Patents
Literature
83 results about "One-way delay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
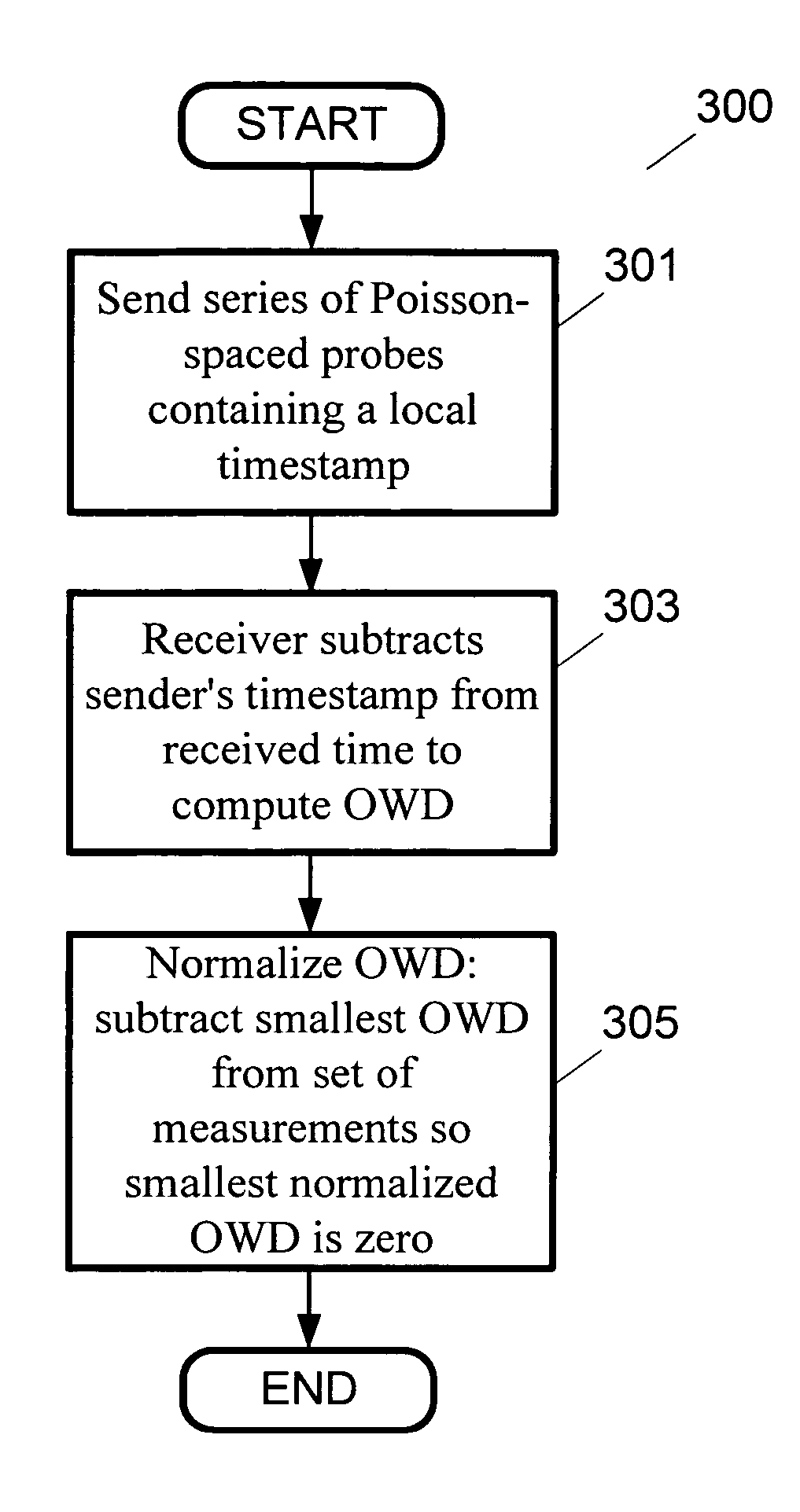
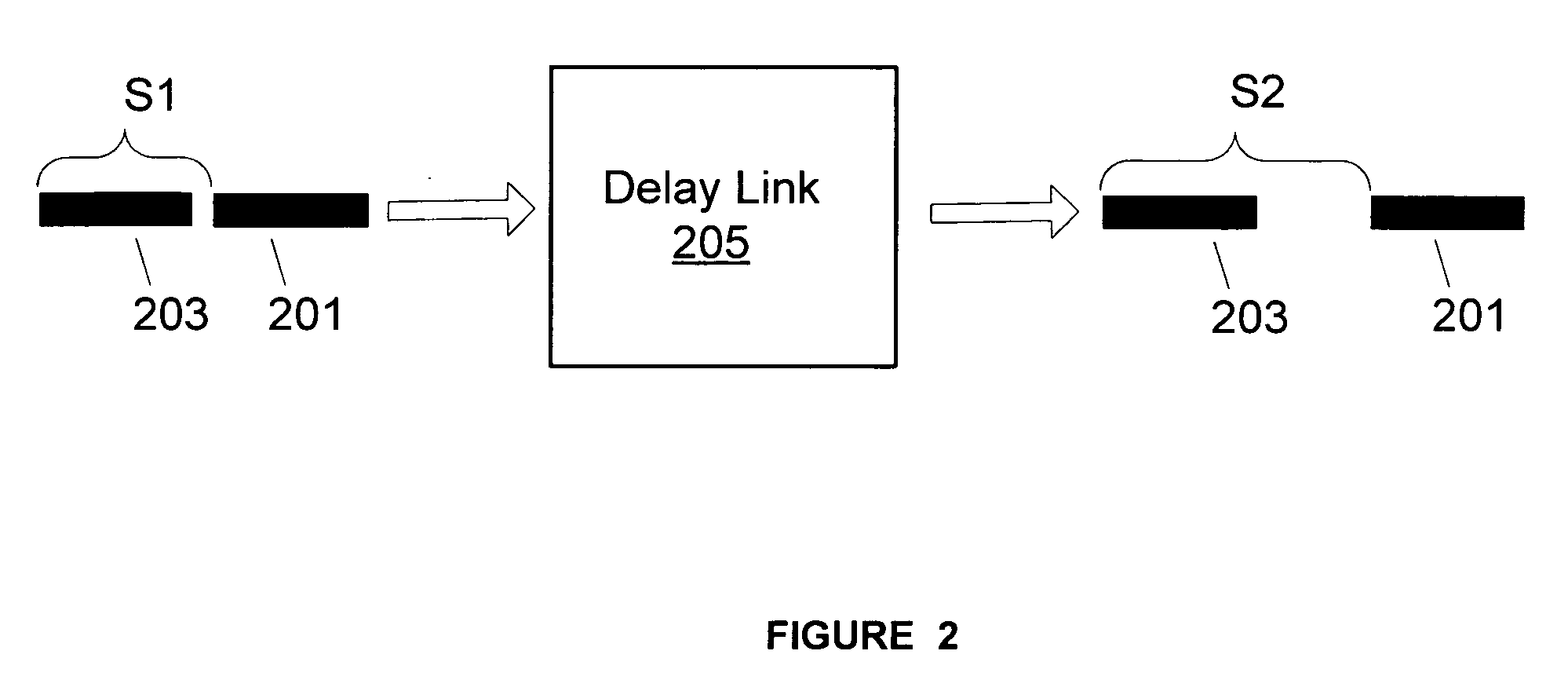
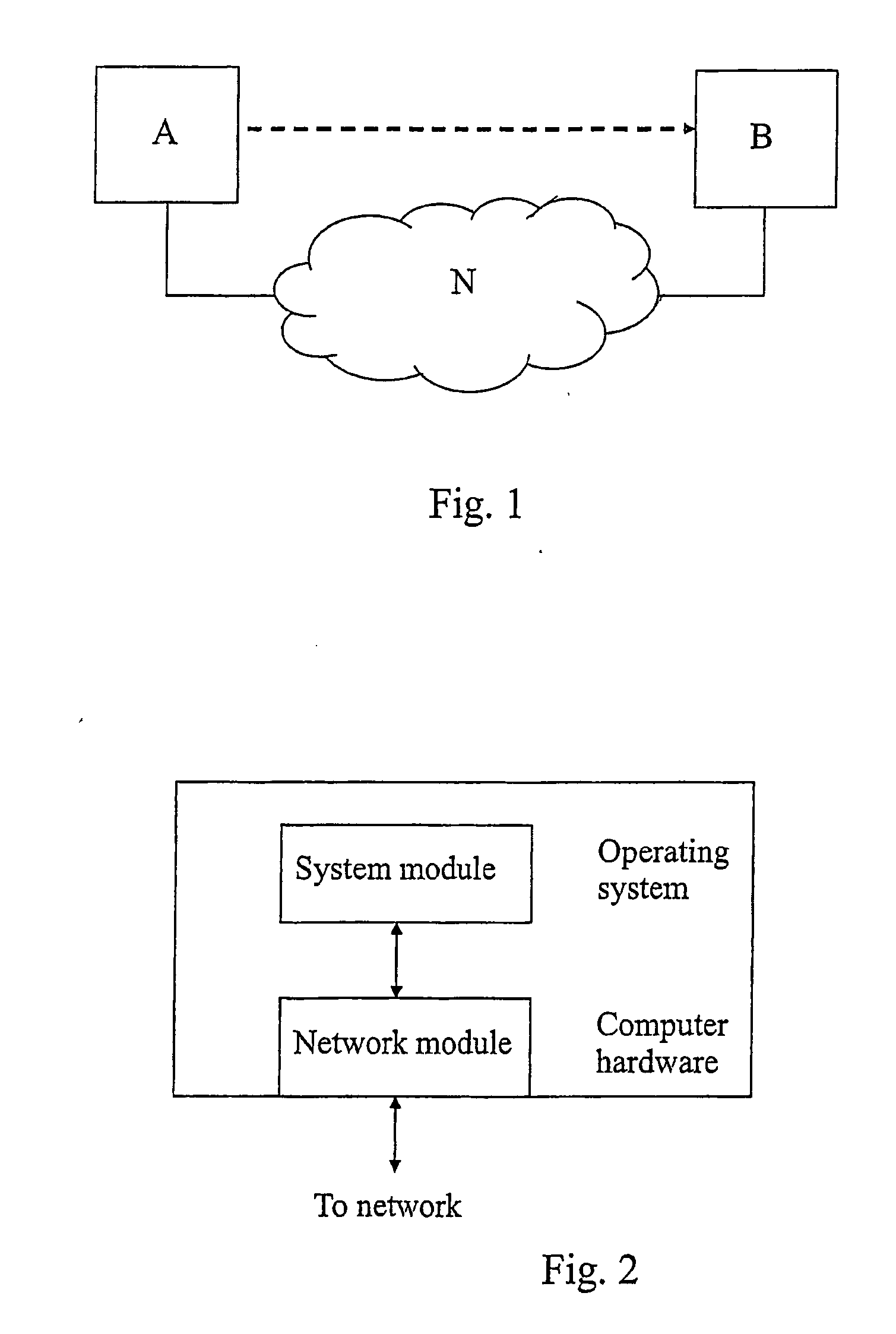
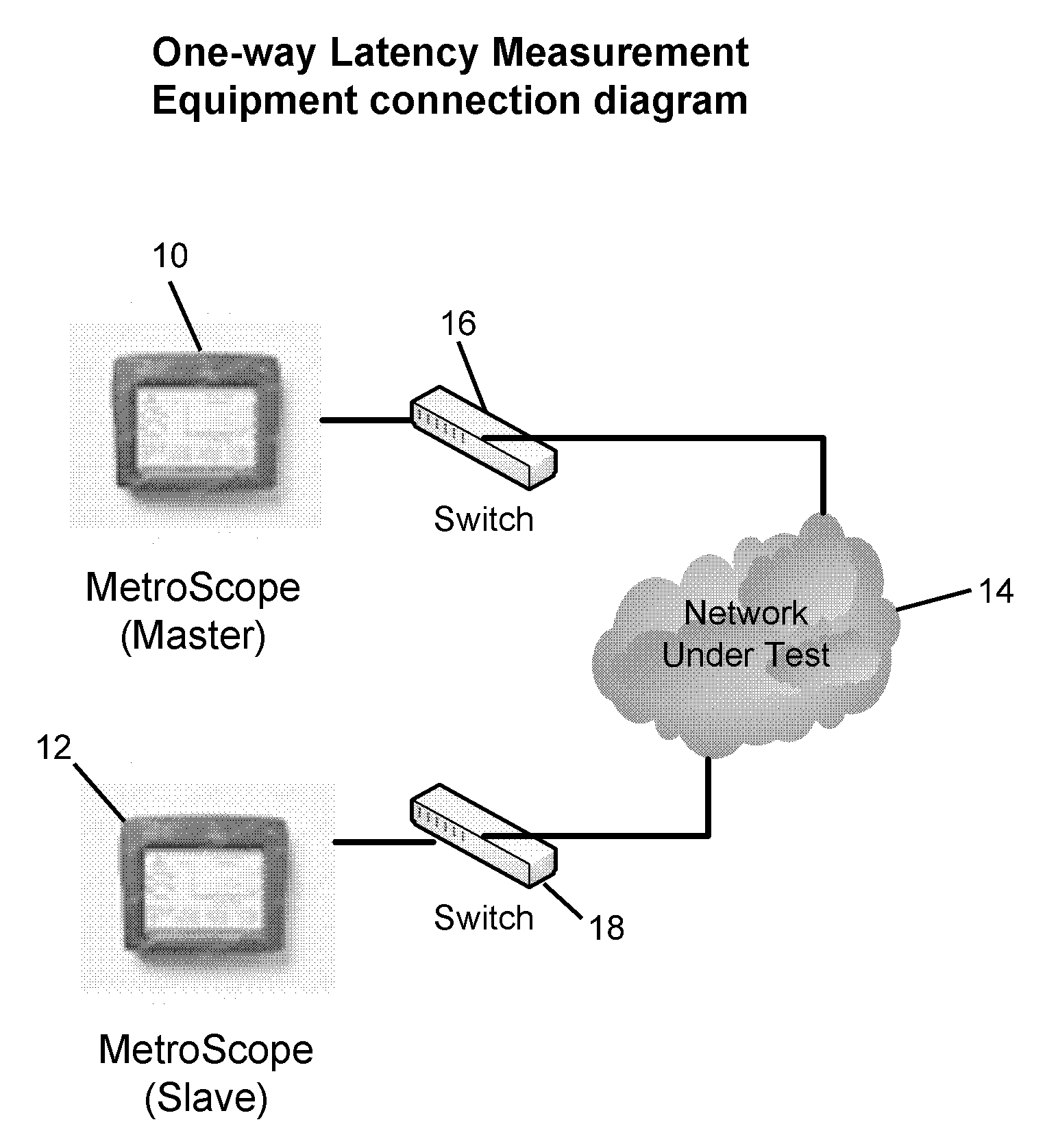
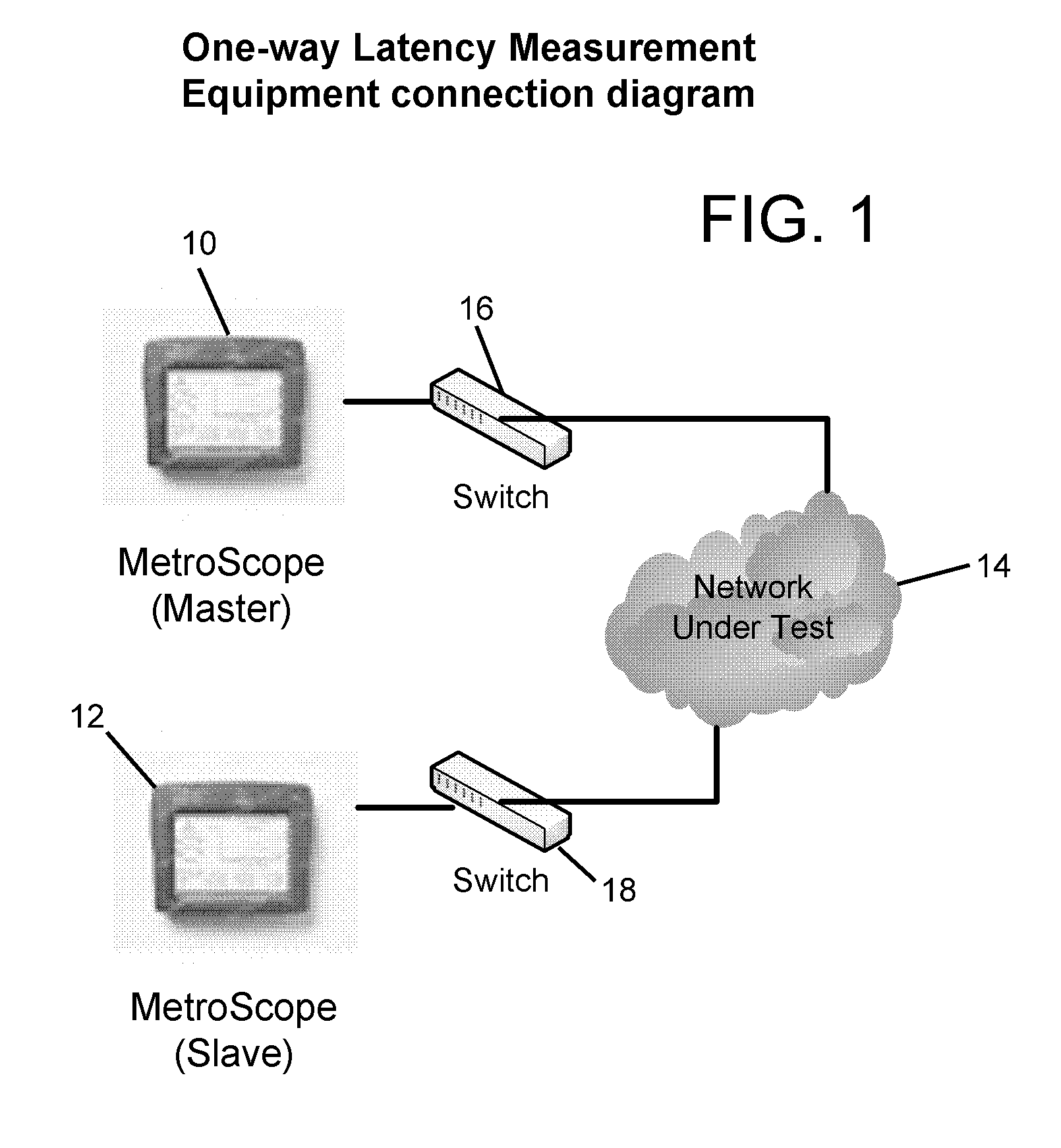
One-Way Delay, abbreviated as OWD, is a common term in IP network monitoring, and differs from Round-Trip Time. The ping utility calculates the RTT, that is, the time to go and come back to a host. This does not assure that the go and back paths are the same in terms of congestion, number of hops, or Quality of Service. In order to avoid such problems, OWD concept comes into play. The One-Way Delay value is calculated between two synchronized points A and B of an IP network, and it is the time in seconds that a packet spends in travelling across the IP network from A to B. The transmitted packets need to be identified at source and destination in order to avoid packet loss or packet reordering. The measurement method makes obvious that this value is substantially different from the Round-Trip Time/2 value.
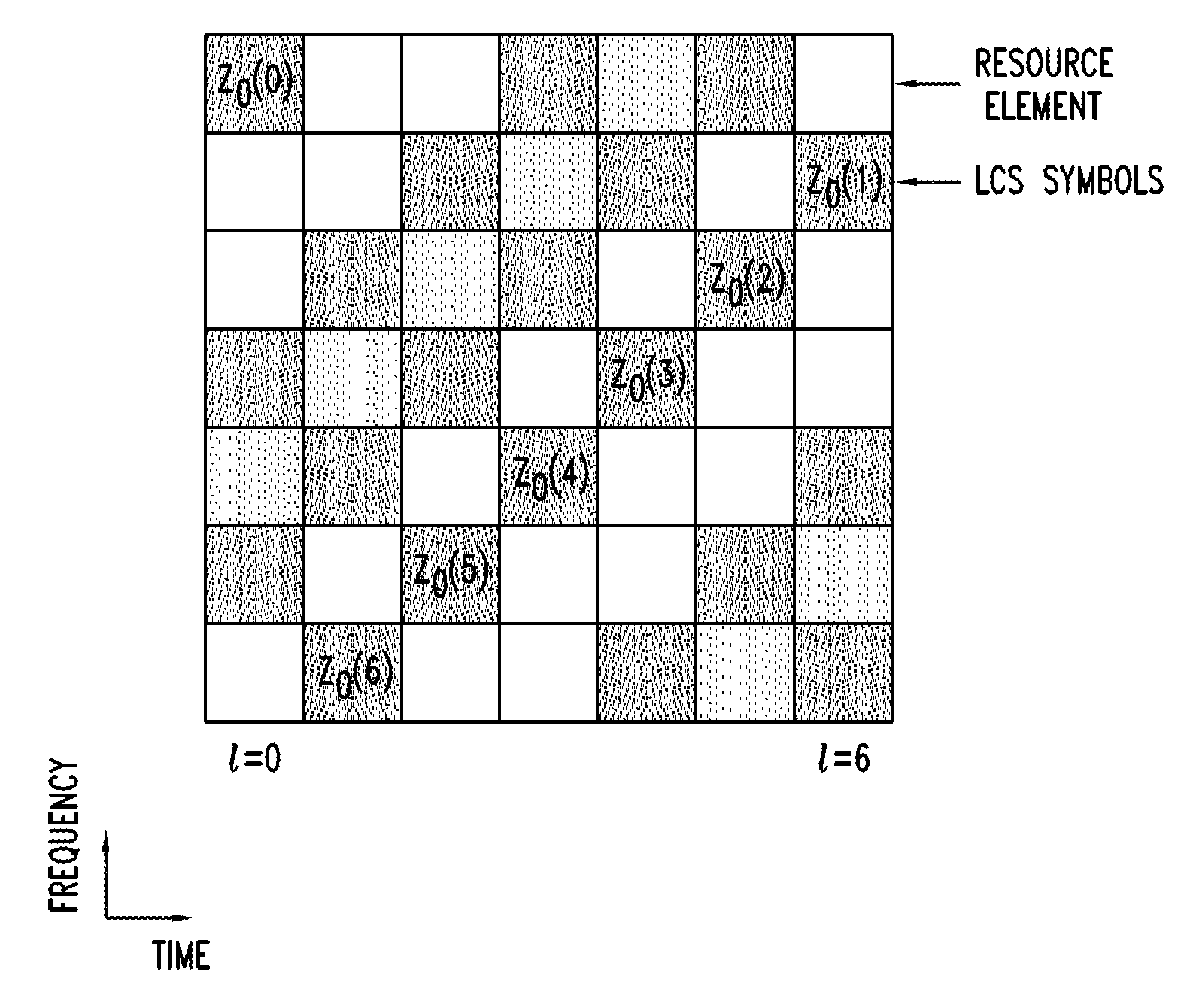
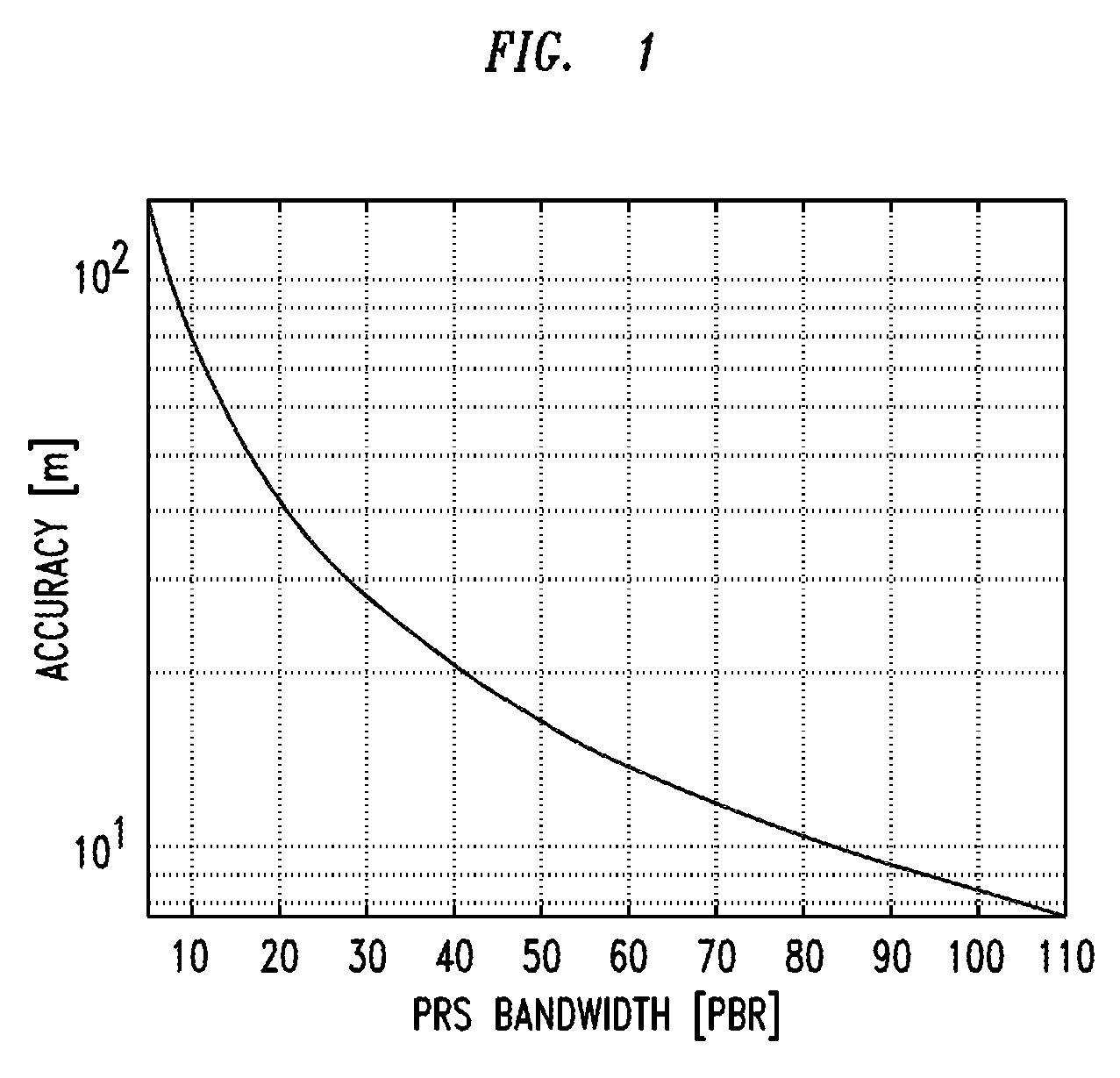
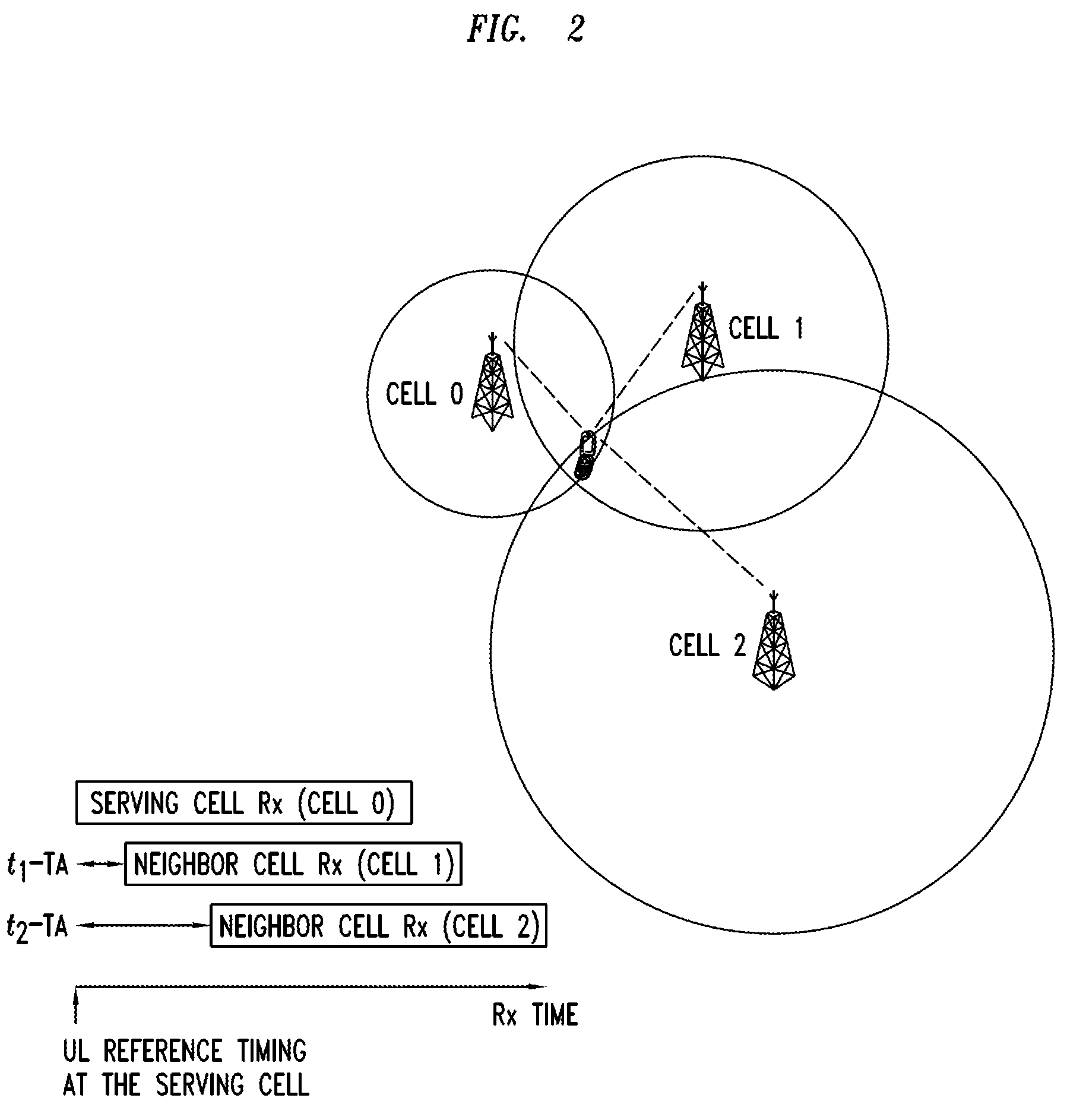
Method And Apparatus for UE Positioning in LTE Networks
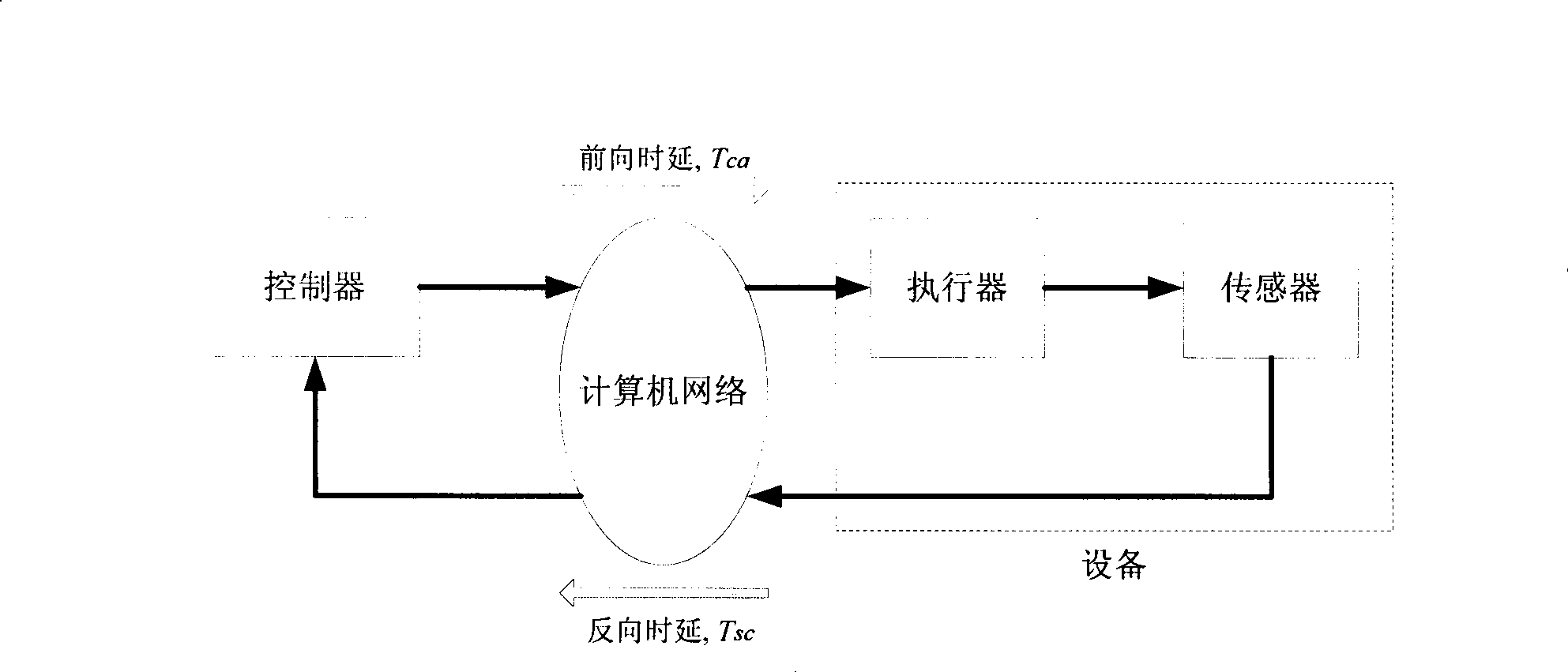
Methods and apparatuses are provided for user equipment positioning in networks. An example method includes computing a location of a user equipment (UE). The computing includes joint scheduling of UL subframes and receiving a Up Link Positioning Reference Signal (UL-PRS). The computing is performed by a network equipment that serves at least one cell site. The UL-PRS is received in a known subframe. The computing may also include estimating an arrival time the UL-PRS from the UE for a plurality of cell sites. In another embodiment, the computing includes determining a one-way delay between
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
