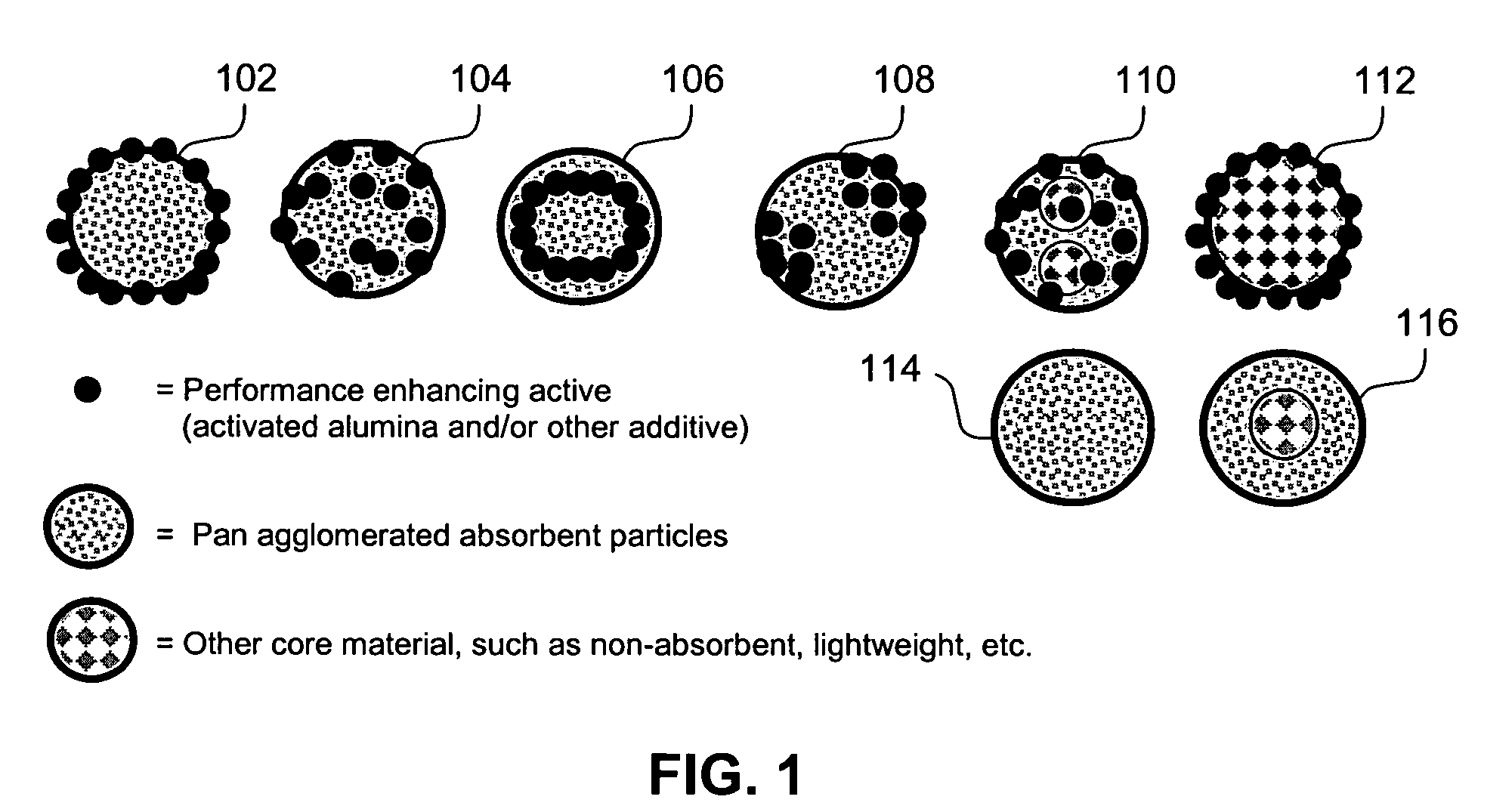
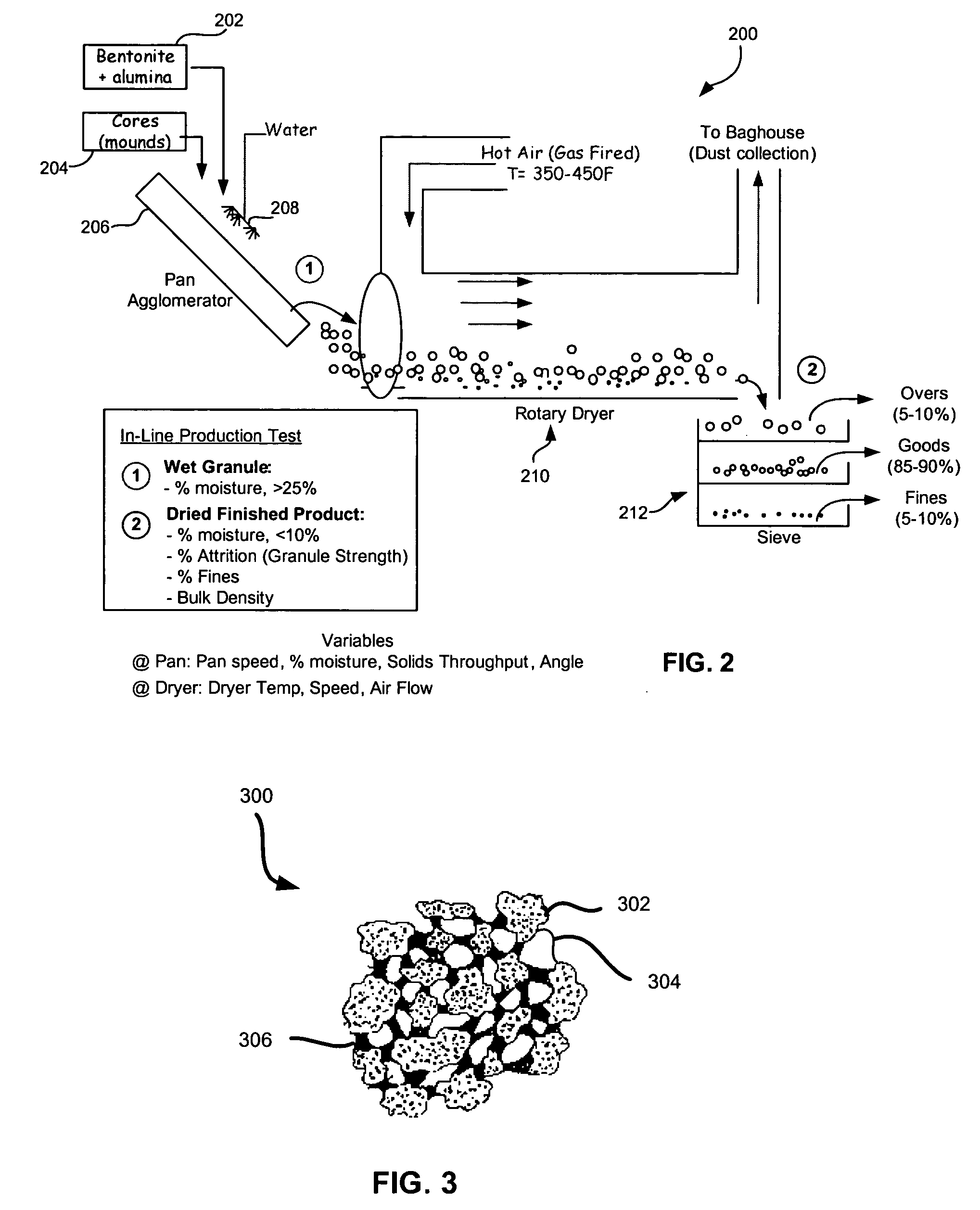
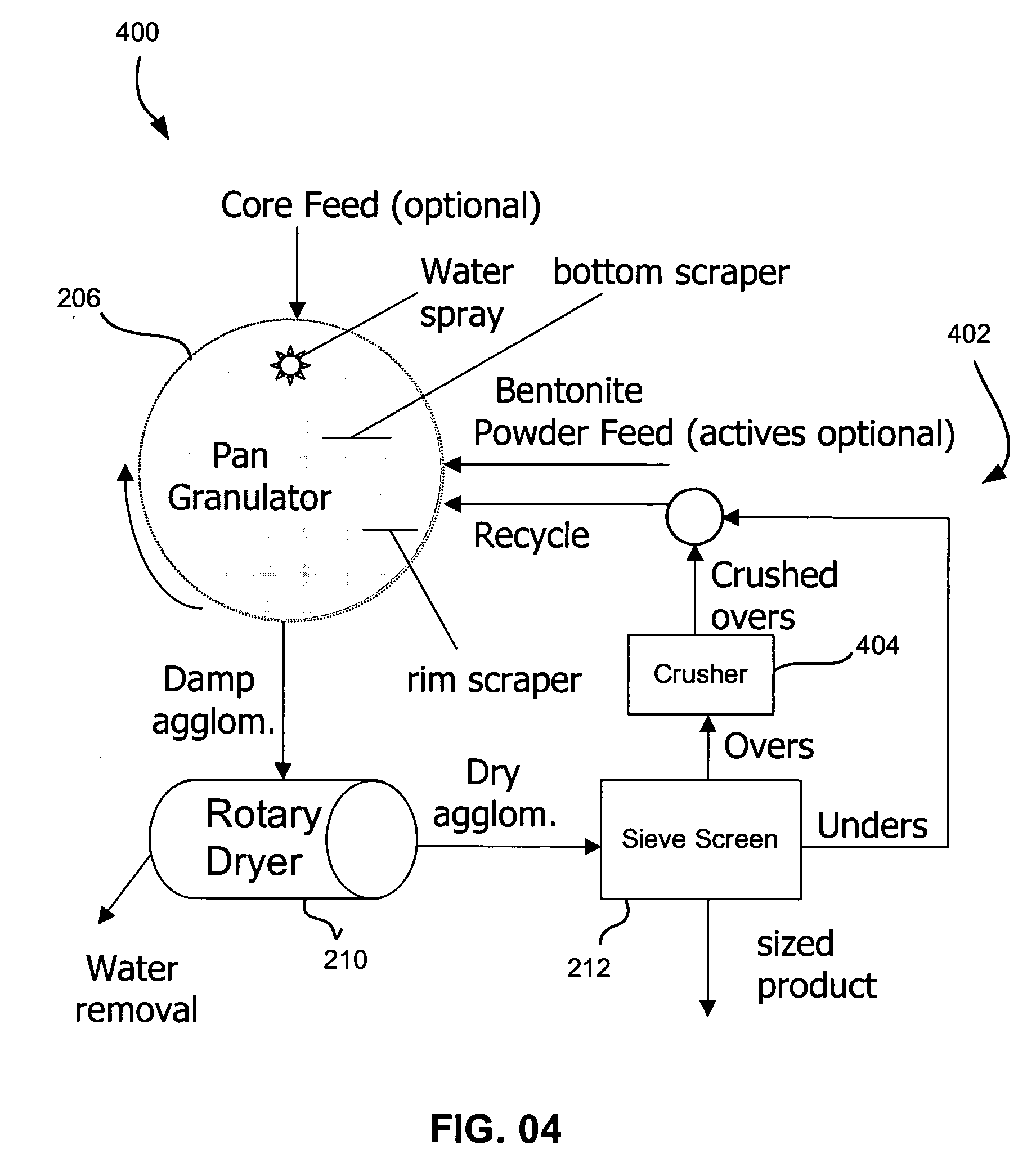
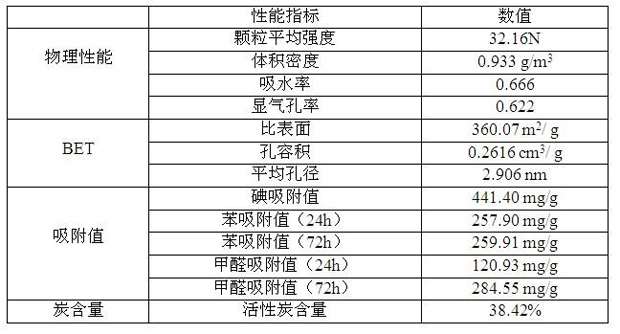
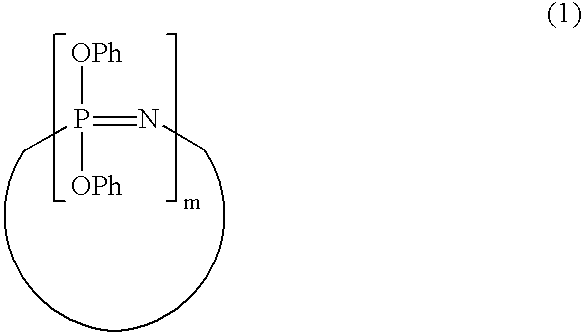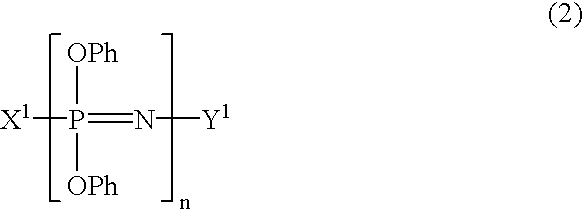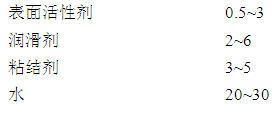Patents
Literature
972 results about "Activated alumina" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Activated alumina is manufactured from aluminium hydroxide by dehydroxylating it in a way that produces a highly porous material; this material can have a surface area significantly over 200 m²/g. The compound is used as a desiccant (to keep things dry by absorbing water from the air) and as a filter of fluoride, arsenic and selenium in drinking water. It is made of aluminium oxide (alumina; Al₂O₃). It has a very high surface-area-to-weight ratio, due to the many "tunnel like" pores that it has. Activated alumina in its phase composition can be represented only by metastable forms (gamma-Al₂O₃ etc.). Corundum (alpha-Al₂O₃), the only stable form of aluminum oxide, does not have such a chemically active surface and is not used as a sorbent.
