Patents
Literature
139 results about "Link budget" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
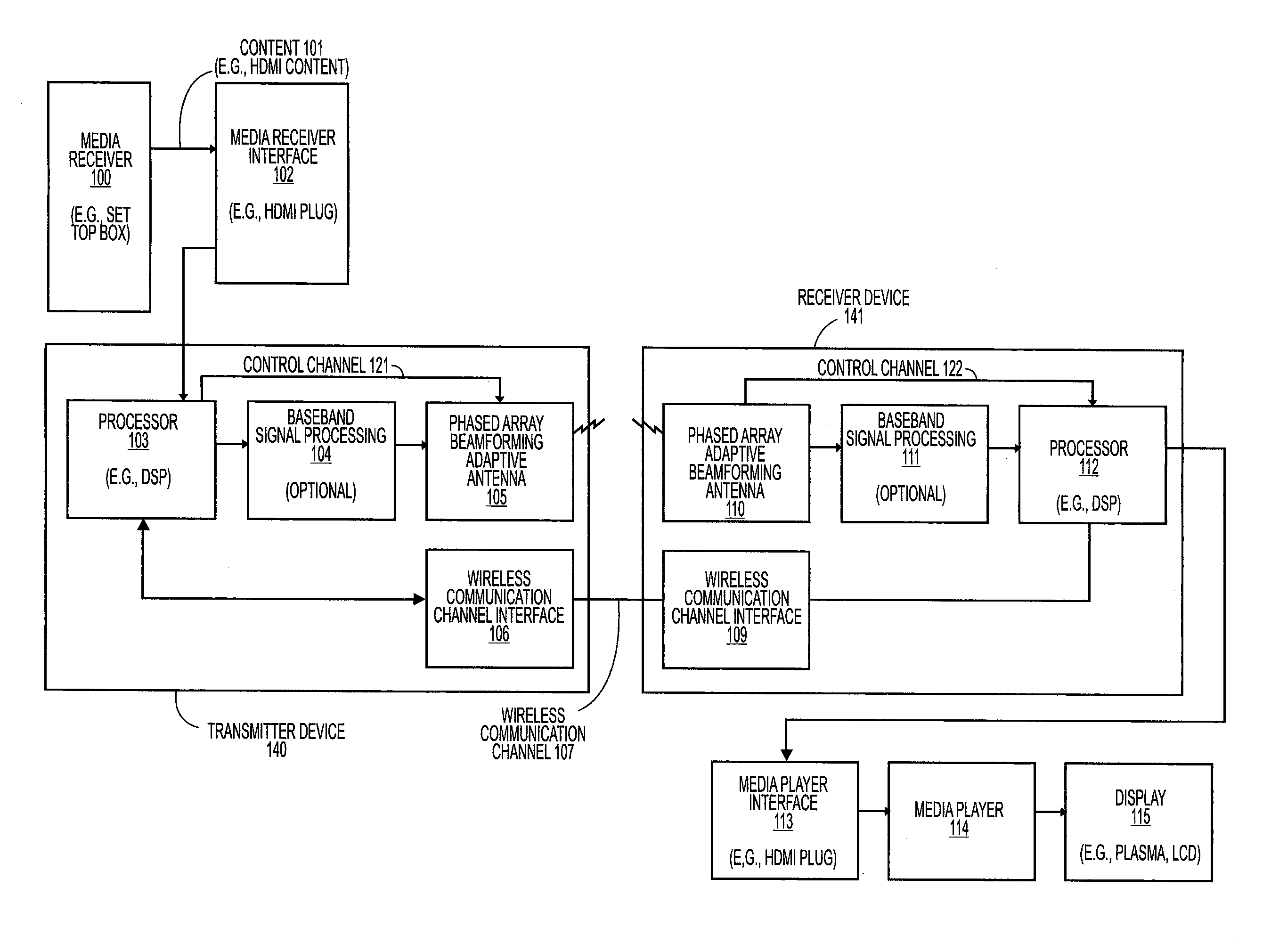
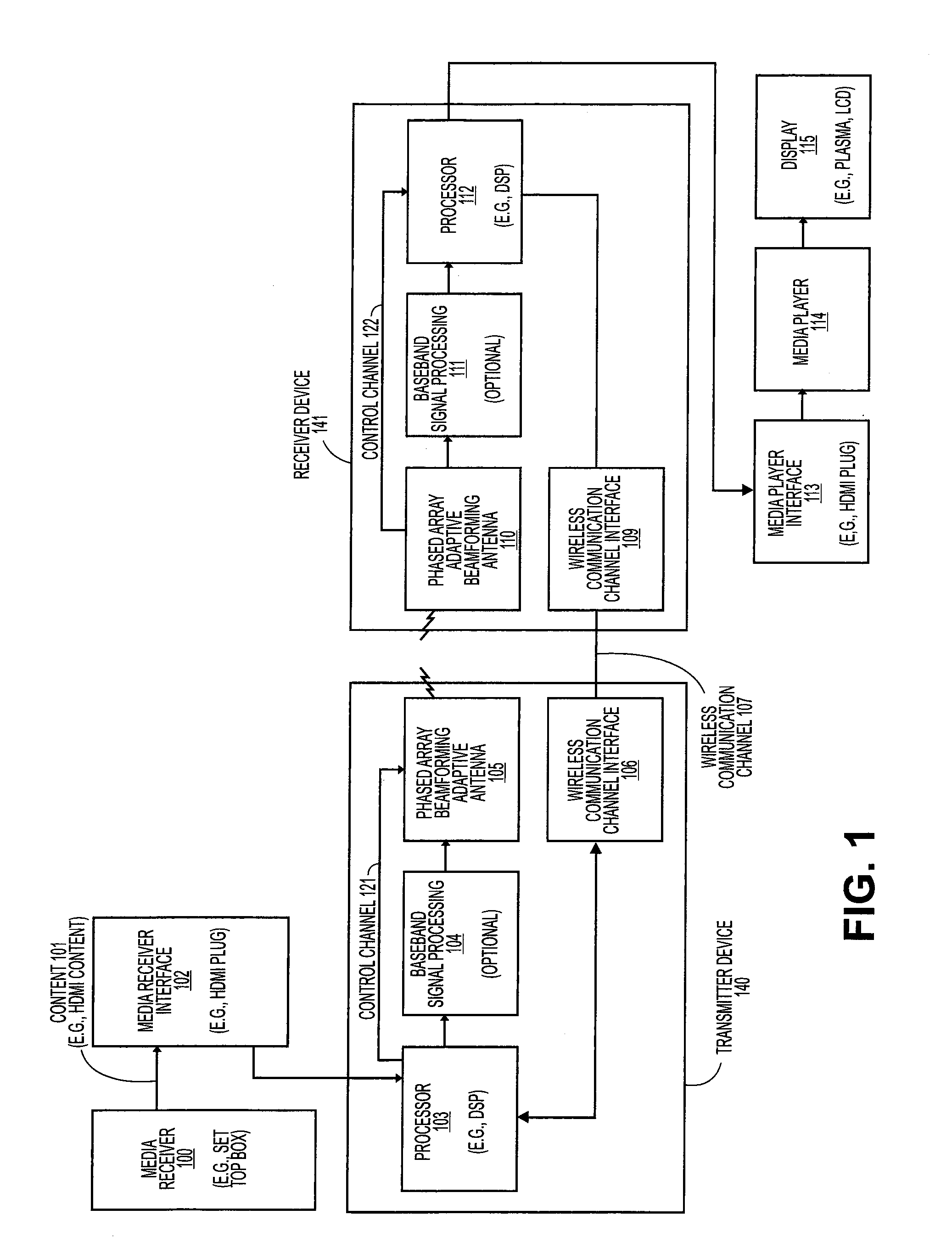
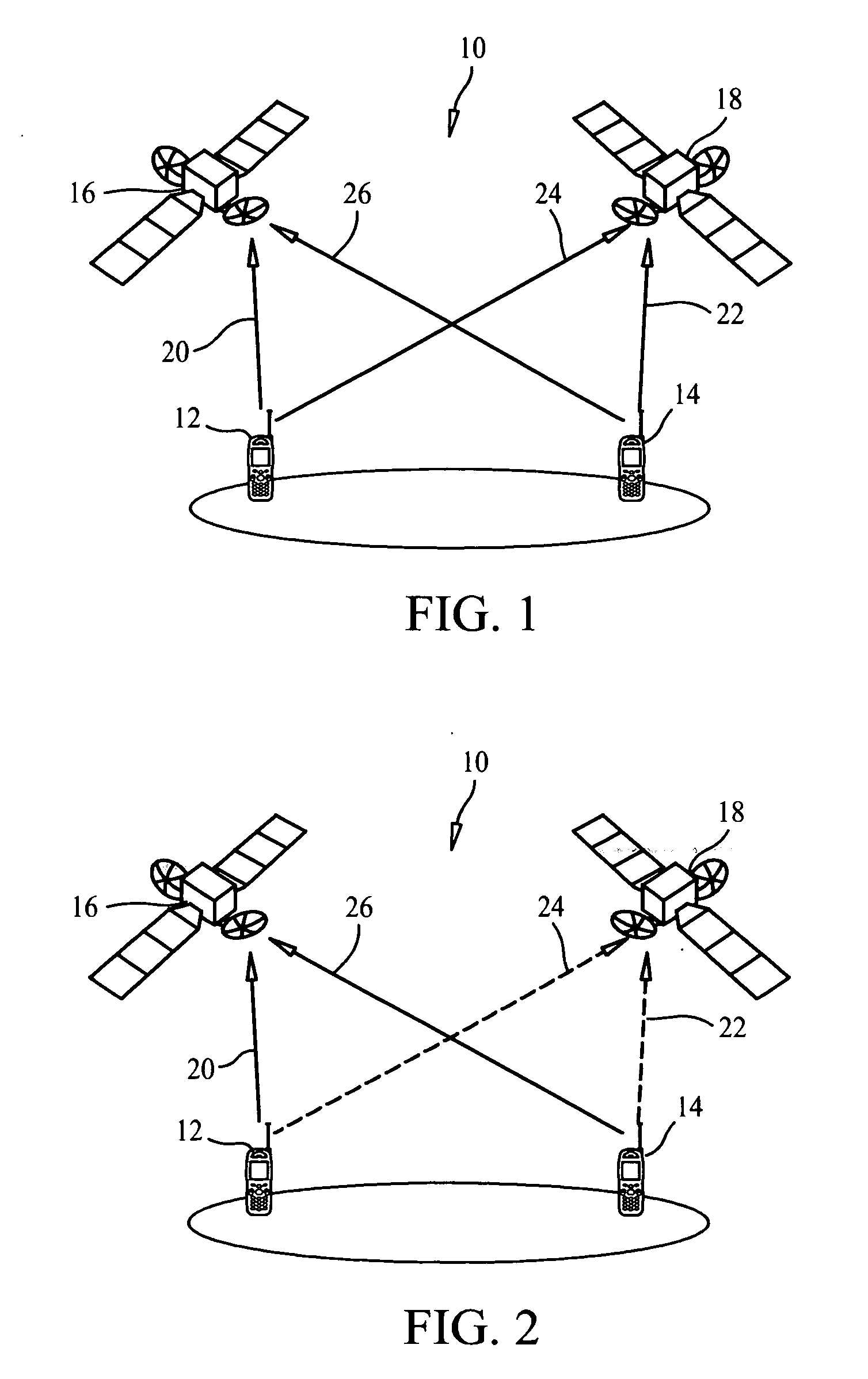
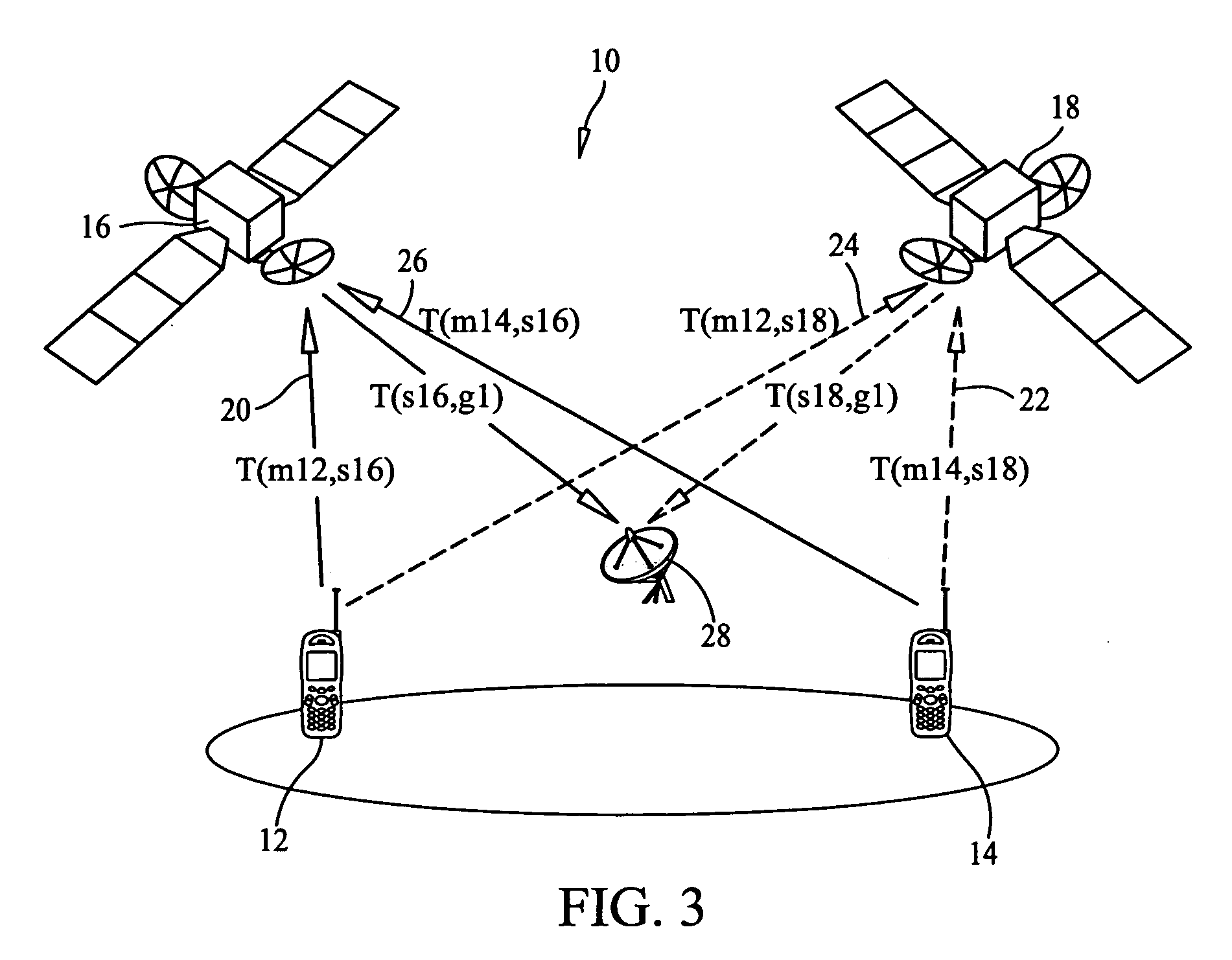
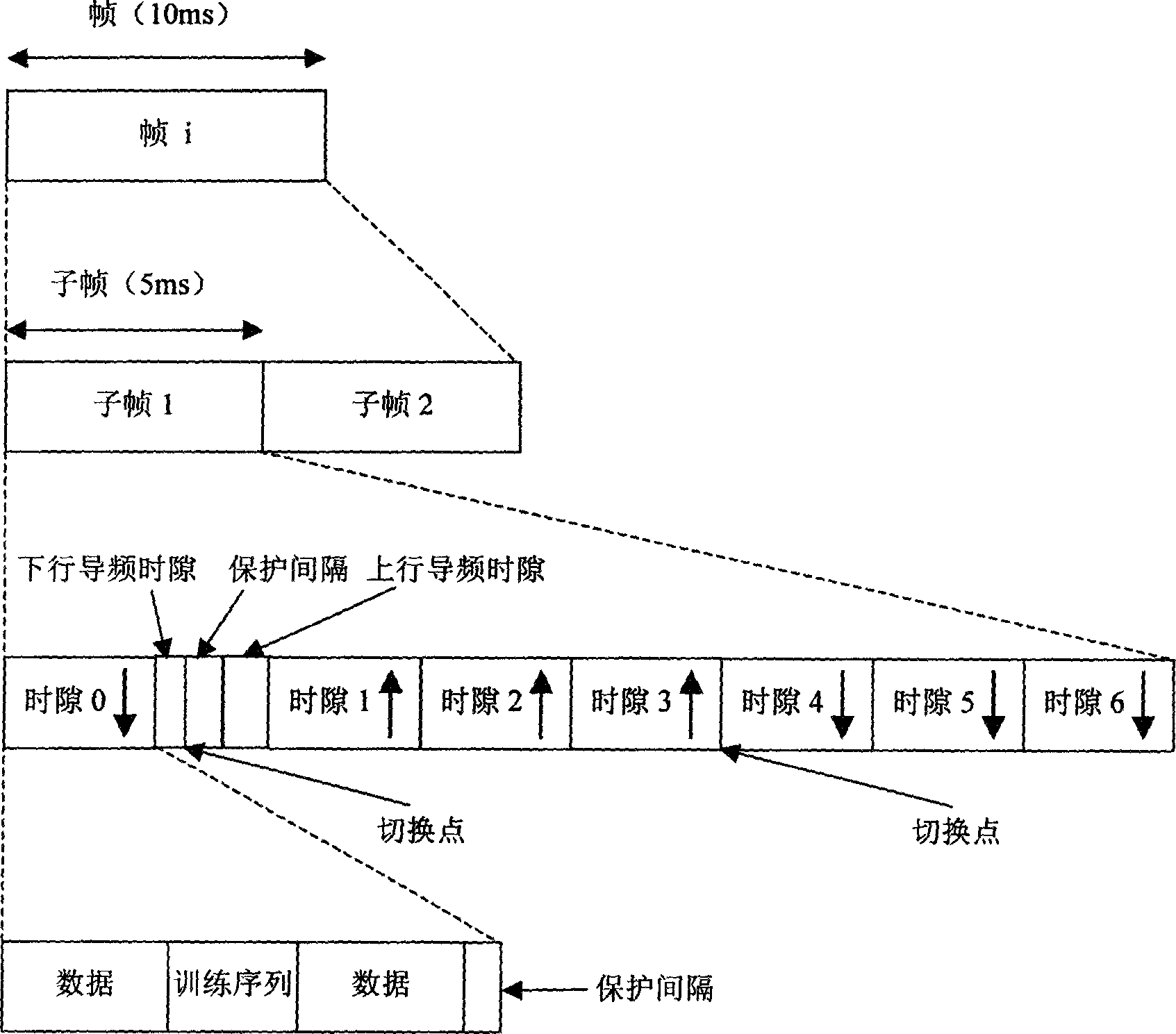
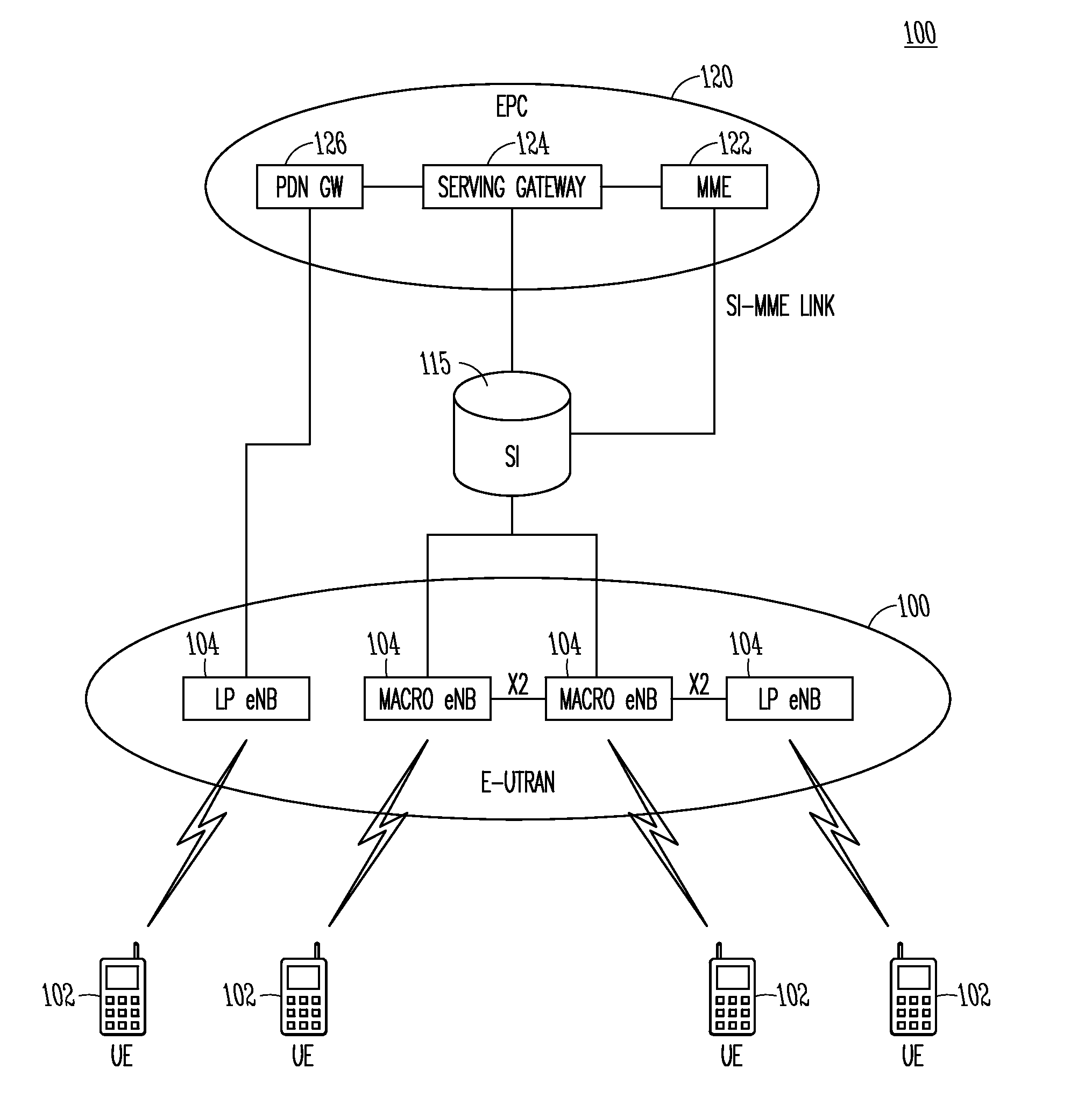
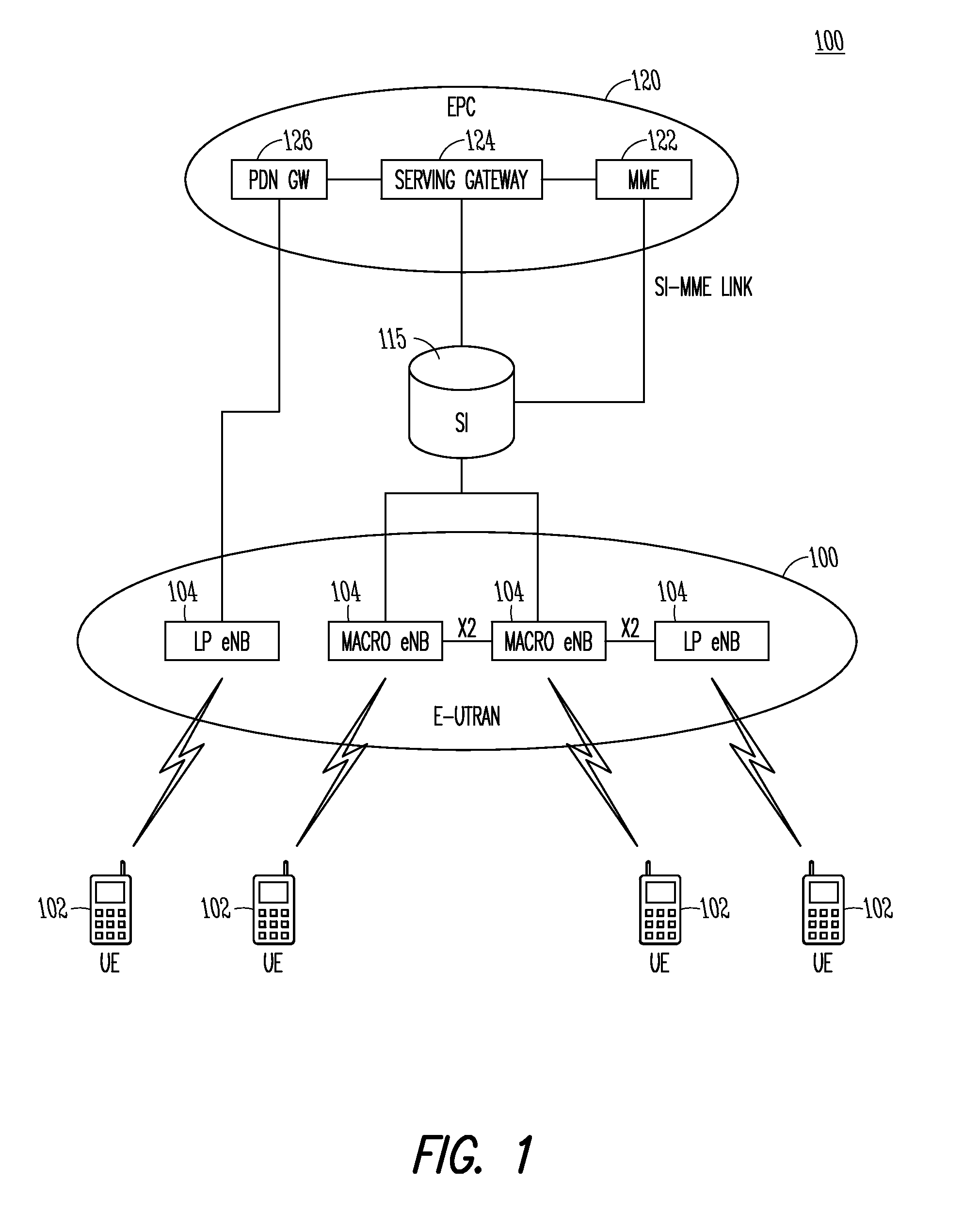
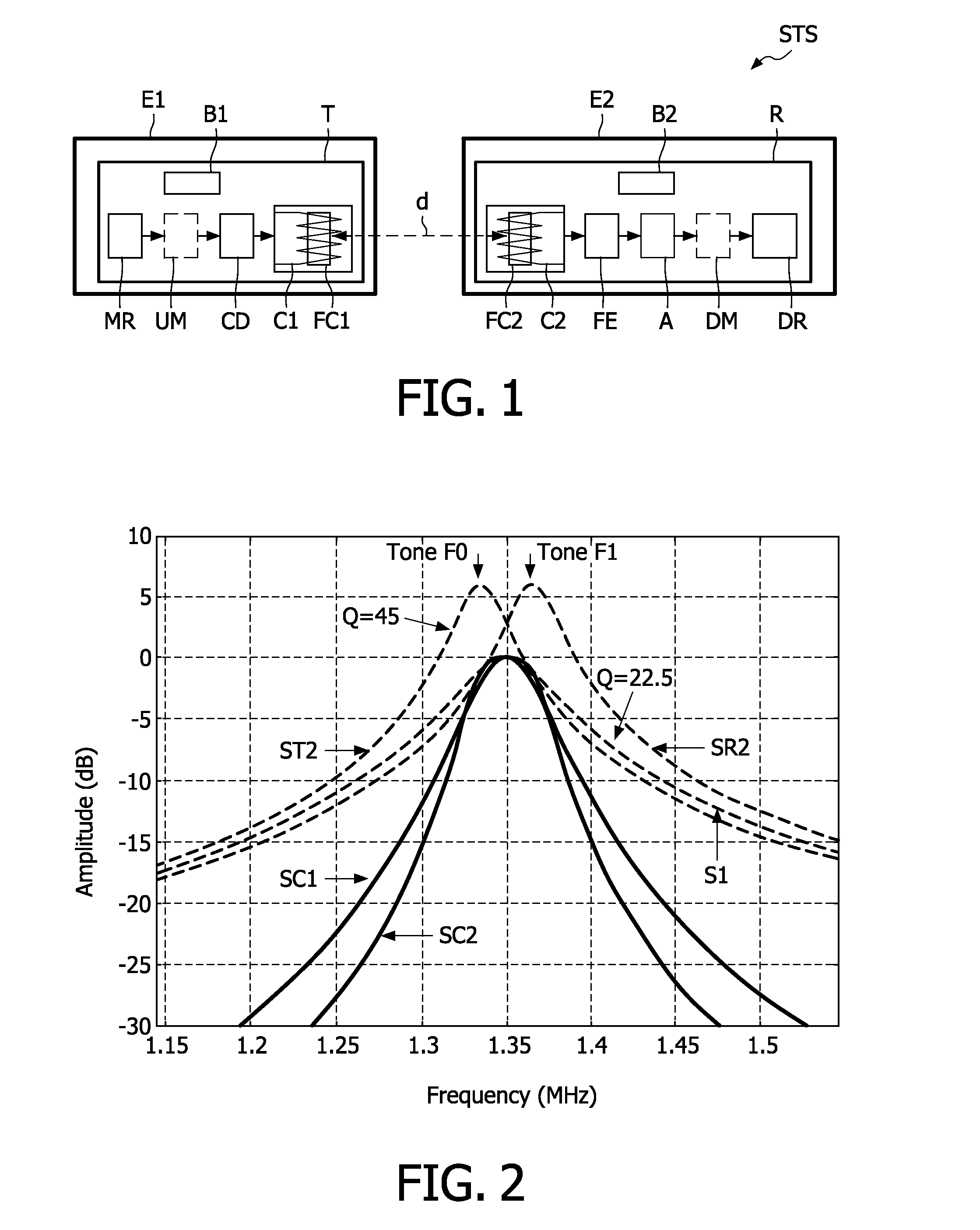
A link budget is an accounting of all of the gains and losses from a transmitter, through a medium (free space, cable, waveguide, fiber, etc.) to the receiver in a telecommunication system. It accounts for the attenuation of the transmitted signal due to propagation, as well as the antenna gains and feedline and other losses. Randomly varying channel gains such as fading are taken into account by adding some margin depending on the anticipated severity of its effects. The amount of margin required can be reduced by the use of mitigating techniques such as antenna diversity or frequency hopping.
