Patents
Literature
108 results about "Nanomesh" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
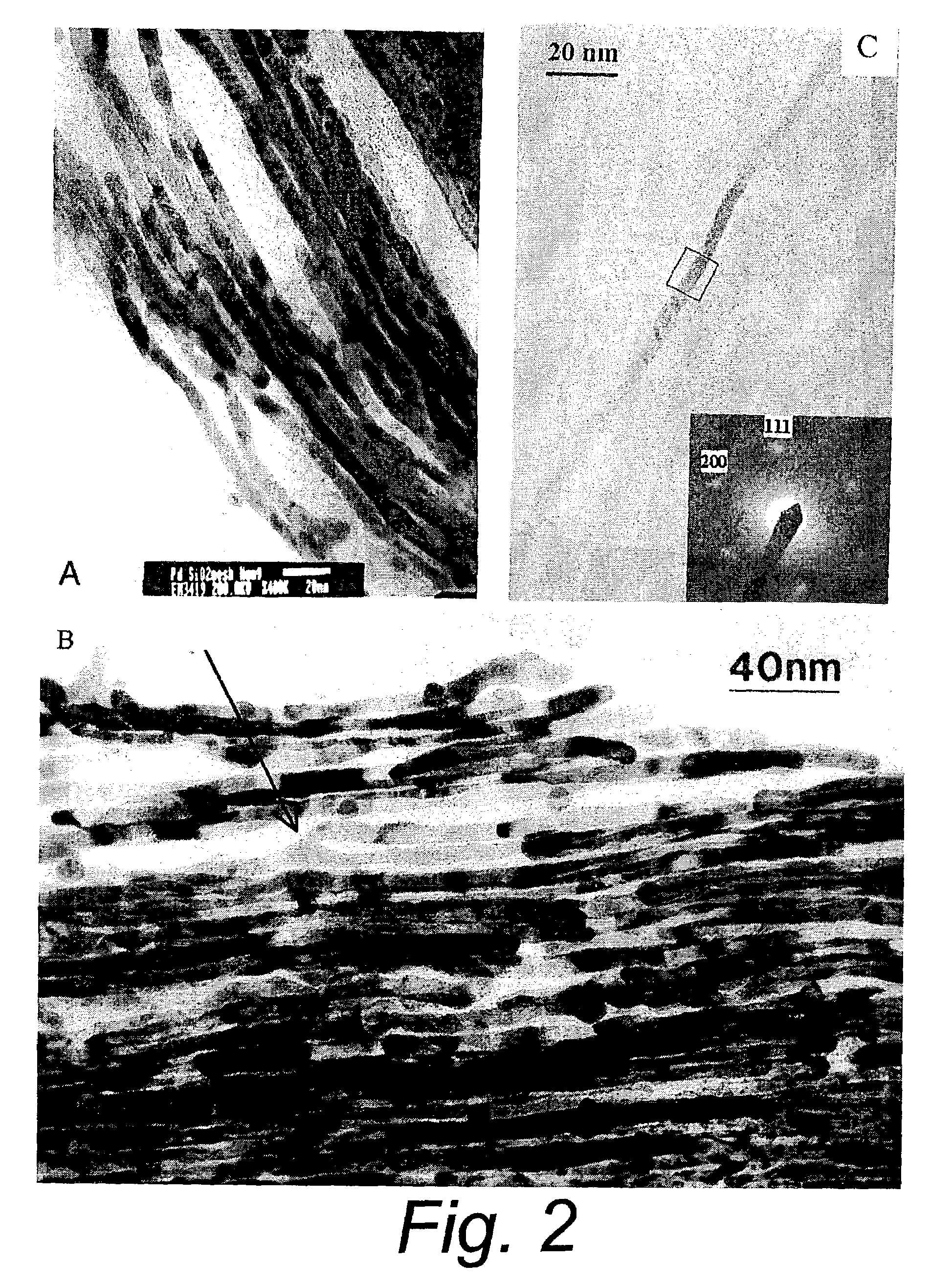
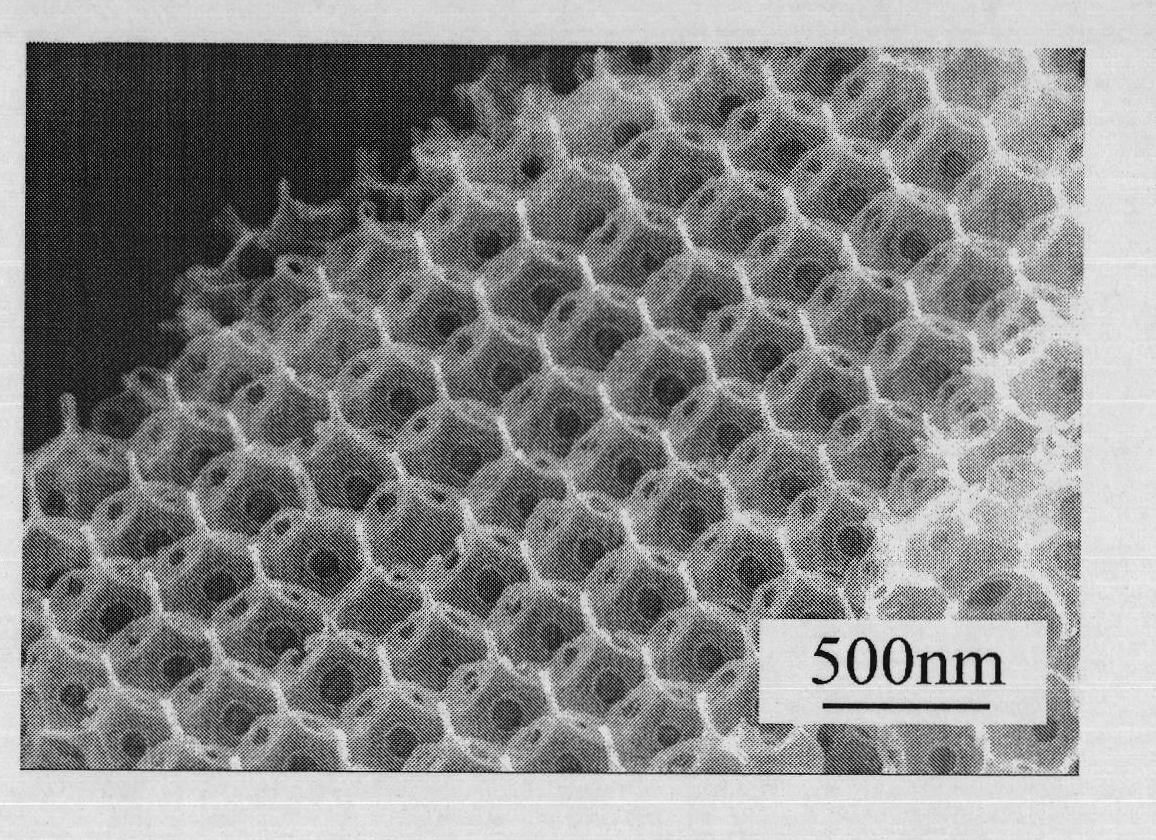
The nanomesh is a inorganic nanostructured two-dimensional material, similar to graphene. It was discovered in 2003 at the University of Zurich, Switzerland . It consists of a single layer of boron (B) and nitrogen (N) atoms, which forms by self-assembly into a highly regular mesh after high-temperature exposure of a clean rhodium or ruthenium surface to borazine under ultra-high vacuum.
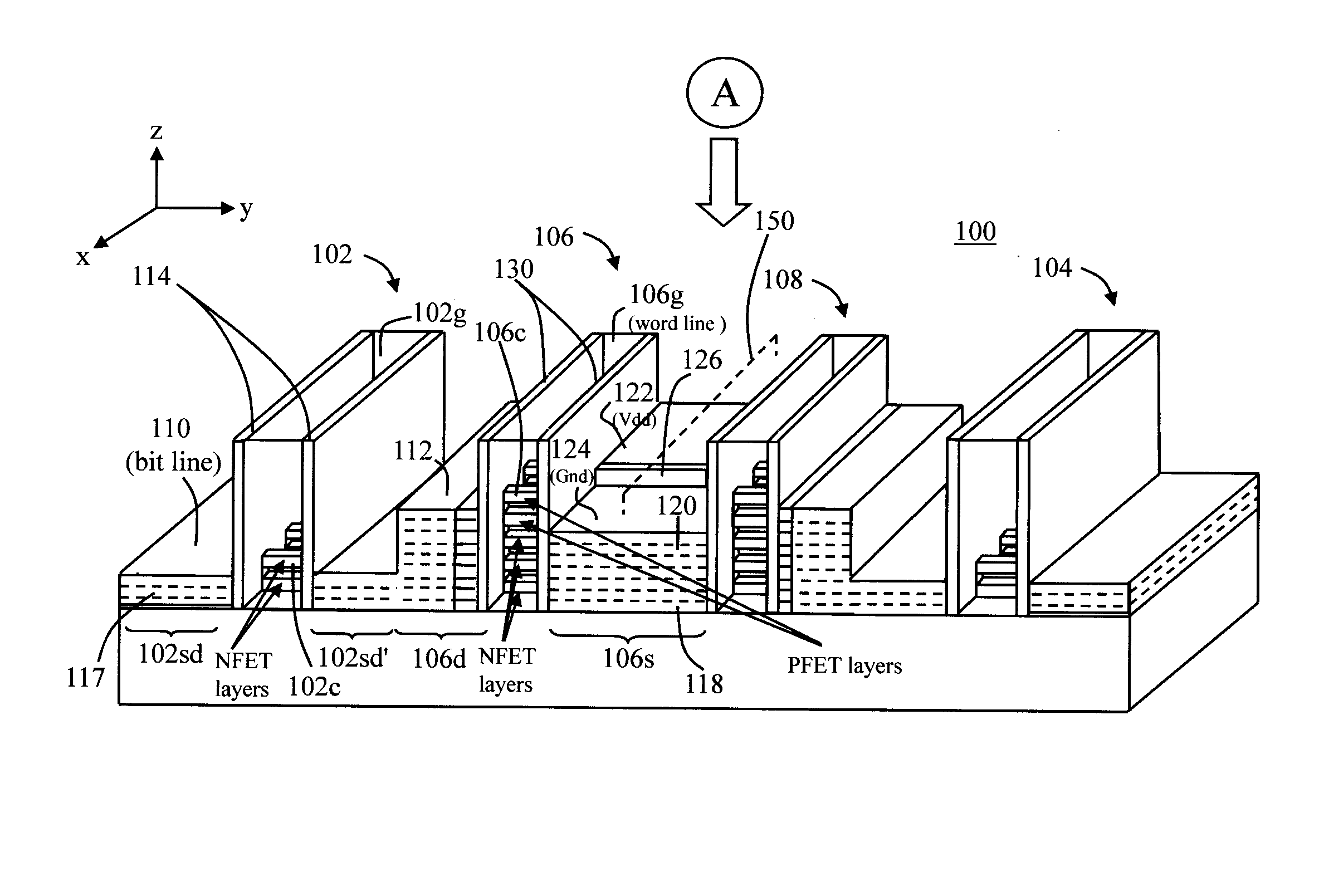
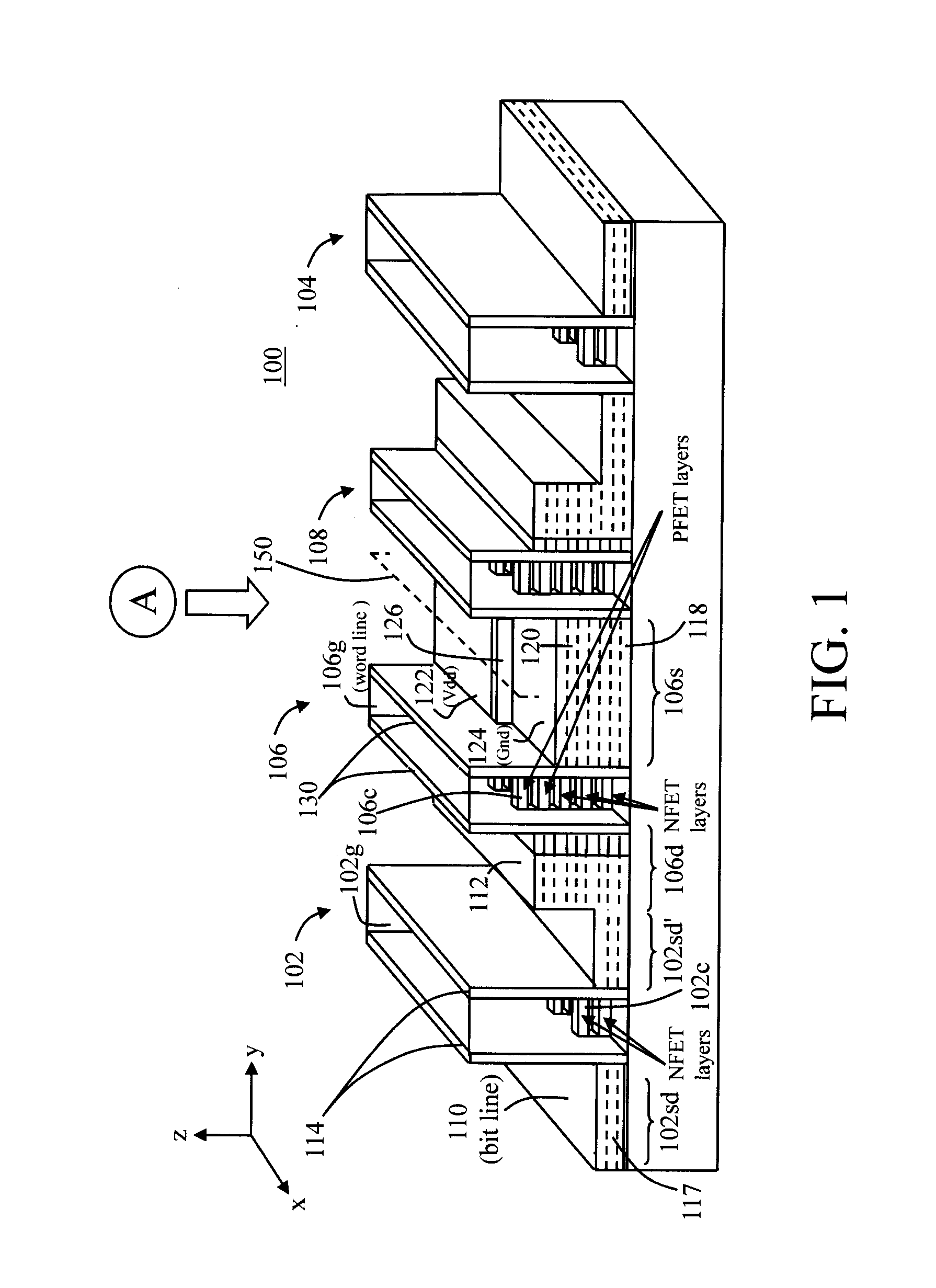
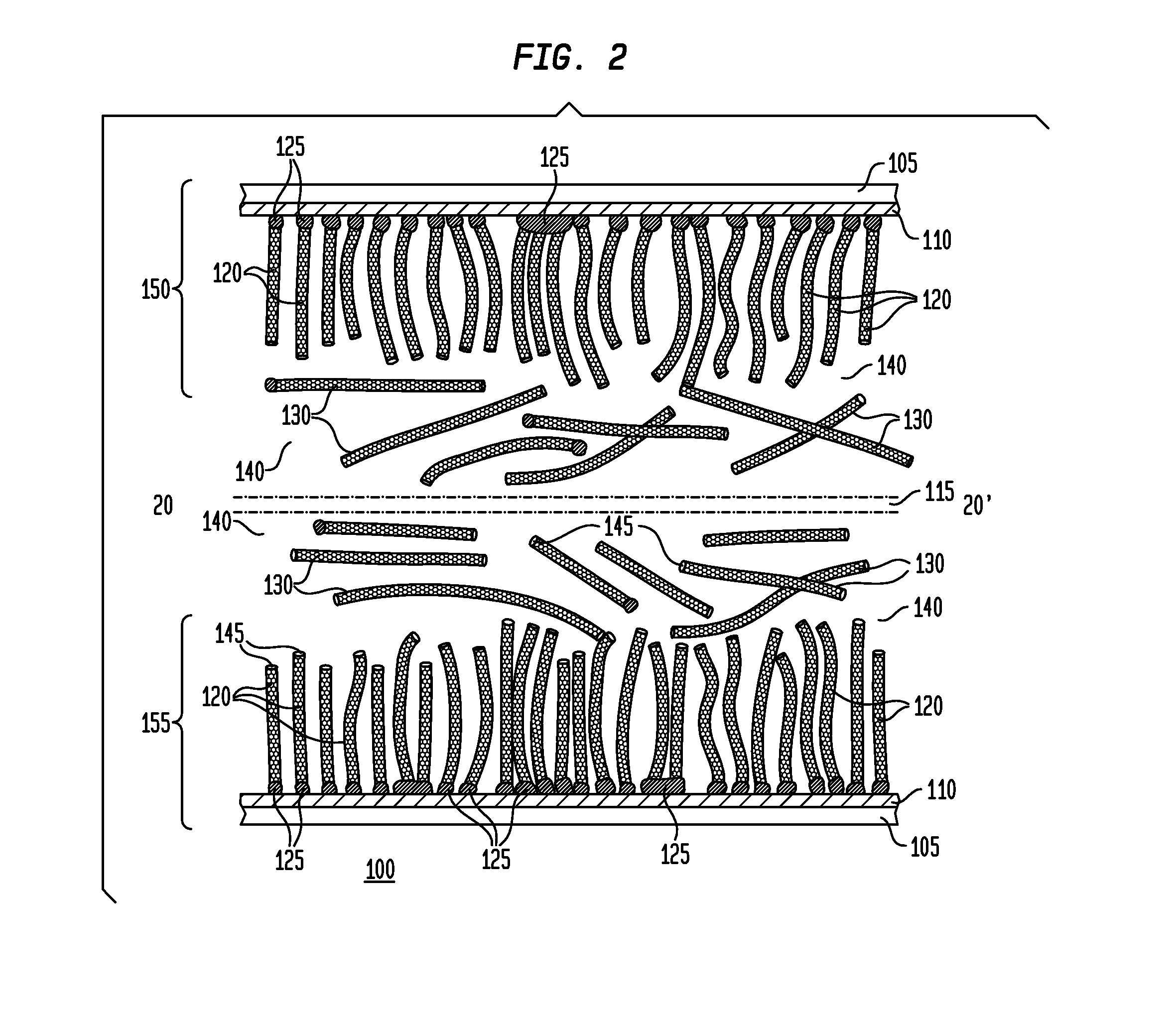
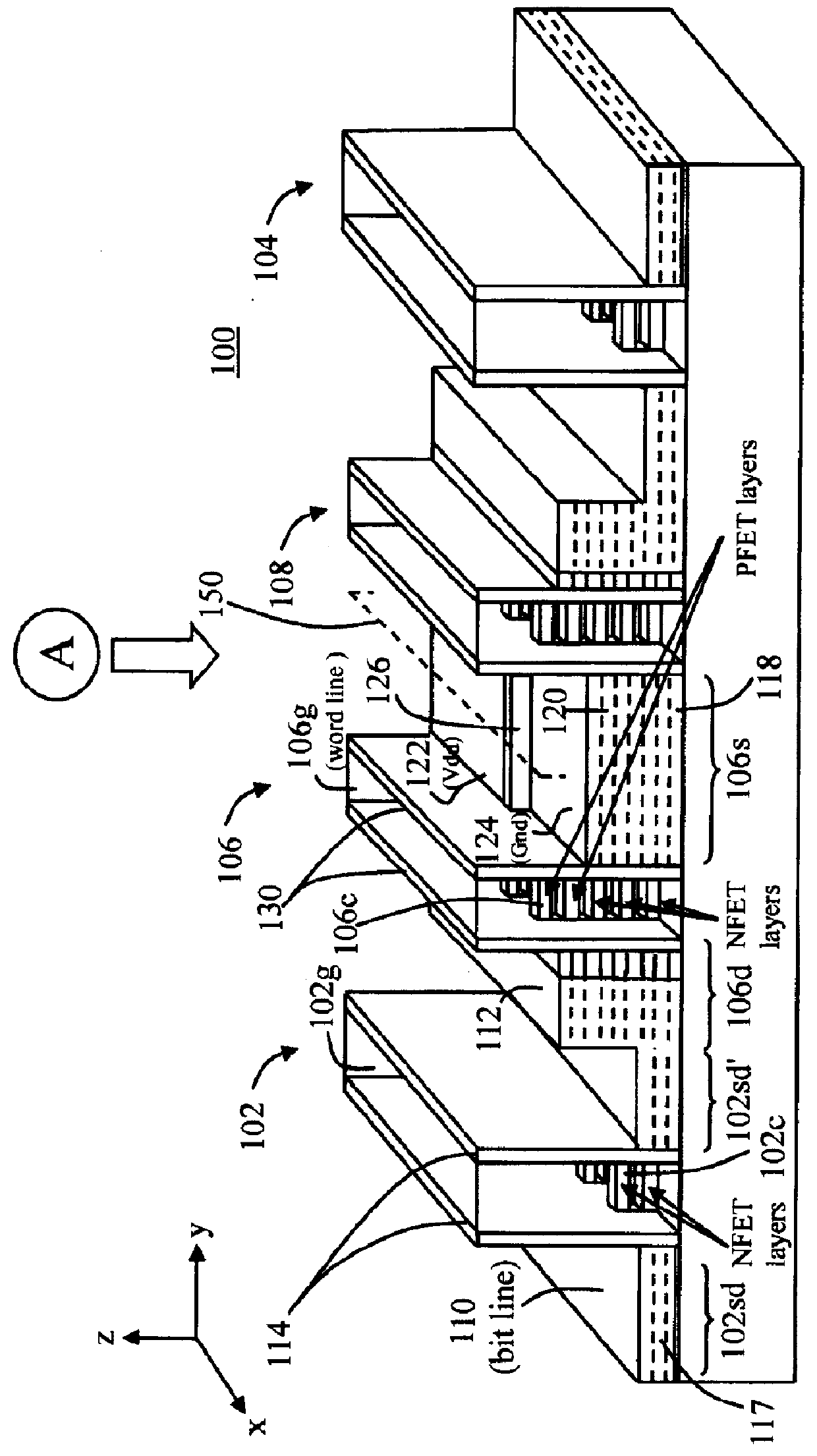
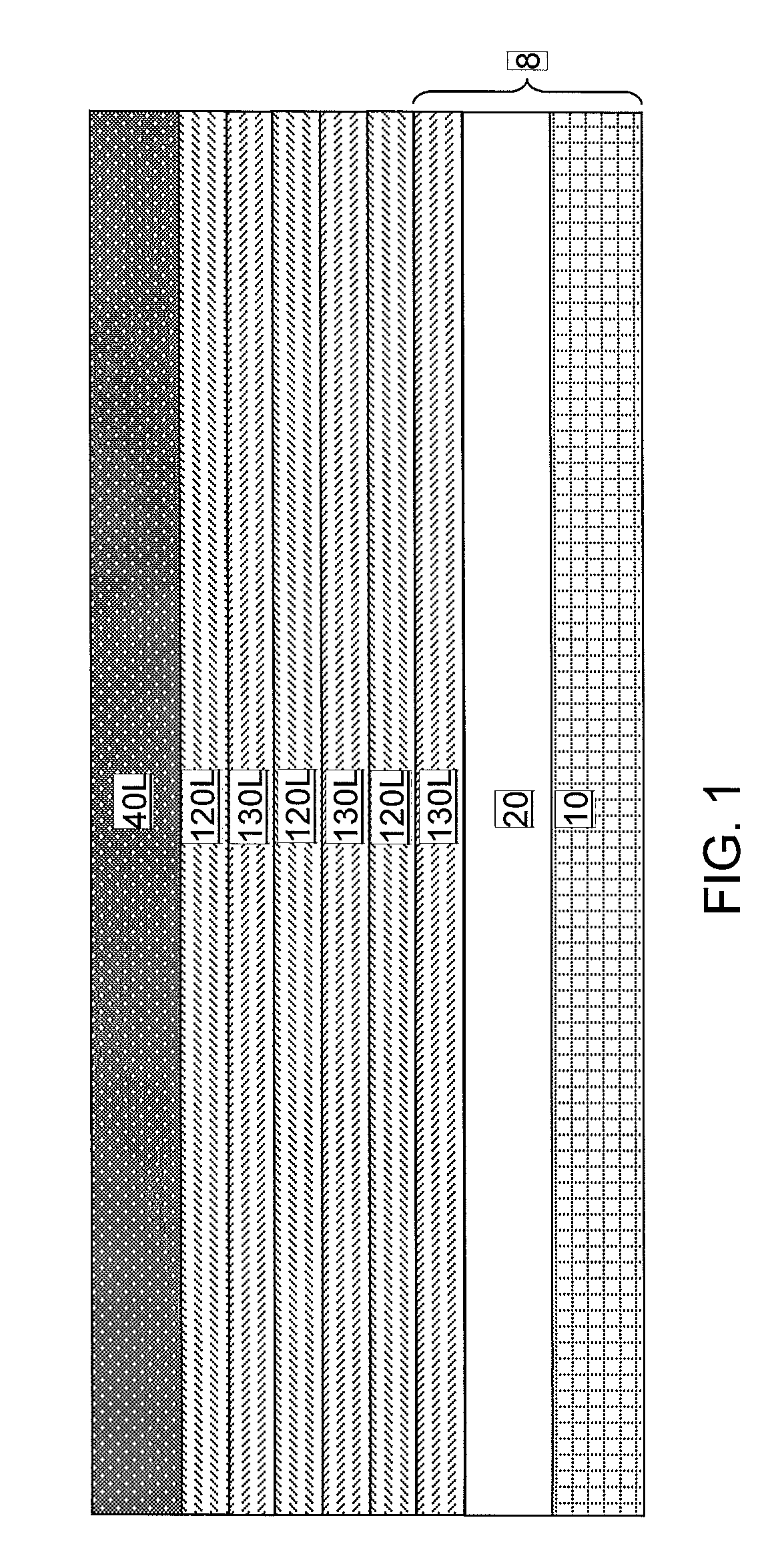
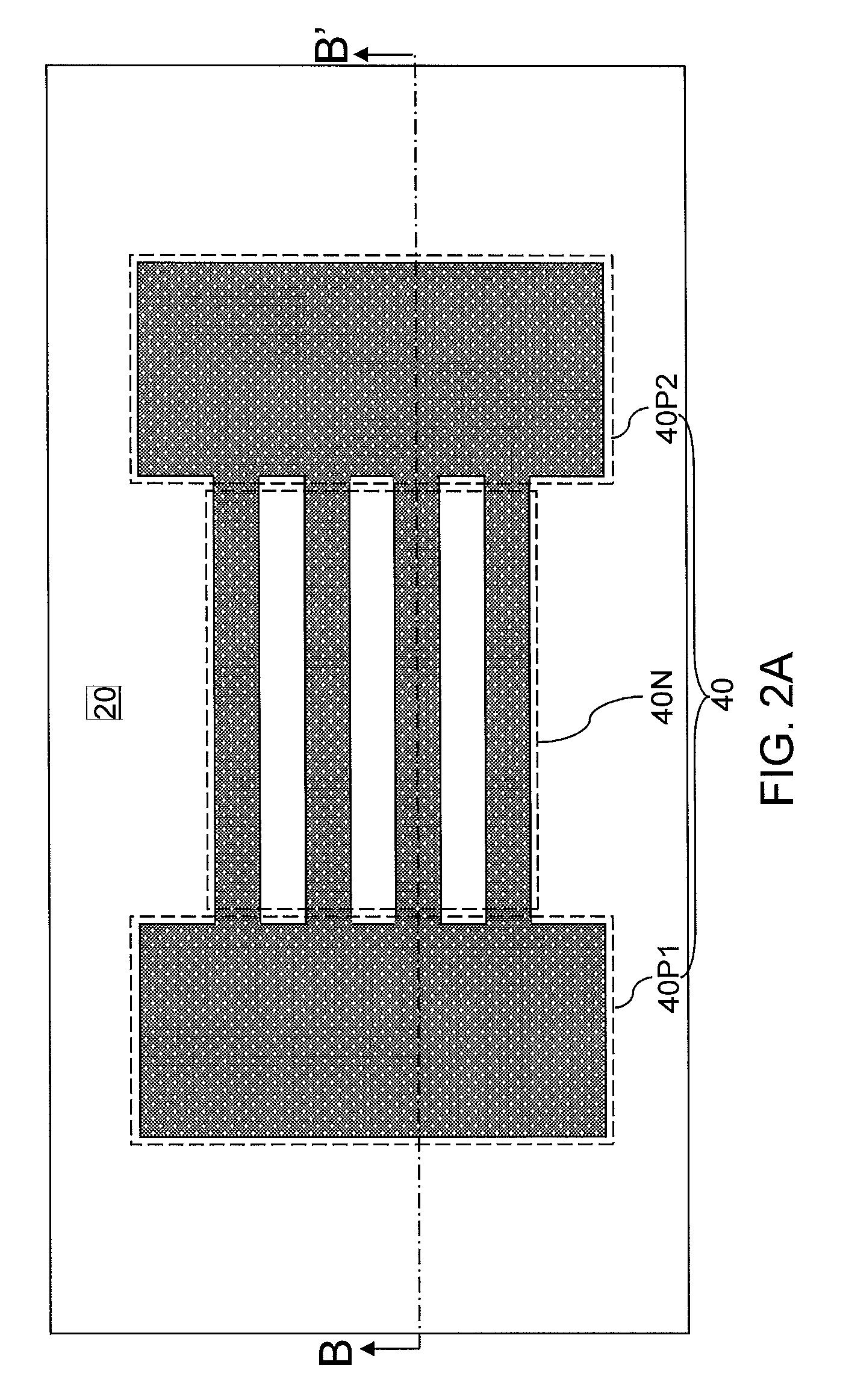
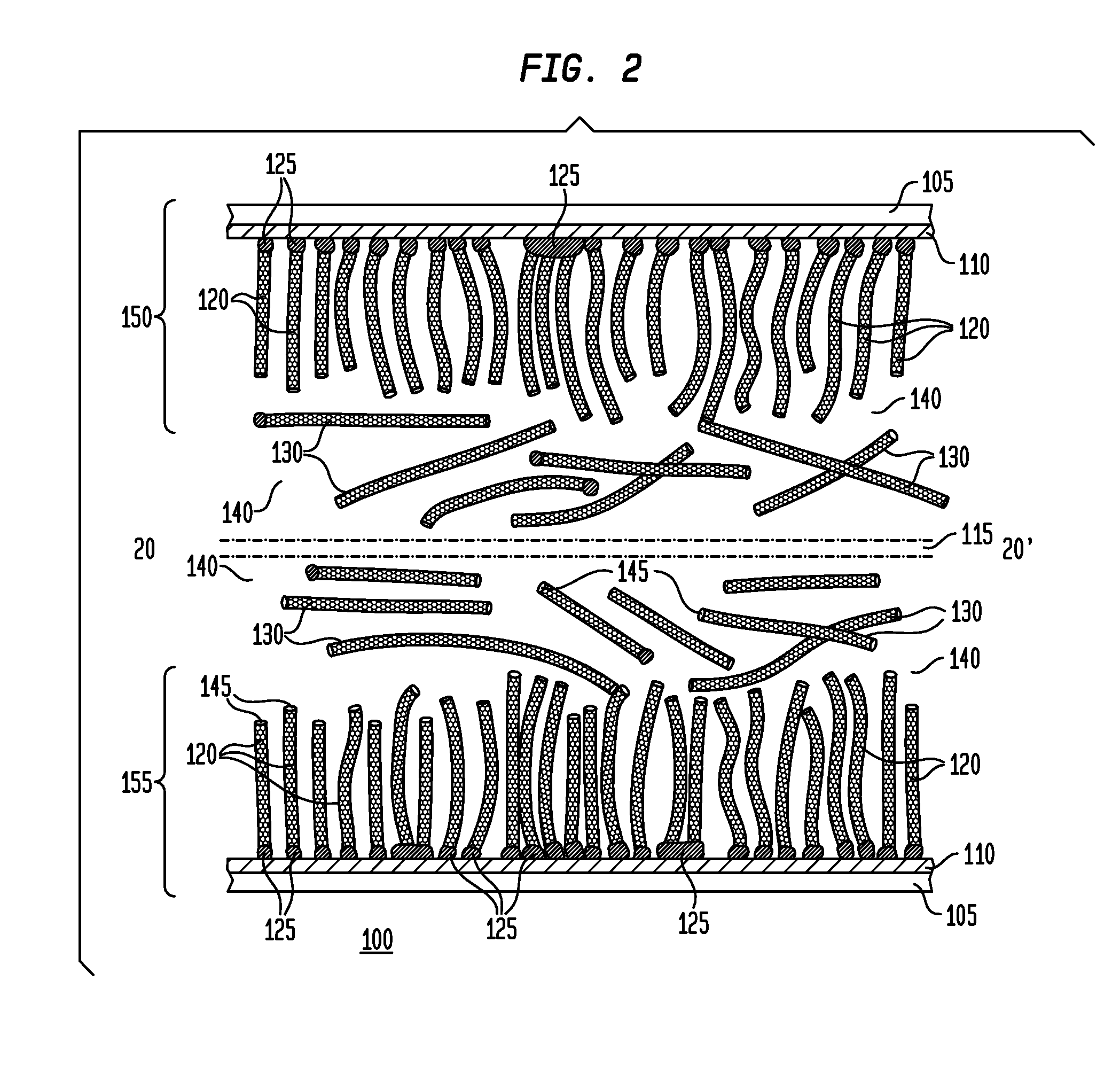
Nanomesh SRAM Cell
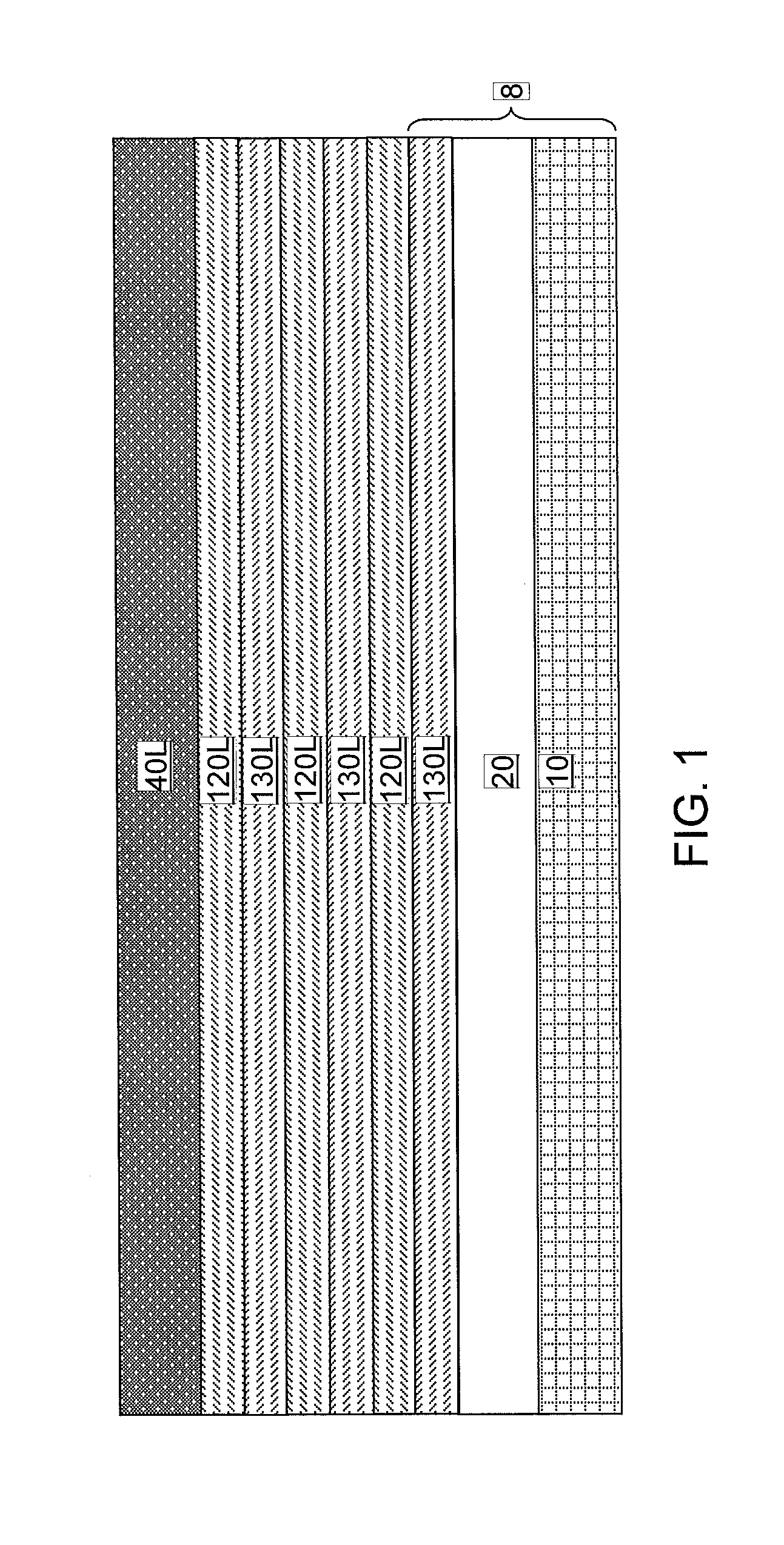
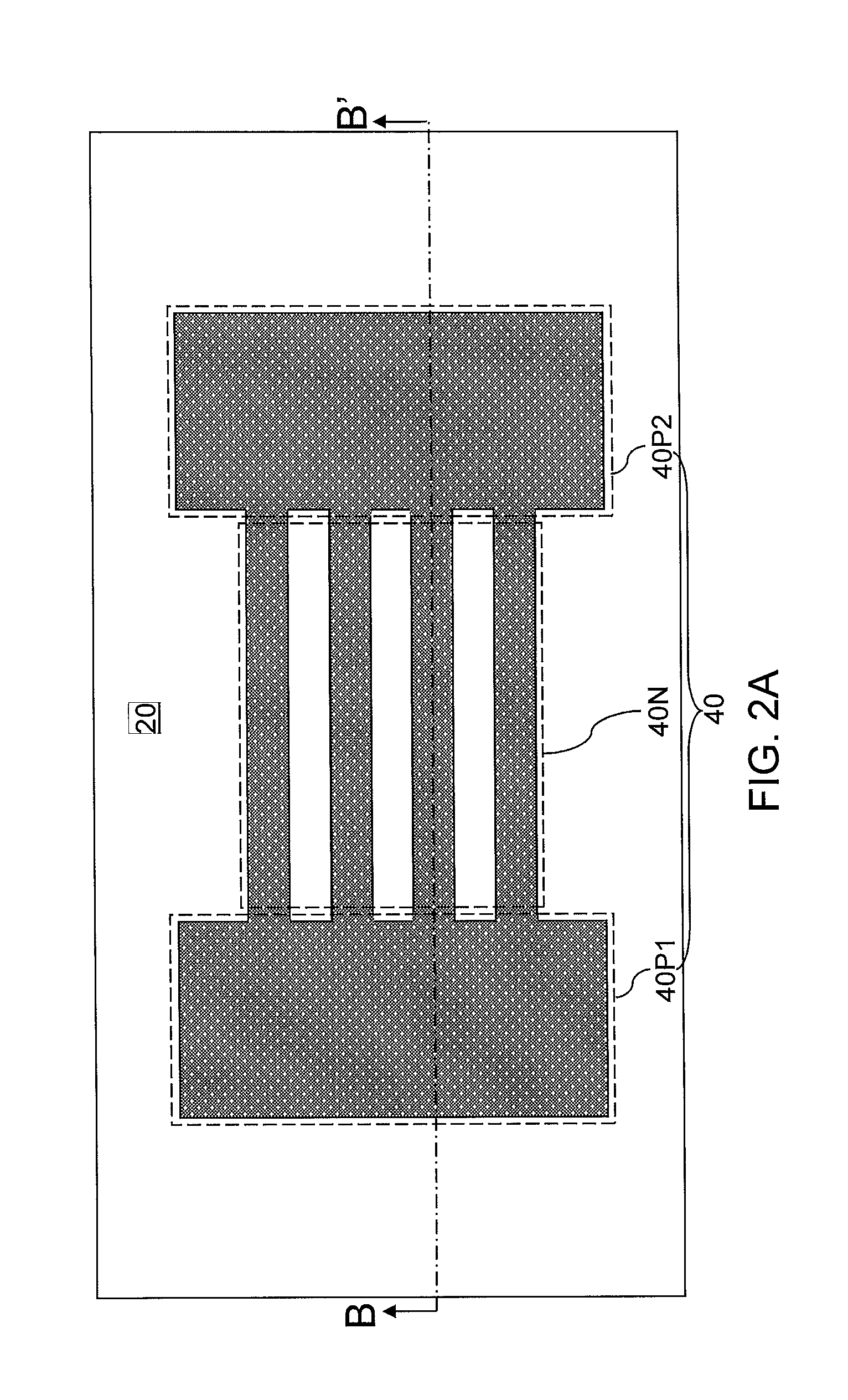
Nanowire-based devices are provided. In one aspect, a SRAM cell includes at least one pair of pass gates and at least one pair of inverters formed adjacent to one another on a wafer. Each pass gate includes one or more device layers each having a source region, a drain region and a plurality of nanowire channels connecting the source region and the drain region and a gate common to each of the pass gate device layers surrounding the nanowire channels. Each inverter includes a plurality of device layers each having a source region, a drain region and a plurality of nanowire channels connecting the source region and the drain region and a gate common to each of the inverter device layers surrounding the nanowire channels.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Composite-coated lithium iron phosphate and preparation method therefor, and lithium ion battery
ActiveUS20180097228A1Improve conductivityHigh activityMaterial nanotechnologyElectrode thermal treatmentNanonetworkConductive polymer
A composite-coated lithium iron phosphate in a three-dimensional nanonetwork layered structure and a preparation method therefor, and a lithium ion battery, wherein a composite is prepared by compounding a conducting polymer, graphene and a carbon nano tube. The preparation method for the coated lithium iron phosphate comprises the following steps: doping the composite and anhydrous ferric phosphate in situ in the process of preparing the anhydrous ferric phosphate, serving as a lithium iron phosphate precursor, then mixing the composite in-situ doped anhydrous ferric phosphate, a lithium source, a traditional carbon material and a solvent to obtain slurry, spray drying the slurry, and calcining to obtain the composite-coated lithium iron phosphate in a three-dimensional nanonetwork layered structure. The preparation method is simple and has a wide raw material source, low cost and very broad practical application prospect. Serving as an anode material of the lithium ion battery, the coated lithium iron phosphate has higher electrical conductivity and cycling stability, and more excellent comprehensive electrochemical performance.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-replacement gate nanomesh field effect transistor with epitixially grown source and drain