Absorbent composition with improved odor control
InactiveUS20050175577A1Improved odor controlEasy to controlOther chemical processesAnimal housingLitterAbsorbent material
An absorbent composition with improved odor control and suitable for use as an animal litter, comprising an absorbent material, activated alumina, and optional additives.
Owner:THE CLOROX CO
Activated alumina and activated carbon compounded material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101890336AAchieve the perfect combinationEasy to useCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesActivated carbonAir purification
The invention provides an activated alumina and activated carbon compounded material and a preparation method thereof. According to a formula, the material comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 40 to 99 percent of aluminum hydroxide, 1 to 60 percent of activated carbon, and 15 to 35 percent of binder. The material is prepared by uniformly mixing, pelleting, ageing, molding, airing, sintering, rinsing, drying and the like. The invention aims to compound the activated carbon with the activated alumina; on the one hand, the material with a certain shape can be processed, the defects of loose shape, low strength, difficult recovery and the like of the activated carbon are overcome, and the material is easy to recycle; and on the other hand, the adsorption property of the activated alumina material is greatly improved. The method has the advantages of simpleness, practicality, readily available raw materials, low cost and suitability for industrial mass production, and can be widely applied to various fields such as industry, agriculture, environmental protection, air purification, water treatment and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Gas purifying process and gas purifying apparatus
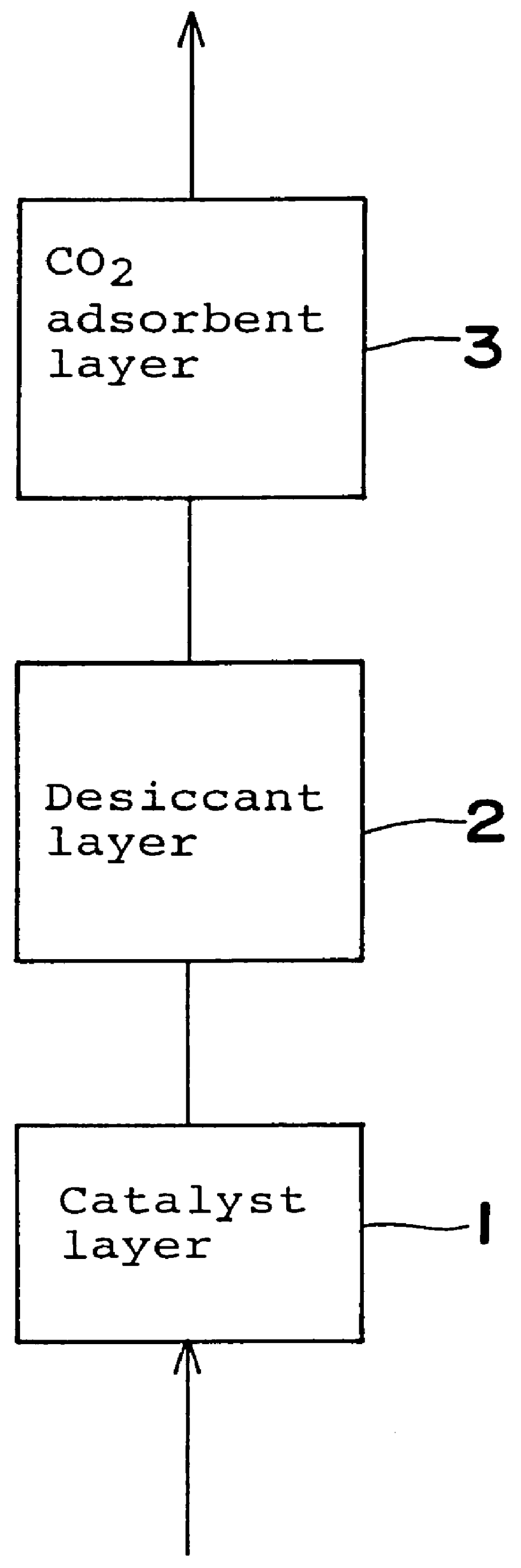
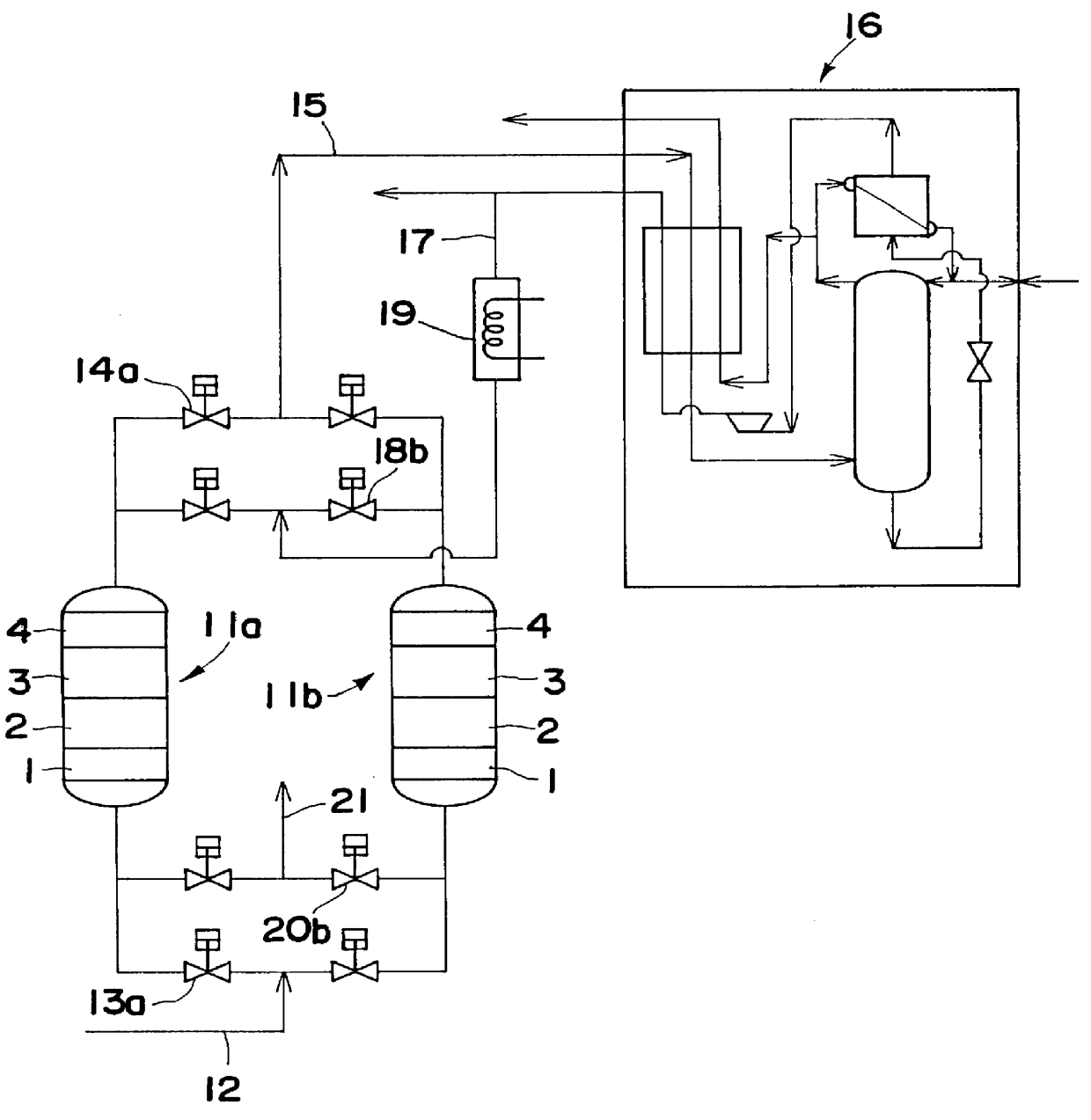
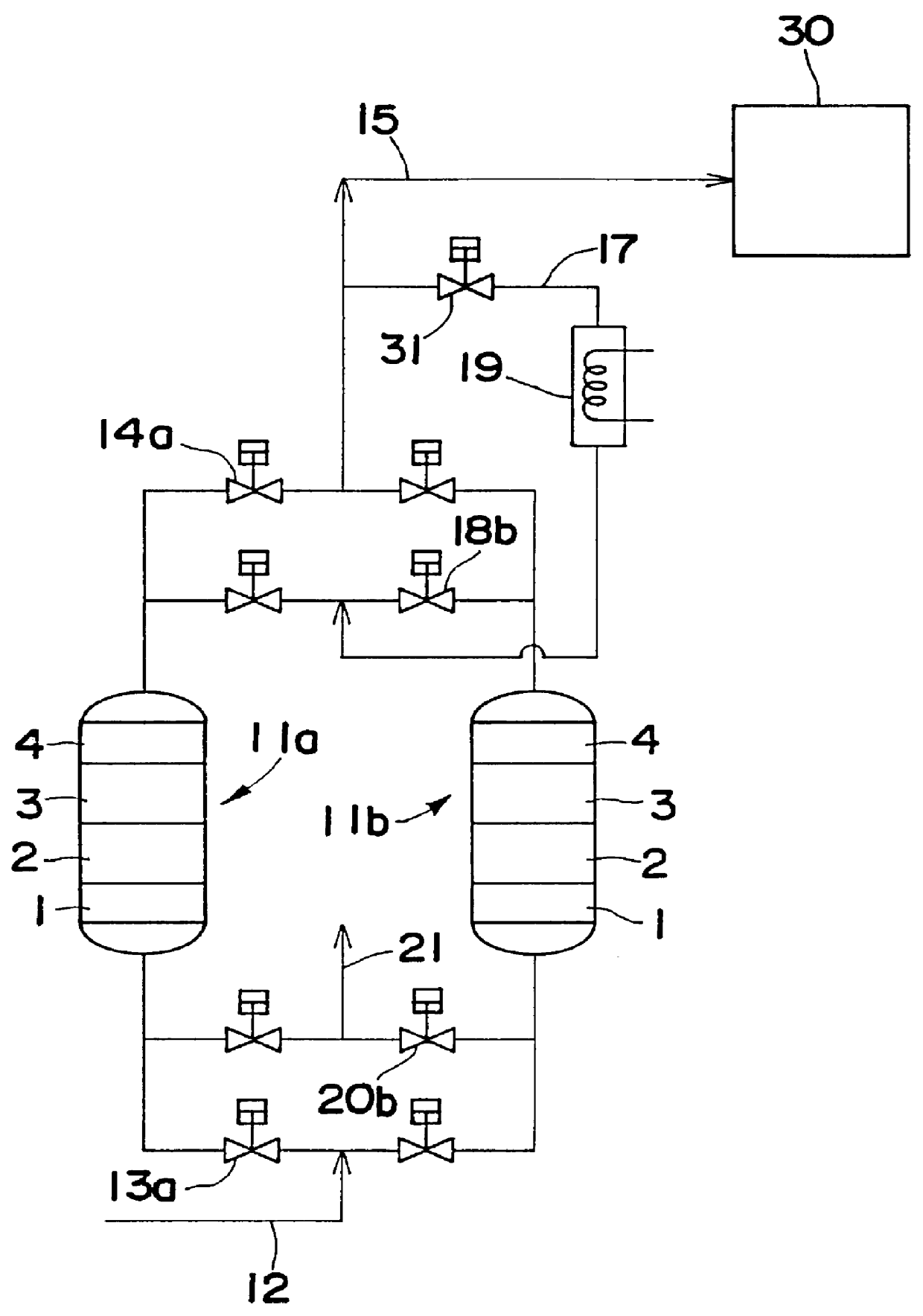
A method is provided for removing water, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide out of a gas, such as air, by passing the gas through a packed column so that the gas sequentially contacts a catalyst consisting of platinum or palladium and at least one member selected from the group consisting of iron, cobalt, nickel, manganese, copper, chromium, tin, lead and cerium wherein the catalyst is supported on alumina containing substantially no pores having pore diameters of 110 Angstroms or less under conditions which oxidize the carbon monoxide in the gas into carbon dioxide; an adsorbent selected from the group consisting of silica gel, activated alumina, zeolite and combinations thereof under conditions in which water is adsorbed and removed from the gas and an adsorbent selected from the group consisting of calcium ion exchanged A zeolite; calcium ion exchanged X zeolite; sodium ion exchanged X zeolite and mixtures thereof under conditions which carbon dioxide is adsorbed and removed from the gas. The gas may also be subjected to a catalyst / adsorbent in the packed column to effect oxidation and removal of hydrogen in the gas.