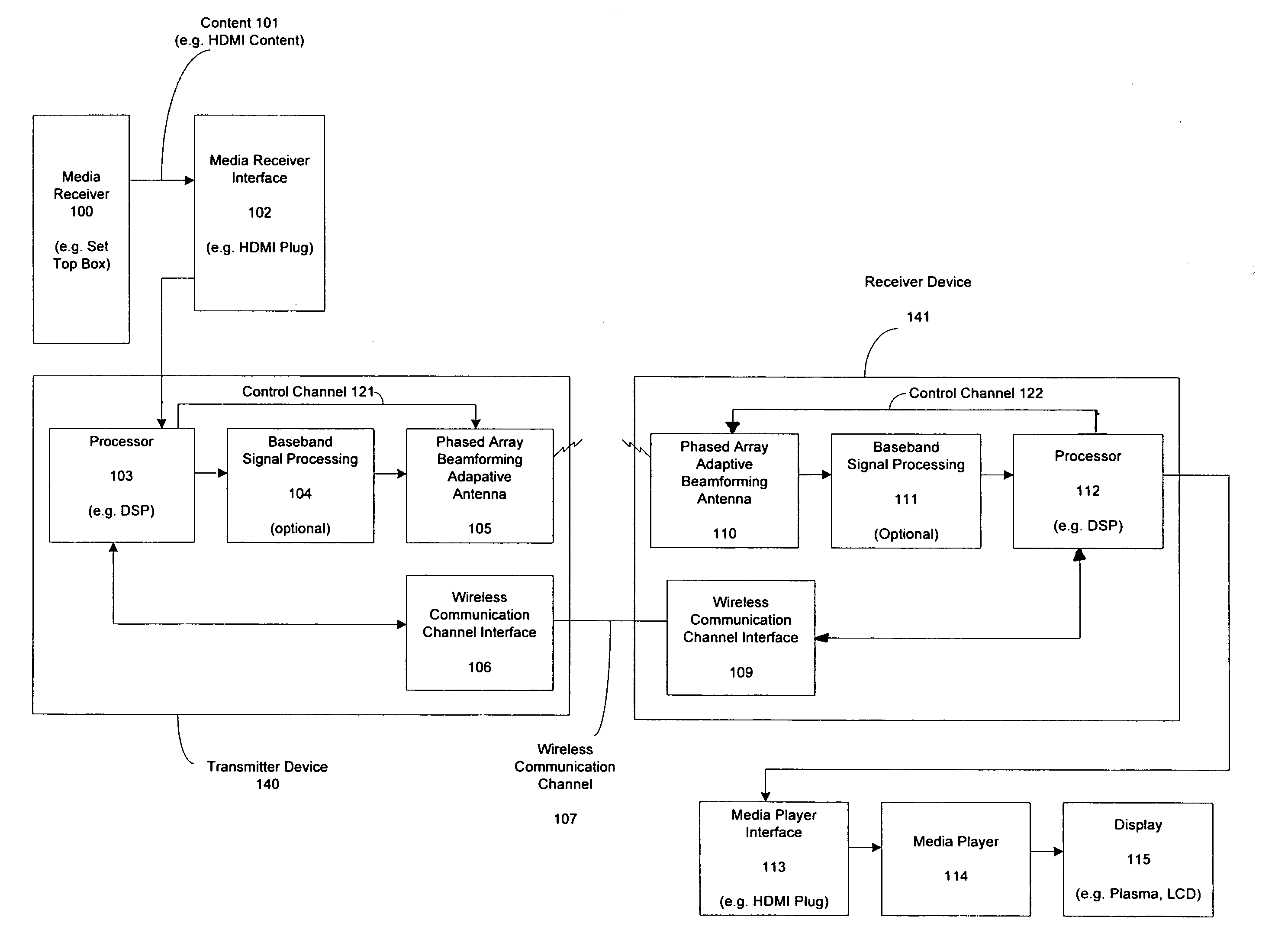
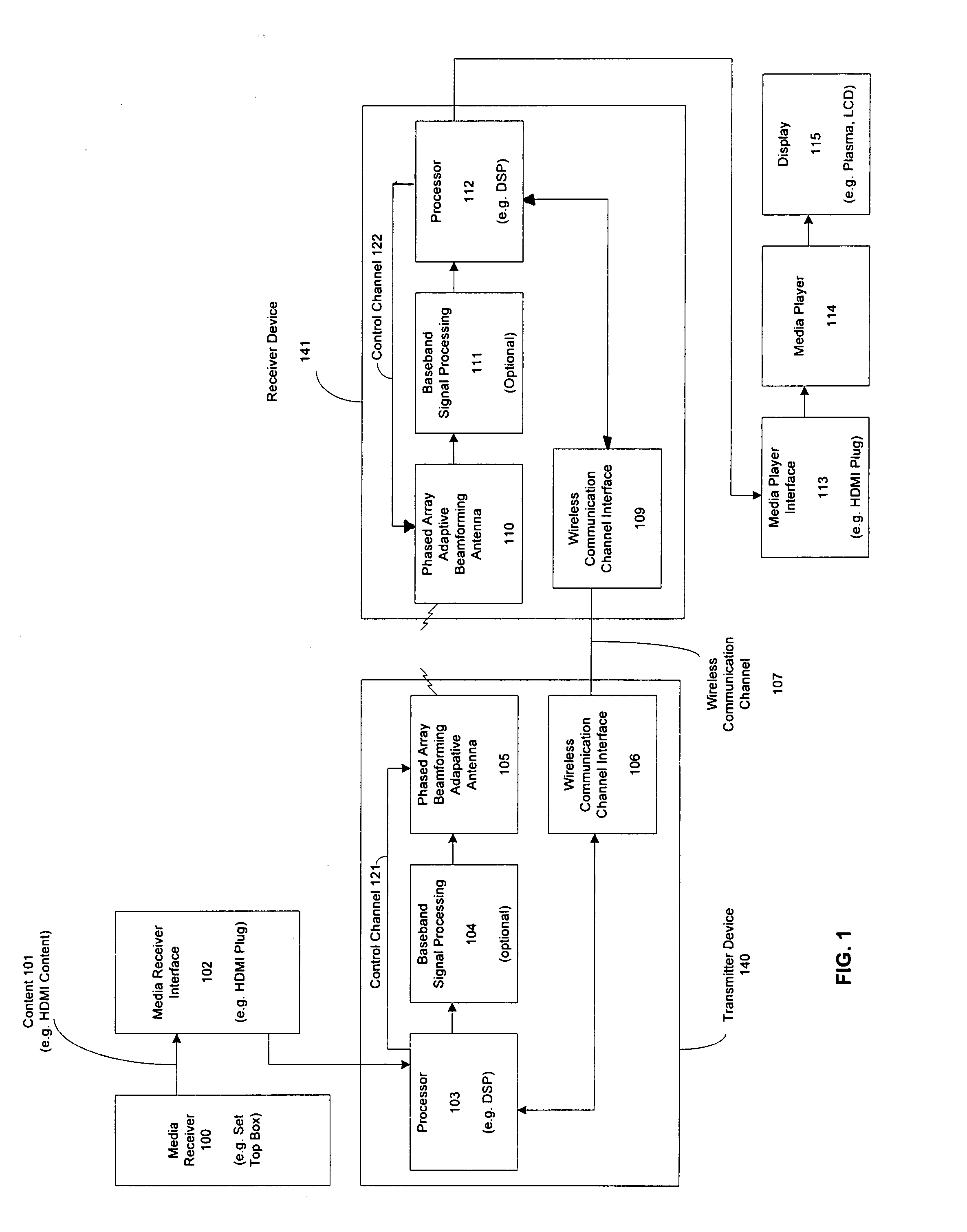
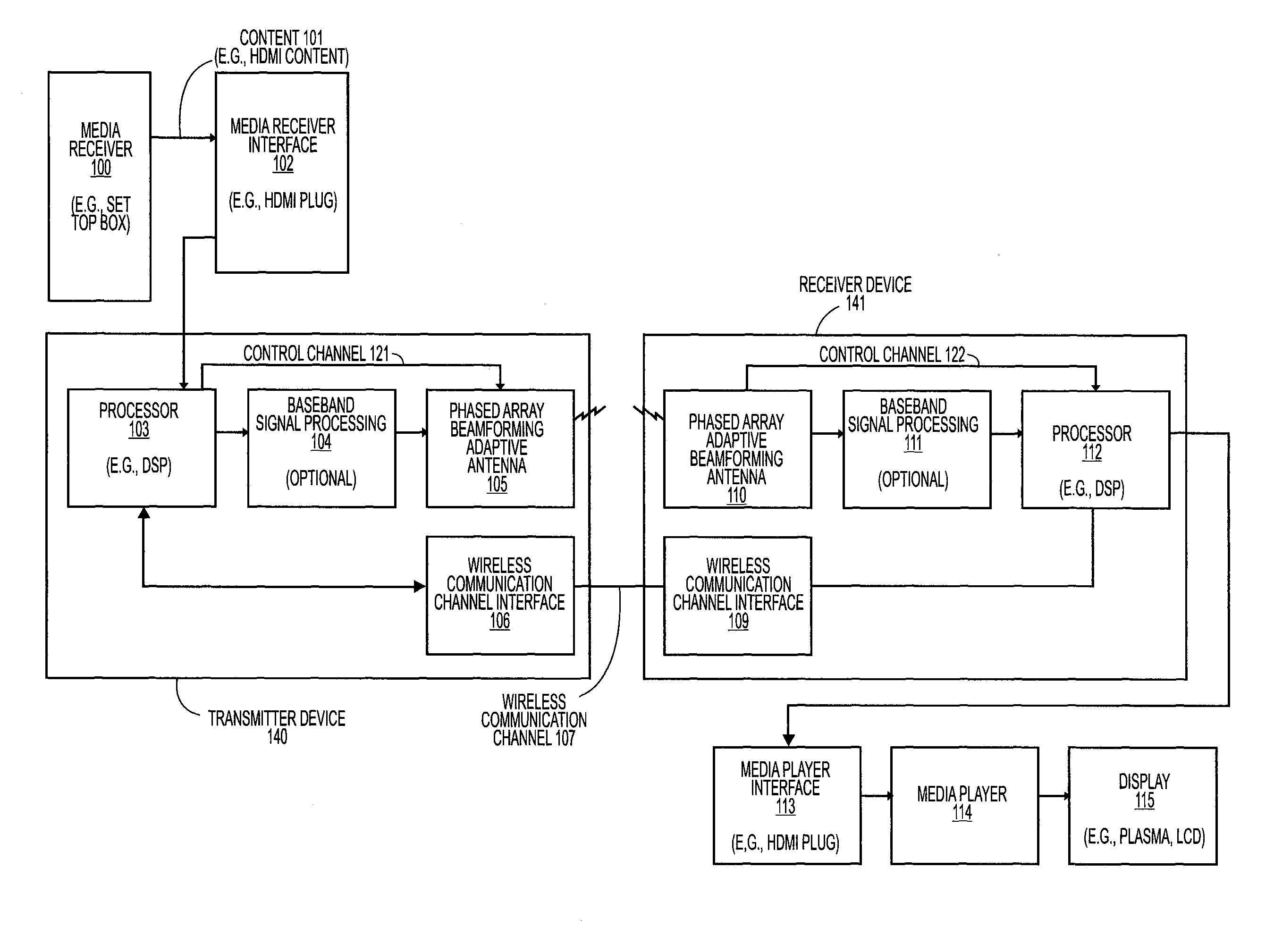
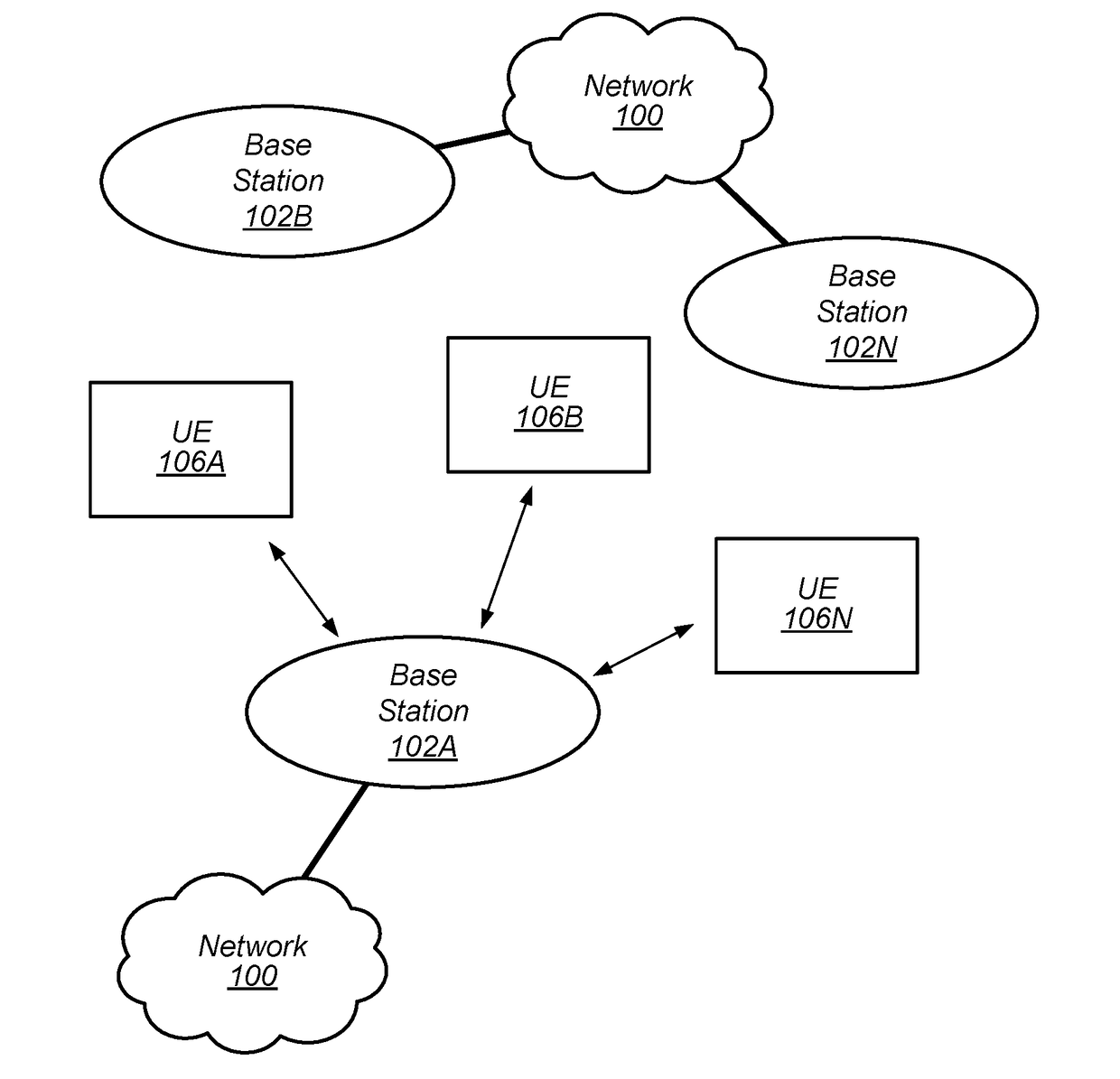
Adaptive beam-steering methods to maximize wireless link budget and reduce delay-spread using multiple transmit and receive antennas
A method and apparatus for adaptive beam-steering are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises performing adaptive beam steering using multiple transmit and receive antennas, including iteratively performing a pair of training sequences, wherein the pair of training sequences includes estimating a transmitter antenna-array weight vector and a receiver antenna-array weight vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adaptive beam-steering methods to maximize wireless link budget and reduce delay-spread using multiple transmit and receive antennas
A method and apparatus for adaptive beam-steering are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises performing adaptive beam steering using multiple transmit and receive antennas, including iteratively performing a pair of training sequences, wherein the pair of training sequences includes estimating a transmitter antenna-array weight vector and a receiver antenna-array weight vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
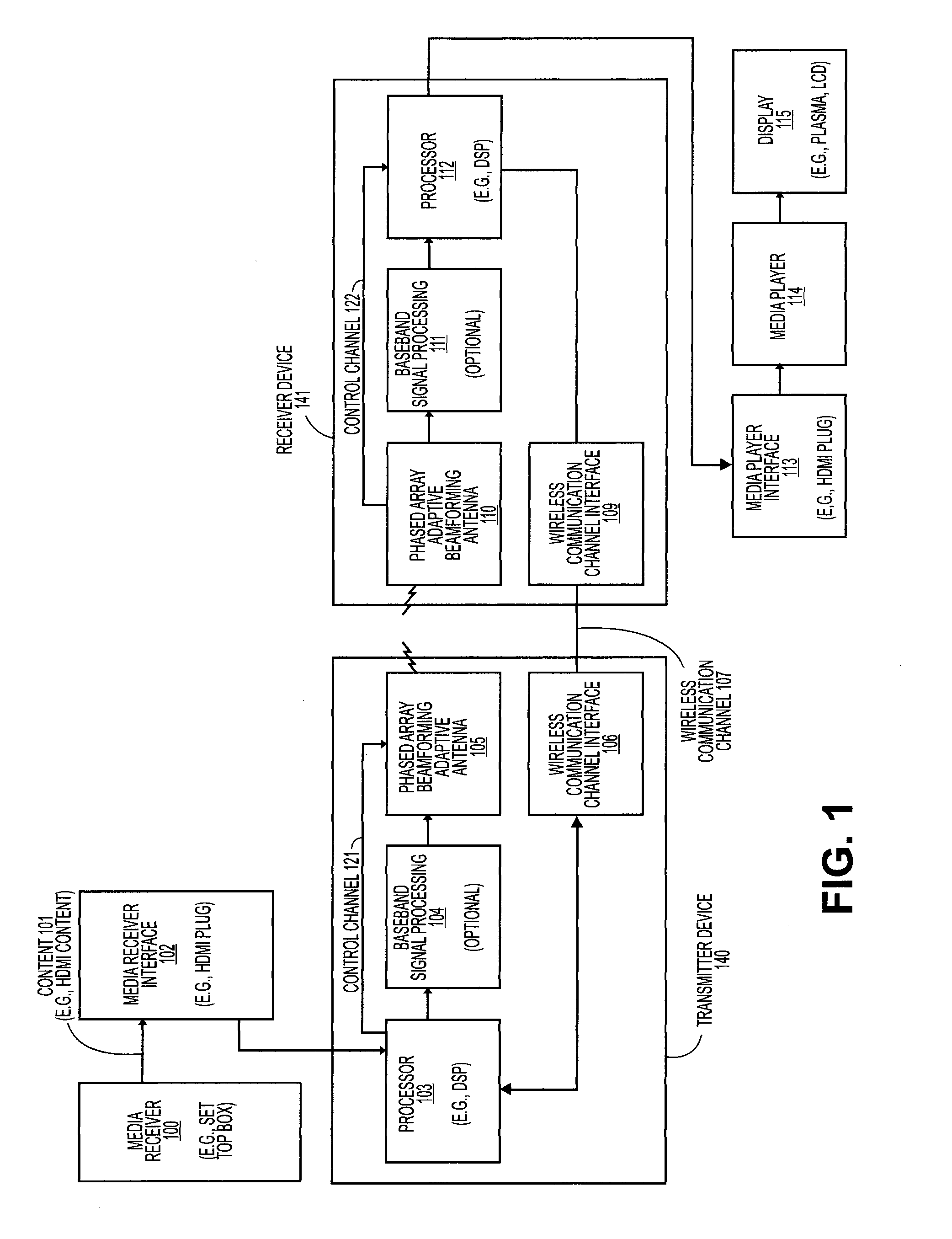
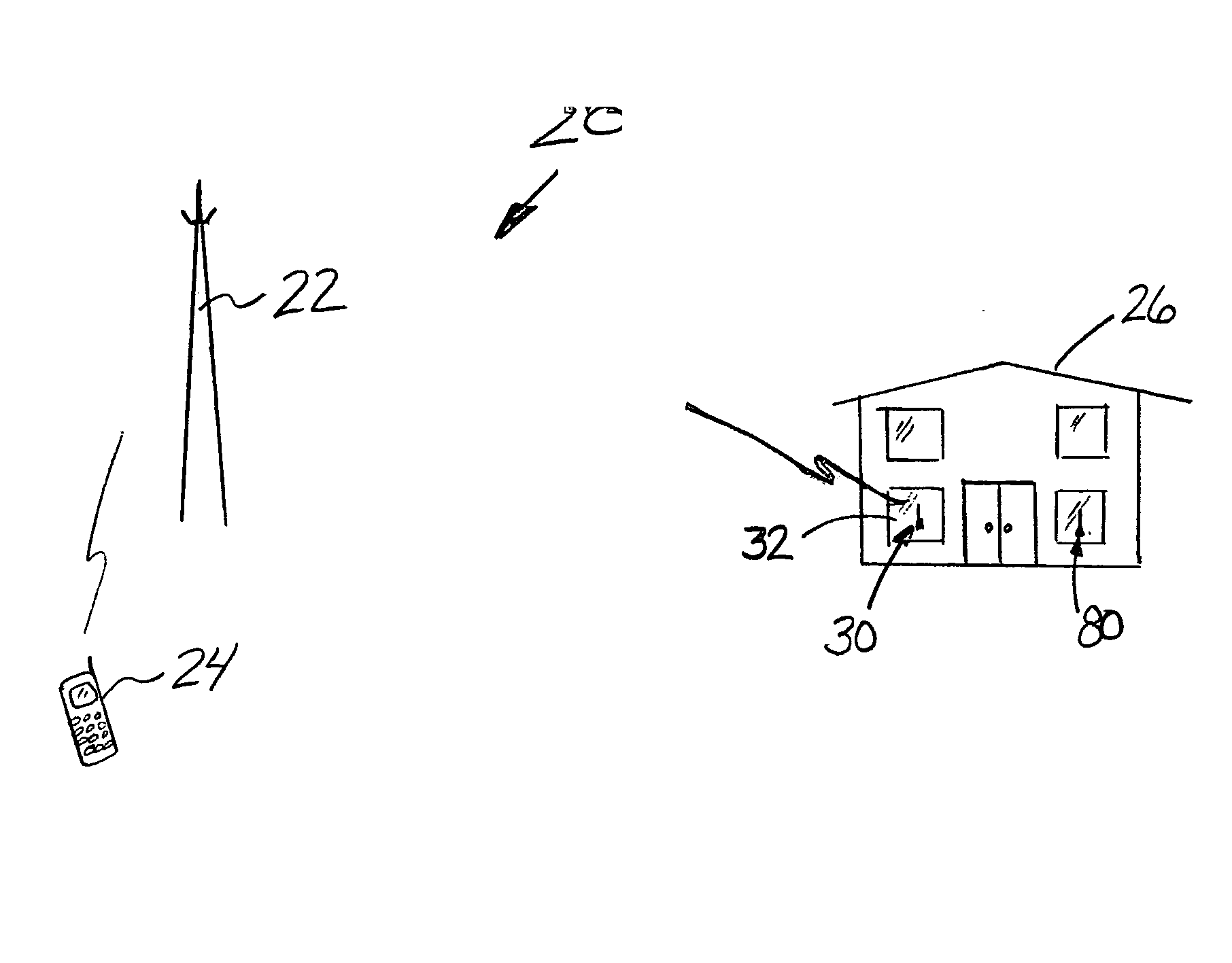
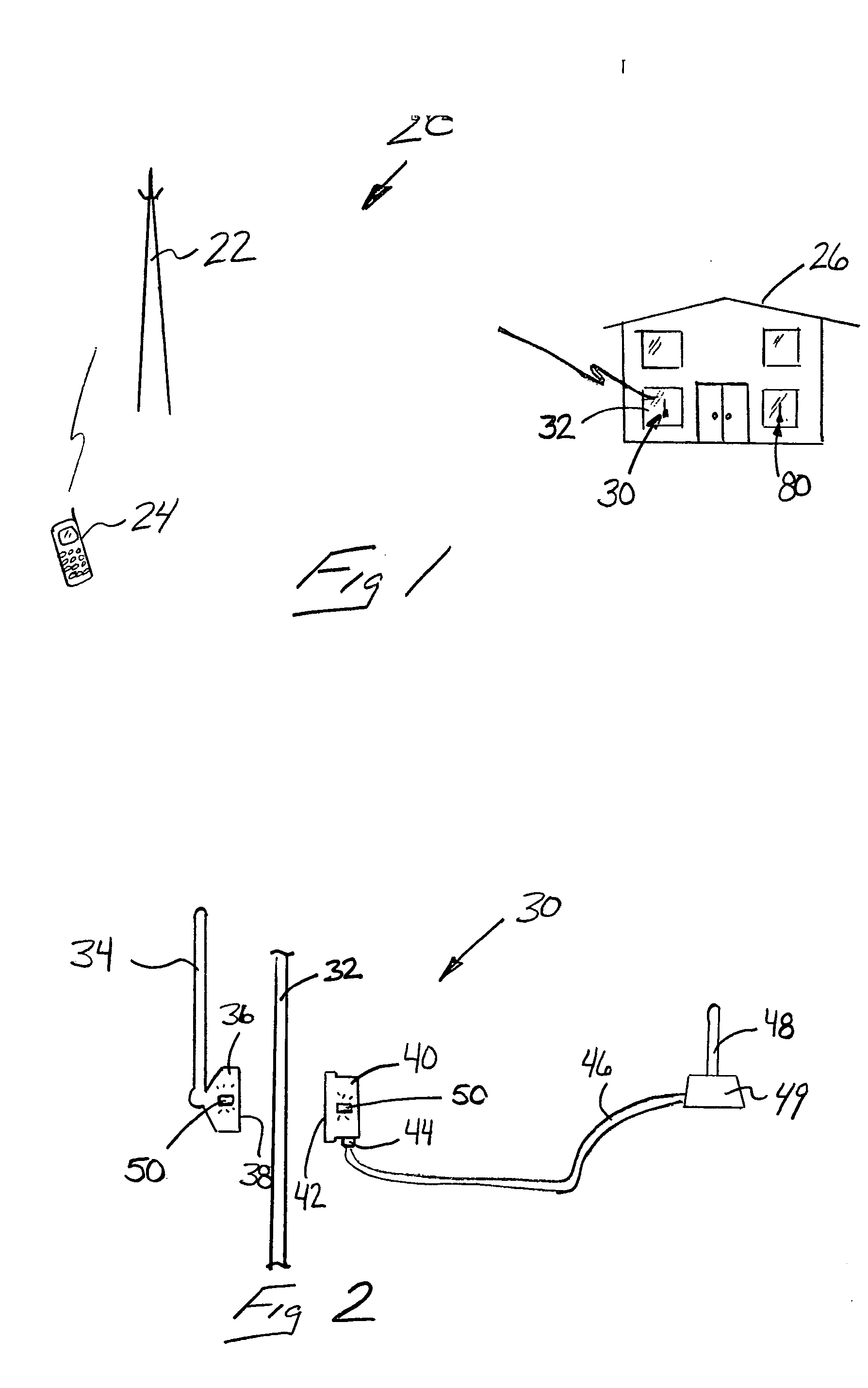
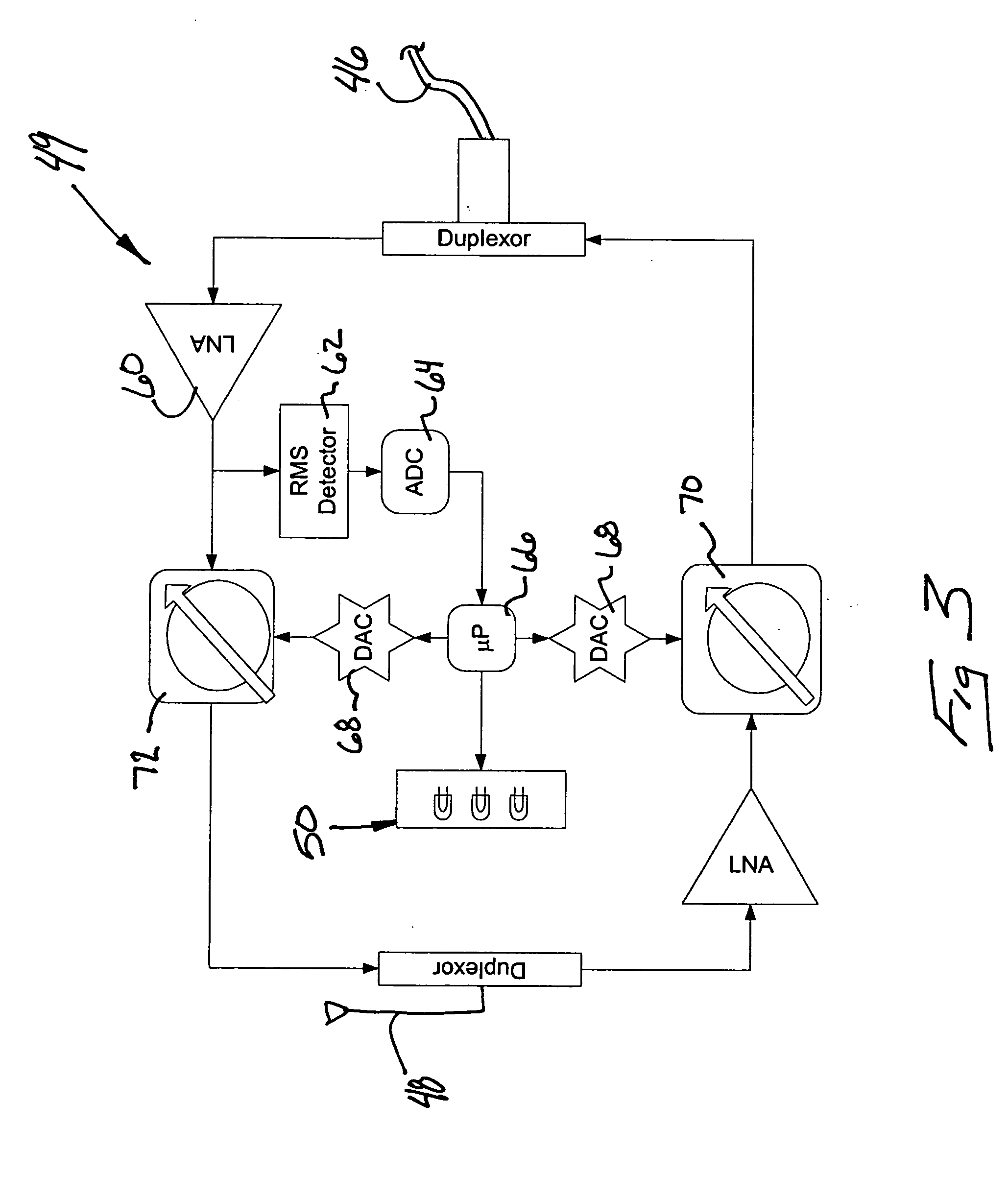
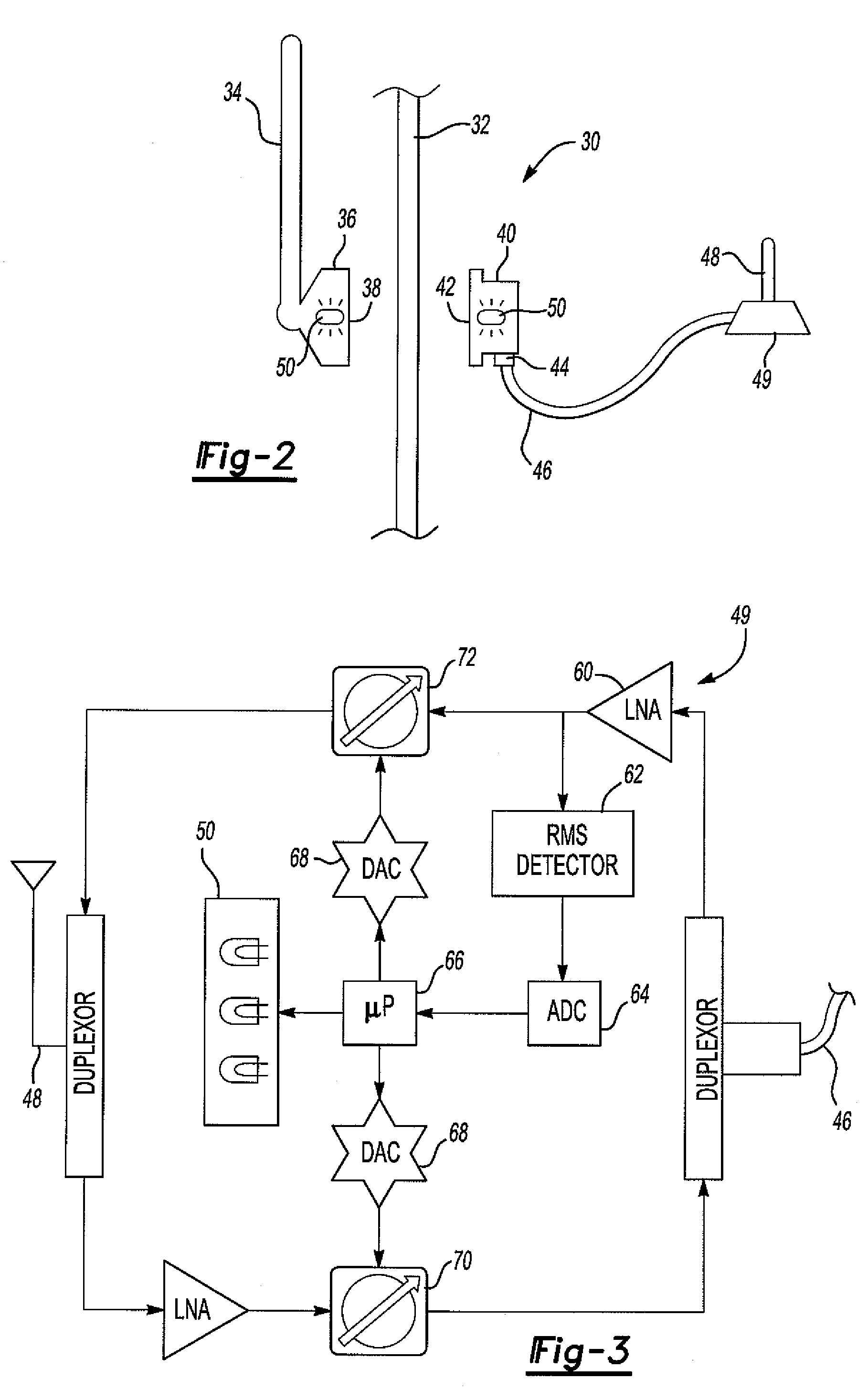
Extending wireless communication RF coverage inside building
ActiveUS20060025072A1High possible repeater gainAvoiding base station receiver desensitizationPower managementResonant long antennasCommunications systemTransceiver
