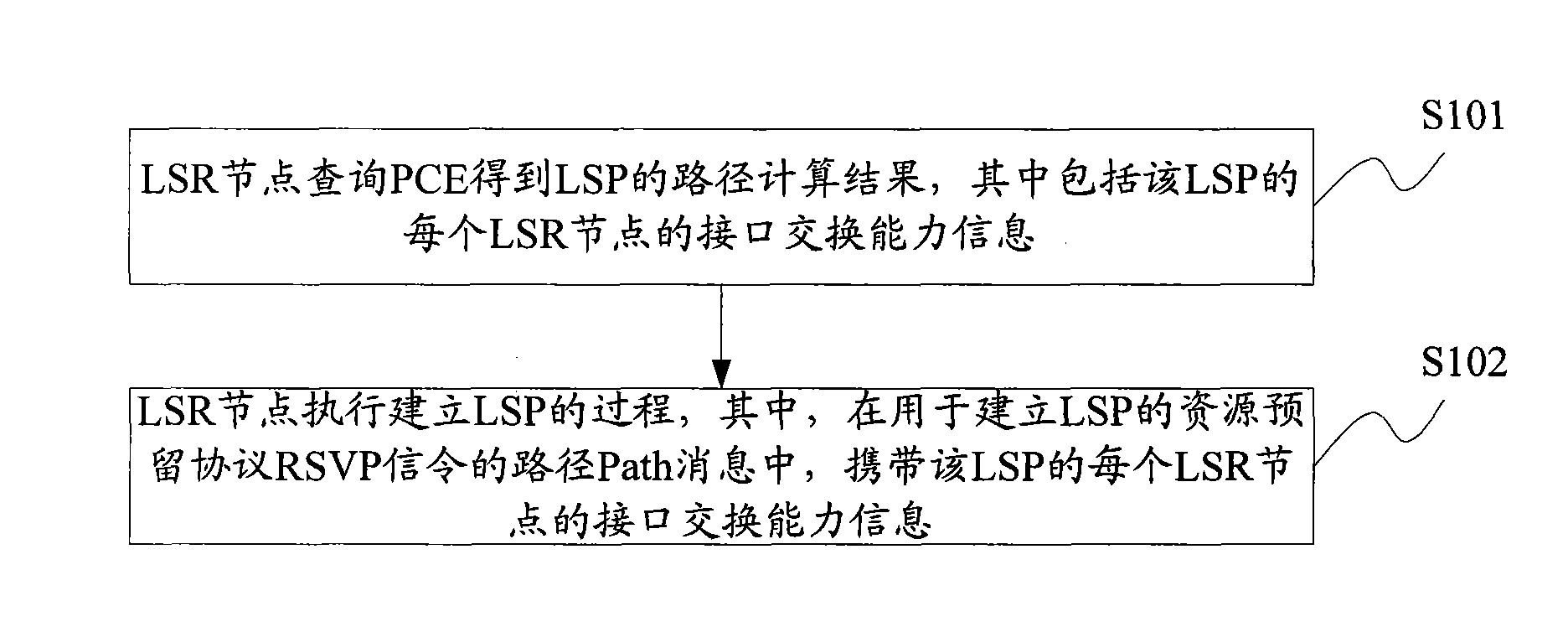
Method, system and device for establishing label switch path
ActiveCN101945048ARealize judgmentRealize automatic triggerData switching networksComputer scienceResource Reservation Protocol
The invention discloses a method, a system and a device for establishing a label switch path (LSP) for realizing the judgment of an LSP boundary so as to automatically trigger the creation of a lower-level LSP. The method for establishing a label switch path (LSP) comprises the following steps: label switch router (LSR) nodes acquire LSP path computation results obtained by inquiring a path computing element (PCE), wherein the path computation result includes interface switching capability information of each LSR node of the LSP; and the LSR nodes execute a process of establishing the LSP, wherein the interface switching capability information of each LSR node of the LSP is carried by a Path message of a path for establishing the resource reservation protocol (RSVP) signaling of the LSP.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and system for providing failure protection in a ring network that utilizes label switching
A working label switched path (LSP) between neighbor label switched routers (LSRs) in a ring network that utilizes label switching is protected by an LSP that connects the neighbor LSRs of the working LSP in an opposite direction to the working LSP. If the working LSP fails, then packets are switched to the protection LSP. Switched packets traverse the protection LSP until they reach the neighbor LSR that they would have reached had the packets traversed the