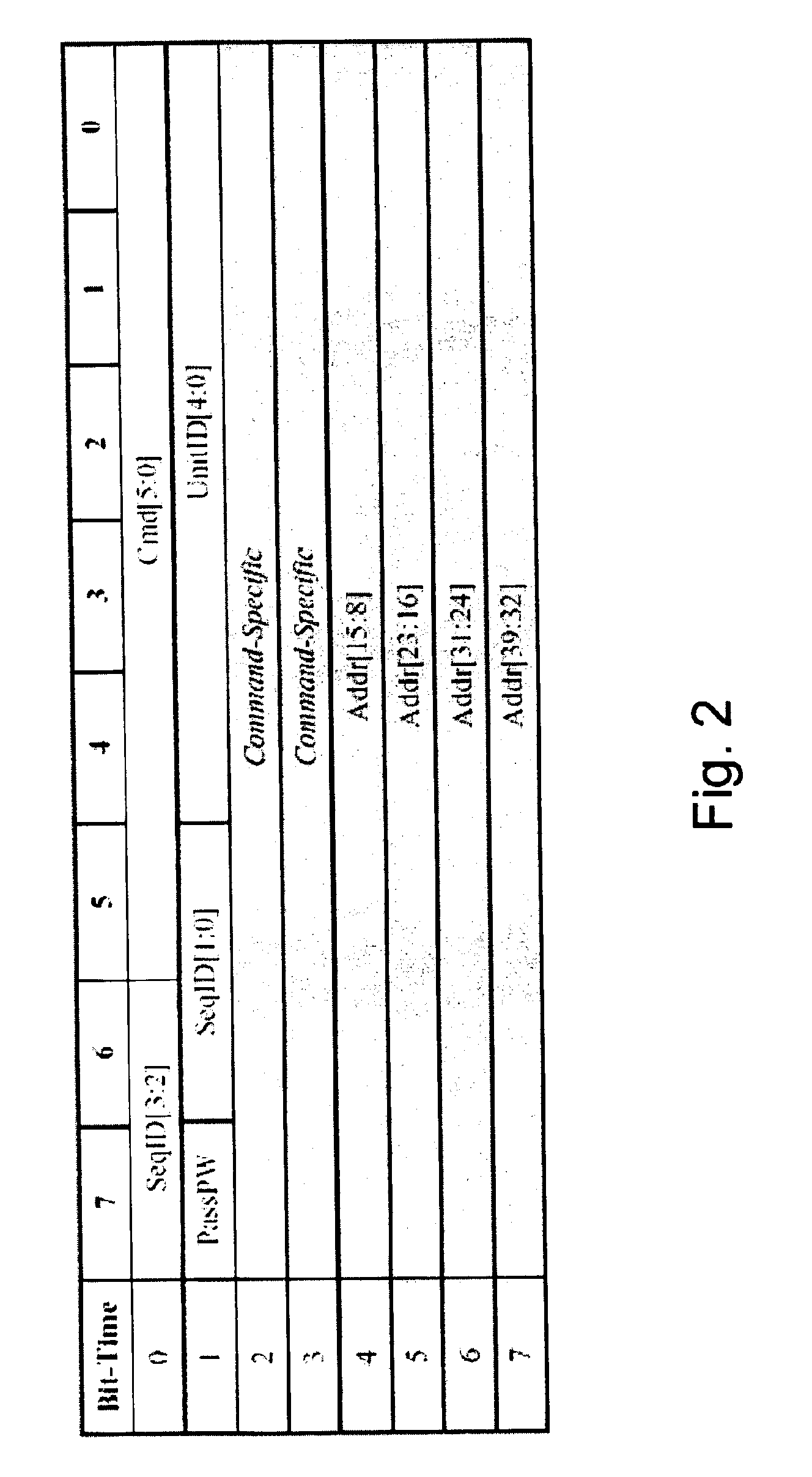
Patents
Literature
205 results about "Symmetric multiprocessing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
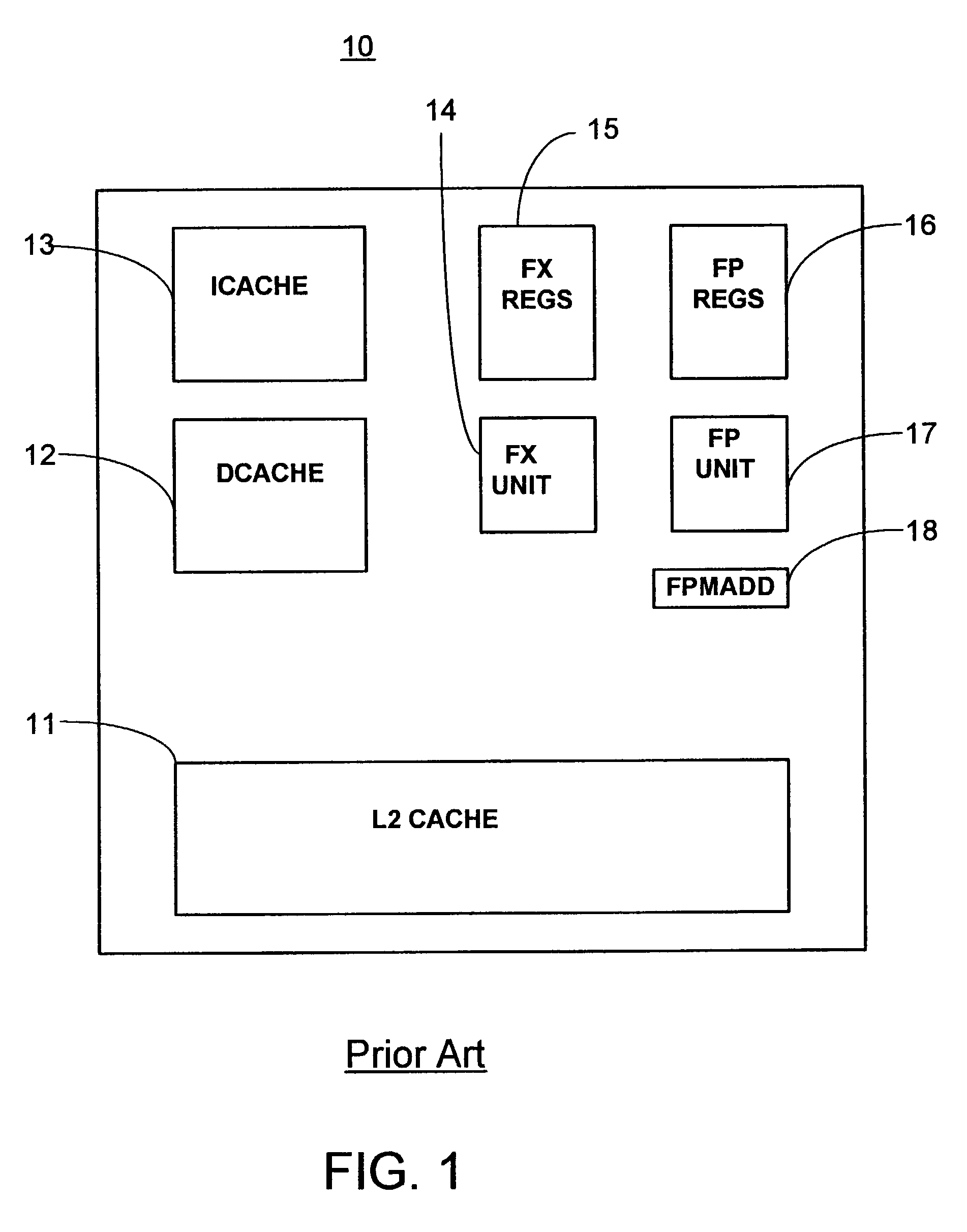
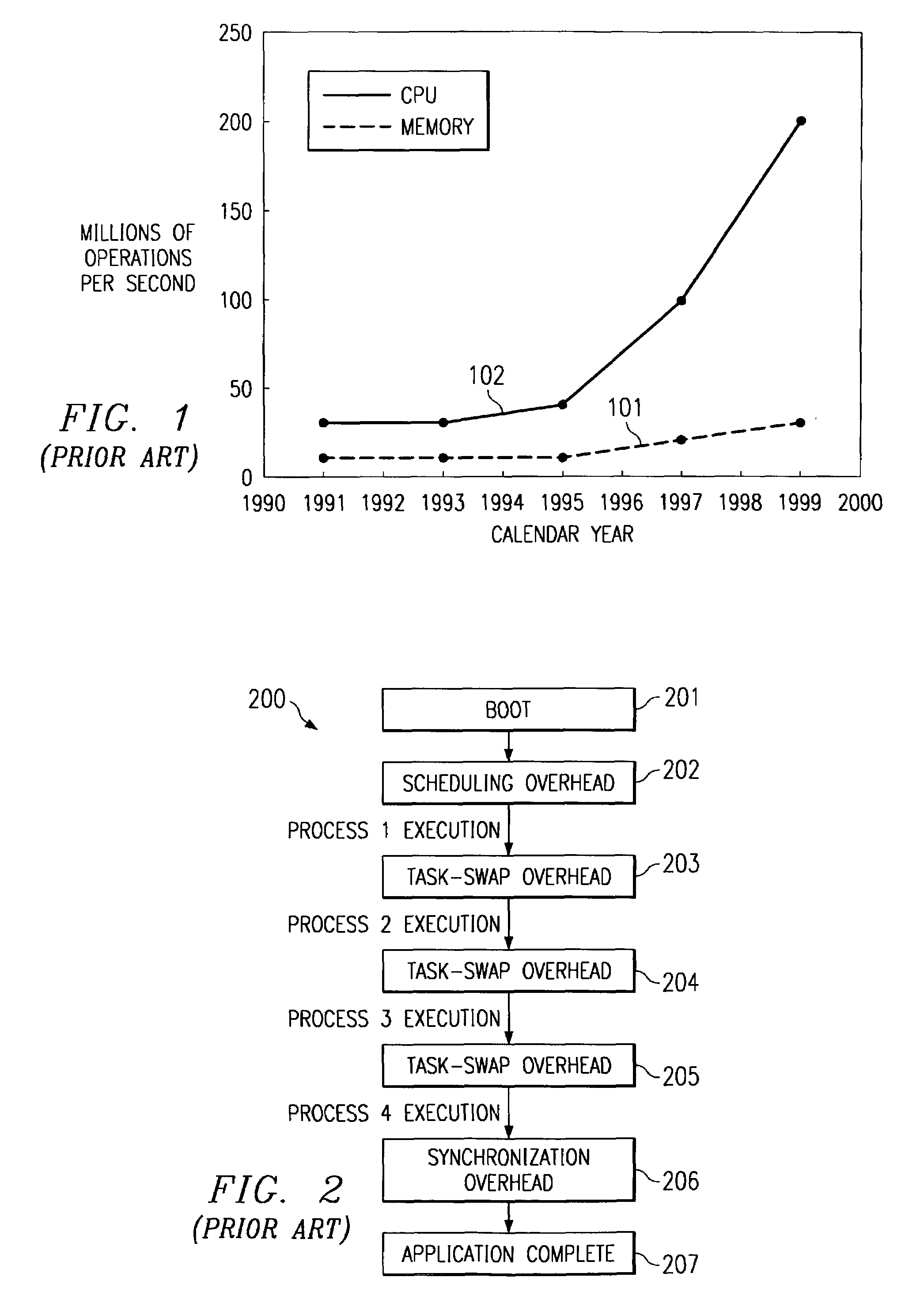
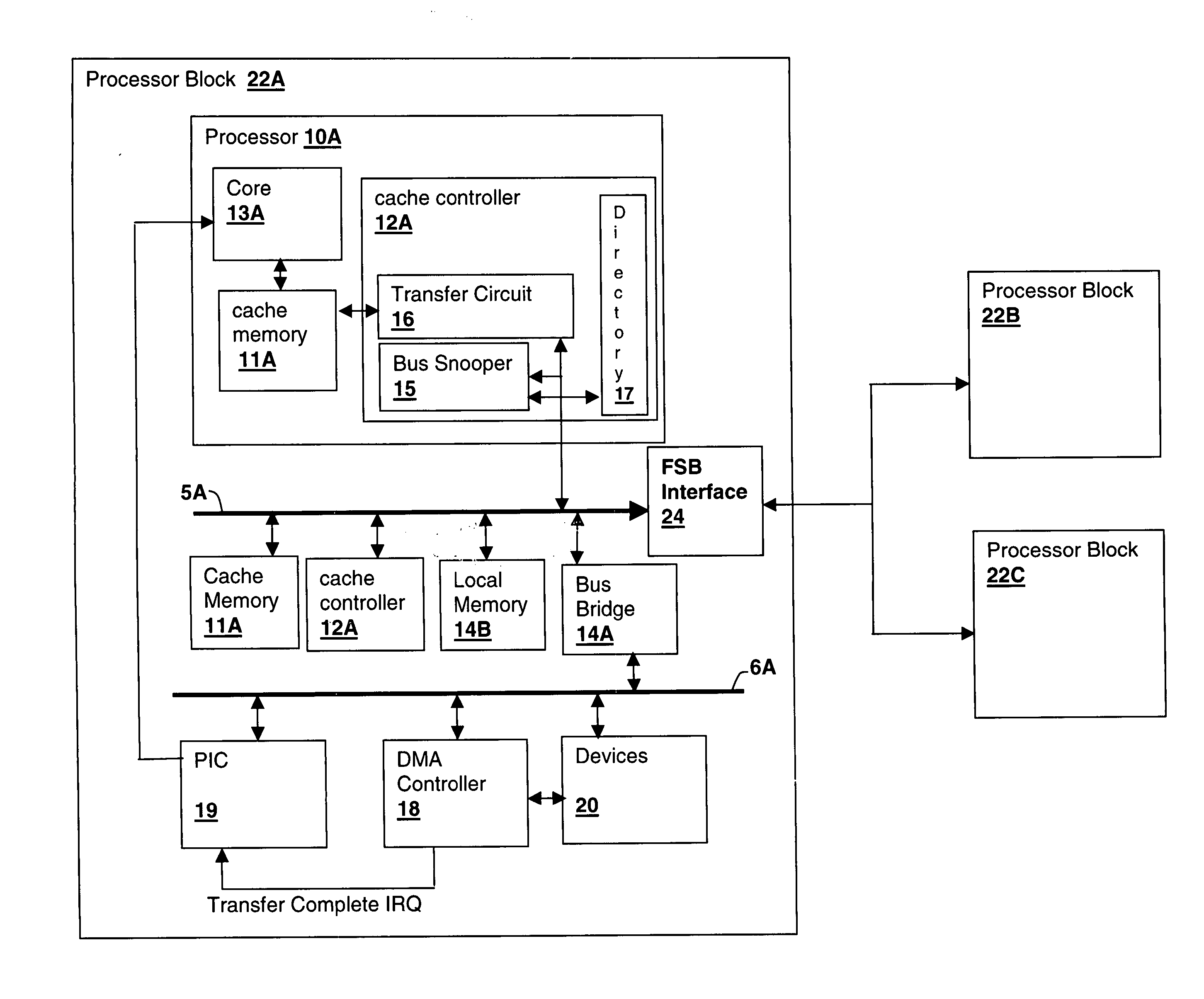
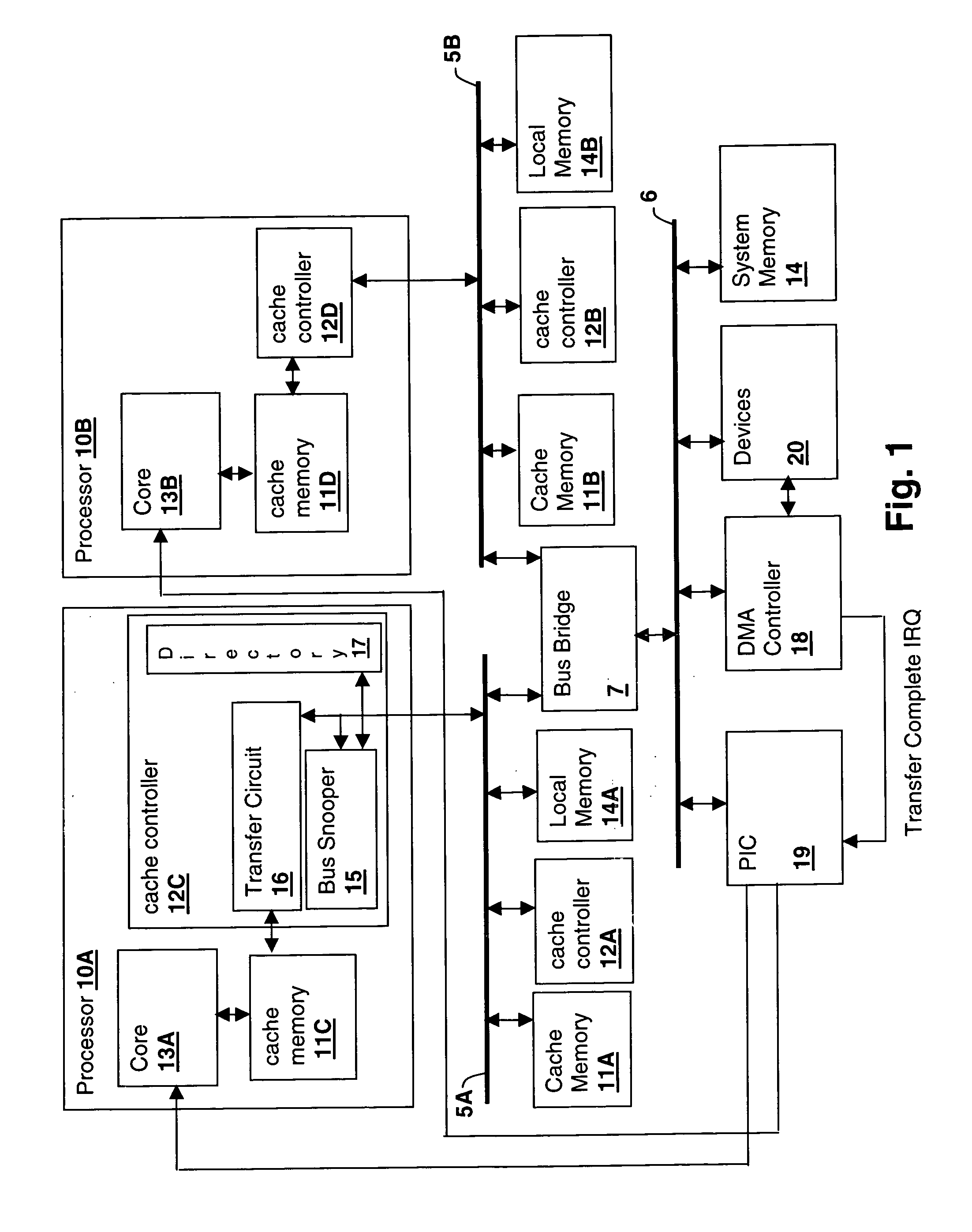
Symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) involves a multiprocessor computer hardware and software architecture where two or more identical processors are connected to a single, shared main memory, have full access to all input and output devices, and are controlled by a single operating system instance that treats all processors equally, reserving none for special purposes. Most multiprocessor systems today use an SMP architecture. In the case of multi-core processors, the SMP architecture applies to the cores, treating them as separate processors.
Method and mechanism for speculatively executing threads of instructions
InactiveUS6574725B1Program initiation/switchingGeneral purpose stored program computerSpeculative executionOperational system
A processor architecture containing multiple closely coupled processors in a form of symmetric multiprocessing system is provided. The special coupling mechanism allows it to speculatively execute multiple threads in parallel very efficiently. Generally, the operating system is responsible for scheduling various threads of execution among the available processors in a multiprocessor system. One problem with parallel multithreading is that the overhead involved in scheduling the threads for execution by the operating system is such that shorter segments of code cannot efficiently take advantage of parallel multithreading. Consequently, potential performance gains from parallel multithreading are not attainable. Additional circuitry is included in a form of symmetrical multiprocessing system which enables the scheduling and speculative execution of multiple threads on multiple processors without the involvement and inherent overhead of the operating system. Advantageously, parallel multithreaded execution is more efficient and performance may be improved.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
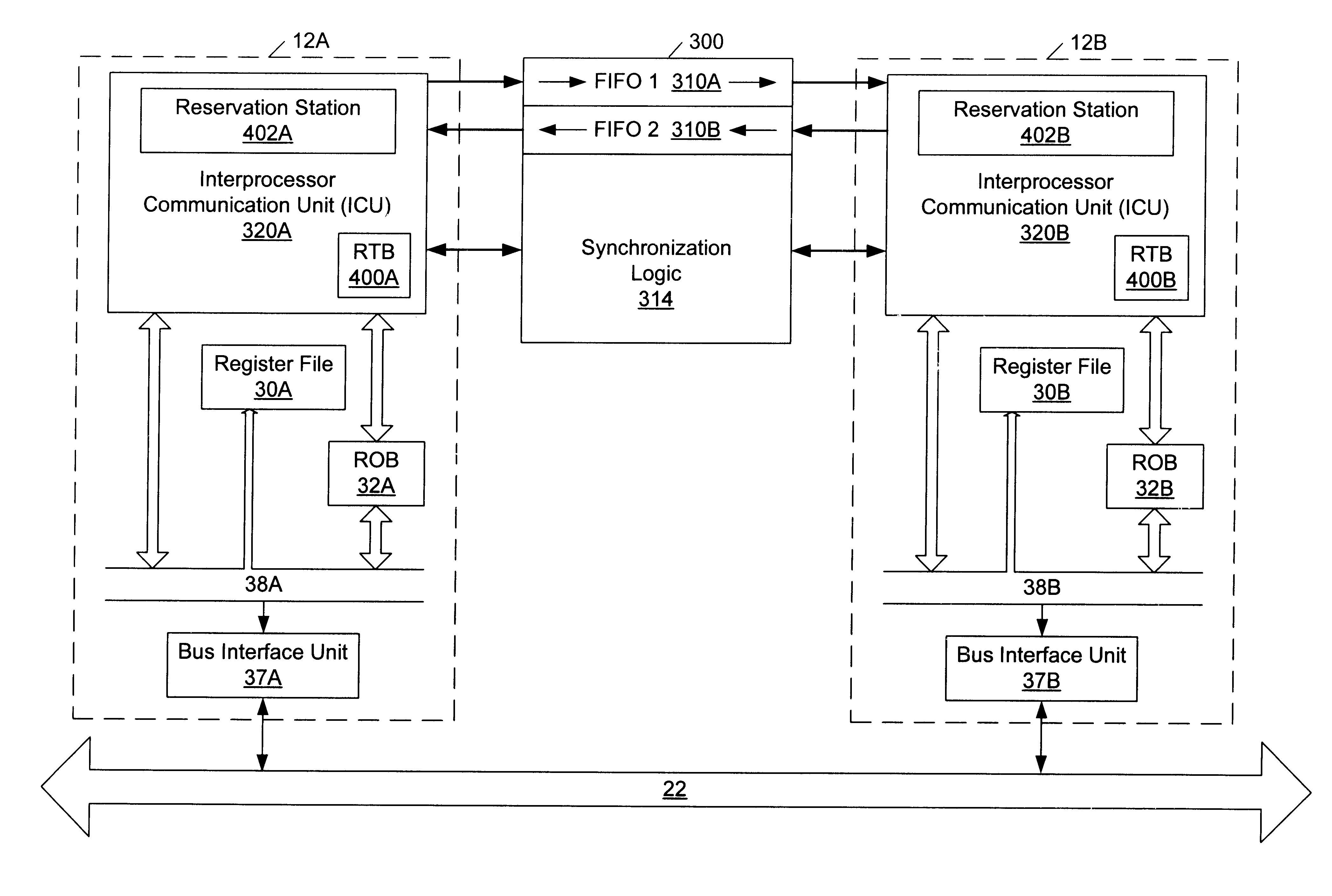
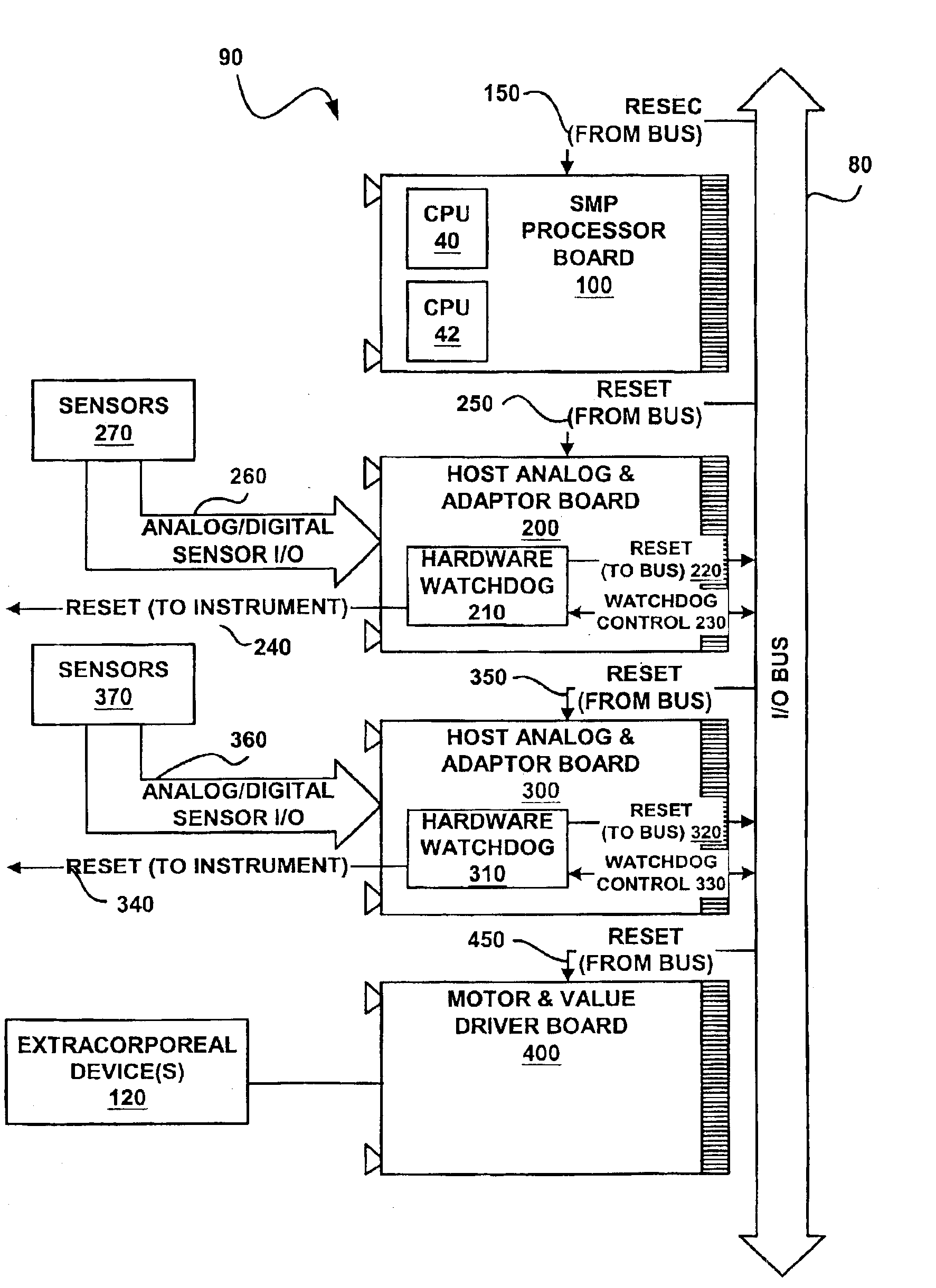
Dialysis machine with symmetric multi-processing (SMP) control system and method of operation
InactiveUS6868309B1Low costImprove performanceMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesLevel controlControl systemSingle point of failure
A method and control system computing platform for a dialysis machine that uses Symmetric Multi-Processing (SMP) architecture. The SMP architecture tightly couples multiple (e.g., 2) independent processors by sharing memory between the processors. A single shared memory is used by both processors in order to facilitate communication between the processors and reduce cost by eliminating the expense of redundant memory. In this way, the two, or in general “N” processors, increase processor throughput by allowing the execution of N processes in parallel while without requiring extra memory and without having a single point of failure in the computer. In the event of a bus failure on the circuit card, the computer is reset using distributed hardware watchdogs. The watchdog reset signal is also sent to the hardware components of the dialysis machine in order to place the system in a safe.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +2
Methods and architecture for enhanced computer performance
InactiveUS20160378545A1Reducing mode switchingReduce limitationsProgram initiation/switchingHardware monitoringOperational systemComputer performance
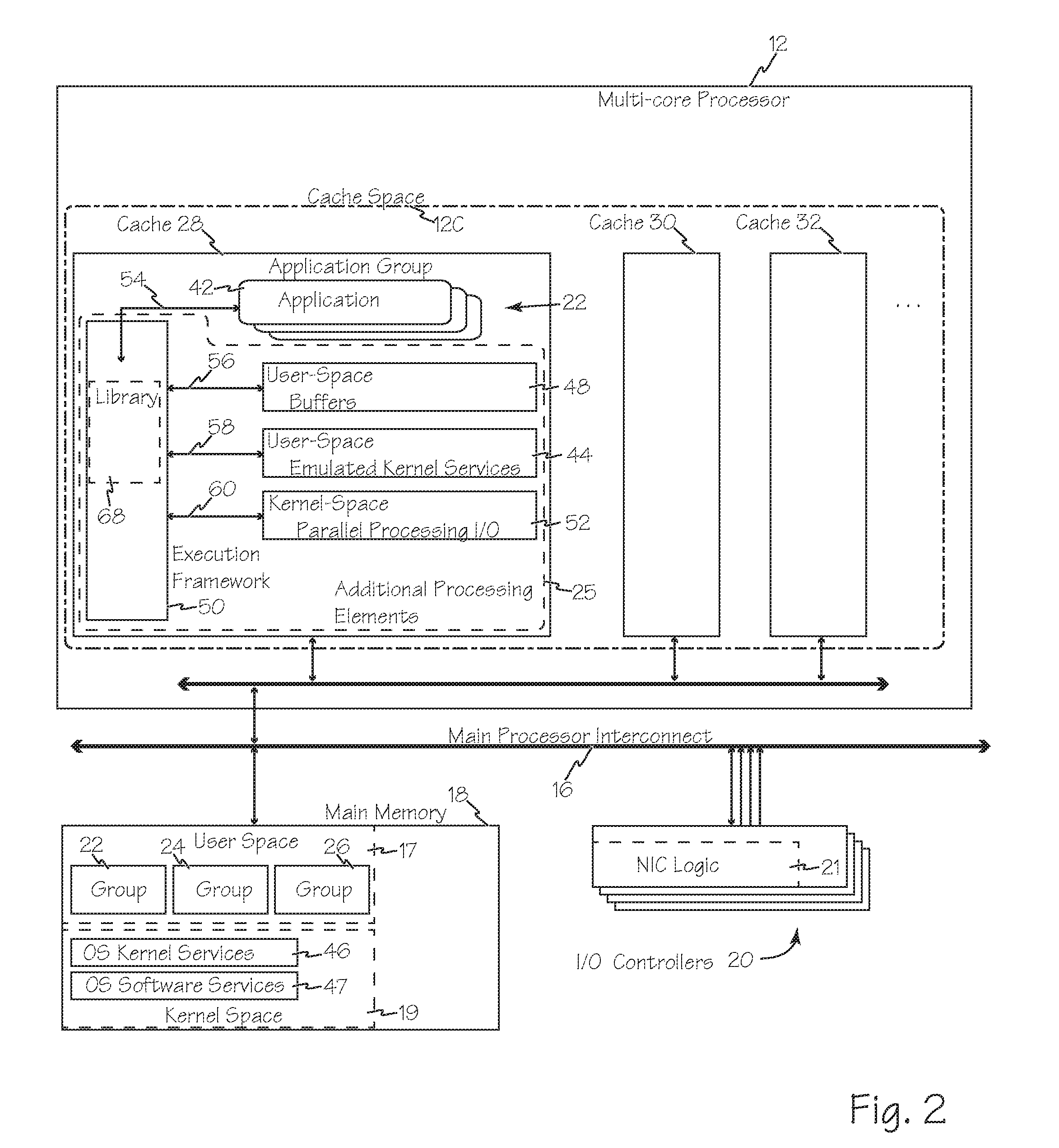
Methods and systems for enhanced computer performance improve software application execution in a computer system using, for example, a symmetrical multi-processing operating system including OS kernel services in kernel space of main memory, by using groups of related applications isolated areas in user space, such as containers, and using a reduced set of application group specific set of resource management services stored with each application group in user space, rather than the OS kernel facilities in kernel space, to manage shared resources during execution of an application, process or thread from that group. The reduced sets of resource management services may be optimized for the group stored therewith. Execution of each group may be exclusive to a different core of a multi-core processor and multiple groups may therefore execute separately and simultaneously on the different cores.