A wireless communication system includes at least one repeater antenna assembly for providing adequate RF coverage within a building, such as a home. An example repeater antenna assembly has an automatically adjustable gain that is controlled responsive to a pathloss associated with a received signal to avoid base station transceiver desensitization and positive feedback. A disclosed assembly avoids base station desensitization and positive feedback. Another disclosed technique maintains a selected minimum link budget within the building.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
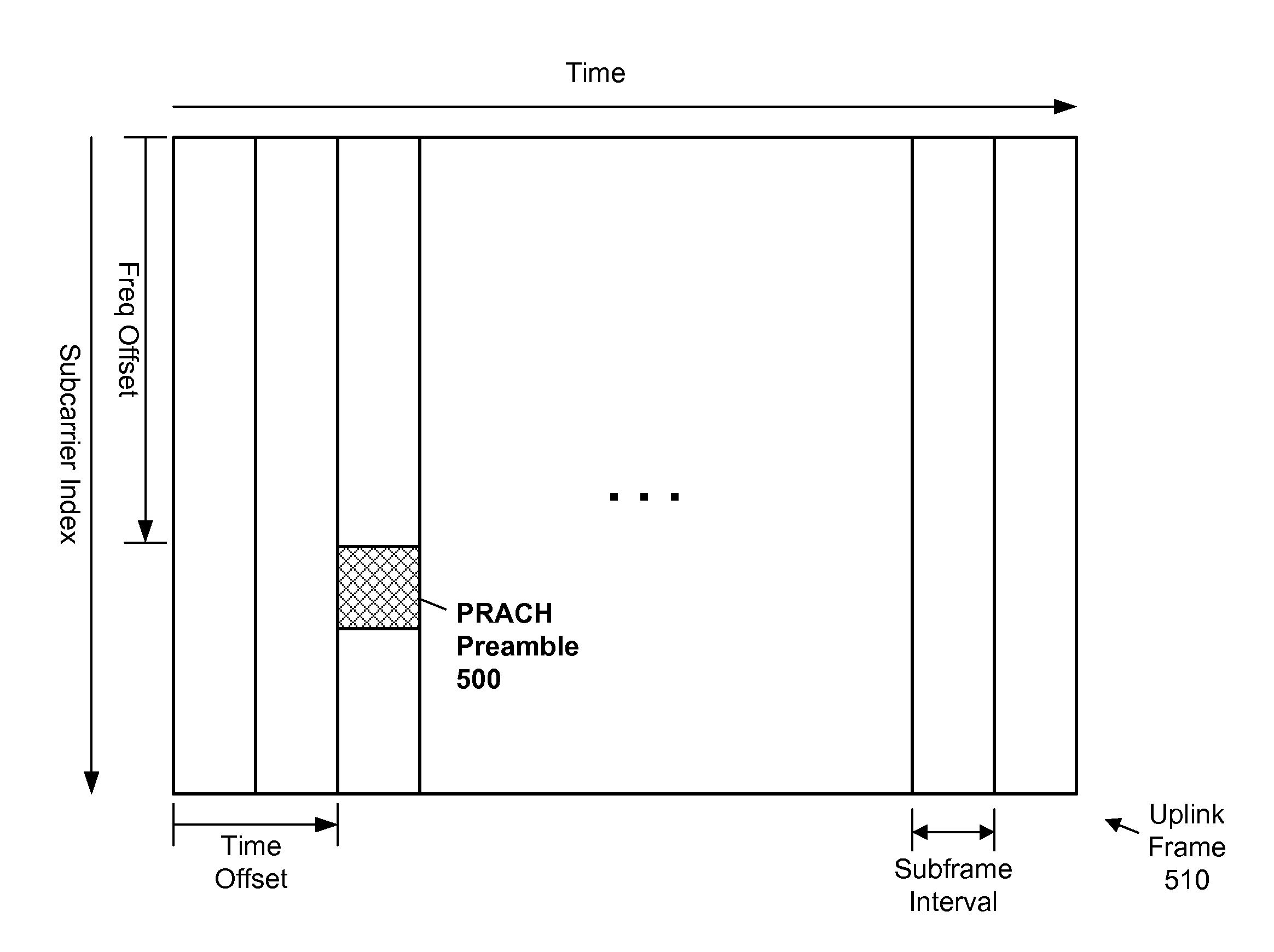
Enhanced PRACH Scheme for Power Savings, Range Improvement and Improved Detection
ActiveUS20150365977A1Big spaceLarge temporal widthError prevention/detection by using return channelPower managementTelecommunicationsRandom-access channel
Enhanced random access procedures for link-budget-limited user equipment (UE) devices are disclosed. A user equipment device may transmit a first message containing a Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH). The PRACH contains instances of a Zadoff-Chu sequence, and may be transmitted repeatedly as part of a single random attempt, to facilitate correlation data combining at the base station. The available Zadoff-Chu sequences may be partitioned among a plurality of sets, each set being associated with a respective Doppler shift range (or frequency hop pattern or time repetition pattern). A UE device may signal Doppler shift (or other information) to the base station by selection of one of the sets. The first PRACH transmission and the following PRACH transmission may occur in consecutive subframes. A UE device may select from a special set of Zadoff-Chu sequences (different from a conventional set of sequences), to signal its status as a link-budget-limited device.
