X-ray fluuorroscopy device
A grid structure and ground grid technology, applied in underwater structures, infrastructure engineering, nets, etc., to achieve the effect of enhancing resistance, enhancing multi-directional performance, and improving flexural modulus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
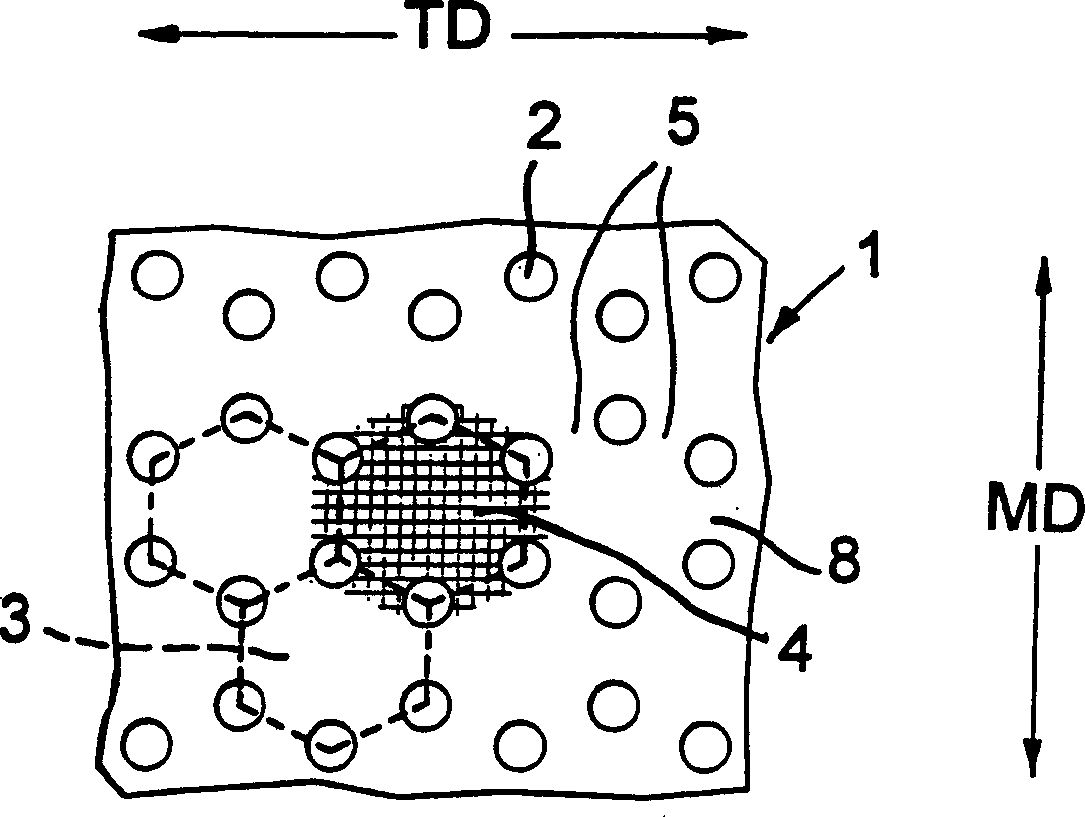
[0073] Figure 7 for figure 1 An enlarged view of a portion of the starting material of , and shows the pitch (distance between centers) of holes 2 . The starting sheet 1 is typically nominally 4.7 mm thick polypropylene with 2% added carbon black, the hole 2 punched to a size of 5 mm diameter. It will be seen that the hexagons 3 do not have sides of equal length, but are slightly shortened in the MD, and within each hexagon 3, the distances between the two opposing holes 2 on the (18.5) MD axis of the hexagon 3 The ratio of the distance between the centers to the distance between the other remaining pairs of opposite holes 2 (21.7 mm) is 0.85:1 (or 1:1.17). The primary MD pitch:secondary MD pitch ratio was 2.625:1, and the ratios between the center distance separating adjacent holes and the diameter of the holes were 2.1:1 and 2.06:1, respectively.
[0074] Starting material 1 was first (imaginary MD) stretched to a draw ratio of 3.86:1 and allowed to relax to a draw rati...
