Three-dimensional imaging system and method in deep scattering medium
A three-dimensional imaging and medium technology, applied in the direction of material excitation analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of phosphor imaging and low efficiency of three-dimensional images
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
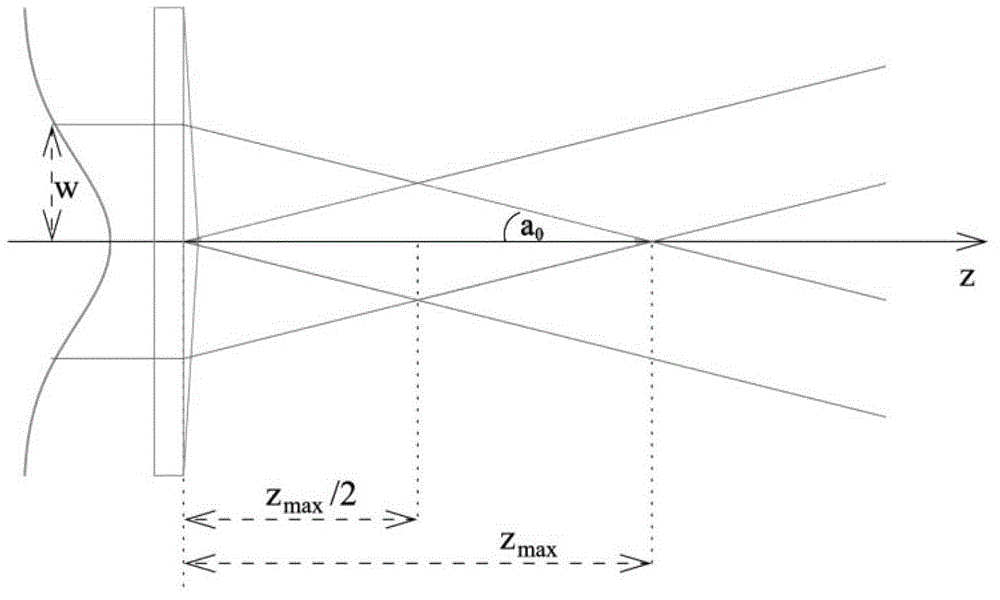
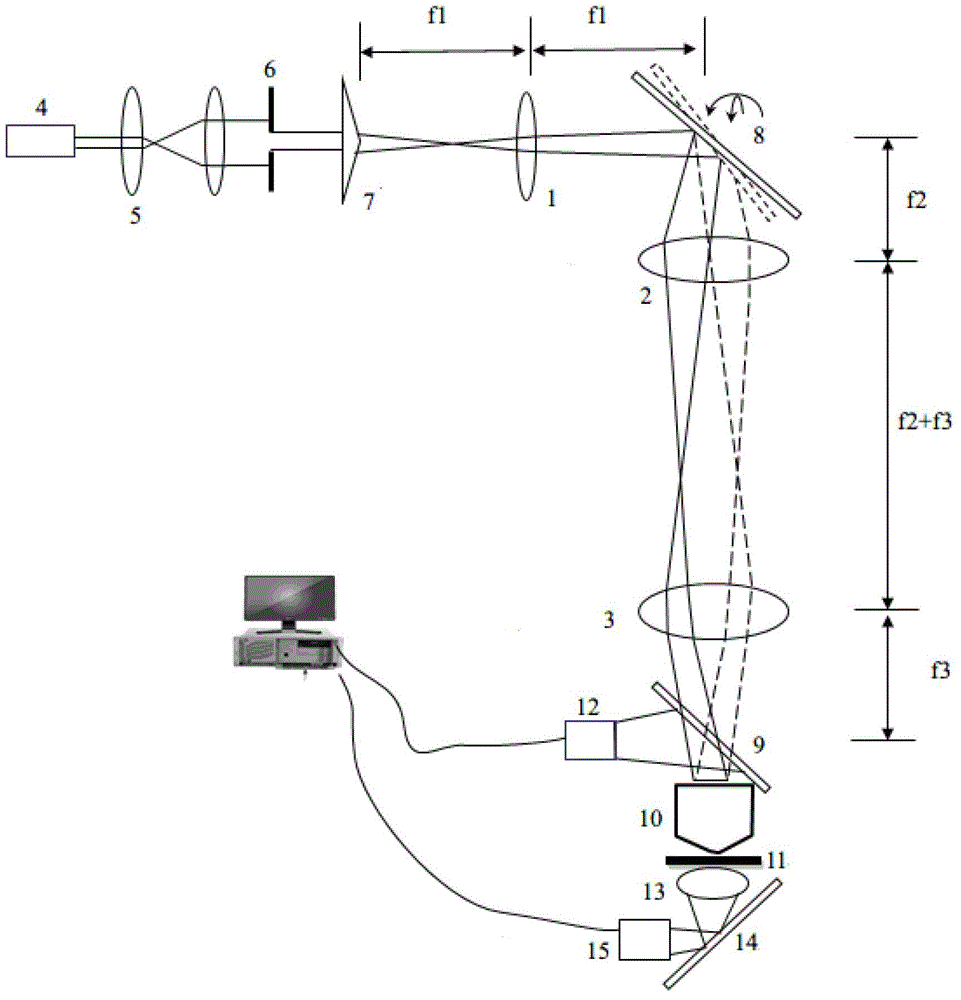
[0050] In order to efficiently excite the two-photon fluorescence in the fluorescently labeled sample and scan the sample at high speed, the excitation light source generally adopts an ultrashort pulse mode-locked laser with a high repetition rate (such as 80MHz). For example, the Mai Tai ultrafast femtosecond laser from