Patents
Literature
64 results about "Bit stuffing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
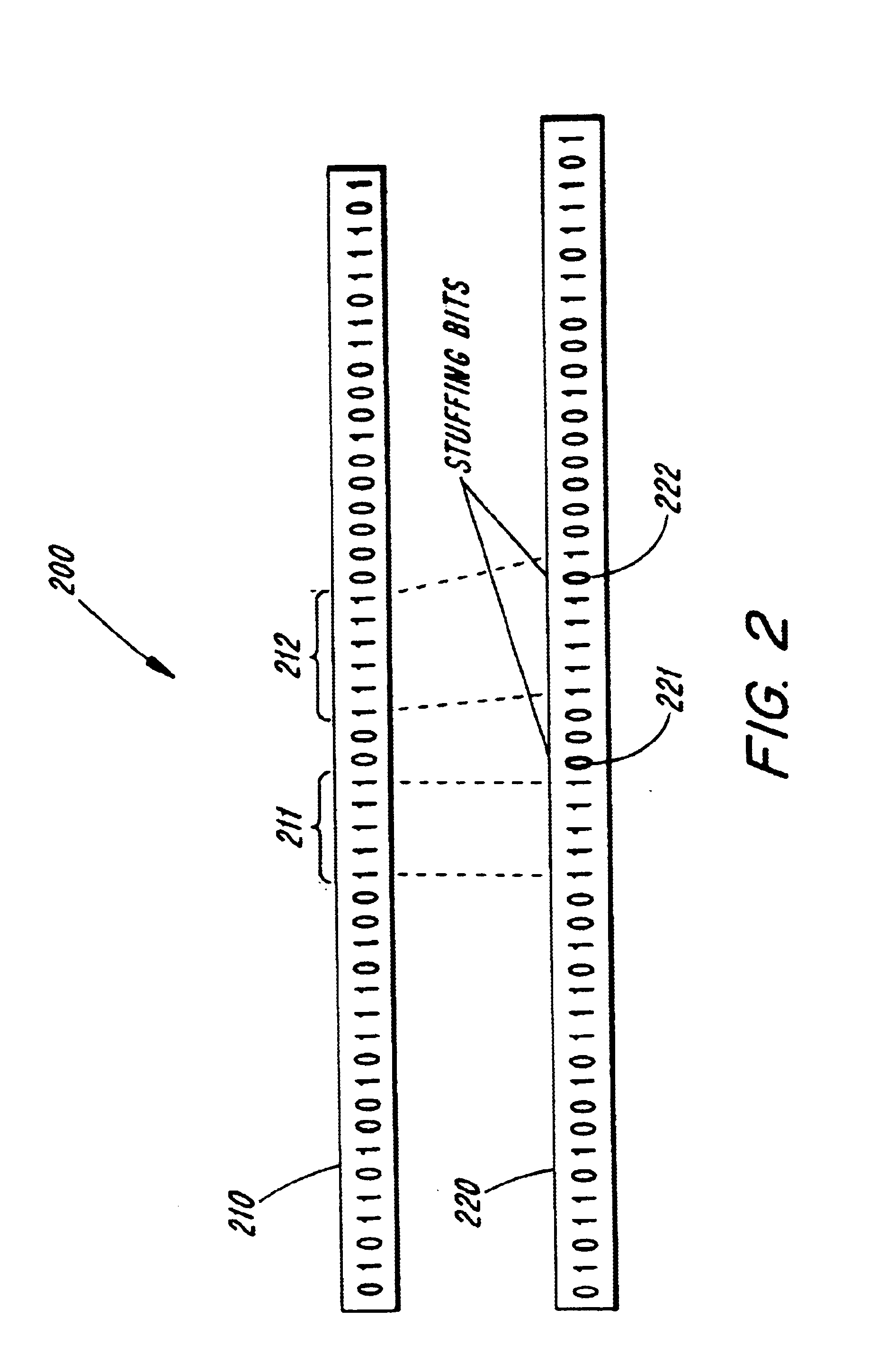
In data transmission and telecommunication, bit stuffing (also known—uncommonly—as positive justification) is the insertion of non-information bits into data. Stuffed bits should not be confused with overhead bits.
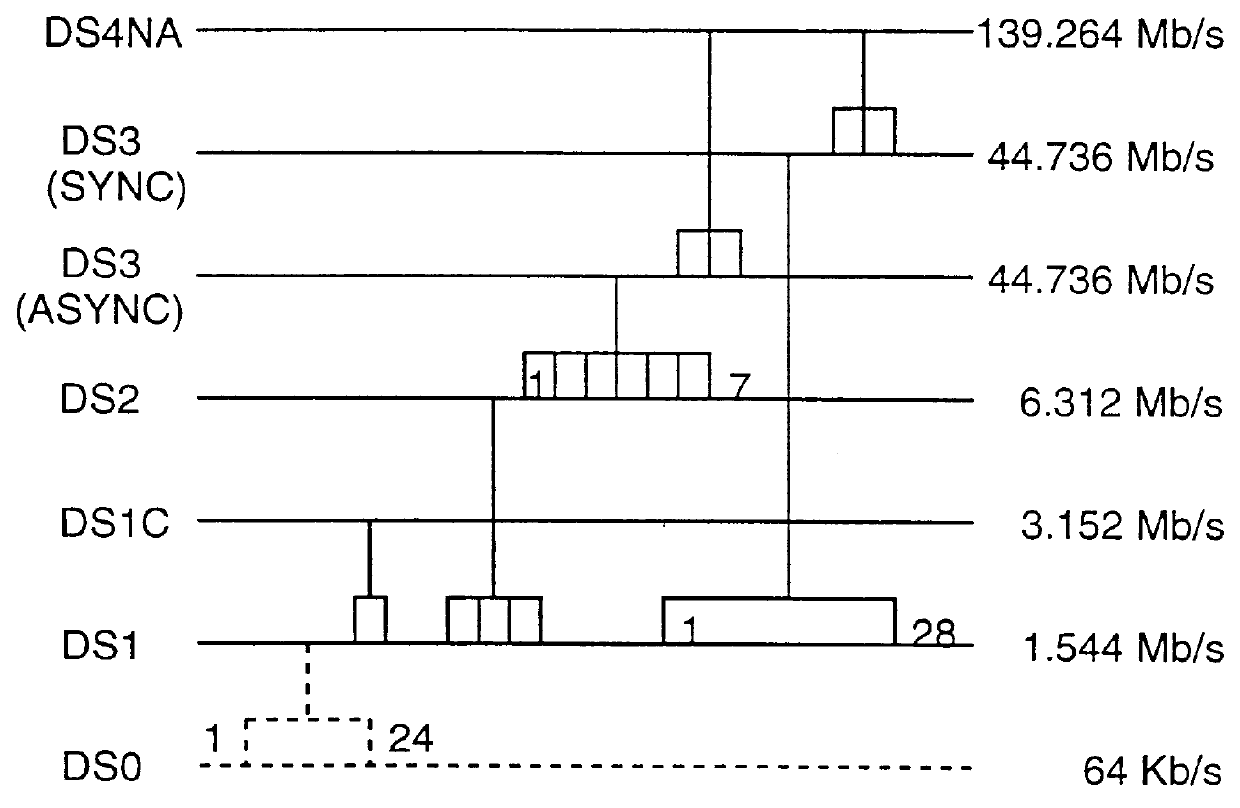
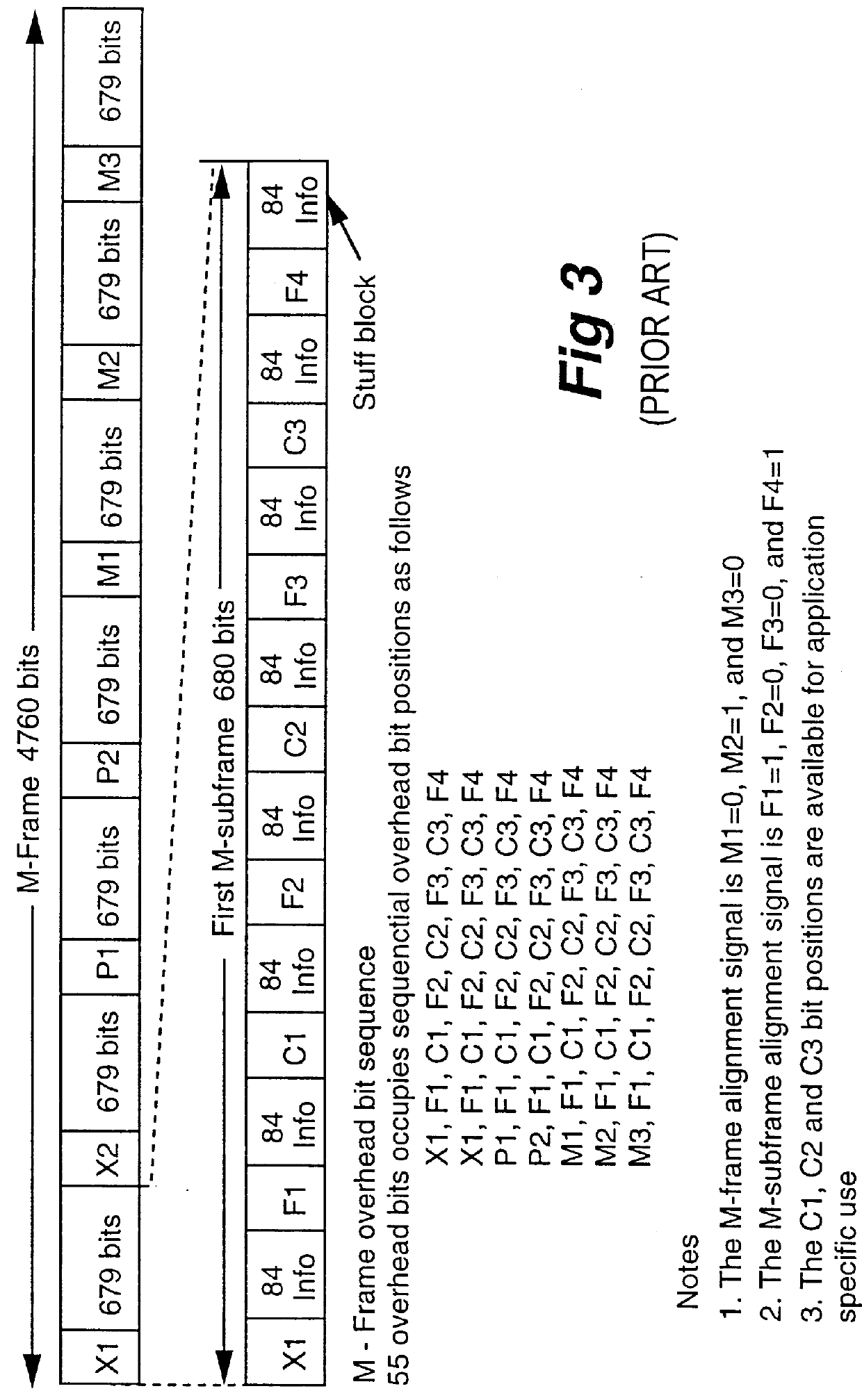
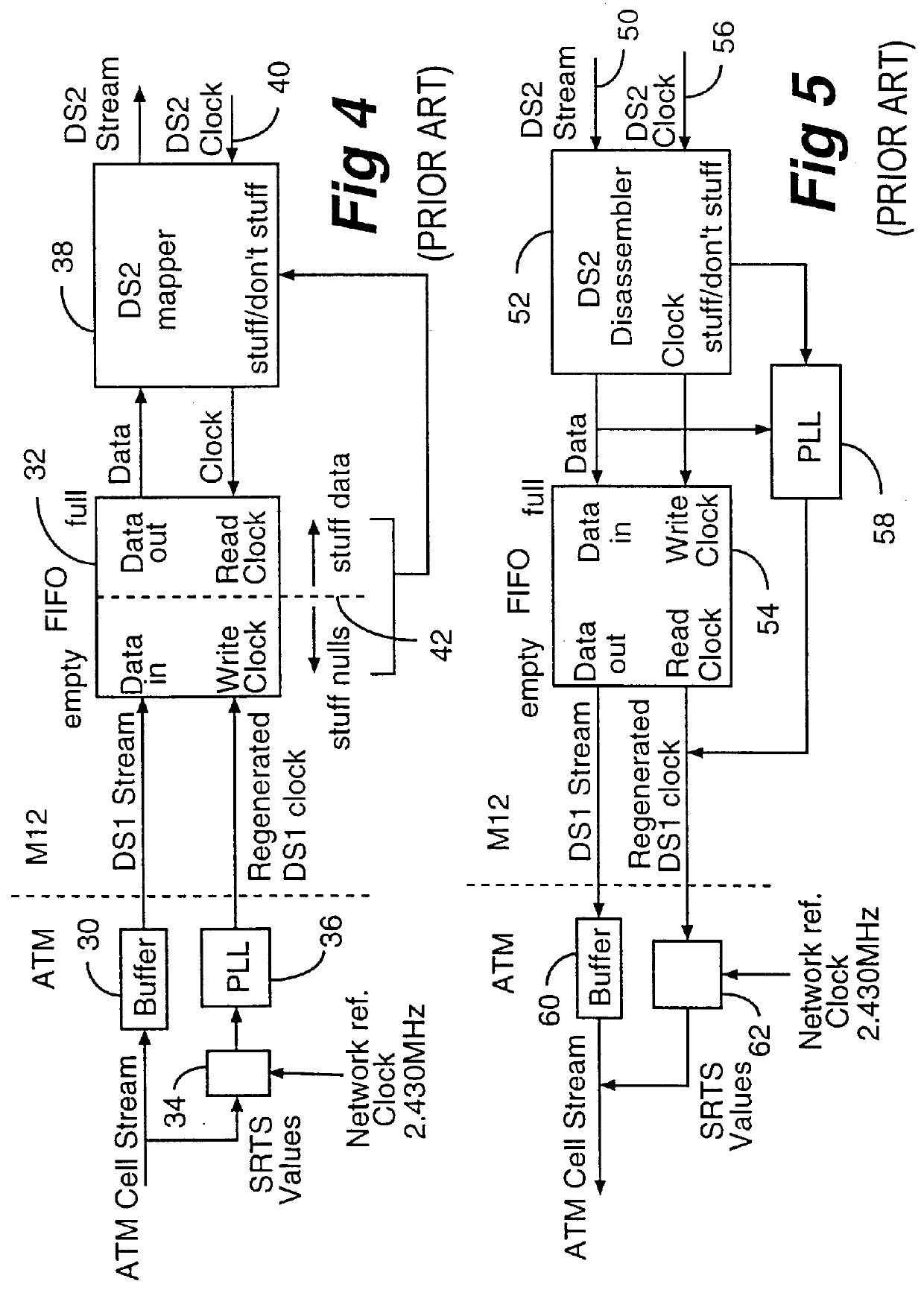
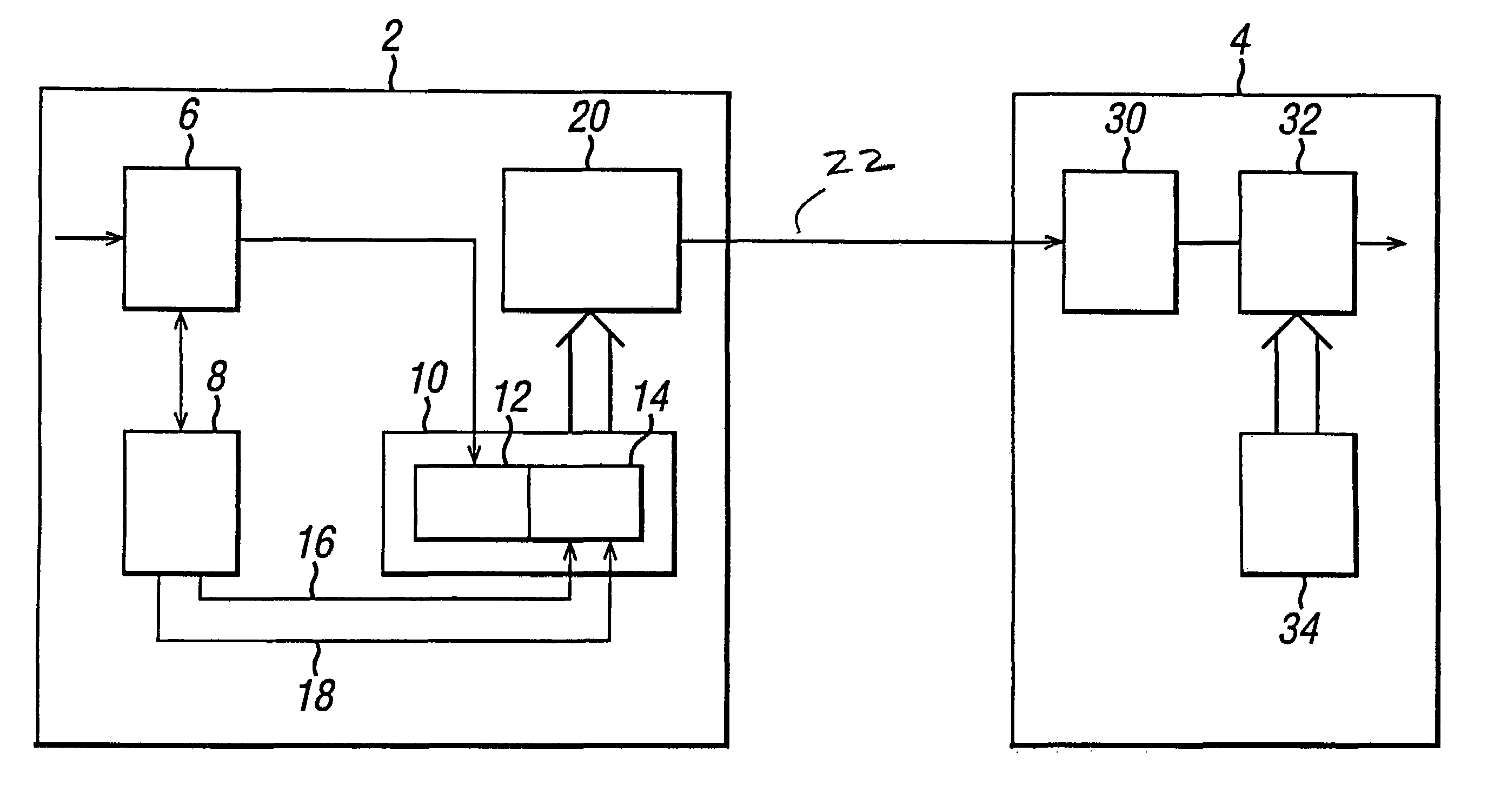
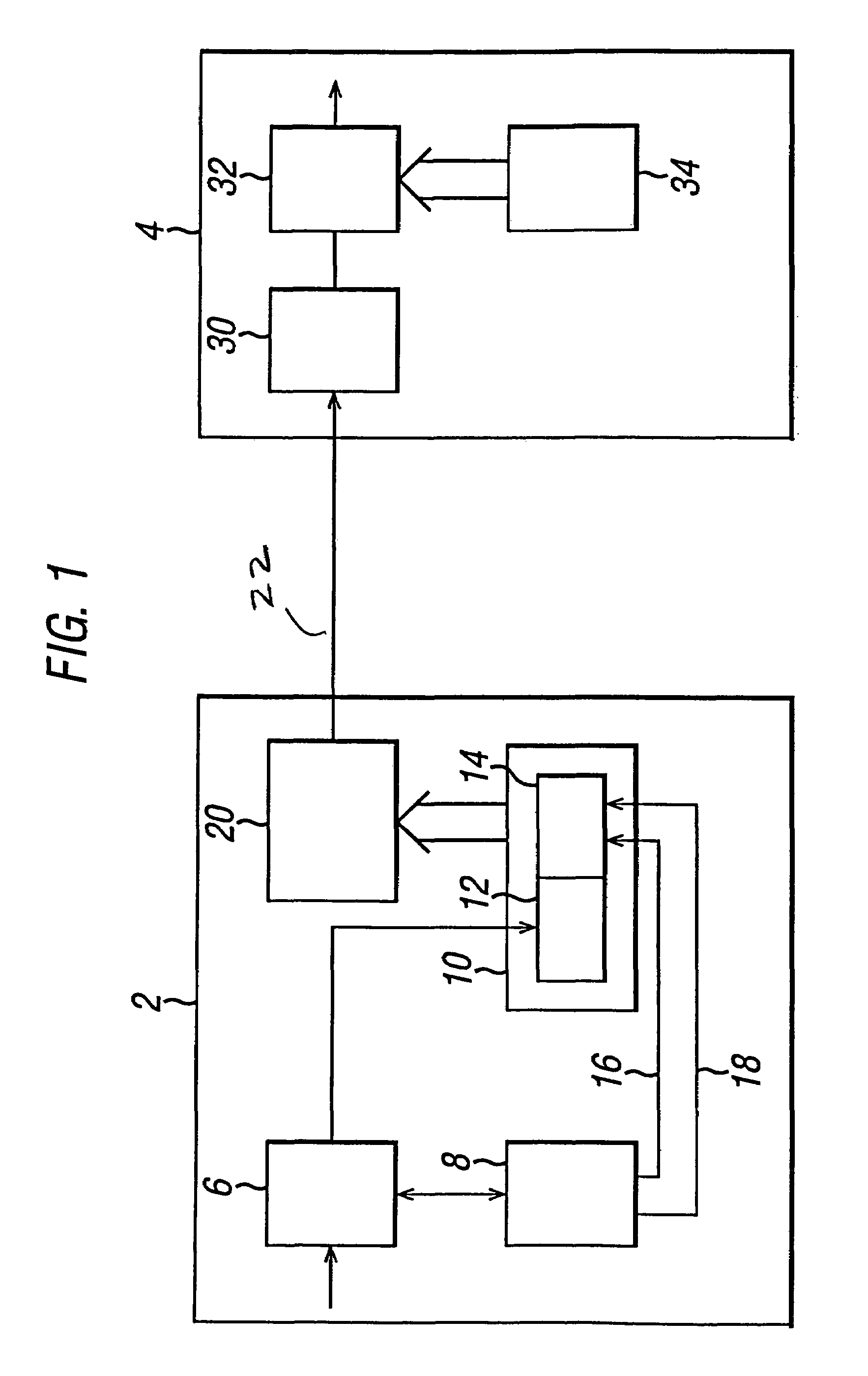
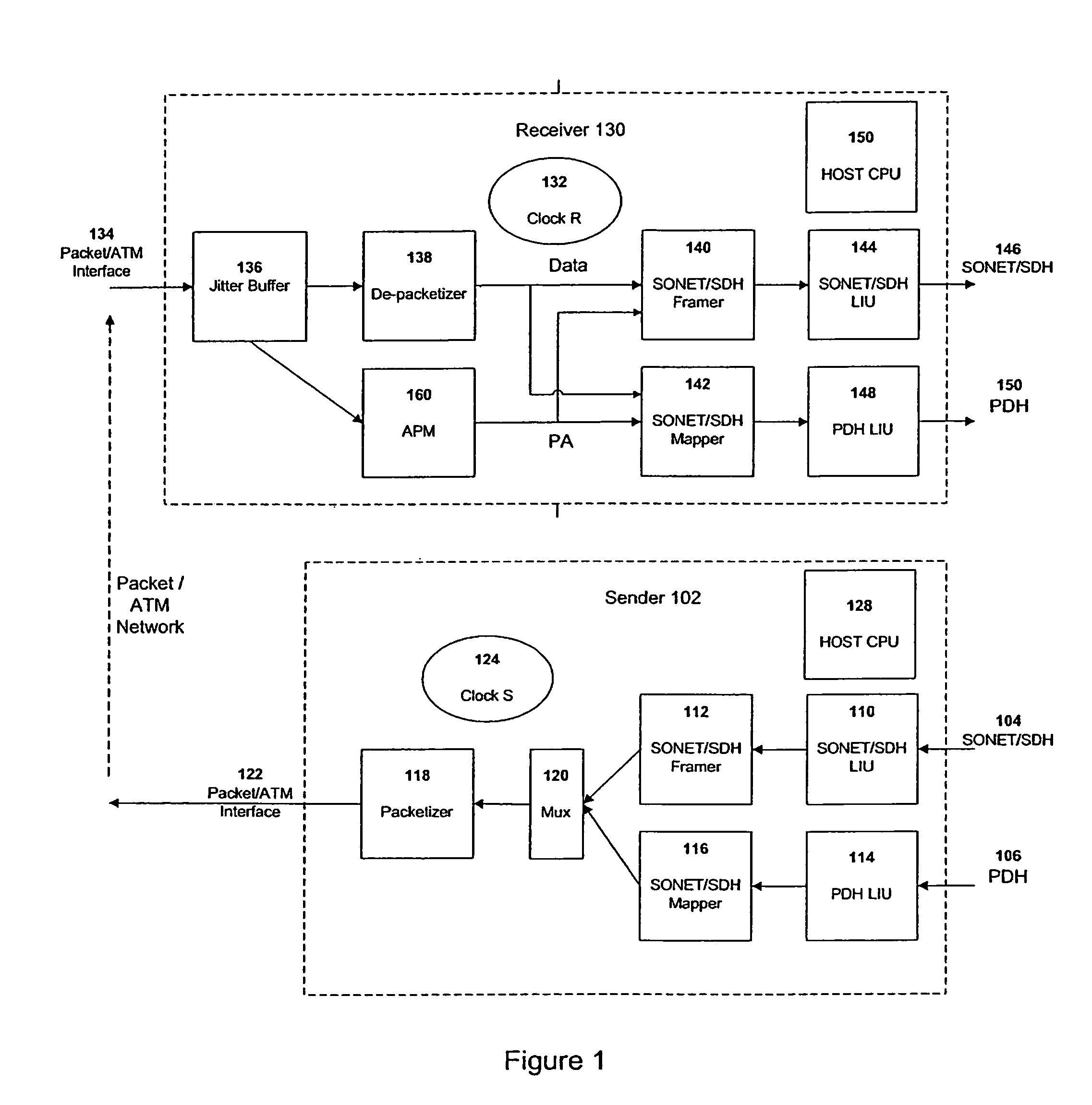
Method of and apparatus for multiplexing and demultiplexing digital signal streams
Multiplexing and demultiplexing are commonplace for an efficient bandwidth utilization in telecommunications. SRTS (Synchronous Residual Time Stamp) technique is widely used for timing recovery in processing of digital signal streams. The bit stuffing is also prevalent for various purposes, one being rate adjustment. The invention performs the SRTS technique entirely digitally to monitor the rate of slower speed signal streams in relation to the rate of a higher speed stream. The digital implementation permits the use of context switching for processing a plurality of digital signal streams. As the result, hardware requirement is greatly reduced.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
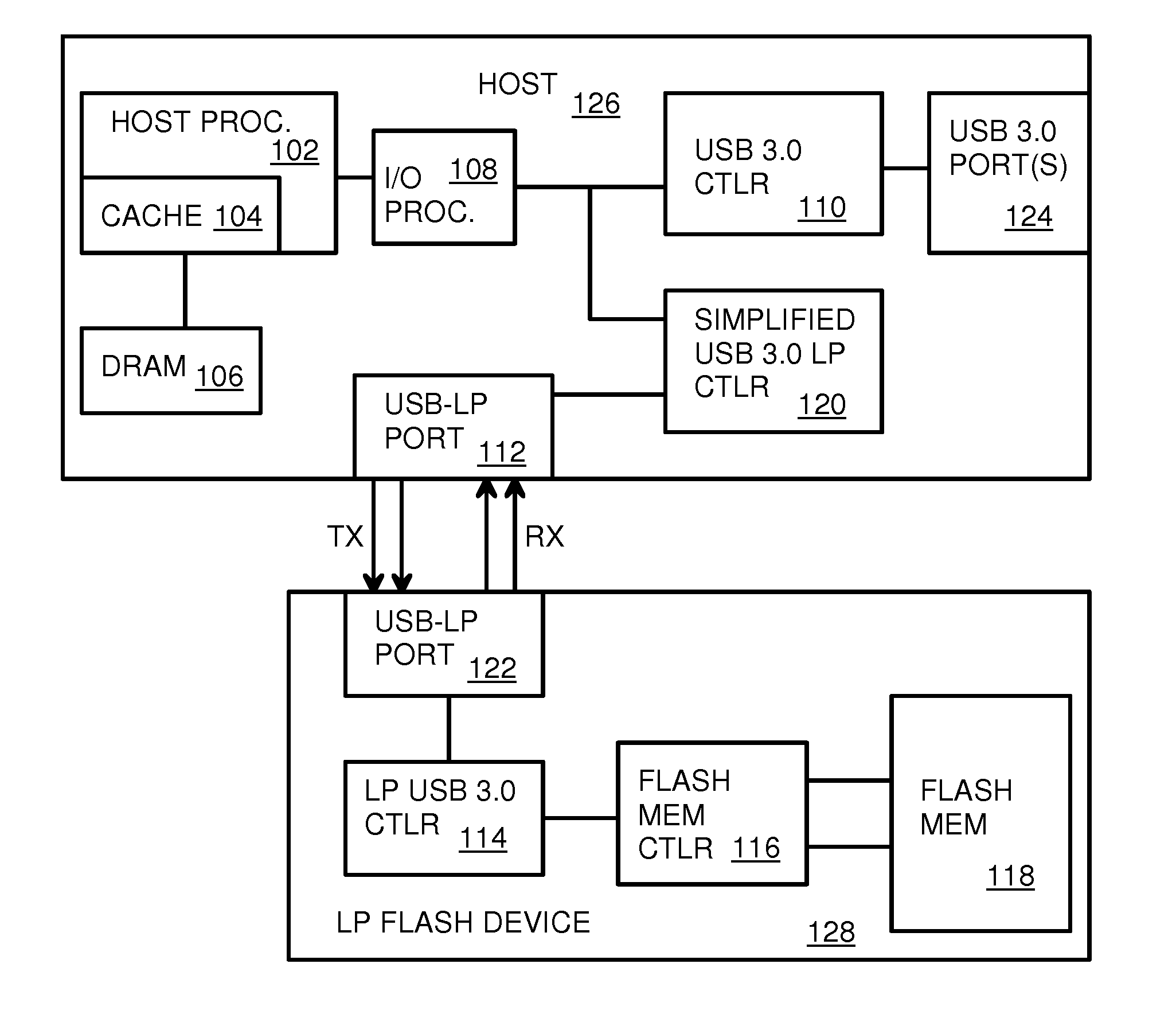
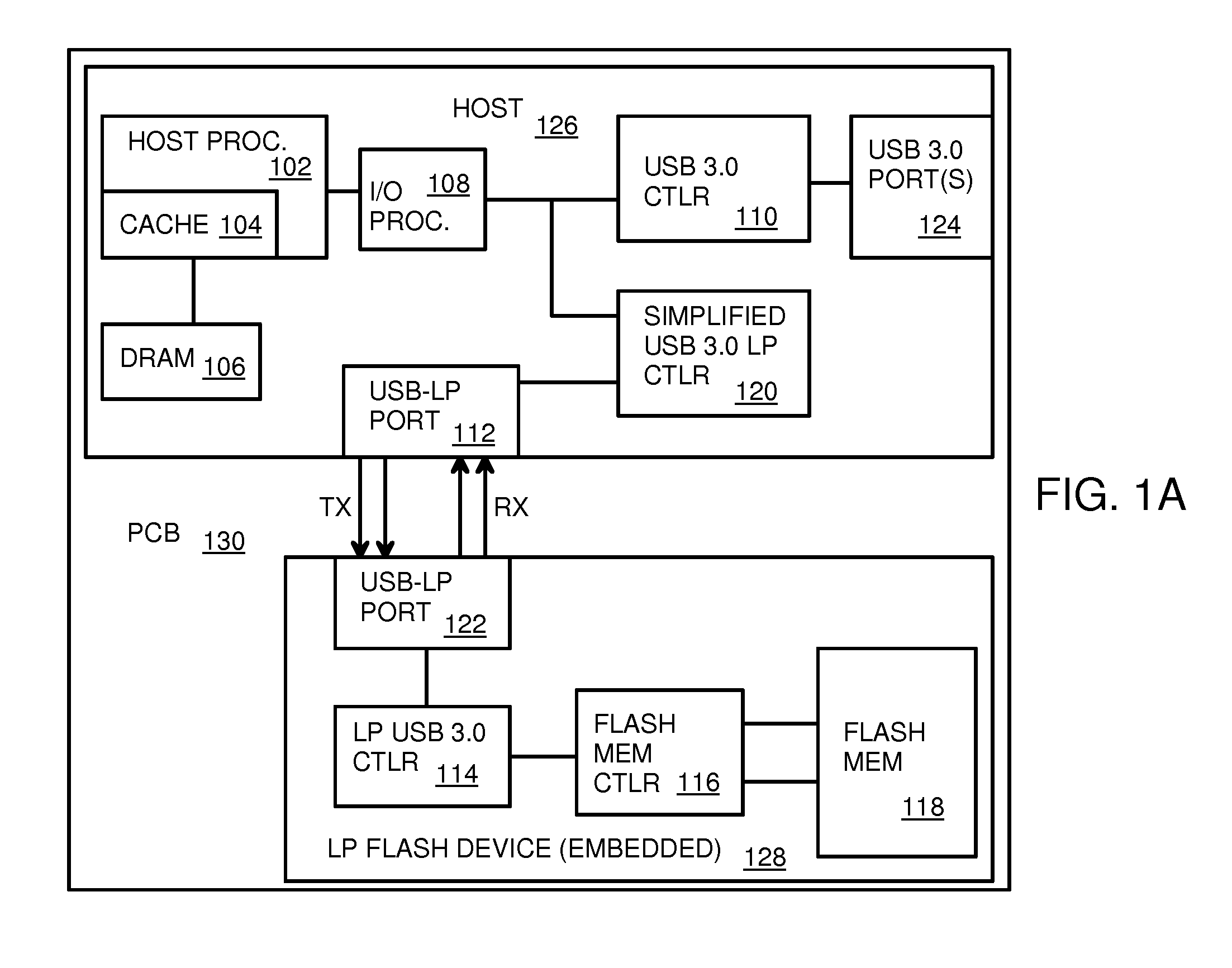
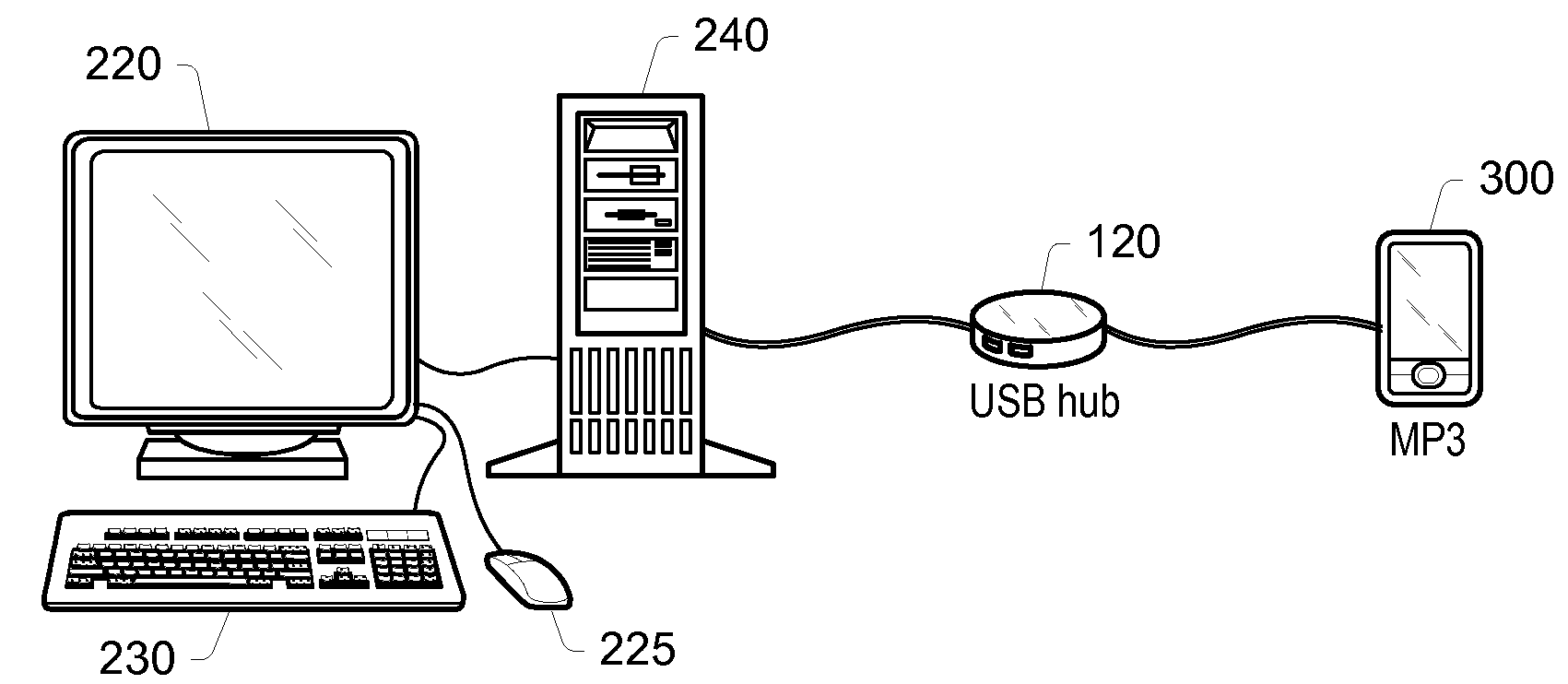
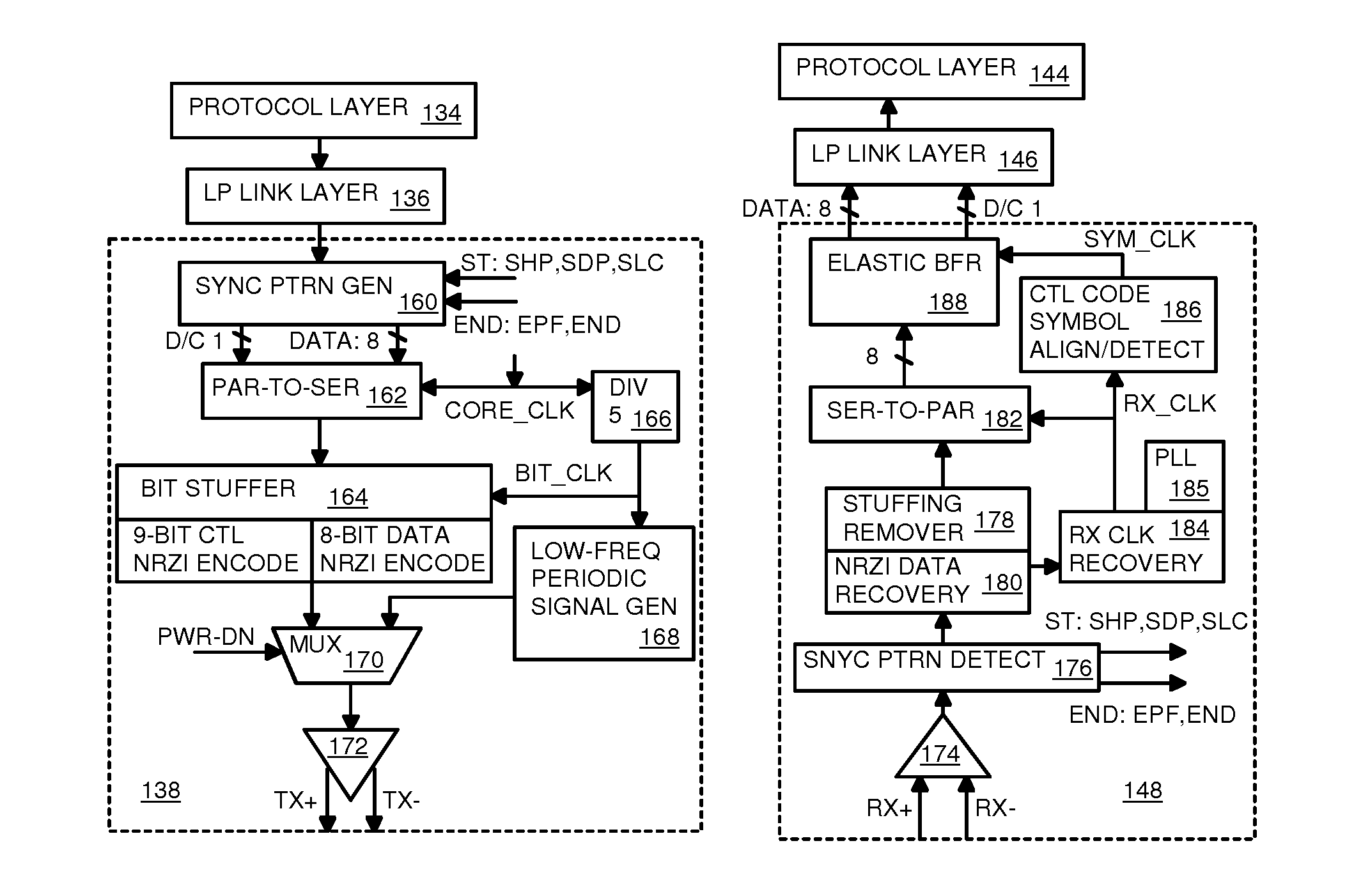
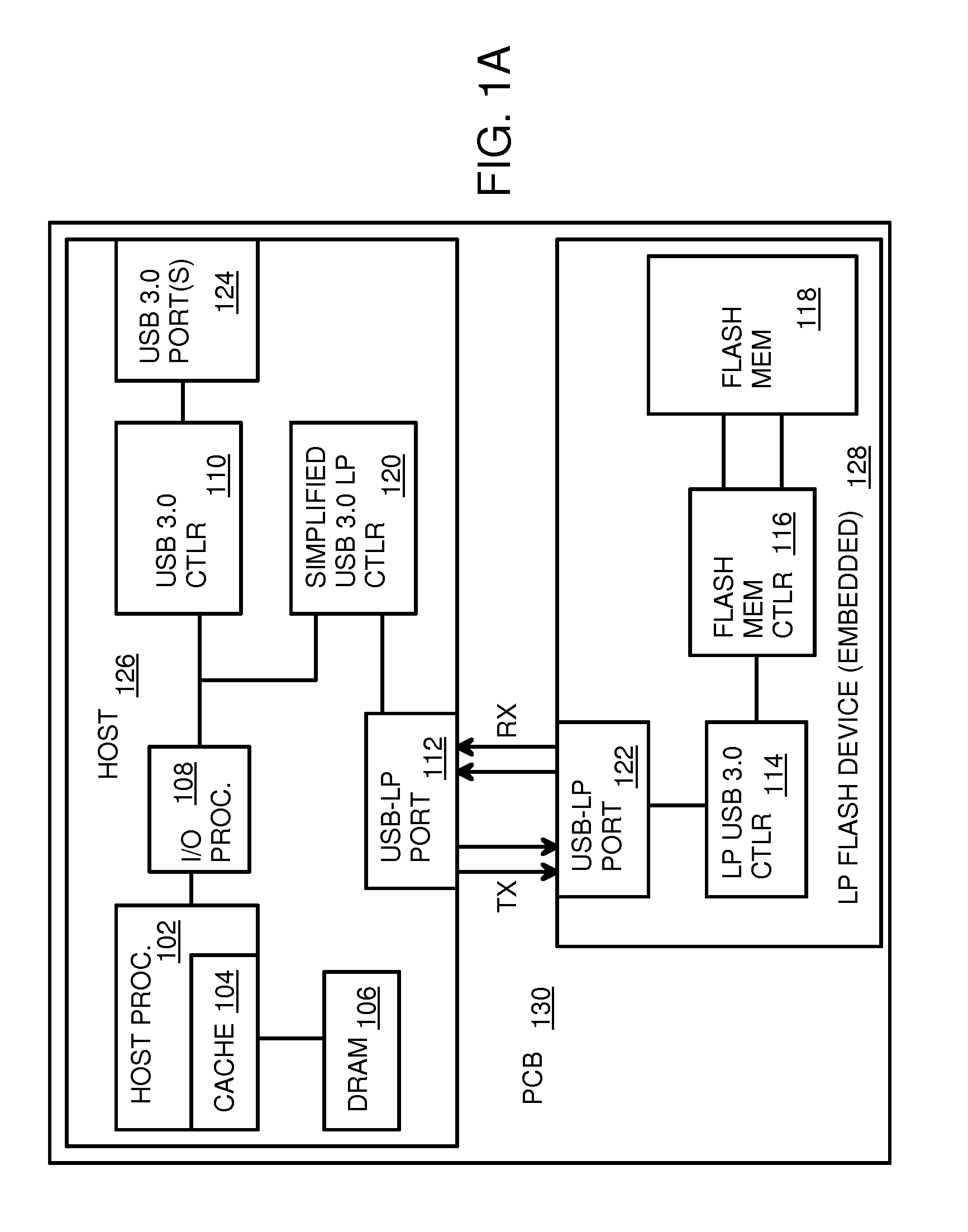
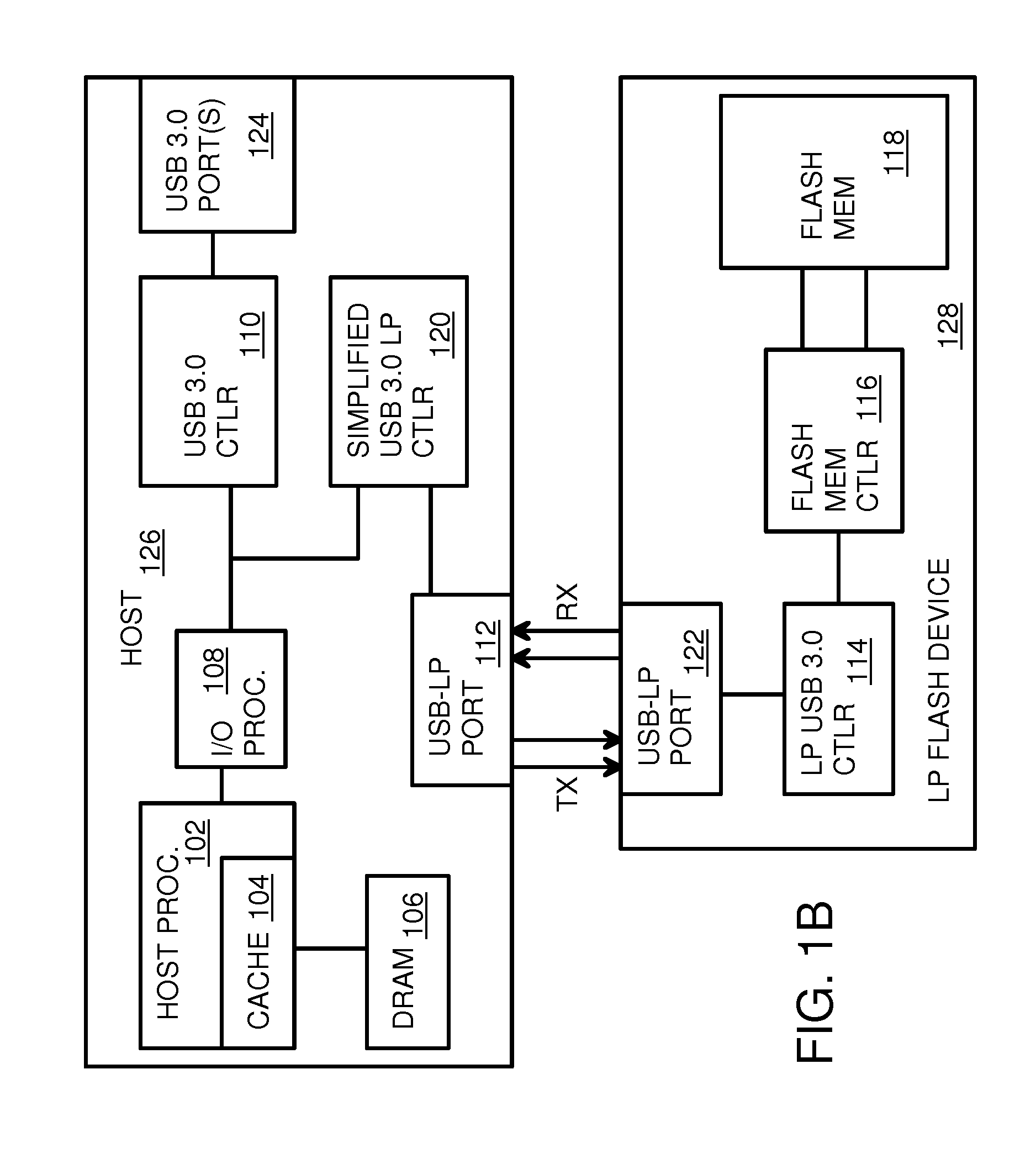
Low-Power USB SuperSpeed Device with 8-bit Payload and 9-bit Frame NRZI Encoding for Replacing 8/10-bit Encoding
A Low-power flash-memory device uses a modified Universal-Serial-Bus (USB) 3.0 Protocol to reduce power consumption. The bit clock is slowed to reduce power and the need for pre-emphasis when USB cable lengths are short in applications. Data efficiency is improved by eliminating the 8 / 10-bit encoder and instead encoding sync and framing bytes as 9-bit symbols. Data bytes are expanded by bit stuffing only when a series of six ones occurs in the data. Header and payload data is transmitted as nearly 8-bits per data byte while framing is 9-bits per symbol, much less than the standard 10 bits per byte. Low-power link layers, physical layers, and scaled-down protocol layers are used. A card reader converter hub allows USB hosts to access low-power USB devices. Only one flash device is accessed, reducing power compared with standard USB broadcasting to multiple devices.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
