Interconnection method of transparent interconnection network of lots of links in different places and operator edge device
A transparent interconnection and multi-link technology, applied in the field of network interconnection, can solve problems such as slow convergence, waste of bandwidth, and traffic impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0067] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
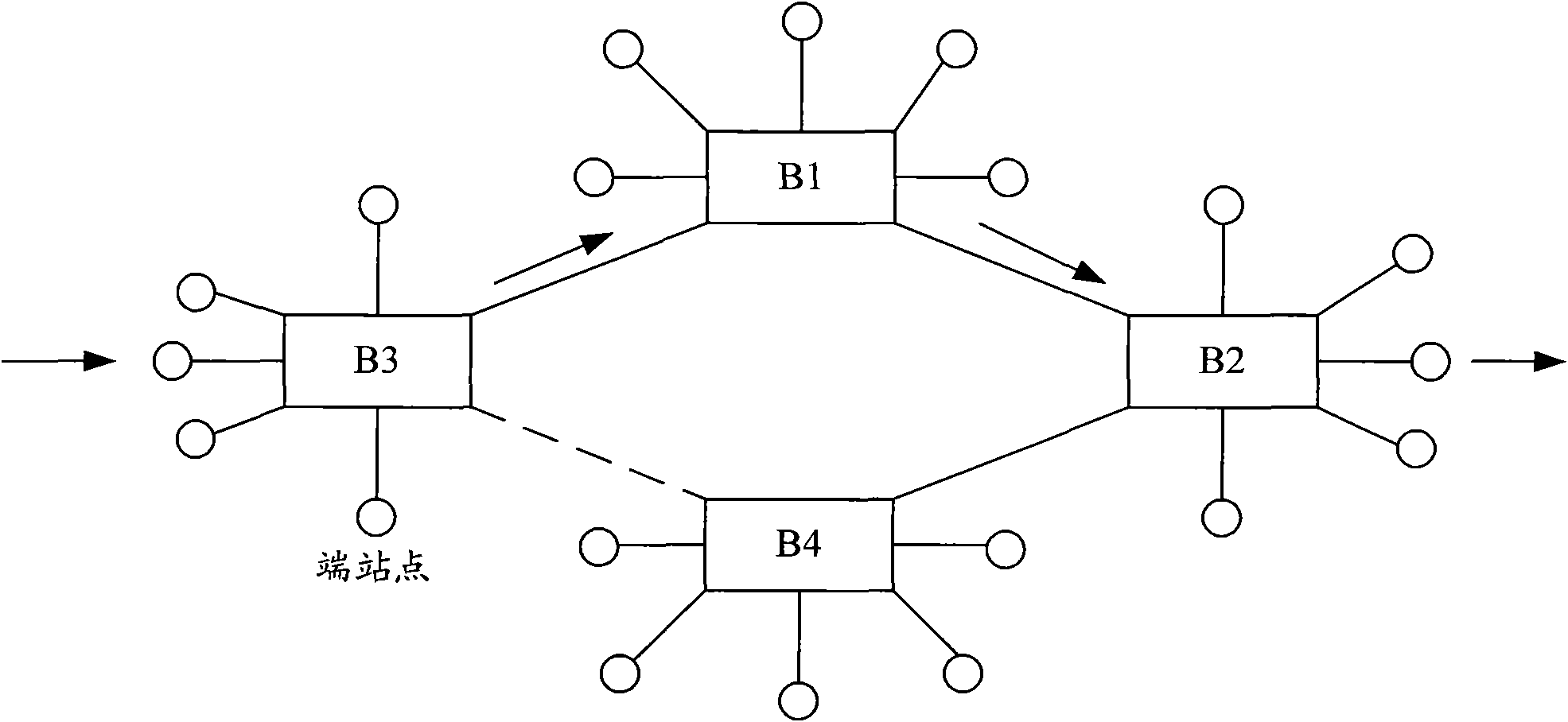
[0068] Figure 10 A schematic diagram of Layer 2 networking for remote interconnection of TRILL networks provided by the embodiment of the present invention, as shown in Figure 10 As shown, sites 1 and 2 are remote sites of the same VPN: VPN A, and sites 3 and 4 are remote sites of the same VPN: VPN B. Sites 1, 2, and sites 3 and 4 realize remote interconnection through MPLS L3VPN.