Owner:APL SOFTWARE INC
Method and apparatus to distribute interrupts to multiple interrupt handlers in a distributed symmetric multiprocessor system
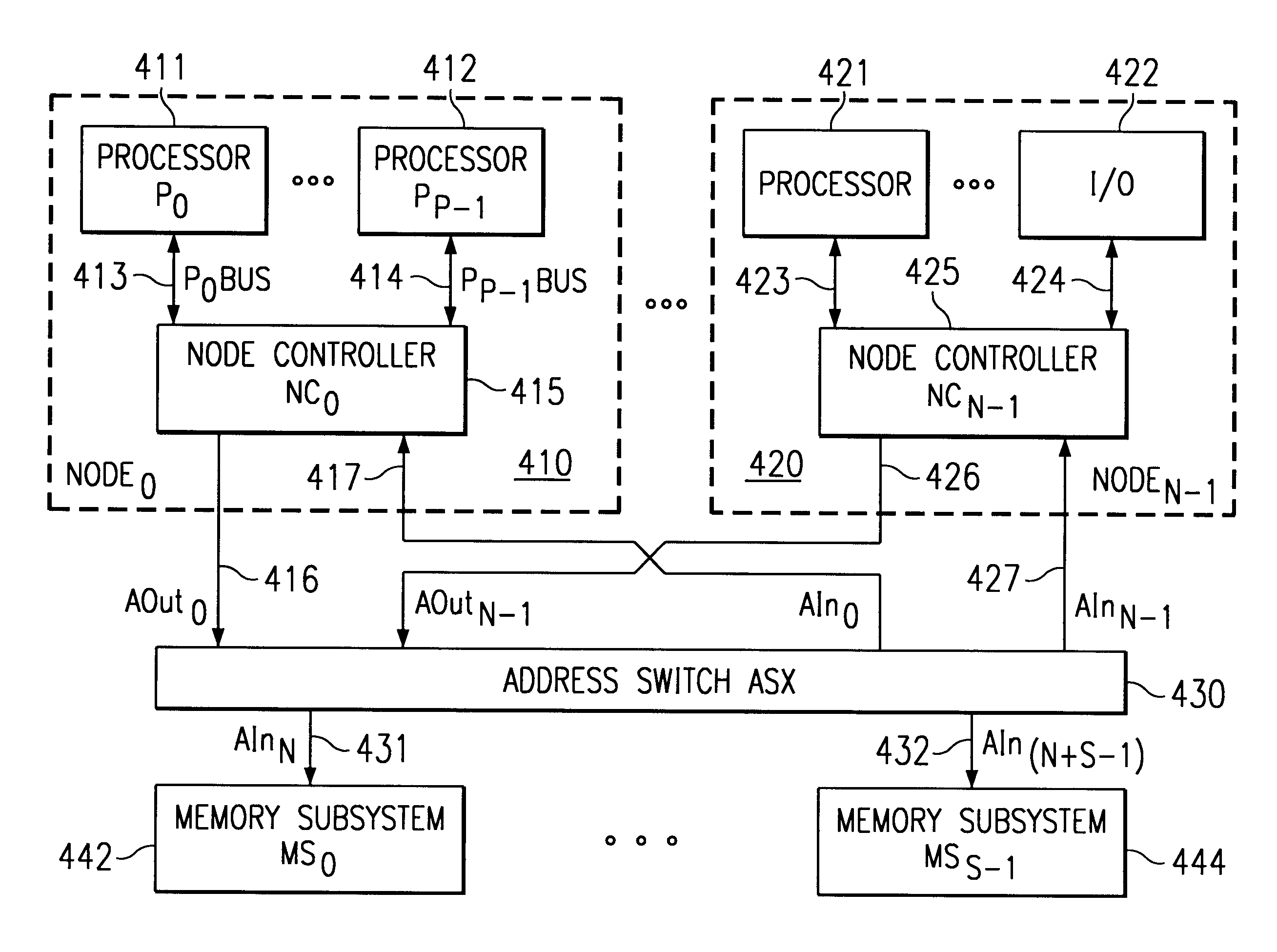
A distributed system structure for a large-way, symmetric multiprocessor system using a bus-based cache-coherence protocol is provided. The distributed system structure contains an address switch, multiple memory subsystems, and multiple master devices, either processors, I / O agents, or coherent memory adapters, organized into a set of nodes supported by a node controller. The node controller receives transactions from a master device, communicates with a master device as another master device or as a slave device, and queues transactions received from a master device. Since the achievement of coherency is distributed in time and space, the node controller helps to maintain cache coherency. The node controller also implements an interrupt arbitration scheme designed to choose among multiple eligible interrupt distribution units without using dedicated sideband signals on the bus.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
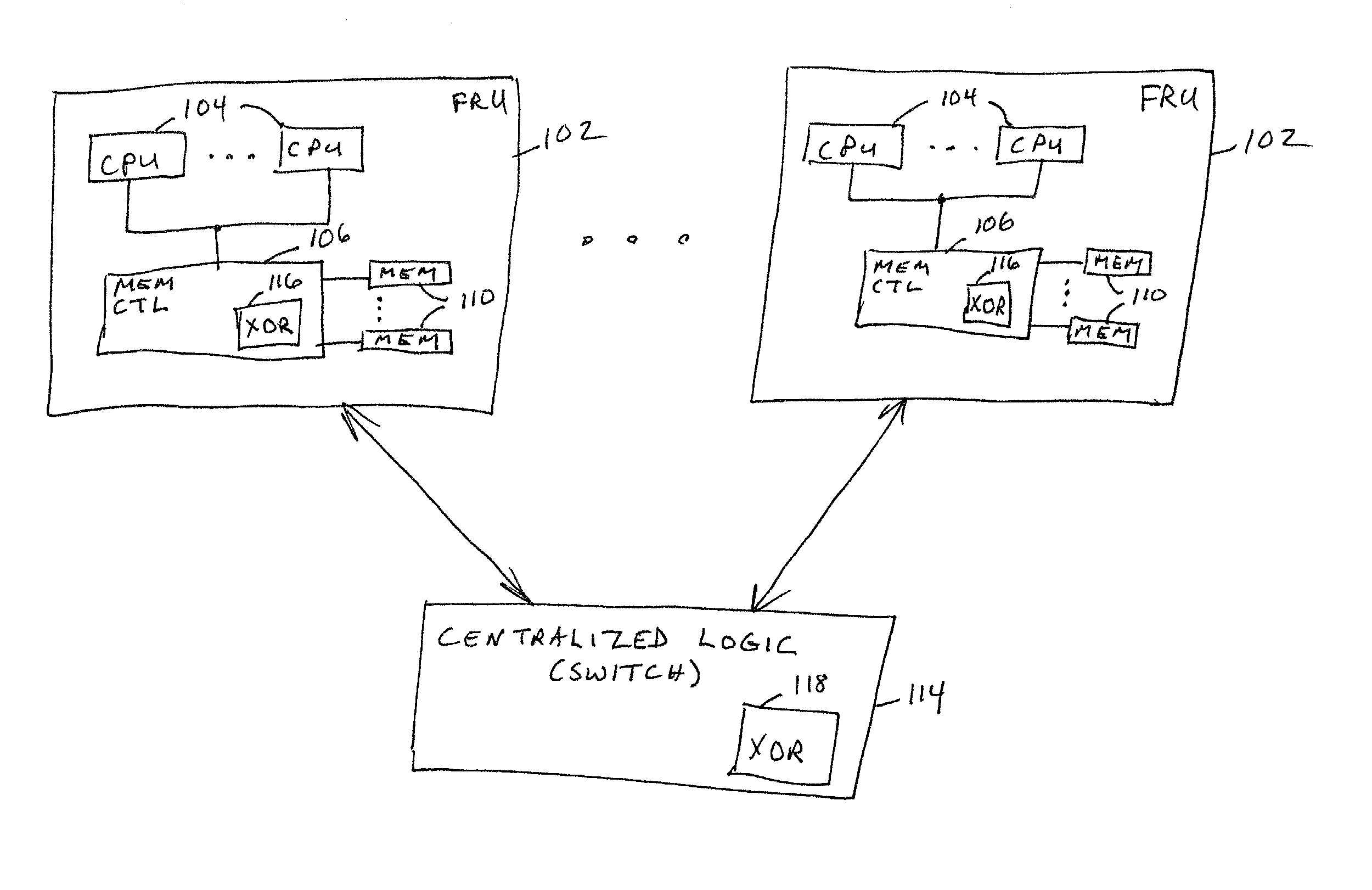
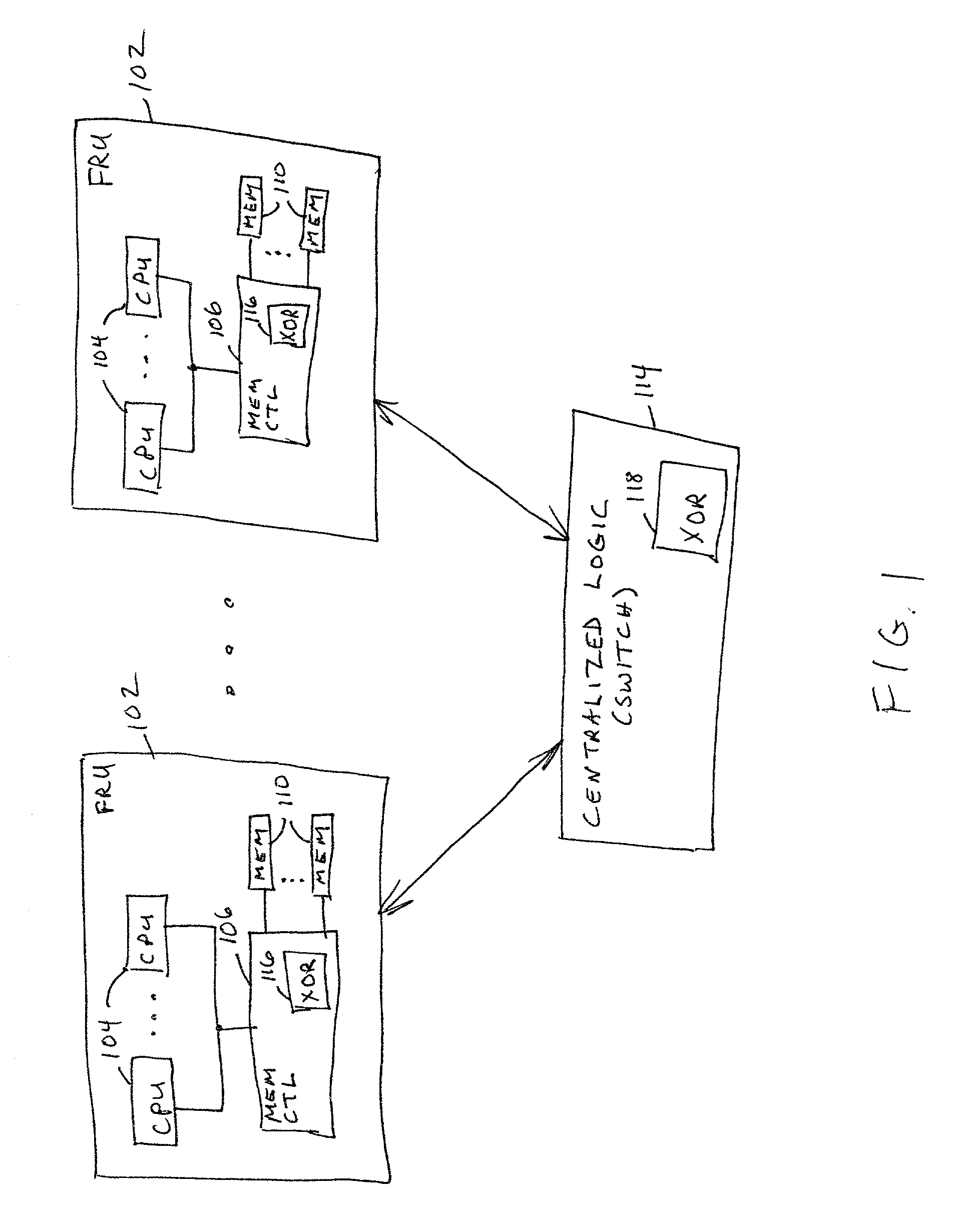
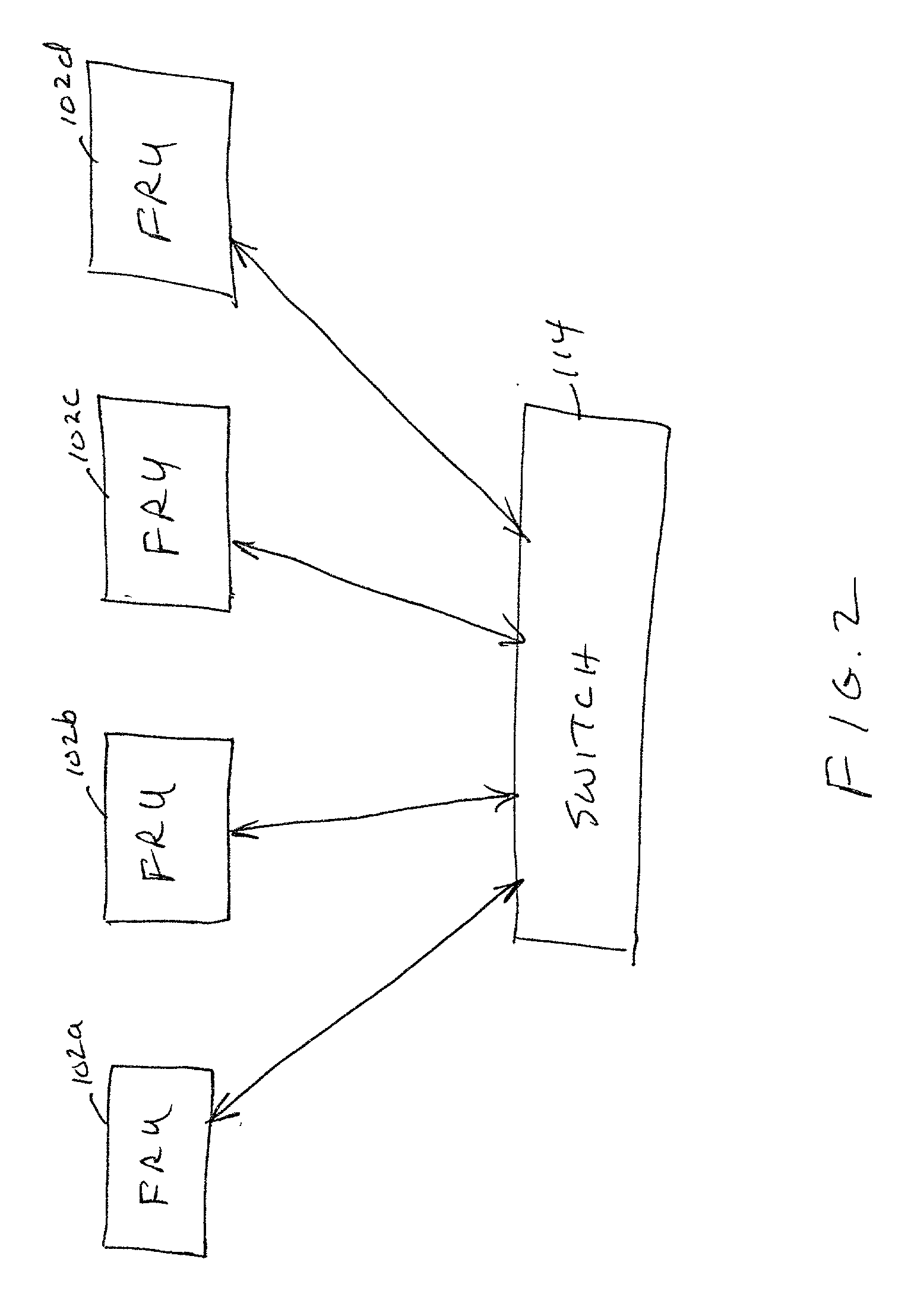
Data redundancy in a hot pluggable, large symmetric multi-processor system
ActiveUS20030172330A1Fault toleranceReduce the numberStatic storageRedundant data error correctionFault toleranceRAID
A computer system includes a plurality of field replaceable units, each having volatile memory and at least one CPU. The FRUs communicate with each other via centralized logic. A RAID data fault tolerance technique is applied to the system so that an FRU can be lost or removed without loss of its data. An exclusive OR engine is included in the centralized logic or distributed among the FRUs. The RAID logic can restripe itself upon removal or addition of a FRU.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Method and apparatus to eliminate processor core hot spots
Methods and apparatus are provided for eliminating hot spots on processor chips in a symmetric multiprocessor (SMP) computer system. Some operations, in particular, floating point multiply / add, repetitively utilize portions of a processor chip to the point that the average power of the affected portions exceeds cooling capabilities. The localized temperature of the affected portions can then exceed design limits. The current invention determines when a hot spot occurs and task swaps the task to another processor prior to the localized temperature becoming too hot. Moving of tasks to processors that have data affinity with the processor reporting a hot spot is considered. Further considerations include prioritizing unused processors and those processors that have not recently reported a hot spot.
Owner:IBM CORP
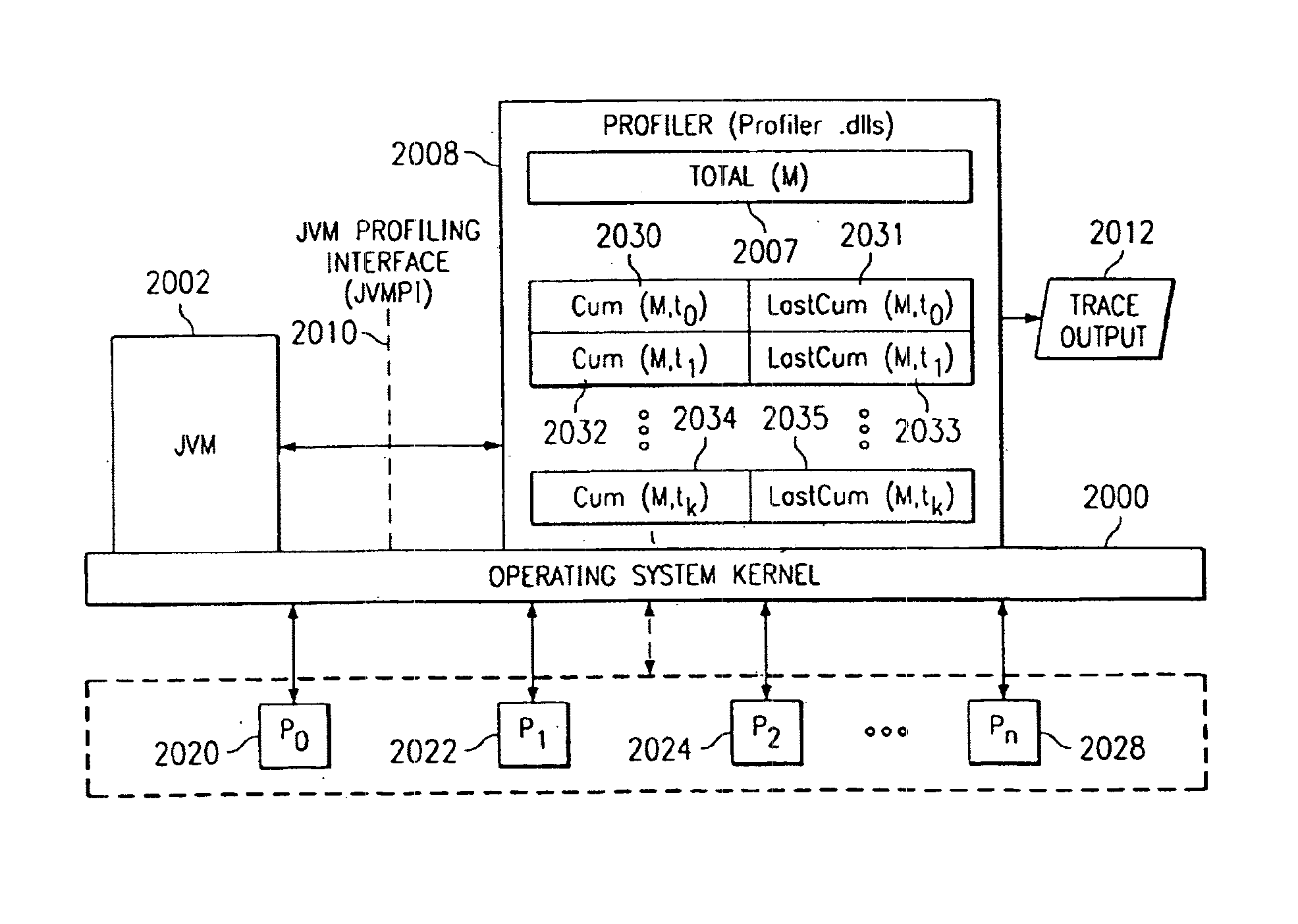
Method and system for apportioning changes in metric variables in an symmetric multiprocessor (SMP) environment
A method and system for monitoring performance of a program using global metric variables to provide the support in an symmetric multiprocessor (SMP) system. A Java virtual machine (Jvm) either calls the profiler whenever bytes are allocated or provides an interface to allow the profiler to determine the value of the change in the metric for the current thread. The profiler then applies the changes to a metric for the current thread. Alternatively, per processor data areas are maintained for storing per processor metric values. Whenever a thread switch occurs or there is a request for the metric on a specified thread, an operating system kernel updates the thread level metric values with changes in the values per processor metrics.
Owner:IBM CORP
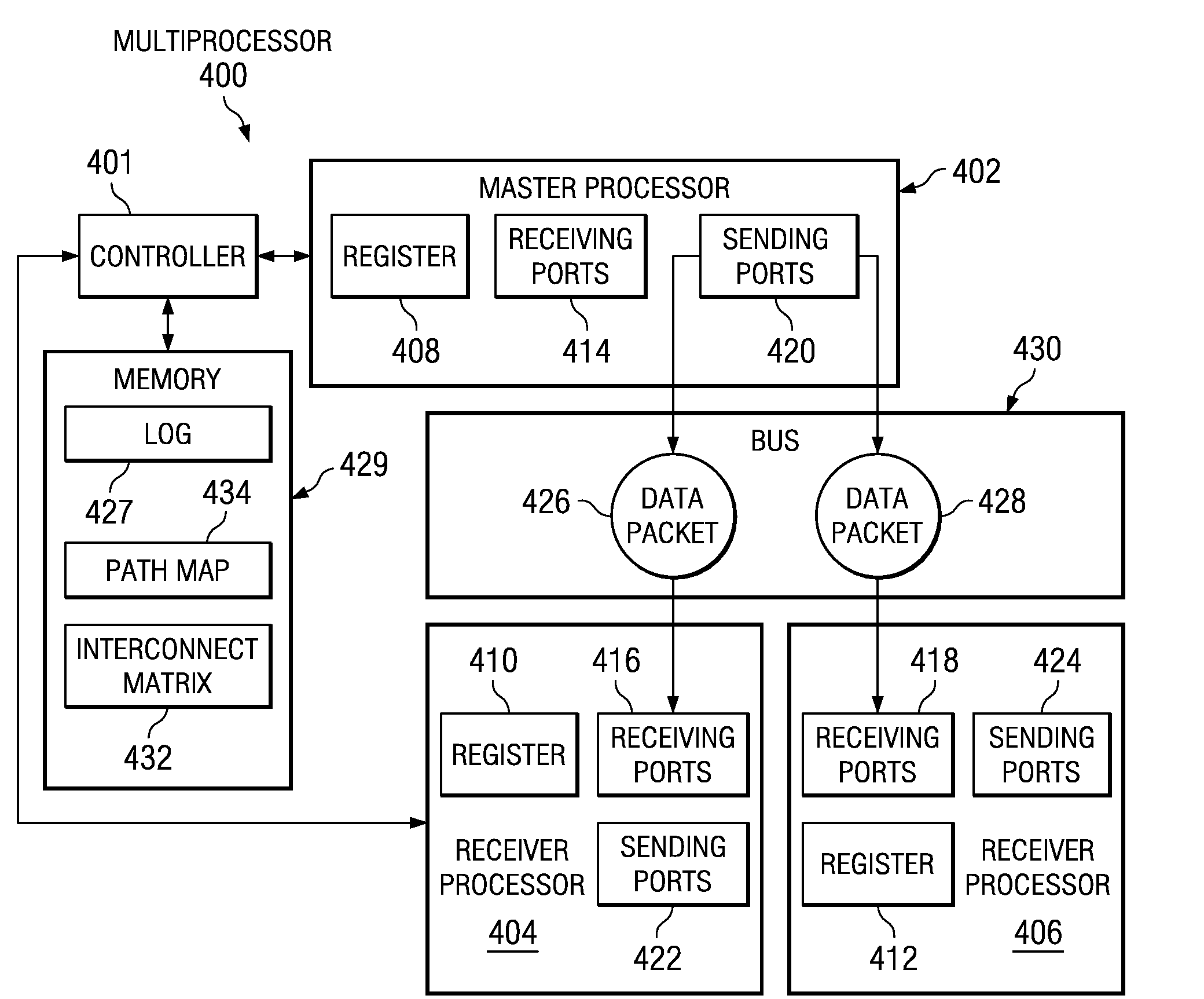
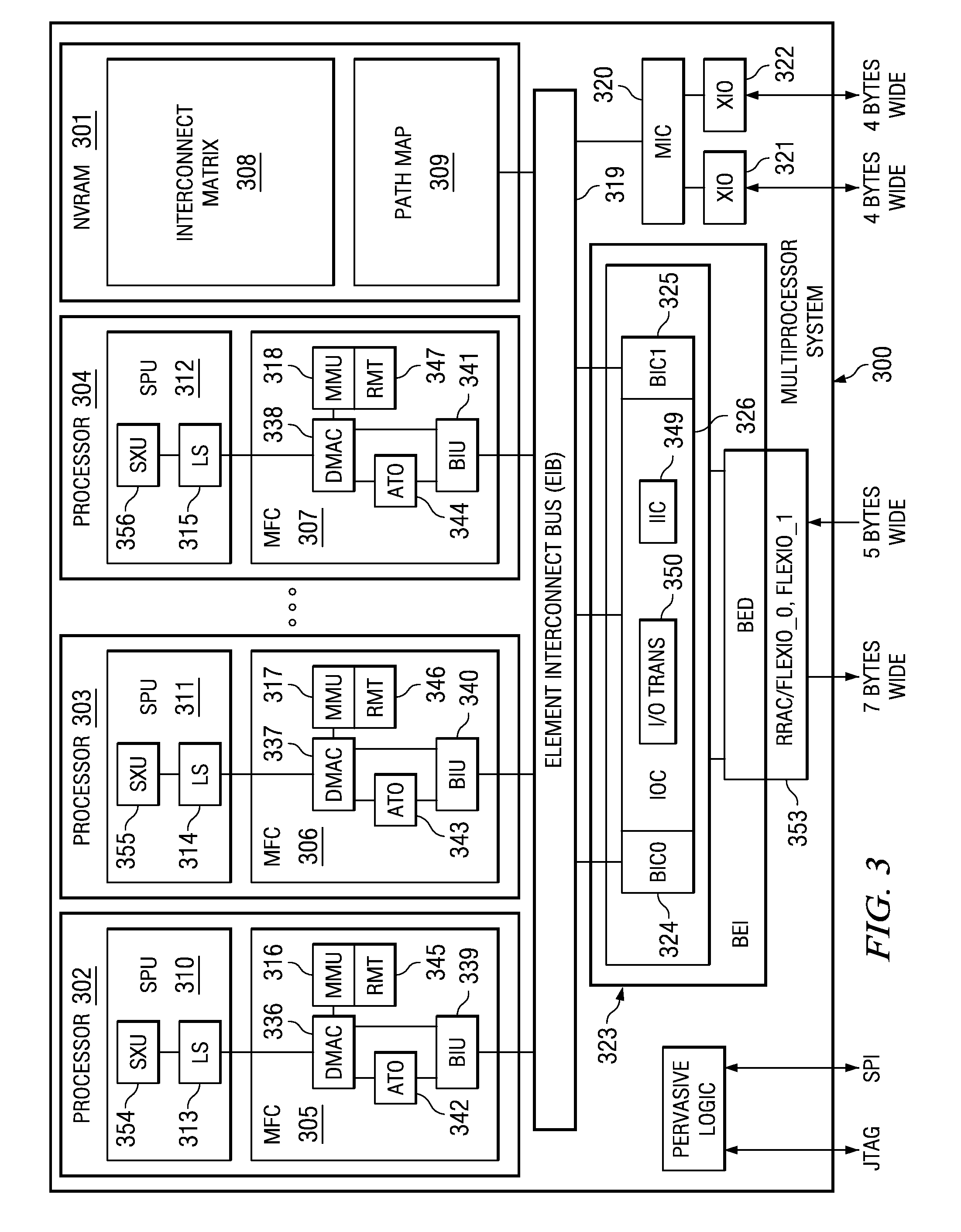
Method and Apparatus for Self-Healing Symmetric Multi-Processor System Interconnects
InactiveUS20080168255A1Program control using stored programsGeneral purpose stored program computerSelf-healingComputer architecture
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer program product for managing symmetric multiprocessor interconnects. The process identifies functional communication connections between each processor in a plurality of processors on a multiprocessor to form identified functional communication connections. The process maps every functional communication connection between any two processors in the plurality of processors, based on the identified functional communication connections, to form an interconnect matrix. The process creates a path map using the interconnect matrix. The path map comprises a sequence of communication connections between the plurality of processors. The process initializes the plurality of processors using the path map.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method, system and program product for communicating among processes in a symmetric multi-processing cluster environment
InactiveUS20070174558A1Improve performanceProgram controlMemory systemsCollective communicationSymmetric multiprocessing
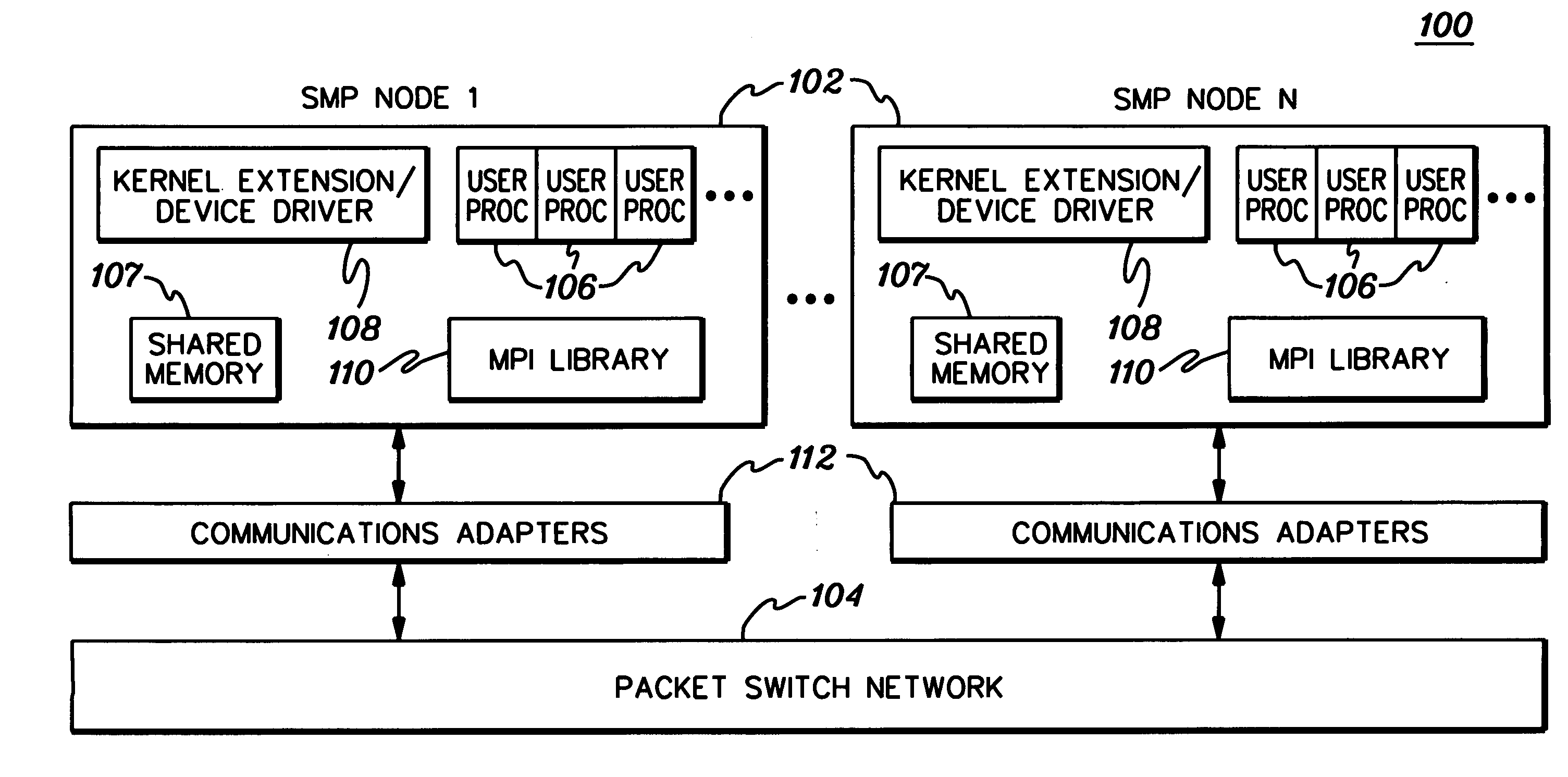
A facility is provided for communicating among processes in a symmetric multi-processing (SMP) cluster environment wherein at least some SMP nodes of the SMP cluster include multiple processes. The facility includes transferring intra-nodal at an SMP node messages of a collective communication among processes employing a shared memory of the SMP node; and responsive to the intra-nodal transferring, concurrently transferring inter-nodal multiple messages of the collective communication from n SMP node(s) to m other SMP node(s), wherein at least one of n or m is greater than one. The concurrently transferring is performed by multiple processes of at least one of the n SMP node(s) or the m other SMP node(s). More particularly, the facility includes concurrently transferring inter-nodal the multiple messages from one of: one SMP node to multiple other SMP nodes, multiple SMP nodes to one other SMP node, or multiple SMP nodes to multiple other SMP nodes.