An alternating stack of two different semiconductor materials is patterned to include two pad regions and nanowire regions. A semiconductor material is laterally etched selective to another semiconductor material to form a nanomesh including suspended semiconductor nanowires. Gate dielectrics, a gate electrode, and a gate cap dielectric are formed over the nanomesh. A dielectric spacer is formed around the gate electrode. The semiconductor materials in the two pad regions and physically exposed portions of the nanomesh are removed employing the dielectric spacer and the gate cap dielectric as an etch mask. A source region and a drain region are epitaxially grown from end surfaces of the nanomesh.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method of and Printable Compositions for Manufacturing a Multilayer Carbon Nanotube Capacitor
InactiveUS20110204020A1Increase powerImprove cycle lifeMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismElectrical conductorCatalyst nanoparticles
Multilayer carbon nanotube capacitors, and methods and printable compositions for manufacturing multilayer carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are disclosed. A first capacitor embodiment comprises: a first conductor; a plurality of fixed CNTs in an ionic liquid, each fixed CNT comprising a magnetic catalyst nanoparticle coupled to a carbon nanotube and further coupled to the first conductor; and a first plurality of free CNTs dispersed and moveable in the ionic liquid. Another capacitor embodiment comprises: a first conductor; a conductive nanomesh coupled to the first conductor; a first plurality of fixed CNTs in an ionic liquid and further coupled to the conductive nanomesh; and a plurality of free CNTs dispersed and moveable in the ionic liquid. Various methods of printing the CNTs and other structures, and methods of aligning and moving the CNTs using applied electric and magnetic fields, are also disclosed.
Owner:NTHDEGREE TECH WORLDWIDE
Method for Exfoliation of Hexagonal Boron Nitride
ActiveUS20110045223A1Simplify the chemical processEasy post-processingNitrogen compoundsLayered productsBulk crystalOrganic solvent
A new method is disclosed for the exfoliation of hexagonal boron nitride into mono- and few-layered nanosheets (or nanoplatelets, nanomesh, nanoribbons). The method does not necessarily require high temperature or vacuum, but uses commercially available h-BN powders (or those derived from these materials, bulk crystals) and only requires wet chemical processing. The method is facile, cost efficient, and scalable. The resultant exfoliated h-BN is dispersible in an organic solvent or water thus amenable for solution processing for unique microelectronic or composite applications.