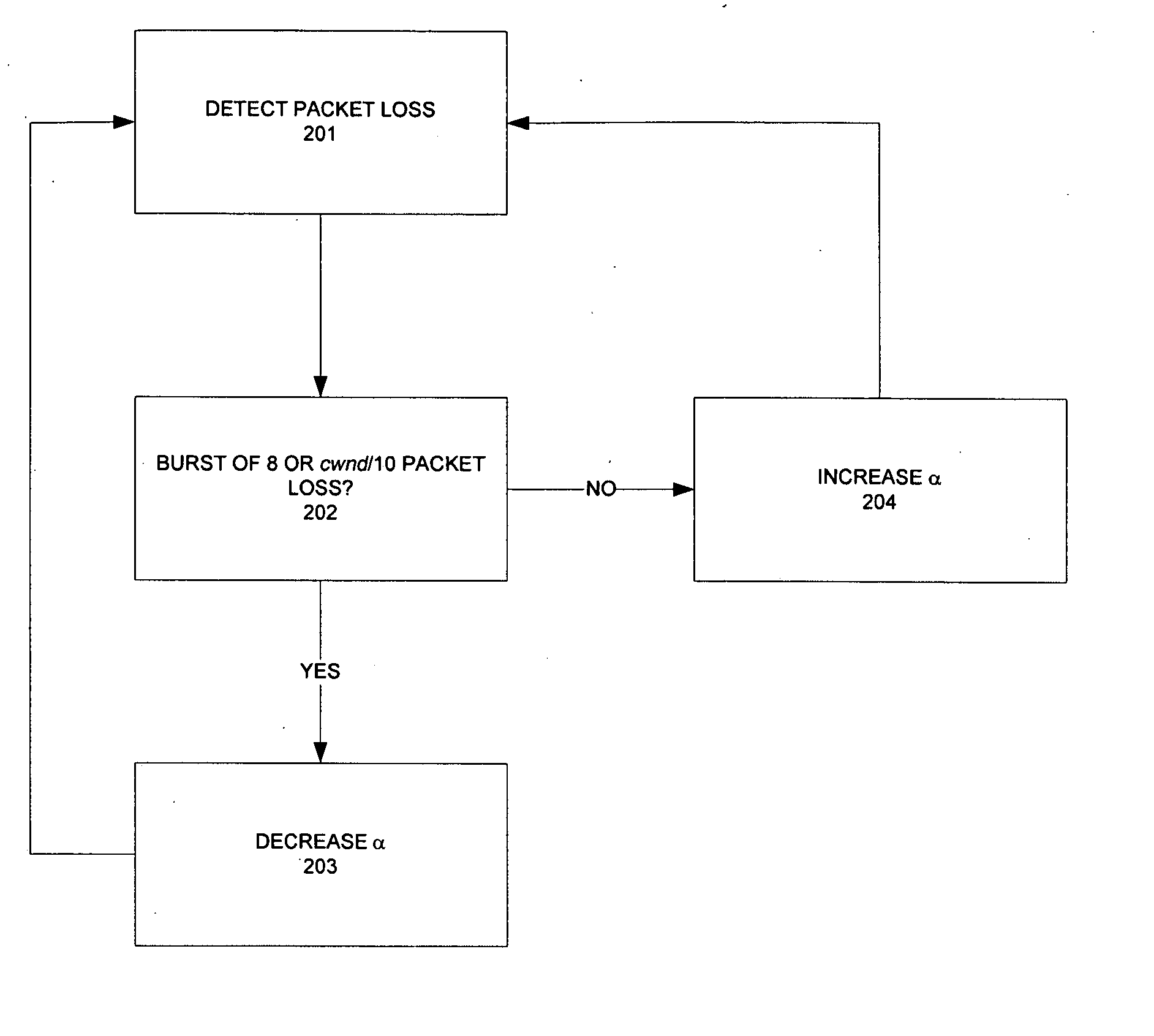
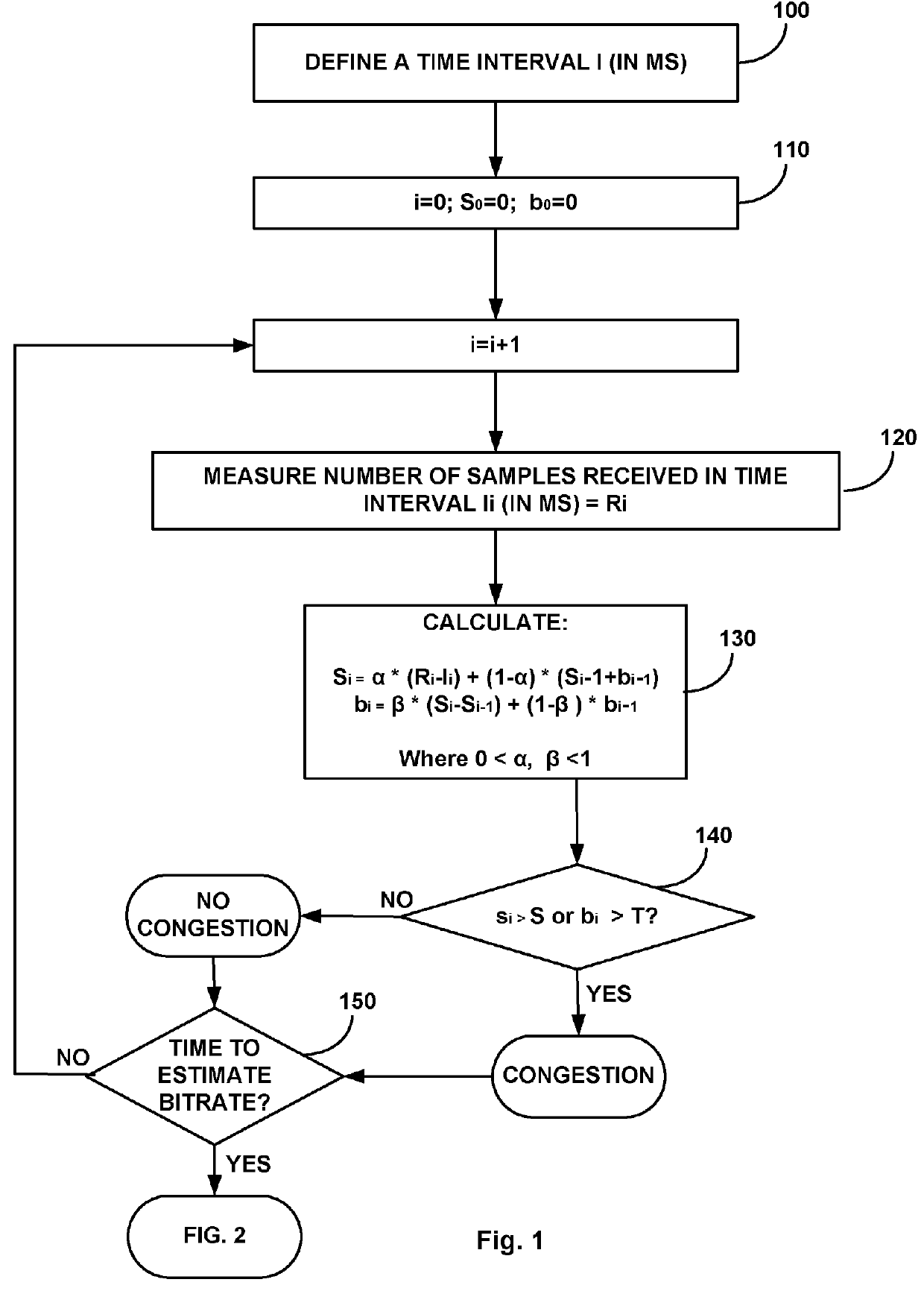
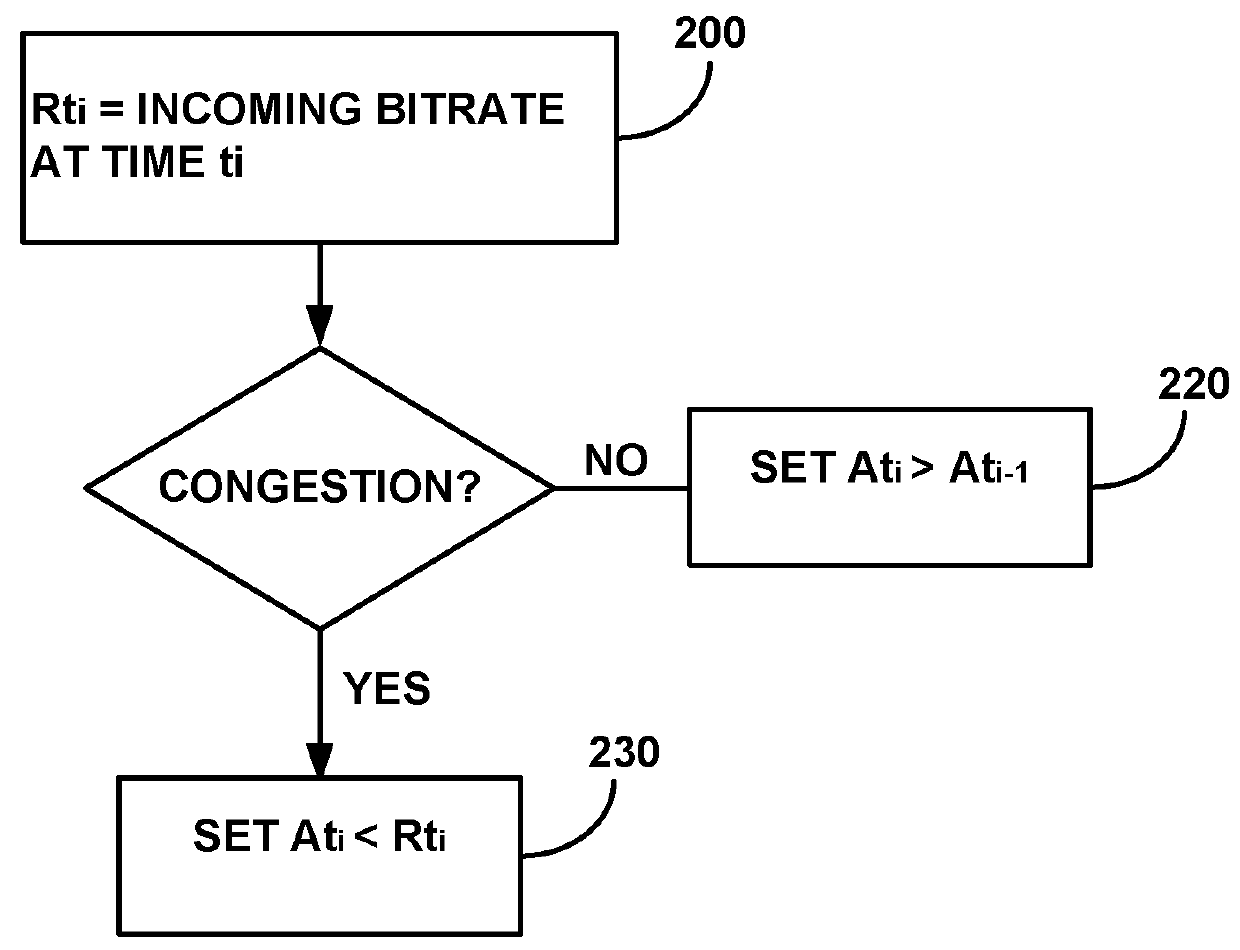
Method and apparatus for network congestion control using queue control and one-way delay measurements
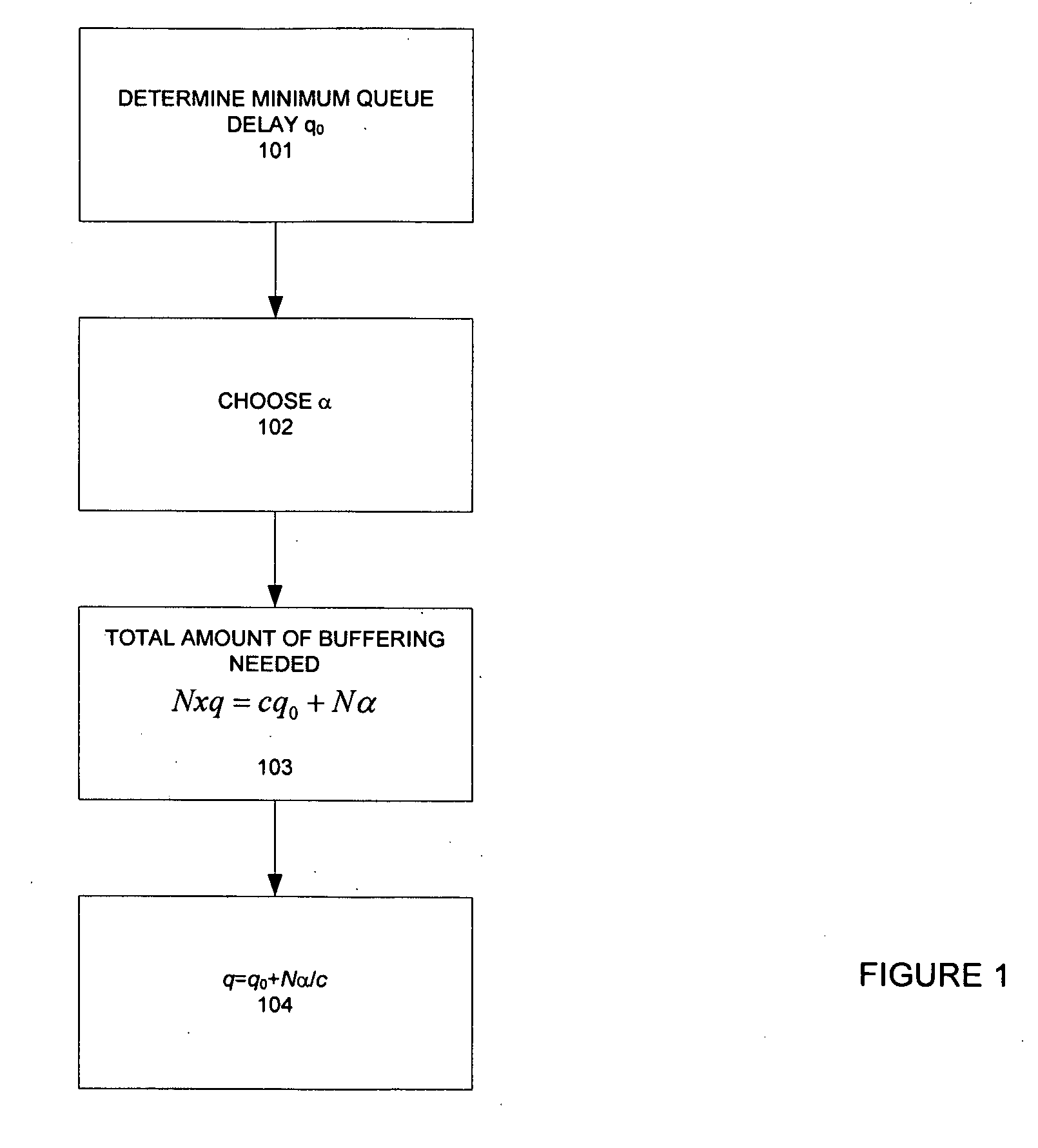
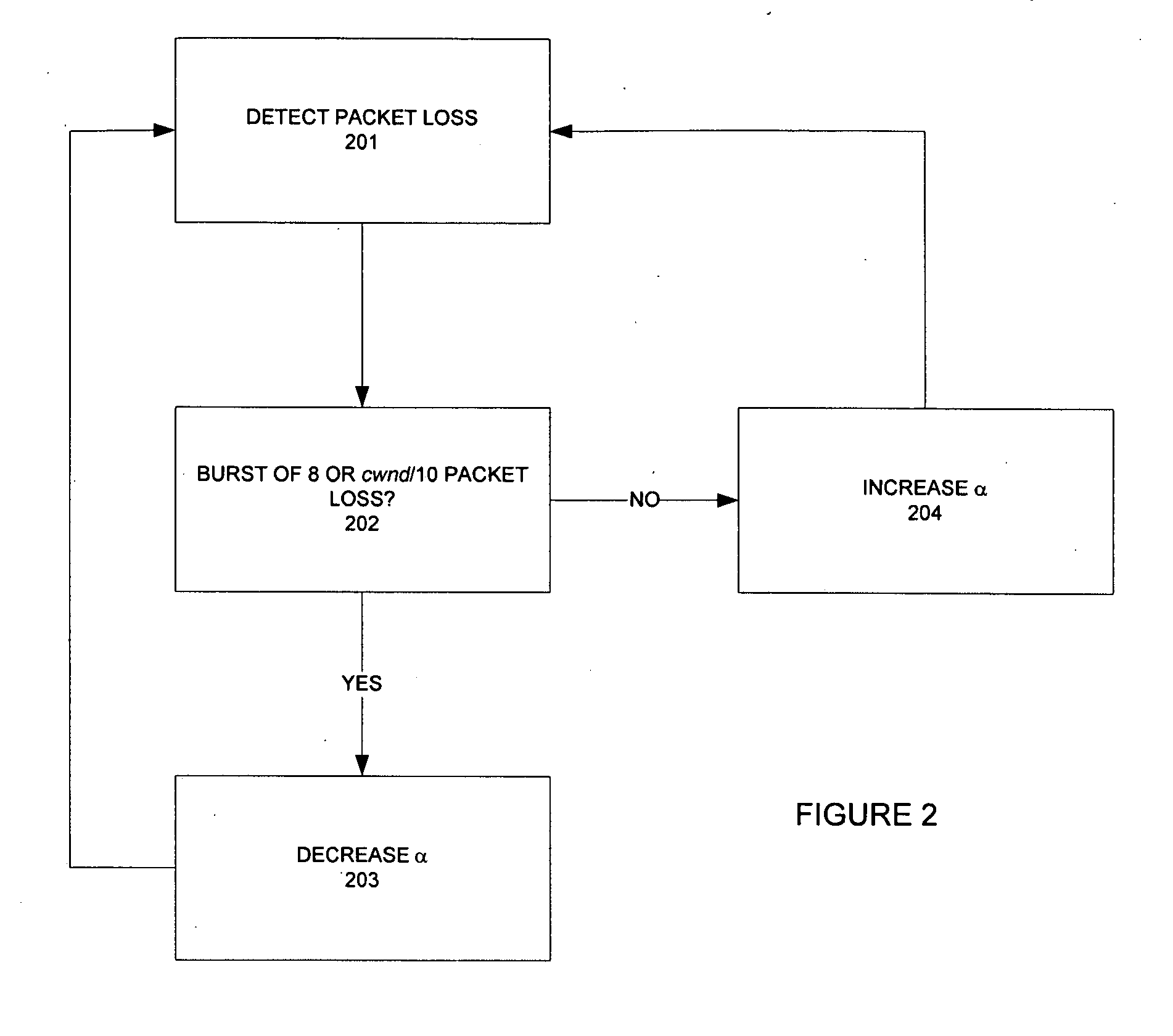
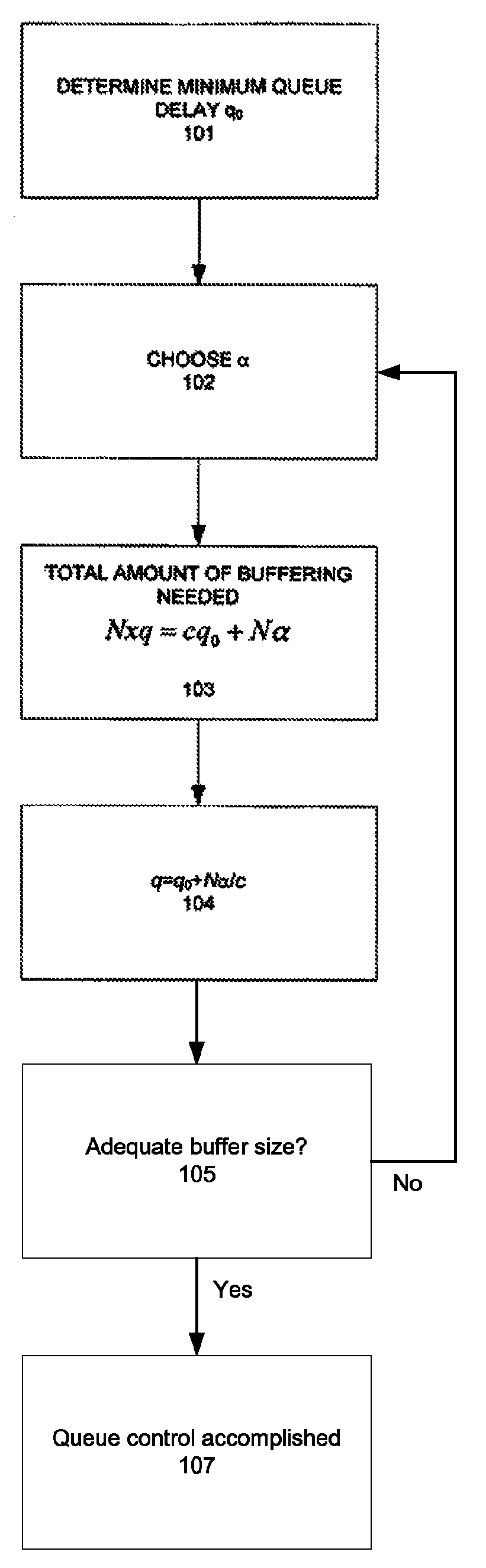
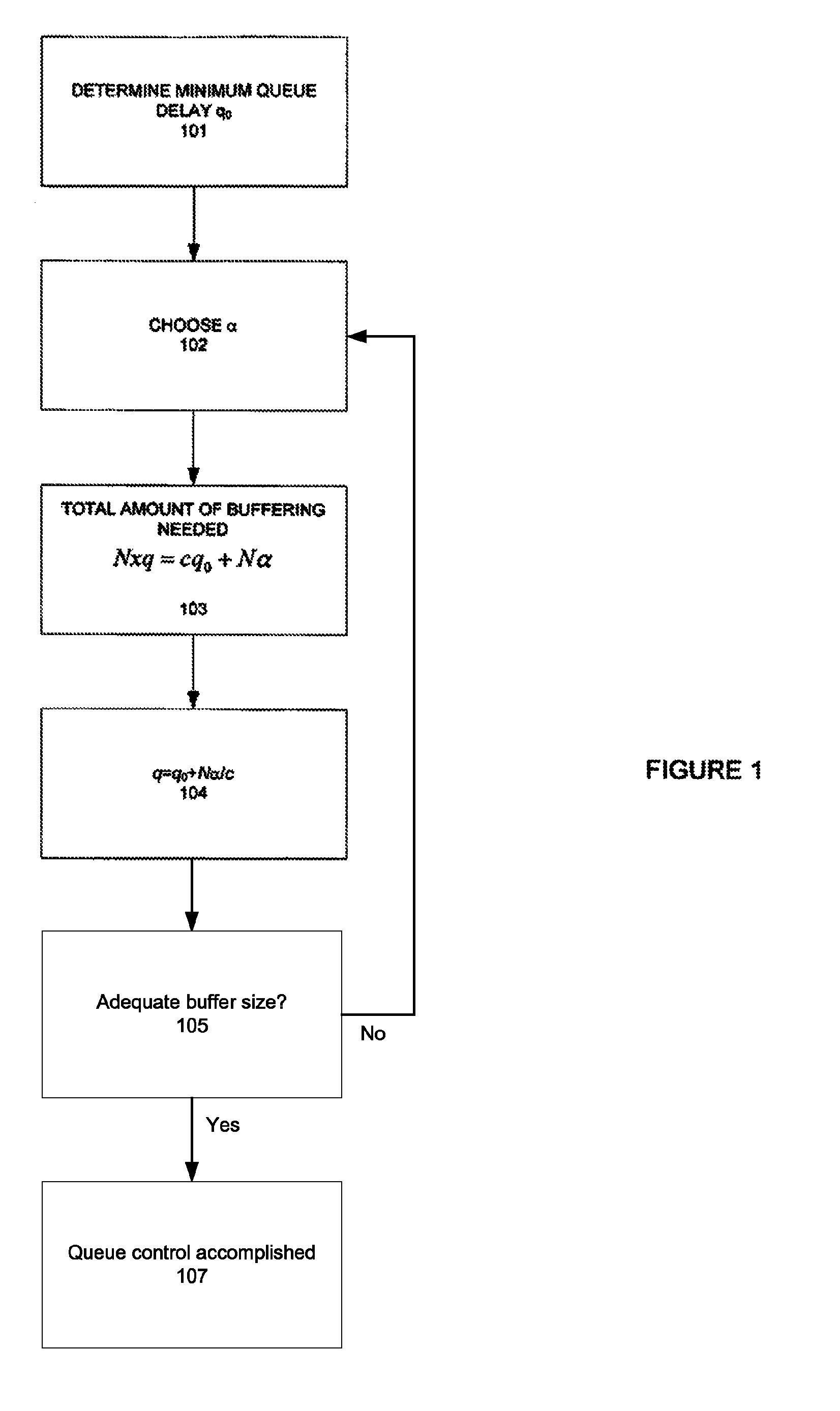
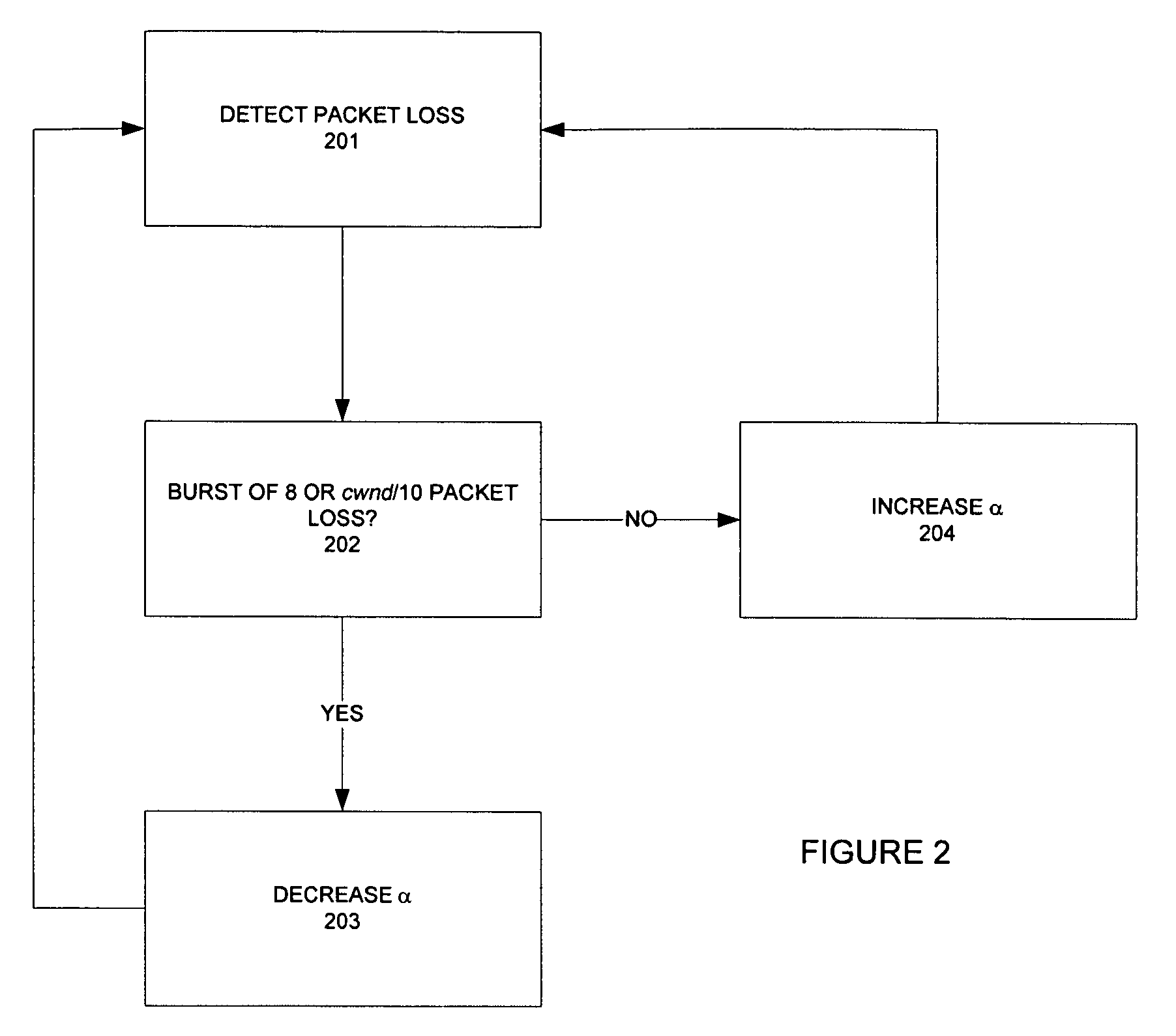
The invention provides a congestion control scheme that is a delay based scheme that includes a scalable queue size and one-way queueing delay measurement to reduce network congestion. Queue size is managed by queue control, a scalable utility function, dynamic alpha tuning, and / or randomized alpha tuning. One-way queueing delay is accomplished by measuring backward queueing delay management using various methods of estimating the receiver clock period. Embodiments include estimating the receiver clock period using single sample and multiple sample periods. The system includes a method for detecting route change.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Bandwidth estimation in broadband access networks
ActiveUS20060215574A1Accurate bandwidth estimationAccurate bandwidthError preventionTransmission systemsIdle timeBroadband
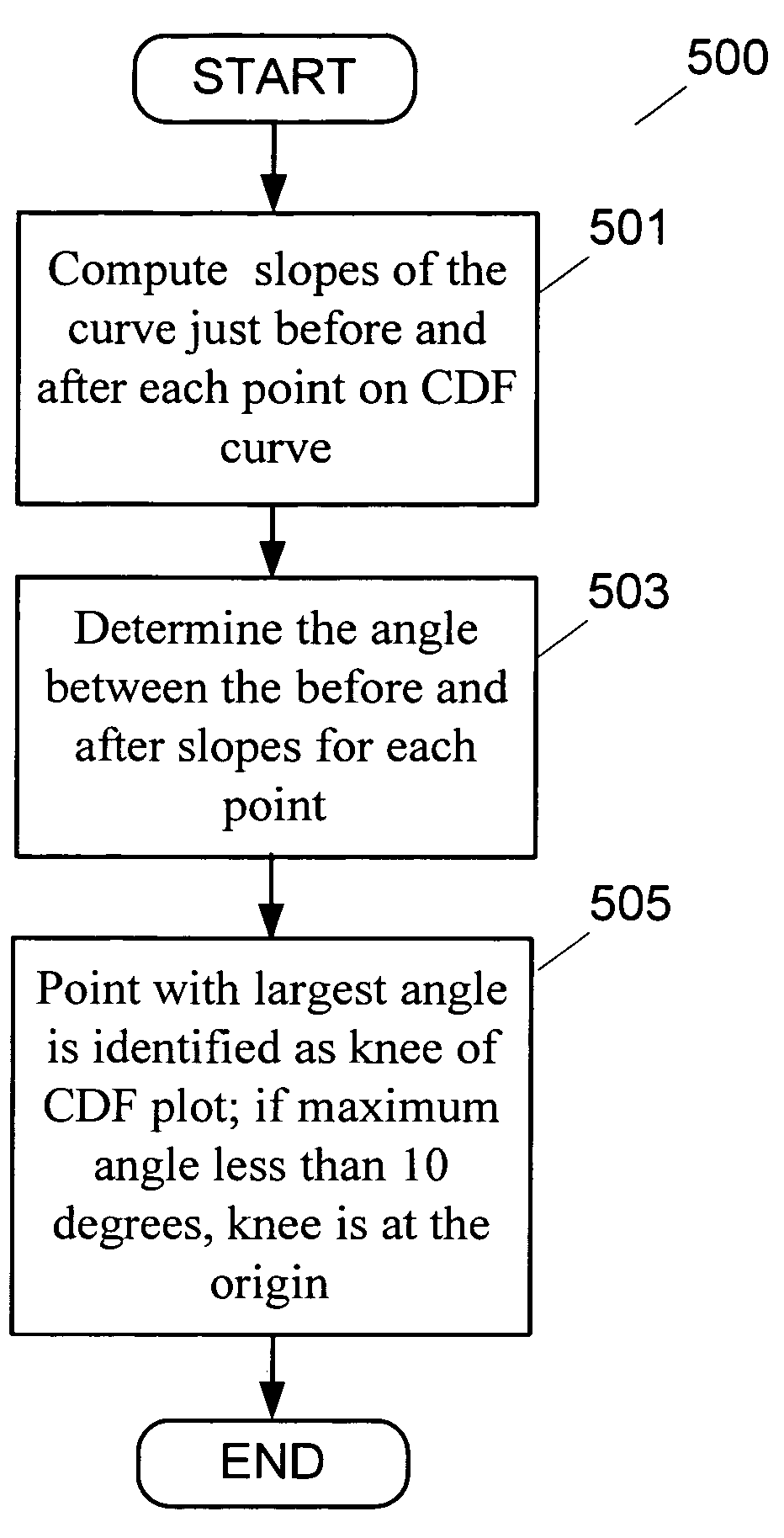
Measurement systems according to embodiments of the invention allow accurate bandwidth estimation even in non-FIFO scheduling and frame-level contention environments. In an embodiment of the invention, the approximate fraction of time that a link is idle is found by probing for idle periods (“gaps”). The fraction of idle time is then multiplied by the capacity to obtain an estimate of the available bandwidth. Gap time is estimated in an embodiment of the invention fraction by gathering samples of one-way delay (OWD) over the link in question. After the OWD is normalized and plotted, the knee in the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of OWD samples is used to identify the fraction of time that the channel is idle.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