Owner:IBM CORP
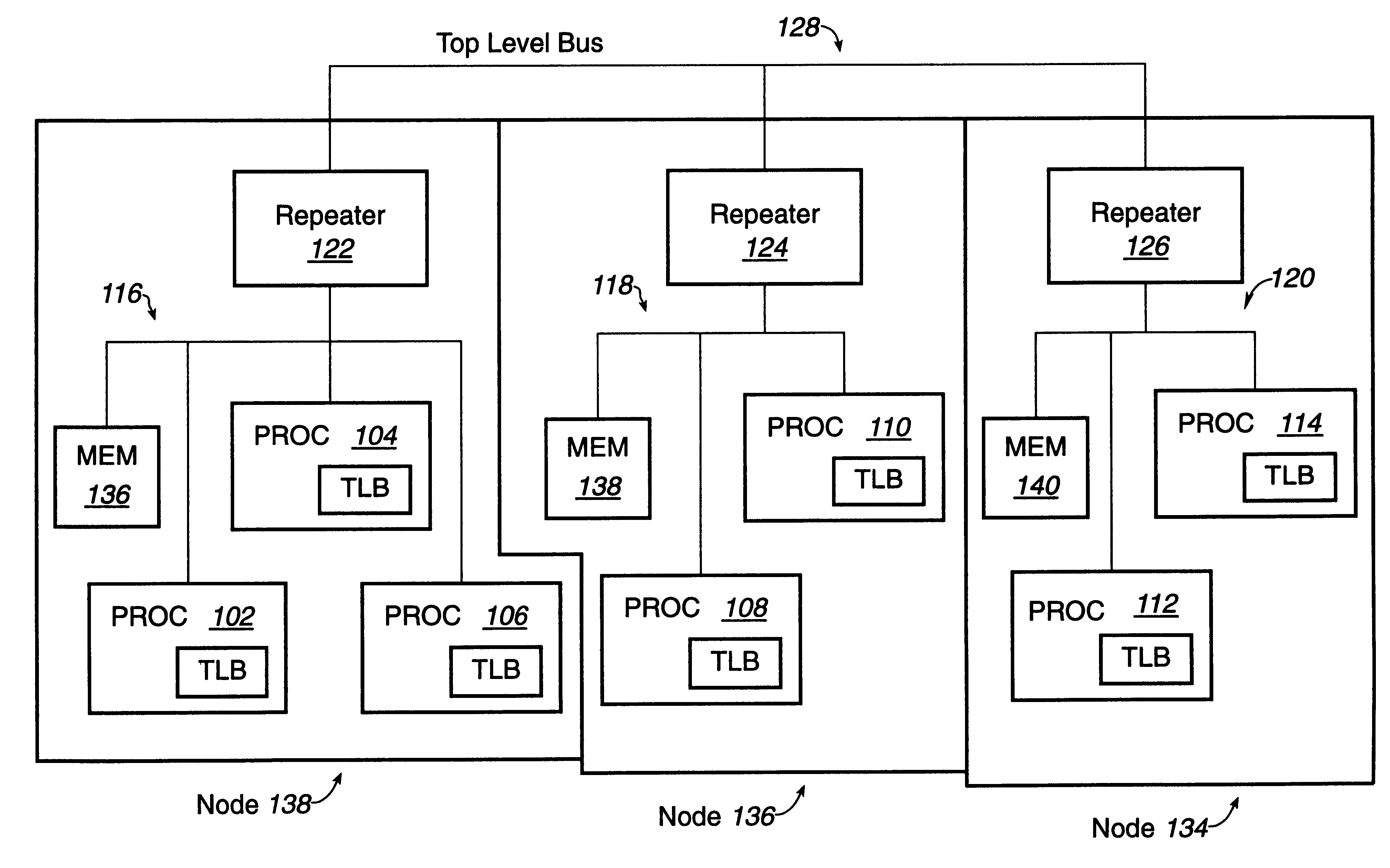
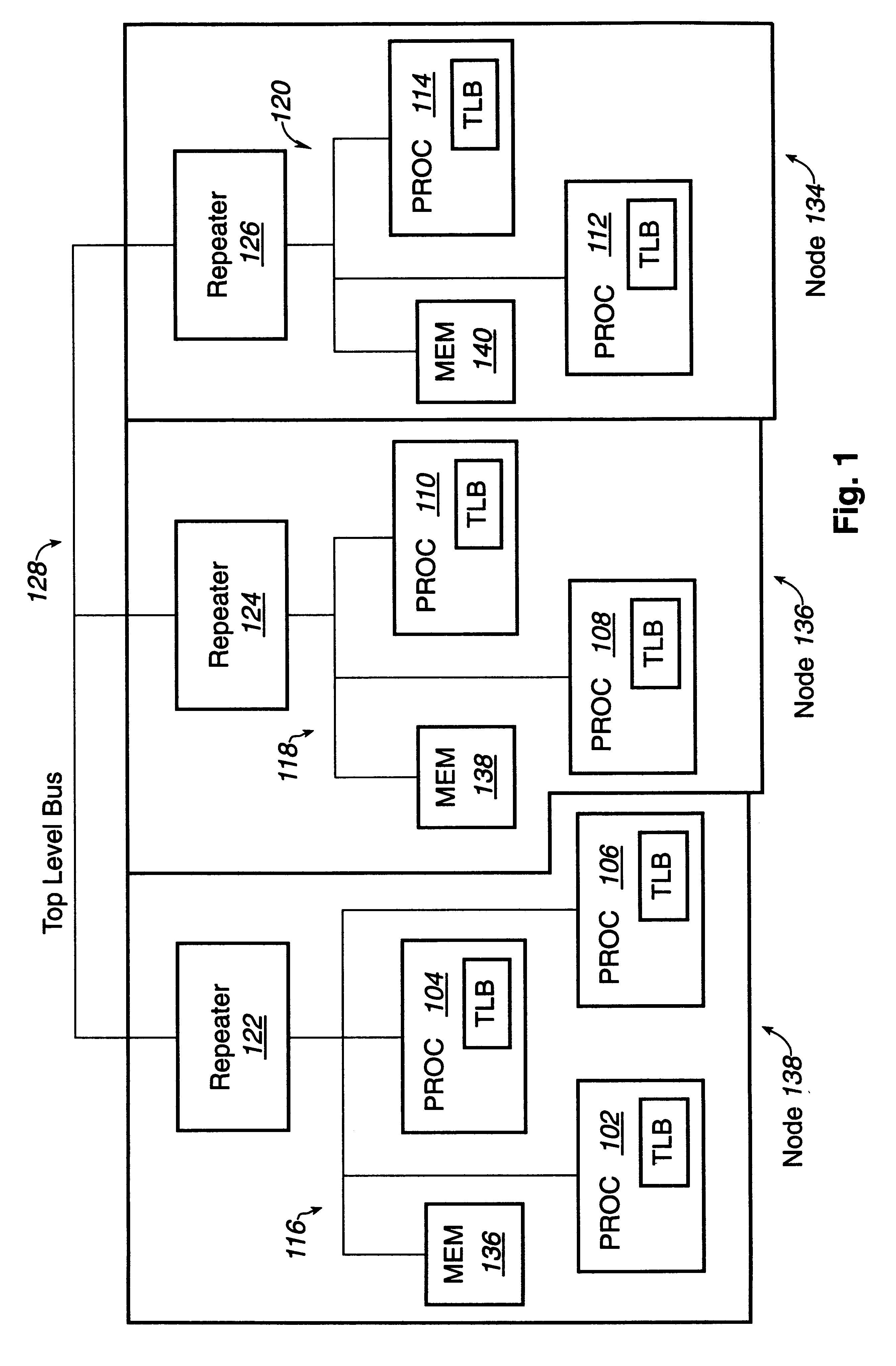
Distributed symmetric multiprocessing computing architecture
ActiveUS20110125974A1Shorten the progressMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsSupercomputerGlobal address space
Example embodiments of the present invention includes systems and methods for implementing a scalable symmetric multiprocessing (shared memory) computer architecture using a network of homogeneous multi-core servers. The level of processor and memory performance achieved is suitable for running applications that currently require cache coherent shared memory mainframes and supercomputers. The architecture combines new operating system extensions with a high-speed network that supports remote direct memory access to achieve an effective global distributed shared memory. A distributed thread model allows a process running in a head node to fork threads in other (worker) nodes that run in the same global address space. Thread synchronization is supported by a distributed mutex implementation. A transactional memory model allows a multi-threaded program to maintain global memory page consistency across the distributed architecture. A distributed file access implementation supports non-contentious file I / O for threads. These and other functions provide a symmetric multiprocessing programming model consistent with standards such as Portable Operating System Interface for Unix (POSIX).
Owner:ANDERSON RICHARD S
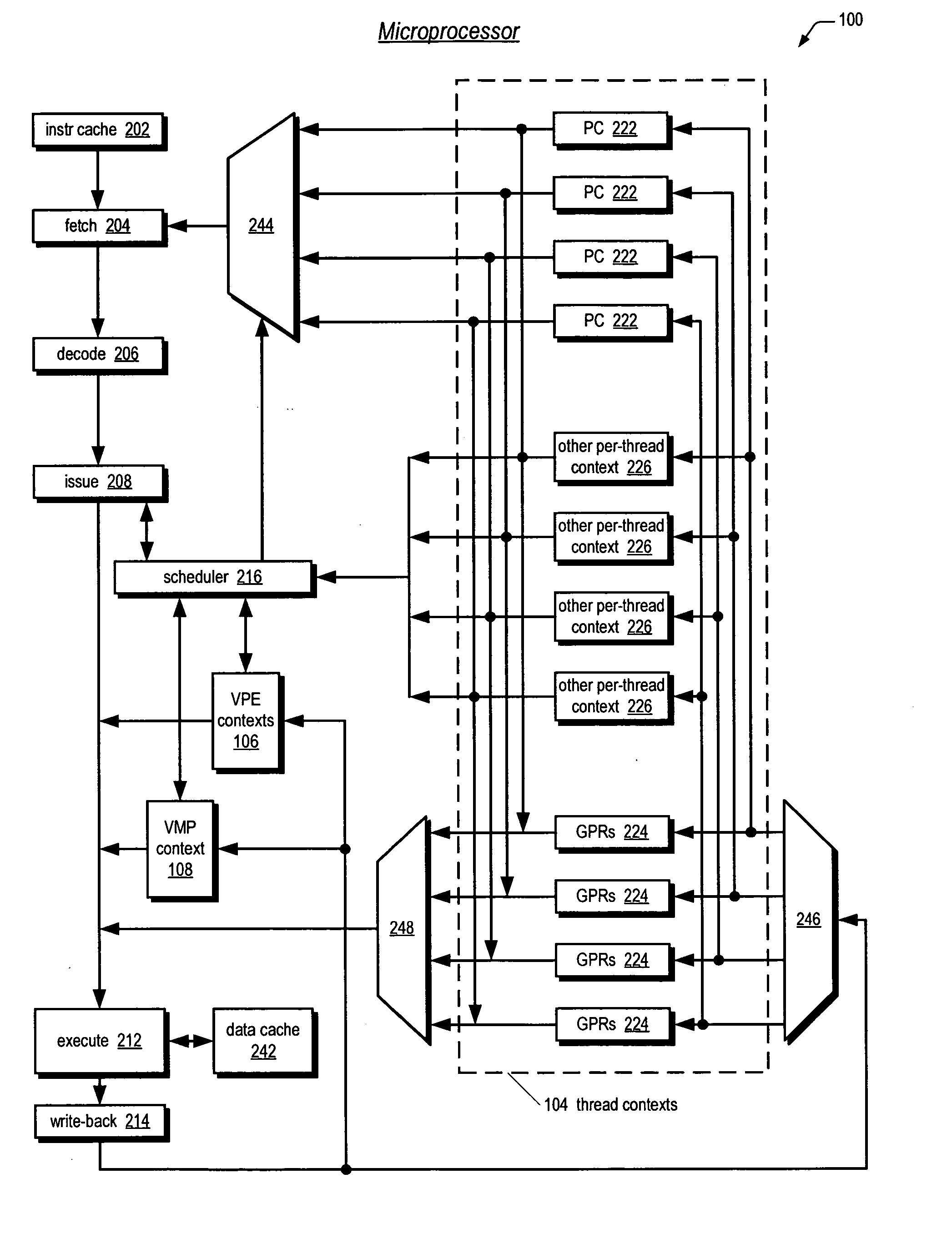
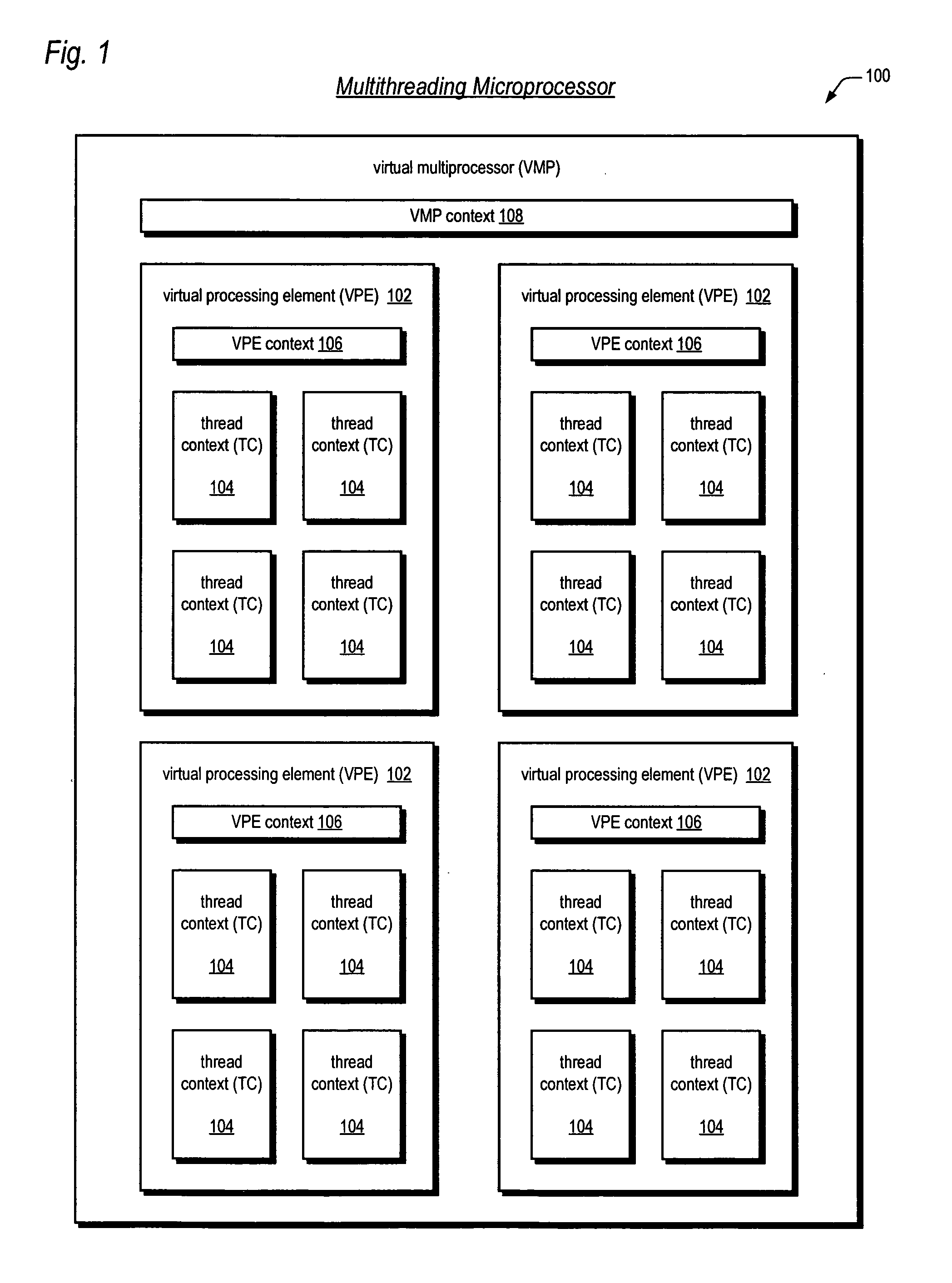
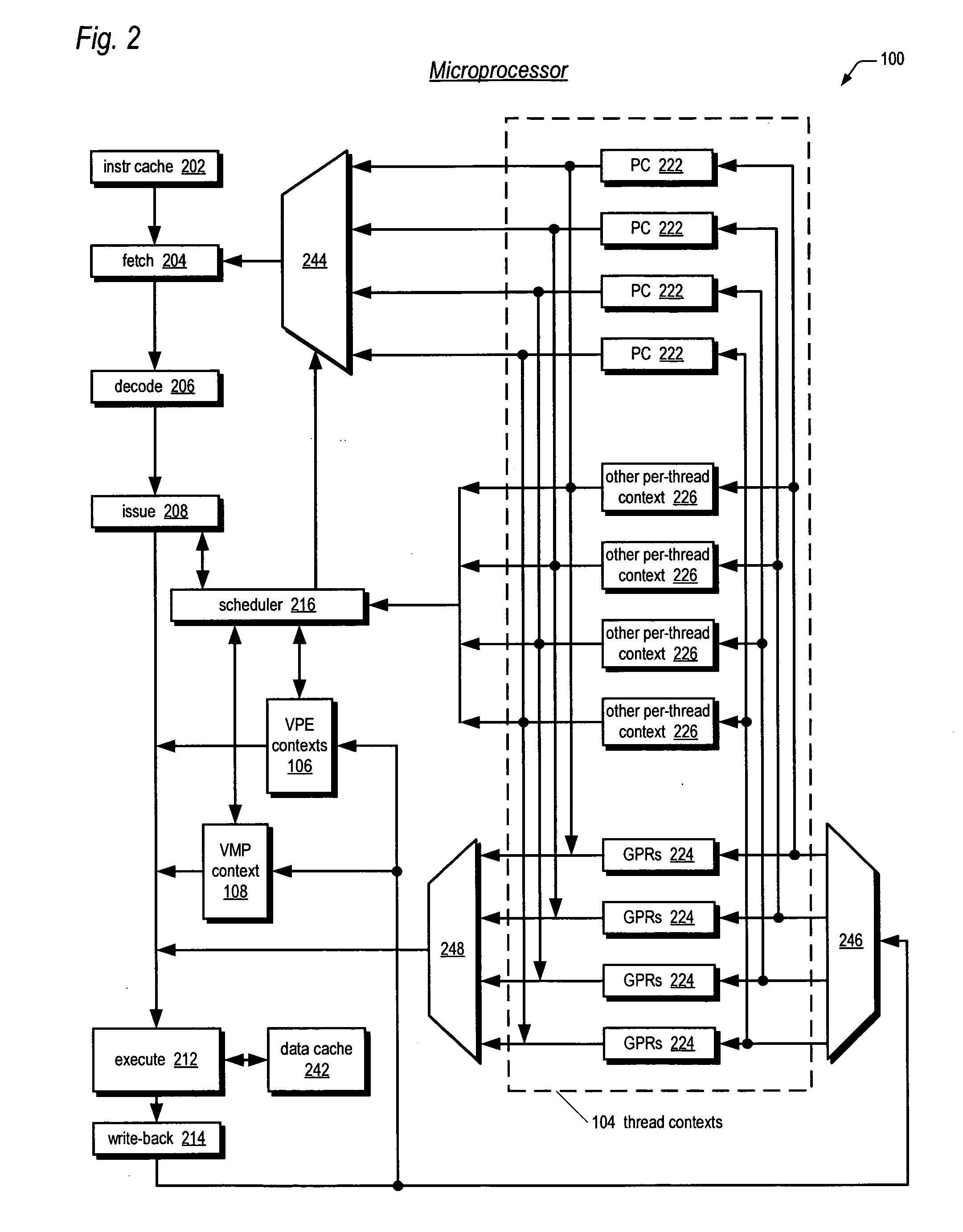
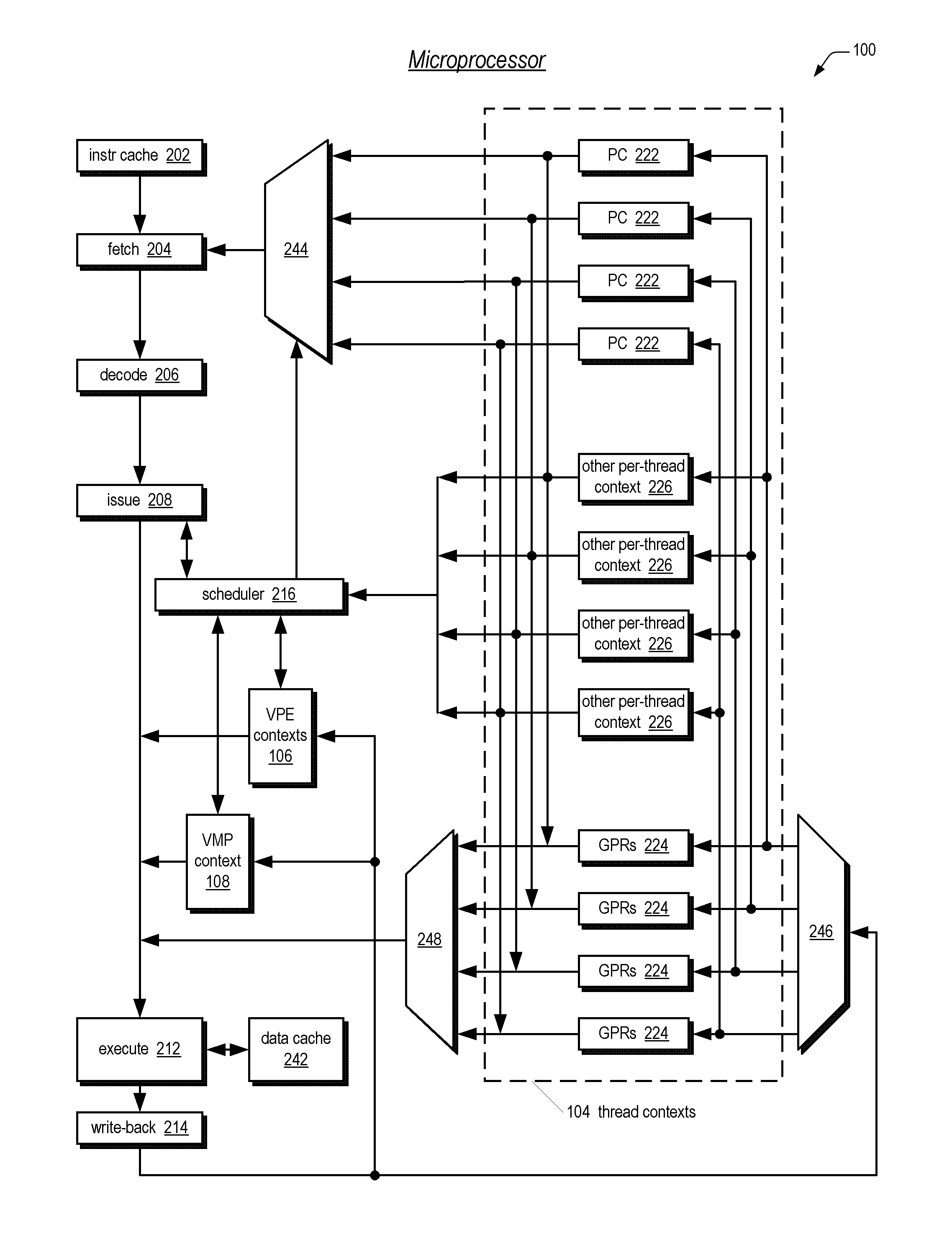
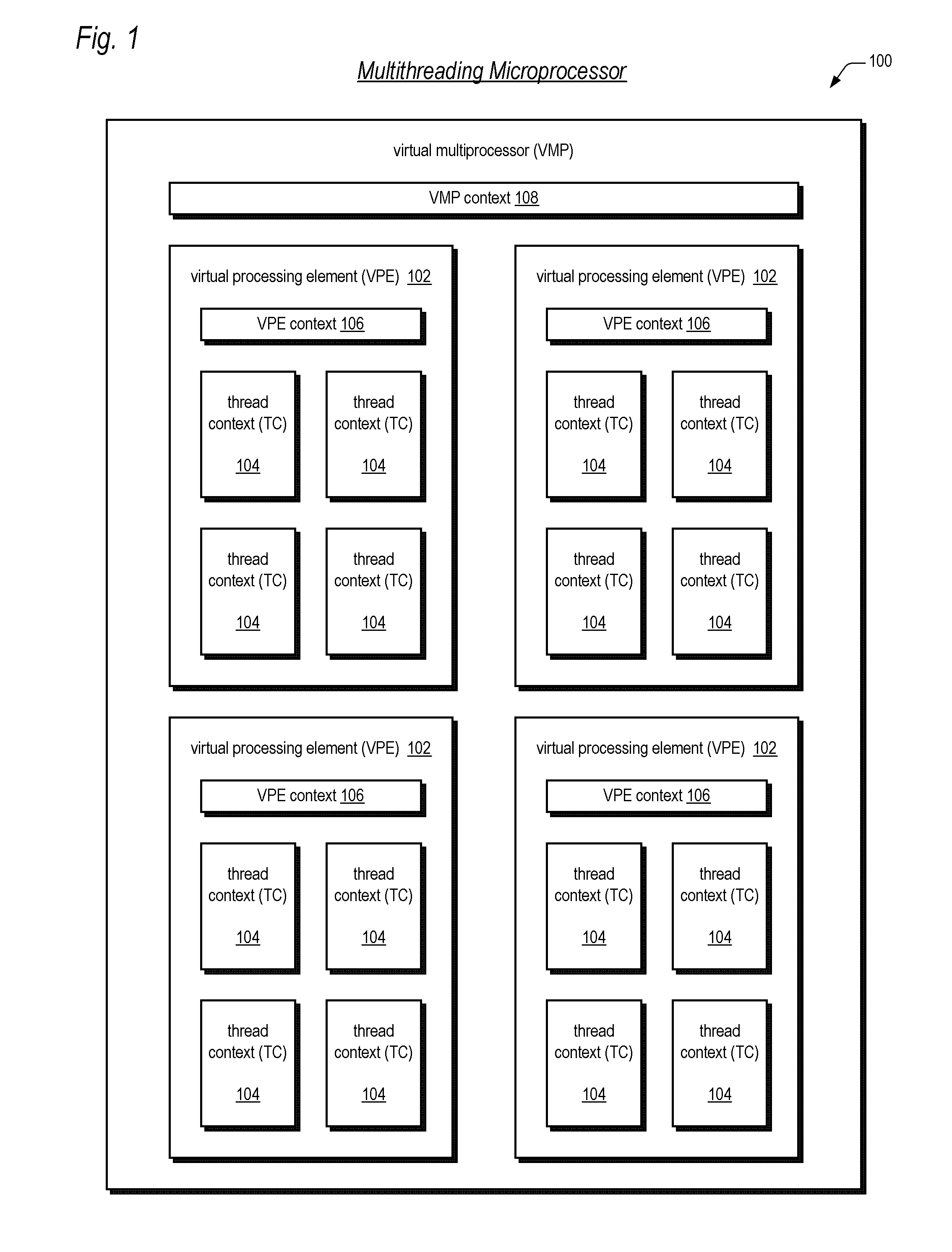
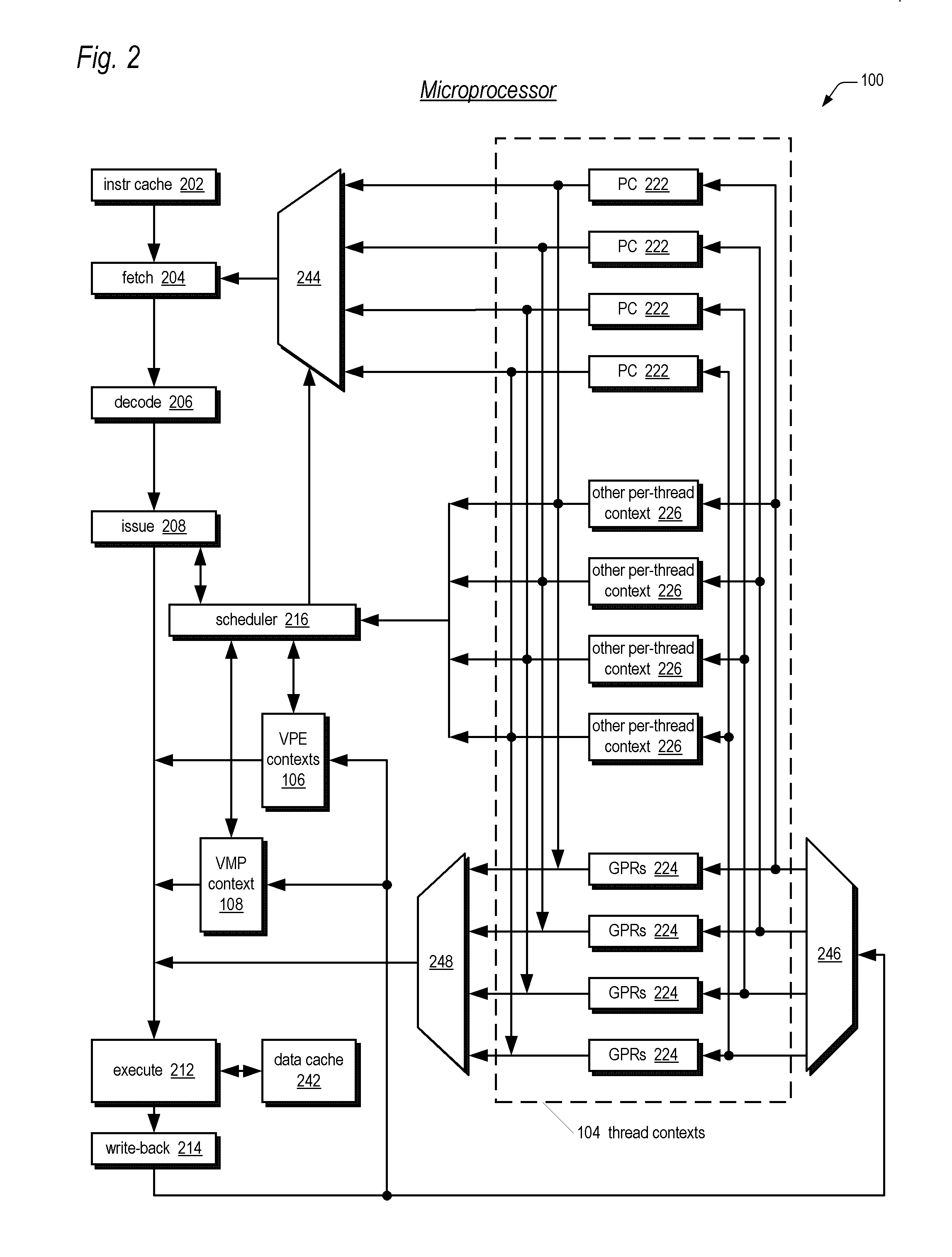
Symmetric multiprocessor operating system for execution on non-independent lightweight thread contexts
InactiveUS20060195683A1Lightweight in of areaLightweight in of powerEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsGeneral purposeUser Privilege
A multiprocessing system is disclosed. The system includes a multithreading microprocessor including a plurality of thread contexts (TCs), each having a program counter and a general purpose register set for executing a thread. The microprocessor also includes a shared privileged resource, shared by the plurality of TCs rather than being replicated for each of the plurality of TCs, and privileged to be managed only by operating system-privileged threads rather than by user-privileged threads. The system also includes a multiprocessor operating system (OS), configured to manage the shared privileged resource, and to schedule execution of both the operating system-privileged threads and the user-privileged threads on the plurality of TCs.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
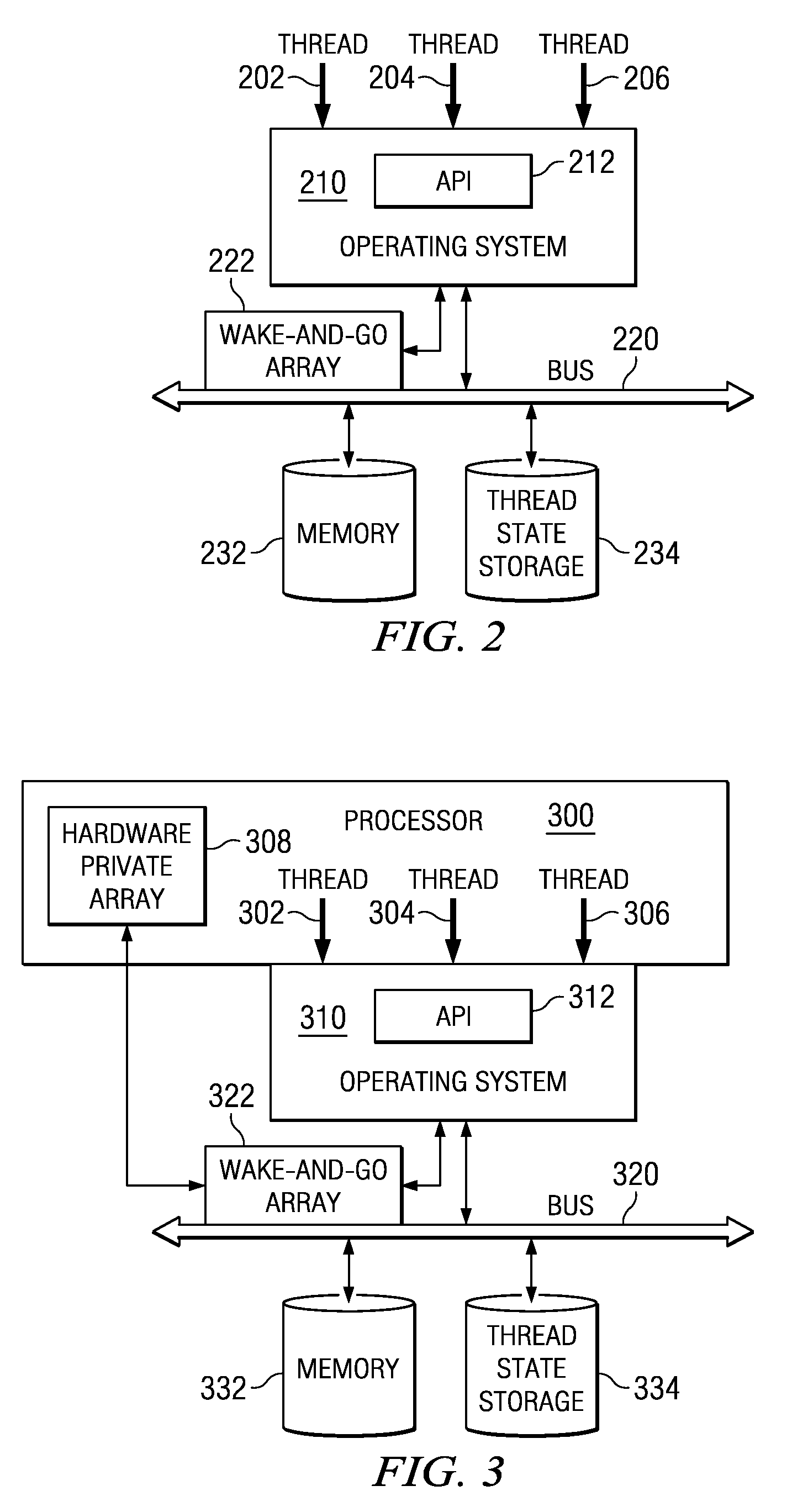
Wake-and-Go Mechanism with Data Monitoring
ActiveUS20090199029A1Energy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementOperational systemArray data structure
