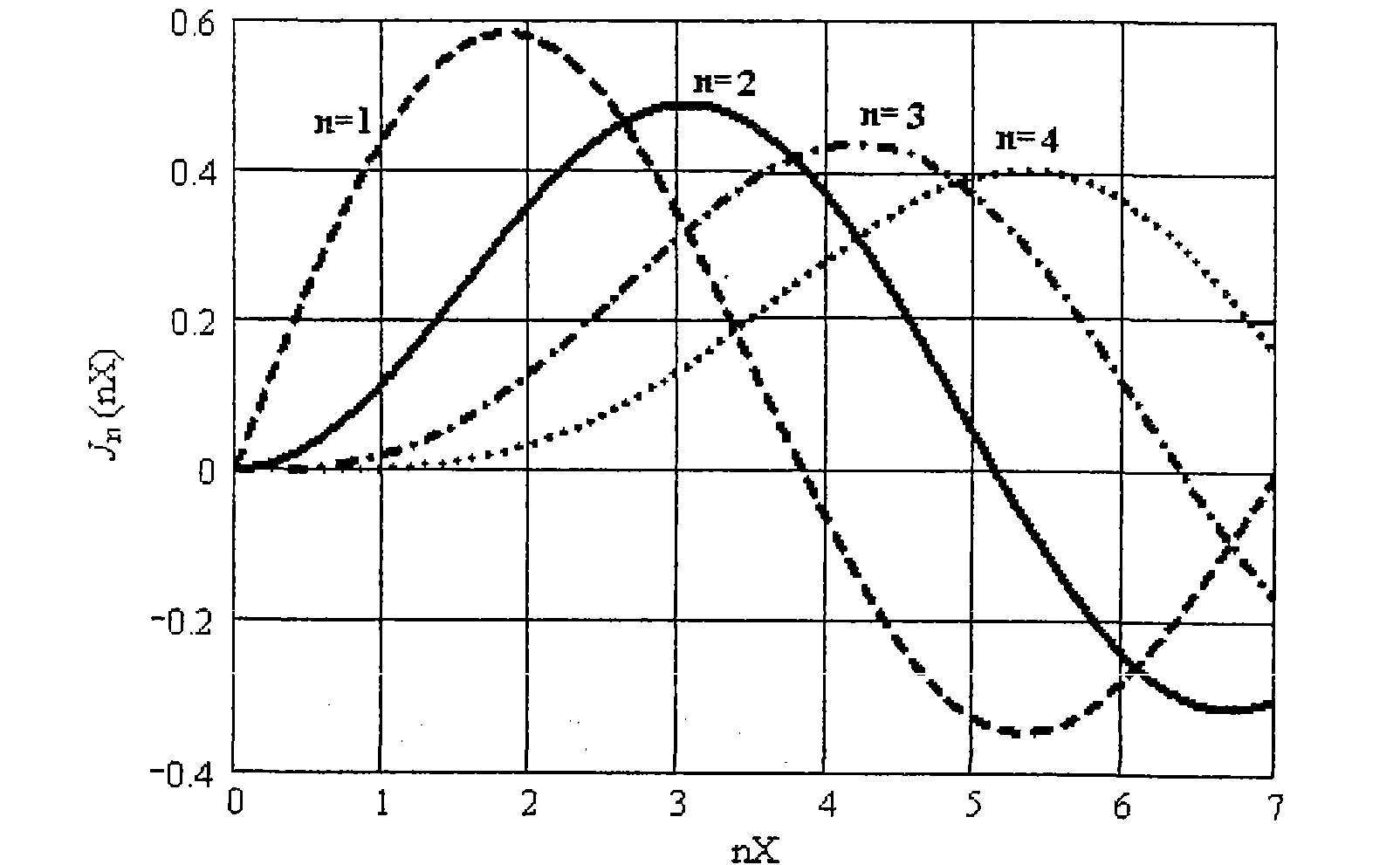
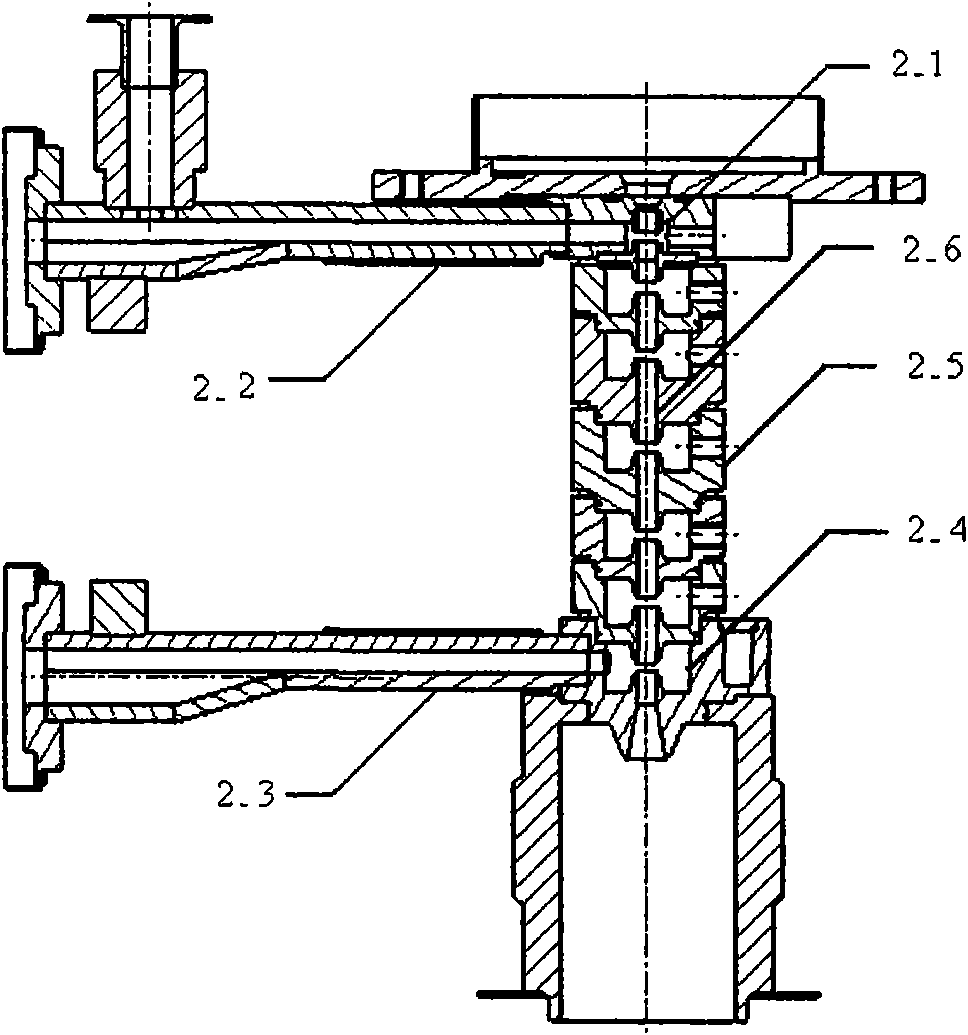
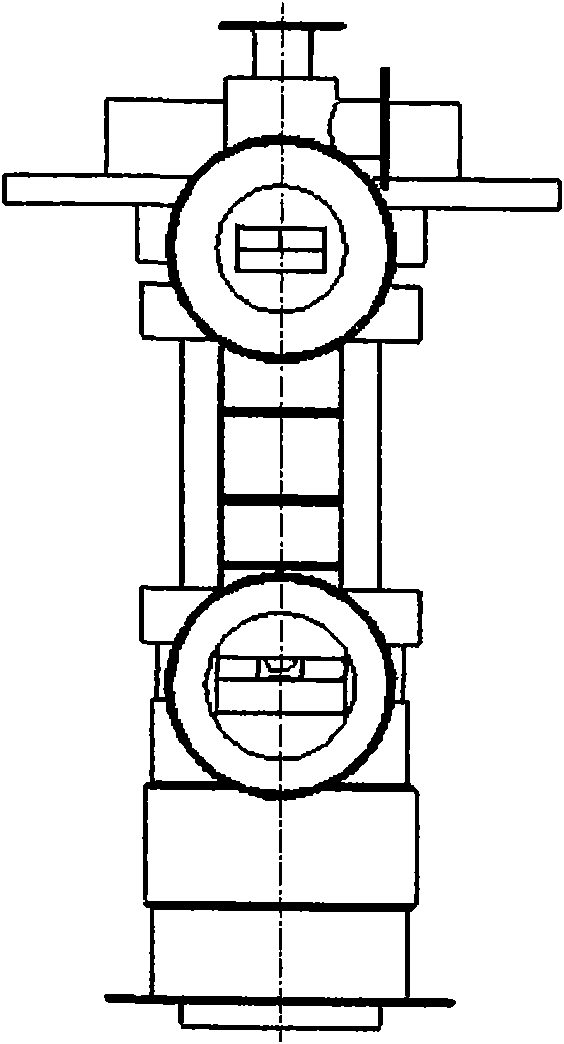
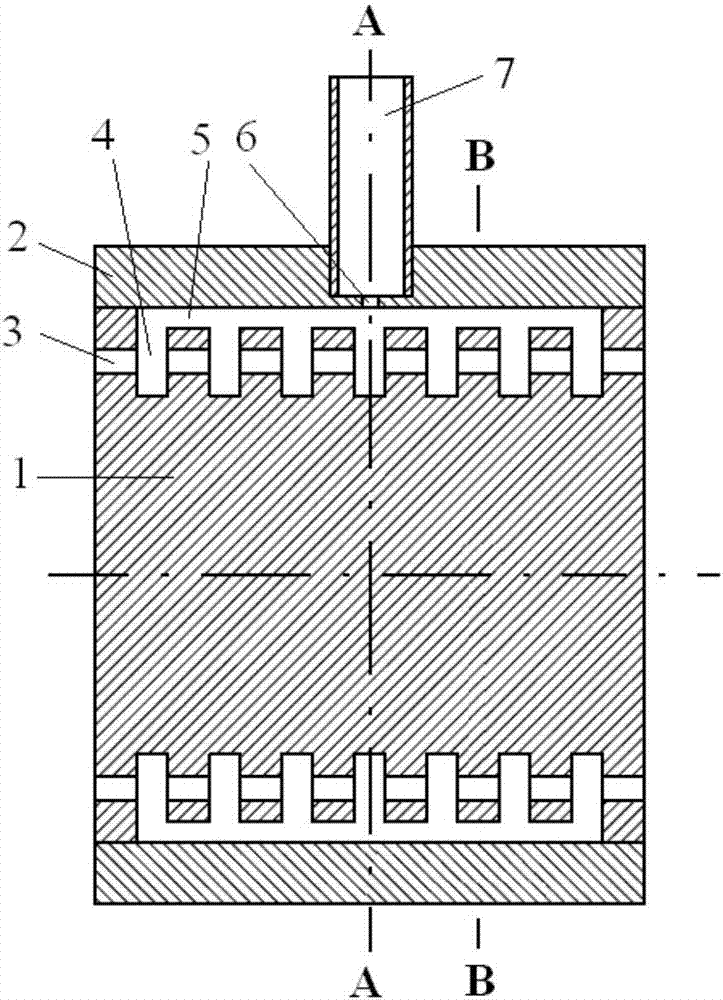
Patents
Literature
247results about "Klystrons" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
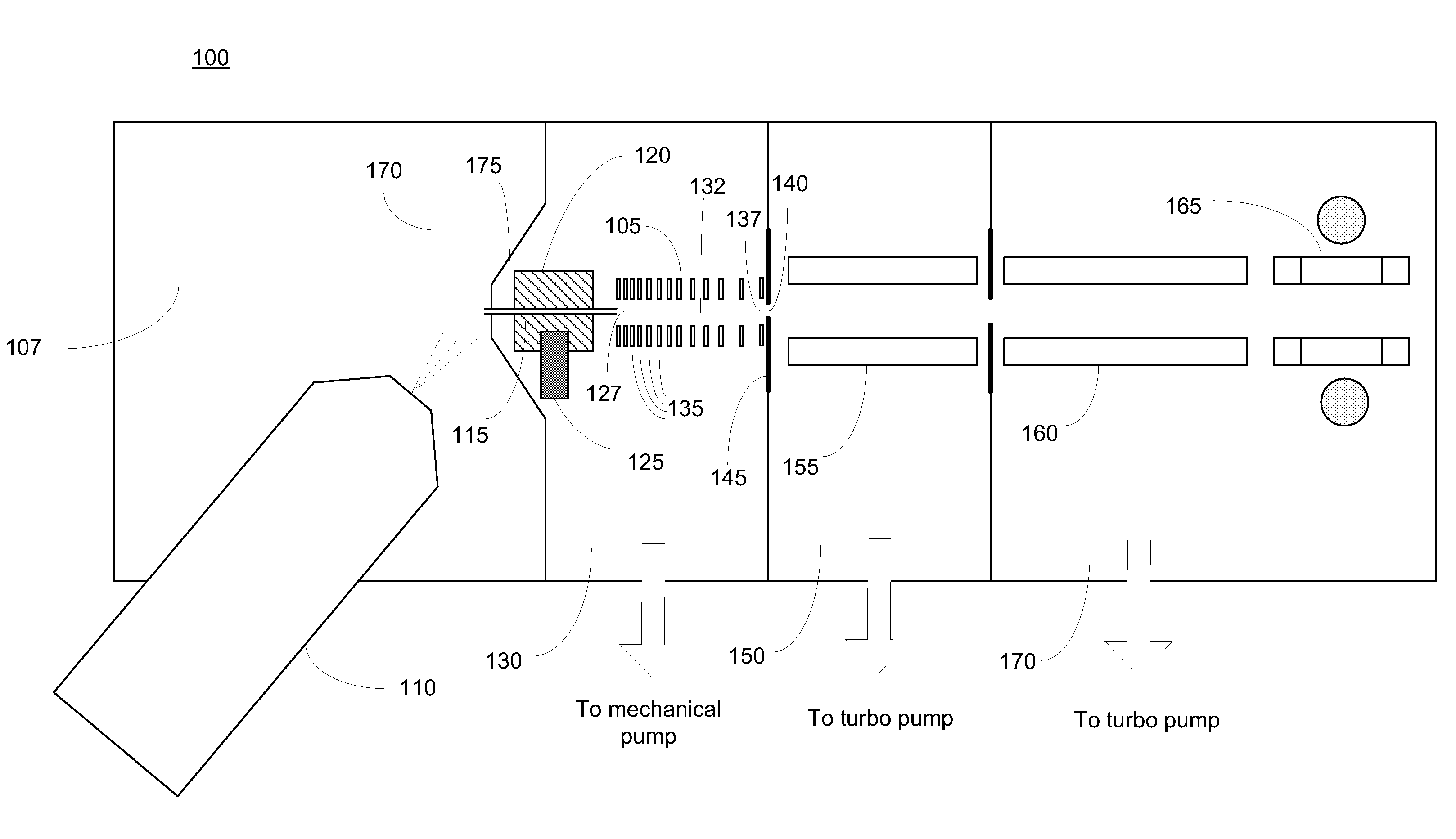
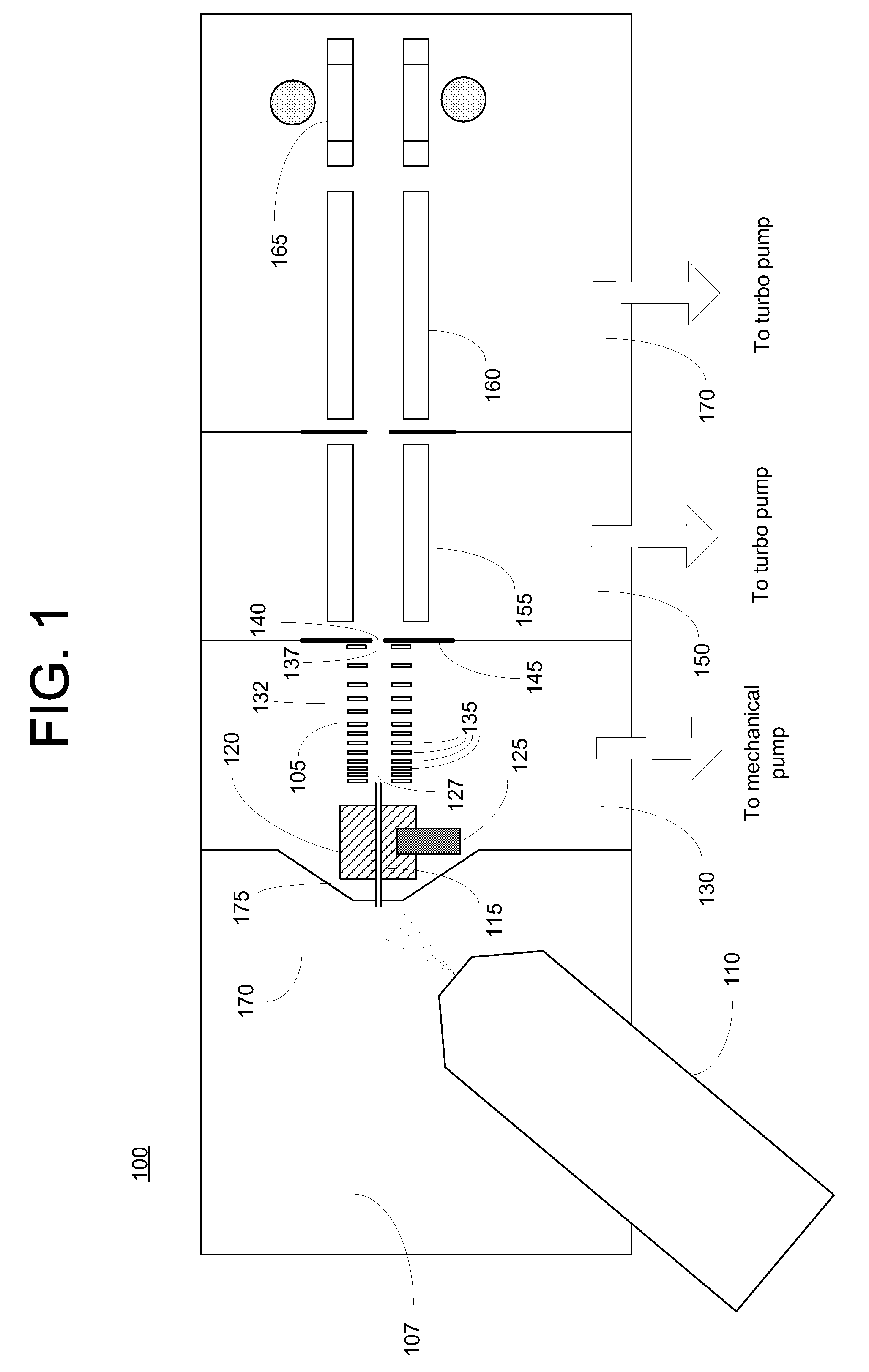
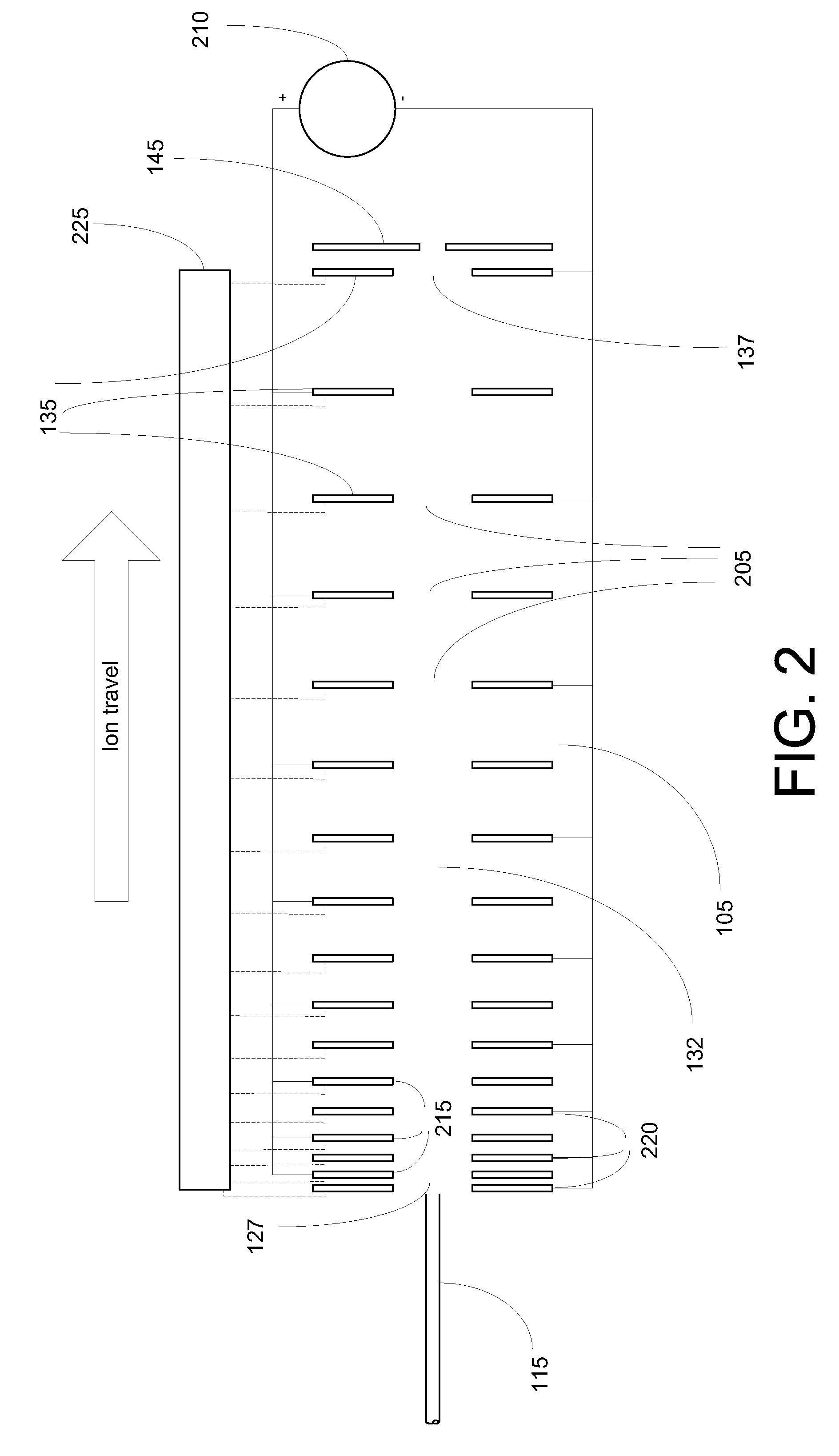
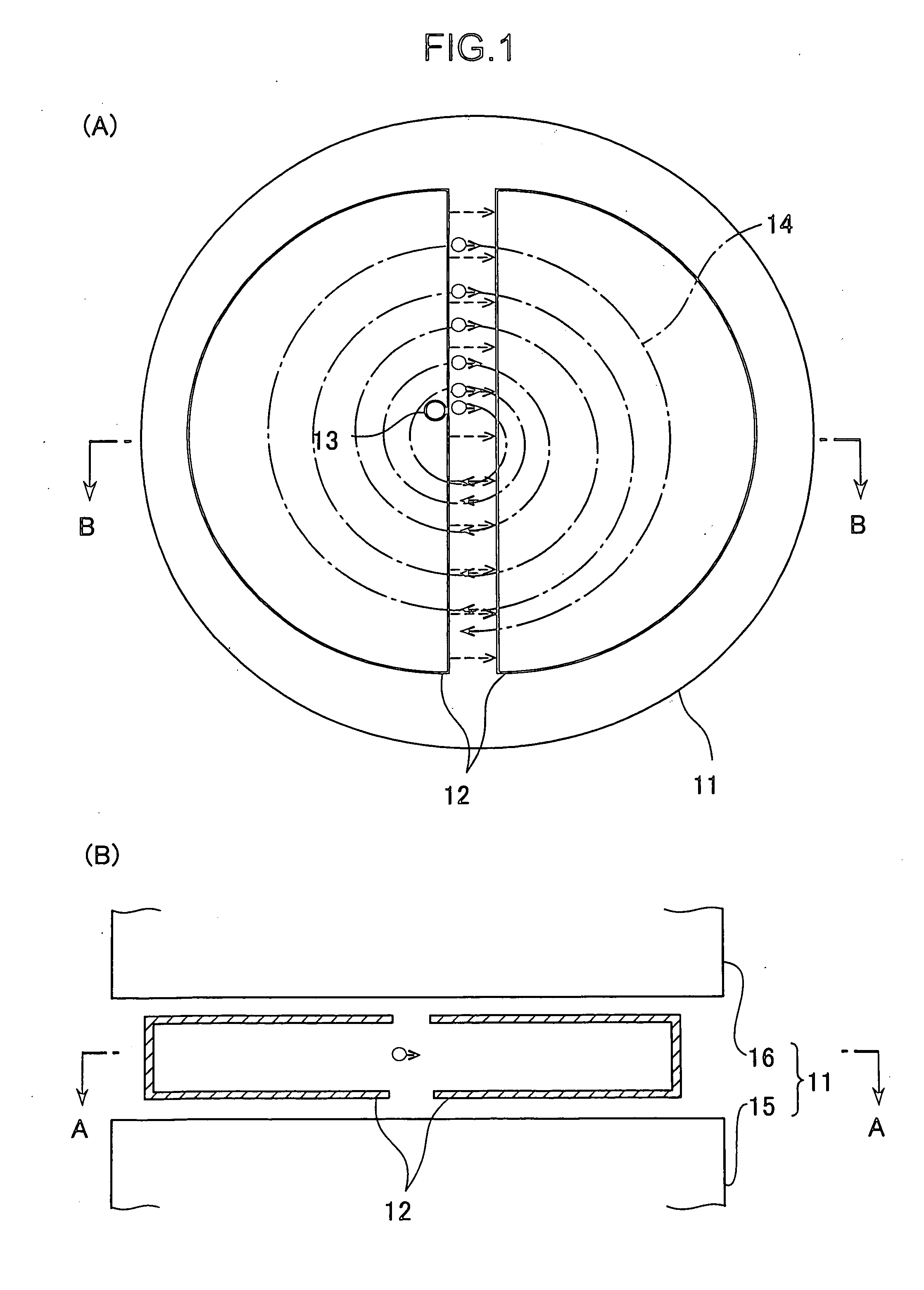
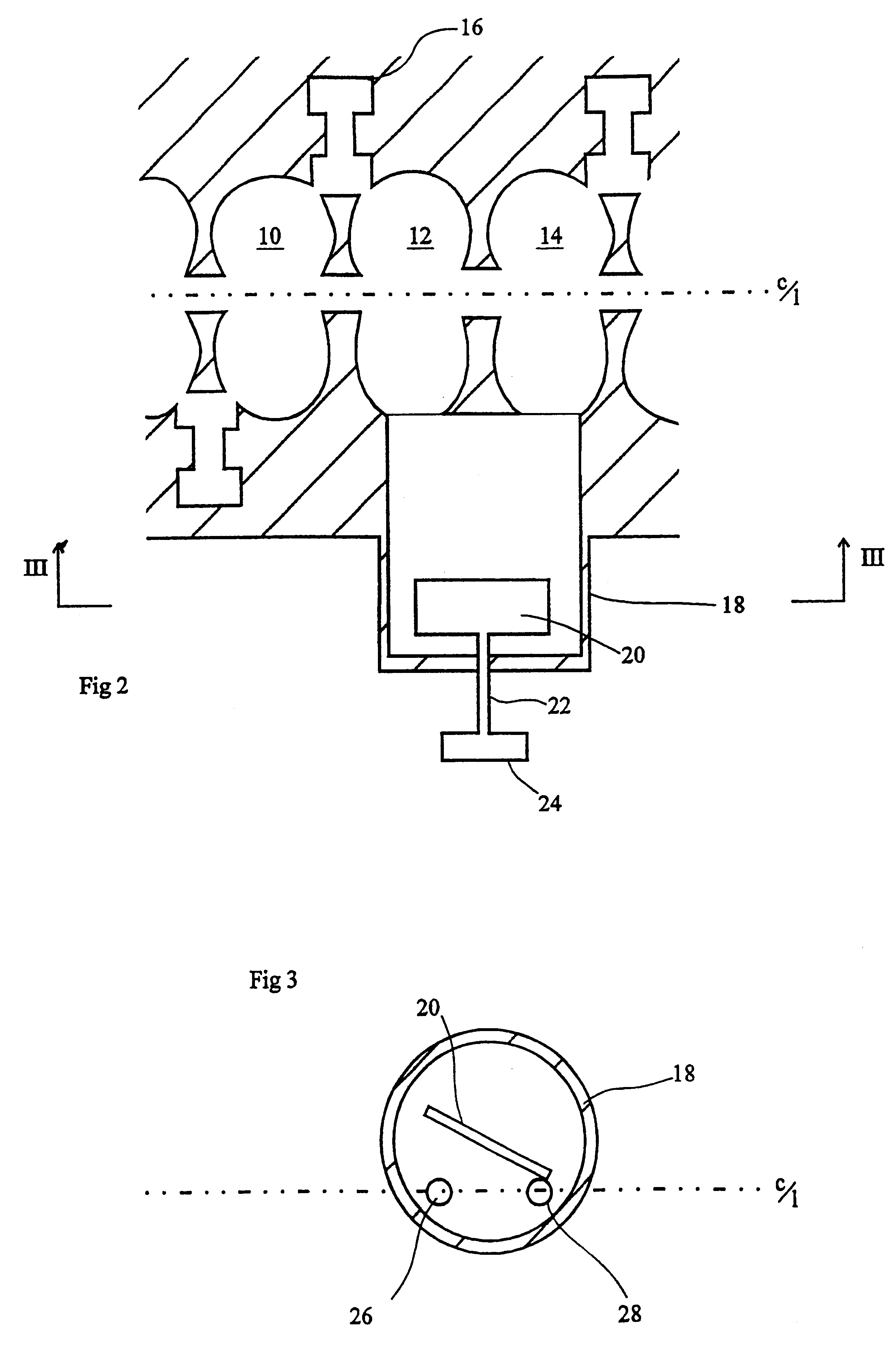
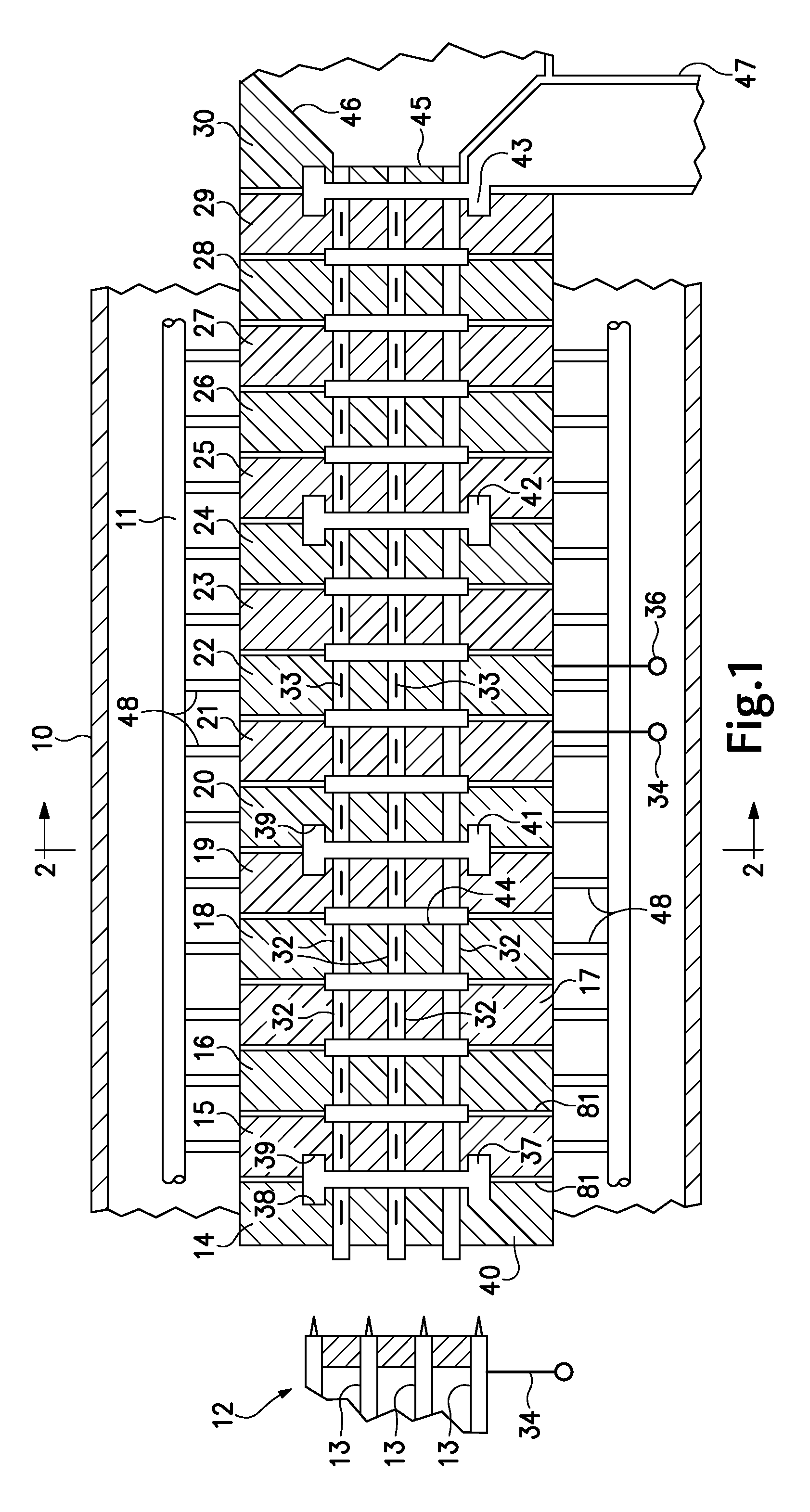
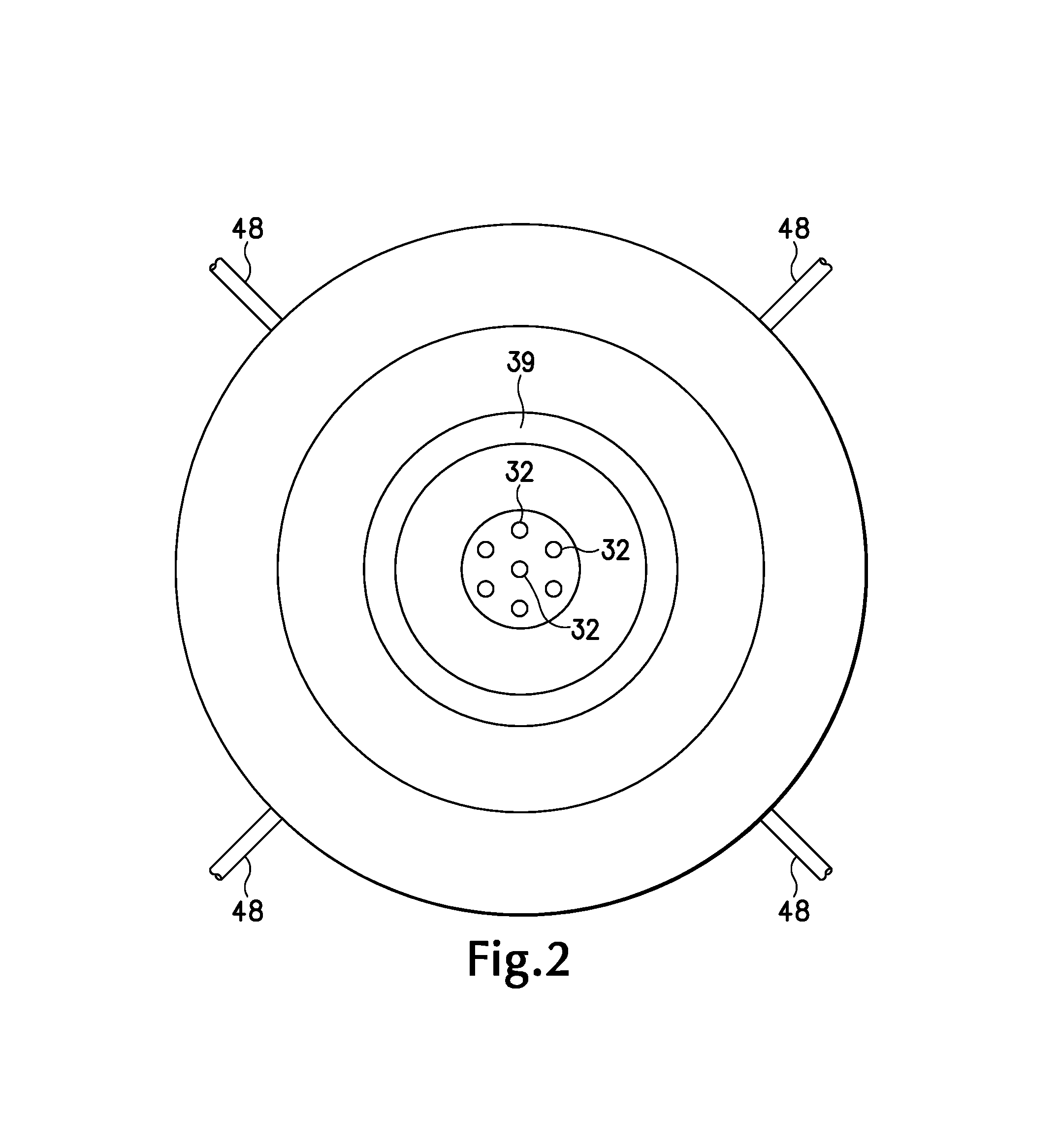
Ion transport device and modes of operation thereof
ActiveUS7781728B2Reduce streamingElectrostatic separatorsParticle separator tubesVoltage amplitudeLight beam
A device for transporting and focusing ions in a low vacuum or atmospheric-pressure region of a mass spectrometer is constructed from a plurality of longitudinally spaced apart electrodes to which oscillatory (e.g., radio-frequency) voltages are applied. In order to create a tapered field that focuses ions to a narrow beam near the device exit, the inter-electrode spacing or the oscillatory voltage amplitude is increased in the direction of ion travel.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
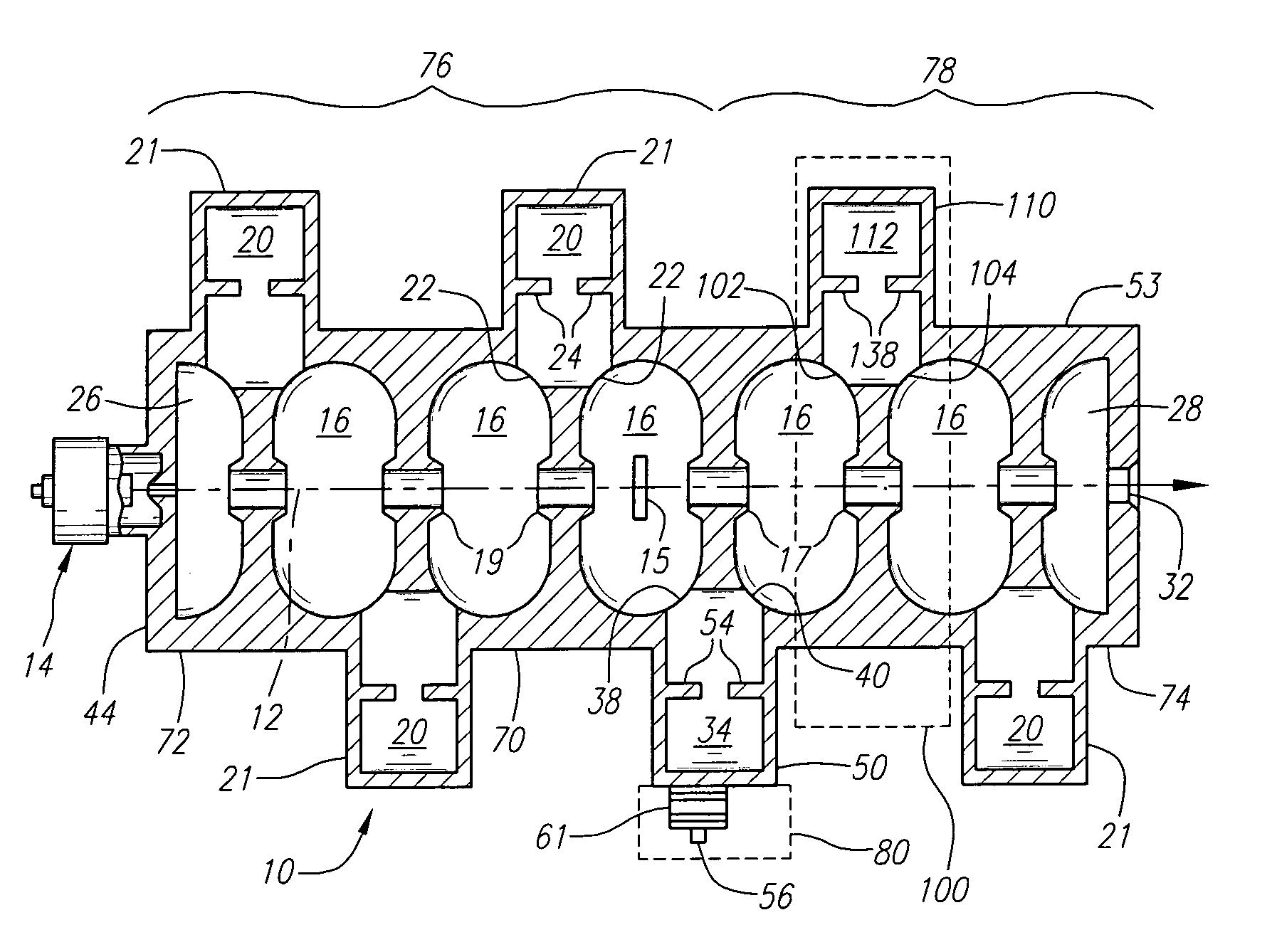
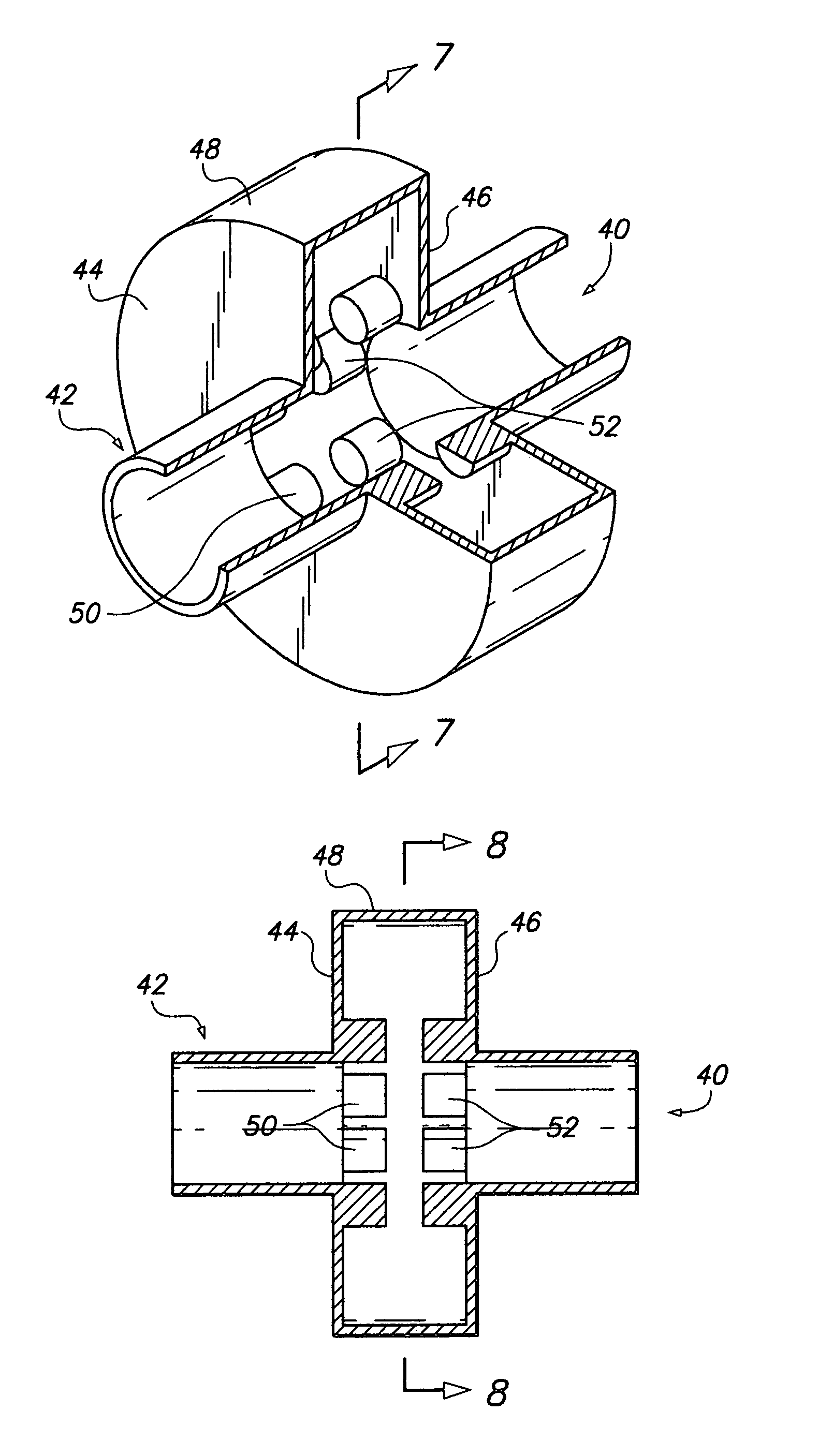
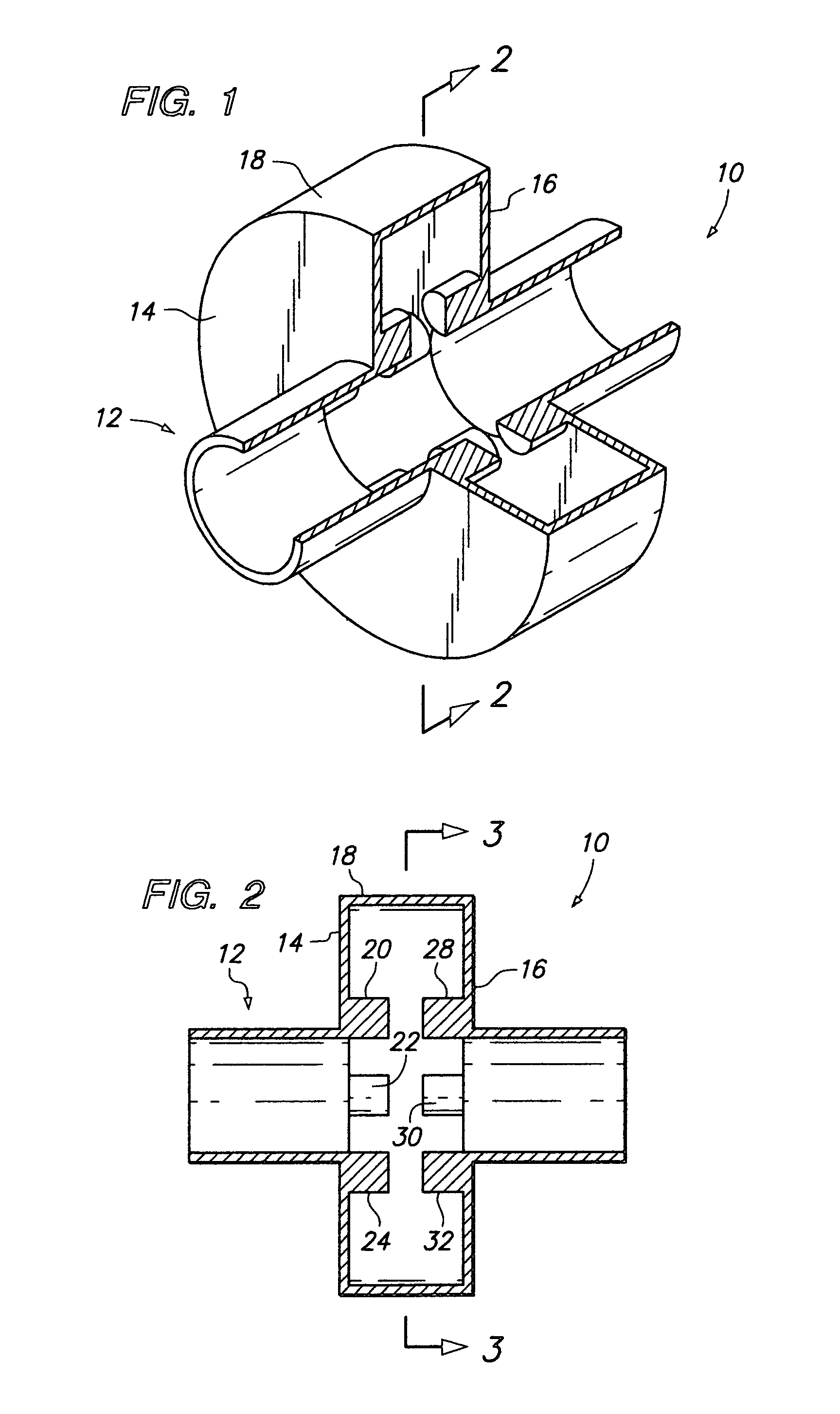
Standing wave particle beam accelerator
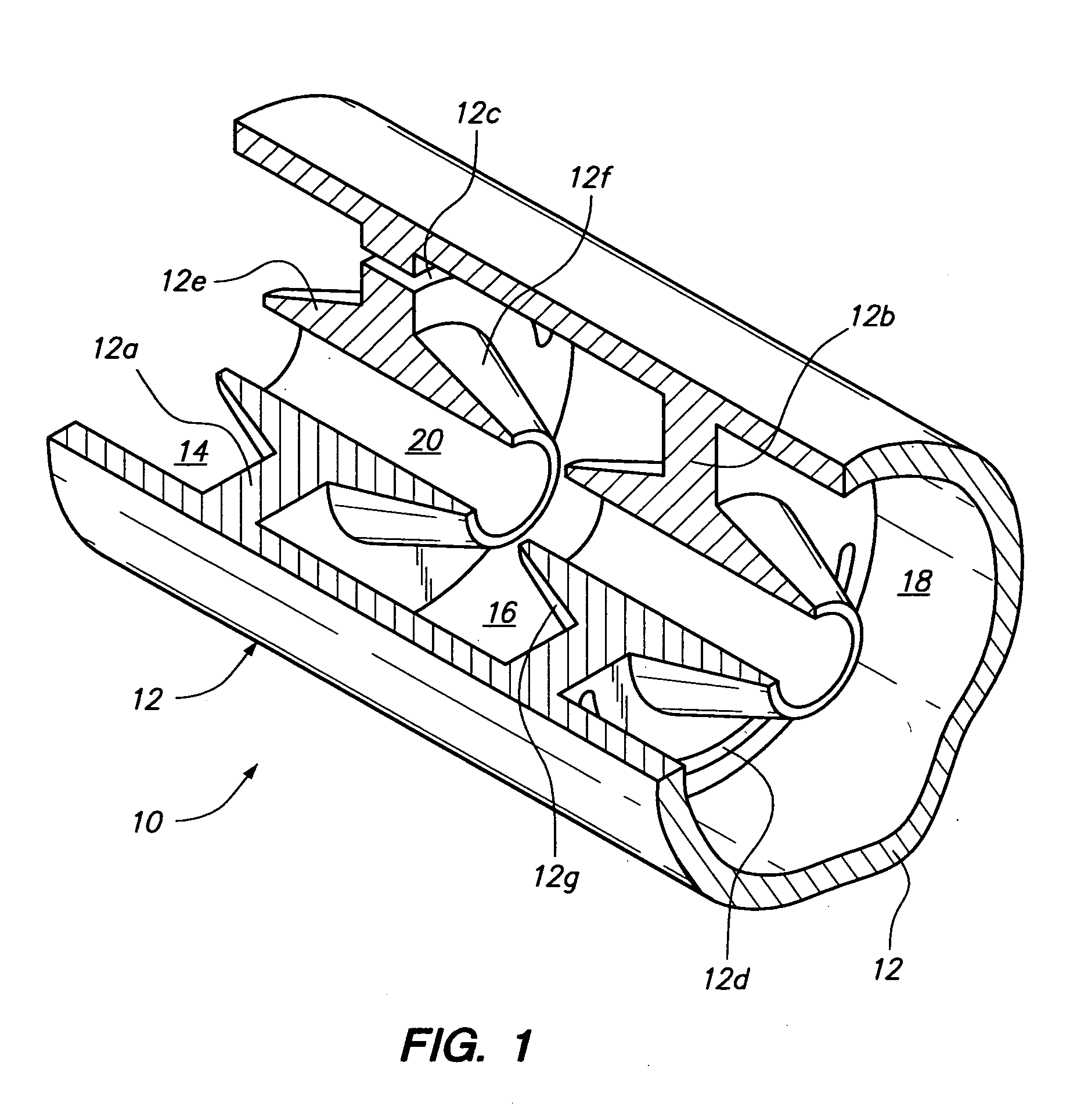
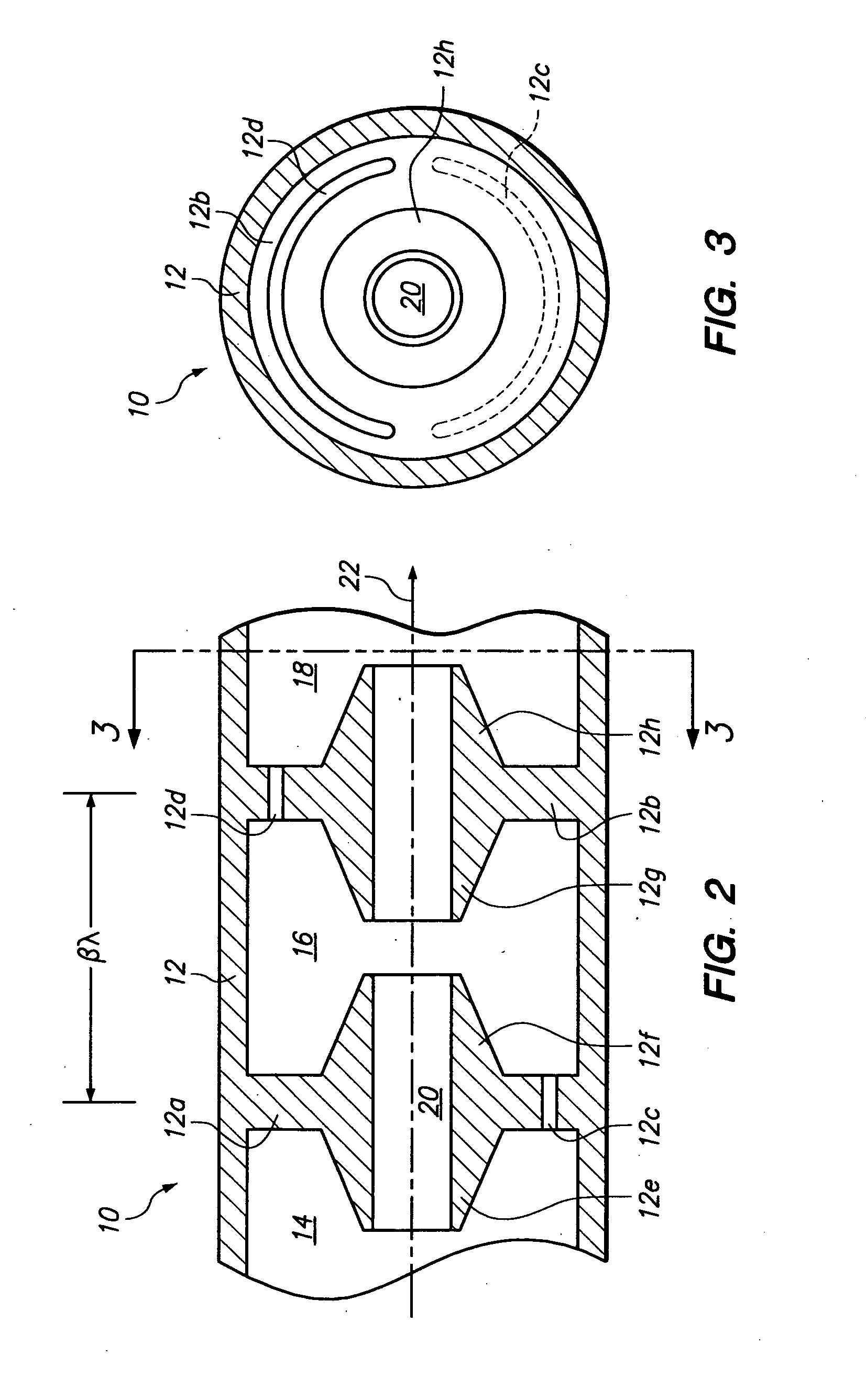
ActiveUS7339320B1Enhanced interactionWide bandwidthLinear acceleratorsKlystronsCapacitanceParticle accelerator
An accelerator for accelerating a particle beam includes a main body having a plurality of electromagnetic cavities coupled in series, and a first coupling body having a first side cavity coupled to one of the electromagnetic cavities through a first opening, and to another of the electromagnetic cavities through a second opening, wherein the first opening and the second opening have different configurations. The accelerator further includes a pair of conductive capacitively coupled noses secured to side walls of the first coupling body, wherein the pair of noses have equal lengths.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC +1
X-ray source employing a compact electron beam accelerator
InactiveUS6864633B2Beam energy is maximizedRadiation is minimizedLinear acceleratorsKlystronsLight beamX-ray
A standing wave electron beam accelerator and x-ray source is described. The accelerator has a plurality of on-axis resonant cells having axial apertures electrically coupled to one another by on-axis coupling cells having axial apertures. The accelerator includes a buncher cavity defined in part by an apertured anode and a half cell. The buncher cavity is configured to receive electrons injected through said anode aperture and r.f. focus them into a beam which is projected along the axis through said apertures. An x-ray target is supported in spaced relationship to said accelerator by a support having a smaller diameter than the accelerator.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
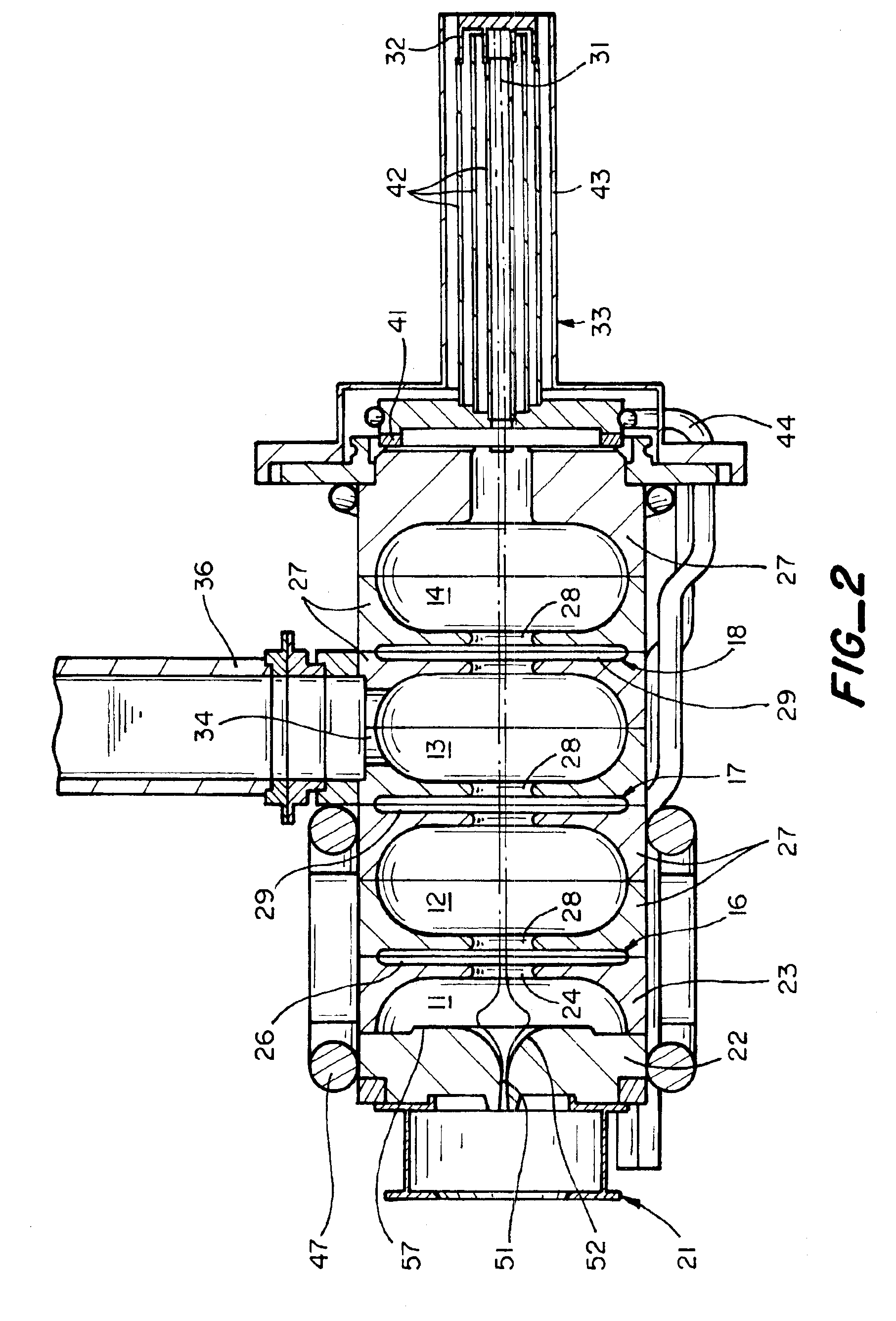
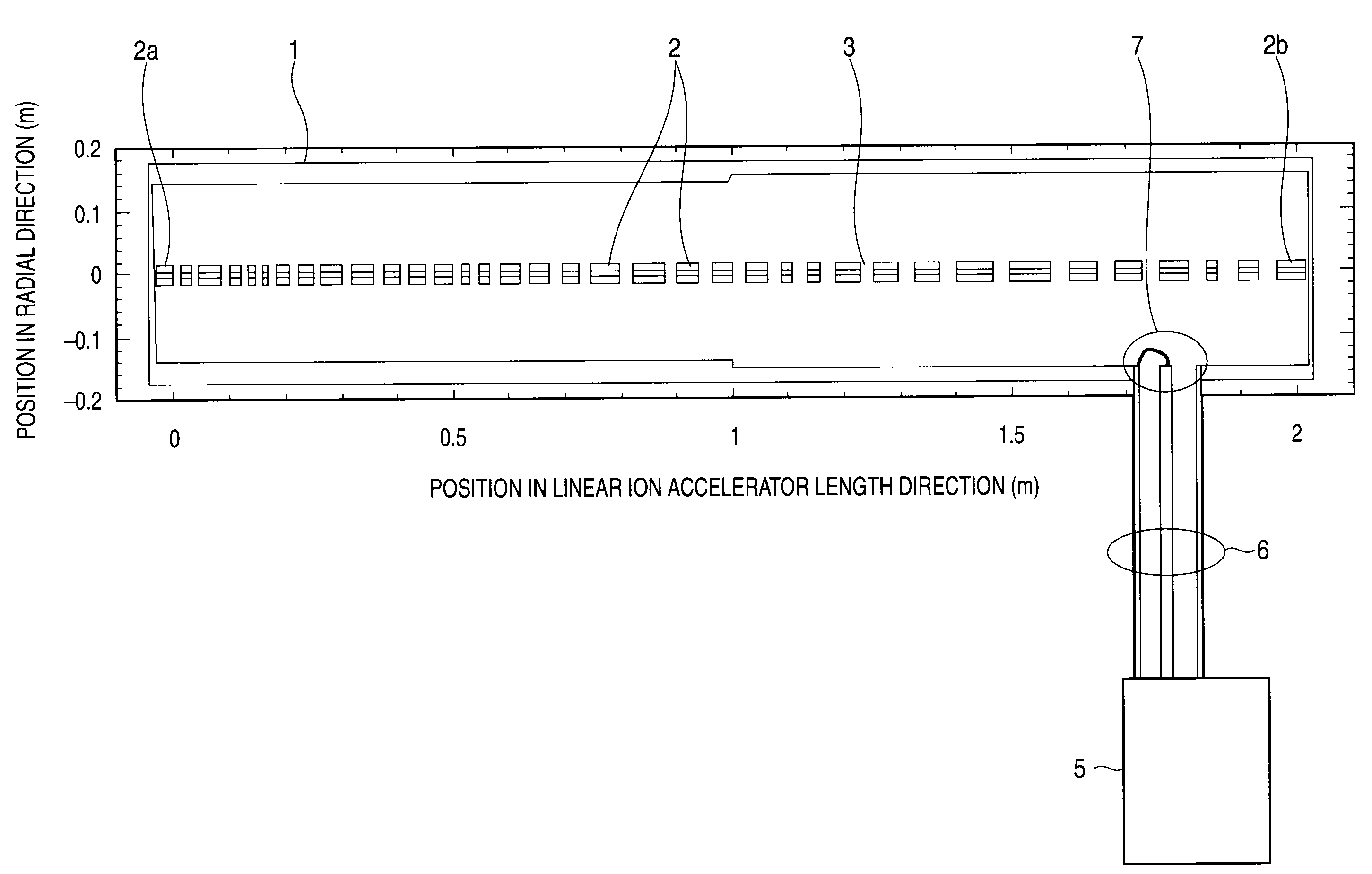