Owner:NASA
Hybrid nanomesh structures
An alternating stack of first and second semiconductor layers is formed. Fin-defining mask structures are formed over the alternating stack. A planarization dielectric layer and first and second gate cavities therein are subsequently formed. The first and second gate cavities are extended downward by etching the alternating stack employing a combination of the planarization layer and the fin-defining mask structures as an etch mask. The second semiconductor material is isotropically etched to laterally expand the first gate cavity and to form a first array of semiconductor nanowires including the first semiconductor material, and the first semiconductor material is isotropically etched to laterally expand the second gate cavity and to form a second array of semiconductor nanowires including the second semiconductor material. The first and second gate cavities are filled with replacement gate structures. Each replacement gate structure laterally can surround a two-dimensional array of semiconductor nanowires.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
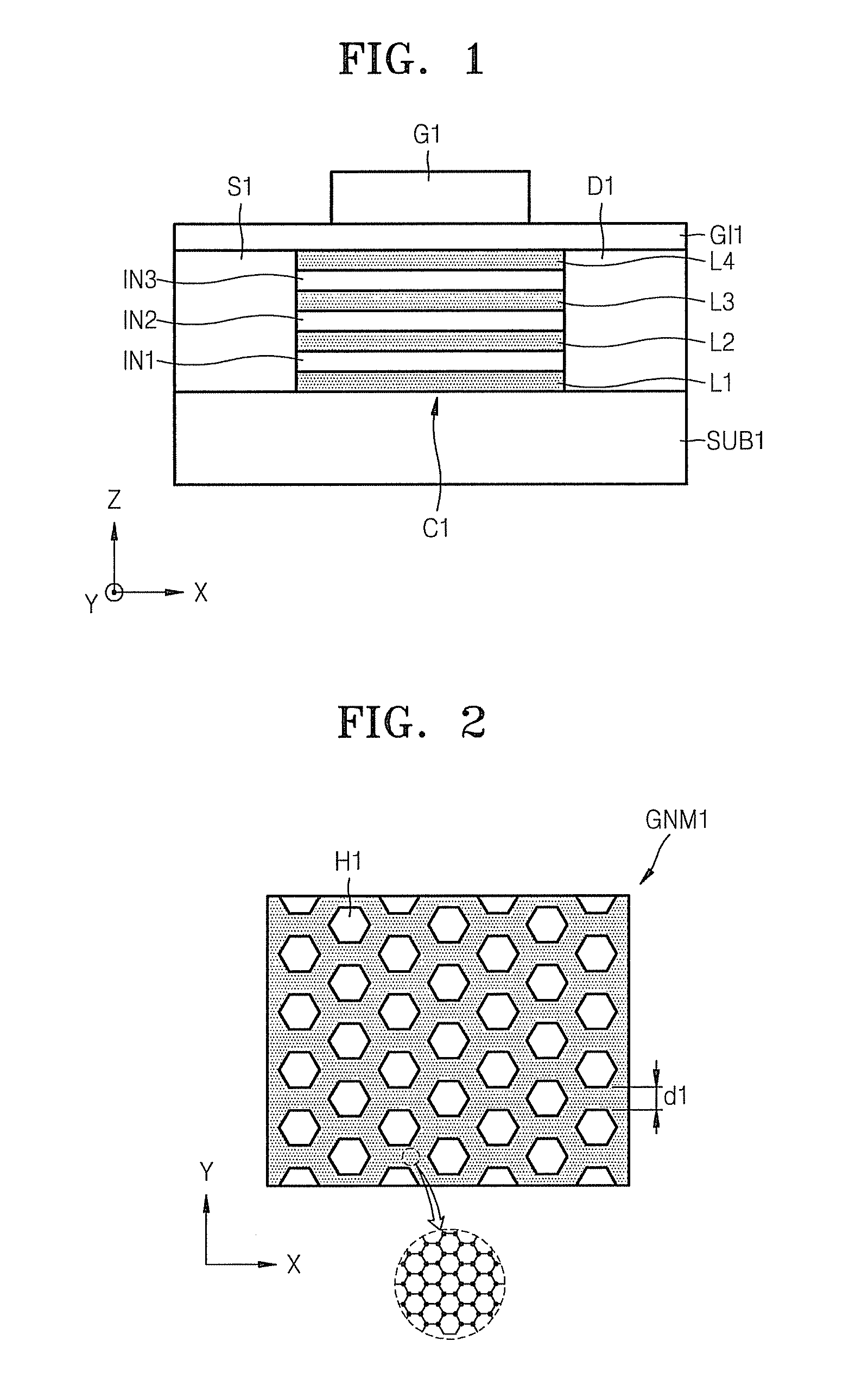
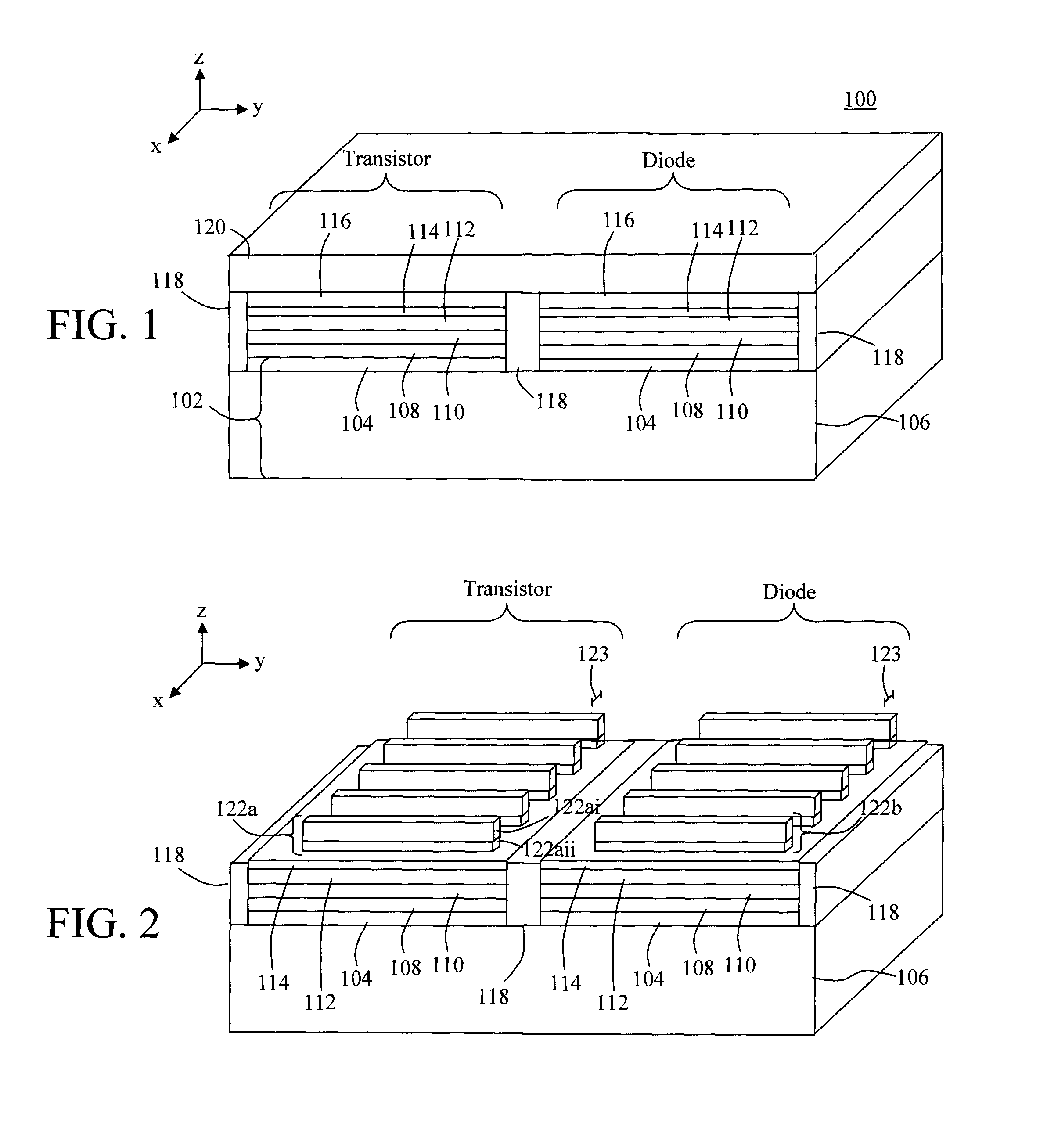
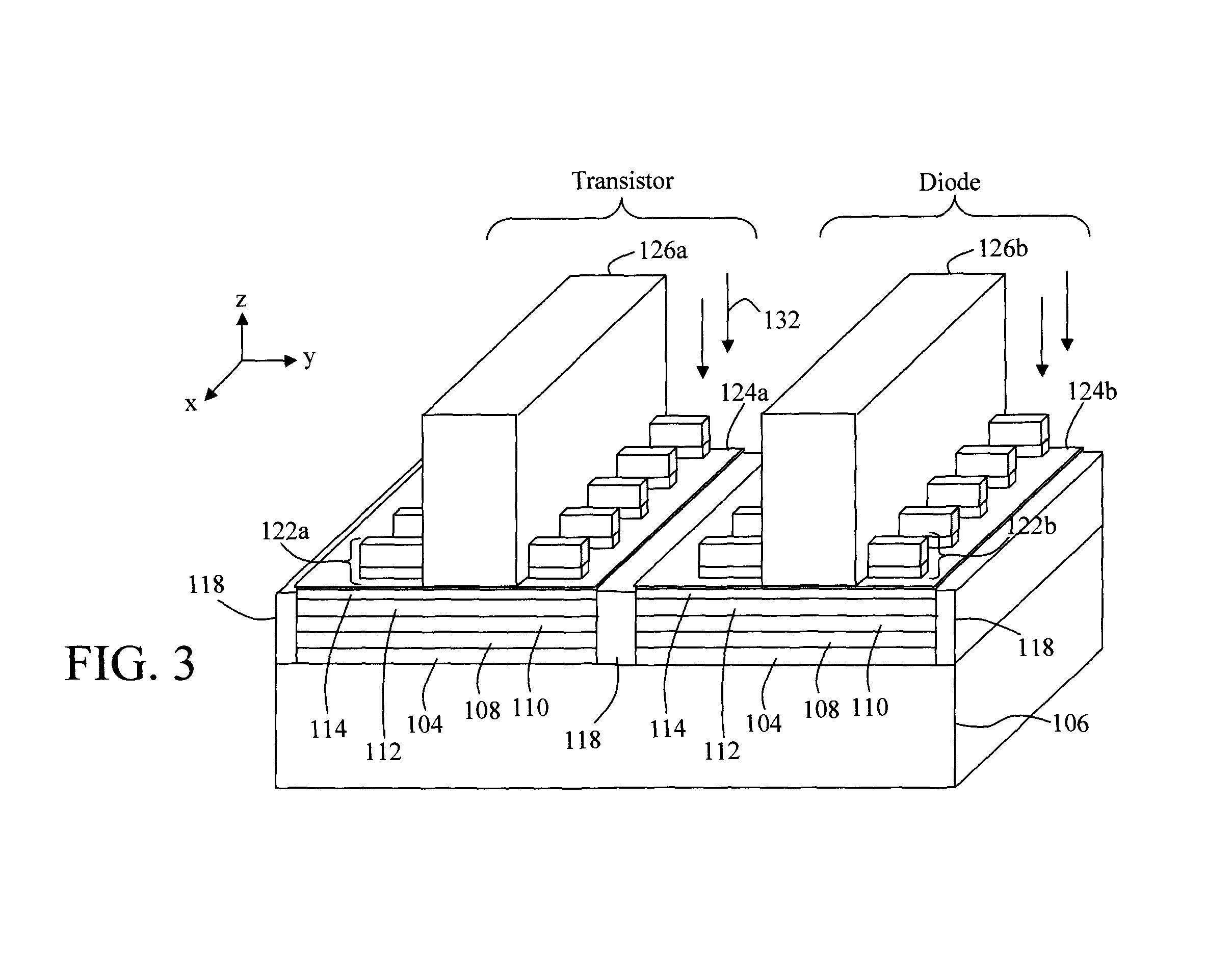
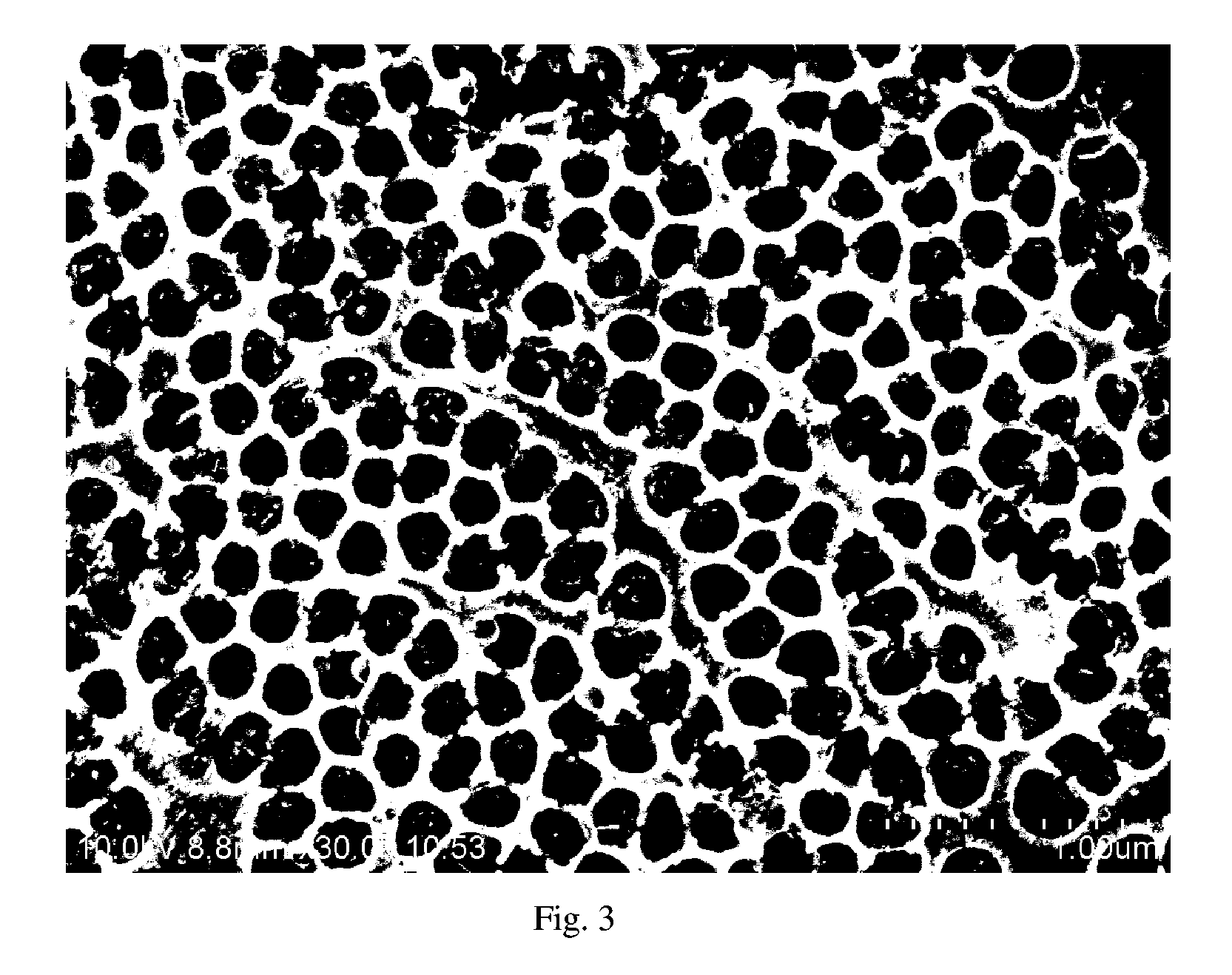
Semiconductor Device, Method Of Manufacturing The Same, And Electronic Device Including The Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20120248414A1Improve uniformityImprove running characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsDevice materialEngineering
An example embodiment relates to a semiconductor device including a semiconductor element. The semiconductor element may include a plurality of unit layers spaced apart from each other in a vertical direction. Each unit layer may include a patterned graphene layer. The patterned graphene layer may be a layer patterned in a nanoscale. The patterned graphene layer may have a nanomesh or nanoribbon structure. The semiconductor device may be a transistor or a diode. An example embodiment relates to a method of making a semiconductor device including a semiconductor element.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Process for the preparation of metal-containing nanostructured films
InactiveUS7001669B2Sufficient structural integrityHigh mechanical strengthNanotechLayered productsNanowireMesoporous silica
Metal-containing nanostructured films are prepared by electrodepositing a metal-containing composition within the pores of a mesoporous silica template to form a metal-containing silica nanocomposite. The nanocomposite is annealed to strengthen the deposited metal-containing composition. The silica is then removed from the nanocomposite, e.g., by dissolving the silica in an etching solution to provide a self-supporting metal-containing nanostructured film. The nanostructured films have a nanowire or nanomesh architecture depending on the pore structure of the mesoporous silica template used to prepare the films.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND
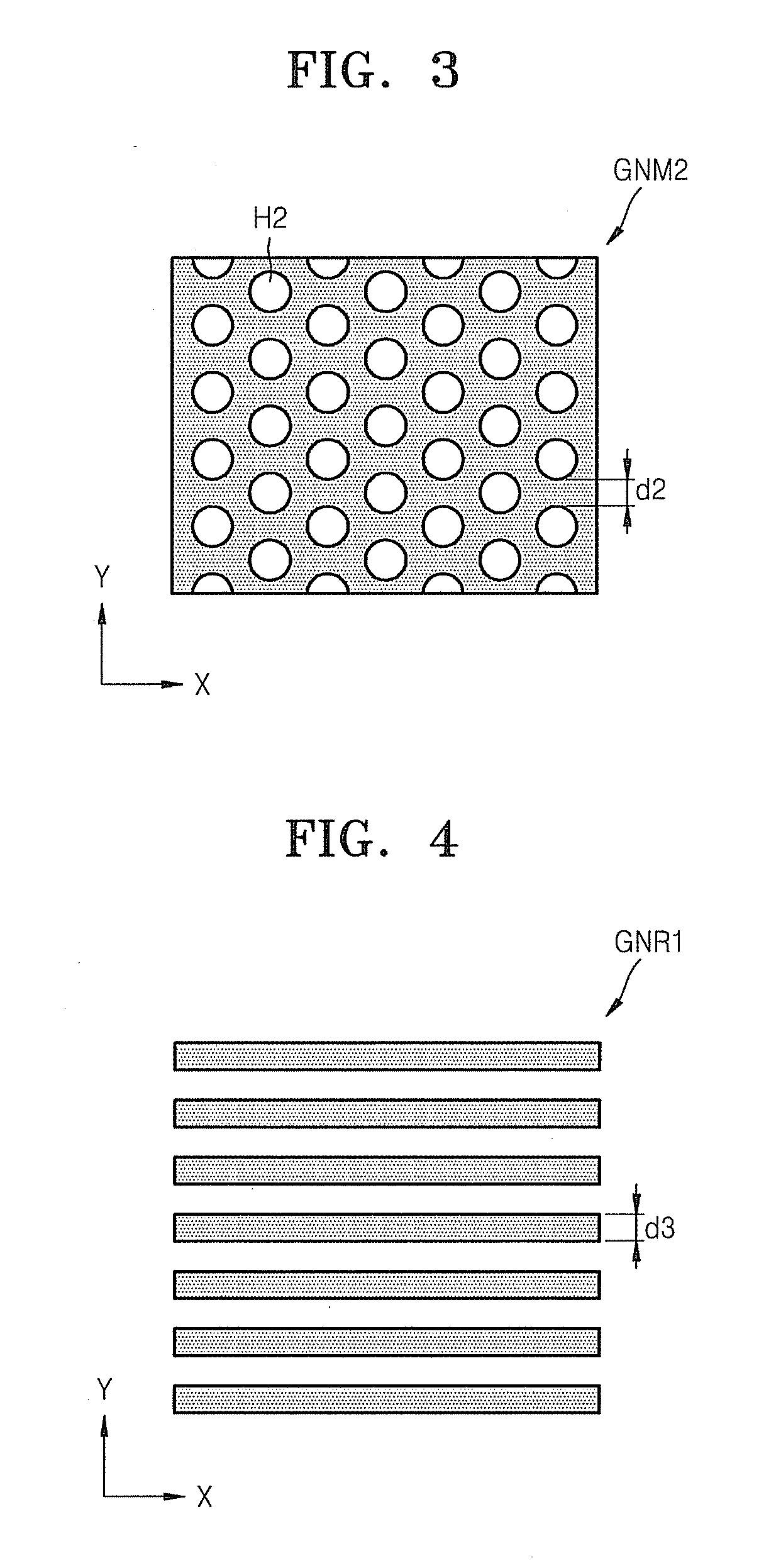
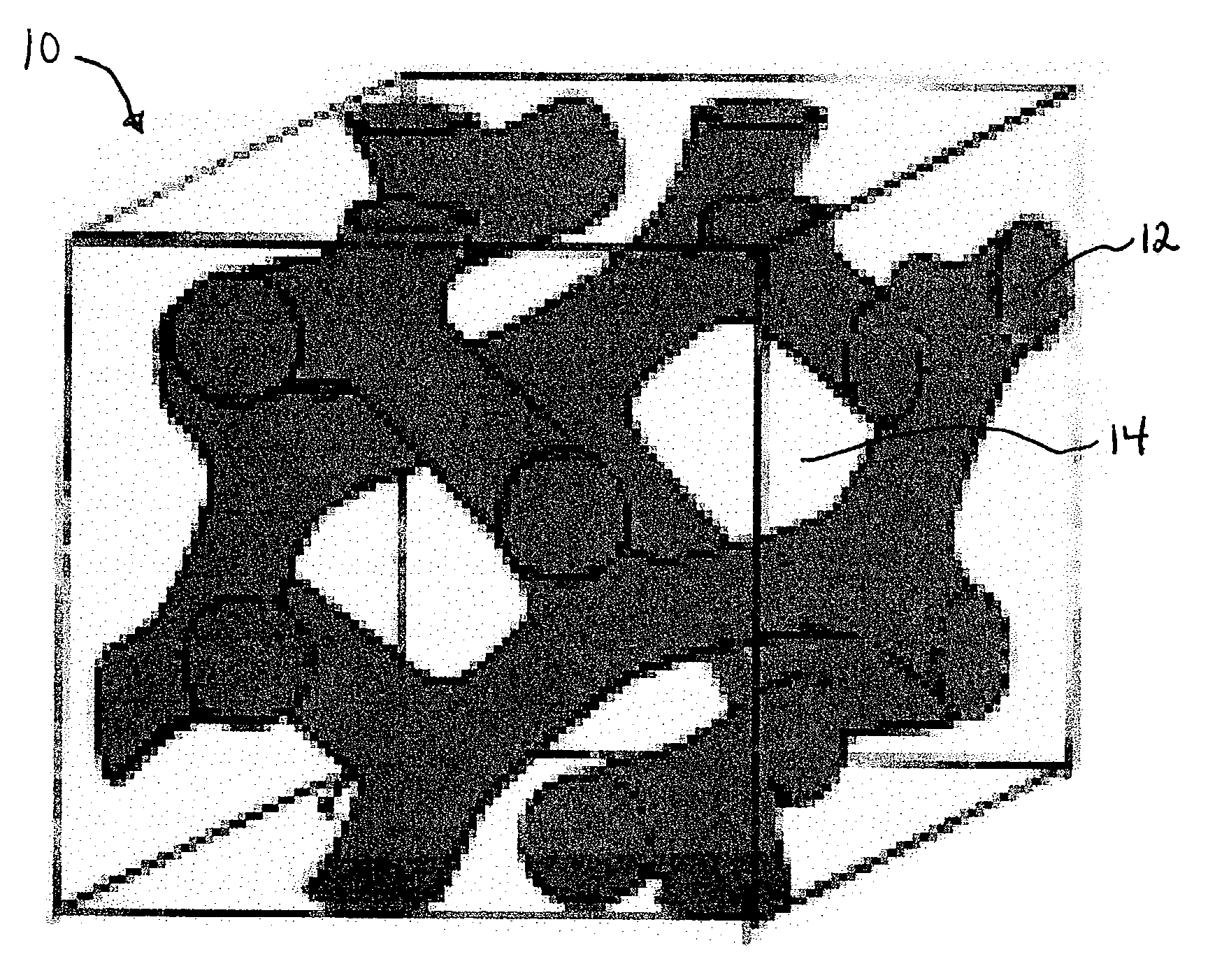
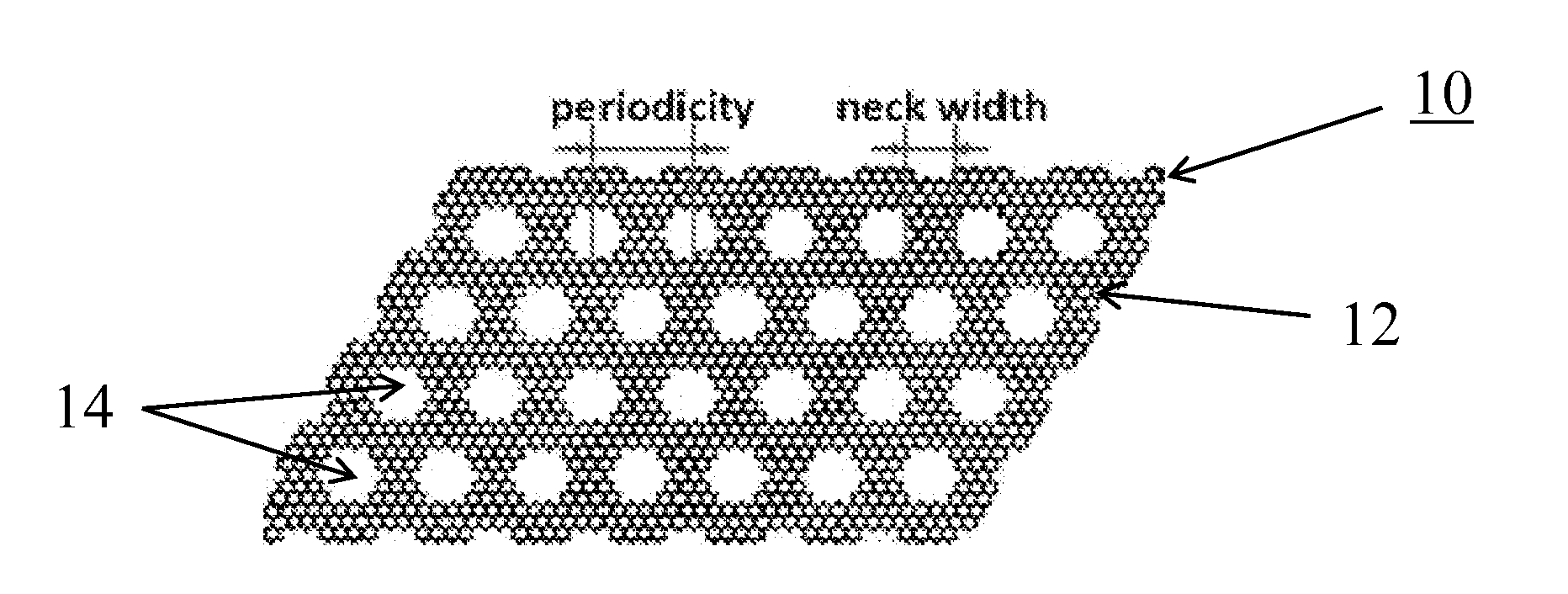
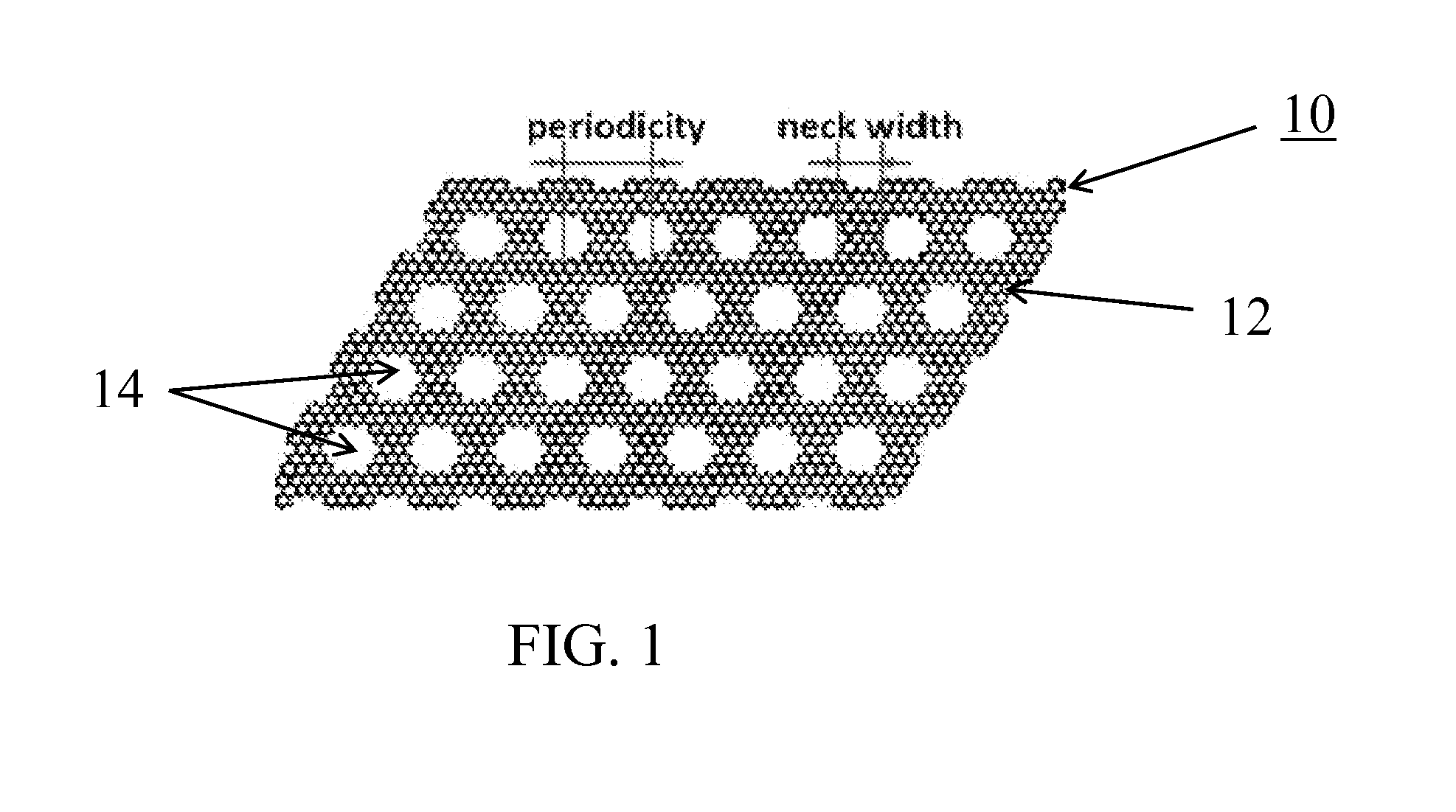
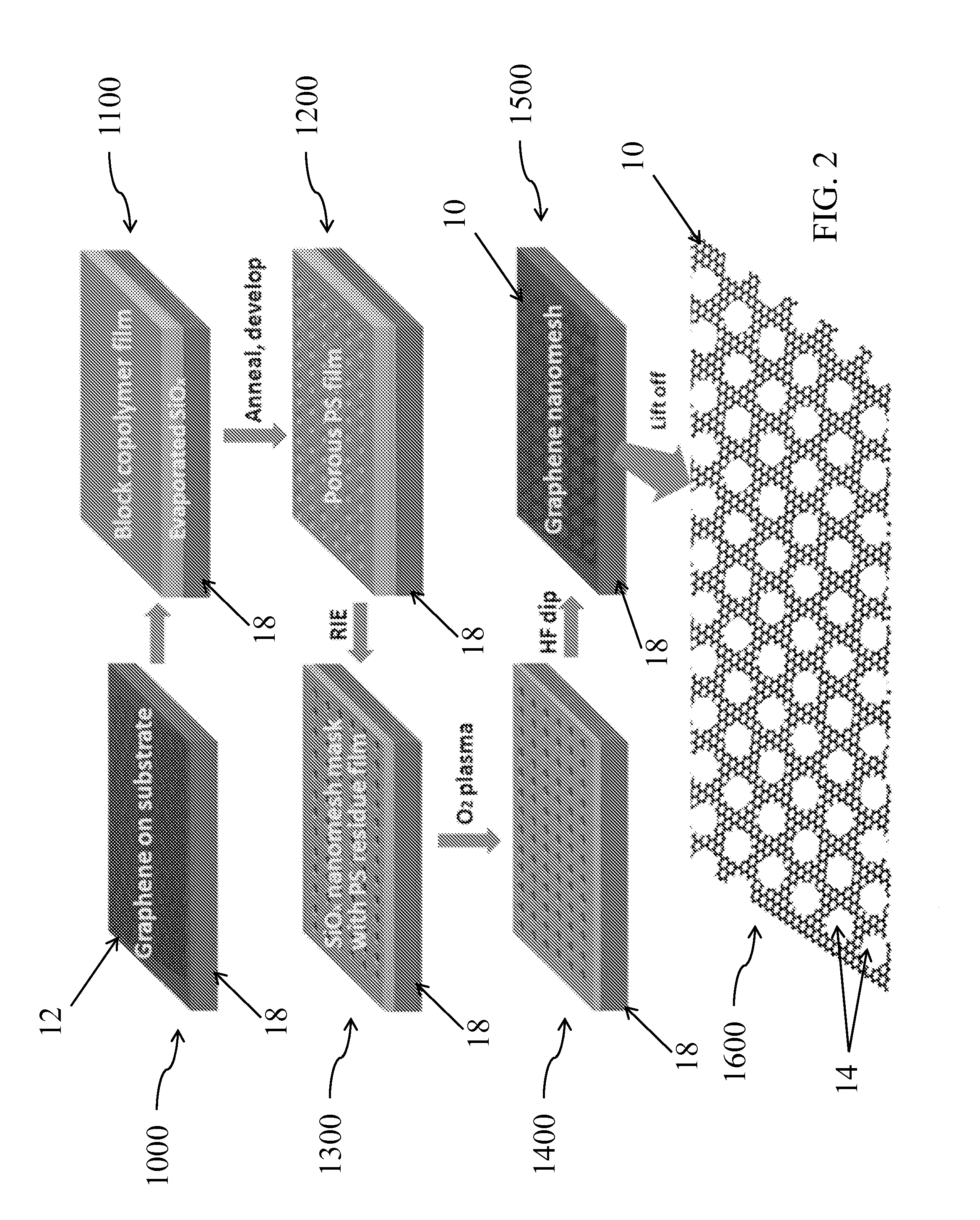
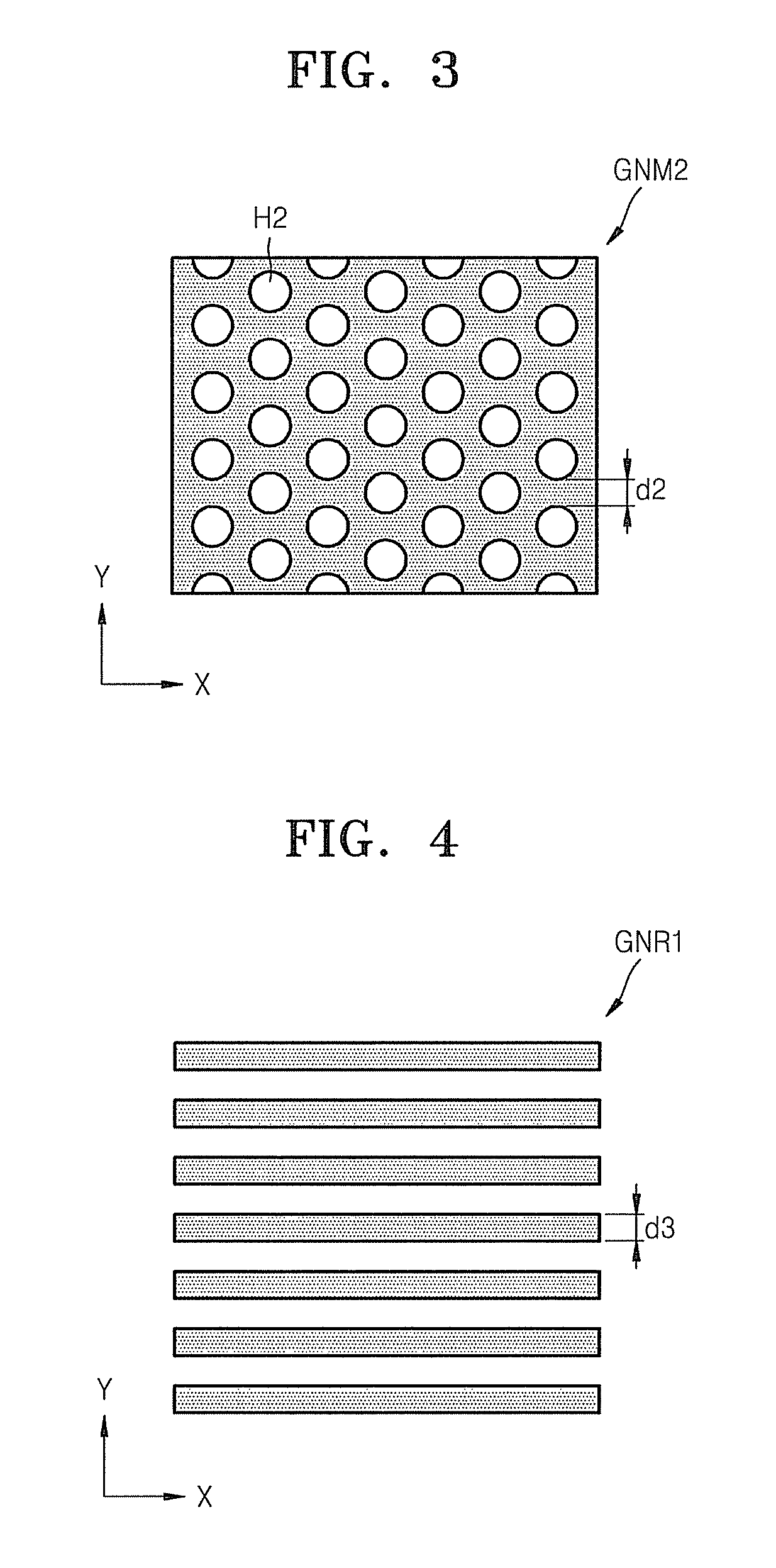
Graphene nanomesh and method of making the same
InactiveUS20120301953A1Uniform periodicityUniform widthMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGraphene nanoribbonsGraphene flake