A wake-and-go mechanism is provided for a data processing system. The wake-and-go mechanism recognizes a programming idiom, specialized instruction, operating system call, or application programming interface call that indicates that a thread is waiting for an event. The wake-and-go mechanism updates a wake-and-go array with a target address, expected data value, and comparison type associated with the event. The thread then goes to sleep until the event occurs. The wake-and-go array may be a content addressable memory (CAM). When a transaction appears on the symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) fabric that modifies the value at a target address in the CAM, logic associated with the CAM performs a comparison based on the data value being written, expected data value, and comparison type.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for backup a parallel server data storage system
InactiveUS6658589B1Safe and effective backupSafe and effective and restoreData processing applicationsRedundant operation error correctionMulti processorParallel processing
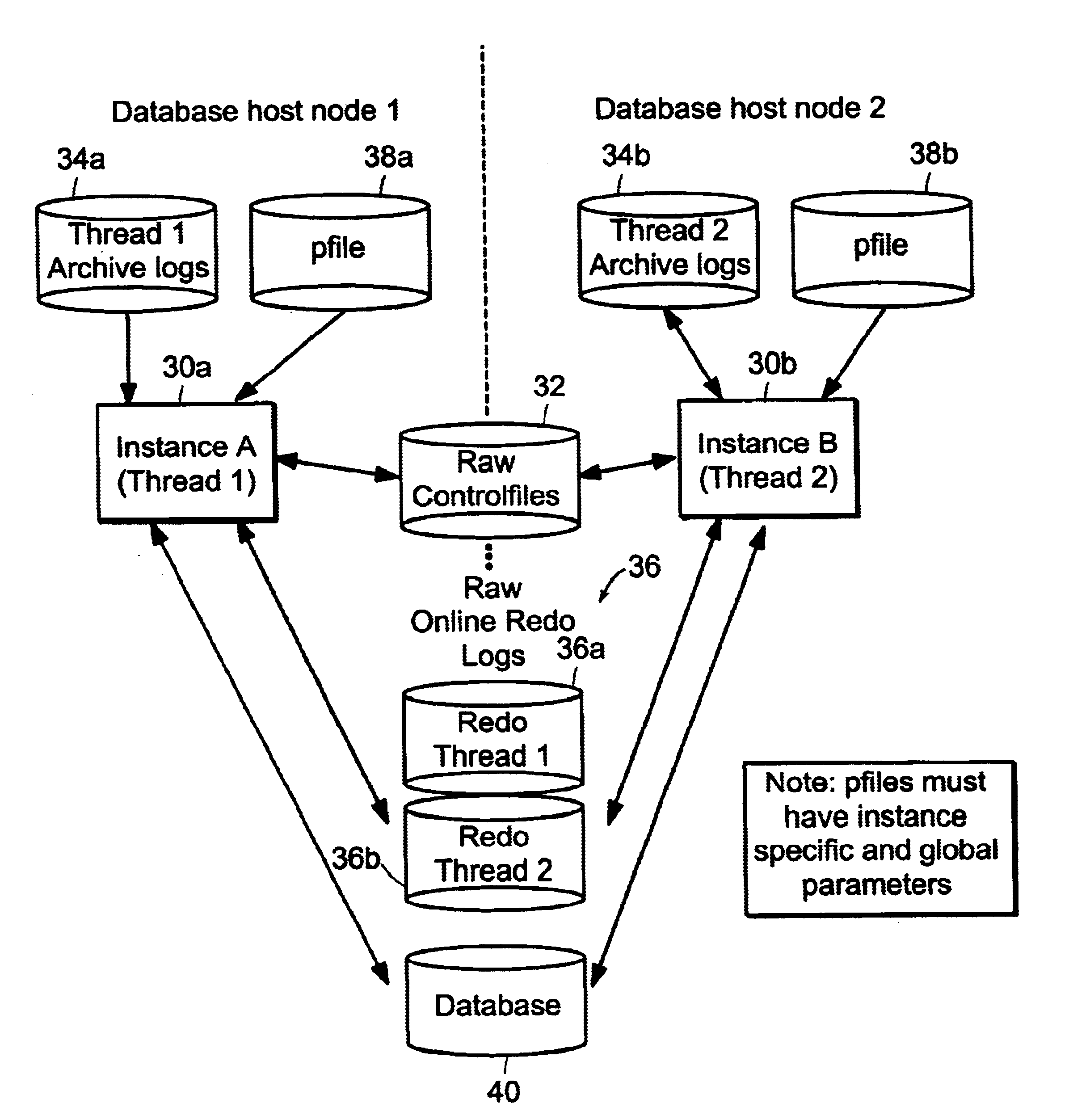
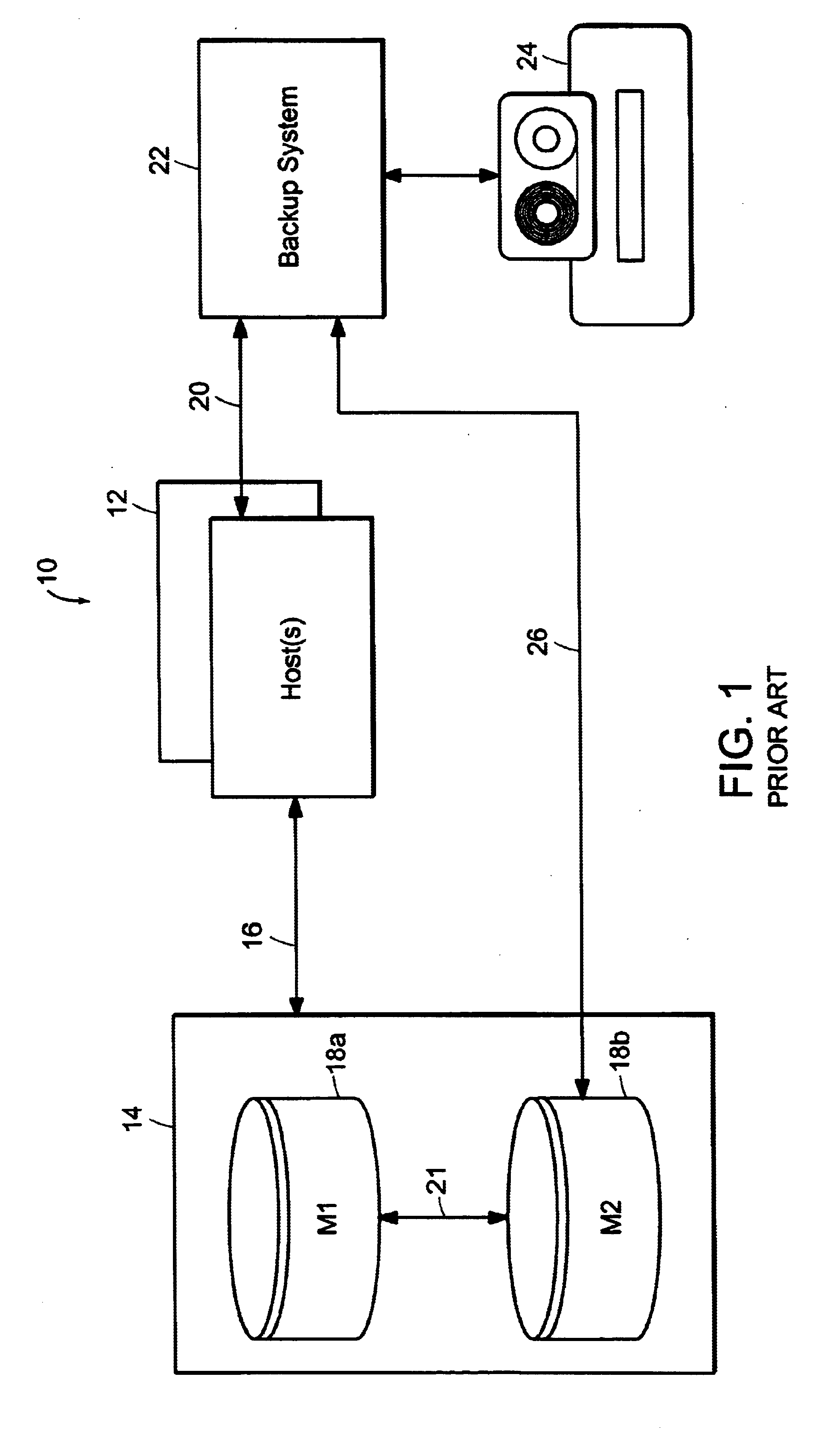
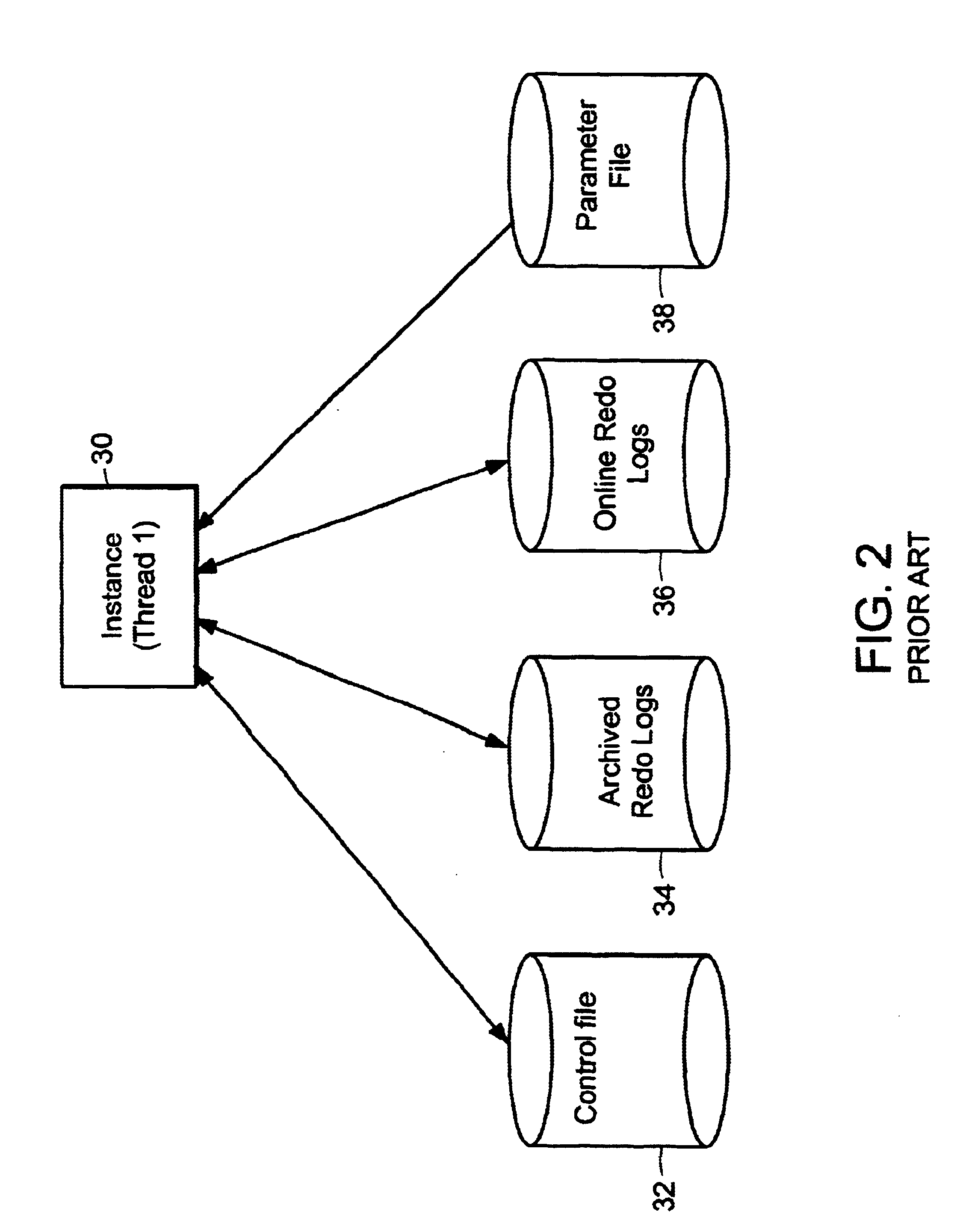
A system and method for safe and effective backup and restore of parallel server databases stored in data storage systems. Parallel server databases allow multiple nodes in MPP (Massively Parallel Processor) or SMP (Symmetric Multi-Processor) systems to simultaneously access a database. Each node is running an instance (thread) which provides access to the database. The present invention allows for online or offline backup to be performed from any node in the system, with proper access to all control files and logs, both archived and online, whether the files are stored in raw partitions in the data storage system, or local on certain nodes. Two different types of external restore supported: complete external restore and partial external restore. In a complete external restore, all spaces will be restored to the most recent checkpoint that was generated while creating an external backup. If users lose only a portion of the data (which is more typically the case), a partial external restore may be performed.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
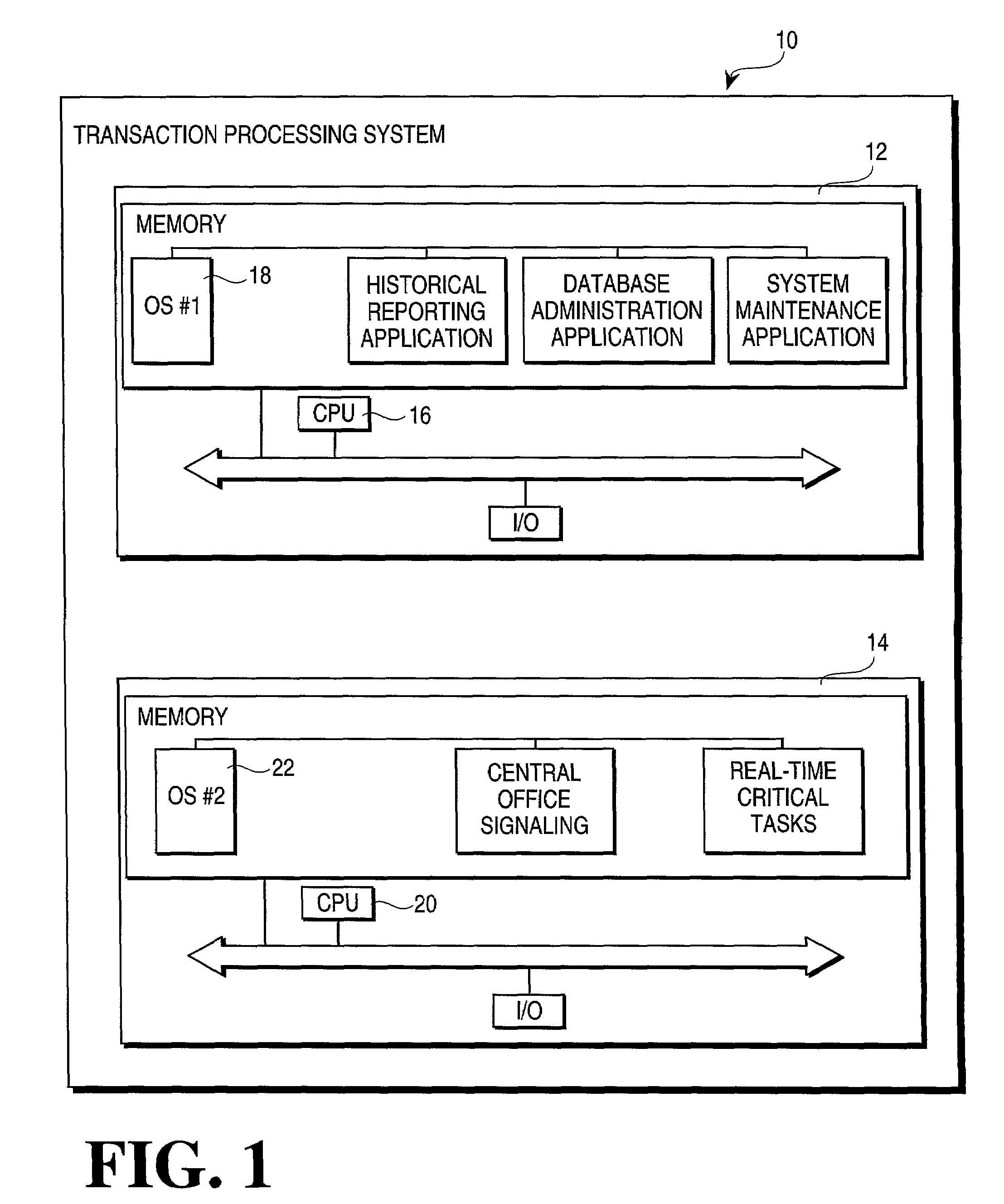
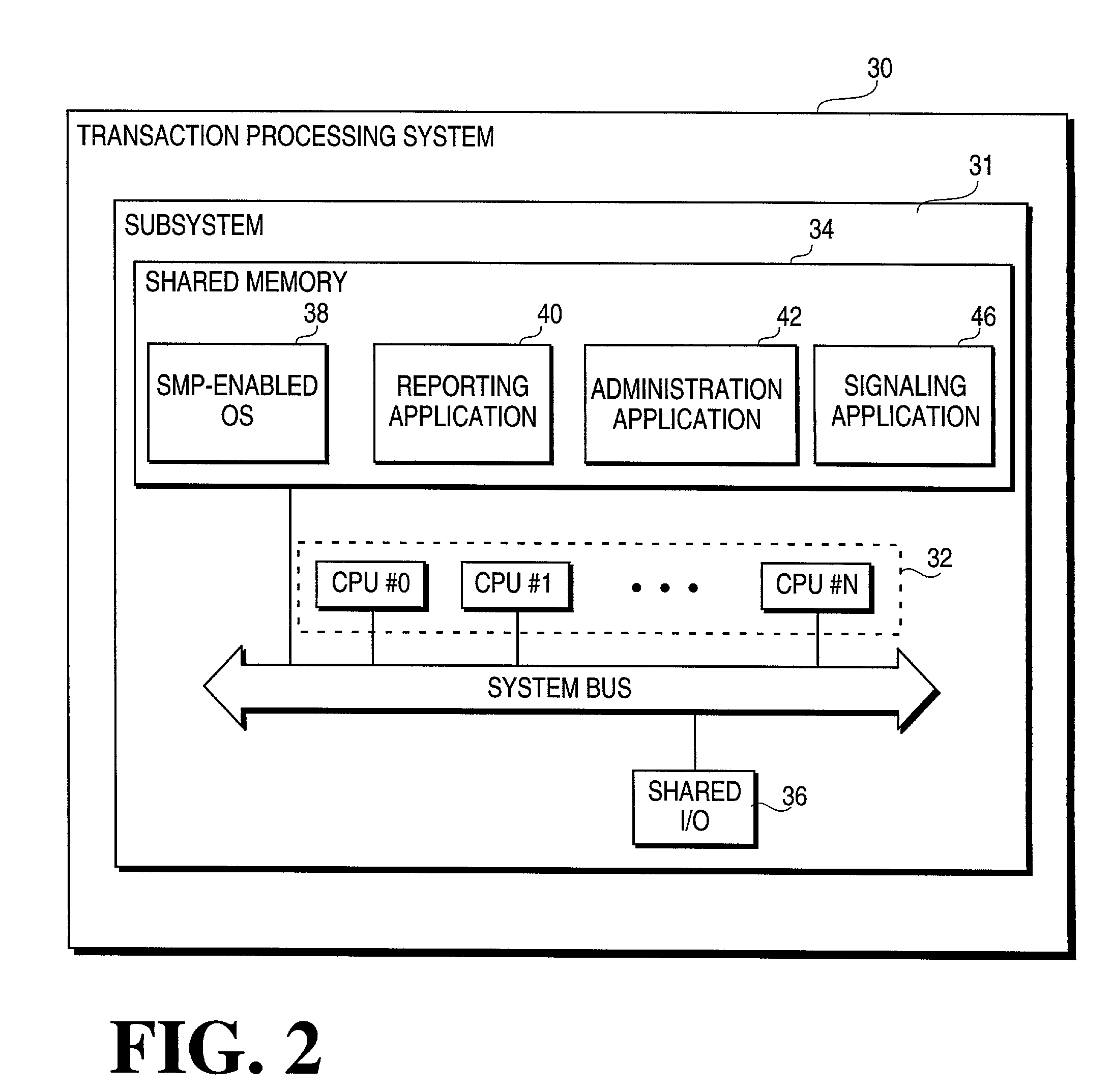
Methods and apparatus for executing a transaction task within a transaction processing system employing symmetric multiprocessors
InactiveUS7401112B1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsMulti processorTransaction processing system
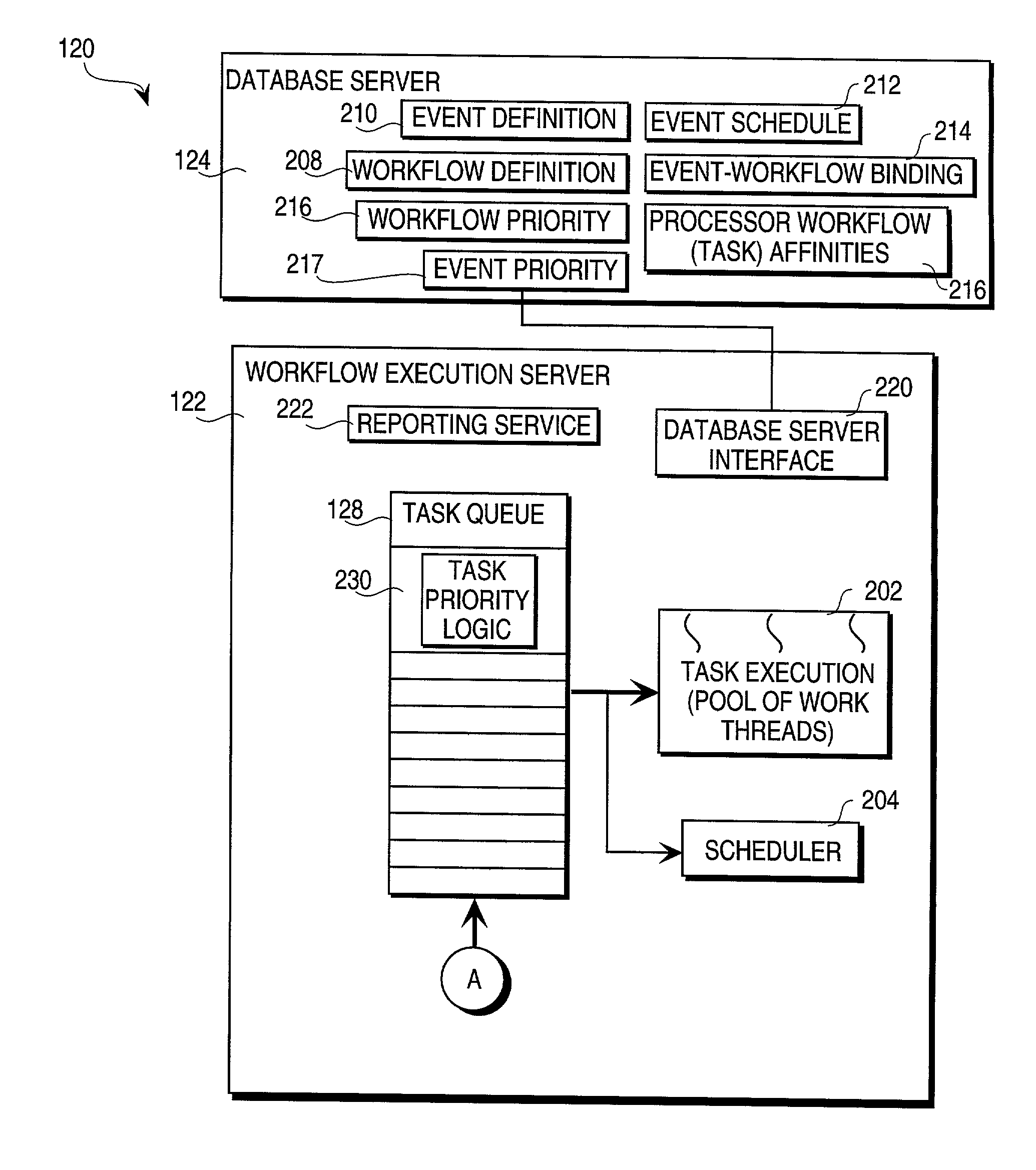
A method of executing a transaction task within a transaction processing system includes, responsive to an event, the steps of identifying a workflow associated with the event. A transaction task, that at least partially executes the workflow, is distributed to an available thread within a pool threads operating within a multiprocessor system, that may be a Symmetrical Multiprocessor (SMP) system.