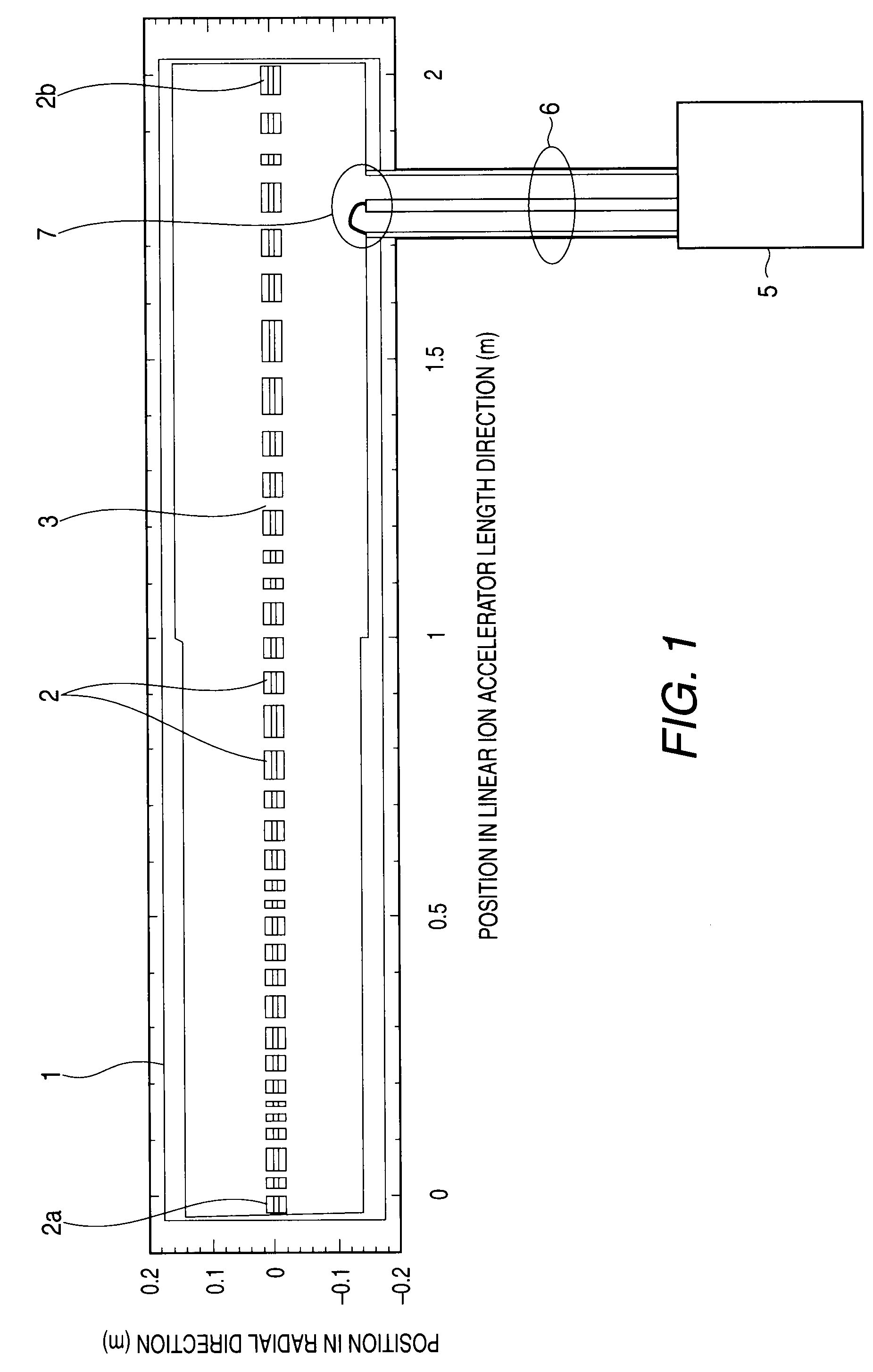
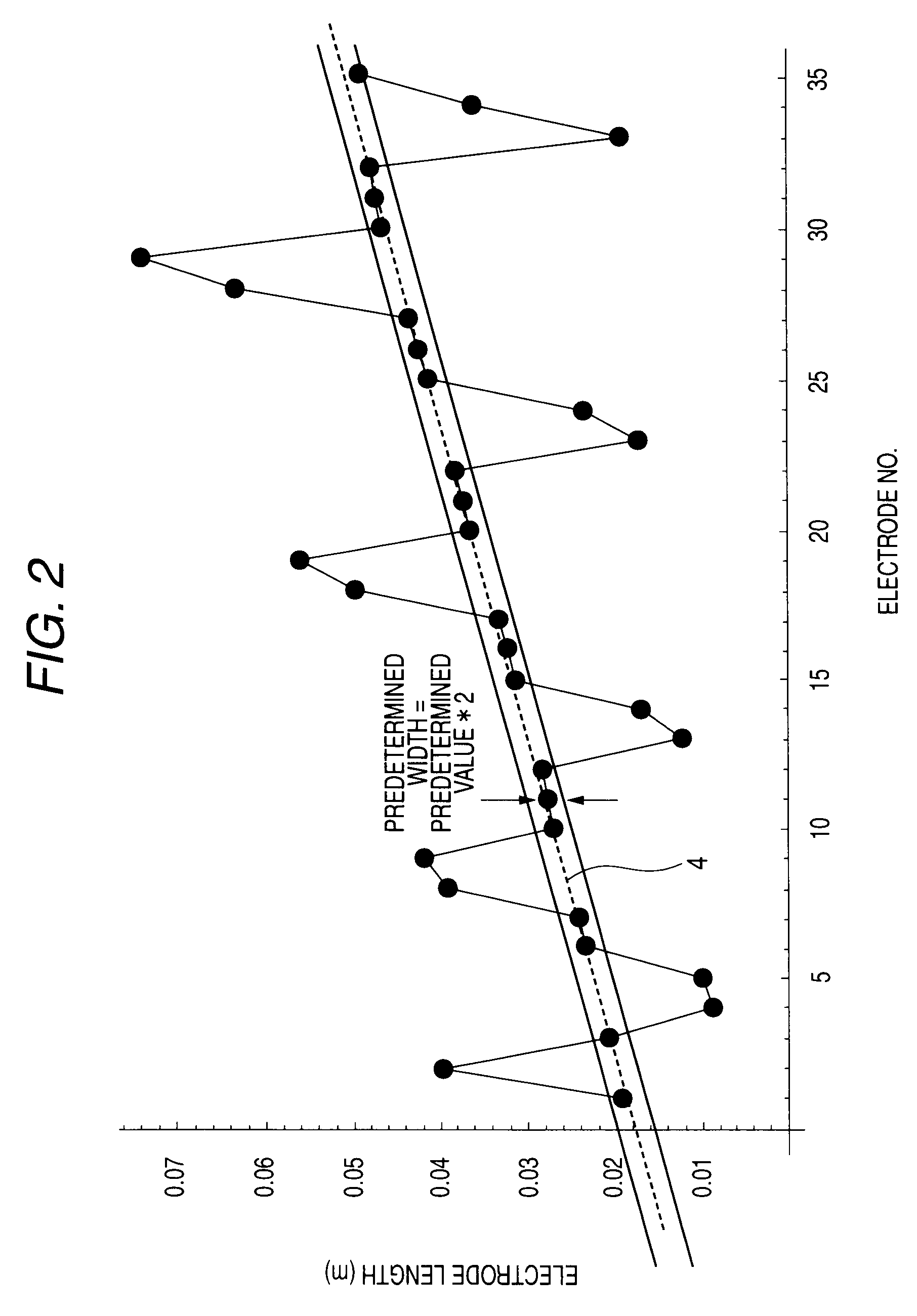
Linear ion accelerator
ActiveUS7609009B2Affect produced by the space charge effect is increasedEasy to divergeStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsIon beamIon acceleration
The electrode lengths of a plurality of electrodes linearly arranged in an acceleration cavity are proportional to the velocity of a traveling ion beam. Further, the electrode length is so designated that, in each half of a predetermined cycle in the ion beam direction of travel, the absolute value of a difference, relative to a length that is proportional to the beam traveling velocity is equal to or greater than a value corresponding to the phase width of the traveling ion beam, is provided for electrodes that do not exceed three units and that are fewer than electrodes allotted to half the predetermined cycle.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Dual-plunger energy switch
InactiveUS20070035260A1Increase productionHigh energyLinear acceleratorsKlystronsHigh energyParticle beam
A dual-plunger energy switch assembly for standing wave linear particle beam accelerators capable of operating in a higher energy mode and a lower energy mode employs two mechanical plungers that can be extended different distances inside two side cavities of the linear accelerator. When the linear accelerator is operated in the higher energy mode, both plungers are retracted out of the side cavities. To achieve high output while the linear accelerator is operated in the lower energy mode, the two plungers are radially inserted into the two side cavities to adjust the electromagnetic accelerating field along the length of the accelerator, e.g., one plunger is inserted into a side cavity so that the plunger touches the smile surface of the side cavity, while the second plunger is inserted into a second side cavity so that the plunger is adjacent to, but not touching, the smile surface of the side cavity.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Dual-plunger energy switch
InactiveUS7239095B2Increase productionHigh energyLinear acceleratorsKlystronsParticle beamHigh energy
A dual-plunger energy switch assembly for standing wave linear particle beam accelerators capable of operating in a higher energy mode and a lower energy mode employs two mechanical plungers that can be extended different distances inside two side cavities of the linear accelerator. When the linear accelerator is operated in the higher energy mode, both plungers are retracted out of the side cavities. To achieve high output while the linear accelerator is operated in the lower energy mode, the two plungers are radially inserted into the two side cavities to adjust the electromagnetic accelerating field along the length of the accelerator, e.g., one plunger is inserted into a side cavity so that the plunger touches the smile surface of the side cavity, while the second plunger is inserted into a second side cavity so that the plunger is adjacent to, but not touching, the smile surface of the side cavity.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