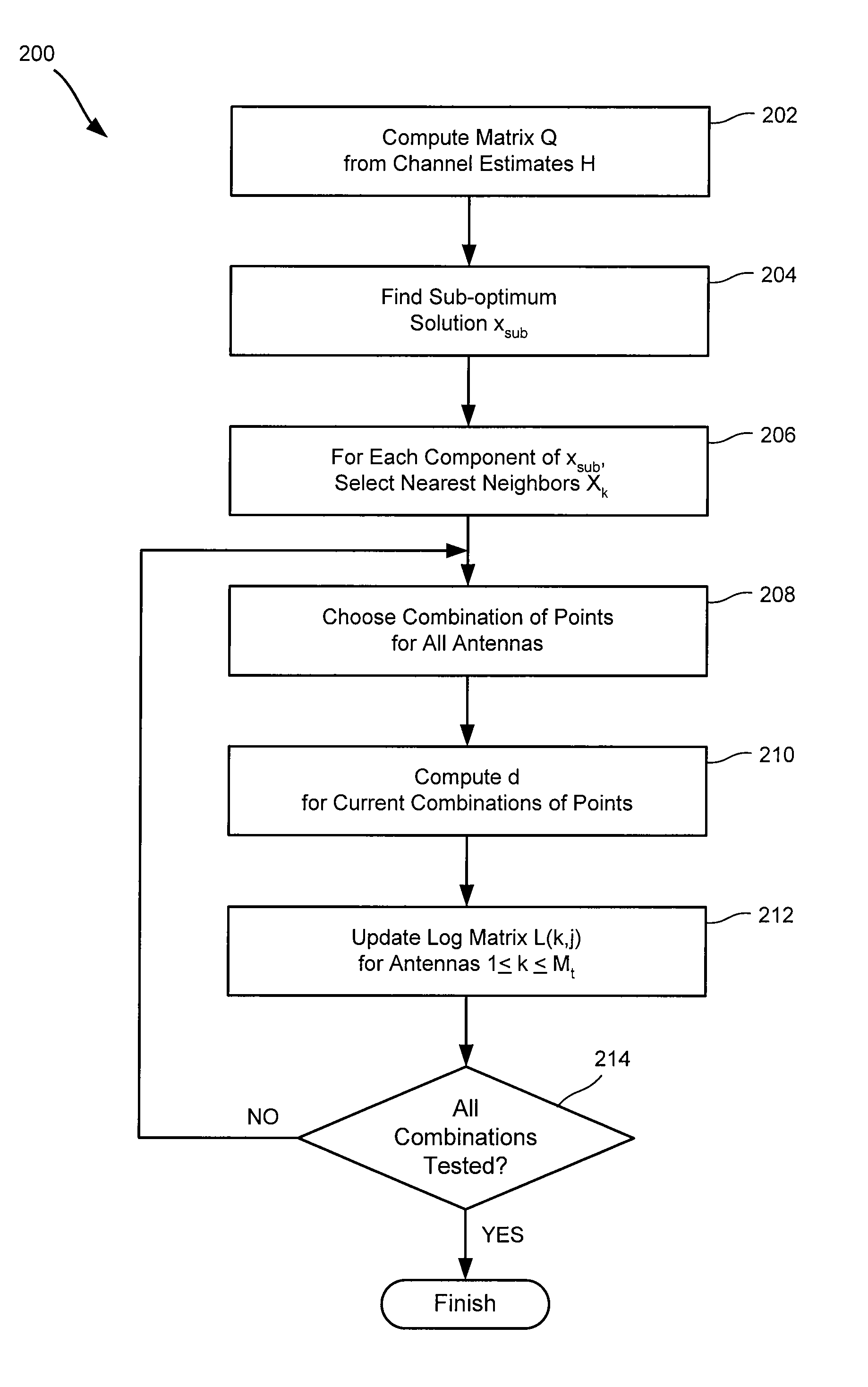
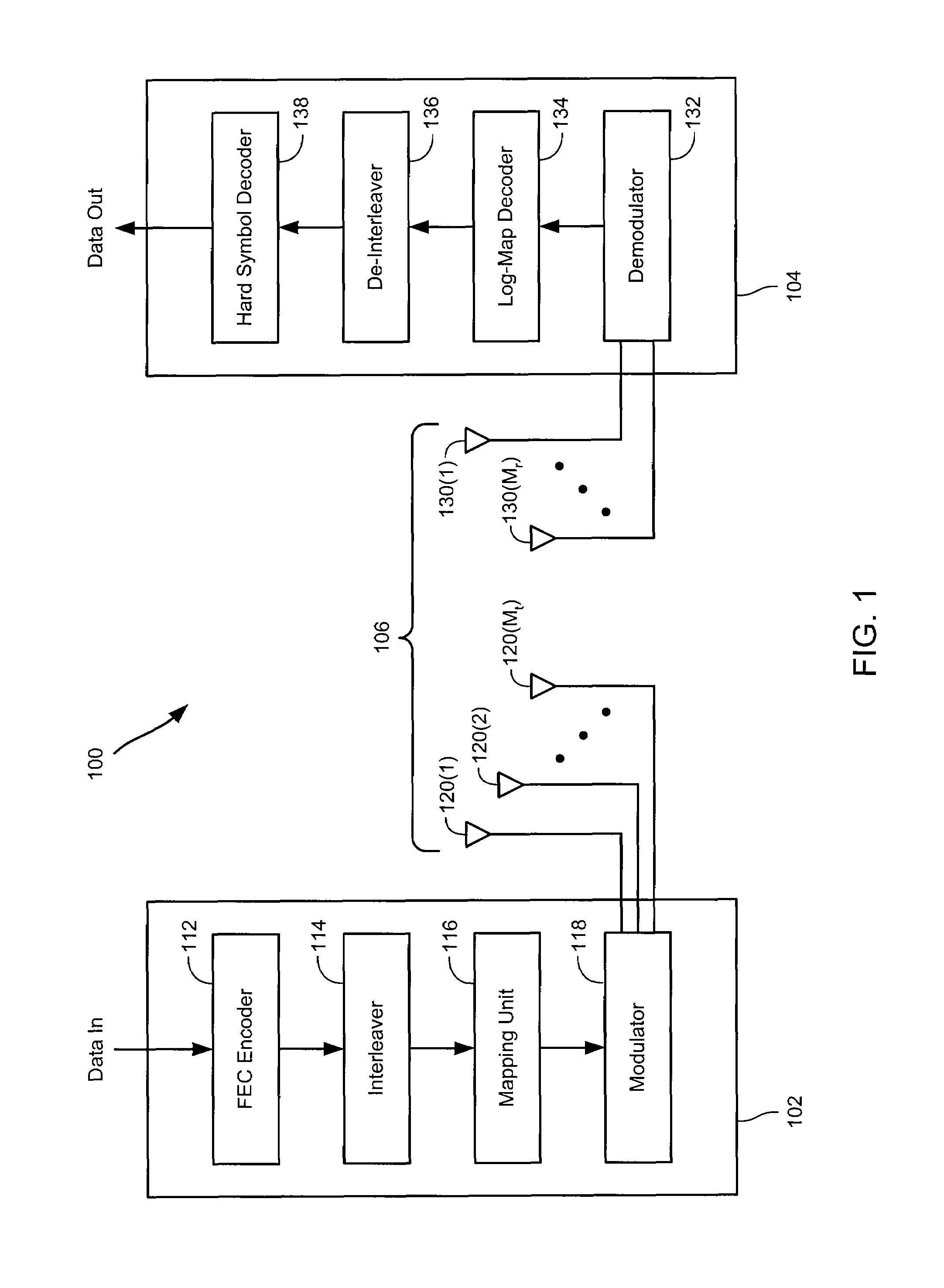
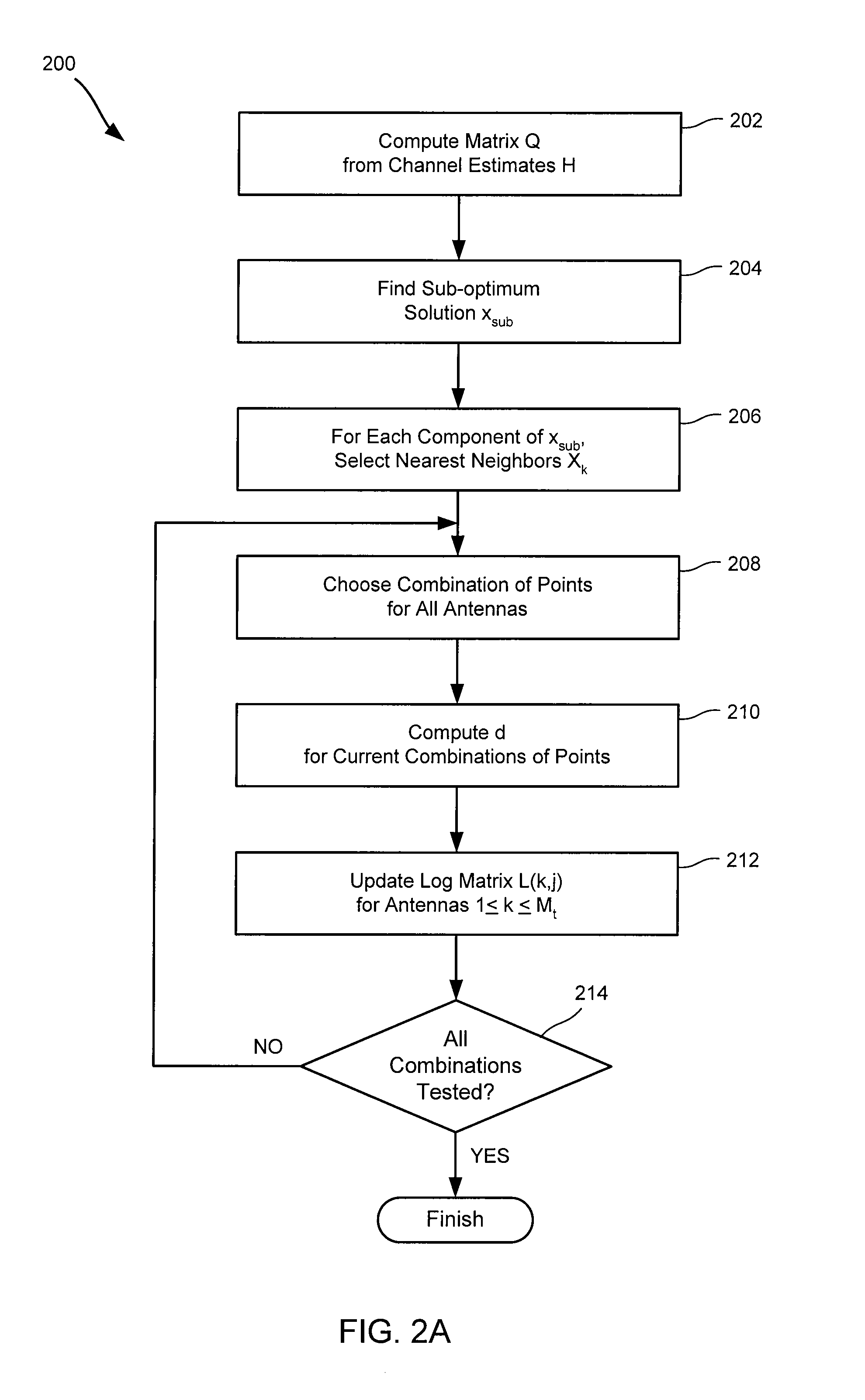
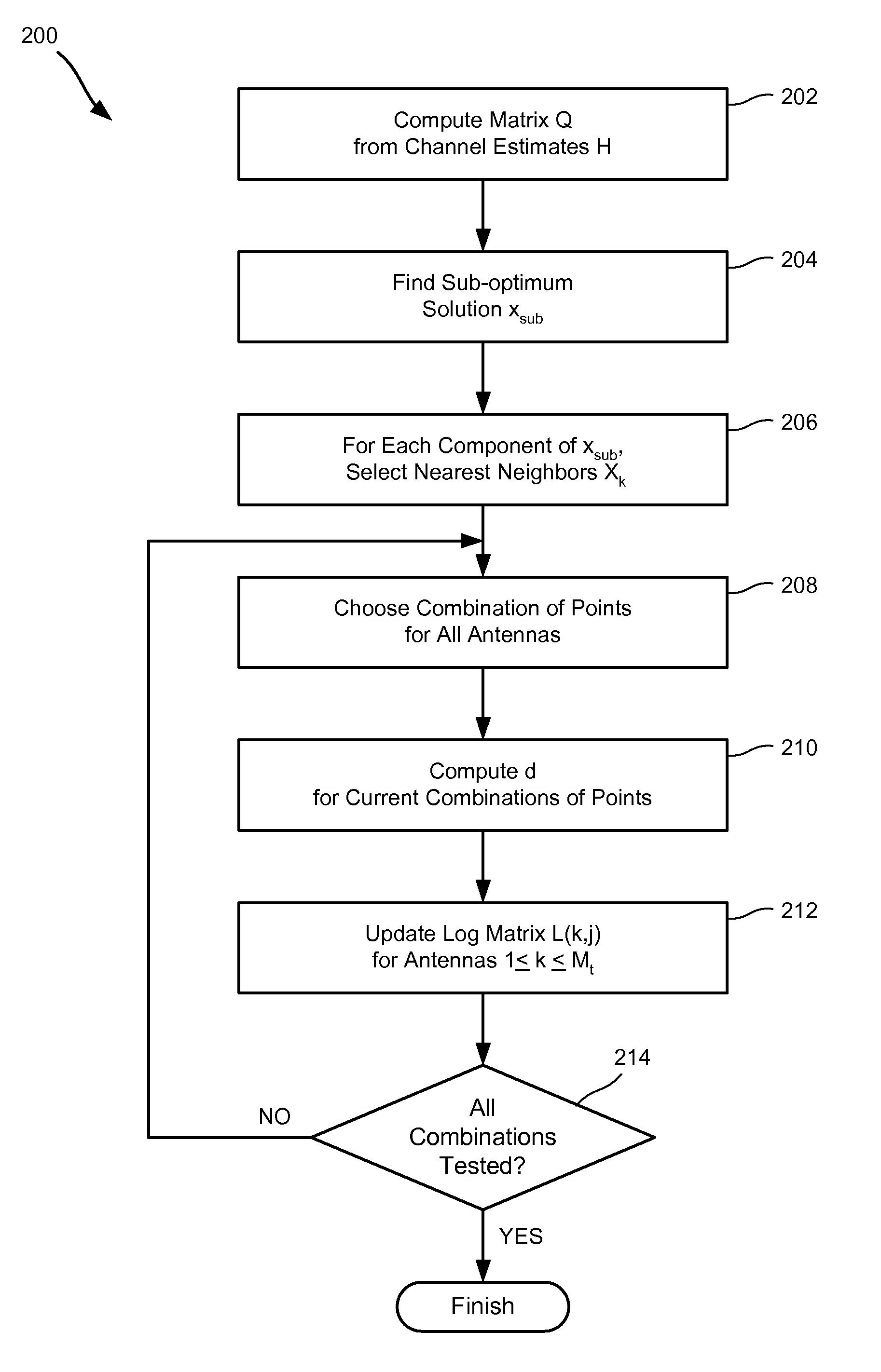
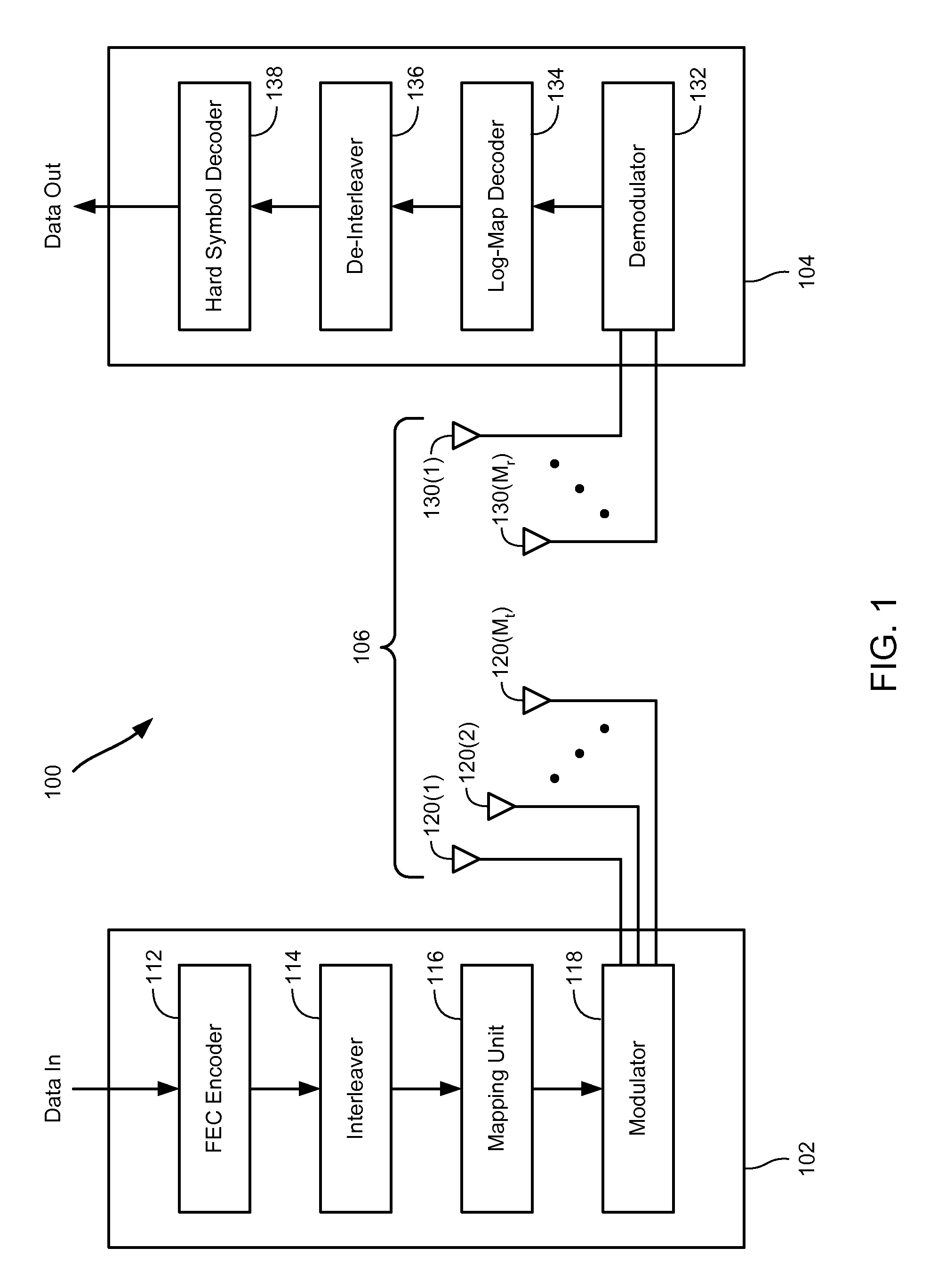
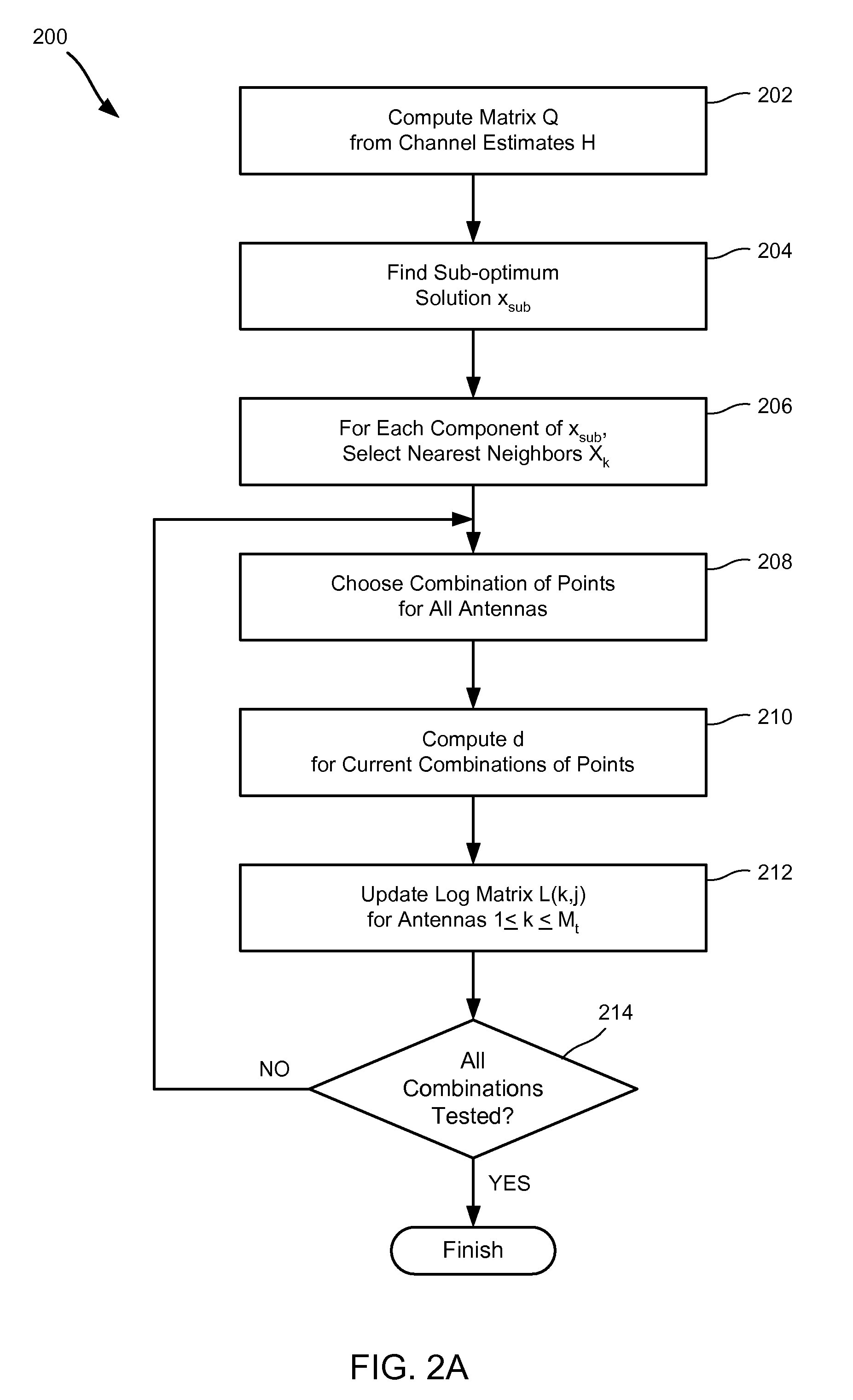
Soft symbol decoding for MIMO communication systems with reduced search complexity
InactiveUS7245666B1Reduce search complexityReduce in quantityPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRound complexitySymbol decoding
Soft symbol decoder algorithms for multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) receivers reduce the search complexity by searching over fewer than all possible combinations of transmitted symbols to compute log metrics for each transmitted bit from each transmit antenna. In one algorithm, a sub-optimal set of transmitted symbols is computed and the transmitted symbols are restricted to neighboring constellation points of the sub-optimal set. In another algorithm, all constellation points are searched for every antenna except one. In yet another algorithm, constellation points are searched excluding more than one antenna. The non-searched antenna(s) can be handled by either a bit stuffing or a soft slicing technique.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
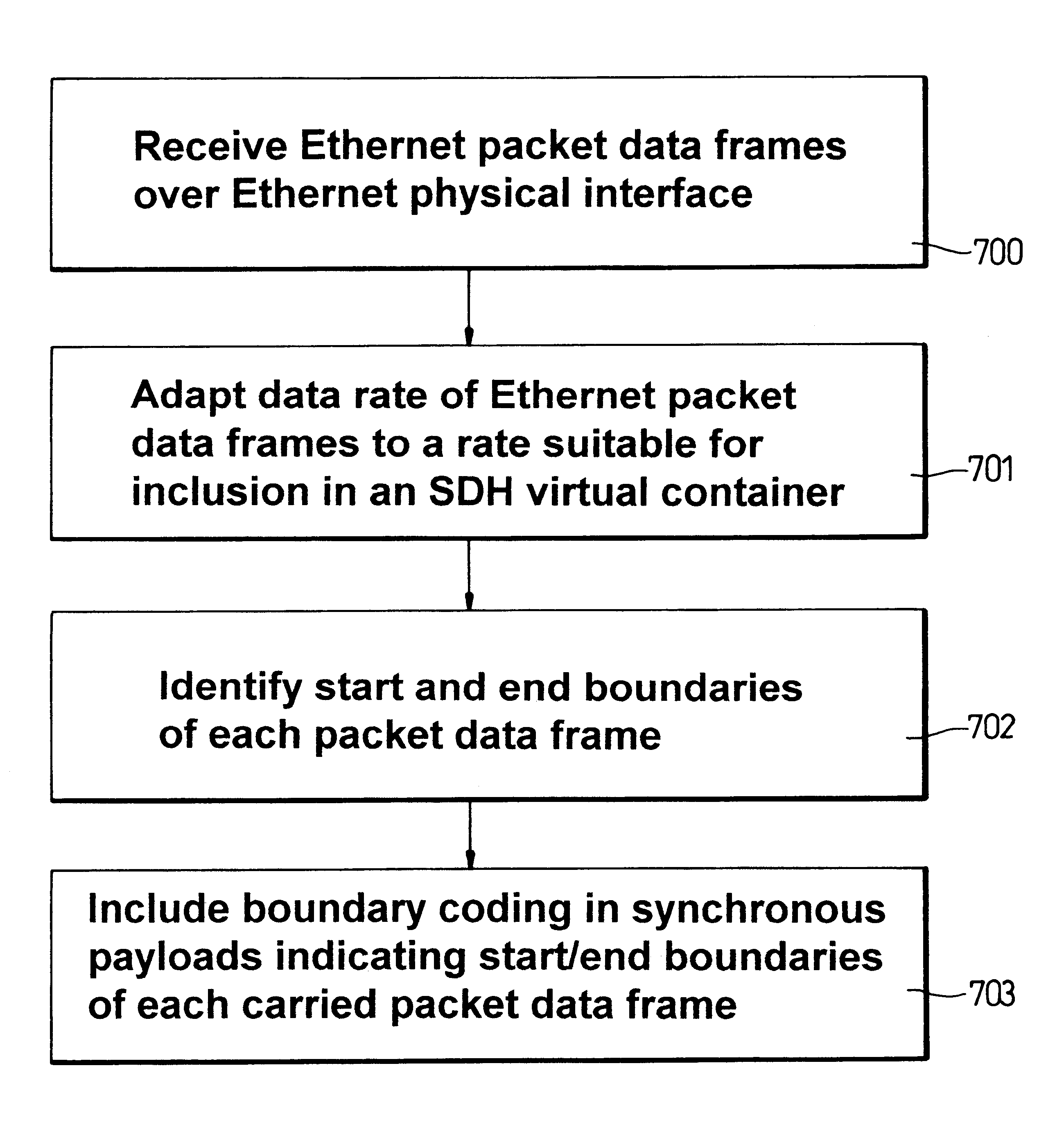
Payload mapping in synchronous networks
There is disclosed a method of carrying frame based data, eg Ethernet data, over a synchronous digital hierarchy network in order to provide local area network type functionality over a wide area network coverage. Specific embodiments disclose methods of mapping Ethernet data frames into SDH virtual containers, and distinguishing start and end boundaries of the Ethernet data frames within the virtual container payloads, by a selection of encoding methods including a segmentation, pointer methods, bit stuffing methods and byte stuffing methods. Data frames are encoded with a code which designates a boundary of each frame, and the encoded frames are input into a synchronous data channel.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
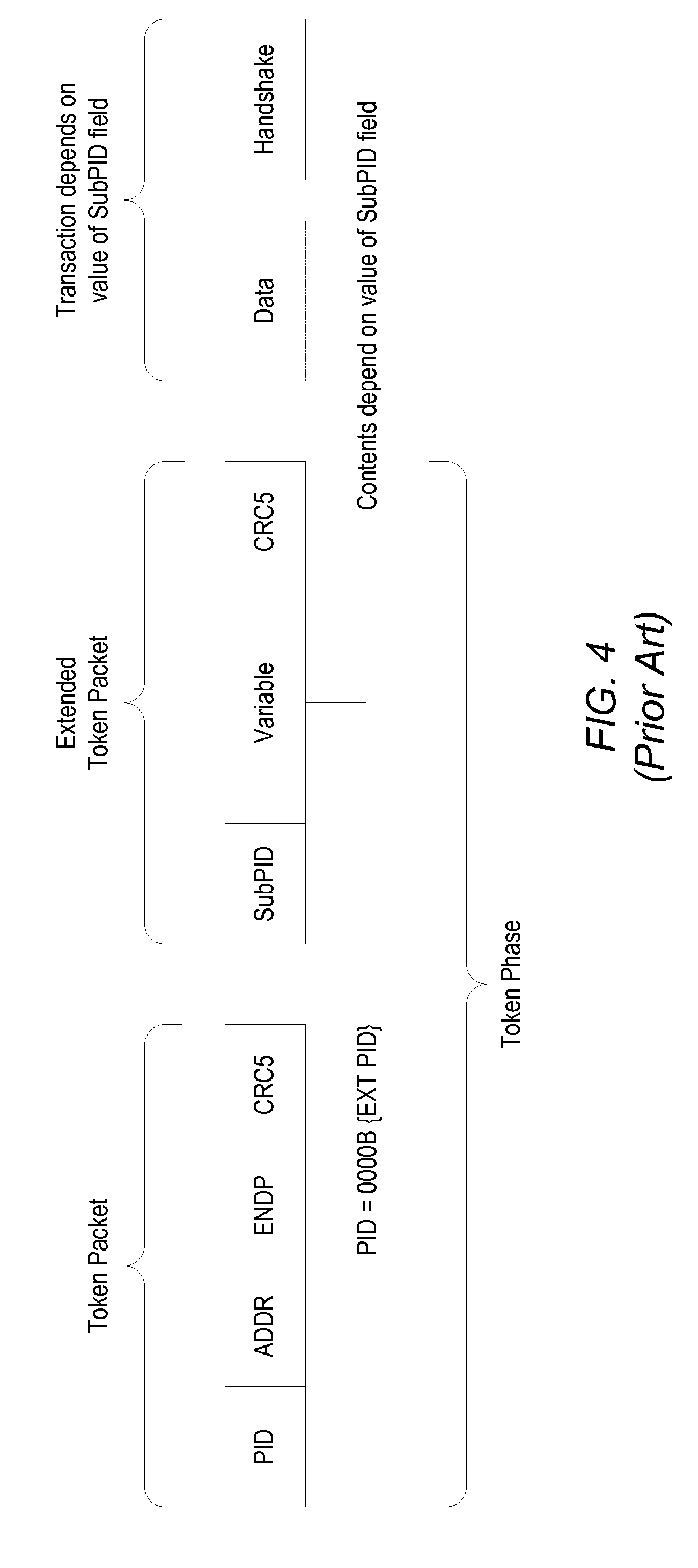