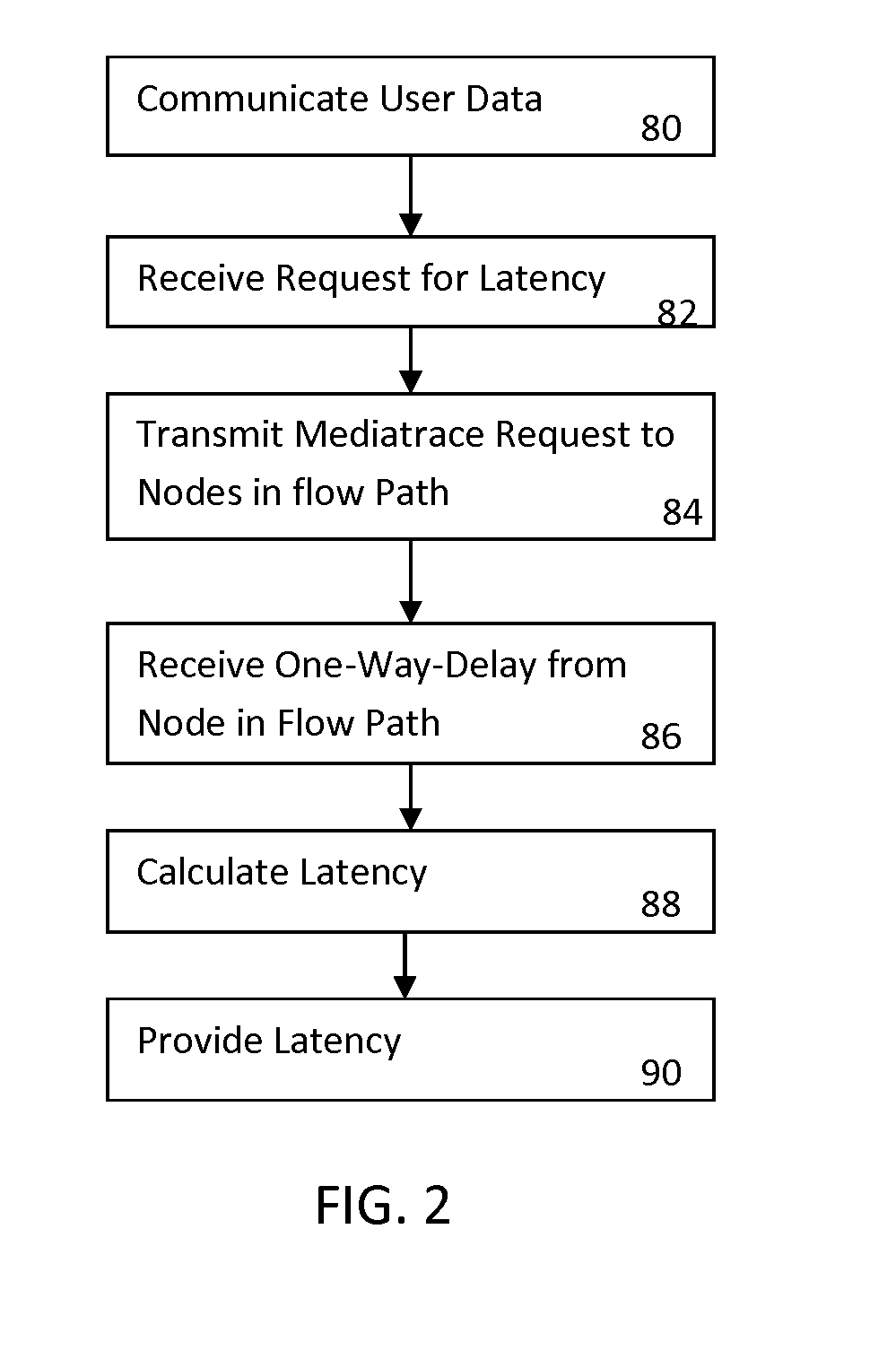
Calculating Latency in Computer Networks
In one implementation, data is communicated along a communications route in a network. A mediatrace request is generated for the communications route. Responses to the mediatrace request are received from along the communications route. The hop-by-hop latency is passively measured, from the responses, with one-way delay along the communications route in the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Transmitter, Receiver And Communication System
InactiveUS20080095247A1Minimizing dataMinimize disturbanceEnergy efficient ICTPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesStreaming dataPacket loss
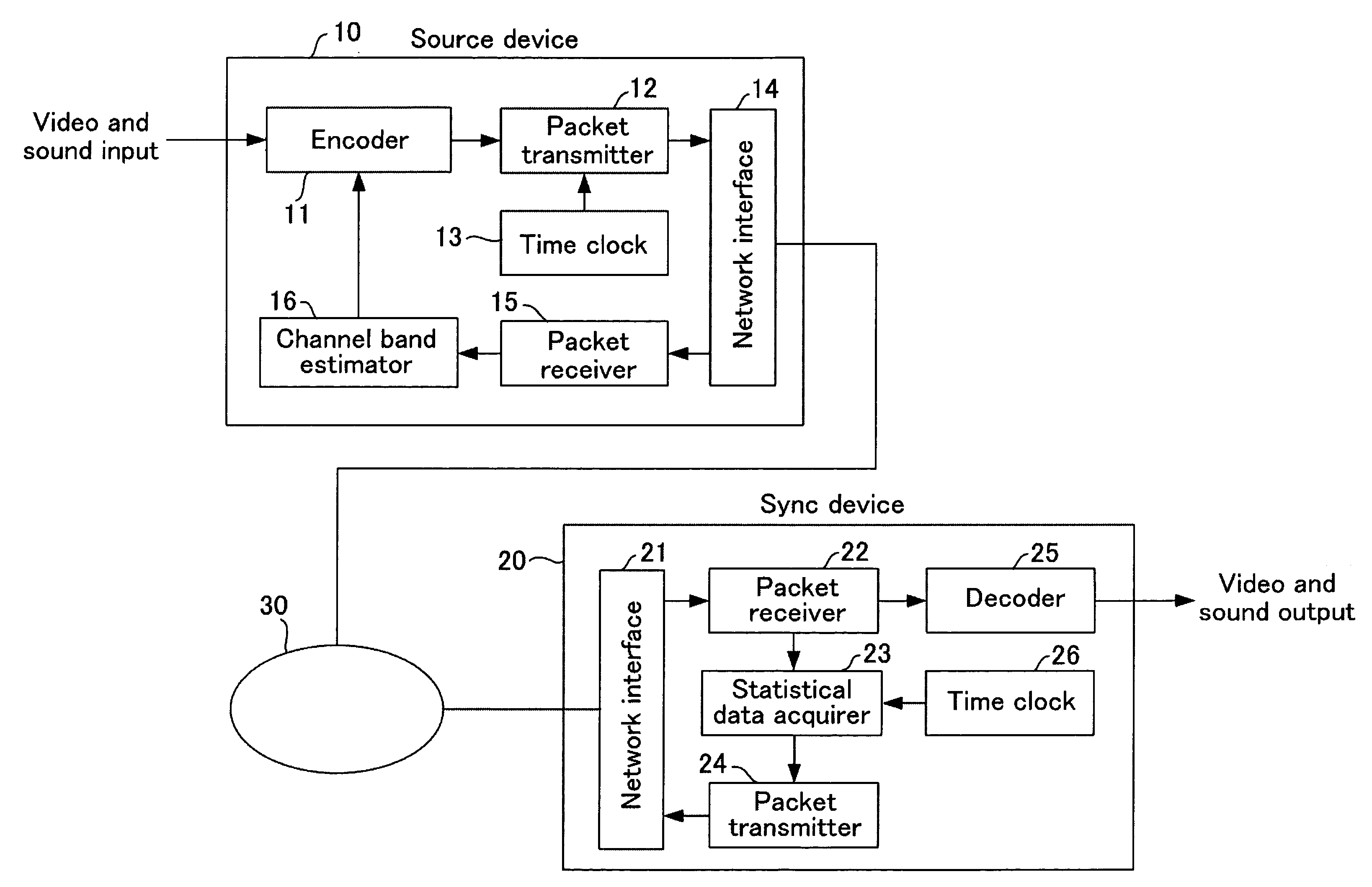
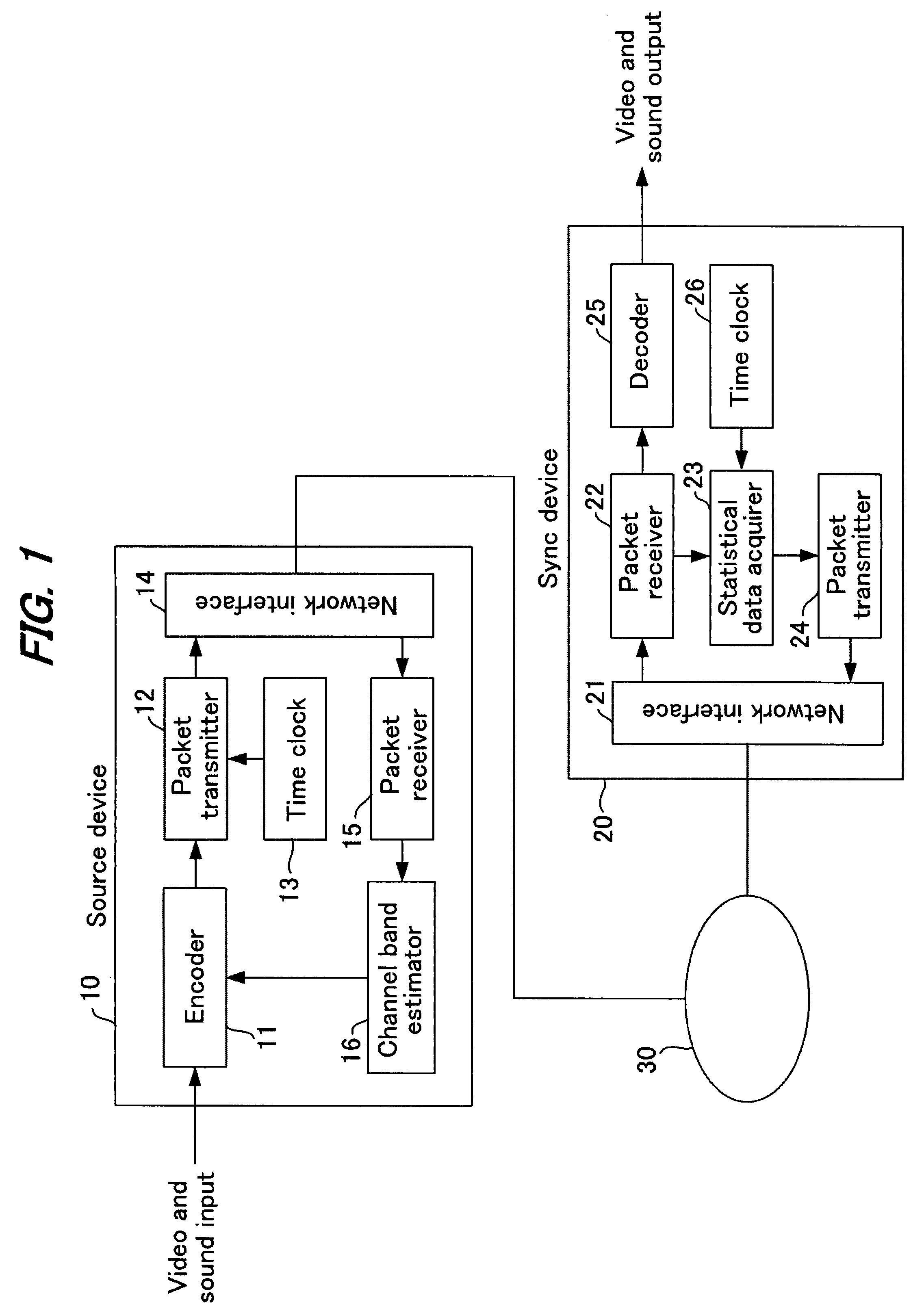
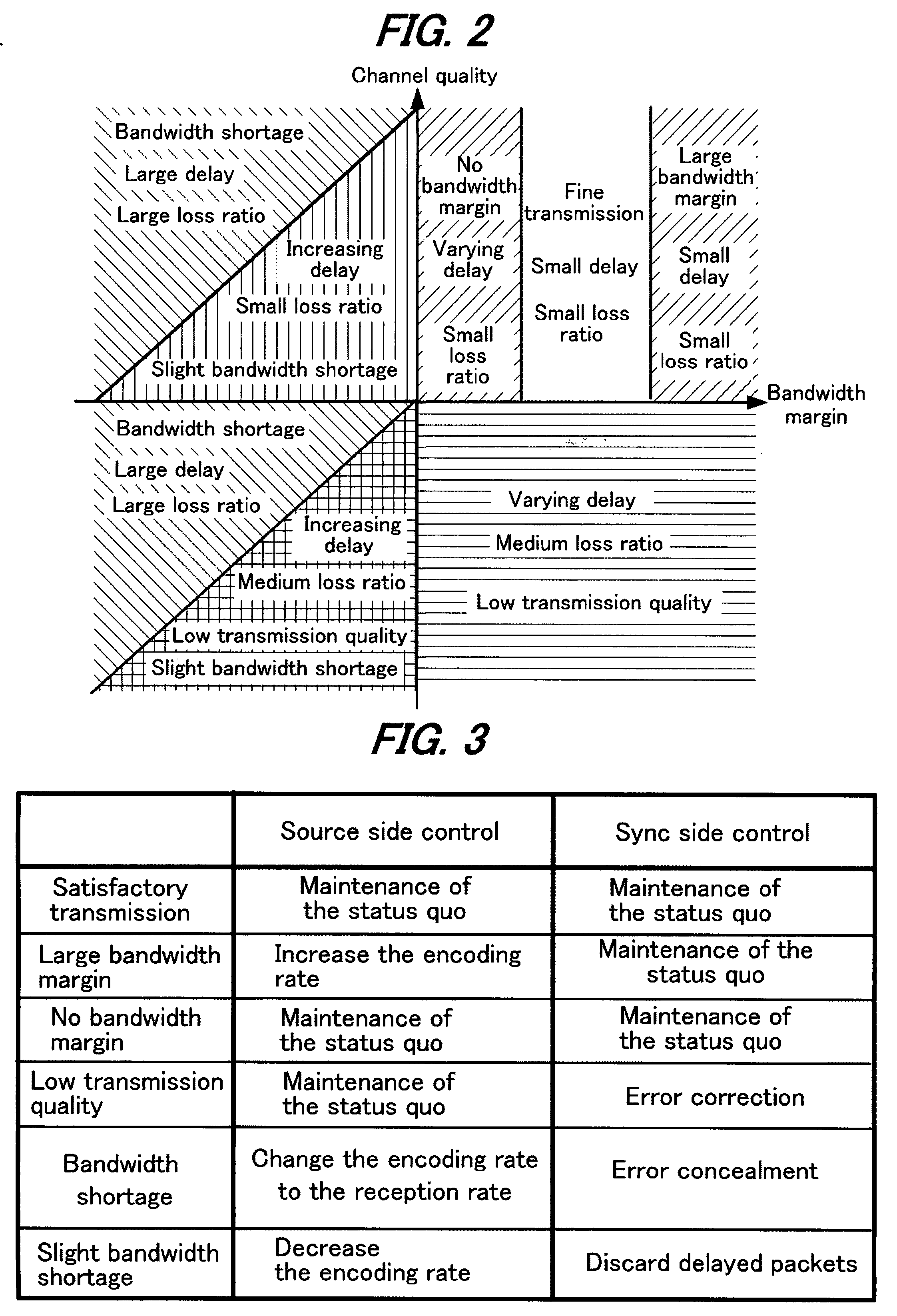
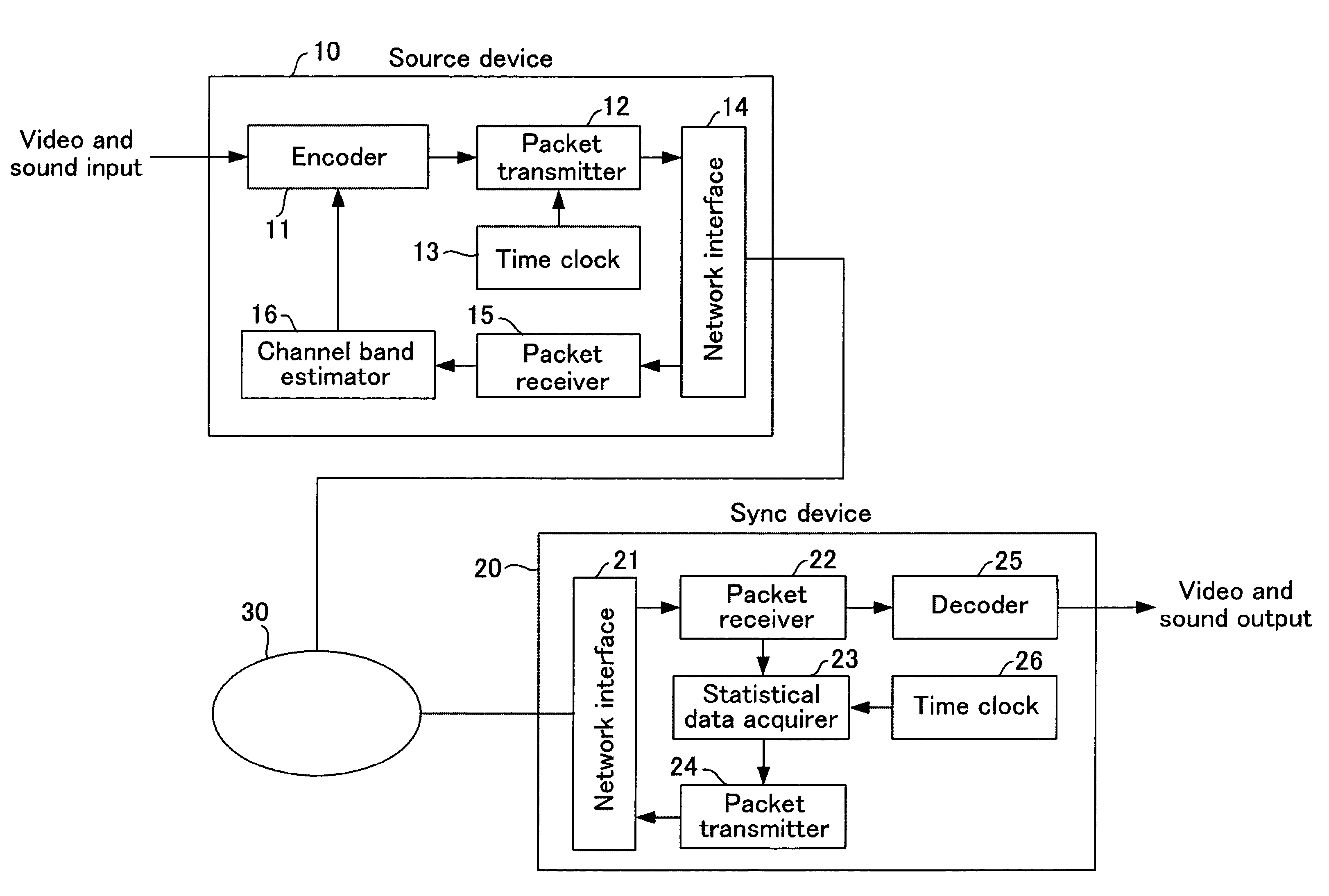
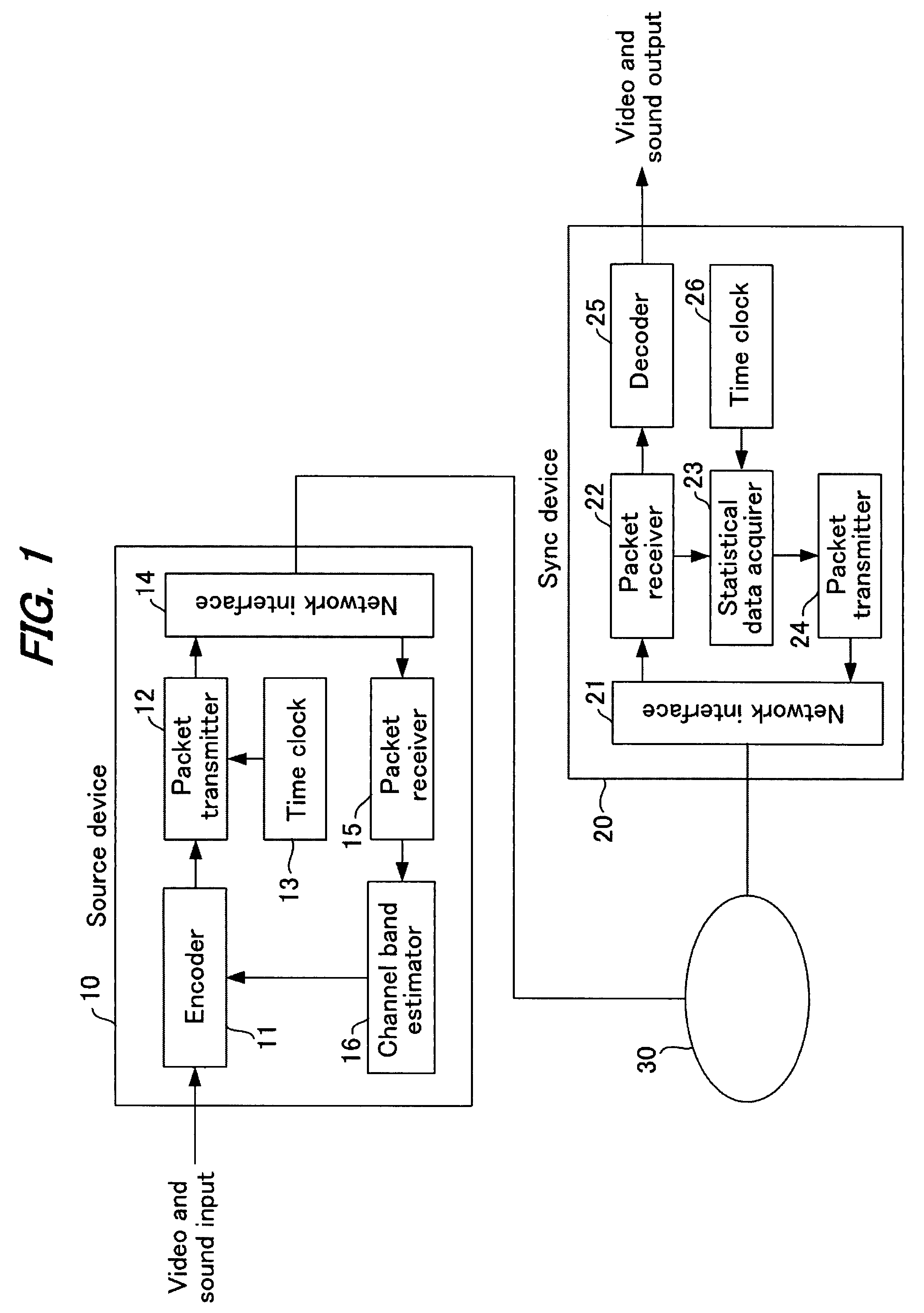
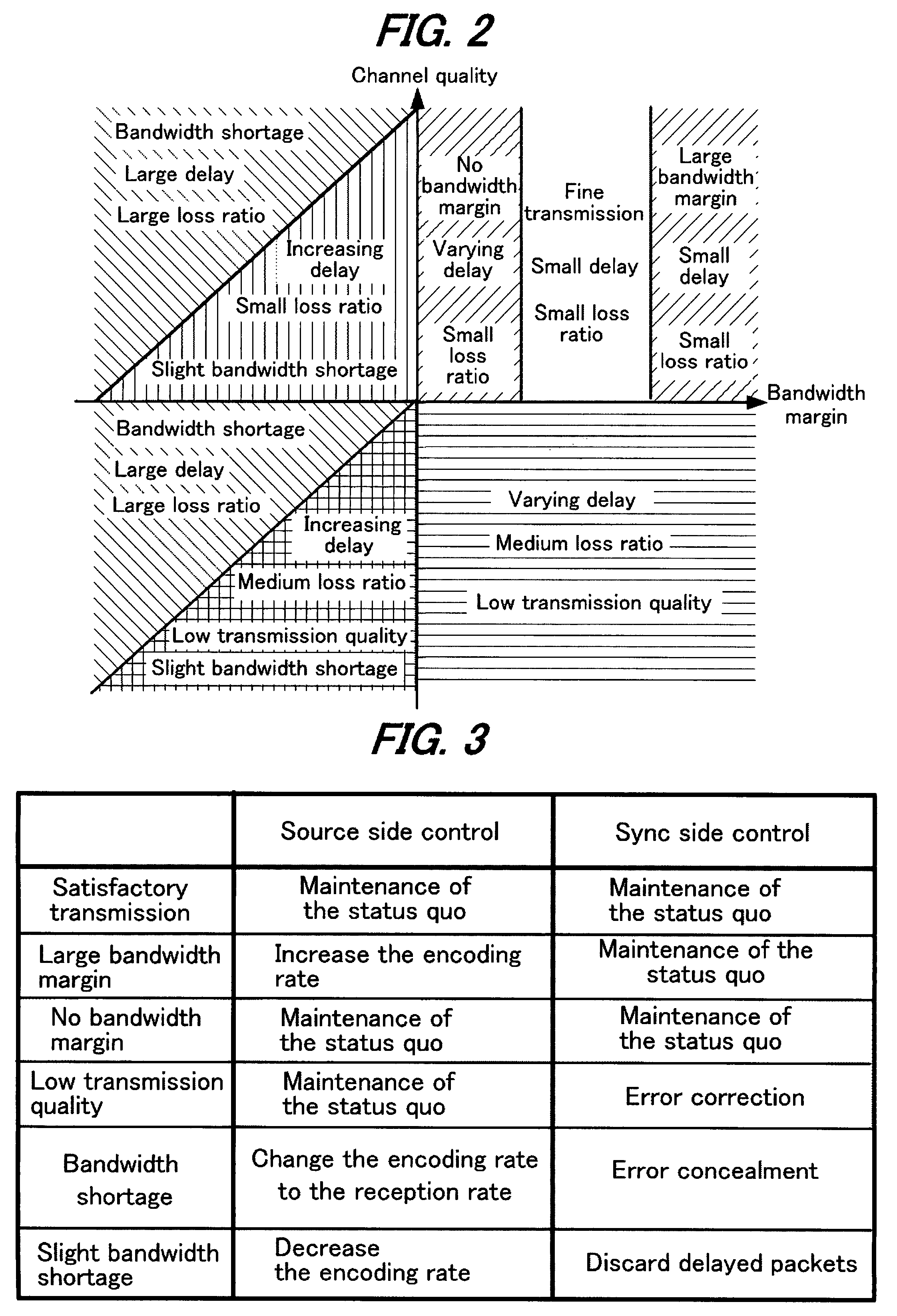
A source device 10 transmits streaming data. In a packet receiver 22 of a sync device 20, statistical data acquirer 23 calculates statistical data such as one-way delay time, packet loss ratio, reception rate and the like from the received streaming data and transmits it to the source device. The statistical information received by source device 20 is extracted by a packet receiver 15 and input to a channel band estimator 16. The channel band estimator 16 gives encoder 11 instructions to provide optimal encoding based on the transmission delay. Upon this, the transmission delay is calculated by assuming the minimum value of the communication delay from the start of transmission as zero. Control is performed by determining the delay time and packet loss ratio in data transmission and considering, based on these, the channel quality and bandwidth margin, so as to provide the optimal transmission bit rate or encoding rate.