Owner:APPLE INC
Adaptive beam-steering methods to maximize wireless link budget and reduce delay-spread using multiple transmit and receive antennas
ActiveUS20100178884A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsElectromagnetic wave modulationDelay spreadBeam steering
A method and apparatus for adaptive beam-steering are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises performing adaptive beam steering using multiple transmit and receive antennas, including iteratively performing a pair of training sequences, wherein the pair of training sequences includes estimating a transmitter antenna-array weight vector and a receiver antenna-array weight vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
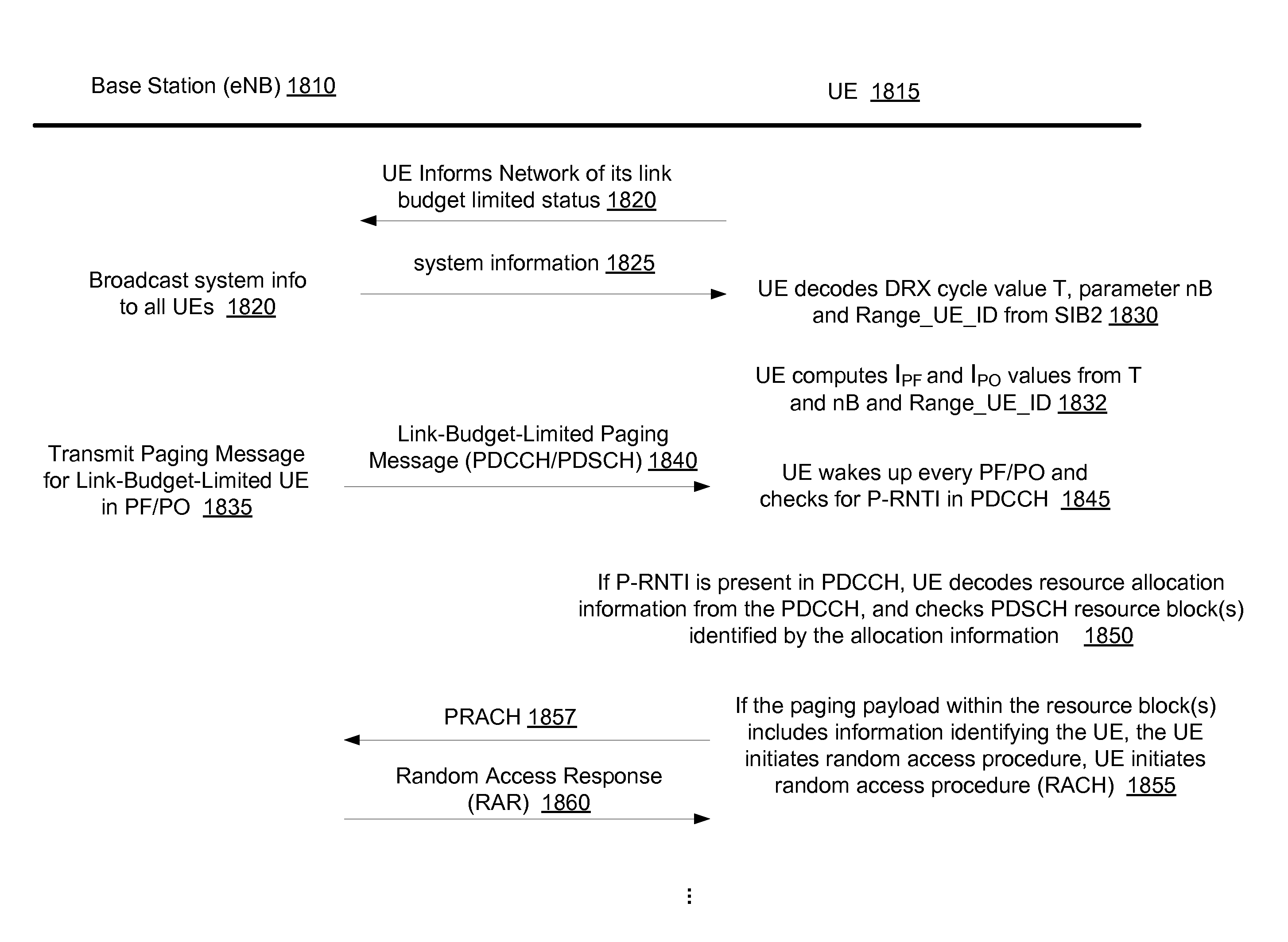
Coverage constrained devices and paging method
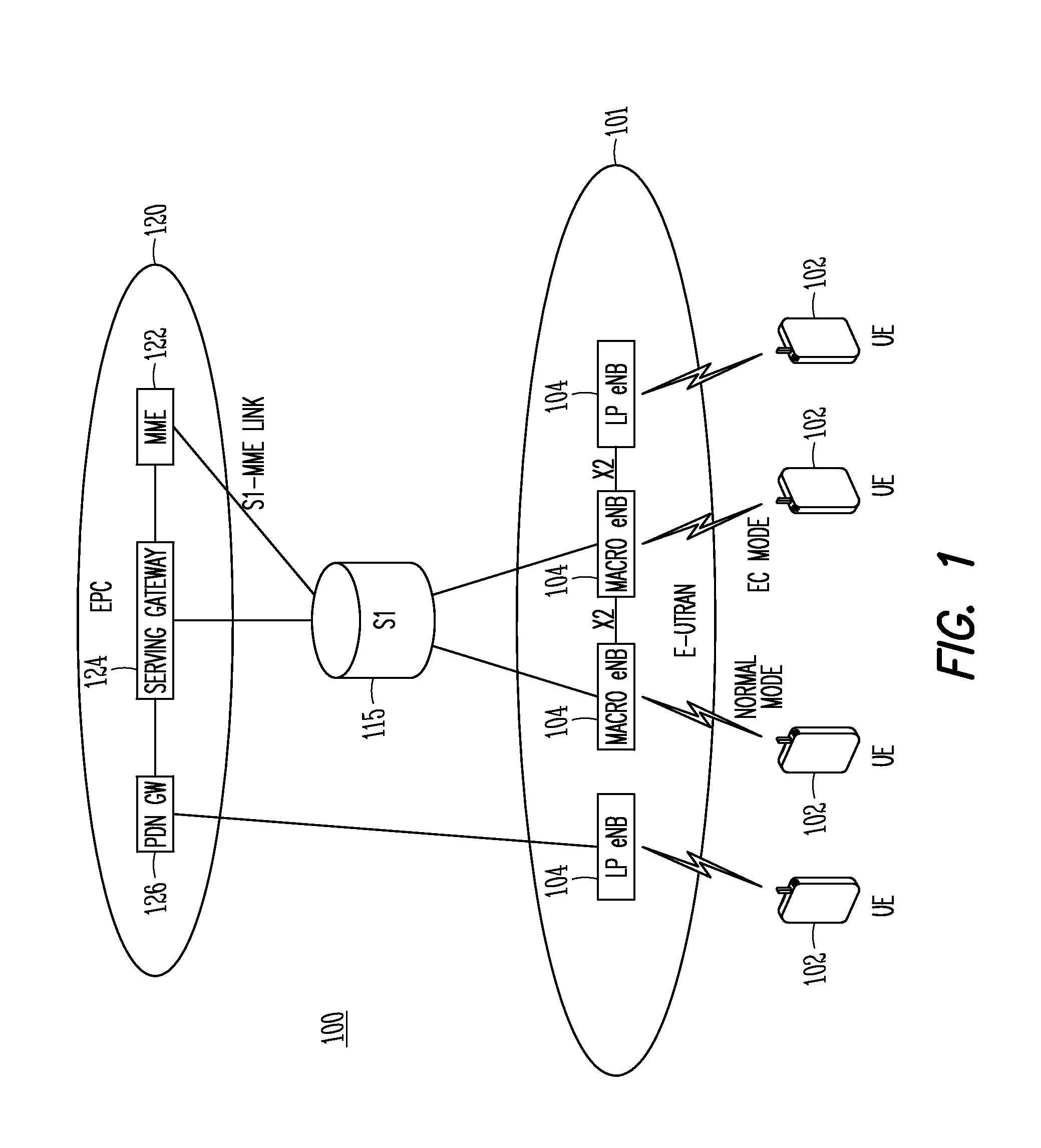
Devices and methods of paging user equipment (UE) are generally described. An evolved Node-B (eNB) may transmit legacy and extended coverage paging messages having different Paging Radio Network Temporary Identifiers (P-RNTIs) to UEs. Each extended coverage paging message may contain the same information, which coverage constrained UEs may combine to achieve a predetermined link budget and subsequently decode. The coverage constrained UEs may ignore legacy paging messages prior to decoding the legacy paging messages. The extended coverage paging messages may be transmitted in non-legacy paging occasions that may span multiple paging cycles. Each paging cycle may contain 0, 1 or multiple extended coverage paging occasions. The UE may be provided the physical resource blocks (PRBs) used for the extended coverage paging message through a system information message. The PRBs may be assigned as a fixed or semi-statically assigned set of PRBs or a dynamically assigned set of PRBs.
Owner:APPLE INC
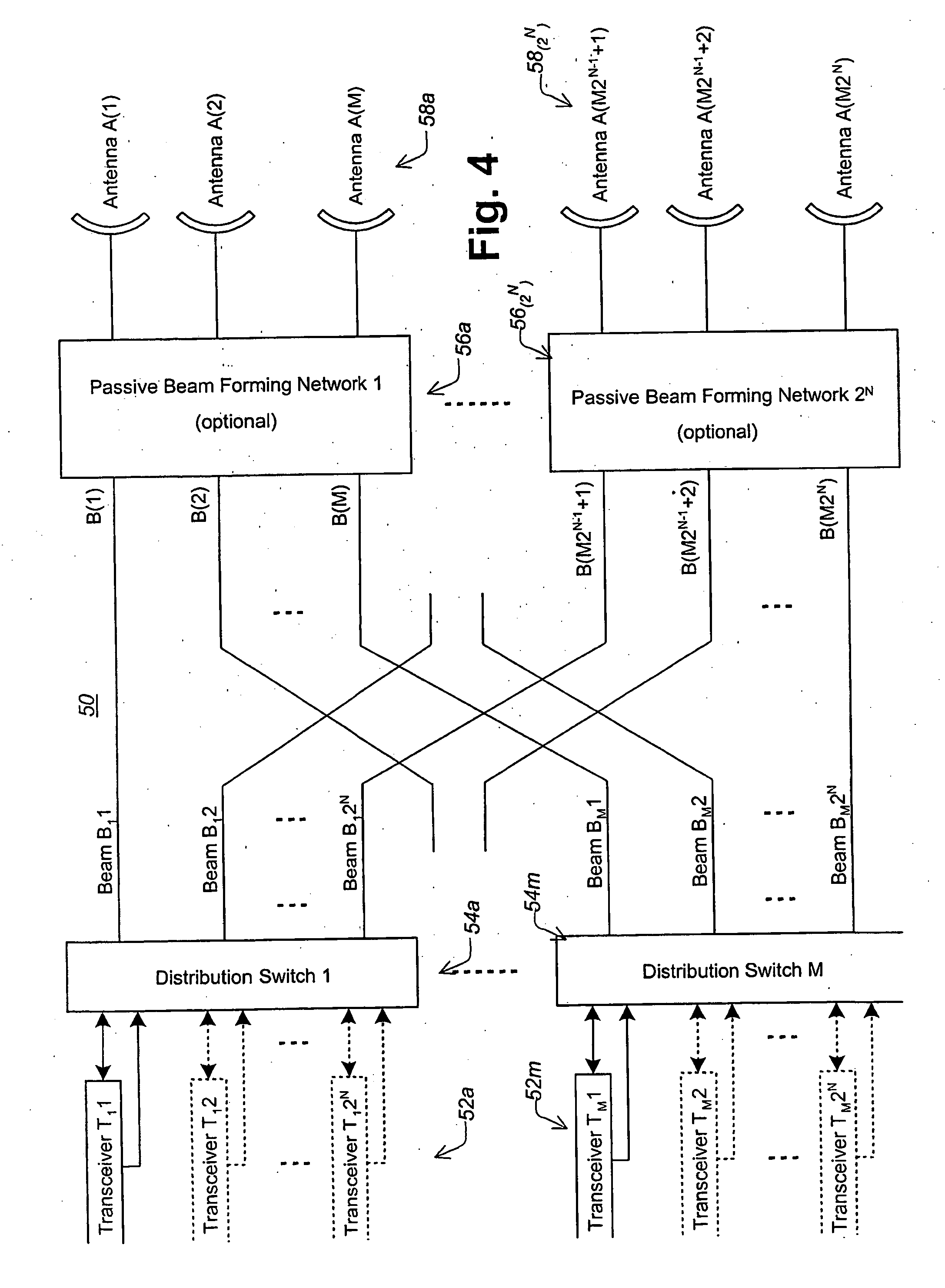
Method and apparatus for beam steering in a wireless communications systems
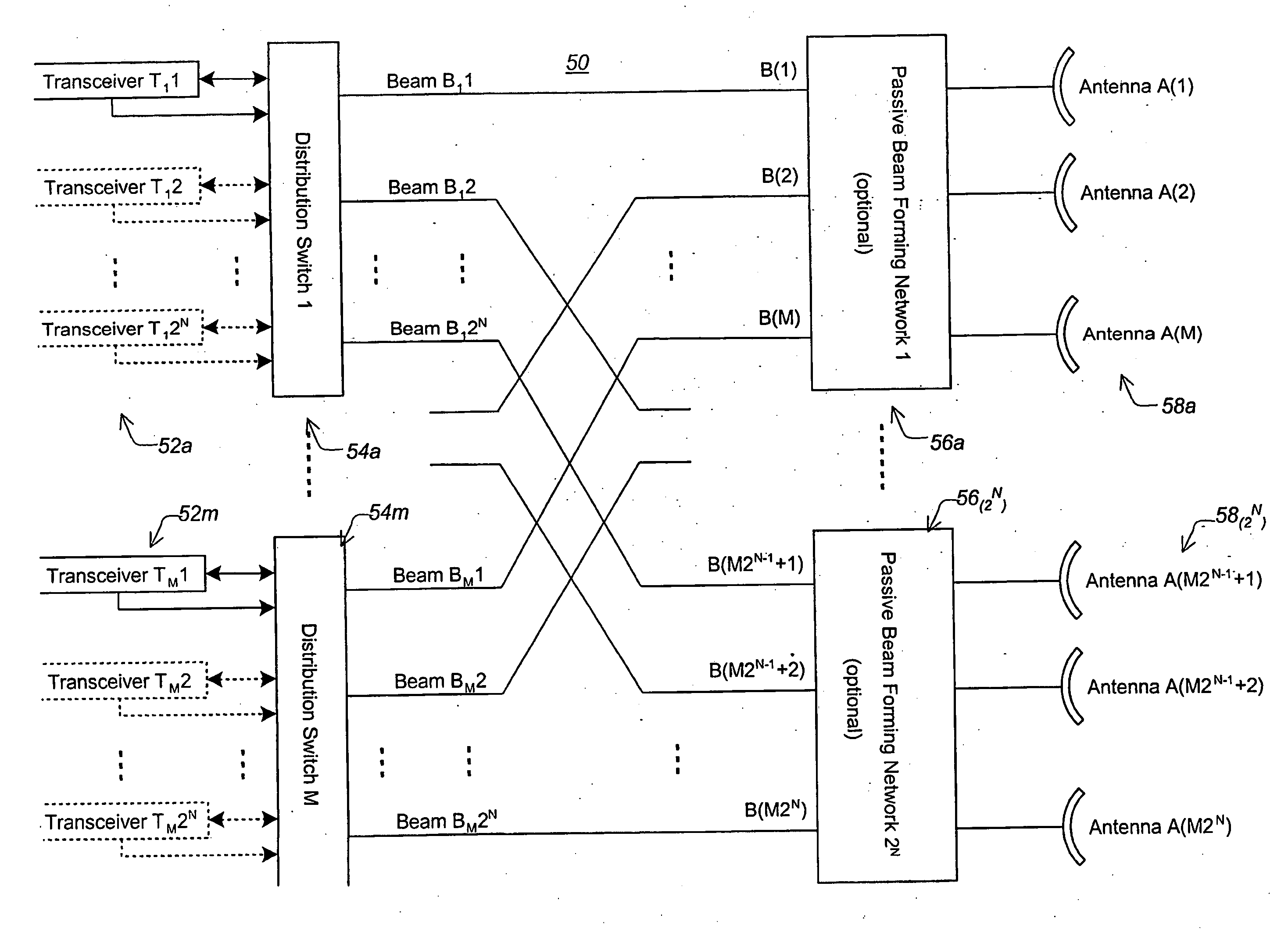
InactiveUS20050148370A1Reduce system costLow costAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentTransceiverCommunications system
A med and apparatus is provided that allows M transceivers to transmit / receive using M2N distinct beams using passive beam steering. This provides for the use of arbitrary narrow beams with a number of transceivers that is a fraction of the number of beams but ensures 360° coverage. In other words it permits significant improvements in the link budget with a minimal rise in the cost of the BS. The apparatus includes M distribution switches applied 2N passive beam forming networks each coupled to M antennas. The method and apparatus ate compatible with TDMA in the downlink and in the uplink.