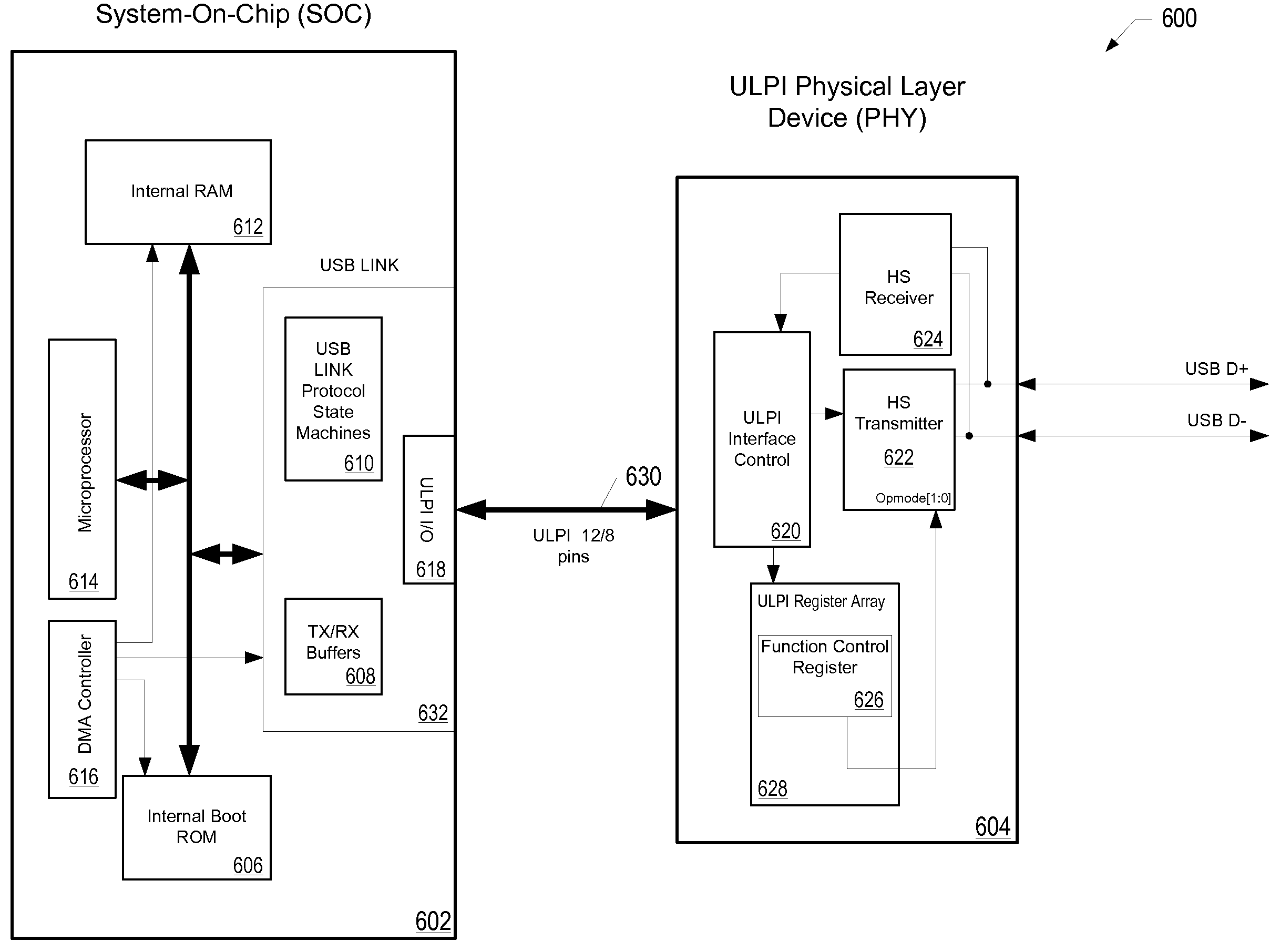
Physical Device (PHY) Support Of The USB2.0 Link Power Management Addendum Using A ULPI PHY Interface Standard
A protocol may enable support of the USB 2.0 LPM (Link Power Management) Addendum by a ULPI PHY (Universal Serial Bus Transceiver Macrocell Low-Pin Interface Physical Layer Device), facilitating transmitting the reserved PID (Physical Interface Device) token, used in the LPM Extended Transaction, through a ULPI bus. Bits [3:0] of a ULPI Tx Cmd (Transmit Command) byte may be reused, with the value of those bits being 4′b0 for a transmission (normally indicating a No PID transmission), by configuring the ULPI PHY to qualify the selected four Tx Cmd bits (bits [3:0] of the Tx Cmd) with the Opmode code. The ULPI PHY may thereby interpret bits [3:0] of the Tx Cmd byte based on the value of the Opmode, and may not transmit the Extended PID when the Opmode is set to 2′b10, that is, when the Opmode is indicative of bit-stuffing and NRZI encoding being disabled, for example during a Chirp transmission. When the Opmode code is set to 2′b0, indicative of normal bit-stuffing, and the Tx Cmd bits [3:0] are set to 4′b0 during a transmission (Tx Cmd bits[7:6]=2′b01), then the PHY may transmit the Extended PID, followed by the rest of the extended transaction onto a USB.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
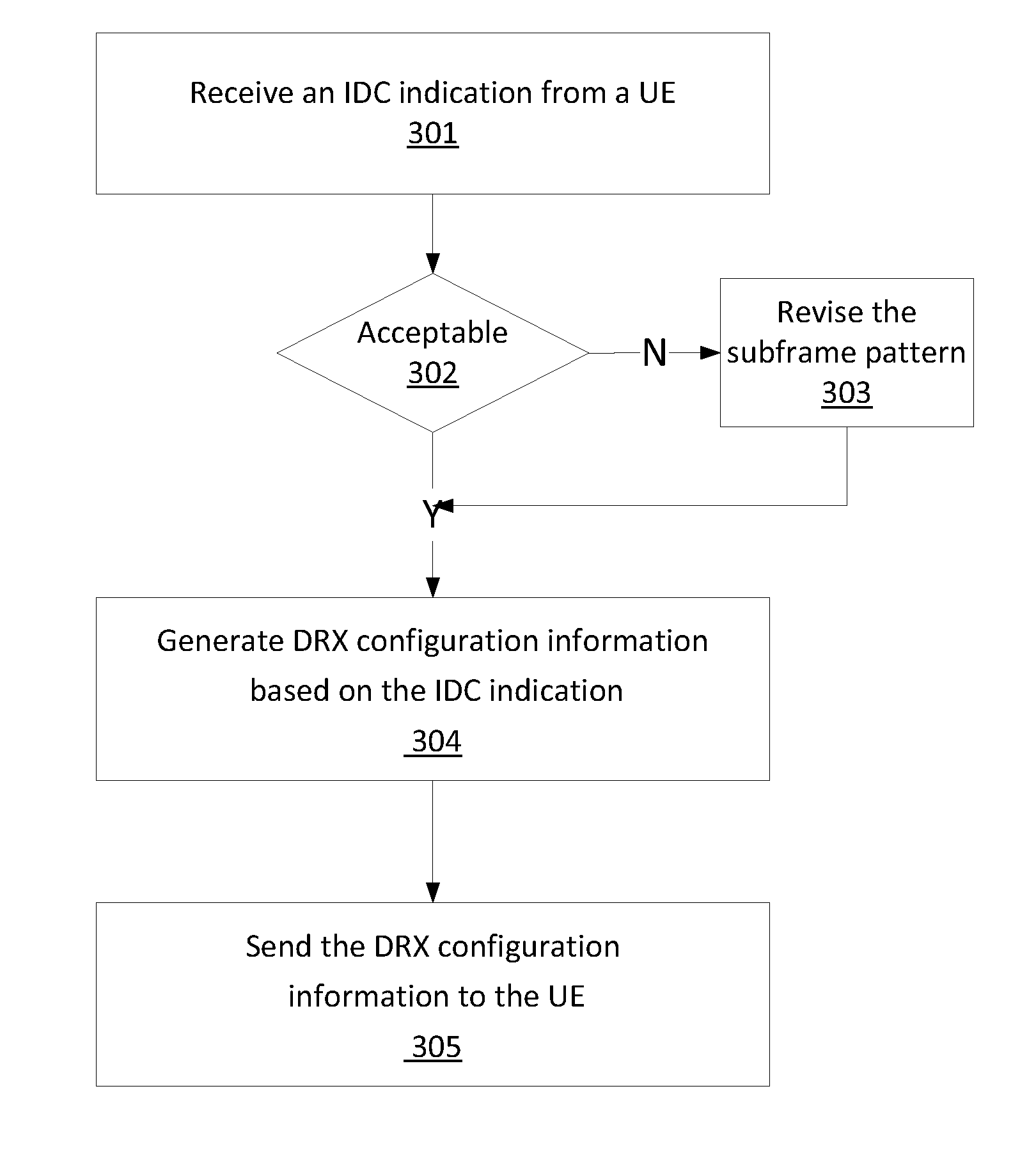
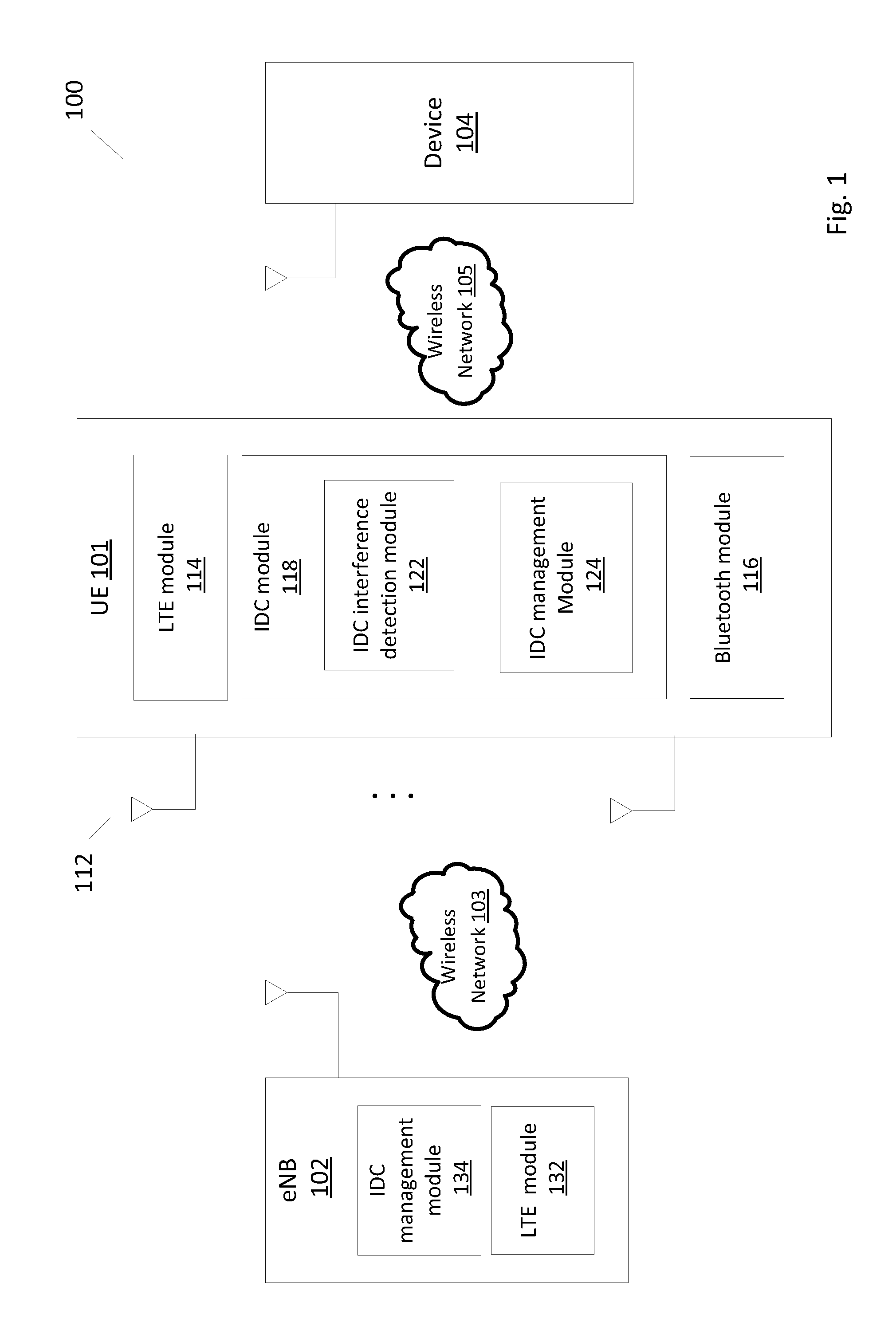
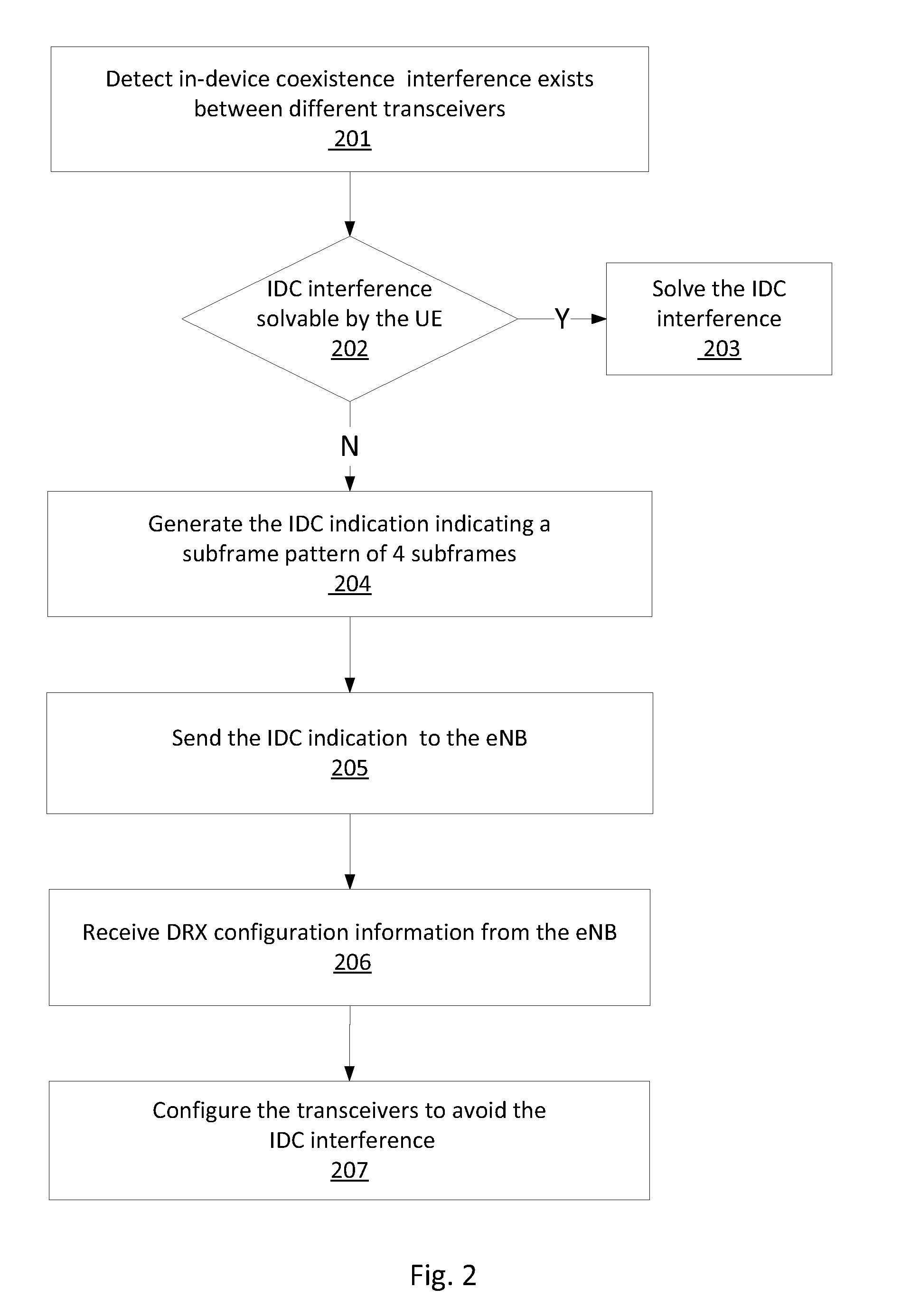
Method, apparatus and system for handling in-device coexistance interference in a wireless network
ActiveUS20140247759A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageCriteria allocationComputer hardwareWireless sensor network
A device, method and system of handling in-device coexistence (IDC) interference in a wireless network, may comprise detecting the IDC interference between a first communication module operating over a first protocol and a second communication module operating over a second protocol; generating an IDC indication having a bit string comprising four bits, wherein the four bits correspond to a subframe pattern comprising four subframes, a value of a bit of the bit string indicates whether an enhanced node B (eNB) is requested to abstain from using a subframe of the four subframes of the subframe pattern; and transmit the IDC indication to the eNB via a wireless network.