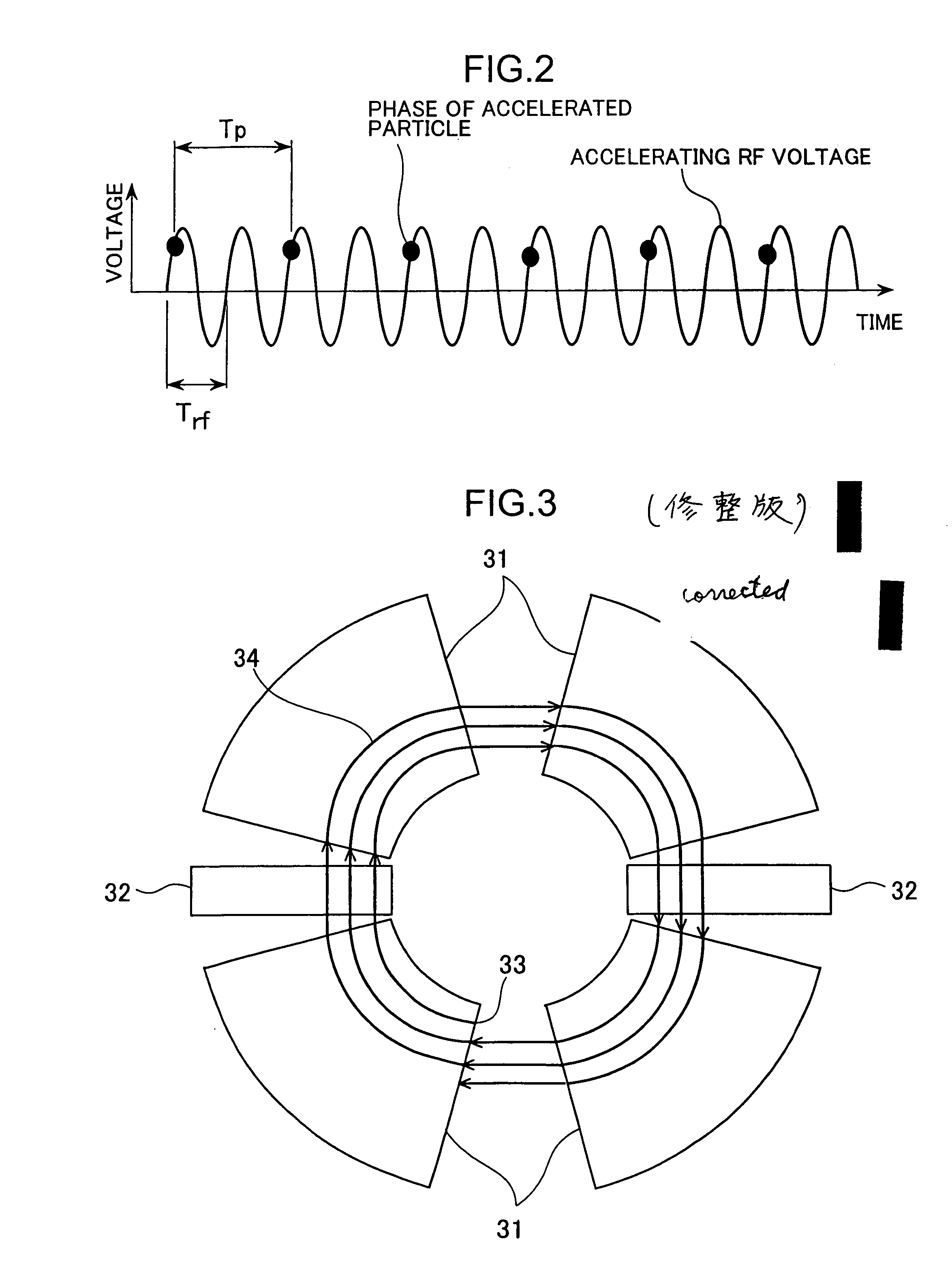
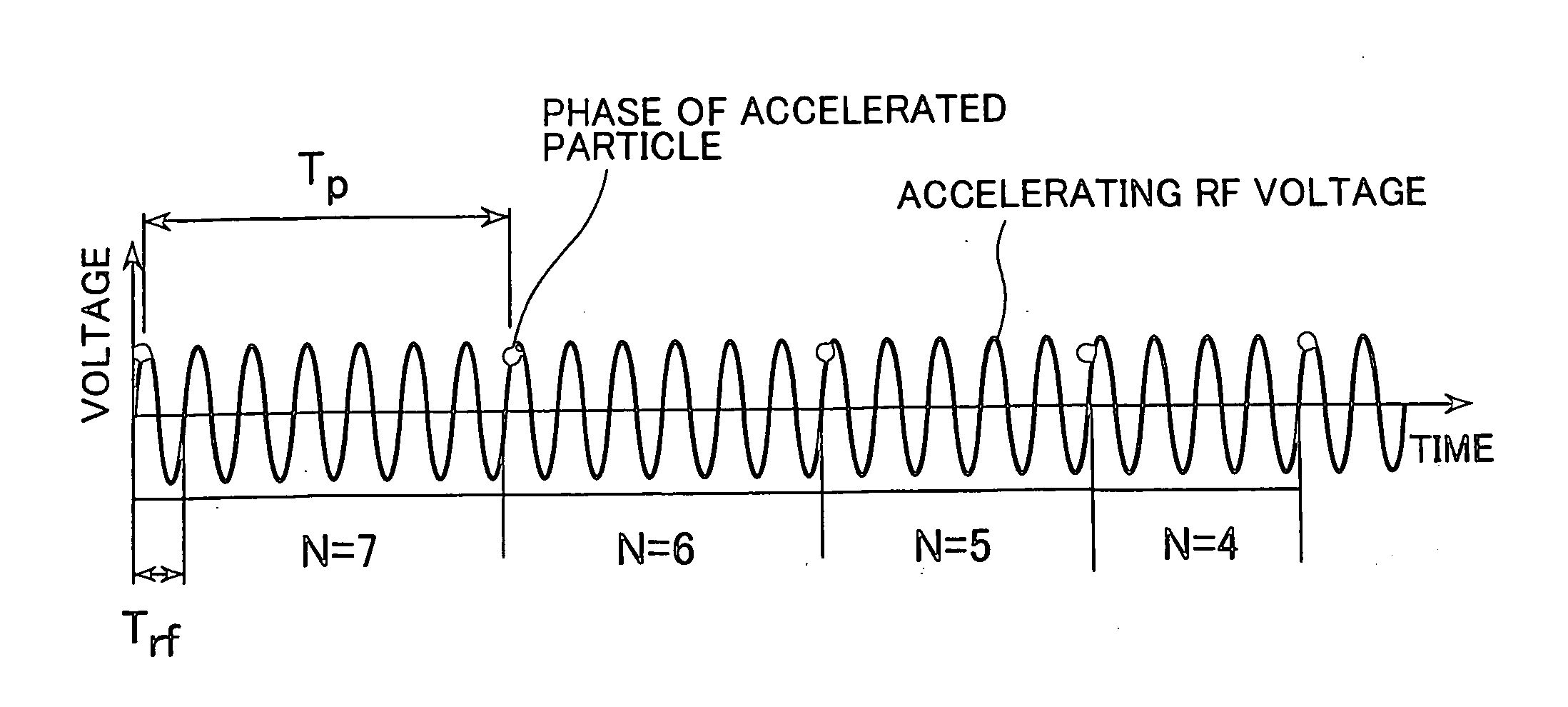
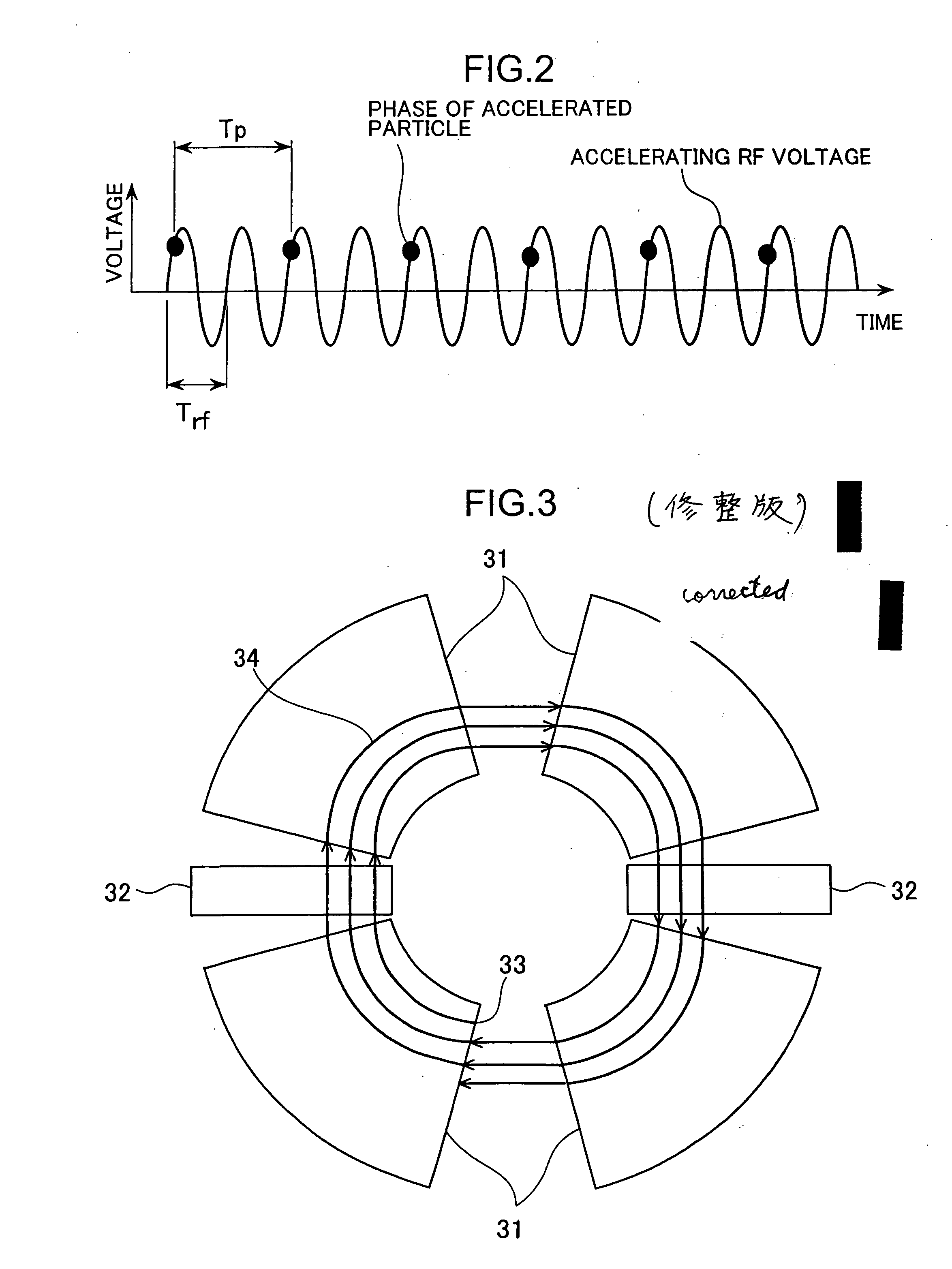
Spiral orbit charged particle accelerator and its acceleration method
InactiveUS7262565B2High energyIncreasing magnet sizeMagnetic resonance acceleratorsKlystronsParticle acceleratorHarmonic
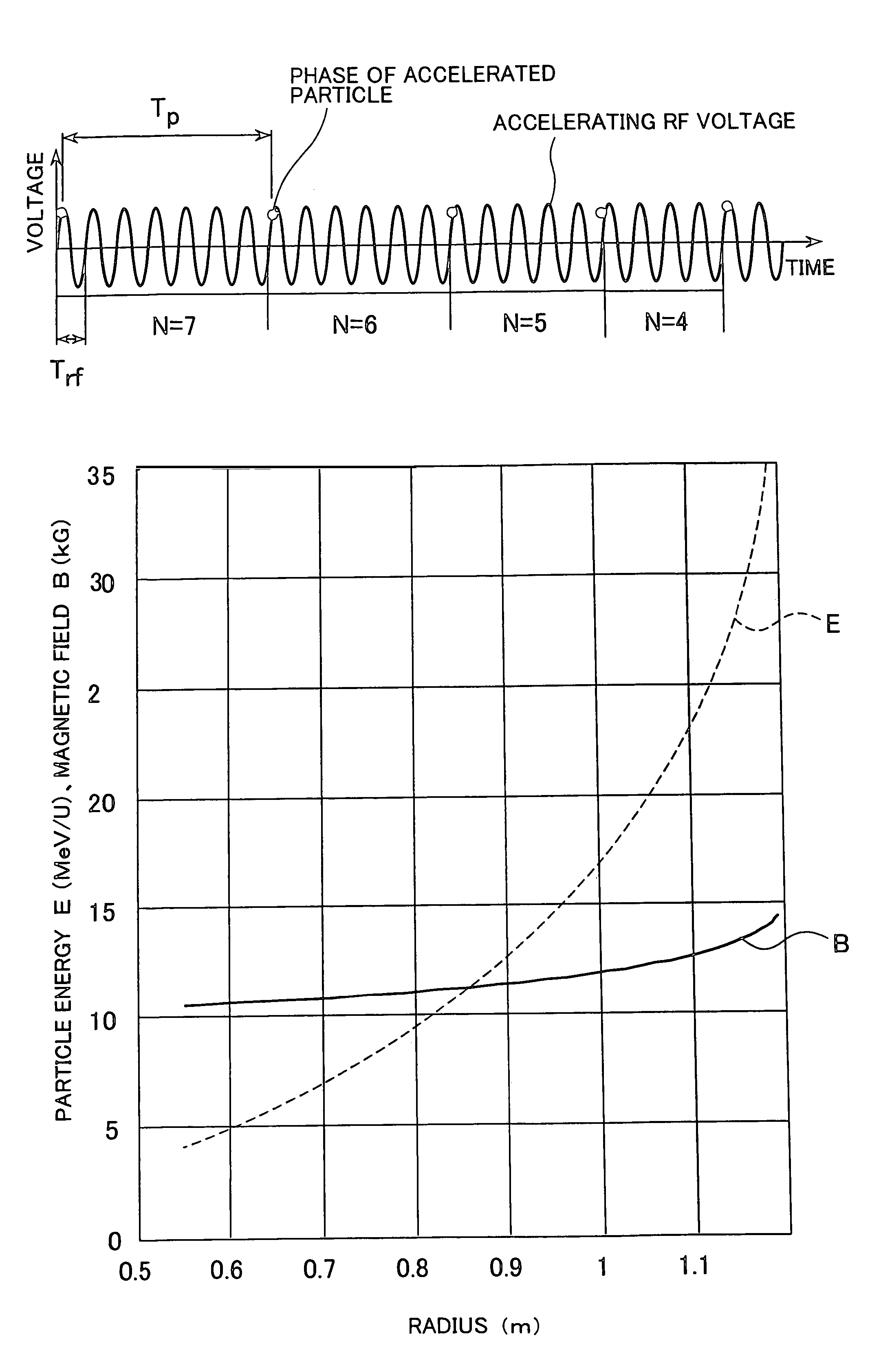
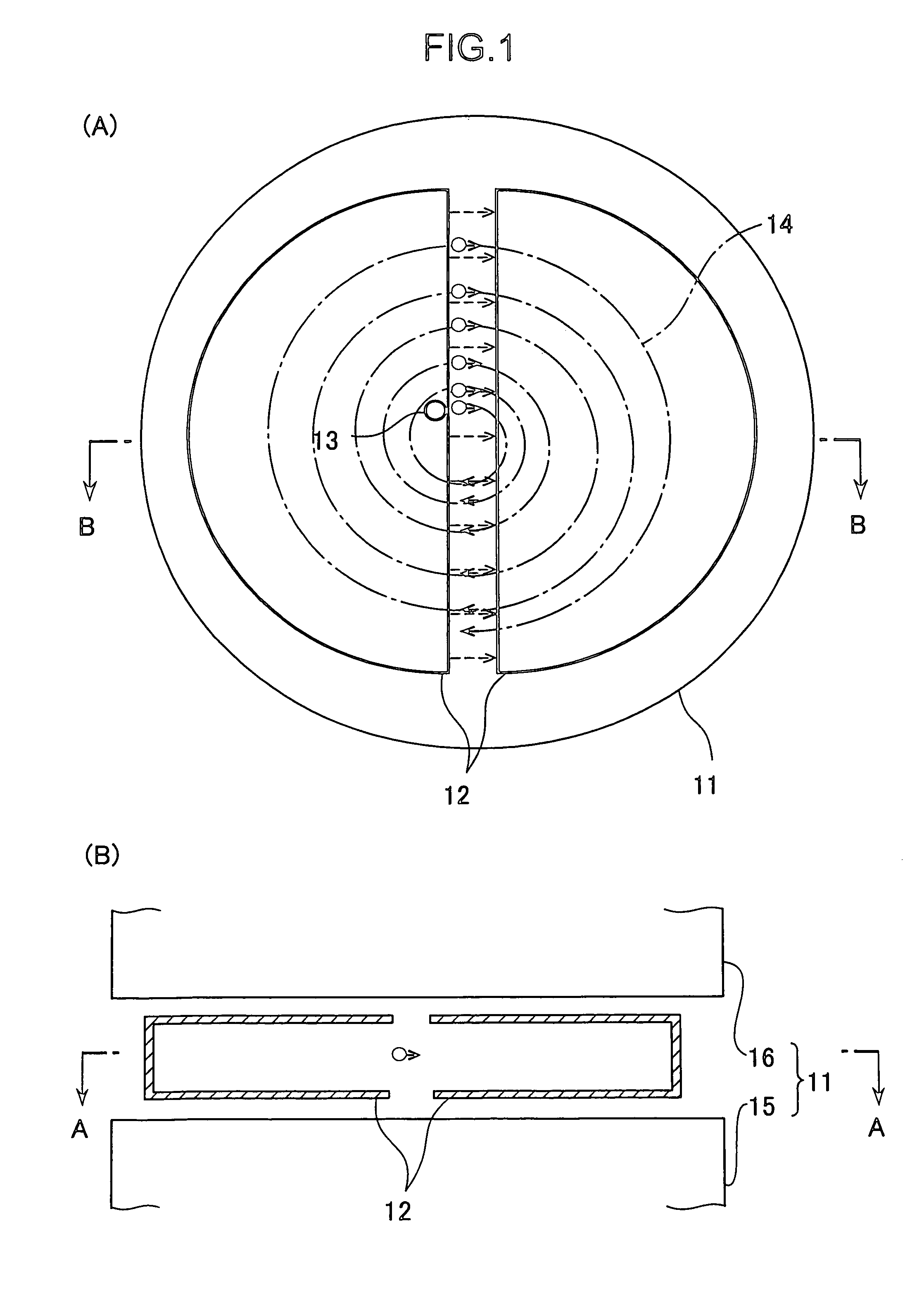
According to the present invention, a non-isochronous magnetic field distribution in which the magnetic field increases as the radius increases is formed and a distribution of fixed-frequency accelerating RF voltage is formed, said non-isochronous magnetic field distribution and said distribution of fixed-frequency accelerating RF voltage being formed so that a harmonic number defined as a ratio of the particle revolution period to the period of the accelerating RF voltage decreases in integer for every particle revolution.
Owner:NAT INST OF RADIOLOGICAL SCI
Spiral orbit charged particle accelerator and its acceleration method
InactiveUS20060175991A1High energy gainIncreasing magnet sizeMagnetic resonance acceleratorsKlystronsHarmonicOrbit
According to the present invention, a non-isochronous magnetic field distribution in which the magnetic field increases as the radius increases is formed and a distribution of fixed-frequency accelerating RF voltage is formed, said non-isochronous magnetic field distribution and said distribution of fixed-frequency accelerating RF voltage being formed so that a harmonic number defined as a ratio of the particle revolution period to the period of the accelerating RF voltage decreases in integer for every particle revolution.
Owner:NAT INST OF RADIOLOGICAL SCI
Multi-section particle accelerator with controlled beam current
InactiveUS7208890B2Reducing and eliminating reflectionEasy transferLinear acceleratorsKlystronsParticle acceleratorAccelerated particle
Owner:SCANTECHIBS IP HLDG
Linac for ion beam acceleration
InactiveUS6888326B2Effective reduction in overall dimensionSatisfies requirementLinear acceleratorsMachines/enginesIon beamDrift tube
A drift tube linear accelerator (linac) that can be used for the acceleration of low energy ion beams. The particles enter the linac at low energy and are accelerated and focused along a straight line in a plurality of resonant accelerating structures interposed by coupling structures up to the desired energy. In the accelerating structures, excited by an H-type resonant electromagnetic field, a plurality of accelerating gaps is provided between drift tubes supported by stems, for instance alternatively horizontally and vertically disposed. A basic module composed of two accelerating structures and an interposed coupling structure, or a modified coupling structure connected to a RF power generator, is if necessary linked to a vacuum system and equipped with one or more quadrupoles.
Owner:FOND PER ADROTERAPIA ONCOLOGICA TERA
Linear accelerator
InactiveUS6376990B1Good flexibilityGreat flexibility.TheTravelling-wave tubesElectric arc lampsElectrical resistance and conductanceRelative magnitude