A graphene nanomesh includes a sheet of graphene having a plurality of periodically arranged apertures, wherein the plurality of apertures have a substantially uniform periodicity and substantially uniform neck width. The graphene nanomesh can open up a large band gap in a sheet of graphene to create a semiconducting thin film. The periodicity and neck width of the apertures formed in the graphene nanomesh may be tuned to alter the electrical properties of the graphene nanomesh. The graphene nanomesh is prepared with block copolymer lithography. Graphene nanomesh field-effect transistors (FETs) can support currents nearly 100 times greater than individual graphene nanoribbon devices and the on-off ratio, which is comparable with values achieved in nanoribbon devices, can be tuned by varying the neck width. The graphene nanomesh may also be incorporated into FET-type sensor devices.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
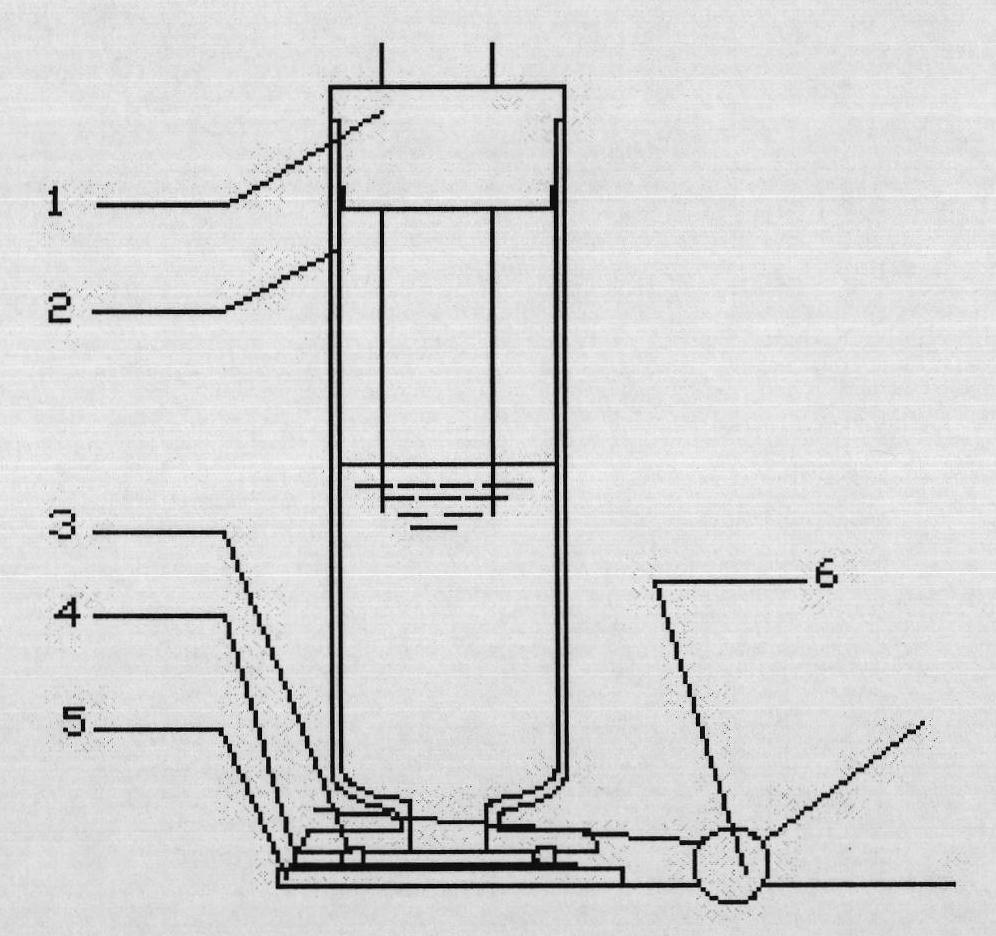
Method for preparing metallic submicron microsphere array film and electric deposition device
InactiveCN101844743AUniform particle sizeAchieve full fillNanostructure manufactureMicrospherePhotonics
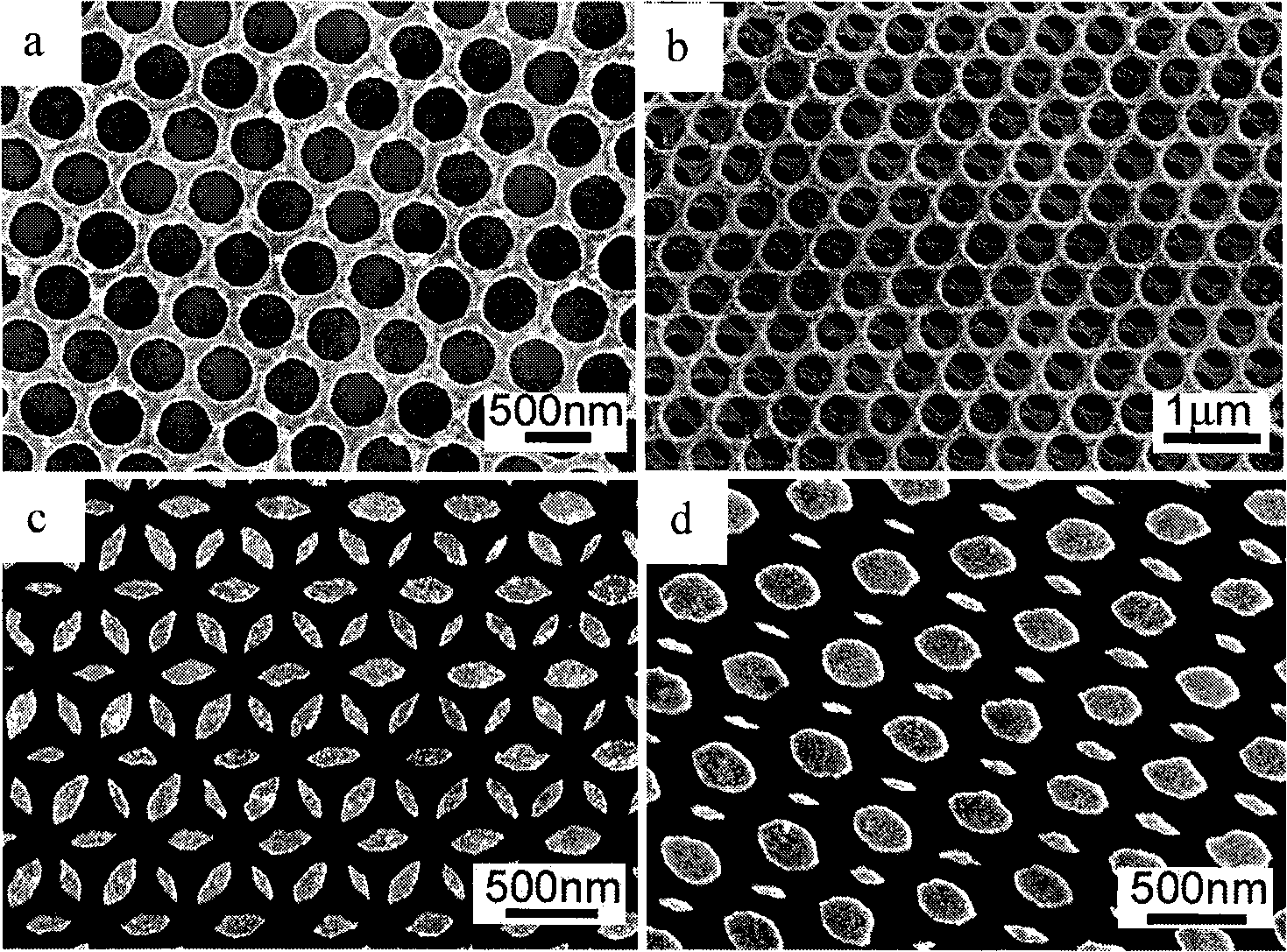
The invention relates to a method for preparing a metallic submicron microsphere array film and an electric deposition device. The method comprises the following steps of: vertically self-assembling polystyrene microspheres to obtain an ordered microsphere array film grown on conductive glass, synthesizing a silicon dioxide macroporous nano net by using the ordered microsphere array film as an initial template and adopting a sol-gel method, and obtaining the metallic submicron microsphere array film attached to the conductive glass by using the nano net as a second-step template and adopting an electrochemical deposition method. The electric deposition device comprises a glass tube filled with electroplating liquid; a tube orifice is sealed by using a plug containing platinum opposite electrodes and a silver / silver chloride reference electrode on the upper part of the glass tube; and the lower part of the glass tube is connected with an inverse opal film attached to the surface of the conductive glass through an O-shaped gasket and fixed on the inverse opal film. The method solves the problem of difficulty in preparing the high-ordered metallic microsphere array film, and lays a foundation for researching three-dimensional photonic band gap performance of a metallic microsphere array, particularly silver spheres with special optical property.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Nanomesh SRAM Cell
Nanowire-based devices are provided. In one aspect, a SRAM cell includes at least one pair of pass gates and at least one pair of inverters formed adjacent to one another on a wafer. Each pass gate includes one or more device layers each having a source region, a drain region and a plurality of nanowire channels connecting the source region and the drain region and a gate common to each of the pass gate device layers surrounding the nanowire channels. Each inverter includes a plurality of device layers each having a source region, a drain region and a plurality of nanowire channels connecting the source region and the drain region and a gate common to each of the inverter device layers surrounding the nanowire channels.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method for exfoliation of hexagonal boron nitride
ActiveUS8303922B2Simple processEasy to processNitrogen compoundsLayered productsBulk crystalOrganic solvent
A new method is disclosed for the exfoliation of hexagonal boron nitride into mono- and few-layered nanosheets (or nanoplatelets, nanomesh, nanoribbons). The method does not necessarily require high temperature or vacuum, but uses commercially available h-BN powders (or those derived from these materials, bulk crystals) and only requires wet chemical processing. The method is facile, cost efficient, and scalable. The resultant exfoliated h-BN is dispersible in an organic solvent or water thus amenable for solution processing for unique microelectronic or composite applications.