Owner:APPLE INC
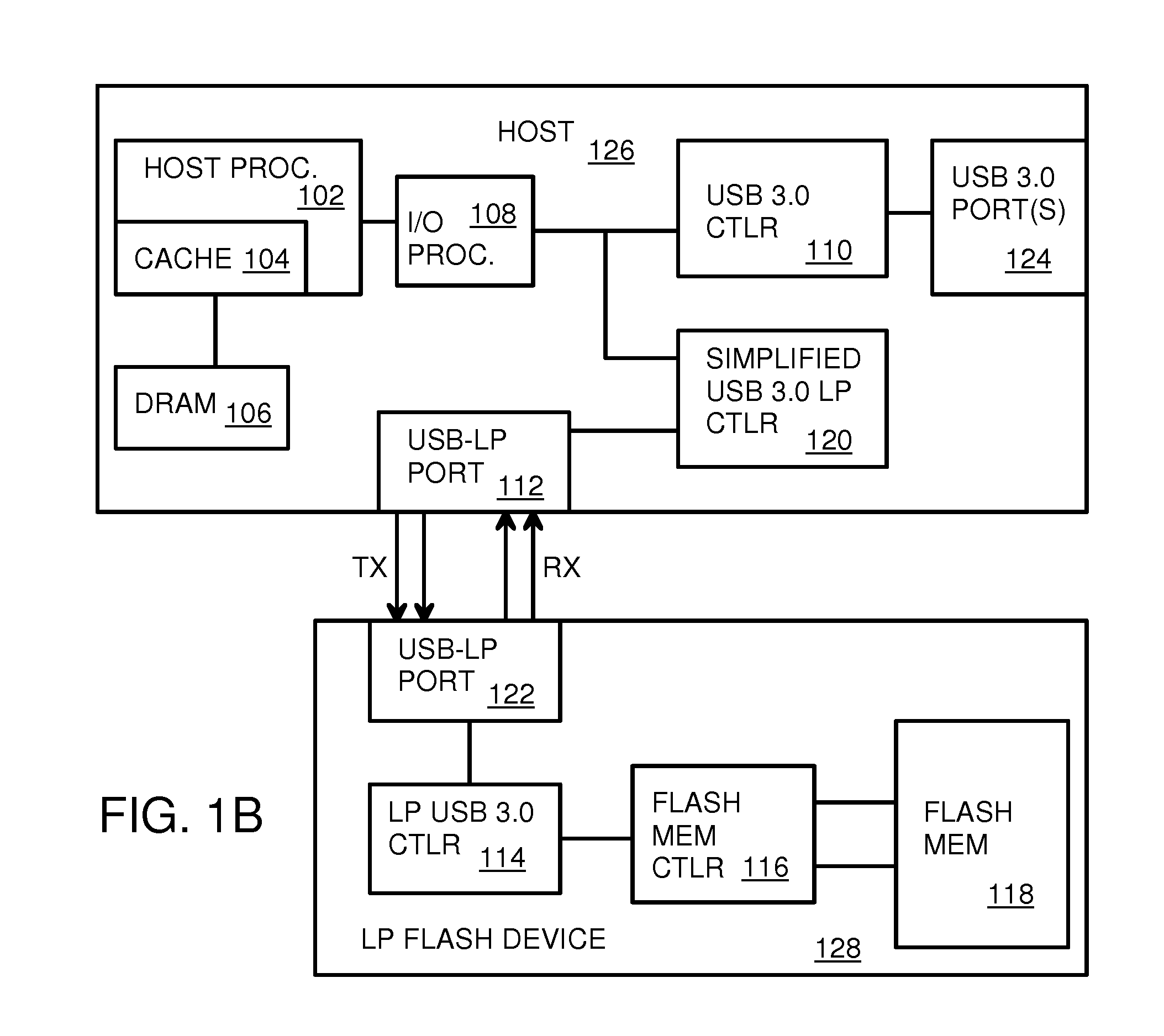
Low-power USB superspeed device with 8-bit payload and 9-bit frame NRZI encoding for replacing 8/10-bit encoding
A Low-power flash-memory device uses a modified Universal-Serial-Bus (USB) 3.0 Protocol to reduce power consumption. The bit clock is slowed to reduce power and the need for pre-emphasis when USB cable lengths are short in applications. Data efficiency is improved by eliminating the 8 / 10-bit encoder and instead encoding sync and framing bytes as 9-bit symbols. Data bytes are expanded by bit stuffing only when a series of six ones occurs in the data. Header and payload data is transmitted as nearly 8-bits per data byte while framing is 9-bits per symbol, much less than the standard 10 bits per byte. Low-power link layers, physical layers, and scaled-down protocol layers are used. A card reader converter hub allows USB hosts to access low-power USB devices. Only one flash device is accessed, reducing power compared with standard USB broadcasting to multiple devices.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
One-way hashing function construction method and system based on built-in chaos mapping
InactiveCN101296079APrevent tamperingKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationHash functionCollision resistance
The invention provides a method and a system for structuring expandable one-way hash function based on embedded chaotic mapping. The structuring method comprises the following steps of: receiving the scheduled chaotic mapping, an initial value, a cipherkey and a message to be treated so as to generate a group of initial buffer value chaotic sequence; using the chaotic sequence to bit-stuff the message so as to divide the stuffed message pad into subblocks with the same length; carrying out Boolean operation to the initial buffer value sequence group and one of the subblocks and taking the result as a new buffer value sequence group; carrying out the Boolean operation again to the new buffer value sequence group and another subblock from the subblocks with preset order until finishing the Boolean operation to all subblocks; cascading of final output, which is taken as the one-way hash function value sequence of the message. Therefore, the structuring method is simple and easy for operation, which effectively realizes the diffusing and mixing of the message and has obvious enhancement in the aspects of security, collision resistance and operation speed.
Owner:SONY CHINA
Frame synchronization in data communication system
InactiveUS6983031B2Easy to implementSimple hardware implementationTime-division multiplexSynchronising arrangementCommunications systemConsecutive frame
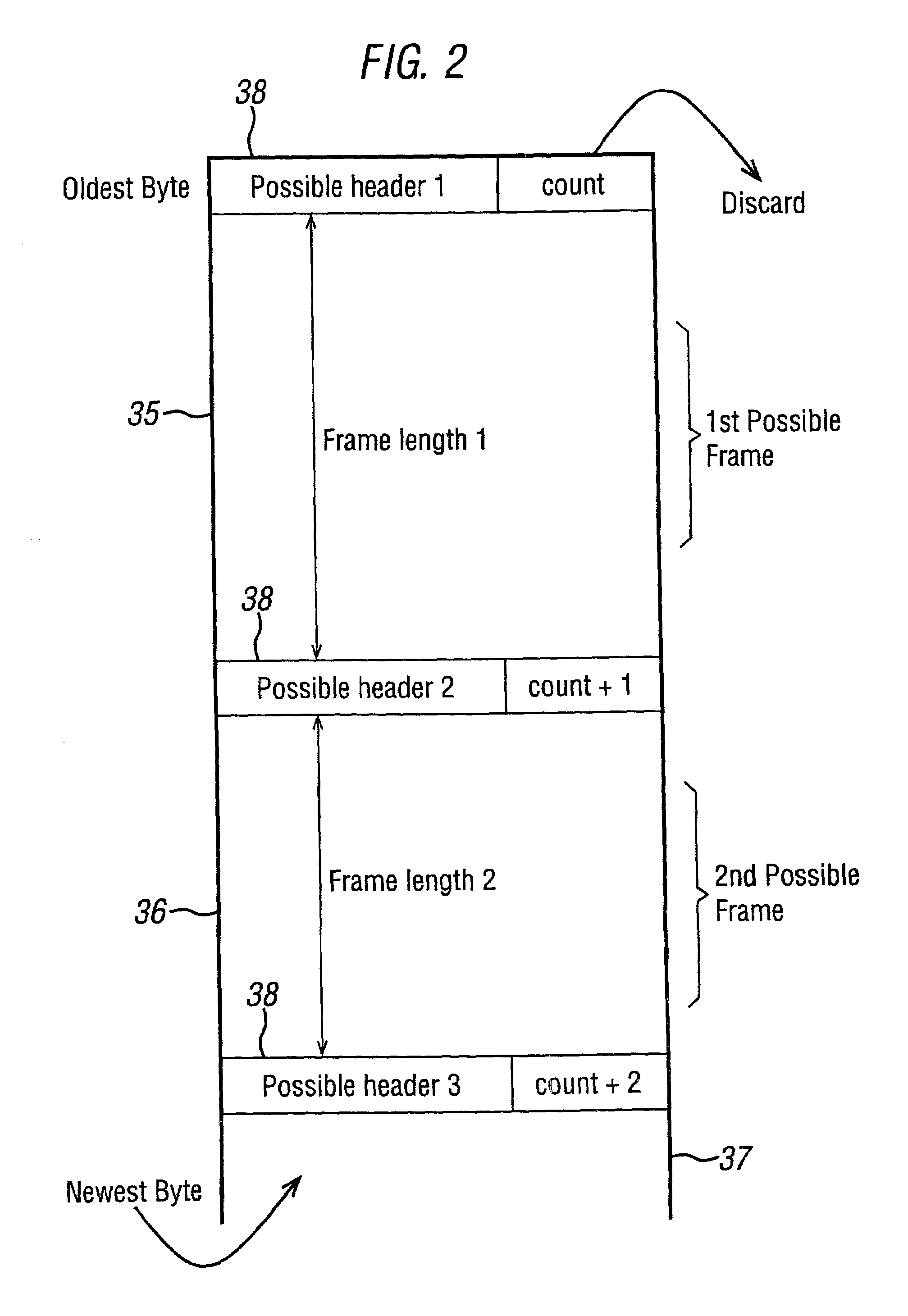
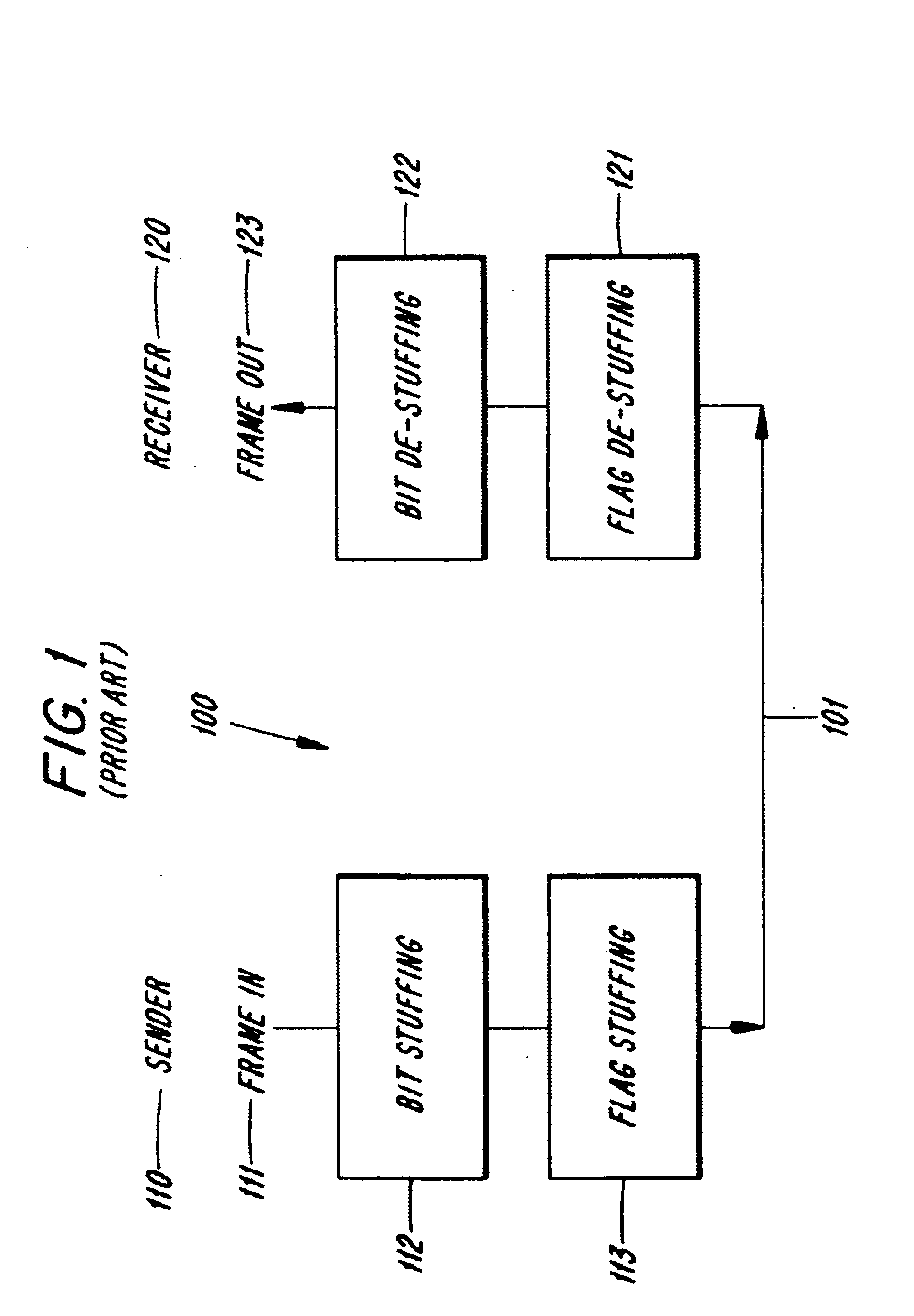
In order to provide a simple and reliable means of frame synchronization in a serial data communication system, which avoids the problem of ‘bit-stuffing’ in known HDLC systems, the data communication system comprises a transmitter arranged to transmit data as a sequence of frames, each frame comprising a synchronization section and a payload section of data, and the transmitter including in the synchronization section of each frame a count value of a sequence of count values (a part of a predetermined code sequence), wherein successive frames contain successive count values (other parts of the predetermined code sequence) The receiver includes a FIFO buffer for storing three successively received frames, and a processor for assessing the stored data within the frames in order to locate and recognize the count values, whereby to synchronize to the received frames.
Owner:AGERE SYST GUARDIAN
Limited error raster compression
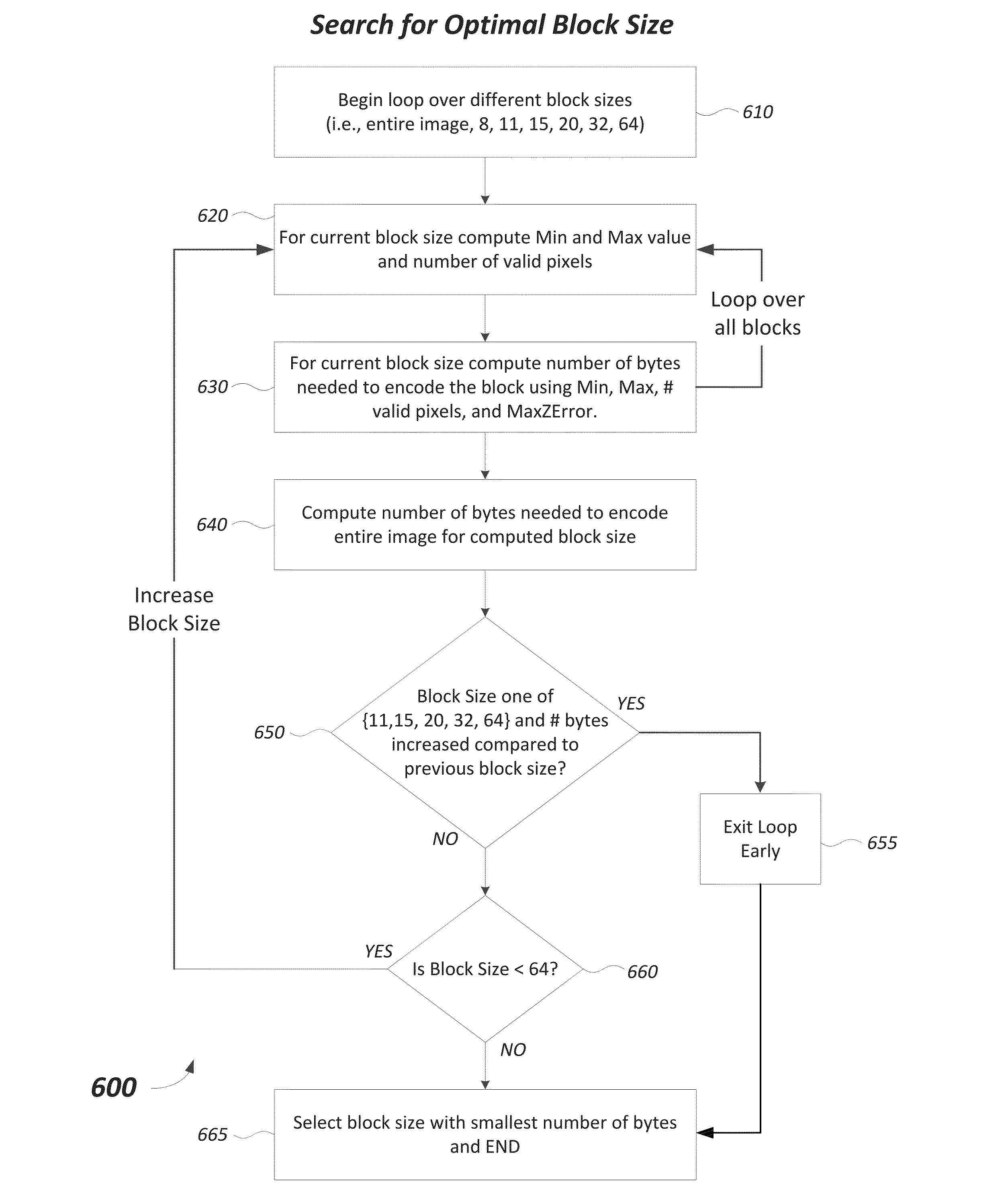
Embodiments of the invention relate to an image or raster compression method for a multi-dimensional array of pixels. A user specifies a maximum error allowable per pixel for the compression algorithm. The raster is divided into a number of pixel blocks where each pixel is quantized and bit stuffed based on a number of block statistics including the maximum error allowable. The size of the pixel blocks is limited to two (e.g., 8×8 and 16×16) to save processing time with little difference in compression. A Look-Up Table (LUT) is used instead for certain types of data where it is more efficient.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL SYST RES INST
Method and apparatus for constant throughput rate adaptation
InactiveUS6859465B1Time-division multiplexTransmitter/receiver shaping networksRate adaptationFlag sequence
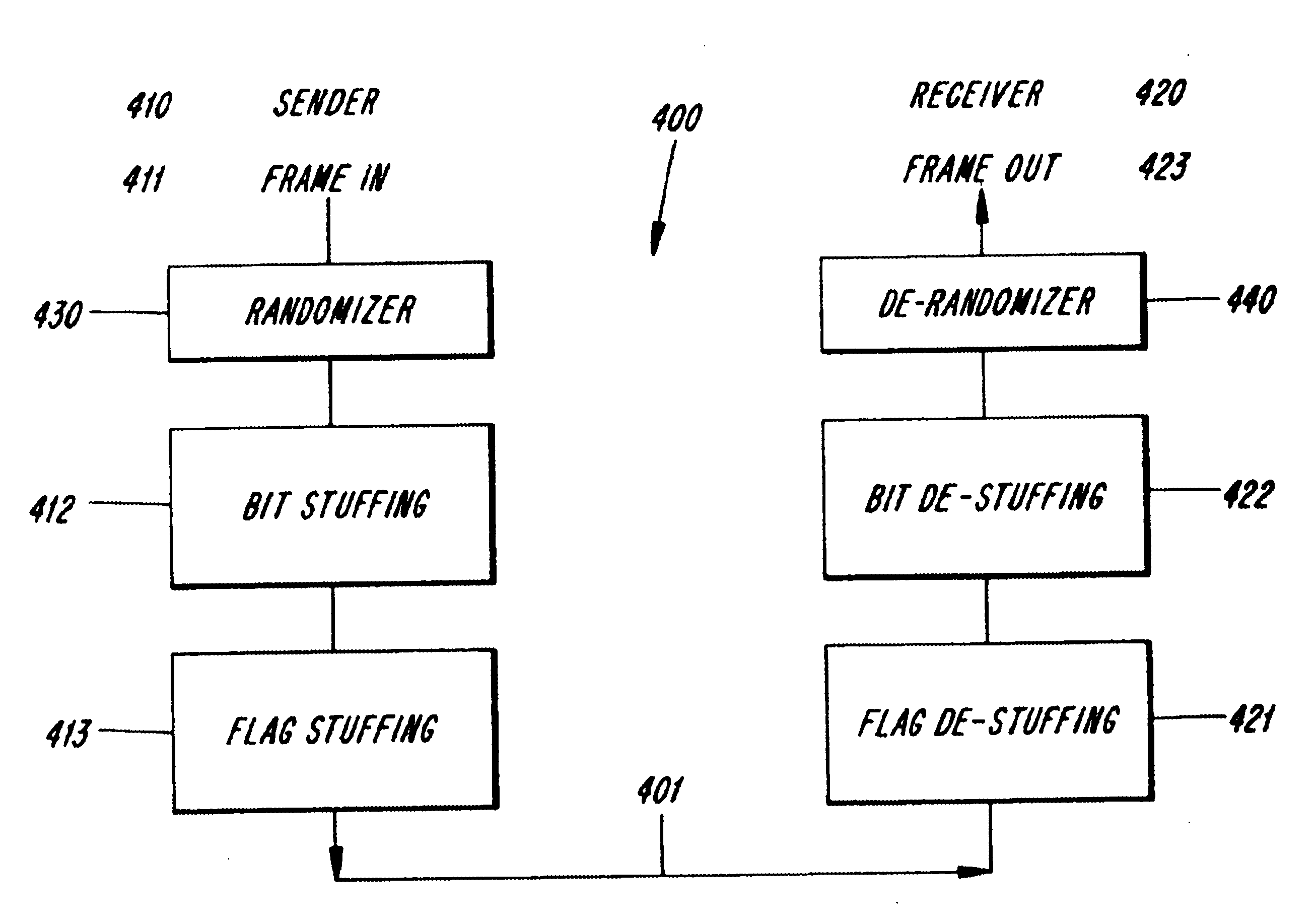
A method and apparatus is described for providing rate adaptation between a first node and a second node in a data communication environment employing bit stuffing and having a link budget of B bits per second. One or more N-sized frames of user data are randomized at the first node according to a predetermined random sequence to produce randomized N-sized frames which are then de-randomized at the second node according to the random sequence. N is the size of the N-sized frames in bits. Occurrences of a flag sequence related event is detected for in the N-sized frames after randomizing, and up to n bits are inserted in the N-sized frames according to a bit stuffing protocol. By performing randomizing before inserting, n and N are selected such that n+N does not exceed B. The bits are then removed such that de-randomizing can be performed. Randomizing includes combining N-sized frames with a random sequence and de-randomizing includes uncombining the N-sized frames with the random sequence. Alternatively, one or more random sequences may be used in randomizing and de-randomizing. Inserting up to n bits further includes determining a distribution of stuffing bits n according to h(n,N) for the N-sized frames such that n and N are selected so that n+N does not exceed B.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
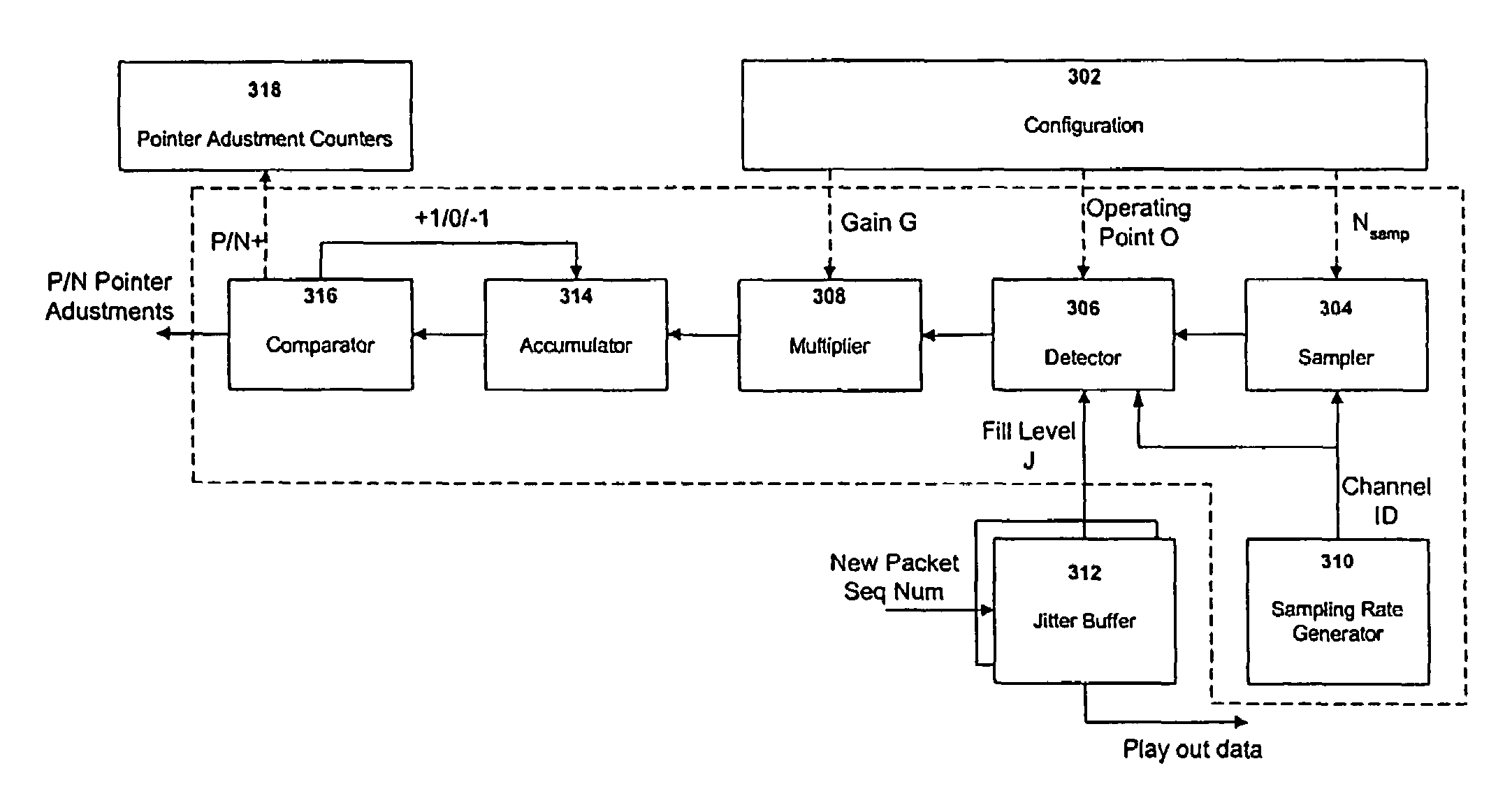
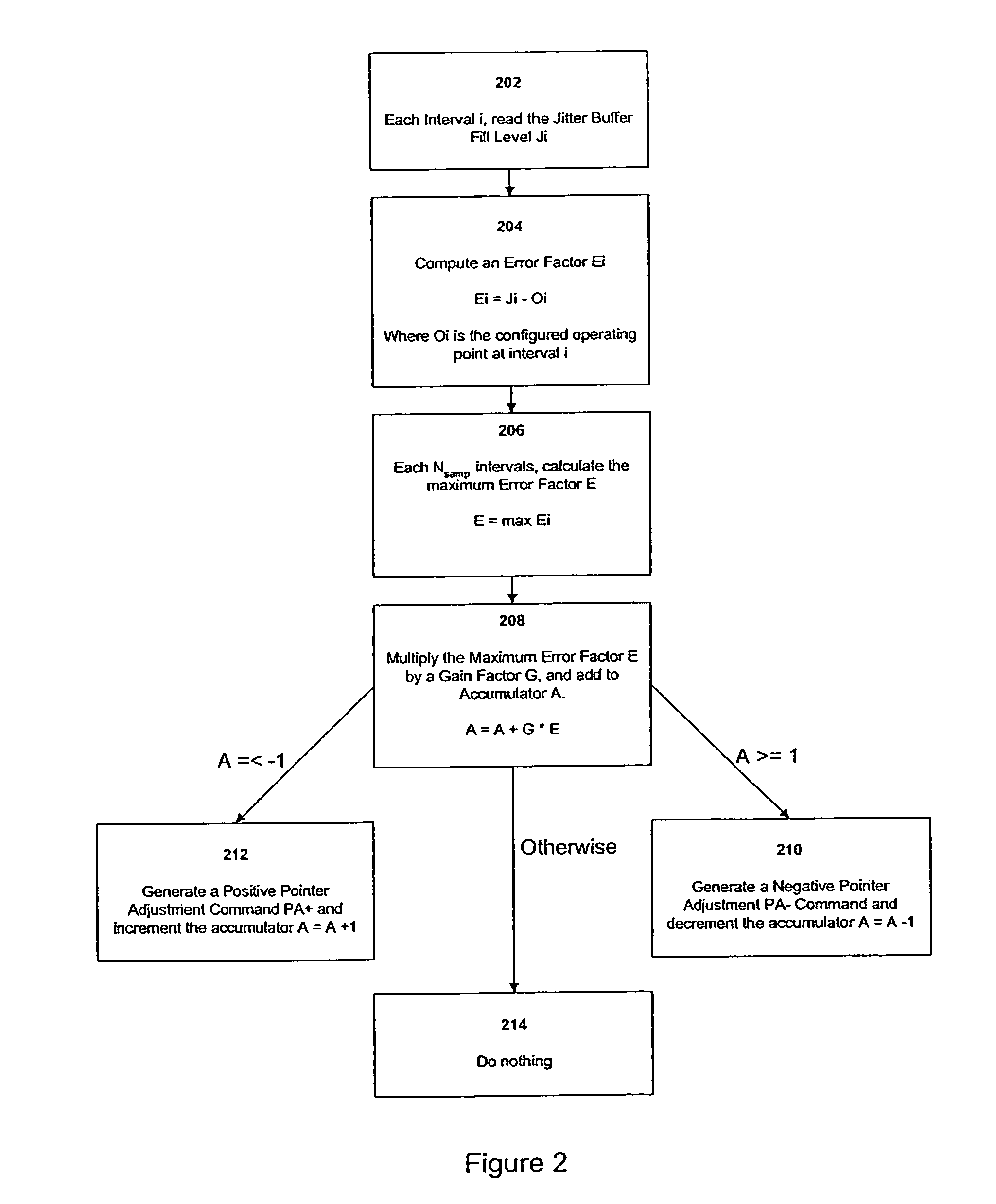
Methods and systems for adaptive rate management, for adaptive pointer management, and for frequency locked adaptive pointer management
InactiveUS7436858B2Good flexibilityPrevent wrong actionTime-division multiplexLoop networksExchange networkPacket switched
An adaptive rate management method and system for adapting a receiver rate to a transmission rate in a packet switch network comprises determining an error value at a sample rate, obtaining an updated accumulator value based on said error value Es at a decimated sample rate, and generating an appropriate rate command and changing said accumulator value at the decimated rate based on the updated accumulator value. The method may be adapted for either adapter point management or bit stuffing. When applied to adapter point management (APM), the method generates pointer adjustments for rate management. In a frequency locked APM preferred embodiment of the method and system, pointer adjustments in an interval are generated at a constant rate based on an average pointer adjustment value calculated in previous intervals.