Owner:NIPPON SANSO CORP
Active alumina/active carbon composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102319557ASolve the strength problemSolve the problem of longevityCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesActivated carbonSludge
The invention discloses an active alumina / active carbon composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material comprises the following ingredients: 70-90 weight portions of sludge, 10-30 weight portions of active carbon, and 15-35 weight portions of binder, and is prepared by uniformly mixing, pelleting, aging, molding, drying in the air, sintering, rinsing and drying. Using sludge as raw material has an important meaning to environmental protection and recycling of waste. The invention has the advantages of simple preparation method, easy obtainment of raw material, and low cost, and can be widely applied in the fields of industry, agriculture, environmental protection, air cleaning, water treatment and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for preparing benzene adsorption material by using waste activated alumina
InactiveCN102274713AImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesDispersed particle separationBenzeneOrganic matter
The invention relates to a method for preparing a benzene adsorbing material by utilizing a discarded activated aluminum oxide. In the method, an activated aluminum oxide / active carbon composite material which has a high adsorption effect on benzene is prepared by cleaning, filtering and drying the discarded activated aluminum oxide and by closed heat treatment at low temperature. In the method, due to the adoption of a closed low-temperature heat treatment mode, holes which are blocked in the discarded activated aluminum oxide can be perforated, and organic matters adsorbed to the discarded activated aluminum oxide can be directly discomposed and carbonized and stored in the aluminum oxide holes to form active carbon, so air pollution is reduced. The method has a novel process, is simple, easy and low in cost and has a high environment friendliness and economic value, and wastes can be turned into wealth.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Adsorbents for pressure swing adsorption systems and methods of use therefor
InactiveUS7713333B2Reduce frequencyMaintain purityGas treatmentIsotope separationPurification methodsSorbent
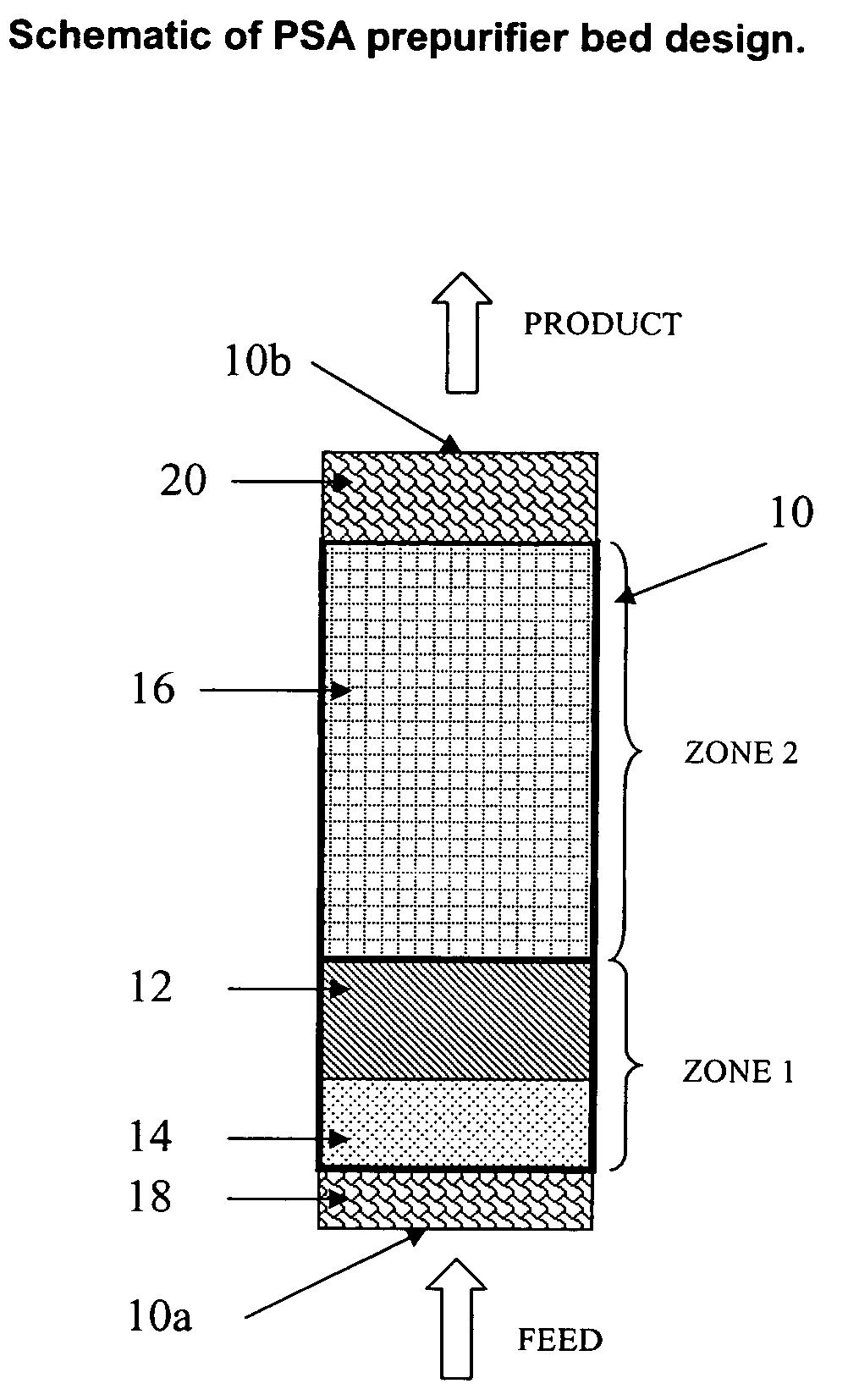
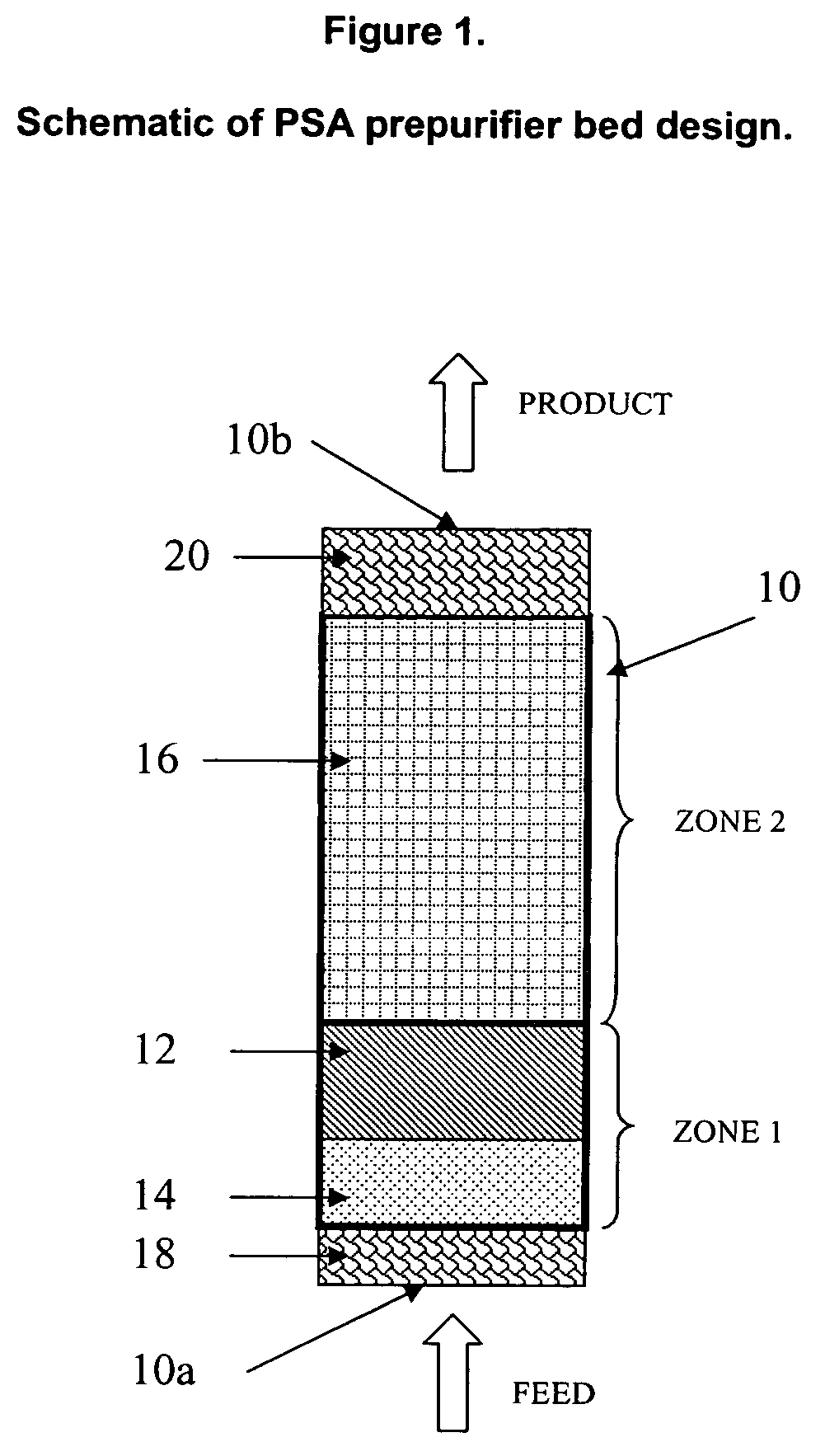
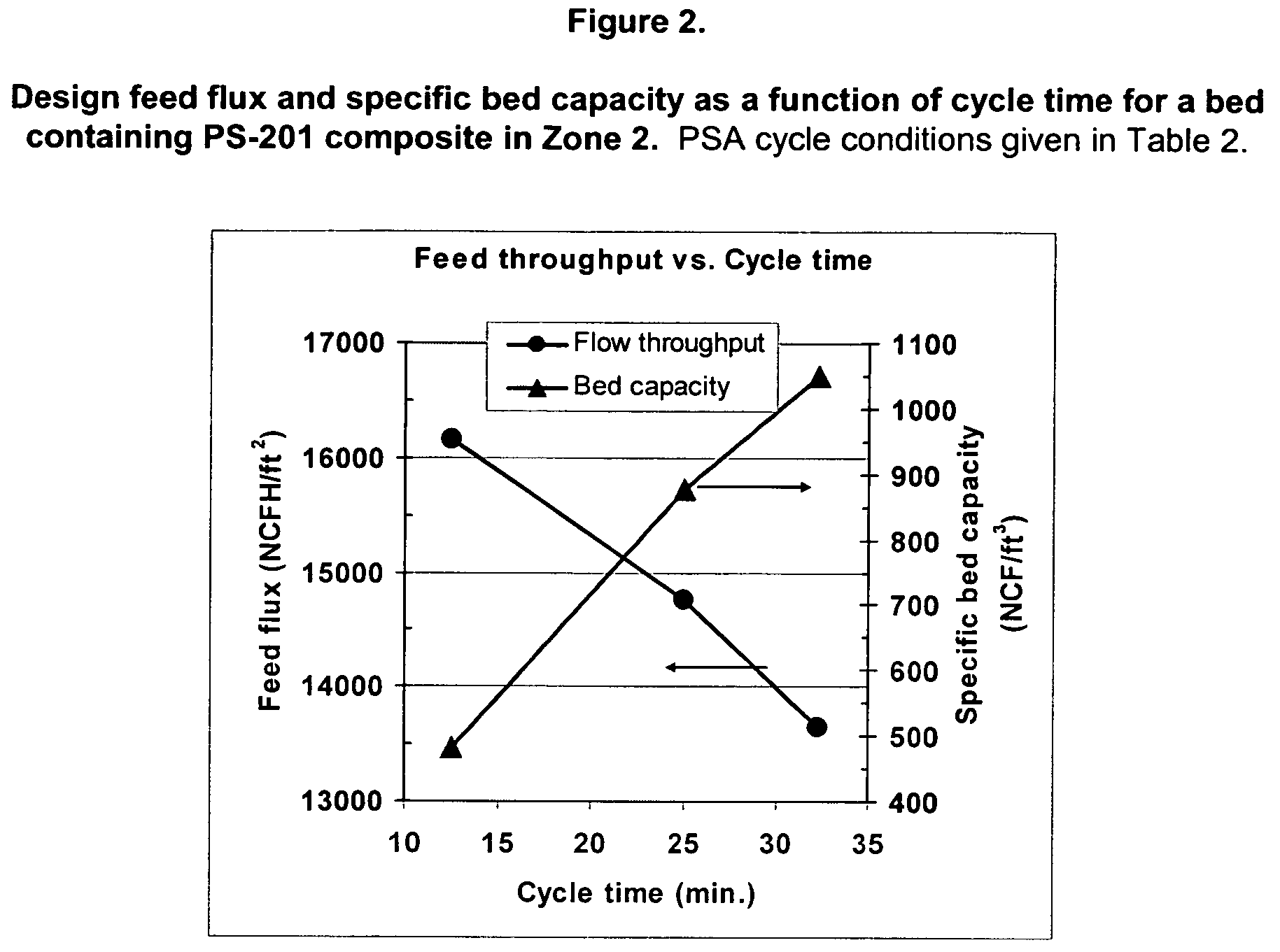
The present invention relates generally to adsorbents for use in pressure swing adsorption (PSA) prepurification processes. The invention more particularly relates to the design of adsorbent zones to be used in PSA prepurification processes that are expected to provide for extensions in PSA cycle time, thereby reducing blowdown loss and operating costs associated with the process. One particular embodiment of the present invention includes a first adsorption zone containing activated alumina and a second adsorption zone of an alumina-zeolite mixture or composite adsorbent in which the volume of the first zone does not exceed 50% of the total volume of the first and second zone.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Adsorptive duct for contaminant removal, and methods
A duct for passage of air therethough; one particular use for the duct is as a passage for intake air for a vehicle engine. The duct has an interior, adsorptive region that is adapted to remove contaminants from the air stream passing therethrough. The adsorptive region includes adsorptive material such as carbon (usually activated carbon), activated alumina, zeolites, metal oxides or ion exchange resin. The duct inhibits diffusion of uncombusted gasoline back through the duct from the engine, after the engine has been shut off.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Process for preparing active alumina
InactiveCN1420082AIncrease profitAvoid or suppress generationAlkali-metal aluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide preparationHigh concentrationPorosity
A process for preparing the active aluminium oxide includes preparing the solution of sodium metaaluminate from powdered aluminium hydroxide and sodium hydroxide, introducing high-concentration CO2 gas mixture, colloidizing at 20-70 deg.C, regulating pH=9-11, filtering, washing the filtered cake, drying at 60-100 deg.C to obtain alpha-AlO(OH), and calcining at 500-700 deg.C. Its advantages are high reaction speed, low CO2 consumption and low cost.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for adsorption of phosphate contaminants from water solutions and its recovery
