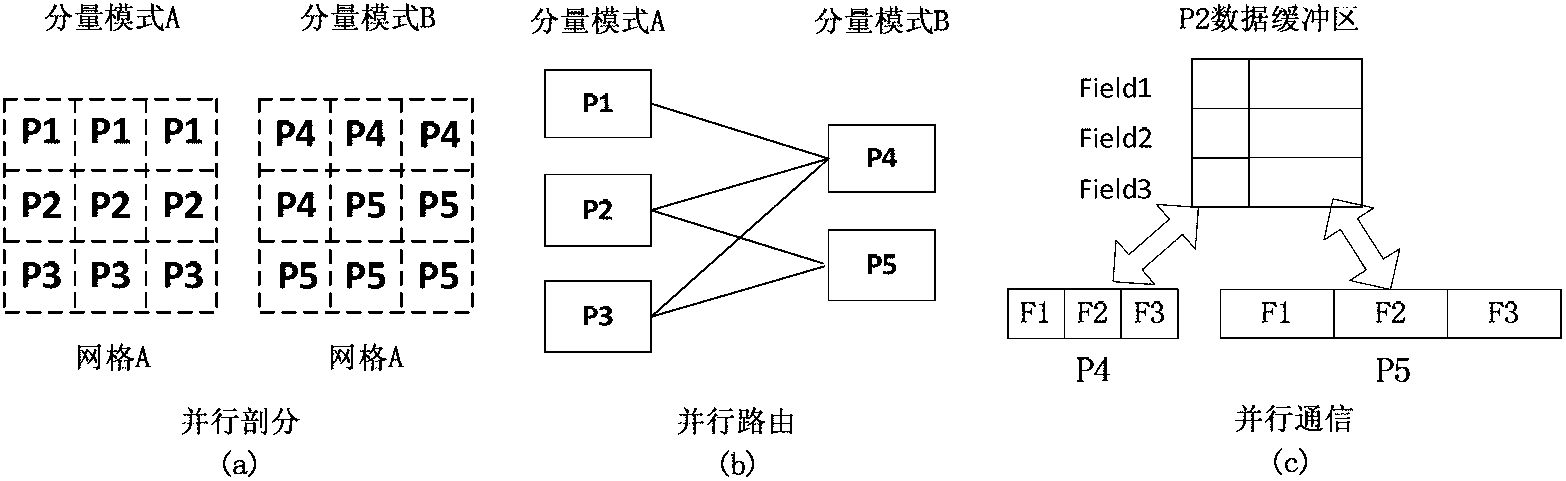
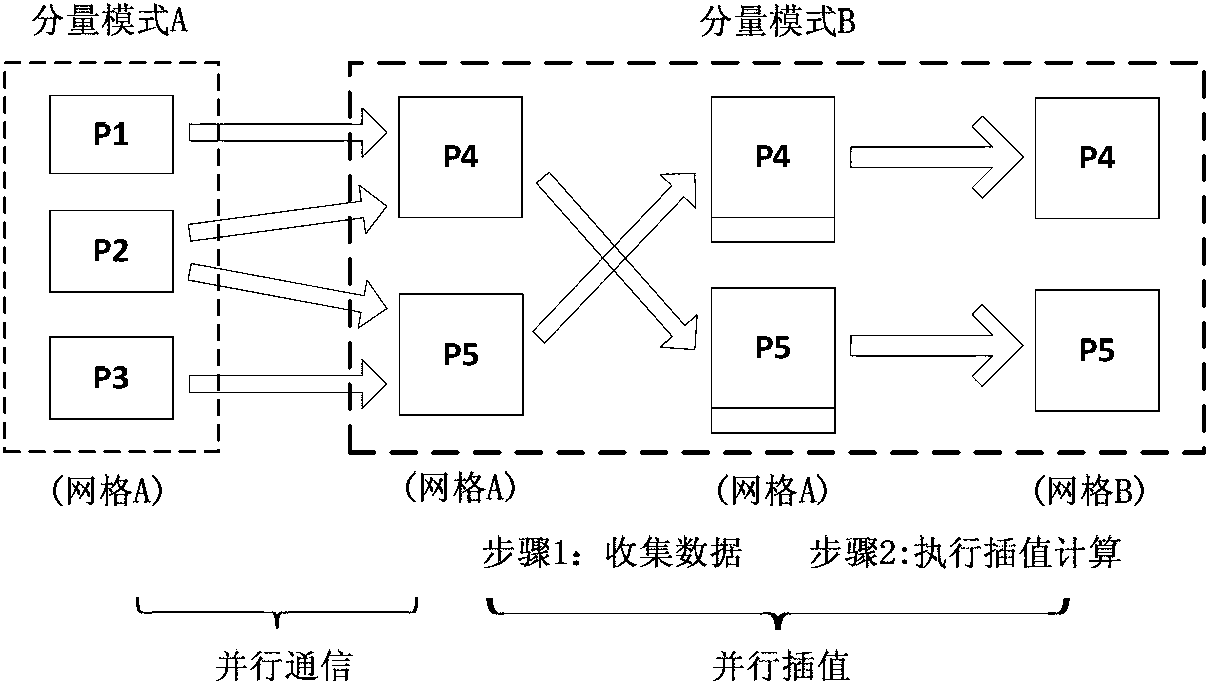
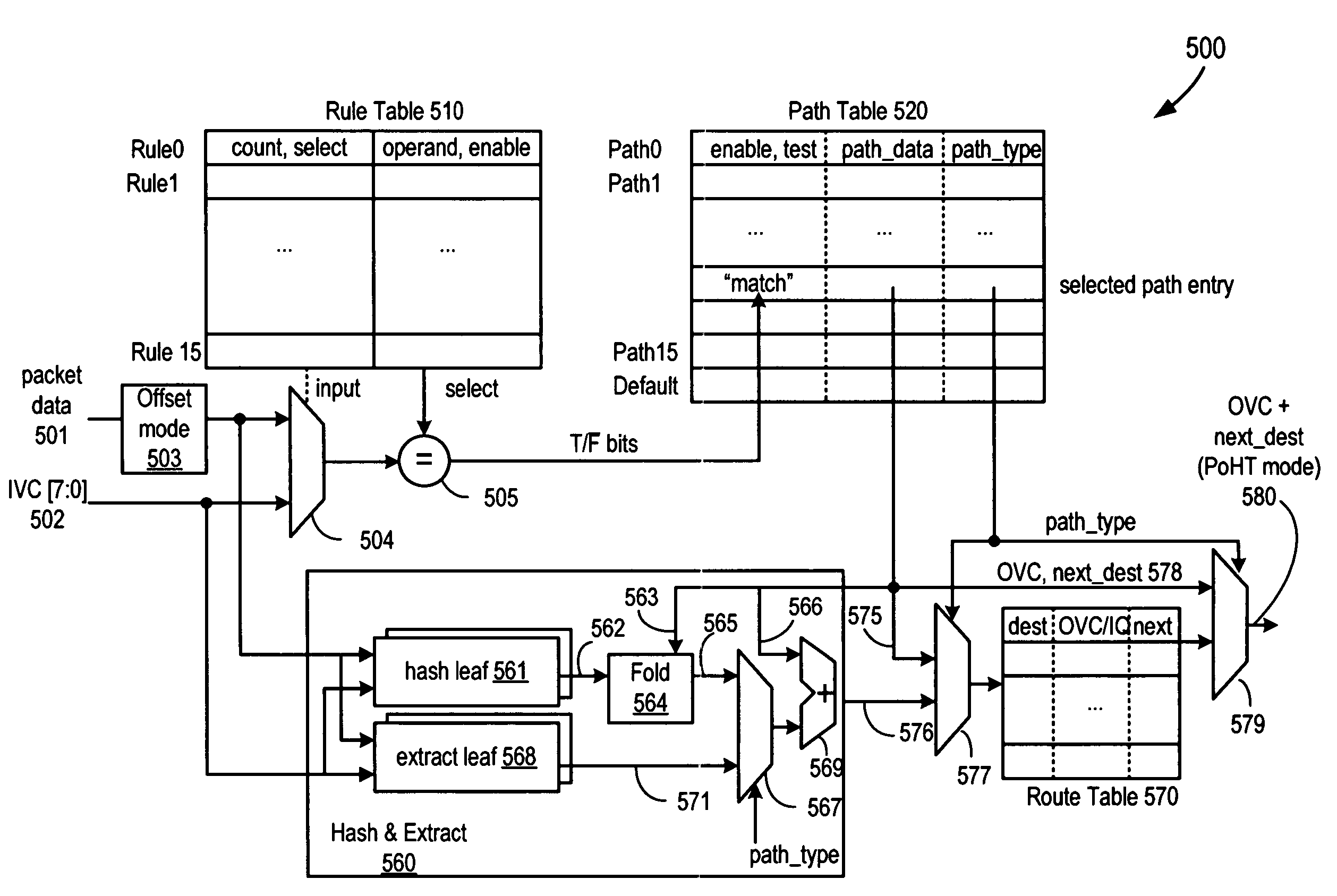
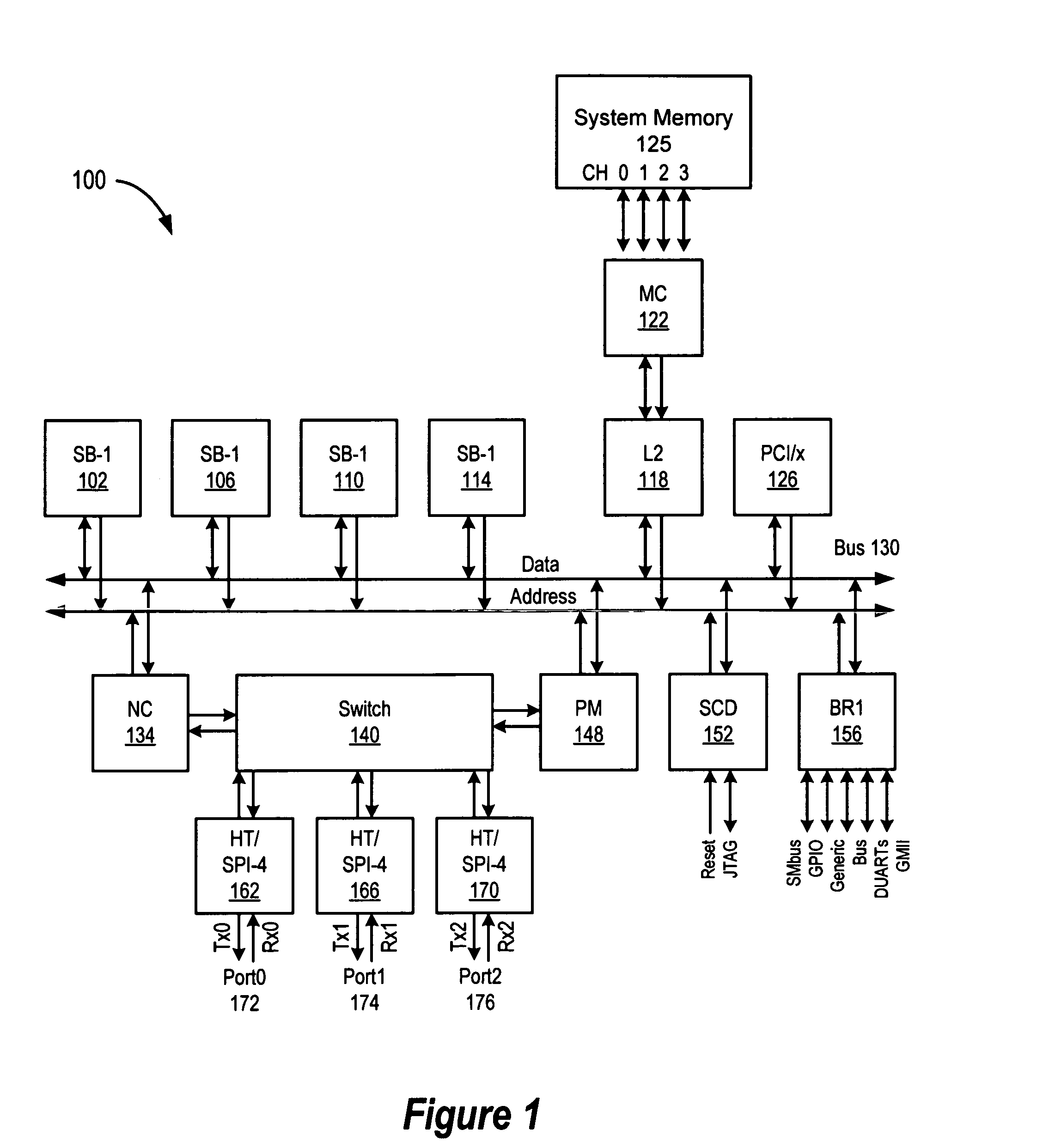
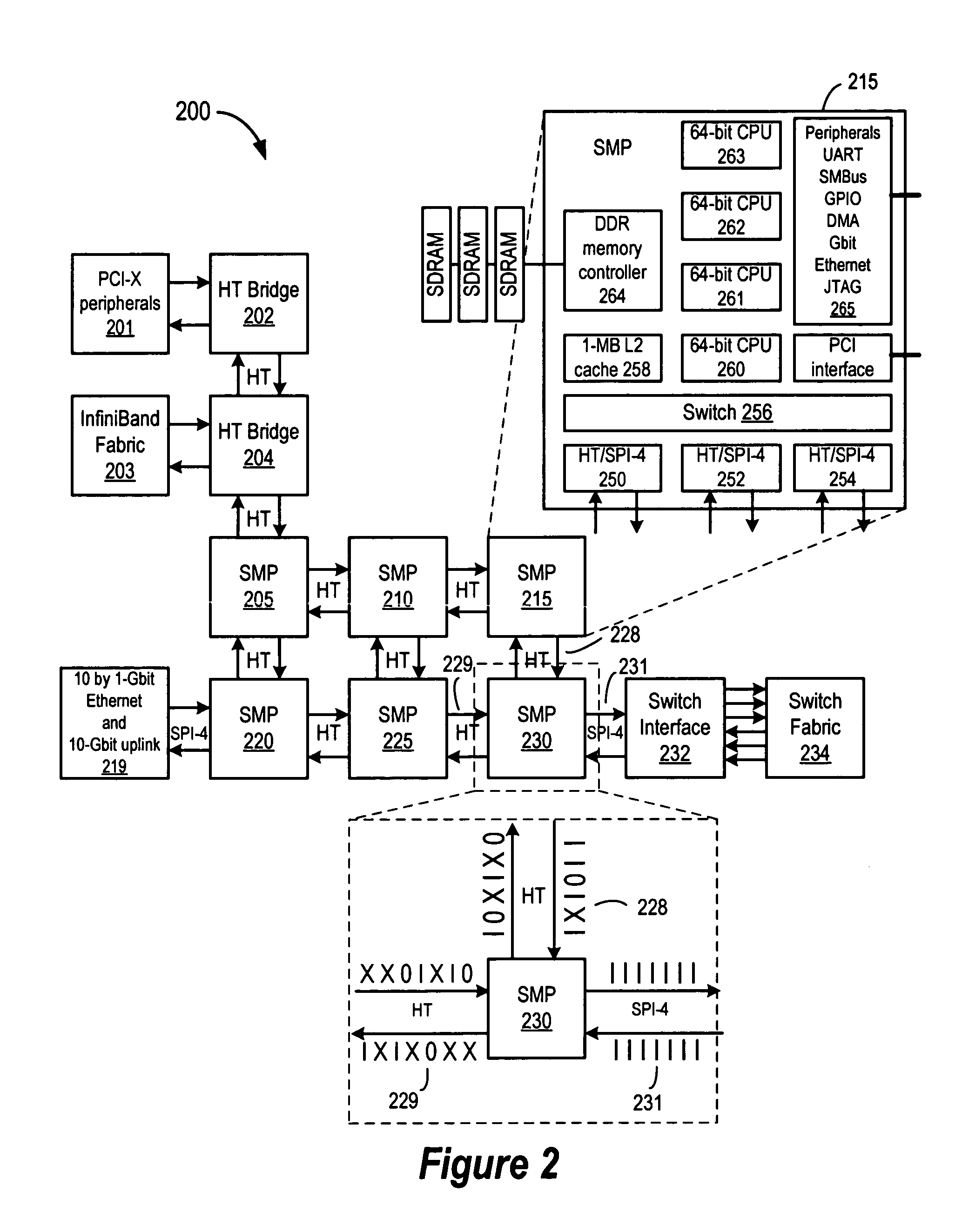
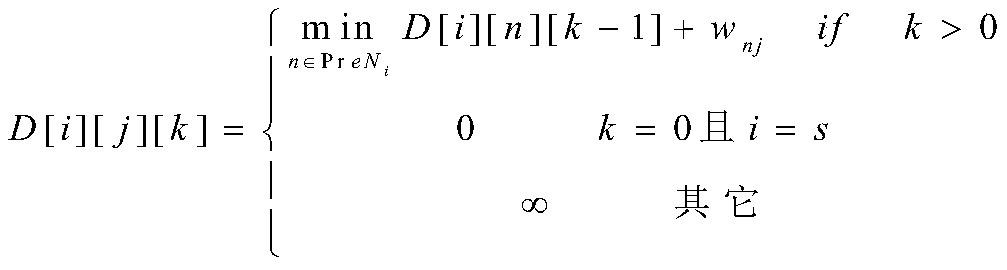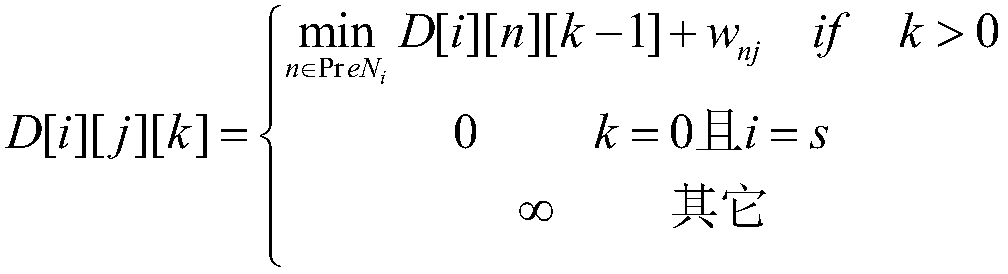Patents
Literature
35 results about "Parallel routing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Parallel routings (sometimes also referred to as parallel sequences) are used when multiple manufacturing operations/processes can or is need to be performed simultaneously by routing the material that is being worked on to multiple work centers.
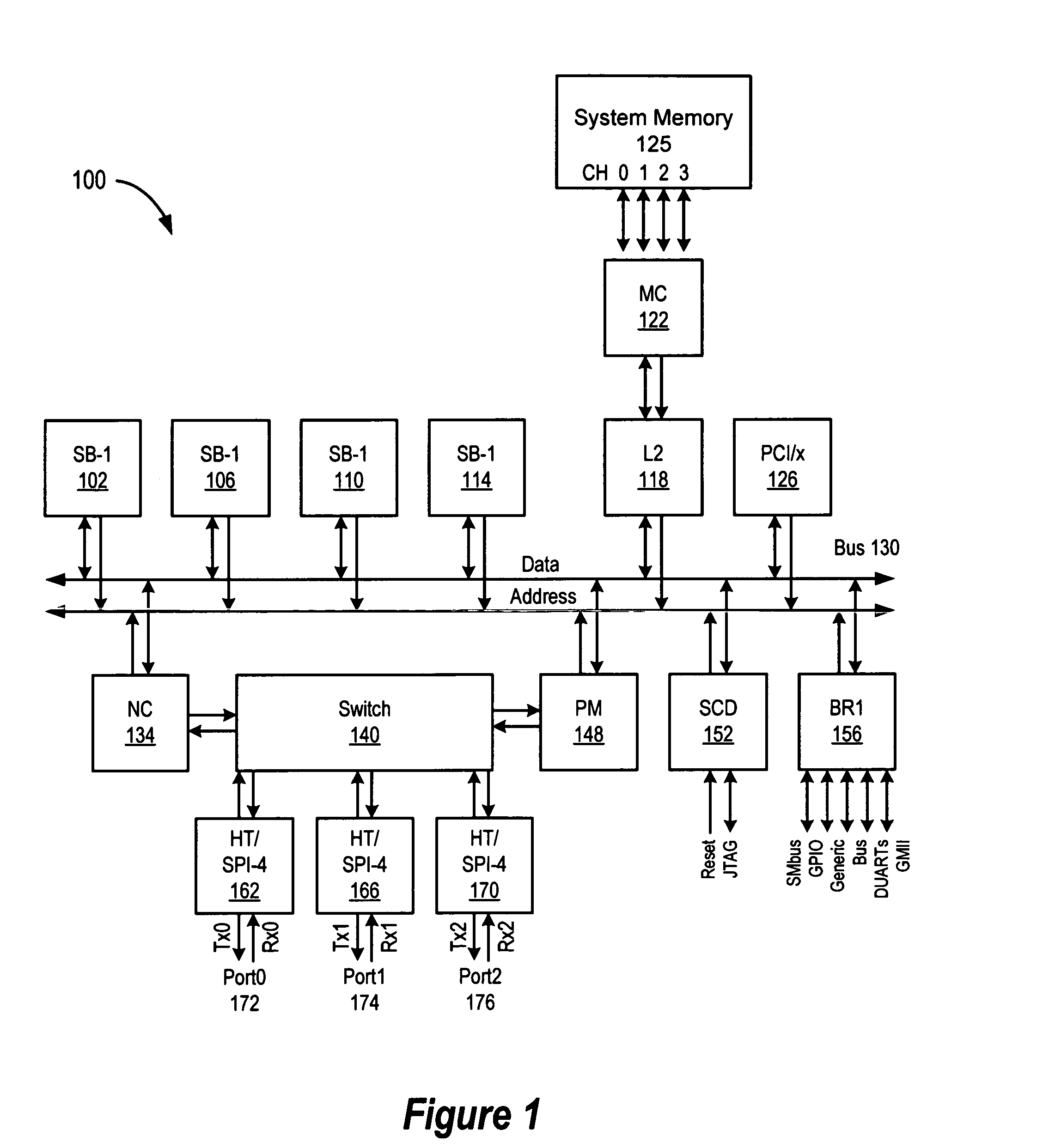
Apparatus and methods providing redundant routing in a switched network device
InactiveUS6628649B1Improve fault toleranceHigh degreeMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationData transmissionData loss
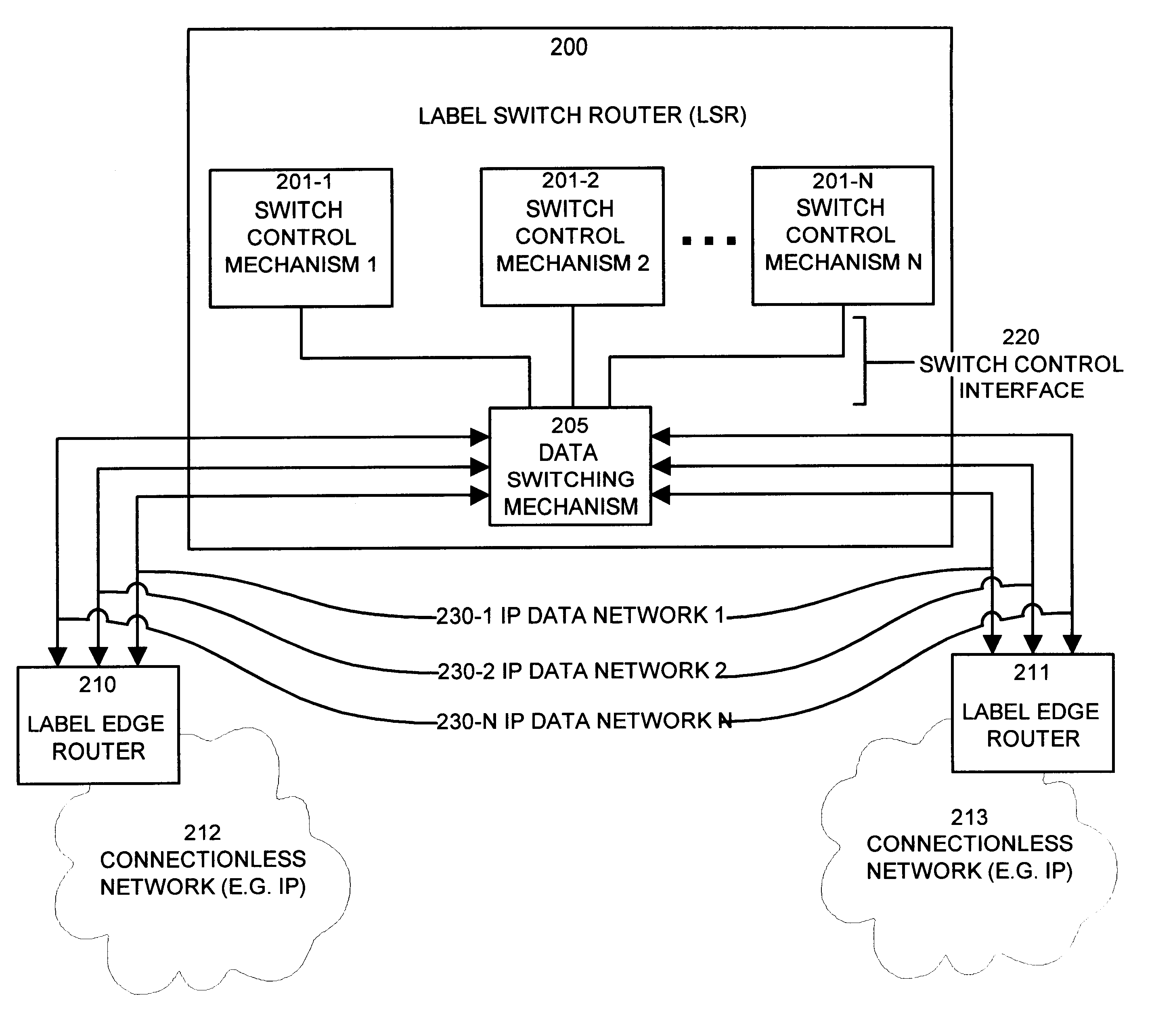
The invention provides unique architectures and techniques for routing redundancy in a data switch configured to use label switching. Multiple label switch controllers (LSCs) each operate concurrently but independently of each other to provide routes through a data switching mechanism. Preferred embodiments provide a plurality of LSCs offering MPLS capabilities coupled to a single switch, such as an ATM switch. The similarly configured LSCs each can concurrently support a route for data (e.g., labeled ATM cells) within the data switching mechanism in parallel, thereby providing the ability to support redundant and multiple parallel data networks. The configuration is called a label switch router (LSR). A fully-meshed embodiment allows selected routes to share bandwidth on ports, while a fully parallel embodiment provides separate ports for selected routes. Since each LSC provides parallel routes with the other LSCs in an LSR, a communications between an LSR and a label edge router (LER) can use multipath routing to concurrently distribute data equally across the parallel routes for each destination. Alternatively, unipath routing techniques can select one route for use for each destination from the available routes concurrently offered by each LSC. In the event of a failure of one of the LSCs, multipath routing implementations can exclude transmission of data onto the failed network, while continuing to use the other parallel networks supported by non-failed LSCs in a concurrent manner. Alternatively, if a failure occurs with unipath routing, a new route offered by another LSC can be selected for data transfers. In either case, the LSC that fails does not need to provide state or connection information to the LSCs that operate subsequently to the failure, since they are already configured in parallel to support the same route. Upon an LSC failure, switch resources such as bandwidth that were used by the failed LSC are made available to the remaining non-failed LSCs. The design allows failures are handled gracefully without diminished network capacity or data loss resulting in a highly reliable routing capability provided within connection-based or circuit-switched networks.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
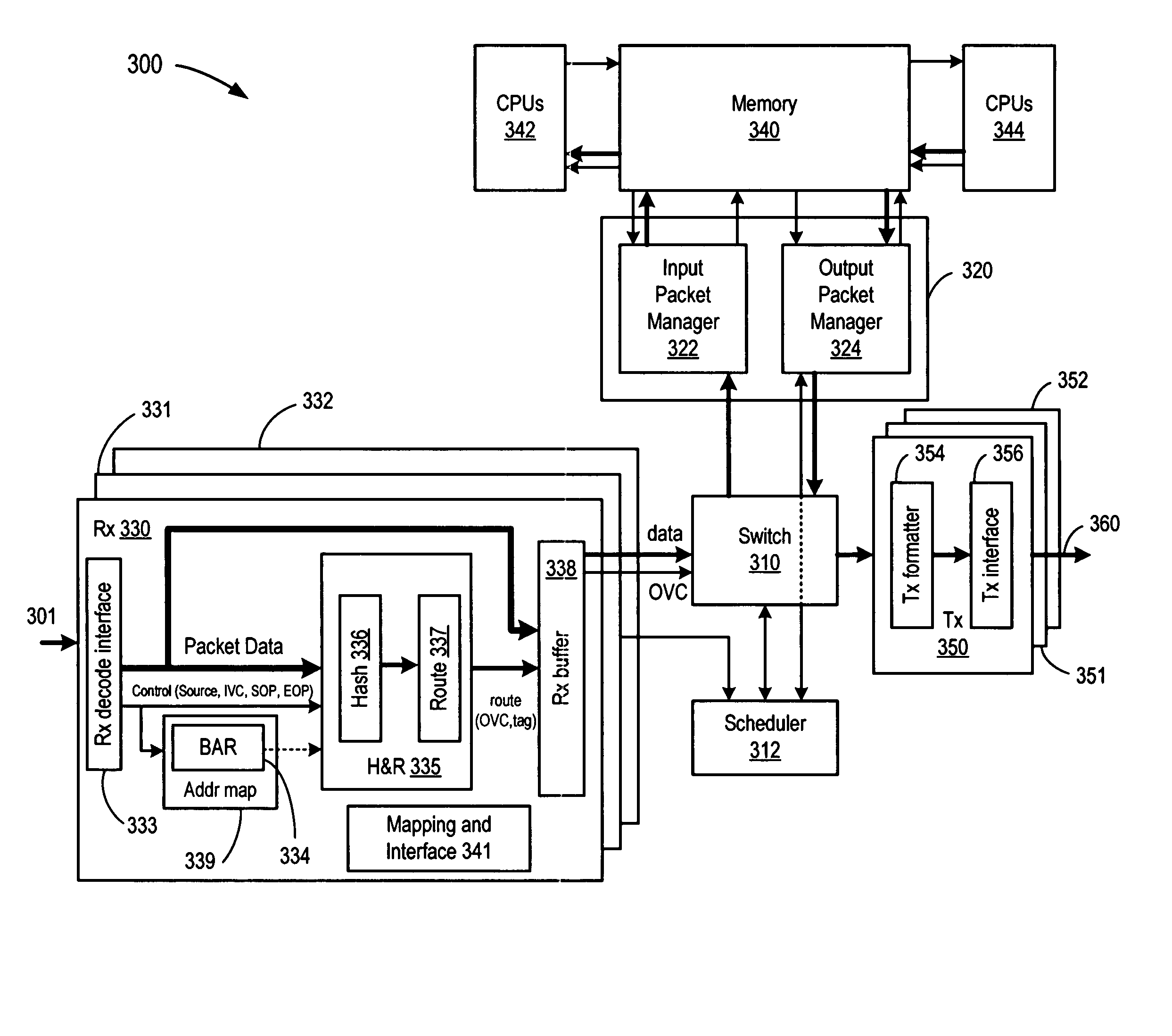
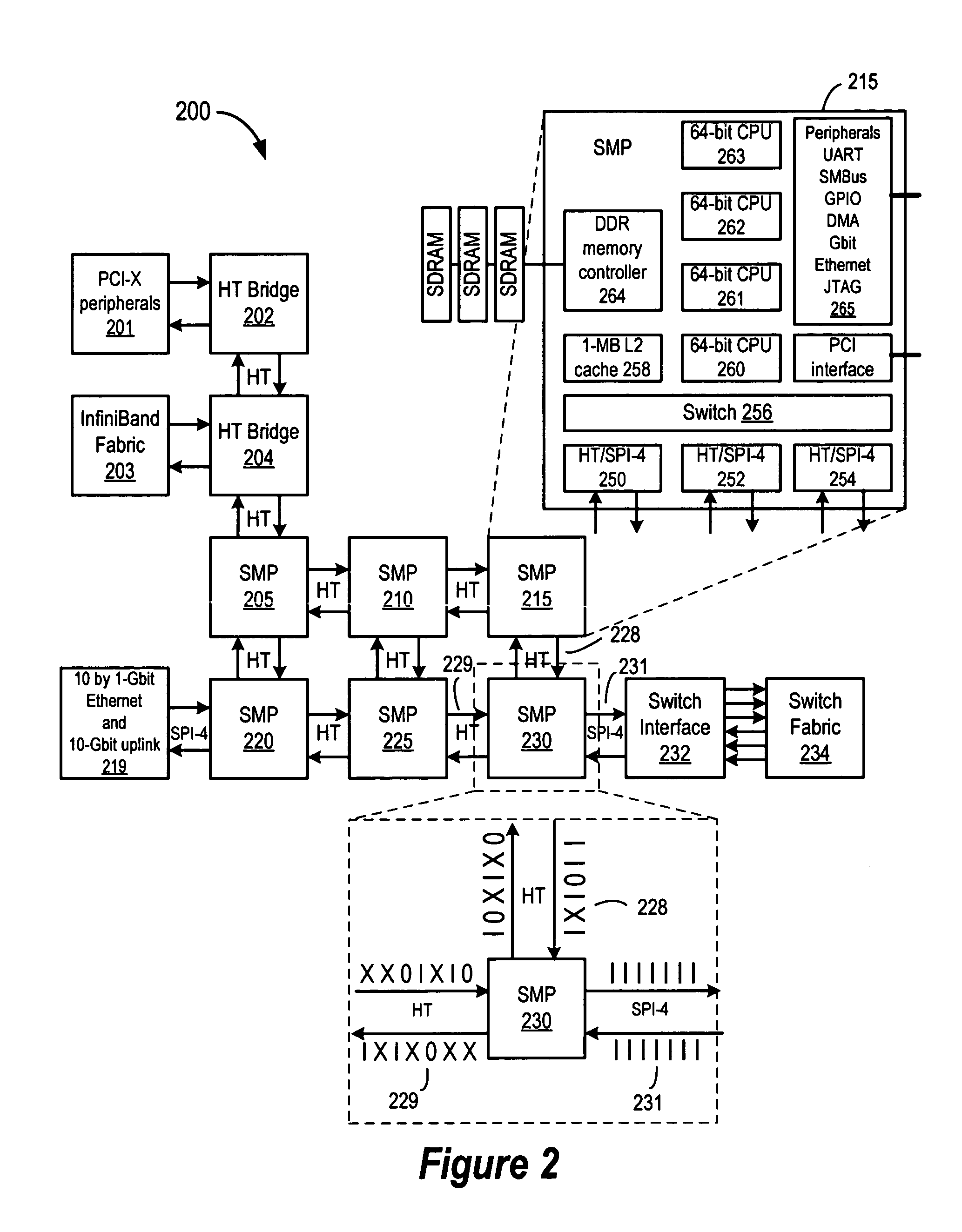
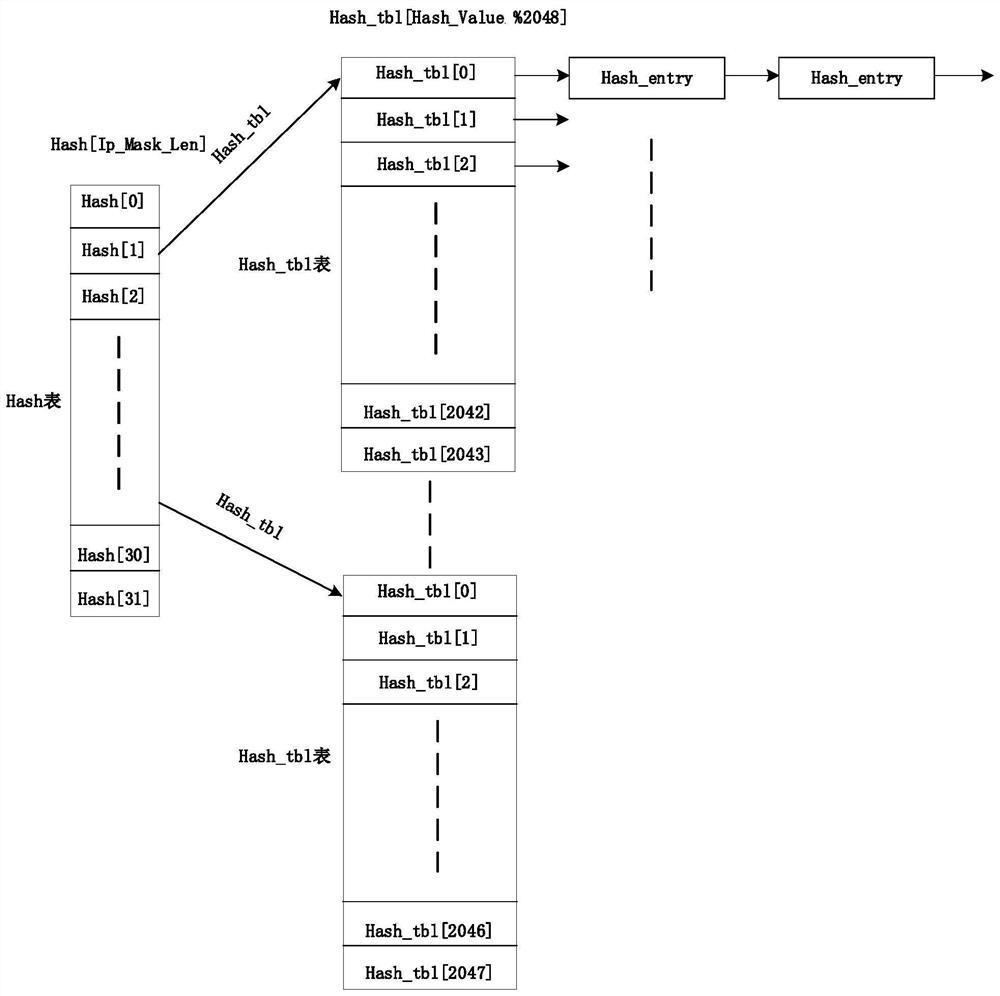
Hash and route hardware with parallel routing scheme
A multiprocessor switching device substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described in connection with a parallel routing scheme for calculating routing information for incoming packets. Using the programmable hash and route routing scheme, a hash and route circuit can be programmed for a variety of applications, such as routing, flow-splitting or load balancing.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
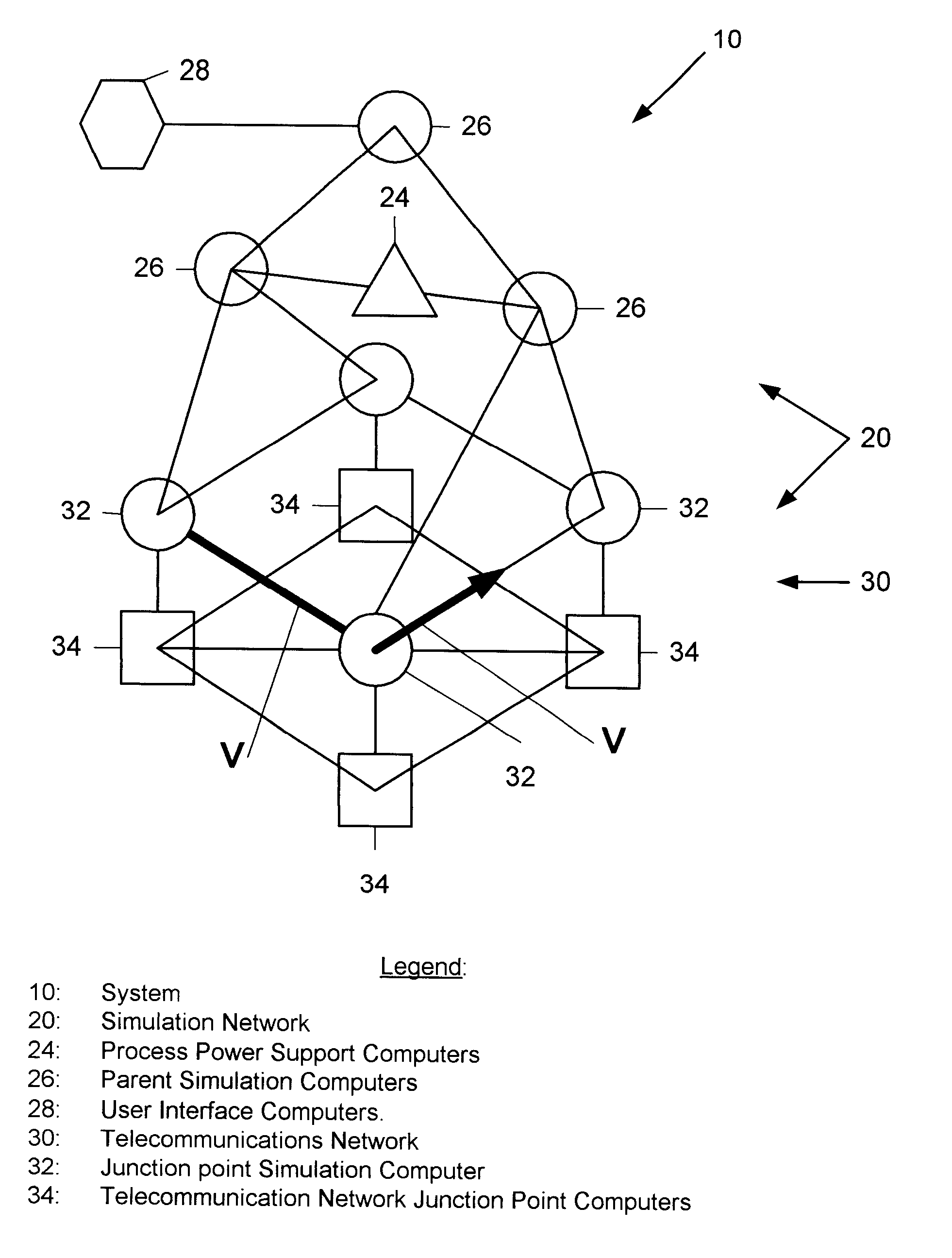
Parallel computer network and method for telecommunications network simulation to route calls and continuously estimate call billing in real time
InactiveUS6614893B1Use minimizedPower maximizationMultiplex system selection arrangementsInterconnection arrangementsTelecommunications networkAnalog computer