Owner:REDLINE COMM
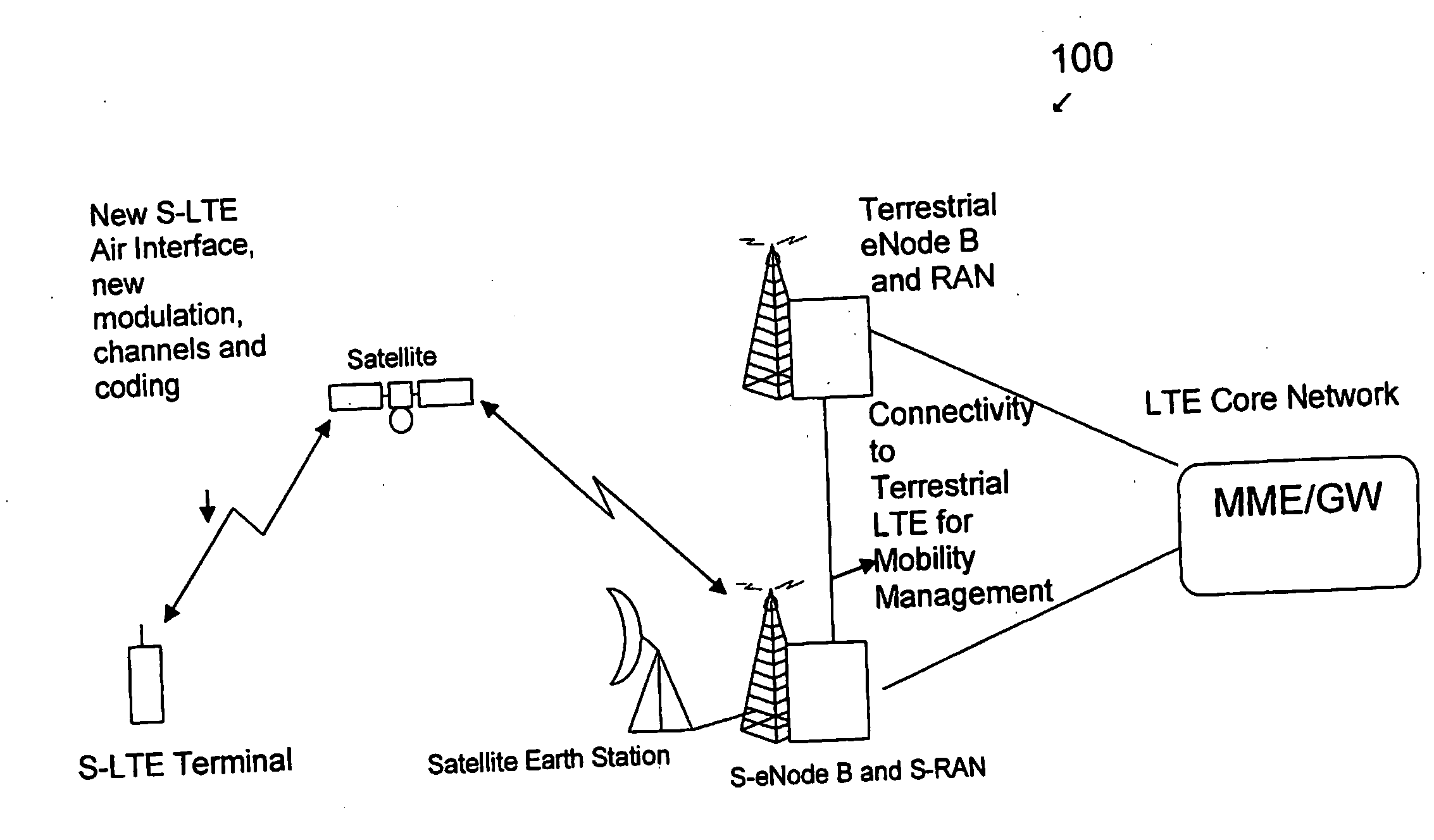
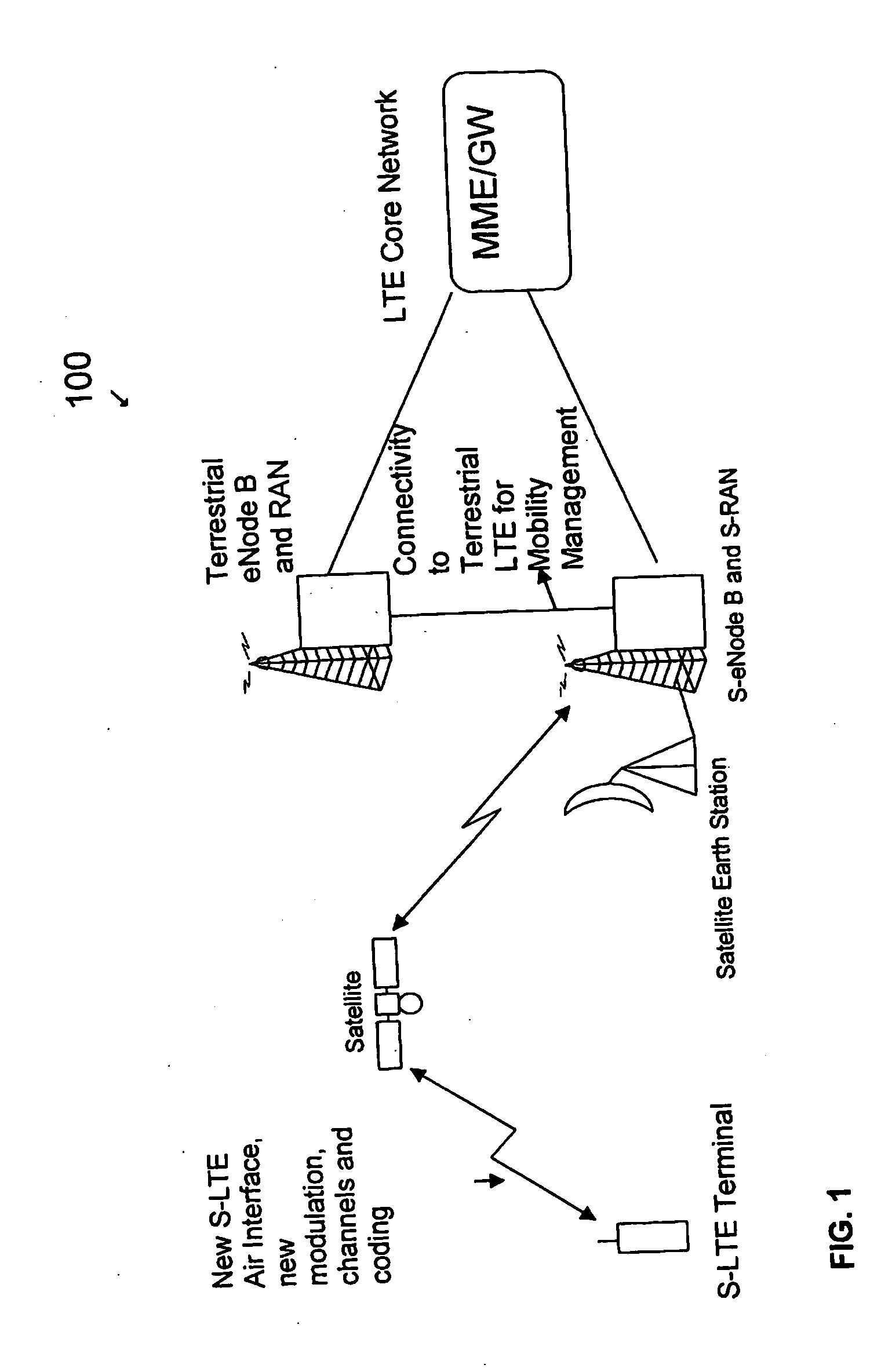
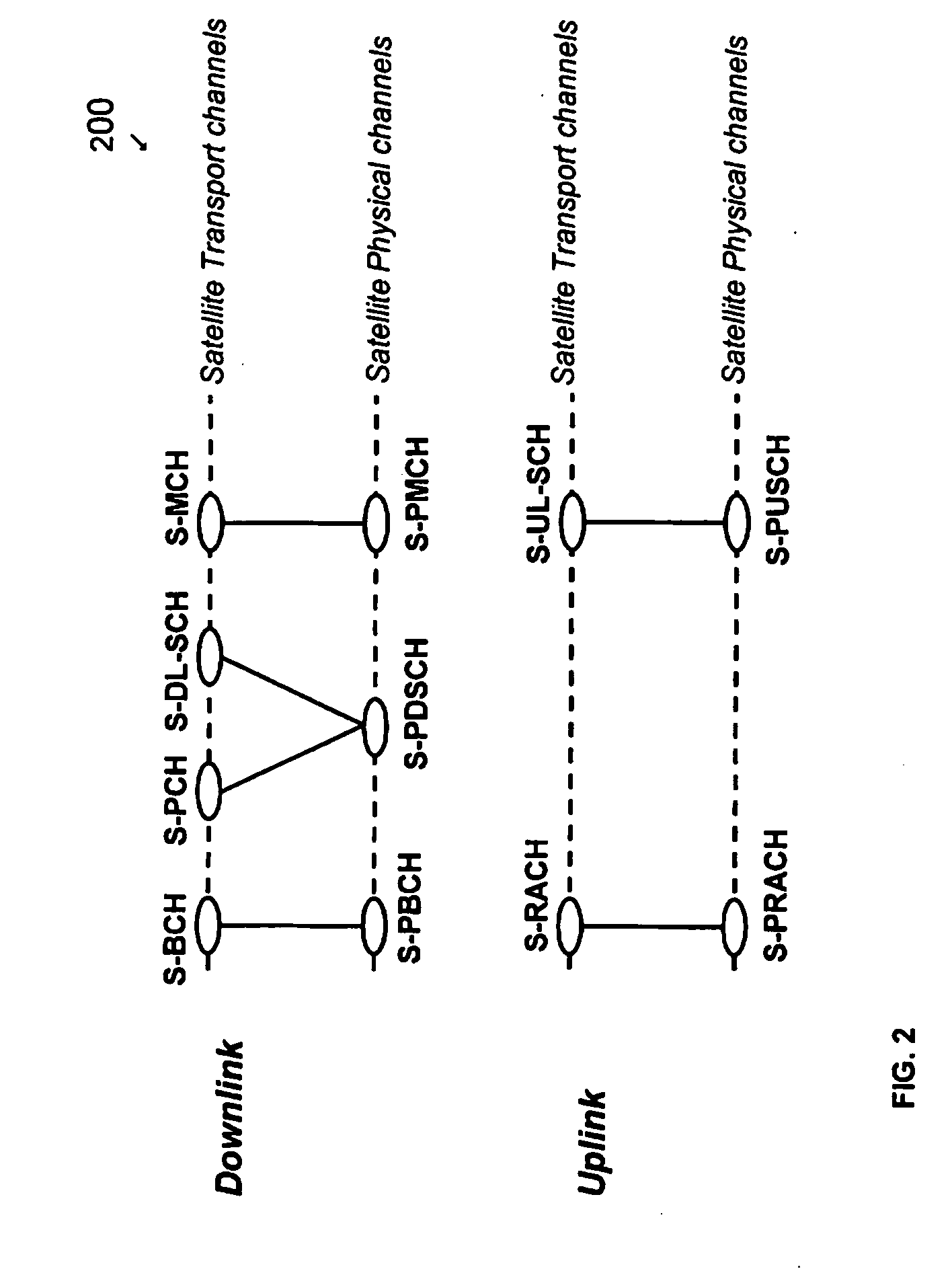
System and method for satellite-long term evolution (s-lte) air interface
InactiveUS20100068993A1Facilitates broadband high-speed dataRadio transmissionDifferentiatorAir interface
An air interface for use with a mobile satellite system that extends the baseline LTE interface modulation and coding from 3GPP. The LTE OFDM and S-FDMA technologies are used in the lowest FDD E-UTRA assigned bandwidth of 1.4 MHz but can be extended up to 7 other bands. The key differentiator for S-LTE from LTE would be the use of 32-ary Amplitude Phase Shift Keying (32-APSK) in the uplink channel for S-FDMA with LDPC and turbo coding and 64-QAM in the downlink channel for OFDM with LDPC and turbo coding. This new mechanism for S-LTE with new combination of coding will allow a robust channel model for S-LTE air interface and will enable the S-LTE air interface to have an efficient link budget. The S-LTE air interface of the present invention can be implemented in 700 MHz, 1.5 GHz, 2.1 GHz and 2.6 GHz bands or any future bands allocated for the specific air interface.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Mechanisms to Facilitate Random Access by Link-Budget-Limited Devices
ActiveUS20170019932A1Sure easyIncrease successConnection managementLower station broadcast interaction arrangementComputer hardwareCurrent cell
Mechanisms enabling link-budget-limited (LBL) devices to more effectively perform random access may include: (1) broadcasting a Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH) configuration index (PCI) reserved for LBL devices; (2) configuring LBL devices to use a PCI that is offset from the conventional PCI of current cell; (3) configuring LBL devices to transmit PRACH messages using an alternative set of subframes, different from conventionally-defined subframe set; (4) configuring LBL devices to transmit PRACH messages on odd frames when the conventional PRACH configuration specifies even frames; (5) configuring LBL devices to generate and use extra PRACH preambles that are not used by non-LBL devices; (6) configuring LBL devices to use group B preambles while non-LBL devices are configured to use group A preambles; and (7) boosting power of a random access response message after an Nth random access failure with preamble conforming to an LBL-reserved pattern of preambles.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and system for diversity using orthogonal frequency/division multiplexing
ActiveUS20080159419A1Improving overall link budgetSynchronisation arrangementTransmission path divisionPropagation timeTime-division multiplexing
A method and system for achieving a link budget improvement in a diverse OFDM radio system by addressing the timing misalignment issue that can occur due to the differences in propagation time in signals between mobile stations and Radio Access Nodes. Timing misalignment is shared or split between the primary path to a primary Radio Access Node and a diverse path to a diverse Radio Access Node. The relative timing offsets between mobile stations are adjusted, the mobile stations are grouped into zones using a variety of different grouping techniques, and the transmission for each mobile station is scheduled, using one or more of a variety of scheduling techniques.
Owner:APPLE INC
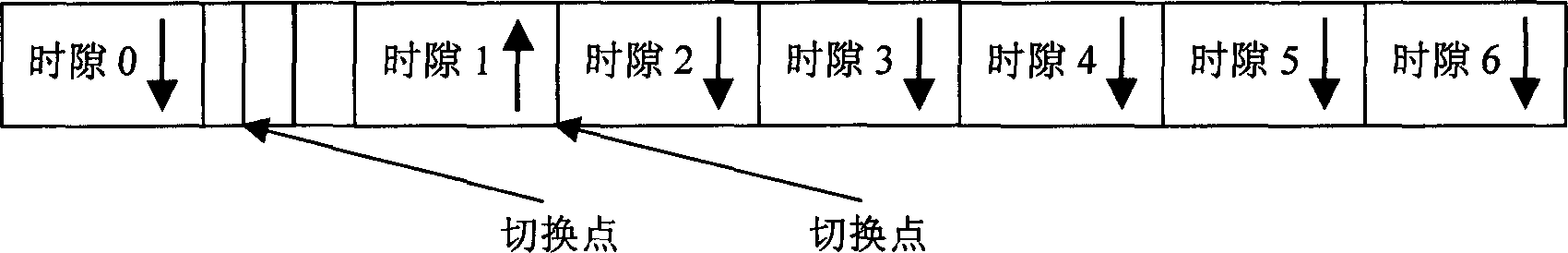
Method for reducing small-region interference in time-division synchronous CDMA accessing system
InactiveCN1816198AOptimizationReduce distractionsNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTD-SCDMAChannel power
Base on different types of service in each region of system, the method allows TD-SCDMA system configures different numbers of time slots for upward and downward services for the region smartly. The said method is only applied to adjacent sub zones in configuration area, where there are different numbers of time slots for upward and downward services. Based on link estimation of investigated user device, and result report for measured channel power of interference signal up or down link, network controller determines whether a time slot is assigned to the investigated user device in order to reduce mutual interference between adjacent sub zones with different service time slots being configured. The network controller also carries out periodic monitoring for switching number inside sub zone in the said two adjacent sub zones in order to overcome influence on channel allocation caused by time varying character of interference signal so as to optimize allocation and raise capacity.
Owner:诺基亚西门子通信系统技术(北京)有限公司
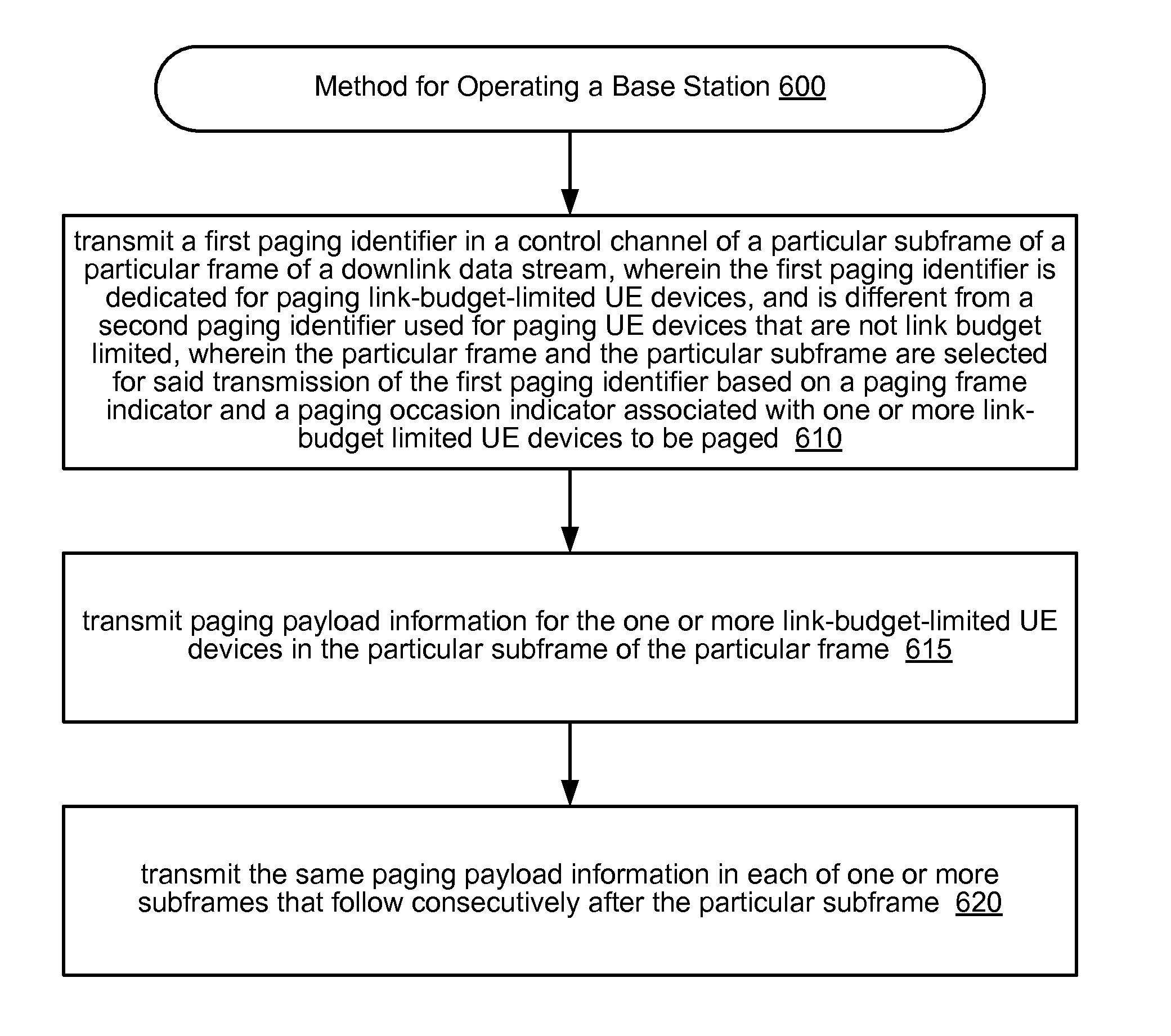
Paging Mechanisms for Link-Budget-Limited User Devices
ActiveUS20160066296A1Increase the number ofGreater improvement in link marginConnection managementPagingUser equipment
Various mechanisms for paging link-budget-limited (LBL) devices are disclosed, including: (1) transmitting paging message with non-conventional paging identifier; (2) transmitting paging message(s) with increased power; (3) repeating transmission of paging message to support combining at receiver. Various mechanisms for UE device to signal LBL status are disclosed, including, transmitting status flag or special value of DRX cycle to network node as part of tracking area update and / or attach request. The network node informs a base station of the device's LBL status as part of a paging message. (The network node may, e.g., assign an S-RNTI to the LBL device from a reserved subset of S-RNTI space.) The base station invokes a paging enhancement mechanism when paging an LBL device. Alternatively, the base station may page UE devices without knowledge of LBL status, e.g., by counting paging attempts for a given UE, and boosting power after the Nth paging attempt.
Owner:APPLE INC
USPL-FSO lasercom point-to-point and point-to-multipoint optical wireless communication
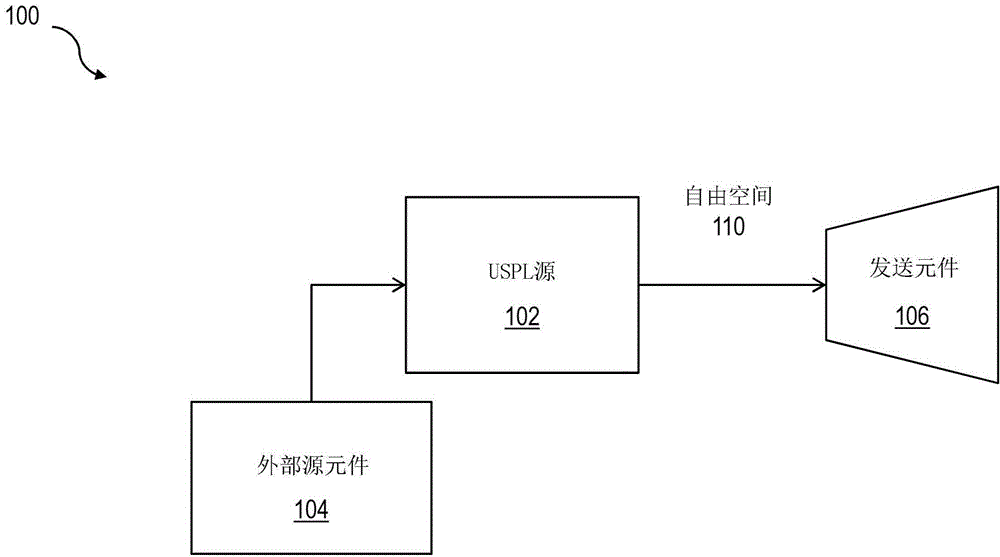
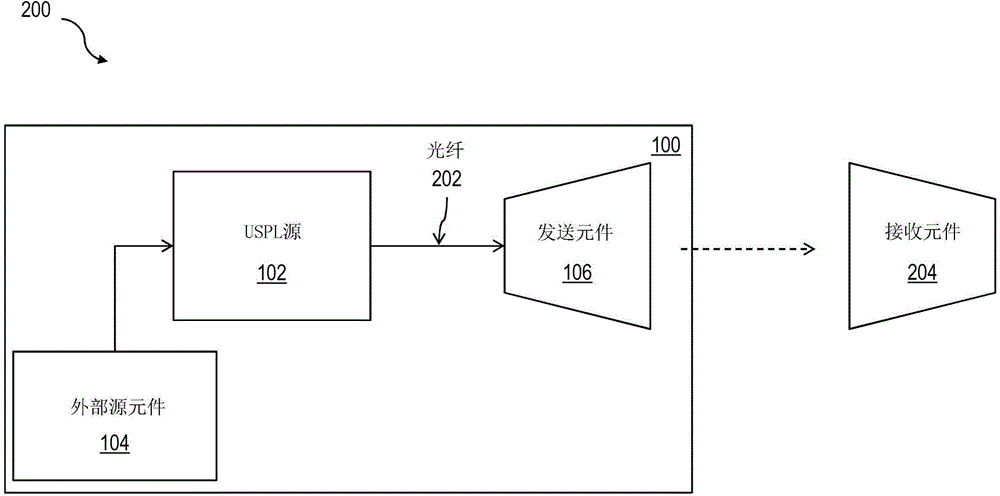
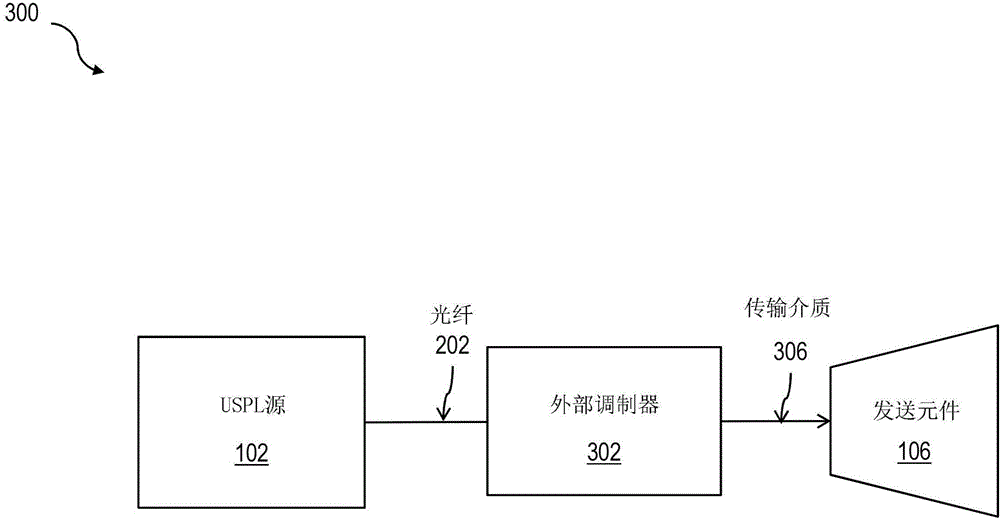
ActiveCN104160640APolarisation multiplex systemsWavelength-division multiplex systemsOptical propagationUltrasound attenuation
Enhancements in optical beam propagation performance can be realized through the utilization of ultra-short pulse laser (USPL) sources for laser transmit platforms, which are can be used throughout the telecommunication network infrastructure fabric. One or more of the described and illustrated features of USPL free space-optical (USPL-FSO) laser communications can be used in improving optical propagation through the atmosphere, for example by mitigating optical attenuation and scintillation effects, thereby enhancing effective system availability as well as link budget considerations, as evidenced through experimental studies and theoretical calculations between USPL and fog related atmospheric events.