Owner:RESOLUTE NETWORKS
Dictionary coding compression method without storage of dictionary
A dictionary coding compression method without the storage of a dictionary contains the following steps of: a, generating a determined complete test set by the adoption of an automatic test mode generation tool and recoding the test vector number as N; b, cascading all the test vectors, namely cascading the tail of a vector with the head of another vector, and recording as S; c, establishing an irrational number dictionary list, beginning integers a and b with 2, storing the first t values of the continuously calculated values according to a binary system, establishing a dictionary with the corresponding index being a and b until a=m and b=n, wherein t, m and n are all integers and the values are adjusted according to an actual compression situation; d, coding, carrying out bitwise comparison between S from the beginning and the dictionary list, taking the longest one which is compatible with the dictionary list, recording the corresponding compatible length k and the corresponding indexes x and y, removing the front k values from S, and repeating the step d until S is empty. The invention has the following advantages: memory capacitance is greatly minimized, unrelated bit stuffing is not required, and the efficiency is high.
Owner:詹文法
USB interface drive device based on FPGA technology
InactiveCN101145146AHigh speed data transmissionSuitable for real-time data collection occasionsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCode moduleReal-time data
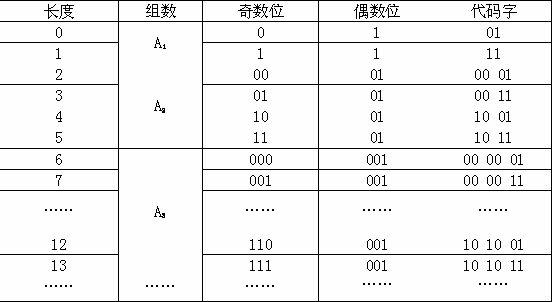
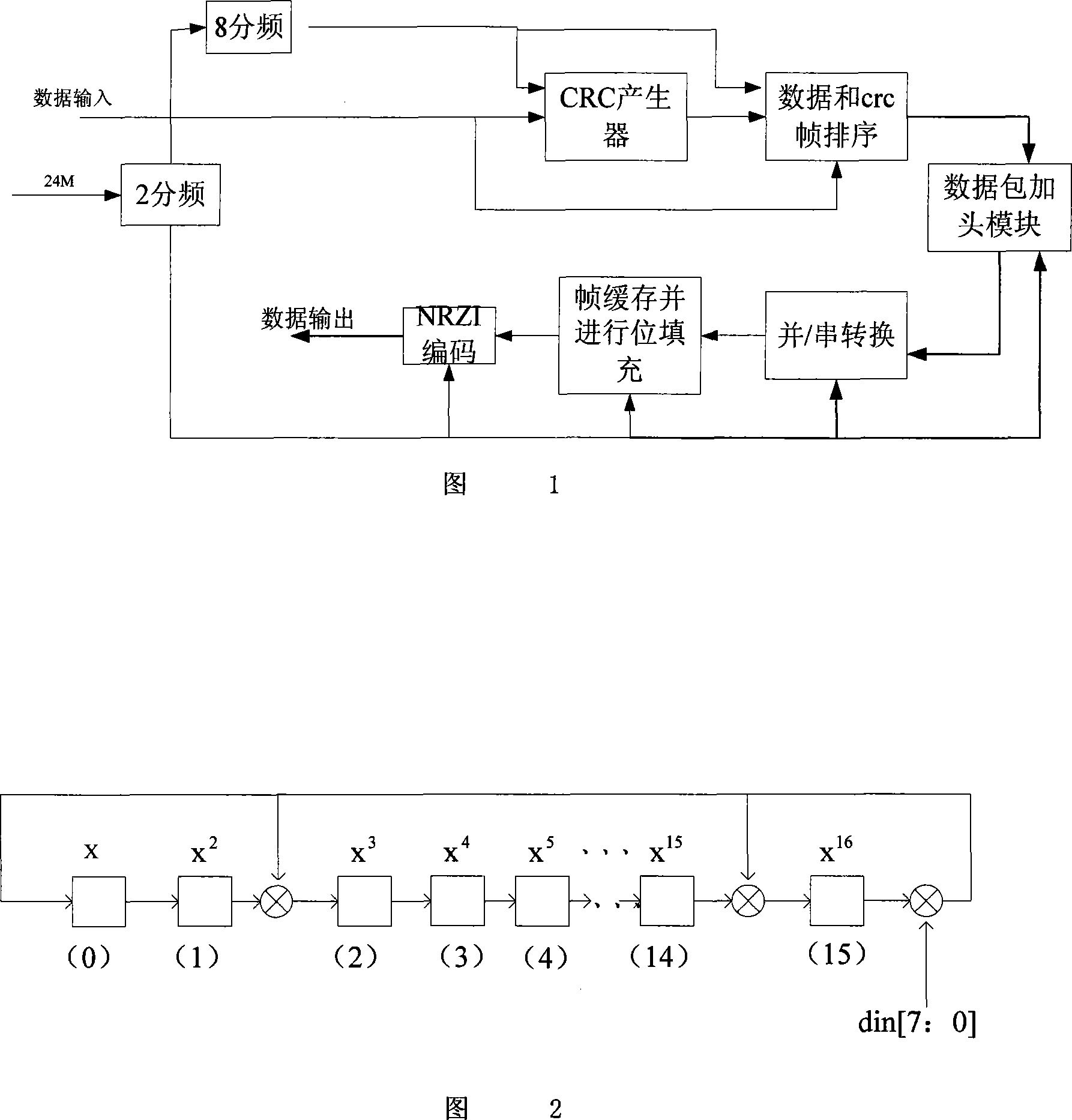
The present invention relates to a drive unit for a USB interface based on the technology of FPGA, consisting of a reset end for an overall setting and an external clock which comprises two clock domains. The USB interface comprises a data producing module, a CRC inspecting module, a sorting module of data and CRC checking codes, a parallel-serial conversion module, a bit stuffing module, an NRZI coding module and a data outputting module. The present invention provides a drive unit for a USB interface that is high-speed in data transmission, is applicable to occasions of real-time data collecting and based on the technology of the FPGA.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for distributing filling bit in split code word
InactiveCN101431396AEffective distributionFrame Error Rate (FER) performance balanceError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionBit numberingBlock number
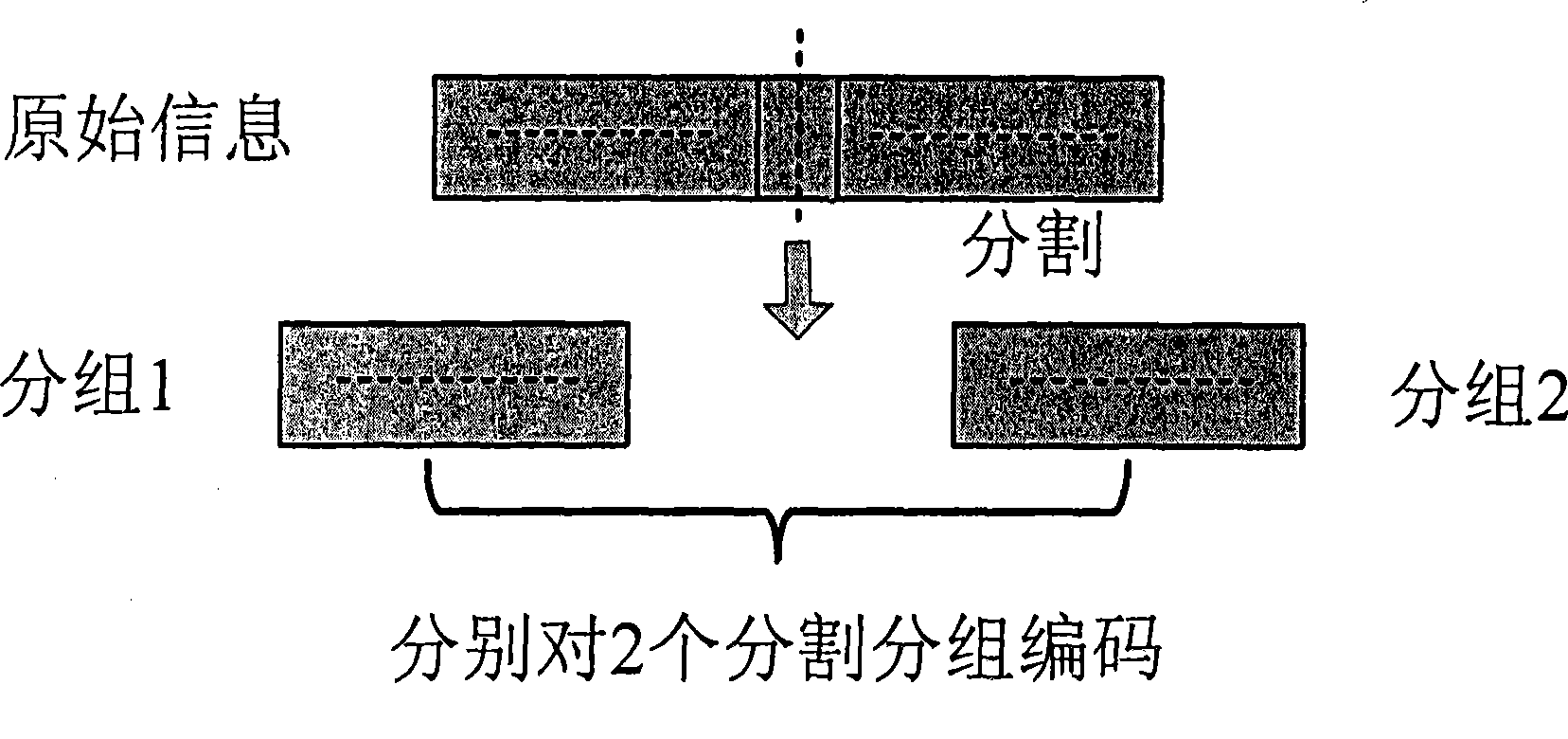
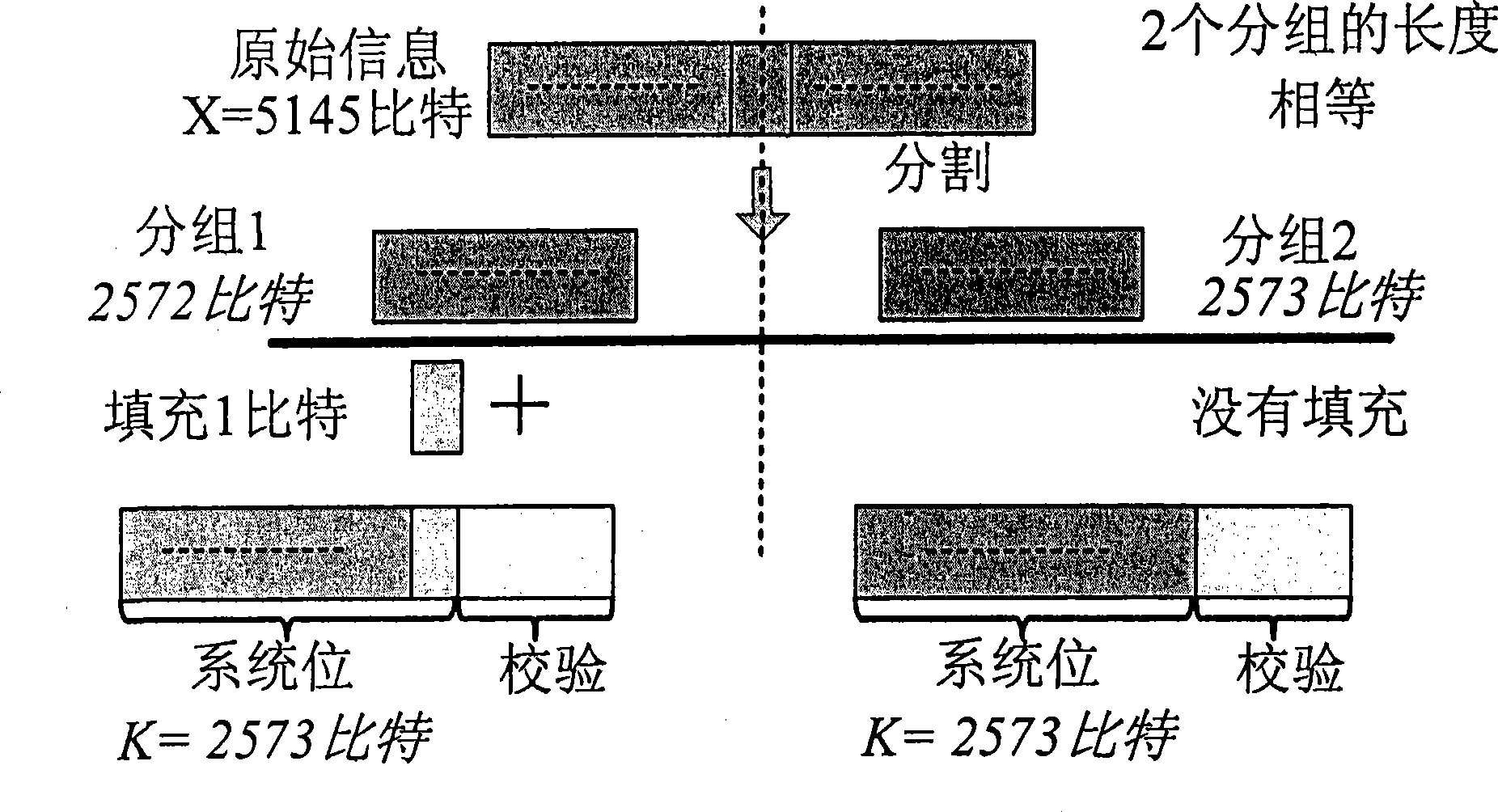
The present invention discloses a method for bit allocating and bit stuffing in encoding block and comprises the following procedures: segmenting original information bit sequence by length of encoding block that supported by channel coding to determine encoding block numbers that need segmented by; selecting two encoding block at least whose length discrete value nearby which supported by channel coding according to numbers of determined encoding block and length of encoding block that supported so as to have the least stuffing bit numbers that introduced by selected at least two encoding blocks; distributing required stuffing bit numbers to all encoding blocks which have smaller block length equally. As replacement, all stuffing bit can be distributed to each encoding block by proportional distribution to make bit rate of each corresponding encoding block approximately equal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for encoding ultra short code length density parity check code
ActiveCN101465655AGood coding performanceImprove performanceError preventionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsRound complexityComputer architecture
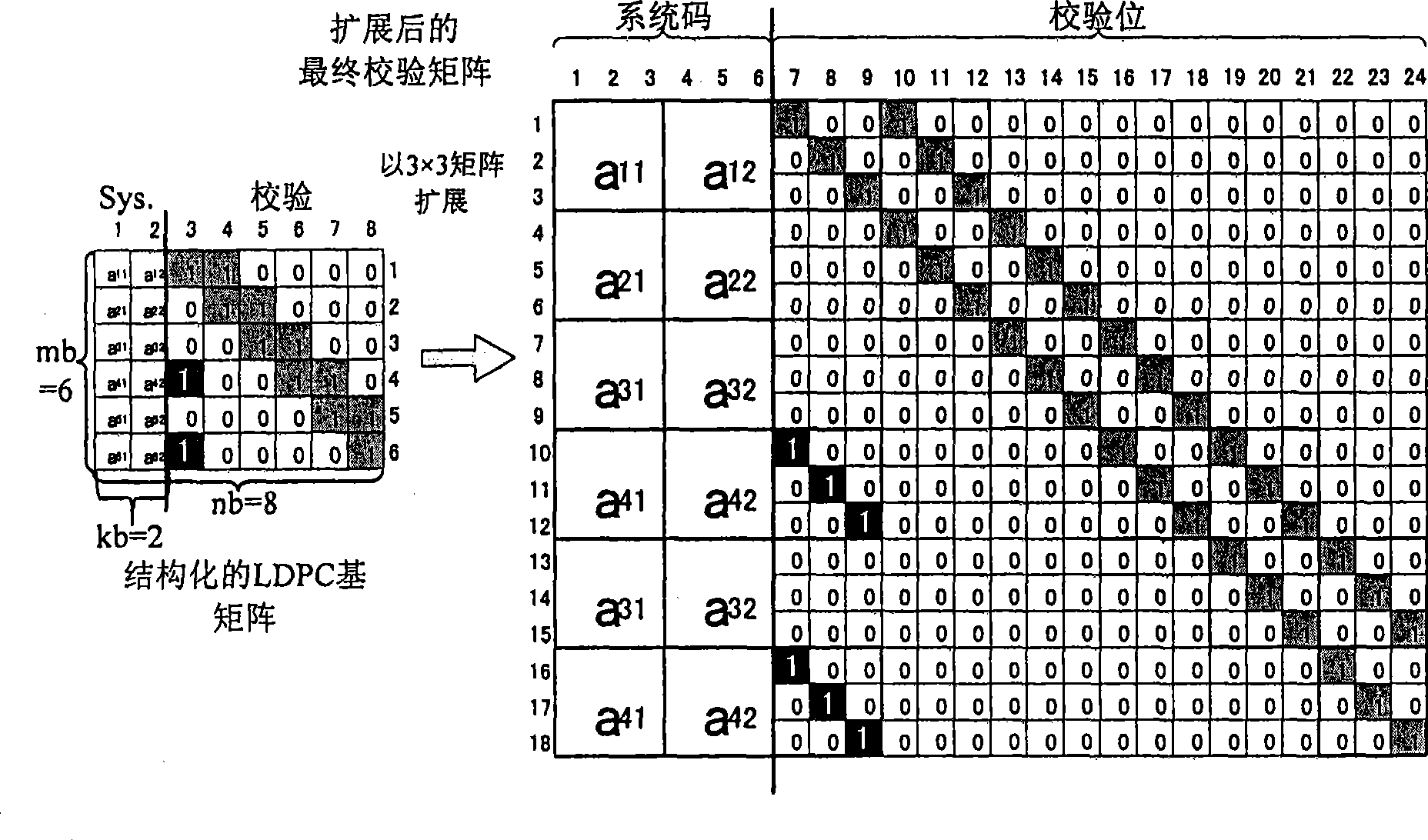
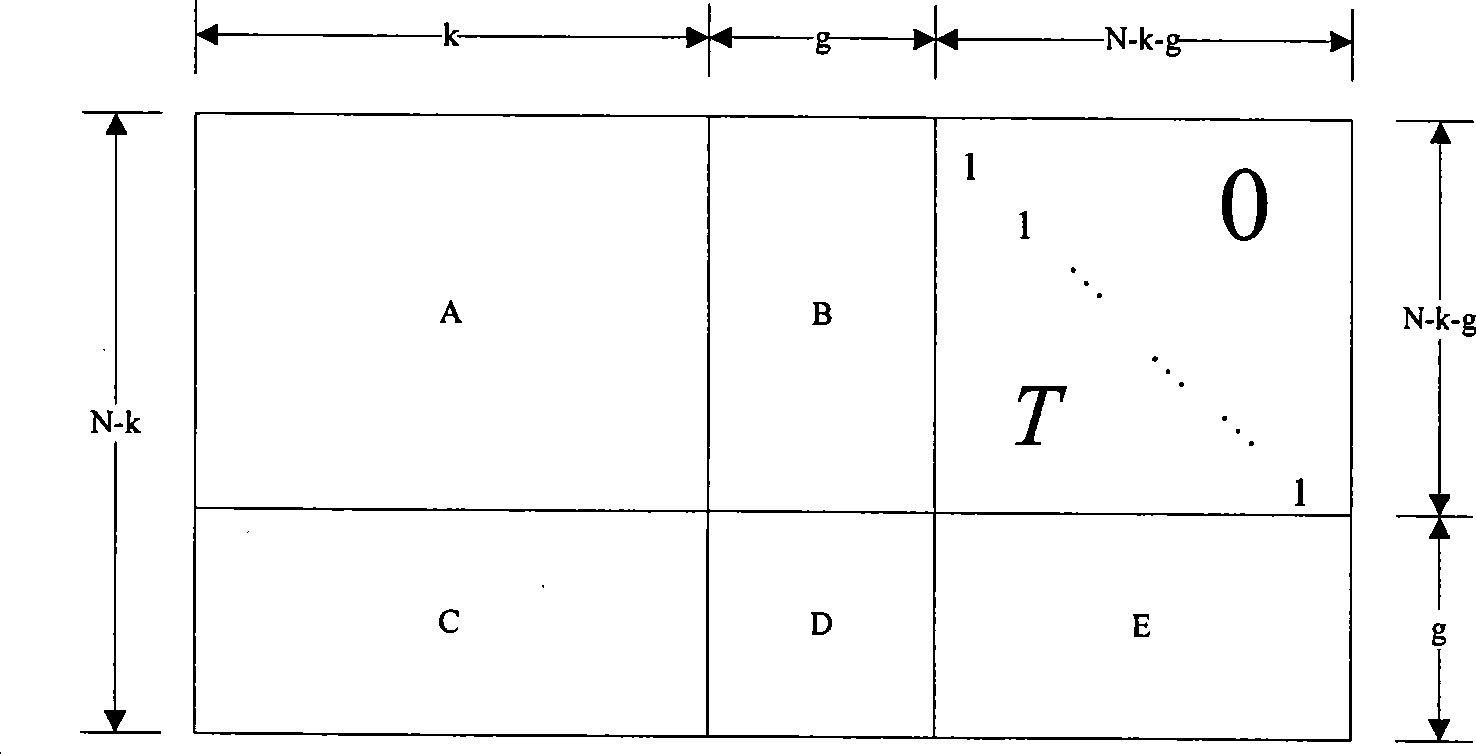
The invention relates to a coding method for very short code-length density parity check code, which belongs to communication channel coding technical field; the coding method includes that a very short LDPC coding code has the code length of 372bits and code rate of 1 / 2; the operations of codeword overlapping, information bit shortening, check bit stuffing, check bit deletion and codeword random interleaving are performed on the obtained LDPC code to realize very short LDPC code coding with other code length and code rate. The coding method proposed in the invention has no loss on coding performance, even has better performance on local points. Meanwhile, compared with coding method based on completely-random structure matrix, the coding method in the invention is realized with very low complexity, and facilitates hardware implementation and has strong application prospect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
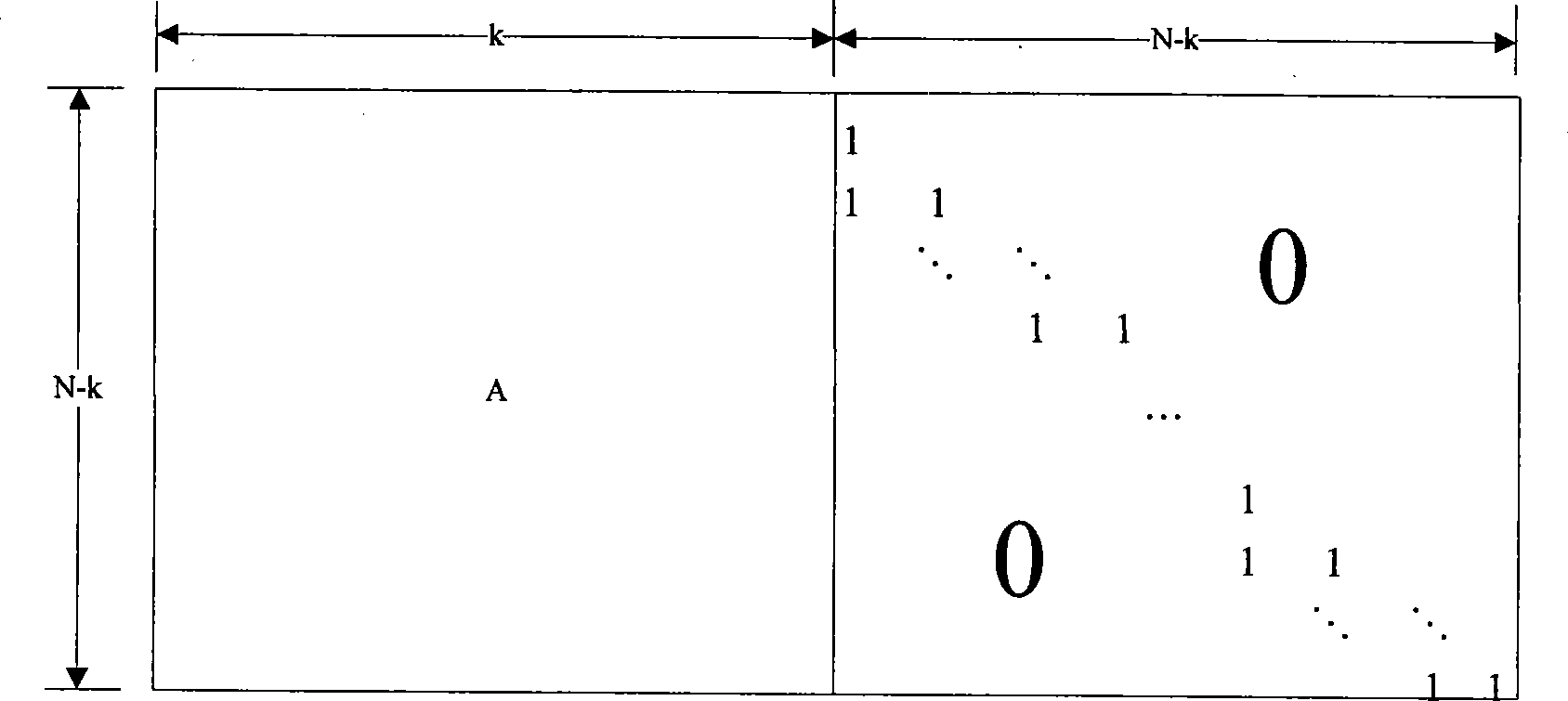
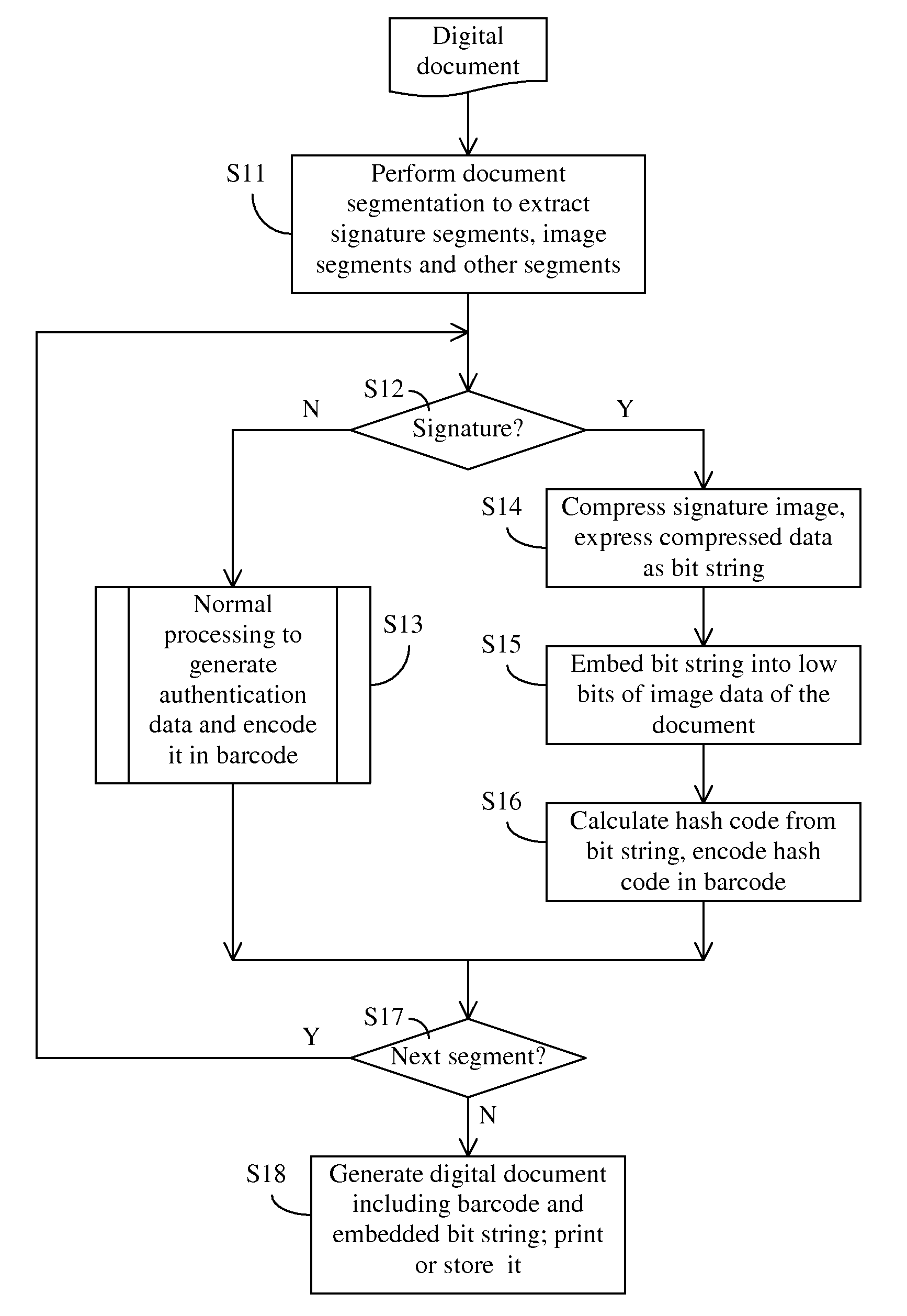
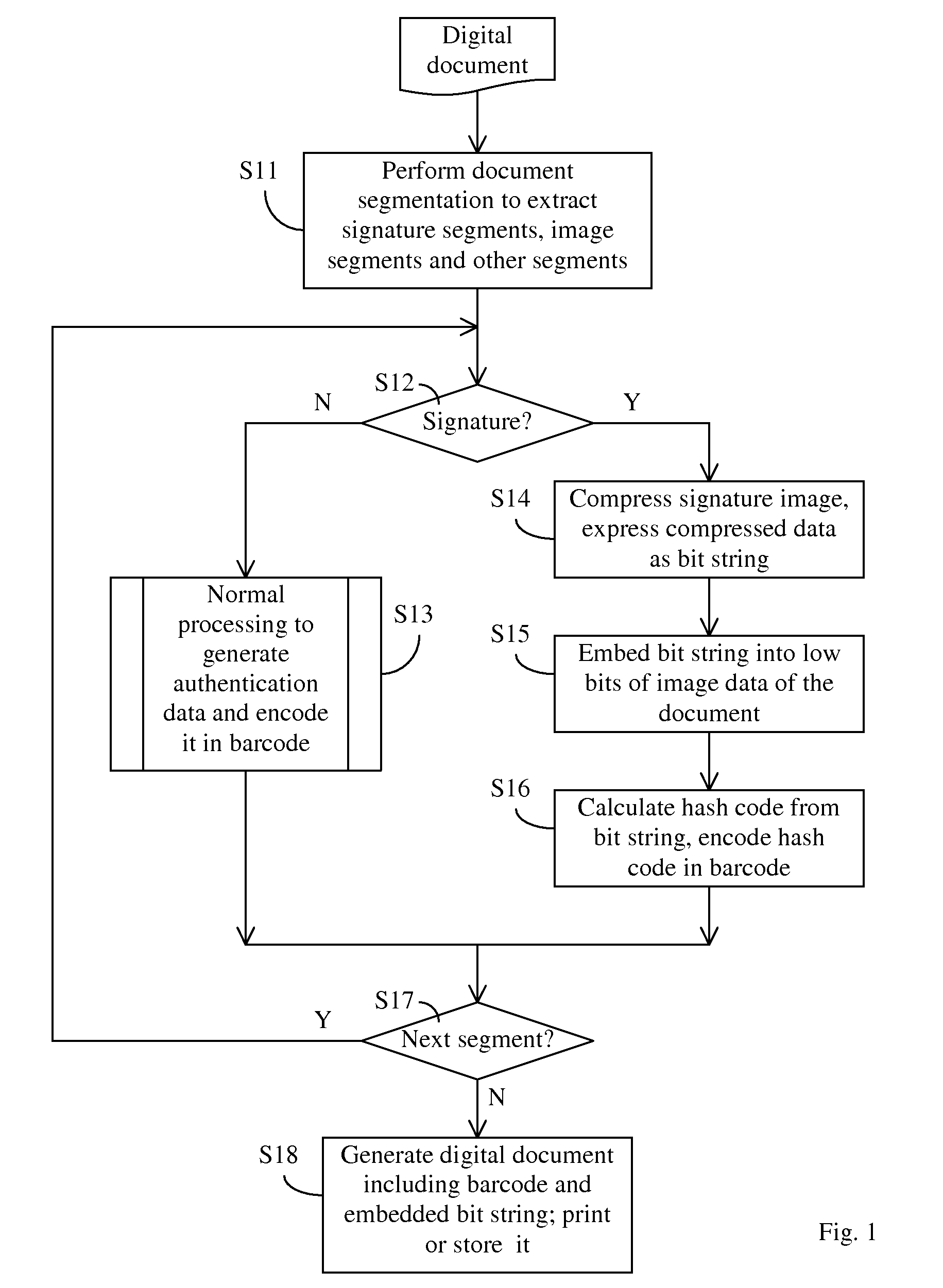
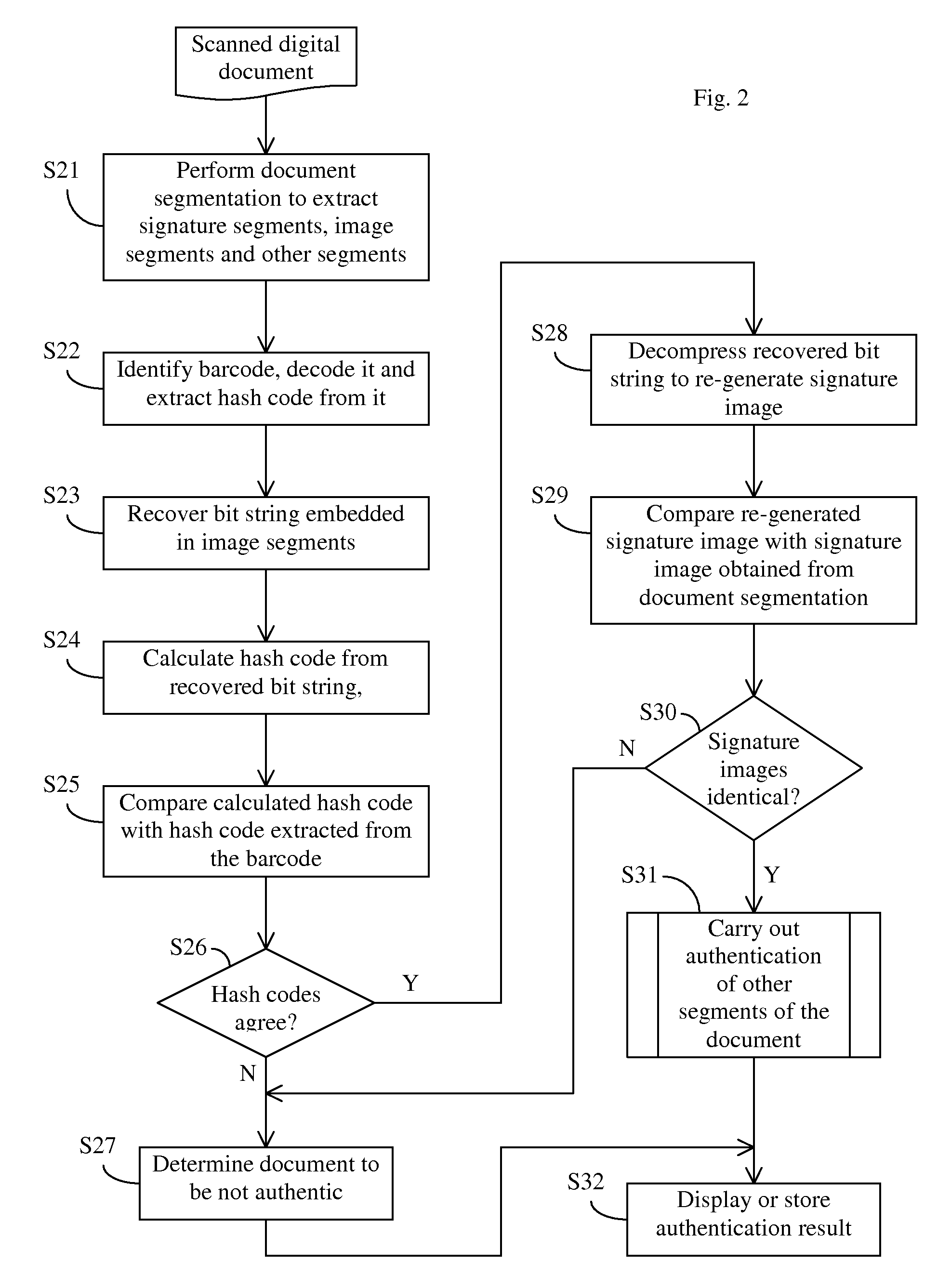
Method of self-authenticating a document while preserving critical content in authentication data
ActiveUS8595503B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareImage resolution