This device allows the variation of the coupling between two points in an RF circuit in a very simple way while maintaining the RF phase relationship and varying the relative magnitude of the RF fields. The device is characterized by a simple mechanical control of coupling value, that has negligible effect on the phase shift across the device. This is achieved by the simple rotation of the polarisation of a TE111 mode inside a cylindrical cavity. Such a device does not contain resistive elements, and the sliding mechanical surfaces are free from high RF currents. This device finds an application in standing wave linear accelerators, where it is desirable to vary the relative RF field in one set of cavities with respect to another, in order that the accelerator can operate successfully over a wide range of energies.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
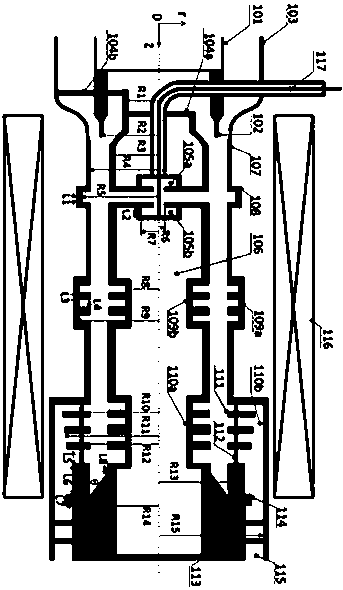
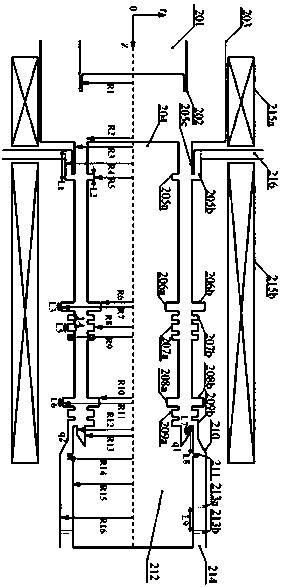
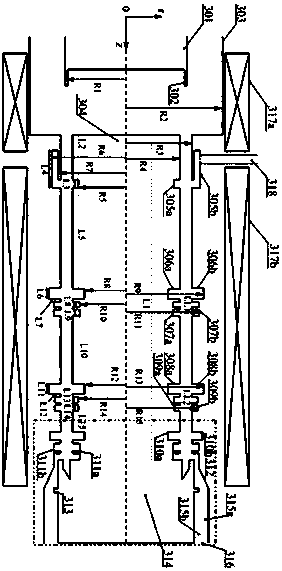
X-band high gain and high efficiency triaxial relativistic klystron amplifier
ActiveCN109599316AHigh gainHigh Gain High EfficiencyKlystronsTransit-tube coupling devicesKlystronElectrical conductor
An X-band high gain and high efficiency triaxial relativistic klystron amplifier comprises a cathode holder 301, a cathode 302, an anode outer cylinder 303, an inner conductor 304, a modulation cavity305, a first reflection cavity 306, a first cluster cavity 307, a second reflection cavity 308, a second cluster cavity 309, a third reflection cavity 310, an extraction cavity 311, a cone waveguide312, a feedback loop 313, an electron collector 314, a support rod 315, a microwave output port 316, a solenoid magnetic field 317, and an injection waveguide 318, wherein the overall structure is rotationally symmetric about the central axis OZ axis. The amplifier, by rationally designing the electromagnetic structure of the device, overcomes the shortages such as complex structure, and relatively low gain (about 40 dB), efficiency (less than 30%) and output microwave power (about 1 GW) of axial injection or lateral dual-port injection in the existing X-band triaxial relativistic klystron amplifier, and realizes the high-gain, high-efficiency, and high-power microwave output of the triaxial relativistic klystron amplifier in the X-band.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
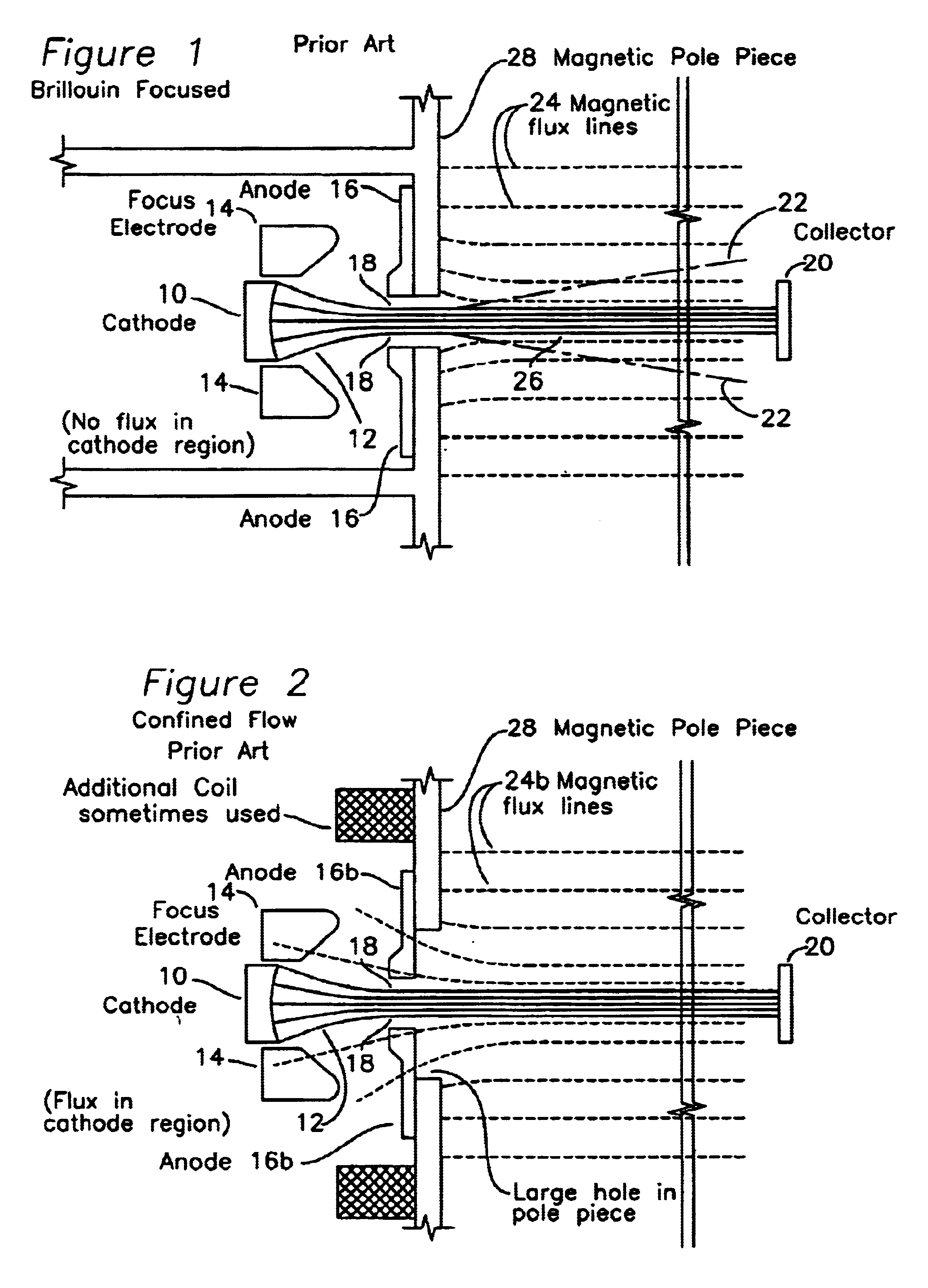
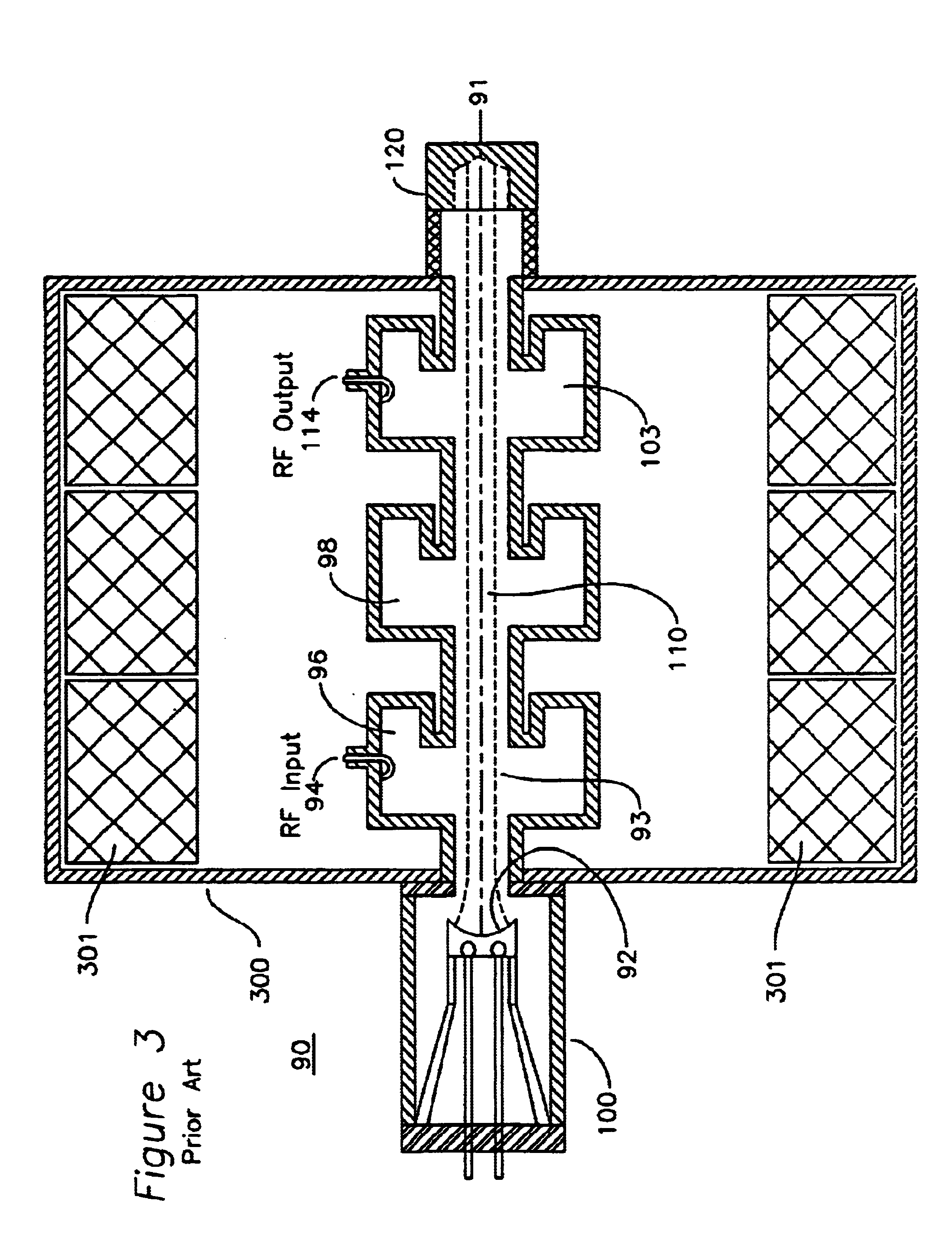
Electron gun for a multiple beam klystron using magnetic focusing with a magnetic field corrector
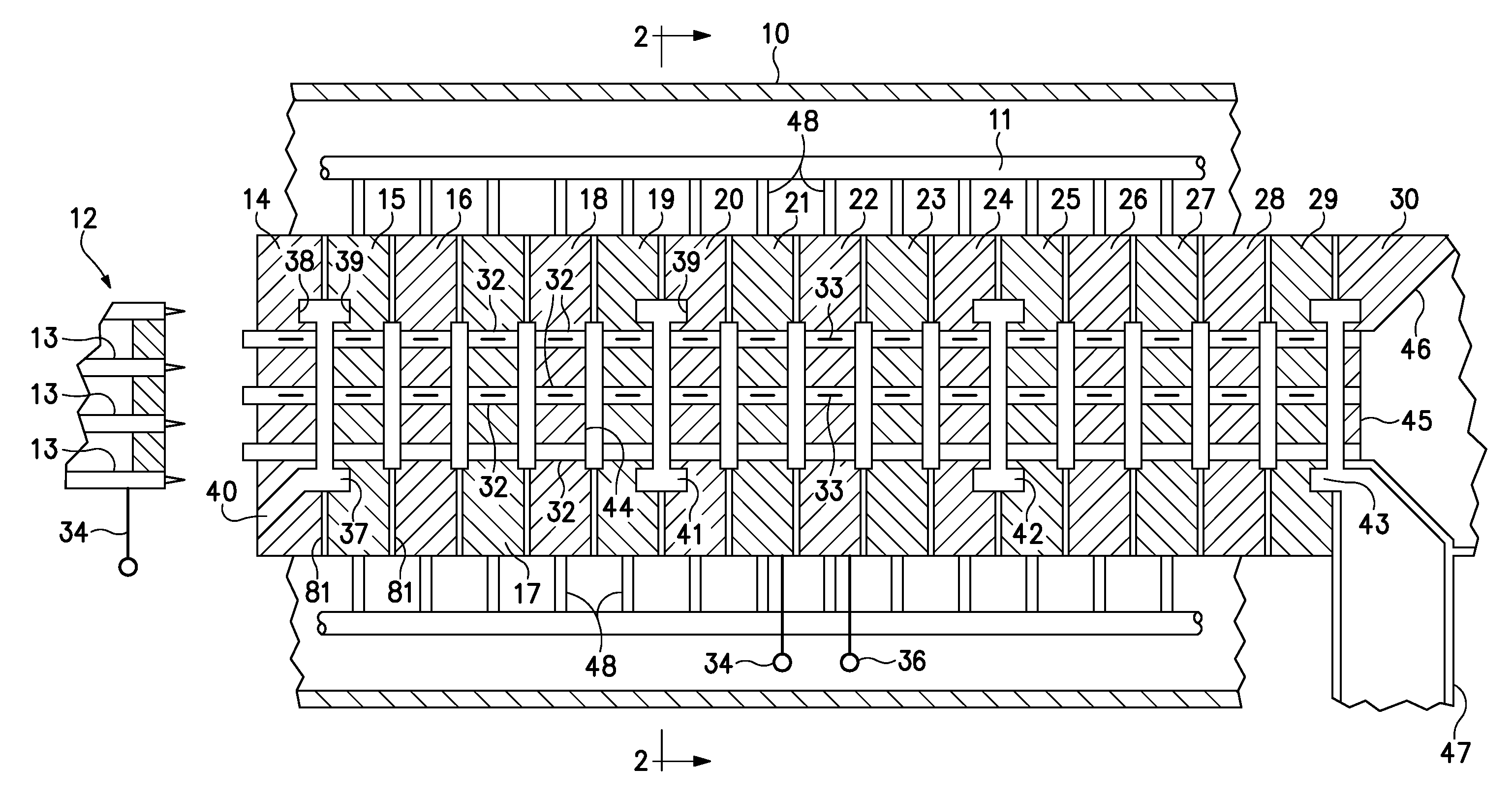
InactiveUS6847168B1High gainHigh bandwidthTransit-tube focussing arrangementsKlystronsResonant cavityKlystron
An RF device comprising a plurality of drift tubes, each drift tube having a plurality of gaps defining resonant cavities, is immersed in an axial magnetic field. RF energy is introduced at an input RF port at one of these resonant cavities and collected at an output RF port at a different RF cavity. A plurality of electron beams passes through these drift tubes, and each electron beam has an individual magnetic shaping applied which enables confined beam transport through the drift tubes.