A telecommunications call routing and billing computer system includes a telecommunications network including a junction point including a call routing switching device, and including two call routing links meeting at the junction point and in communication with each other through the call routing switching device; and a call routing simulation network including a junction point simulation computer located at the junction point and in communication with the call routing switching device and the two call routing links. A method of placing a call through such a telecommunications network includes the steps of: placing one junction point simulation computer at each telecommunications network call junction point; for each call placed with the telecommunications network, plotting a call routing vector through the simulation network with forward chaining through the junction point simulation computers; and sending routing vector information back through the simulation network with rearward chaining to direct the call along a parallel routing vector through the telecommunications network. The method preferably includes the additional steps of: monitoring buffer levels of telecommunications network junction point computers with the simulation computer at each junction point; and using the buffer level information to shunt calls from telecommunications network junction point computers having smaller buffers to those having larger buffers.
Owner:PAIZ RICHARD S
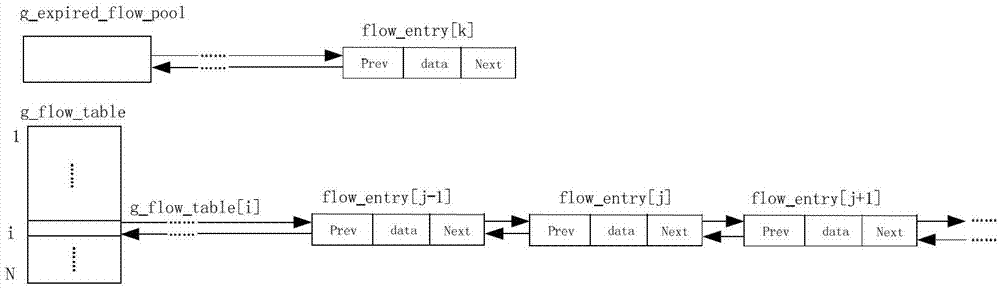
Unlocked flow table routing lookup algorithm adopting high-speed parallel execution manner
ActiveCN102938000ASolve processing performance bottlenecksAchieve securitySpecial data processing applicationsData transmissionParallel routing
The invention relates to a routing lookup algorithm, and in particular relates to an unlocked flow table routing lookup algorithm adopting a multi-core processor high-speed parallel execution manner. In the multi-core processor parallel execution environment, a flow table design structure having the number corresponding to the core number is adopted, the manner of combining control planes with data planes in multiple cores is used, and a delete operation for entries in the flow table can be divided into two relatively independent stages, namely FLOW-INVALID and FLOW-DELETE stages, so that the multiple cores can read and write one flow table at the same time without relying on the control of a resource lock. The unlocked flow table routing lookup algorithm adopting the multi-core processor high-speed parallel execution manner solves the data processing bottleneck problem caused by the existing flow table design method during the multi-core processor parallel execution process, realizes safety and rapidness of data transmission during the multi-core processor parallel execution process, and improves the high-capacity system routing lookup speed and the parallel routing lookup performance.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
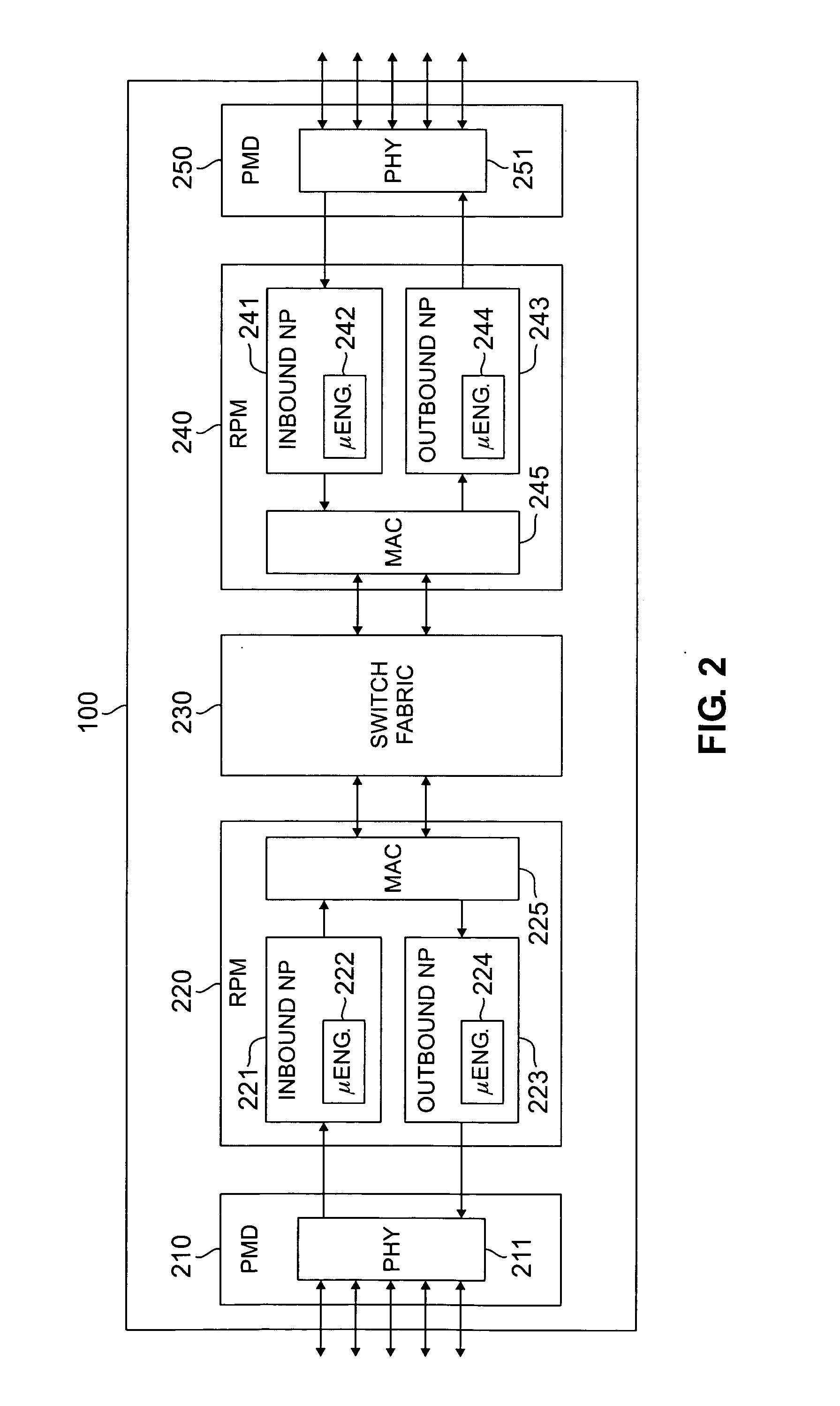
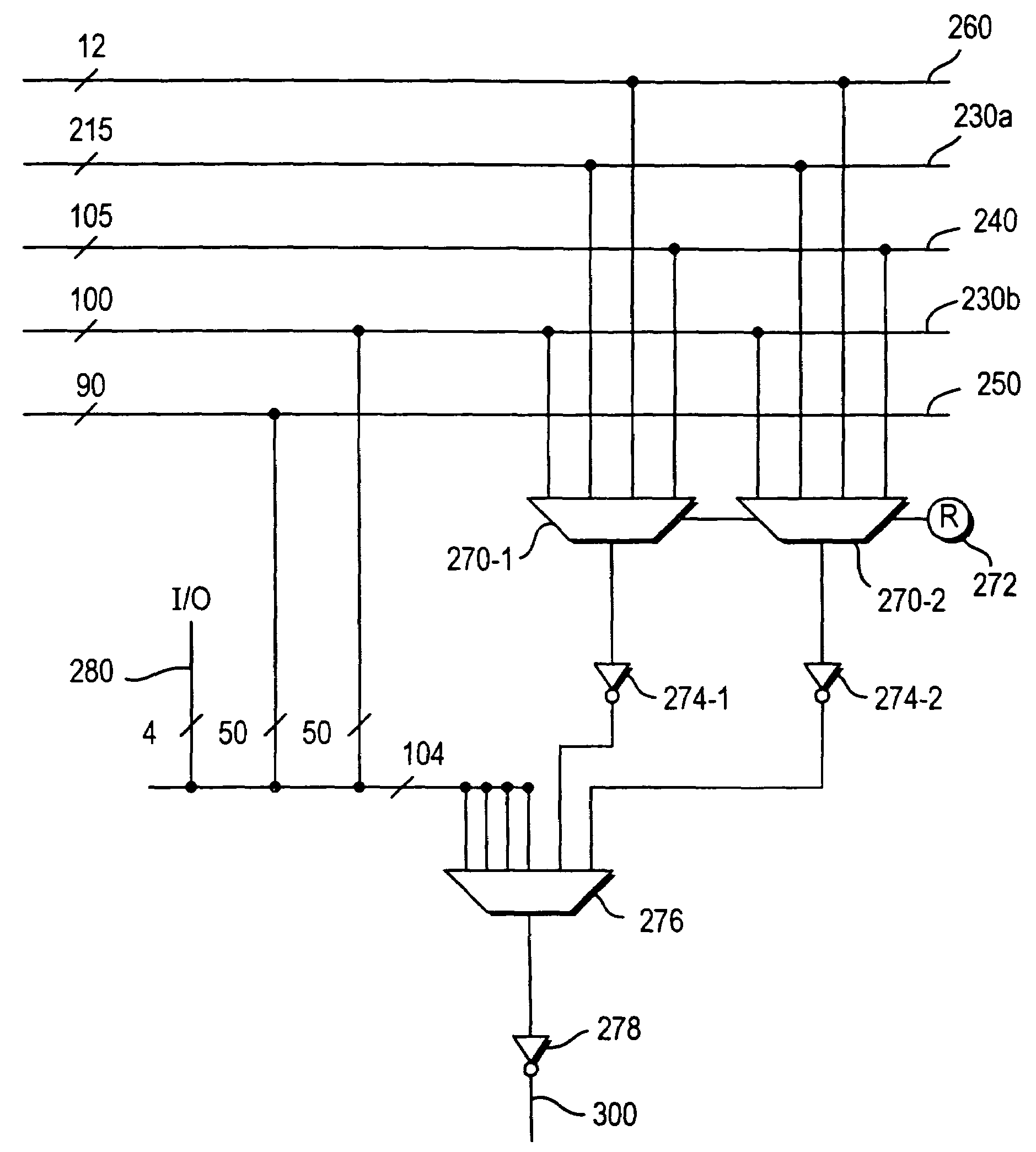
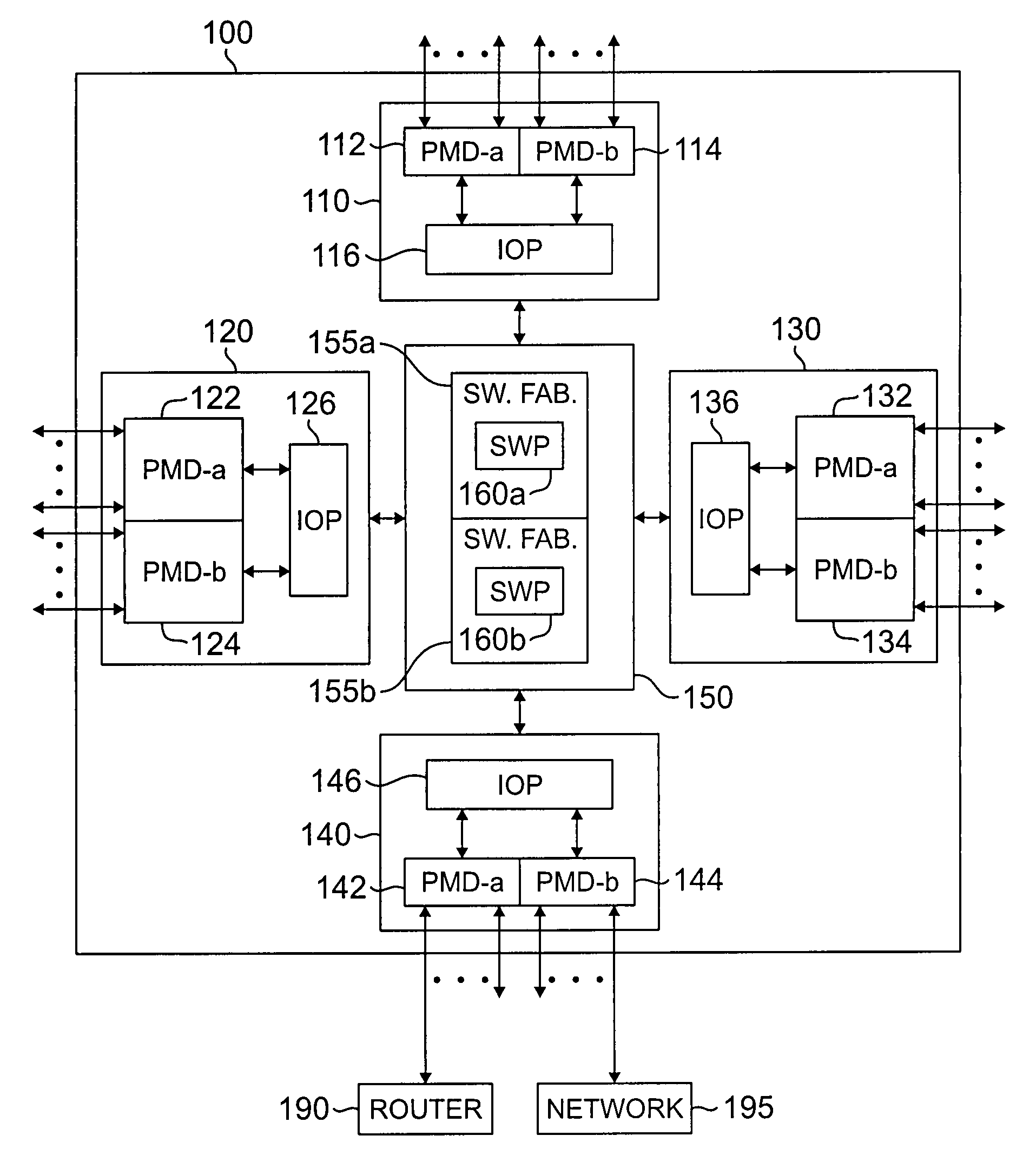
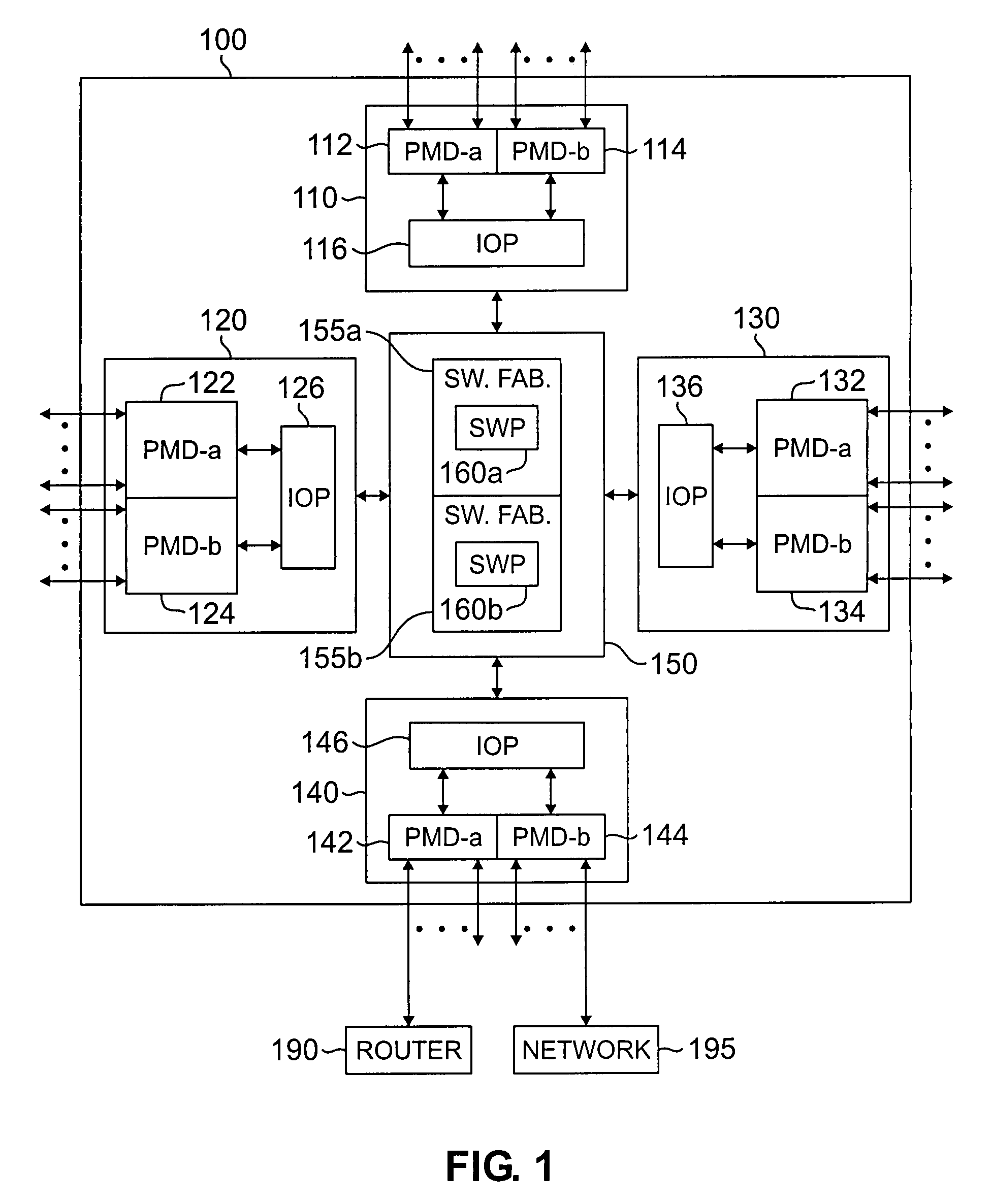
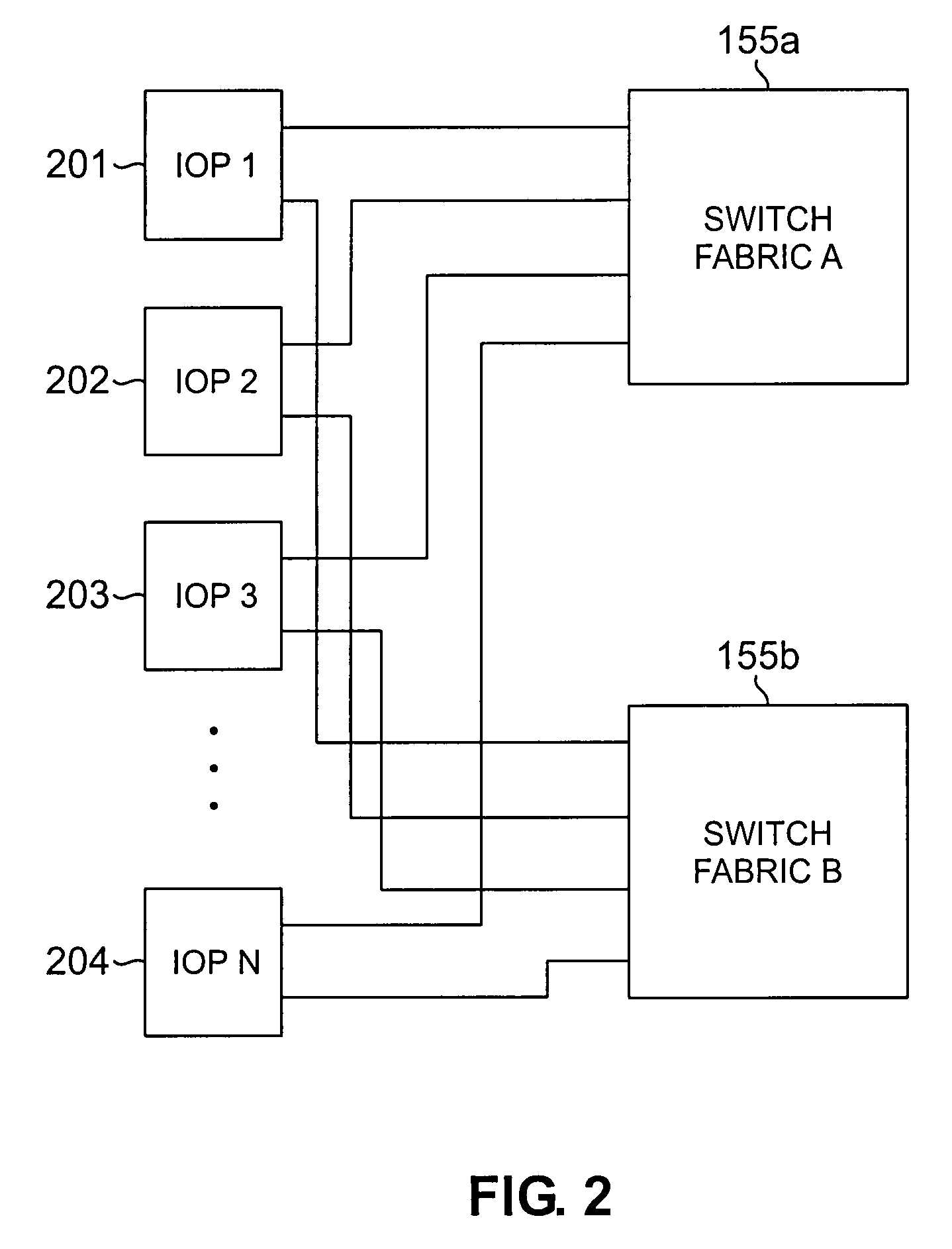
Apparatus and method for maintaining packet sequencing in a parallel router
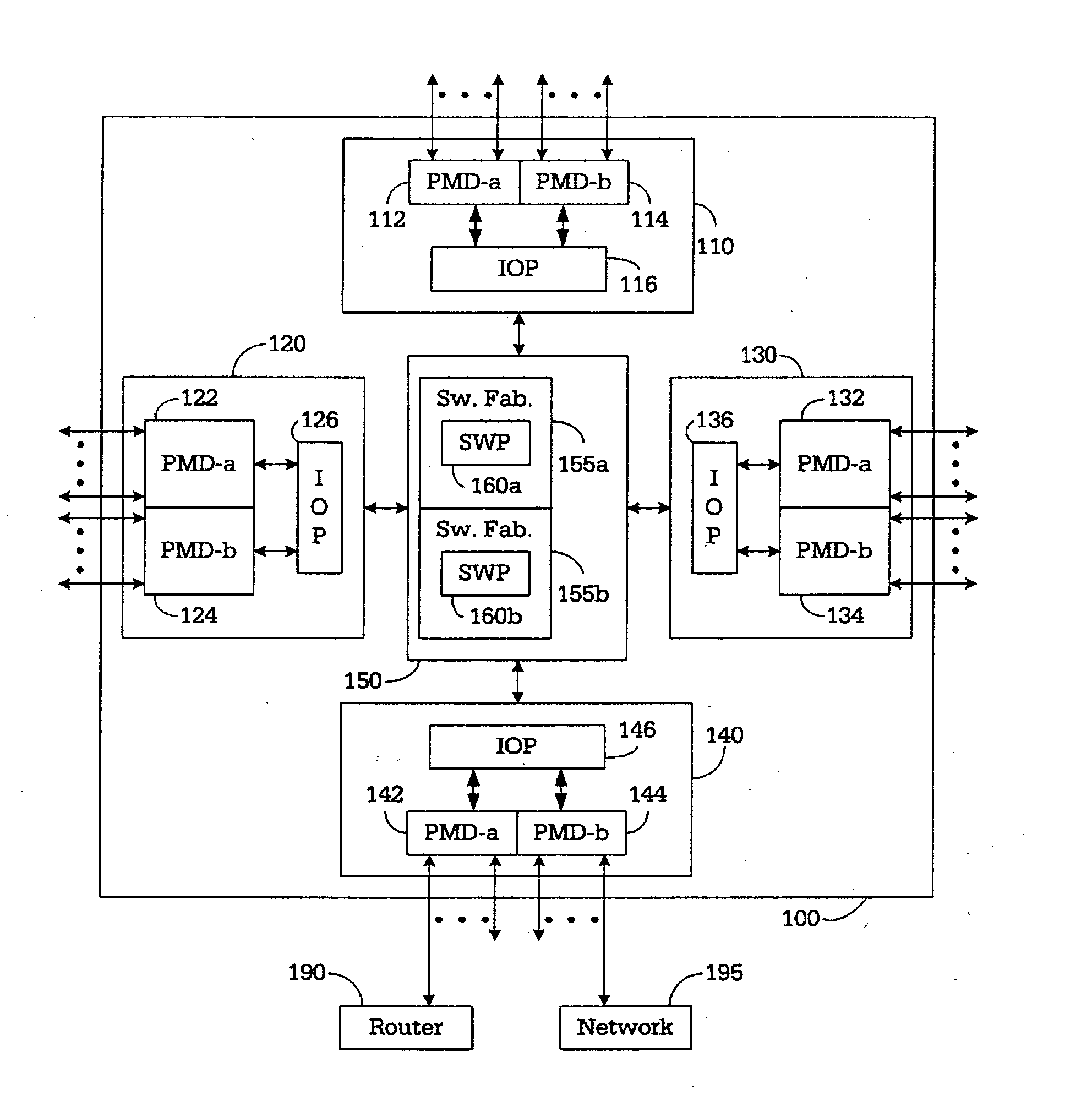
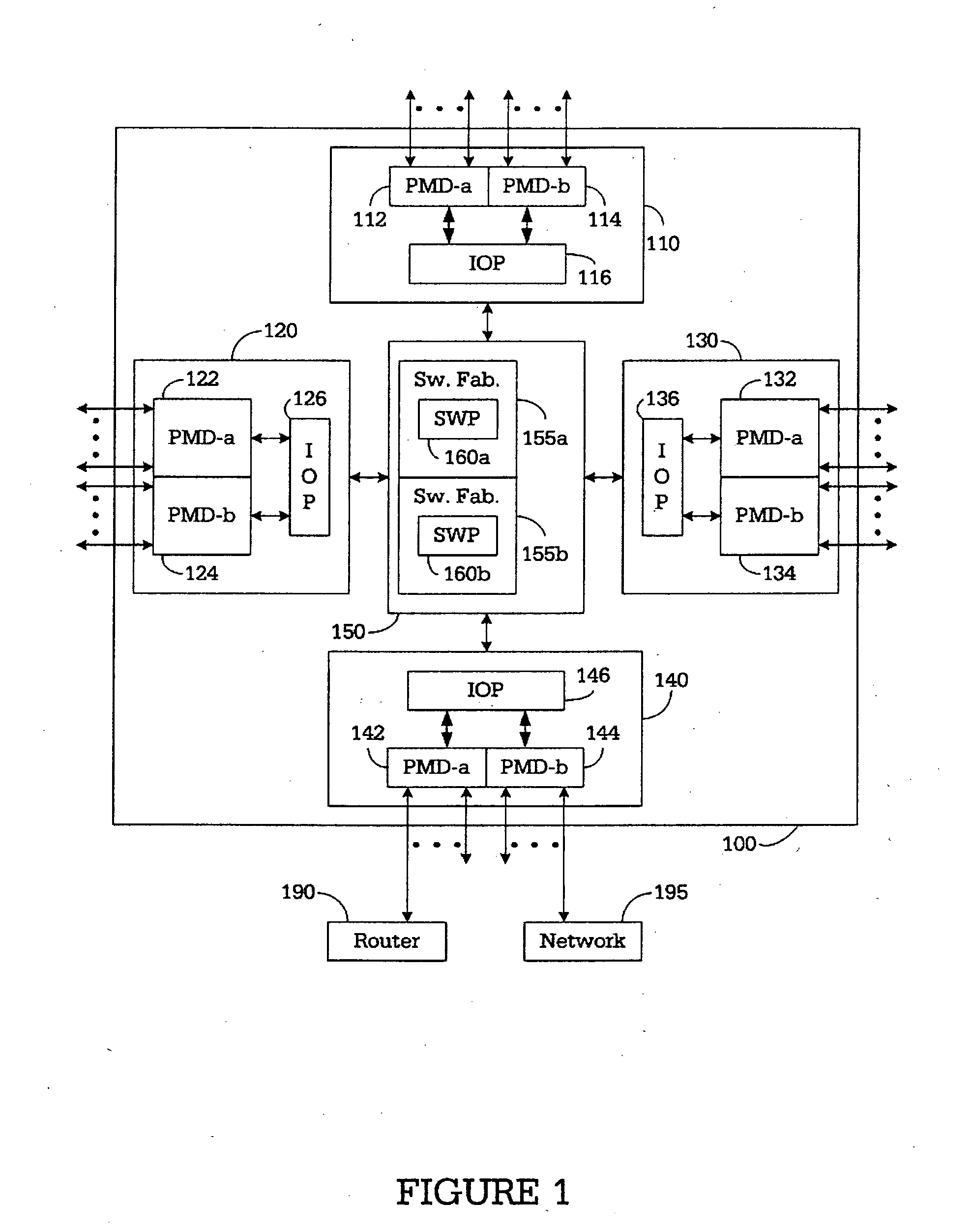
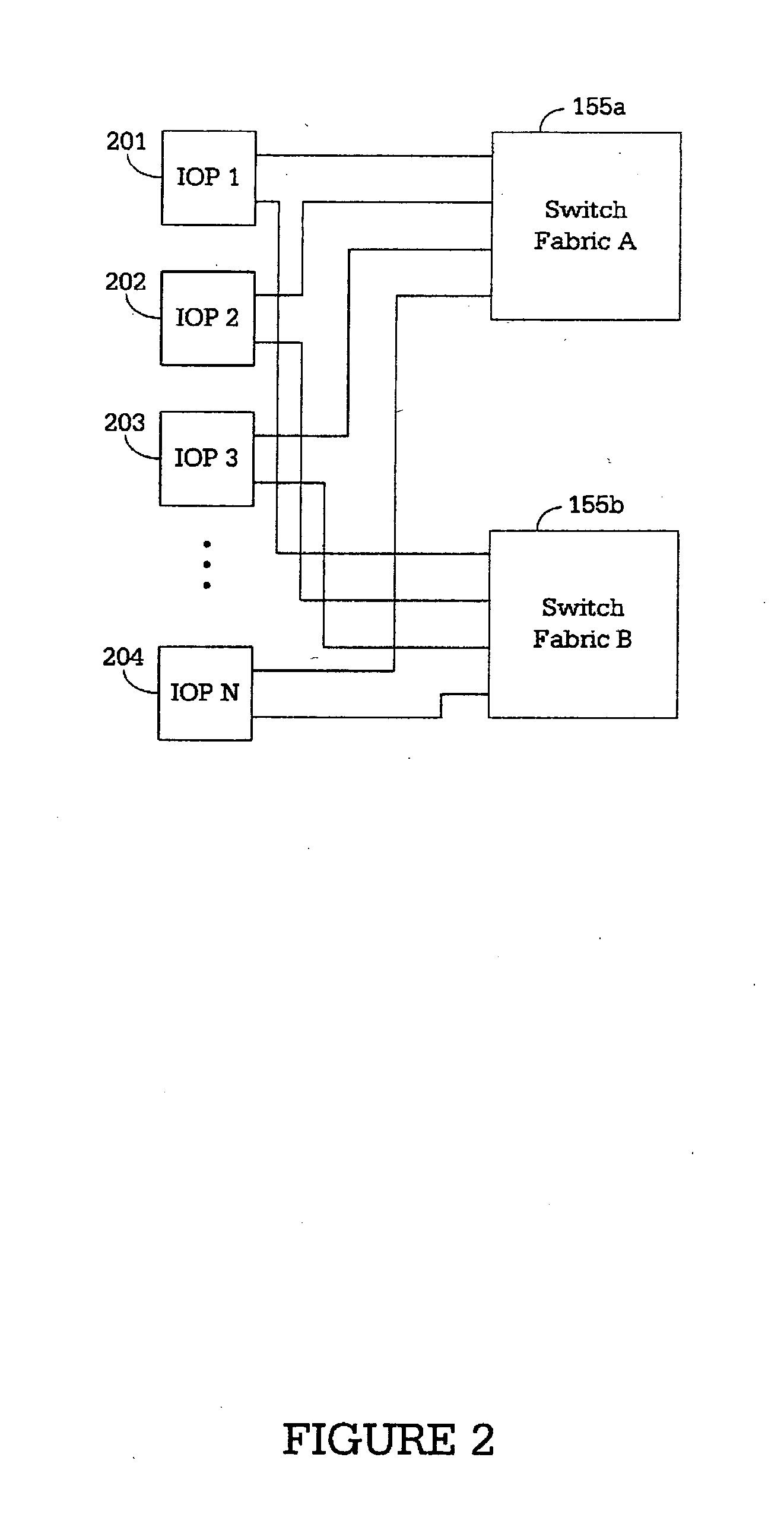
A router for interconnecting N interfacing peripheral devices. The router comprises: i) a first switch fabric; ii) a second switch fabric; and iii) a plurality of routing nodes coupled to the first and second switch fabrics. Each of the routing nodes comprises an input-output processing (IOP) module for forwarding received data packets to other ones of the IOP modules via the first and second switch fabrics. A first one of the IOP modules forwards received data packets directed to a second one of the IOP modules by alternating between the first and second switch fabrics for each sequential data packet directed to the second IOP module. Breaks in the alternating sequence identify failed links and cause all traffic to be sent via the remaining good link. Support for multiple IOP modules and switch fabrics also is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
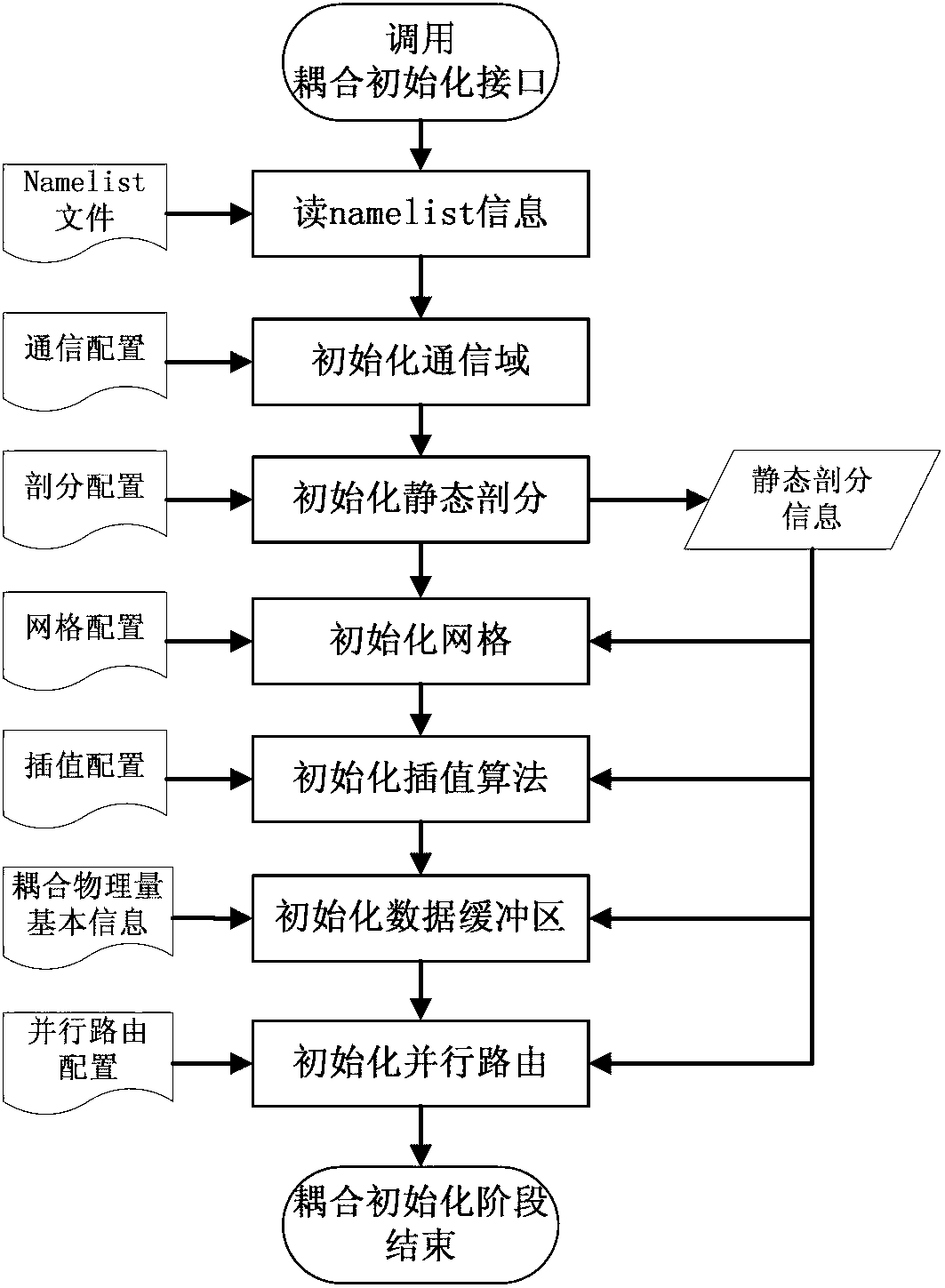
Parallel coupling method for global system mode
ActiveCN102707932AEliminate communication operationsReduce the number of communicationsInterprogram communicationConcurrent instruction executionEnd stagesCoupling
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Hash and route hardware with parallel routing scheme
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Parallel route searching method and system for eliminating longest prefix match search
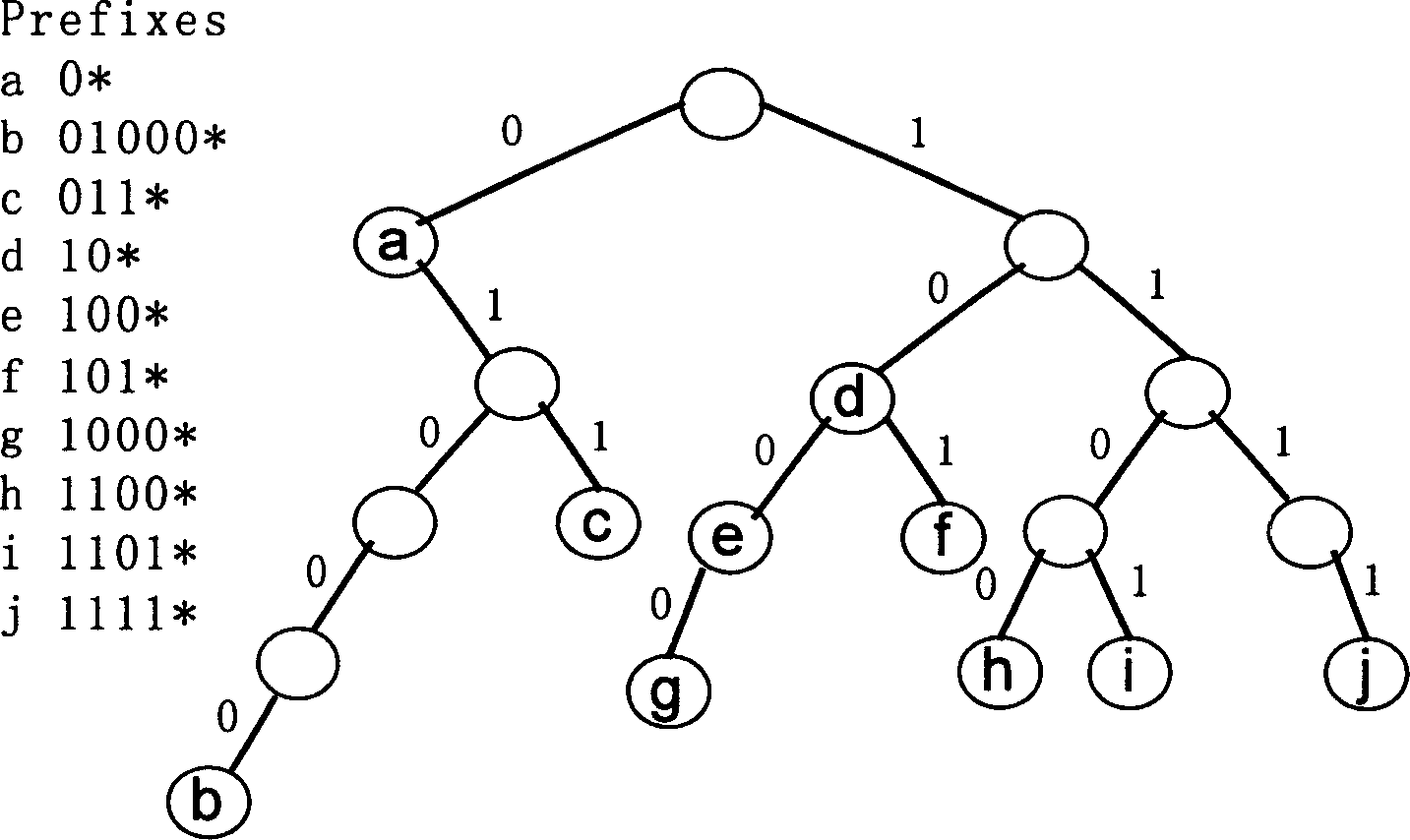
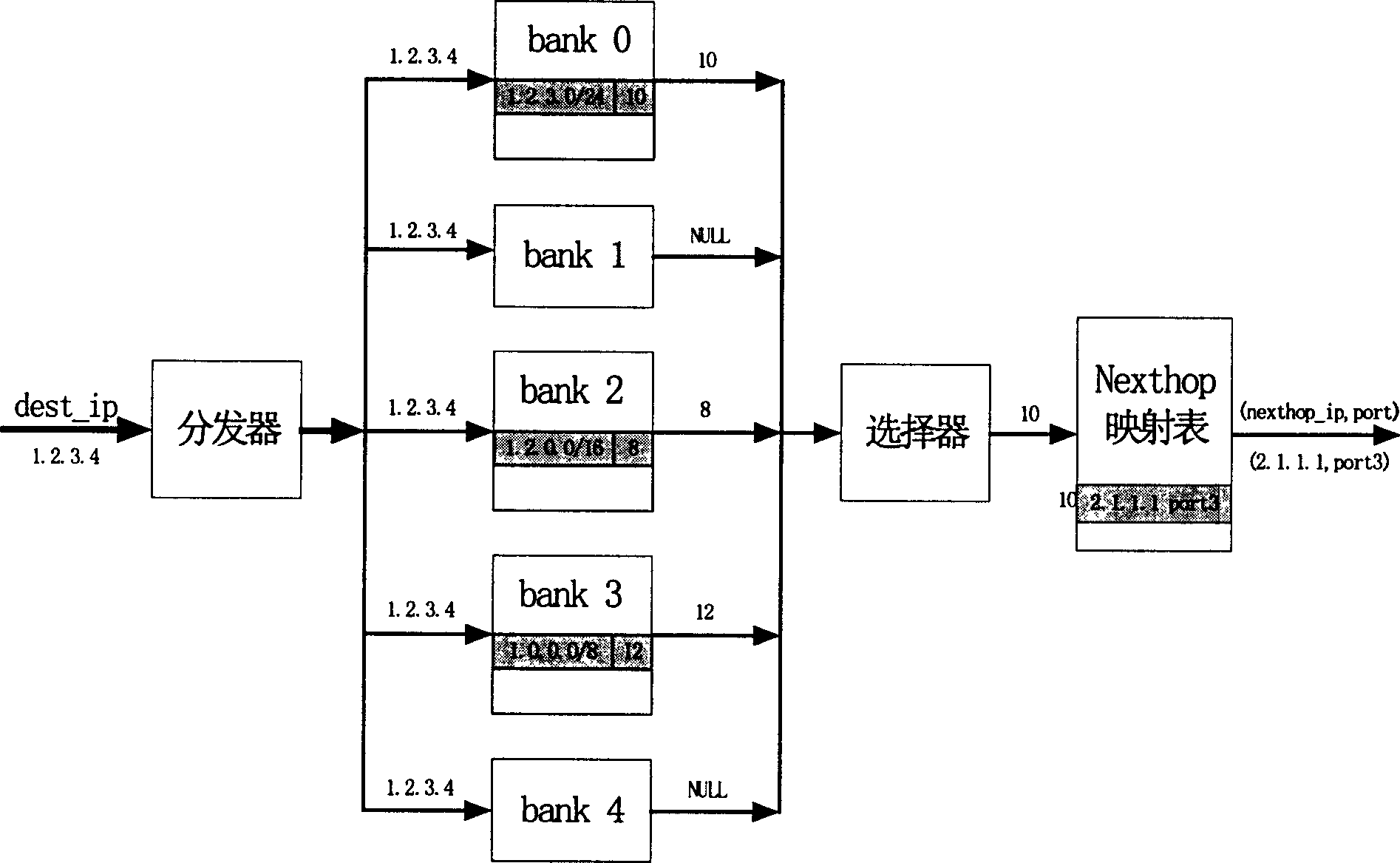
