Large field-of-view bionic compound eye visual system adopting dome light cone
A bionic compound eye and vision system technology, applied in the field of bionic vision and sensing, can solve the problems of staying in the initial verification, high technical complexity, low luminous flux, etc., so as to reduce the difficulty of optical design and optimization, and solve the problem of serious imaging defocus. , the system structure is compact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The present invention will be further illustrated below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments. This embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention. It should be understood that these embodiments are only used to illustrate the present invention and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
[0027] The following examples are preferred embodiments of the present invention:
[0028] (1) System structure composition
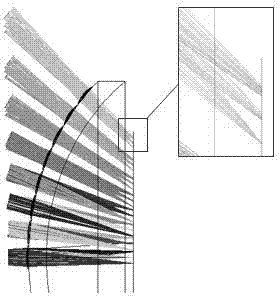
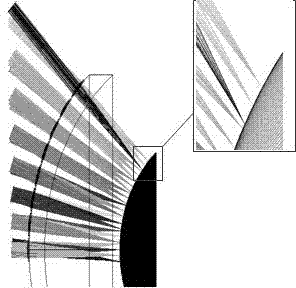
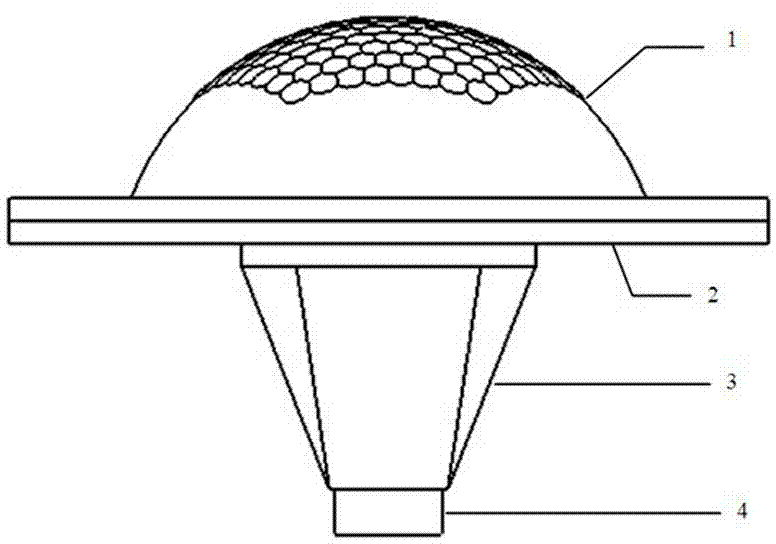
[0029] The overall structure of the compound eye optical system based on the above principles is as follows: figure 2 shown. The system includes a curved fly-eye lens 1, an aperture stop 2, a dome light cone 3, an image detector 4, and related assembly parts and an image acquisition platform connected in sequence.
[0030] Such as figure 2 As shown, assuming that the incident light comes from infinity, the incident light from all directions within the total ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com