Owner:ASPECT COMM +1
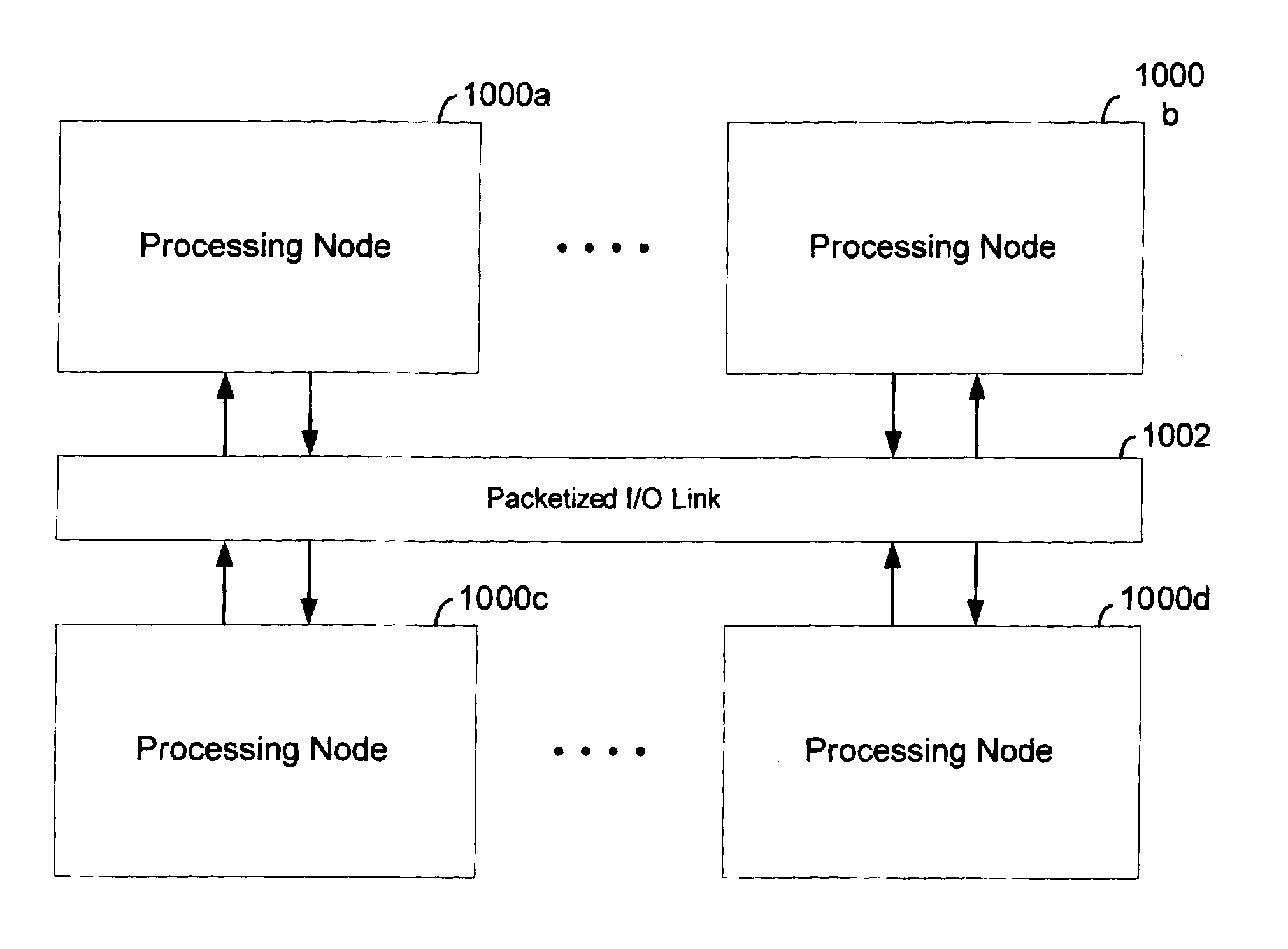
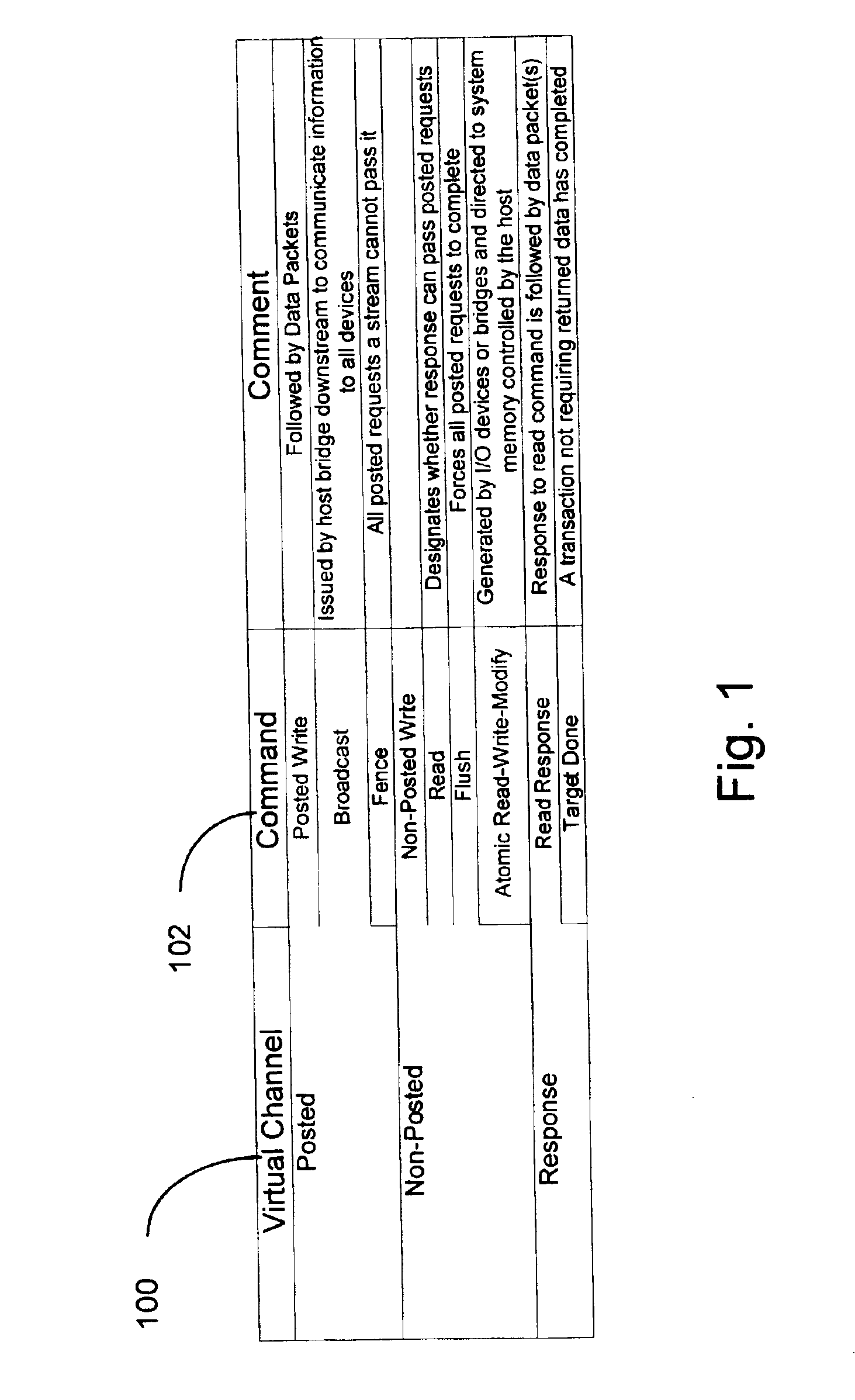
Scalable cache coherent distributed shared memory processing system
A packetized I / O link such as the HyperTransport protocol is adapted to transport memory coherency transactions over the link to support cache coherency in distributed shared memory systems. The I / O link protocol is adapted to include additional virtual channels that can carry command packets for coherency transactions over the link in a format that is acceptable to the I / O protocol. The coherency transactions support cache coherency between processing nodes interconnected by the link. Each processing node may include processing resources that themselves share memory, such as symmetrical multiprocessor configuration. In this case, coherency will have to be maintained both at the intranode level as well as the internode level. A remote line directory is maintained by each processing node so that it can track the state and location of all of the lines from its local memory that have been provided to other remote nodes. A node controller initiates transactions over the link in response to local transactions initiated within itself, and initiates transactions over the link based on local transactions initiated within itself. Flow control is provided for each of the coherency virtual channels either by software through credits or through a buffer free command packet that is sent to a source node by a target node indicating the availability of virtual channel buffering for that channel.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
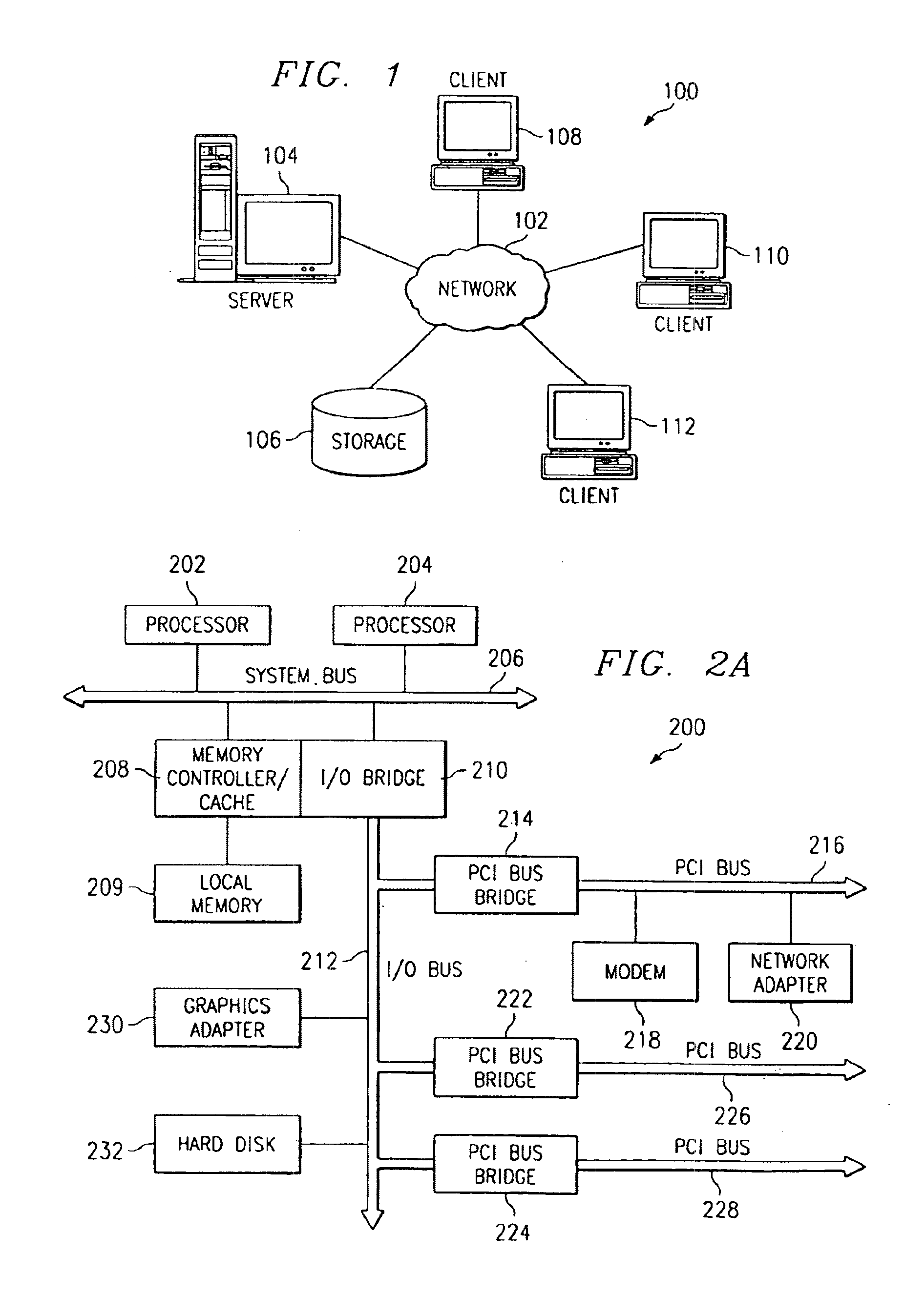
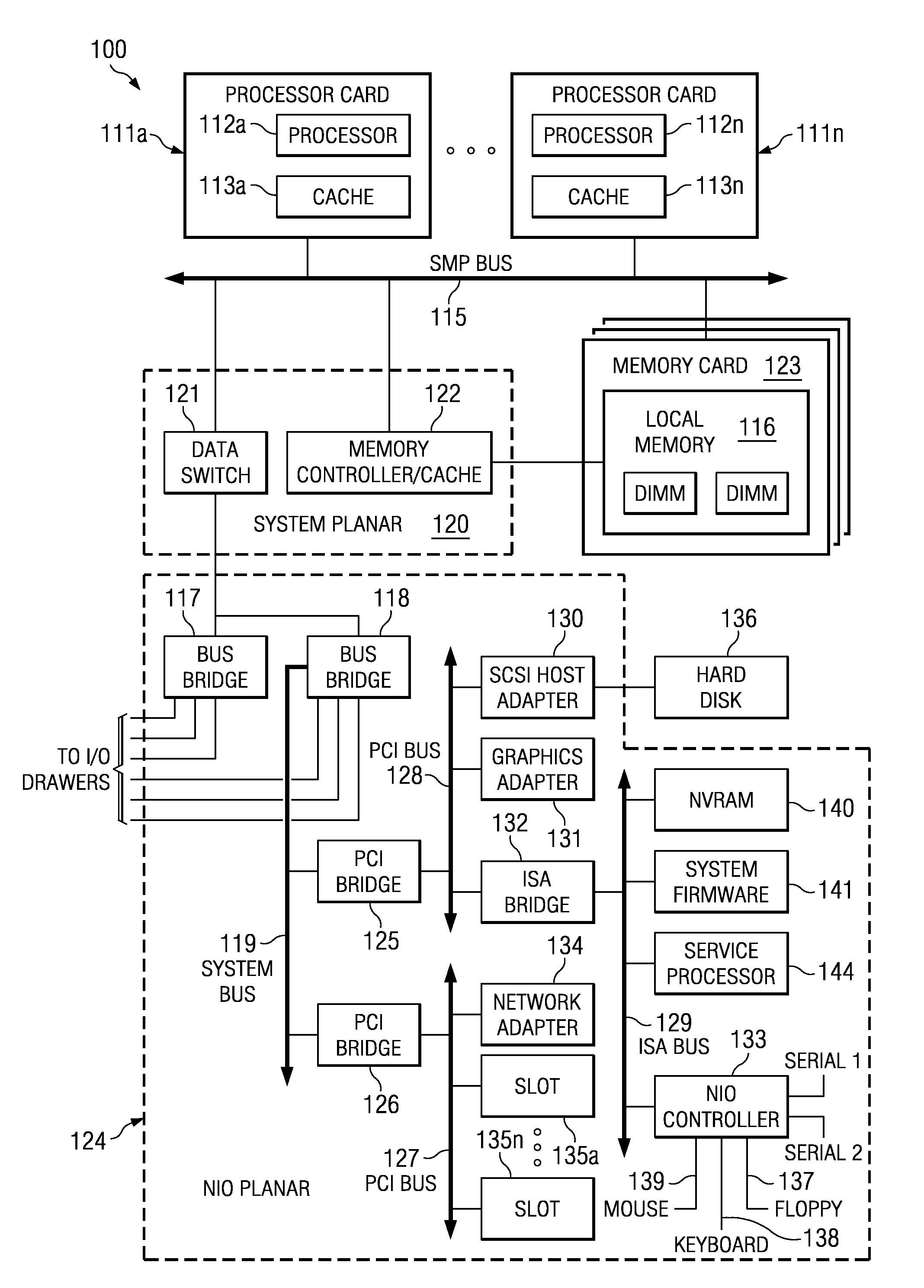
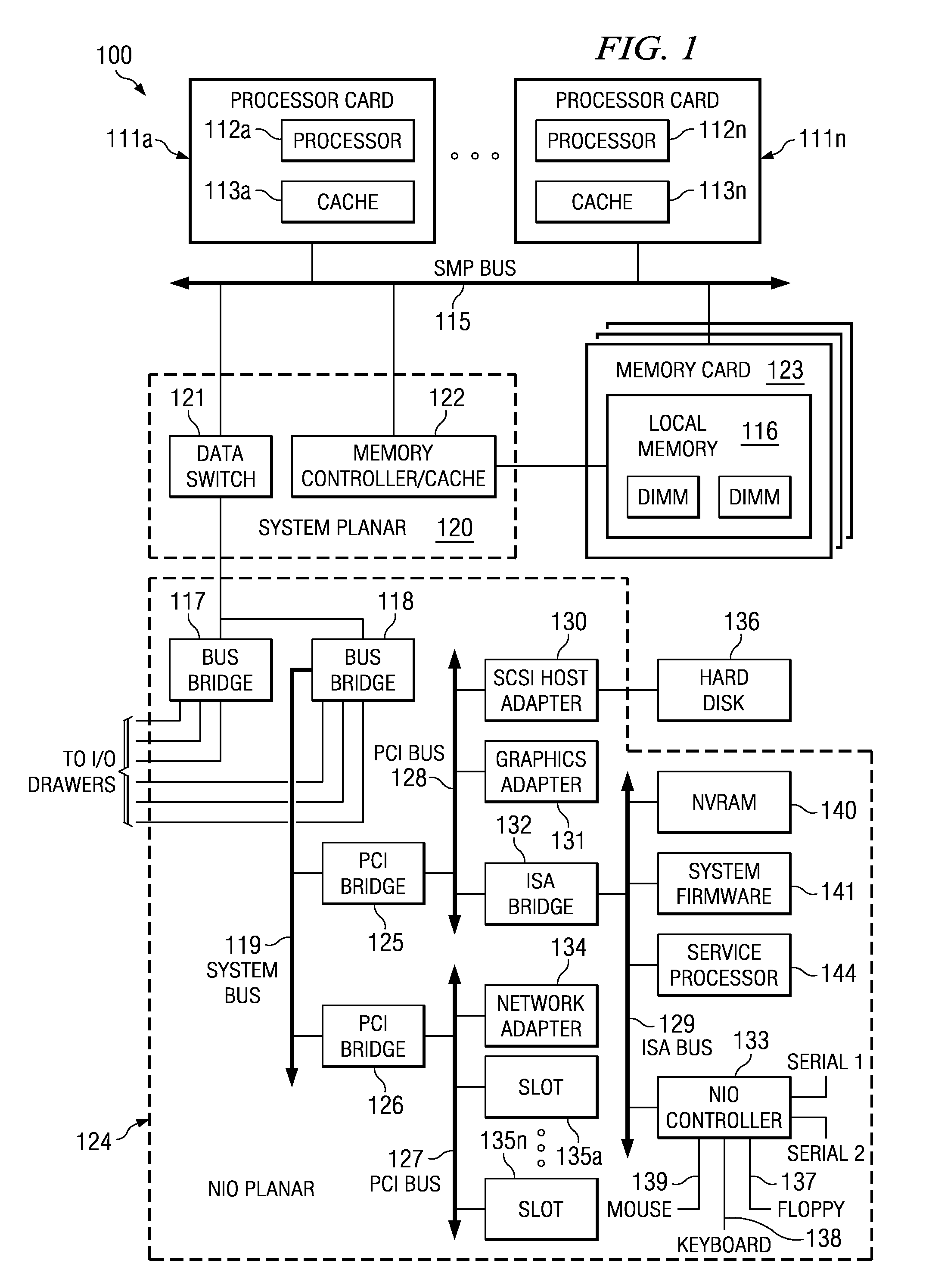
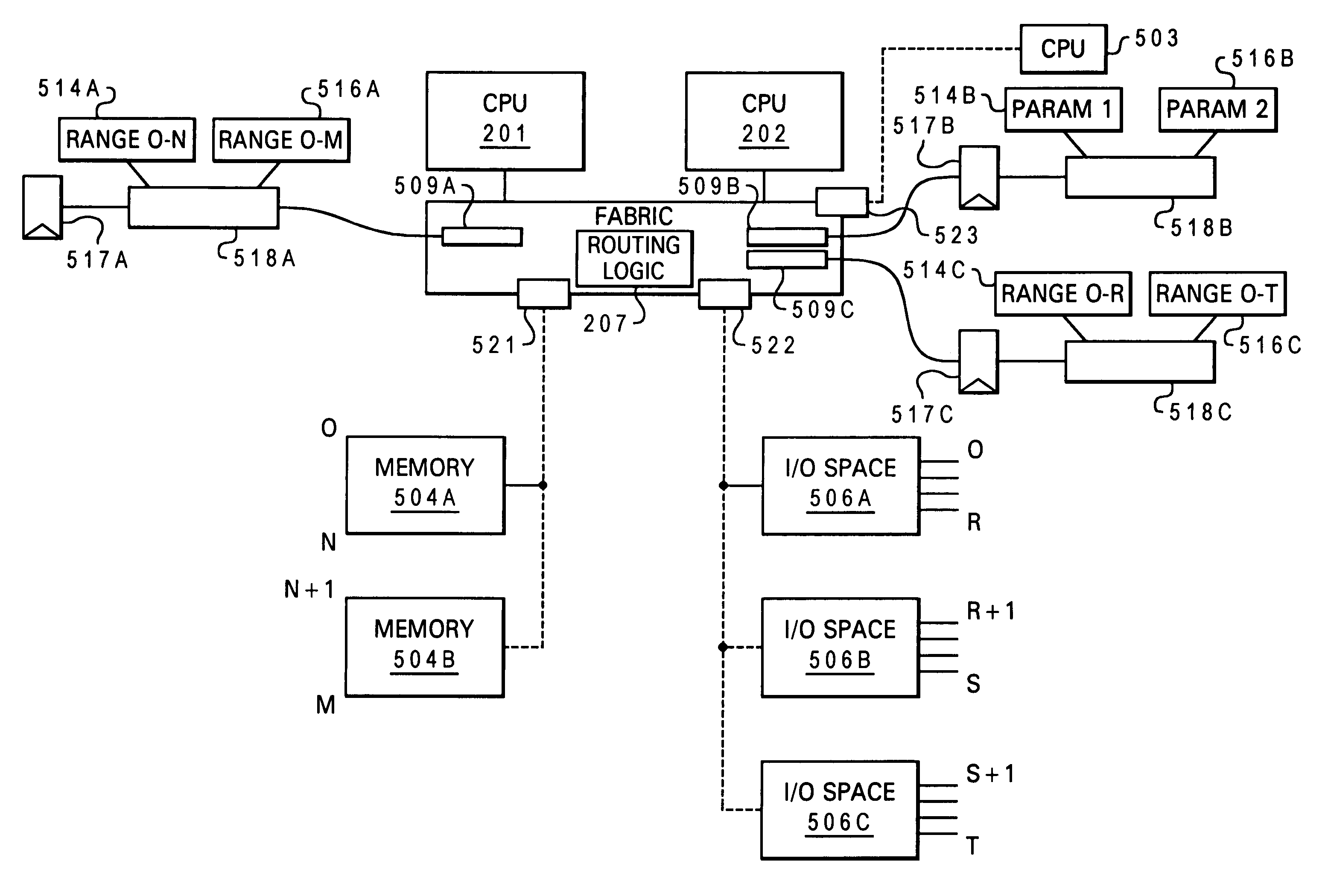
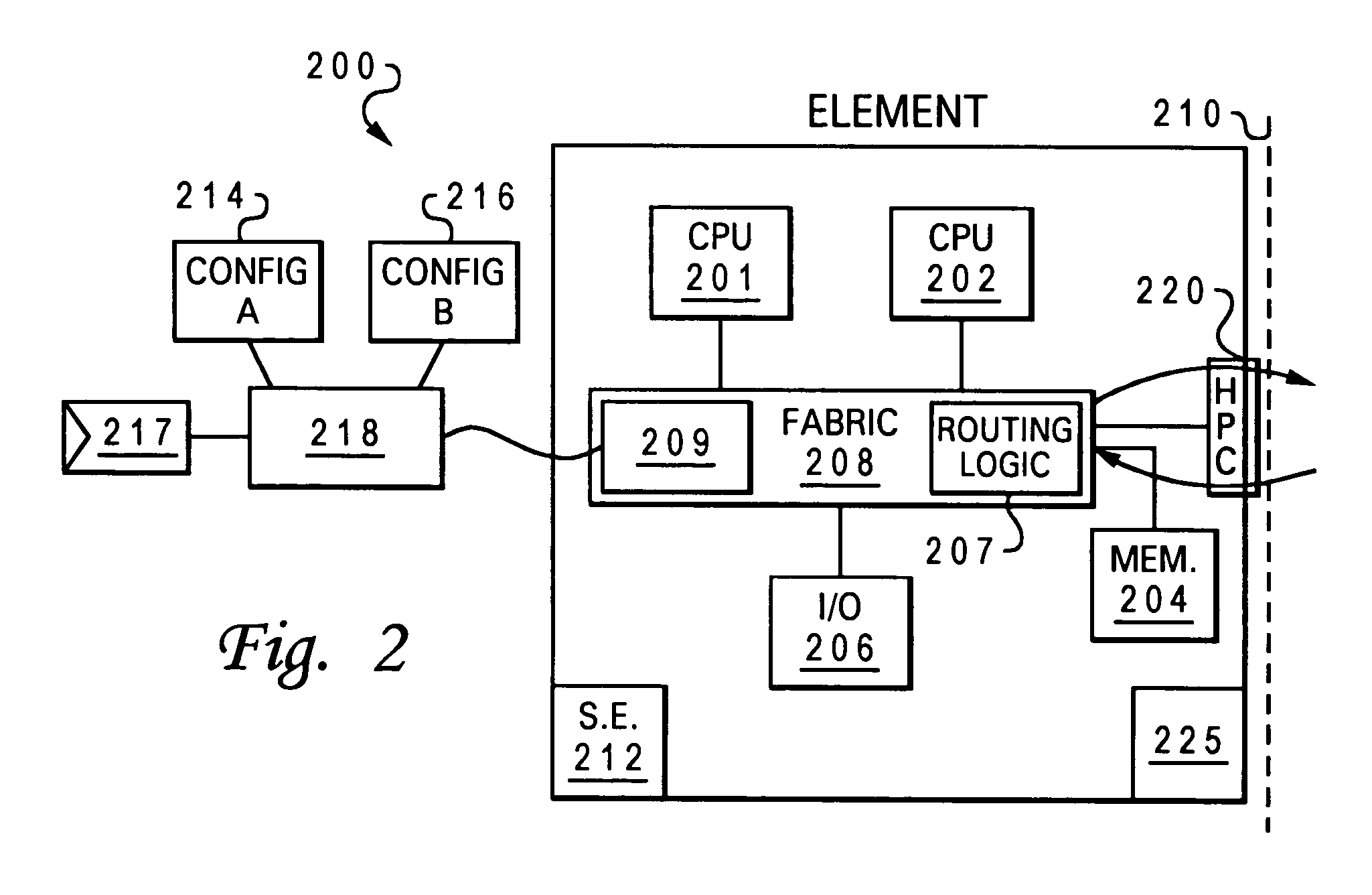
Non-disruptive, dynamic hot-add and hot-remove of non-symmetric data processing system resources
InactiveUS20040215864A1Interprogram communicationDigital computer detailsData processing systemNon symmetric
A data processing system that provides non-disruptive, hot-plug functionality for several major hardware components, namely processors, memory and input / output (I / O) channels. The data processing system comprises an original processor, original memory and an original I / O channel each interconnect via an interconnect fabric. The data processing system also comprises a service element and an operating system (OS). The interconnect fabric comprises wiring and hardware and software logic components that enable both the hot-plug addition (or removal) of additional processors, memory and I / O channels and the on-the-fly re-configuration features required to support the various expansions or removals of the additional components. The various components are added without disrupting the processing of the existing components and become immediately available for utilization within the enhanced system.
Owner:IBM CORP
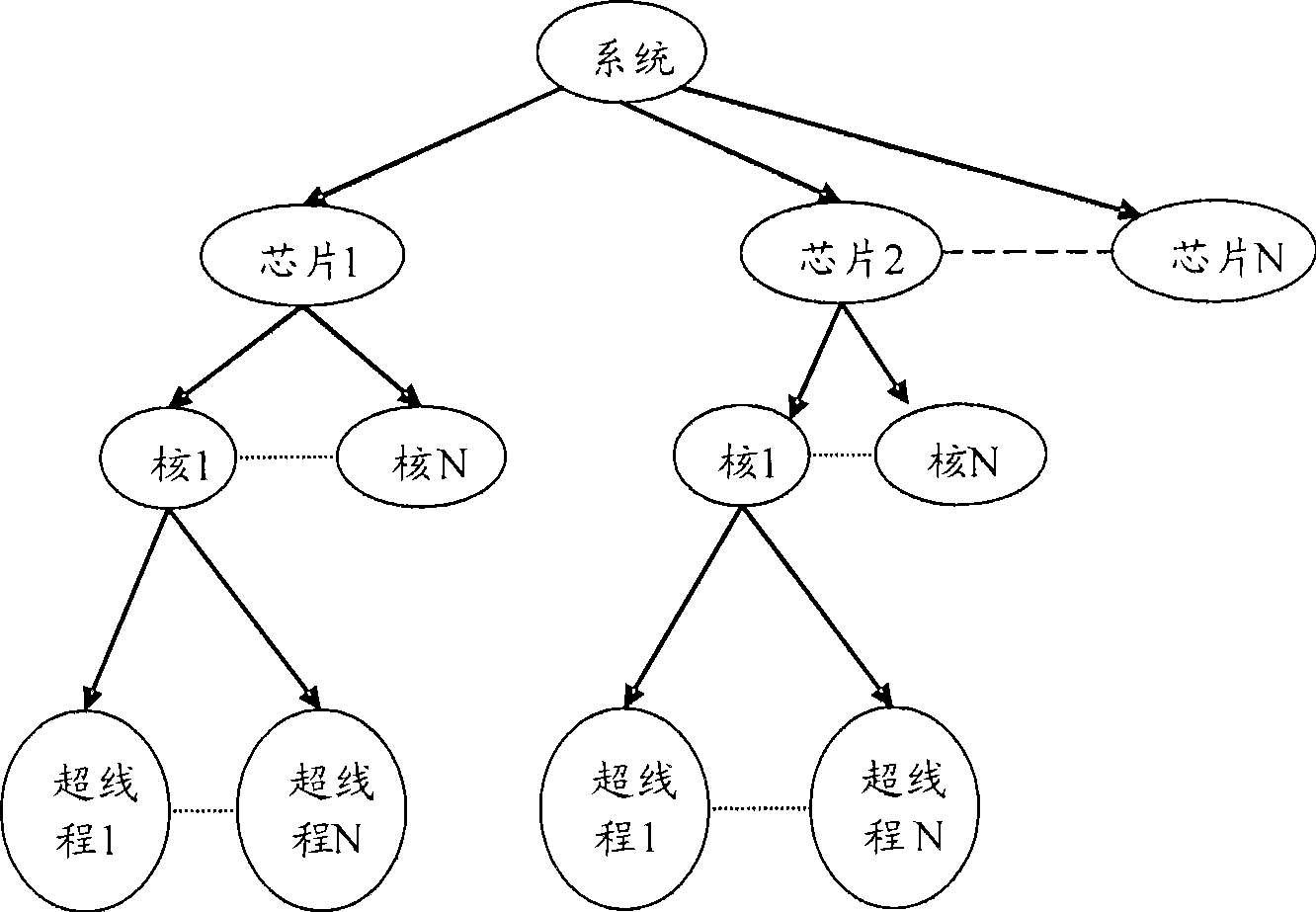
Load equilibration scheduling method and device
ActiveCN101458634AGood real-time responsivenessReduce computational overheadMultiprogramming arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionMaximum differenceDistributed computing
The present invention provides a load balances scheduling method and apparatus, wherein, the method comprises: step one, a load balance monitoring module of periodic duty is started up for monitoring the distribution of task priority of each processing unit in multiprocessor system, and when the distribution unbalance of the task priority of each processing unit is monitored and the maximum difference value of the task priority distribution exceeds the preset threshold value, the load balance monitoring module can determine a source processing unit, a target processing unit and the priority of the task scheduling to be performed, and can launch a load balance scheduling message to related load balance processing module; and step two, the relating load balance processing module can execute the task scheduling according to the task priority distribution of each processing unit and relations between processing units, thereby the task load on each processing unit in a symmetrical multiprocessor system can be reached to balance.