working LSP. Time-to-live (TTL) values of packets that traverse the protection LSP are adjusted to account for the number of hops on the protection LSP so that the TTL values of the packets are the same after traversing the protection LSP as they would have been had they traversed the working LSP. After traversing the protection LSP packets can be switched back to the working LSP or switched to a next hop LSP.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
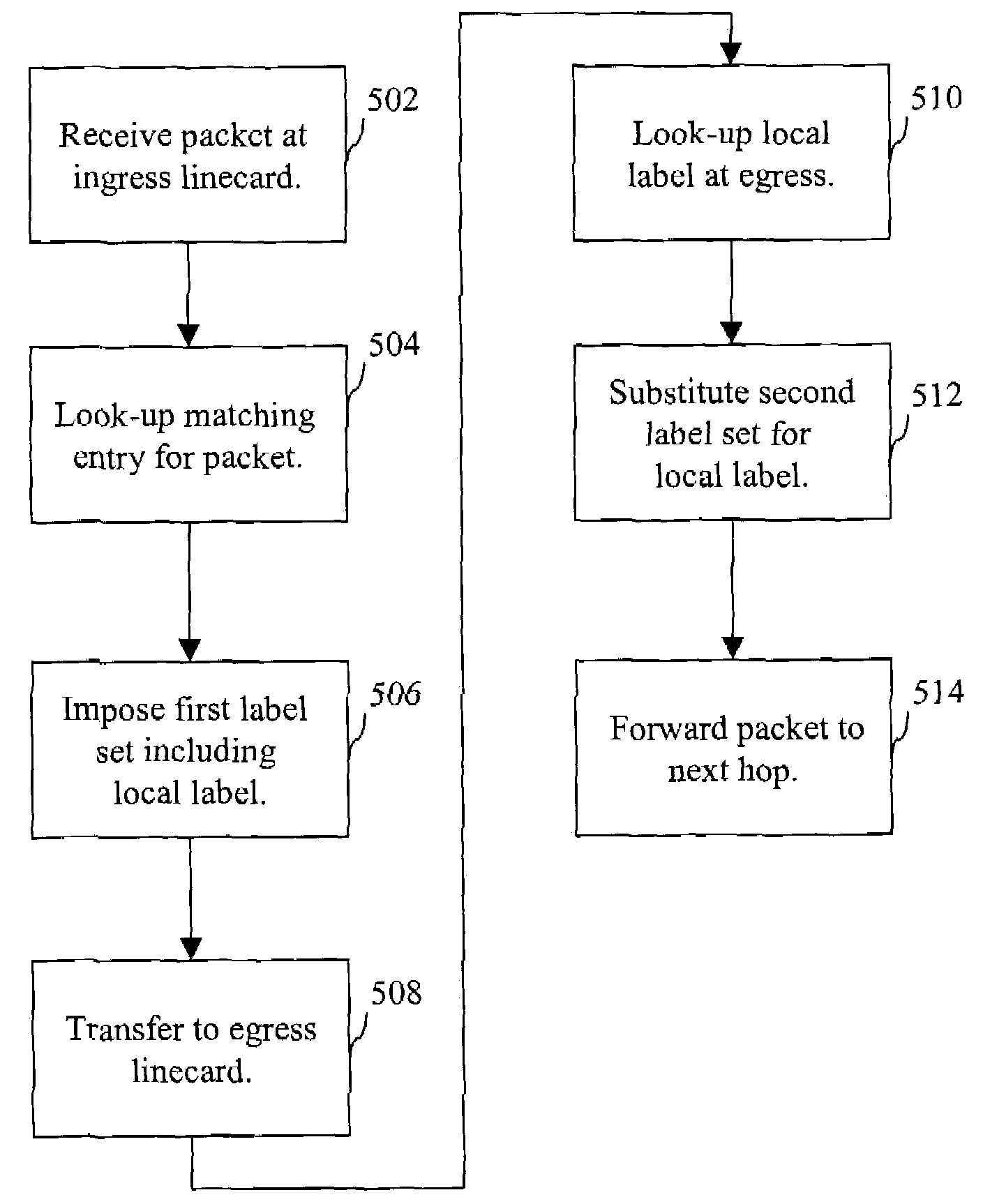
Distributed imposition of multi-level label stack using local label
ActiveUS7319699B1Improve scalabilityImprove performanceData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsComputer scienceLabel switch router
Improved scalability and performance for label switched routers are provided. Large numbers of interfaces may be readily accommodated. In one implementation, label imposition is divided between ingress and egress linecards so that the interface supporting a given service can be the one to impose any needed corresponding label.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Fast rerouting method and label exchange router
ActiveCN101431466ASolve the problem of handling simultaneous failuresImprove stabilityNetworks interconnectionTelecommunicationsMessage processing
The invention relates to a quick rerouting method in communication technology field and label switching router. The label switching router comprises: route message judging module, a first judging module, a second judging module and route message processing module. The route message processing module judges if the received message is