Sepctra-Physics can be used, which has a wide spectral adjustment range (690nm~1040nm), and can excite common fluorescent markers to produce two-photon fluorescence. The pulse width is generally selected between 100 and 200 femtoseconds, and a larger pulse width will reduce the two-photon excitation efficiency, thereby weakening the excitation depth of the Bessel beam.
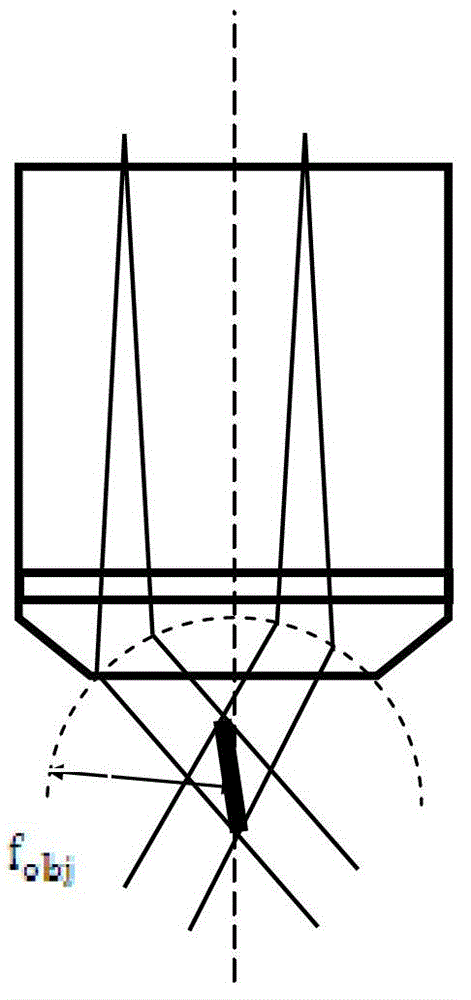
[0051] The microscope objective serves both as a component for scanning Bessel beams and as a component for reverse fluorescence collection in the present invention. In order to enable the scanning field to have a better Bessel focusing field at different scanning angles, it is advisable to us...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com