Owner:ZTE CORP
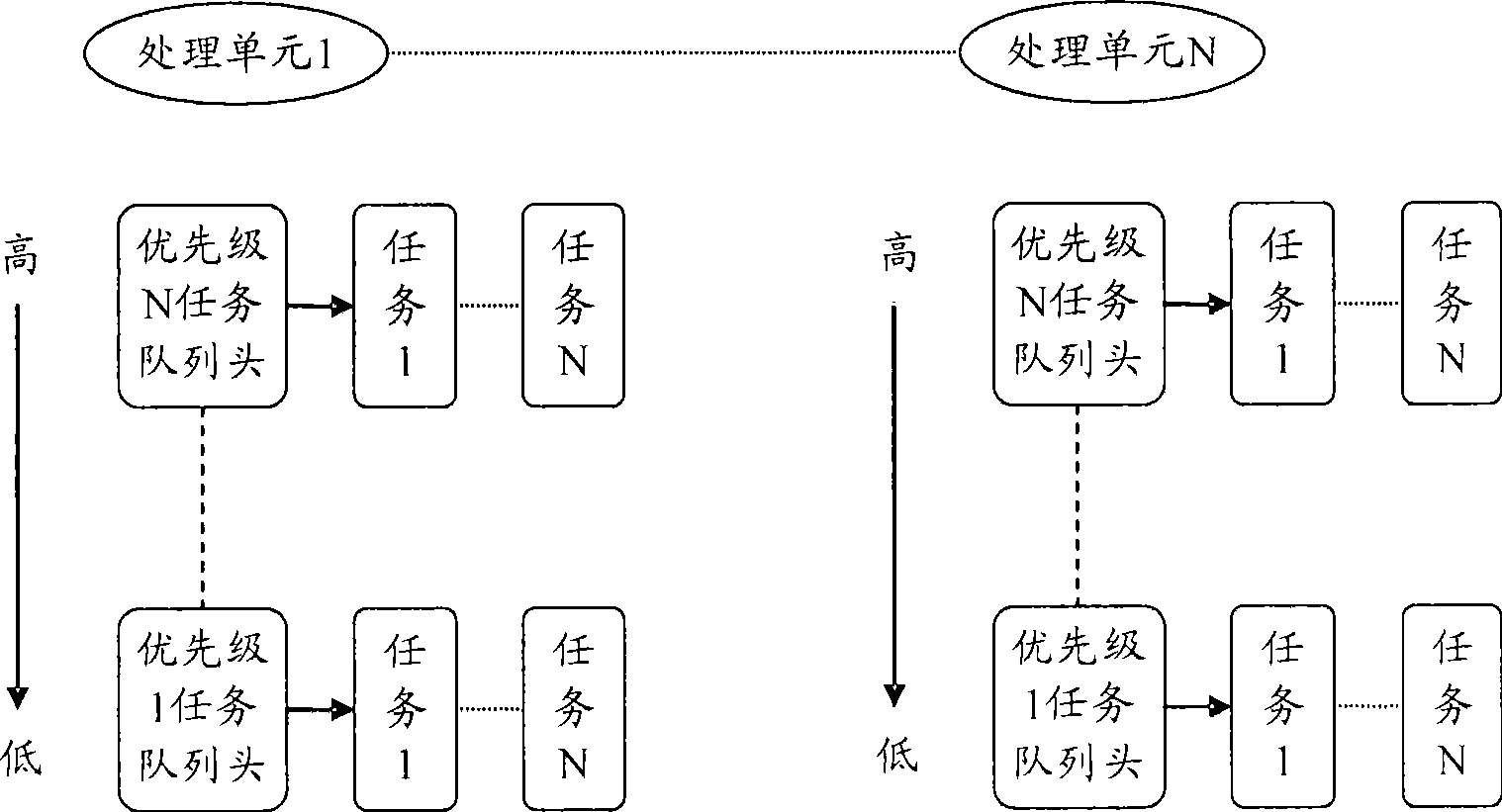
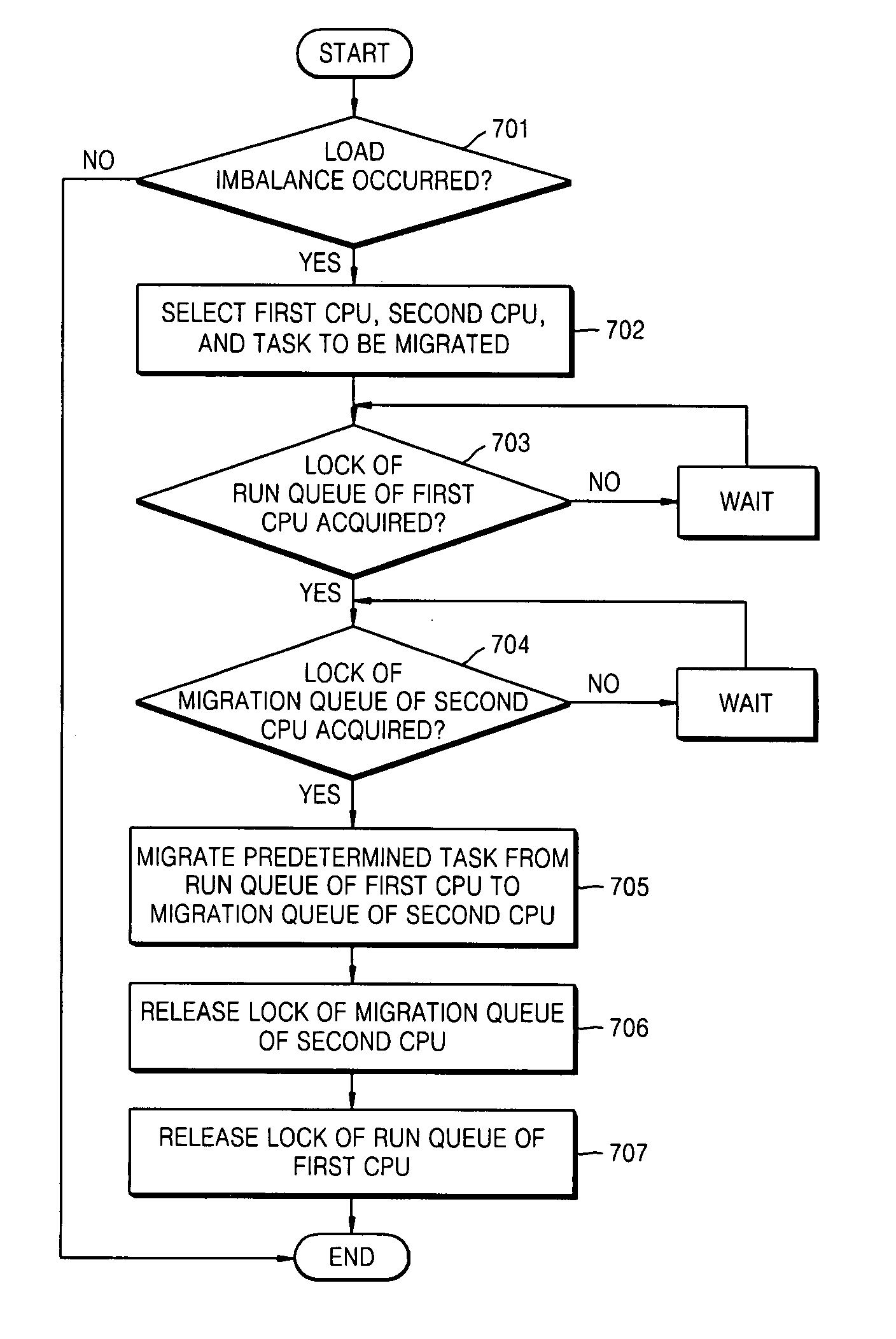
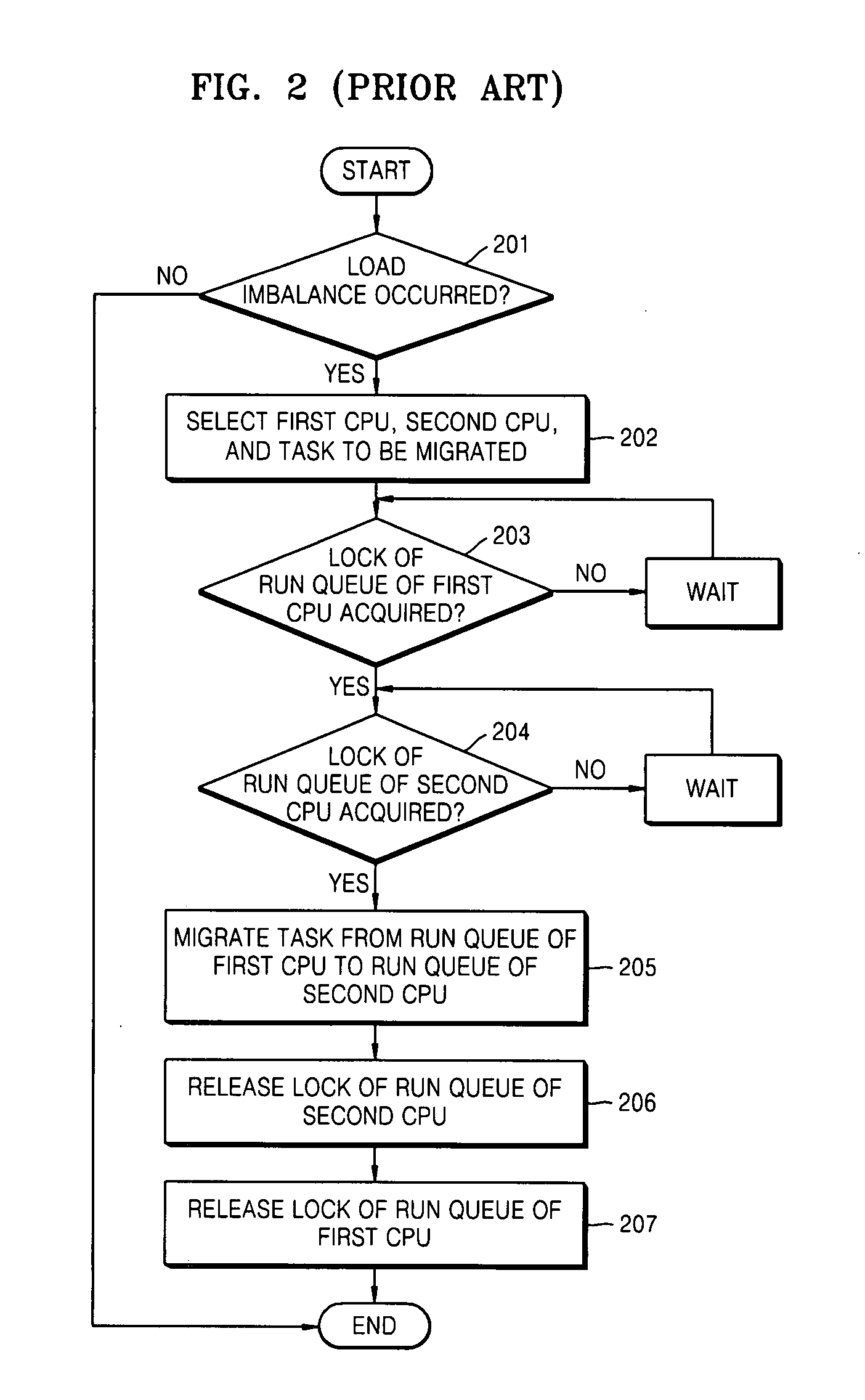
Load balancing method and apparatus in symmetric multi-processor system
InactiveUS20090019449A1Prevents delay in response timeLong waiting timeResource allocationMemory systemsSymmetric matrixSymmetric multiprocessing
Provided are a load balancing method and a load balancing apparatus in a symmetric multi-processor system. The load balancing method includes selecting at least two processors based on a load between a plurality of processors, from among the plurality of processors, migrating a predetermined task stored in a run queue of a first processor to a migration queue of a second processor, and migrating the predetermined task stored in the migration queue of the second processor to a run queue of the second processor. Accordingly, a run queue of a processor is not blocked while migrating a task, an immediate response of the run queue is possible, and a waiting time of a scheduler is reduced. Consequently, the scheduler can speedily perform context switching, and thus performance of the entire operating system is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for performing asynchronous writes to database logs using multiple insertion points
InactiveUS6131094AImprove write throughputData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalMulti processorTransaction log
A method in a symmetric multi-processor computer system for increasing database transaction log performance by pipelining transaction log buffers. The method includes the steps of inserting a log record into a log buffer stored in a volatile memory of the computer system. Next, the log buffer is queued for eventual delivery to a persistent storage device. Then the log buffer is dequeued from the queue set in the previous step. Following this, a transfer of the contents of the log buffer to the persistent storage device is initiated. A wait is imposed on the process for the completion of the transfer of the contents of the log buffer to the persistent storage device in order to guarantee that the contents are safely stored in the persistent storage device in the original serial order as received.
Owner:UNISYS CORP
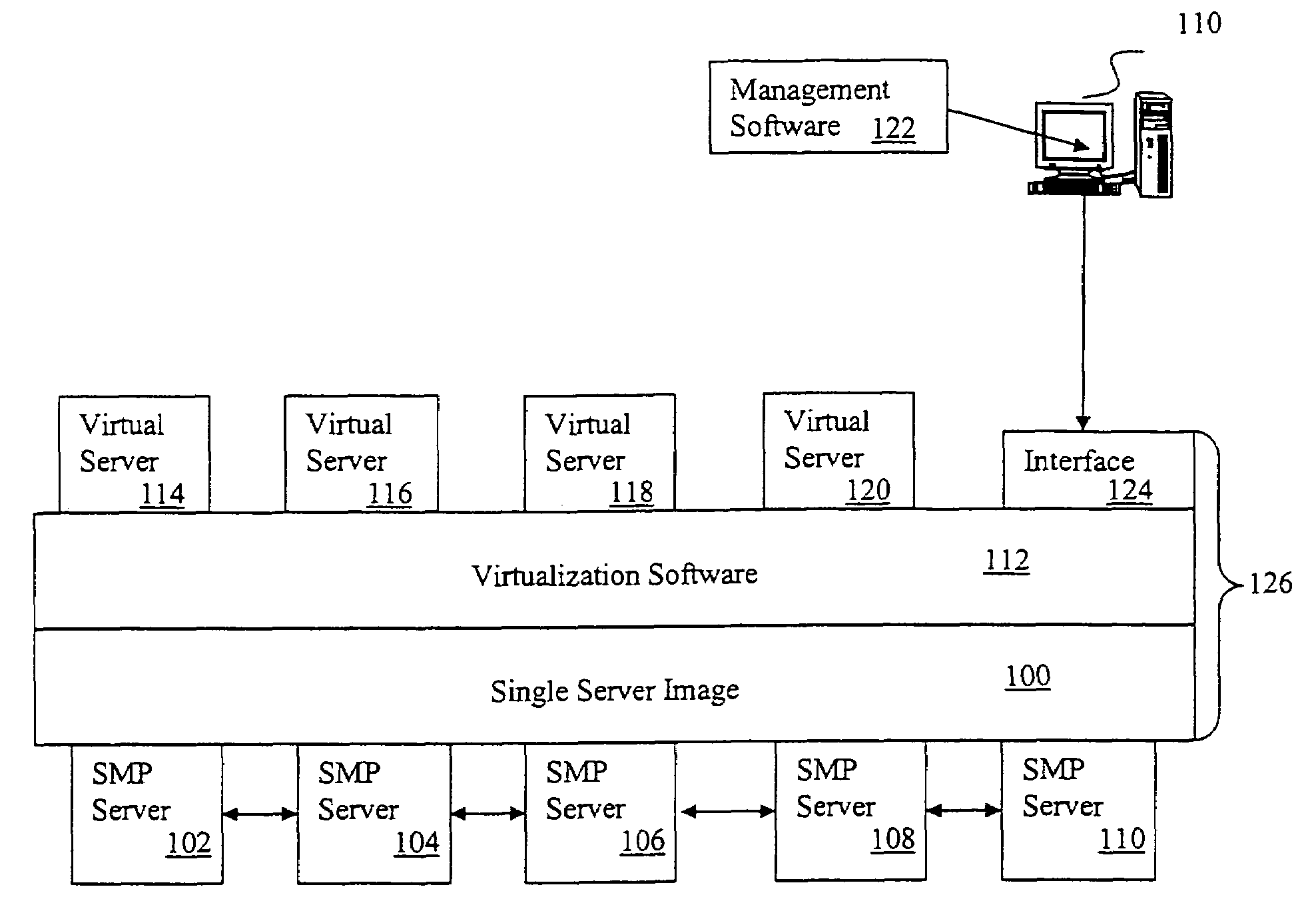
Virtualization and server imaging system for allocation of computer hardware and software
ActiveUS7533385B1Improve resource utilizationMultiprogramming arrangementsTransmissionVirtualizationResource utilization
A system for improving resource utilization across a cluster of interconnected symmetric multiprocessor (“SMP”) servers is provided. The system includes single system image (“SSI”) software that represents the cluster of SMP servers as a single virtual SMP server and virtualization software that partitions the virtual SMP server into virtual servers. The system may also include virtual infrastructure management software that is used to partition the virtual SMP server into the virtual servers. A method for using SMP servers is further provided. The method includes representing the SMP servers as a virtual SMP server and partitioning the virtual SMP server into virtual servers. The method may also include allocating and reallocating processes across the physical SMP servers.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
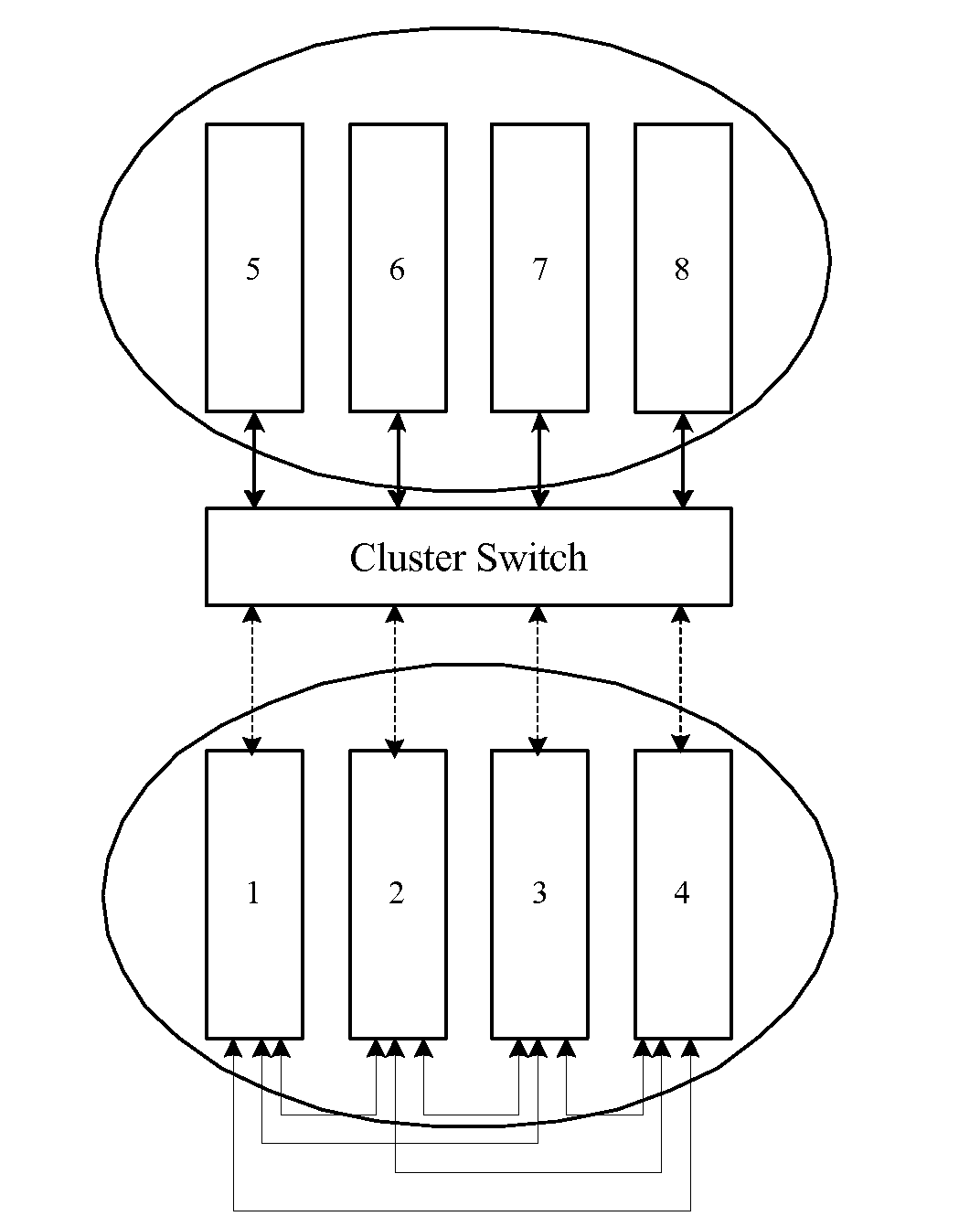
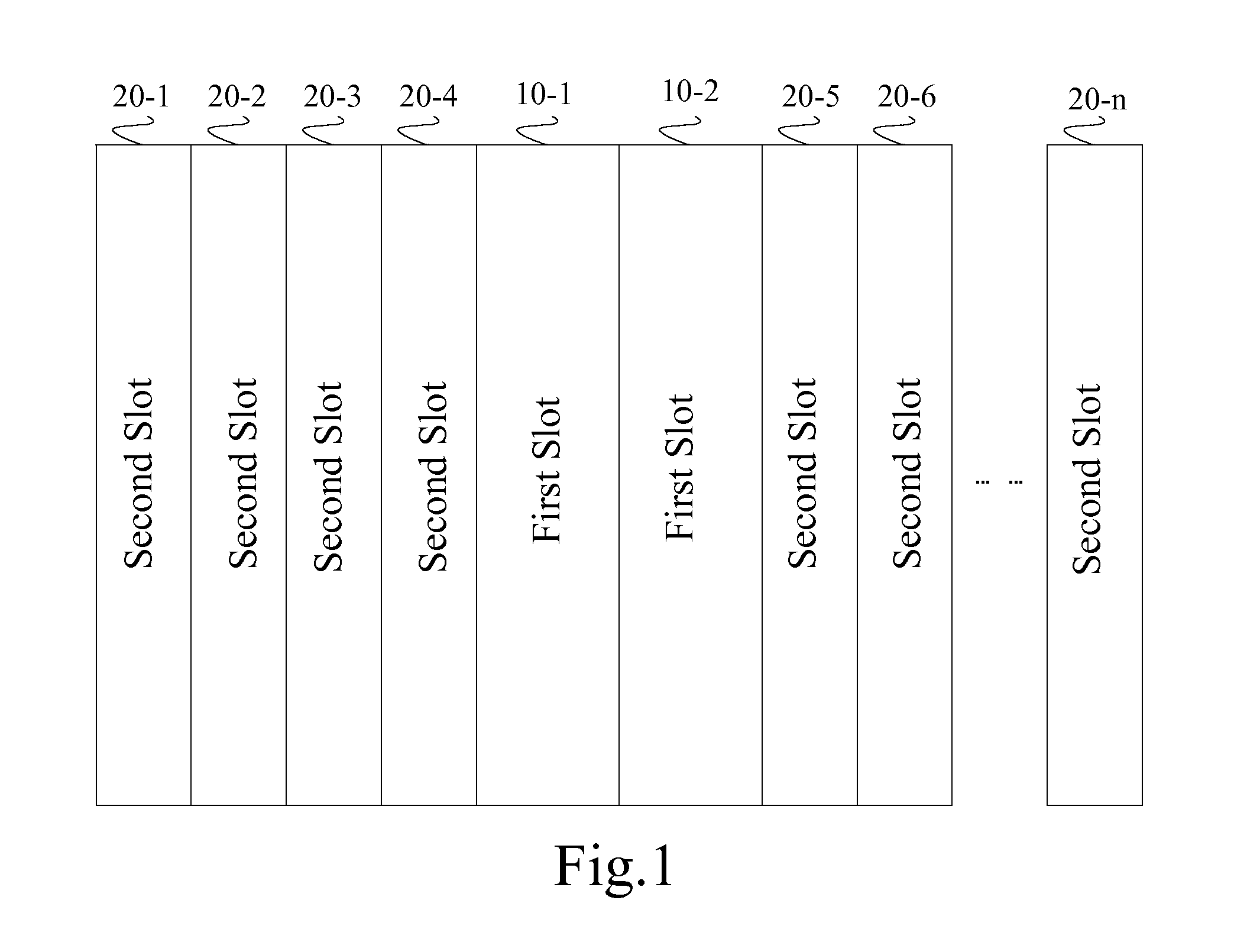
Server
ActiveUS20080250181A1Minimizing user costImprove scalabilityDigital data processing detailsComponent plug-in assemblagesComputer scienceSymmetric multiprocessing
The present invention relates to the field of communications, in particular, to a server for solving the problem related to the incompatibility between normal blades and multi-processing blades in a conventional server. The server according to an embodiment of the invention includes a backboard, on which backboard wiring and a first slot are disposed. At least two second slots are further disposed on the backboard. Both a first interface configured to be connected to a normal blade and a second interface configured to be connected to a multi-processing blade are disposed on each of the second slots, the first interface being connected to a corresponding Cluster Switch interface disposed on the first slot via the backboard wiring, and the second interface being interconnected directly via the backboard wiring or being connected to a corresponding Symmetrical Multi-Processing Switch interface disposed on the first slot via the backboard wiring.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Instruction set reconciliation for heterogeneous symmetric-multiprocessor systems