received from bypass tunnel; if the received message is received from bypass tunnel, then judges if the protected tunnel passes head node of bypass tunnel employing the present node as fusion node, if the protected tunnel does not pass head node, then discards the route message or receives the route message; if the route message is received from ordinary route of non-bypass tunnel, then judges if the head node of bypass tunnel currently used is in route recording object of route message received from the ordinary route, if the head node is not in route recording object, then receives the route message or discards the route message received from the ordinary route. The invention effectively solves problem of adjacent double link failure under nesting protection through changing processing flow of node for route error message and route message.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
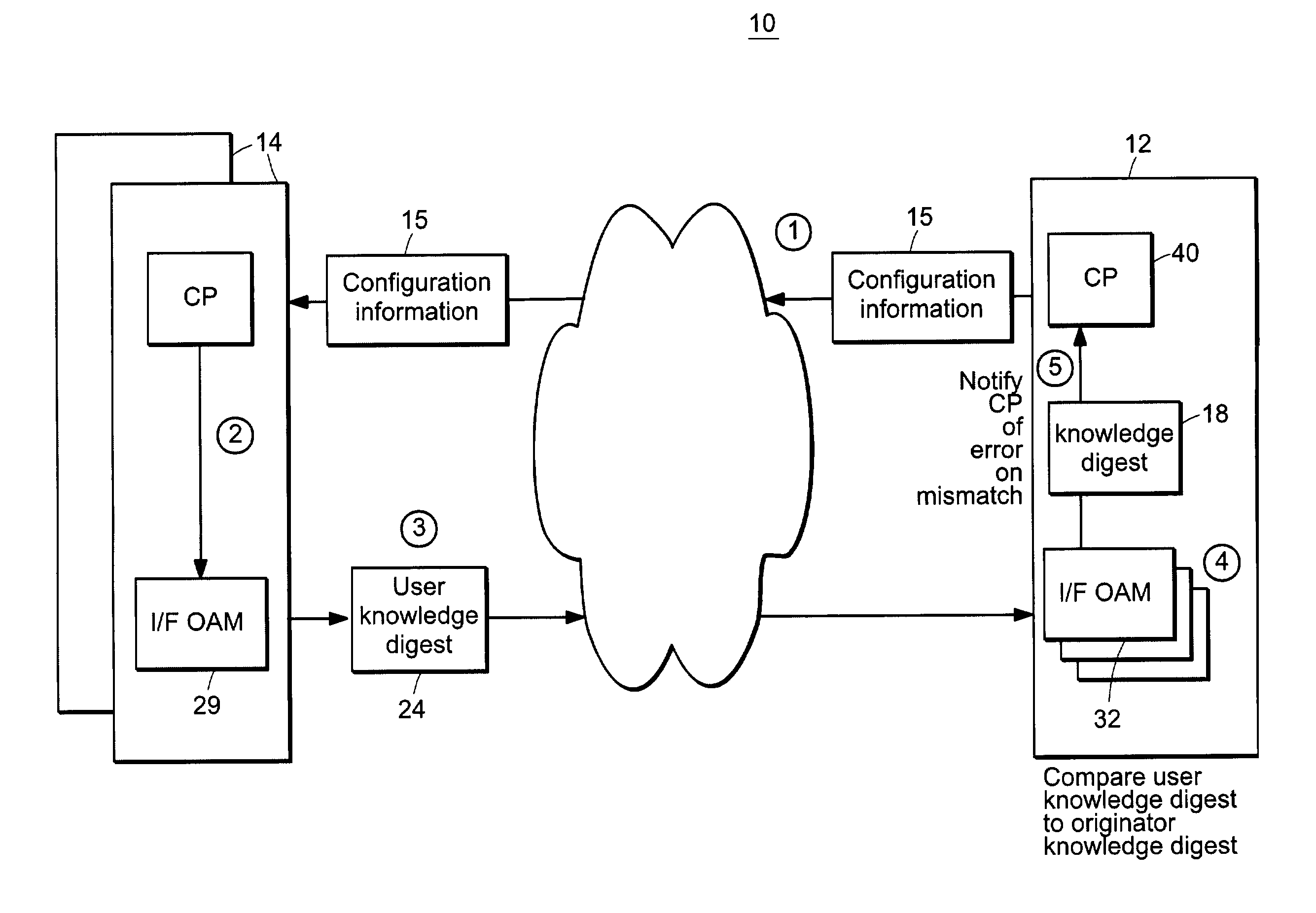
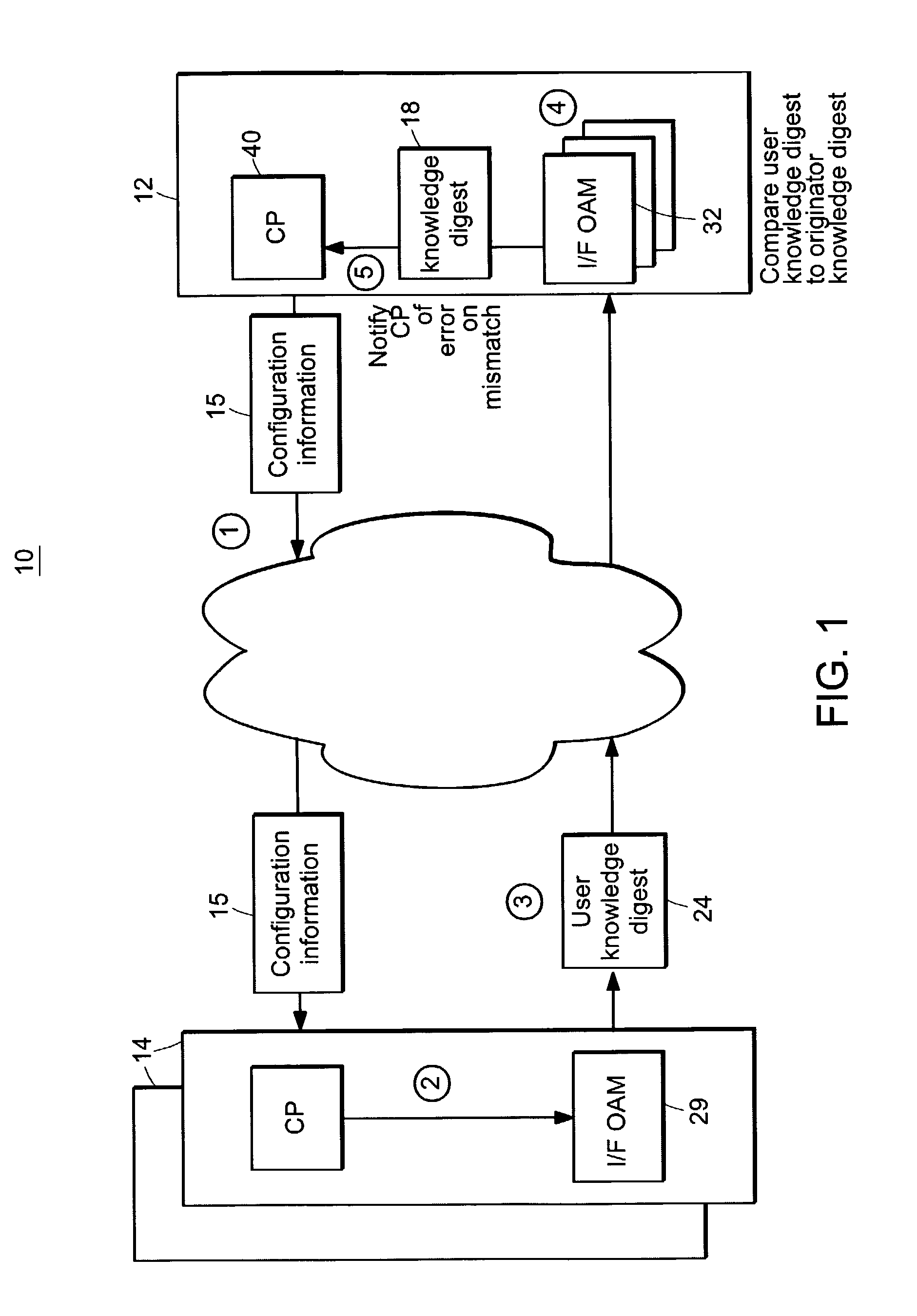
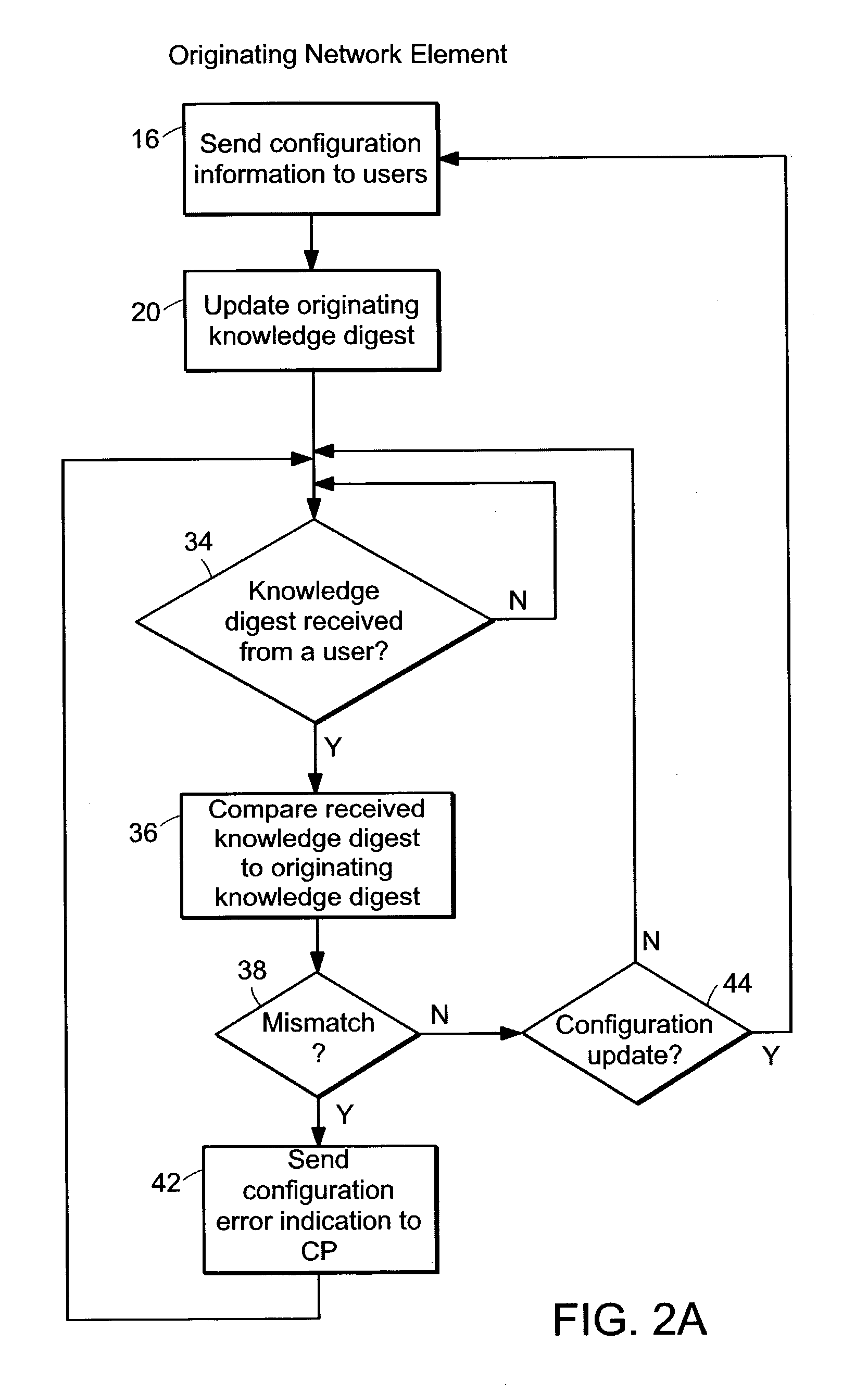
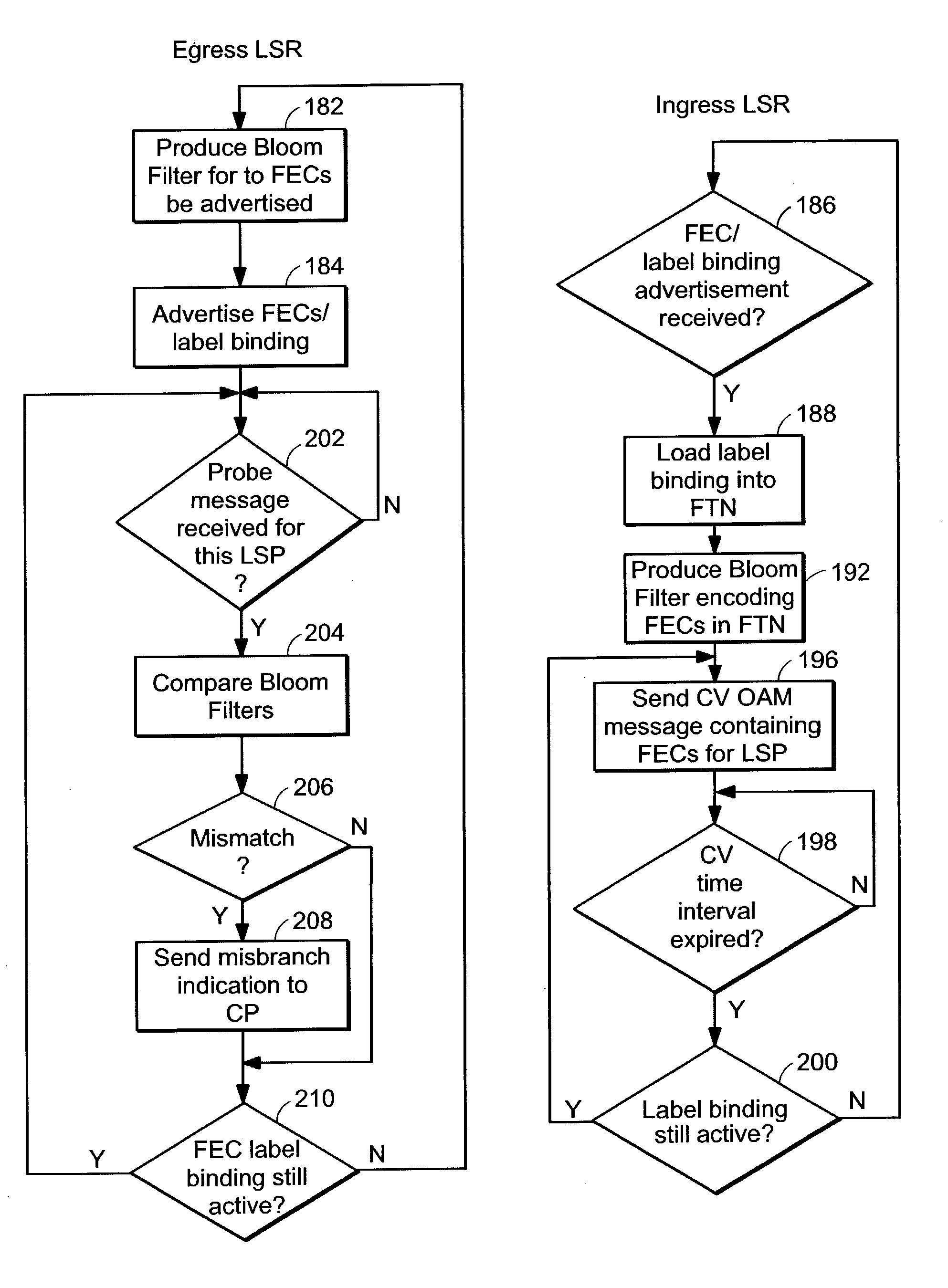
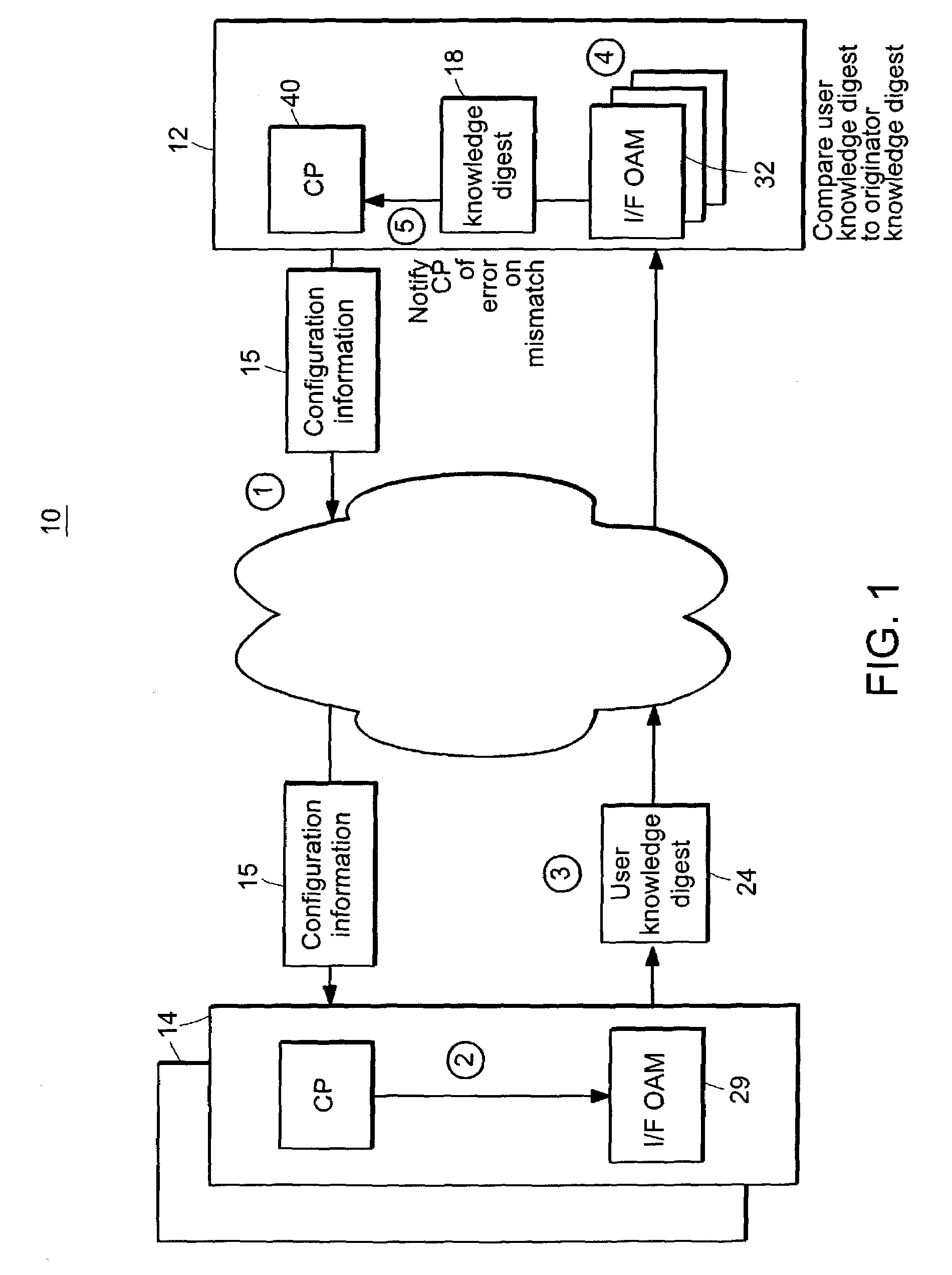
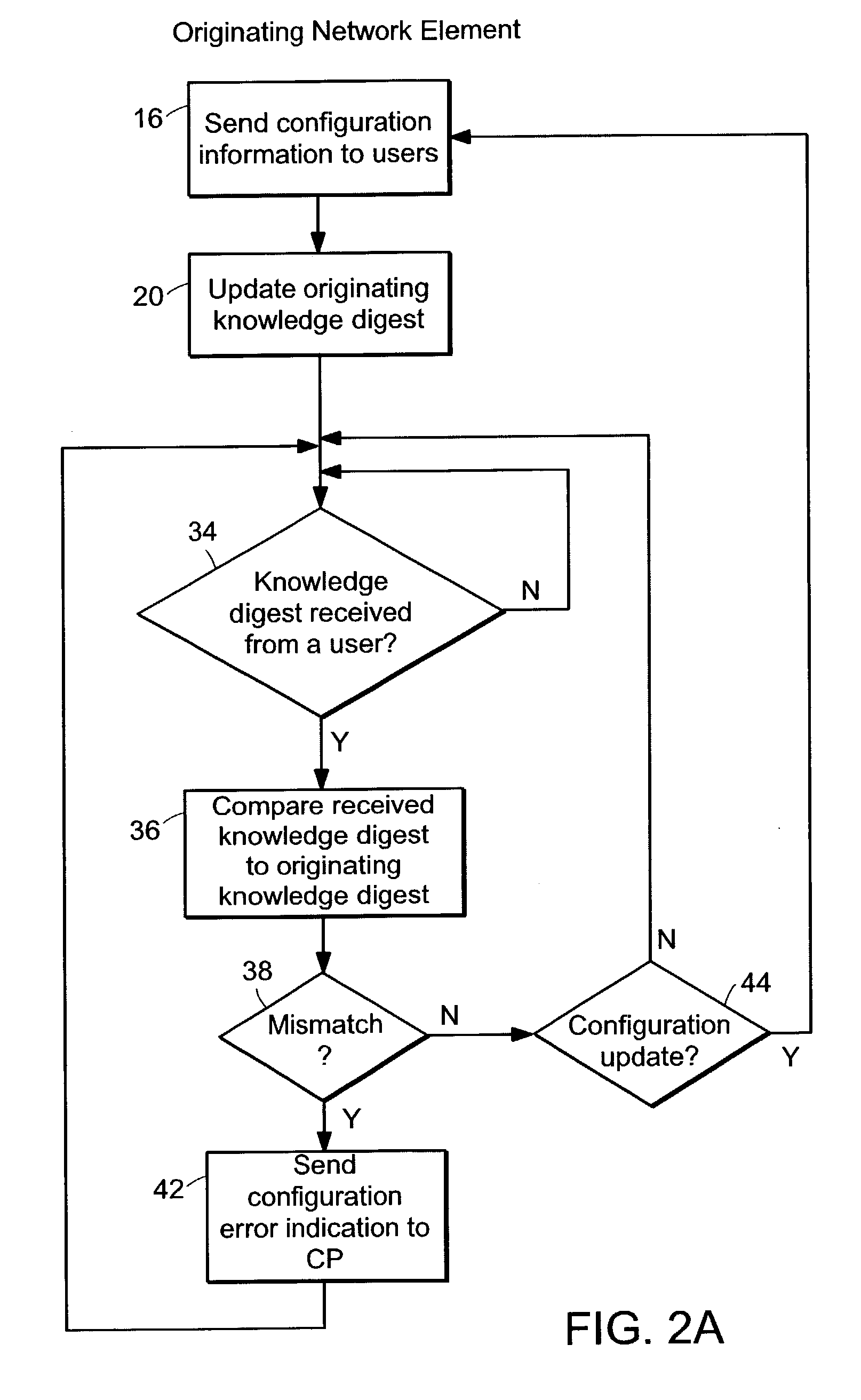
Connectivity assessment for label distribution protocol (LDP) networks
InactiveUS7680923B1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksBloom filterComputer science
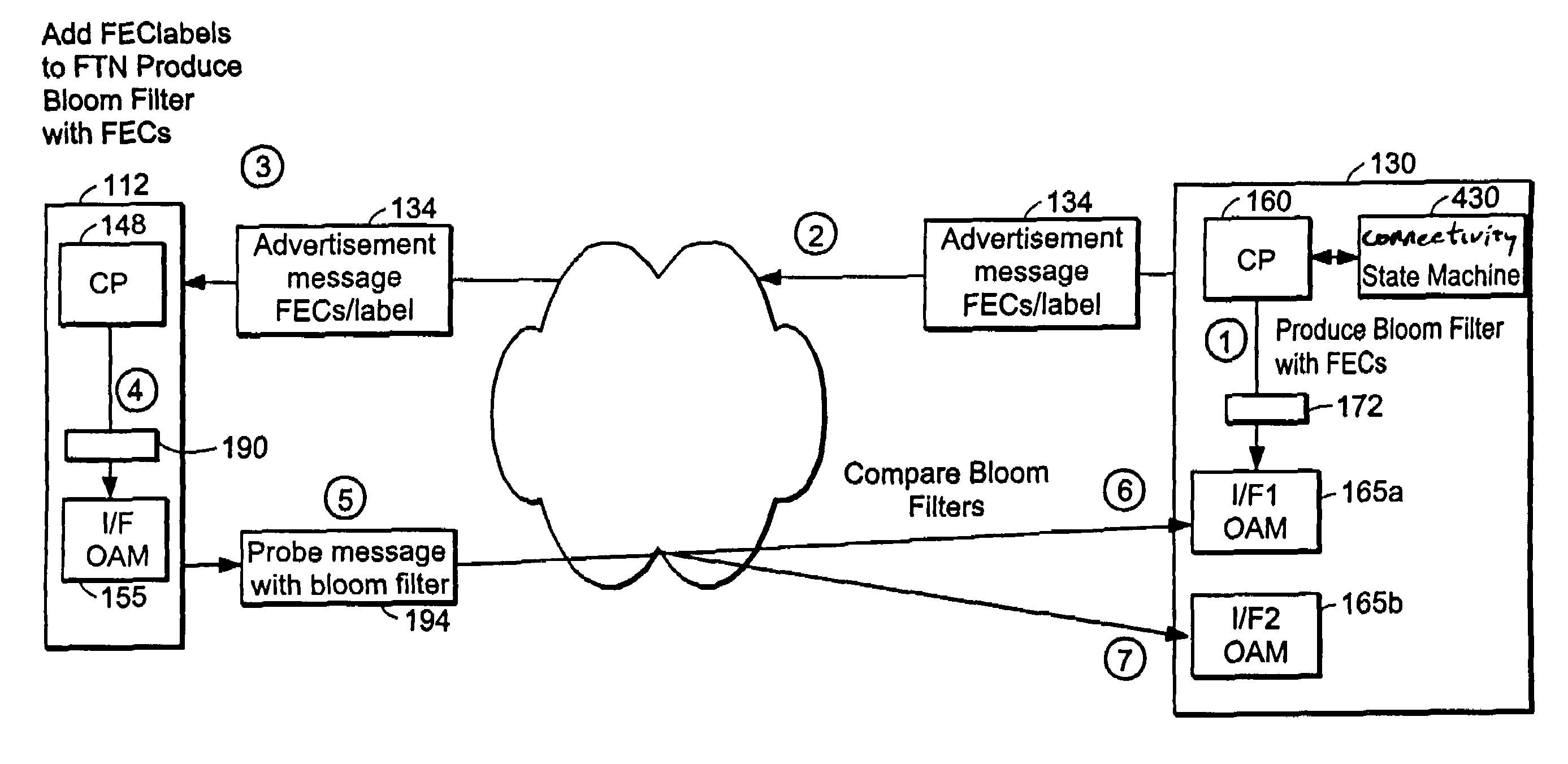
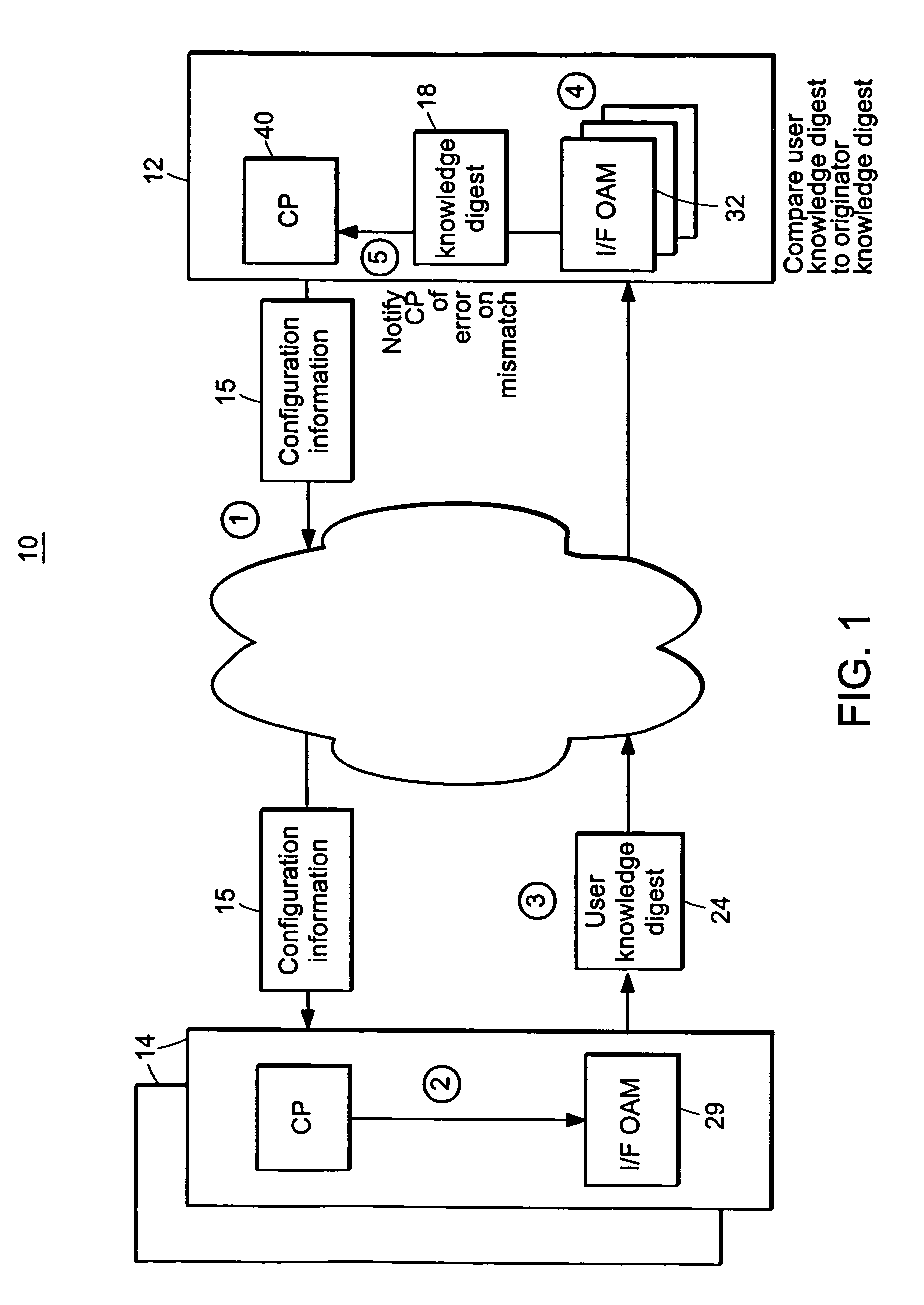
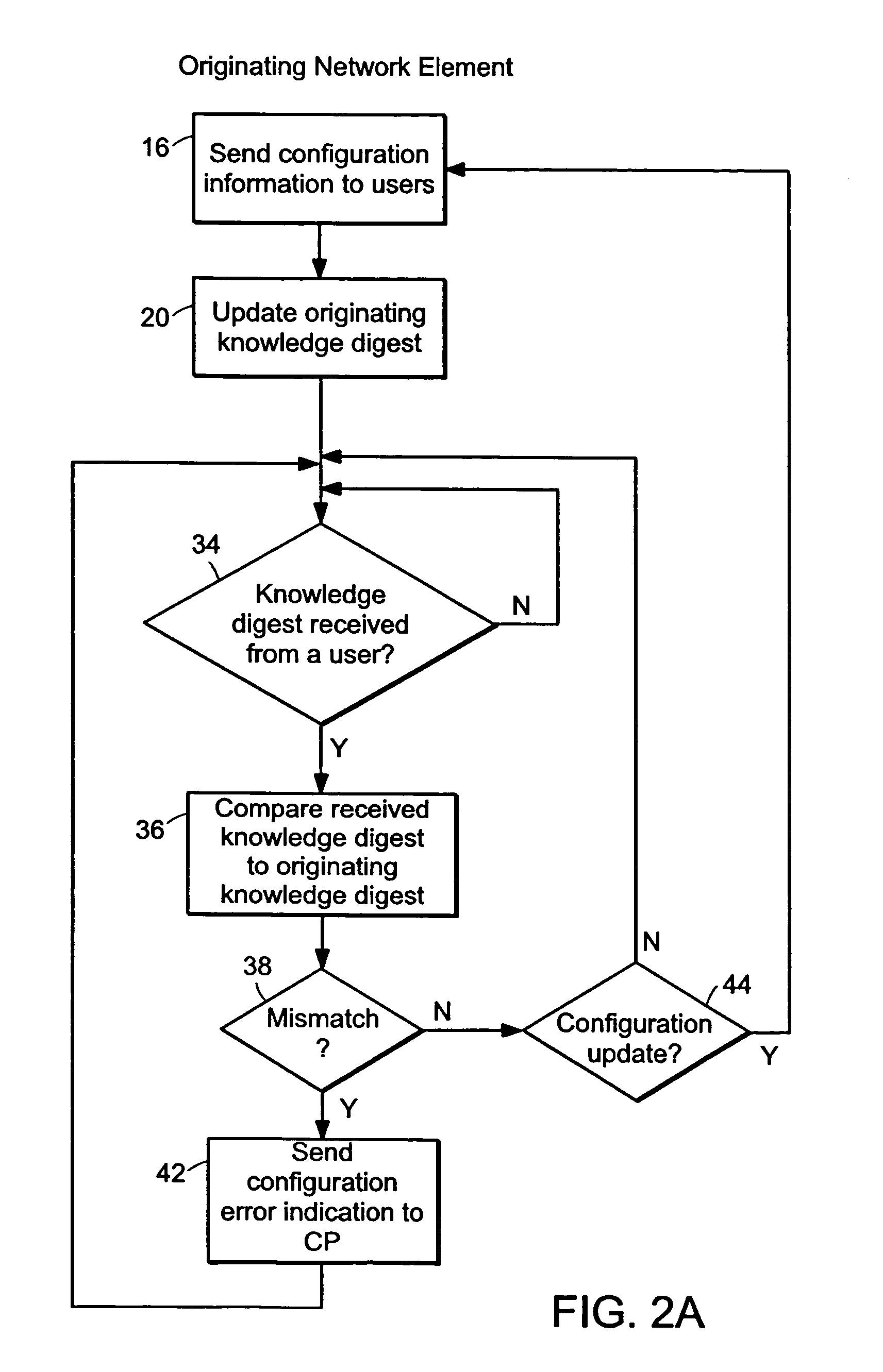