Owner:SHARP KK
Communication terminal which perform low-delay communication by using a broadband line
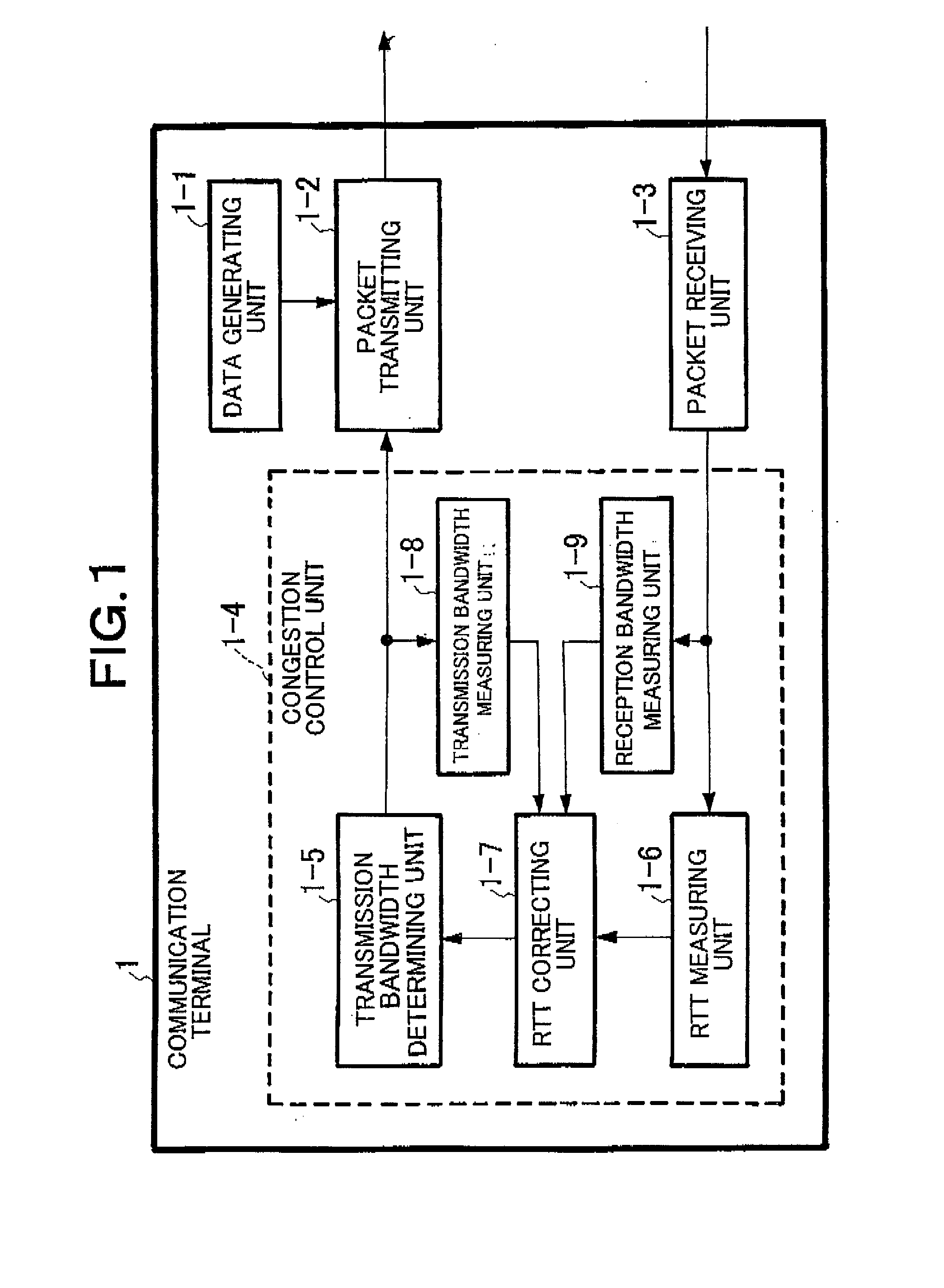
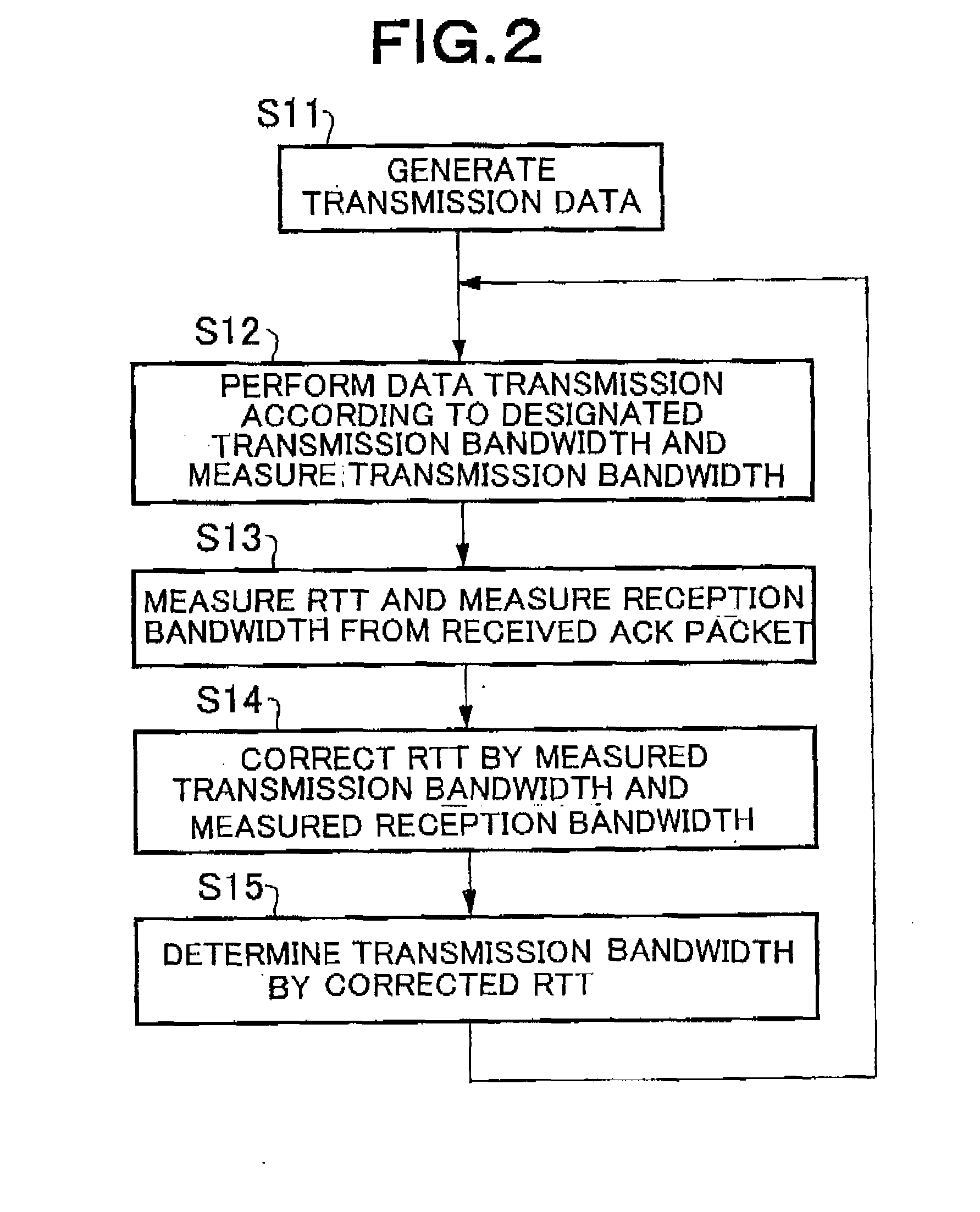
ActiveUS20080212480A1Reduce latencyExpand the transmission rangeError preventionTransmission systemsRound-trip delay timeDelayed time
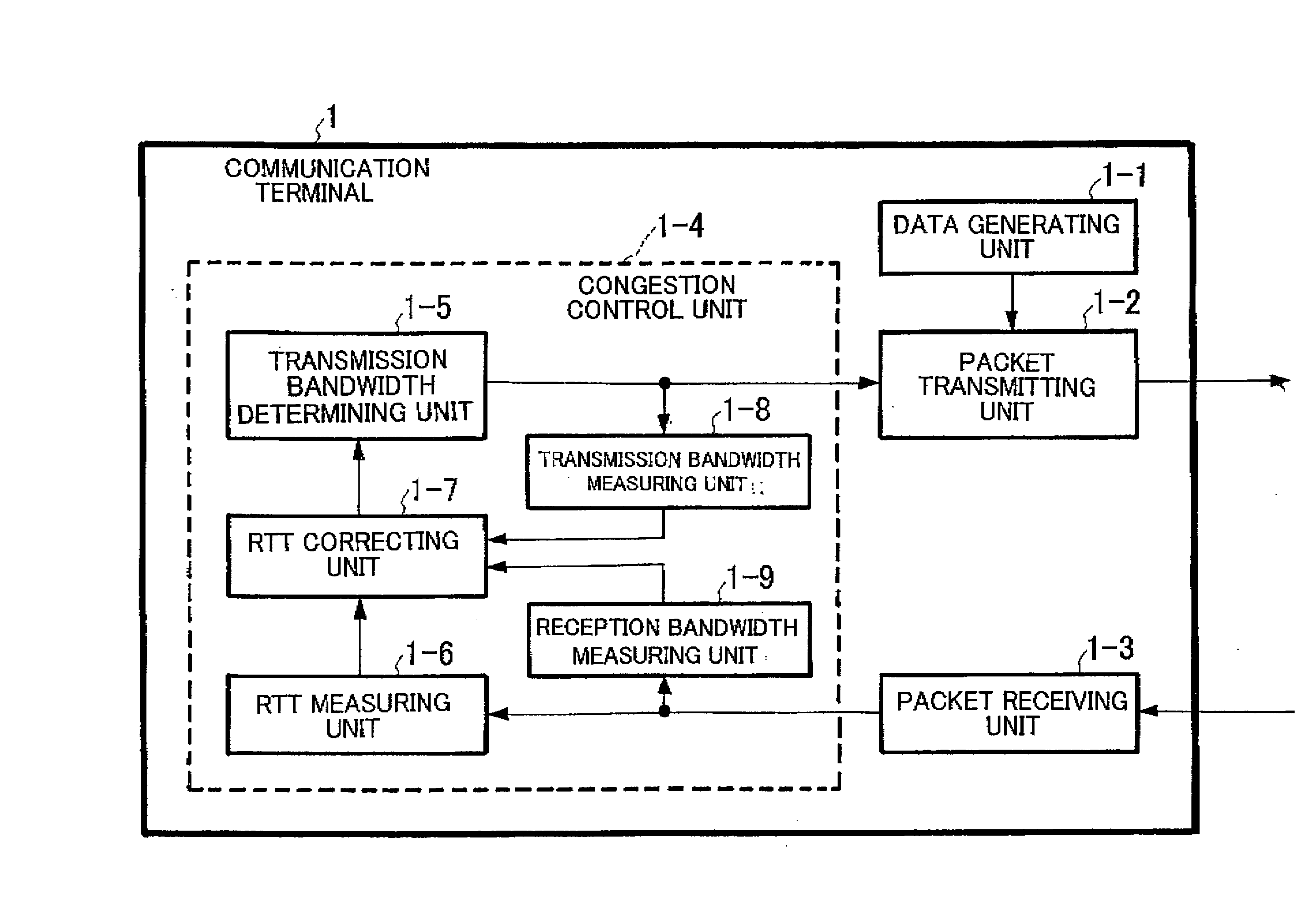
A communication terminal which sets a communication session between a plurality of communication terminals through a network to perform data transmission and reception includes a measuring unit which measures round-trip delay time (RTT) or one-way delay time between the communication terminals for performing transmission and reception on the basis of the received acknowledgement, a reception bandwidth measuring unit which measures a reception bandwidth in a reception terminal of the communication terminals on the basis of the received acknowledgement, a correcting unit which corrects a value of the round-trip delay time or the one-way delay time by using at least the reception bandwidth, and a transmission bandwidth determining unit which determines a transmission bandwidth on the basis of the value of the corrected round-trip delay time or the corrected one-way delay time.
Owner:NEC CORP
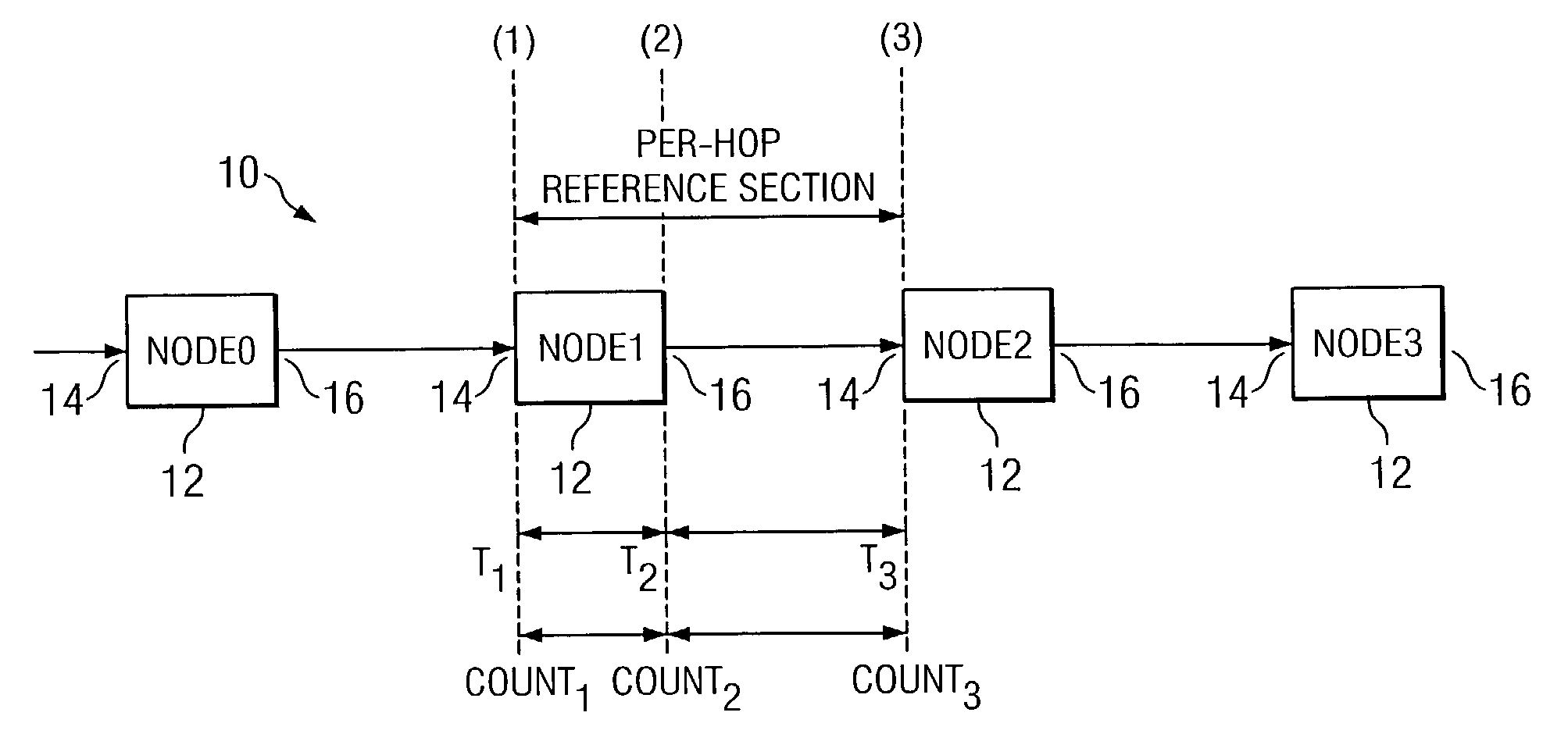
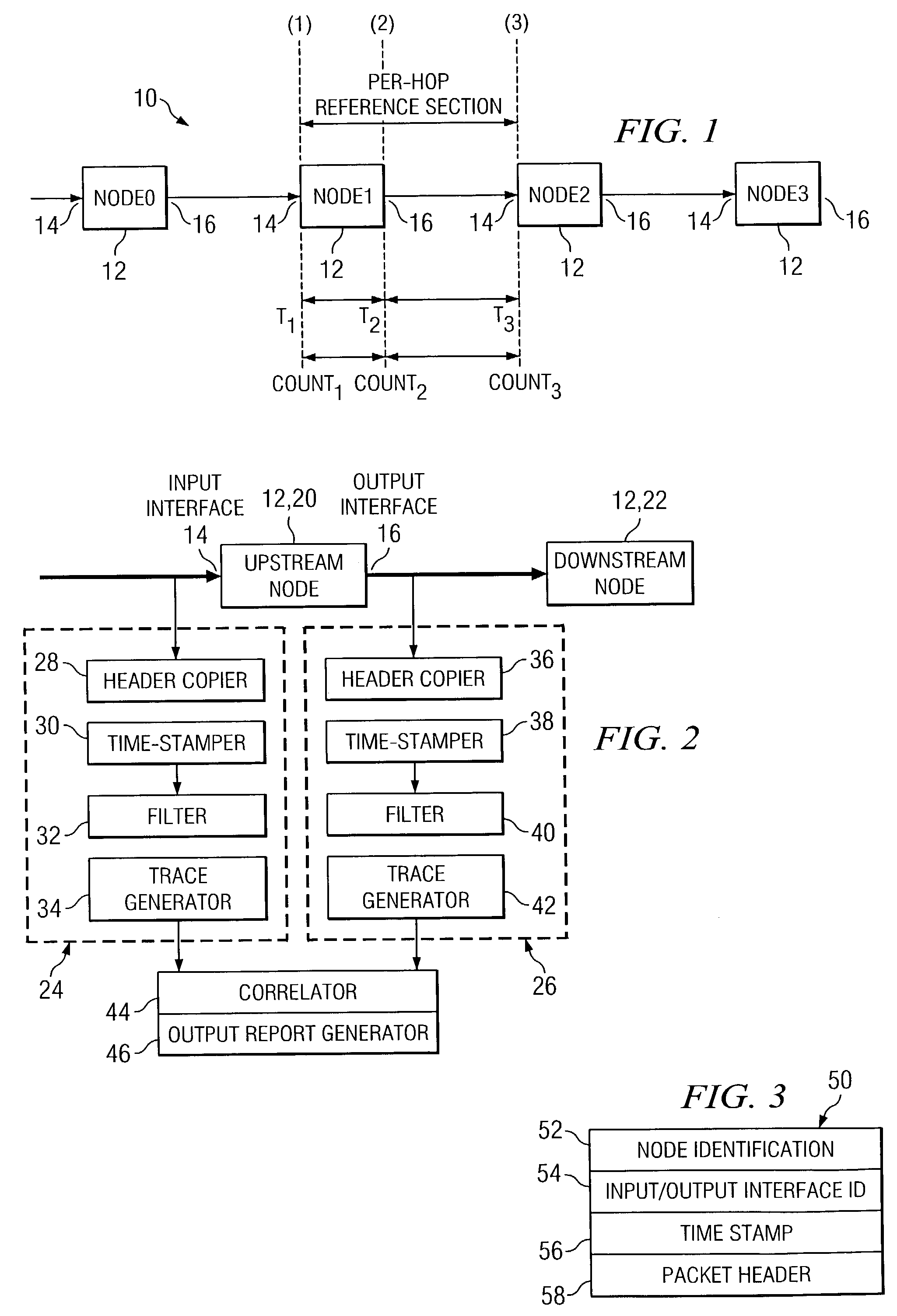
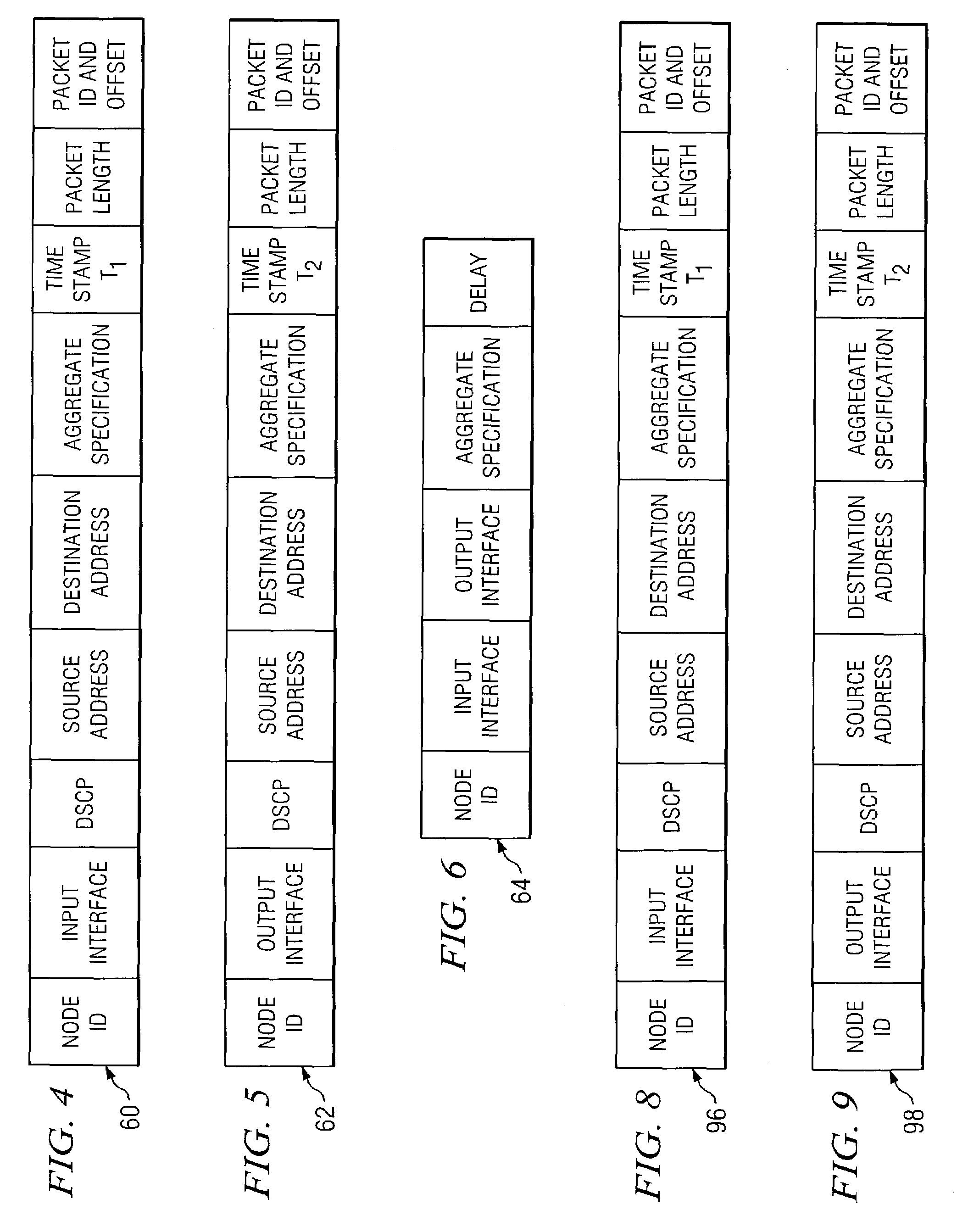
Measurement architecture to obtain per-hop one-way packet loss and delay in multi-class service networks
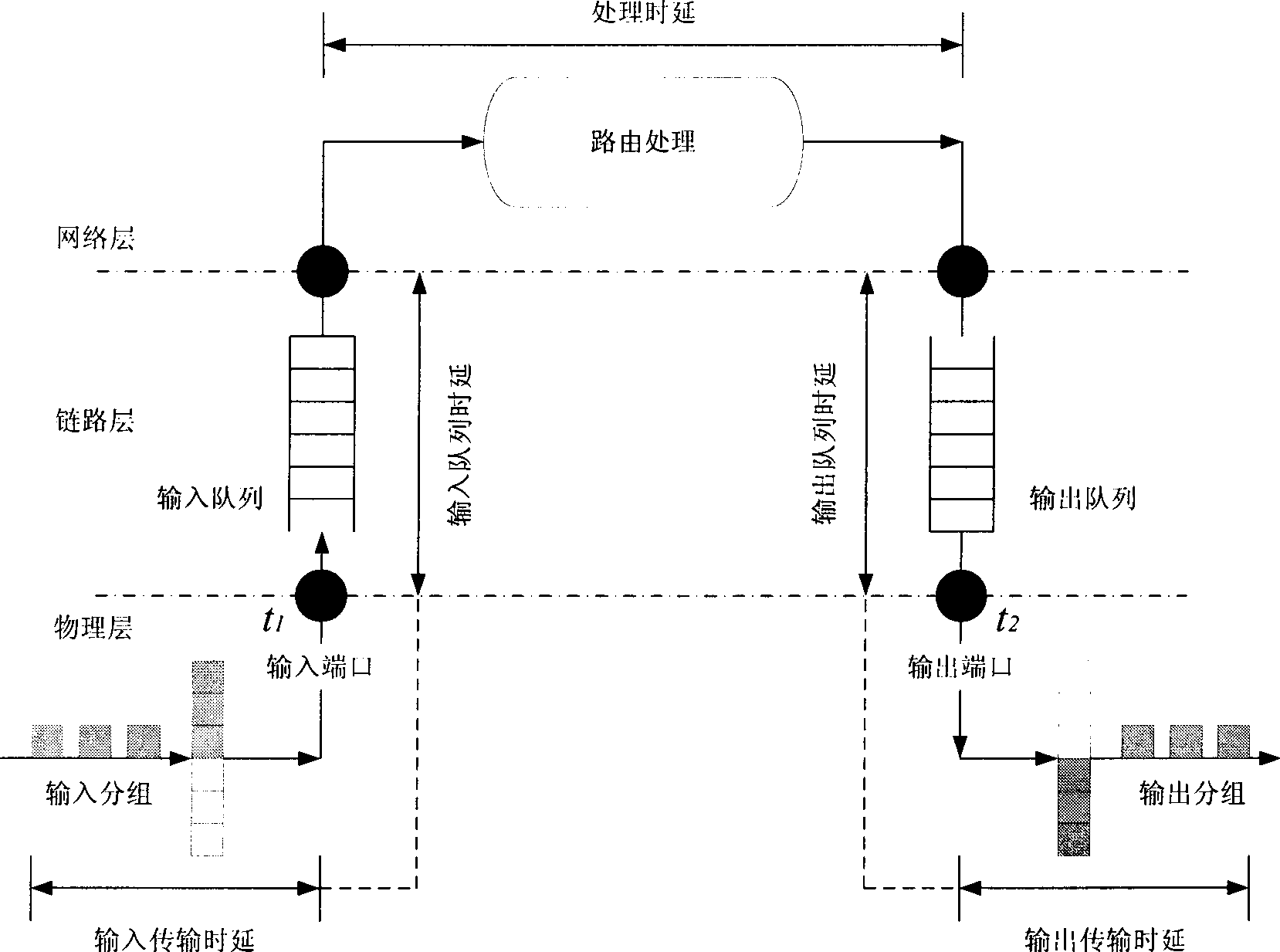
An architecture for measurement of per-hop, one-way delay includes a input observation circuit (24) at the input interface of a node (12) and a output observation circuit (26) at the output interface (16) of a node (12). The input observation circuit (24) copies and time stamps the headers of incoming packets, and filters packets according to an aggregate definition. Similarly, the output observation circuit (26) copies and time stamps the headers of outgoing packets, and filters packets according to the aggregate definition. The incoming and outgoing traces are correlated to calculate a delay measurement. A packet loss measurement uses input observation circuits (72a and 72b) at the input interfaces (14) of upstream and downstream nodes (20 and 22) and an output observation circuit 74 at the output interface (16) of the upstream node. The observation circuits (72a, 72b and 74) determine the number of lost packets across a node and between nodes, according to an aggregate definition.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
VOIP bandwidth management
A computerized method of optimizing audio quality in a voice stream between a sender and a receiver VoIP applications, comprising: defining by the receiver time intervals; determining by the receiver at the end of each time interval whether congestion exists, by calculating (i) one-way-delay and (ii) trend, using double-exponential smoothing; estimating by the receiver a bandwidth available to the sender based on said calculation; sending said estimated bandwidth by the receiver to the sender; and using by the sender said bandwidth estimate as maximum allowed send rate.