Embodiment 2
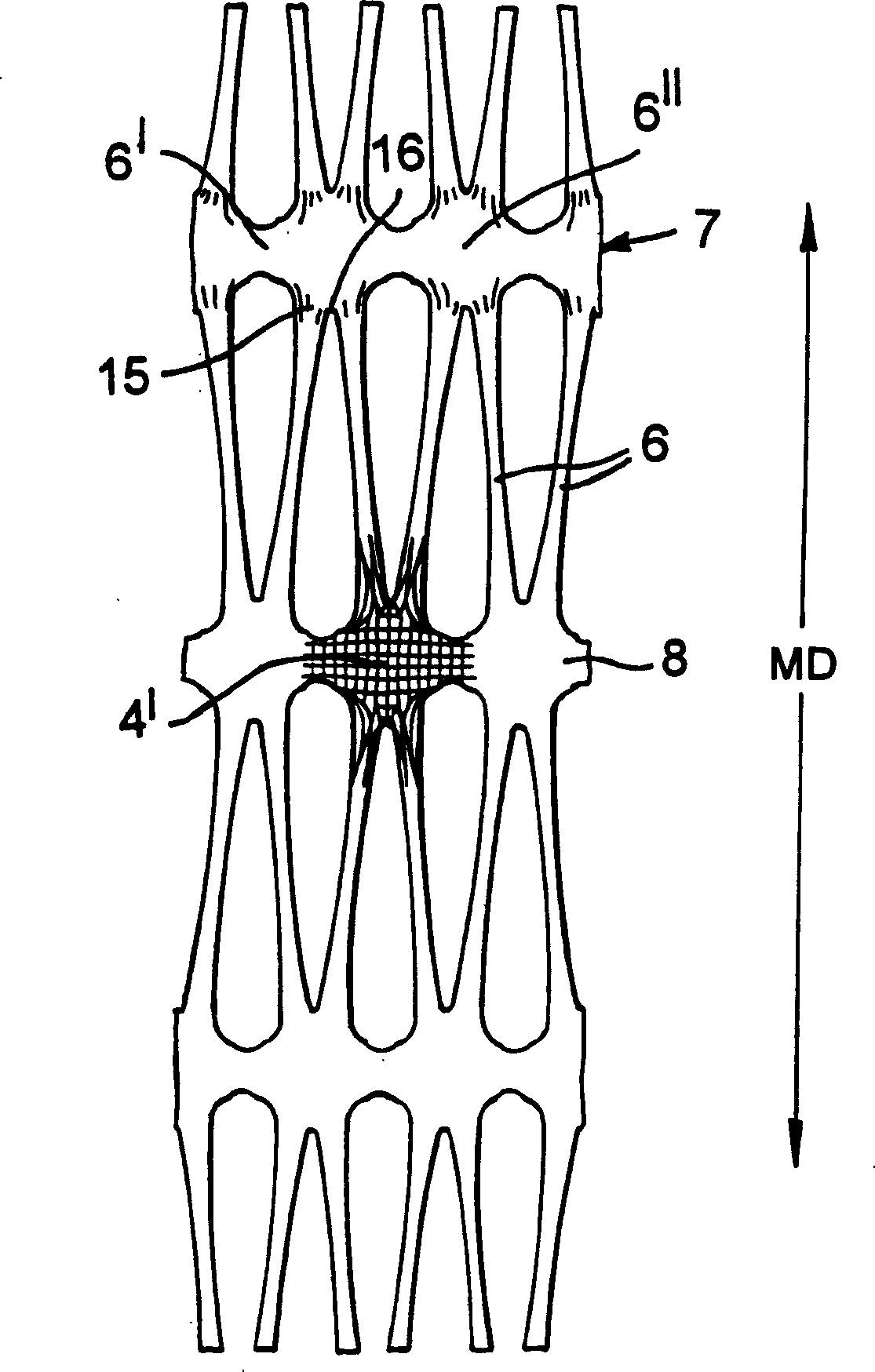
[0077] Figure 8 corresponds to Figure 7 , but if Figure 8 Dimensions shown in may vary. Hexagon 3 has sides of equal length. The punching size for hole 2 is also 5mm in diameter. The ratio between the distance separating the centers of adjacent holes 2 measured along the line connecting the centers and the width of the holes 2 was 2.30:1. Other parameters are:
[0078] Starting flake thickness - 4.7 mm.
[0079] Primary MD Pitch: Secondary MD Pitch - 2.6:1.
[0080] MD distance between centerlines of adjacent bars 6 after first stretching - 60mm
[0081] TD junction center / joint center distance after first stretch (after relaxation)—21.3mm
[0082]TD junction center / joint center distance after second stretch (after relaxation) - 69.3 mm
[0083] Intermediate MD stretch ratio (before relaxation) - 3.82:1
[0084] Intermediate TD stretch ratio (before relaxation) - 3.31:1 (including relaxation allowance)
[0085] Final MD stretch ratio (after relaxation) - 3.76:1 ...