Probe and stop probe messages associated with an ingress access point are processed at an egress label switched router. The ingress access point may consist of an identifier of an ingress network element, in combination with a LSP identifier provided by the ingress network element. Auto-registration is performed upon receipt of a probe message indicating an ingress access point not currently being tracked. In the event that a probe message is received indicating an ingress access point not currently being tracked, the egress label switched router adds an entry to a tracking data structure, and a central processor is notified. Each entry within the tracking data structure stores information for a corresponding ingress access point, including knowledge digests from probe messages and an indication of the time a last previous probe message was received. As probe and stop probe messages are received, the knowledge digests they include are compared with the knowledge digests stored in the corresponding tracking table entries. In the event of a conflict between a received knowledge digest and a stored knowledge digest, a predetermined action is taken, such as generation of a misbranching alarm. The knowledge digests may, for example, be Bloom Filters. In the event a stop probe message is received for an ingress access point associated with one of the entries in the tracking table, the corresponding tracking entry is removed.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Label switching router
InactiveUS6895008B2Reduce processData switching by path configurationComputer scienceLabel switch router
In a label switching router placed at one end of an LSP set by using CRLDP, a bidirectional LSP setup TLV preparing portion prepares a bidirectional LSP setup TLV included in a bidirectional setup label request message transmitted in an up direction to a label switching router placed at the other end of the LSP. Based on an external bidirectional LSP setup request accepted by a bidirectional LSP setup accepting portion, a bidirectional LSP setup TLV analyzer analyzes the bidirectional LSP setup TLV in the message. When the message is received from the label switching router at the other end, a bidirectional LSP processor performs an LSP setup request in a down direction as opposed to the up direction. Based on the analyzed result by the bidirectional LSP setup TLV analyzer, and an explicit route preparing portion prepares an explicit route on which a router to be relayed in the down direction is prescribed. Based on an explicit route preparing request from the bidirectional LSP processor, explicit route preparing portion notifies the prepared route to the bidirectional LSP processor.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Automation fallback to P2P LSPs for mLDP built multipoint-trees
ActiveUS20070217428A1Special service provision for substationData switching by path configurationCore routerComputer science
A method of using a point-to-point (P2P) label switched path (LSP) to transmit multicast data packets partially through a multiprotocol label switched (MPLS) network when one or more label switched routers (LSRs) of the MPLS are not multicast label distribution protocol (mLDP) enabled. The P2P LSP can be used to transmit multicast data packets to the head end of a point-to-multipoint (P2MP) LSP created with mLDP enabled LSRs. The P2MP LSP can be used to transmit the multicast data packets through