Owner:VIBER MEDIA S A R L
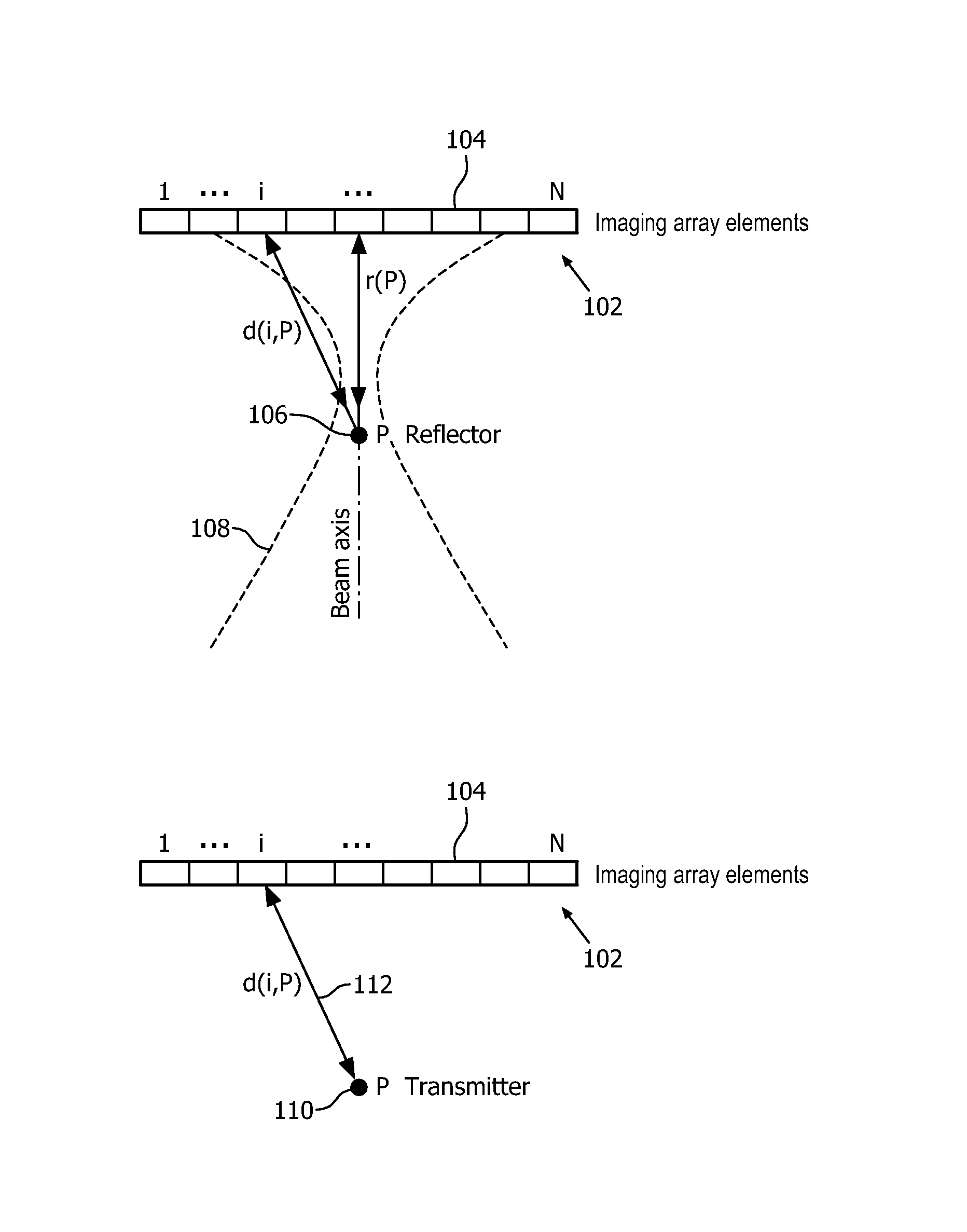
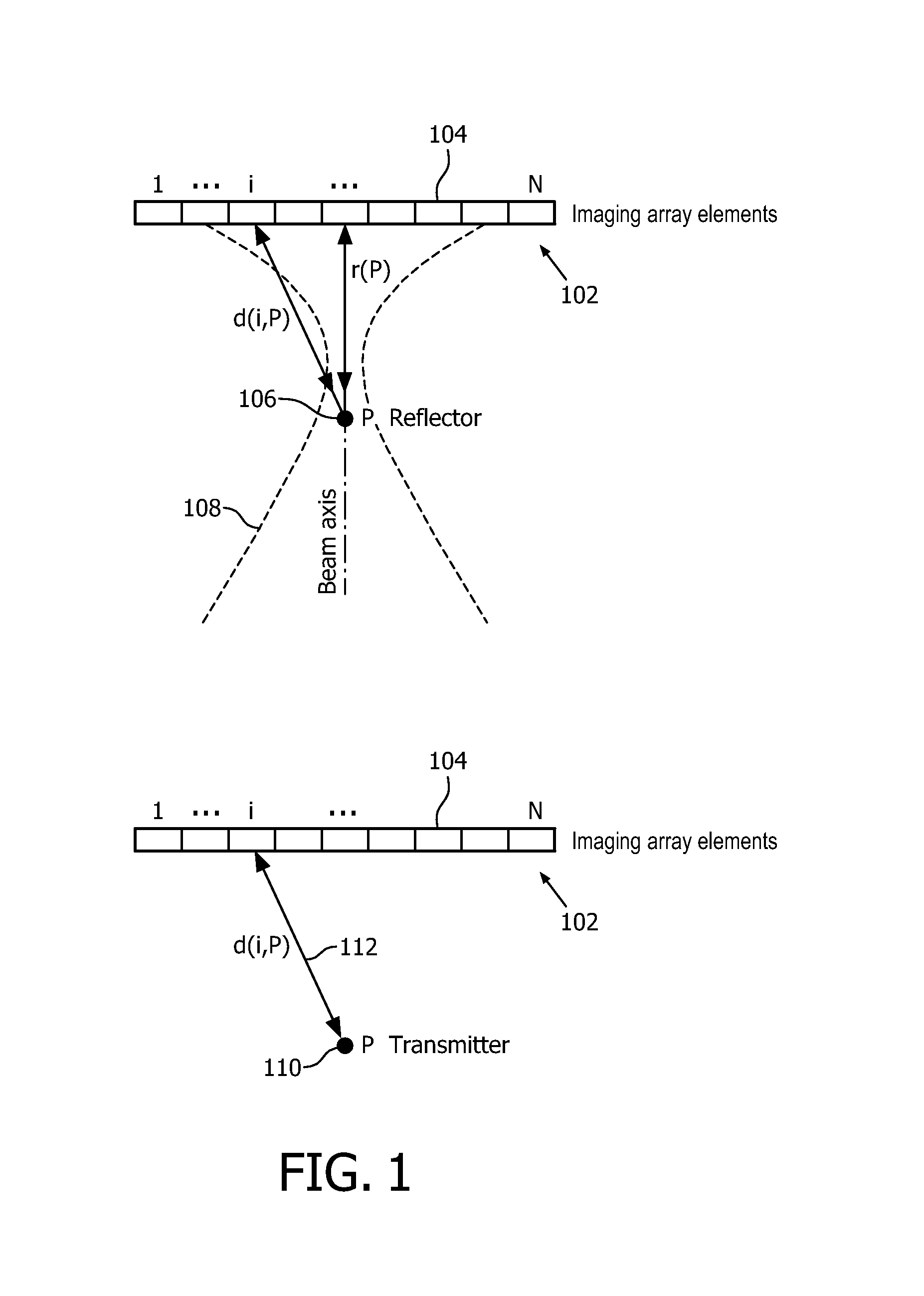
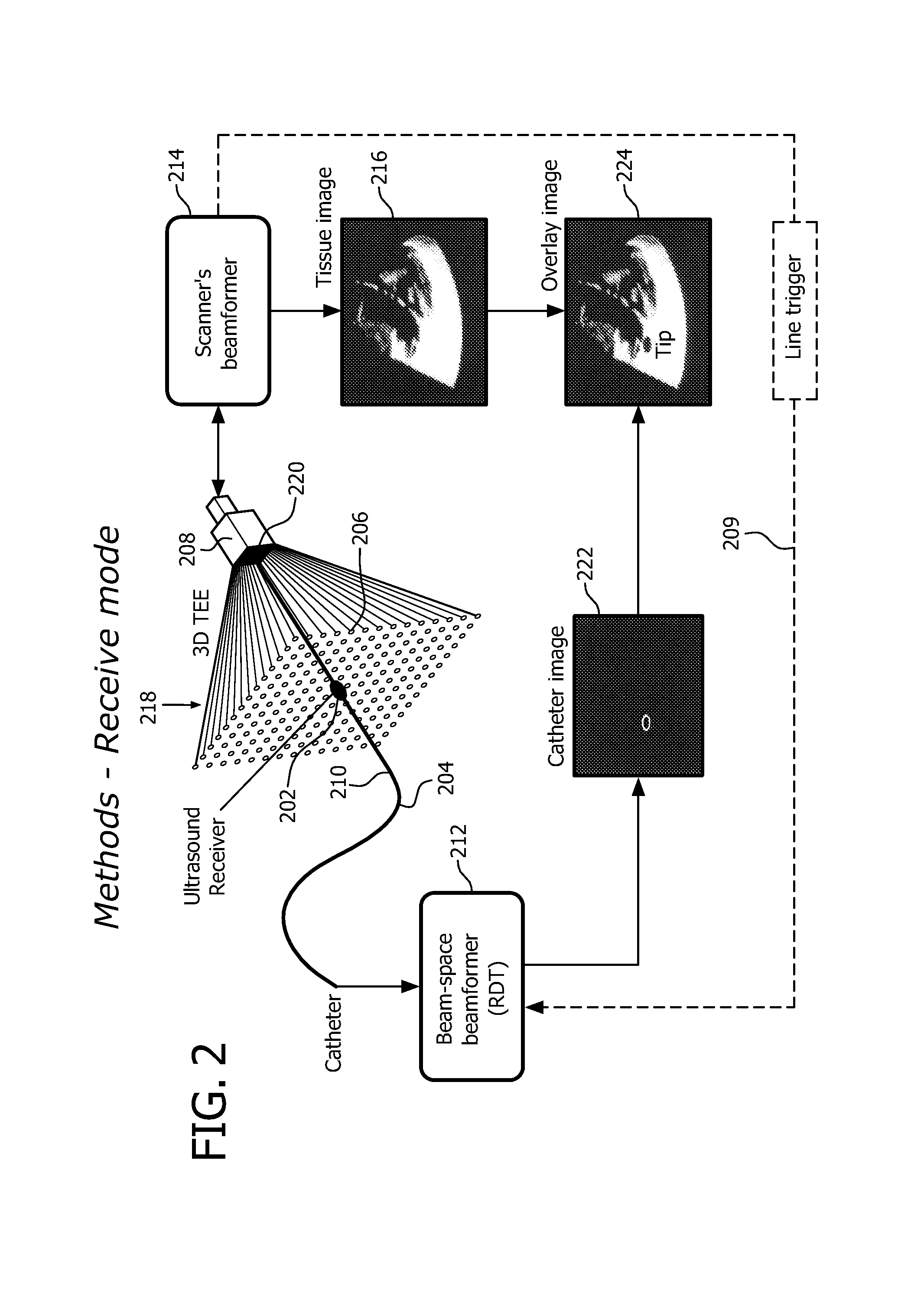
Ultrasonic tracking of ultrasound transducer(s) aboard an interventional tool
ActiveUS9282946B2Improve accuracyAccurate imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgical navigation systemsSonificationUltrasonic sensor
In one aspect, an ultrasound receive beamformer is configured for one-way only beamforming of transmissive ultrasound using one-way delays. The receive beamforming in some embodiments is used to track, in real time, a catheter, needle or other surgical tool within an image of a region of interest. The tool can have embedded at its tip a small ultrasound transmitter or receiver for transmitting or receiving the transmissive ultrasound. Optionally, additional transducers are fixed along the tool to provide the orientation of the tool.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
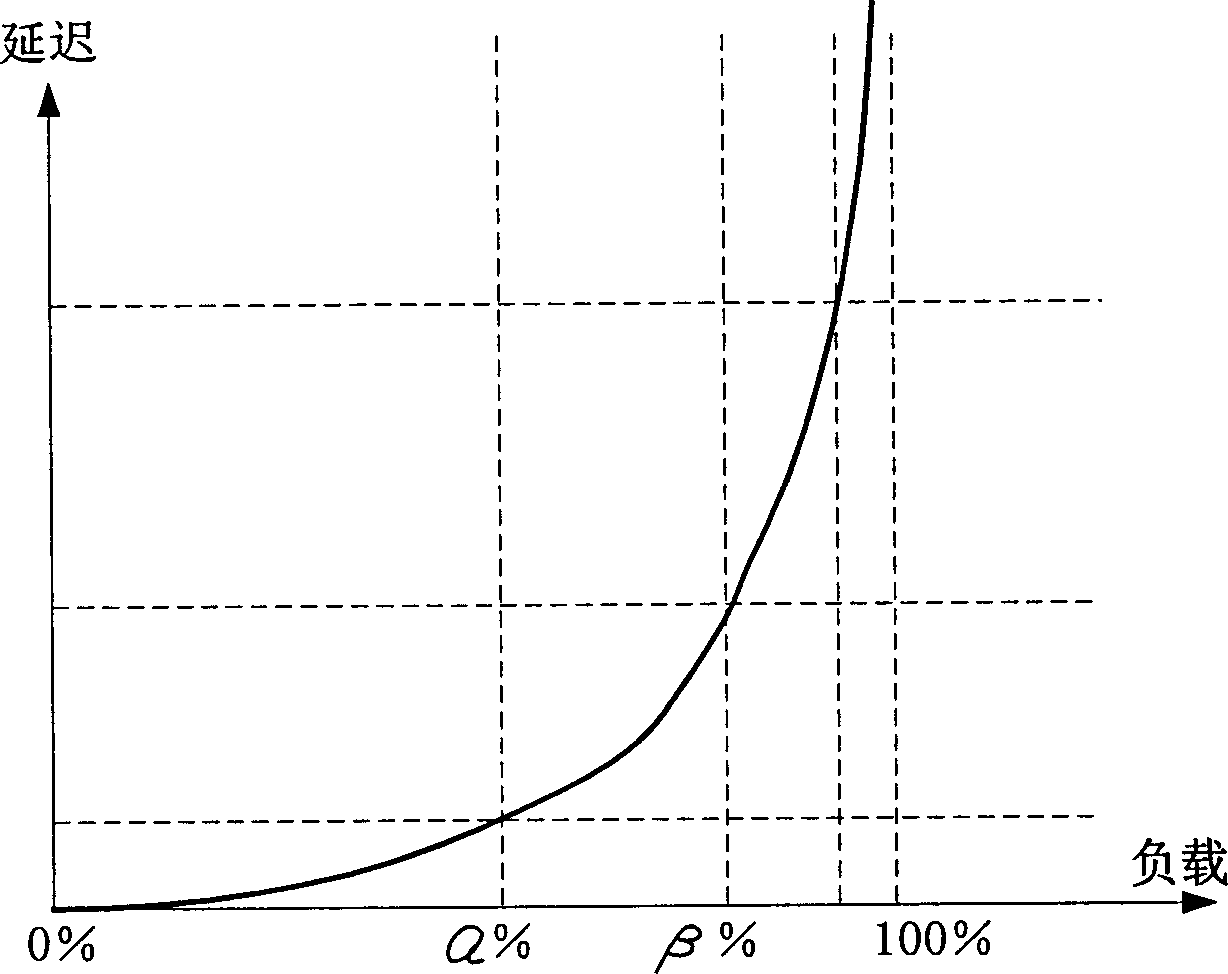
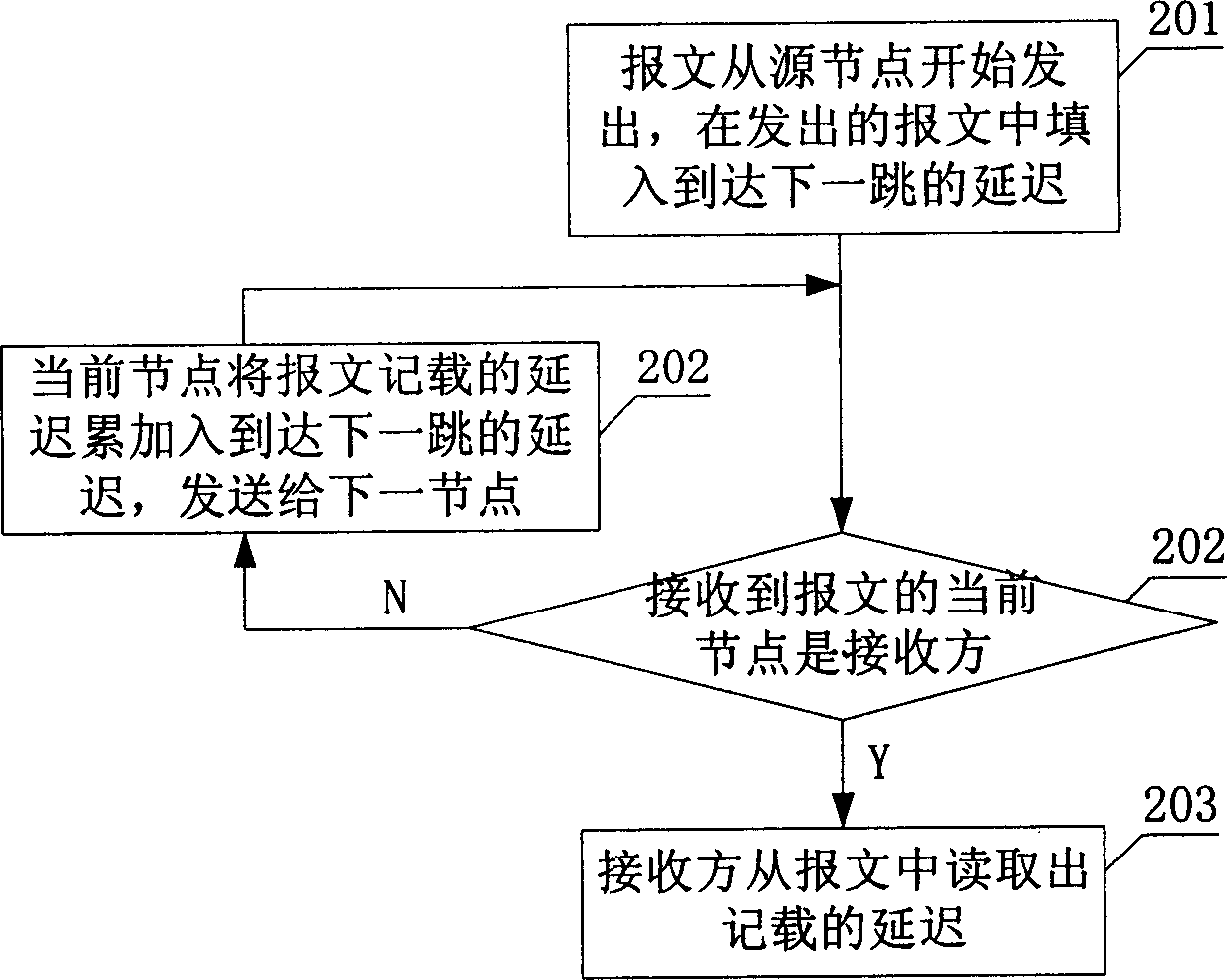
One-way delay measuring method
InactiveCN1812350ARealize measurementReduce complexityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorData switching networksTotal delayOne-way delay
This invention provides a kind of measuring method for unidirectional delay, which is message transmission delay from transmitting part to receiving part. It concludes: A) transmitting part keeps the delay to the neighboring next node in the current message and transmits it to the neighboring next node; B) the node, which receives the said message, is used as current transmitting part. Step A is repeated until current node is receiving part; C) receiving part abstracts each delay kept in the message and calculates total delay. Or when transmitting message to next node every time, the kept delays are accumulated. This invention does not need time synchronism between network node facilities to achieve precise unidirectional delay measuring.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Method and device for probing available bandwidth
ActiveCN108234224AImprove communication qualityDoes not affect communication qualityData switching networksPacket lossCommunication quality
The invention discloses a method and a device for probing an available bandwidth, belonging to the field of internet technology. The method comprises the steps of: receiving first probing data packetssent by a sending end every preset time period; calculating a delay value of one-way delay of the first probing data packets within the current time period; and when the delay value of one-way delayis determined to change suddenly, taking the receiving rate calculated according to the data volume of the first probing data packets as an available bandwidth within the current time period. The method and the device do not rely on multimedia data packets, but probe based on the first probing data packets special for probing an available bandwidth. Since the first probing data packets do not contain related data of audio and video communication, the loss does not affect the communication quality, and the packet loss probability of each kind of data packets in a network is the same. When the network is congested, in the presence of the first probing data packets, the lost multimedia data packets are less than those in the prior art, so that the audio and video communication quality is obviously improved. Therefore, the probing method is more reasonable.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Jitter buffering system and method of jitter buffering
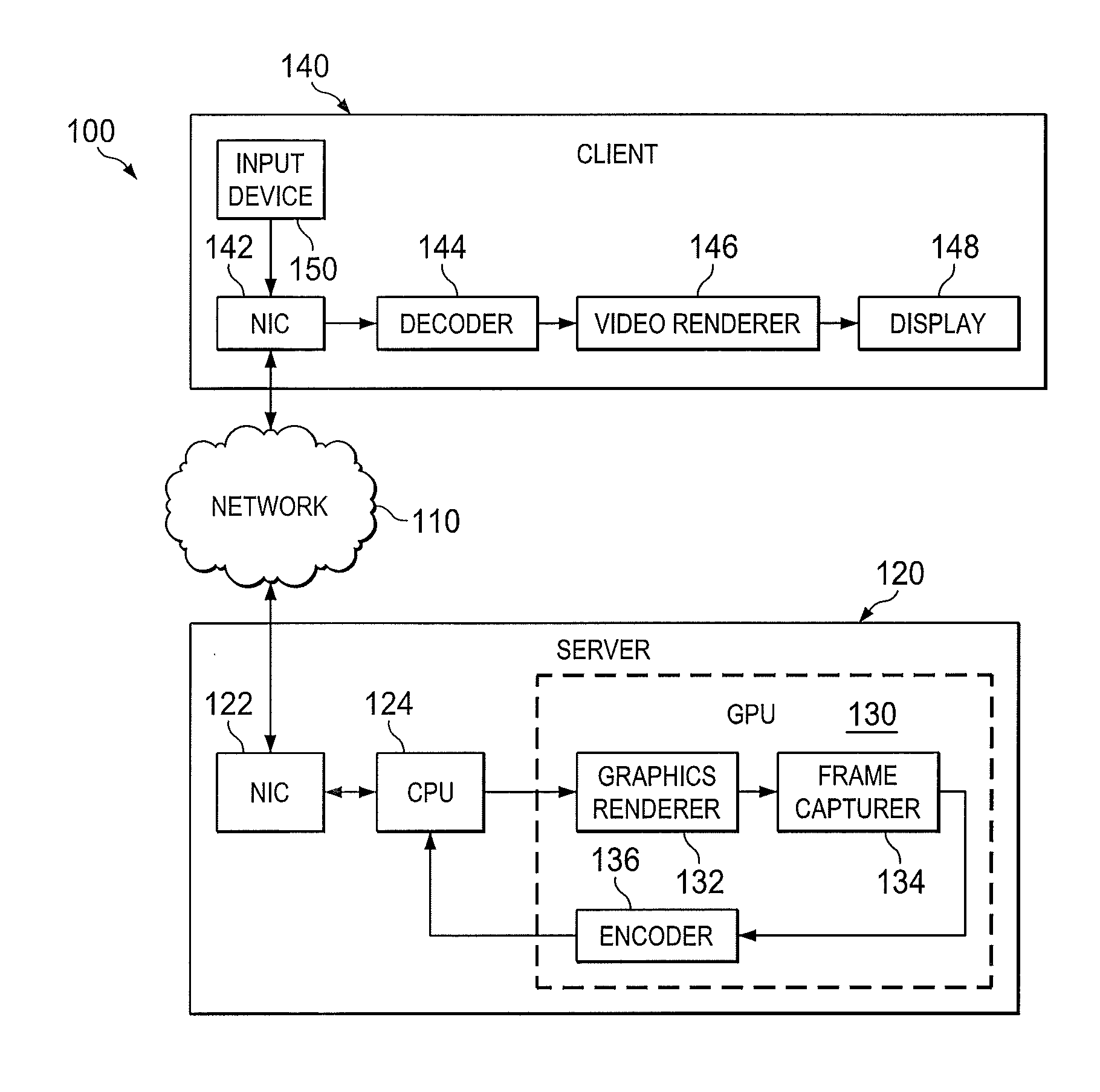
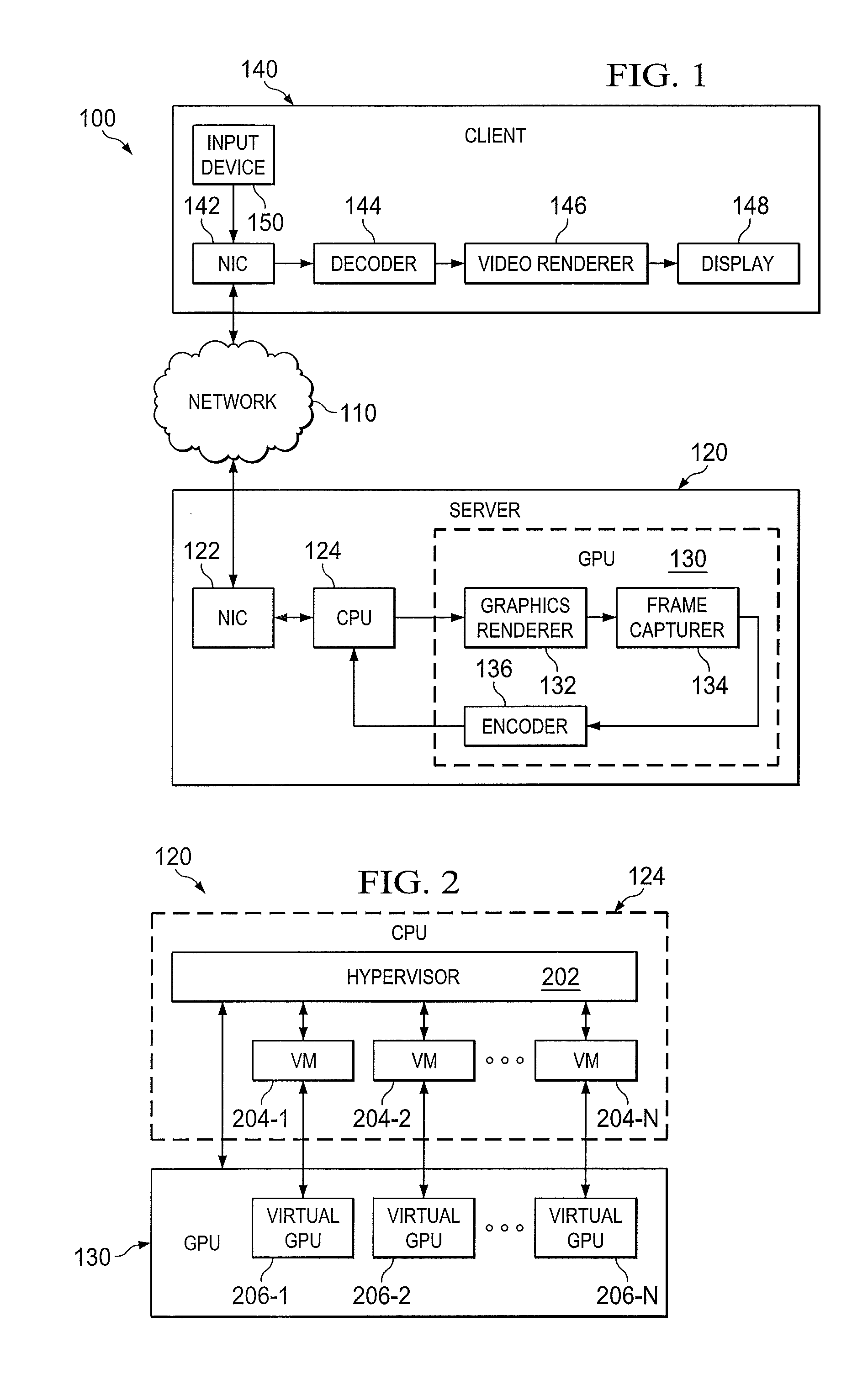
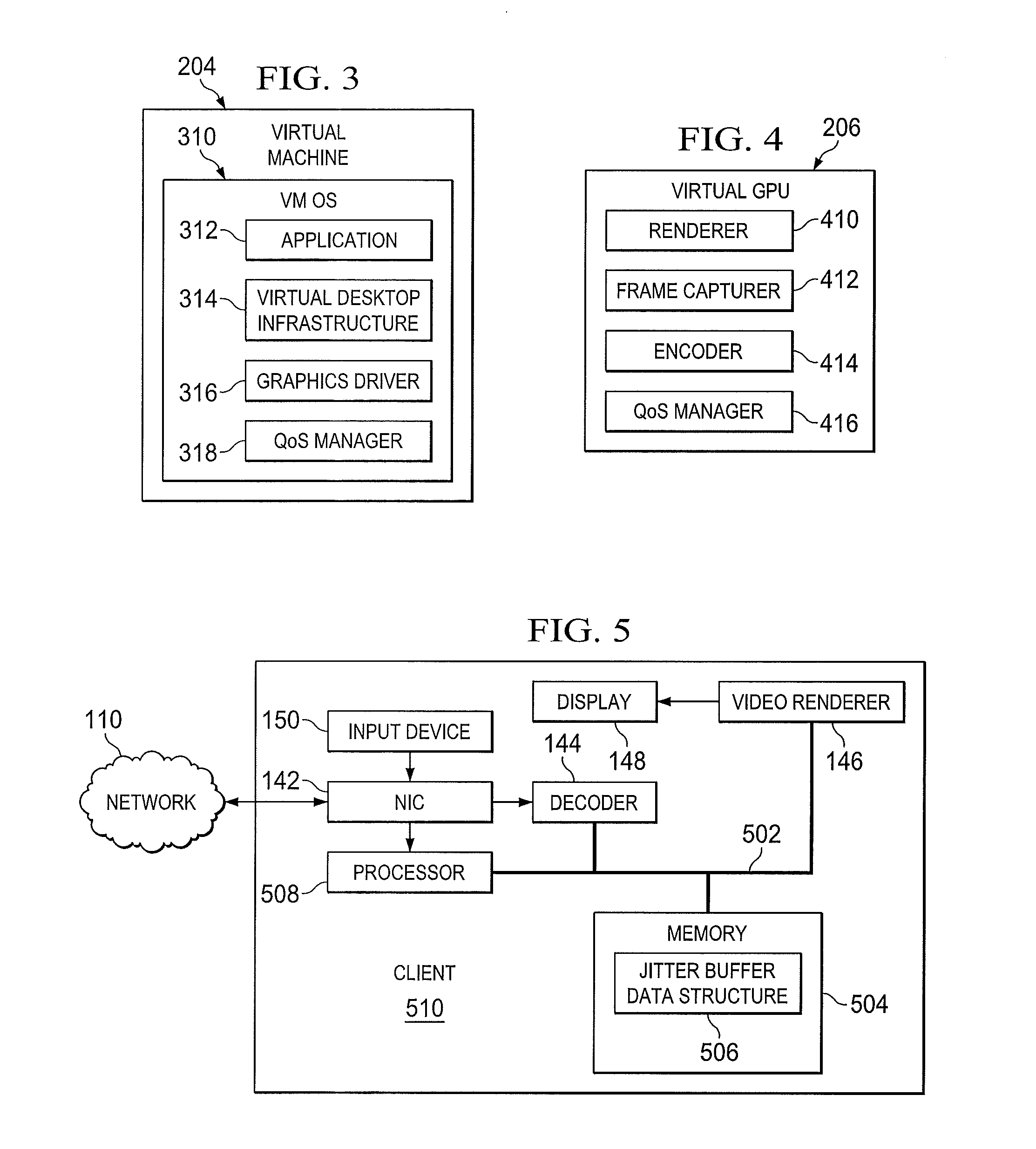
ActiveUS20140281017A1Multiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionNetwork interfaceOne-way delay
A jitter buffering system and a method of jitter buffering. The jitter buffering system may be embodied in a quality of service (QoS) management server, including: (1) a network interface controller (NIC) configured to receive one-way-delay statistics regarding a video stream transmitted to a client, and (2) a processer configured to employ the one-way-delay statistics to calculate and recognize jitter and subsequently generate a command for the client to enable jitter buffering.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method for Obtaining Accurate Wire Transmission Delay in Time Synchronization
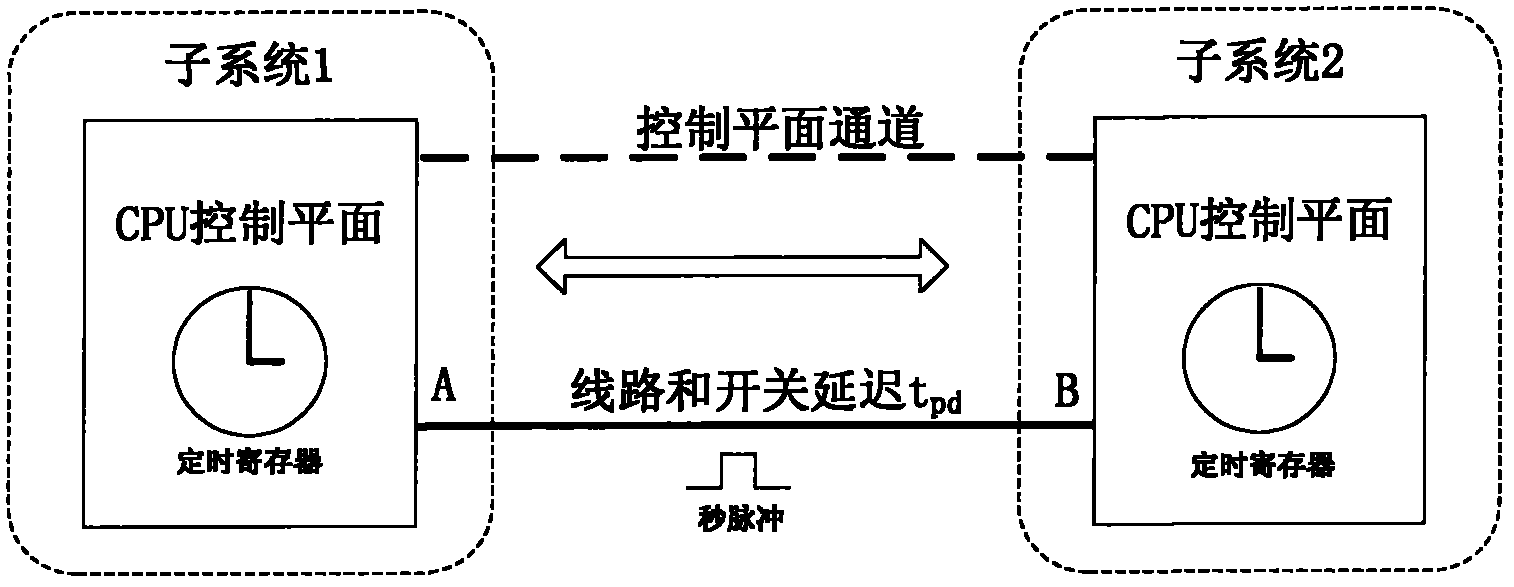
ActiveCN102291233APrecise time synchronizationMeet the requirements of normal operationSynchronising arrangementEngineeringSystem time
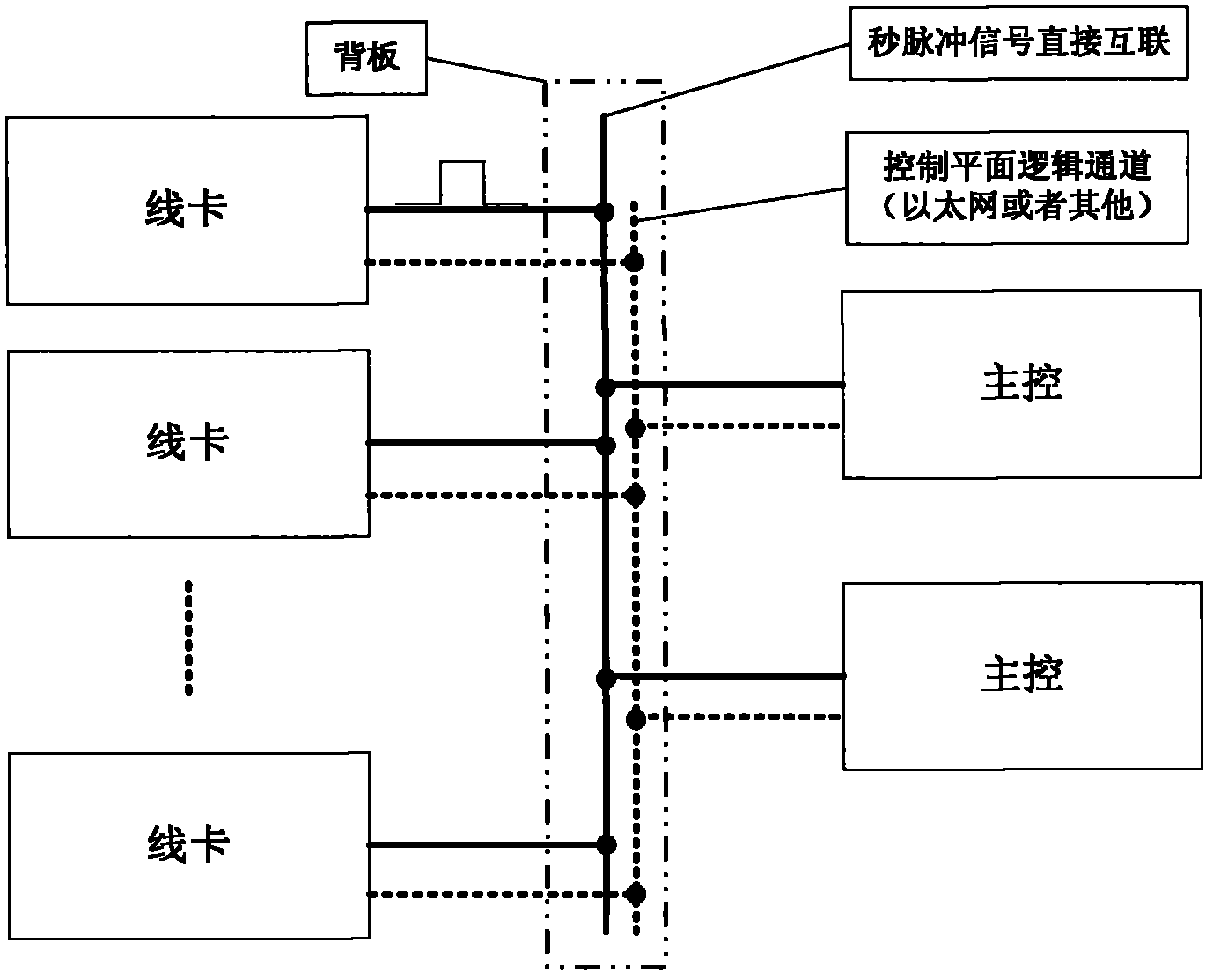
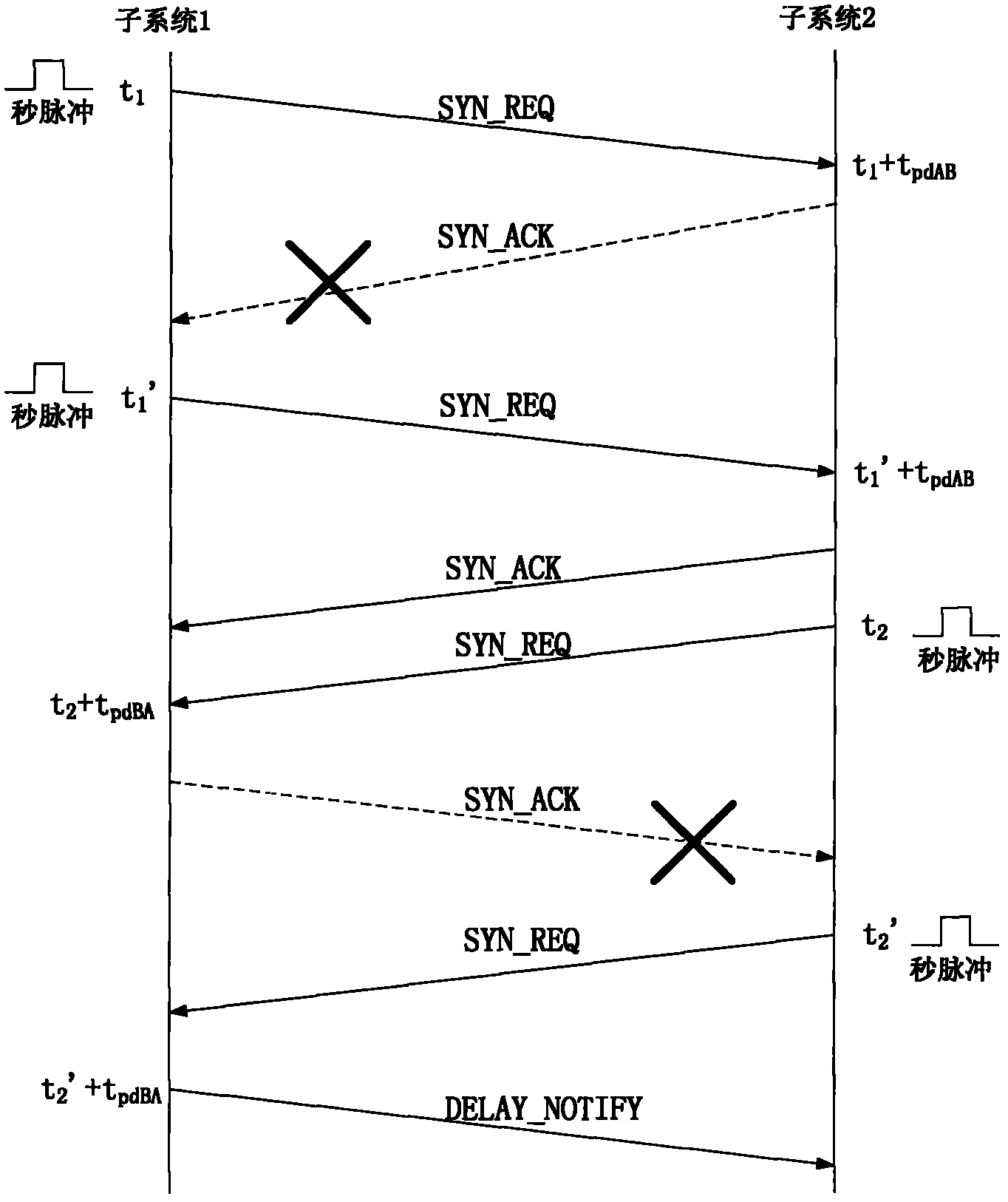