An improved document authentication method in which critical content, such as signatures, is preserved at a high-resolution in the authentication data carried on the self-authenticating document. When generating authentication data, signatures are compressed without down-sampling to preserve their resolution and quality. The compressed signature data (a bit string) is embedded in an image segment on the document. For example, each bit of the bit string is stored in the low bits of one or more image pixels. A hash code is calculated from the bit string and stored in a barcode printed on the document. To authenticate a scanned-back document, the bit string is recovered from the image segment. A hash code is calculated from the recovered bit string and compared to the hash code extracted from the barcode. The signatures re-generated from the recovered bit string are compared to the signatures in the scanned document.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA LAB U S A INC
Physical device (PHY) support of the USB2.0 link power management addendum using a ULPI PHY interface standard
A protocol may enable support of the USB 2.0 LPM (Link Power Management) Addendum by a ULPI PHY (Universal Serial Bus Transceiver Macrocell Low-Pin Interface Physical Layer Device), facilitating transmitting the reserved PID (Physical Interface Device) token, used in the LPM Extended Transaction, through a ULPI bus. Bits [3:0] of a ULPI Tx Cmd (Transmit Command) byte may be reused, with the value of those bits being 4′b0 for a transmission (normally indicating a No PID transmission), by configuring the ULPI PHY to qualify the selected four Tx Cmd bits (bits [3:0] of the Tx Cmd) with the Opmode code. The ULPI PHY may thereby interpret bits [3:0] of the Tx Cmd byte based on the value of the Opmode, and may not transmit the Extended PID when the Opmode is set to 2′b10, that is, when the Opmode is indicative of bit-stuffing and NRZI encoding being disabled, for example during a Chirp transmission. When the Opmode code is set to 2′b0, indicative of normal bit-stuffing, and the Tx Cmd bits [3:0] are set to 4′b0 during a transmission (Tx Cmd bits[7:6]=2′b01), then the PHY may transmit the Extended PID, followed by the rest of the extended transaction onto a USB.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
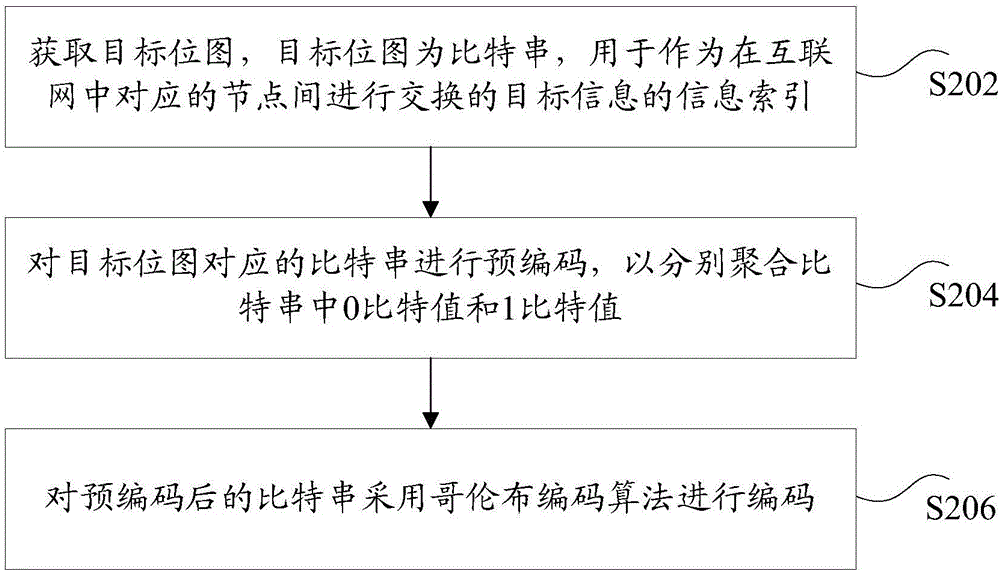
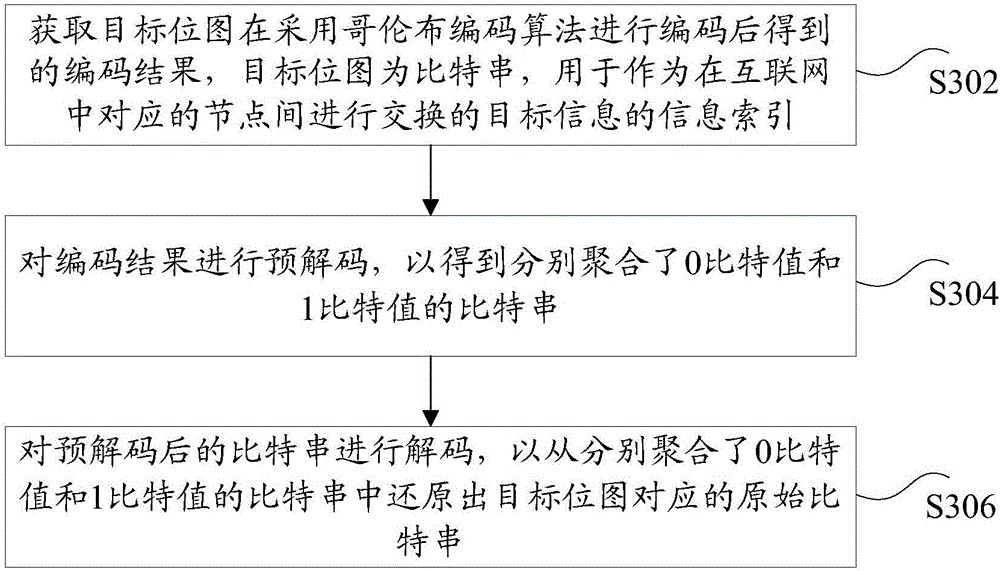
Coding method and device and decoding method and device of information bitmap
ActiveCN106815875AReduce transmission overheadReduce the difficulty of encoding and decodingImage codingDigital video signal modificationComputer hardwareDecoding methods
The invention discloses a coding method and device and a decoding method and device of an information bitmap. The coding method comprises: a target bitmap is obtained, wherein the target bitmap being a bit string is used as an information index of target information of exchanging between corresponding nodes in an internet network; precoding is carried out on the bit string corresponding to the target bitmap to realize aggregation of 0 bit values and 1 bit values in the bit string; and the bit string after precoding is coded by using a Golomb coding algorithm. Therefore, a technical problem of high transmission cost and large coding and decoding difficulty because of direct Golomb coding on an information bitmap according to the correlated technique can be solved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Soft symbol decoding for MIMO communication systems with reduced search complexity
InactiveUS7421035B1Reduce search complexityReduce in quantityPolarisation/directional diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRound complexitySymbol decoding
Soft symbol decoder algorithms for multiple input, multiple output (MIMO) receivers reduce the search complexity by searching over fewer than all possible combinations of transmitted symbols to compute log metrics for each transmitted bit from each transmit antenna. In one algorithm, a sub-optimal set of transmitted symbols is computed and the transmitted symbols are restricted to neighboring constellation points of the sub-optimal set. In another algorithm, all constellation points are searched for every antenna except one. In yet another algorithm, constellation points are searched excluding more than one antenna. The non-searched antenna(s) can be handled by either a bit stuffing or a soft slicing technique.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
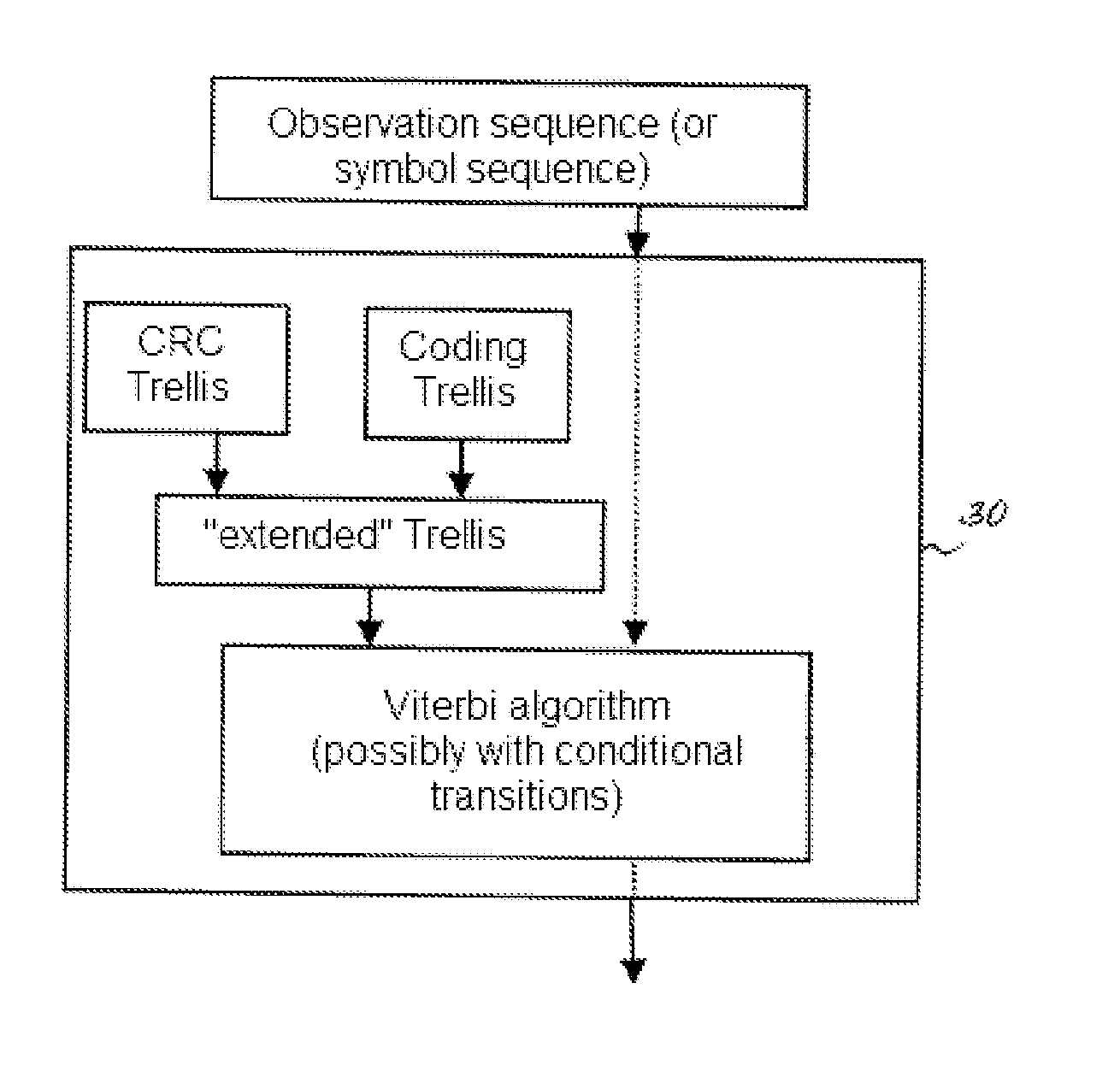
Decoding method and decoder
ActiveUS20130275841A1Other decoding techniquesError correction/detection using trellis codingDecoding methodsFinite-state machine
The method according to the invention relates to the decoding of a sequence of symbols, the sequence of symbols having been generated by: calculating a CRC value for an initial message; combining the initial message and the CRC value so as to produce a transformed message; and, encoding the transformed message. The decoding comprises: generating a number of path hypotheses via a trellis diagram corresponding to the trellis diagram of a finite-state machine comprising the encoder and the CRC generator, in which the encoder and the CRC generator are supplied with the same input. According to a preferred embodiment of the method, the trellis diagram is adapted to take into account bit stuffing possibly inserted in the transformed message before encoding.