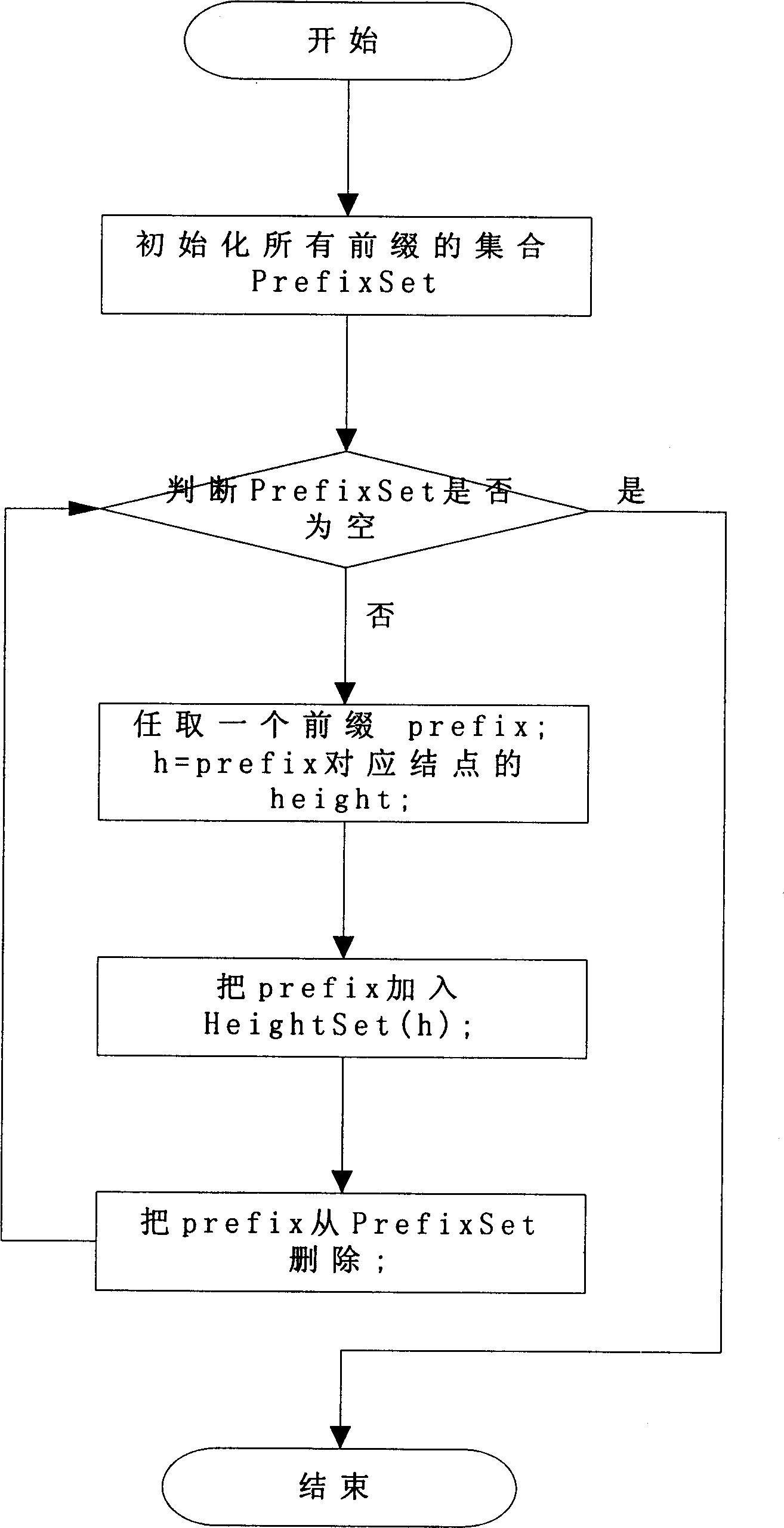
InactiveCN1529454ASimple designImprove search speedData switching networksSelection arrangementsStatic random-access memoryGate array
The invention belonging to technical area for searching Internet IP address in high speed possesses characters: based on searching structure of dichotomy tree, prefix partition is carried out for prefix of all routes according to principle that node heights of current nodes are equal; then, searching for next jumping out port to forward information is carried out concurrently by using search framework in high commonality for some nonoverlapping prefix sets divided from the above said step. The searching system includes distributor, bank unit set, selector and mapper. The said distributor and selector are composed of field programmable gate array (FPGA). The mapper includes static random access memory (SRAM). The said bank unit set is composed of cascaded FPGA and SRAM. The invention also discloses a method for balancing prefix set. Experimental verifies that the invention increases searching speed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
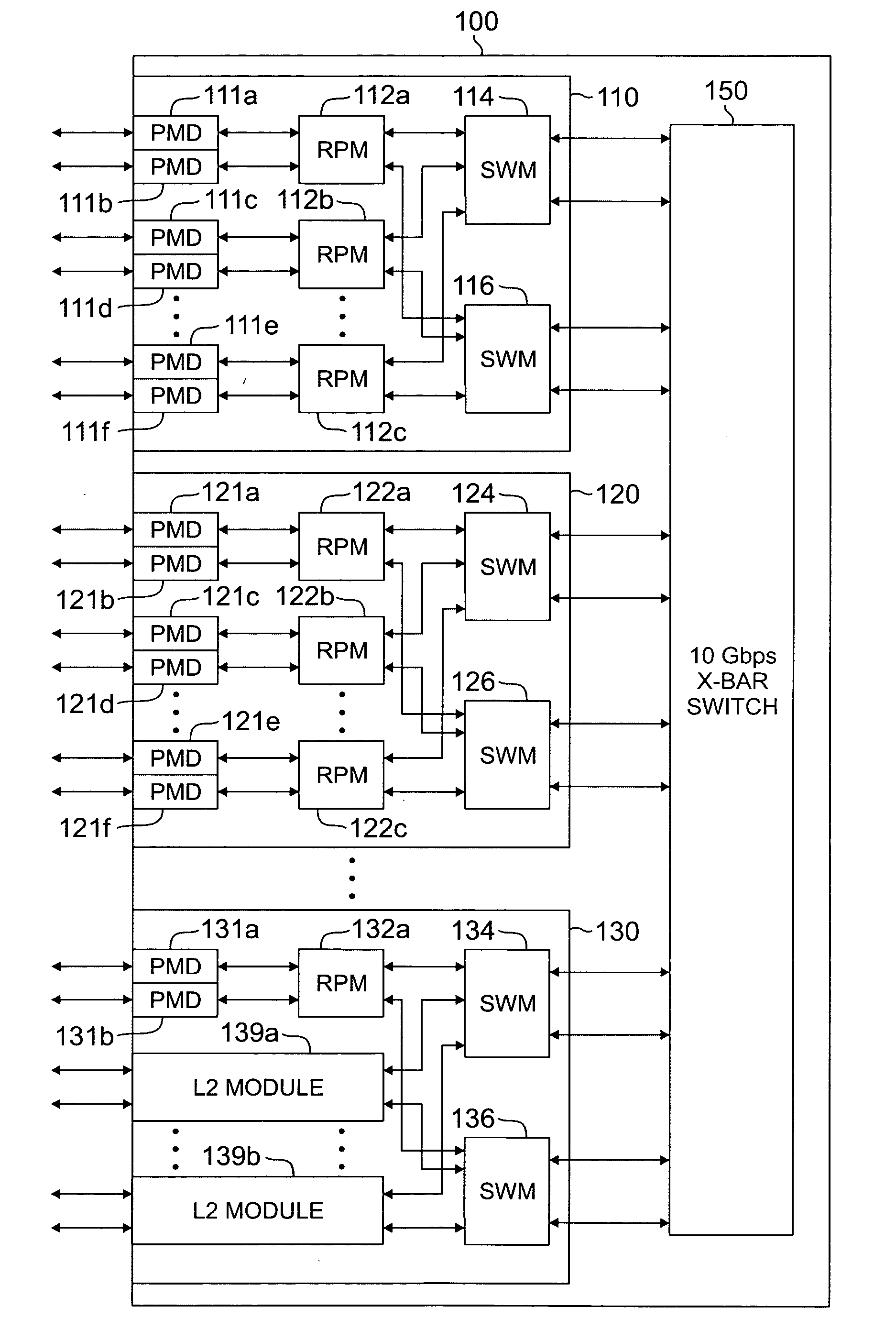
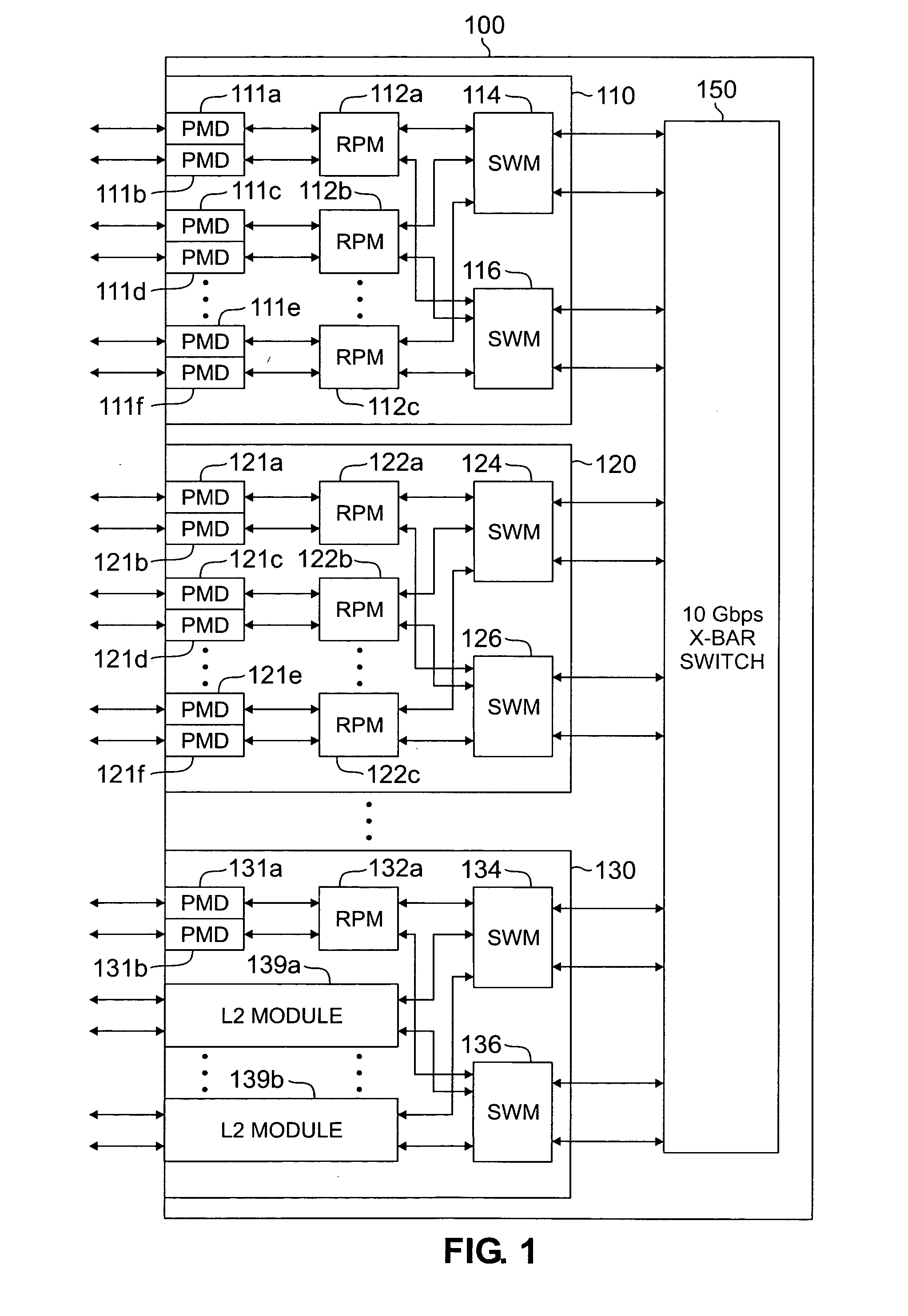
Apparatus and method for maintaining high-speed forwarding tables in a massively parallel router
A router for interconnecting external devices coupled to the router. The router comprises a switch fabric and a plurality of routing nodes coupled to the switch fabric. Each of the routing nodes exchanges data packets with the external devices via network interface ports and with other routing nodes via the switch fabric. A first routing node comprises an inbound network processor capable of receiving incoming data packets from a network interface port; an outbound network processor capable of transmitting data packets to the network interface port; and a shared memory for storing forwarding table information used by the inbound and outbound network processors. The shared memory comprises an inbound upper bank capable of storing forwarding table information accessed by the inbound network processor and an inbound lower bank capable of storing forwarding table information accessed by the inbound network processor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Interconnection and input/output resources for programmable logic integrated circuit devices
InactiveUS6989689B2Increase speedIncrease the propagation speedComputation using non-contact making devicesSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceComputer module
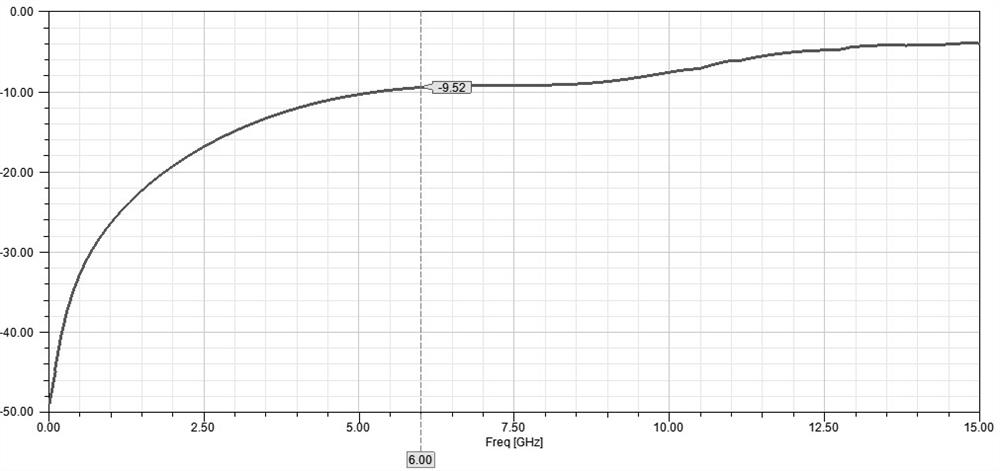
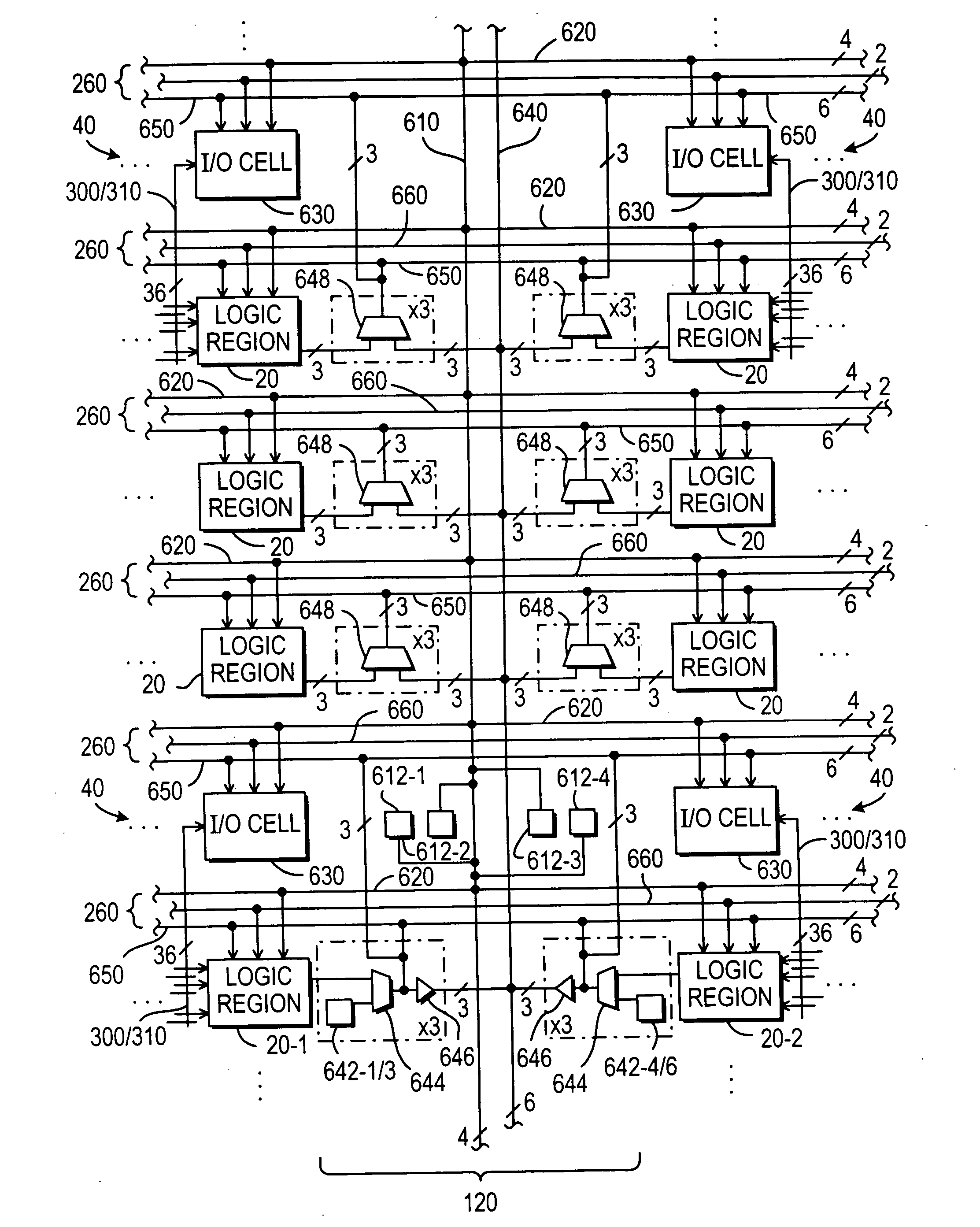
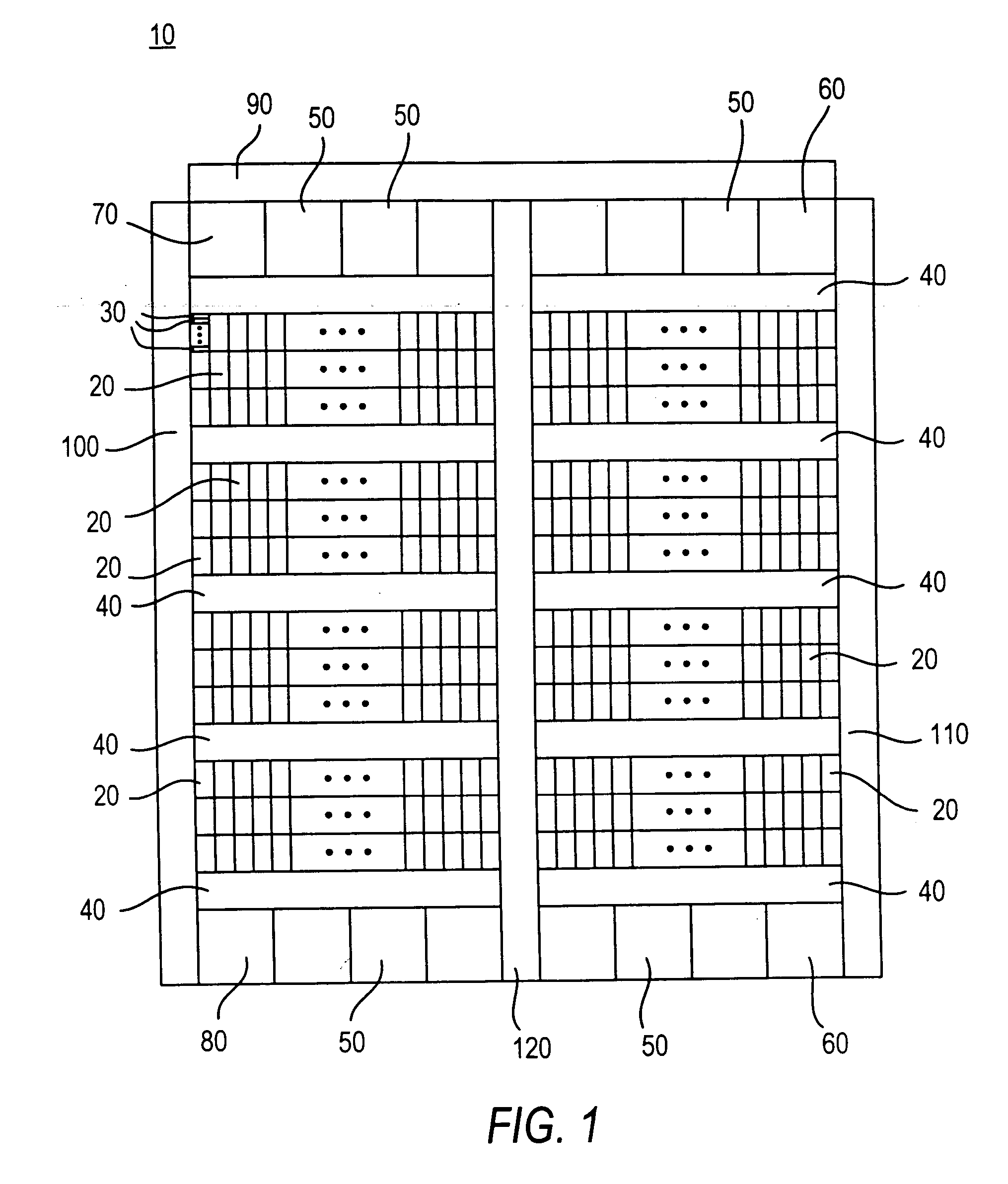
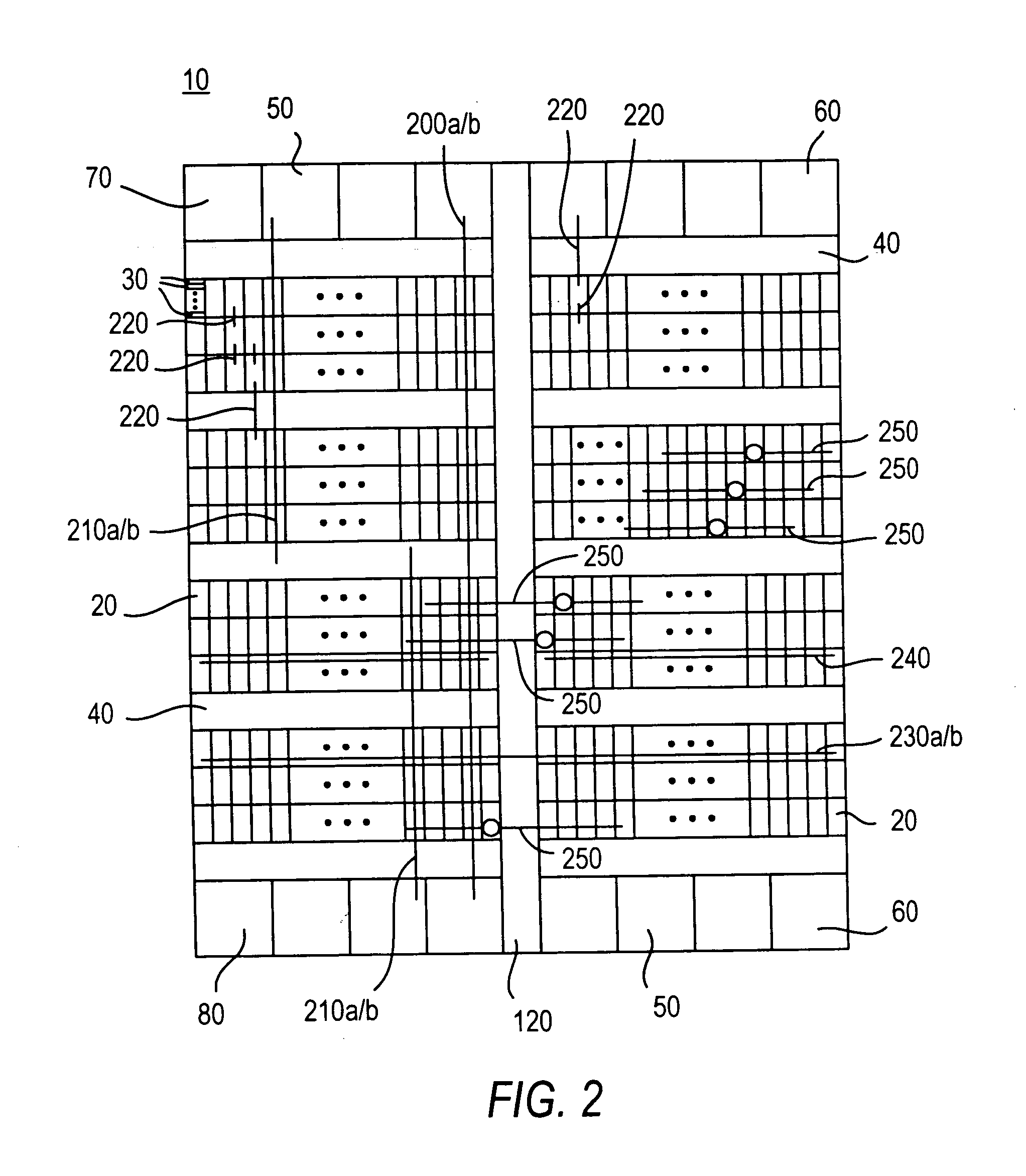
A programmable logic integrated circuit device has a plurality of regions of programmable logic disposed on the device in a plurality of intersecting rows and columns of such regions. Interconnection resources (e.g., interconnection conductors, signal buffers / drivers, programmable connectors, etc.) are provided on the device for making programmable interconnections to, from, and / or between the regions. At least some of these interconnection resources are provided in two forms that are architecturally similar (e.g., with similar and substantially parallel routing) but that have significantly different signal propagation speed characteristics. For example, a major or larger portion of such dual-form interconnection resources may have what may be termed normal signal speed, while a smaller minor portion may have significantly faster signal speed. Secondary (e.g., clock and clear) signal distribution may also be enhanced, and so may be input / output circuitry and cascade connections between adjacent or nearby logic modules on the device.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
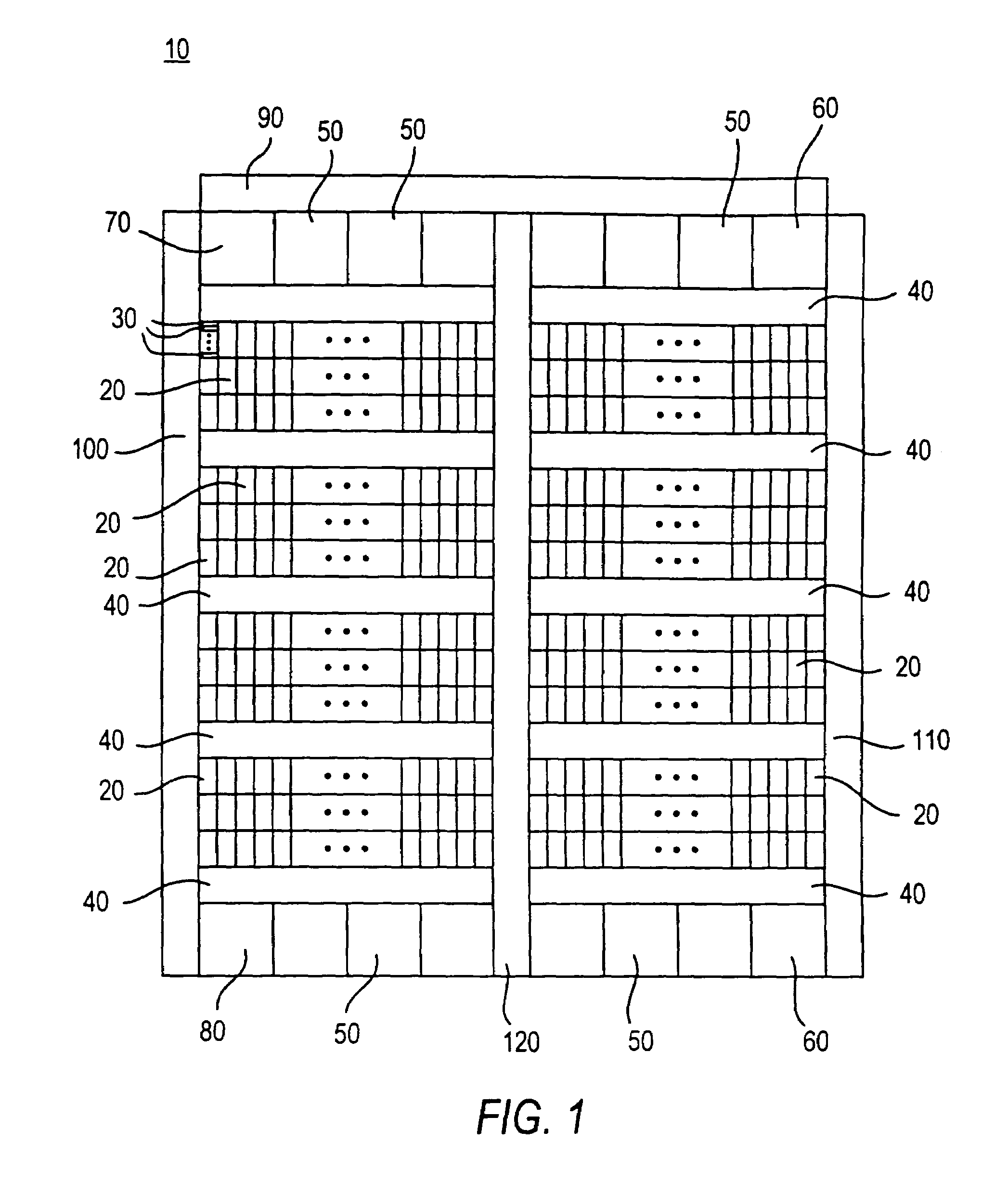
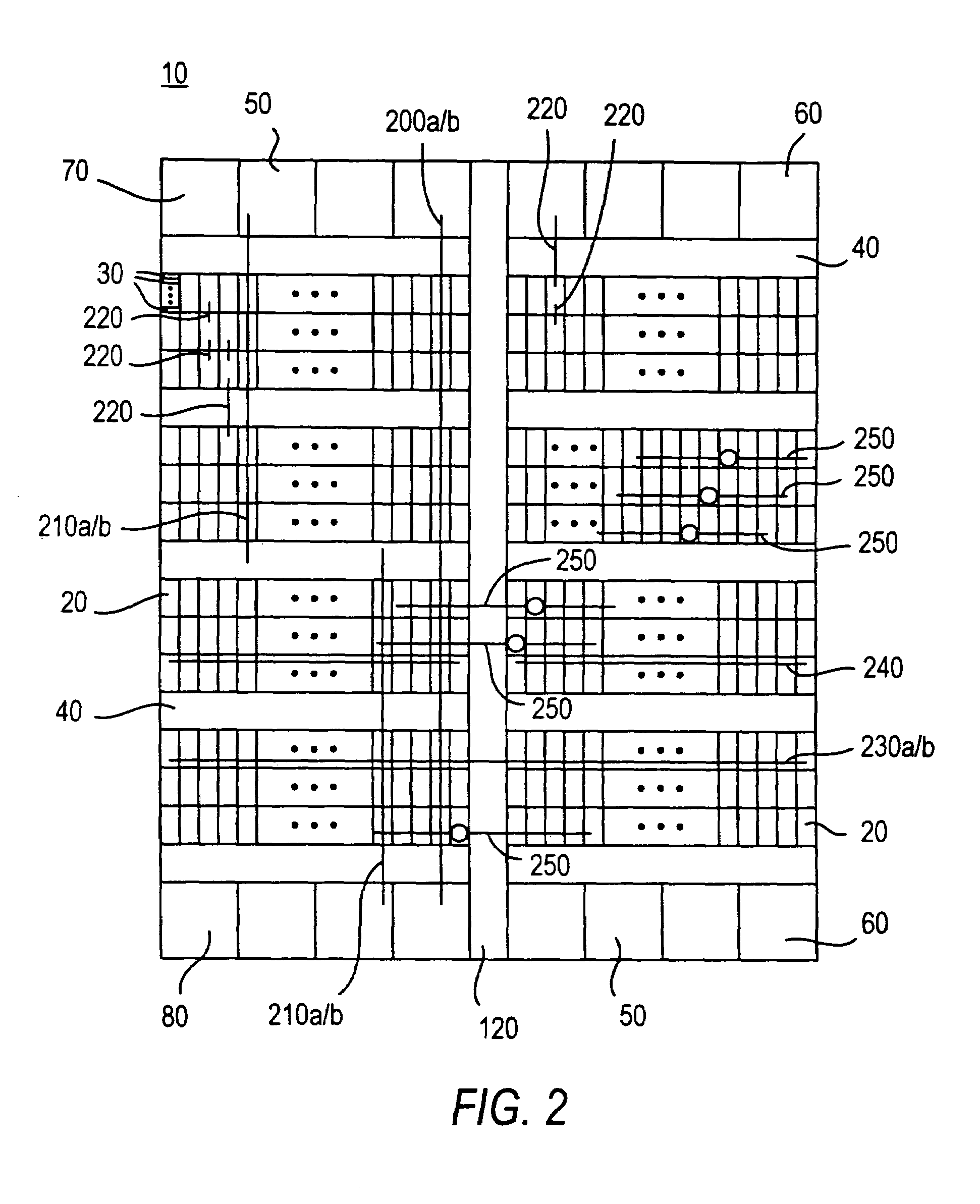
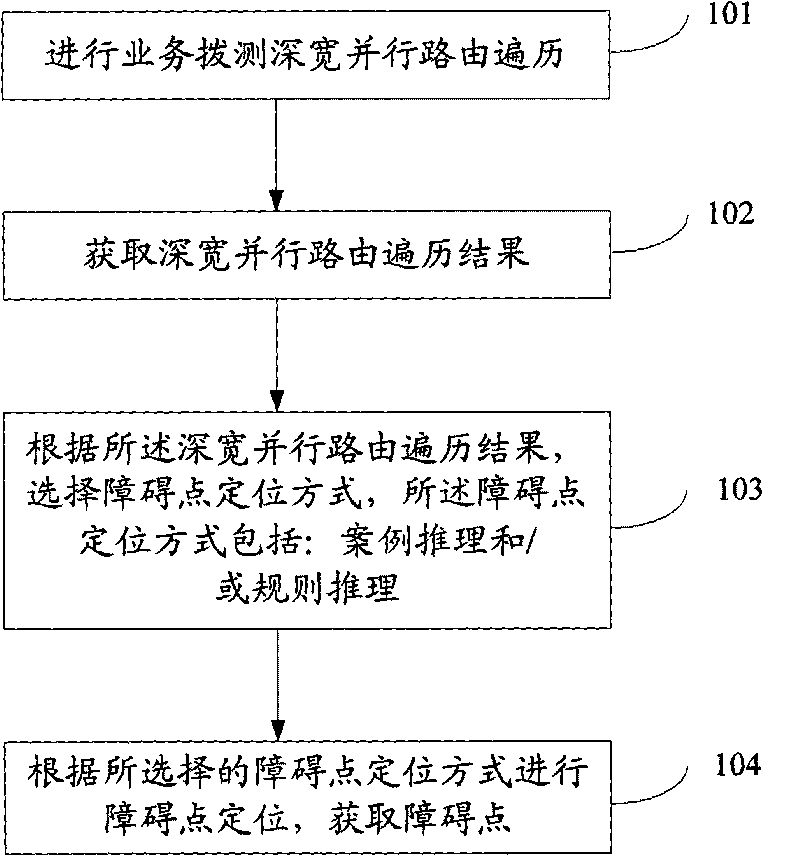
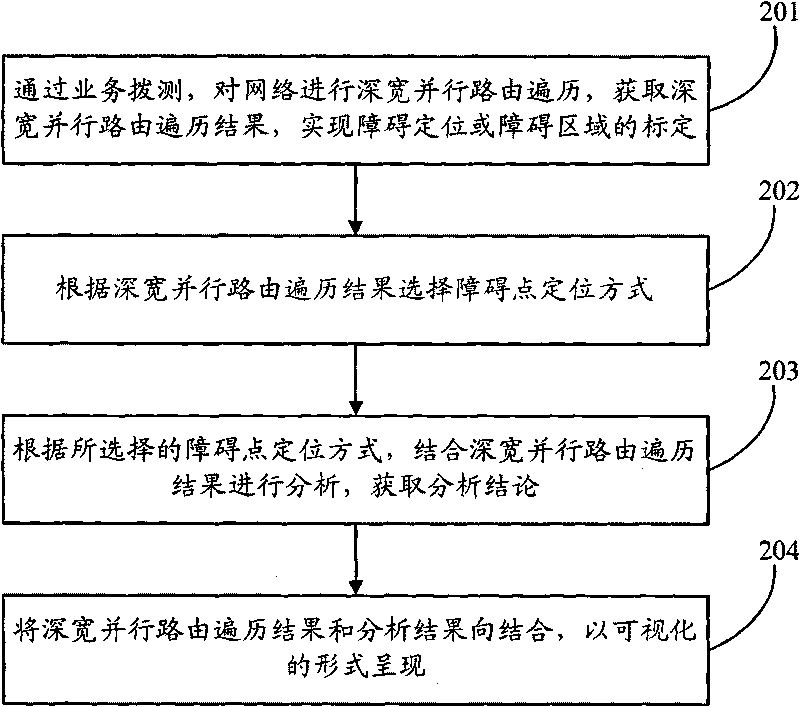
Method and device for automatically positioning fault points
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a device for automatically positioning fault points. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out dialling test height and width parallel routing traversal for service; obtaining the result of the height and width parallel routing traversal; according to the result of the height and width parallel routing traversal, selecting a fault point positioning mode, wherein the fault point positioning mode comprises: case-based reasoning and / or rule-based reasoning; according to the selected fault point positioning mode, positioning the fault point, and obtaining the fault point. The invention realizes that the fault points can be accurately and automatically positioned.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP ZHEJIANG