Owner:ATTOCHRON
Adaptive beam-steering methods to maximize wireless link budget and reduce delay-spread using multiple transmit and receive antennas
A method and an apparatus for adaptive beam-steering are disclosed. In one embodiment, the method comprises performing adaptive beam steering using multiple transmit and receive antennas, including iteratively performing a pair of training sequences, wherein the pair of training sequences includes estimating a transmitter antenna-array weight vector and a receiver antenna-array weight vector.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
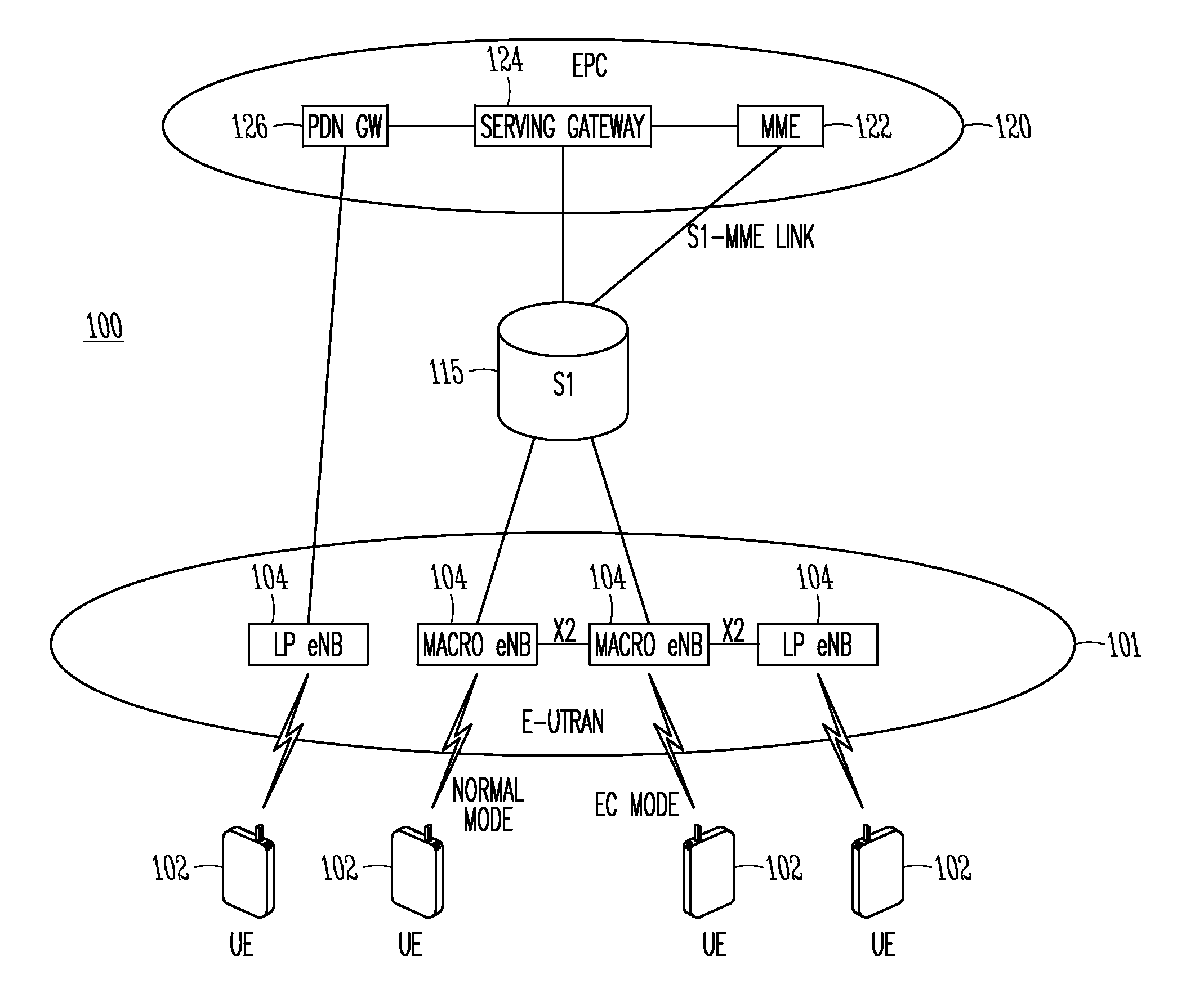
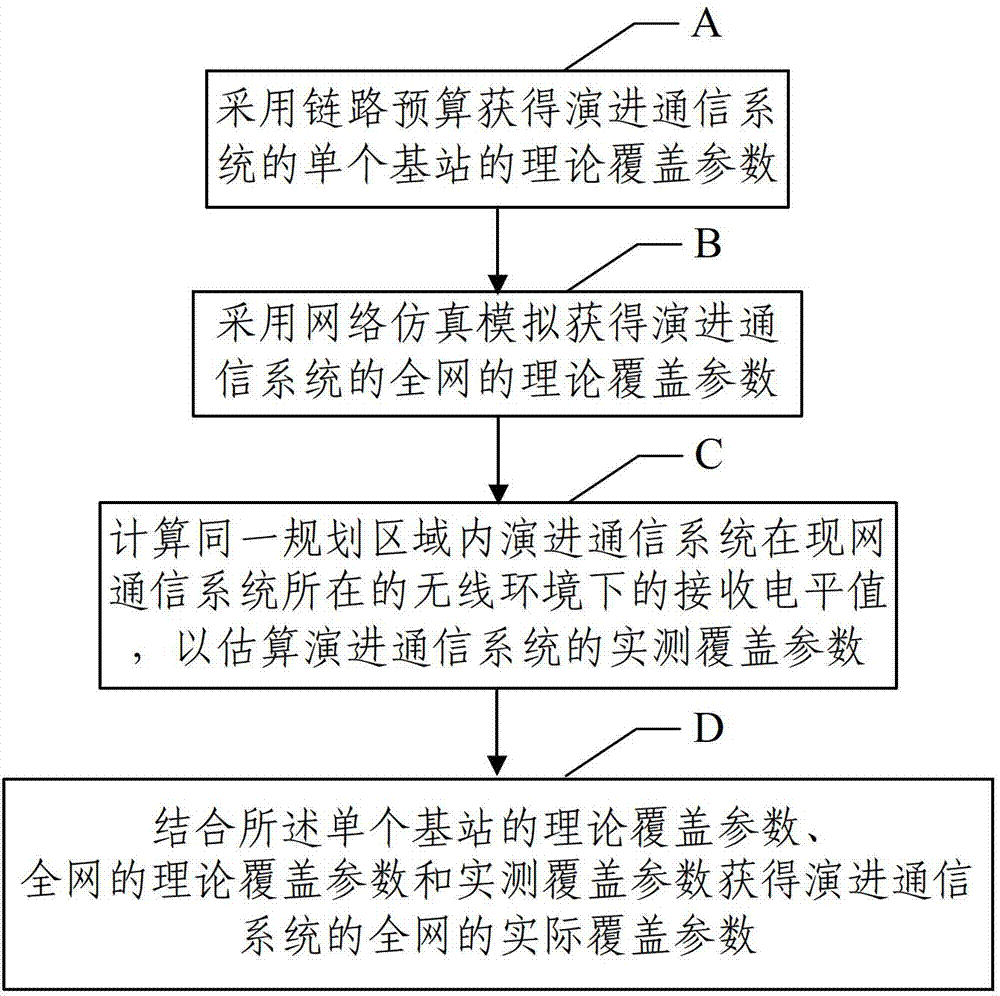
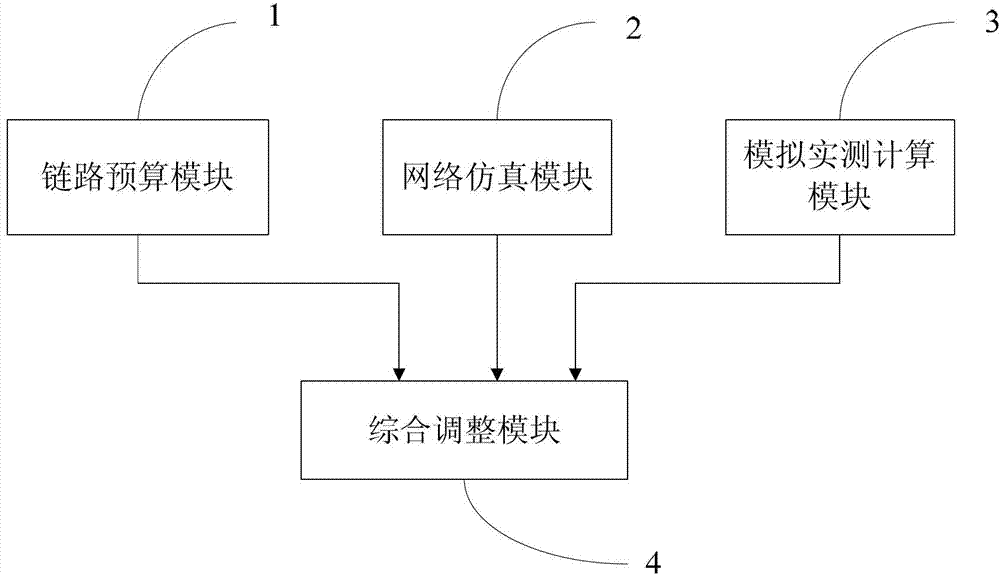
Network coverage planning method and device of evolution communication system
The invention provides a network coverage planning method and device of an evolution communication system. The method comprises the steps of: obtaining a theoretical coverage parameter of a single base station of the evolution communication system by using a link budget; obtaining the theoretical coverage parameters of the whole network of the evolution communication system by using network analogue simulation; calculating a reception level value of the evolution communication system in a same planning area under a wireless environment of the current network communication system by means of measurement and report data of a terminal in the current network communication system corresponding to the evolution communication system and the relation between the current network communication system and the reception level of the evolution communication system so as to estimate simulated actual measurement coverage parameters of the evolution communication system; and planning the coverage parameters of the whole network of the evolution communication system according to the theoretical coverage parameter of the single base station, the theoretical coverage parameters of the whole network and the simulated actual measurement coverage parameters. With the adoption of the invention, the network coverage plan is more accurate so that the network established is closer to an expected coverage target.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Ran paging mechanism to enable enhanced coverage mode
Devices and methods of enhanced coverage (EC) paging are generally described. An evolved Node-B (eNB) may transmit multiple EC paging messages to user equipment (UE) over at least one paging cycle. Each EC paging message may contain the same paging information. The UE may combine the individual EC paging messages to achieve a predetermined link budget and subsequently may decode the EC combined paging message to determine whether the combined paging message is directed to the UE. The EC paging messages may contain information for more than one UE and a legacy P-RNTI or a specific P-RNTI for EC mode UEs. The EC paging messages may be transmitted in legacy occasions over several paging cycles or non-legacy paging occasions over one or more paging cycles. The EC paging messages may be transmitted in continuous or non-continuous subframes in a particular paging cycle.
Owner:APPLE INC
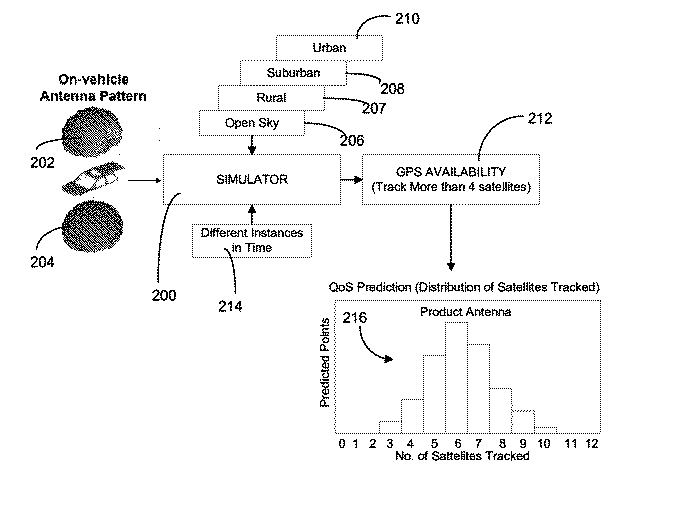
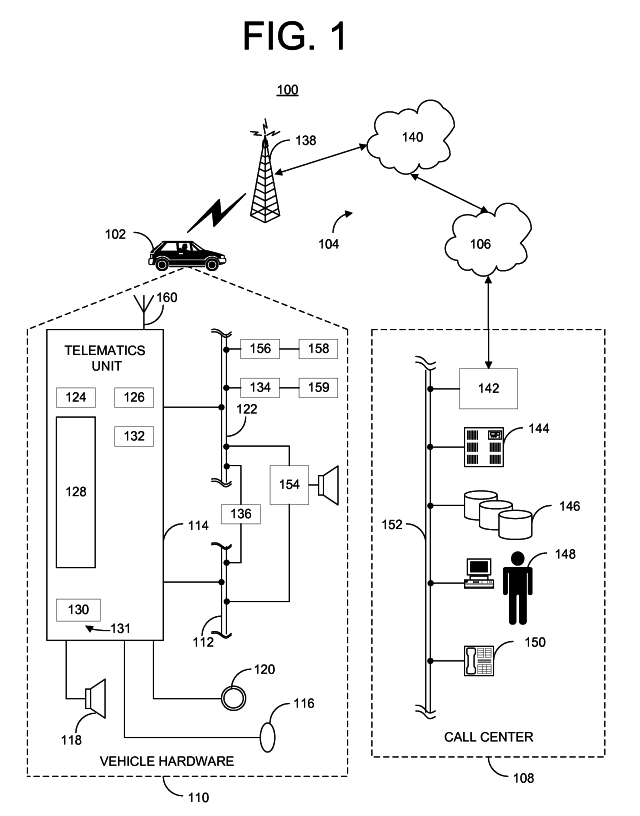
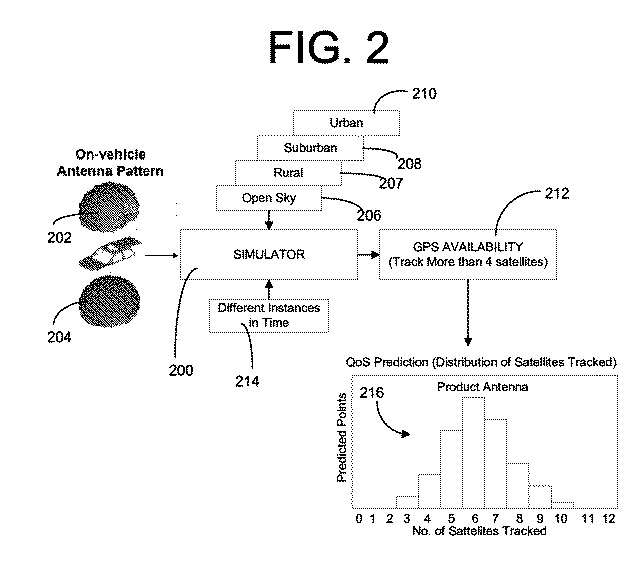
Methods and Simulation Tools for Predicting GPS Performance in the Broad Operating Environment
InactiveUS20090243914A1Good choiceAnalogue computers for electric apparatusSatellite radio beaconingAntenna radiation patternsGps receiver
To facilitate GPS hardware selection and evaluate performance of vehicle integrated GPS hardware, including various types of GPS antennas and receivers, within different vehicle operating environments, embodiments of the invention are used to provide a simulator which does not require physical GPS hardware to simulate GPS system performance. Preferably, the simulator randomly generates one or more GPS system link budget variables, within predetermined performance bounds, in order to predict GPS system performance in a specific vehicle operating environment for a given antenna radiation pattern and / or GPS receiver. The simulator employs a Monte Carlo technique to evaluate the GPS system performance based on generated pools of link budget variables.
Owner:GENERA MOTORS LLC
Extending wireless communication RF coverage inside building
ActiveUS7406300B2Prevent desensitizationAvoid feedbackPower managementResonant long antennasTransceiverCommunications system
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
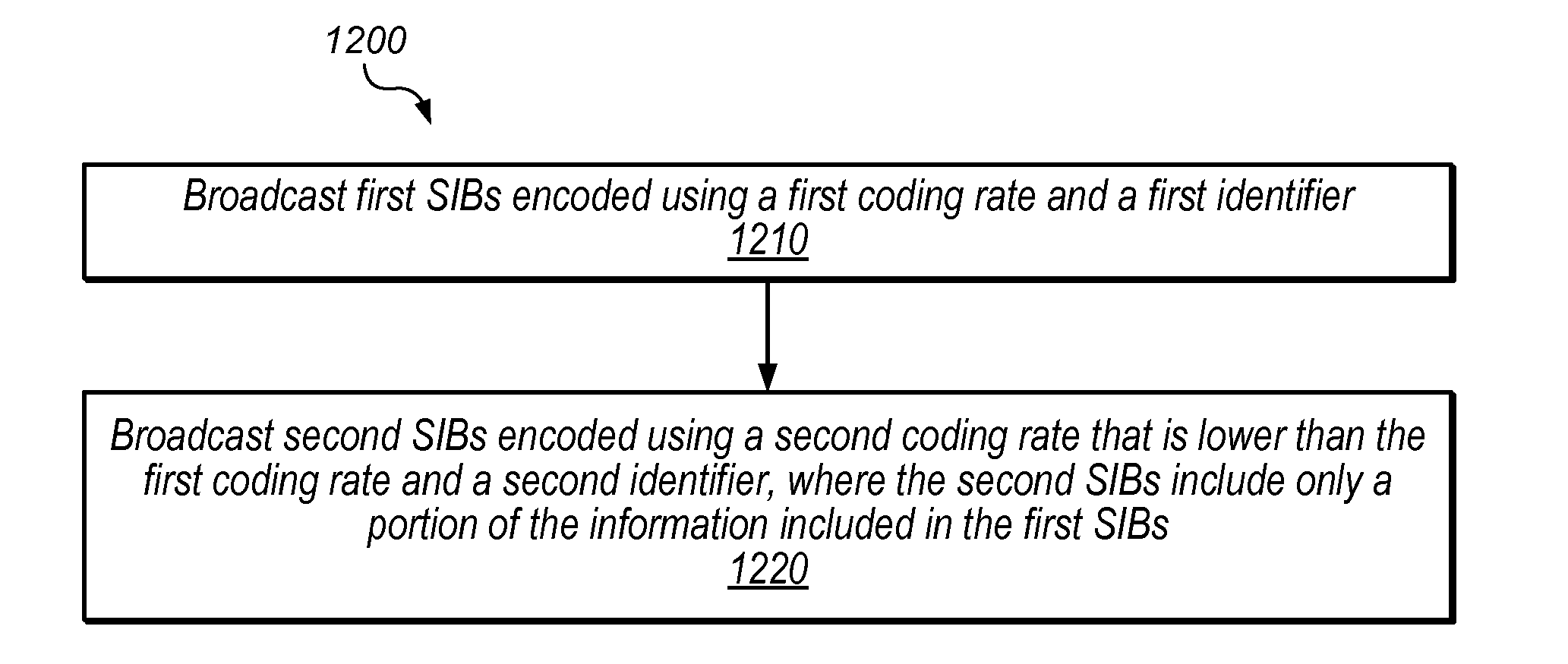
Compressed System Information for Link Budget Limited UEs in a Radio Access Network
ActiveUS20160150506A1Limited budgetAssess restrictionWireless commuication servicesRadio access technologyRadio access network
Techniques are disclosed relating to broadcasting and receiving system information in a radio access network (RAN). In one embodiment, a base station includes at least one antenna, at least one radio, configured to perform cellular communication using a radio access technology (RAT), and one or more processors coupled to the radio. In this embodiment, the base station is configured to broadcast first system information blocks (SIBs) encoded using a first coding rate and a first identifier. In this embodiment, the base station is also configured to broadcast second SIBs encoded using a second coding rate that is lower than the first coding rate and a second identifier. In this embodiment, the second SIBs include only a portion of the information included in the first SIBs and the second SIBs are usable by user equipment devices (UEs) having a limited link budget to determine access parameters for the base station.
Owner:APPLE INC
Enhanced Paging Schemes and Connected-State DRX
For paging user devices that are link budget limited (LBL), a base station transmits a special ID that is used by said devices to identify a paging frame and / or a paging occasion. When transmitting a paging message for an LBL device, the base station may use: (a) larger aggregation and larger CFI (than conventionally allowed) and (b) a larger number of resource blocks (than conventionally allowed) for paging payload. If paging messages for LBL devices saturate the paging frame capacity, the base station may allocate a plurality of special IDs. If paging messages for LBL devices and / or other data transfers saturate network capacity, at least a subset of the LBL devices may be directed to enter a connected-state discontinuous reception (DRX) mode, wherein those devices will remain in connected mode and periodically check for resource allocations. Paging payload information may be repeatedly transmitted in successive subframes, to support soft combining.
Owner:APPLE INC
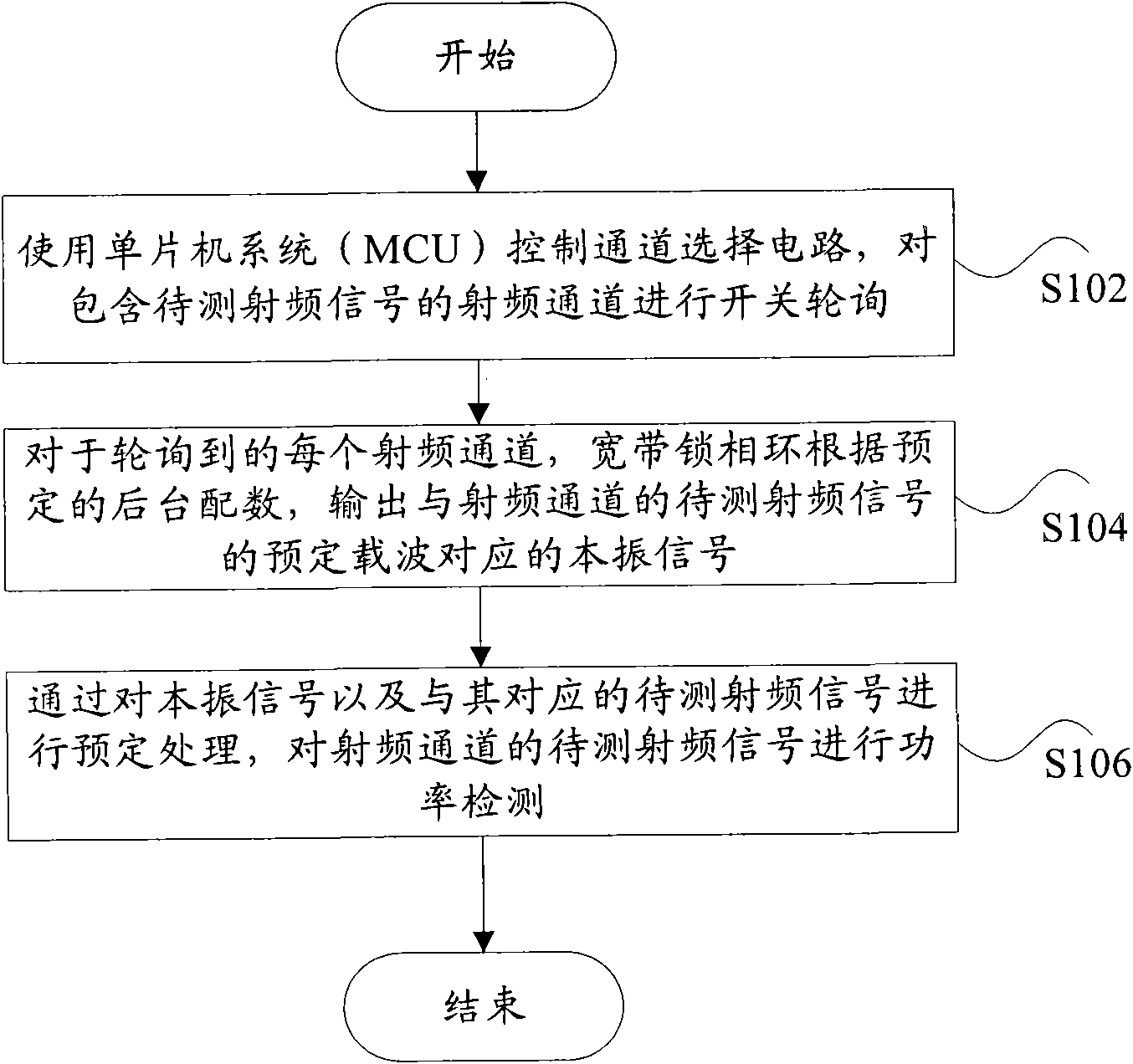
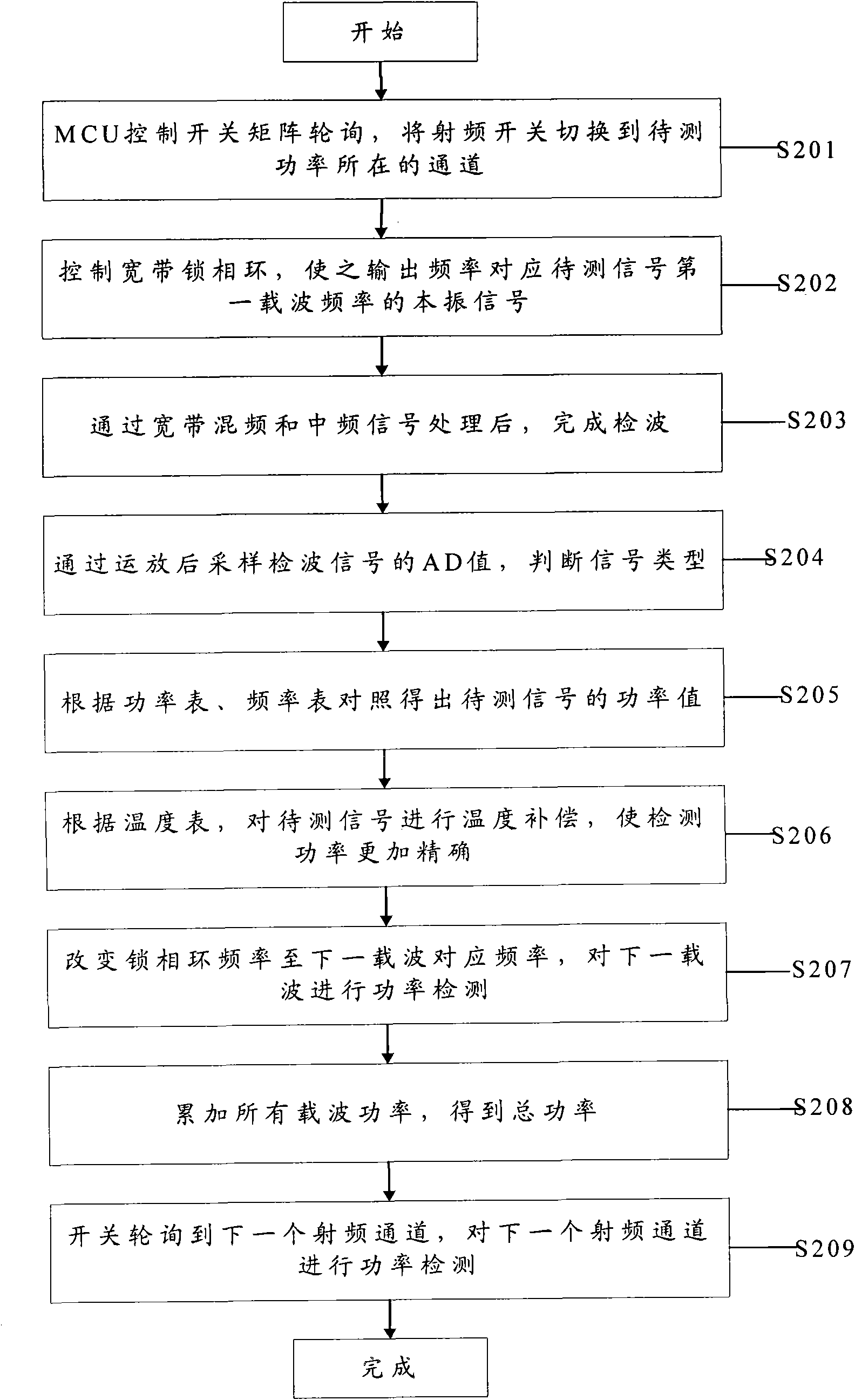
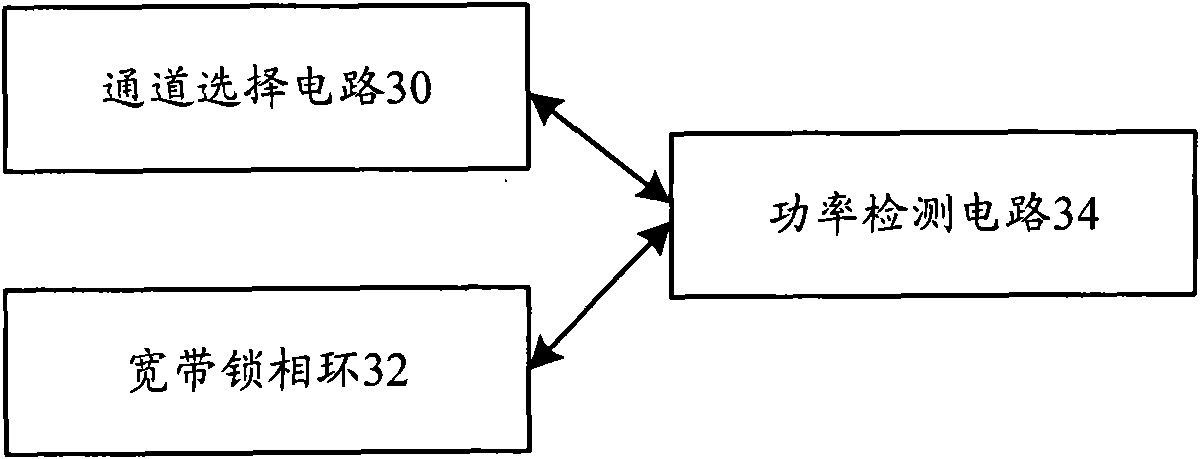
Method and device for detecting broadband power
ActiveCN101635943AMeet the needs of wideband detectionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementMulti bandLocal oscillator signal
The invention discloses a method and a device for detecting broadband power. The method comprises the following steps: using a channel selection circuit to perform switch polling on a radio-frequency channel comprising radio-frequency signals to be measured; for each polled radio-frequency channel, according to the scheduled background number, outputting local oscillator signals corresponding to scheduled carriers of the radio-frequency signals to be measured of the radio-frequency channel by a broadband phase-locked loop; and performing power detection on the radio-frequency signals to be measured of the radio-frequency channel by performing scheduled processing on the local oscillator signals and the radio-frequency signals to be measured corresponding to the local oscillator signals. Through the technical scheme, the detection of a multi-band broadband is achieved, the development cost and the link budget are saved, and the precision and the application range of the power detection are effectively improved.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Random Access Procedures for Link Budget Constrained Wireless Devices
ActiveUS20160366705A1Raise the possibilityHigh strengthWireless communicationComputer scienceLink budget
This disclosure relates to accommodating link budget constrained wireless devices performing random access procedures. A base station may detect a preamble message from a wireless device. It may be determined that the preamble message is received from a link budget constrained wireless device. Characteristics of a response message may be selected based at least in part on determining that the preamble message is received from a link budget constrained wireless device. The response message may be transmitted to the link budget constrained wireless device using the selected characteristics.