Owner:CENT NAT DETUD SPATIALES C N E S
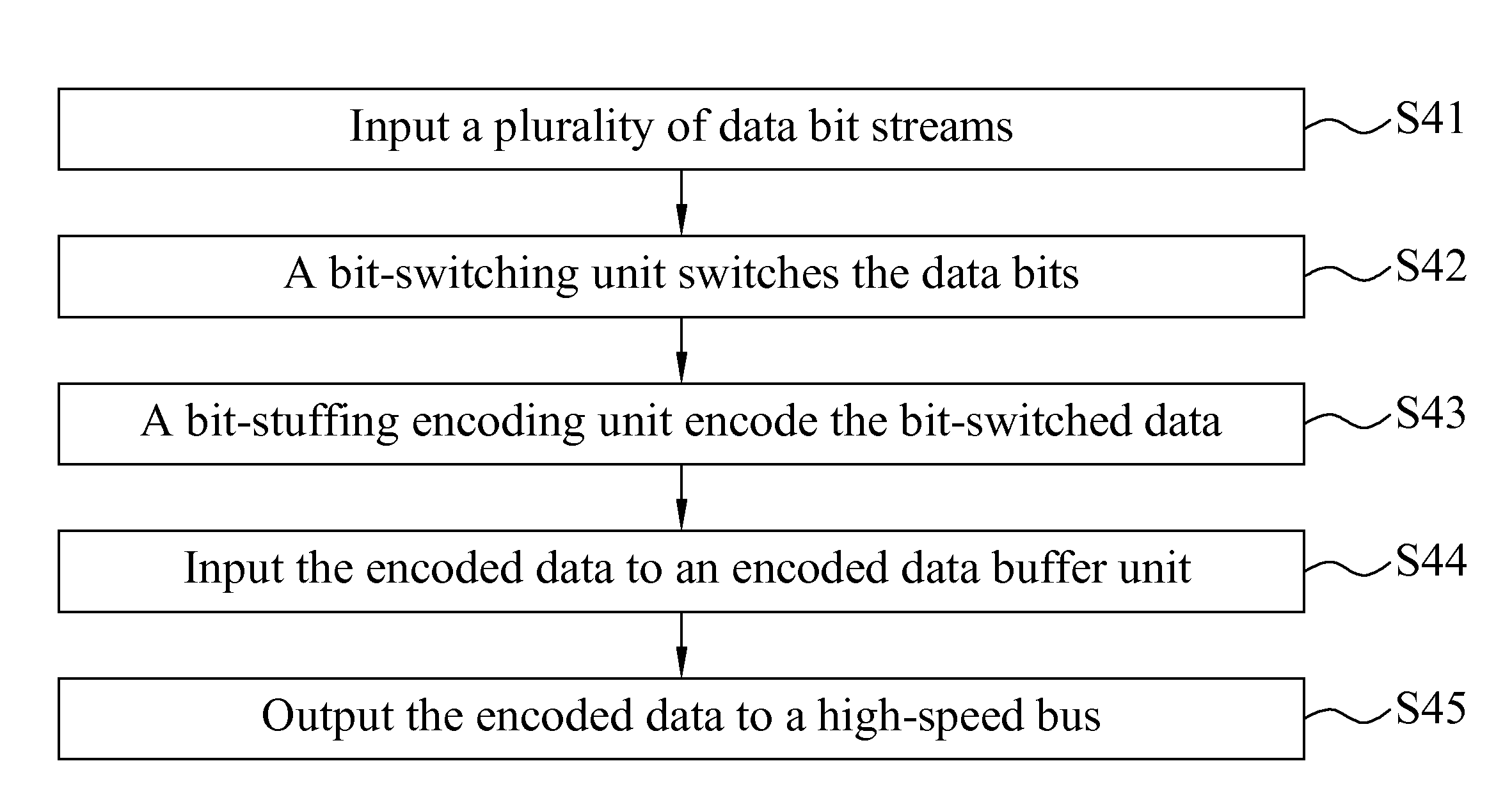
Bit-stuffing method for crosstalk avoidance in high-speed buses
InactiveUS20110222622A1High bit rateReduce complexityTime-division multiplexSecret communicationCrosstalkData buffer
This invention discloses a bit-stuffing method for crosstalk avoidance in high-speed buses, which comprises the steps of inputting a plurality of data bit streams in parallel to a data input buffer; the data input buffer sequentially inputting data bits of the data bit streams to a bit-switching unit, and the bit-switching unit switching the data bits to generate bit-switched data; parallelly inputting the bit-switched data to a bit-stuffing encoding unit; the bit-stuffing encoding unit performing bit-stuffing encoding on the bit-switched data to generate encoded data bits and inputting the encoded data bits to an encoded data buffer; and the encoded data buffer outputting the encoded data to a high-speed bus. The encoded data bits passed through the high-speed bus are decoded using a bit-removing method to recover the data bit streams.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Semiconductor device, unique ID of semiconductor device and method for verifying unique ID
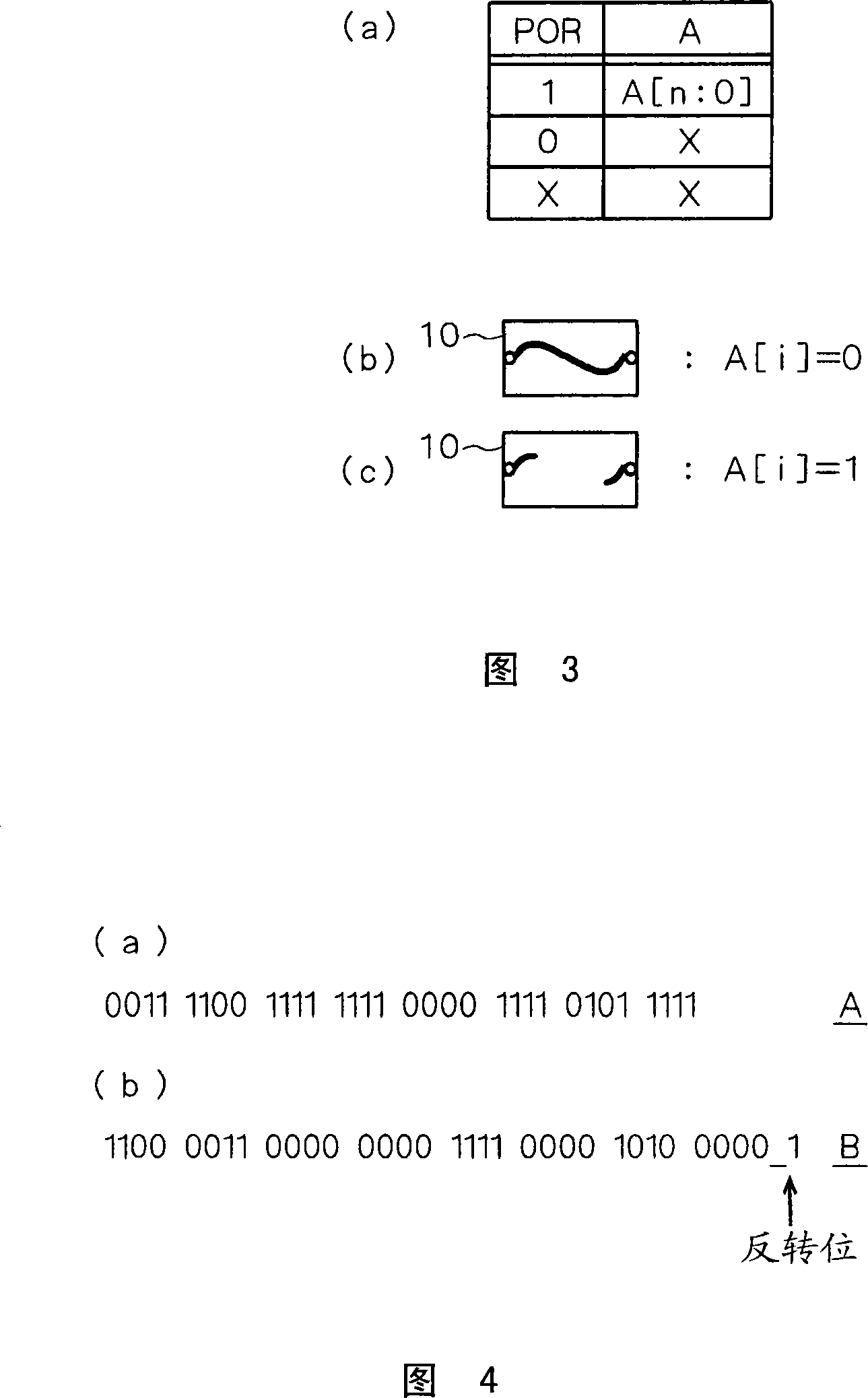
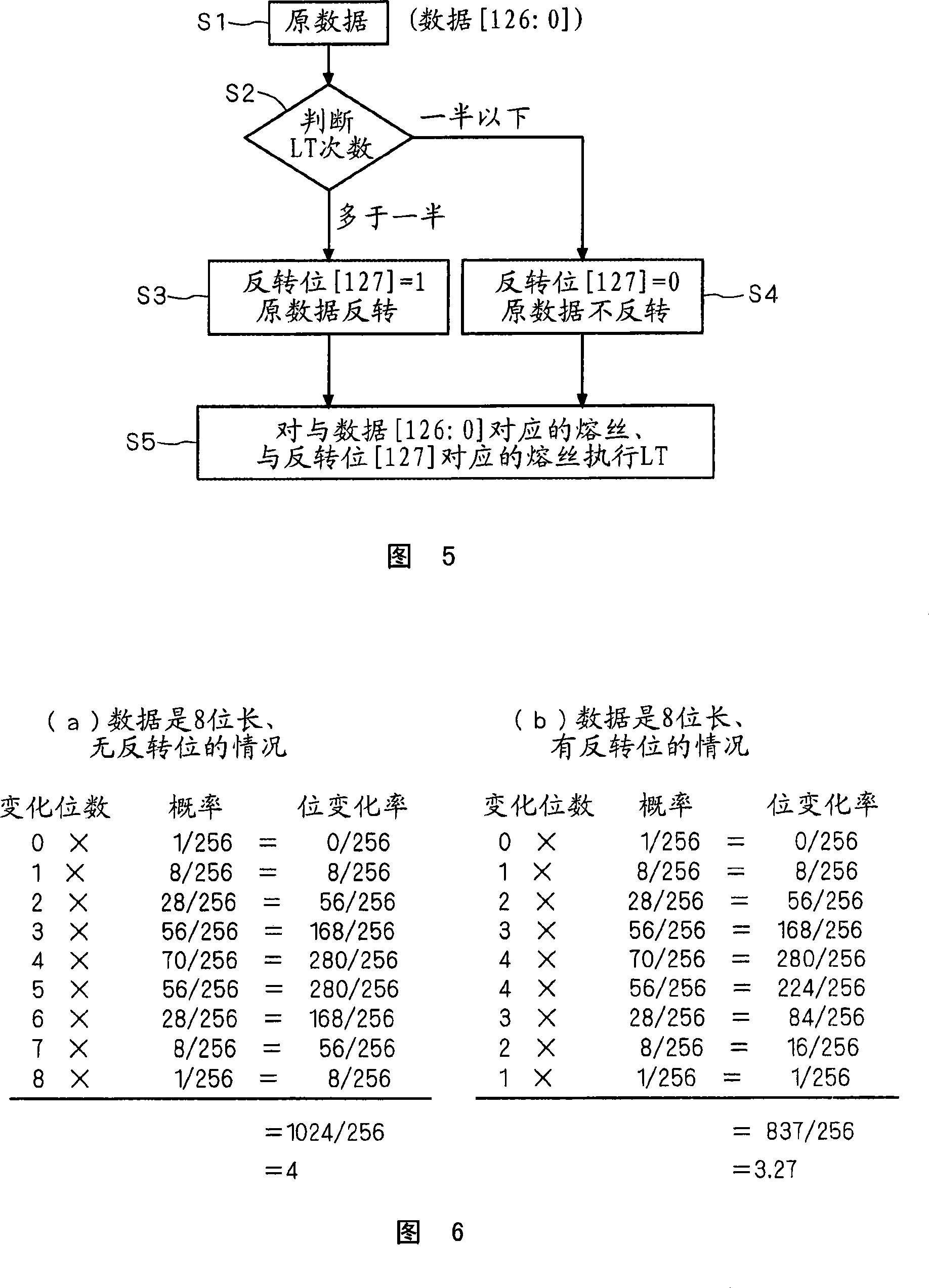
InactiveCN101086757AReduce laser trimming timesShorten production timeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesValidation methodsOriginal data
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device, a unique ID of the semiconductor device and a method for verifying the unique ID. Thus, original data (bit string) having 127-bit length [126:0] is inputted at step S1 . Then, it is determined whether the number of bits of ''1'' in the bit string [126:0] inputted at the step S 1 is more than the half of the bits of the bit string (that is, not less than 64) or not at step S2 . When the number is not less than 64, the process proceeds to step S3 . At the step S3 , the bit string [126:0] is inverted and an invert bit [127] is set to ''1''. Then, the process proceeds to step S5 . At the step S5 , the fuse corresponding to the bit string [126:0] and the bit [127] are cut by LT.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Message processing method and device
Embodiments of the invention provide a message processing method. The method comprises the steps that a first node receives a first message, wherein the first message carries a first bit string, the first bit string comprises M bit sets, each bit set is corresponding to one node group, a value of the bit set is used for indicating whether a target node of the first message comprises a corresponding node group, and M is an integer greater than or equal to 1; and the first node determines whether to send the first message to a second node according to the first bit string and a second bit string, wherein the second bit string comprises N bit sets, each bit set is corresponding to one node group, a value of the bit set is used for indicating whether a related node of the first node comprisesa node belonging to a corresponding node group, and N is an integer greater than or equal to 1. The node needs to store the second bit string alone and does not need to store complex forwarding tableentries, whether the message is to forwarded is determined according to the first bit string and the second bit string, and the node is required of low calculation capability.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
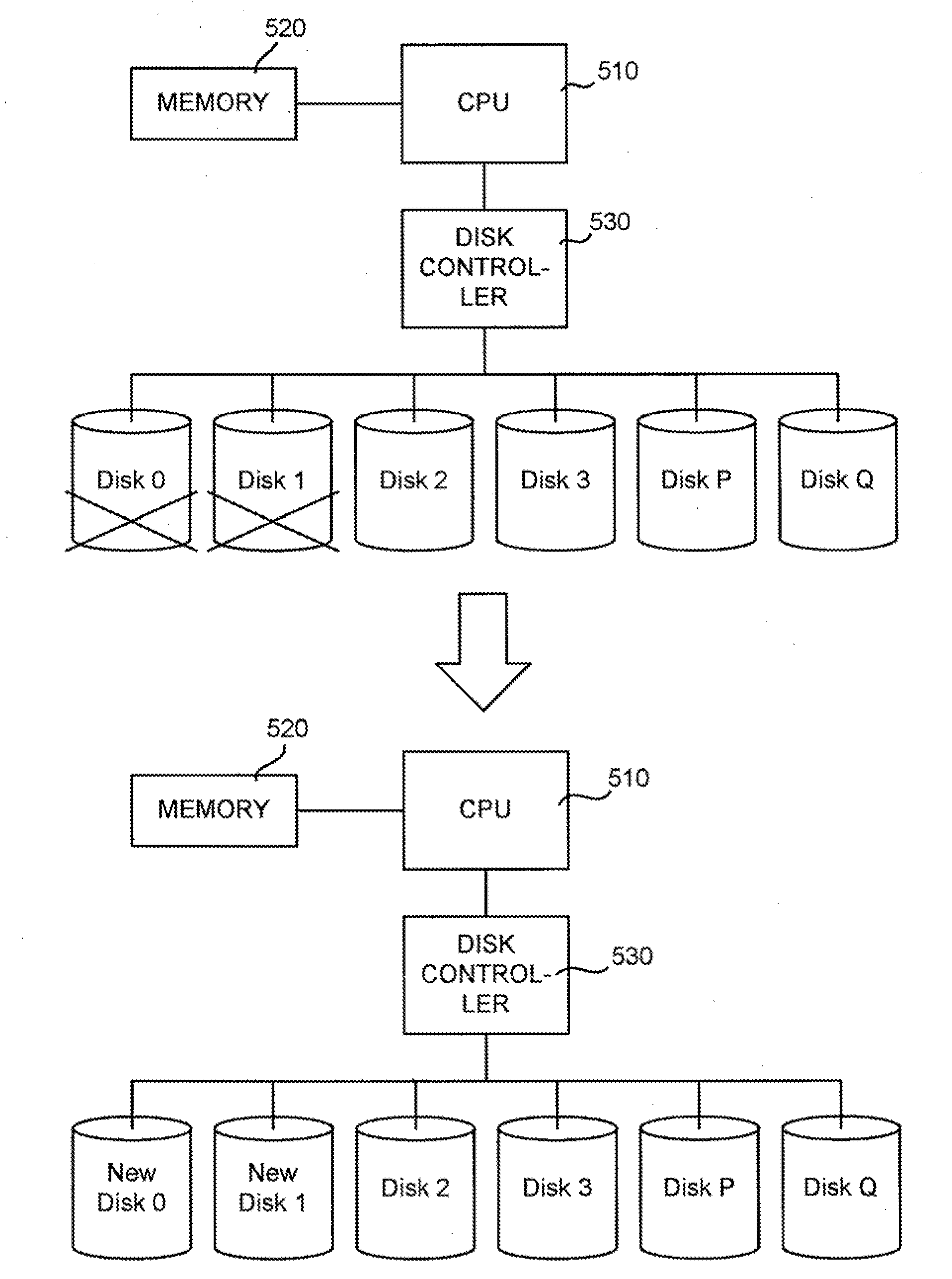
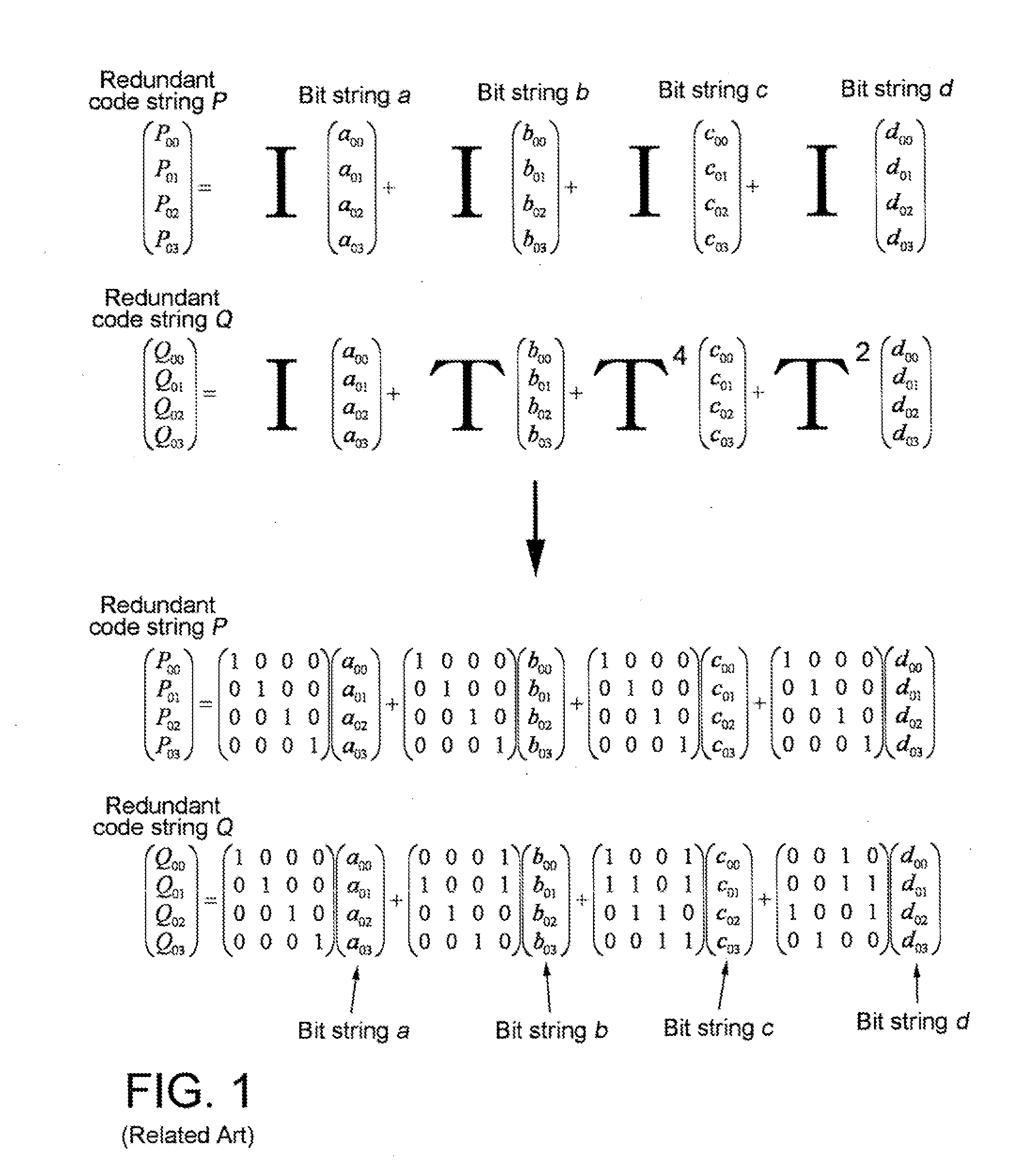
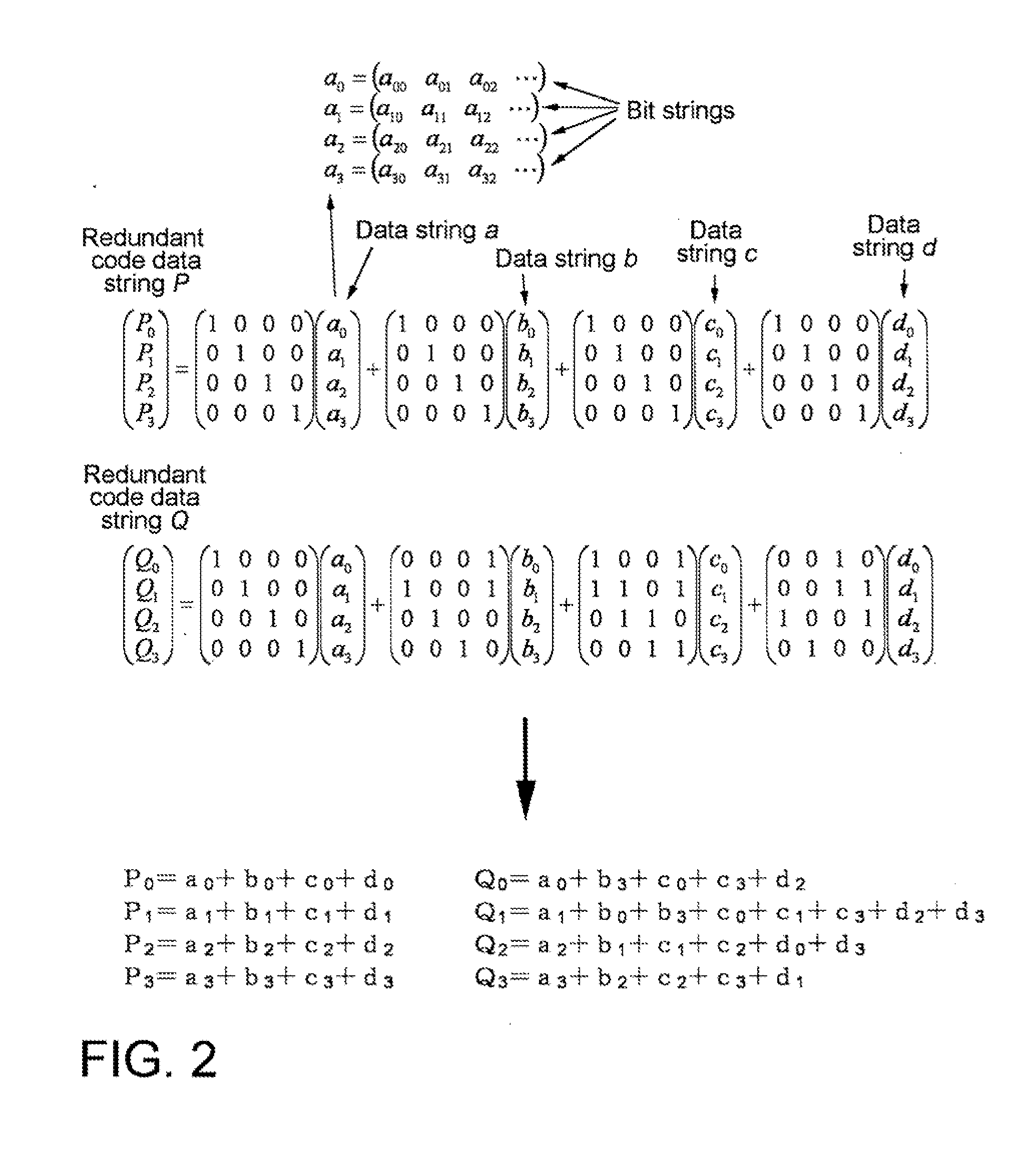
Redundant code generation method and device, data restoration method and device, and raid storage device
ActiveUS20100251071A1Increase speedGenerate redundant codeMemory loss protectionCode conversionRAIDAs element
A redundant code generation method includes: dividing original data into data strings; dividing each data string into a number of bit strings that accords with an extended Galois field operation; storing each of the bit string in a different memory area of a memory; and executing an exclusive OR operation among vectors, which are extracted from the respective bit strings stored in the memory, according to an operational expression to compute bit strings that make up redundant code data strings without carrying out a bit shift operation within the vectors. A predetermined plural number of bits is taken as a data unit and the number of bits as elements constituting each vector is equal to the data unit. The operational expression includes a companion matrix of a primitive polynomial of the Galois field and defined the generation of the redundant code data strings.
Owner:NEC CORP
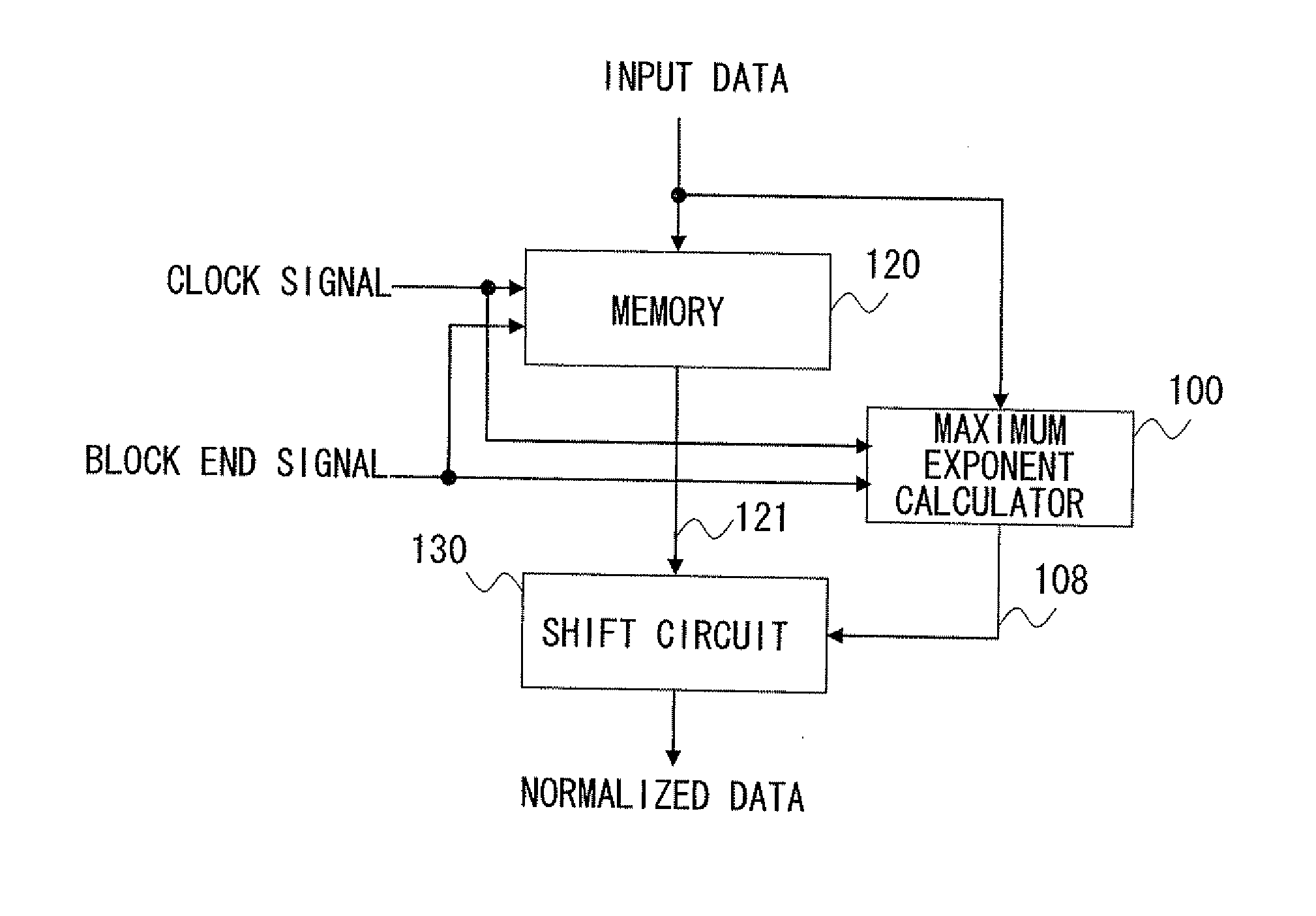
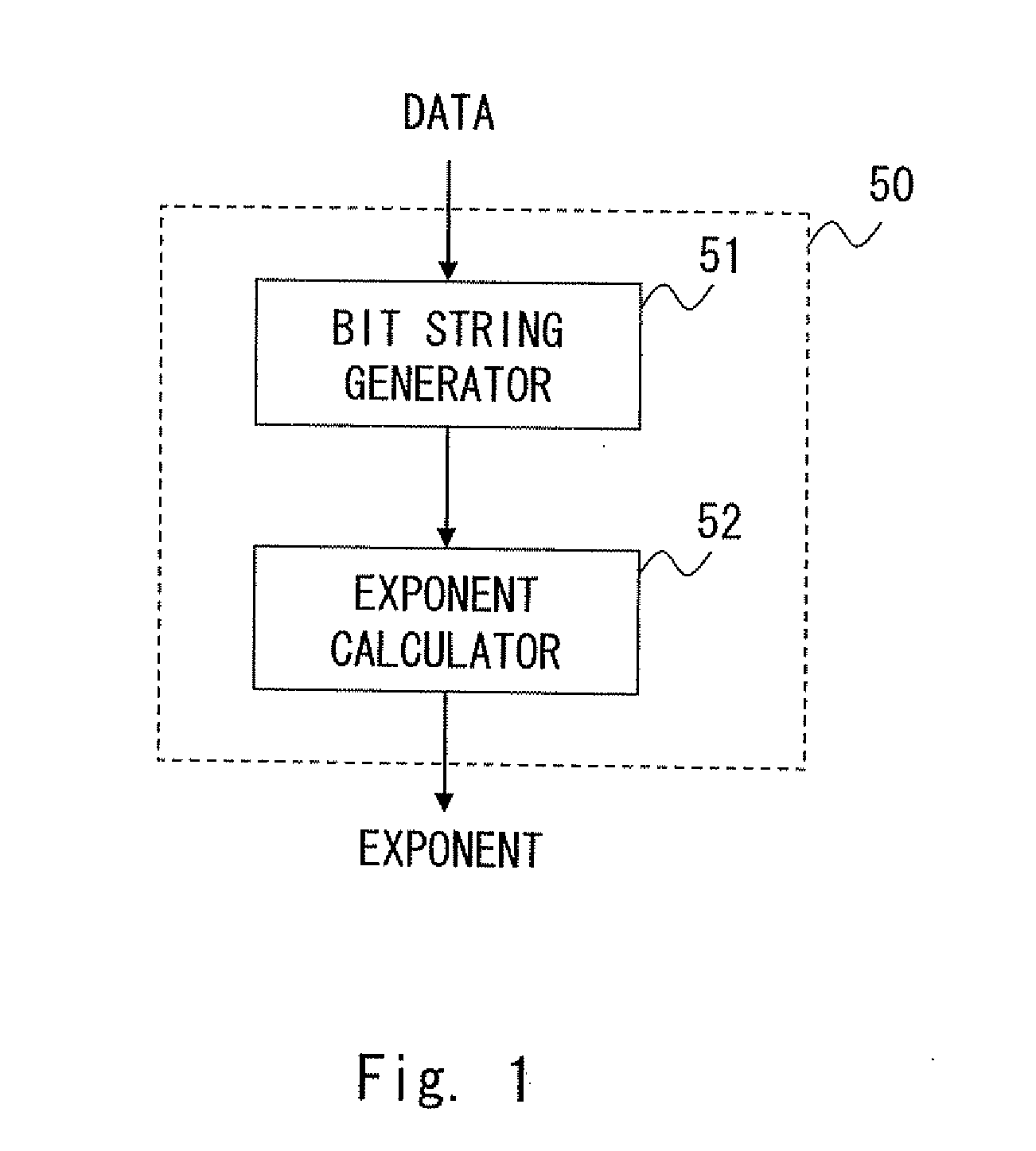
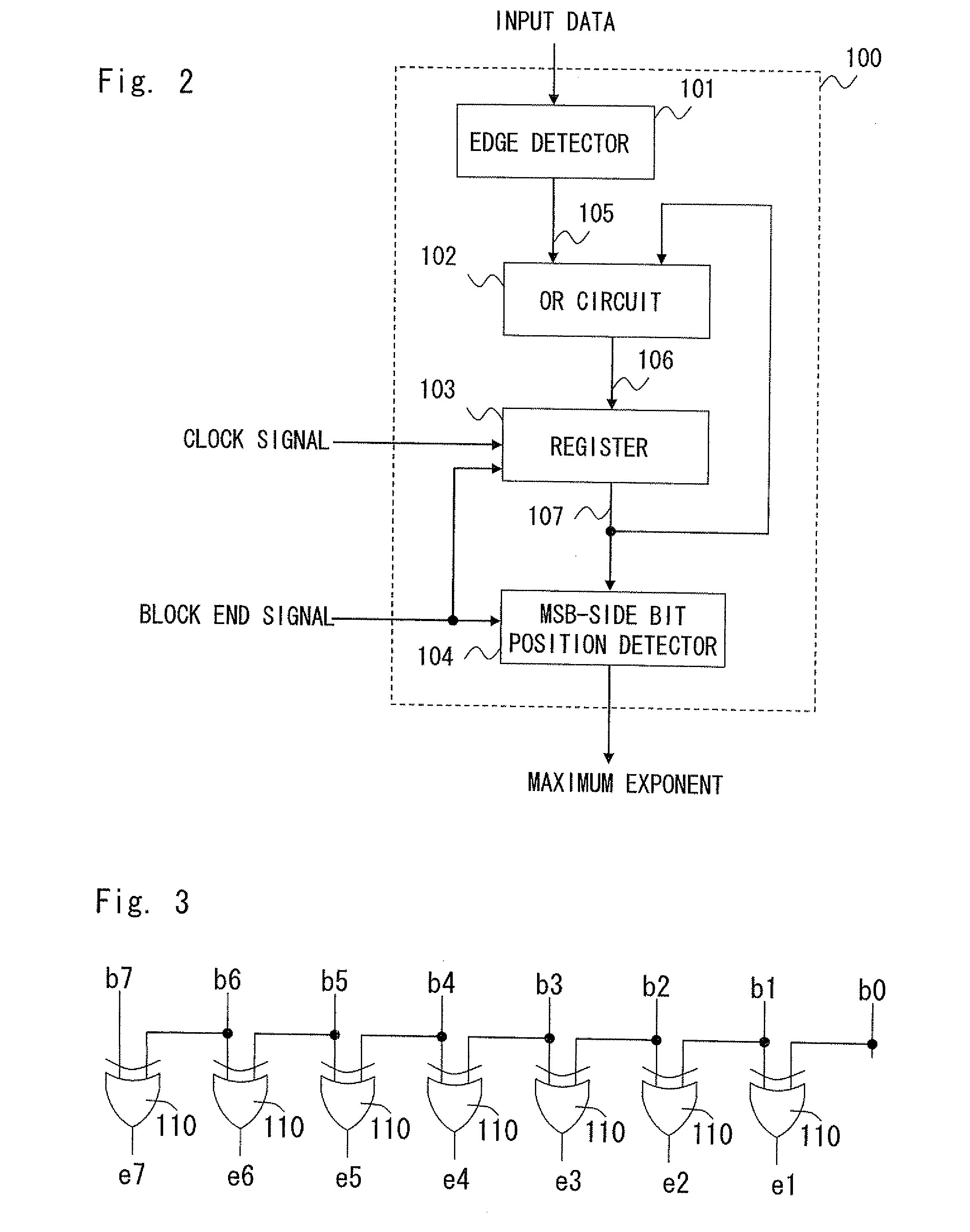
Semiconductor integrated circuit and exponent calculation method
InactiveUS20120117337A1Speedup of calculationCircuit scale be reducedDigital data processing detailsCode conversionComputer scienceCalculation methods
Provided is a semiconductor integrated circuit and an exponent calculation method that, when normalizing a plurality of data by a common exponent, speed up exponent calculation and reduce circuit scale and power consumption. When normalizing a plurality of data by a common exponent, a semiconductor integrated circuit calculates the exponent of the plurality of data. Included is a bit string generator that generates a second bit string containing bits having a transition value indicating that values of adjacent bits are different or a non-transition value indicating that values of adjacent bits are not different for each pair of adjacent bits of a first bit string constituting the data, and an exponent calculator that calculates the exponent of the plurality of data based on bit position of the transition value of a plurality of second bit strings generated from a plurality of first bit strings respectively constituting the plurality of data.