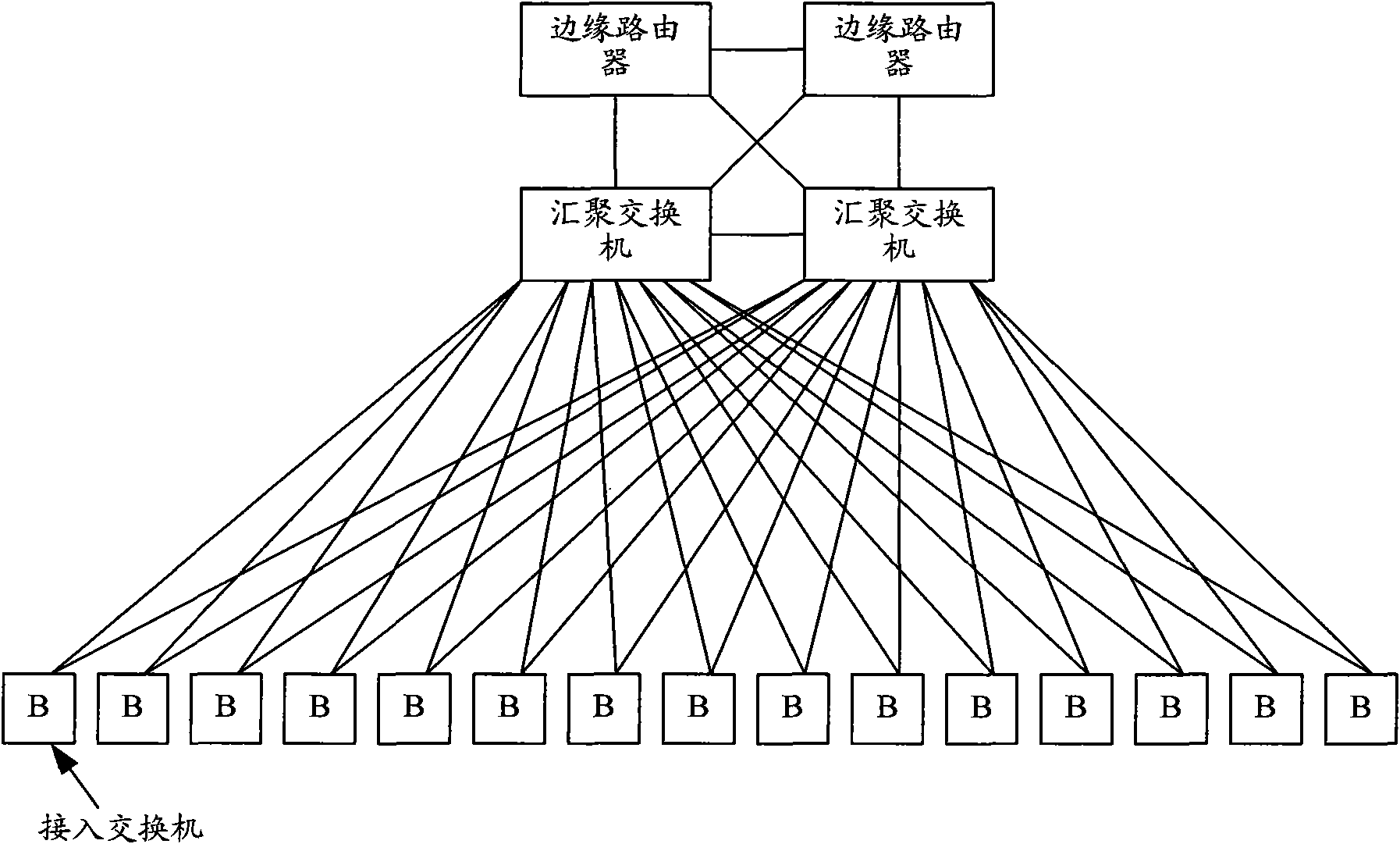
[0069] In practical applications, each TRILL network may contain more VPN sites, and the network diagram at this time can be obtained by figure 2 It can be obtained by simple expansion, and will not be drawn one by one here.