Owner:NASA
Nitrogen hybridized carbon nanohorn-graphite nanocomposite, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103515627AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCatalyst carriersPtru catalystMaterials science
The invention discloses a nitrogen hybridized carbon nanohorn-graphite nanocomposite, a preparation method thereof and application of the nanocomposite as a catalyst carrier. A nanometer composite catalyst provided by the invention is composed of the nitrogen hybridized carbon nanohorn-graphite nanocomposite and a transition metal and / or transition metal alloy nano-cluster, wherein the mass percentage content of the transition metal and / or transition metal alloy nano-cluster is 0.1 to 80%, the size of the transition metal and / or transition metal alloy nano-cluster is 0.5 to 20 nm, and the transition metal and / or transition metal alloy nano-cluster is dispersed in a porous nanometer network formed by nitrogen hybridized carbon nanohorns and graphite. As a fuel cell catalyst, the nanometer composite catalyst has excellent electrocatalytic activity and stability in reactions like oxygen reduction and methanol oxidation.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Preparing method of metal chalcogenide nanomesh material
InactiveCN103910340AAperture controllableControllable hole arrangementMaterial nanotechnologyMolybdenum sulfidesMetal chalcogenidesMesoporous material
The invention discloses a preparing method of a metal chalcogenide nanomesh material. A mesoporous material is adopted as a template material. The metal chalcogenide nanomesh material is prepared by steps of: preparing a metal precursor into a solution, filling a pore channel space of the mesoporous template material with the solution so as to prepare a mesoporous material loading the metal precursor; mixing the mesoporous material loading the metal precursor with a chalcogenide precursor and putting the mixture into a heating space of a heating device, or putting the mesoporous material loading the metal precursor and the chalcogenide precursor side by side into the heating space of the heating device; raising the temperature rapidly to 300-900 DEG C under the protection of carrier gas and maintaining the temperature for 15-600 min; adding a template corroding agent into the obtained solid powder so that the mesoporous material is fully dissolved in the template corroding solution; and filtering and drying the filter cake. The metal chalcogenide nanomesh material is obtained by synthesis for the first time. The preparation method is free of use of precious metals, free of vacuum conditions, simple in synthetic process, and prone to large-scale production.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Non-replacement gate nanomesh field effect transistor with pad regions
A gate-first processing scheme for forming a nanomesh field effect transistor is provided. An alternating stack of two different semiconductor materials is patterned to include two pad regions and nanowire regions. A semiconductor material is laterally etched selective to another semiconductor material to form a nanomesh including suspended semiconductor nanowires. A stack of a gate dielectric, a gate electrode, and a gate cap dielectric is formed over the nanomesh. A dielectric spacer is formed around the gate electrode. An isotropic etch is employed to remove dielectric materials that are formed in lateral recesses of the patterned alternating stack. A selective epitaxy process can be employed to form a source region and a drain region.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
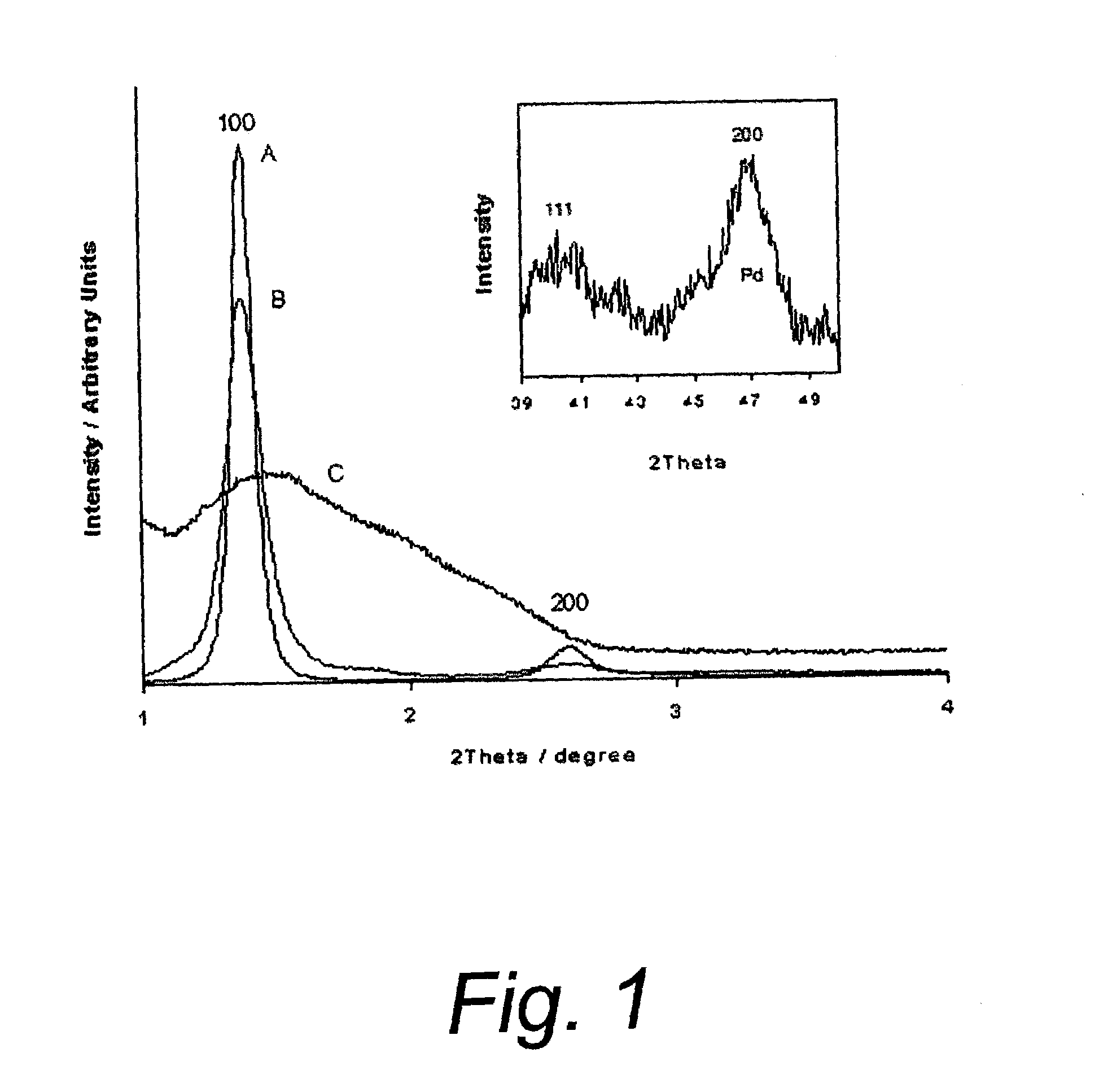
Methods of making platinum and platinum alloy catalysts with nanonetwork structures
InactiveUS7700520B2NanotechOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsNanonetworkPt element
This invention relates to the preparations of noble metal catalysts, i.e., platinum and platinum alloys, on suitable supports with nanonetwork structures and high catalytic efficiencies. A compact structure of a monolayer or a few layers is formed by self-assembly of organic polymer, e.g., polystyrene (PS), nanospheres or inorganic, i.e., silicon dioxide (SiO2), nanospheres on a support surface. In the void spaces of such a compact arrangement, catalyst is formed by filling with catalyst metal ion-containing aqueous solution and reduced by chemical reduction, or formed by vacuum sputtering. When using organic polymer nanospheres as the starting or structure-directing material, the polymer particles are removed by burning at a high temperature and the catalyst having a nanonetwork structure is obtained. In the case of using silicon dioxide nanospheres as the starting material, silicon dioxide particles are dissolved with hydrofluoric acid solution and evaporated away leading to formation of a similar nanonetwork structure made of catalyst. The catalysts prepared by these methods possess characteristics of robust in structure, uniform in hole size and high in catalytic surface area. Their main applications include uses as catalysts in direct methanol and proton exchange membrane fuel cells, as well as in chemical reactors, fuel reformers, catalytic converters, etc.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Preparation method for precious metal and transition metal nanowires and nano reticular material
ActiveCN107326209AEasy to prepareNothing producedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNanowireQuenching
The invention discloses a preparation method for precious metal and transition metal nanowires and a nano reticular material, and belongs to the field of nanomaterial preparation. The preparation method comprises the following steps that firstly, a Cu-Zr-Al-Ag non-crystal alloy thin belt is prepared by adopting a solution fast quenching method; then a suitable corrosive liquid is selected, chemical de-alloying processing is conducted, Zr and Al elements are removed, and a nanoporous copper silver composite material is obtained; after the end of the corrosion process, the nanoporous copper silver composite material is washed repeatedly through distilled water and absolute ethyl alcohol, after the nanoporous copper silver composite material is dried by air, precious metal or transition metal atom clusters are sputtered onto the surface of the nanoporous copper silver composite material through ion sputtering equipment, the precious metal or transition metal nanowires grow out, the diameter of the nanowires is 10-100 nm, and the nanowires grow continuously in a staggered mode to form the nano reticular material. The preparation method is simple and convenient in technology, economical and controllable in process, a prepared precious metal nanonet shows the good performance such as surface enhanced raman scattering (SERS), the broad application prospects in optics, electricity, catalysis, biology and other areas are achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Nitrogen/sulfur-doped three-dimensional carbon nano-network supporting molybdenum disulfide nano-material and preparation of the nano-material
The invention relates to a nitrogen / sulfur-doped three-dimensional carbon nano-network supporting molybdenum disulfide nano-material, and a preparation method and an application of same. The nano-material is formed by supporting molybdenum disulfide nano-sheets on a nitrogen / sulfur-doped three-dimensional carbon nano-network, wherein the molybdenum disulfide nano-sheets are 100-300 nm in size, thickness of the nitrogen / sulfur-doped three-dimensional carbon is 1-10 nm, and radius of the three-dimensional graphene network is 10-50 [mu]m. Mass percentage ratio of the molybdenum disulfide to the total carbon quantity is 0.3-0.8:0.5-0.2.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
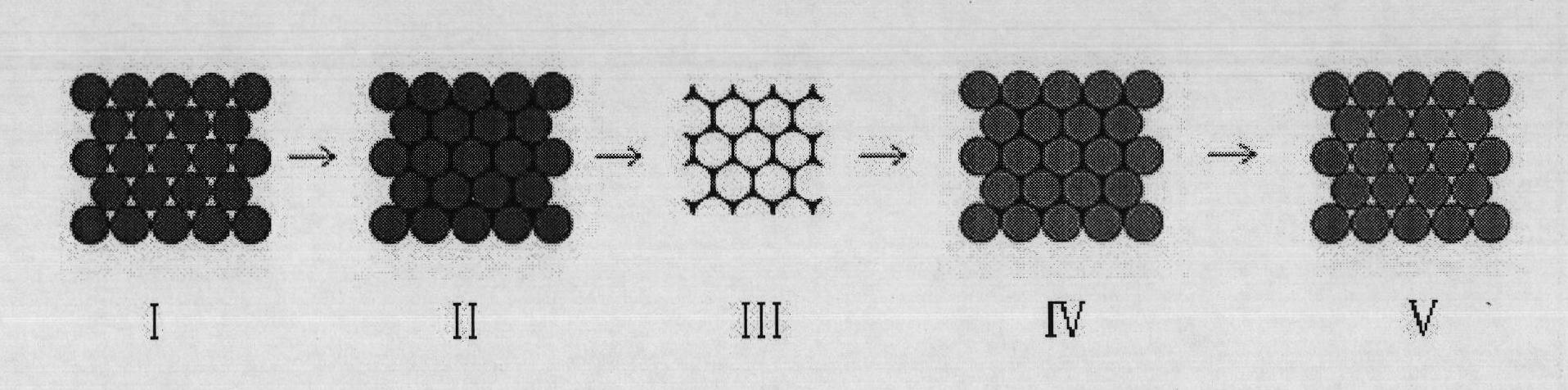
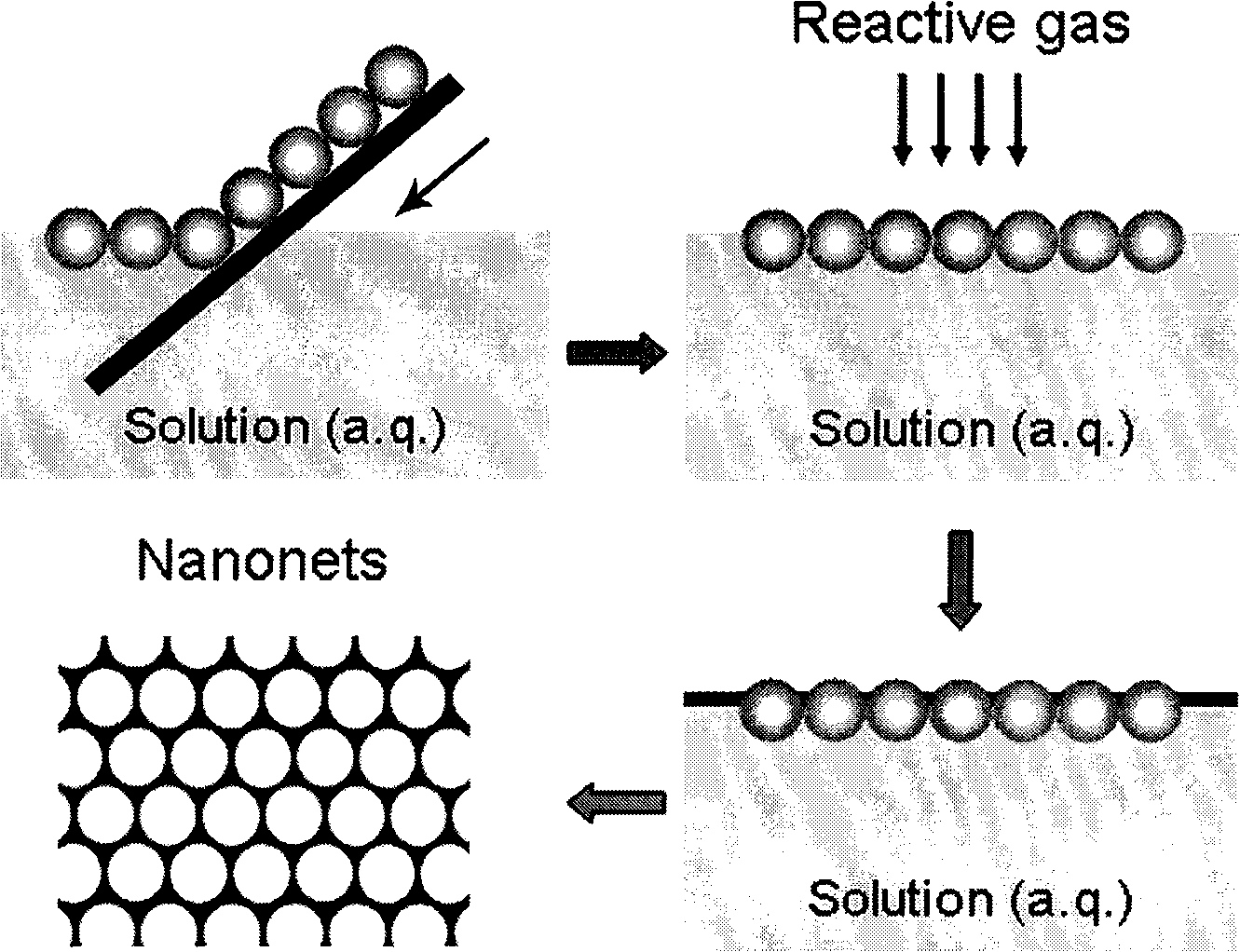
Method for preparing nano-mesh film
InactiveCN101538008AHigh mechanical strengthGood flexibilityIndividual molecule manipulationChemical reactionRoom temperature
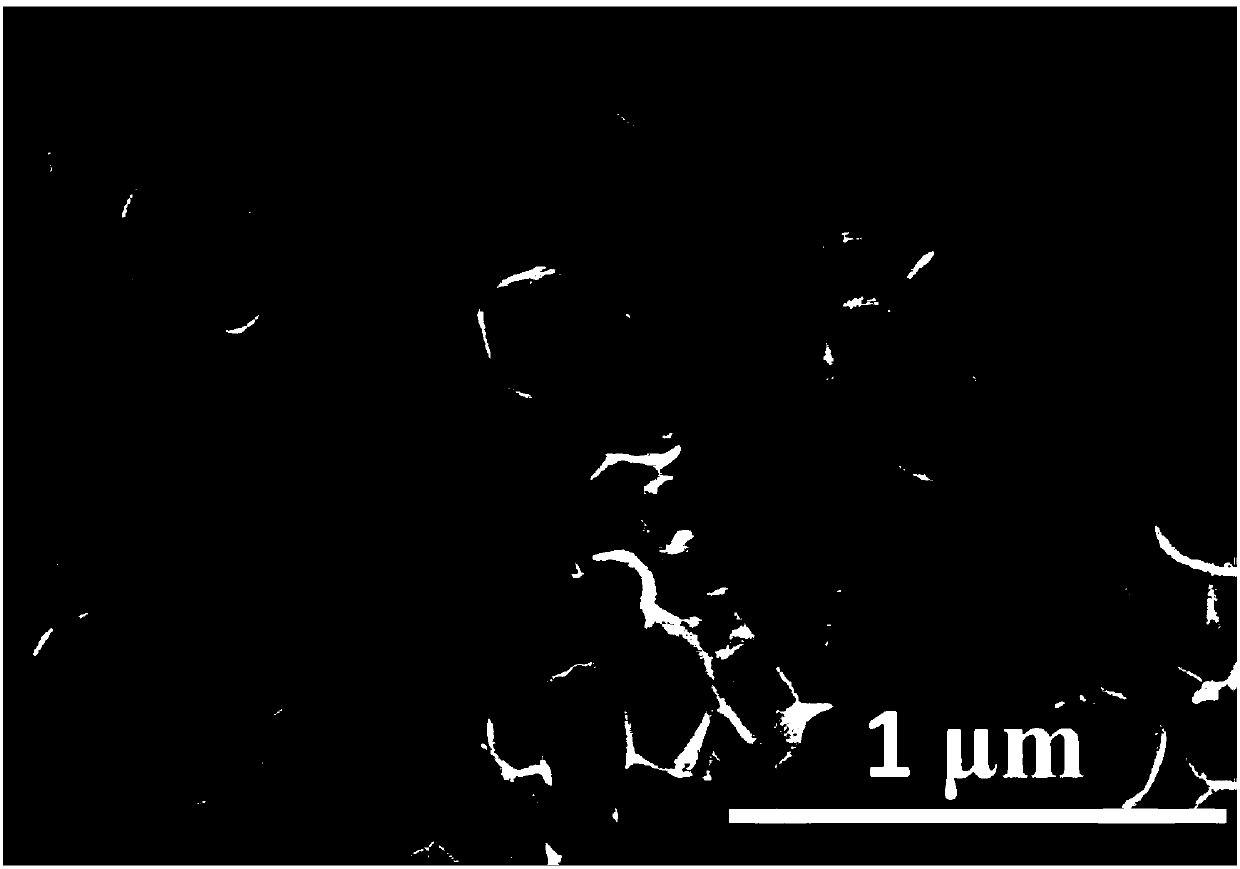
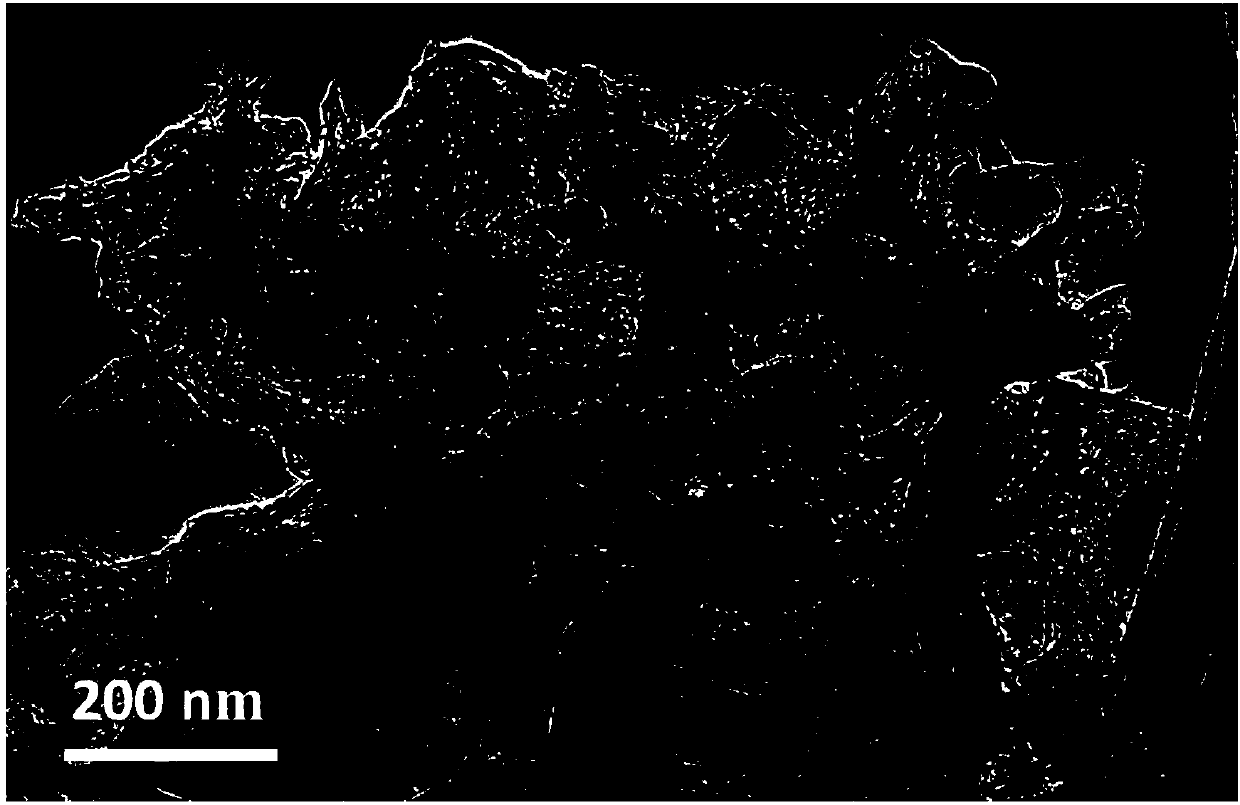
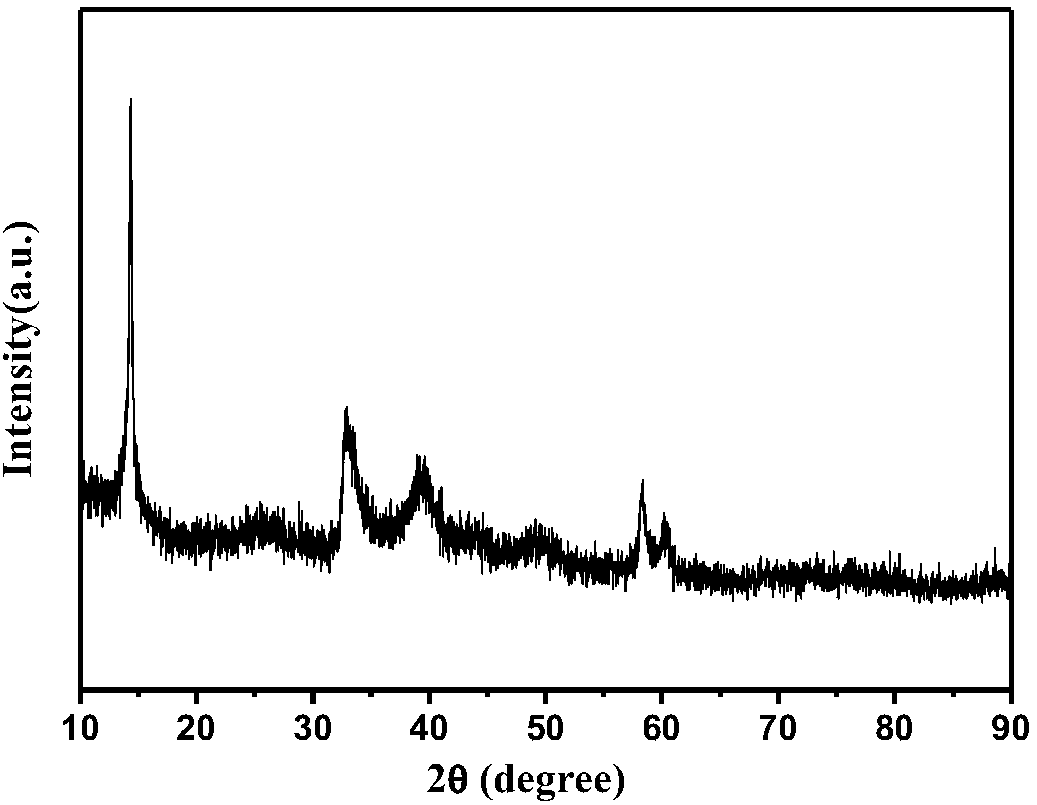
The invention discloses a method for preparing a nano-mesh film, comprising the following steps: monolayer colloidal crystal which floats at the surface of reaction solution is taken as a masking film; reaction gas is injected on the surface of the reaction solution; the reaction gas reacts with the reaction solution on an gas-solution interface; a reaction product is deposited on the liquid surface which is not covered by the colloidal crystal; after the colloidal crystal is removed, a nano-mesh film is obtained. The invention has simple operation, high production and cheap reagents, does not need any special apparatus, can be realized by chemical reaction at room temperature, and is generally used for preparing various inorganic nano-meshes. The nano-mesh film has high regularity and large area, convenient movement, easy assembly to multilayer nano-mesh, and the like, and has potential using value in the fields such as nanoprocessing, optical device, sensing, sieving, etc.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
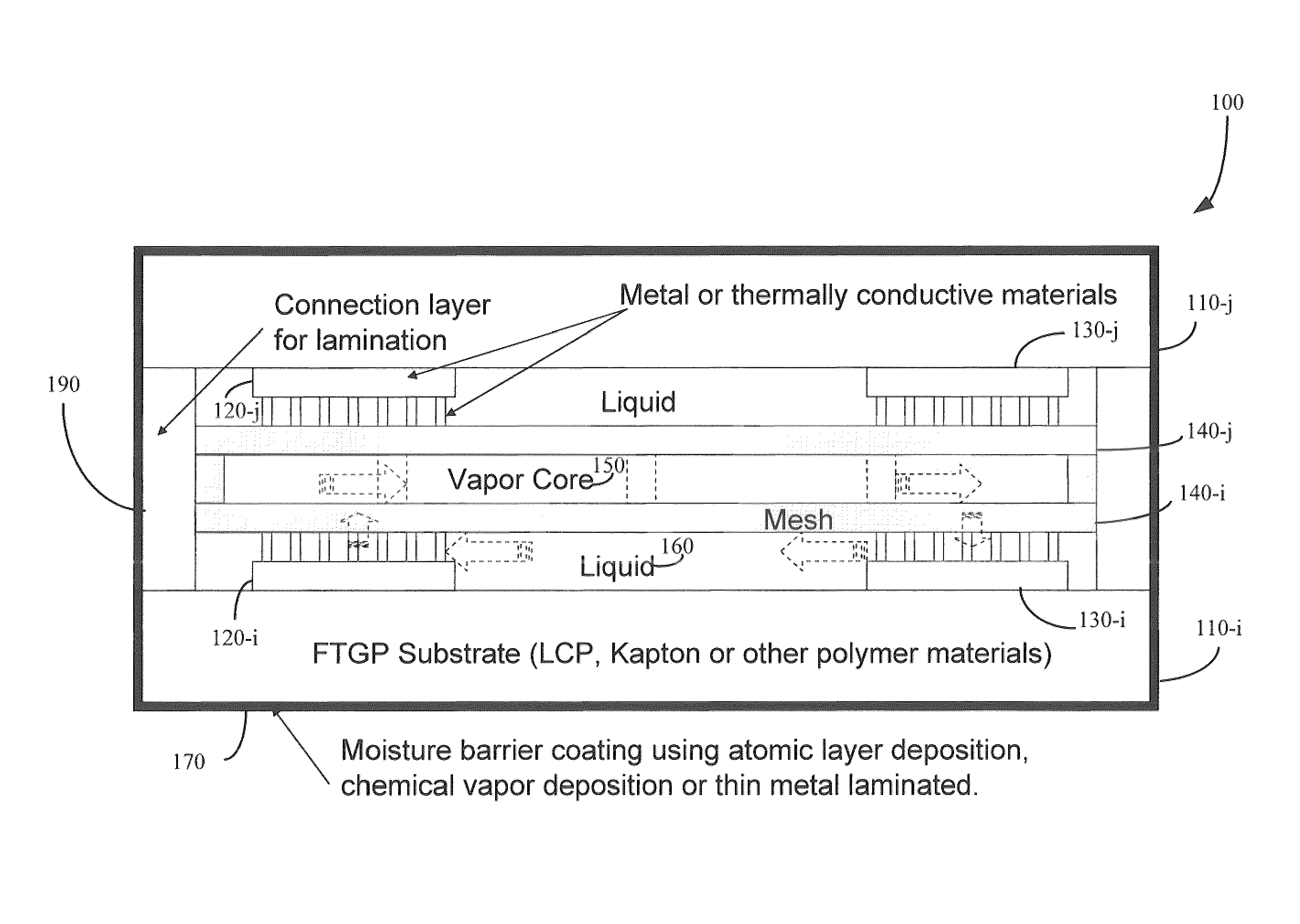
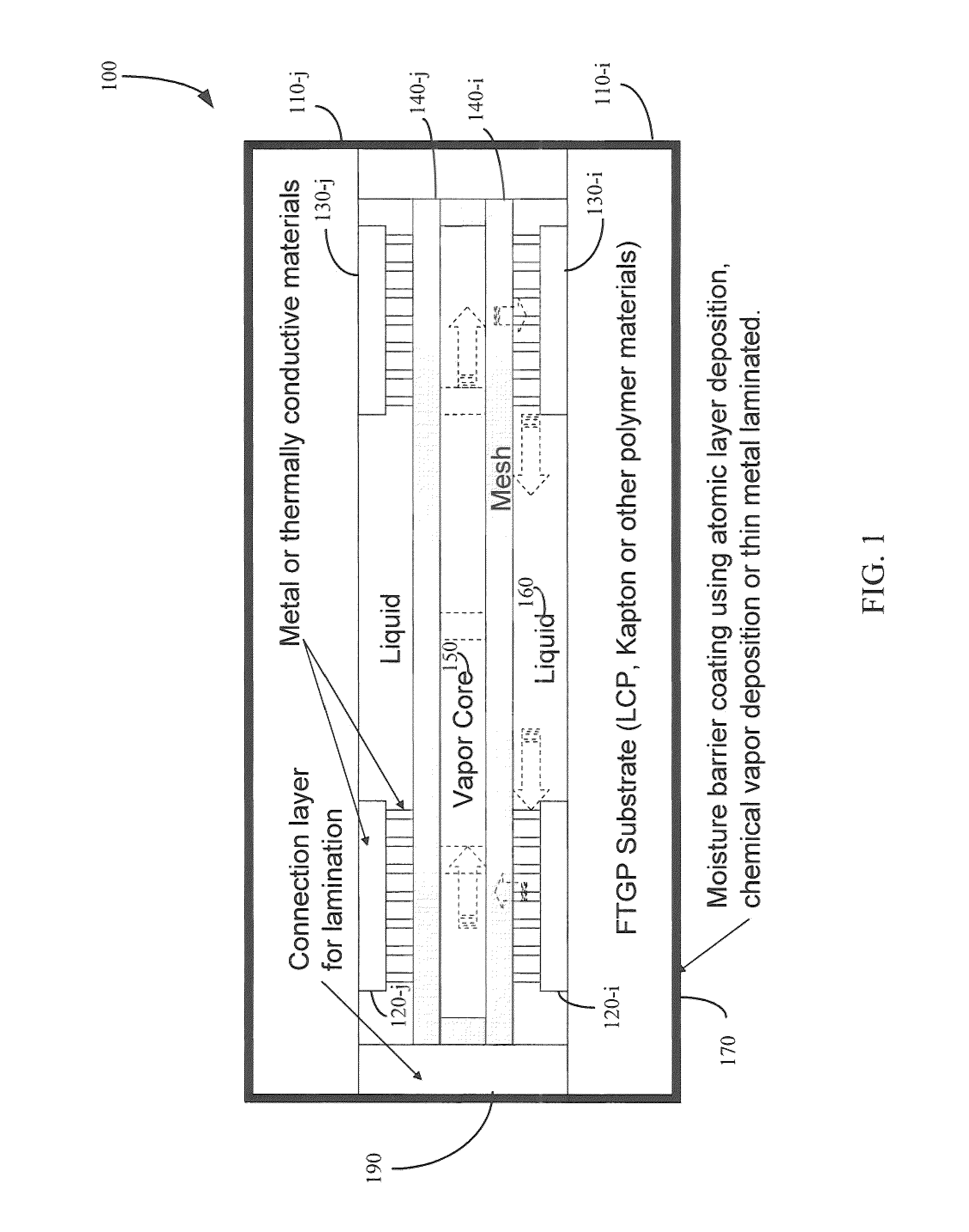
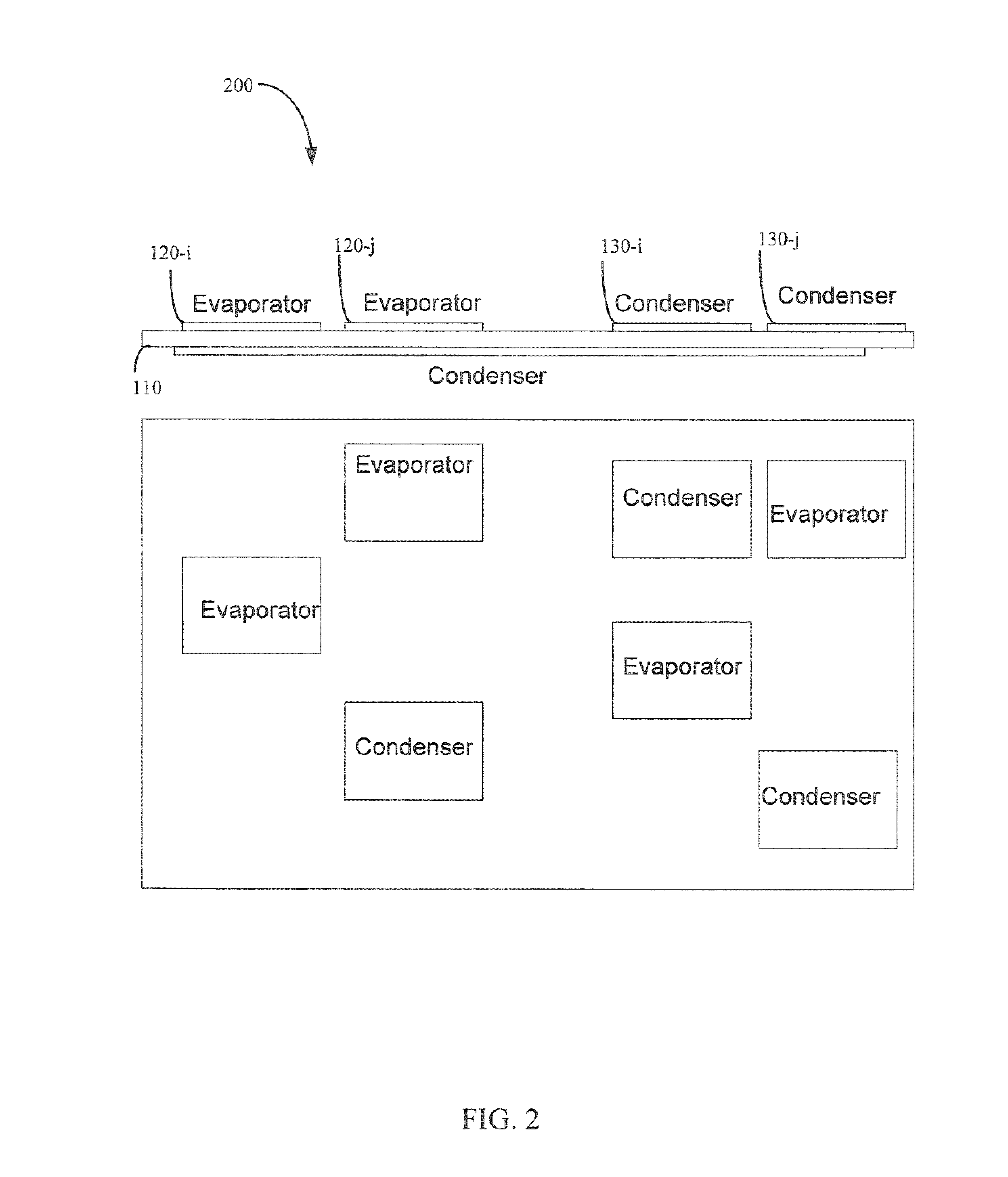
Flexible thermal ground plane and manufacturing the same
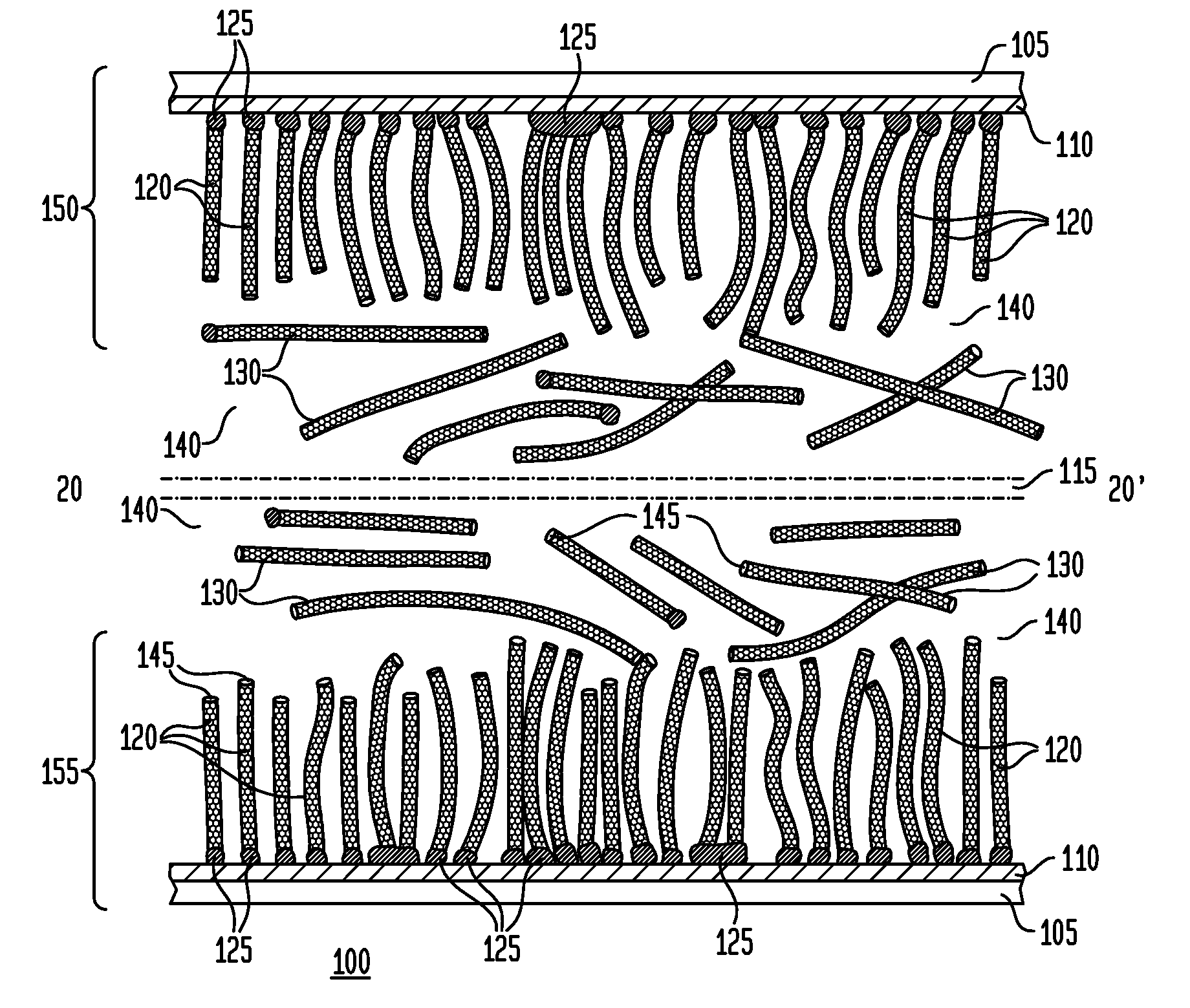
ActiveUS9163883B2Improve thermal performanceImprove heat transfer performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGround planeNanomesh
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are disclosed for flexible thermal ground planes. A flexible thermal ground plane may include a support member. The flexible thermal ground plane may include an evaporator region or multiple evaporator regions configured to couple with the support member. The flexible thermal ground plane may include a condenser region or multiple condenser regions configured to couple with the support member. The evaporator and condenser region may include a microwicking structure. The evaporator and condenser region may include a nanowicking structure coupled with the micro-wicking structure, where the nanowicking structure includes nanorods. The evaporator and condenser region may include a nanomesh coupled with the nanorods and / or the microwicking structure. Some embodiments may include a micromesh coupled with the nanorods and / or the microwicking structure.
Owner:KELVIN THERMAL TECH
Controlled assembly of charged nanoparticles using functionalized graphene nanomesh
InactiveUS8835686B2Material nanotechnologyNanostructure assemblyChemical treatmentTargeted nanoparticles
A method, an apparatus and an article of manufacture for attracting charged nanoparticles using a graphene nanomesh. The method includes creating a graphene nanomesh by generating multiple holes in graphene, wherein each of the multiple holes is of a size appropriate to a targeted charged nanoparticle, selectively passivating the multiple holes of the graphene nanomesh to form a charged ring in the graphene nanomesh by treating the graphene nanomesh with chemistry yielding a trap with an opposite charge to that of the targeted nanoparticle, and electrostatically attracting the target charged nanoparticle to the oppositely charged ring to facilitate docking of the charged nanoparticle to the graphene nanomesh.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP +1
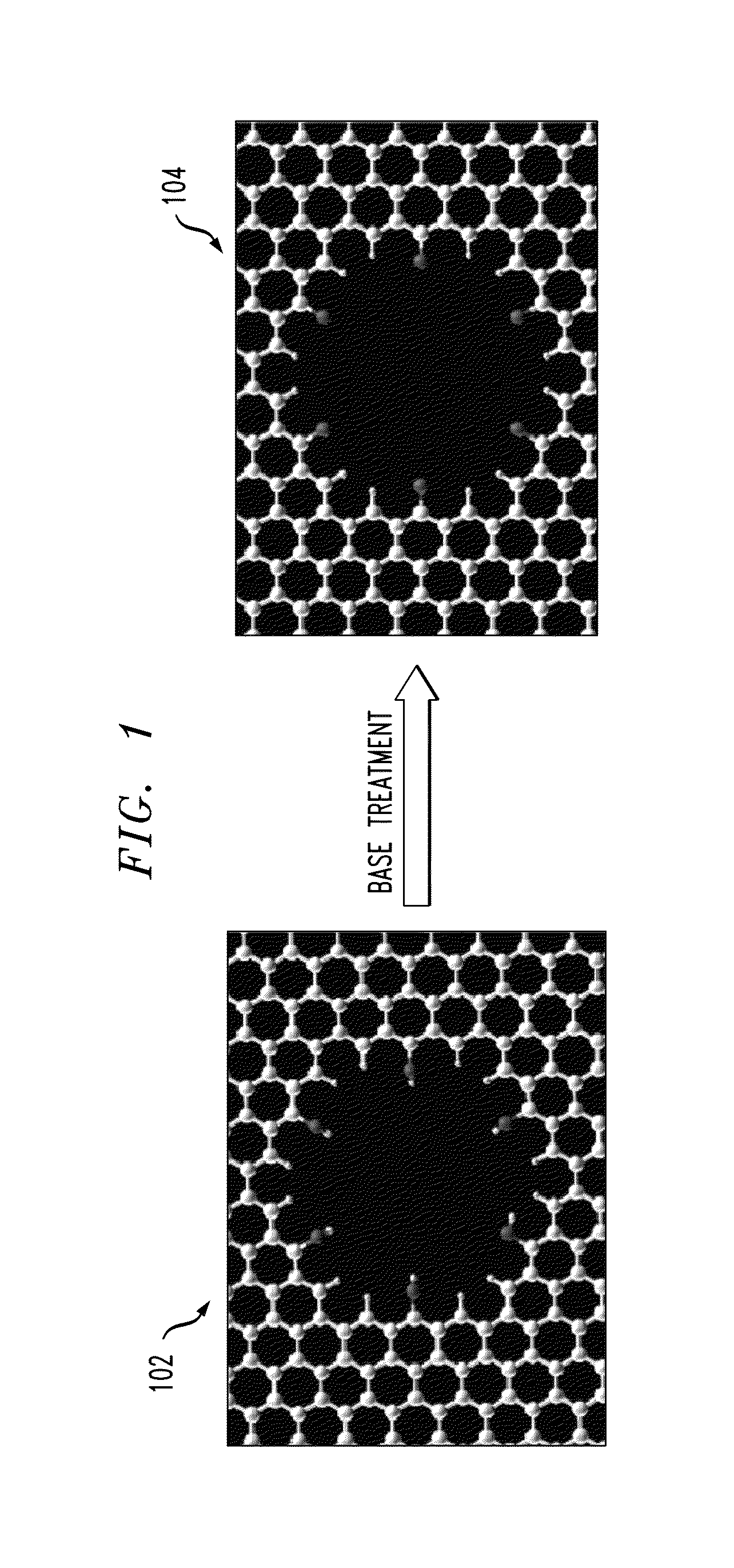
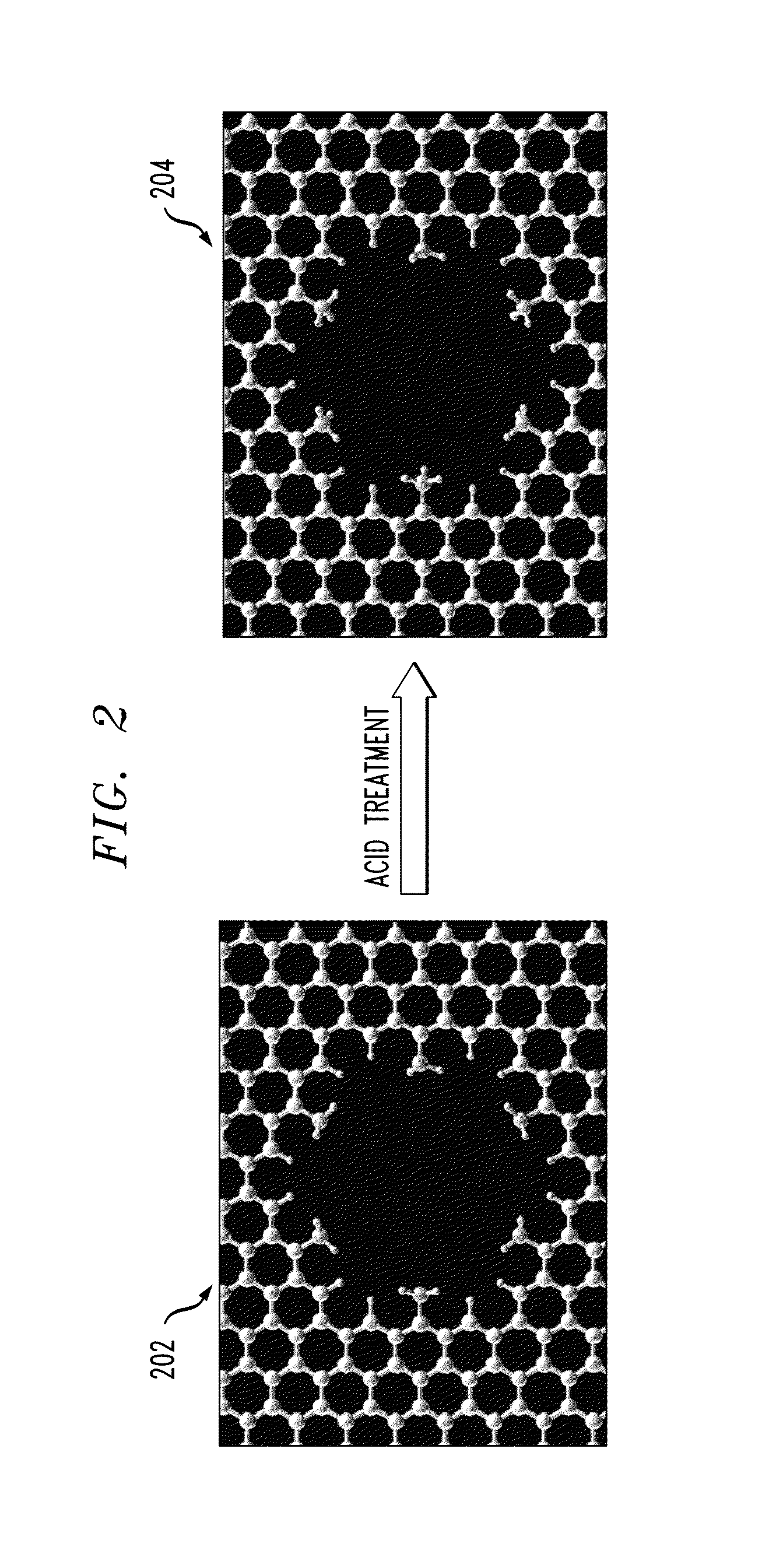
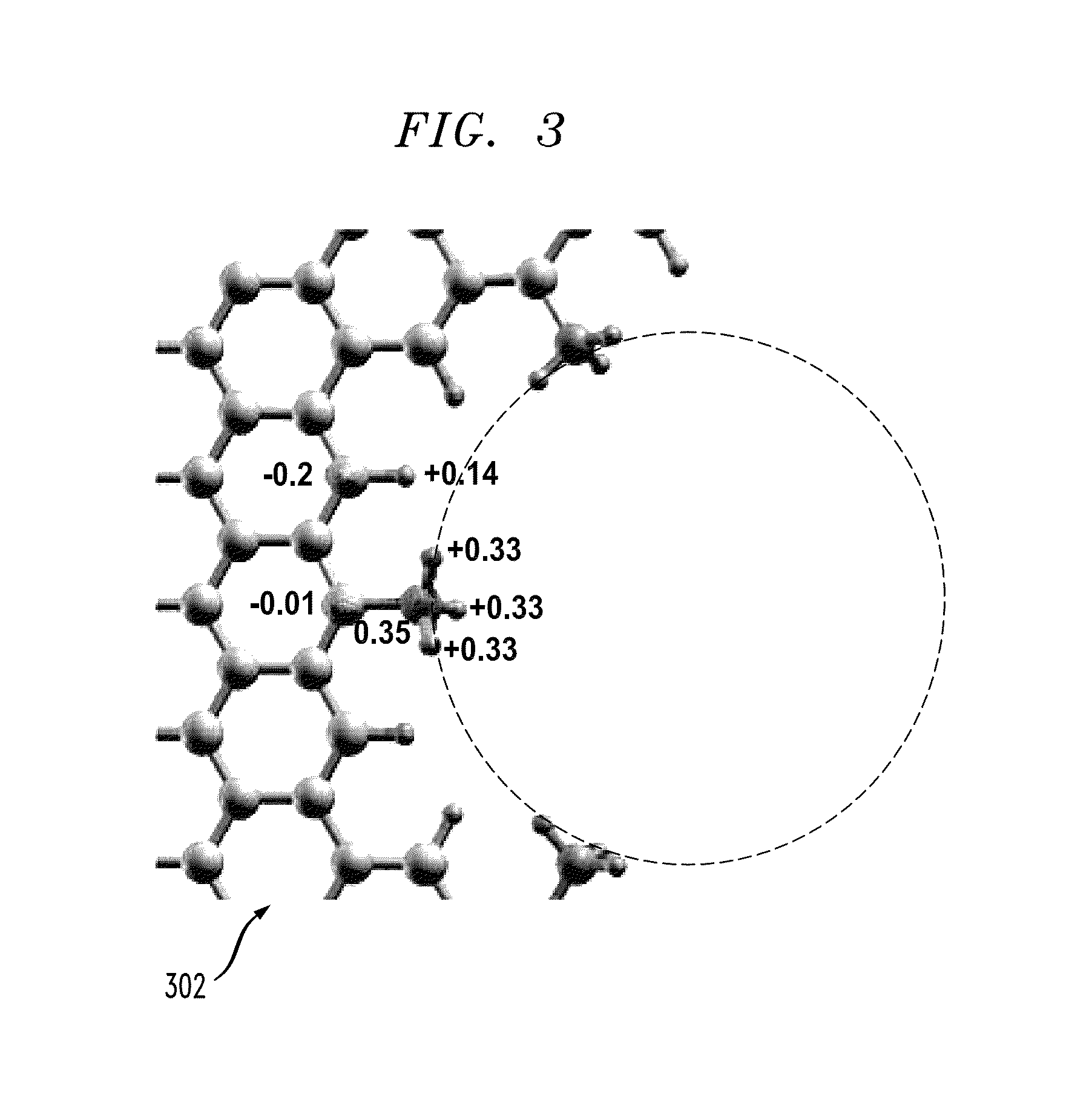
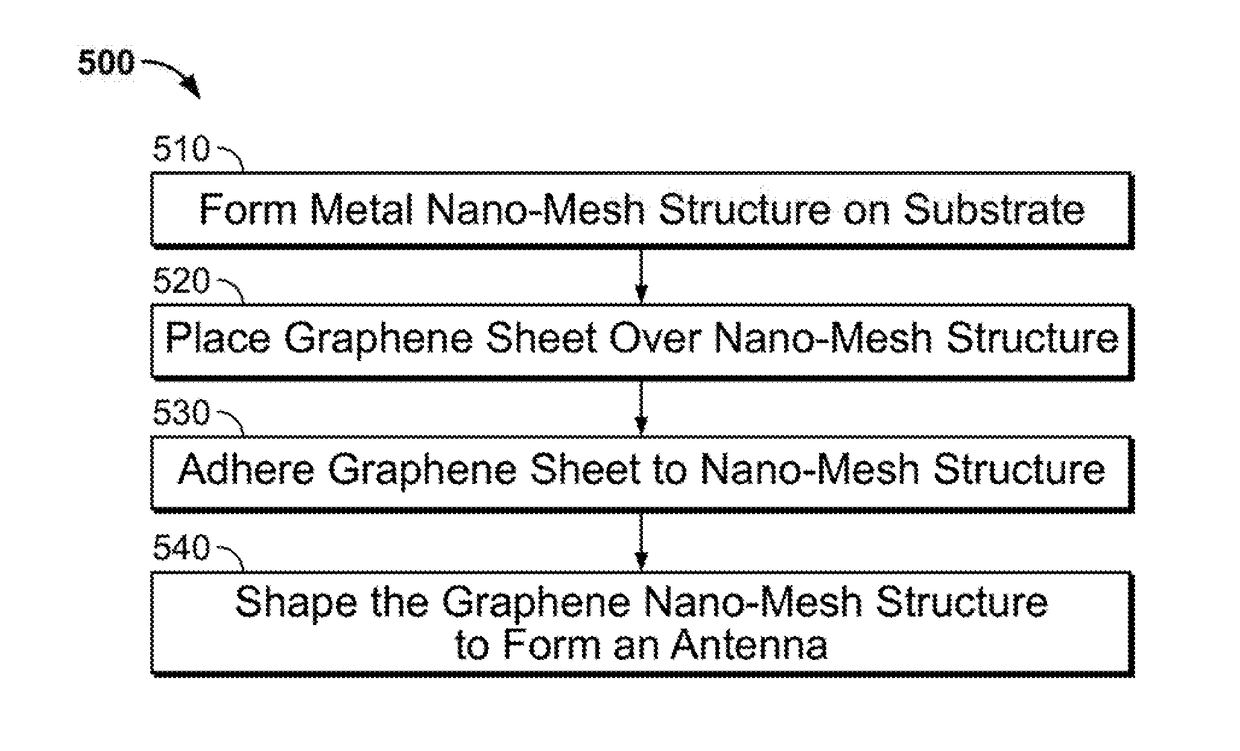
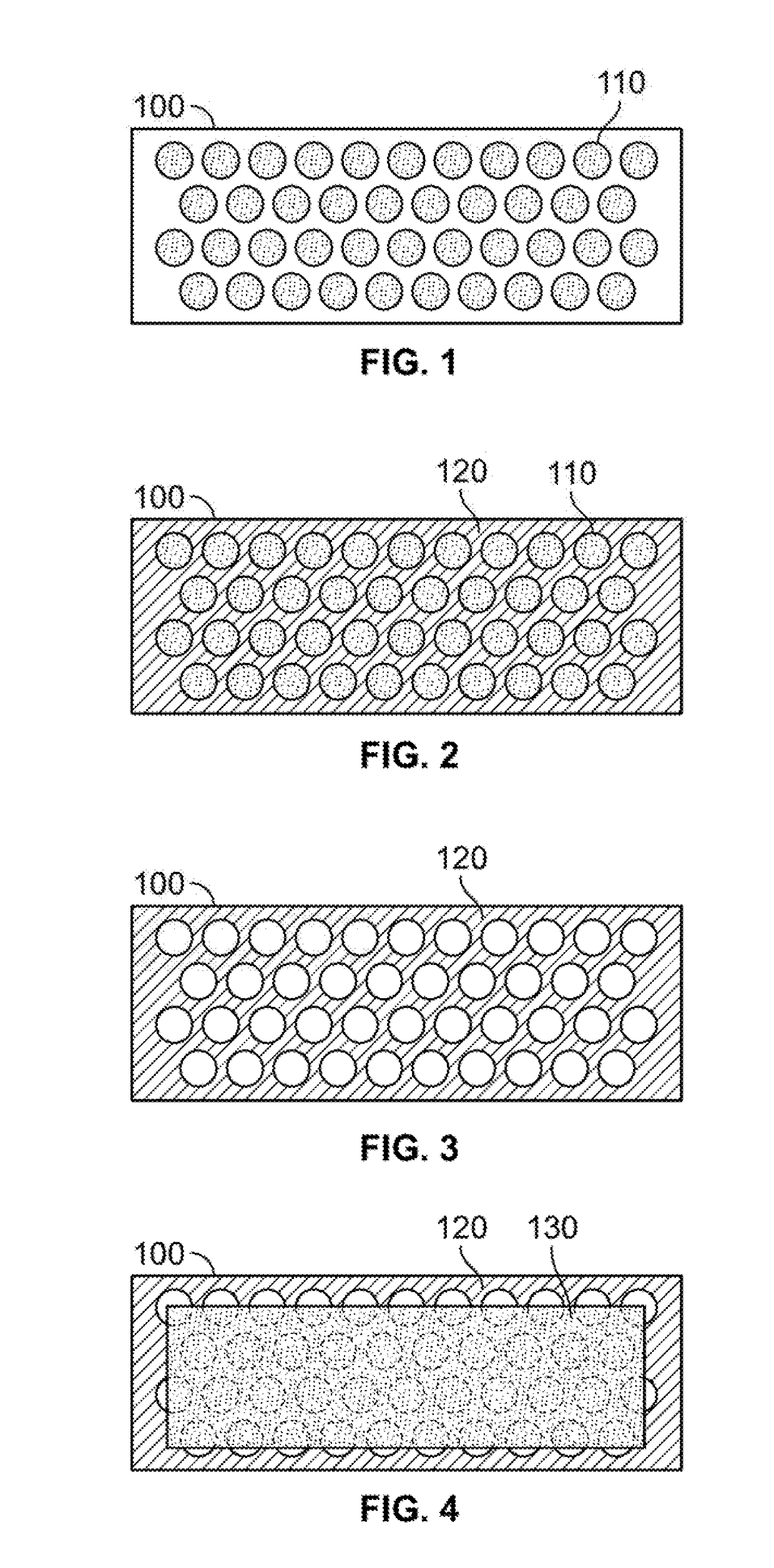