The invention relates to a method for acquiring accurate line transmission delay during time synchronization. The method comprises the following steps: a subsystem is selected as a main subsystem; an auxiliary subsystem is selected; the main subsystem sends a pulse per second at t1 time, and the pulse per second reaches the auxiliary subsystem after line transmission delay tpdBA; after the auxiliary subsystem receives the pulse per second, the auxiliary subsystem starts a timing register; the auxiliary subsystem computes that the time of the auxiliary subsystem is delayed for tpdAB compared with the main subsystem by combining with a counting time value Delta t' from a current time value; the auxiliary subsystem sends the pulse per second to the main subsystem at t2 time, and when the pulse per second reaches the main subsystem after the line transmission delay tpdBA, the time value t3 of the main subsystem is recorded at the time; and the one-way delay tpd of the main subsystem and the auxiliary subsystem is computed through tpd=(tpdBA+tpdAB) / 2=(t3-t2). According to the method disclosed by the invention, the one-way or two-way accurate line transmission delay of a system can be accurately obtained, and therefore delay is convenient to subsequentially compensate.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
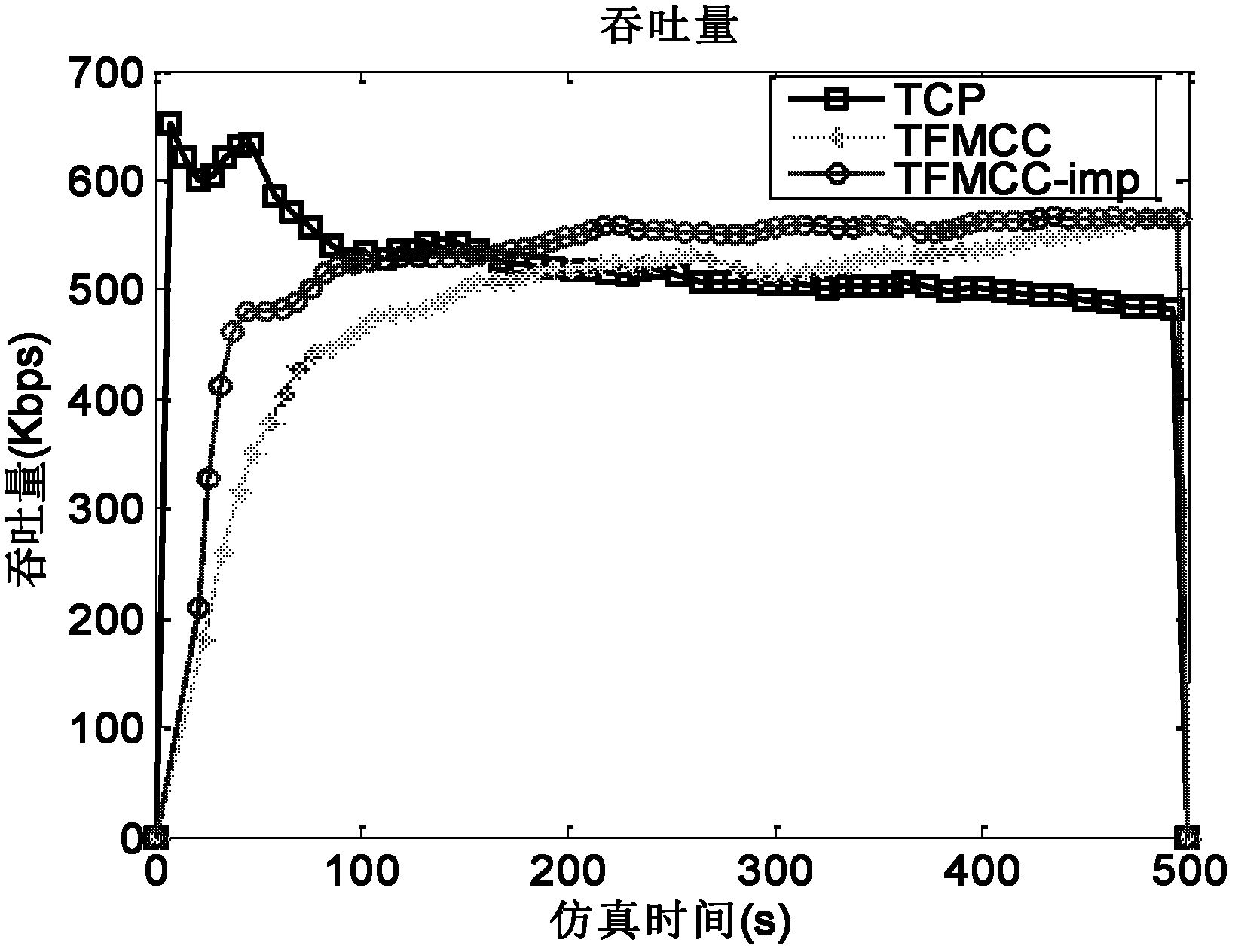
Improved-transmission control protocol-friendly multicast congestion control (TFMCC)-protocol-based communication method
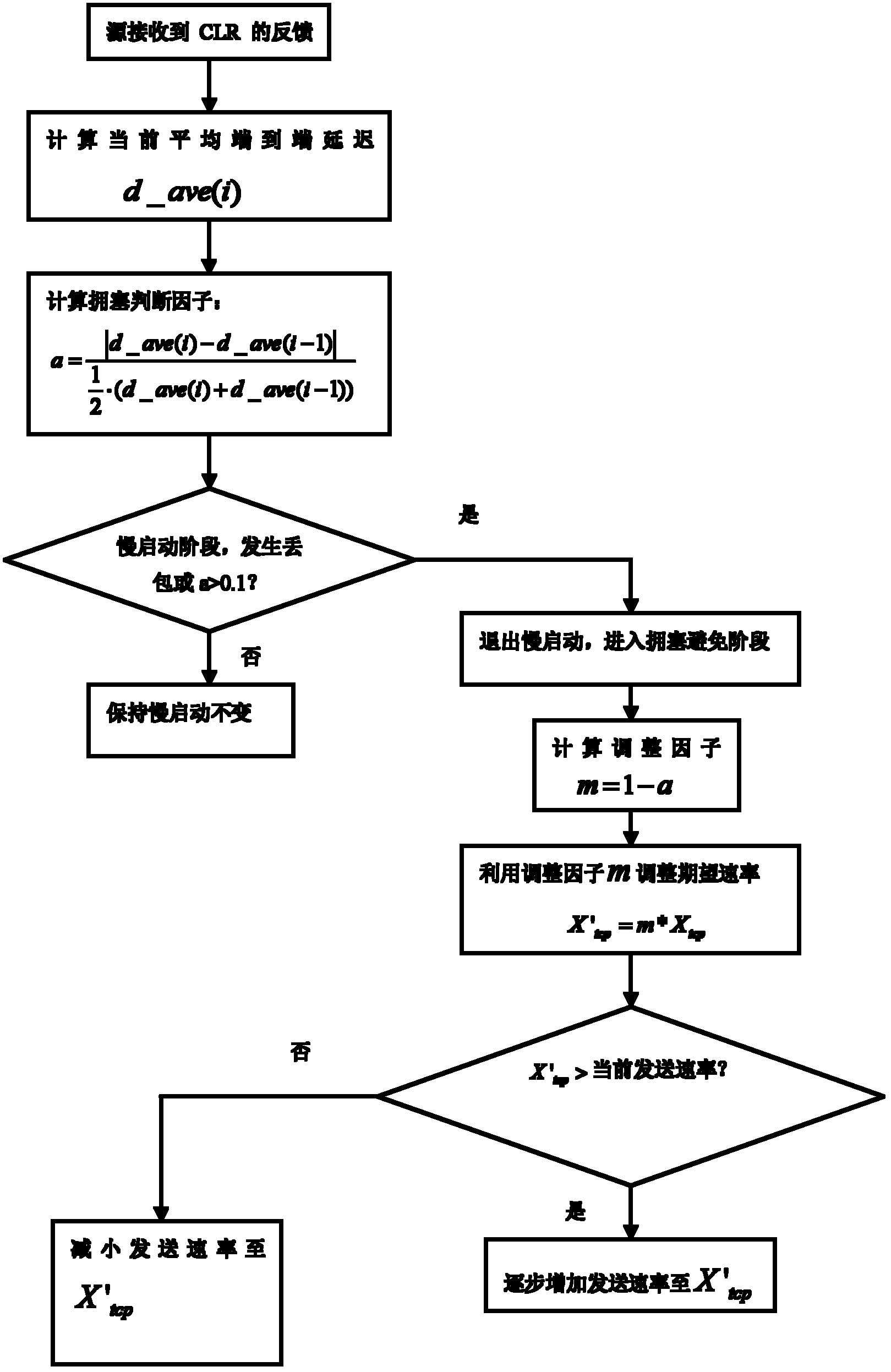
The invention discloses an improved-transmission control protocol-friendly multicast congestion control (TFMCC)-protocol-based communication method, which is implemented by the following steps of: every time when a source receives a feedback data packet from a current limiting receiver (CLR), computing end-to-end one-way delay jitter between the source and the CLR according to effective timestamp information in the feedback data packet, and computing a congestion judgment factor by utilizing the delay jitter to judge congestion; and computing a correction factor by utilizing the congestion judgment factor to regulate expected throughput and further regulate a transmission rate. In the method, the transmission rate is regulated by calculating the end-to-end delay jitter between the source and the CLR as a congestion signal, and the end-to-end delay jitter of a TFMCC protocol is effectively controlled, thereby effectively reducing the jitter of the protocol, average end-to-end delay, average end-to-end delay jitter, an average packet loss rate and the like, improving the stability and overall performance of the TFMCC protocol, and making the protocol better serve a multicast protocol and more suitable for the transmission of multimedia services.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Streaming communication device, streaming communication method, and streaming communication system
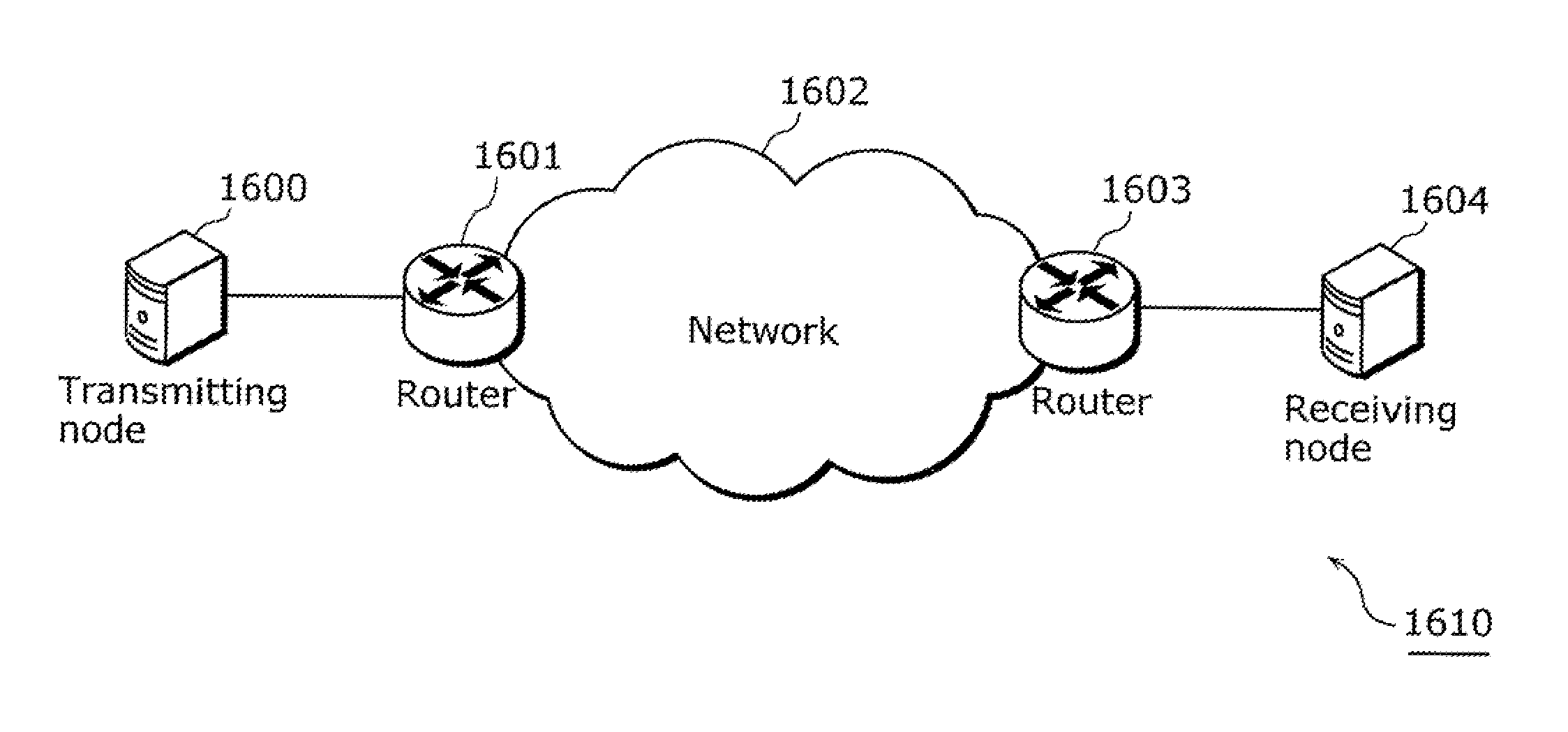
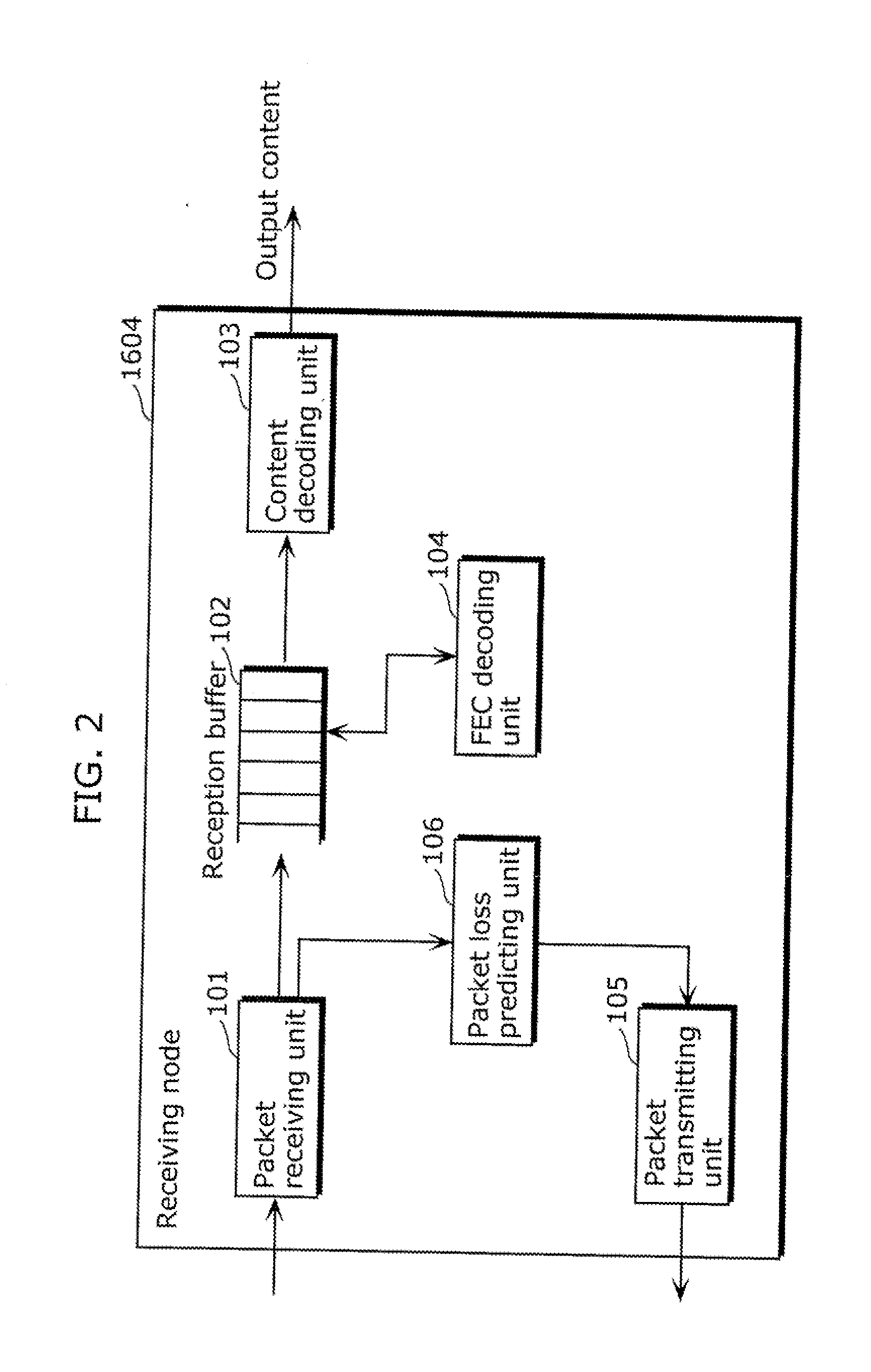
ActiveUS20110110260A1Accurate estimateReduce loss rateError preventionTransmission systemsPacket lossCommunications system
A streaming communication device which accurately estimates a packet which will be lost in the future. A streaming communication device which transmits or receives a stream via a router over a packet-switched network, the streaming communication device including: an accumulating unit (204) configured to accumulate a one-way delay that is a time period between transmission and reception of a packet which includes a small segment of the stream; a detecting unit (202) configured to detect a sign of a packet loss by identifying a tendency toward an increase in the one-way delay accumulated in the accumulating unit (204); and an estimating unit (203) configured to estimate, when the sign is detected, a loss packet from a degree of the increase in the one-way delay accumulated in the accumulating unit (204), the loss packet being a packet which will be lost.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method, a Computer Program Product, and a Carrier for Indicating One-Way Latency in a Data Network
ActiveUS20070268850A1High precision latency measurementImprove accuracyFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCarrier signalOne-way delay
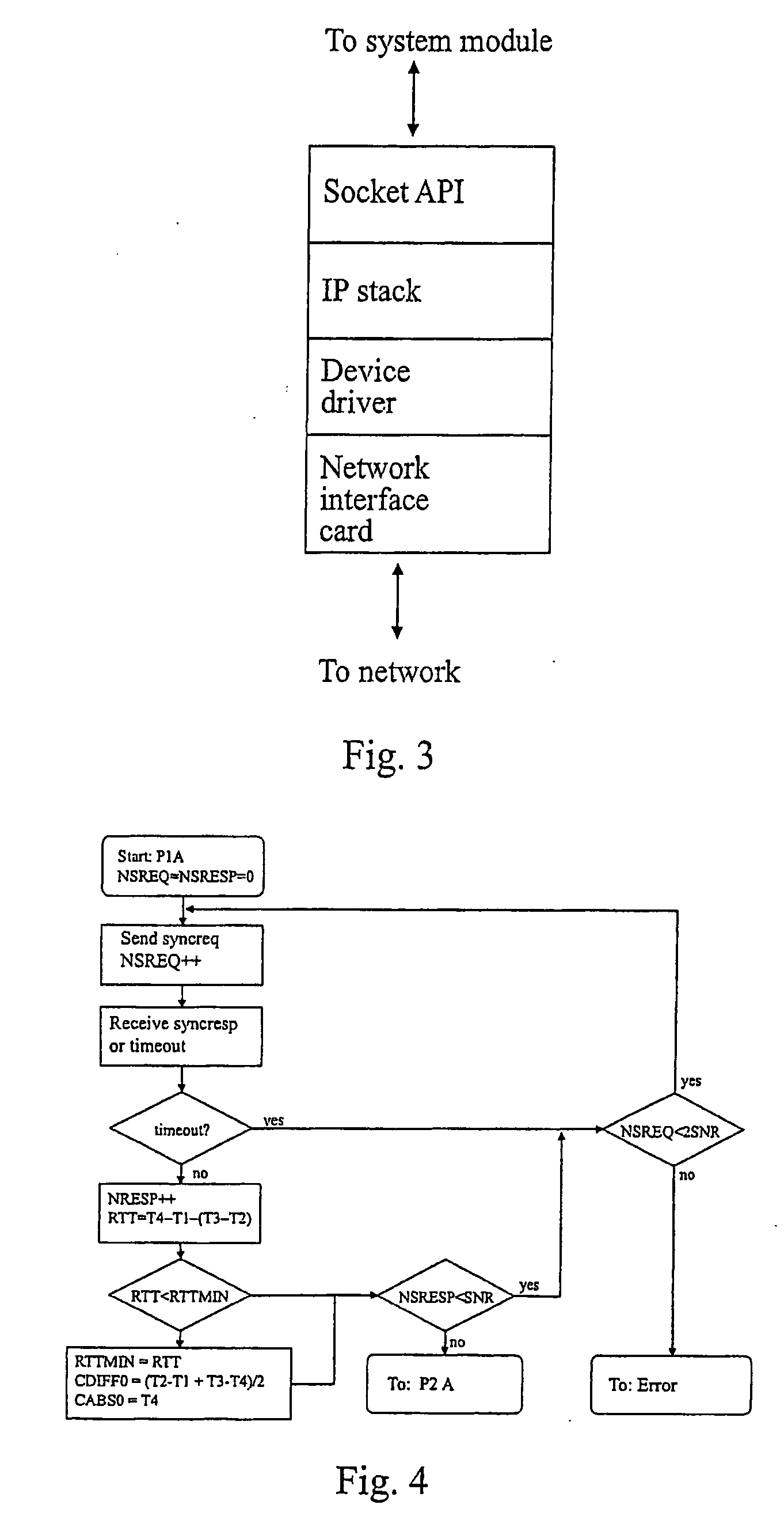
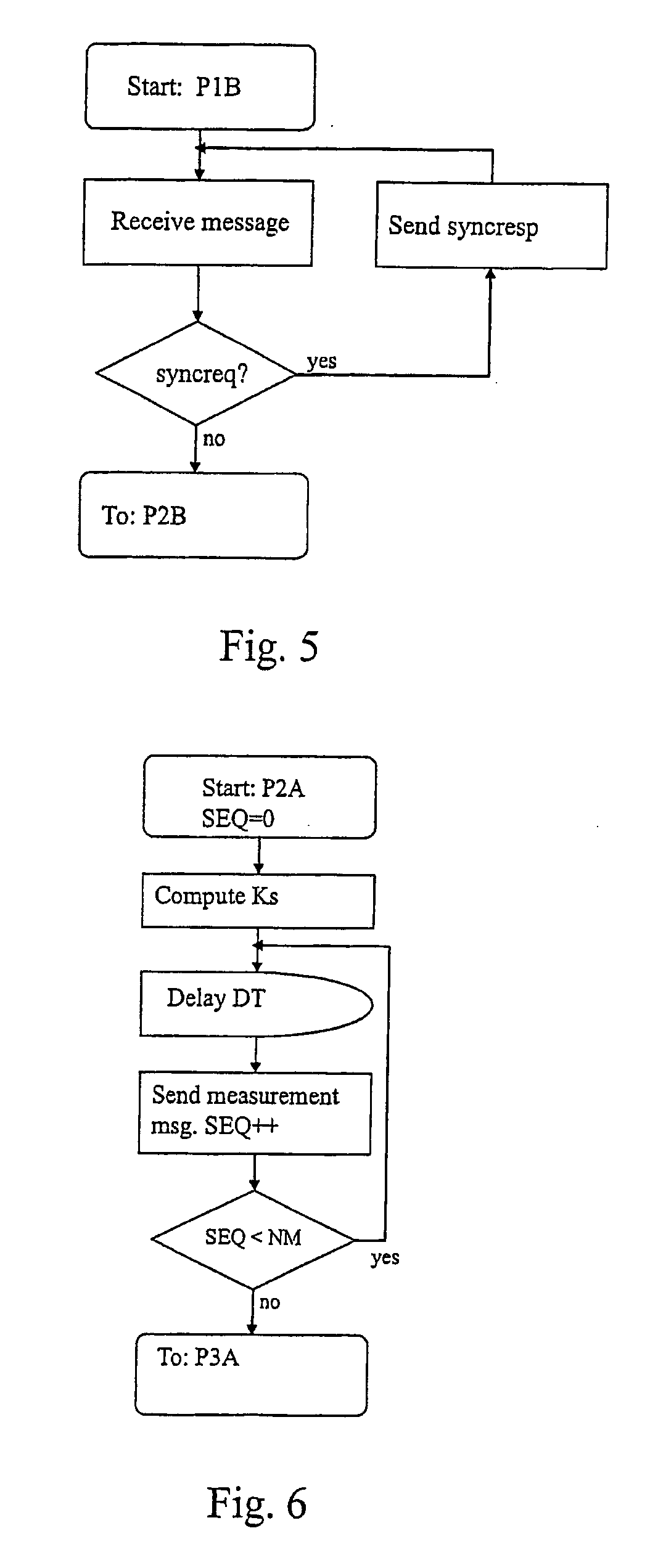
Disclosed herein is a method, a computer program product, and a carrier for indicating one-way latency in a data network (N) between a first node (A) and a second node (B), wherein the data network (N) lacks continuous clock synchronization, comprising: a pre-synchronisation step, a measuring step, a post-synchronisation step, an interpolation step, and generating a latency profile. The present invention also relates to a computer program product incorporating the method, a carrier comprising the computer program product, and a method for indicating server functionality based on the first aspect.