[0070]The following gives the specific implementation of remote sites such as: site 1, 2, site 3, 4 how to achieve remote interconnection:
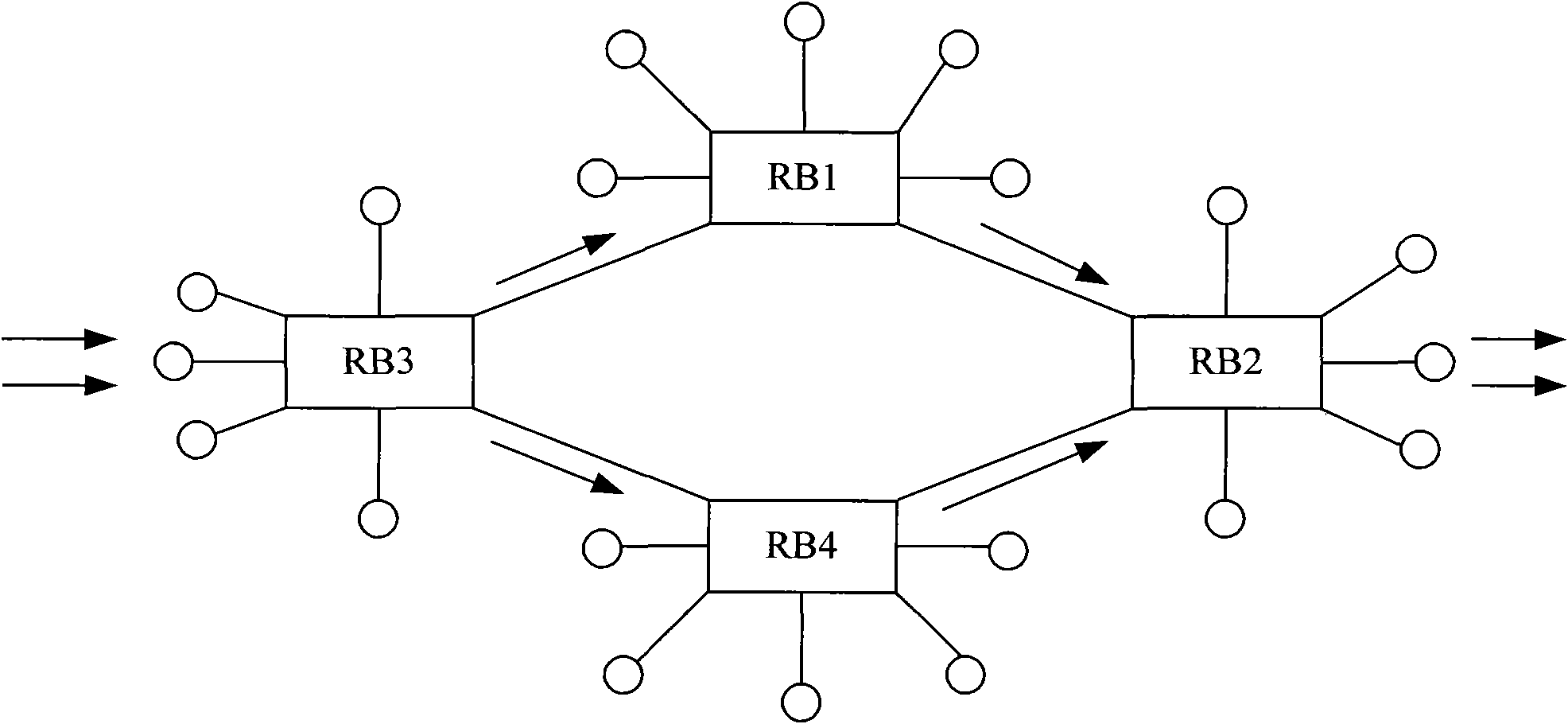
[0071] Figure 11 The flow chart of the TRILL network remote interconnection method p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com