Multi-threaded track assignment
ActiveUS20110055789A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingCircuit design
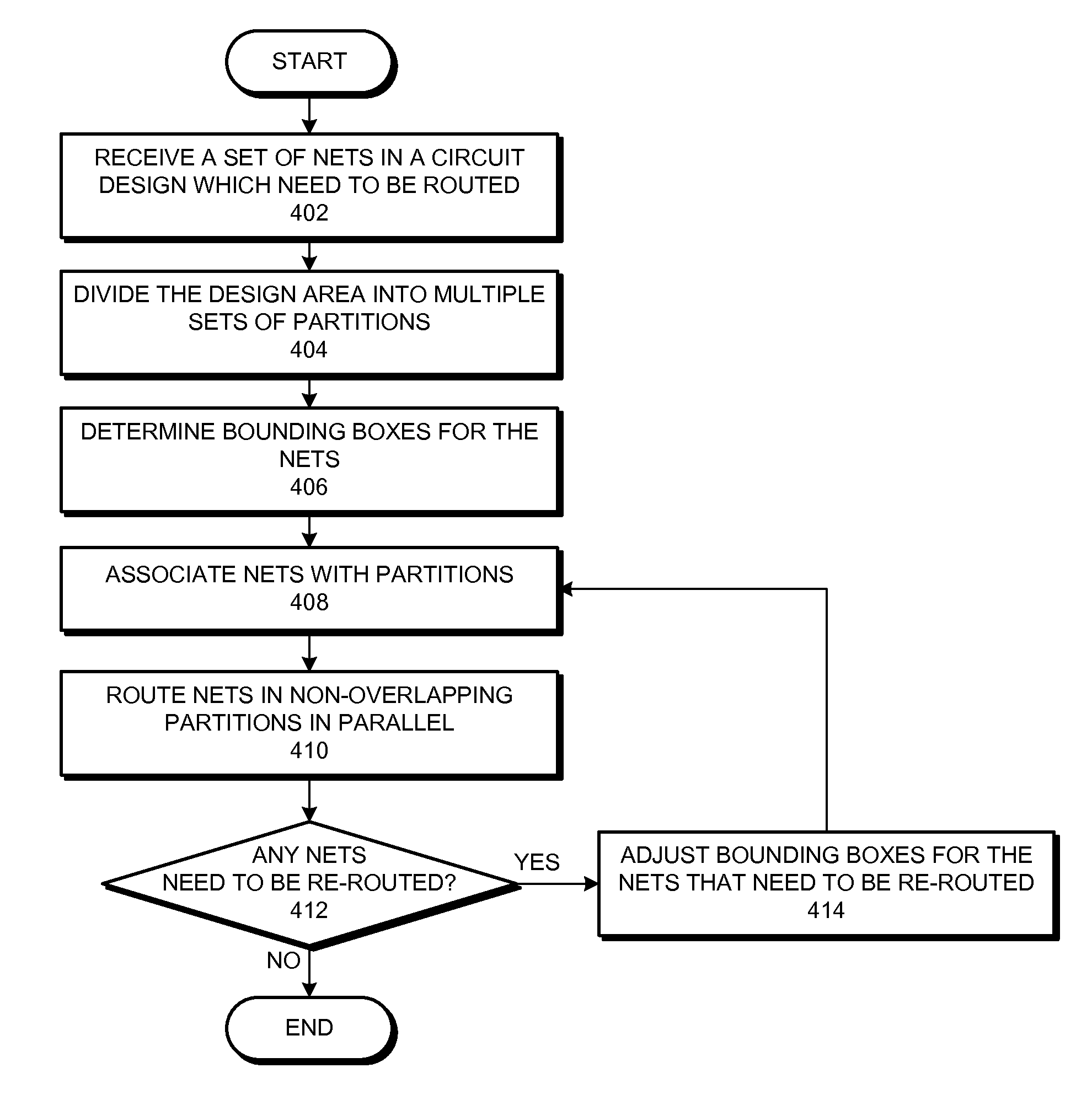
Some embodiments provide techniques and systems for routing nets in a circuit design in parallel. During operation, the system can receive a first set of partitions for a circuit design, wherein each partition in the first set of partitions extends across the circuit design along a first direction. Next, the system can perform, in parallel, track assignment in the first direction on non-overlapping partitions in the first set of partitions. The system can then receive a second set of partitions for the circuit design, wherein each partition in the second set of partitions extends across the circuit design along a second direction which is different from the first direction. Next, the system can perform, in parallel, track assignment in the second direction on non-overlapping partitions in the second set of partitions. In some embodiments, each track assignment process being performed in parallel performs track assignment on a different net.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Interconnection and input/output resources for programmable logic integrated circuit devices
InactiveUS6894533B2Double speedHalve propagation time of signalComputation using non-contact making devicesSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceComputer module
A programmable logic integrated circuit device has a plurality of regions of programmable logic disposed on the device in a plurality of intersecting rows and columns of such regions. Interconnection resources (e.g., interconnection conductors, signal buffers / drivers, programmable connectors, etc.) are provided on the device for making programmable interconnections to, from, and / or between the regions. At least some of these interconnection resources are provided in two forms that are architecturally similar (e.g., with similar and substantially parallel routing) but that have significantly different signal propagation speed characteristics. For example, a major or larger portion of such dual-form interconnection resources may have what may be termed normal signal speed, while a smaller minor portion may have significantly faster signal speed. Secondary (e.g., clock and clear) signal distribution may also be enhanced, and so may be input / output circuitry and cascade connections between adjacent or nearby logic modules on the device.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
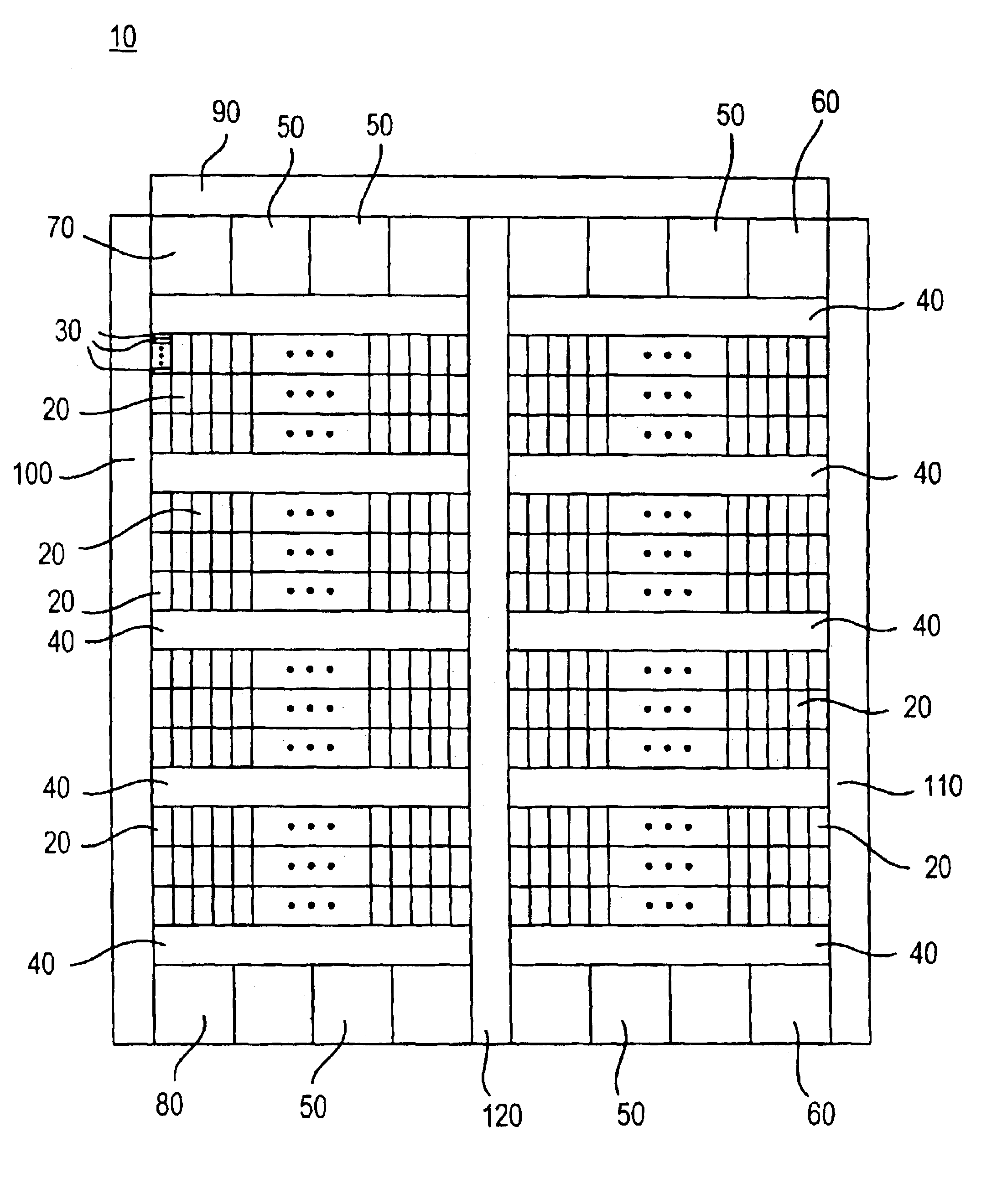
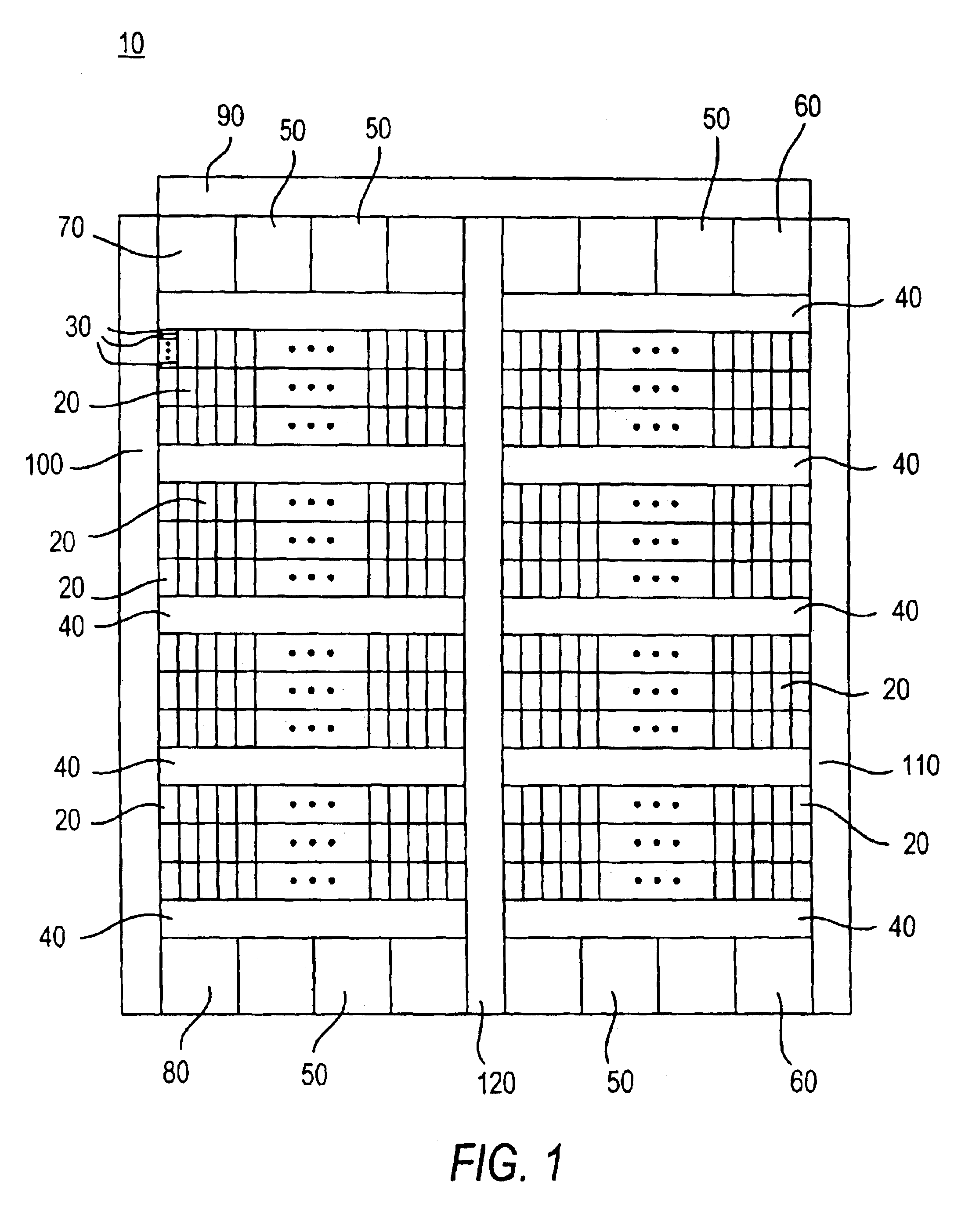
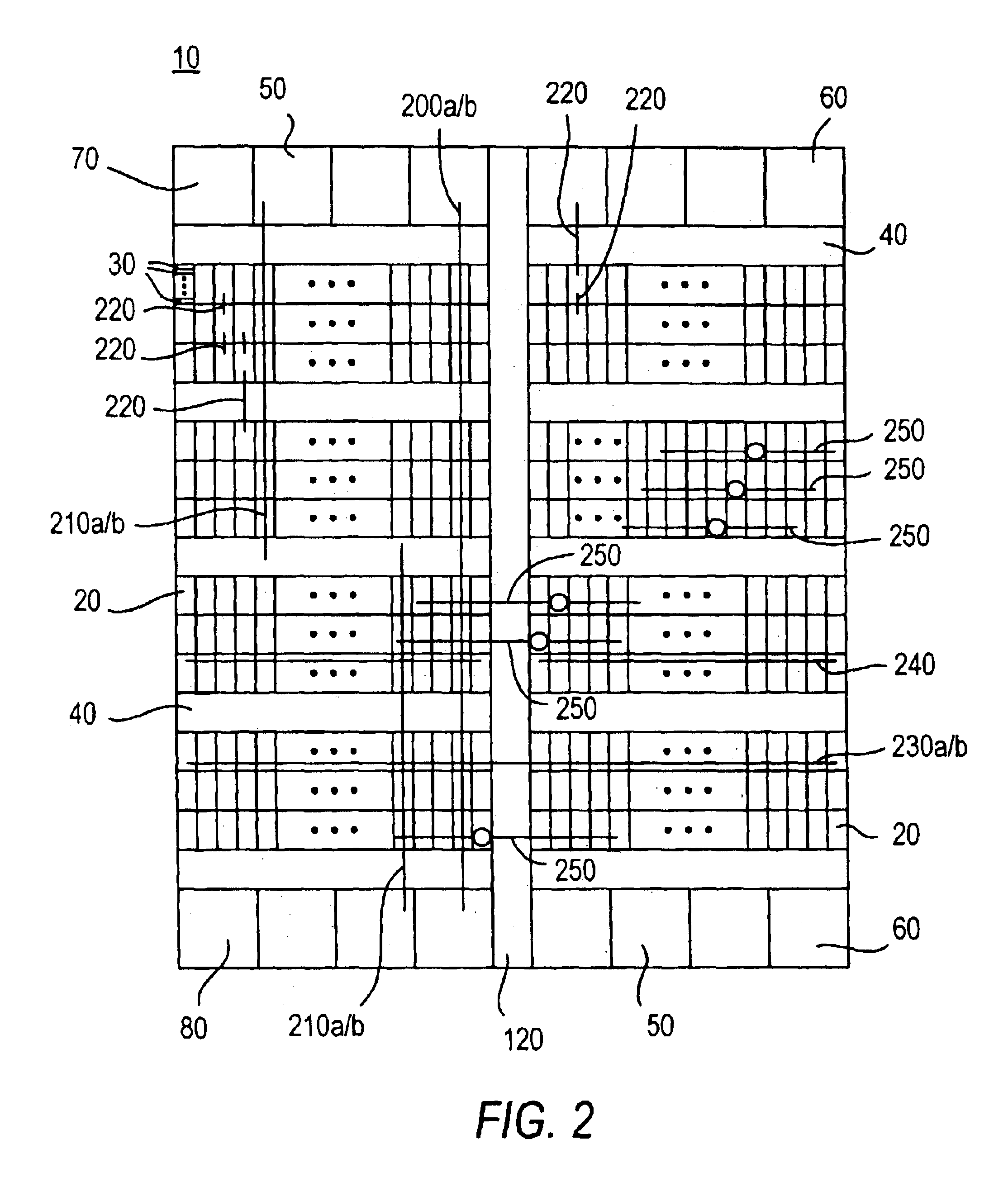
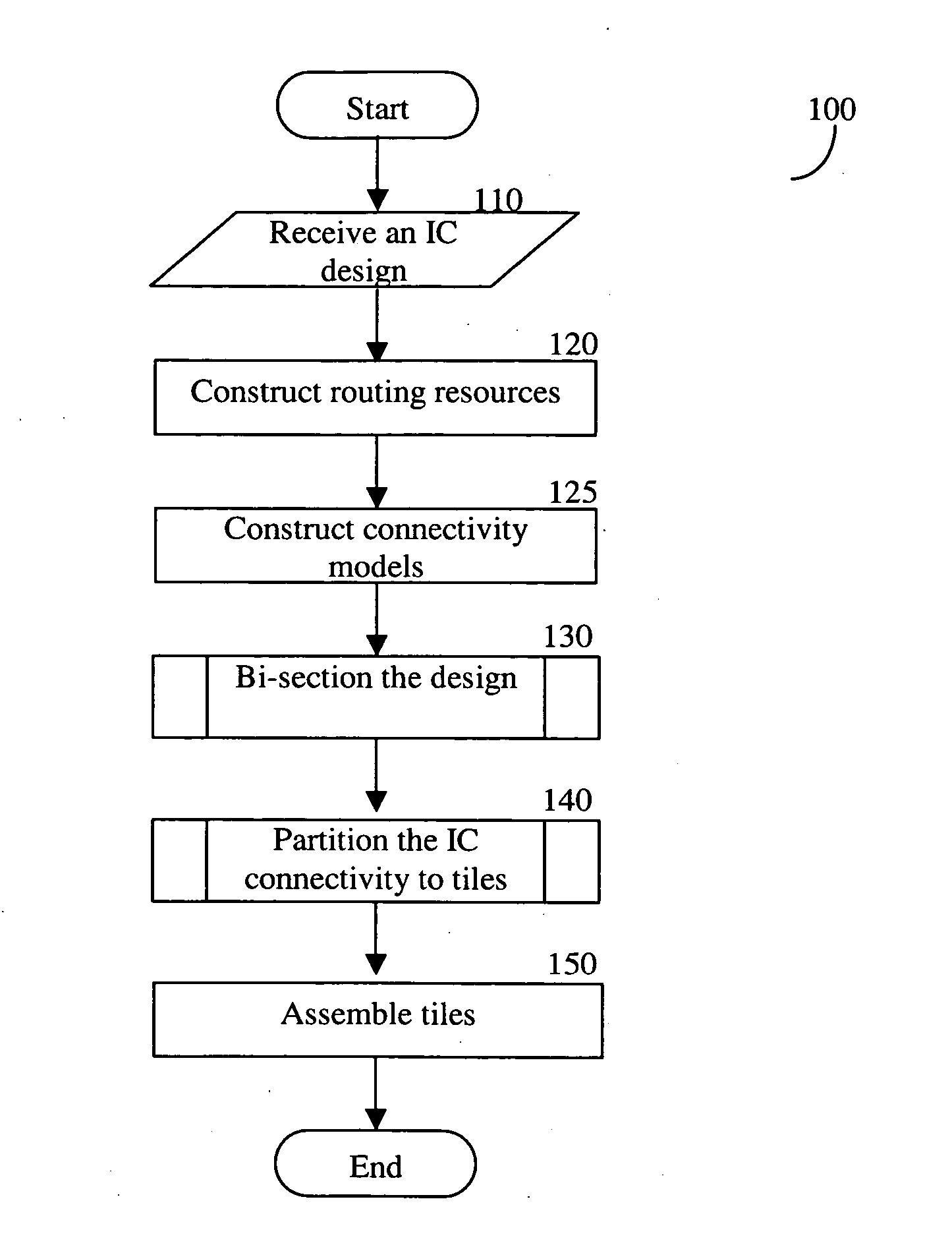
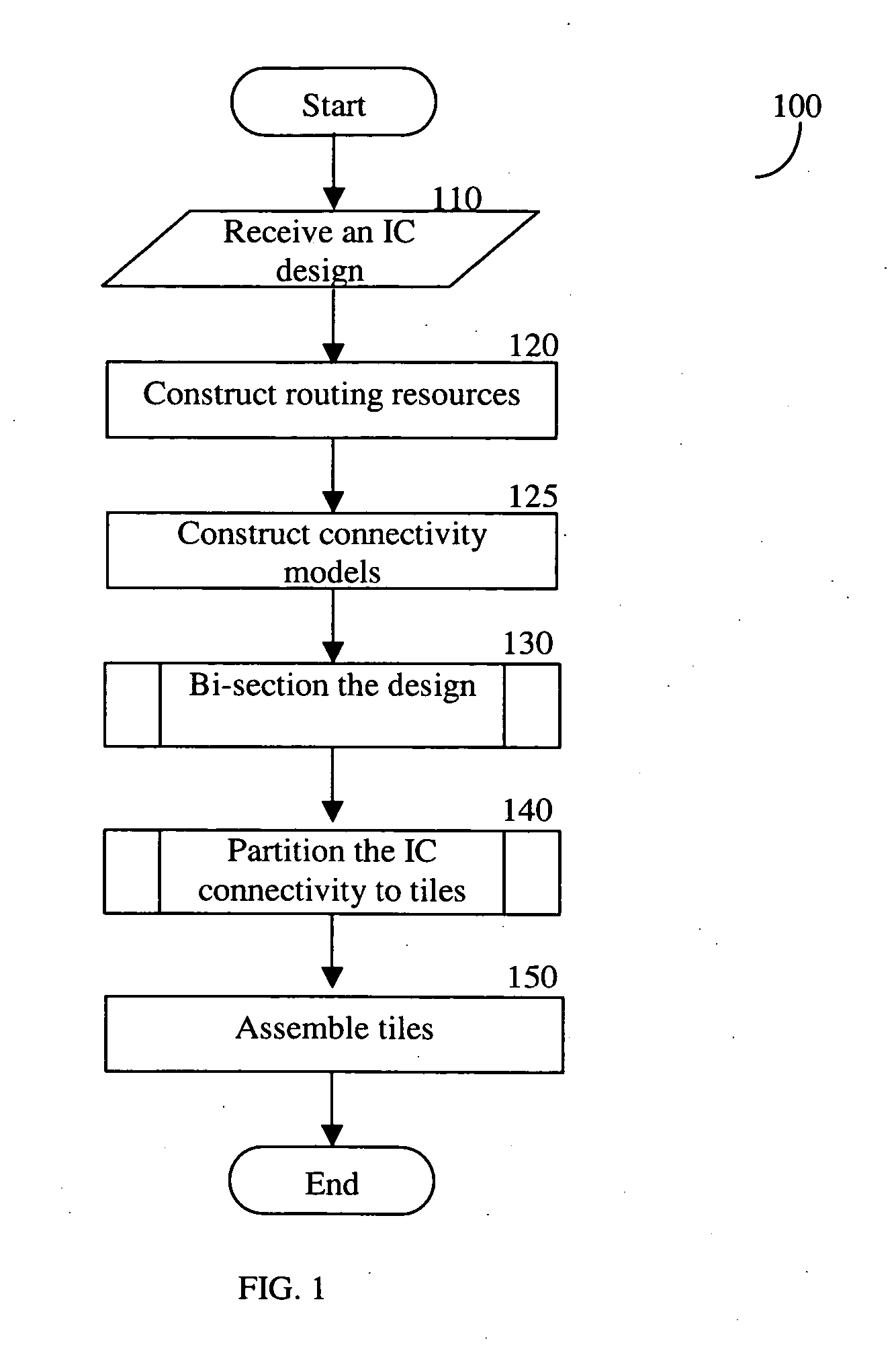
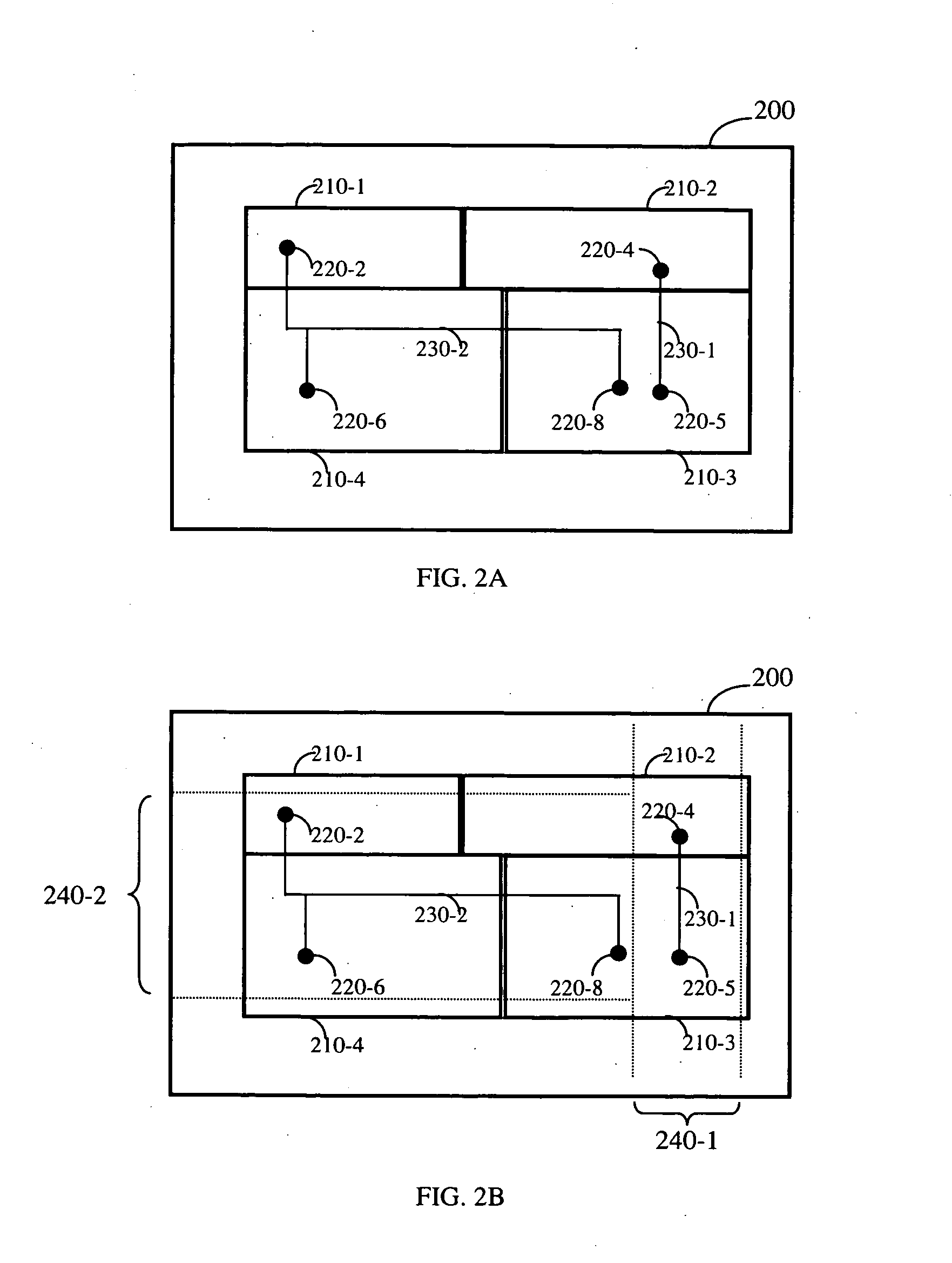
Methods for tiling integrated circuit designs
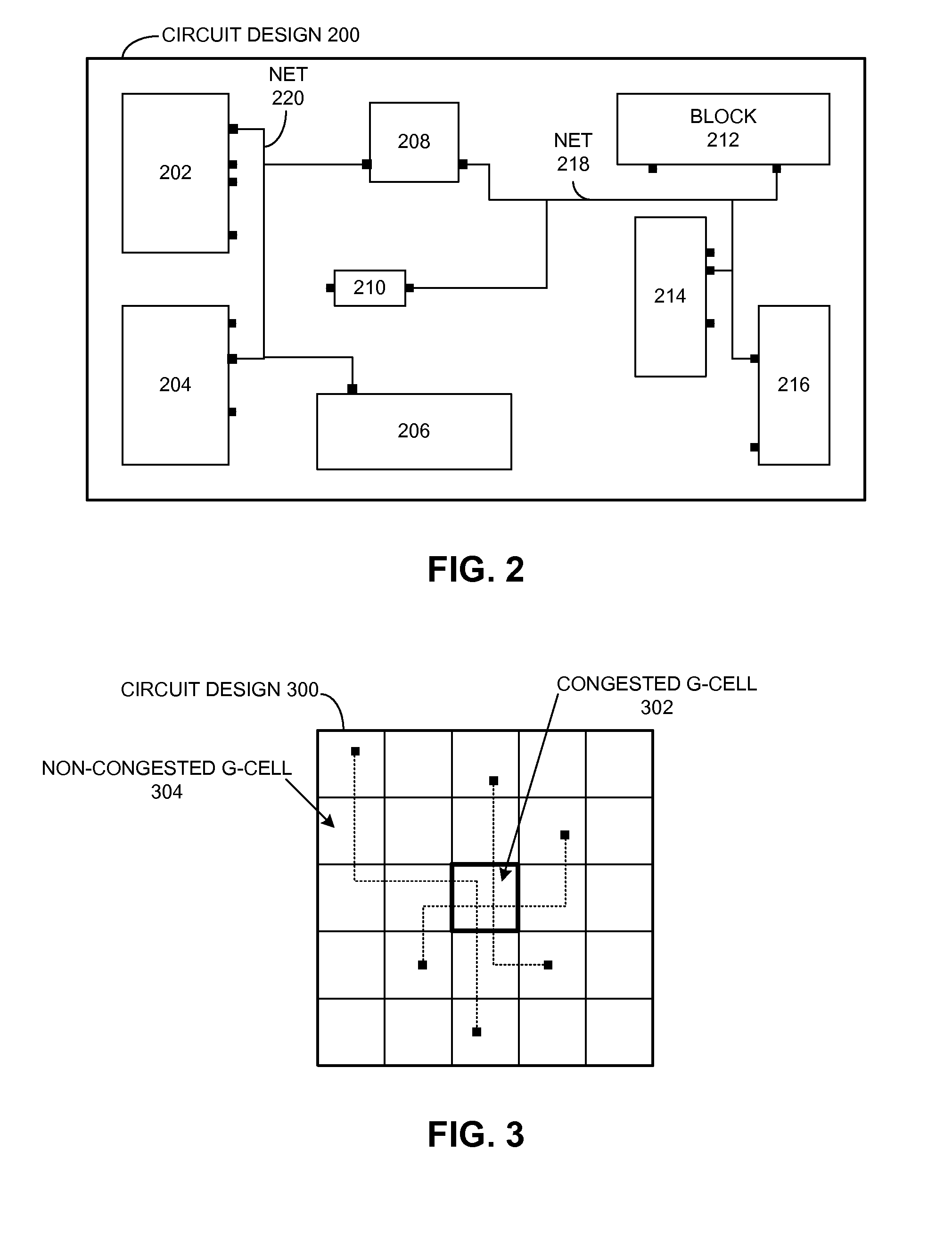
Methods for routing in the design of integrated circuits (ICs) to simplify the routing task. The method includes dividing a given IC design into a limited number of non-overlapping tiles, and then routing all tiles in parallel, each tile being independently routed by a standard router. Thereafter, routed tiles are assembled to form a routing solution for the entire IC. Details of exemplary methods are disclosed.
Owner:ATHENA DESIGN SYST
Multi-channel DDS chip substrate packaging structure and method
ActiveCN112133687AReduce crosstalkReduce couplingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransmission channelGround plane
The invention discloses a multi-channel DDS (Direct Digital Synthesizer) chip substrate packaging structure and method, which are used for designing wiring of multi-channel differential pair signals,layout of a power supply ground plane and arrangement of bonding fingers and leading-out ends. The differential pair of each channel adopts an arc-shaped routing and non-parallel routing mode; power supply ground planes are laid in the horizontal direction, the lower layer and the lower layer of the differential pair, the power supply ground planes of all the channels are independent of one another and keep a certain isolation distance, crosstalk and coupling between the power supply ground planes of all the channels are reduced, signal loss of the multi-channel DDS chip is remarkably reduced,and isolation between all transmission channels is improved. The technical problems that in the prior art, attenuation of multi-channel DDS chip signals is increasingly serious, and the isolation degree between transmission channels is increasingly low are solved.