the MPLS network to intended receivers that are external to the MPLS network. When configuring the P2MP LSP, an mLDP enabled LSR receives a first message from a non-mLDP enabled MPLS core router in response to sending a label mapping message to the non-mLDP enabled MPLS core router. In response, a directed LDP session is created between the mLDP enabled LSR and an edge LSR in one embodiment in response to receiving the first message from an MPLS enabled core router. The directed LDP session can be used to transmit a label mapping message to an ingress LSR.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and system for implementing protection switching in multi-protocol label switching network
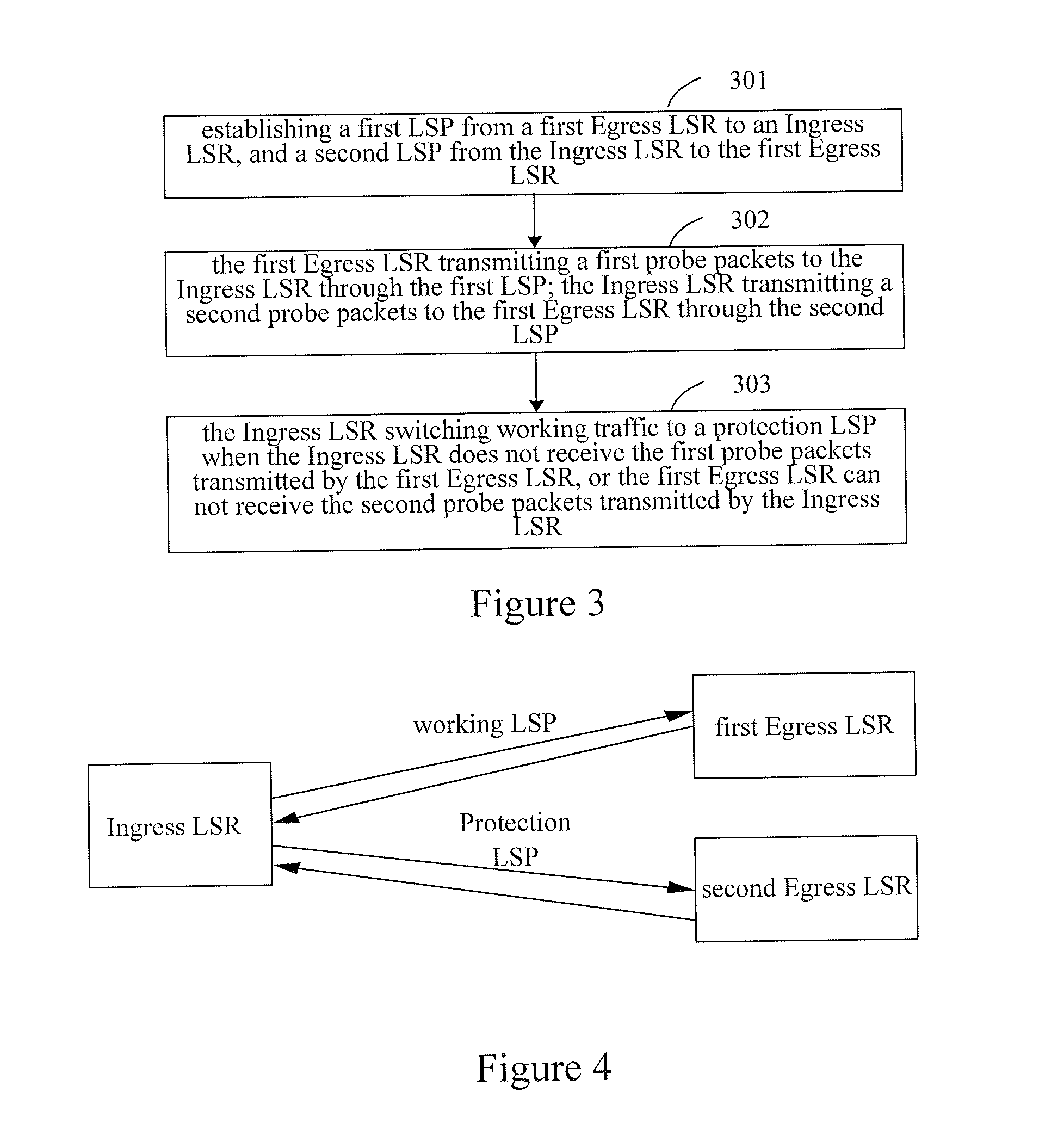
ActiveUS20070242605A1Improve securityError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityMulti protocol
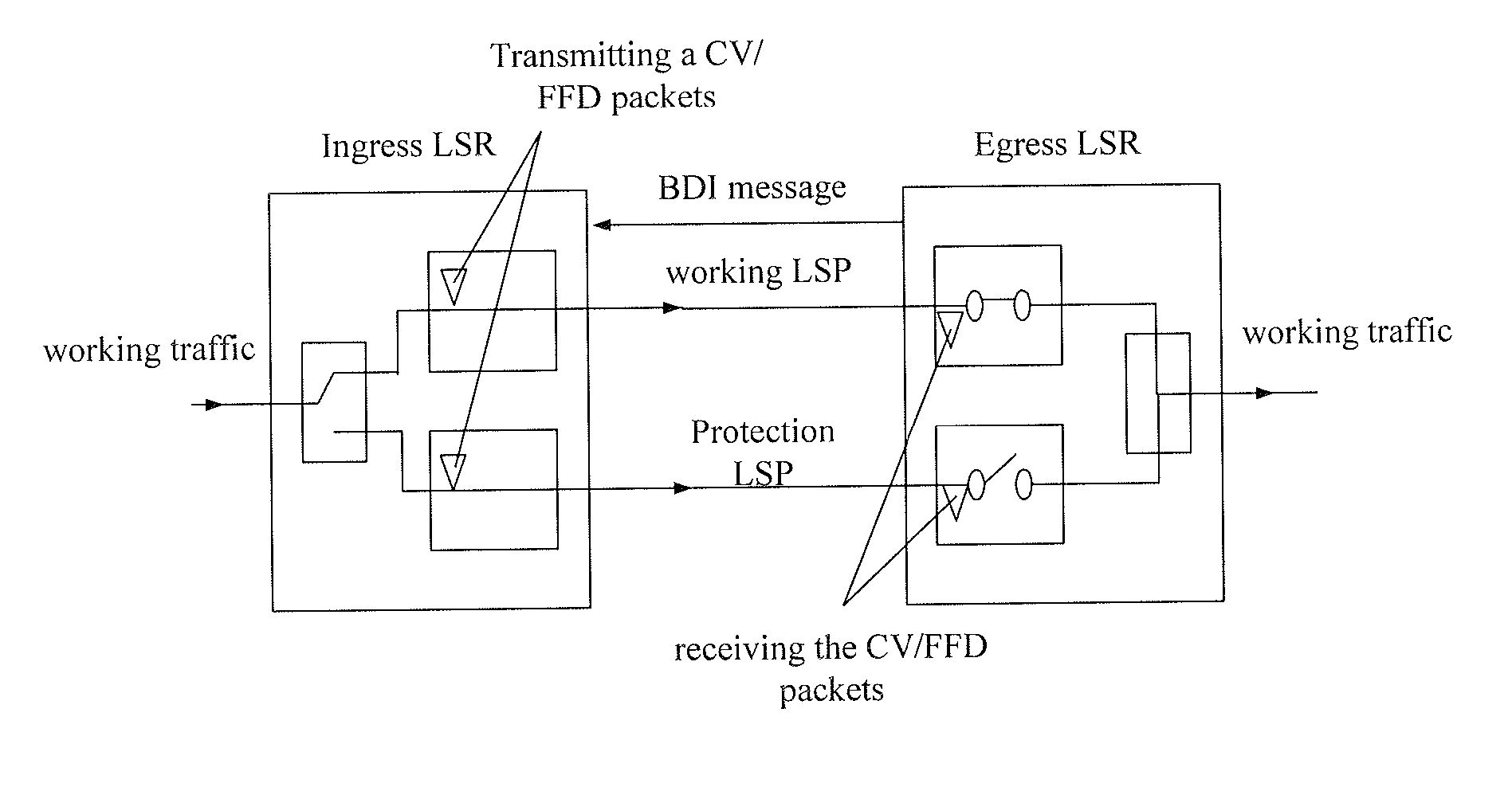
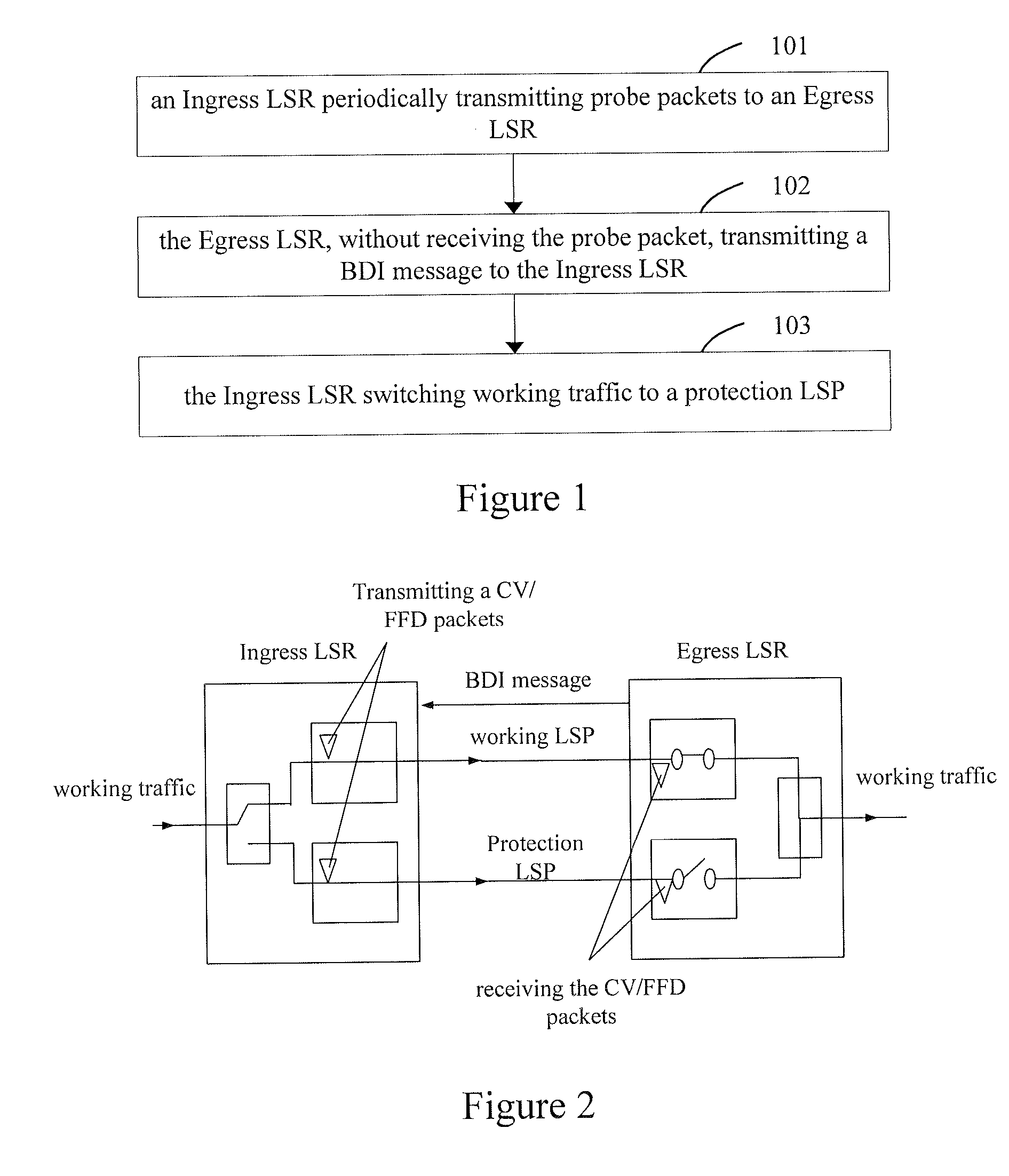
The embodiments of the present invention provide a method and a system for implementing protection switching in Multi-protocol Label Switching (MPLS) network, the method includes: transmitting by a first Egress Label Switched Router (LSR) first probe packets to an Ingress LSR via a first Label Switching Path (LSP); switching by the Ingress LSR working traffic to a third LSP terminated at a second Egress LSR when the Ingress LSR does not receive the first probe packets. According to the embodiments of the present invention, the Ingress LSR may learn the failure of the Egress LSR according to the result of receiving the probe packets when a failure of the Egress LSR occurs, and switches