InactiveUS20100243571A1Prevent precipitationReduce concentrationMaterial nanotechnologyIon-exchanger regenerationSorbentSludge
Aqueous fluid polluted with phosphate contaminants is mixed with or passed through an adsorbent material selected from: (i) particles of oxides or hydroxides of transition metals, aluminum oxides or hydroxides, TiO2, or mixtures thereof, or (ii) particles of activated carbon, activated alumina, aluminum oxide, activated TiO2, TiO2, mineral clay, zeolite, or an ion exchanger loaded with nanoparticles of oxides or hydroxides of transition metals, aluminum oxides or hydroxides or TiO2, or mixtures thereof, to yield aqueous fluid purified from phosphate. The adsorbent material is further regenerated by increasing the pH of the adsorbent sludge, concentrated phosphate solution or a phosphate crystal slurry is recovered as well.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Purificant for adsorbing formaldehyde and method of preparing the same
InactiveCN101279237AAvoid uneven loadImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesMolecular sieveDesorption
The invention relates to a formaldehyde purificatory absorbent and a preparation method thereof, which belongs to the technical field of a purificant and a preparation method thereof. The formaldehyde purificatory absorbent uses a porous material as a carrier and the carrier is one or more of activated alumina, sea-foam and zeolite molecular sieve. The preparation method relates to that a steeping fluid is placed into a beaker, added with carrier powders at a steeping temperature ranging from 20 DEG C to 60 DEG C, stirred for 2 through 6 hours, dried at the temperature ranging from 100 DEG C to 140 DEG C after being filtrated and then porphyrized with a mortar. The steeping fluid adopts a strong oxidizer potassium permanganate and is diluted to an acid solution and an organic amine solution of 3 to 8 percent by de-ionized water. The method of the invention adopts the strong oxidizer as an active component and carries out the steeping of the carrier after the active component is coordinated with the solution, when the active component is of even load bearing, thus being able to oxidize the adsorbed formaldehyde molecule to be carbon dioxide desorption and forming the cycle adsorption to enlarge the adsorption capacity thereof. Besides, the method of the invention adopts the acid solution and the organic amine to carry out the steeping modification of the carrier, which improves the characteristics of the carrier, like the structure in the pores or on the surface, the polarity and so on, and enhances the adsorption ability to formaldehyde.
Owner:张宏
Preparation process for large pore volume and light bulk density activated alumina
InactiveCN102730724AChange the stacking methodFine grainAluminium oxides/hydroxidesWater vaporSodium aluminate
The invention relates to a preparation process for large pore volume and light bulk density activated alumina, and belongs to the technical field of activated alumina preparation. According to the process, an aluminum sulfate solution and a sodium aluminate solution form a glue in a stainless steel neutralization kettle through a continuous co-current flow method; then an aging treatment is performed for a certain time in a stainless steel aging washing tank; the resulting material is pressed to a plate and frame filter press with a material pressing pump to carry out continuous washing to prepare primary pseudo-boehmite particles with large grains; the removed filter cake is acidified, and proper amounts of a pore expanding agent and a surfactant are added during the acidification process to carry out forming; the formed wet balls are placed in a drying box to carry out drying; and the dried small balls are loaded into a calcination activation furnace to carry out high temperature calcination and pore expanding. The process of the present invention has characteristics of low cost and low equipment corrosion, can performs continuous washing cycle, and has advantages of low wastewater discharging, less pollution, and the like. With the process of the present invention, the production cycle can be reduced, the labor intensity can be reduced, and various performance indicators of the prepared gamma-Al2O3 can meet the international advanced level after pore expanding by water vapor.