Owner:CHENGDU CORPRO TECH CO LTD
Interconnection and input/output resources for programmable logic integrated circuit devices
InactiveUS20070030029A1Increase speedIncrease the propagation speedComputation using non-contact making devicesSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorInterconnection
A programmable logic integrated circuit device has a plurality of regions of programmable logic disposed on the device in a plurality of intersecting rows and columns of such regions. Interconnection resources (e.g., interconnection conductors, signal buffers / drivers, programmable connectors, etc.) are provided on the device for making programmable interconnections to, from, and / or between the regions. At least some of these interconnection resources are provided in two forms that are architecturally similar (e.g., with similar and substantially parallel routing) but that have significantly different signal propagation speed characteristics. For example, a major or larger portion of such dual-form interconnection resources may have what may be termed normal signal speed, while a smaller minor portion may have significantly faster signal speed. Secondary (e.g., clock and clear) signal distribution may also be enhanced, and so may be input / output circuitry and cascade connections between adjacent or nearby logic modules on the device.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Parallel route searching method and system
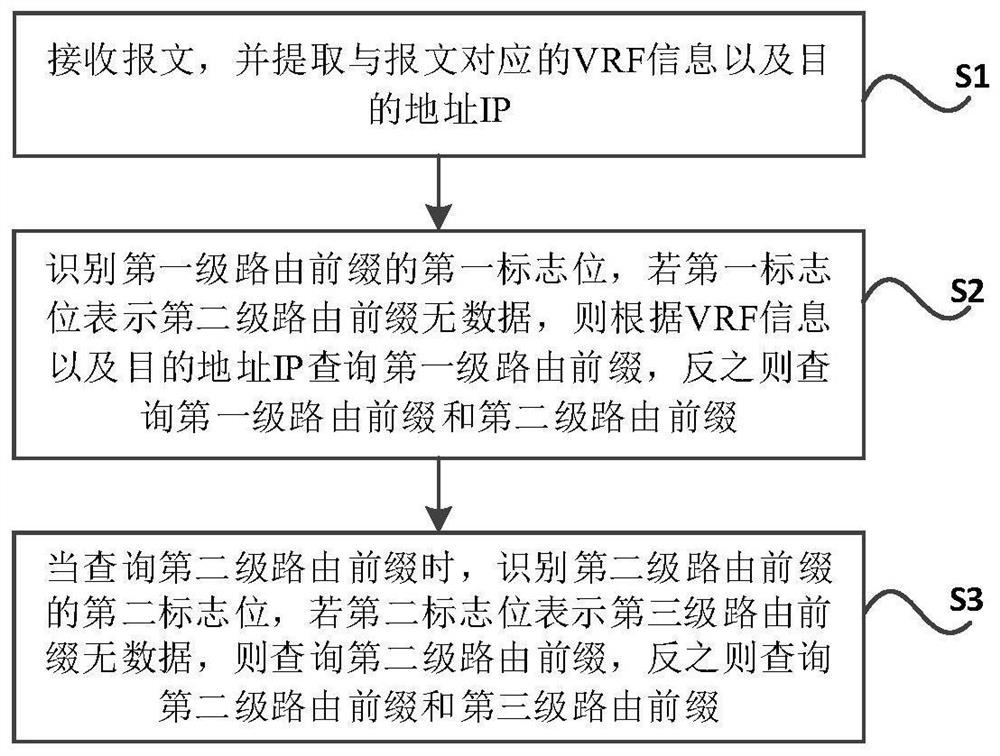
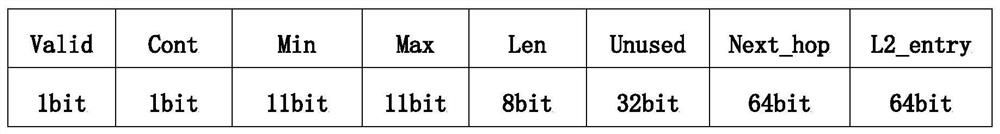
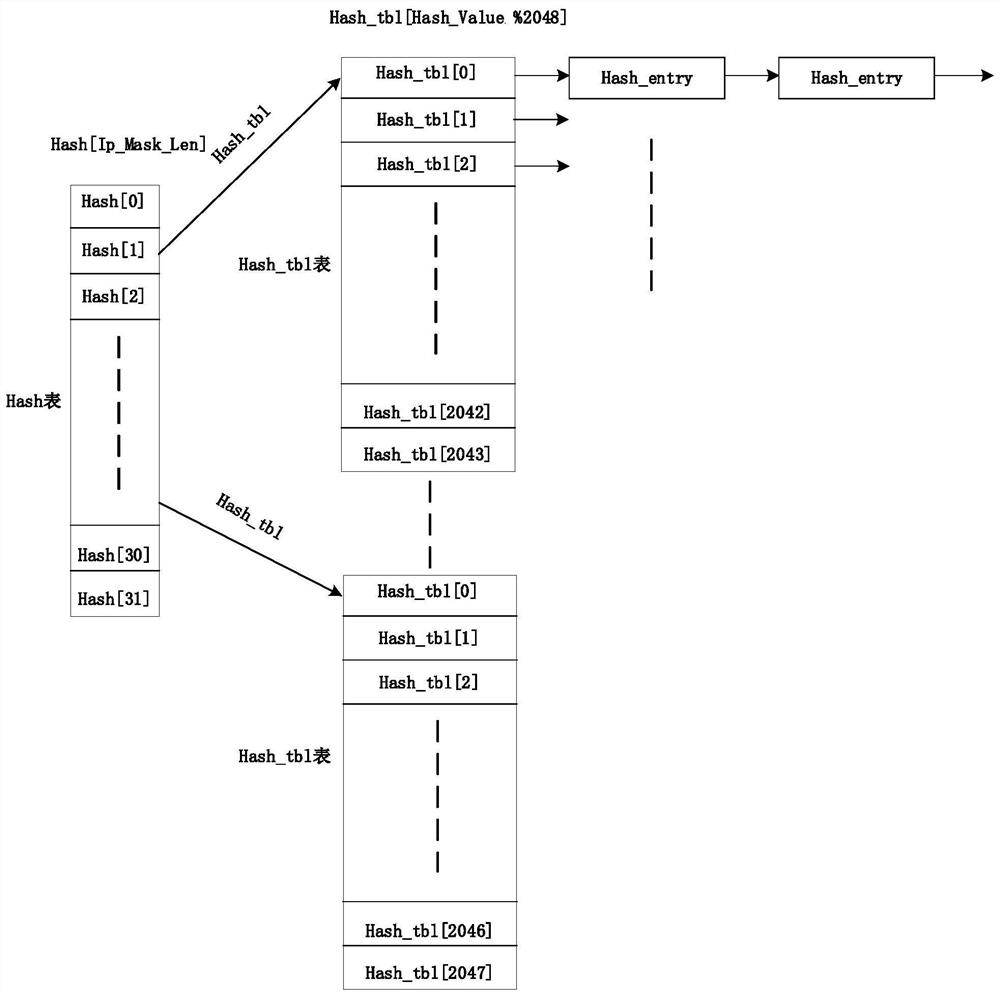
ActiveCN112235197AEasy to findEliminate limitationsData switching networksComputer networkEngineering
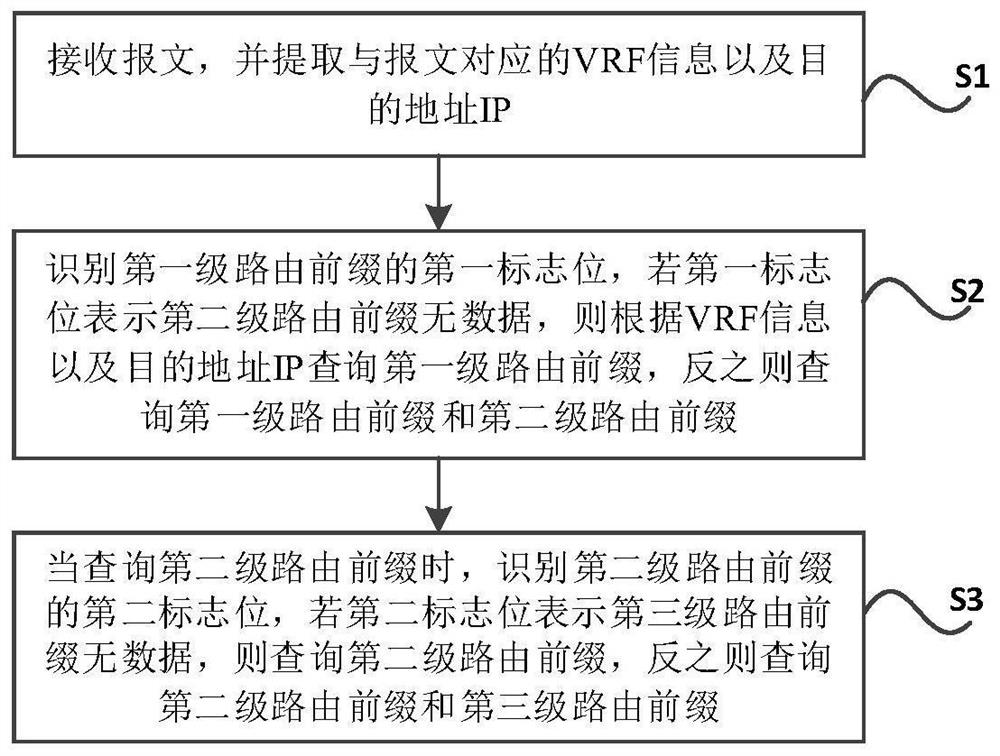
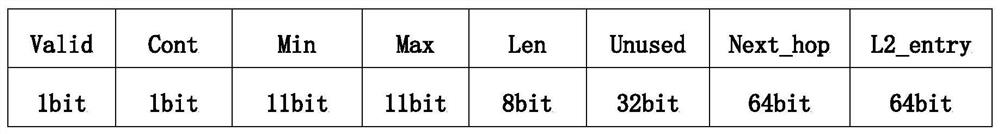
The invention discloses a parallel route searching method and system, and relates to the technical field of communication, and the method comprises the following steps: receiving a message, and extracting VRF information and a destination address IP corresponding to the message; identifying a first flag bit of the first-level routing prefix, if the first flag bit indicates that the second-level routing prefix has no data, querying the first-level routing prefix according to the VRF information and the destination address IP, and otherwise, querying the first-level routing prefix and the second-level routing prefix; and when querying the second-level routing prefix, identifying a second flag bit of the second-level routing prefix, if the second flag bit indicates that the third-level routing prefix has no data, querying the second-level routing prefix, and otherwise, querying the second-level routing prefix and the third-level routing prefix. According to the method, the multi-level routing prefix is adopted, a multi-level data storage structure which is simple and convenient to search is provided, and the limitation of the existing parallel routing search method is eliminated.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Synchronized parallel processing of rows of data with dependencies by determining start time for processors
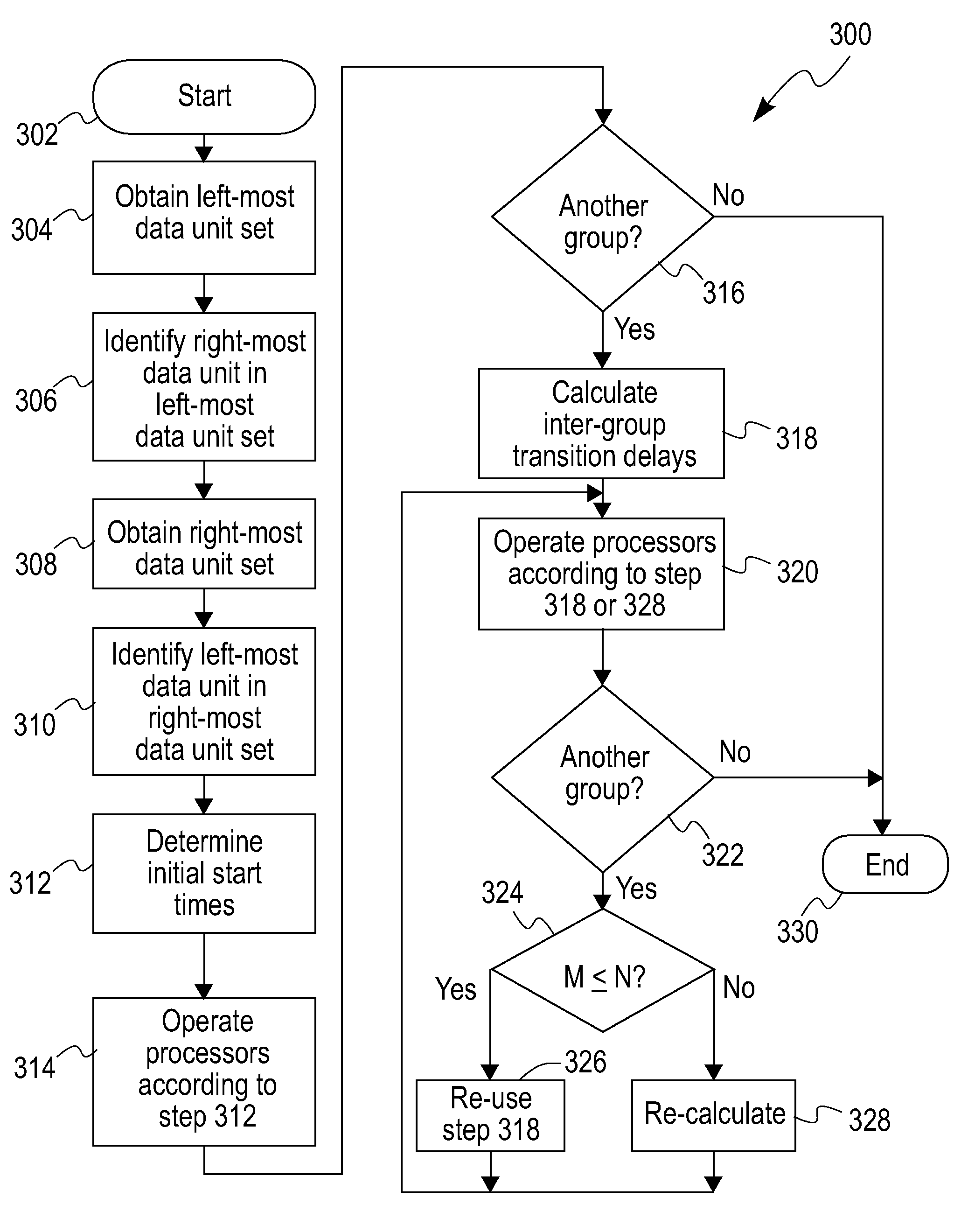
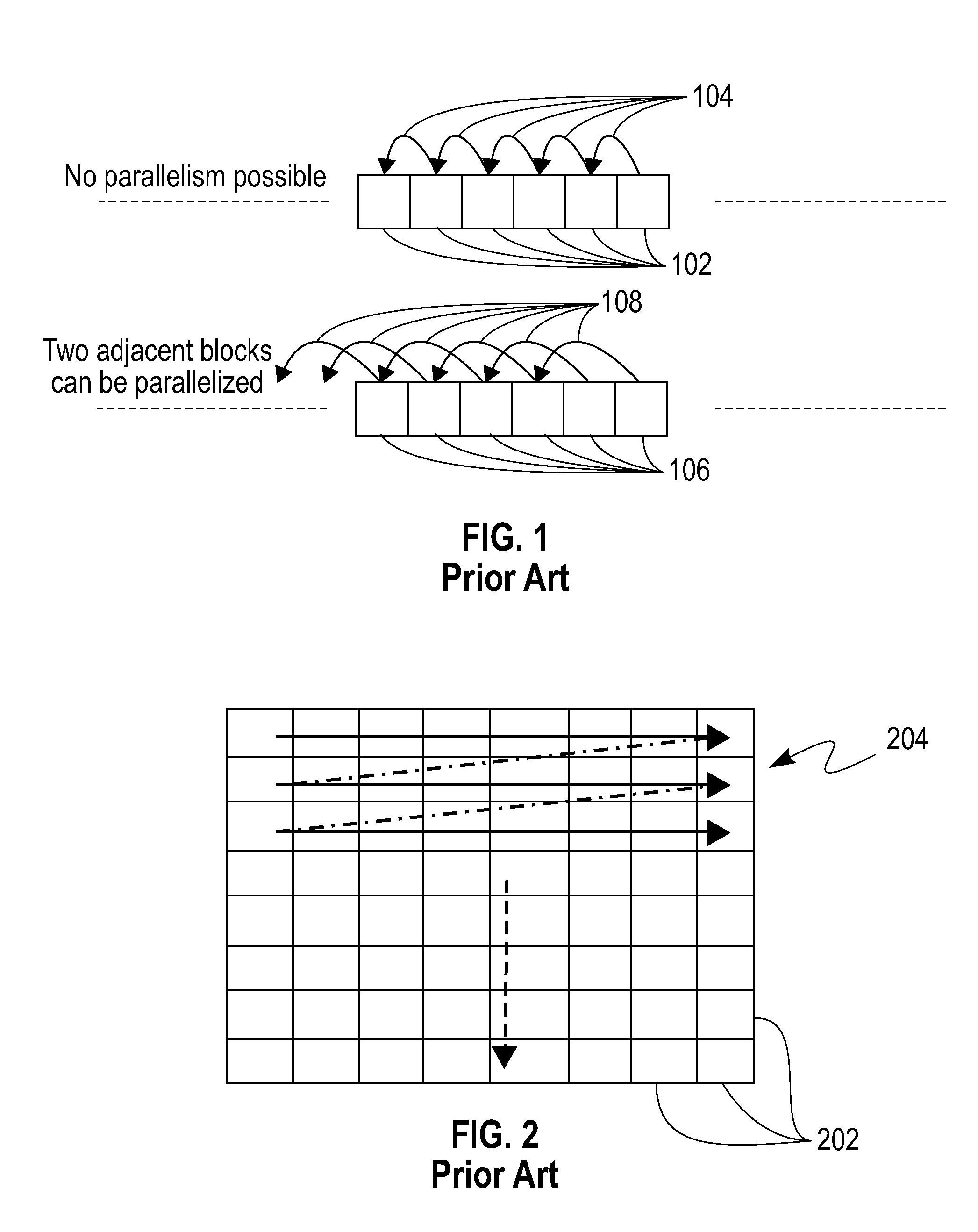
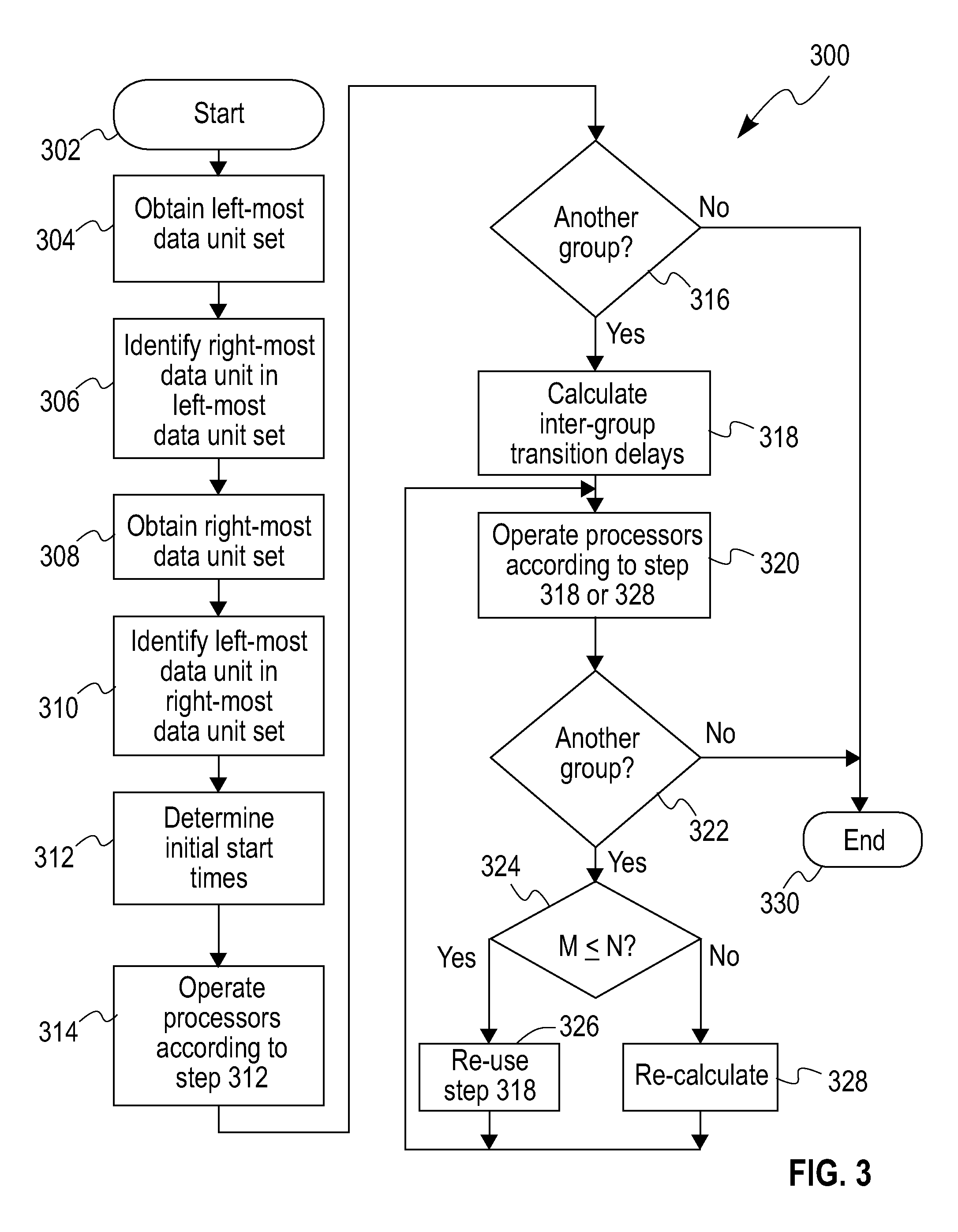
InactiveUS8156364B2Multiple digital computer combinationsProcessor architectures/configurationDependency structureStart time
A method (which can be computer implemented) for processing a plurality of adjacent rows of data units, using a plurality of parallel processors, given (i) a predetermined processing order, and (ii) a specified inter-row dependency structure, includes the steps of determining starting times for each individual one of the processors, and maintaining synchronization across the processors, while ensuring that the dependency structure is not violated. Not all the starting times are the same, and a sum of absolute differences between (i) starting times of any given processor, and (ii) that one of the processors having an earliest starting time, is minimized.
Owner:IBM CORP
Chip on film (COF) and COF carrier tape