the working traffic correspondingly. Moreover, the working LSP and protection LSP are not terminated at a same Egress LSR, but correspond to different Egress LSRs which greatly improves the security of the MPLS network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and apparatus for processing label distribution protocol conversation, label switching router
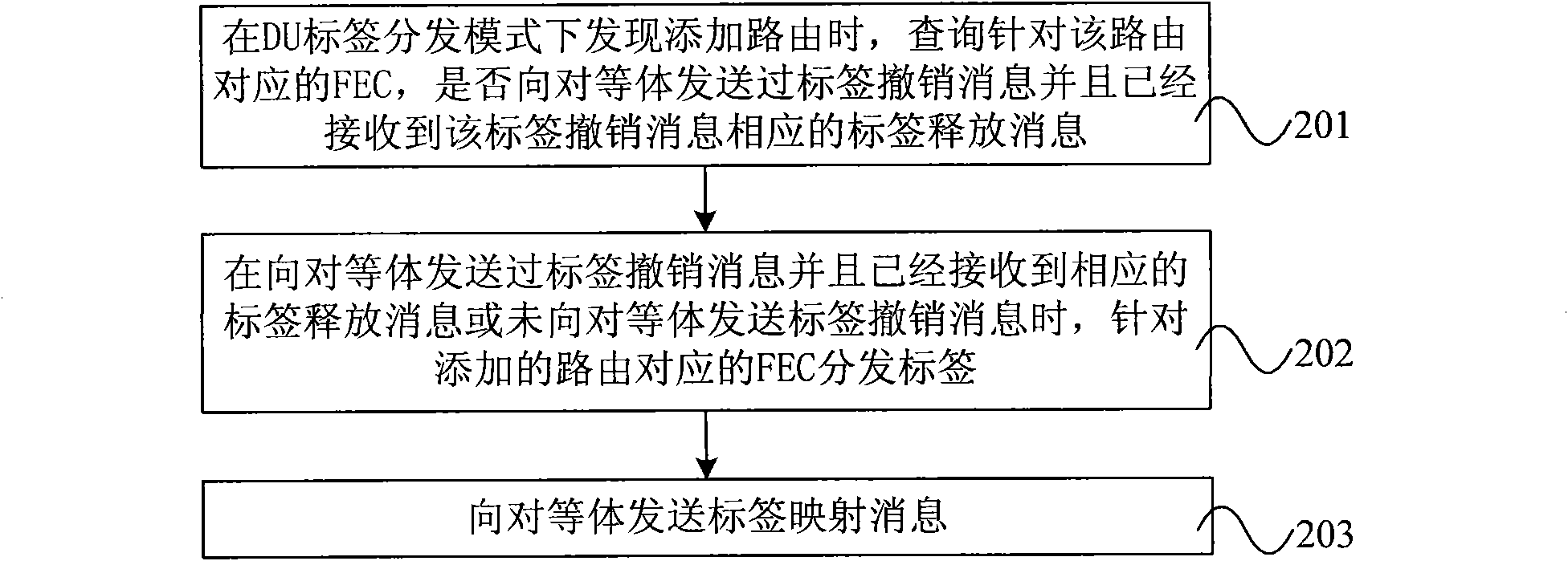
ActiveCN101656666AAvoid inconsistenciesGuaranteed normal forwardingData switching networksForwarding equivalence classDistributed computing
The embodiment of thehe present invention discloses a method and apparatus for processing label distribution protocol conversations, and a label switching router. The method includes steps: when discovering addion of a route in a mode of actively distributing DU label on the downstream, enquiring whether a forwarding equivalence class FEC corresponding with the route, sends label canceling messageto a peer and receives a corresponding label releasing message of the label canceling message or not; when the peer has sent the label canceling message and has received the corresponding label releasing message, or does not have sent the label canceling message, distributing a label for the FEC; sending a label mapping message to the peer, wherein the label mapping message includes the FEC and distributed label. The embodiment of the invention is capable of avoiding that forwarding items of the peers are different due to deletion of the route and rapid addition of the route in a DU mode, ensuring normal forwarding of packets, so as to ensure communication service quality effectively.