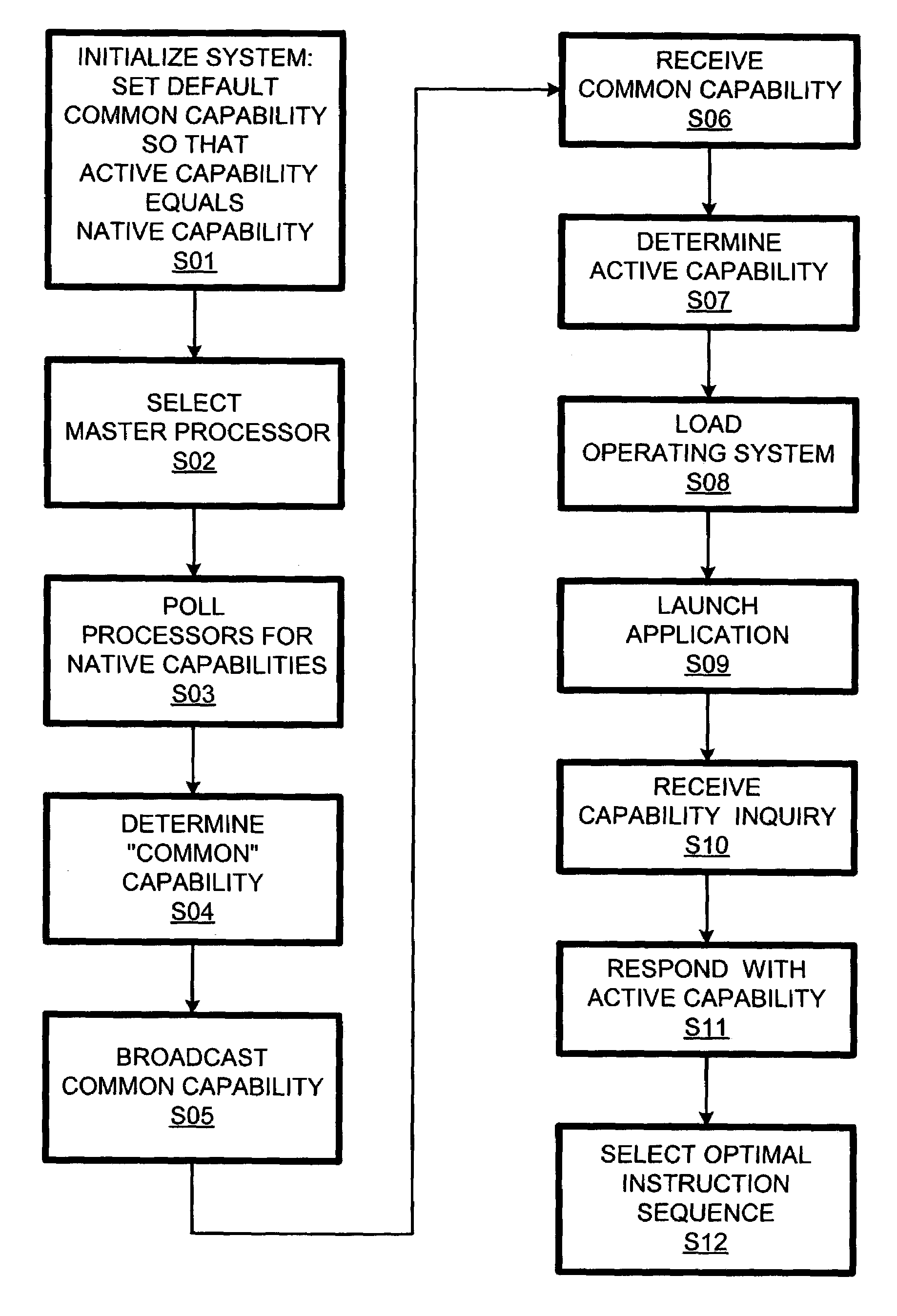
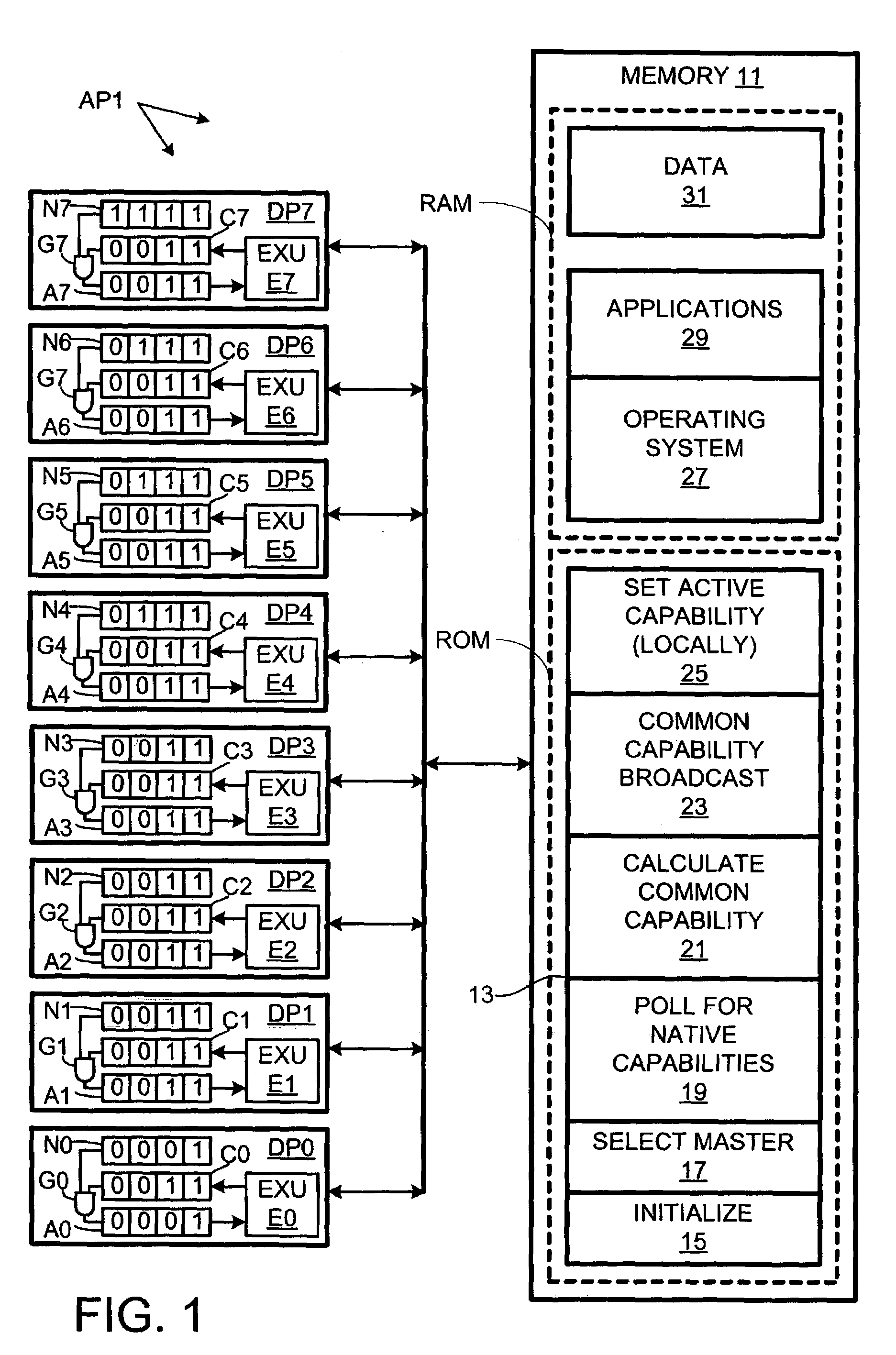
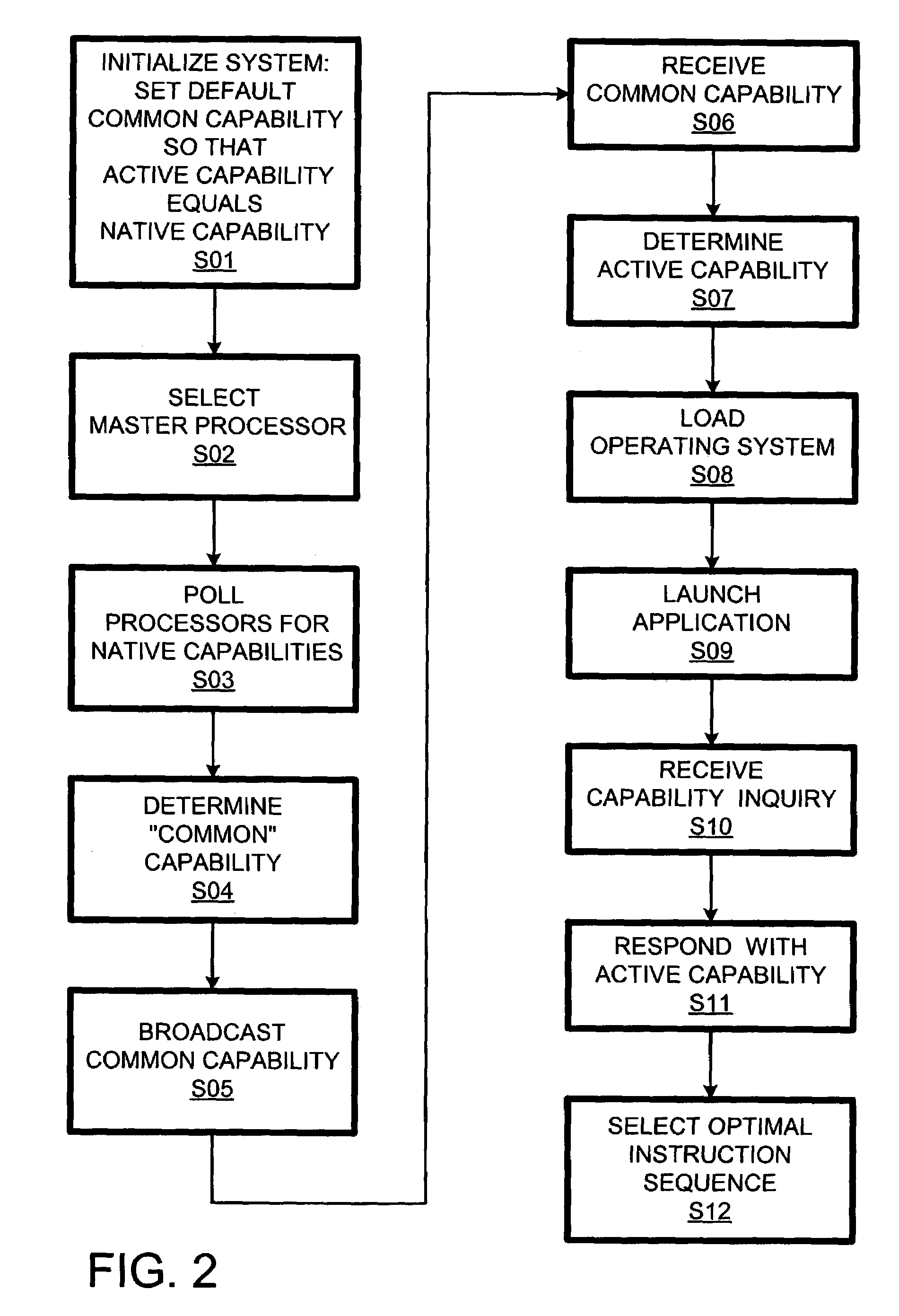
ActiveUS7080242B2Improve performanceResource allocationDigital computer detailsMulti processorSymmetric multiprocessor system
In a symmetric multiprocessing system using processors (DP0–DP7) of different capabilities (instruction sets), a processor responds (S11) to a query regarding its capabilities (instruction set) with its “active” capability, which is the intersection of its native capability and a common capability across processors determined (S04) during a boot sequence (13). The querying application (29) can select (S12) a program variant optimized for the active capability of the selected processor. If the application is subsequently subjected to a blind transfer to another processor, it is more likely than it would otherwise be (if the processors responded with their native capabilities) that the previously selected program variant runs without encountering unimplemented instructions.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
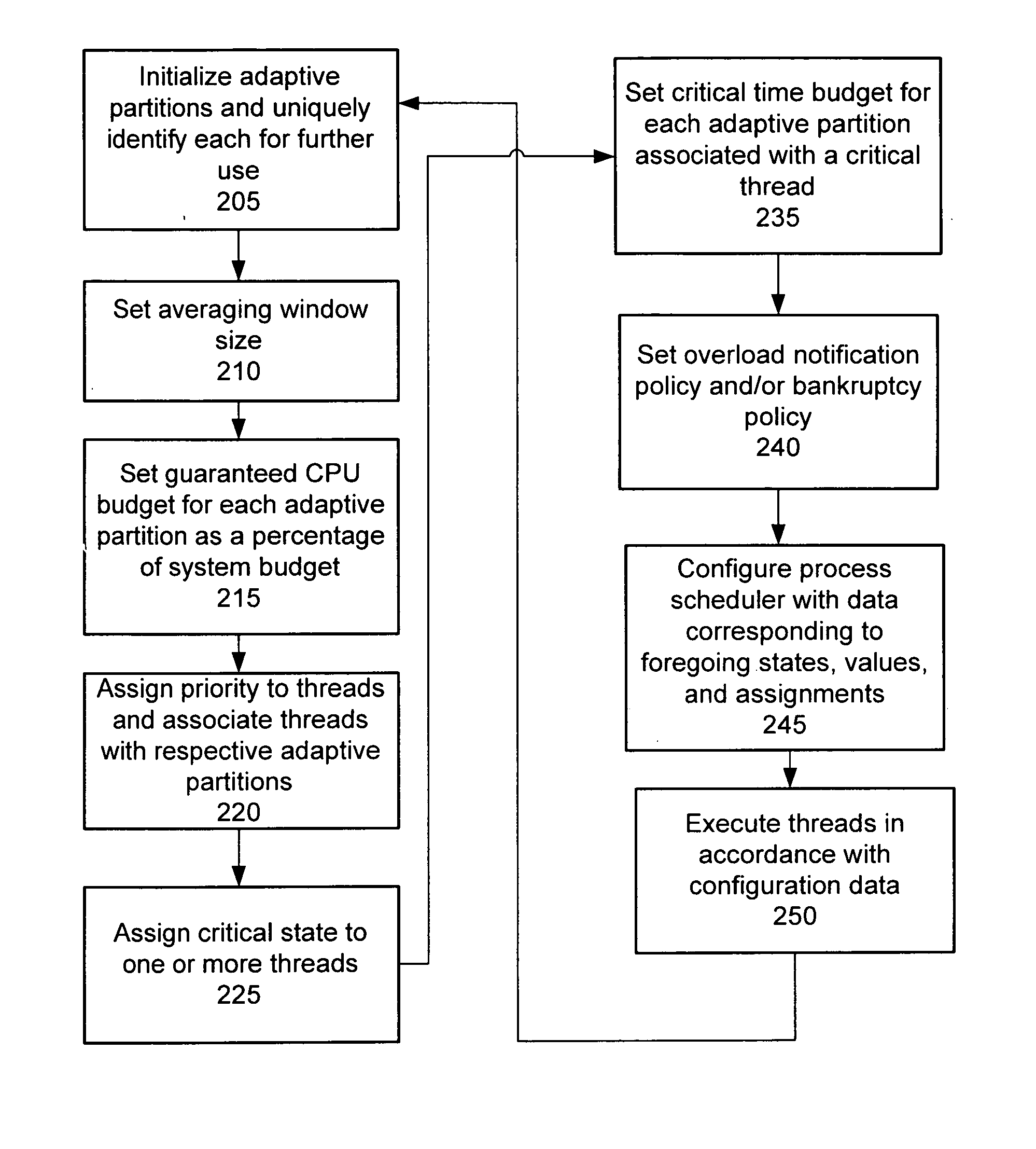
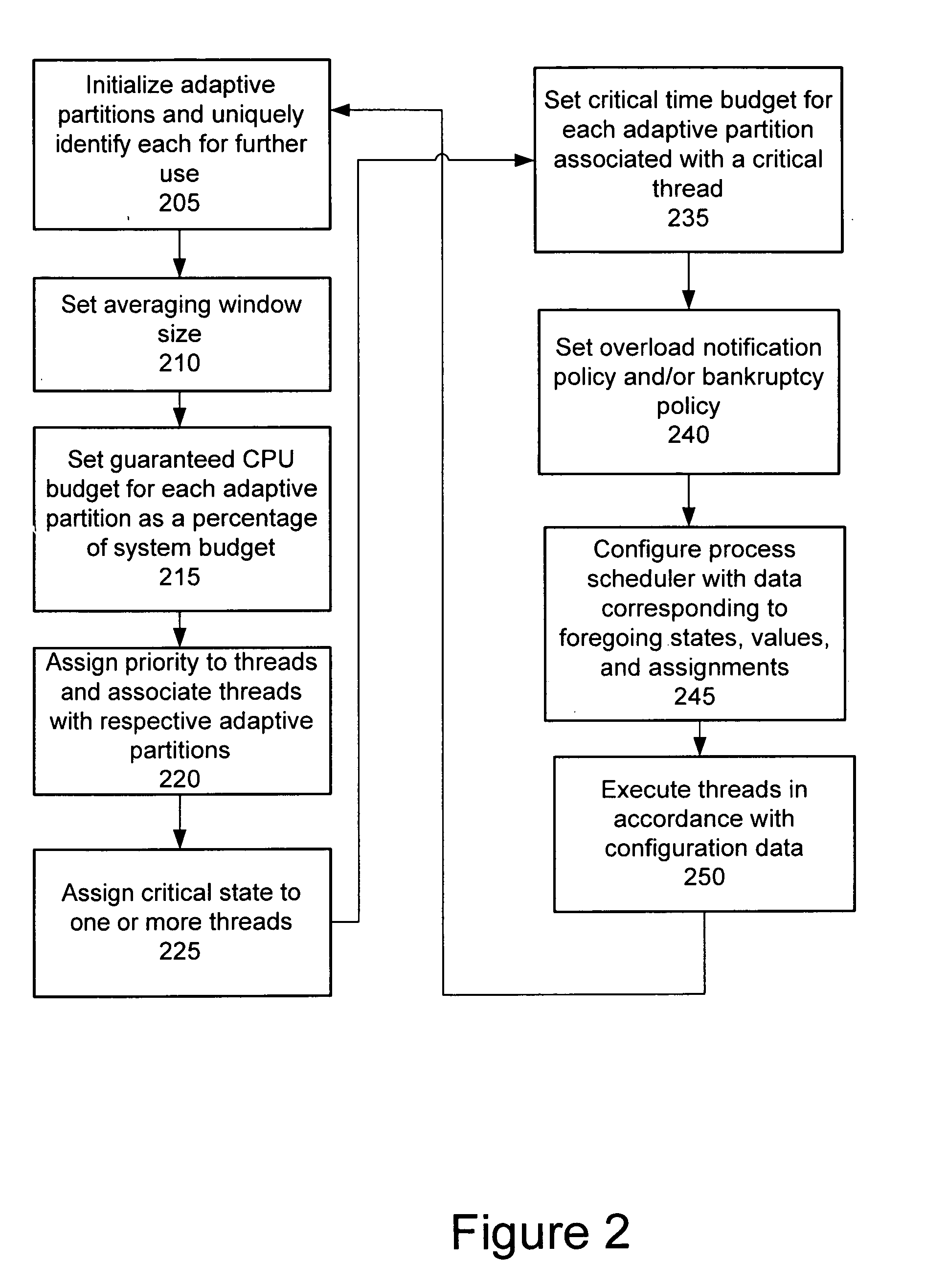
Process scheduler employing adaptive partitioning of process threads
ActiveUS20070226739A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsParallel computingSymmetric multiprocessing
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
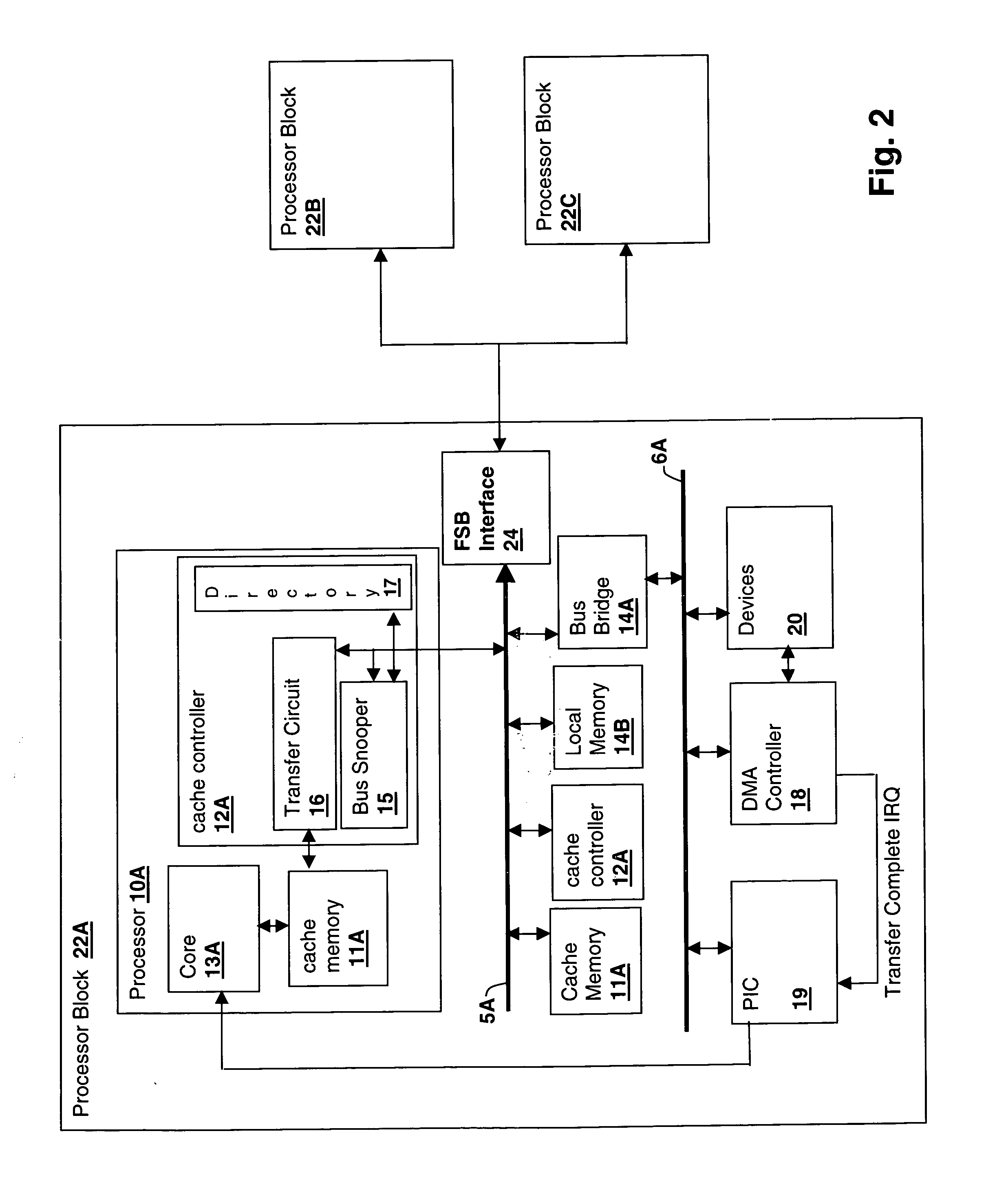
Embedded symmetric multiprocessor system with arbitration control of access to shared resources
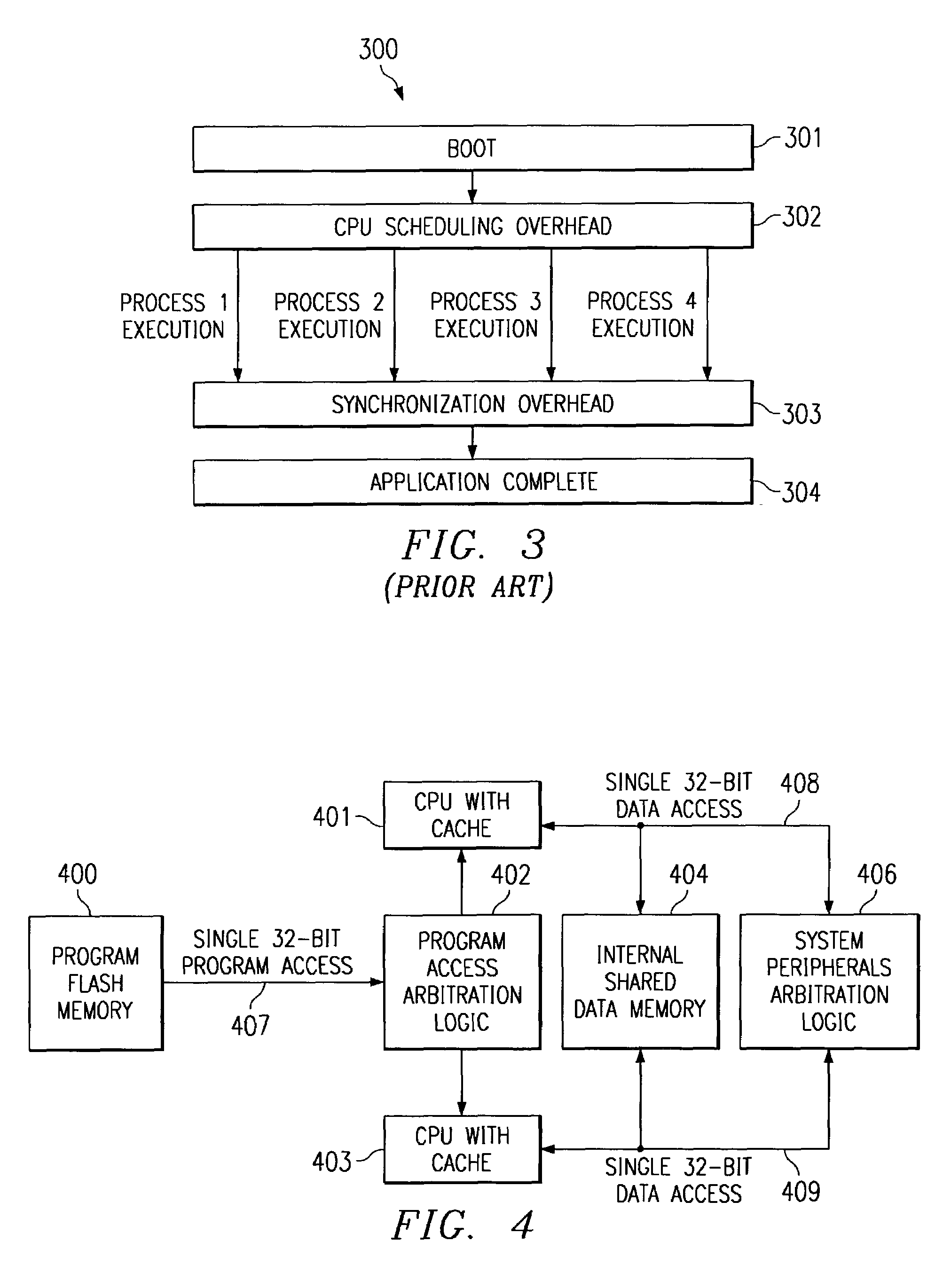
InactiveUS7237071B2Low costImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory bankSingle chip
A single chip, embedded symmetric multiprocessor (ESMP) having parallel multiprocessing architecture composed of identical processors includes a single program memory. Program access arbitration logic supplies an instruction to a single requesting central processing unit at a time. Shared memory access arbitration logic can supply data from separate simultaneously accessible memory banks or arbitrate among central processing units for access. The system may simulate an atomic read / modify / write instruction by prohibiting access to the one address by another central processing unit for a predetermined number of memory cycles following a read access to one of a predetermined set of addresses in said shared memory.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Method and system for managing cache injection in a multiprocessor system
A method and apparatus for managing cache injection in a multiprocessor system reduces processing time associated with direct memory access transfers in a symmetrical multiprocessor (SMP) or a non-uniform memory access (NUMA) multiprocessor environment. The method and apparatus either detect the target processor for DMA completion or direct processing of DMA completion to a particular processor, thereby enabling cache injection to a cache that is coupled with processor that executes the DMA completion routine processing the data injected into the cache. The target processor may be identified by determining the processor handling the interrupt that occurs on completion of the DMA transfer. Alternatively or in conjunction with target processor identification, an interrupt handler may queue a deferred procedure call to the target processor to process the transferred data. In NUMA multiprocessor systems, the completing processor / target memory is chosen for accessibility of the target memory to the processor and associated cache.
Owner:IBM CORP
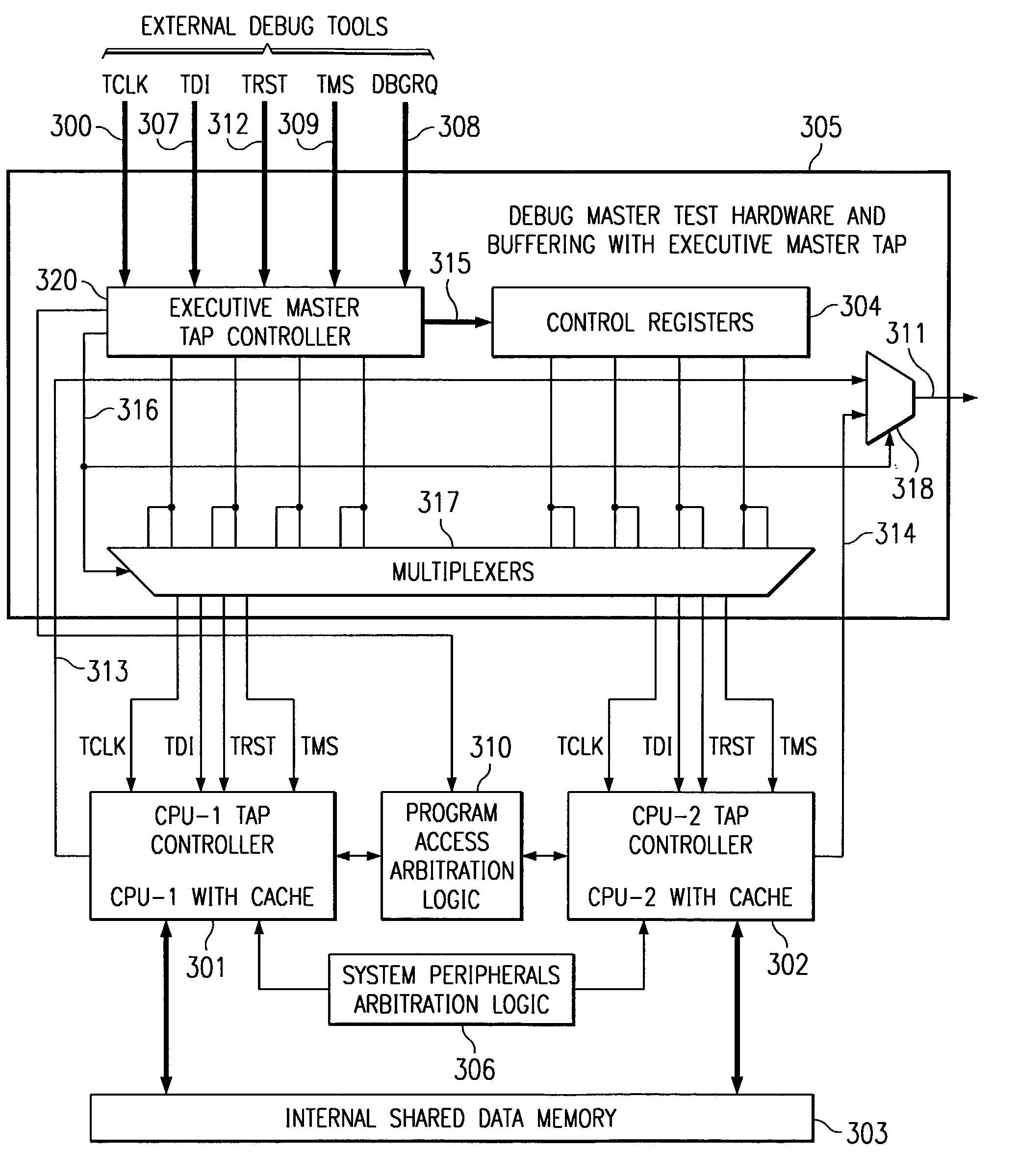
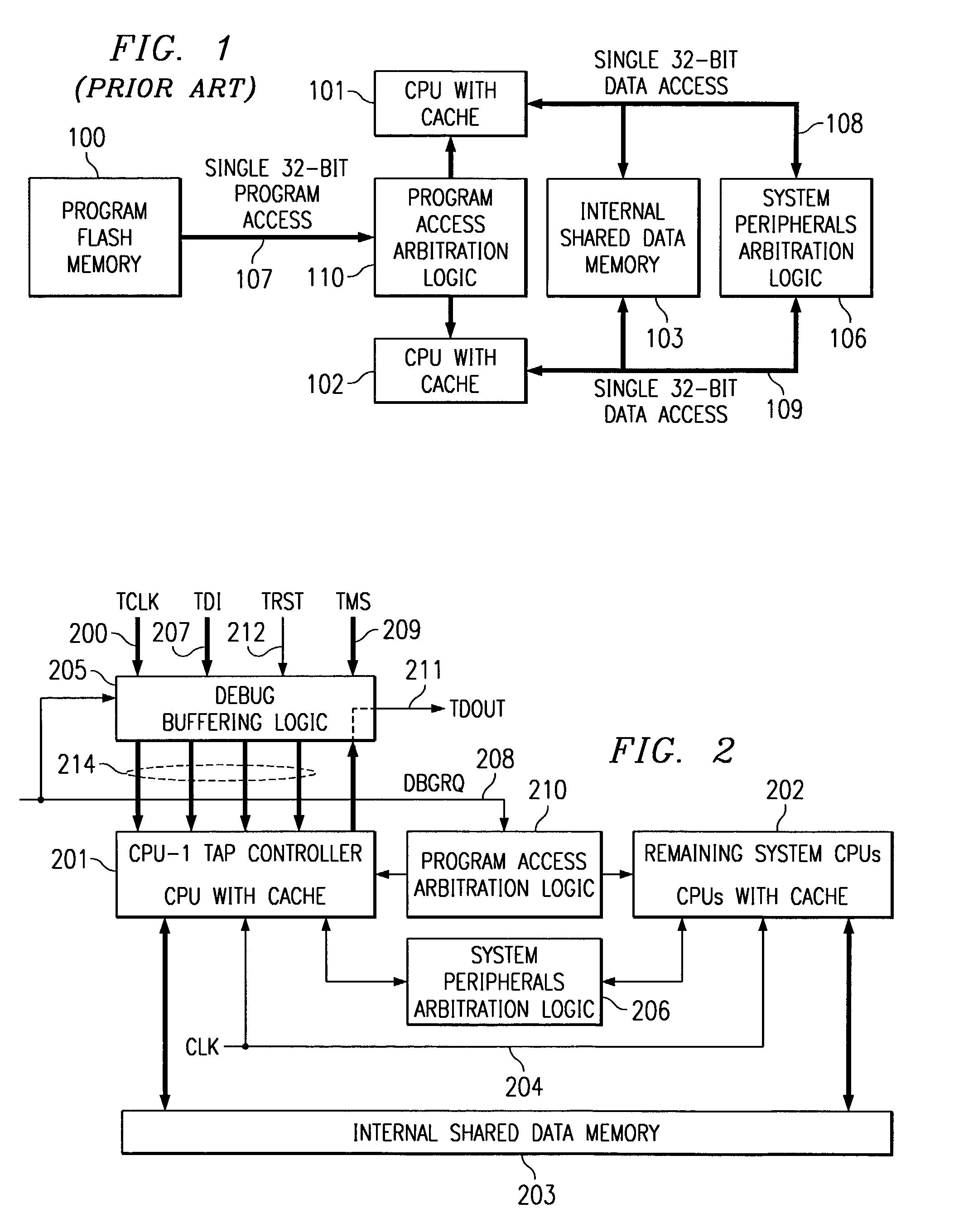
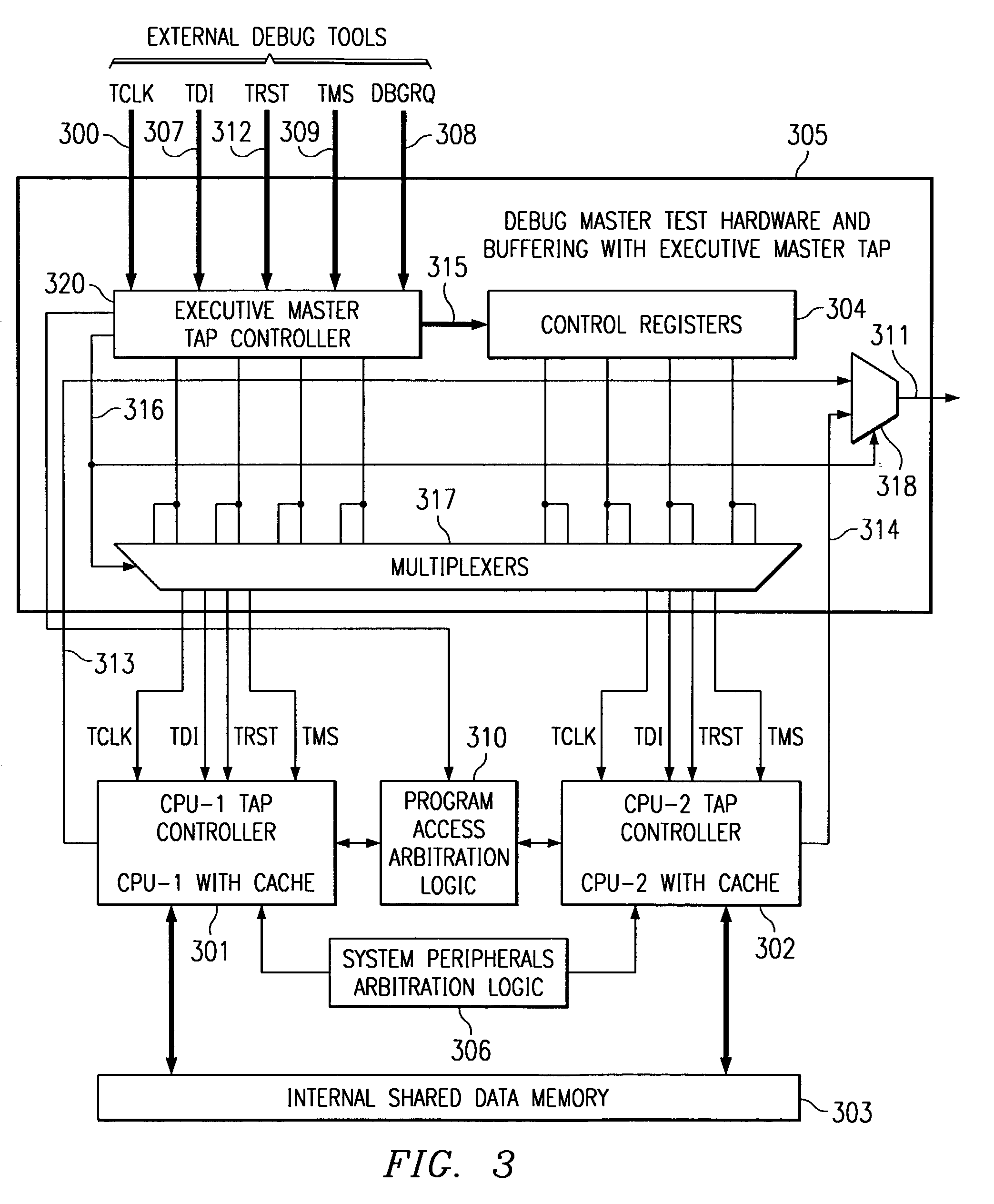
Embedded symmetric multiprocessor system debug
ActiveUS7010722B2Low advantageReduce development costsElectronic circuit testingFunctional testingMultiplexerNormal mode
A test signal multiplexer receives supplies external test signals to a selected debug master central processing unit in a symmetrical multiprocessor system and debug slave signals to debug slave central processing units. An executive master test access port controller responds to the external test signals and controls the test signal multiplexer. A control register loadable via the executive master test access port stores the debug slave signals. A test data output multiplexer connects the test data output line of the selected debug master central processor unit to an external test data output line. The external test signals includes a debug state signal supplied to each central processing unit. This selects either a normal mode or a debug mode at each central processor unit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