Owner:JIANGSU JINGJING NEW MATERIALS
Gas storage and delivery system for pressurized containers
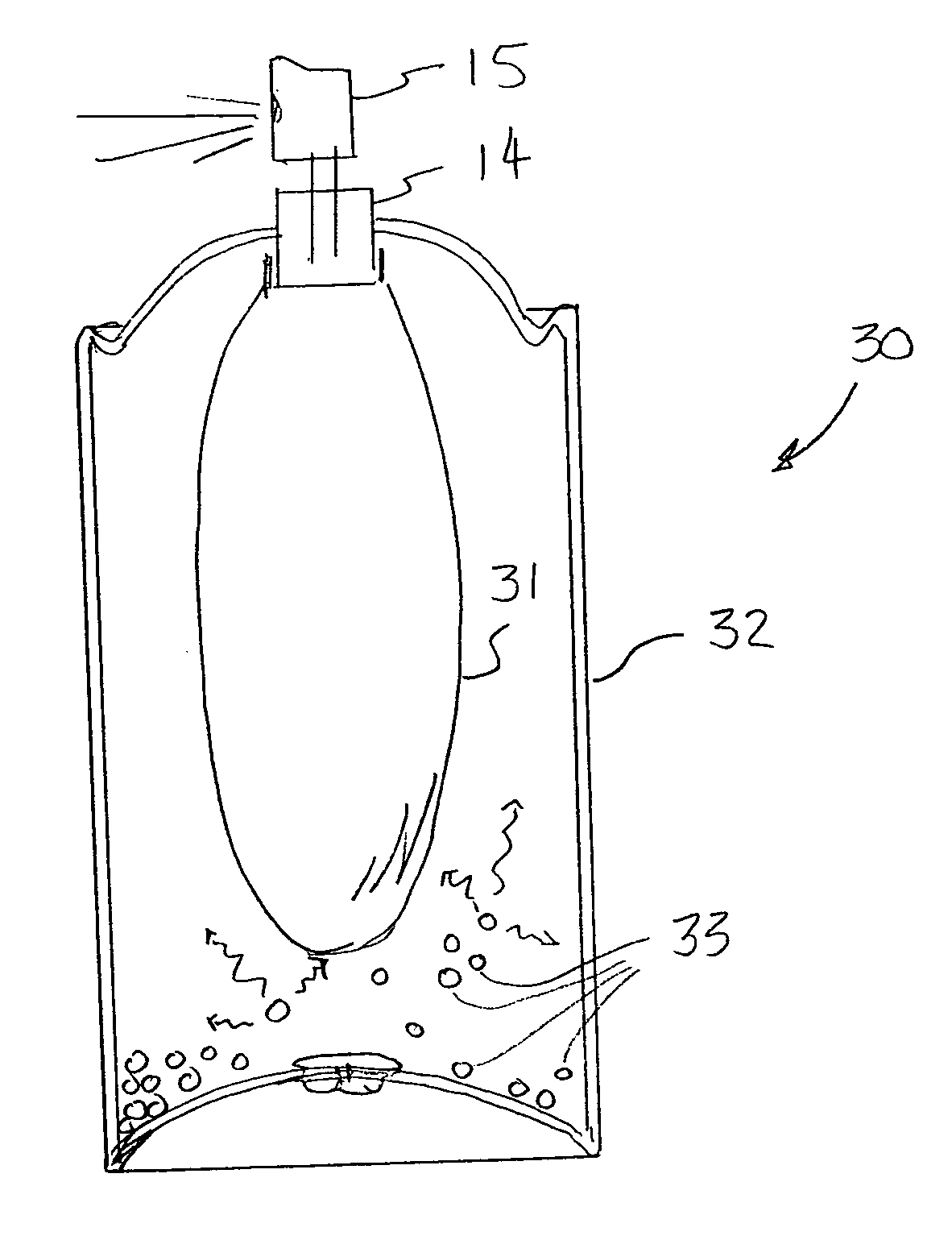
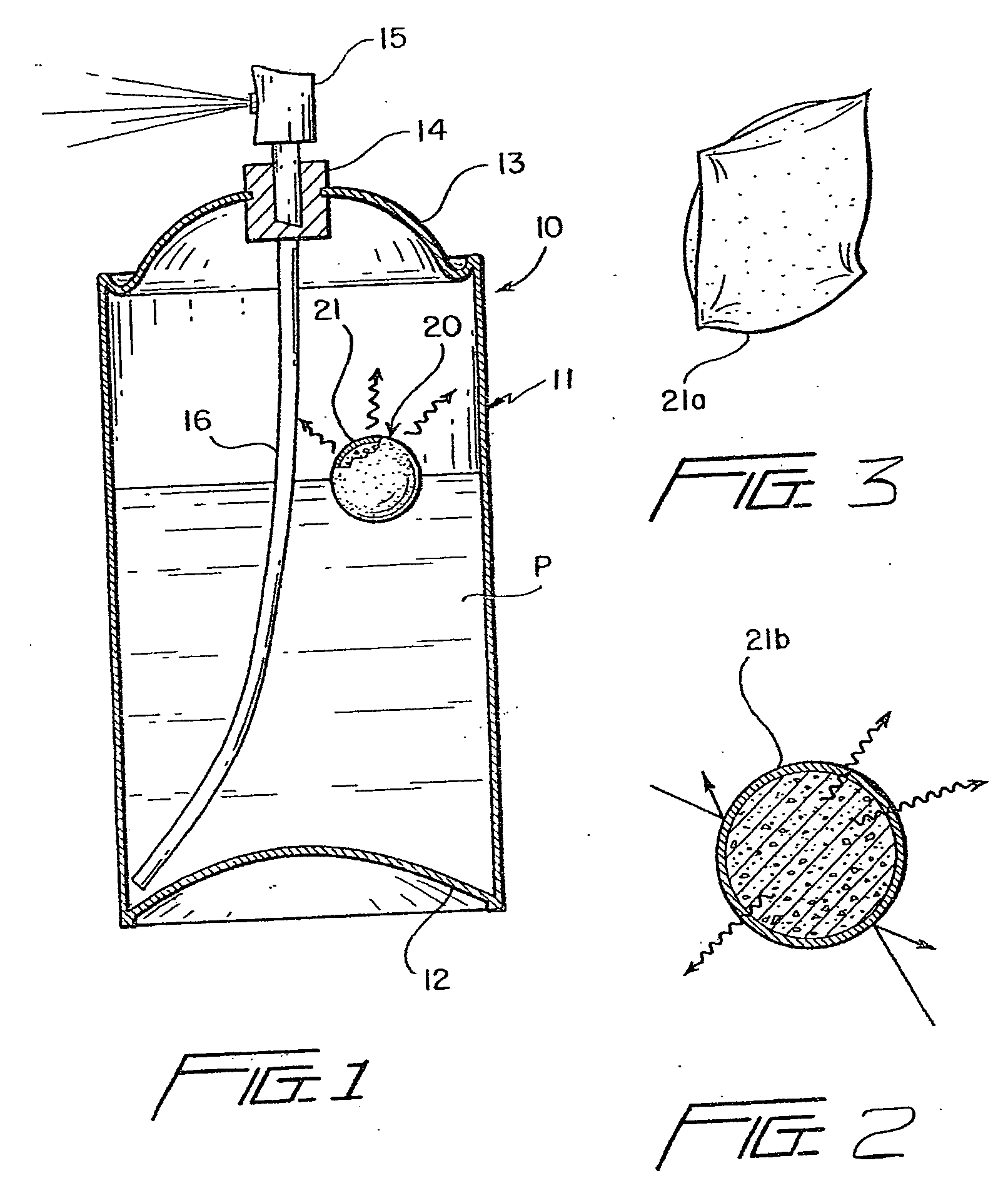
InactiveUS20050274737A1Consistent and uniform and acceptable spray patternFine foamOpening closed containersBottle/container closureSodium bicarbonateDesorption
A gas adsorption material containing a desired quantity of gas is placed in a pressurized container along with a product to be dispensed, and as pressure in the container is depleted during use, stored gas is released into the container to maintain pressure in the container within a predetermined range. The material may be in contact with the product, or it may be isolated from the product, and is known as a pressure swing adsorption (PSA) system, wherein adsorption of gas into the material occurs at a high pressure, and desorption of gas from the material occurs at a low pressure. Such devices are capable of storing under pressure a volume of gas 18 to 20 times the volume of the material. A preferred adsorbent gas storage material is granular activated carbon, or a carbon fiber composite molecular sieve (CFCMS). Other materials, such as zeolite, starch-based polymers, activated alumina, silica gel, and sodium bicarbonate, or mixtures thereof, may be used, although they generally are not as effective as activated carbon. The adsorbent material may be in granular, powdered, or pellet form, or a mass of the material may be formed into variously shaped cohesive bodies, such as balls, tubes, cubes or rods, or sheets or screens which may be flat or curved or folded into various shapes, such as, for example, an accordion-like fold.
Owner:LIM WALTER K
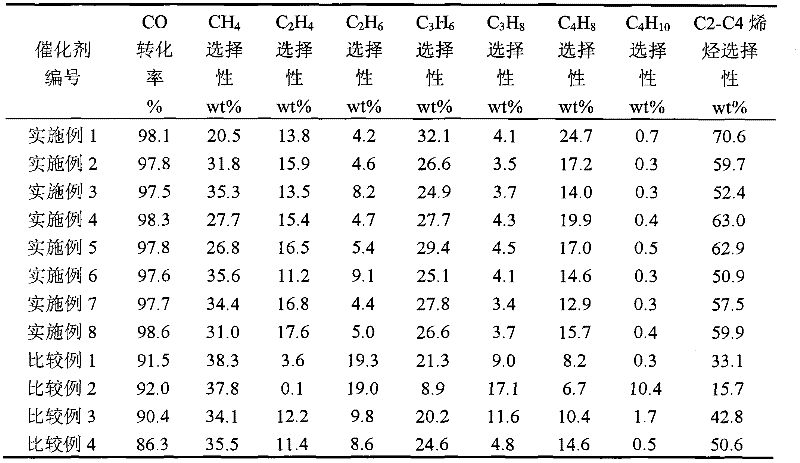
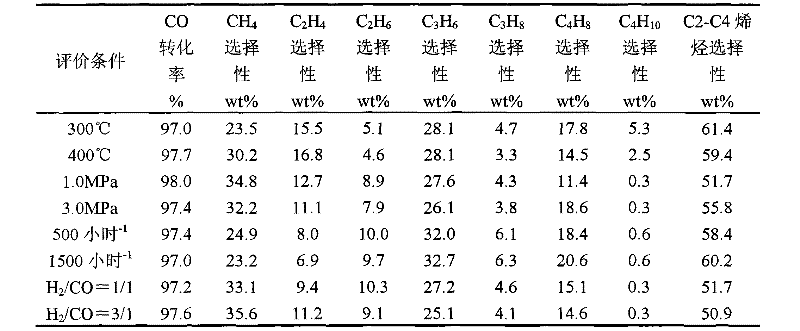
Method for preparing low-carbon olefin by synthetic gas one-step technology
ActiveCN102452878AHighly uniform dispersionIncrease the number ofHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesCatalyst activation/preparationSyngasFixed bed
The invention relates to a method for preparing a low-carbon olefin by a synthetic gas one-step technology. The method aims at solving a problem that based on the prior art, a low-carbon olefin preparation process adopting a fixed bed Fischer-Tropsch synthesis technology has a low CO conversion rate and poor low-carbon olefin selectivity. The method solves the problem well by adopting a technical scheme of low-carbon olefin preparation adopting a fixed bed catalyst, wherein the technical scheme is characterized in that active alumina is utilized as a carrier; supported active ingredients contain compounds having an atomic ratio chemical formula of Fe100AaBbOx; A represents at least one of Cu and Mn; and B represents an alkali metal K. The method provided by the invention can be utilized for low-carbon olefin industrial production adopting synthetic gas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
High temperature-resistant activated alumina material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102745729AEase of mass productionSimple processAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationRoom temperaturePeptization
The present invention provides a high temperature-resistant activated alumina material and a preparation method thereof. The alumina material is prepared by the following steps: mixing macroporous pseudo-boehmite, high viscosity pseudo-boehmite and an additive by using water; uniformly stirring at a rotation speed of 100-1000 r / min; adding dilute nitric acid with a concentration of 30% to carry out a reaction until the pH value is 2.0-5.5 and the solution is at the peptization state, and then aging for 3-6 hours at a temperature of 80-100 DEG C while stirring; adding a pore-forming agent at a room temperature, and carrying out uniform stirring, pulping, spraying and drying; and carrying out calcination at a temperature of 900 DEG C to prepare the alumina. The alumina material of the present invention has advantages of convenient mass production, high specific surface, and the like, wherein the specific surface of the alumina material of the present invention can be maintained more than 110 m<2> / g for a long time at a temperature of 1000-1100 DEG C. In addition, the preparation method of the alumina material has characteristics of simple process and low cost.