Owner:NEC CORP
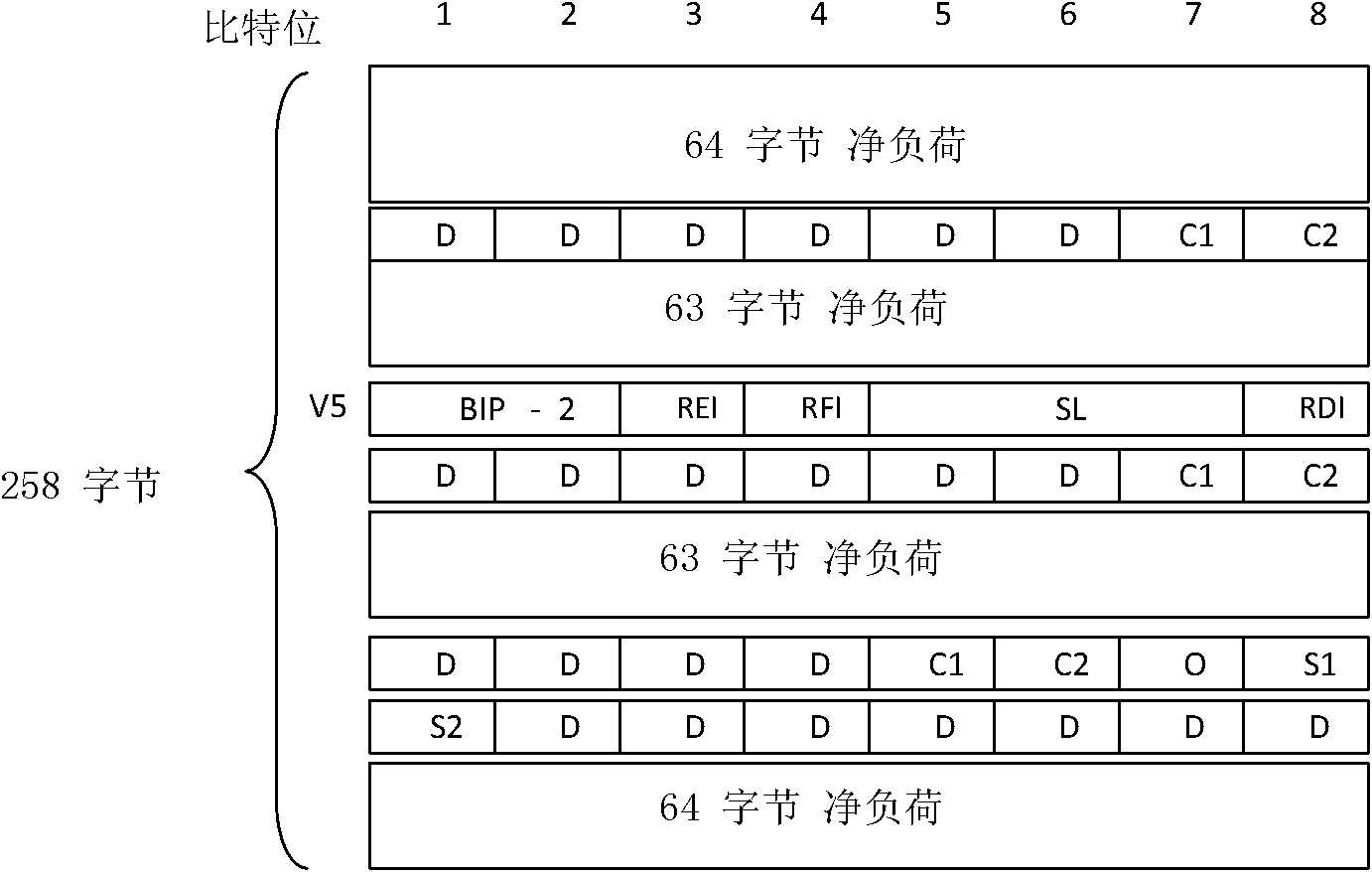
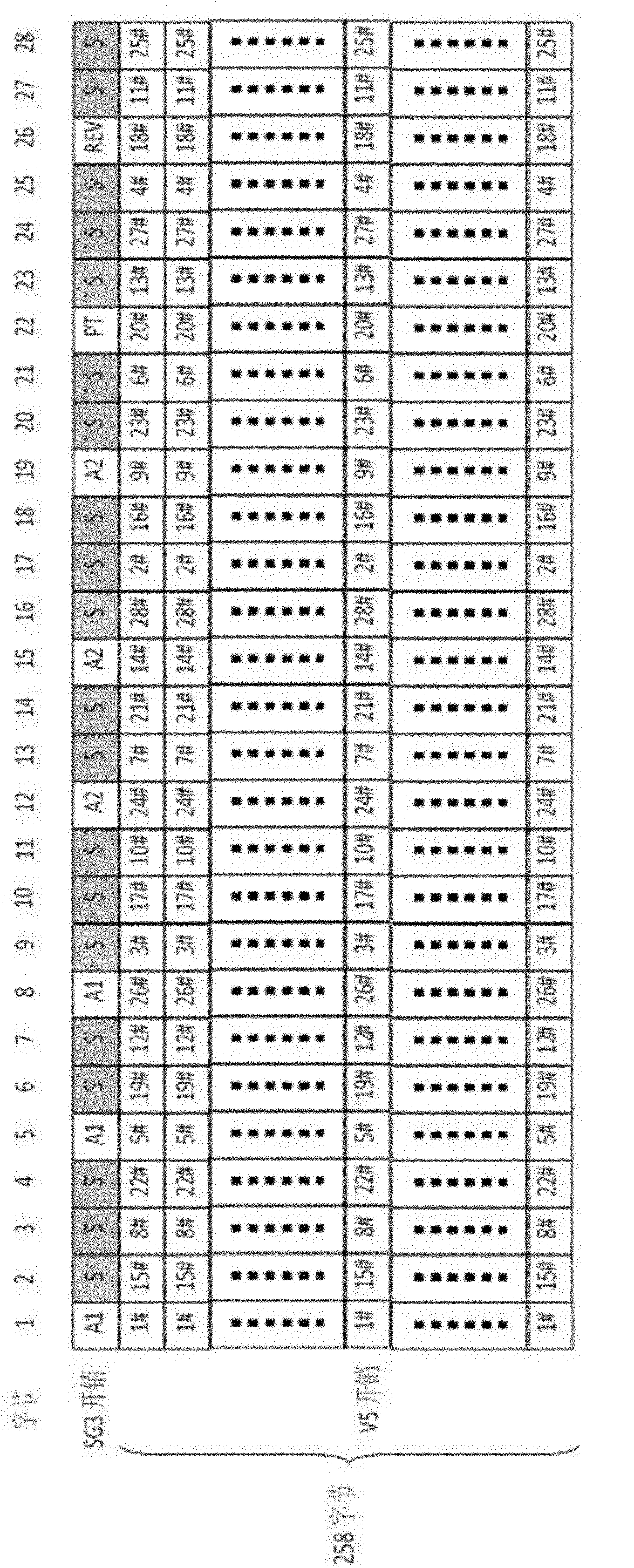
Enhancement-type PDH (plesiochronous digital hierarchy) frame format suitable for microwave communication and mapping method
ActiveCN102025438AImprove transmission performanceReduce Overhead FieldsMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexMicrowavePlesiochronous digital hierarchy
The invention relates to an enhancement-type PDH (plesiochronous digital hierarchy) frame format suitable for microwave communication and a mapping method. The frame comprises an SG3 frame which comprises overhead of 8 bytes, stuffing of 20 bytes and data payload. In the method, synchronization and desynchronization are realized by utilizing a control bit stuffing mechanism and a CE1 frame. The enhancement-type PDH frame format has the advantages that the transmission of various PDH speeds, performance alarming and protection are supported, less overhead is occupied, the bandwidth use ratio is utilized, and valuable microwave resources are solved. Compared with the traditional SDH protocol, a great quantity of overhead bytes are decreased, thus greatly improving the bandwidth use ratio, and greatly enhancing the transmission ability of a microwave network; and the enhancement-type PDH frame format is suitable for various microwave communication equipment, and ensures that the product integrated level is improved, and the complexity levels of the system hardware and software are lowered.
Owner:杭州依赛通信有限公司
LDPC encoding method based on bit stuffing
ActiveCN104143992AImprove real-time processing speedReduce complexityError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsParallel encodingDesign methods
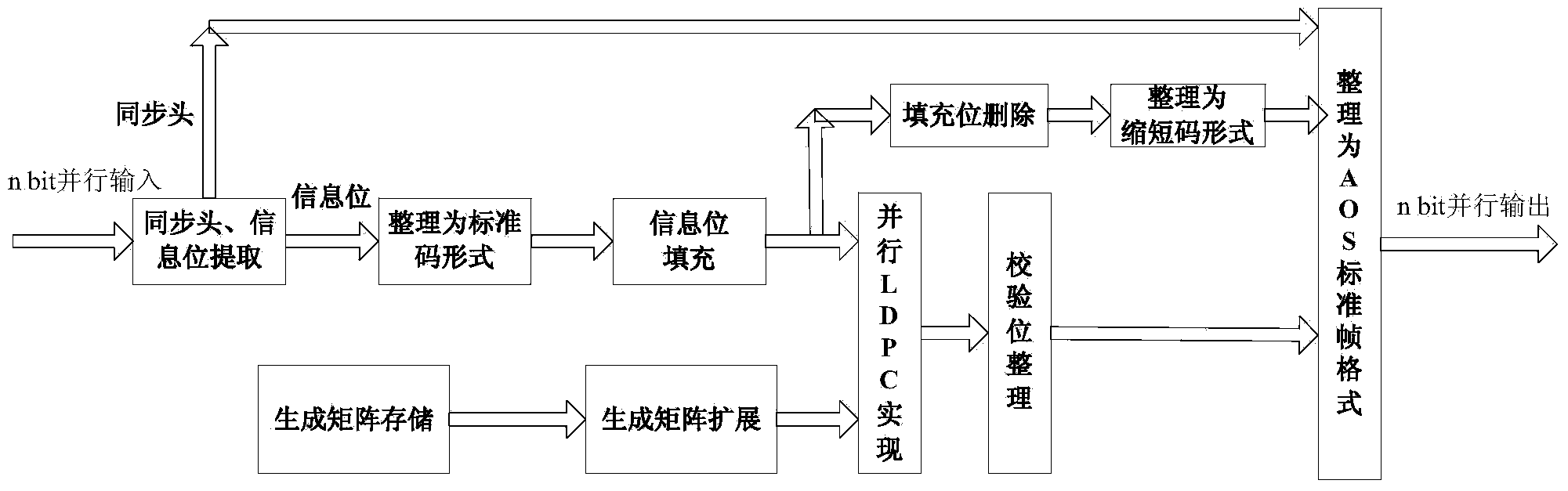
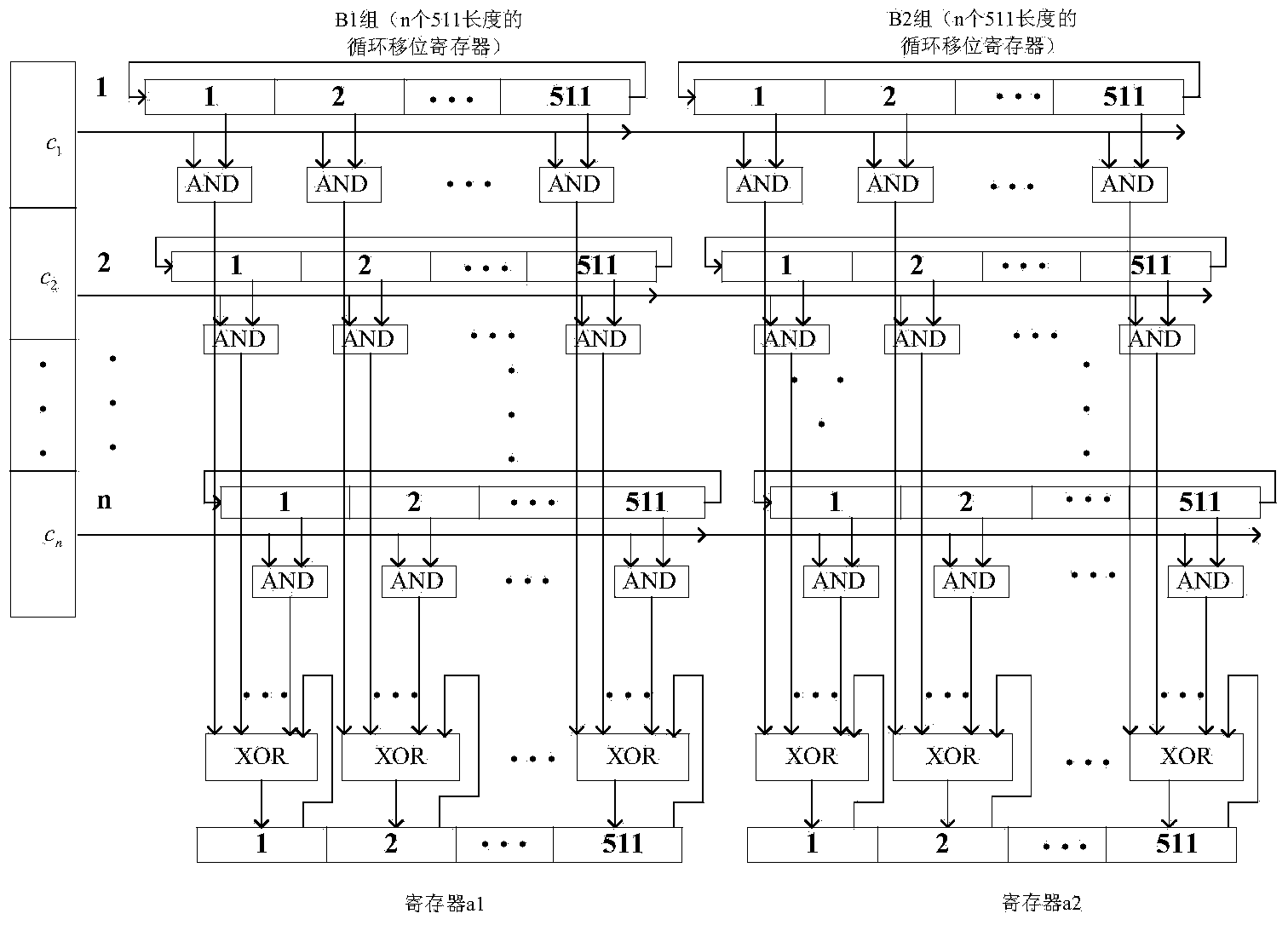
An LDPC encoding method based on bit stuffing is characterized by comprising the steps that (1) synchronous head and information bit extraction is performed on received AOS standard frame data, and n bit parallel information bit data flow capable of performing parallel encoding is obtained through information bit sorting and bit stuffing; (2) extension is performed to generate a matrix; (3) LDPC parallel encoding is performed to generate a check bit; (4) sorting is performed to form AOS standard frame format data flow for output. The LDPC encoding method based on bit stuffing has the advantages of being low in hardware overhead, high in processing speed and applicability, easy to implement in an engineering mode, stable and reliable; besides, the design method has obvious advantages in application in the aerospace field.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Data Encoding/Decoding Method and Related Device Capable of Lowering Signal Power Spectral Density
InactiveUS20090085779A1Lowering signal power spectral densityLow power spectral densityIndividual digits conversionComputer architectureData encoding
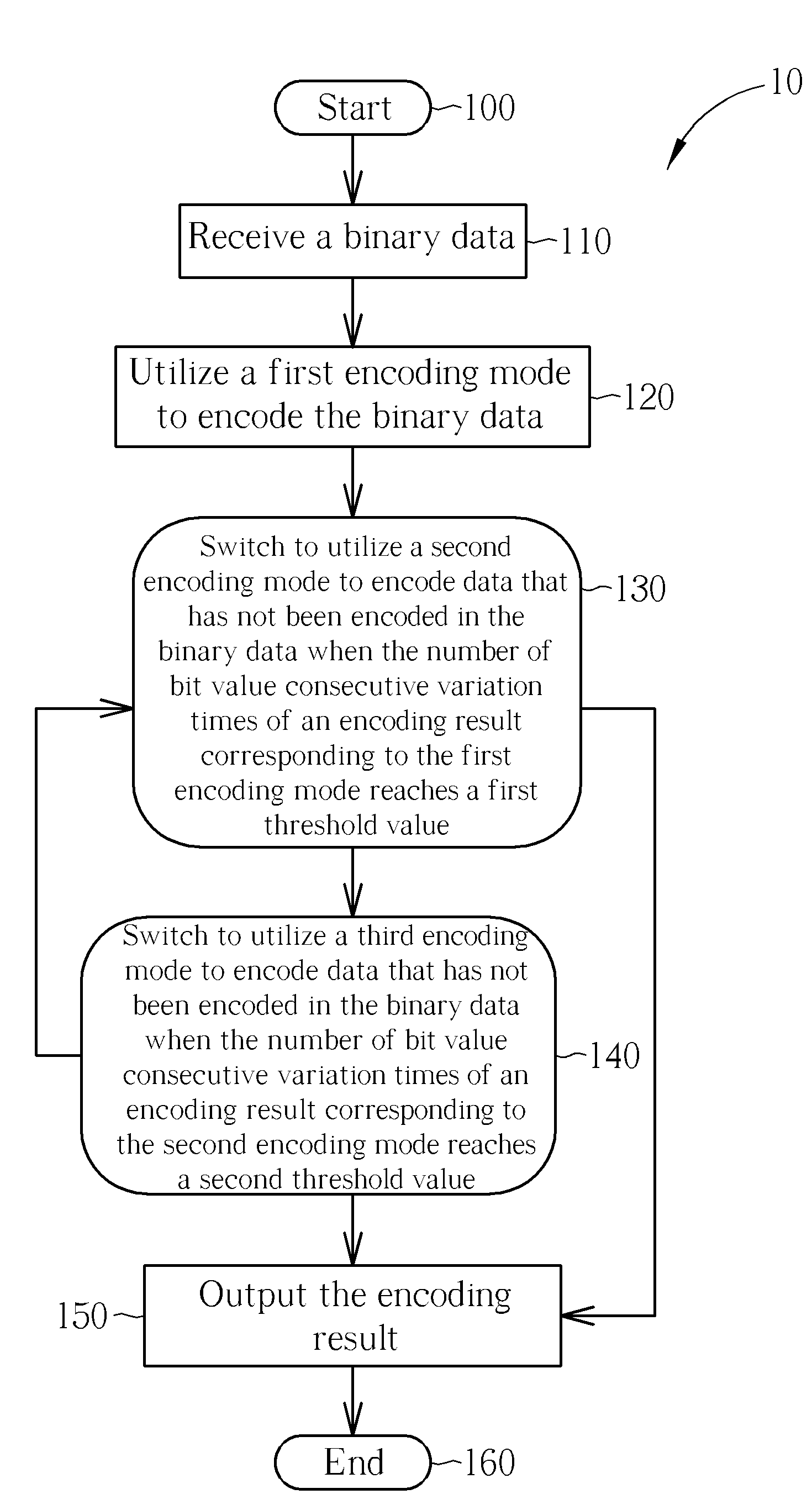
A data encoding and decoding method capable of lowering signal power spectral density for a binary data transmission system is disclosed. The data encoding method includes receiving binary data, performing adaptive mode tracking encoding for the binary data to generate a first encoding result, performing bit stuffing encoding for the first encoding result to generate a second encoding result, performing bit stationary state resuming encoding for the second encoding result to generate a third encoding result, and outputting the third encoding result.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Rate adaption within a TDM switch using bit stuffing
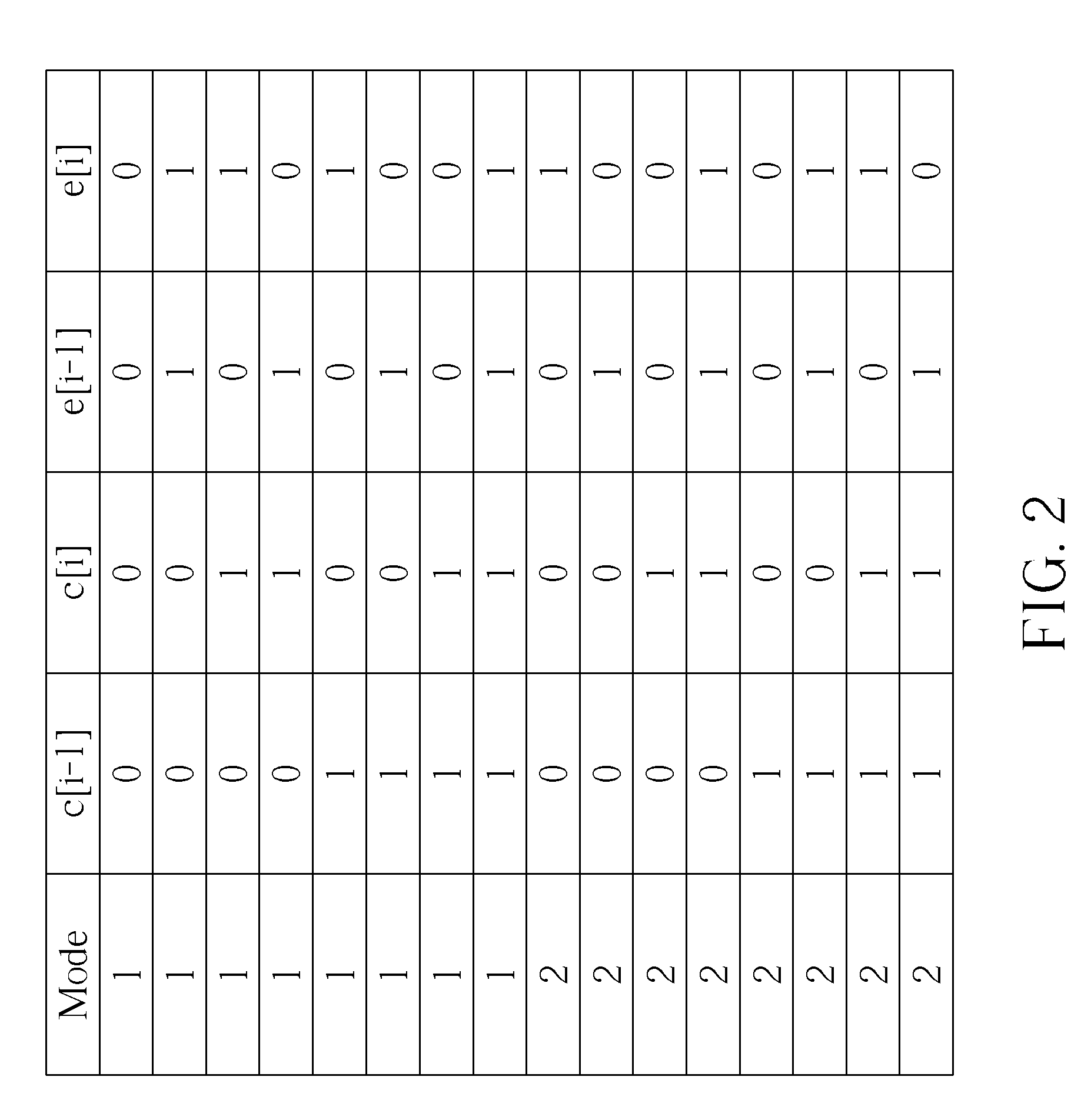
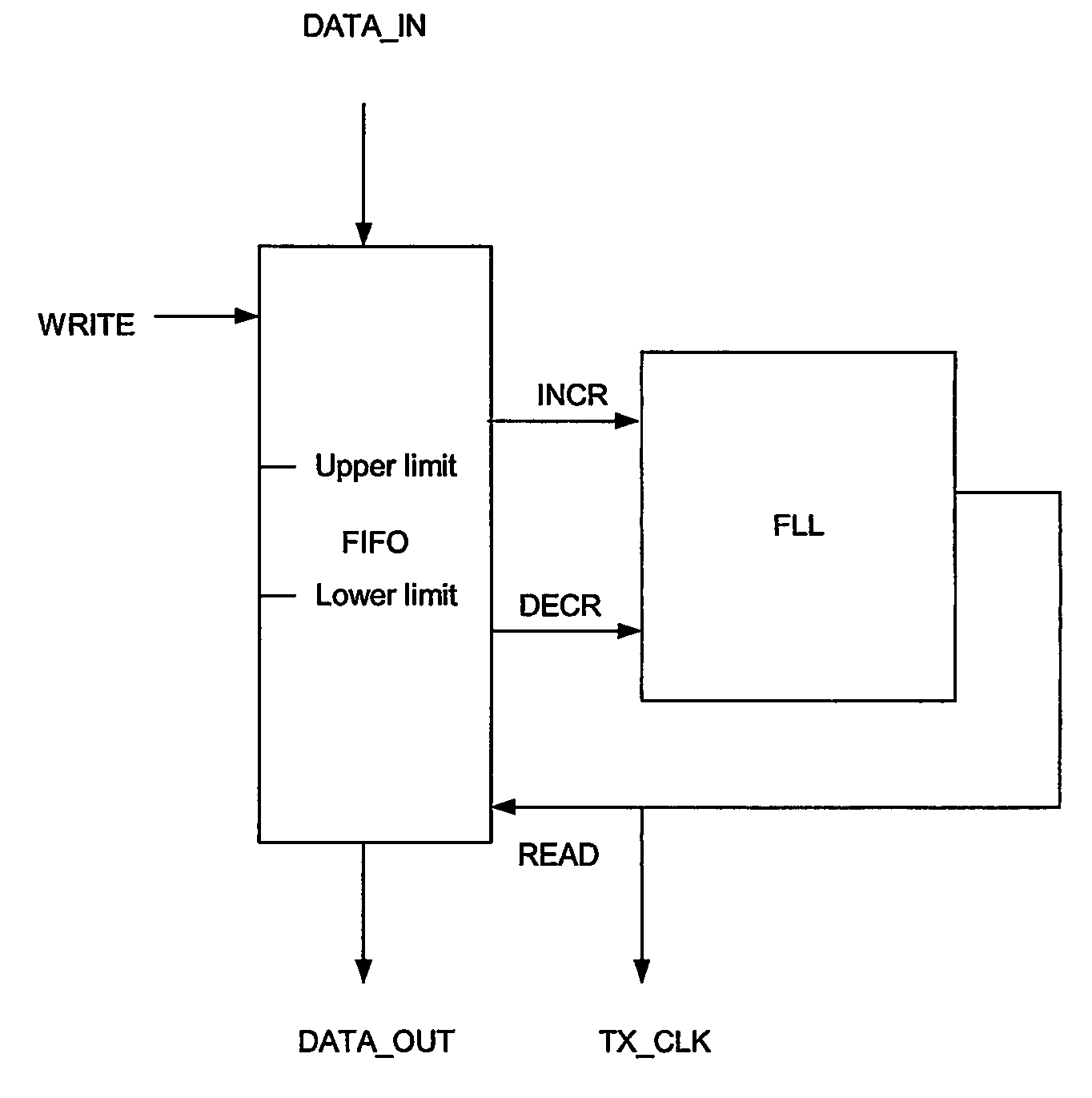
InactiveUS7372862B2Avoid introducingExcellent jitter and frequency stabilityError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsComputer hardwareRate adaptation
The present invention discloses a method and an arrangement providing transmission of data through a node, e.g. a switch, having different input and output line interfaces in a wide range of data speed, without introducing any loss of bits, but still maintaining the nominal bit rate. This is achieved by means of a very simple and flexible implementation. At the receiving side of the switch, one extra bit per frame is transferred over the time slot bus of the switch if the number of bits in the corresponding FIFO of the input line exceeds a predefined upper limit. In contrast, one bit less per frame is transferred if the number of bits in the corresponding FIFO of the input line goes below a predefined lower limit. At the transmitting side of the switch, a FLL circuit regulates the data rate out of the FIFOs. The FLL circuit is implemented as a P-regulator having i.a. the fill degree of the FIFO as a direct input. Consequently, excellent jitter and frequency stability are achieved, and because of not using an I-component, the FLL circuit becomes stable.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com