InactiveCN102237334AIncrease the number ofLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesChip on filmSemiconductor device
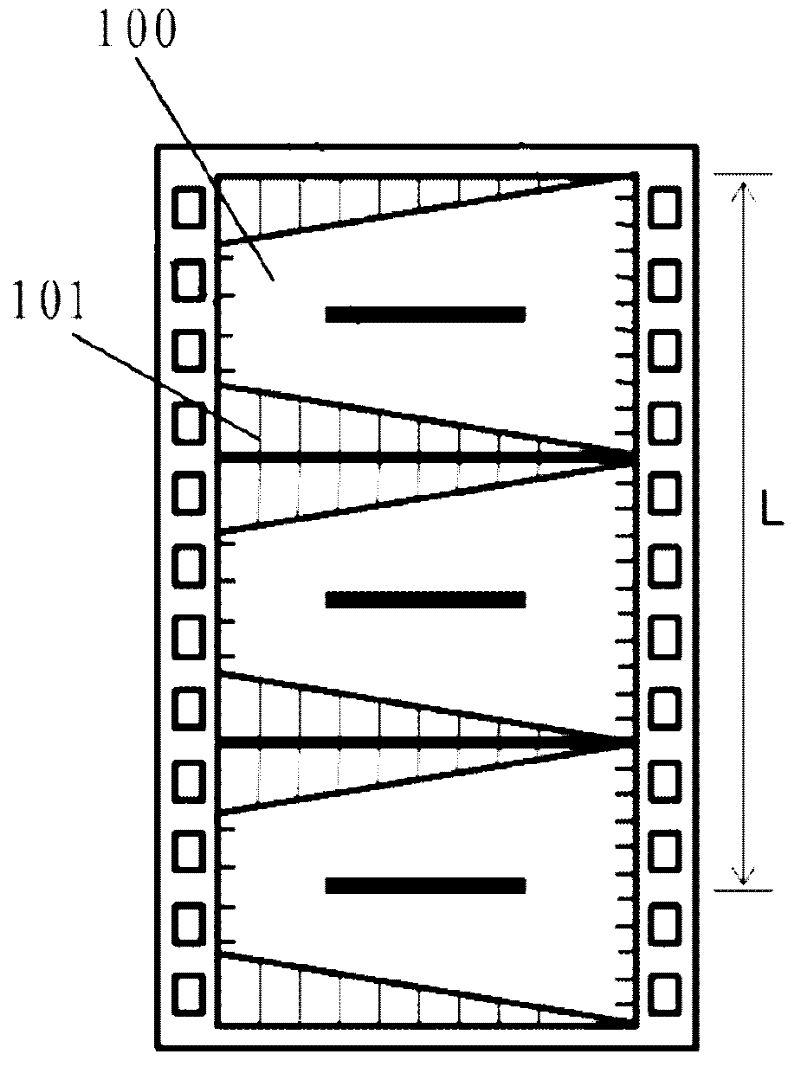
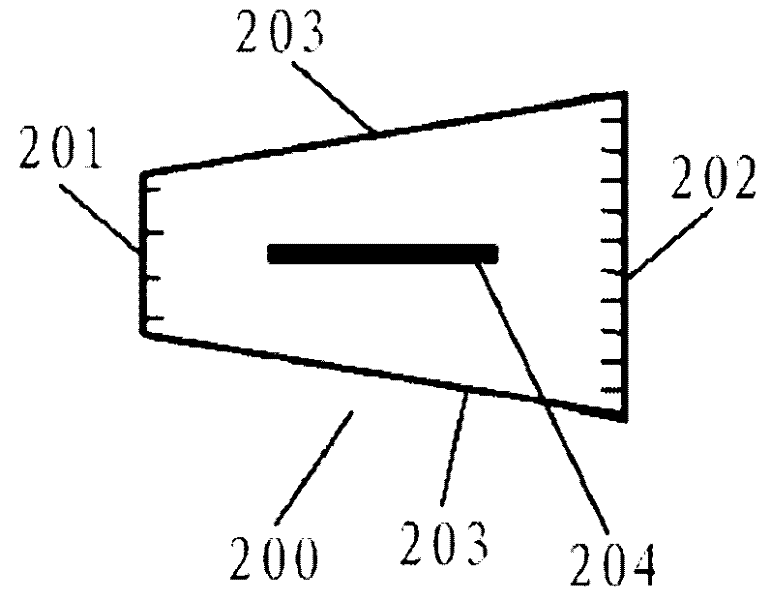
The invention discloses a chip on film (COF) carrier tape. The COF carrier tape comprises a COF tape consisting of a plurality of COFs which are connected sequentially, and a carrier connected with the COF tape, wherein each COF has a trapezoidal shape consisting of two parallel routing edges and two non-parallel side edges; between two adjacent COFs, the long routing edge of one COF and the short routing edge of the other COF are connected with each other and positioned on the same straight line; and the other short routing edge and the other long routing edge of the two COFs are connected with each other and positioned on the same straight line. The invention provides the COF which has the trapezoidal shape consisting of two parallel routing edges and two non-parallel side edges. The COF saves materials; and in a carrier tape type semiconductor device, the number of COFs can be increased on the carrier tape with a specified length and the cost can be reduced greatly.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Interleaved parallel routing workflow pattern based on colored spiking neural membrane system
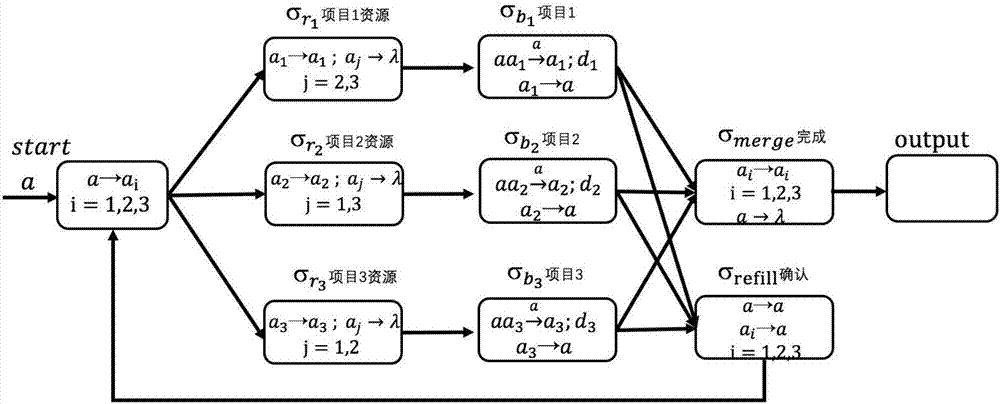
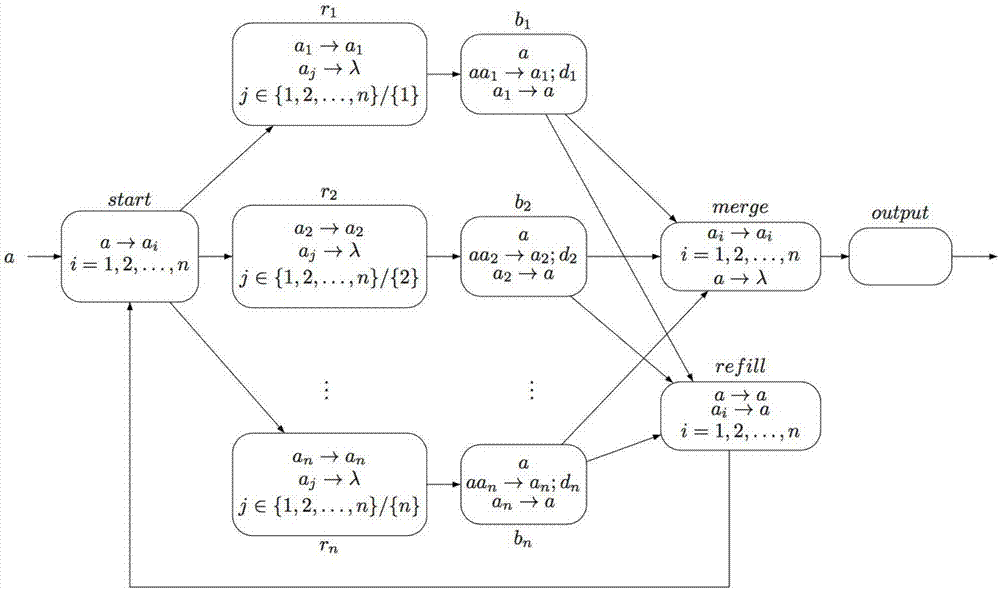
The invention provides an interleaved parallel routing workflow pattern based on a colored spiking neural membrane system. Based on the fact that a colored spiking neural membrane system is distributed, parallel and easy to model, interleaved parallel routing in a workflow pattern is simulated through a colored spiking neural membrane system, and rules are designed for each working point. Finally, a logically clear interleaved parallel routing workflow pattern is obtained.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Apparatus and method for maintaining packet sequencing in a parallel router
A router for interconnecting N interfacing peripheral devices. The router comprises: i) a first switch fabric; ii) a second switch fabric; and iii) a plurality of routing nodes coupled to the first and second switch fabrics. Each of the routing nodes comprises an input-output processing (IOP) module for forwarding received data packets to other ones of the IOP modules via the first and second switch fabrics. A first one of the IOP modules forwards received data packets directed to a second one of the IOP modules by alternating between the first and second switch fabrics for each sequential data packet directed to the second IOP module. Breaks in the alternating sequence identify failed links and cause all traffic to be sent via the remaining good link. Support for multiple IOP modules and switch fabrics also is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
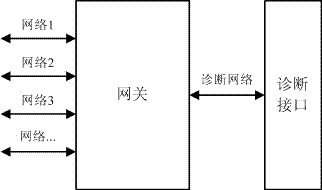
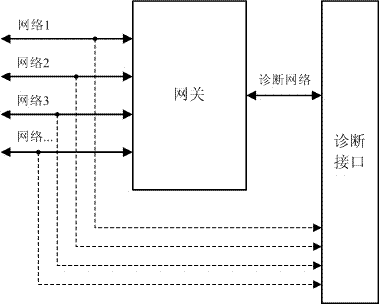
Automobile network routing system and method
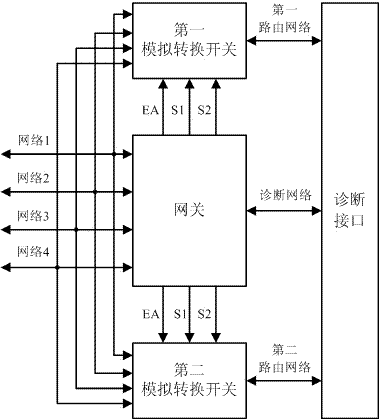
InactiveCN106998280AGuaranteed closureEnsure safetyNetwork connectionsBus networksDiagnostic dataEngineering
The invention provides an automobile network routing system and method. The automobile network routing system comprises a gateway that is connected with a diagnostic network and at least one analog change-over switch that is in hardwired connection with the gateway, wherein the input end of the analog change-over switch is connected with an entire automobile bus network, and the output end of the analog change-over switch is connected with a routing network; and the gateway is configured to make the entire automobile bus network communicate with the routing network and perform routing by controlling the state of the analog change-over switch when receiving a routing service request from the diagnostic network. According to the automobile network routing system and method provided by the invention, the deficiency of a traditional routing scheme in routing applications of diagnostic interfaces of the automobile gateway can be solved by adopting a controllable hardwired connection technical scheme, the parallel routing from multiple automobile bus networks to the diagnostic interfaces can be realized, the monitoring, acquisition and analysis of the diagnostic data of an automobile bus can be facilitated, the utilization efficiency of the automobile bus data can be increased, and thus the related diagnosis of the automobile bus can be more efficient, and the closure and security of the bus data can be ensured.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AUTOMOBILE GROUP CO LTD