Owner:浙江欧信环保科技有限公司
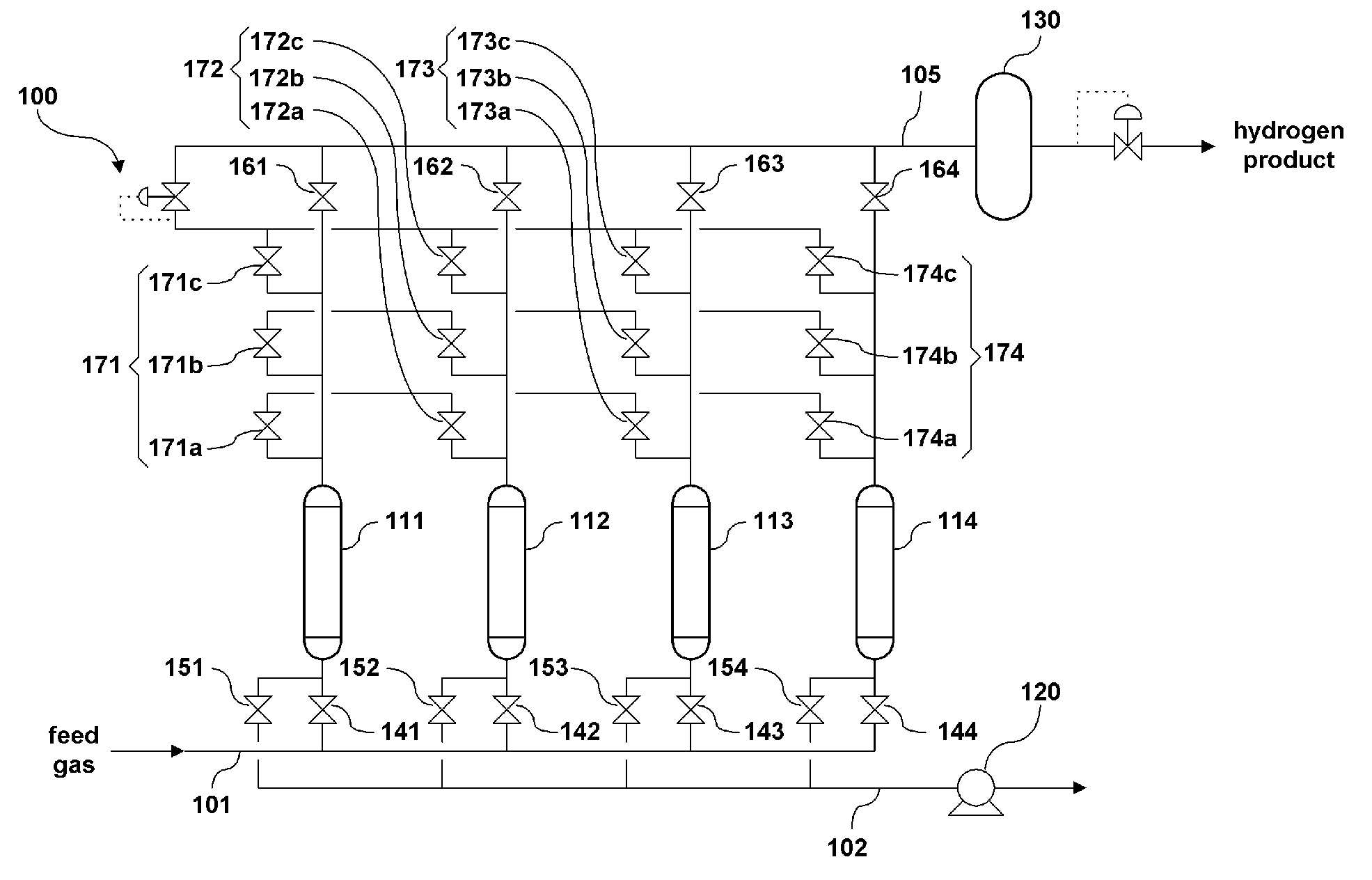
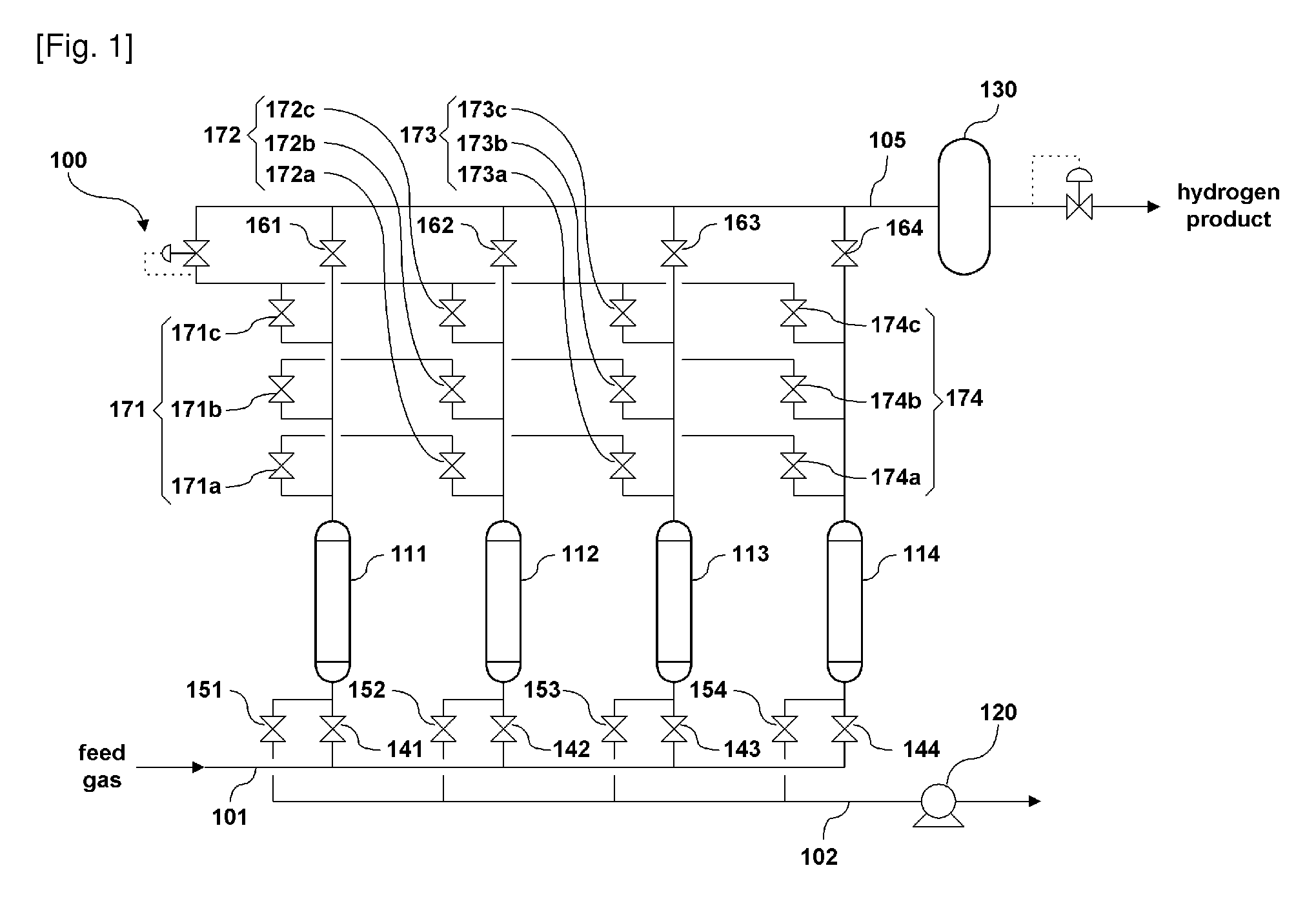
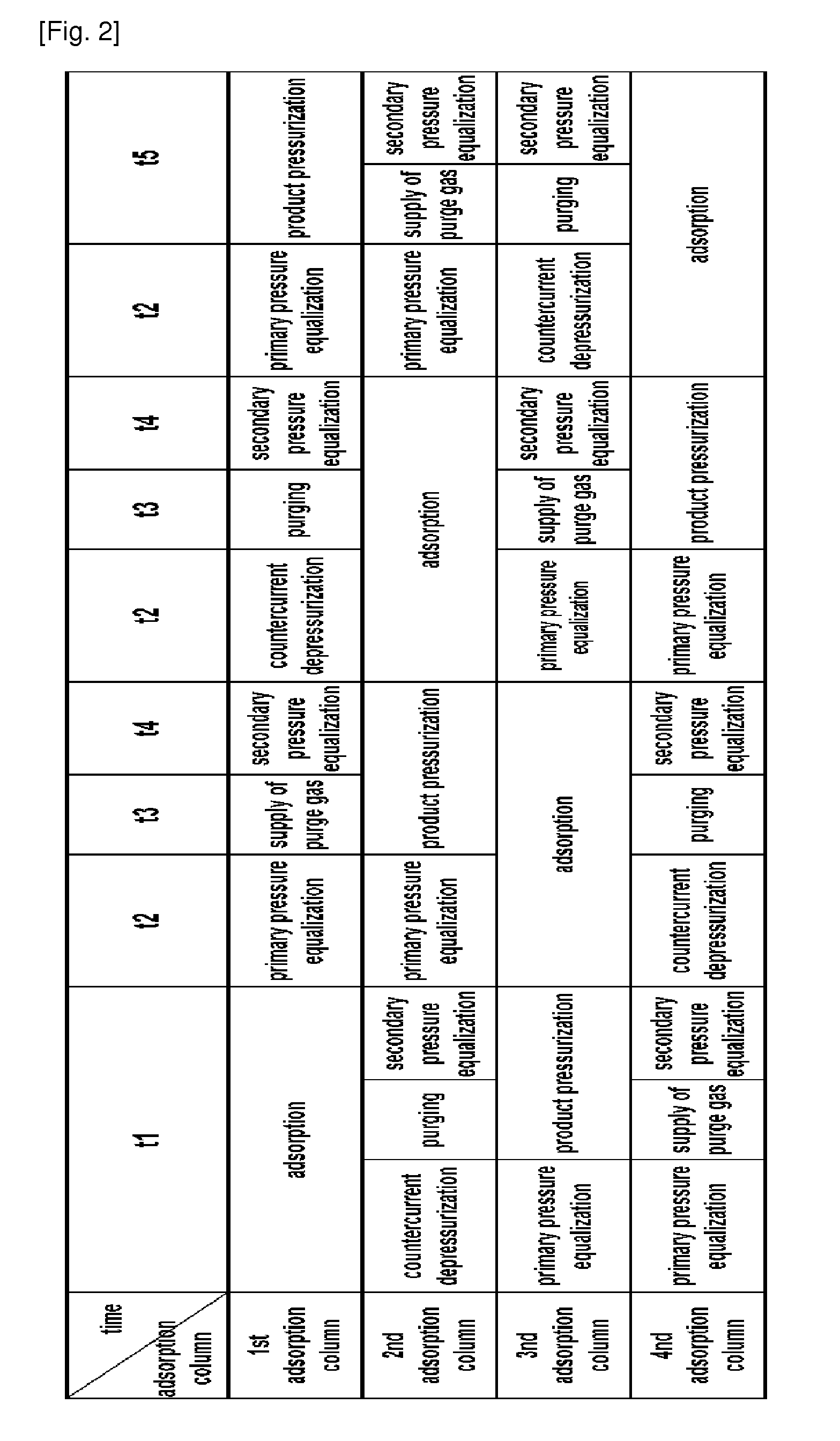
Pressure swing adsorption apparatus and method for hydrogen purification using the same
ActiveUS20110005391A1Increase heightImprove adsorption efficiencyProductsGas treatmentActivated carbonPurification methods
Disclosed are a pressure swing adsorption apparatus for hydrogen purification and a hydrogen purification method using the same. The pressure swing adsorption apparatus for hydrogen purification includes a plurality of adsorption columns connected with a feed supply pipe, a hydrogen storage tank for collecting purified hydrogen from the adsorption columns, and valves for opening or closing a plurality of pipes connected to the respective adsorption columns, and the adsorption columns are packed with adsorbent beds of active alumina or silica gel, activated carbon, zeolite 13X, zeolite 5A, and a carbon monoxide-selective adsorbent other than the zeolite 5A, in order to remove carbon dioxide, methane, and carbon monoxide from a hydrogen-containing gas mixture supplied through the feed supply pipe, and the content of carbon monoxide in the discharged hydrogen is minimized through sequential adsorption on the adsorbents in the adsorption columns. The content of carbon monoxide in the purified hydrogen product can be decreased to 10 ppm or less, thus facilitating the production of highly pure hydrogen products.