Owner:ACCEDIAN NETWORKS
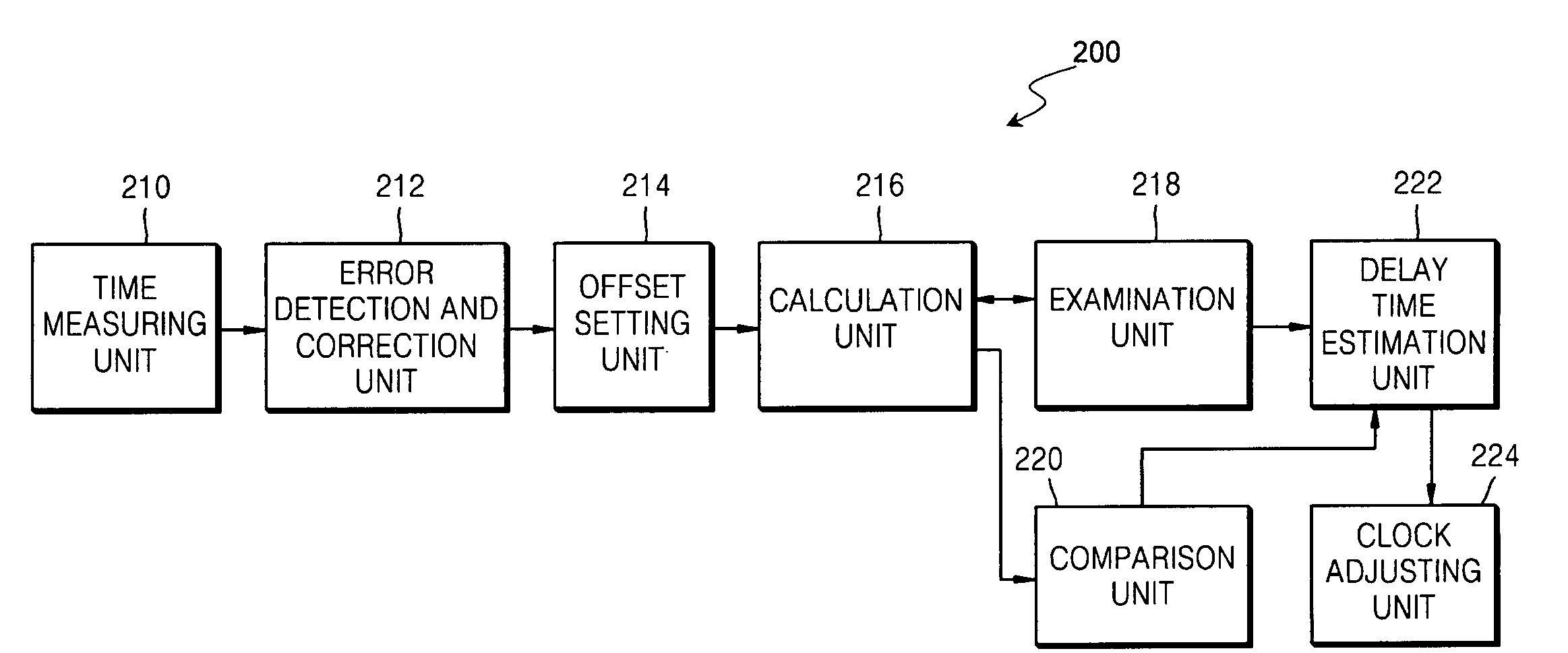
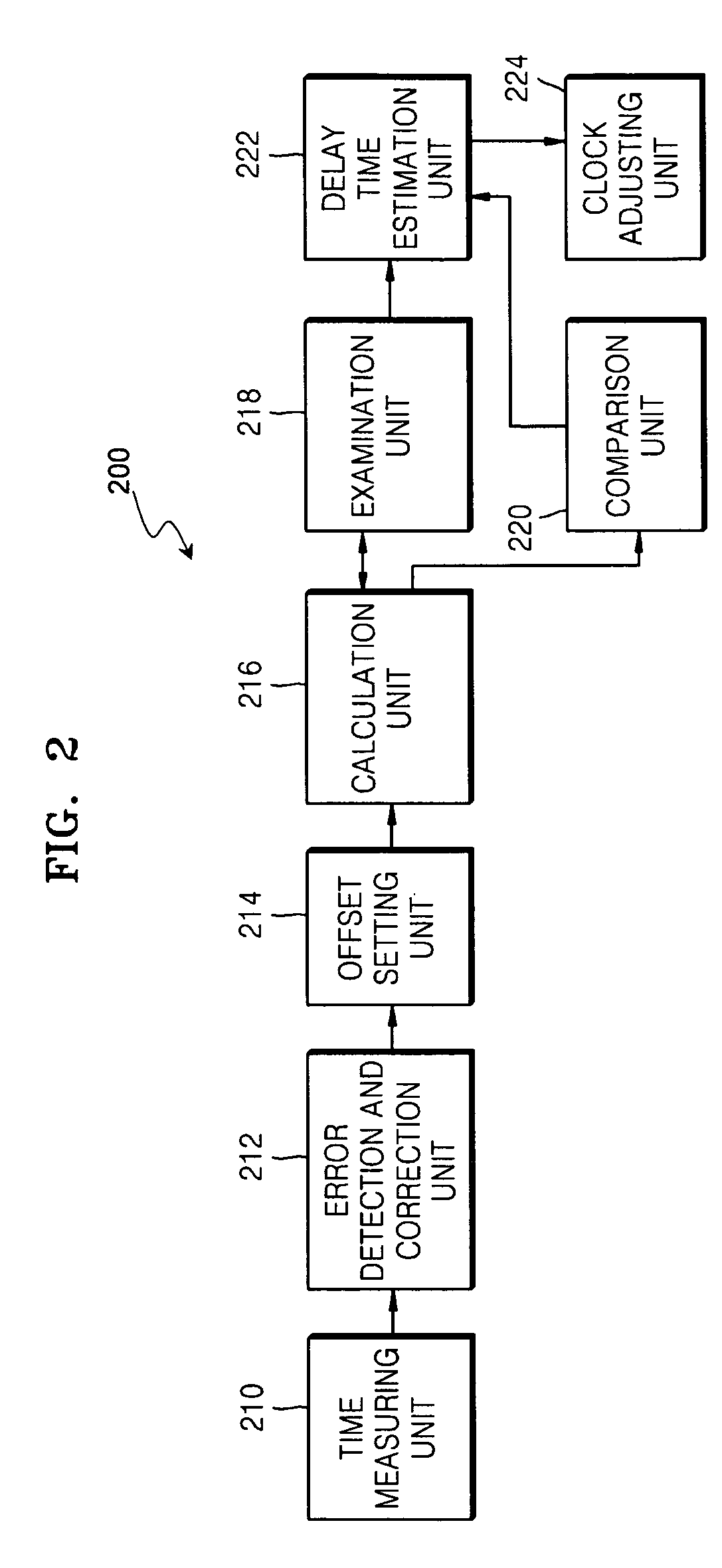
One-way delay time estimation method and apparatus and clock synchronization method and apparatus using the same
An apparatus for and method of estimating a one-way delay time between two hosts and an apparatus and method of clock synchronization using the same. The two hosts are connected to a network and communicate a predetermined packet; k-th, (k+1)-th, and (k+2)-th transmission times are measured at the first host, and k-th, and (k+1)-th transmission times are measured at the second host; a time difference of the m-th transmission time is measured at the first and second host, where m is k or k+1, and by using the measured transmission times, an m-th one-way delay time is calculated. If the time difference is identical to the calculated one-way delay time, a value equal to or less than the calculated one-way delay time is determined as the estimated one-way delay time. Accordingly, the estimation error of a one-way delay time is reduced for both symmetrically and asymmetrically connected hosts.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP +1
Data communication system, backup server, and communication control apparatus
InactiveUS7689644B2Avoid trafficData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunications systemBackup path
In order to distribute multicast packets, using different multicast addresses and avoiding fault points, a backup server is installed close to a master and converts backup multicast packets and sends them as master multicast packets to the client. At this time, backup multicast packets are delayed and sent while the delay is determined from an allowable retransmission time, a one-direction delay to the client, a time required to detect linkage problems, and a time required to establish backup paths and so on.
Owner:KDDI CORP
Hybrid unidirectional time delay estimation method suitable for network control system
InactiveCN101394324AGuaranteed accuracyHigh precisionData switching by path configurationEstimation methodsControl system
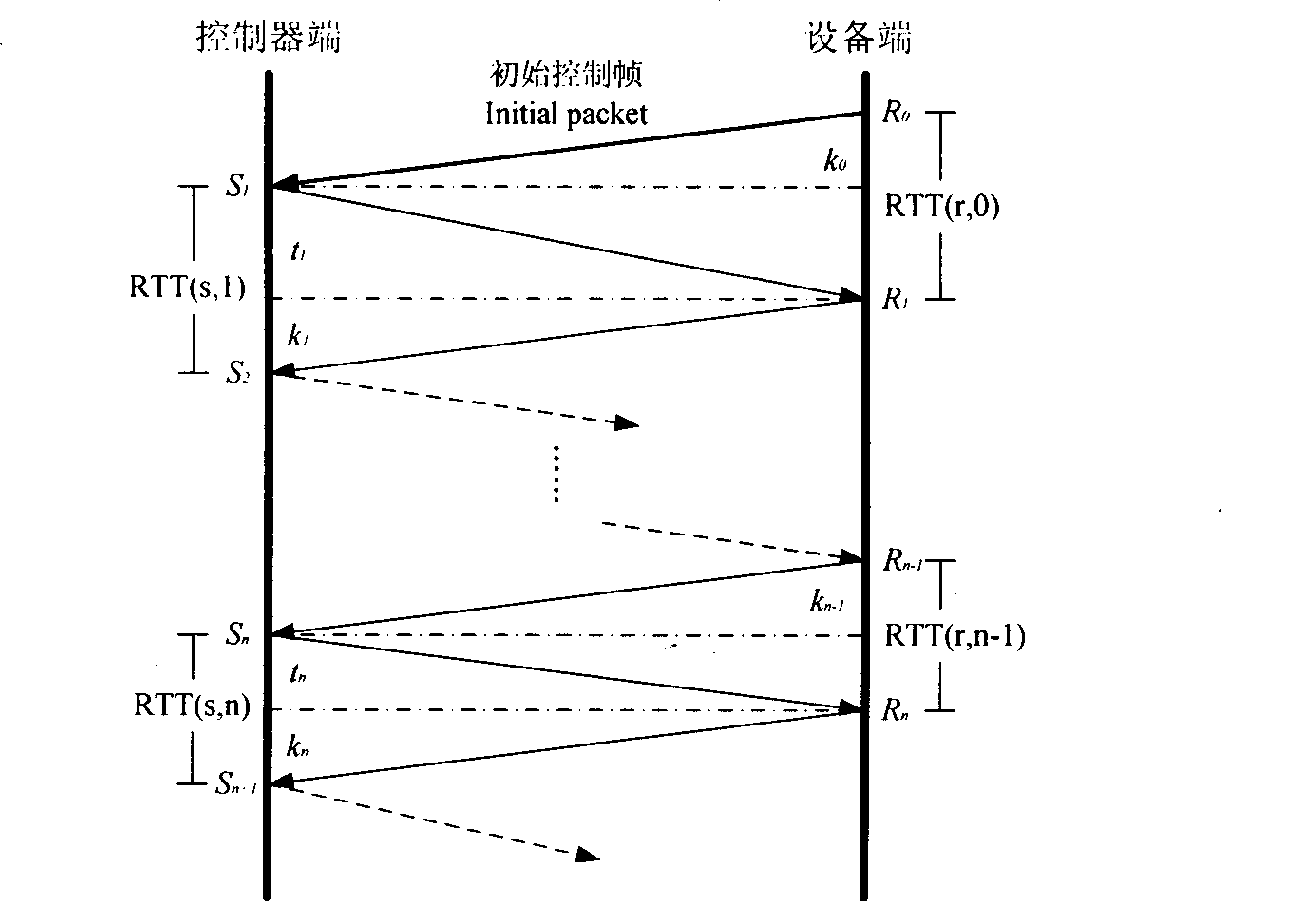
The invention relates to a mixed type one-way delay estimation method, which is suitable for a network control system (NCS). The method comprises the following steps: (1) estimating the one-way delay of a start control initial frame sent from an actuator in the NCS by adopting an online measuring method which is based on router delay compositional analysis, so as to obtain a relatively precise estimated value; and (2) respectively estimating through a series of calculations which are based on rebound trip time (RTT) values recorded by local clocks at both ends of the system and use the obtained start control initial frame estimated value as a reference scalar to obtain the one-way delay values in the forward channel and the backward channel of the NCS. The method not only effectively overcomes the oversized system overhead defect of the online estimation method, but also has remarkably improved precision of the estimated value compared with the prior end-to-end one-way delay estimation method, so as to achieve the purpose of effectively and accurately estimating the one-way delay of the NCS.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for measuring directionally differentiated (one-way) network latency
InactiveUS20100293243A1Simple methodMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTimestampPrimary station
Determining directionally differentiated latency in a network by use of master and slave test instruments to record latency measurements in their native time bases, and retrieving test instrument latency frame transmit / receive timestamps from the master and slave and converting them to the time base of one of the master or slave by use of the offset calculation, utilizing 3 bounce timestamp exchange, providing one-way latency measurement with resolution of less than 100 μs, using internal clocks in the test instruments, without requirement of expensive external time base technology.
Owner:JOHN FLUKE MFG CO INC
Bandwidth estimation in broadband access networks
ActiveUS7675856B2Accurate bandwidthError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsIdle timeBroadband
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Measurement one way delay method and equipment thereof, and communication system
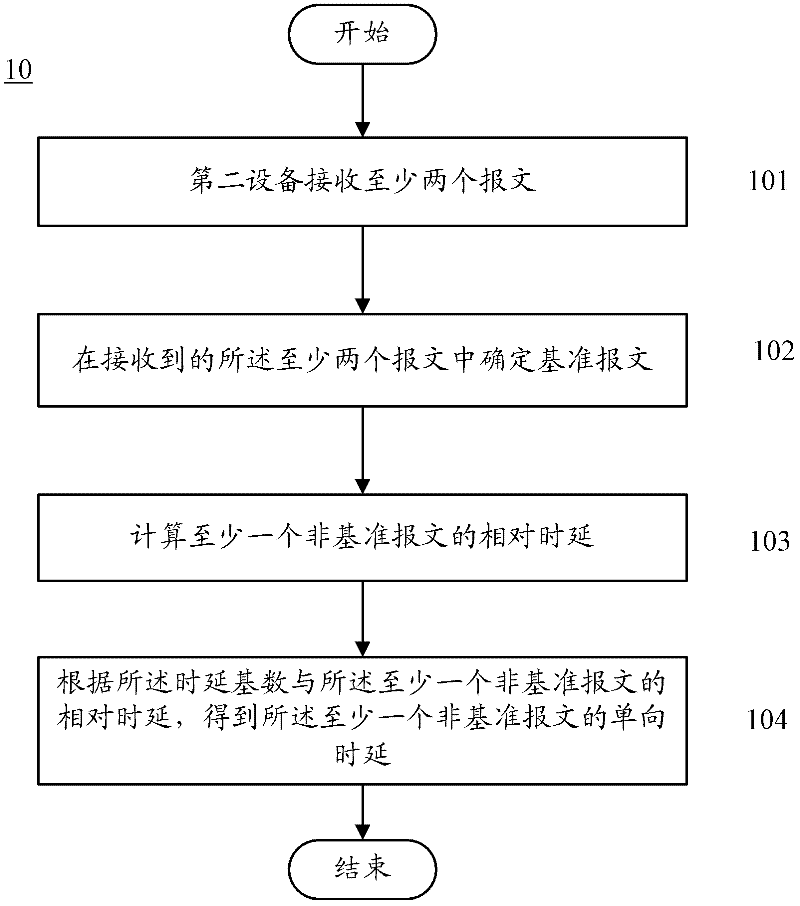
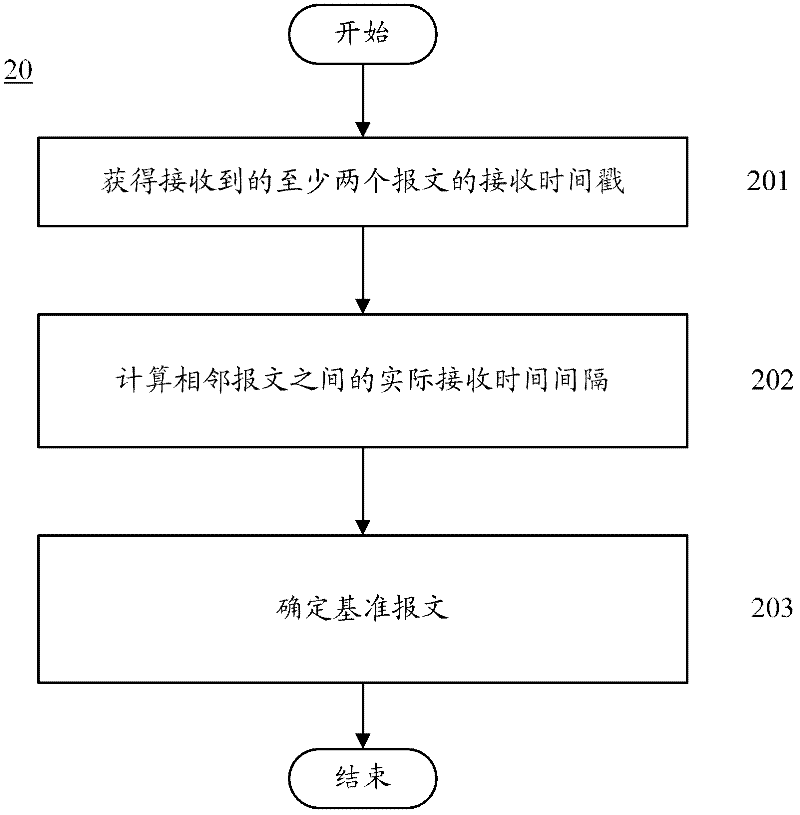
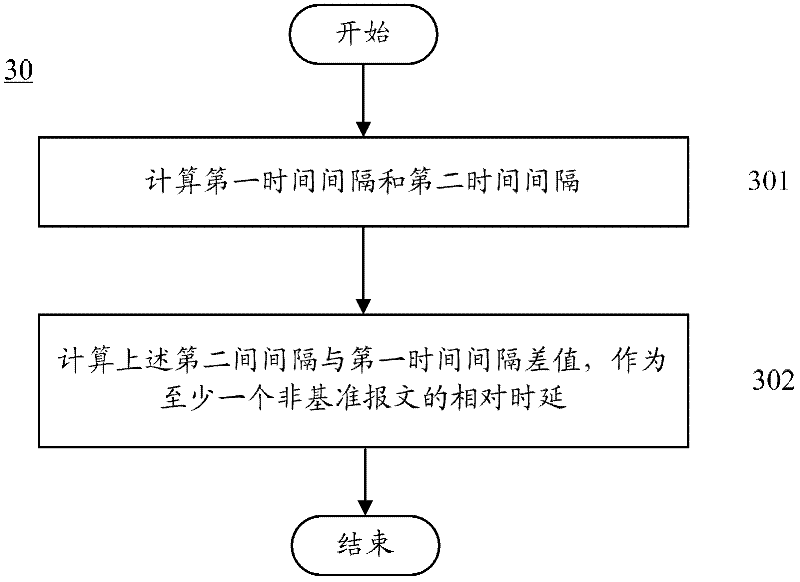
ActiveCN102227110AAvoid occupyingReduce the burden onData switching networksCommunications systemOne-way delay
The embodiment of the invention provides a measurement delay method and equipment thereof, and a communication system. The method comprises the following steps that: second equipment receives at least two messages, which are sent by first equipment in a preset interval of time; a reference message is determined between the received at least two messages, wherein the one way delay of the reference message is a delay radix; relative delay of at least one non-reference message is calculated, wherein the non-reference message is the other message except the reference message between the at least two messages; and one way delay of the at least non-reference message is obtained according to the delay radix and the relative delay of the at least non-reference message.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Transmitter
InactiveUS8281356B2Minimizing dataMinimize disturbanceEnergy efficient ICTFrequency-division multiplex detailsStreaming dataPacket loss
A source device 10 transmits streaming data. In a packet receiver 22 of a sync device 20, statistical data acquirer 23 calculates statistical data such as one-way delay time, packet loss ratio, reception rate and the like from the received streaming data and transmits it to the source device. The statistical information received by source device 20 is extracted by a packet receiver 15 and input to a channel band estimator 16. The channel band estimator 16 gives encoder 11 instructions to provide optimal encoding based on the transmission delay. Upon this, the transmission delay is calculated by assuming the minimum value of the communication delay from the start of transmission as zero. Control is performed by determining the delay time and packet loss ratio in data transmission and considering, based on these, the channel quality and bandwidth margin, so as to provide the optimal transmission bit rate or encoding rate.
Owner:SHARP KK
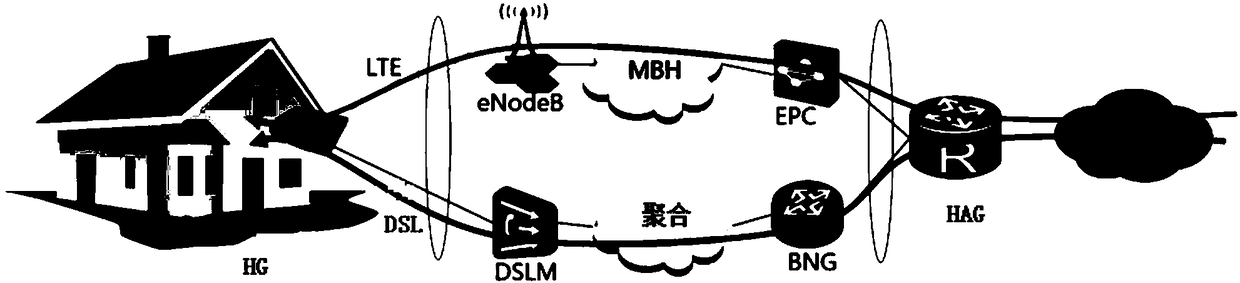
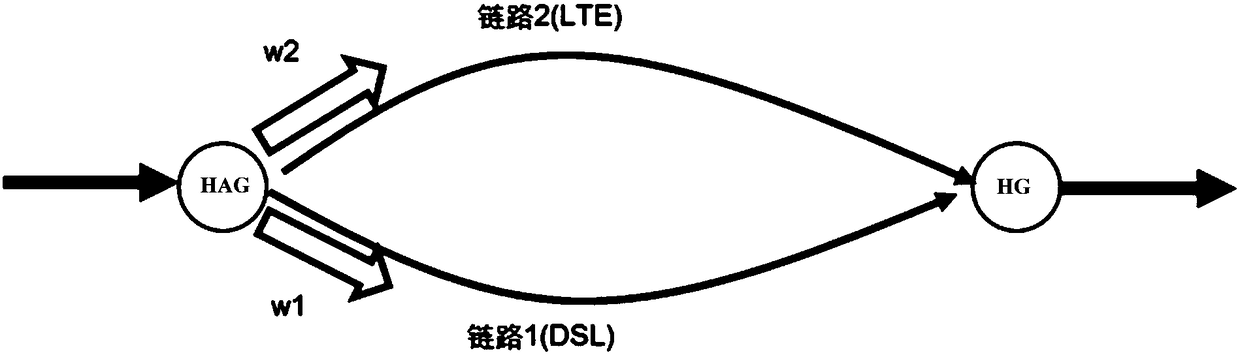
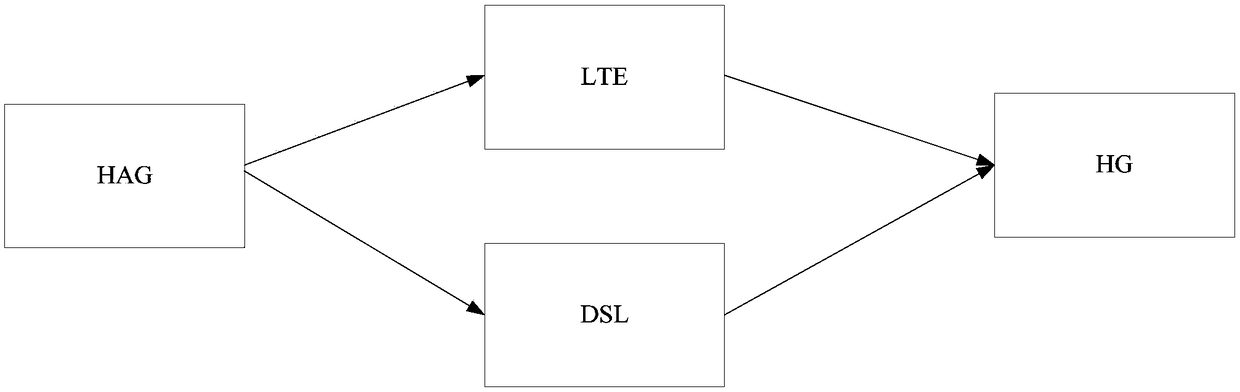
Message transmission method and hybrid access gateway
ActiveCN108234338AImprove transmission efficiencyControl one-way delayNetwork connectionsPacket lossCommitted information rate
The invention relates to a message transmission method and a hybrid access gateway. The method comprises the following steps: receiving a message of which the destination is a home gateway sent by network side equipment through the hybrid access gateway; and when that a first transmission link is congested and a second transmission link is not congested is detected, acquiring a first CIR (Committed Information Rate) of the first transmission link and a second CIR of the second transmission link, classifying the message into a first class message and a second class message, transmitting the first class message through the first transmission link, and transmitting the second class message through the second transmission link. Thus, the first transmission link and the second transmission linkcan be accessed into the hybrid access gateway when the first transmission link is congested and the second transmission link is not congested, and the hybrid access gateway can control the one-way delay of the first transmission link and the second transmission link by reasonably allocating messages transmitted by the second transmission link, so that the problem of packet loss caused by sortingbuffer overflow is avoided, and the transmission efficiency of link transmission is greatly improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