Owner:APPLE INC
System and method for reception mode switching in dual-carrier wireless backhaul networks
ActiveUS20150382214A1Mitigate disadvantage of knownMitigate of methodError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCarrier signalEngineering
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
System for signal transmission by magnetic induction in a near-field propagation mode, with antenna tuning for link budget optimization
ActiveUS8452233B2Electric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsEngineeringLC circuit
Owner:NXP BV
Transmission of Uplink Control Information for Link-Budget-Limited Devices
ActiveUS20160014810A1Raise the possibilityError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityControl channelUser equipment
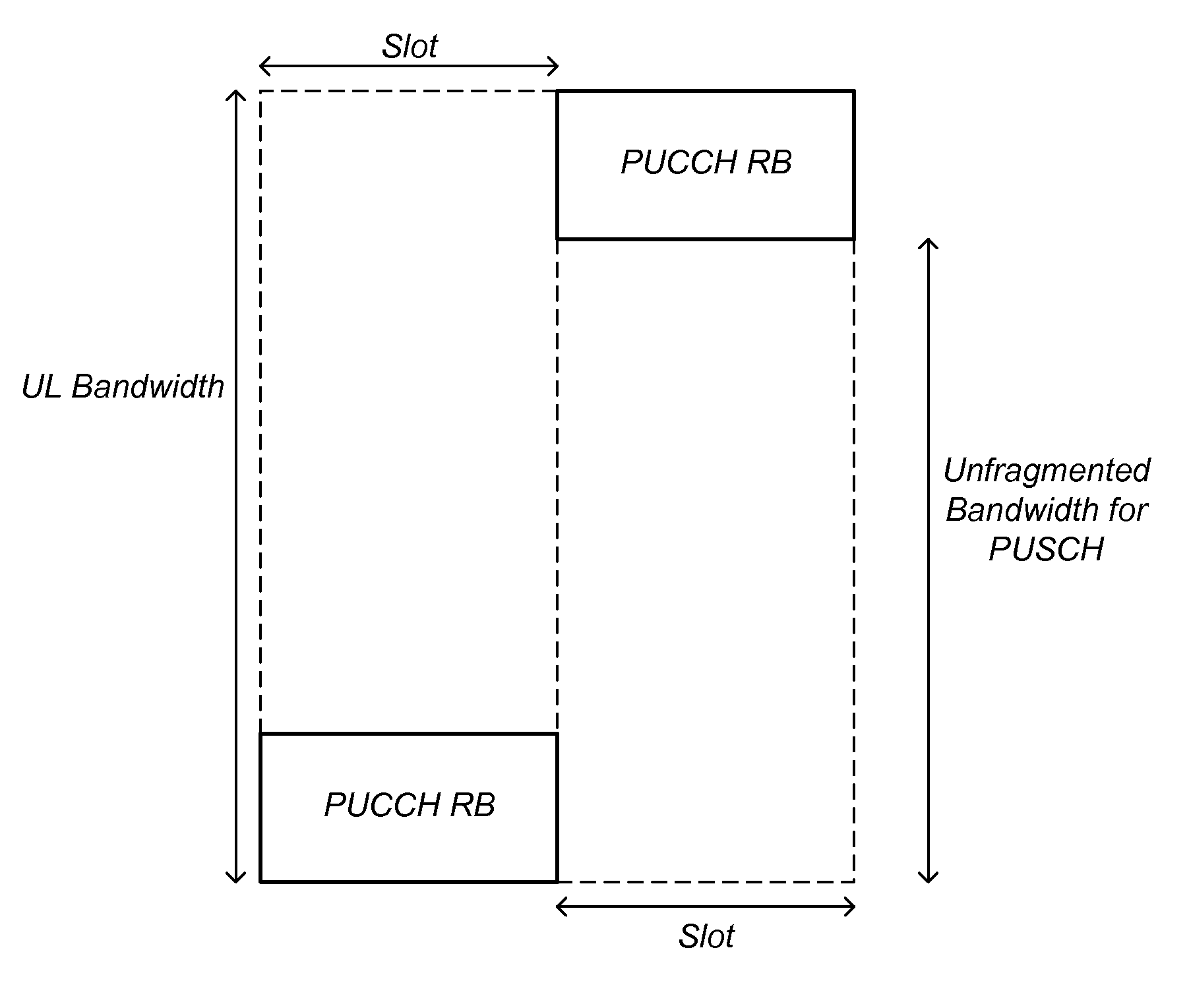
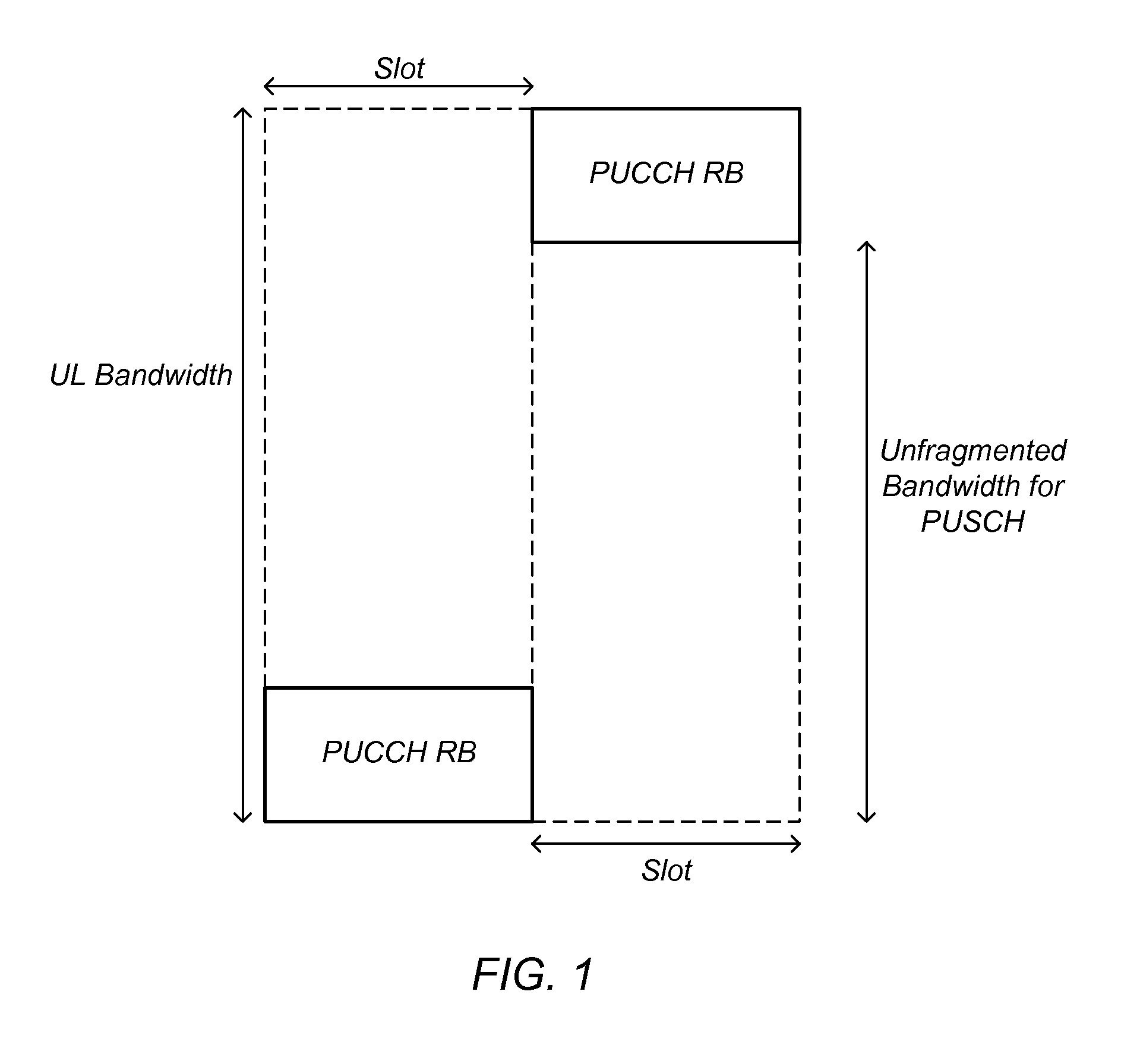
Mechanisms are disclosed for improved transmission of uplink control information by a user equipment (UE) that is link budget limited. In one embodiment, the UE transmits a message to the base station indicating that the UE is link budget limited. In response to the message, the base station sends an uplink grant to the UE, enabling the UE to transmit uplink control information on the physical uplink shared channel (PUSCH) instead of on the Physical Uplink Control Channel (PUCCH). In another embodiment, the base station sends an uplink grant to a link-budget-limited UE each time downlink traffic is transmitted to the UE, enabling the UE to send ACK / NACK feedback on the PUSCH instead of the PUCCH. In another embodiment, the UE transmits a scheduling request (SR) to the base station as part of a random access procedure, enabling the SR to be transmitted on the PUSCH instead of the PUCCH.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and apparatus for constant throughput rate adaptation
InactiveUS6859465B1Time-division multiplexTransmitter/receiver shaping networksRate adaptationFlag sequence
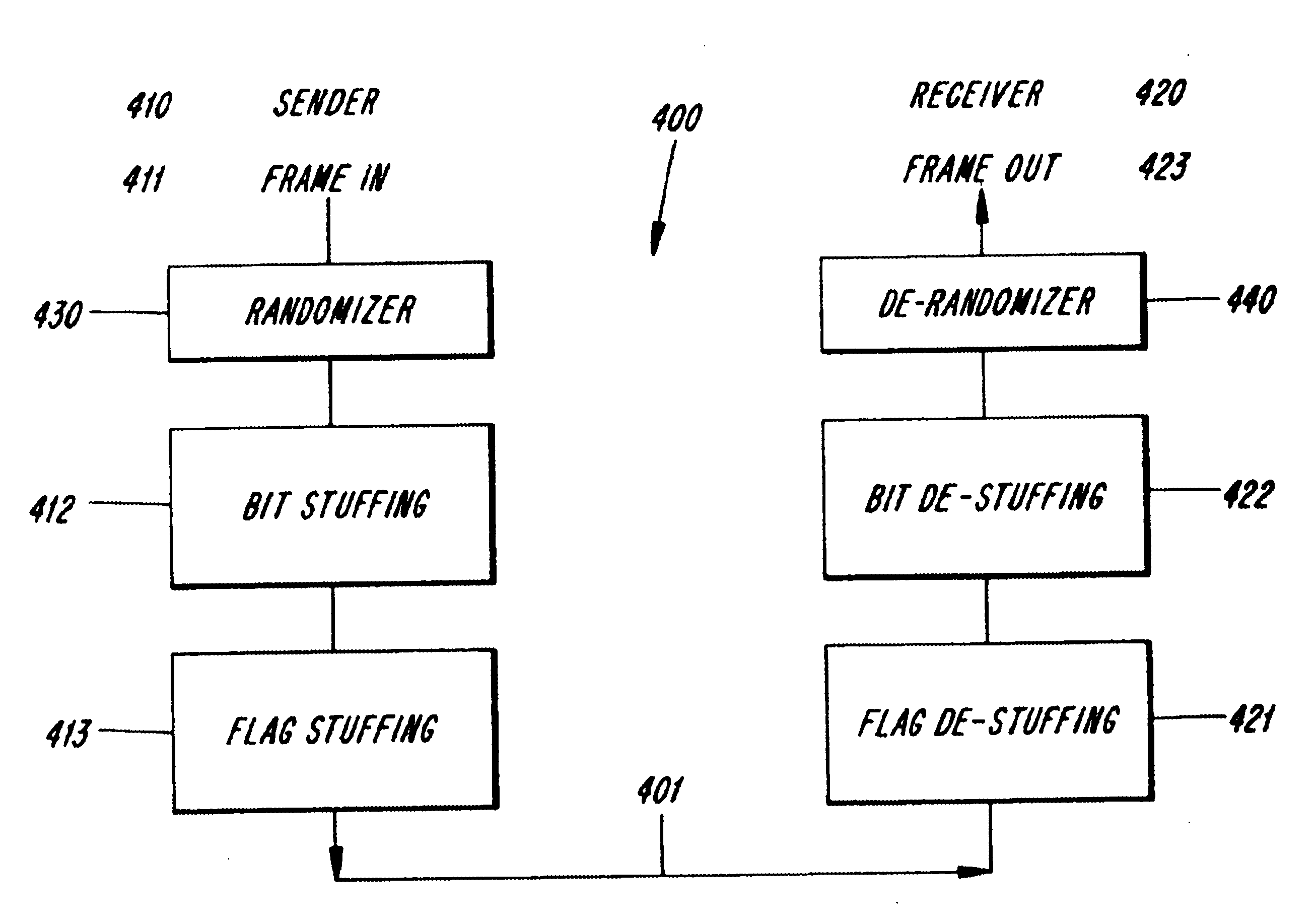
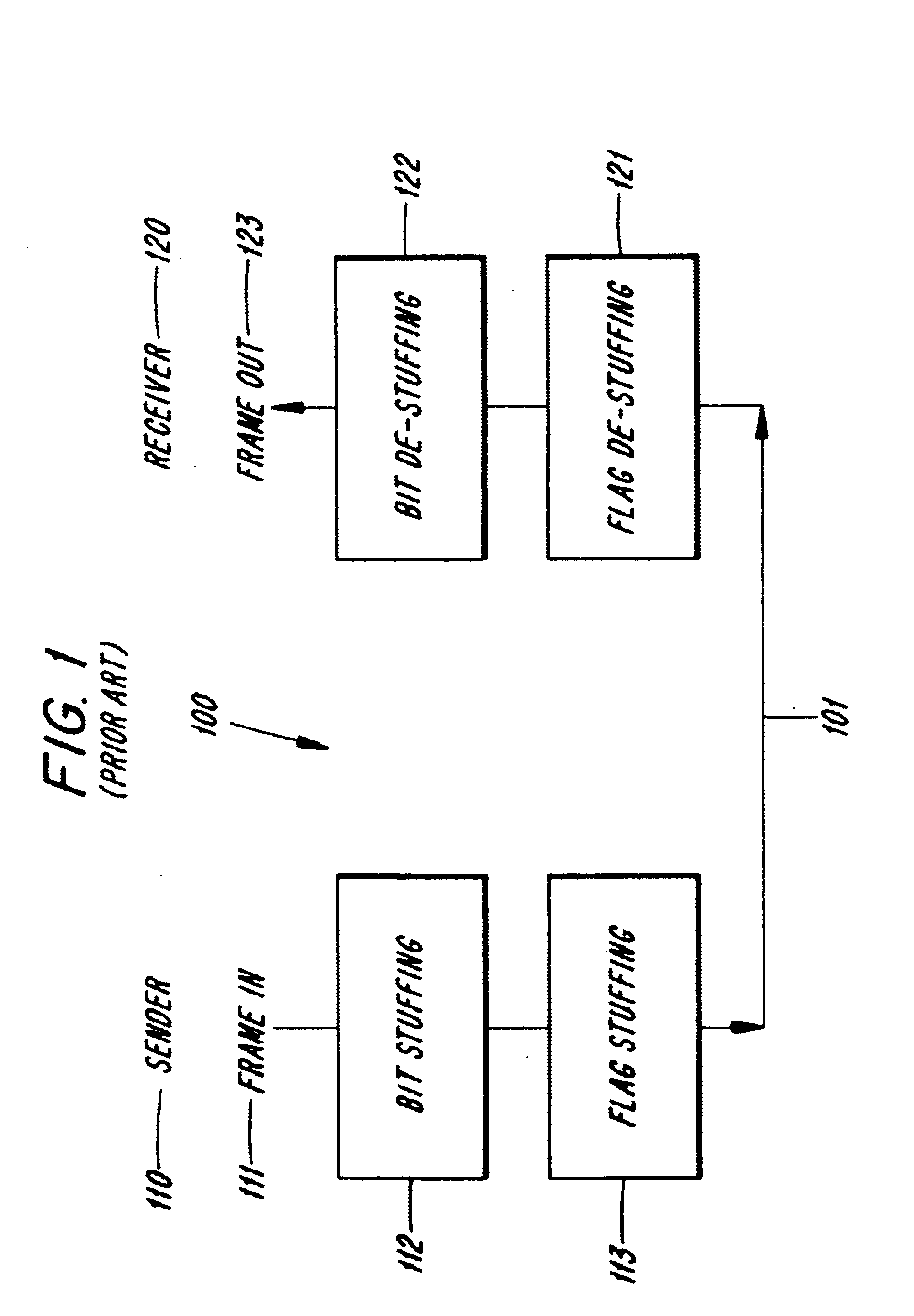
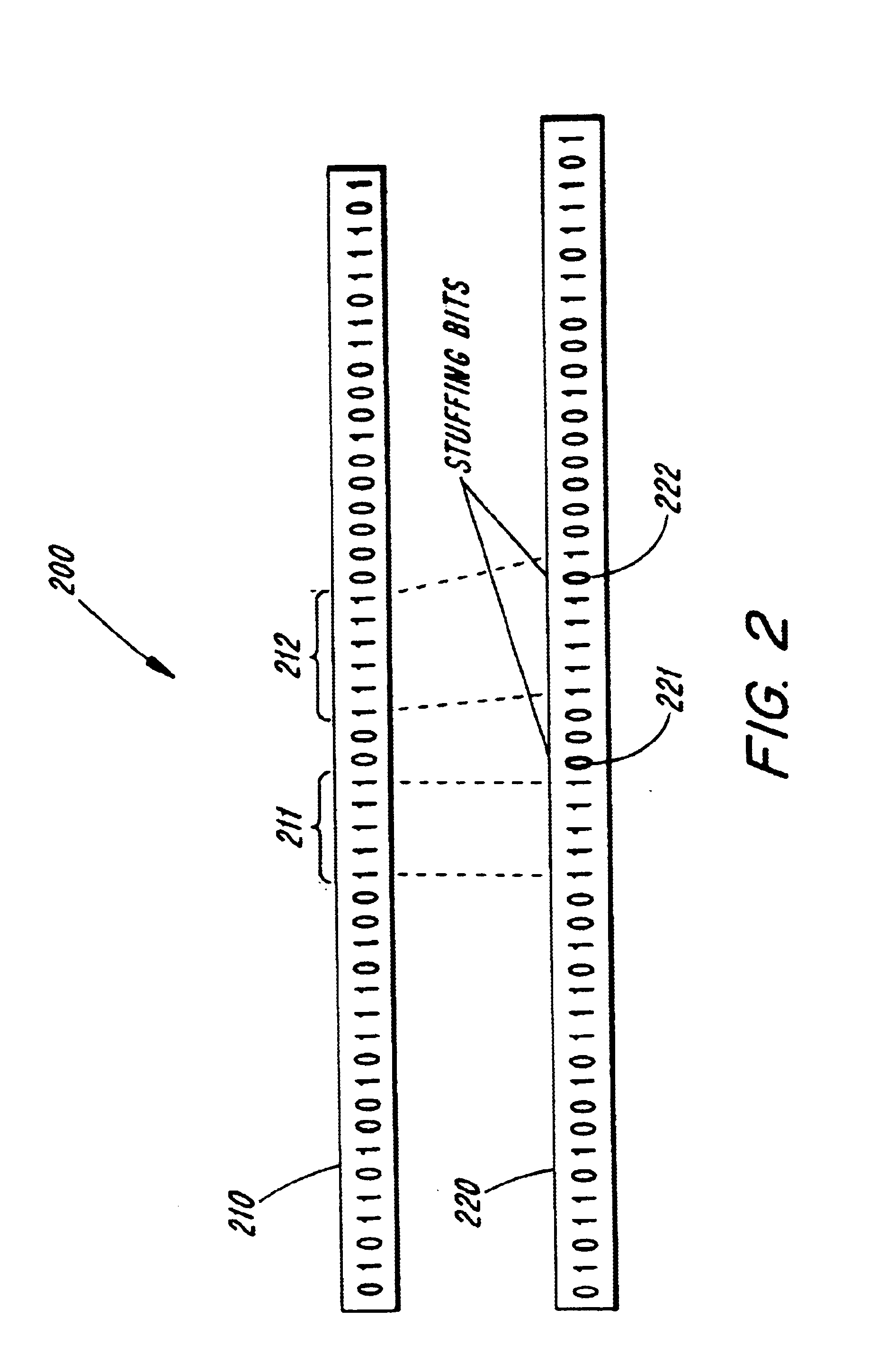
A method and apparatus is described for providing rate adaptation between a first node and a second node in a data communication environment employing bit stuffing and having a link budget of B bits per second. One or more N-sized frames of user data are randomized at the first node according to a predetermined random sequence to produce randomized N-sized frames which are then de-randomized at the second node according to the random sequence. N is the size of the N-sized frames in bits. Occurrences of a flag sequence related event is detected for in the N-sized frames after randomizing, and up to n bits are inserted in the N-sized frames according to a bit stuffing protocol. By performing randomizing before inserting, n and N are selected such that n+N does not exceed B. The bits are then removed such that de-randomizing can be performed. Randomizing includes combining N-sized frames with a random sequence and de-randomizing includes uncombining the N-sized frames with the random sequence. Alternatively, one or more random sequences may be used in randomizing and de-randomizing. Inserting up to n bits further includes determining a distribution of stuffing bits n according to h(n,N) for the N-sized frames such that n and N are selected so that n+N does not exceed B.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Paging Mechanisms for Link-Budget-Limited User Devices
ActiveUS20170135067A1Increase the number ofGreater improvement in link marginConnection managementPagingUser equipment
Various mechanisms for paging link-budget-limited (LBL) devices are disclosed, including: (1) transmitting paging message with non-conventional paging identifier; (2) transmitting paging message(s) with increased power; (3) repeating transmission of paging message to support combining at receiver. Various mechanisms for UE device to signal LBL status are disclosed, including, transmitting status flag or special value of DRX cycle to network node as part of tracking area update and / or attach request. The network node informs a base station of the device's LBL status as part of a paging message. (The network node may, e.g., assign an S-RNTI to the LBL device from a reserved subset of S-RNTI space.) The base station invokes a paging enhancement mechanism when paging an LBL device. Alternatively, the base station may page UE devices without knowledge of LBL status, e.g., by counting paging attempts for a given UE, and boosting power after the Nth paging attempt.