Owner:GENS ENG
Process for producing phenoxyphosphazene compound, flame- retardant resin composition, and flame-retardant resin molding
InactiveUS20030040643A1Quality improvementIncrease resistanceGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAlkanePolymer science
The phenoxyphosphazene compound of the present invention is prepared by treating a phenoxyphosphazene compound with (a) at least one adsorbent selected from activated carbon, silica gel, activated alumina, activated clay, synthetic zeolite and macromolecular adsorbents, (b) at least one reagent selected from metal hydrides, hydrazine, hypochlorites, thiosulfates, dialkyl sulfuric acids, ortho esters, diazoalkanes, lactones, alkanesultones, epoxy compounds and hydrogen peroxide or (c) both the adsorbent and reagent. Incorporation of the phenoxyphosphazene compound prepared by the process of the invention into a synthetic resin achives the following advantages: the synthetic resin can be prevented from discoloration; when the resultant resin composition is stored for a long time, the properties of the synthetic resin, such as heat resistance, weatherability, resistance to discoloration and chemical resistance are not deteriorated; and the resin composition gives a resin composition molded article excellent in properties such as flame retardancy, thermal stability, and moldability.
Owner:OTSUKA CHEM CO LTD
Multifunctional raw gas purifying agent, preparation method and application method thereof
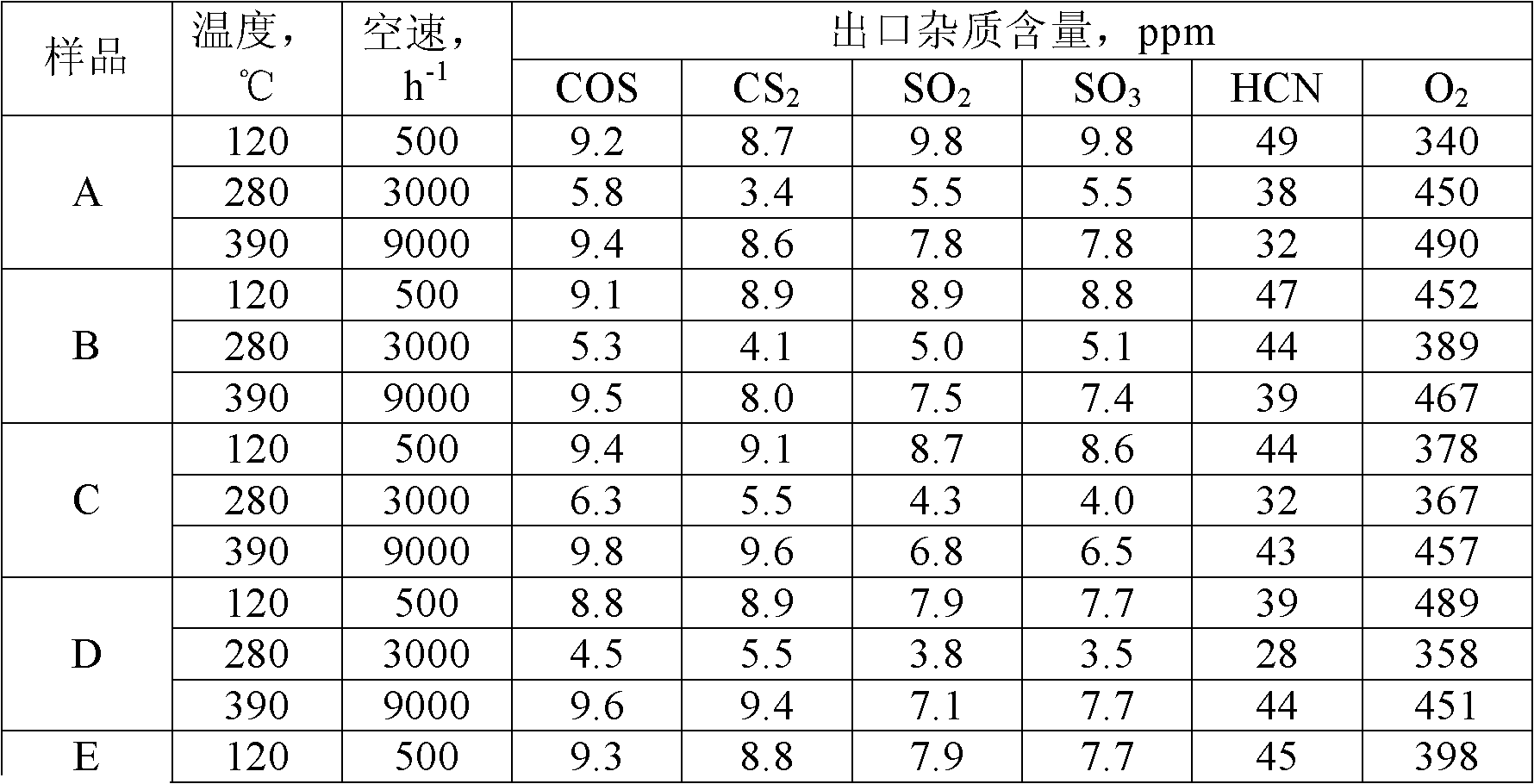
The invention relates to a multifunctional raw gas purifying agent, a preparation method and an application method thereof. According to the present invention, active alumina is adopted as a carrier, and the carrier loads ammonium molybdate, one or two materials selected from copper acetate, zinc acetate, lead acetate, nickel oxalate and ammonium metavanadate, and one material selected from magnesium chloride, potassium carbonate and sodium carbonate to prepare the multifunctional raw gas purifying agent, wherein the mass of the loaded ammonium molybdate is 1-10% of the mass of the carrier, the total mass of the other two or three loaded metal compounds is 10-25% of the mass of the carrier. The preparation method for the multifunctional raw gas purifying agent comprises: impregnating the carrier for 2-6 hours by the metal compound solution; drying for 2-4 hours at a temperature of 120 DEG C; carrying out baking for 4-6 hours at the temperature of 280-350 DEG C to prepare the multifunctional raw gas purifying agent. The multifunctional raw gas purifying agent of the present invention is adopted in the raw gases of water gas, semi-water gas, coke oven gas or IGCC power generation fuel gas to purify COS, CS2, HCN, SO2, SO3 O2 and other impurities, wherein the conversion rates of the COS, the CS2, the HCN, the SO2 and the SO3 are more than or equal to 90%, and the O2 removal rate is more than or equal to 95%.
Owner:HAISO TECH
Lightweight periclase-magnesium aluminate spinel refractory material for rotary cement kiln and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a lightweight periclase-magnesium aluminate spinel refractory material for a rotary cement kiln and a preparation method thereof. According to the scheme, the preparation method comprises the following steps of: uniformly dispersing 0.2 to 4wt% of magnesite micro powder and 0.2 to 4wt% of active alpha alumina micro powder into 5 to 8wt% of binding agent to obtain a modified binding agent; adding 50 to 70wt% of porous periclase-magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic particles to a vacuum agitating machine; vacuumizing to be below 2.5kPa; maintaining the constant pressure for 3 minutes; adding the modified biding agent to the vacuum agitating machine; agitating for 10 minutes; closing a vacuumizing system; then adding 10 to 25wt% of porous periclase-magnesium aluminate spinel ceramic fine powder, 4 to 20wt% of fine magnesia powder, and 1.5 to 4wt% of magnesium aluminate spinel fine powder to the vacuum agitating machine; uniformly agitating; mechanically pressing and modeling; drying; and maintaining the temperature of 1,500 to 1,650 DEG C for 2 to 10 hours. The lightweight periclase-magnesium aluminate spinel refractory material for the rotary cement kiln has the advantages of being low in heat conductivity, high in intensity, high in thermal shock resistance, high in kiln coating performance, and high in resistance to medium erosion.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics and preparation method thereof
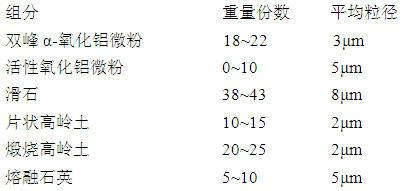
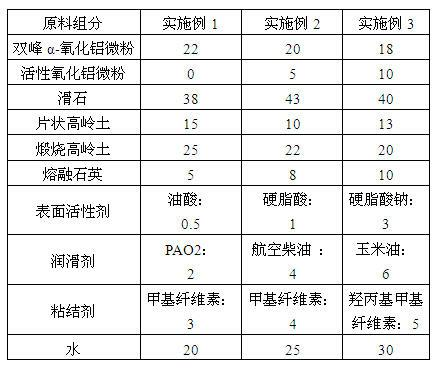
The invention relates to a thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics. The components of the thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics comprise, by weight, 18-22 parts of bimodal alpha-alumina micro powder with the particle size of 3 mum, 0-10 parts of activated alumina micro powder with the particle size of 5 mum, 38-43 parts of talc with the particle size of 8 mum, 10-15 parts of flake kaolin with the particle size of 2 mum, 20-25 parts of calcined kaolin with the particle size of 2 mum, and 5-10 parts of fused quartz with the particle size of 5 mum. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing the bimodal alpha-alumina micro powder and the activated alumina micro powder; (2) uniformly mixing the resulting mixture from the step (1) and a surfactant; (3) uniformly mixing the resulting mixture from the step (2) and the talc; (4) uniformly mixing the resulting mixture from the step (3) with the flake kaolin, the calcined kaolin, the fused quartz, a binder, a lubricant and water; (5) carrying out treatments of forming, drying, sintering and thermal insulation, and then cooling to the room temperature to obtain the thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics. The thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics of the present invention has advantages of high mechanical strength, moderate porosity, and low expansion coefficient. The thermal shock resistance of the thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics is that: the thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics does not crack in three tests at the temperature of 750 DEG C. The thermal shock resistant thin-walled cordierite honeycomb ceramics meets the European IV emission standard.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE YIXING NONMETALLIC CHEM MACHINERY FACTORY
Iolite honeycomb ceramic catalyst for denitrification of flue gas, preparing method and use thereof
InactiveCN1401416ALow costImprove denitrification activityCatalyst carriersDispersed particle separationHigh resistanceFlue gas
A cellular cordierite ceramic catalyst for denitrifying flue gas is composed of cellular cordierite ceramics as the first carrier, the active alumina film (3-5.3 wt.%) as the second carrier and CuO (1.25-15 wt.%) as active component. It is prepared through applying active alumina film on the first carrier, and carrying CuO. Its advantages are low cost, high strength and activity, and high resistance to water and SO2 poisoning.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of low-sodium active aluminum oxide
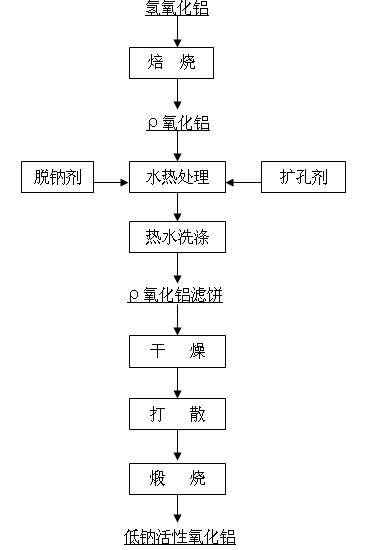
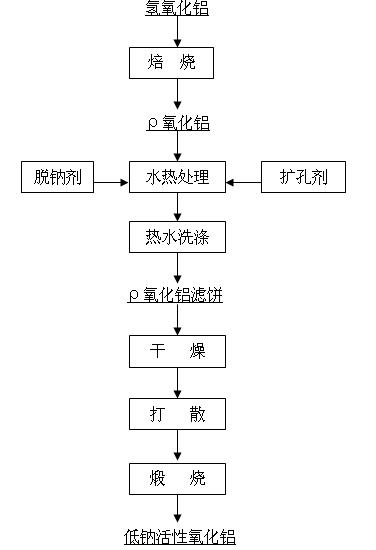
InactiveCN102070169AReduce manufacturing costLarger than surfaceCatalyst carriersAluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide purificationSlurryHeat treating
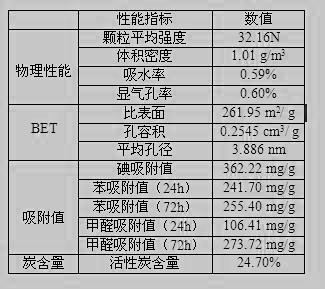
The invention relates to a preparation method of low-sodium active aluminum oxide, in particular to a preparation method of active aluminum oxide used as catalyst carrier for cleaning automobile tail gas. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: roasting aluminum hydroxide to obtain an intermediate product rho aluminum oxide, adding a sodium removal agent and a pore expanding agent to carry out hydrothermal treatment, filtering the treated slurry, washing with hot pure water, drying, dispersing the dried product with a dispersion machine, and calcining to obtain active aluminum oxide. In the method provided by the invention, any one or more than two of nitric acid, acetic acid and citric acid is / are used as the sodium removal agent to wash the intermediate product after the roasting of aluminum hydroxide, thereby lowering the sodium content. The low-sodium active aluminum oxide prepared from aluminum hydroxide has the advantages of larger specific surface, multiple pores, high pore volume, simple preparation method and lower production cost.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
Aluminum-magnesium series lightweight pouring material and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a making method of aluminium-magnesium systemic light-quality casting material, which comprises the following steps: adopting 40-70% aluminium-magnesium porous ceramic particle and 0-20% aluminium-magnesium particle as aggregate; selecting 15-55% fine aluminium-magnesium powder, 2-15% pure calcium aluminate and 2-8% active alpha-aluminium micropowder as substrate; blending the mass; adding 8-25% water, 0.1-0.8% silica powder and 0-3% dehydragent to stir evenly; casting; vibrating; moulding; drying for 8-48h under 110 deg.c.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Architectural decoration material capable of adjusting moisture and reducing harm
ActiveCN101210449AReduce contentHas the function of regulating humidityCovering/liningsSilica gelMoisture