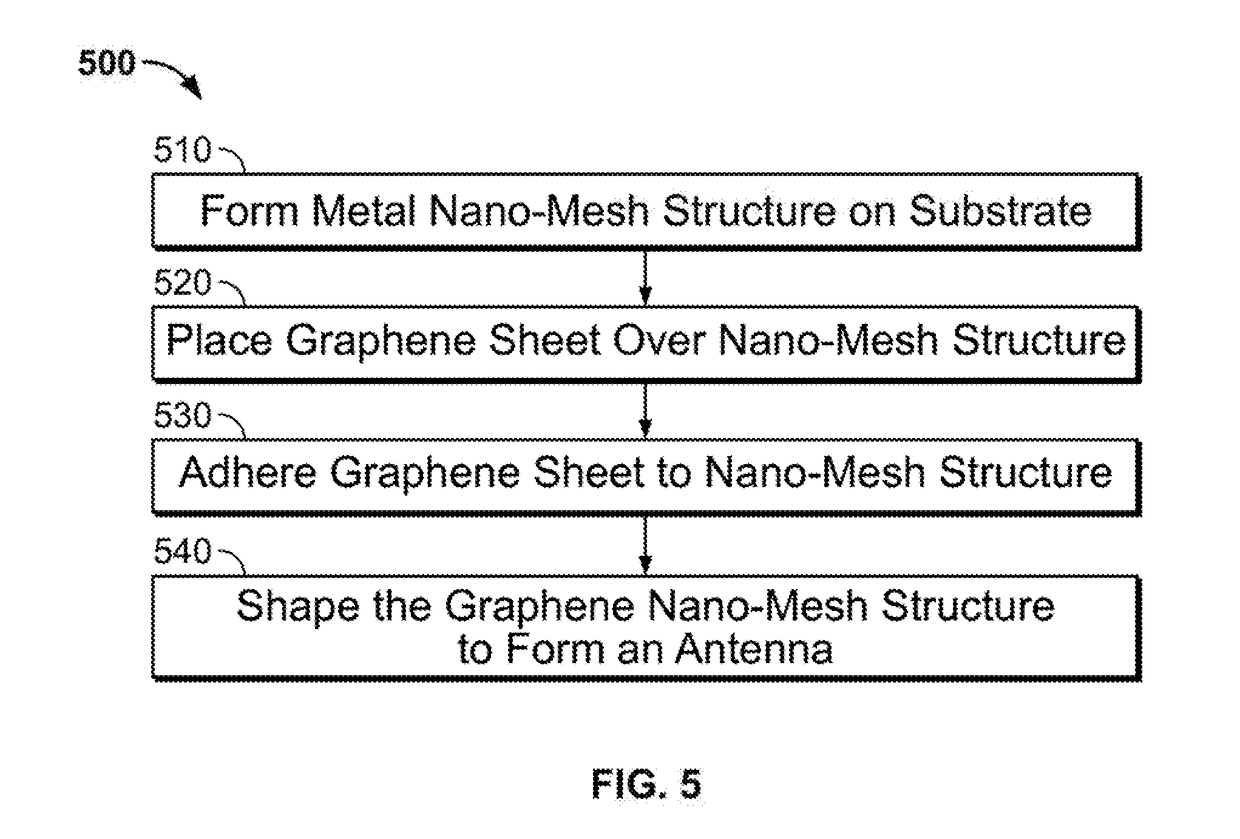
Transparent Antenna Based on Hybrid Graphene/Metal Nanomesh Structures
ActiveUS20180226713A1Guaranteed normal transmissionEfficient receptionRadiating elements structural formsAntenna equipments with additional functionsOptoelectronicsNanometre
A transparent antenna is fabricated by combining a metal nanomesh structure and a graphene sheet. The nanomesh structure is formed on a surface, and the graphene sheet is placed over the nanomesh structure. The graphene sheet is adhered to the nanomesh structure to form a graphene nanomesh structure. The graphene nanomesh structure is shaped to form the transparent antenna that efficiently transmits and receives signals in a desired frequency range yet is optically transparent.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
High-performance positive electrode material, preparation method thereof, and application of positive electrode material in lithium ion battery
ActiveCN111129466AImprove conductivityImproved magnification performanceCell electrodesGrapheneConductive polymerCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses a high-performance positive electrode material, a preparation method thereof and an application of the positive electrode material in a lithium ion battery. The positive electrode material comprises a phosphate-based positive electrode active substance and a composite coating layer coating the surface of the phosphate-based positive electrode active substance, wherein the composite coating layer comprises a first coating material and a second coating material; the first coating is of a three-dimensional nano-network layered structure and comprises a conductive polymer / graphene / carbon nanotube compound, a hydrogen-containing lithium titanium oxide compound and FeF3 (H2O) 0.33, the hydrogen-containing lithium titanium oxide compound and the FeF3 (H2O) 0.33 are dispersed on the surface of the compound in situ, and the second coating is amorphous carbon. In the preparation process of the high-performance positive electrode material, spray drying and heat treatment are combined, so the surface of the phosphate-series positive electrode active substance is uniformly coated with the first coating material with the three-dimensional nano-network layered structure and the amorphous carbon, and the obtained high-performance positive electrode material has the outstanding advantages of relatively high ionic conductivity and electronic conductivity, high specific discharge capacity, high initial coulombic efficiency, good cycling stability, high rate capability and the like.
Owner:LANGFANG GREEN IND TECH CENT +1
Method for manufacturing a suspended single carbon nanowire and piled nano-electrode pairs
ActiveUS20160054659A1High yieldReduction in yieldConductive layers on insulating-supportsAnalysing gaseous mixturesNanowireElectrochemistry
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a suspended single carbon nanowire and piled nano-electrode pairs, and a suspended single carbon nanowire and piled nano-electrode pairs manufactured using said method. A suspended single carbon nanowire, which is manufactured at a high yield by the method for manufacturing a suspended single carbon nanowire according to the present invention, has a minimized dimension, and a suspended carbon nanomesh, which is manufactured at a high yield by the method for manufacturing piled nano-electrode pairs according to the present invention, is thin and dense. The present invention also provides a gas sensor or an electrochemical sensor, to which a suspended single carbon nanowire and piled nano-electrode pairs manufactured by the method according to the present invention are applied.
Owner:UNIST ULSAN NAT INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Semiconductor device, method of manufacturing the same, and electronic device including the semiconductor device
An example embodiment relates to a semiconductor device including a semiconductor element. The semiconductor element may include a plurality of unit layers spaced apart from each other in a vertical direction. Each unit layer may include a patterned graphene layer. The patterned graphene layer may be a layer patterned in a nanoscale. The patterned graphene layer may have a nanomesh or nanoribbon structure. The semiconductor device may be a transistor or a diode. An example embodiment relates to a method of making a semiconductor device including a semiconductor element.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Ternary positive electrode composite material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111092210AReduce surface residual alkaliImprove electronic conductivityCell electrodesGrapheneConductive polymerPolyvinyl alcohol
The invention discloses a ternary positive electrode composite material and a preparation method and application thereof. The composite material comprises a ternary positive electrode material core and a shell coating the surface of the core, and the shell comprises a first coating material and a second coating material; the first coating is of a three-dimensional nano-network layered structure and comprises a conductive polymer / graphene / carbon nanotube compound, a hydrogen-containing lithium titanium oxide compound and FeF3(H2O)0.33, the hydrogen-containing lithium titanium oxide compound andthe FeF3 (H2O) 0.33 are dispersed on the surface of the compound in situ, and the second coating material is a carbonization product of polyvinyl alcohol. The lithium ion battery prepared from the ternary positive electrode composite material has relatively high ionic conductivity and electronic conductivity, and has the outstanding advantages of high specific discharge capacity, high initial coulombic efficiency, high cycling stability and the like.