Owner:CALABAZAS CREEK RES
Slot resonance coupled standing wave linear particle accelerator
InactiveUS20090302785A1Improve effectivenessLinear acceleratorsKlystronsParticle acceleratorPhase difference
A slot resonance coupled, linear standing wave particle accelerator. The accelerator includes a series of resonant accelerator cavities positioned along a beam line, which are connected by resonant azimuthal slots formed in interior walls separating adjacent cavities. At least some of the slots are resonant at a frequency comparable to the resonant frequency of the cavities. The resonant slots are offset from the axis of the accelerator and have a major dimension extending in a direction transverse to the radial direction with respect to the accelerator axis. The off-axis resonant slots function to magnetically couple adjacent cavities of the accelerator while also advancing the phase difference between the standing wave in adjacent cavities by 180 degrees in addition to the 180 degree phase difference resulting from coupling of the standing wave in each cavity with the adjacent slot, such that the signals in each cavity are in phase with one another and each cavity functions as a live accelerating cavity. The resonance frequency of the slot is the comparable to the resonance frequency of the cavities, resulting in coupling of the cavities while also eliminating the need for side-cavity or other off-axis coupling cavities.
Owner:FARTECH
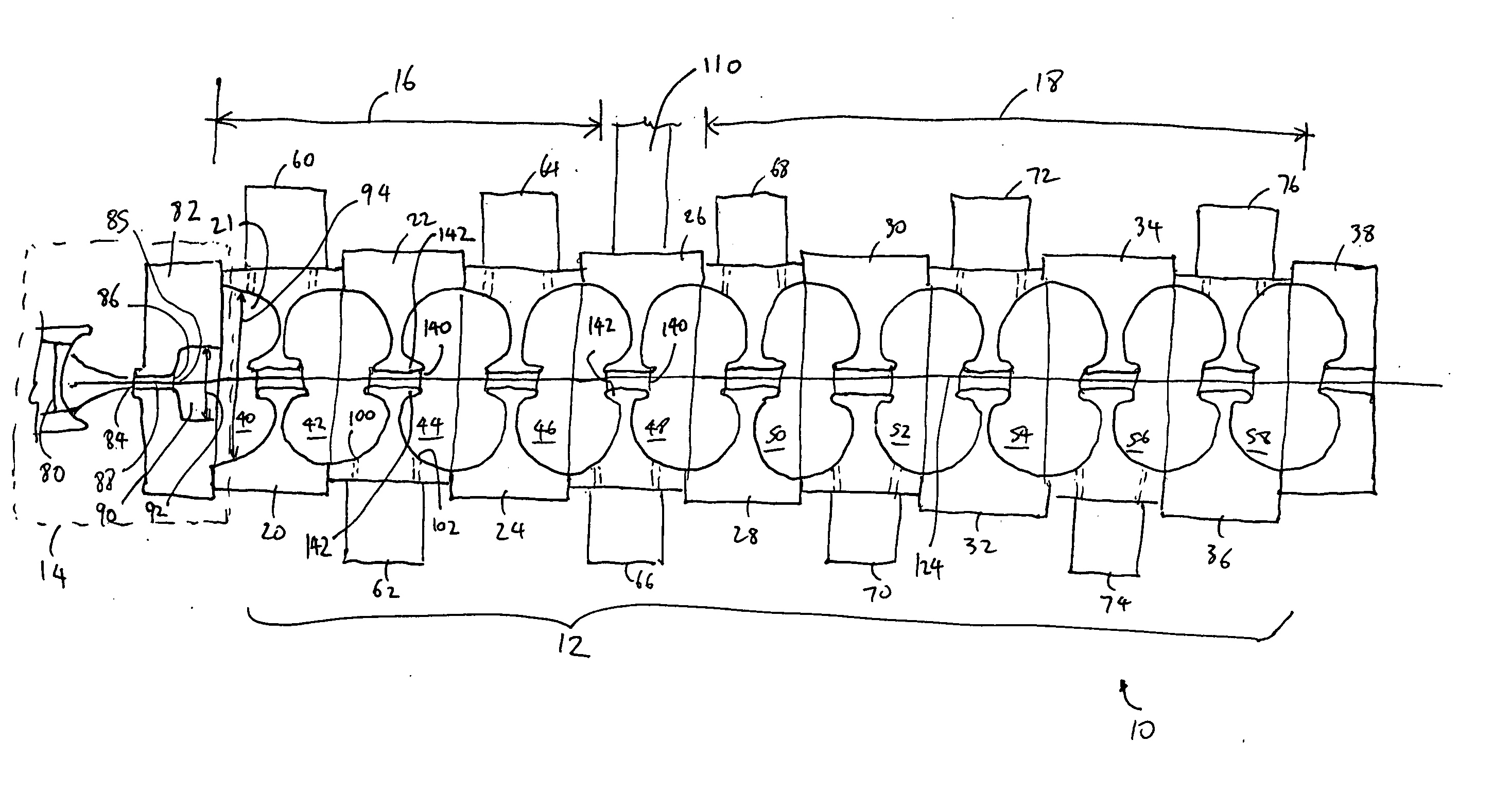
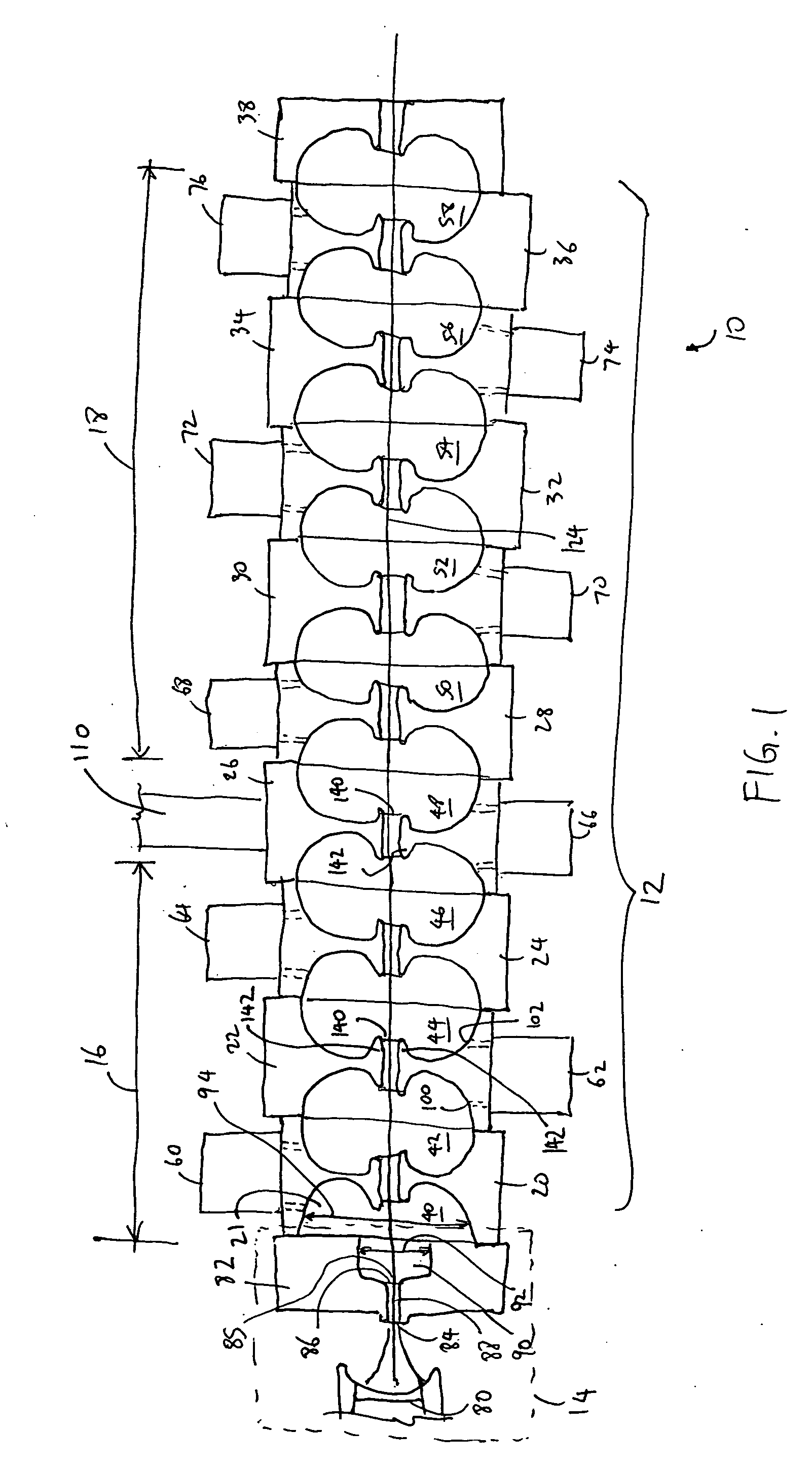
Standing wave particle beam accelerator
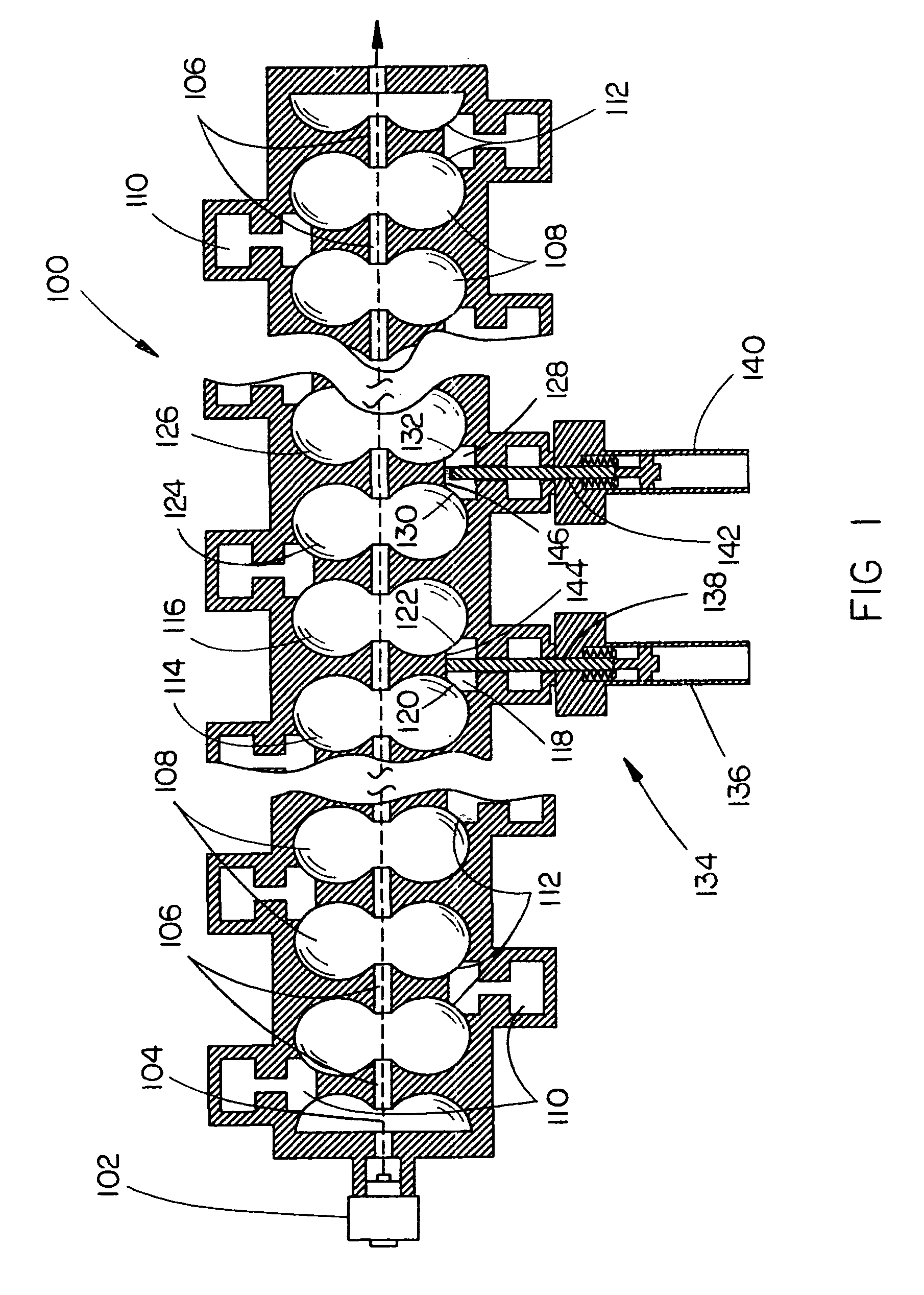
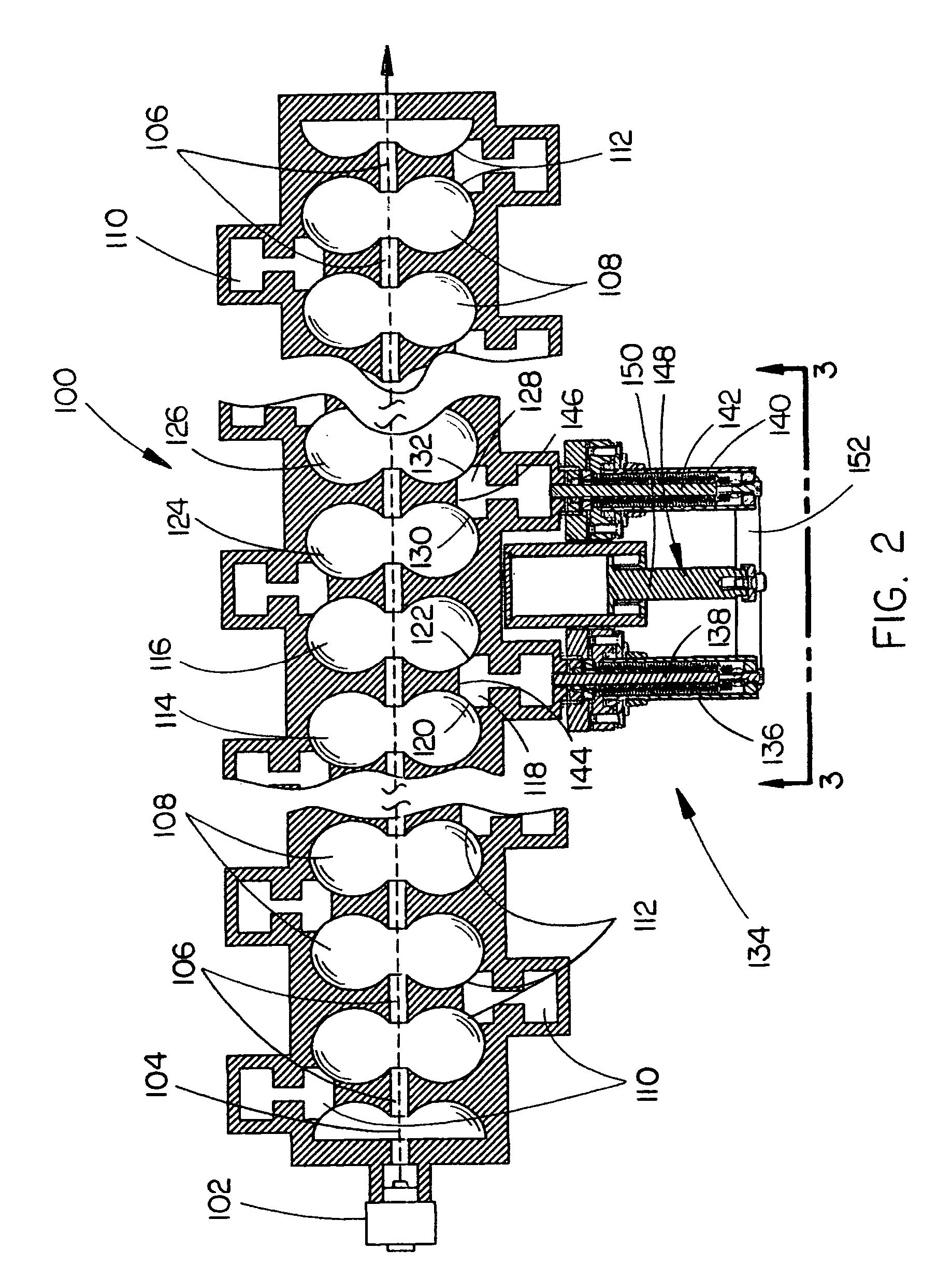
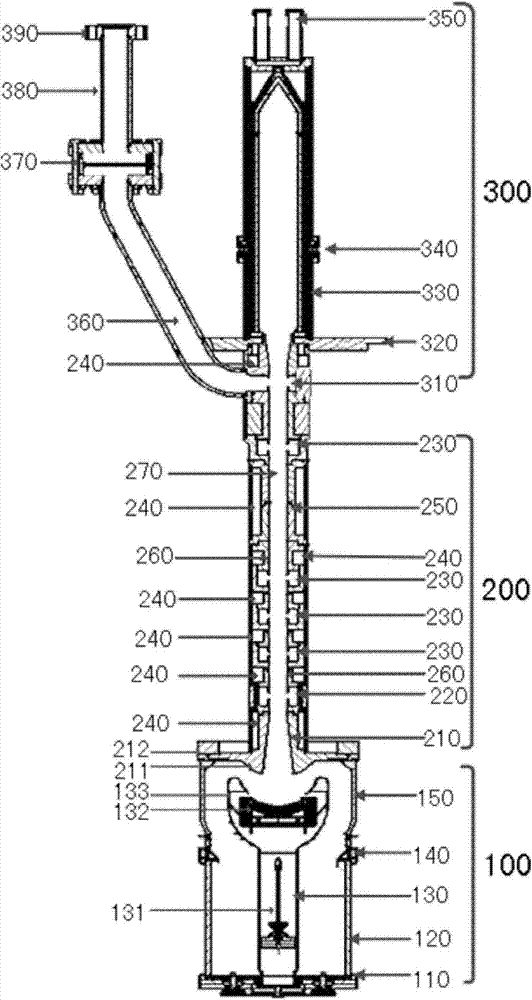
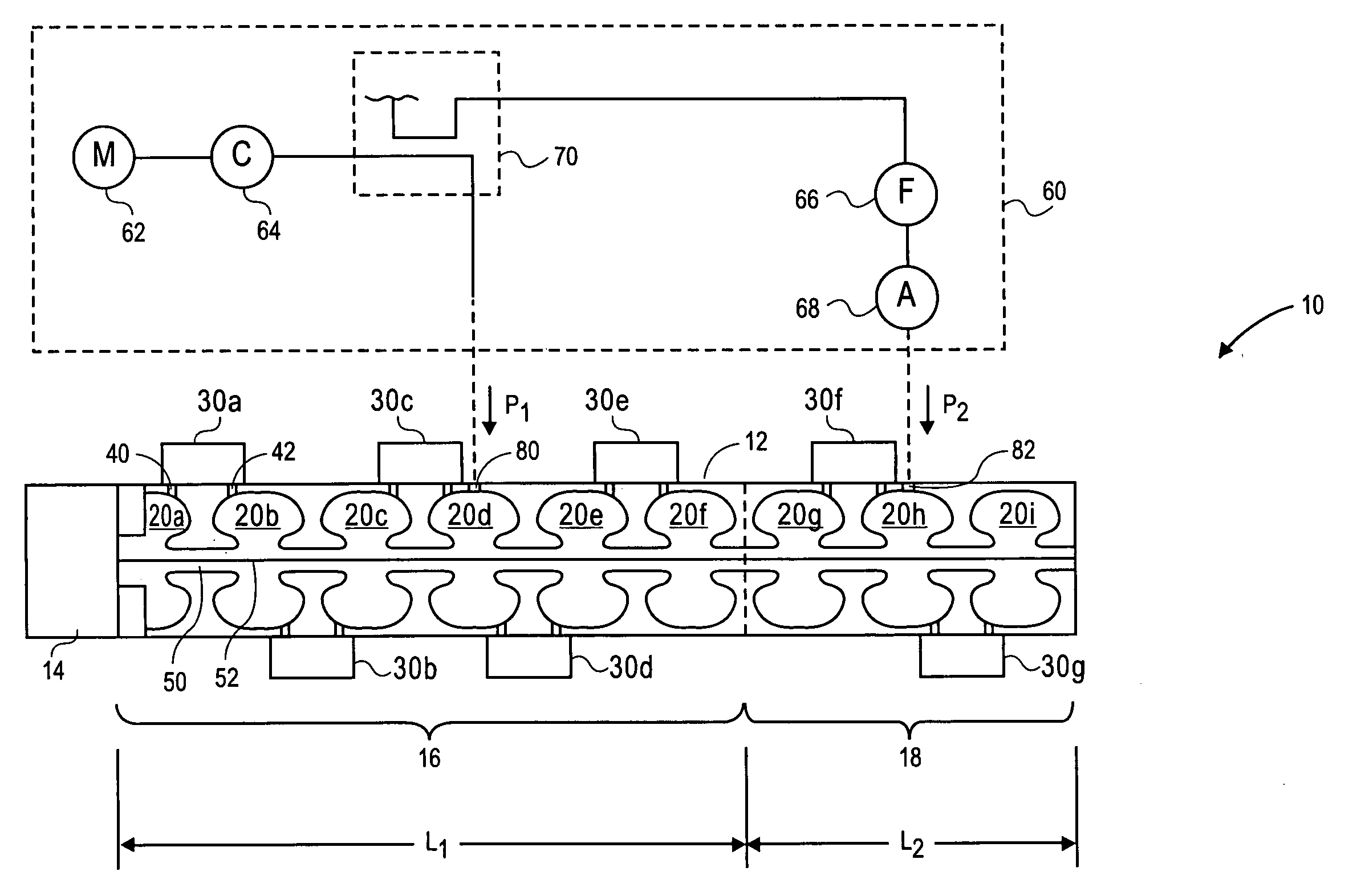
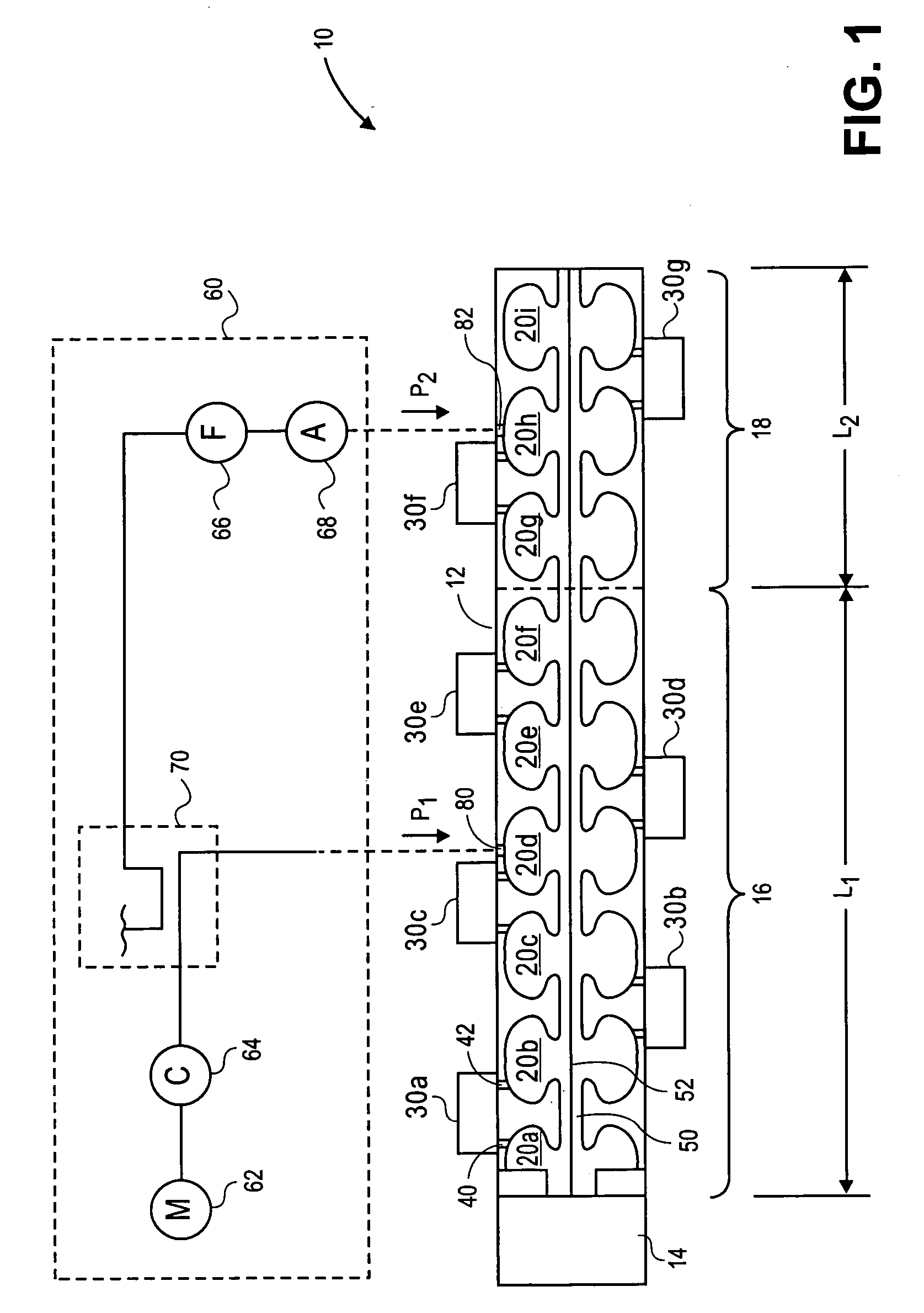
A method for generating an electron beam includes prescribing a location, and generating an envelope of electrons, the envelope having a waist, wherein the generating is performed such that the waist of the envelope is at or adjacent to the prescribed location. A device for generating an electron beam includes a gun source for generating electrons, and a plurality of electromagnetic cavities coupled in series to form a body, the electromagnetic cavities configured to accelerate at least some of the electrons to create a beam of electrons at an energy level having a value between 5 MeV and 20 MeV, the beam of electrons having a cross sectional dimension that is 0.02 λ (or 2 mm) or less.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Multibeam electronic tube with magnetic field for correcting beam trajectory
InactiveUS6486605B1Degrading gainDegrading efficiency characteristicTravelling-wave tubesTransit-tube focussing arrangementsKlystronBeam trajectory
A multibeam electron tube with several approximately parallel electron beams passing through a body. Among the beams, at least some define an interbeam volume, each beam defining the interbeam volume being subjected to a perturbing azimuthal magnetic field induced by all the other beams. The tube includes an element allowing, in at least one conducting element located in the interbeam volume, flow of a reverse current in the opposite direction to that of the current of the beams, this reverse current generating, in the beams defining the interbeam space, a magnetic correction field whose purpose is to oppose the perturbing magnetic field. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention especially apply to the multibeam klystrons or traveling wave tubes.