An architectural decorative material for adjusting humidity and reducing harm includes a substrate and a decorative layer arranged on the surface of the substrate and is characterized in that the decorative layer is a glazed layer containing 0.01-60% of humidity-adjusting and harm-reducing material which is a composite of one or more of the following substances: zeolite, diatomite, allophone, vitreous trass, meerschaum, emathlite, active carbon, silica gel, white carbon black and activated alumina. Compared with prior art, the invention has the advantages of good adjustment of indoor humidity and reduction of harmful gases, as well as good decorative effect.
Owner:堆龙德庆绿家科技有限公司
Gas storage and delivery system for pressurized containers
InactiveUS7185786B2Consistent, uniform and acceptable spray patternBetter aerosolize the productOpening closed containersBottle/container closureSodium bicarbonateDesorption
A gas adsorption material containing a desired quantity of gas is placed in a pressurized container along with a product to be dispensed, and as pressure in the container is depleted during use, stored gas is released into the container to maintain pressure in the container within a predetermined range. The material may be in contact with the product, or it may be isolated from the product, and is known as a pressure swing adsorption (PSA) system, wherein adsorption of gas into the material occurs at a high pressure, and desorption of gas from the material occurs at a low pressure. Such devices are capable of storing under pressure a volume of gas 18 to 20 times the volume of the material. A preferred adsorbent gas storage material is granular activated carbon, or a carbon fiber composite molecular sieve (CFCMS). Other materials, such as zeolite, starch-based polymers, activated alumina, silica gel, and sodium bicarbonate, or mixtures thereof, may be used, although they generally are not as effective as activated carbon. The adsorbent material may be in granular, powdered, or pellet form, or a mass of the material may be formed into variously shaped cohesive bodies, such as balls, tubes, cubes or rods, or sheets or screens which may be flat or curved or folded into various shapes, such as, for example, an accordion-like fold.
Owner:LIM WALTER K
Corundum mullite rock wear-resistant refractory castable
InactiveCN101570442AMeet the use requirementsExcellent medium temperature strengthAluminium hydroxideWear resistant
The invention discloses a corundum mullite rock wear-resistant refractory castable which belongs to refractory materials, aiming at providing an unshaped refractory material with high medium temperature strength and good thermal shock resistance and erosion and wear resistance. According to weight percentages, the invention is formed by evenly mixing 89-96% of wet pug, 2-6% of calcium aluminate cement and 2-5% of bonding agent; the bonding agent is prepared by 20-30% of industrial aluminum hydroxide fine powder, 67-79% of phosphoric acid with concentration being 45% and 1-3% of chromium oxide green fine powder; the wet pug is prepared by taking corundum with certain particle grading or mixture of corundum and mullite as aggregate and adding the bonding agent and additive, the additive is prepared by 60-76% of white alundum powder, 15-25% of activated alumina fine powder, 5-15% of silicon fine powder, 3-8% of sodiumtripolypolyphosphate and 1-8% of sodium borate. The invention is mainly used as an ideal refractory castable for circulating fluid bed boiler lining and cement kiln lining.
Owner:贵阳明通炉料有限公司
Catalytic oxidation catalyst for methyl acetate in organic waste gas and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102247867AEasy to makeSuitable for large-scale productionDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCatalytic oxidationManganese
The invention discloses a catalytic oxidation catalyst for methyl acetate in organic waste gas and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is a supported noble metal alloy catalyst, wherein the noble metal alloy is an arbitrary metal combination of two or more of Pd, Pt, Rh, Au and Ag; the vector is activated alumina and / or titanium dioxide, as well as at least one transition metal oxide whichcomprises metal oxide of manganese, cerium, nickel, lanthanum, copper, vanadium, tungsten, iron, cobalt or chrome; and the weight ratio of the noble metal alloy to the vector is (1:2,000)-(1:5). The catalyst provided by the invention can be used for treating organic waste gas containing methyl acetate, especially for treating waste gas of a PTA (purified terephthalic acid) device, by a catalytic oxidation method; and the catalyst has the advantages of simple preparation, high catalytic oxidation activity, good stability, excellent halogenated hydrocarbon poisoning resistance and high practical application value.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Pu'er tea wine and method for making same
ActiveCN101328459ARaw material hygieneSimple processAlcoholic beverage preparationYeastAlcohol content
The invention relates to a Pu'er tea spirit and a preparation method thereof. The grains undergoing the tea liquor dipping treatment are steamed and subject to fermentation by adding with domesticated yeasts; the fermentation liquor is filtered, sterilized at a high temperature, has the alcohol content reduced to 8 to 20 degrees by drinkable alcohol with the concentration of 95 percent, and is filtered by activated alumina or diatomaceous earth to prepare the clear, rufous, bright and transparent Pu'er tea spirit; the spirit has tea aroma and bouquet of the typical Pu'er tea, is rufous, clear and transparent and is pure and fine in taste. The method of the invention can be also applied to the brewing of black tea, green tea and Oolong tea. The Pu'er tea spirit and the preparation method increase the added values of mid-and low-grade tea leaves, and extract nutrient contents with excellent quality from spirits and teas for people, and simultaneously provide a brand new page for the research of the brewage by the fermentation of tea liquids.
Owner:YUNNAN LONGRUN TEA TECH
Light corundum-mullite refractory brick and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a light corundum-mullite refractory brick and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of evenly dispersing 0.5-1wt% of silicon oxide micro powder and 2-4wt% of active alpha alumina micro powder in 5-8wt% of silica sol to obtain modified silica sol, placing 40-70wt% of porous corundum-mullite ceramic particles in a vacuum mixer, carrying out vacuum pumping until the vacuum is below 2.5 kPa, keeping the constant pressure for three minutes, then pouring the modified silica sol into the vacuum mixer, mixing for ten minutes and closing the vacuum pumping system, pouring 10-25wt% of porous corundum-mullite ceramic fine powder, 10-20wt% of corundum fine powder, 1.5-4wt% of silicon oxide micro powder and 1-3wt% of active alpha alumina micro powder into the vacuum mixer for mixing and mechanical pressing, drying and finally preserving heat at 1400-1600 DEG C for 2-10 hours. The prepared product has the characteristics of controllability in apparent porosity and pore size, low thermal conductivity, good thermal shock stability and strong medium erosion resistance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Catalyst for purifying exhaust gas of natural gas engine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102039146AHigh catalytic activityImprove stabilityDispersed particle separationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsPtru catalystCordierite
The invention discloses a catalyst for purifying exhaust gas of a natural gas engine and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst consists of a carrier, a coating coated on the carrier and catalytic active components loaded on the coating, wherein the carrier of the catalyst is made of a honeycomb cordierite ceramic material, the coating is a mixture of activated alumina, a ceria-zirconia solid solution, a rare-earth oxide, an alkaline-earth metal oxide and a caking agent, and the catalytic active components include a platinum group metal and at least one transition metal composite oxide or one transition metal-rare earth composite oxide. Since the transition metal composite oxide or the transition metal-rare earth composite oxide has high oxidative activity for hydrocarbon, and the rare-earth and alkaline-earth metal oxide in the coating has good stabilization effect on the coating and the active components, therefore, the catalyst disclosed by the invention has high catalytic activity and stability for hydrocarbon compounds, the dosage of precious metal is greatly reduced, and the cost of the catalyst is lowered. Moreover, the catalyst can be used for purifying the exhaust gas of the natural gas engine, and besides, the catalyst can be also used for purifying the exhaust gas of automotive vehicles which take gasoline or liquefied petroleum gas as fuel.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Process for preparing active aluminium oxide
InactiveCN1425612AUniform temperatureUniform concentrationAluminium hydroxide preparationAluminium oxides/hydroxidesAluminium chlorideAluminium hydroxide
The present invention relates to the preparation process of active gamma-Al2O3. The mixed water solution of materials including aluminum chloride, ammonia water, pore expander ammonium oxalate or ammonium citrate, etc. is heated and concentrated to produce aluminum hydroxide precipitate; the precipitate is dried and heated to obtain solid powder and to decompose its NH4Cl, which is recovered from hot gas flow through cooling and crystallization; and the solid powder is roasted at 400-800 deg.c for 3-6 hr to convert into gamma-Al2O3. The present invention produces aluminum hydroxide through evaporation and concentration, rather than neutralization, and aluminium hydroxide is precipitated and separated in a stable and balanced solid-liquid state, and this is favorable to producing aluminium hydroxide grains with homogeneous size.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com