Owner:LANGFANG GREEN IND TECH CENT +1
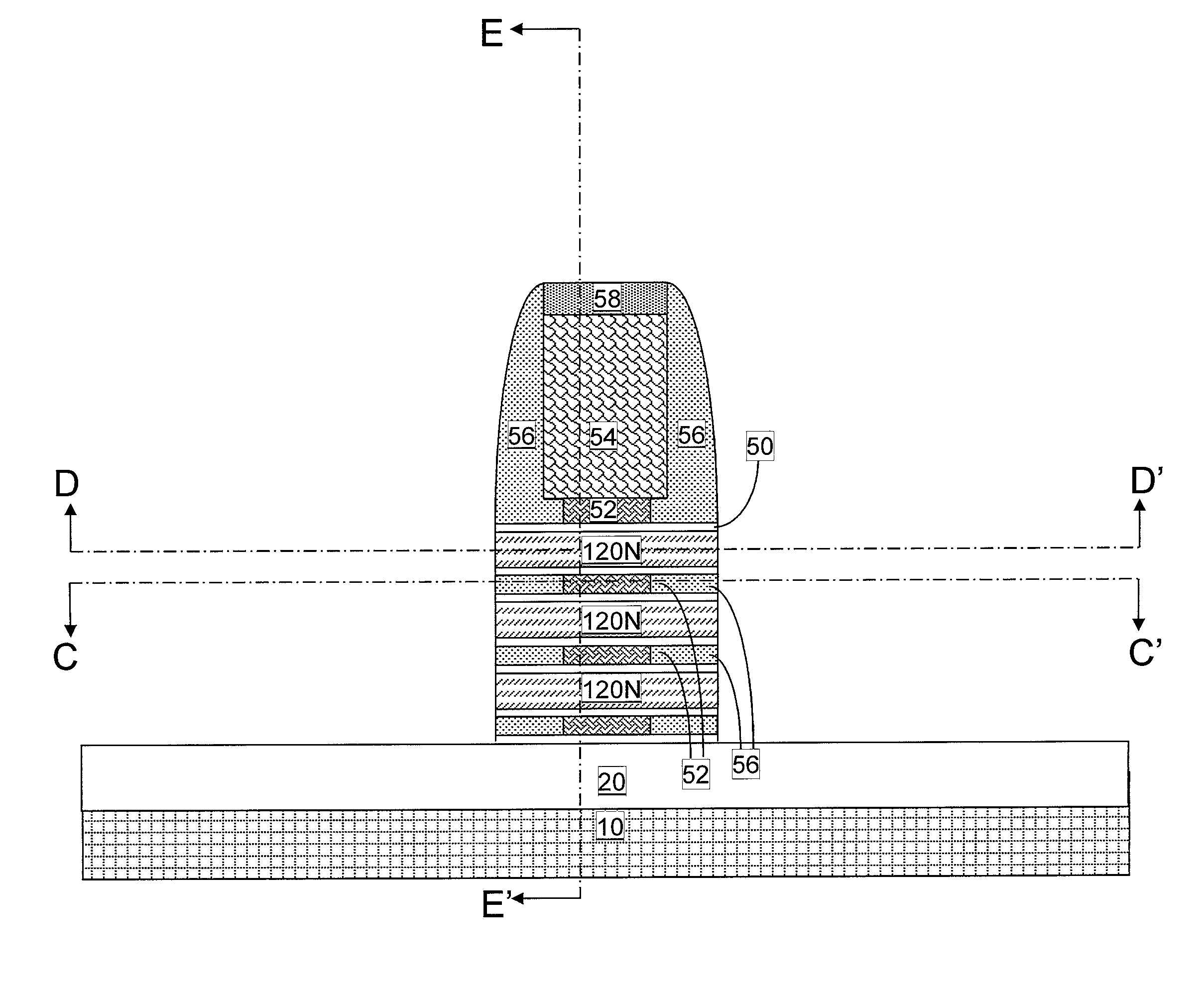
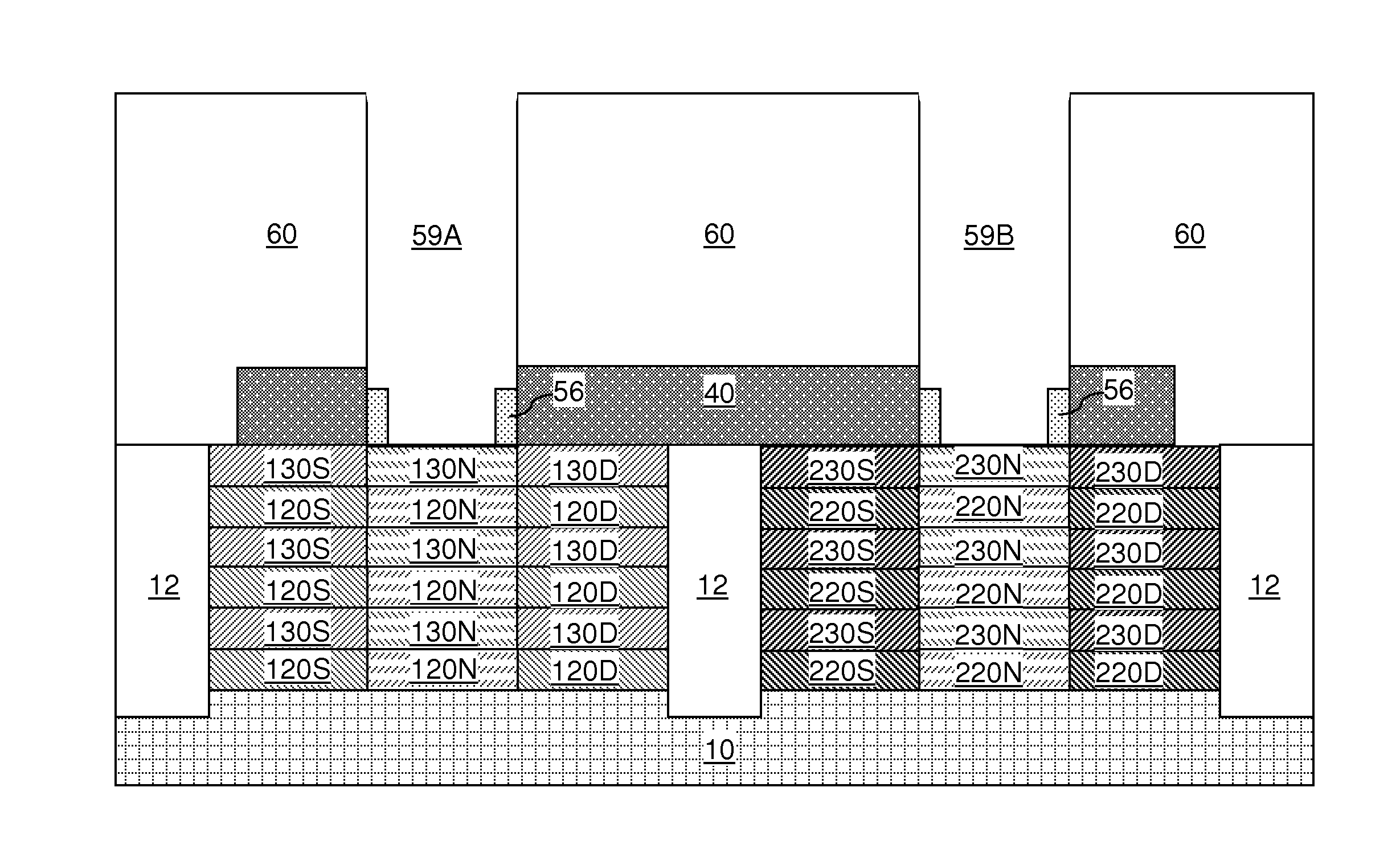
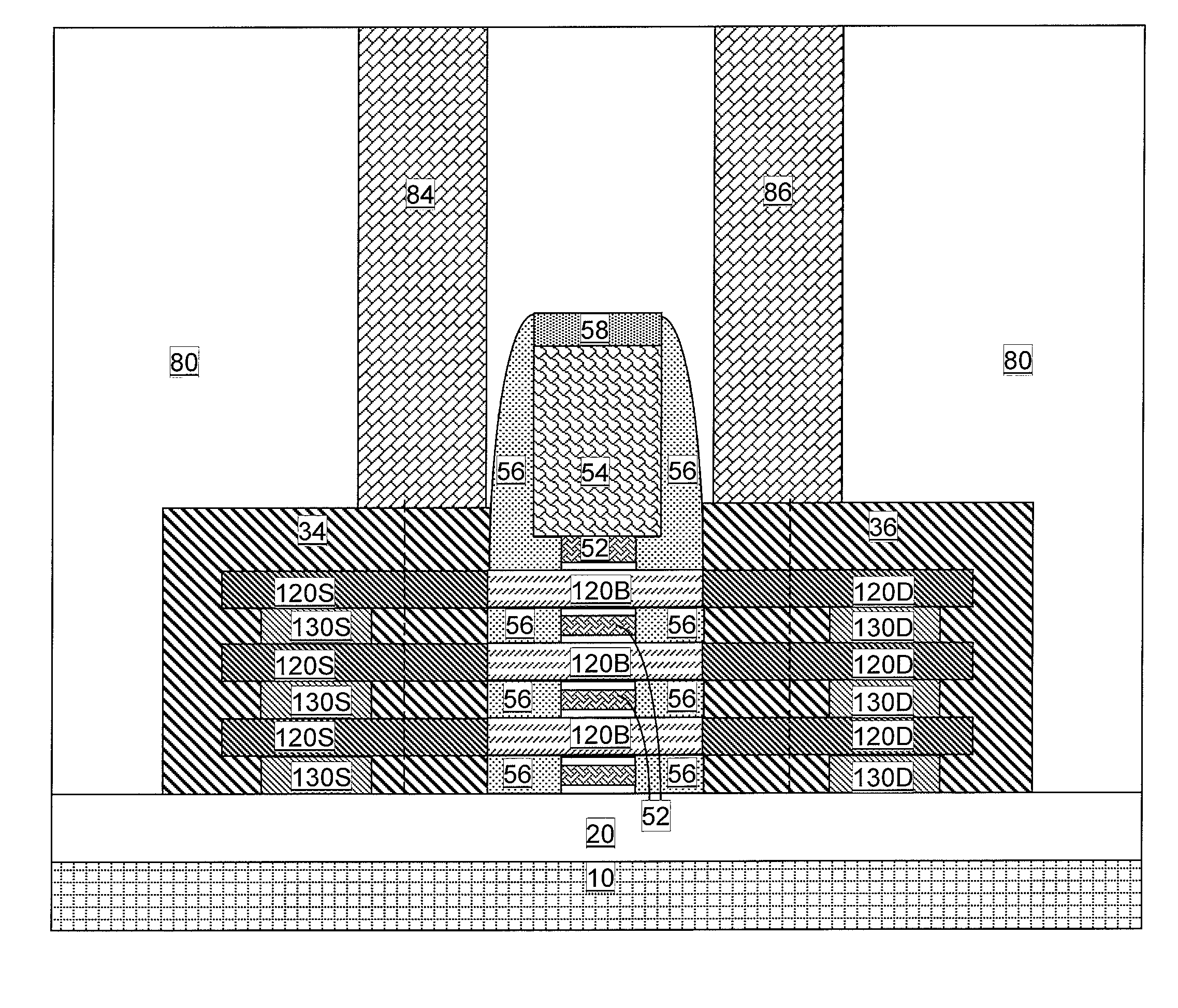
Diode structure and method for wire-last nanomesh technologies
In one aspect, a method of fabricating an electronic device includes the following steps. An alternating series of device and sacrificial layers are formed in a stack on an SOI wafer. Nanowire bars are etched into the device / sacrificial layers such that each of the device layers in a first portion of the stack and each of the device layers in a second portion of the stack has a source region, a drain region and a plurality of nanowire channels connecting the source region and the drain region. The sacrificial layers are removed from between the nanowire bars. A conformal gate dielectric layer is selectively formed surrounding the nanowire channels in the first portion of the stack which serve as a channel region of a nanomesh FET transistor. Gates are formed surrounding the nanowire channels in the first and second portions of the stack.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Methods of making platinum and platinum alloy catalysts with nanonetwork structures
This invention relates to the preparations of noble metal catalysts, i.e., platinum and platinum alloys, on suitable supports with nanonetwork structures and high catalytic efficiencies. A compact structure of a monolayer or a few layers is formed by self-assembly of organic polymer, e.g., polystyrene (PS), nanospheres or inorganic, i.e., silicon dioxide (SiO2), nanospheres on a support surface. In the void spaces of such a compact arrangement, catalyst is formed by filling with catalyst metal ion-containing aqueous solution and reduced by chemical reduction, or formed by vacuum sputtering. When using organic polymer nanospheres as the starting or structure-directing material, the polymer particles are removed by burning at a high temperature and the catalyst having a nanonetwork structure is obtained. In the case of using silicon dioxide nanospheres as the starting material, silicon dioxide particles are dissolved with hydrofluoric acid solution and evaporated away leading to formation of a similar nanonetwork structure made of catalyst. The catalysts prepared by these methods possess characteristics of robust in structure, uniform in hole size and high in catalytic surface area. Their main applications include uses as catalysts in direct methanol and proton exchange membrane fuel cells, as well as in chemical reactors, fuel reformers, catalytic converters, etc.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
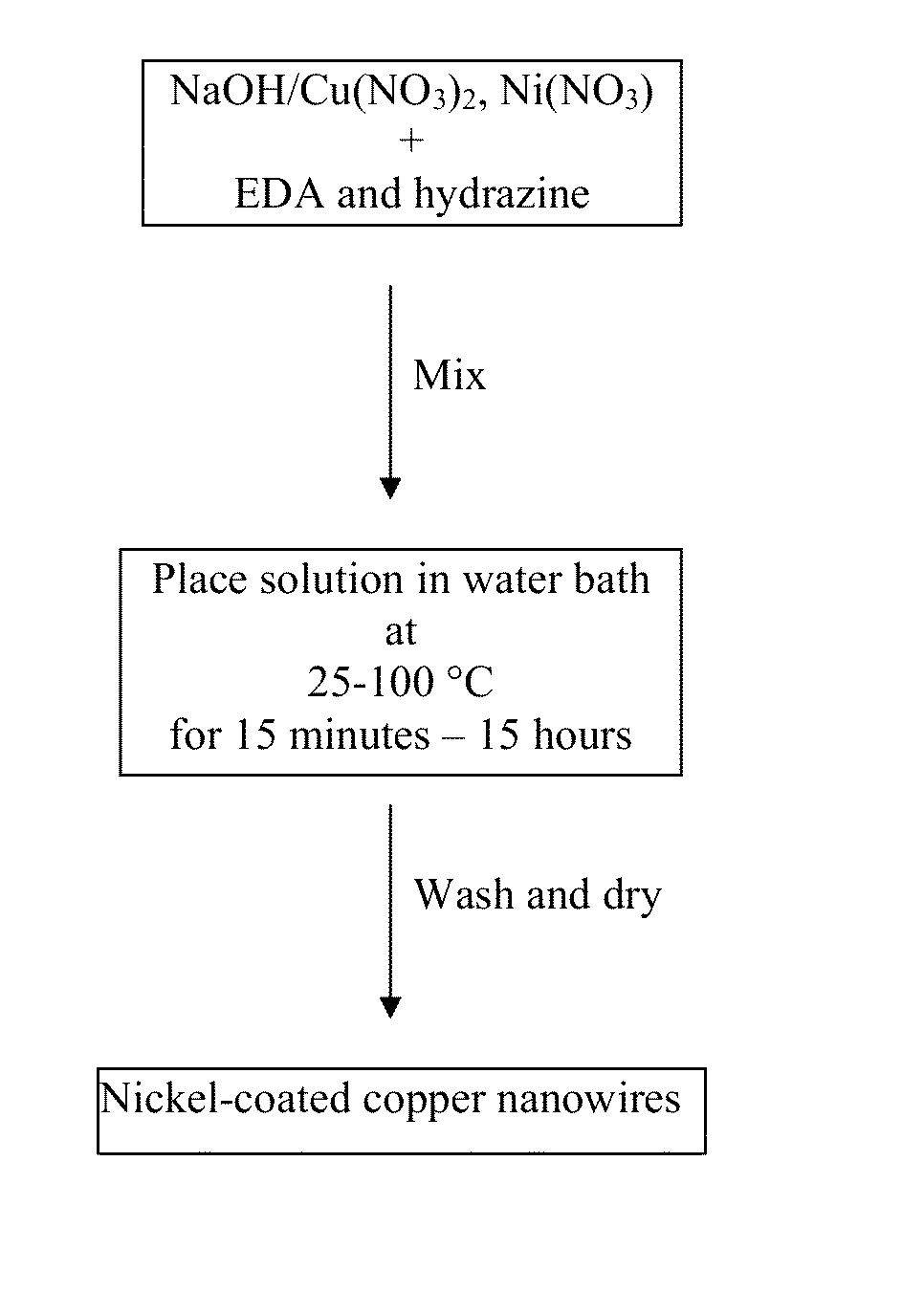
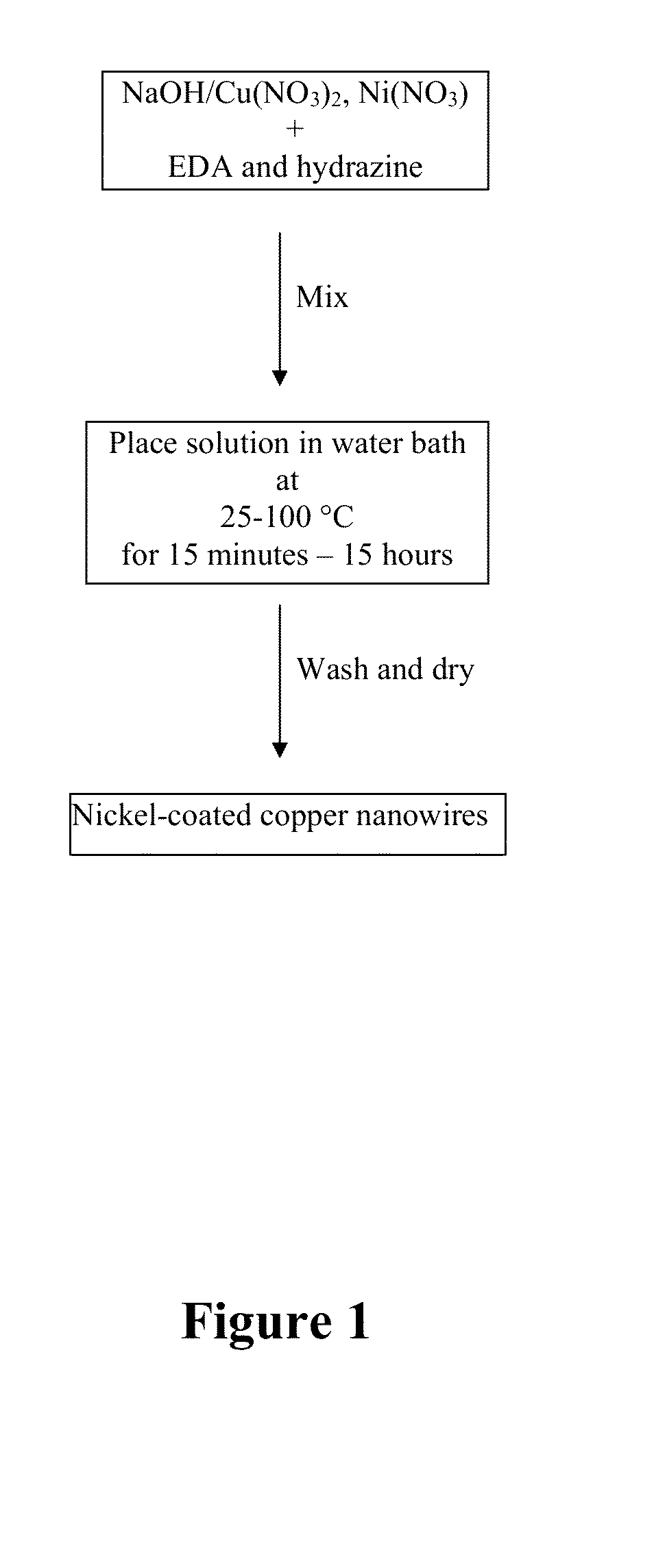
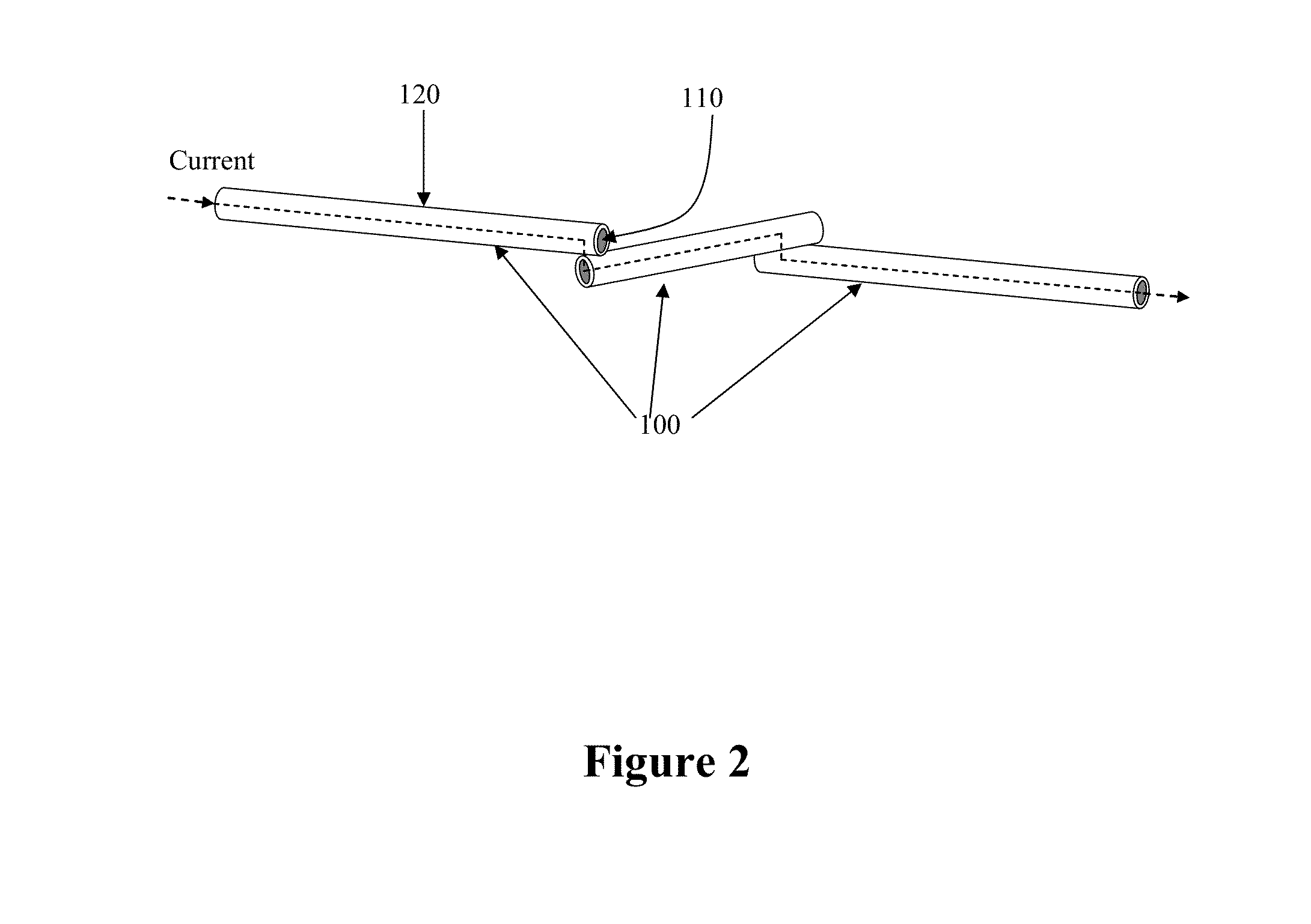
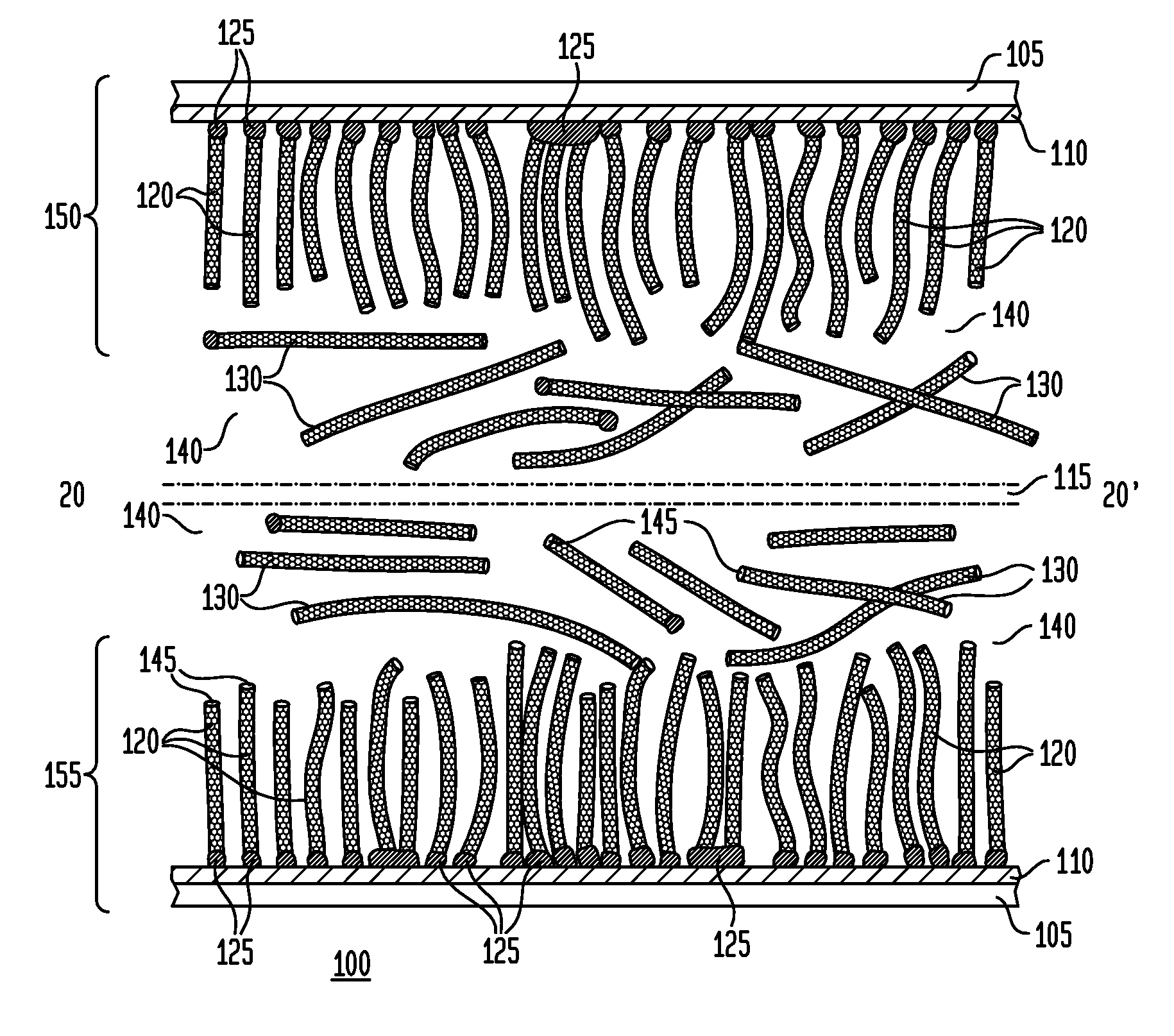
Metal nanowires, nanomesh, and a method of fabrication
The present invention relates to a method of forming copper nanowires with a metallic coating. In a preferred embodiment, the metallic coating is copper. Due to the metal coating, the nanowires become magnetically guidable and chemically stable. As such, the nanowires can be used to form nanomesh. Further, the nanowire and nanomesh of the present invention can be used as transparent electrodes that are used in TV, PC, touch-control, and solar industries.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Multilayer Carbon Nanotube Capacitor
InactiveUS20140139975A1Material nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrolytesElectrical conductorCatalyst nanoparticles
Multilayer carbon nanotube capacitors, and methods and printable compositions for manufacturing multilayer carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are disclosed. A first capacitor embodiment includes: a first conductor; a plurality of fixed CNTs in an ionic liquid, each fixed CNT comprising a magnetic catalyst nanoparticle coupled to a carbon nanotube and further coupled to the first conductor; and a first plurality of free CNTs dispersed and moveable in the ionic liquid. Another capacitor embodiment includes: a first conductor; a conductive nanomesh coupled to the first conductor; a first plurality of fixed CNTs in an ionic liquid and further coupled to the conductive nanomesh; and a plurality of free CNTs dispersed and moveable in the ionic liquid. Various methods of printing the CNTs and other structures, and methods of aligning and moving the CNTs using applied electric and magnetic fields, are also disclosed.
Owner:NTHDEGREE TECH WORLDWIDE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com