Owner:THOMSON TUBES ELECTRONIQUES
S-waveband 12.1% bandwidth klystron
InactiveCN103681177AIncrease powerIncrease the total DC powerTransit-tube collectorsTransit-tube cathodesKlystronMicrowave
The invention provides an S-waveband 12.1% bandwidth klystron which comprises an electron gun assembly, a cluster segment assembly and an output segment assembly. The electron gun assembly is used for emitting an electron beam which moves forwards along a drift channel under the constraint of a magnetic field; the cluster segment assembly modulates the speed and density of the electron beam emitted by the electron gun assembly to generate a high-frequency electron beam; and the output segment assembly makes beam-wave interaction with the high-frequency electron beam provided by the cluster segment assembly, wherein energy of the electron beam is converted into microwaves in an output cavity, and the microwaves are output. The S-waveband 12.1% bandwidth klystron has unique advantages in the aspects of improving the bandwidth and power.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Repetition-frequency low-magnetic-field axial C-waveband high-power microwave device
The invention discloses a repetition-frequency low-magnetic-field axial C-waveband high-power microwave device. The device comprises an anode, a cathode, a guiding magnetic field generator, slow wave structures and a coaxial internal conductor, the anode is internally provided with an emission area and a beam wave interaction area, the cathode is arranged in the emission area, the slow wave structures and the coaxial internal conductor are arranged in the beam wave interaction area of the anode, the cathode is coaxial with the coaxial internal conductor, the slow wave structures are fixed to the inner side of the anode and arranged in the periphery of the coaxial internal conductor, a vacuum cavity is formed by vacuum pumping in the repetition-frequency low-magnetic-field axial C-waveband high-power microwave device, and the vacuum degree of the vacuum cavity does not exceed 10mPa. A baffle plate is arranged between the emission area and the beam wave interaction area. The baffle plate is provided with an annular inlet for guiding high-current electron beams generated by the cathode into the beam wave interaction area, and the diameter of the annular inlet is consistent with that of the cathode. The device is characterized by being capable of generating C-waveband high-power microwaves in repetition frequency and high in the beam wave conversion efficiency.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
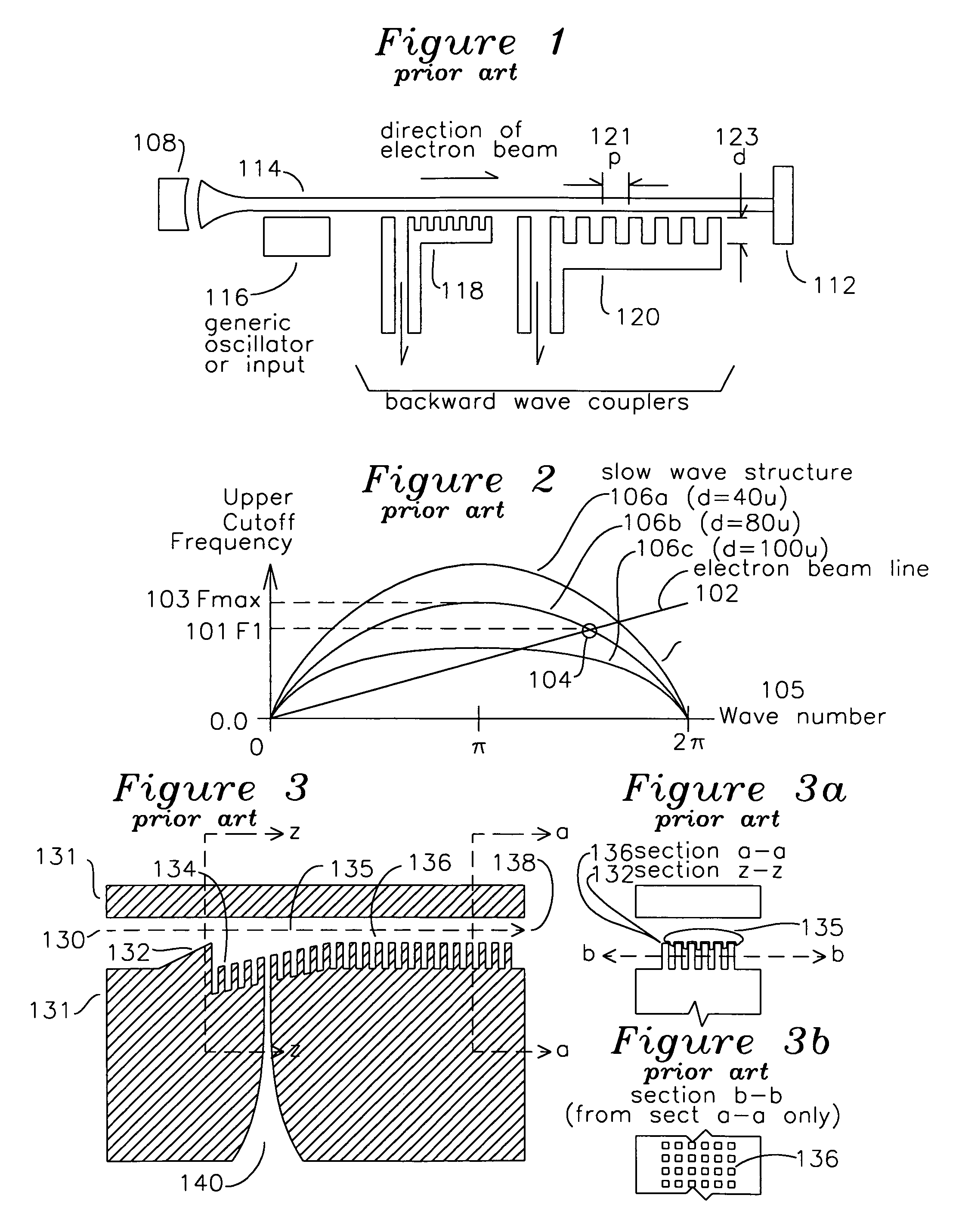
Backward wave coupler for sub-millimeter waves in a traveling wave tube
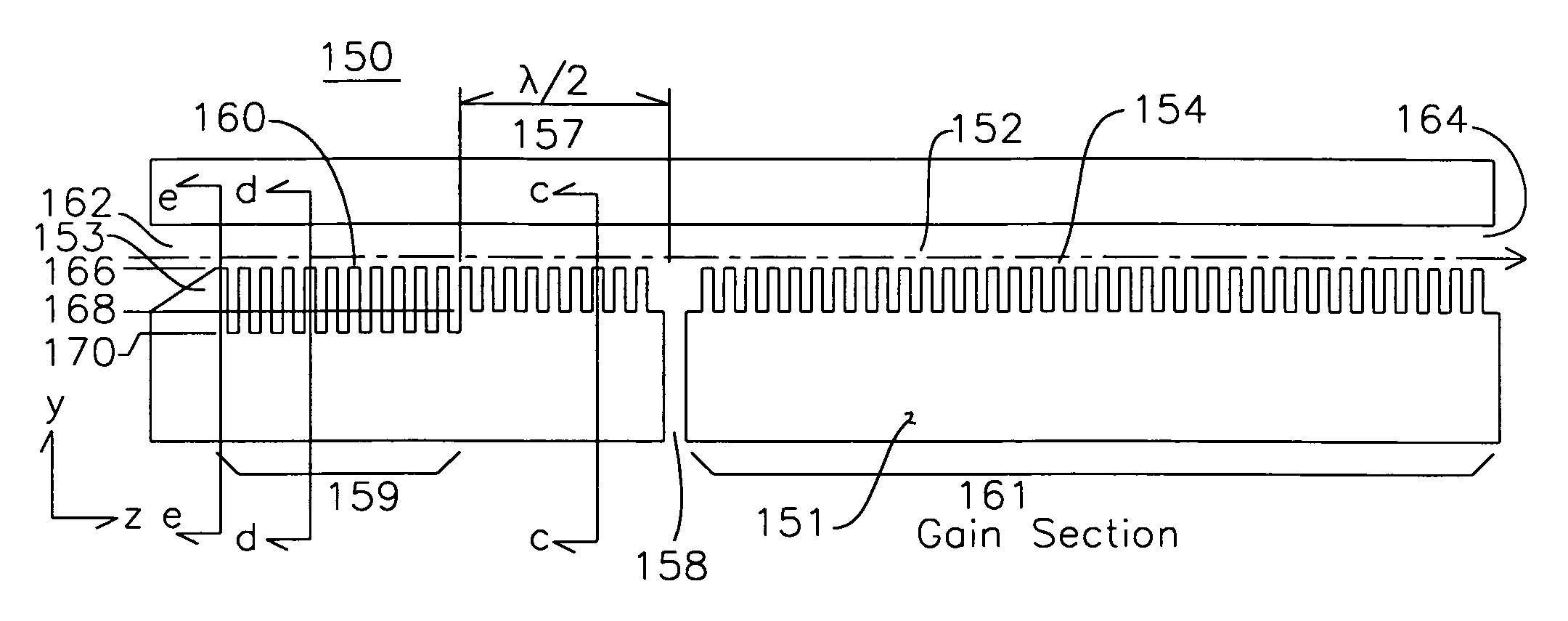
A slow wave structure for coupling RF energy with an electron beam comprises a co-propagating RF section including a plurality of pins having a uniform separation from the plane of an electron beam axis. An output aperture is positioned a half wavelength from a reflection section comprising a change in depth of the pintles, such that RF energy reflected by the change in pintle depth is added to the RF energy traveling with the electron beam. One or more rows of pintles are removed in the region of the output aperture to enhance coupling to the output aperture. The device may include a beam shaper for shaping the electron beam to surround the pintles, and the beam shaper and pintles may share common channels which are longitudinal to the electron beam axis. The slow wave structure may operate in forward and backward wave modes, and may be used in conjunction with other structures to form amplifiers and oscillators.
Owner:CALABAZAS CREEK RES
Vacuum Electronic Devices and Cavities and Fabrication Methods Therefor
The present invention relates to the formation of a vacuum electronics circuit by the fusion bonding of multiple substrate wafers, e.g., silicon, copper, or other suitable conductive material, each etched using DRIE, cut using EDM, or machined by other suitable means. Other aspects of the invention relate to the alignment of a cathode with tube by fusion bonding the cathode wafer to a tube built using the fabrication methods described herein. Yet other aspects involve the alignment of dies or wafers during the fabrication of a vacuum electronics device using the “lego” technique outlined herein. In yet other aspects, fabrication methods are described.
Owner:LOGOS TECH HOLDCO INC
Particle acceleration devices and methods thereof
InactiveUS20090072744A1Provide benefitsPossible to performLinear acceleratorsKlystronsParticle acceleratorPhotonic bandgap
A particle accelerator device structured and arranged for use in a subterranean environment. The particle accelerator device comprising: one or more resonant Photonic Band Gap (PBG) cavity, the one or more resonant PBG cavity is capable of providing localized, resonant electro-magnetic (EM) fields so as to one of accelerate, focus or steer particle beams of one of a plurality of electrons or a plurality of ions. Further, the particle accelerator device may provide for the one or more resonant PBG cavity to include a geometry and one or more material that is optimized in terms of RF power losses, wherein the optimization provides for a PBG cavity quality factor significantly higher than that of an equivalent normally conducting pill-box cavity.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
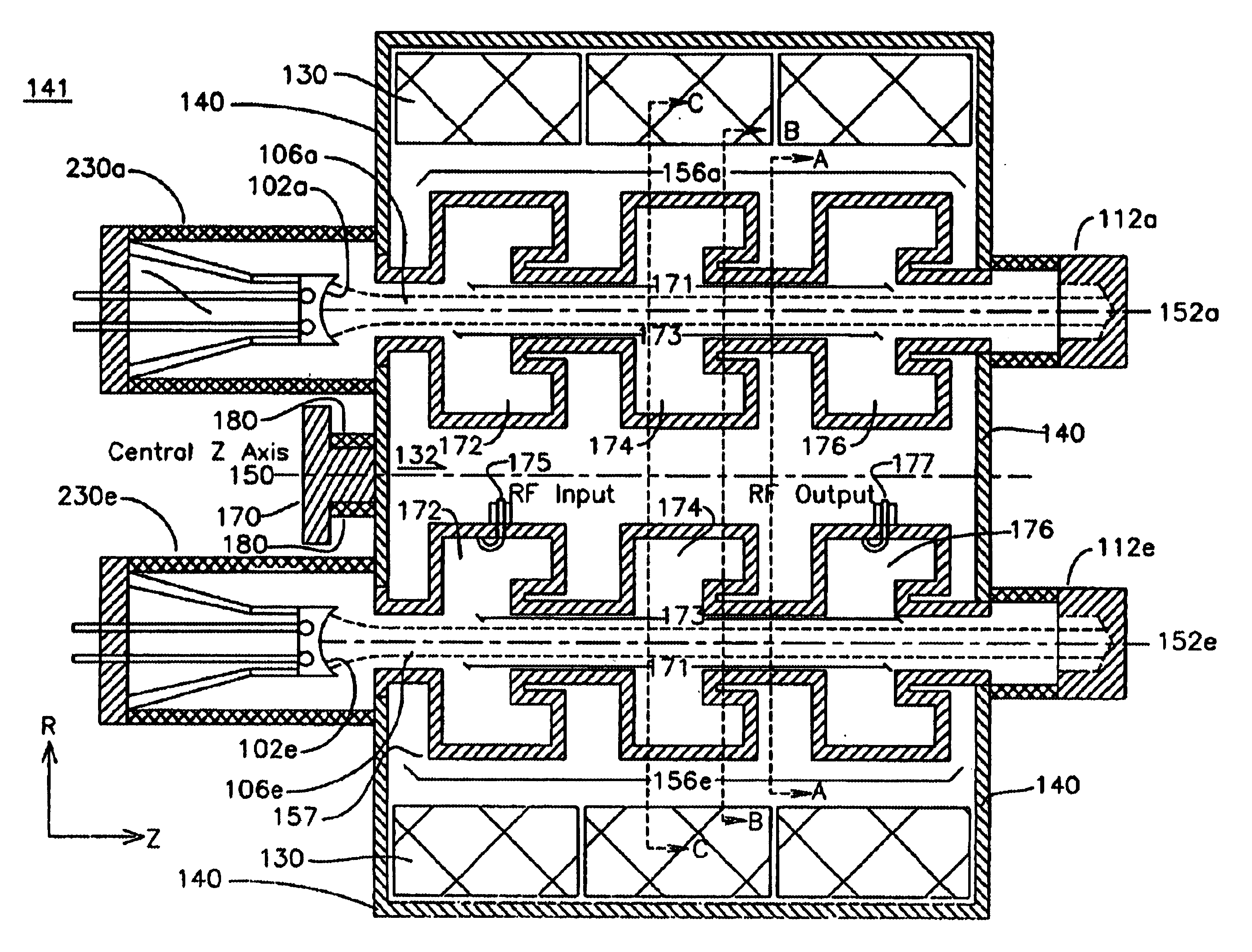
Multi-beam klystron apparatus
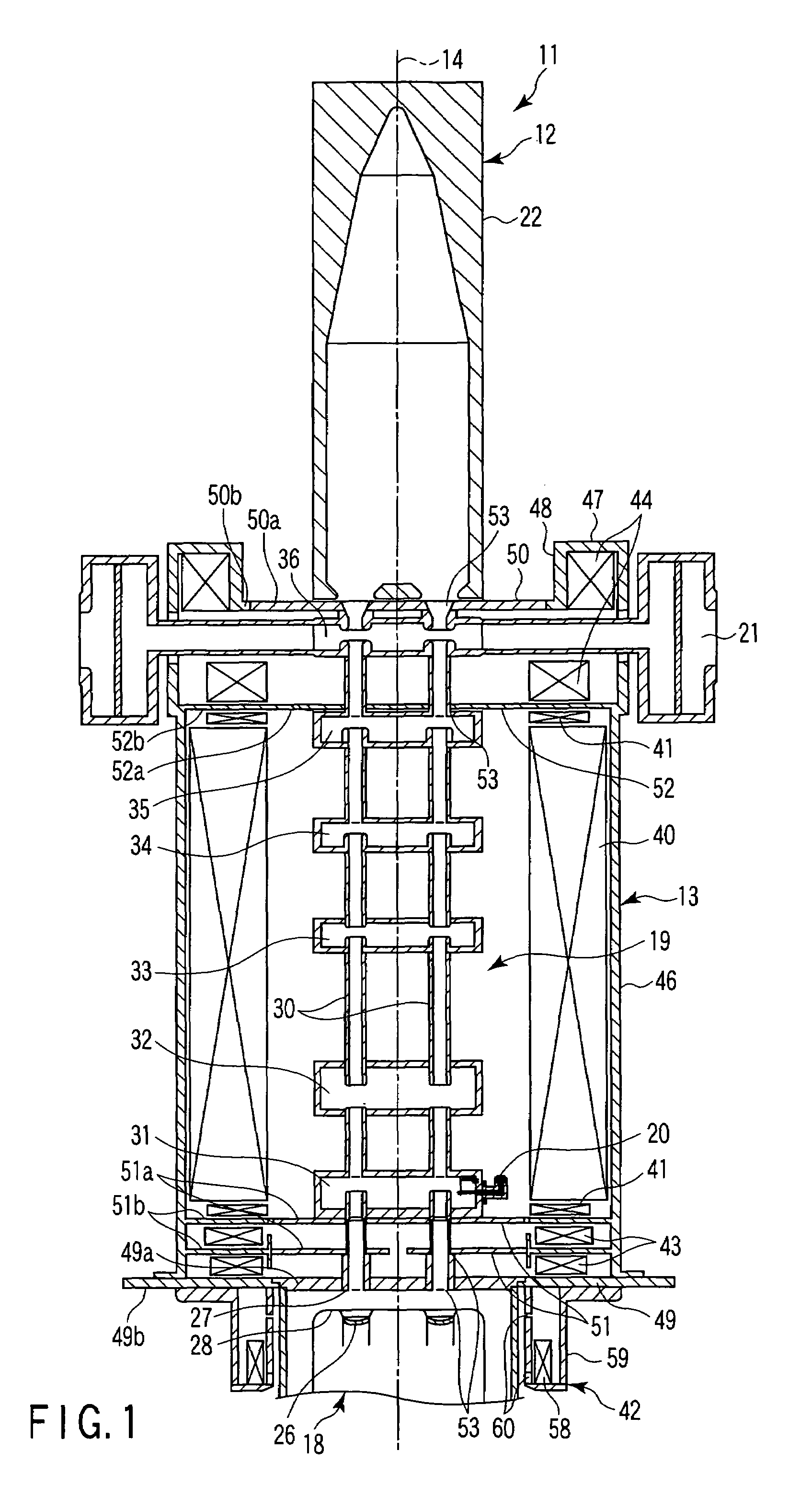
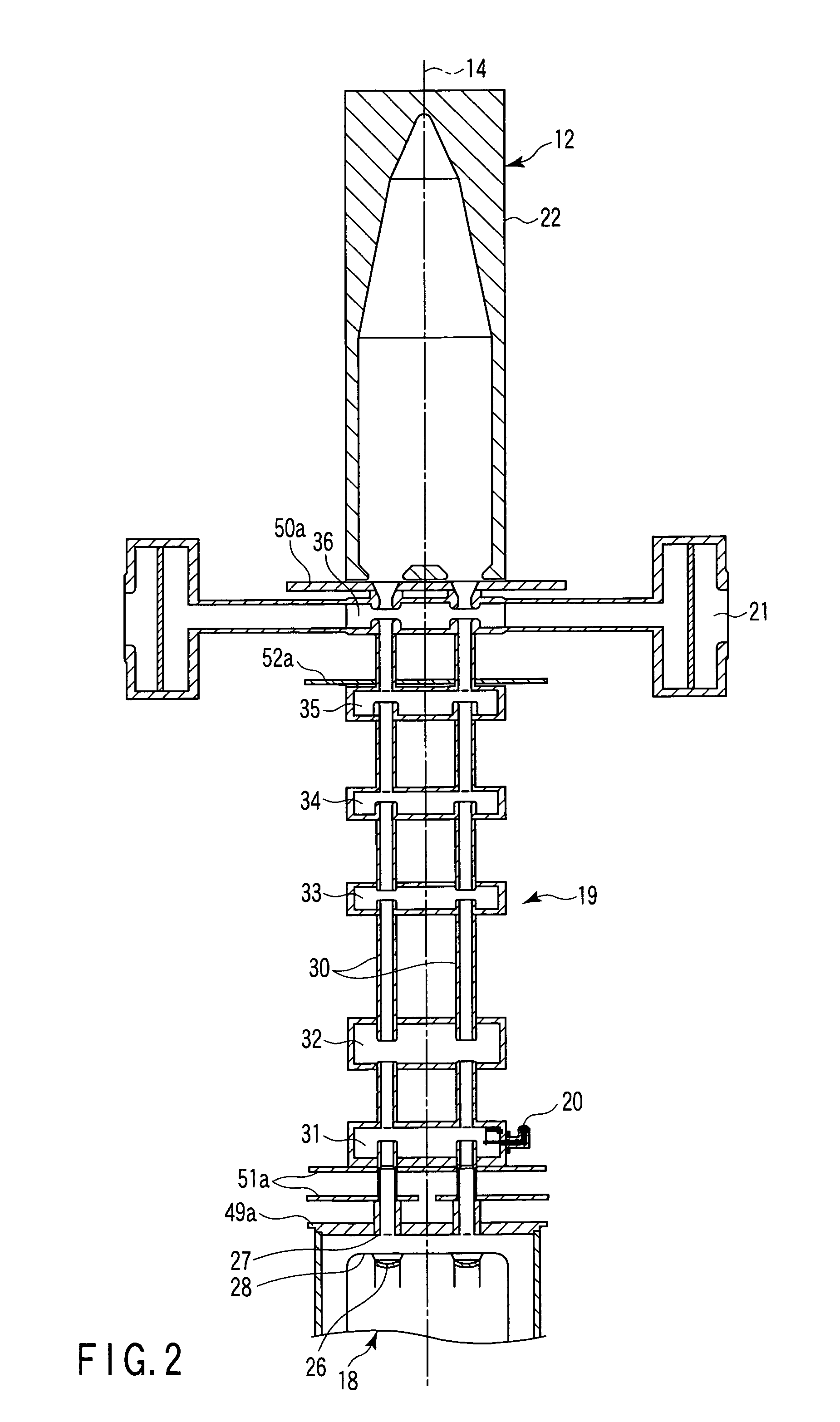
ActiveUS7385354B2High magnetic flux densityAvoid spreadingStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsKlystronLight beam
A multi-beam klystron apparatus is disclosed. A radio-frequency interaction unit pole piece is arranged between a main magnetic field generator and an output-side magnetic field generator. The magnetic circuit formed in the neighborhood of an output cavity of a radio-frequency interaction unit is separated from the magnetic circuit of the main magnetic field generator by the radio-frequency interaction unit pole piece. The output-side magnetic field generator increases the axial magnetic flux density in the neighborhood of the output cavity without curving the electron beams and thus prevents the spread of the electron beams in the neighborhood of the output cavity.