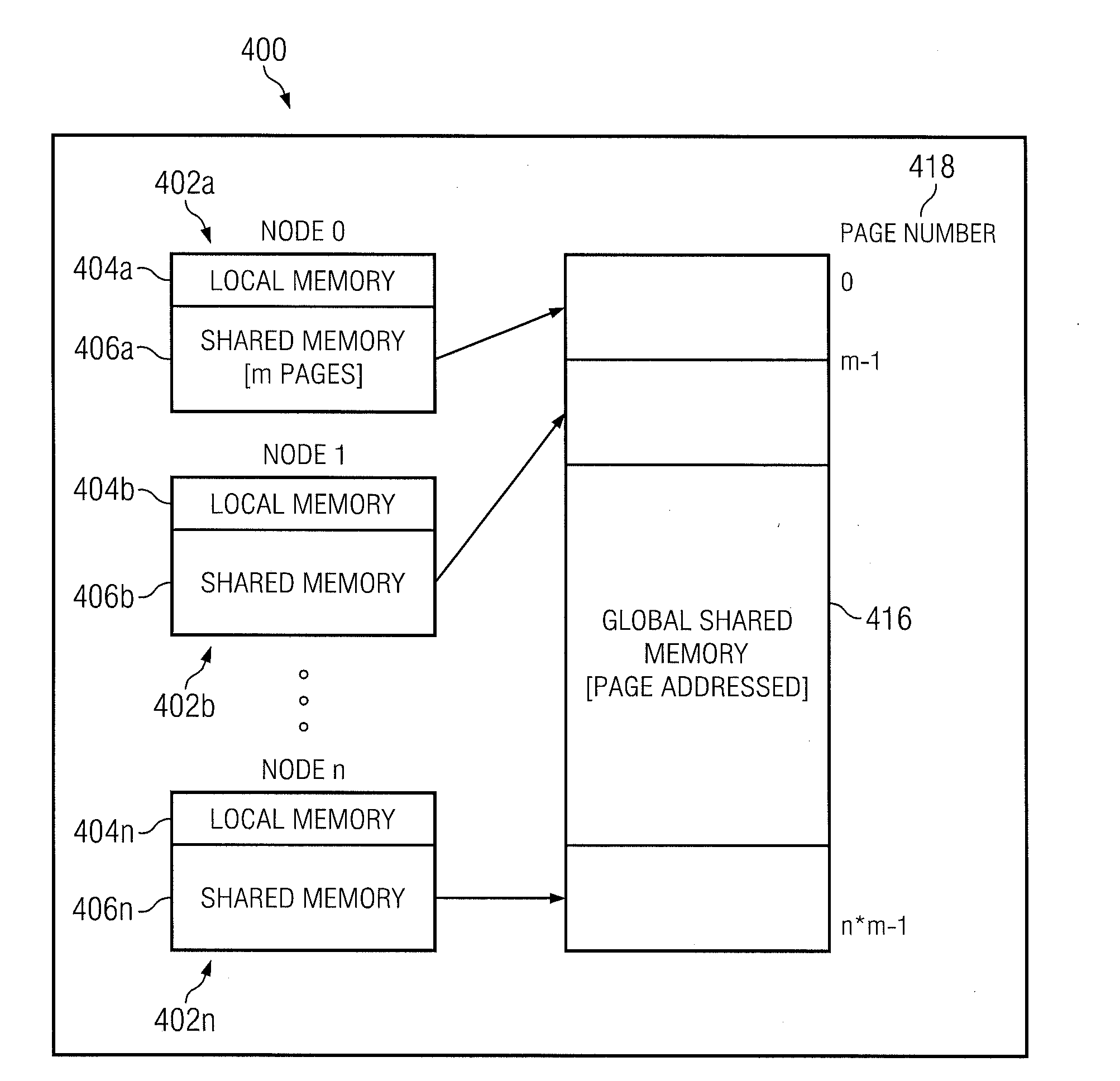
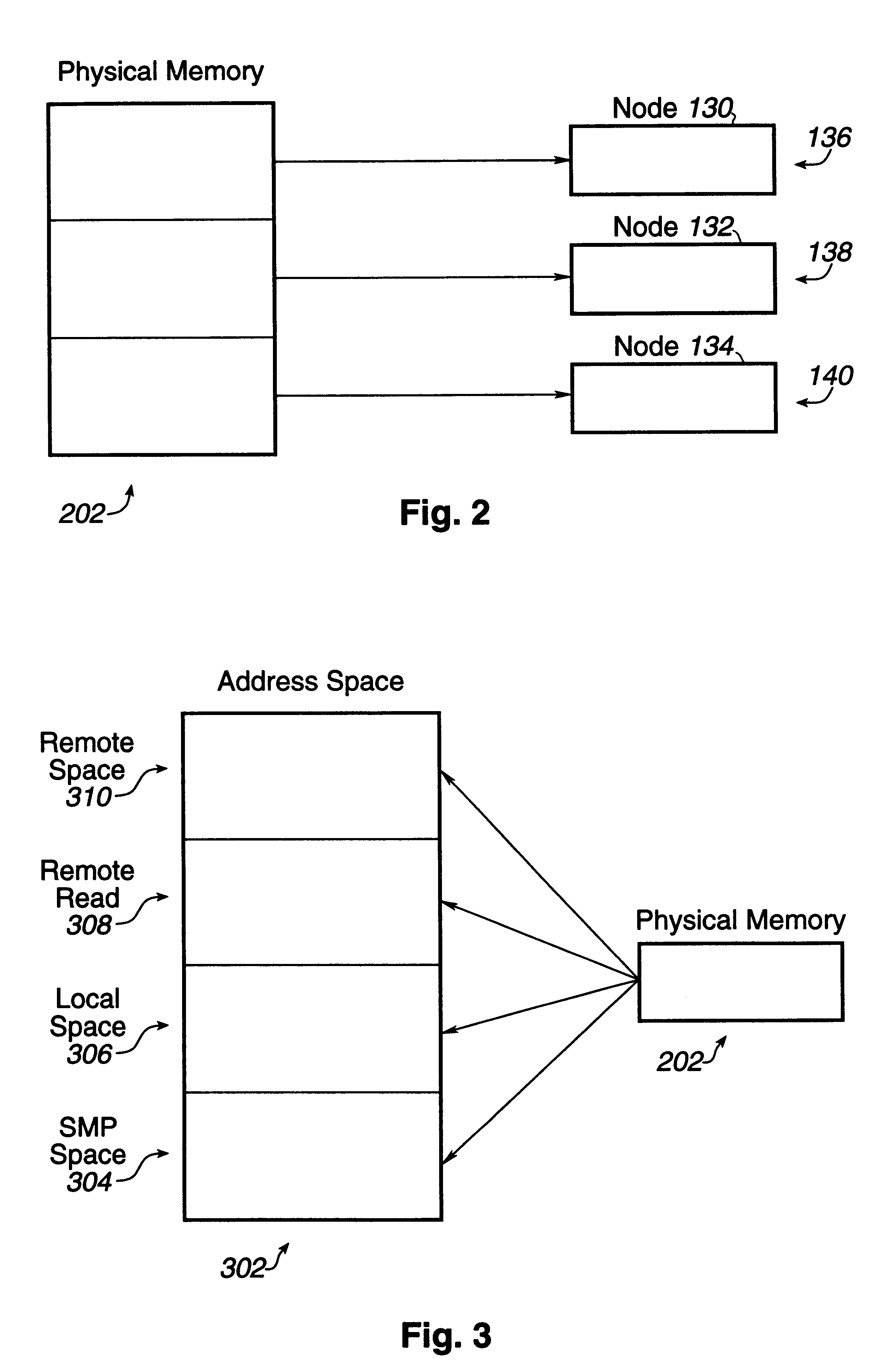
Shared memory system for symmetric multiprocessor systems
InactiveUS6226671B1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiple digital computer combinationsSymmetric multiprocessor systemSymmetric multiprocessing
A shared memory system for symmetric multiprocessing systems including a plurality of physical memory locations in which the locations are either allocated to one node of a plurality of processing nodes, equally distributed among the processing nodes, or unequally distributed among the processing nodes. The memory locations are configured to be accessed by the plurality of processing nodes by mapping all memory locations into a plurality of address partitions within a hierarchy bus. The memory locations are addressed by a plurality of address aliases within the bus while the properties of the address partitions are employed to control transaction access generated in the processing nodes to memory locations allocated locally and globally within the processing nodes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Symmetric multiprocessor operating system for execution on non-independent lightweight thread contexts
InactiveUS20070043935A2Lightweight in of areaLightweight in of powerDigital computer detailsEnergy efficient computingGeneral purposeUser Privilege
A multiprocessing system is disclosed. The system includes a multithreading microprocessor including a plurality of thread contexts (TCs), each having a program counter and a general purpose register set for executing a thread. The microprocessor also includes a shared privileged resource, shared by the plurality of TCs rather than being replicated for each of the plurality of TCs, and privileged to be managed only by operating system-privileged threads rather than by user-privileged threads. The system also includes a multiprocessor operating system (OS), configured to manage the shared privileged resource, and to schedule execution of both the operating system-privileged threads and the user-privileged threads on the plurality of TCs.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
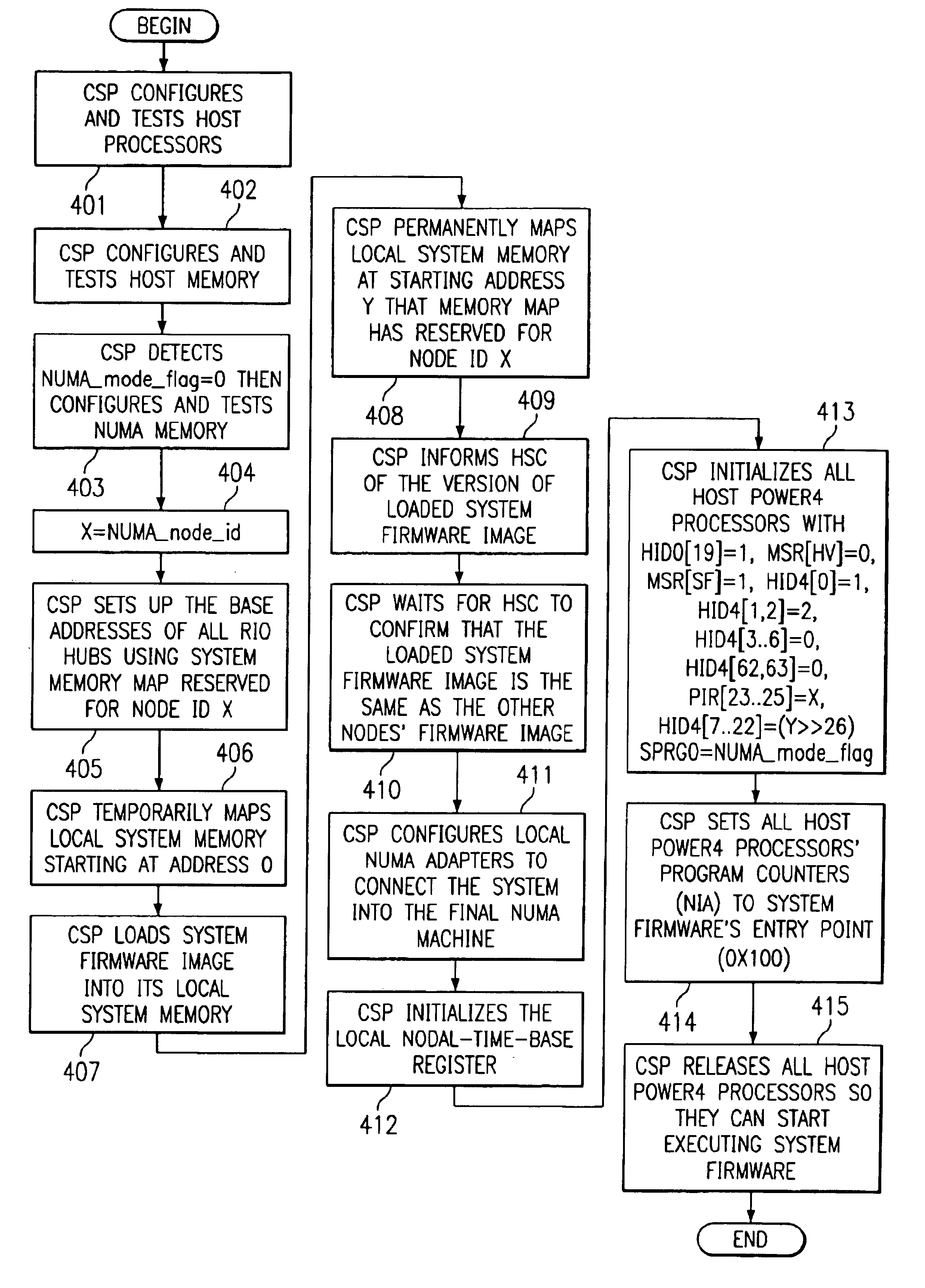
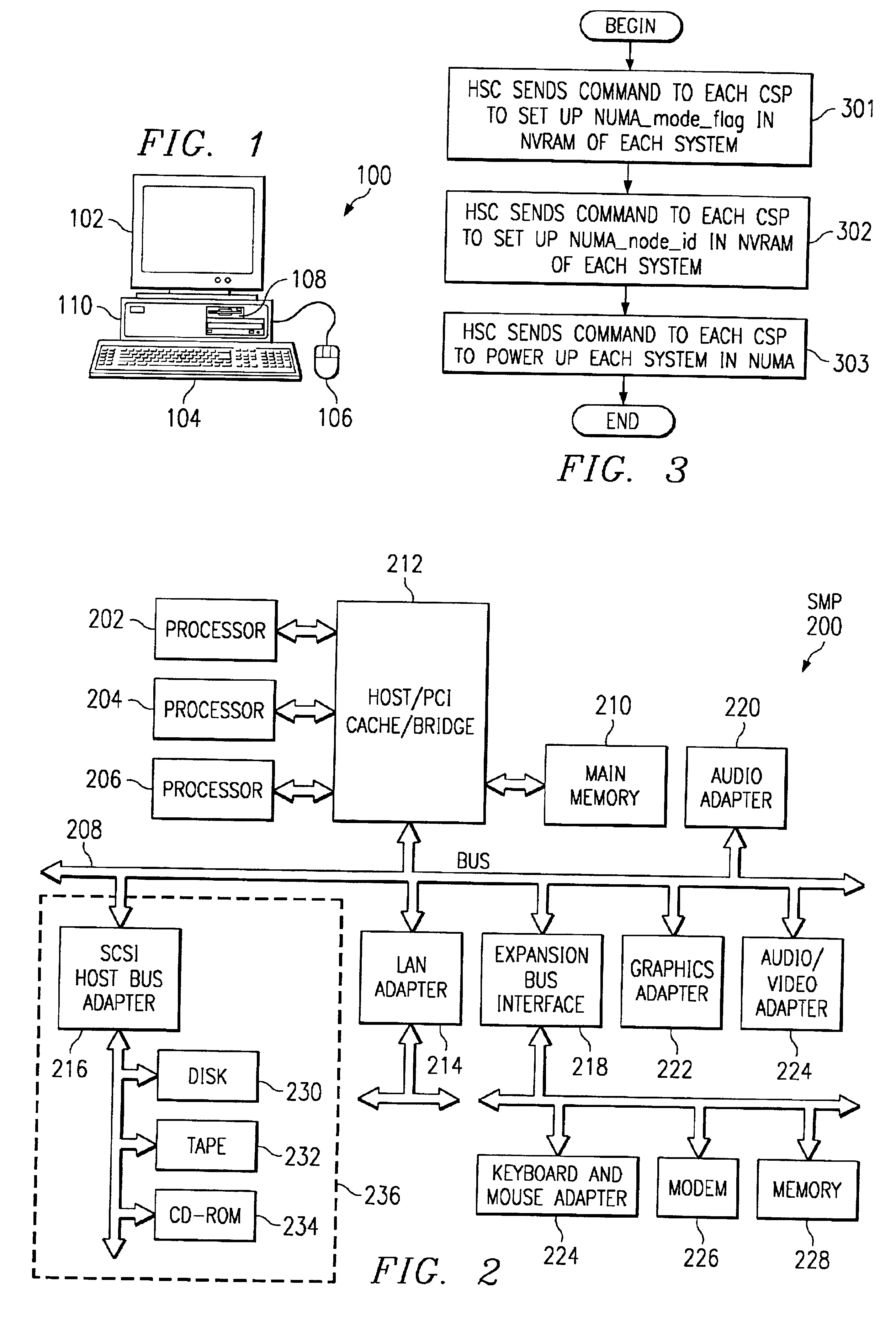
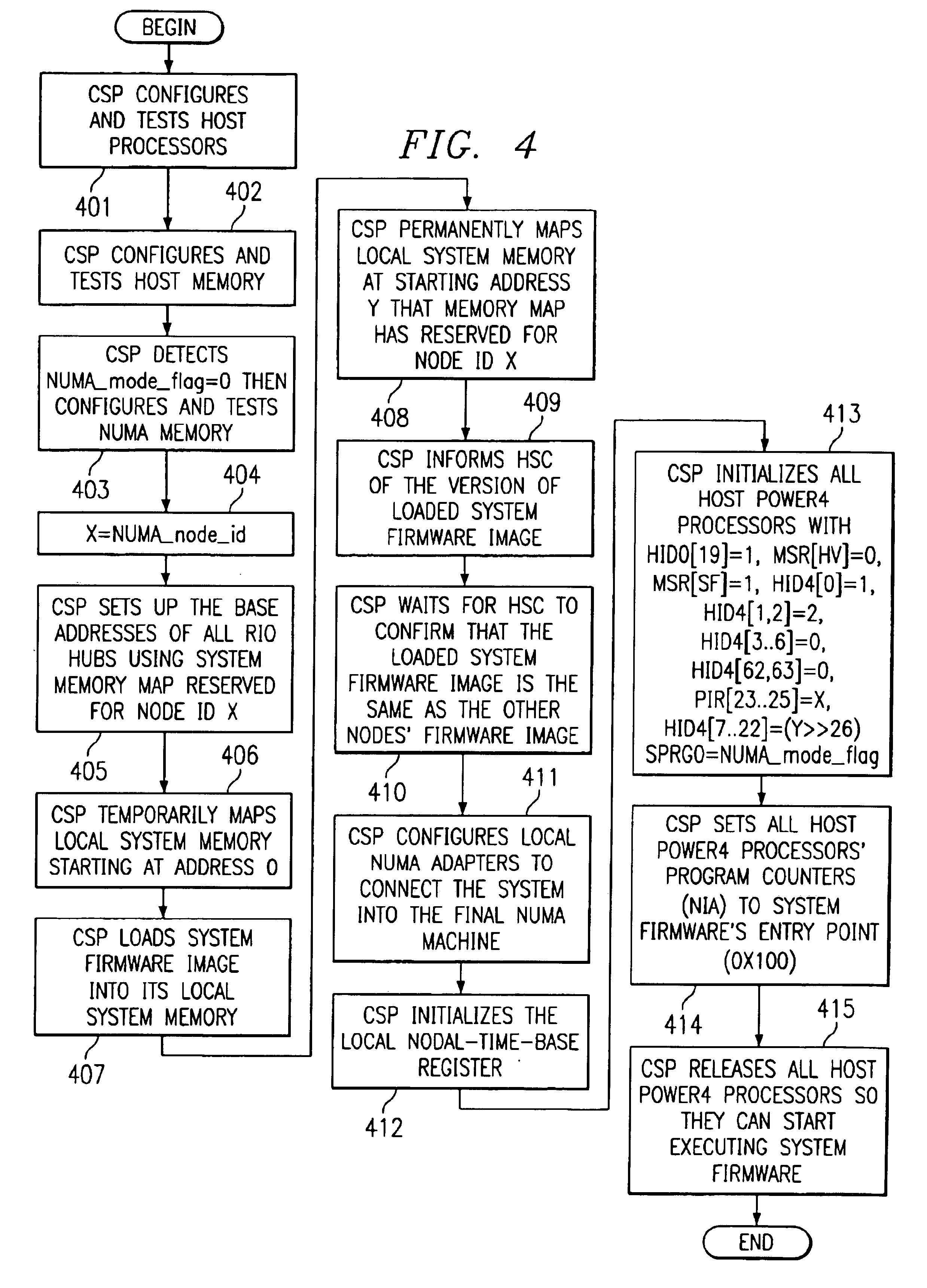
Method and apparatus to concurrently boot multiple processors in a non-uniform-memory-access machine
A method, apparatus and program for booting a non-uniform-memory-access (NUMA) machine are provided. The invention comprises configuring a plurality of standalone, symmetrical multiprocessing (SMP) systems to operate within a NUMA system. A master processor is selected within each SMP; the other processors in the SMP are designated as NUMA slave processors. A NUMA master processor is then chosen from the SMP master processors; the other SMP master processors are designated as NUMA slave processors. A unique NUMA ID is assigned to each SMP that will be part of the NUMA system. The SMPs are then booted in NUMA mode in one-pass with memory coherency established right at the beginning of the execution of the system firmware.
Owner:IBM CORP
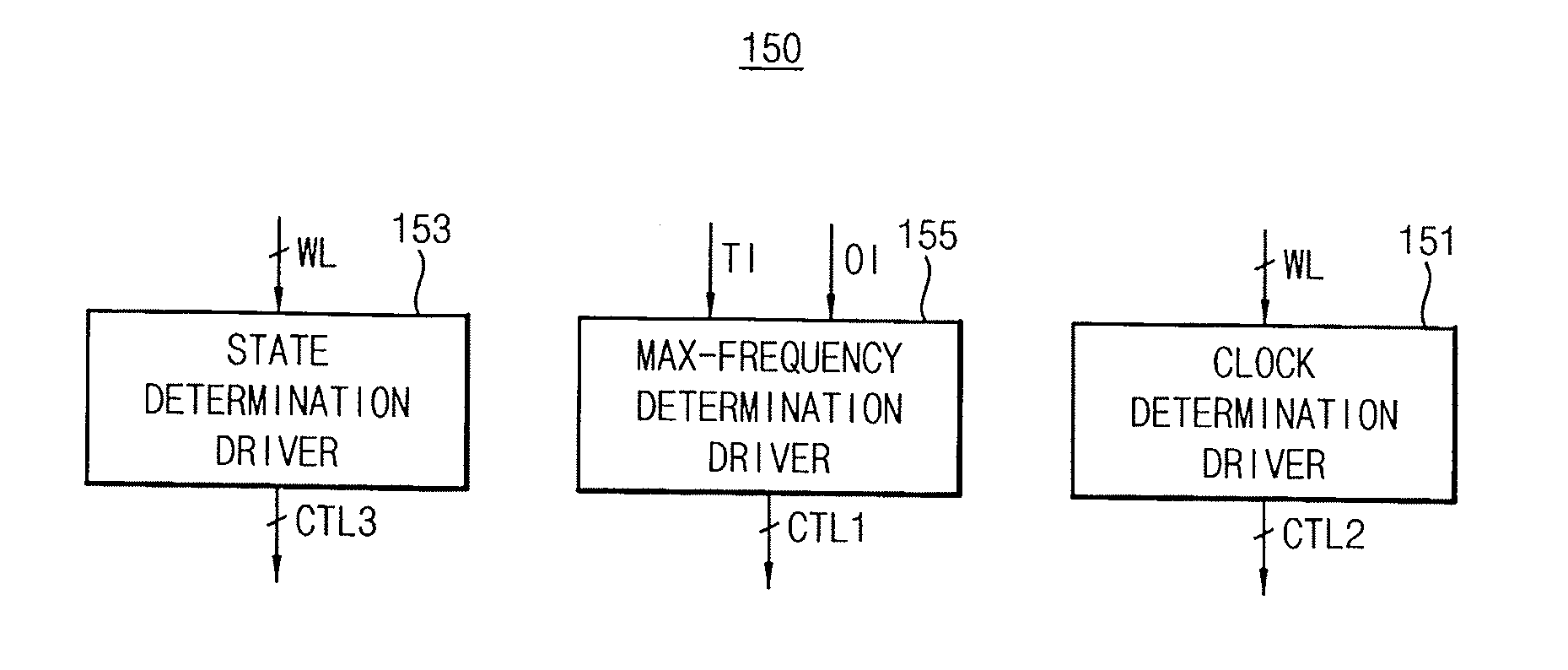
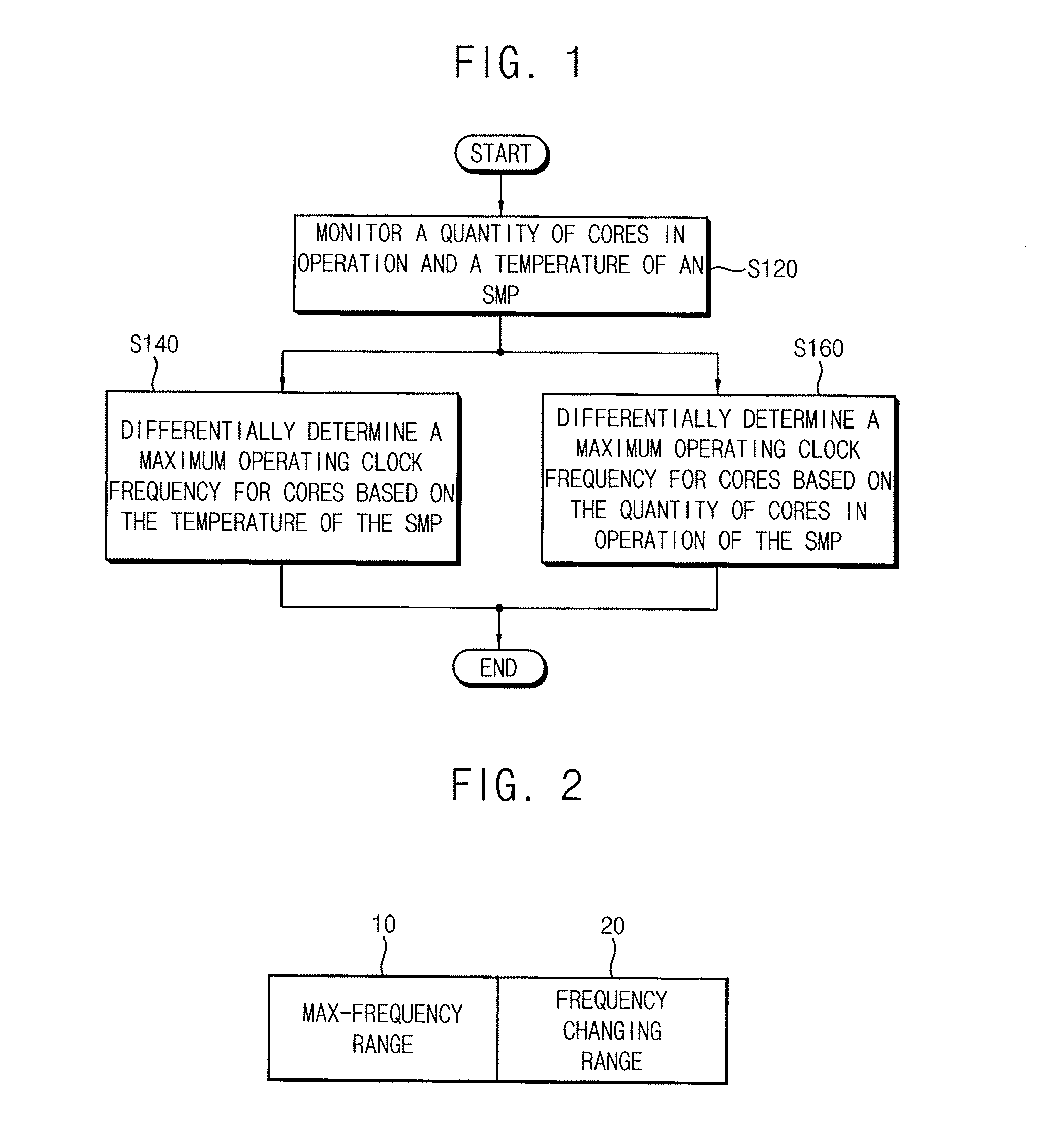
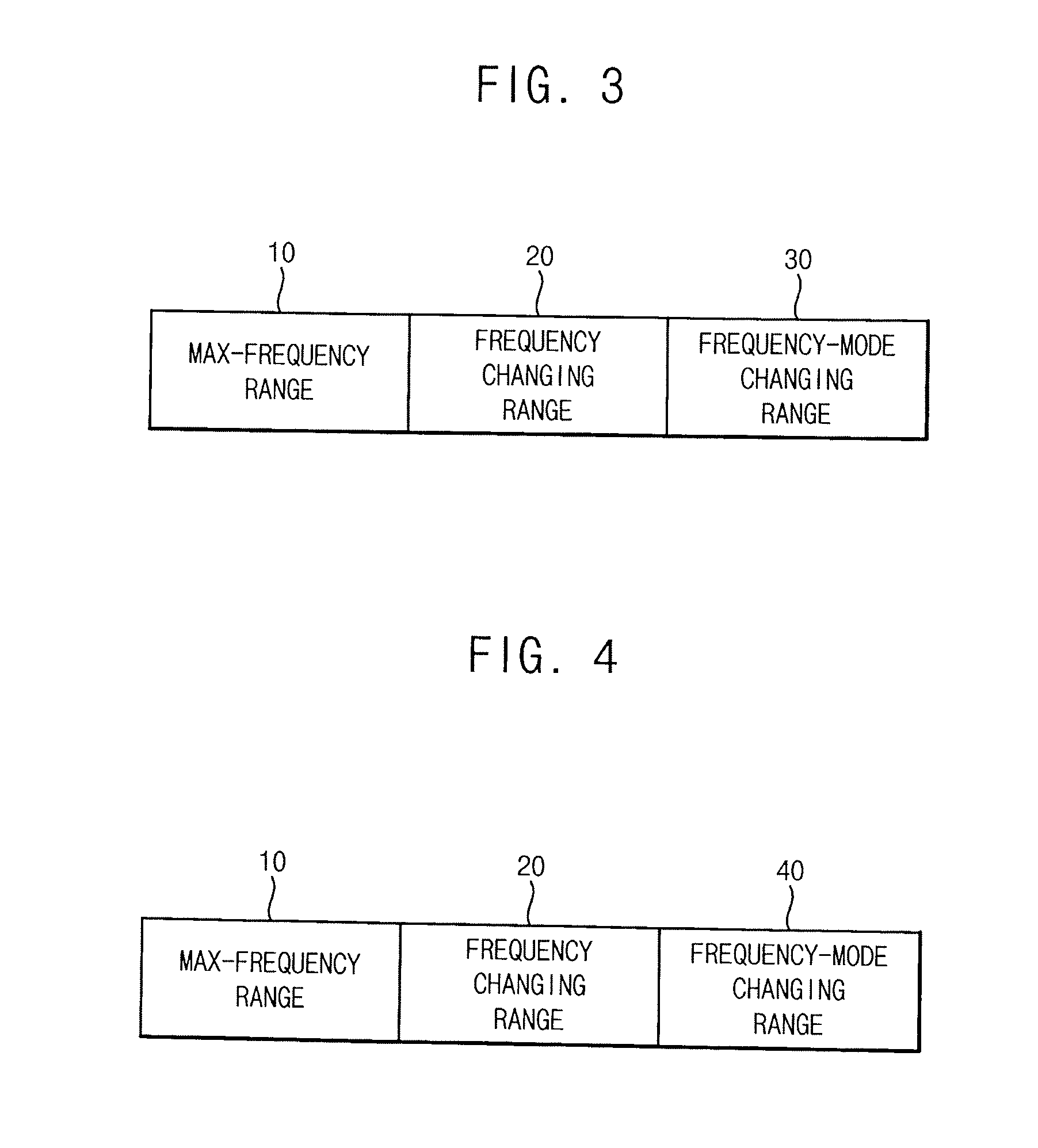
System-on-chip having a symmetric multi-processor and method of determining a maximum operating clock frequency for the same
ActiveUS20150134995A1Reduce heatReduce power consumptionVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringManagement unitMulti processor
A system-on-chip includes a symmetric multi-processor including a plurality of cores, each configured to operate in a high performance operating mode and a low performance operating mode. The system-on-chip further includes a clock management unit configured to provide an operating clock signal to the symmetric multi-processor, a state management unit configured to monitor operating states of the cores, a temperature management unit configured to monitor a temperature of the symmetric multi-processor, and a symmetric multi-processor control unit configured to determine the operating clock signal and the operating states of the cores based on a workload of the symmetric multi-processor. The symmetric multi-processor control unit is further configured to differentially determine a maximum operating clock frequency for the cores based on the temperature and the operating states of the cores, which indicate a quantity of cores that are currently in operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com