Owner:APPLE INC
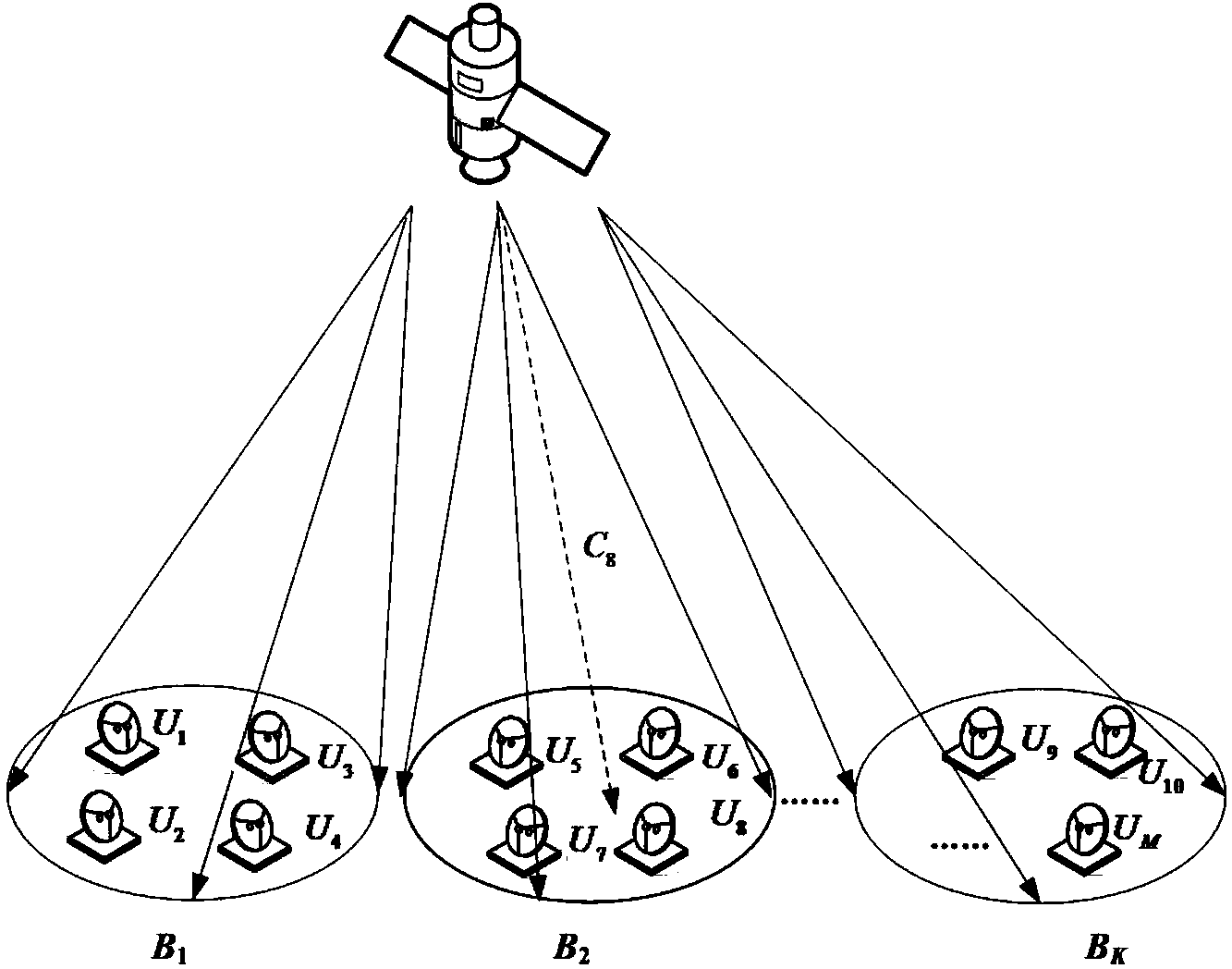
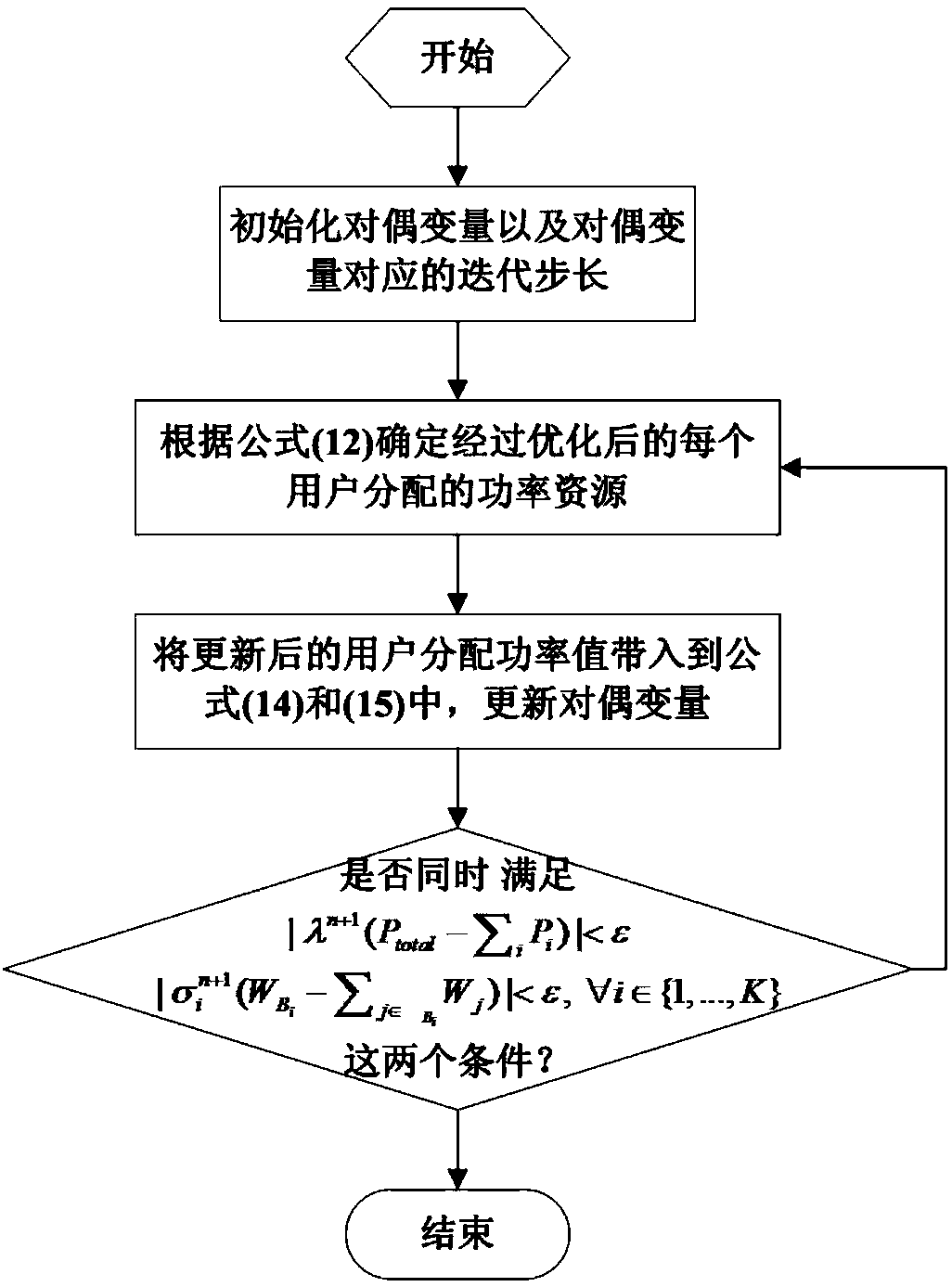
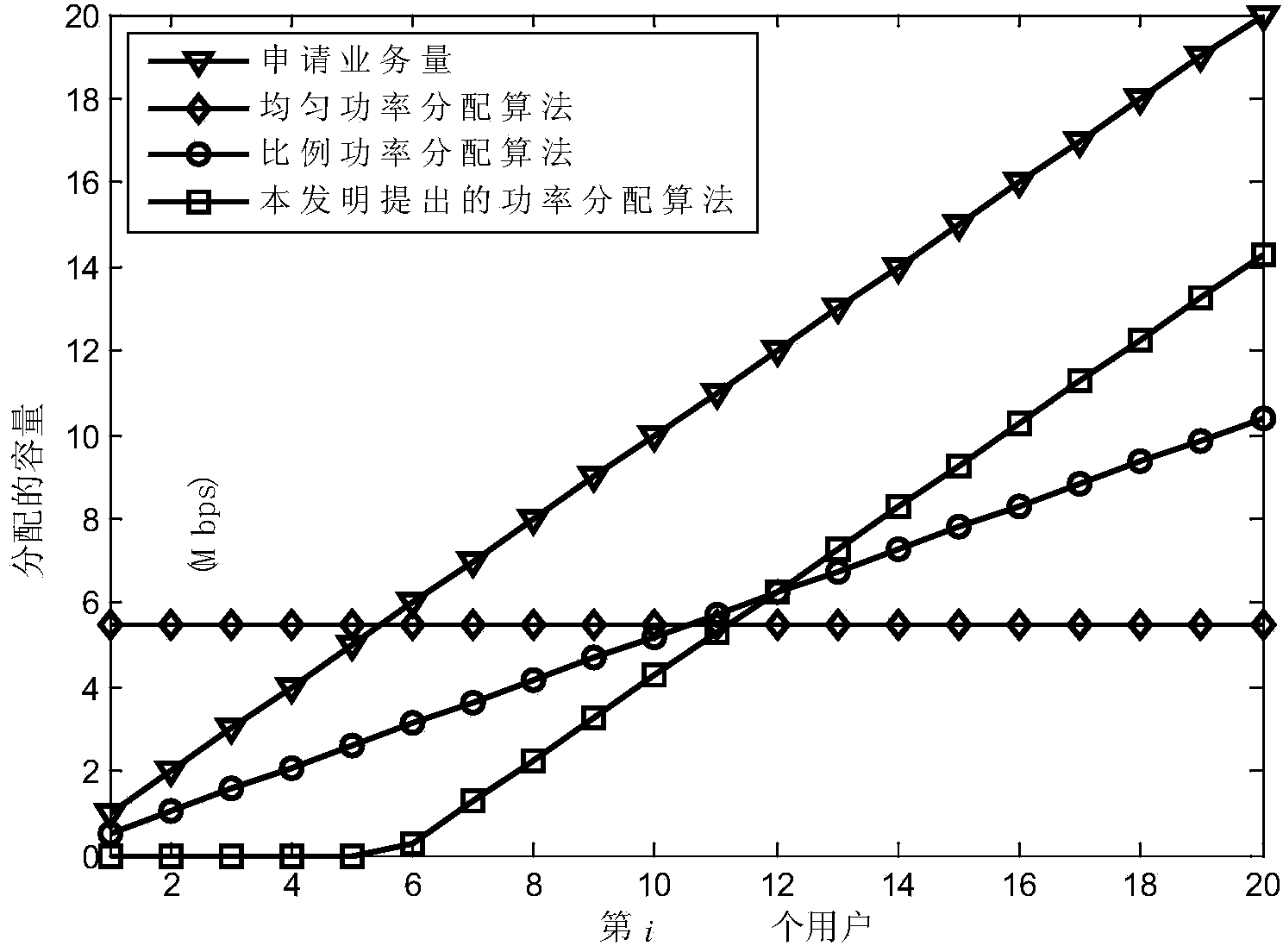
Power distribution method in satellite communication system
ActiveCN103857027AAchieve fairnessImprove practicalityPower managementCommunications systemDistributed power
The invention discloses a power distribution method in a satellite communication system. The power distribution method comprises the steps of firstly, determining the relation between the capacity of each user and distributed power according to a satellite link budget equation in the satellite communication system; then modeling the power distribution problem in the satellite communication system into a non-linear convex optimization problem with constraints; finally, on the basis of the duality theorem, obtaining the optimal power distribution scheme through solution of the duality problem of the optimization problem. Compared with a traditional uniform or proportional power distribution method, the power distribution method has the advantage that on the premise that the whole system capacity is kept unchanged, the fairness of power distribution to each user is improved; in addition, due to the fact that the satellite link budget equation is adopted to calculate the capacity distributed to each user, the distribution result has higher practicability in the actual satellite communication system.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Dynamic Header Compression for Uplink Data for Improving Uplink Link Budget
InactiveUS20180242192A1Small sizeReduced Power RequirementsNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless network protocolsData streamRobust Header Compression
A wireless communication device (UE) may identify a data flow type associated with data packets to be wirelessly transmitted by the wireless communication device over a wireless network during uplink communications. The UE may determine, based on the data flow type, whether to perform header compression for the data packets on a default bearer assigned to the wireless communication device and associated with the data flow for wireless communications over the wireless network. The UE may perform packet header compression for data flow types for which the packet header size is at least a specified percentage of the total packet size. Packet header compression on the default bearer may be enabled at all times, in which case the UE may indicate to the network whether the UE supports header compression on the default bearer. Alternately, the UE may trigger header compression on the default bearer based on application requirements.
Owner:APPLE INC
Method and device for predicting and analyzing WLAN sites
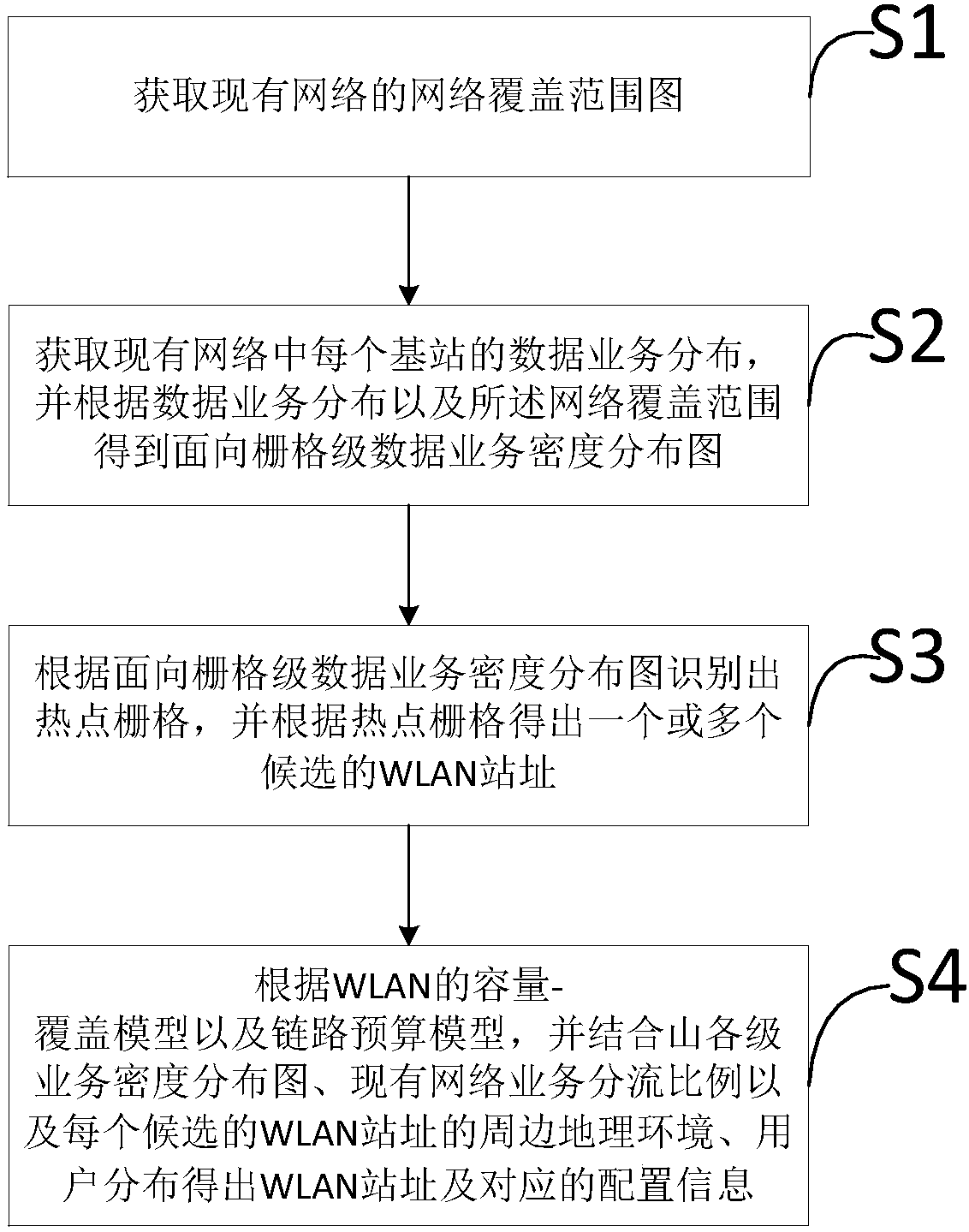
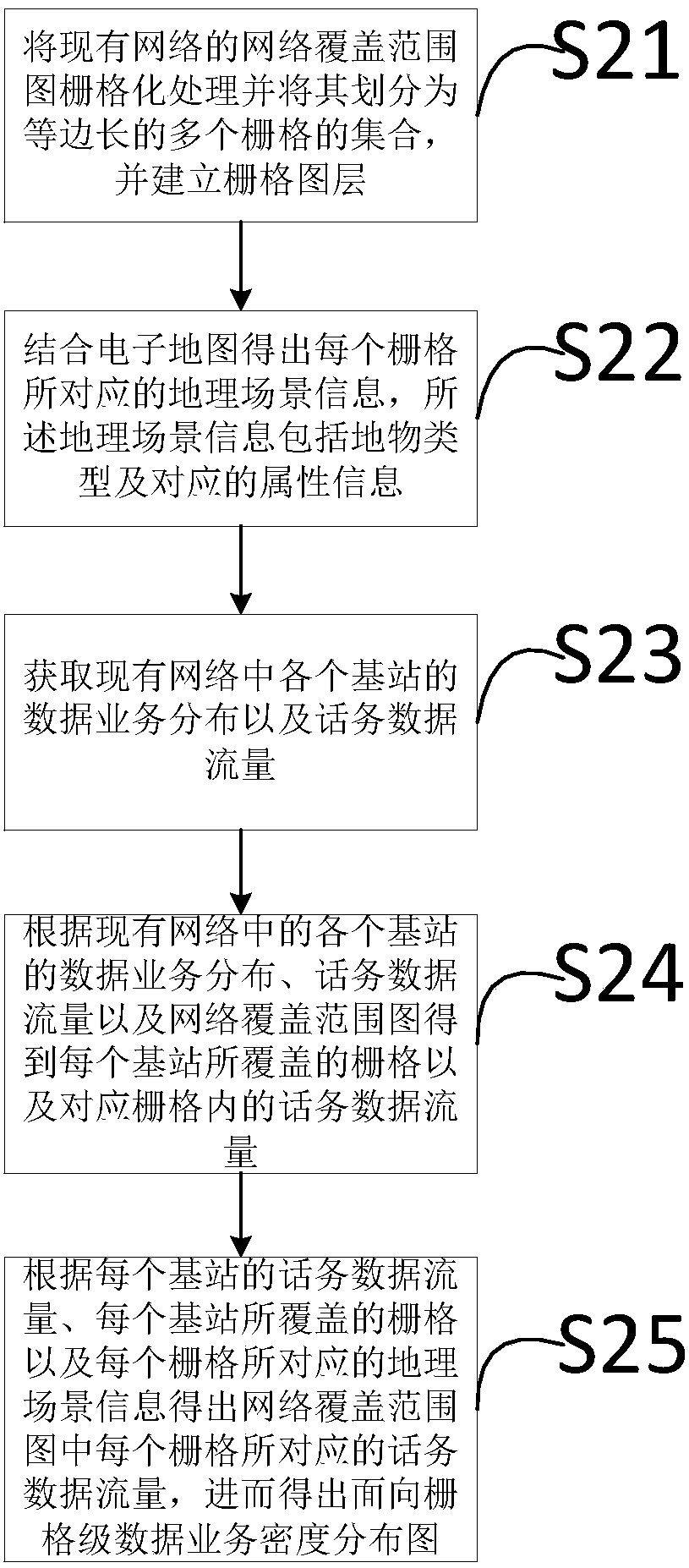
The invention discloses a method and device for predicting and analyzing WLAN sites. The method includes: acquiring the network coverage of an existing network; analyzing, to be more specific, acquiring the data business distribution of each base station in the network, and acquiring a grid-level data business density distribution diagram according to the data business distribution and the networkcoverage; identifying hot spot regions according to the grid-level data business density distribution diagram, and acquiring one or more candidate WLAN sites according to the hot spot regions; selecting the WLAN sites according to a WLAN capacity-coverage model and a link budget module, the grid-level data business density distribution diagram, an existing network business shunt proportion, and the peripheral geographical environment and user distribution of each candidate WLAN sites. The method for predicting and analyzing the WLAN sites is low in cost, little in artificial participation, widely applicable, high in precision and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG TELECOM ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com