Owner:CANON ELECTRON TUBES & DEVICES CO LTD
Common frequency iso-mode whirling traveling-wave klystron amplifier
InactiveCN101329977AConducive to control mode competitionConducive to model competitionKlystronsKlystronAudio power amplifier
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Multibeam klystron
InactiveUS7116051B2Eliminating weight and size and costAccurate focusTransit-tube focussing arrangementsKlystronsMicrowave cavityKlystron
A multibeam, electrostatically focused klystron includes a plurality of conductive members, ones of which are recessed to provide input and output sections of microwave cavities, wherein focusing voltage is applied between those sections. The conductive members are either spaced along the path of multiple beams, or stacked in insulated relation, in either case being supported by glass rods within a glass envelope.
Owner:VANCIL BERNARD K +1
Diagnostic resonant cavity for a charged particle accelerator
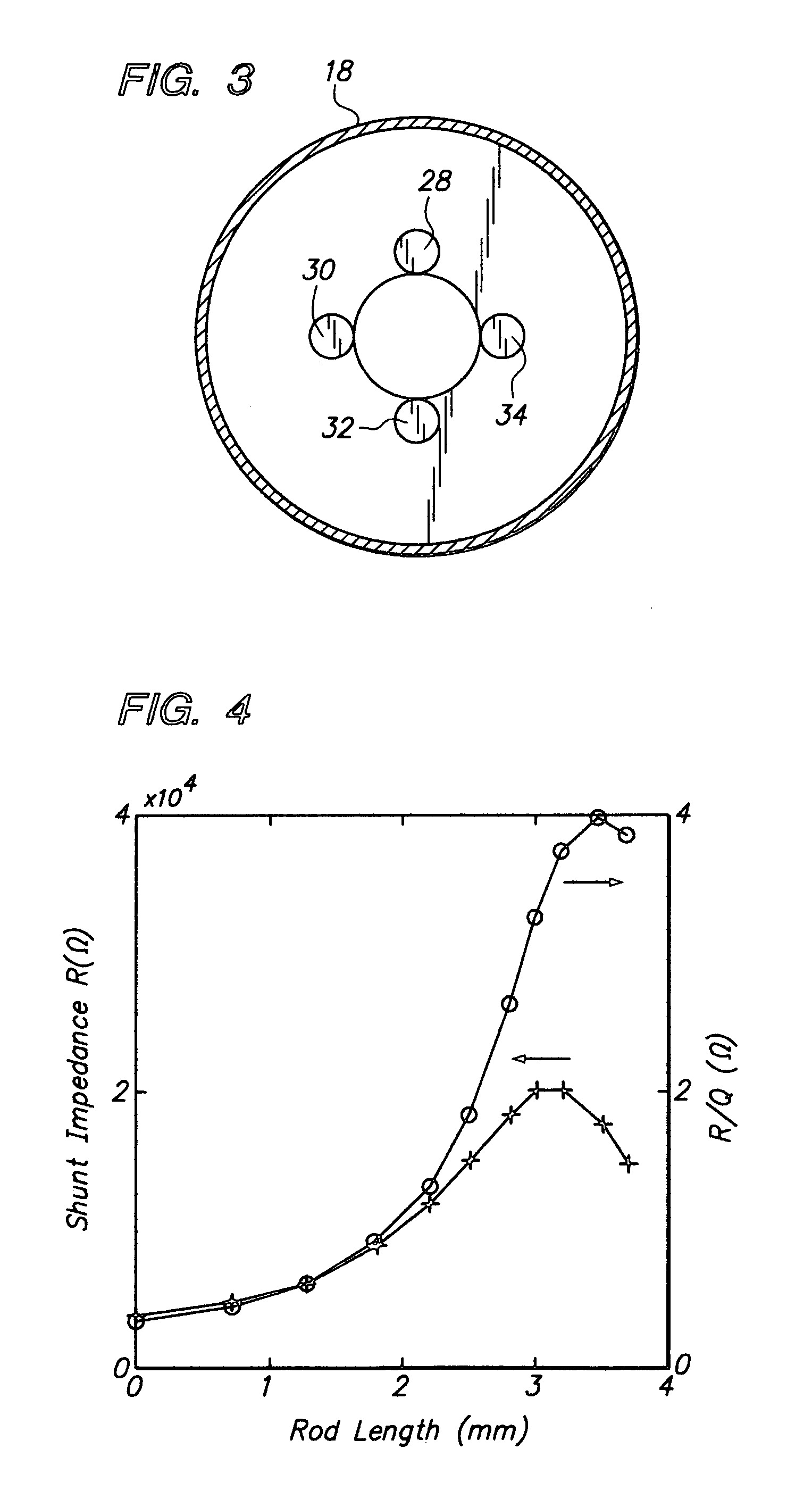
InactiveUS7276708B2Improving impedanceAccurate measurementStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle acceleratorResonant cavity
Disclosed is a diagnostic resonant cavity for determining characteristics of a charged particle beam, such as an electron beam, produced in a charged particle accelerator. The cavity is based on resonant quadrupole-mode and higher order cavities. Enhanced shunt impedance in such cavities is obtained by the incorporation of a set of four or more electrically conductive rods extending inwardly from either one or both of the end walls of the cavity, so as to form capacitive gaps near the outer radius of the beam tube. For typical diagnostic cavity applications, a five-fold increase in shunt impedance can be obtained. In alternative embodiments the cavity may include either four or more opposing pairs of rods which extend coaxially toward one another from the opposite end walls of the cavity and are spaced from one another to form capacitative gaps; or the cavity may include a single set of individual rods that extend from one end wall to a point adjacent the opposing end wall.
Owner:FARTECH
System And Apparatus For Cathodoluminescent Lighting
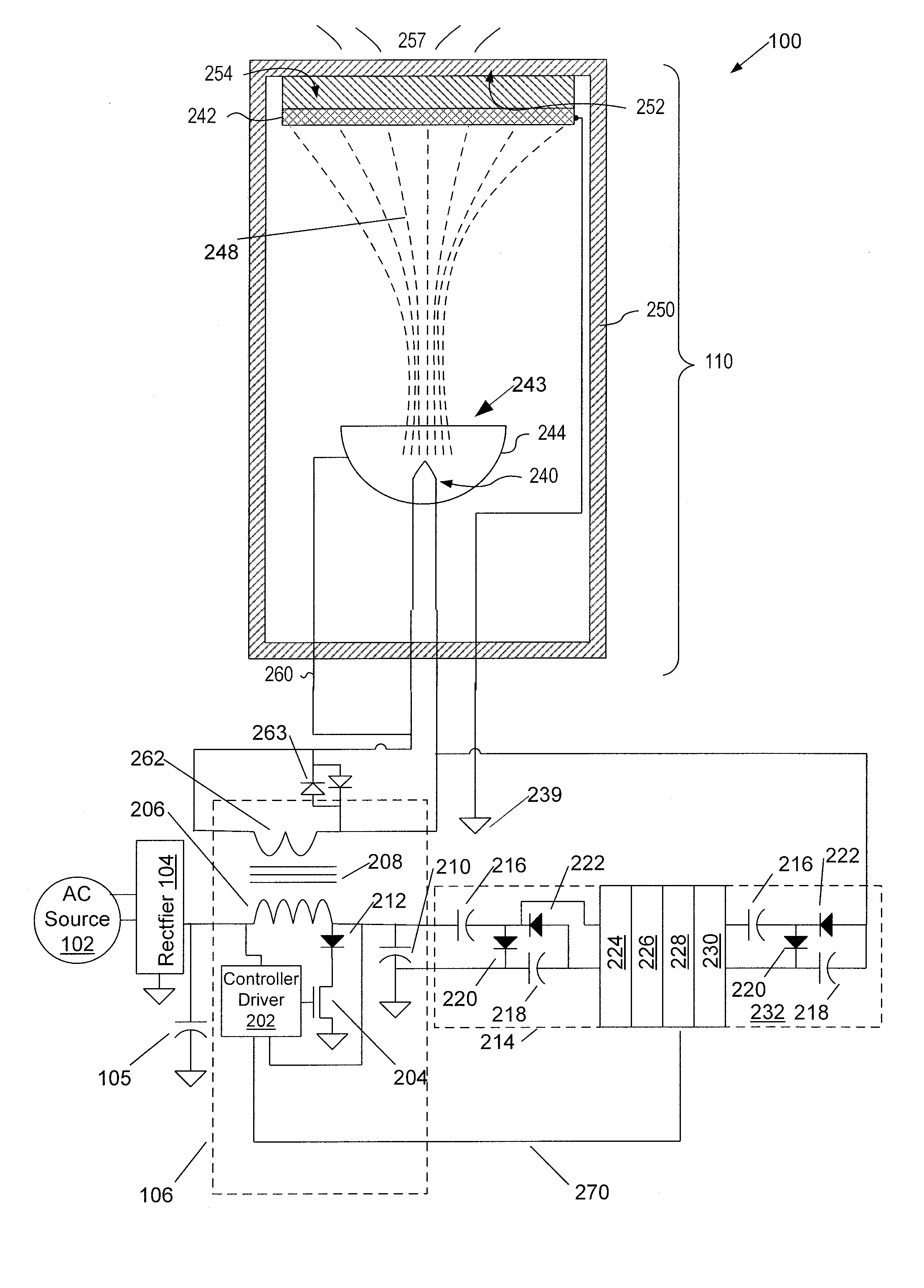
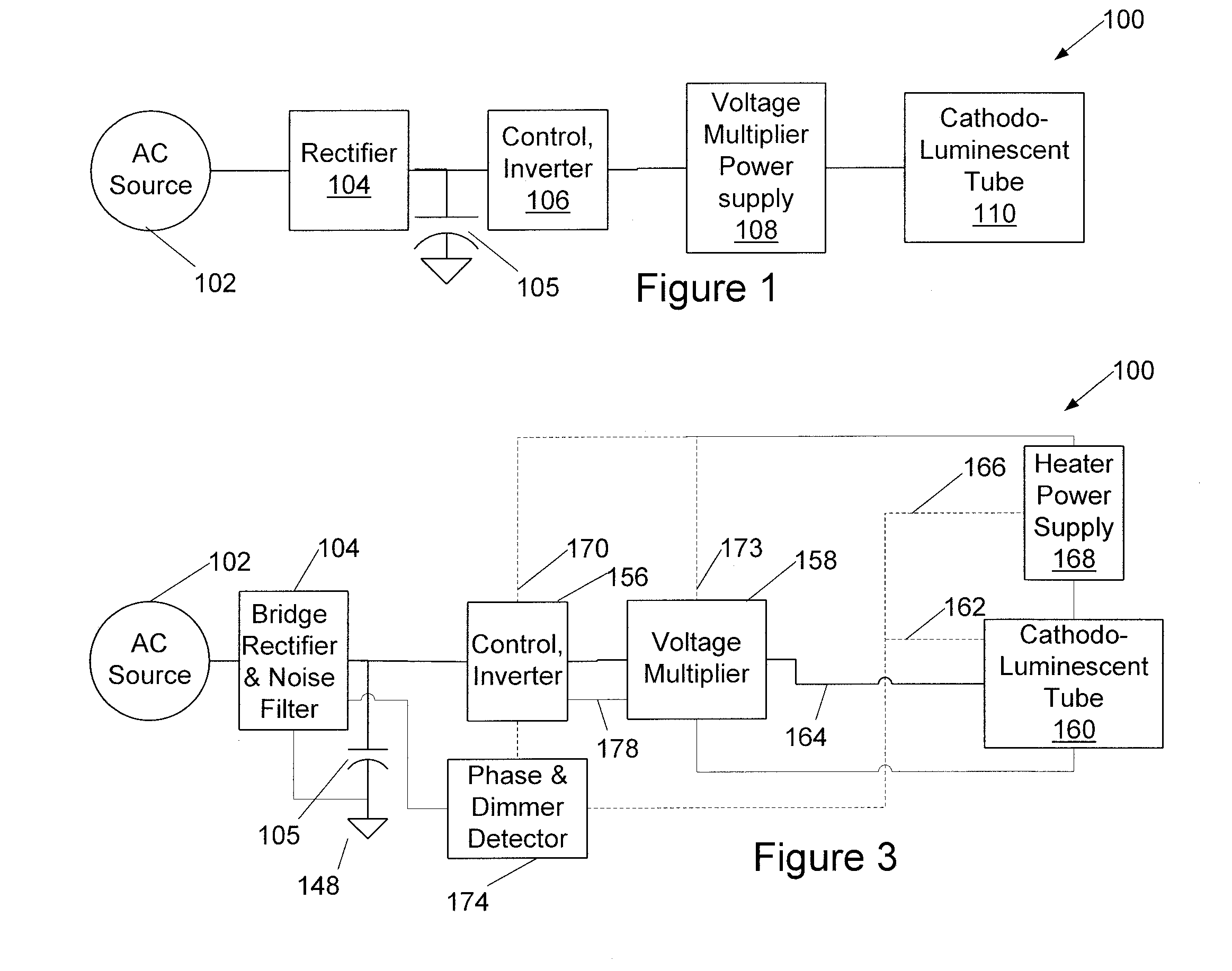
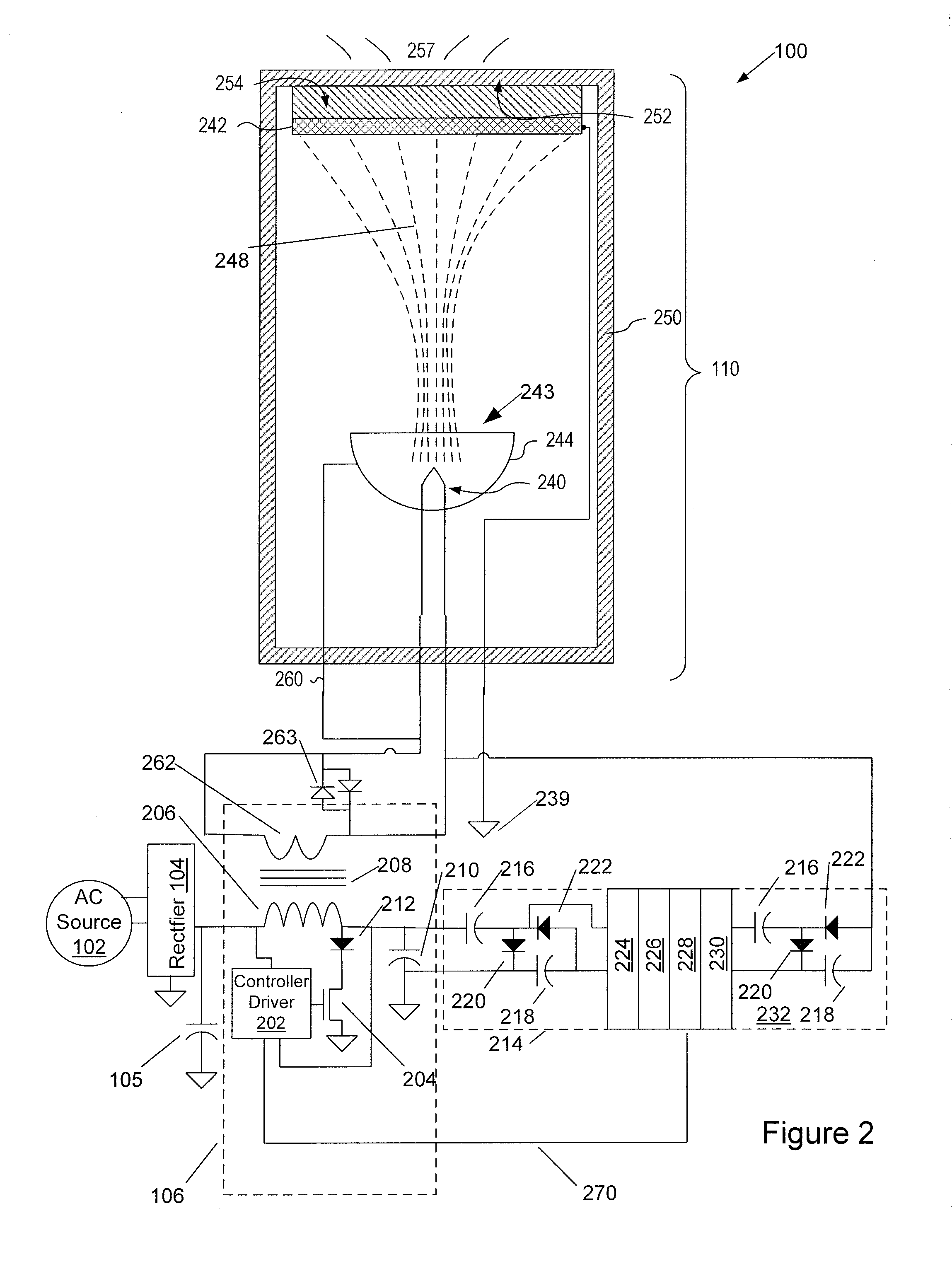
InactiveUS20100097004A1Thermionic cathodesLamp incadescent bodiesElectrical conductorElectron source
Electron sources for a cathodoluminescent lighting system are disclosed. An electron source is a broad-beam reflecting-type electron gun having a cathode for emitting electrons and a reflector and / or secondary emitter electrode and no grids. An alternative electron gun has a cathode having a heater welded to a disk, the disk having an emissive surface on a side facing a dome-shaped defocusing grid and an anode. A lighting system incorporating the electron sources has an envelope with a transparent face, an anode with a phosphor layer to emit light through the face and a conductor layer. The system also has a power supply for providing from five to thirty thousand volts of power to the light emitting device to draw electrons from cathode to anode and excite a cathodoluminescent phosphor, and the electrons transiting from cathode to anode are essentially unfocused. A power-factor-corrected embodiment is also disclosed.