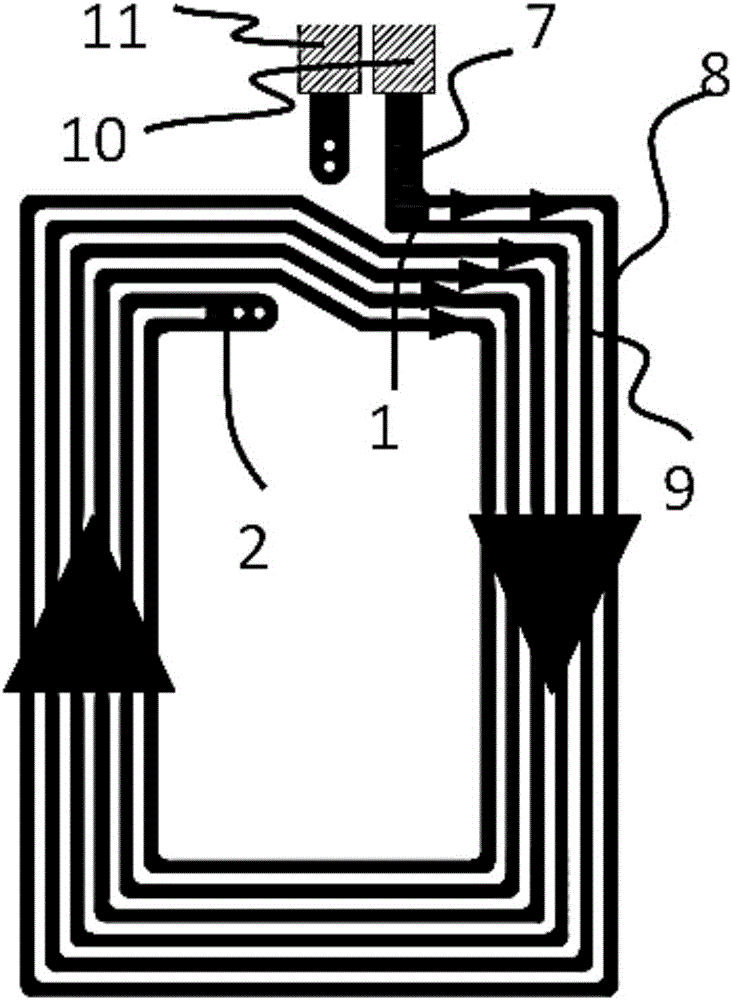
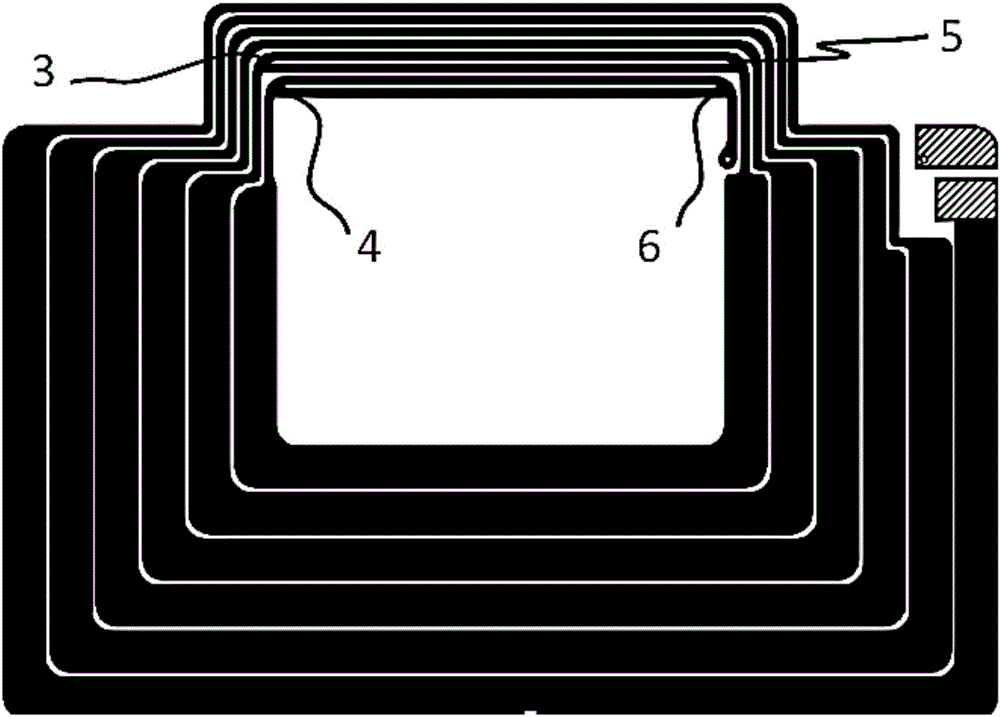
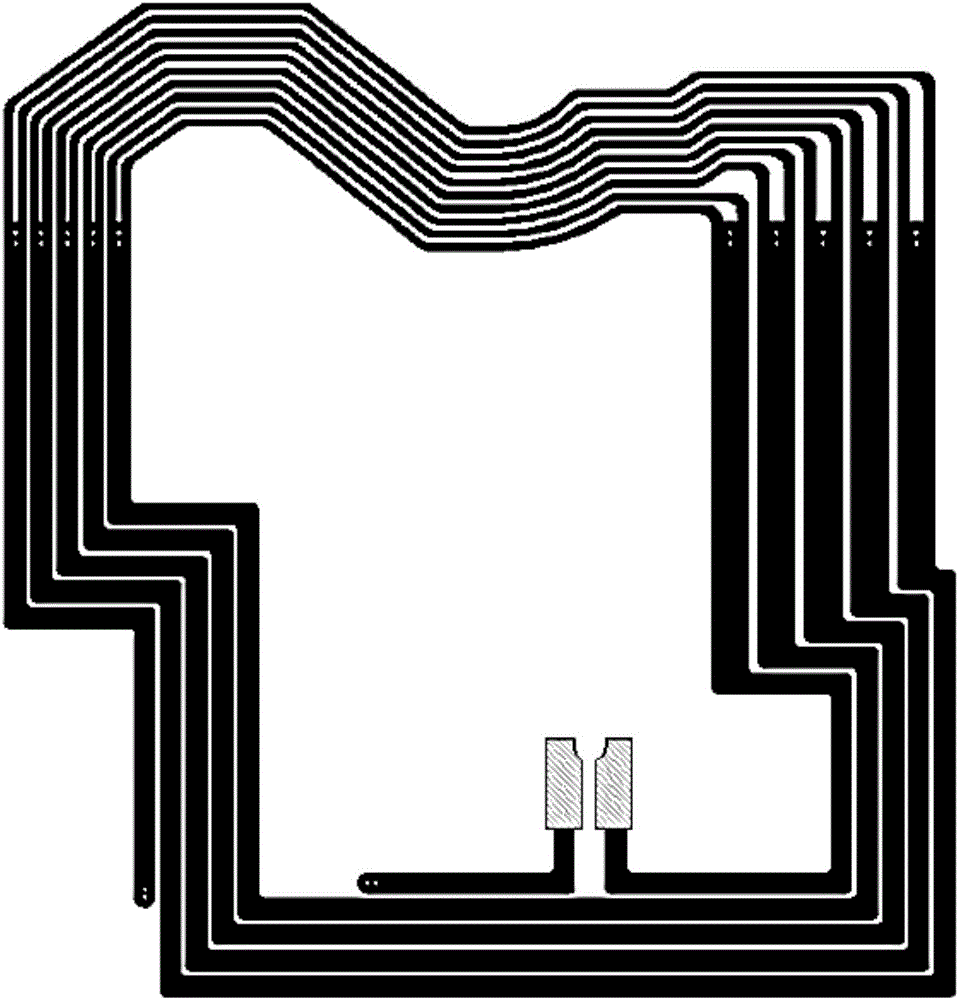
Dual-panel-parallel-routing type NFC antenna
InactiveCN106099347ALower impedanceImprove performanceRadiating elements structural formsLoop antennasClosed loopEngineering
Owner:SHANGHAI DEMAN ELECTRONICS TECH
A Parallel Routing Optimization Method for Elastic Optical Networks
InactiveCN110099003BReduce occupancyCalculation speedData switching networksPathPingConcurrent computation
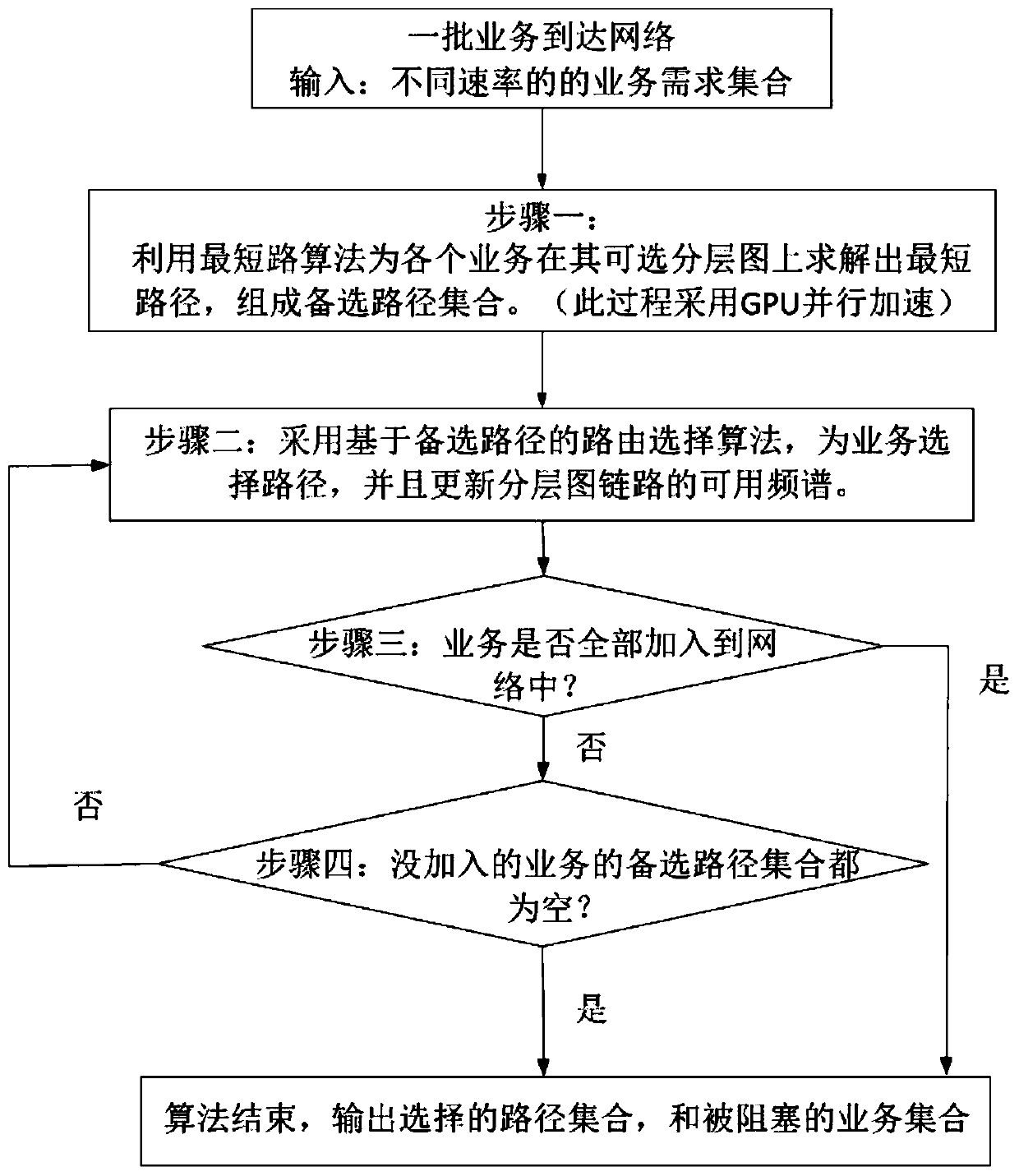
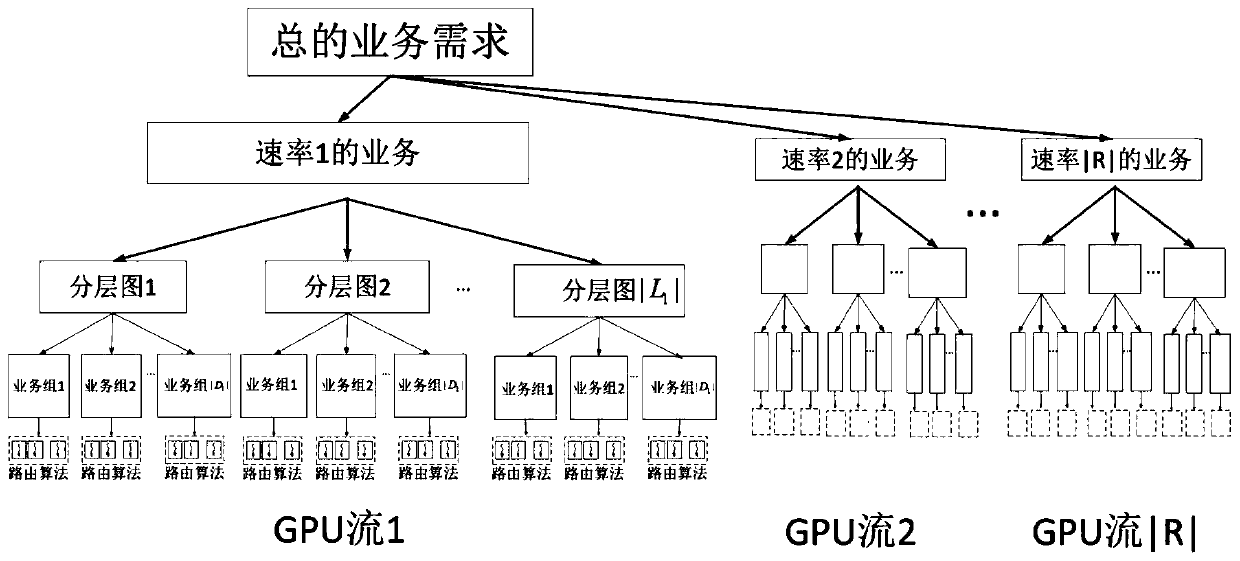
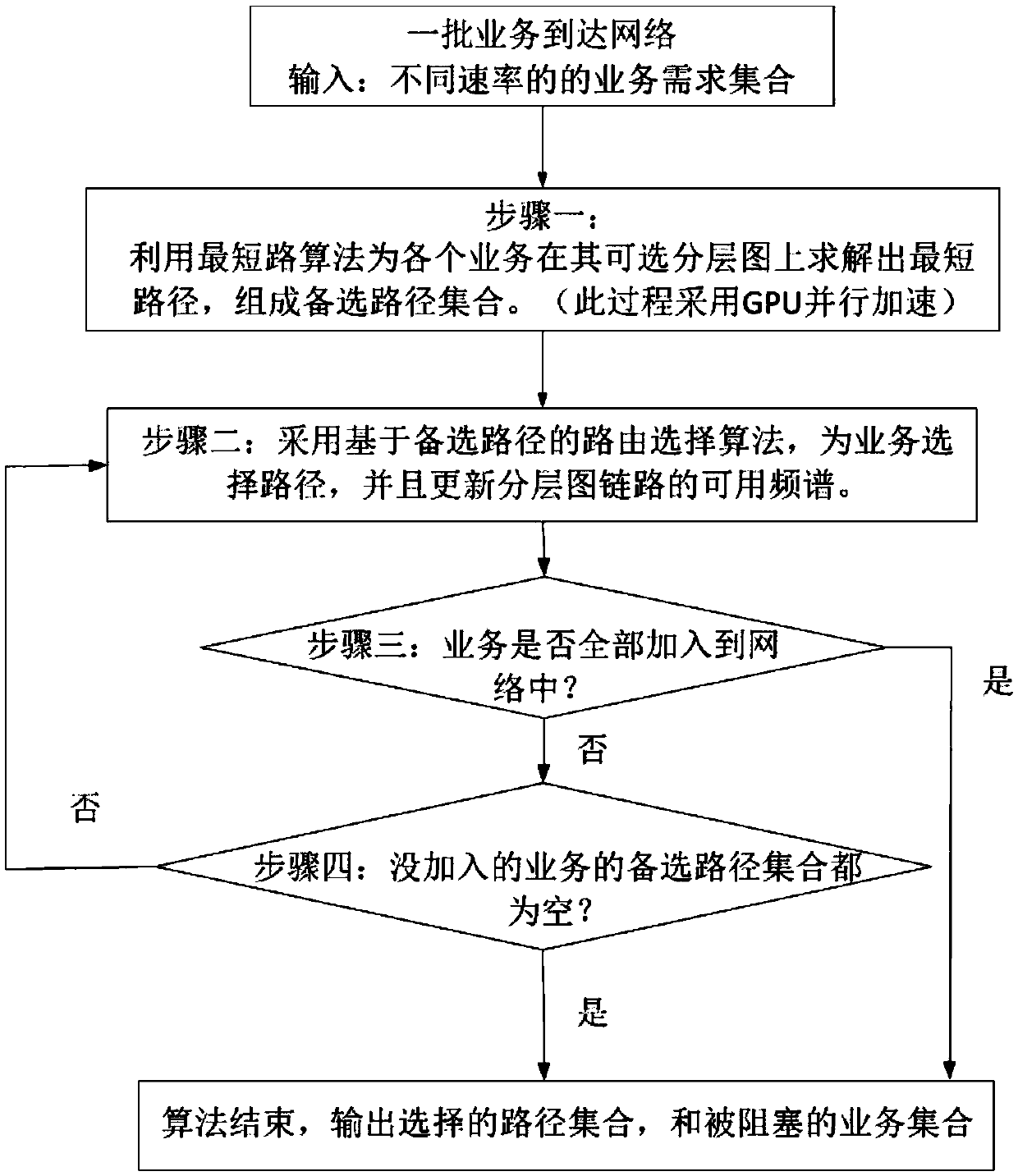
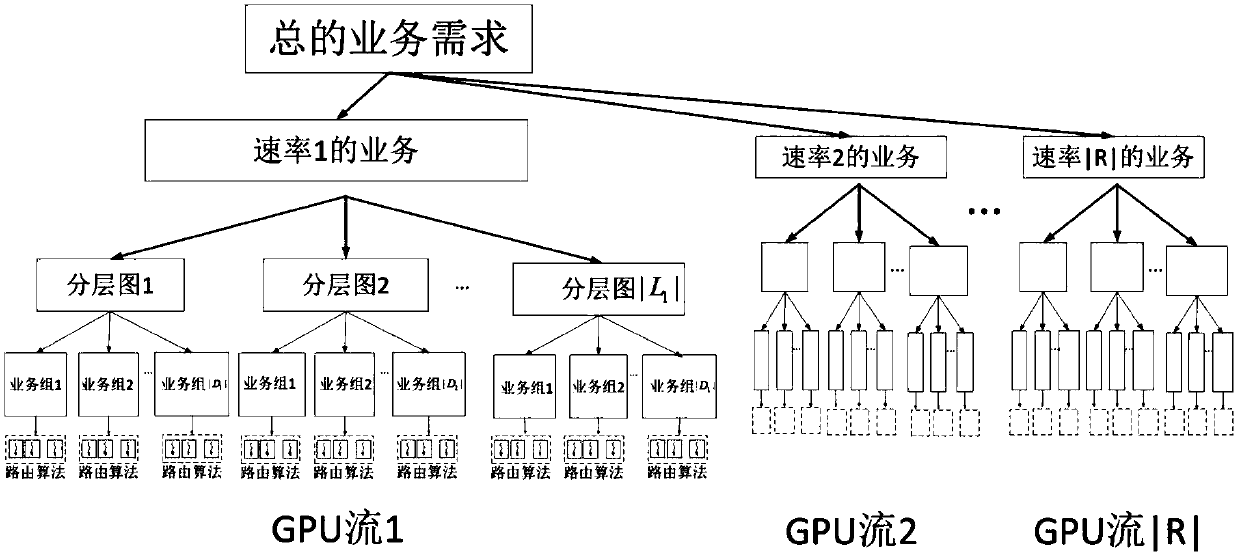
The invention discloses a parallel routing optimization method under an elastic optical network. The method includes: step 1: when a batch of services arrive at the network, use the GPU to solve the shortest path for each service on its available hierarchical graph as Alternative path; Step 2: After calculating the alternative path, use the routing selection algorithm to select a route for the service; Step 3: Determine whether the service can be added to the network, if so, end the algorithm, if not, proceed to Step 4; Step Four: Determine whether the services that have not been added are all blocked services, if so, end the algorithm, and output the path selected by the service, if not, it is necessary to recalculate the route for the services that have not been added, and return to step 1; this method is sufficient Using the powerful parallel computing capability of GPU, the calculation speed of routing optimization algorithm is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Semiconductor structure and chip packaging method
PendingCN114446924AImprove performanceLower requirementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureLead bonding
The invention provides a semiconductor structure and a chip packaging method. The semiconductor structure comprises a substrate, a first chip and a second chip, wherein the first chip and the second chip are arranged on the substrate in parallel; wherein the first chip and the second chip are interconnected directly through a lead bonding process; moreover, for the pins, where high-speed signals need to pass, between the first chip and the second chip, the pins are configured to be oppositely arranged and are connected through parallel routing. According to the embodiment of the invention, through a lead bonding technology between chips, the circuit is shorter in routing, small in occupied space, better in performance of high-speed signals, free of too much change in cost, and even lower in cost. Compared with 2.5 D and 3D packaging, the cost of the embodiment is much lower, the requirement for manufacturing equipment is not high, and the method is very suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:杭州云合智网技术有限公司
A kind of parallel route lookup method and system
The invention discloses a parallel route search method and system, and relates to the technical field of communication. The method includes the following steps: receiving a message, and extracting VRF information and destination address IP corresponding to the message; A flag bit. If the first flag bit indicates that the second-level routing prefix has no data, the first-level routing prefix will be queried according to the VRF information and the destination IP address. Otherwise, the first-level routing prefix and the second-level routing prefix will be queried; When the second-level routing prefix is used, the second flag bit of the second-level routing prefix is identified. If the second flag indicates that the third-level routing prefix has no data, the second-level routing prefix is queried; otherwise, the second-level routing prefix and The third-level routing prefix. The invention adopts the multi-level routing prefix, provides a multi-level data storage structure that is easy to search, and eliminates the limitation of the existing parallel routing search method.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD +1
Apparatus for precisely controlling wire distribution distance
InactiveCN101157436AEasy to implementReduce difficultySemi-permeable membranesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesEngineeringMicromachinings
The invention provides an accurately controlling routing interval device. The device can be used for routing interval accurate control in micromachining technosphere. The device includes at least one movable parallelogram lever. Every parallelogram lever consists of two opposite routing pillows and two connectors. The routing pillow is fixed with a routing comb. Wires are routed in a parallel routing array formed between the routing combs on two opposite routing pillows, and then the vertex angle degree of the parallelogram lever is quantificationally changed, thereby accurately controlling routing interval. The device has the advantages that the structure is simple, the realization is easy, the operation is convenient, the cost is low and the device is steady and reliable. Accurately controlling routing interval can be implemented and the controlling precision can reach micron-grade or submicron-grade. The device provides an advantaged tool for the routing interval accurate control in the micromachining technosphere.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Parallel routing optimization algorithm under elastic optical network
InactiveCN110099003ACalculation speedSolve the problem of long calculation timeData switching networksParallel routingPassive optical network
The invention discloses a parallel routing optimization algorithm under an elastic optical network, and the algorithm comprises the steps: step 1, after a batch of services arrive at the network, using a GPU to solve a shortest path on an available hierarchical graph of each service as an alternative path; step 2, after calculating an alternative path, selecting a route for the service by using aroute selection algorithm; step 3, judging whether the services can be added into the network, if so, ending the algorithm, and if not, performing the step 4; step 4, judging whether the services which are not added are blocked services or not, if yes, ending an algorithm, outputting a path selected for the services, if not, re-calculating a route for the services which are not added, and returning to the step 1. According to the method, the powerful parallel computing capability of the GPU is fully utilized, and the computing speed of the routing optimization algorithm is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
A High-Speed Parallel Lock-Free Flow Table Routing Lookup Method
ActiveCN102938000BSolve processing performance bottlenecksAchieve securitySpecial data processing applicationsRoute searchData transmission
The invention relates to a routing lookup algorithm, and in particular relates to an unlocked flow table routing lookup algorithm adopting a multi-core processor high-speed parallel execution manner. In the multi-core processor parallel execution environment, a flow table design structure having the number corresponding to the core number is adopted, the manner of combining control planes with data planes in multiple cores is used, and a delete operation for entries in the flow table can be divided into two relatively independent stages, namely FLOW-INVALID and FLOW-DELETE stages, so that the multiple cores can read and write one flow table at the same time without relying on the control of a resource lock. The unlocked flow table routing lookup algorithm adopting the multi-core processor high-speed parallel execution manner solves the data processing bottleneck problem caused by the existing flow table design method during the multi-core processor parallel execution process, realizes safety and rapidness of data transmission during the multi-core processor parallel execution process, and improves the high-capacity system routing lookup speed and the parallel routing lookup performance.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
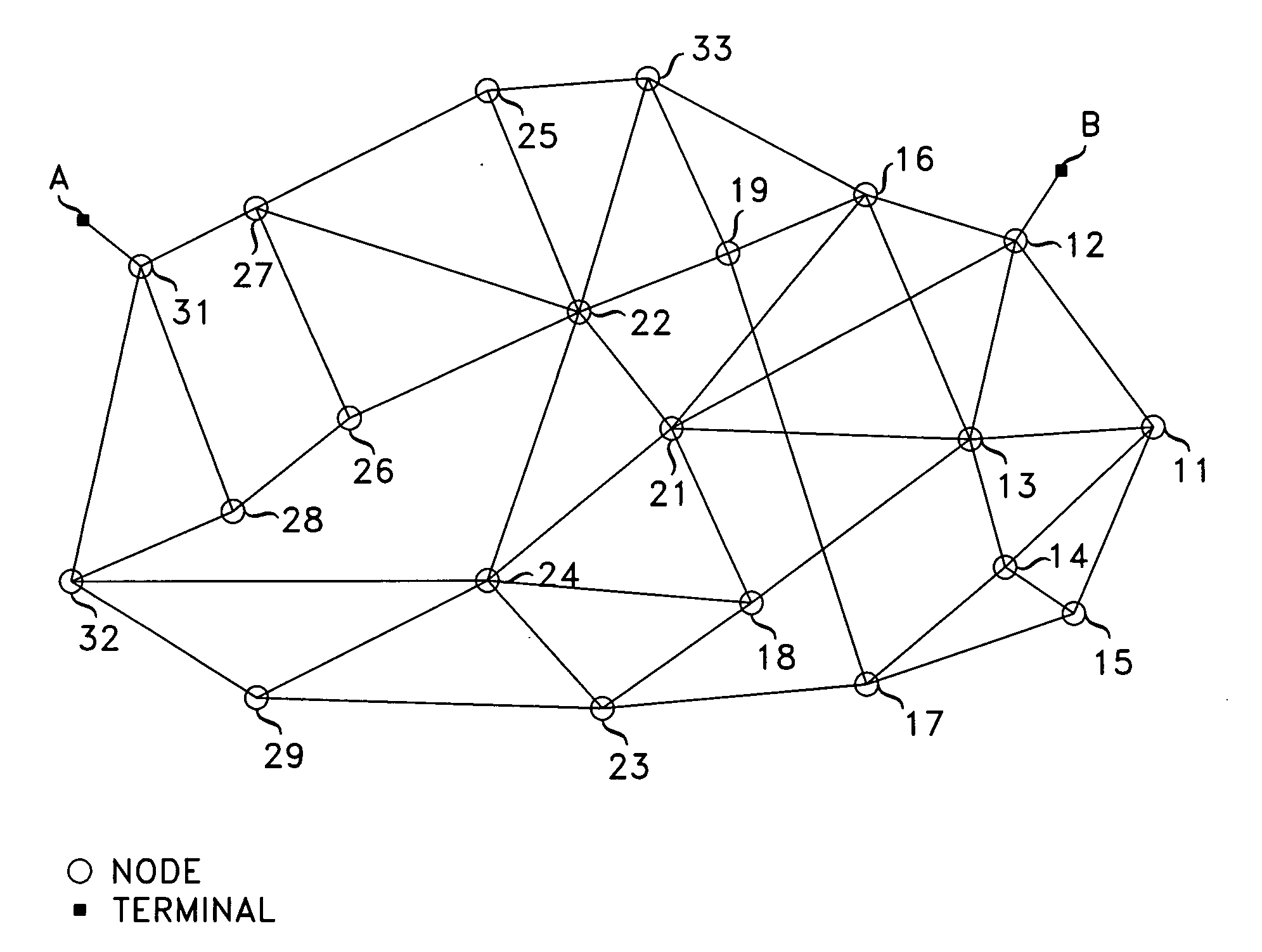
Employing parallel processing for routing calls
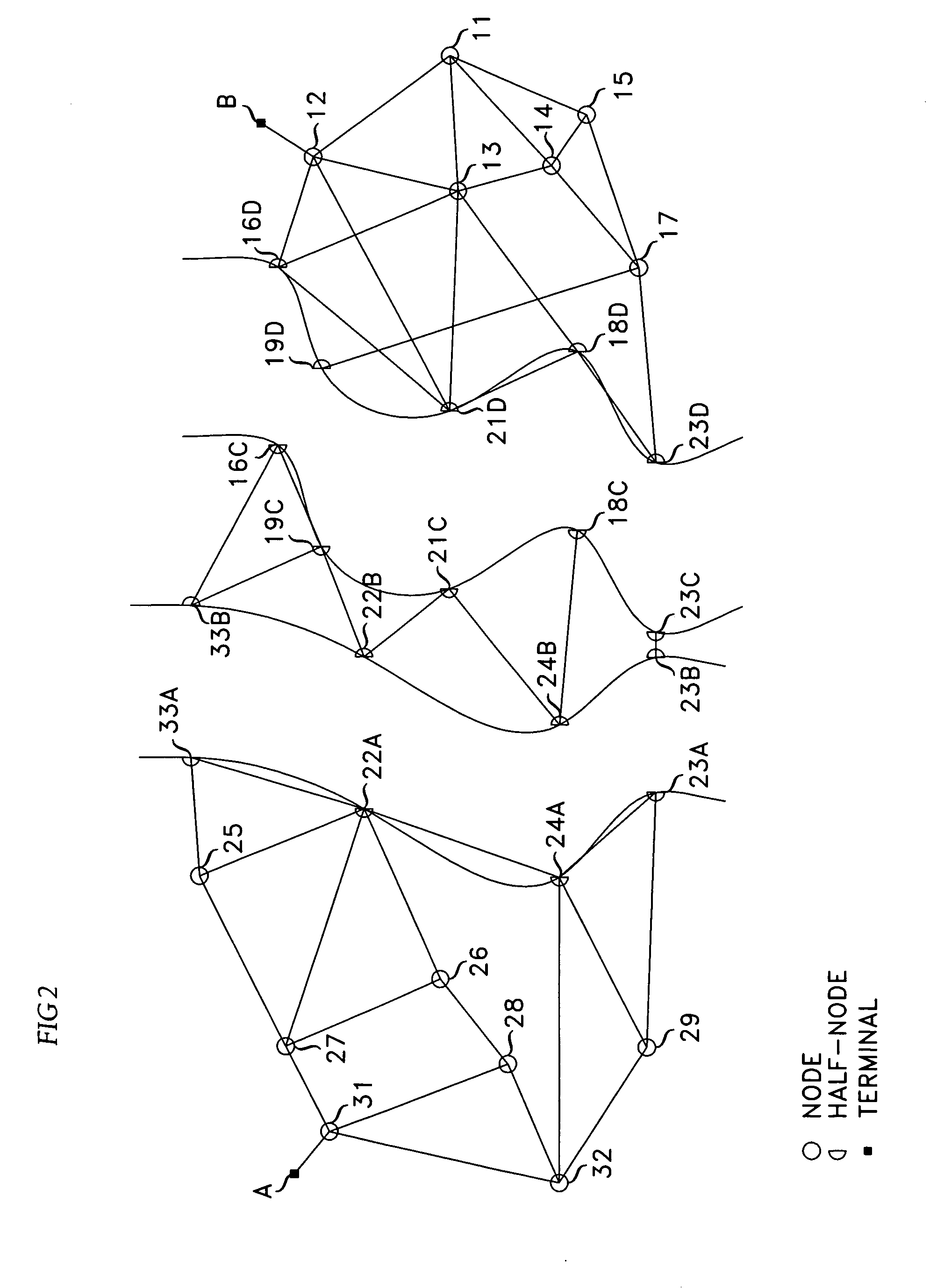
A least-cost path between a pair of nodes A and B of a network is realized by segmenting the network into three or more segments, with nodes A and B being in different ones of the segments, with the third or more other segments being interposed between the segments to which nodes A and B belong, concurrently process the different segment to identify paths and their associated costs, and processing results generated by the different processing units to compute the least-cost path. Advantageously, the segmenting is chosen to equalize the work load of the different processing units so that the units finish their task roughly at the same time.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com