Embodiment 3
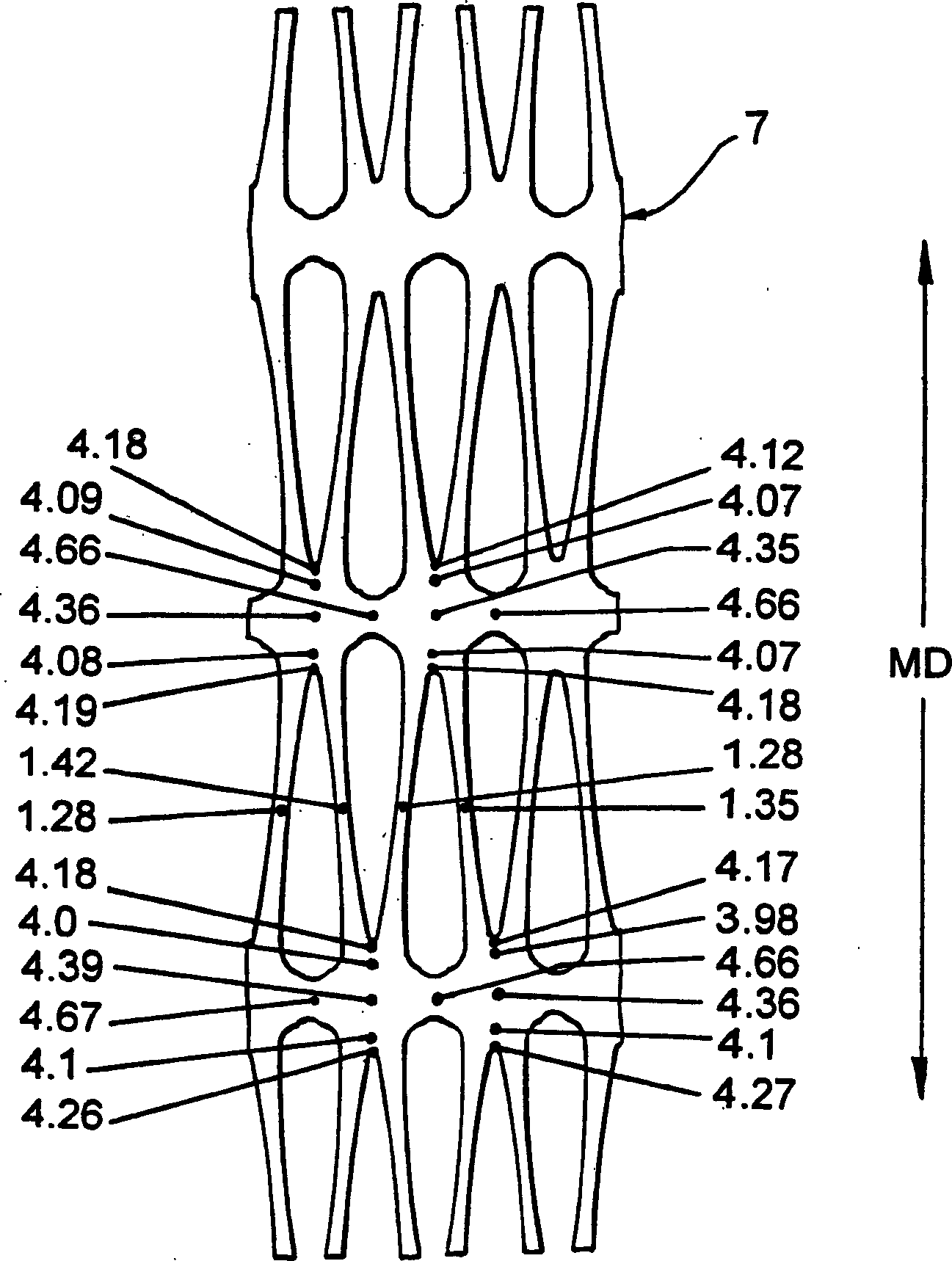
[0100] The thickness, material and punch size of the starting sheet were the same as in Example 1. The imaginary MD pitch is 10.5 mm and the imaginary TD pitch is 9.5 mm. The punches forming the slots 23 had an angle of 116° with radial tips applied to each surface of the material 21 to a depth of 16% of the sheet thickness, forming 32% of the total slotting of the sheet thickness. The MD and TD stretch ratios were 4.00:1 and 2.21:1, respectively. Figure 12 The thickness at different points on the product is shown in millimeters. The geometric measurement extension is 2.3%. The relative lateral displacement was 11.8%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com