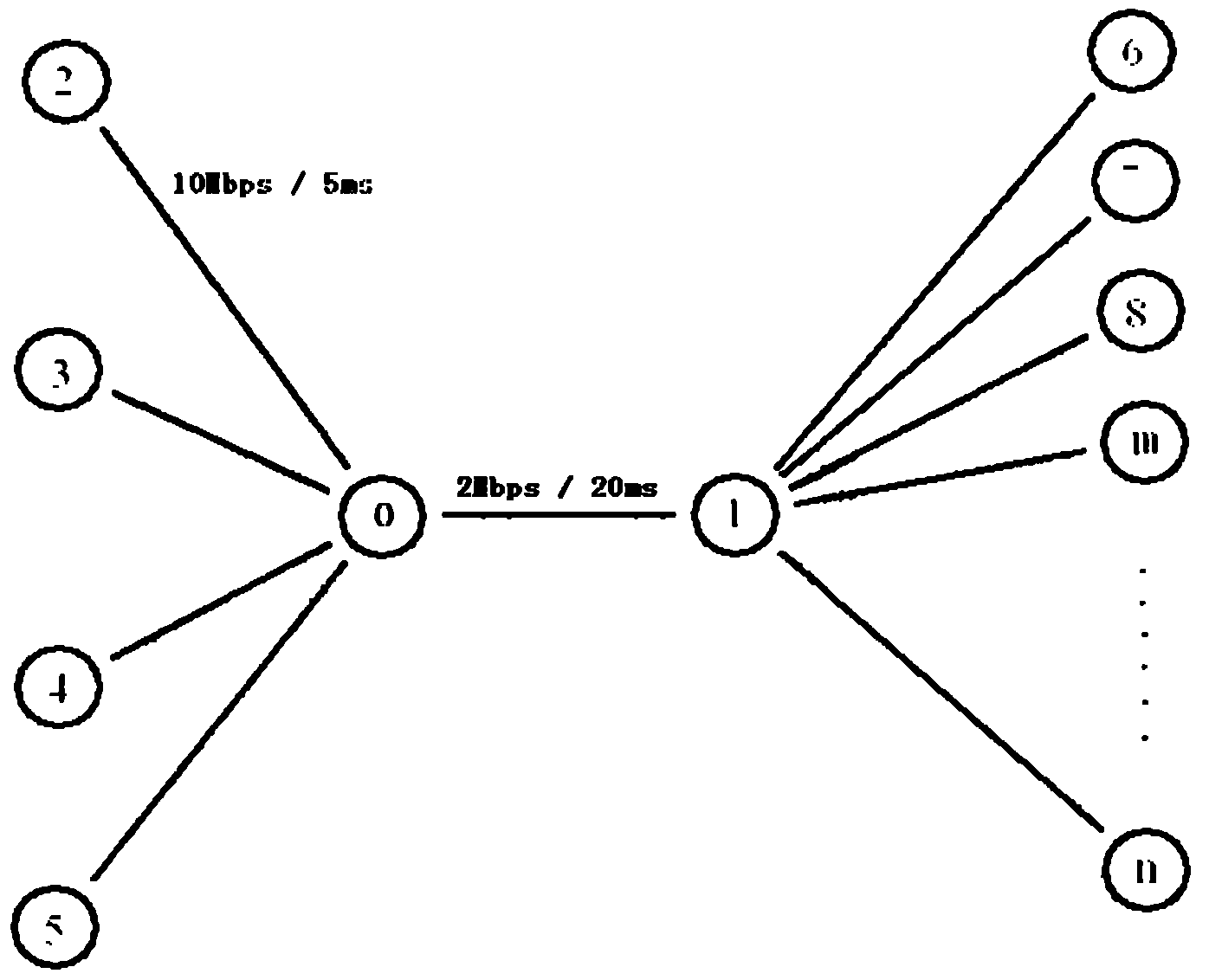
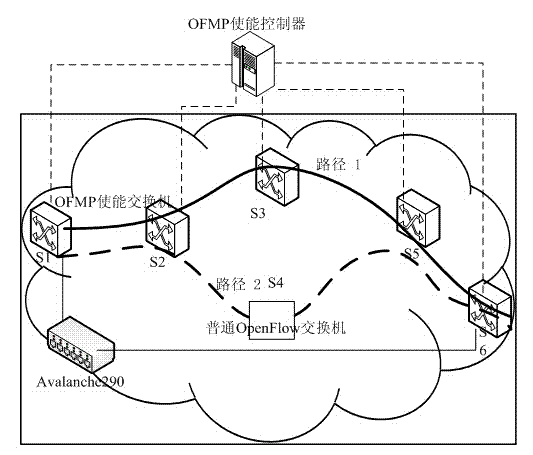
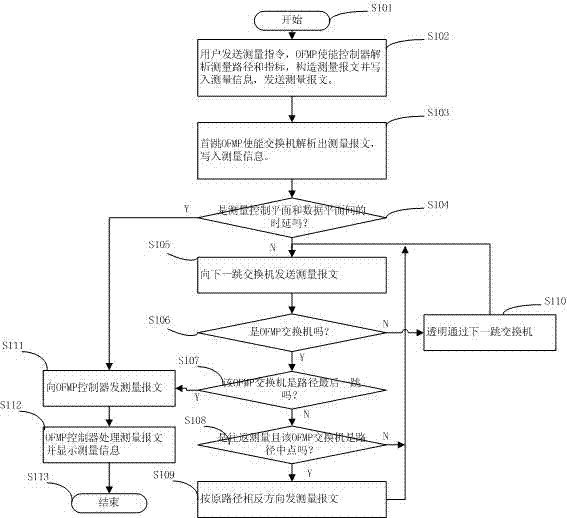
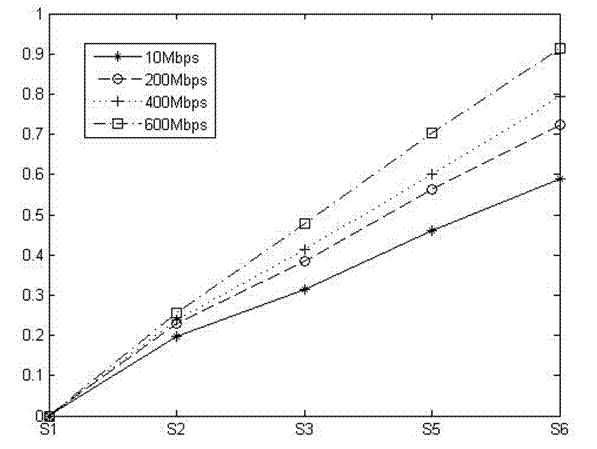
Method for actively measuring end-to-end path performance of OpenFlow network and system adopted by the same
ActiveCN104734907AReduce overheadAddressing the inability to measure end-to-end path performanceData switching networksSynchronising arrangementPacket lossNetwork behavior
The invention provides a method for actively measuring an end-to-end path performance of an OpenFlow network and a system adopted by the same. Aiming at the problem that the end-to-end path performance of the OpenFlow network is currently unable to be measured, the efficient measuring method and the system which use an OpenFlow active measurement protocol OFMP and regard a controller as a center are provided. The measuring method and the system can provide technological means and practical tools for debugging of an SDN control program, quantitative analyzing of an SDN architecture and a mechanism and assessing of network behaviors. Under the condition of clock synchronization of equipment, the system sends one packet so that the end-to-end performance parameters such as routing, a one-way delay, a round trip delay, a piecewise one-way delay, and a delay and a packet loss probability between a control plane and a data plane can be efficiently measured. In addition, under the condition that the clock is desynchronized or not-OFMP enabled equipment is provided, the measuring system can still measure part of major performance indexes, and the advantage that the spending for a processing OFMP is little is provided.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for network congestion control using queue control and one-way delay measurements
The invention provides a congestion control scheme that is a delay based scheme that includes a scalable queue size and one-way queueing delay measurement to reduce network congestion. Queue size is managed by queue control, a scalable utility function, dynamic alpha tuning, and / or randomized alpha tuning. One-way queueing delay is accomplished by measuring backward queueing delay management using various methods of estimating the receiver clock period. Embodiments include estimating the receiver clock period using single sample and multiple sample periods. The system includes a method for detecting route change.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Ethernet performance testing method and device based on point-to-point testing
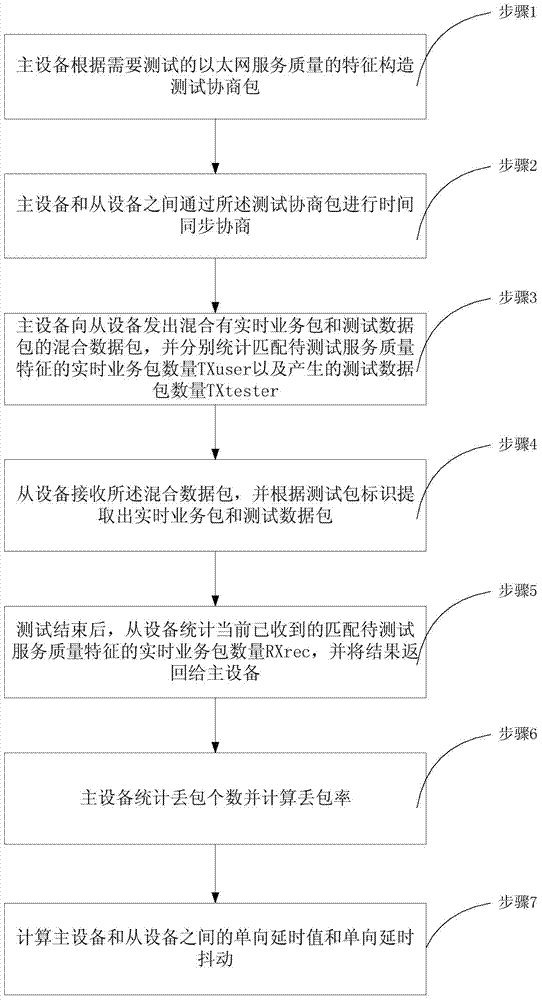
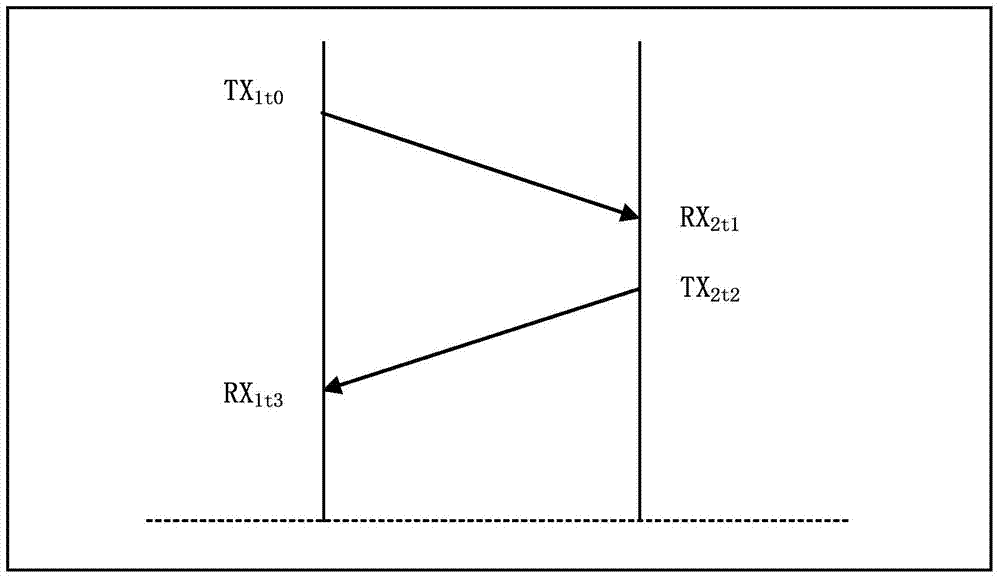
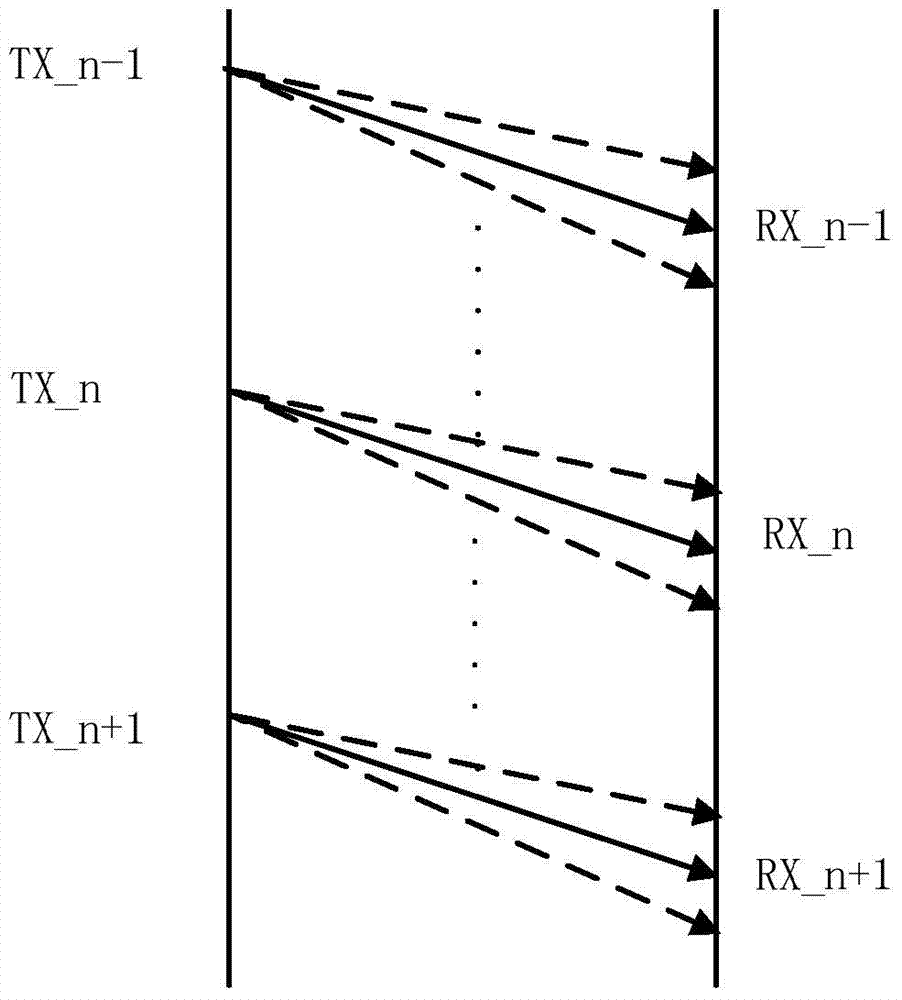
The invention discloses a method and device for testing Ethernet real-time service quality on the basis of point-and-point testing, and belongs to the field of Ethernet performance testing. According to the method, testing data packets with timestamp values are sent back and forth between a master device and a slave device, so that measurement of a one-way delay value and one-way delay jitter is achieved, and synchronous operation is accomplished; according to the device, the master device and the slave device are connected through an intermediate network, the master device is used for generating the testing data packets and leading the testing process, the salve device is used for receiving the data packets, and the testing process of the slave device is controlled by the master device. According to the method and device, due to the fact that delay measurement of the master device and delay measurement of the slave device are carried out according to relative clock adjustment of the master device and relative clock adjustment of the slave device respectively, the synchronizing process of the testing time can be accomplished in two steps, a whole network synchronous clock is not needed, special processing of a middle node device is not needed, the testing environment is simplified, precision, achieved by hardware, of a local timer can be at the microsecond level, and the testing process does not have any influence on the normal service.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Self-adapted method for detecting the clock resetting based on the mode recognition
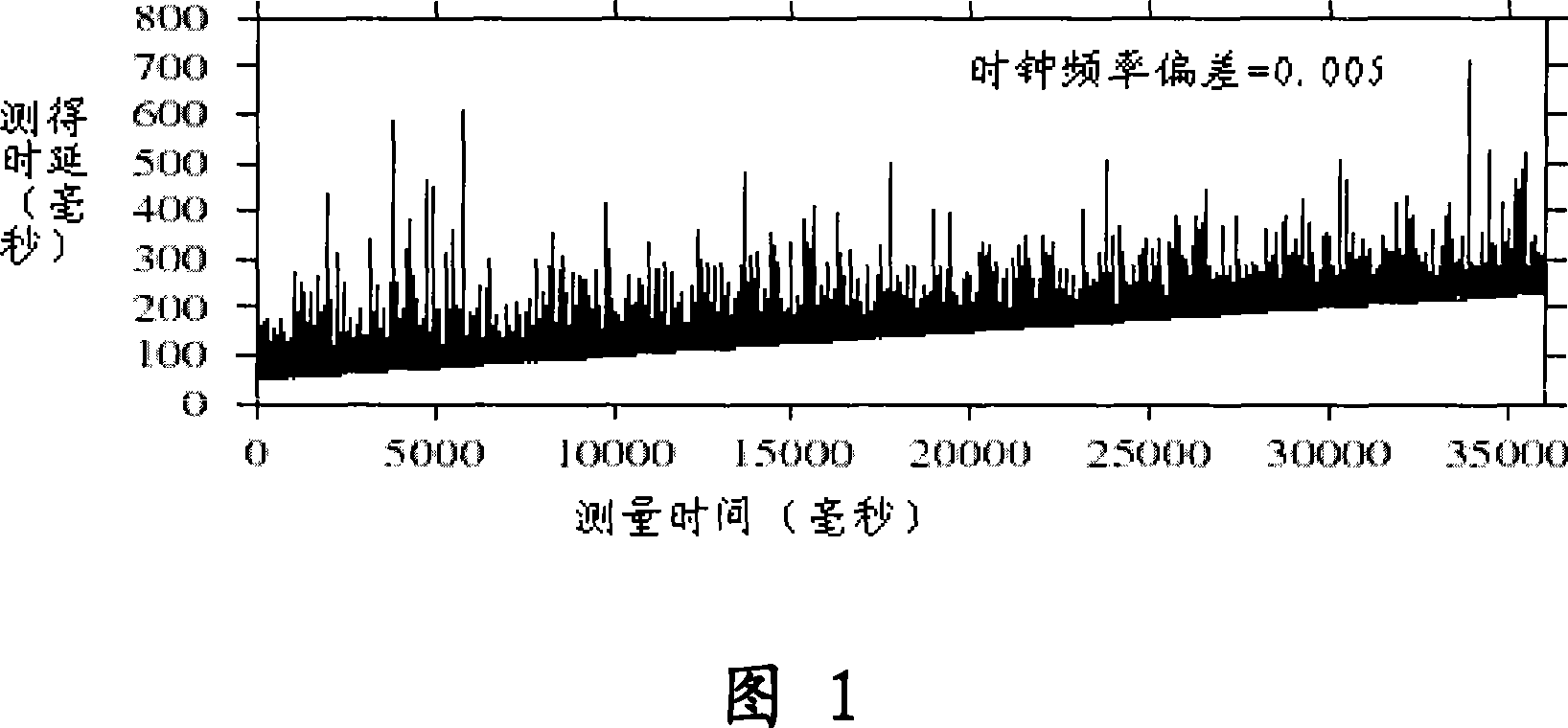
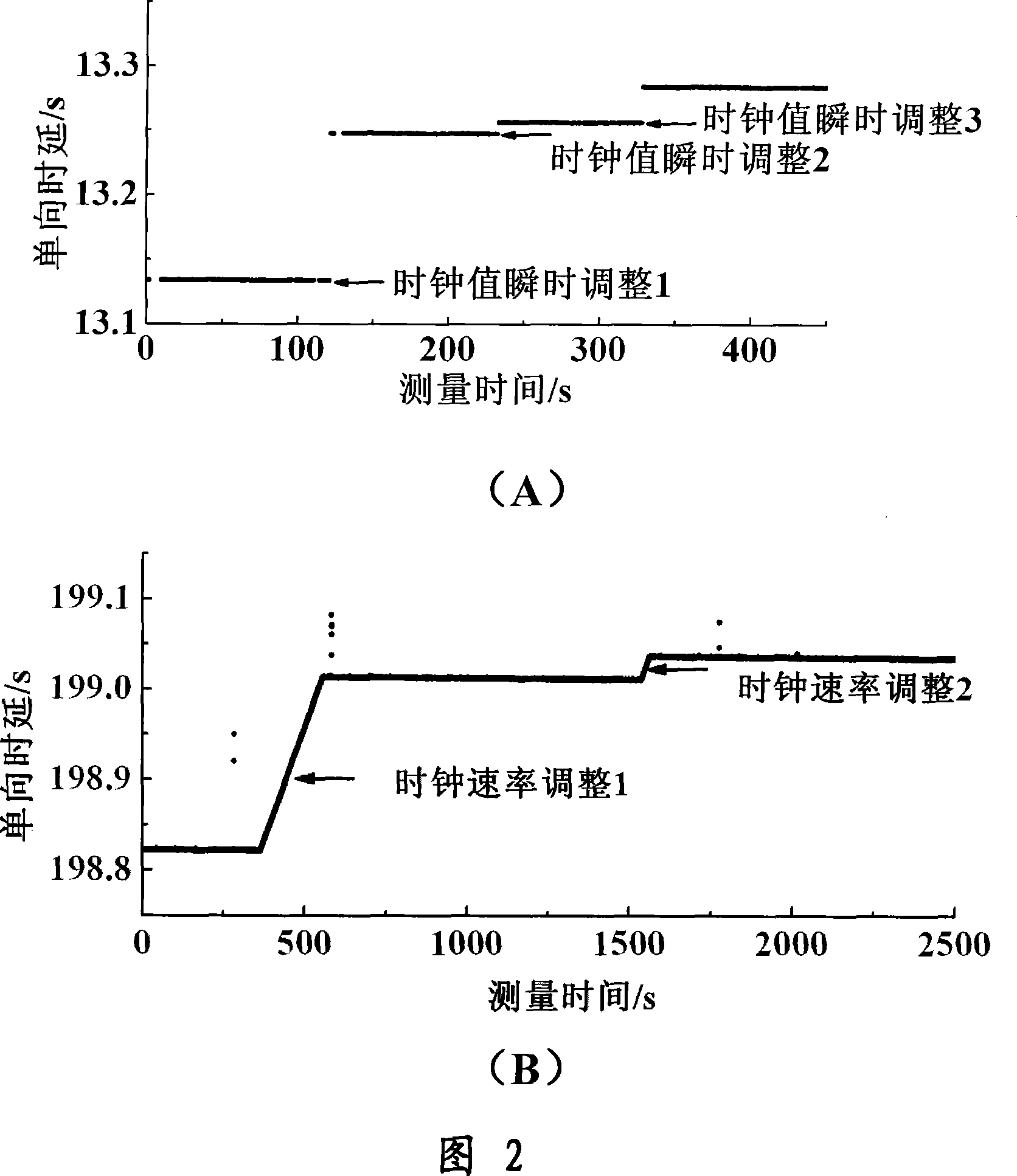
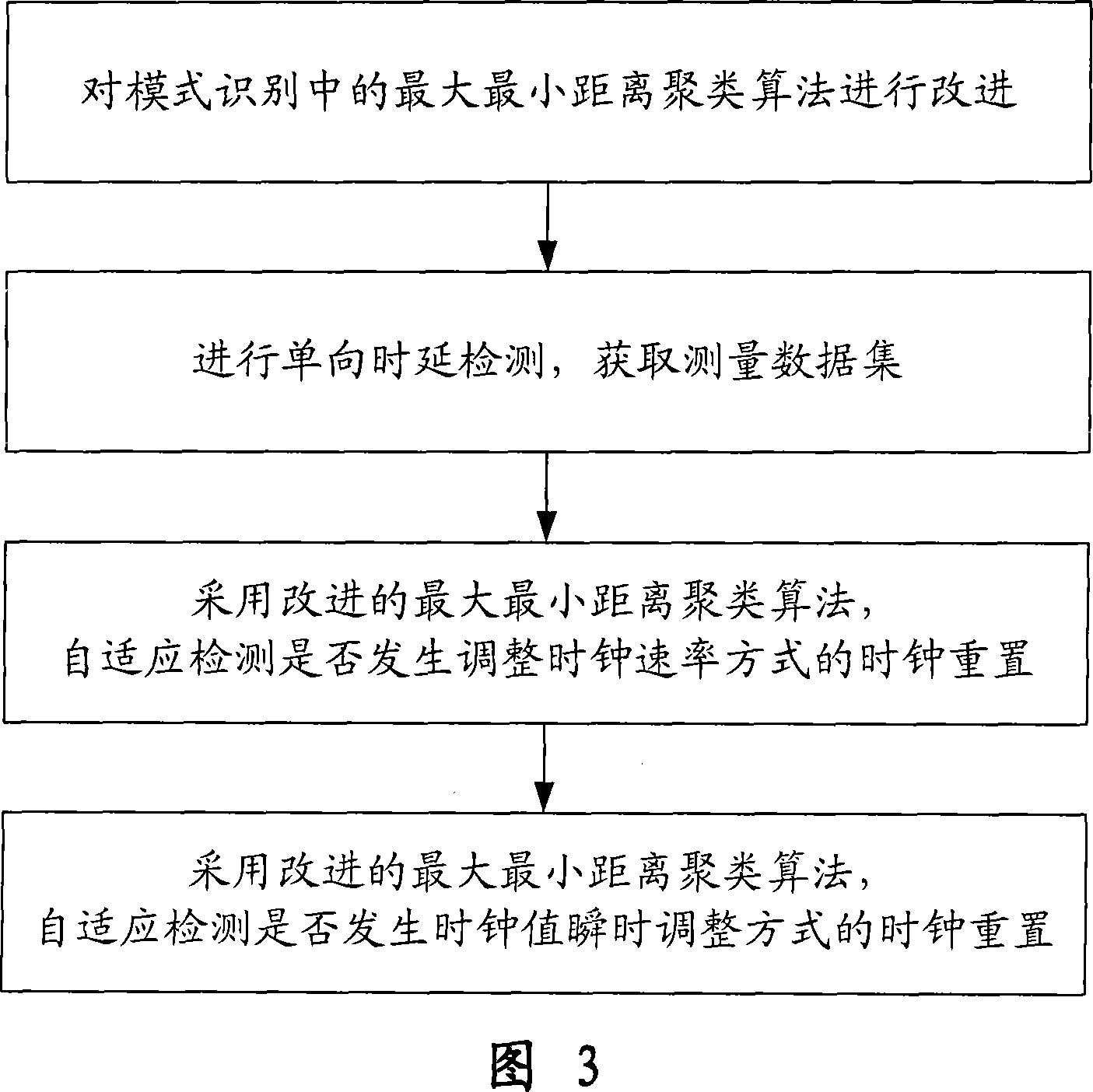
InactiveCN101035038AReduce limitationsImprove accuracyError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorData switching networksCluster algorithmData set
A clock reset detection method based on Adaptive Pattern Recognition, the use of pattern recognition in the improvement of the largest minimum distance clustering algorithm on a one-way delay the processing of data clustering, respectively test for the adaptive re-adjustment methods and the clock rate adjustment means instantaneous value of two different types of time bell replacement, but also to determine the frequency of the clock reset. The main features of the present invention is smaller limitations: the only path forward for a one-way delay measurements to obtain the positive path of one-way delay the measurement data set, we can also use this method to complete adaptive detection and judgment of the two clock reset the type and frequency.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Apparatus and method for performing congestion control in a communication system
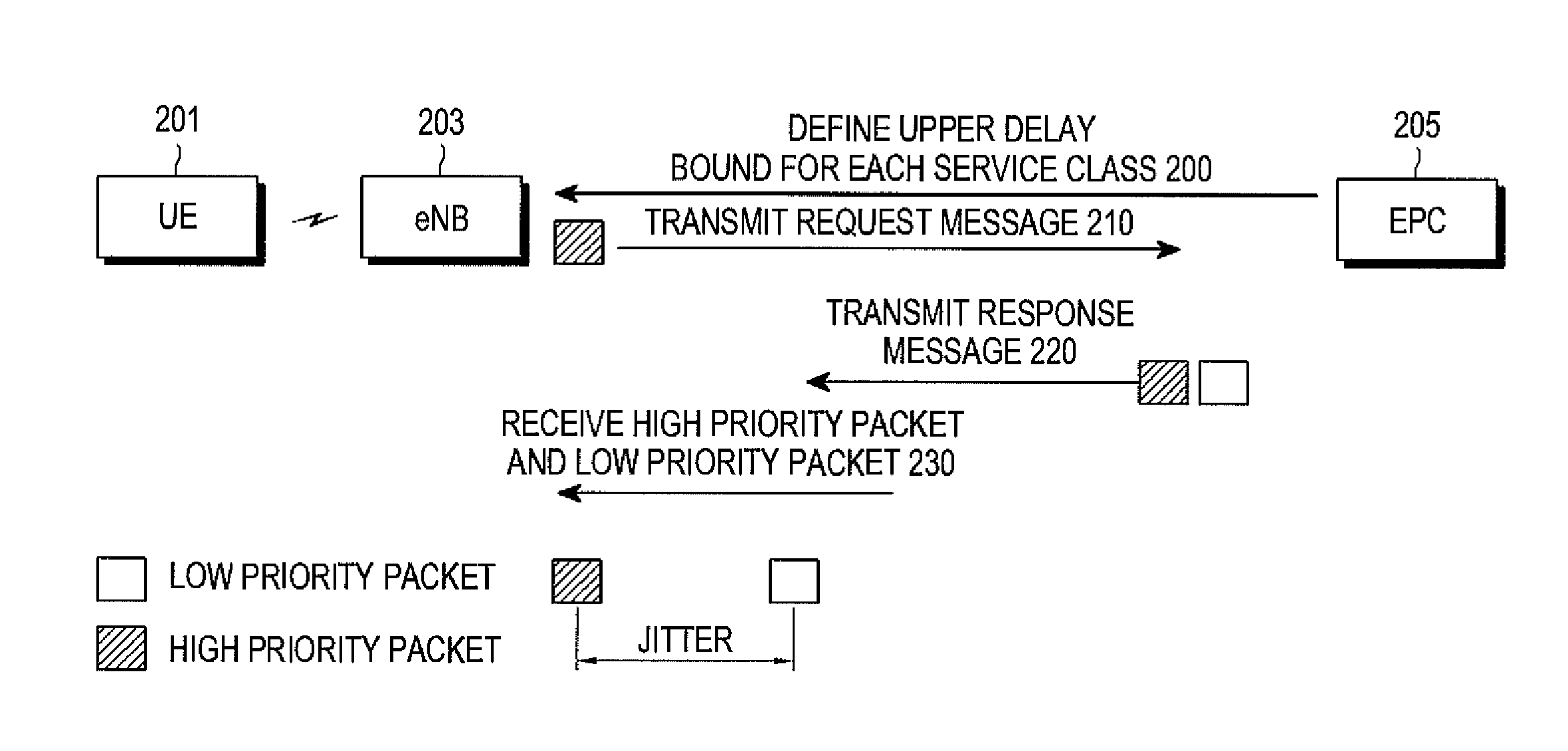
ActiveUS20110170414A1Performance advantageError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemDelayed binding
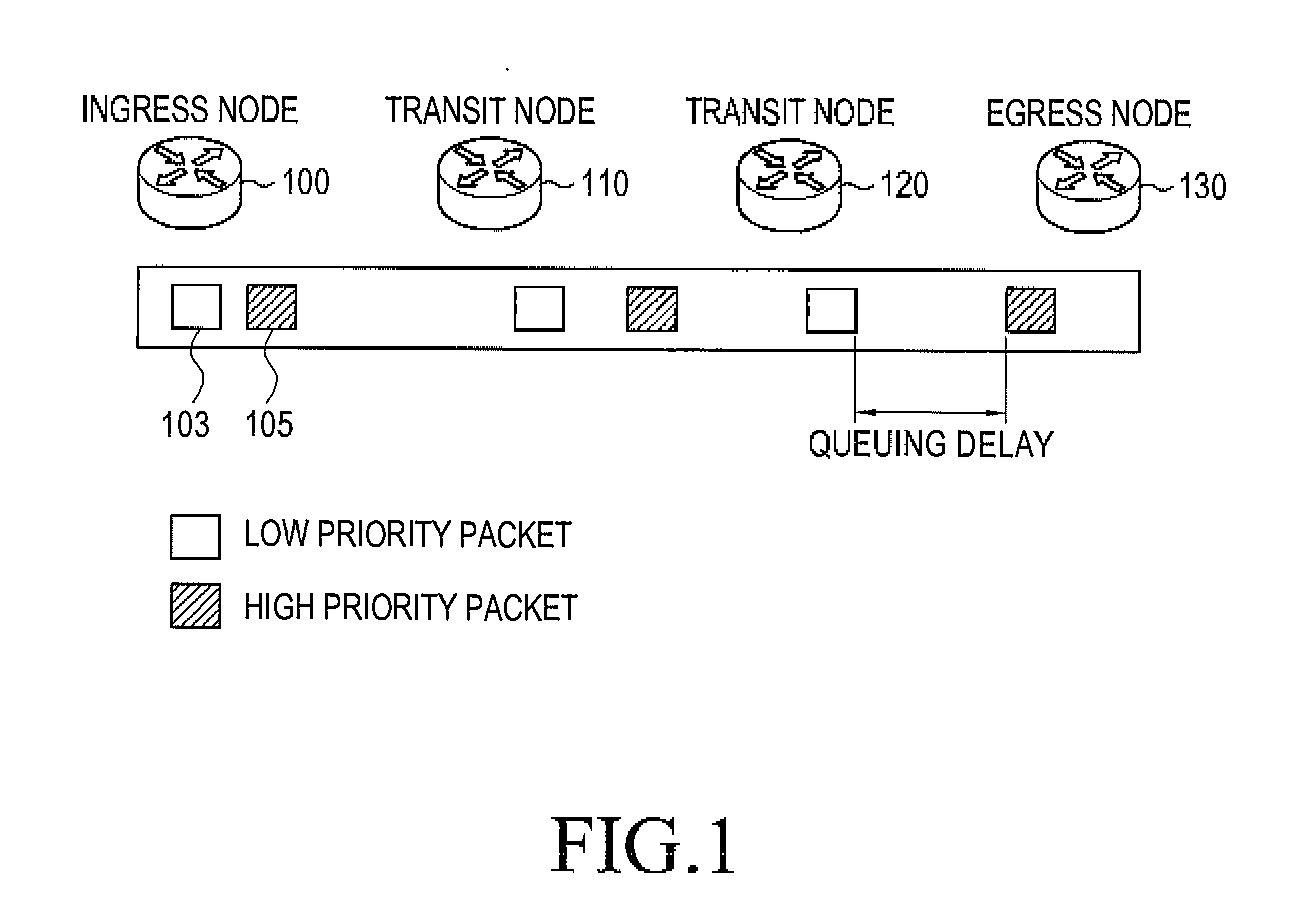
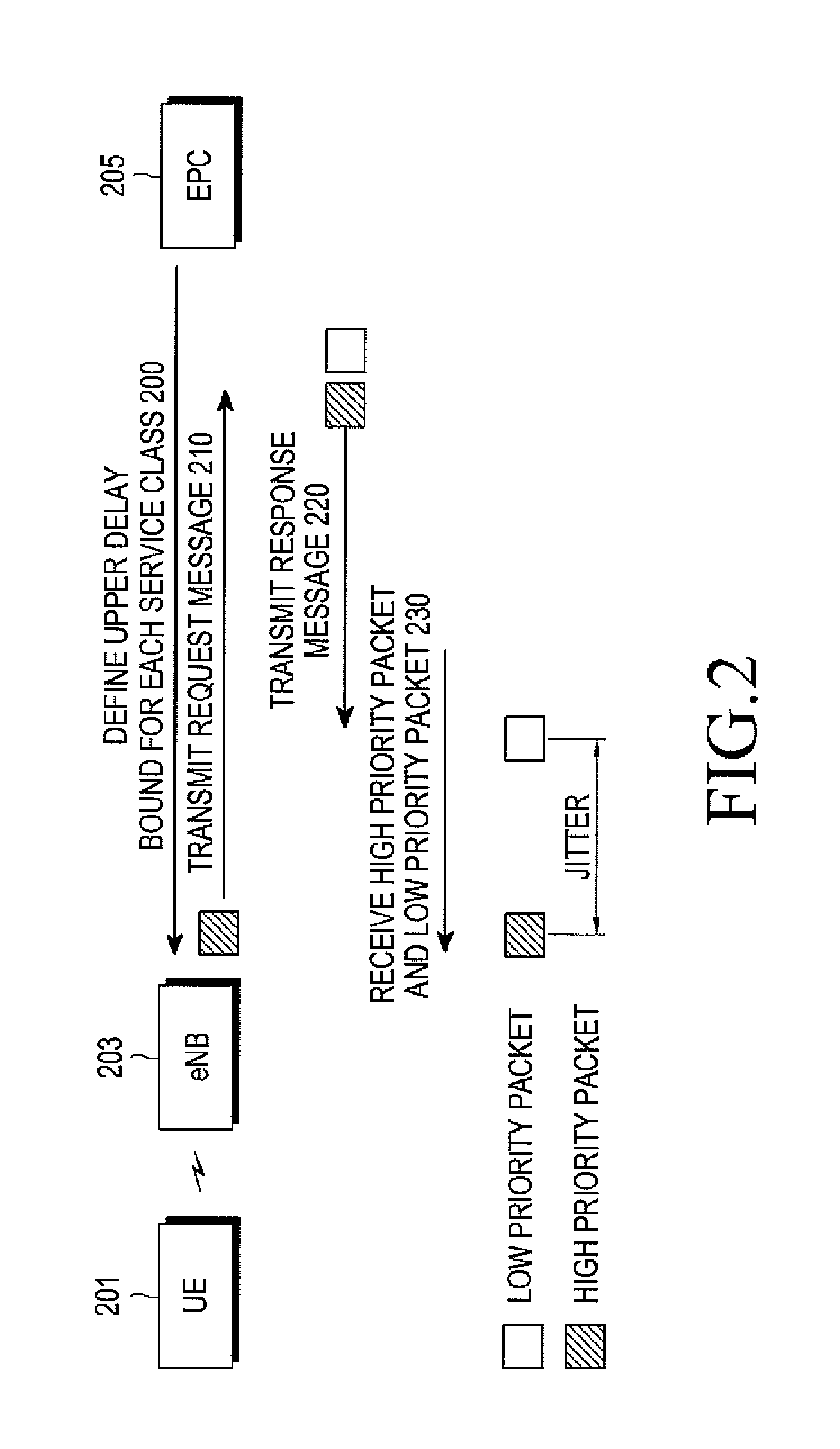
A method for performing congestion control in a communication system. The method includes transmitting a request message to a node using a first packet with a highest priority and receiving a response message corresponding to the request message using the first packet and at least one of a plurality of second packets, estimating a one-way delay of the first packet according to a round trip time for the first packet, converting one of the one-way delay of the first packet and the one-way delay of at least one of the plurality of second packets into a quality of service (QoS) level using a predetermined upper delay bound for a corresponding packet, and converting the converted QoS level into an effective congestion level representing a congestion degree in a network and performing congestion control using the effective congestion level.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
FFT accelerator with high throughput rate
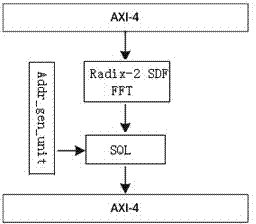
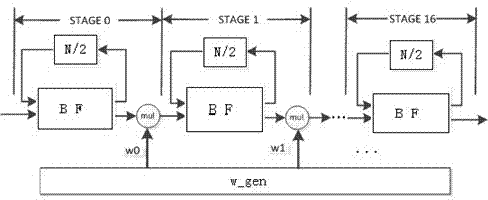
InactiveCN103838704ASave storage resourcesImprove throughputComplex mathematical operationsParallel computingData transmission
The invention relates to an FFT accelerator with a high throughput rate. The FFT accelerator with the high throughput rate is characterized by comprising a data storage module, an address generation module and an FFT acceleration module, wherein the data storage module is used for reading, writing and transmission of data, the address generation module provides a target address of data transmission for the data storage module, and the FFT acceleration module carries out FFT on the data output by the data storage module. The FFT accelerator with the high throughput rate has the advantages that a one-way delayed feedback structure is adopted, the throughput rate is high, and the storage resources in a chip are effectively saved. The FFT accelerator supports expansion interface input on one hand, and supports ping-pong output on the other and. In the data input process, cache space is not needed, the data are fed into an FFT calculation component directly, and FFT calculation is carried out. In the data output process, inverted-order output is carried out through the cache.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com