Owner:RUIJIE NETWORKS CO LTD
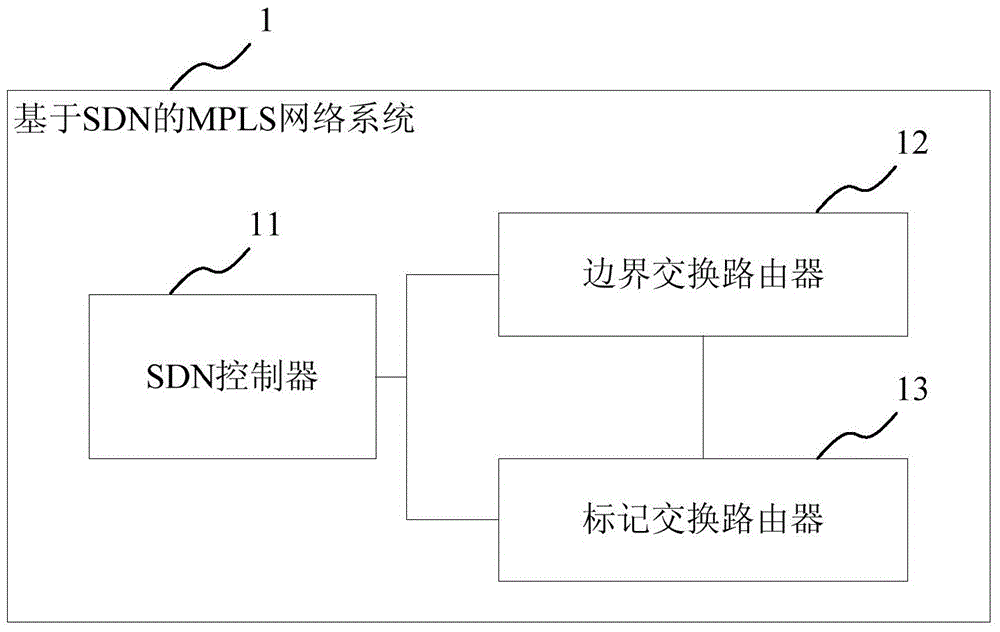
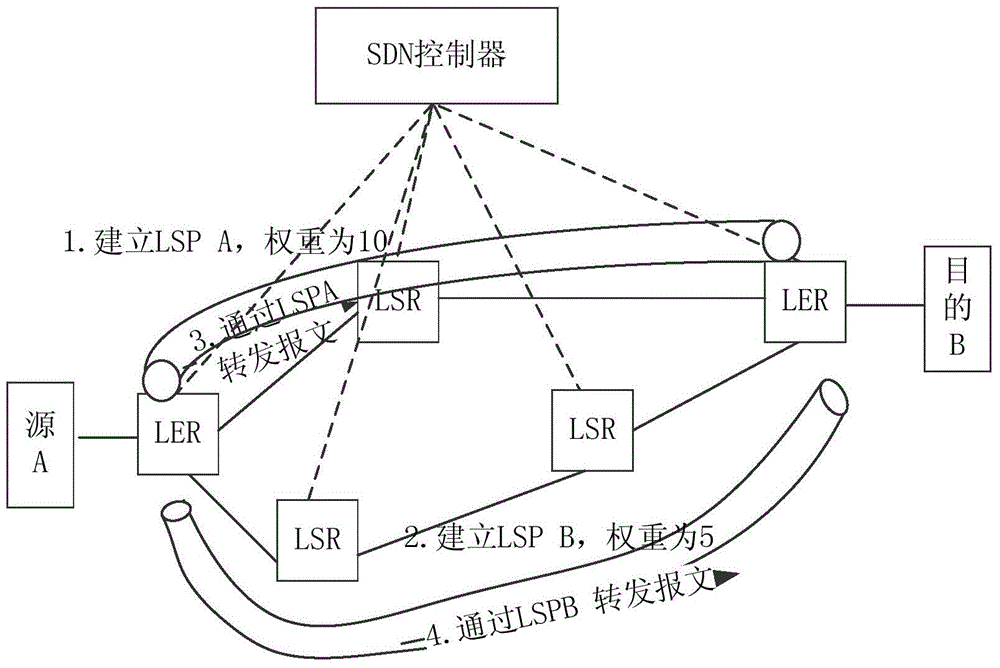
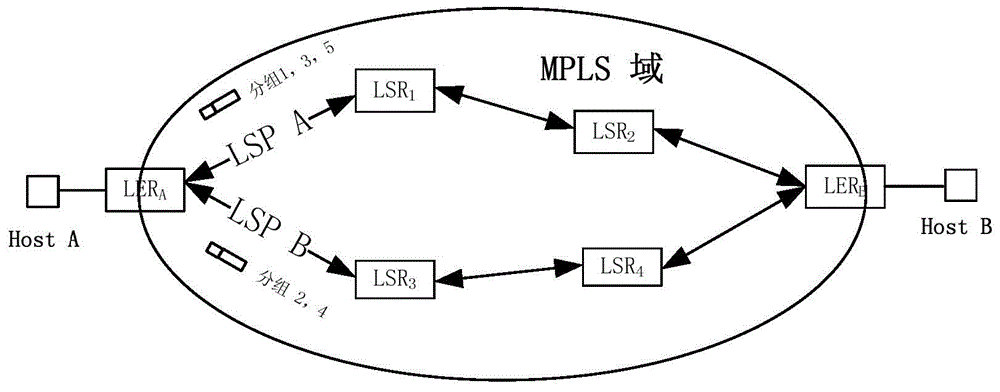
MPLS network control system and method based on SDN
ActiveCN104486218AConvenient collection and analysisEasy to optimizeData switching networksTraffic capacityControl system
The invention discloses an MPLS (Multi-protocol Label Switching) network control system and an MPLS network control method based on SDN (Software Defined Network). The MPLS network control system based on SDN comprises an SDN controller, wherein the SDN controller is used for issuing an IP forwarding table, a label forwarding table and a flow table to a switch; the flow table comprises an IP message for matching according to the targeted IP and a message with the label matching according to the label; the switch comprises a boundary switch router and a label switch router; the boundary switch router is used for receiving the IP forwarding table, the label forwarding table and the flow table, and processing the received messages according to the flow table; the label switch router is used for receiving the label forwarding table and the flow table, and processing the received messages according to the flow table. The technical scheme disclosed by the invention can fully utilize the link resources in the whole network to achieve a better network flow optimization effect.
Owner:北京九云无限网络科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com