Owner:VU1 CORP
Frequency-multiplier klystron and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN101770921AEquivalent multiplier gainGood spectral purityKlystronsManufacture testing/measurementsKlystronFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a frequency-multiplier klystron and a manufacture method thereof, relating to the technique of electron tubes. A microwave actuating signal with the frequency of f is used as an input signal; electron beams are in manual action with multiple resonant cavities of the conventional klystron in vacuum; ultraharmonics components in the Fourier spectrum of the electron beams are obviously increased after good cybotaxis is achieved; an output structure adopts the output structure of a wave band where frequency nf is positioned or utilizes the higher order mode of the conventional structure; the ultraharmonics components of the frequency nf, namely, the input frequency f and the output frequency nf, are derived from the electron beams in high cybotaxis so that the microwave small signal is amplified and the frequency is multiplied to nf from f strictly in integer multiples. The method of the invention is simple and easy to implement, and the manufactured frequency-multiplier klystron can keep comparative frequency multiplication grain, good spectrum purity, wider absolute frequency multiplication bandwidth and higher power capability.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Millimeter wave expansion interaction device adopting coaxial resonant cavities and multi-electron beams
InactiveCN106997838AShorten the lengthHigh impedanceKlystronsOptical light guidesResonant cavityCoupling
The invention belongs to a millimeter wave expansion interaction device in a vacuum electronic device. The millimeter wave expansion interaction device comprises a device body which consists of a shell and a core body, an annular barrel-type coupling channel, circular annular resonant cavities and electron beam channels, output waveguide and coupling holes. The millimeter wave expansion interaction device adopts the cylindrical body and the circular annular resonant cavities which are formed around the axis of the core body in parallel at intervals; the lengths of inner circumference and outer circumference of the resonant cavities are far greater than working wavelengths; 5-19 resonant cavities and 5-20 electron beam channels can be set, and the lengths of the device can be greatly shortened, so that impedance, power capacity and output power of the device can be effectively improved; by means of controlling the radial dimensions of each resonant cavity to be within a range of 2 / 5-3 / 5<lambda> of the working wavelengths <lambda>, the long-term stable operation of the device in base mode state can be ensured; and therefore, the millimeter wave expansion interaction device has the characteristics of capability of improving output power of the device in a base mode state and working performance stability of the device, simple structure, simple and convenient production process, low production cost, long working service life and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Radial EIO (extended interaction oscillator) for high-power source
InactiveCN104658838ALarge power capacityIncrease working currentKlystronsTransit-tube circuit elementsCooling capacityVacuum electronics
The invention discloses a radial EIO (extended interaction oscillator) for a high-power source, belongs to the technical field of vacuum electronics, and relates to a high-power micro-wave and millimeter wave source technology. The invention designs a radial EIO adopting circular sheet electron beam under the limit of the cathode current emission density. The radial EIO comprises two disk bodies, a cathode, an insulated circular ring-shaped piece and an electron beam channel, wherein the disk bodies are symmetrically arranged in the longitudinal direction, and each disk body is provided with a control anode head and circular ring-shaped grooves. The EIO can obtain higher power under small current density by increasing the electron emission area and an electron beam channel area; compared with EIOs adopting other structures, the EIO can meet the requirement for high-power output; the EIO has better cooling capacity, and meanwhile, due to the specific cylindrical symmetry structure, machining becomes simple, and the assembly error can be effectively reduced; the cathode of an electron-optical system is located in the center of a device, the structure is compact, and the shock-proof performance is better.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
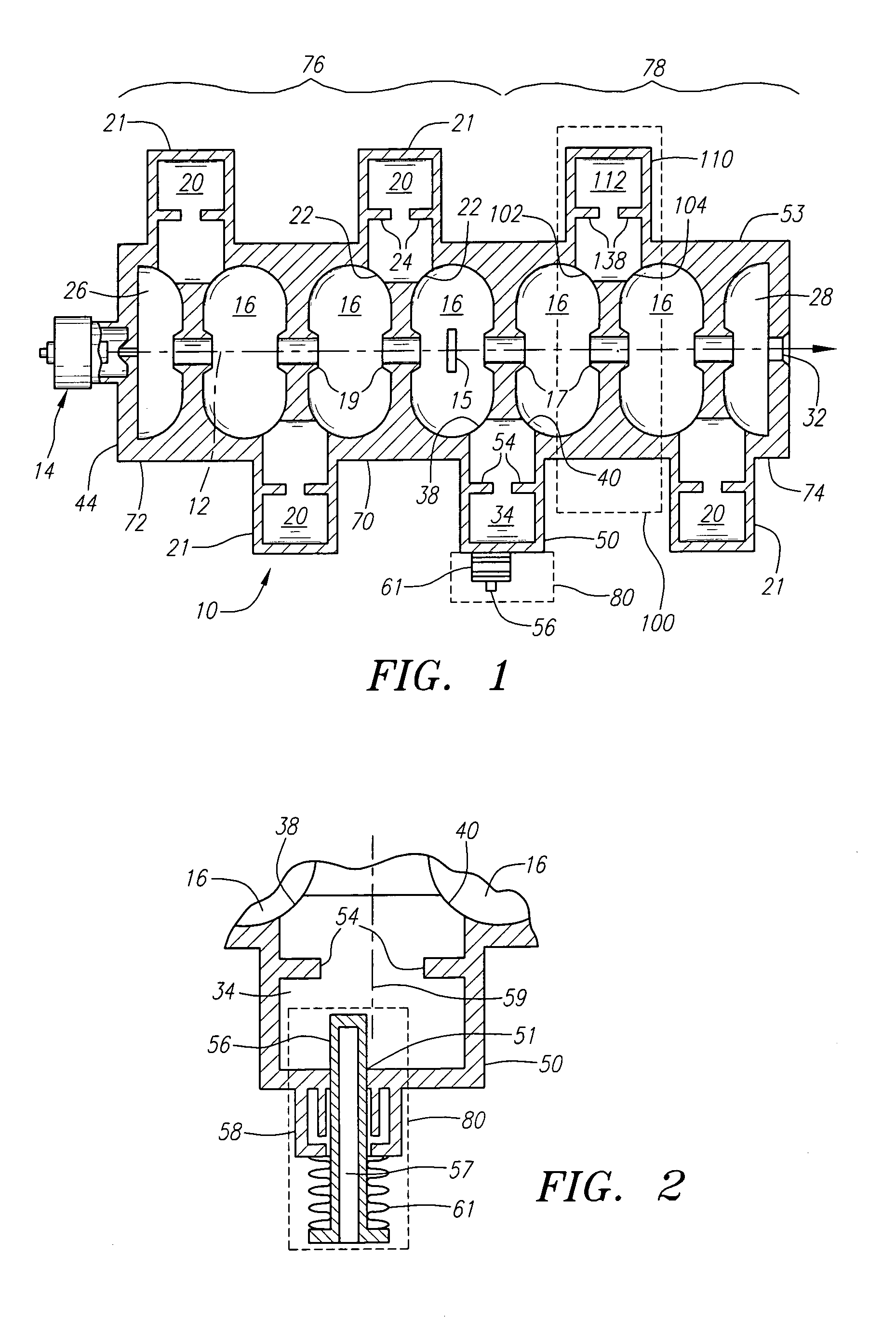
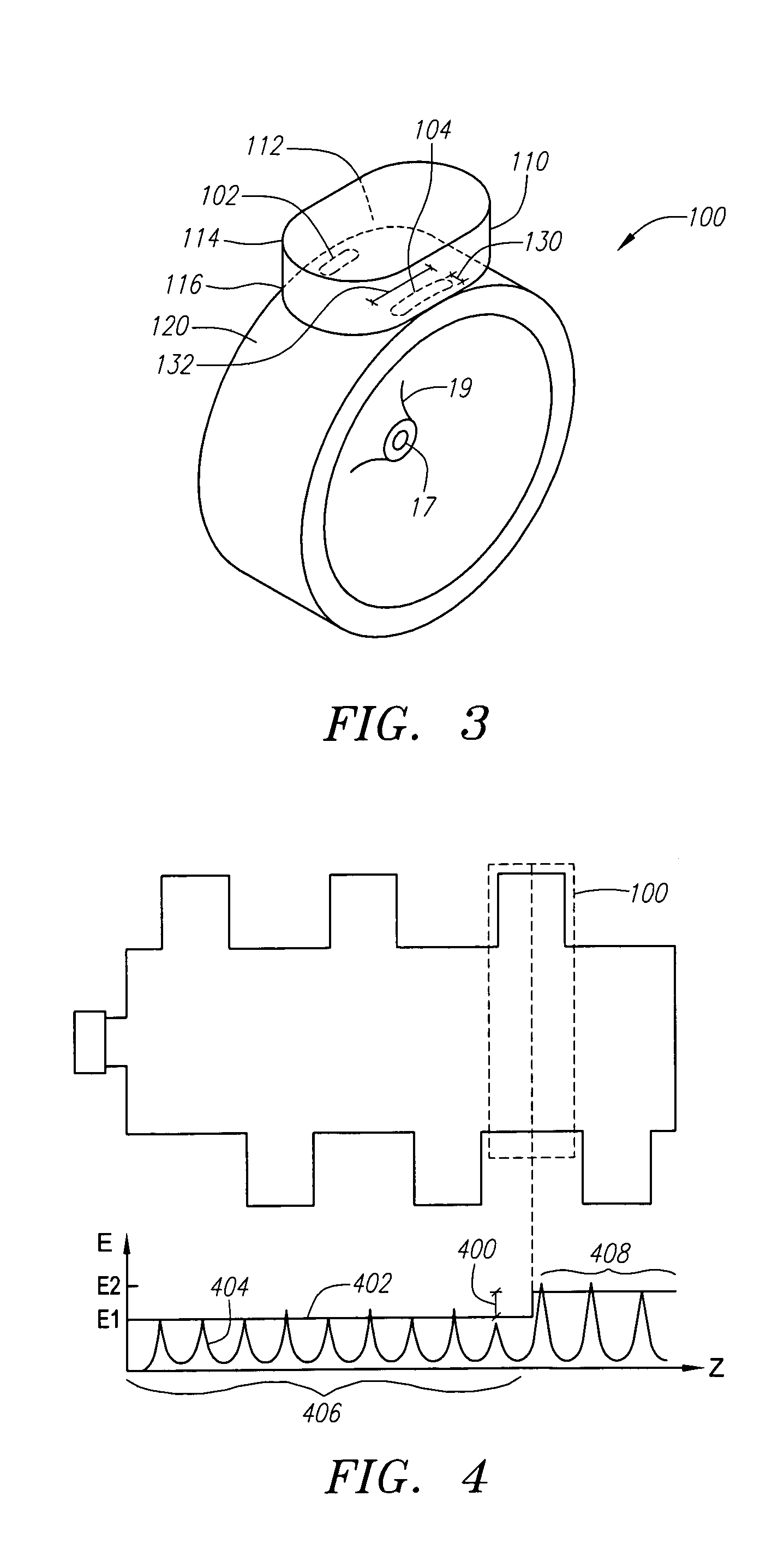
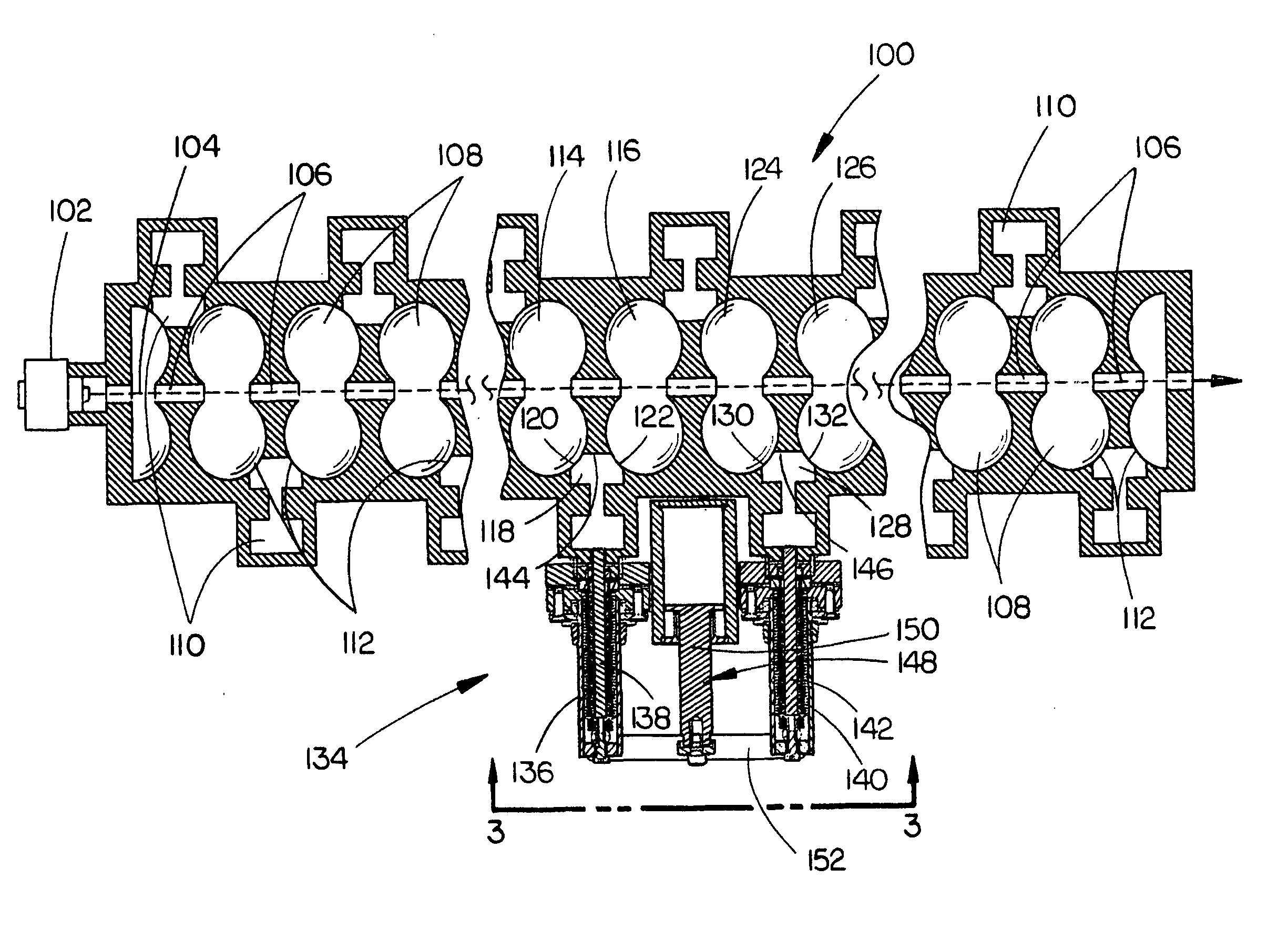
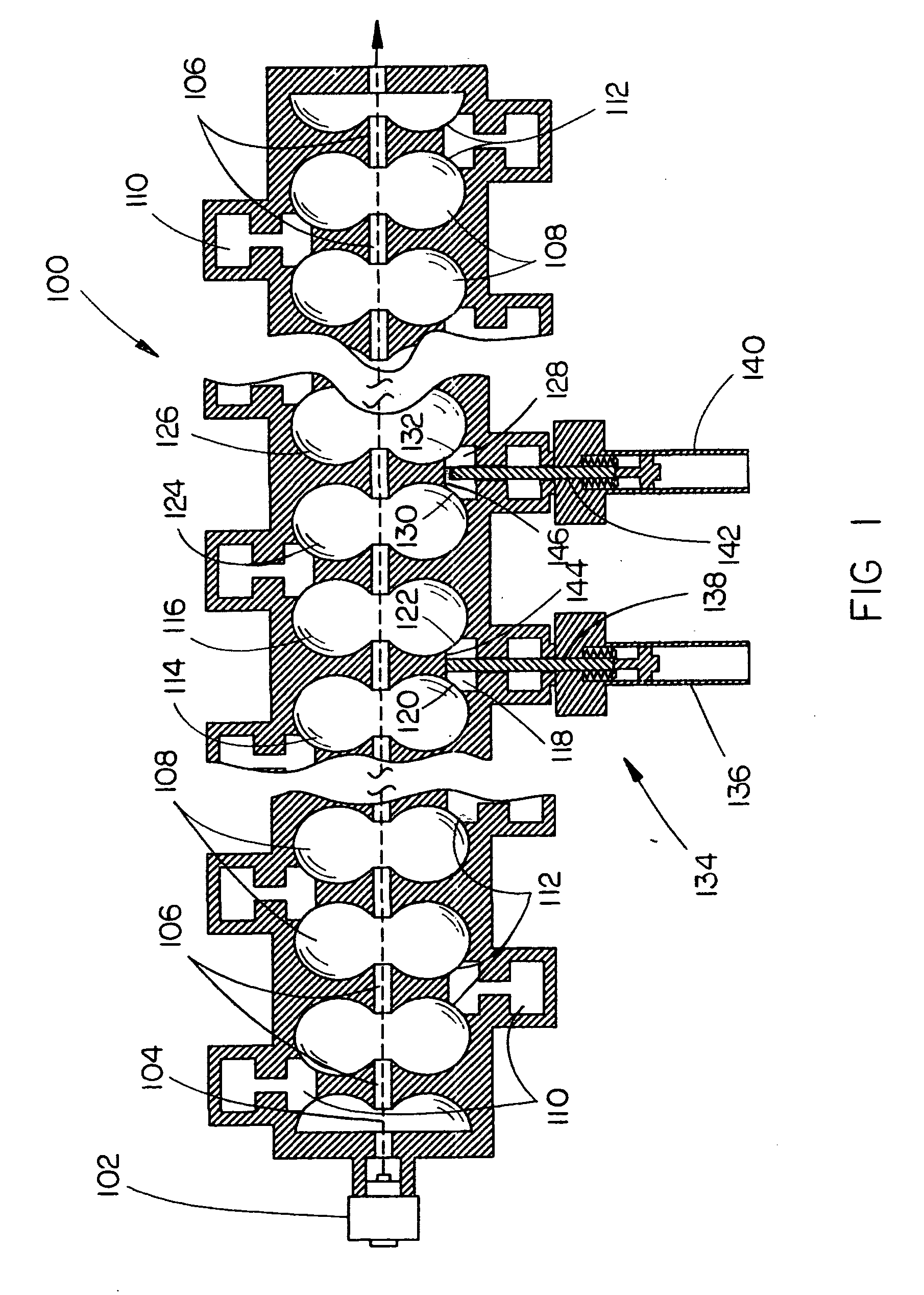
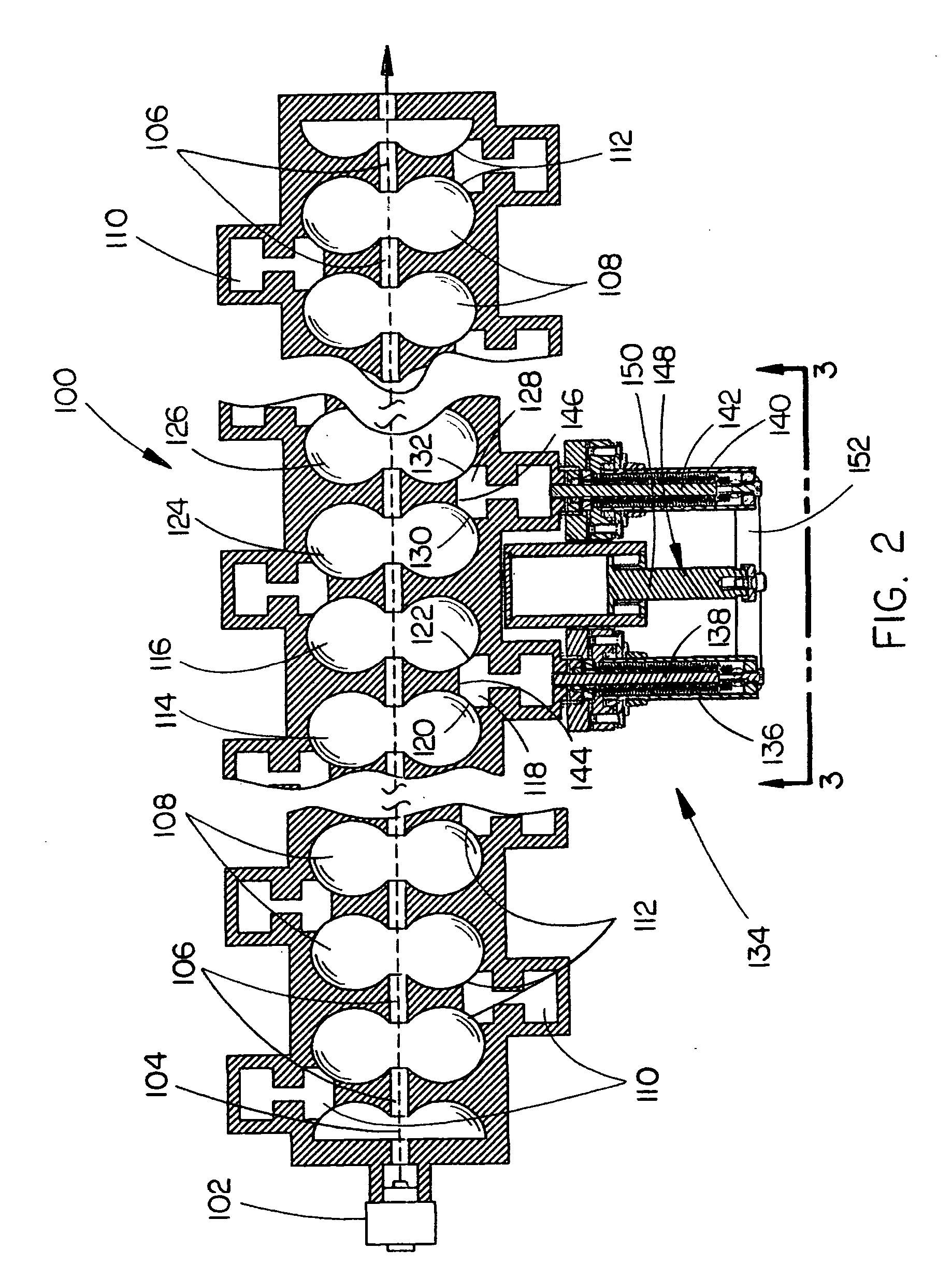
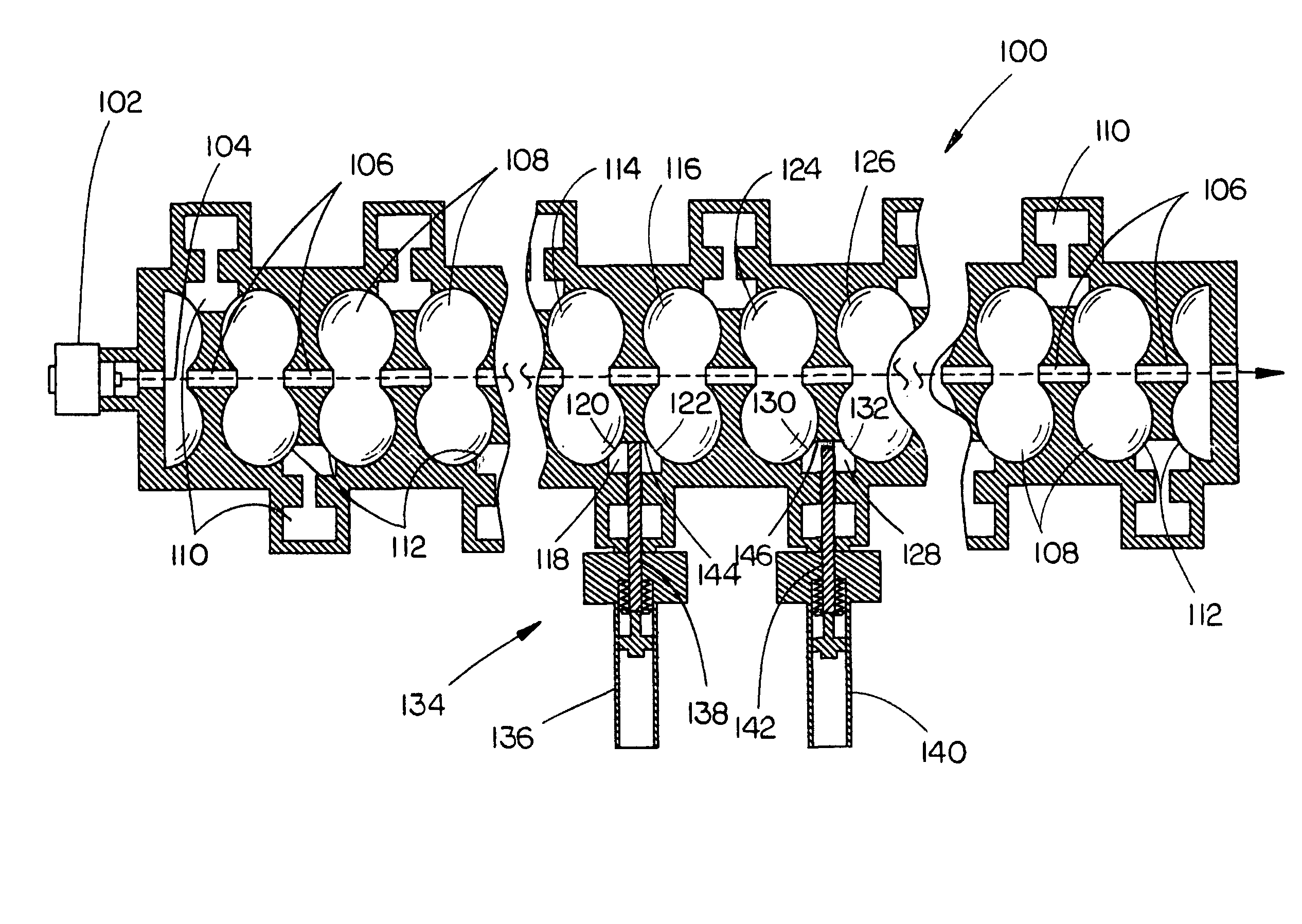
Standing wave particle beam accelerator having a plurality of power inputs
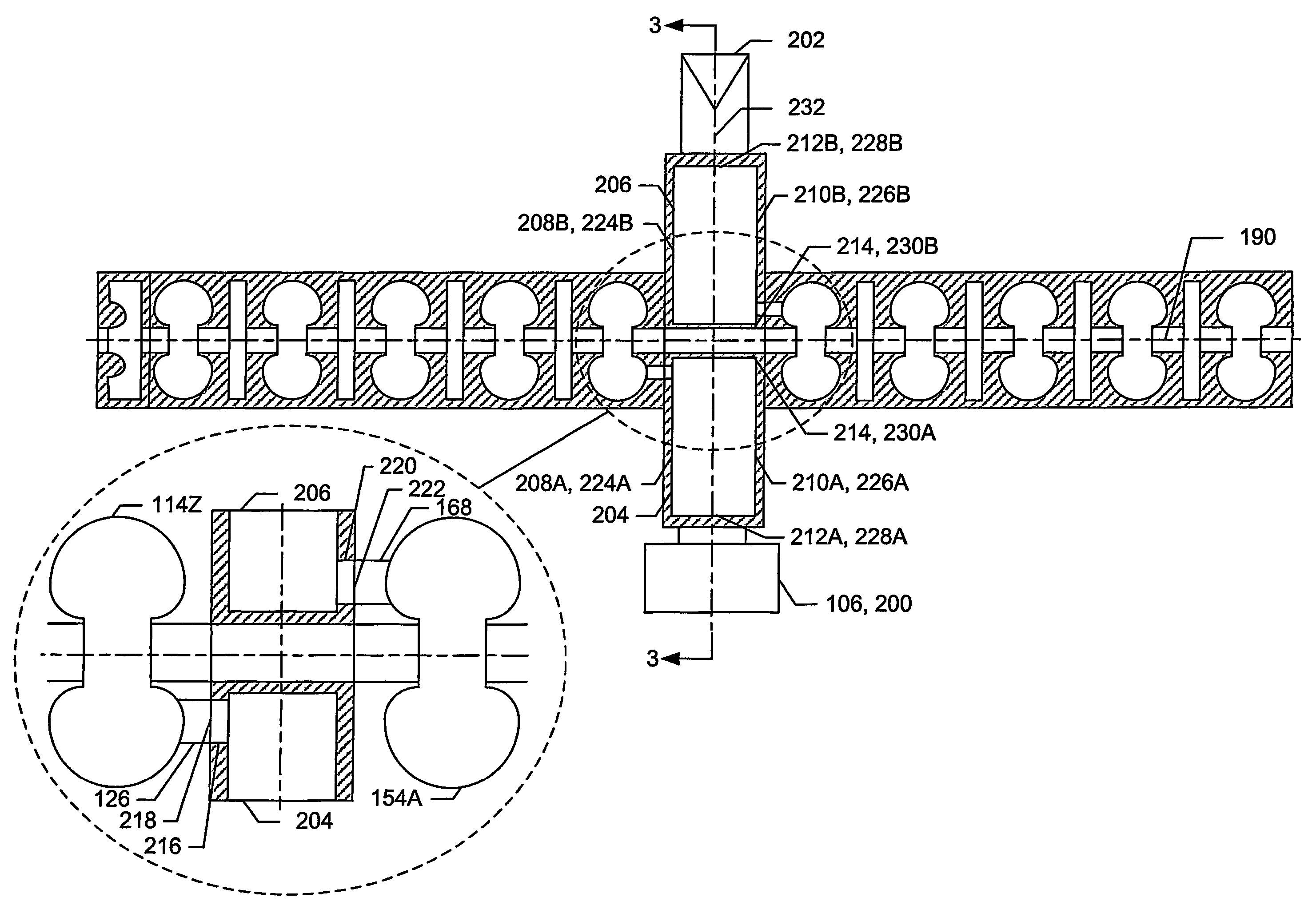
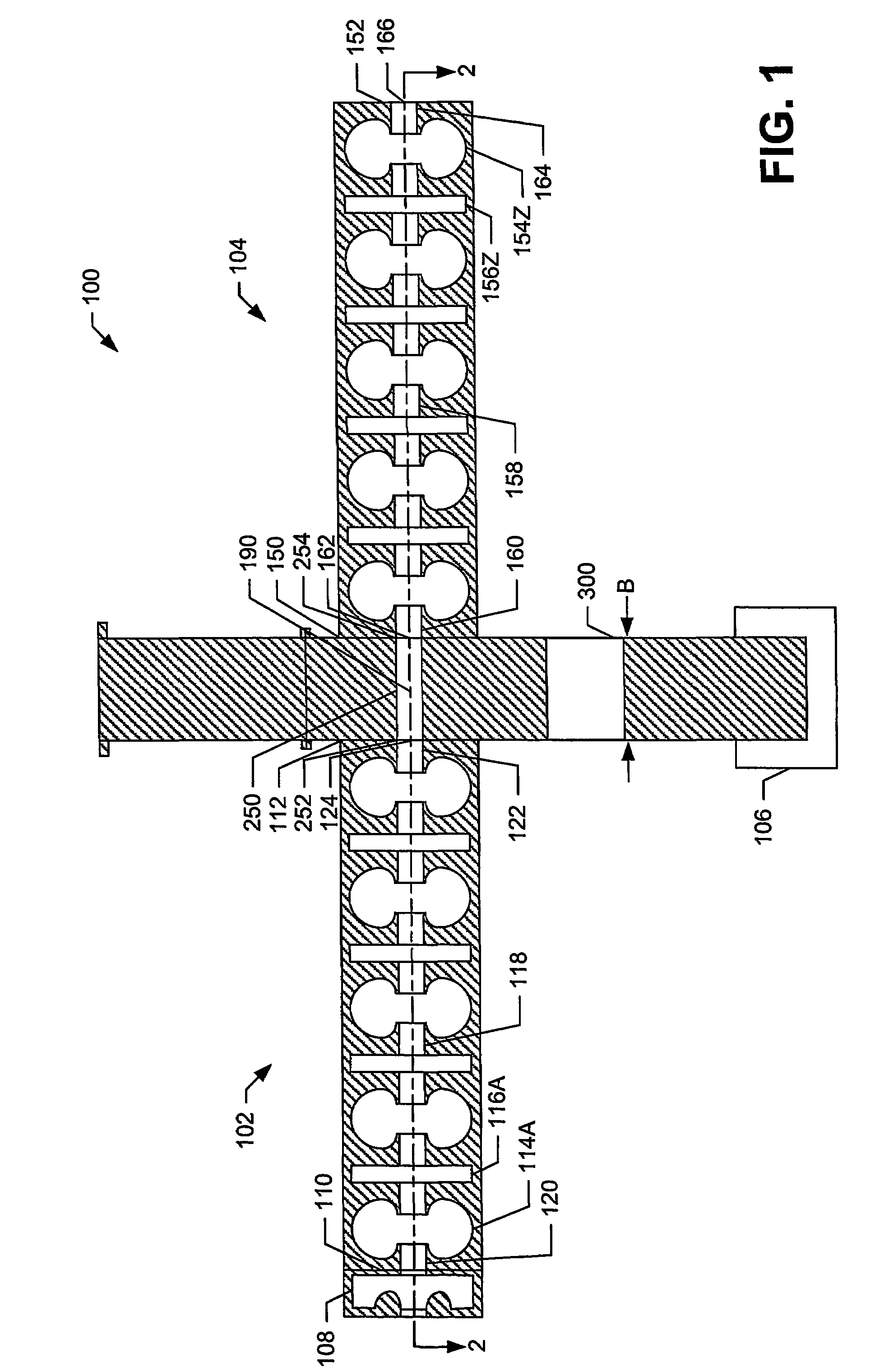
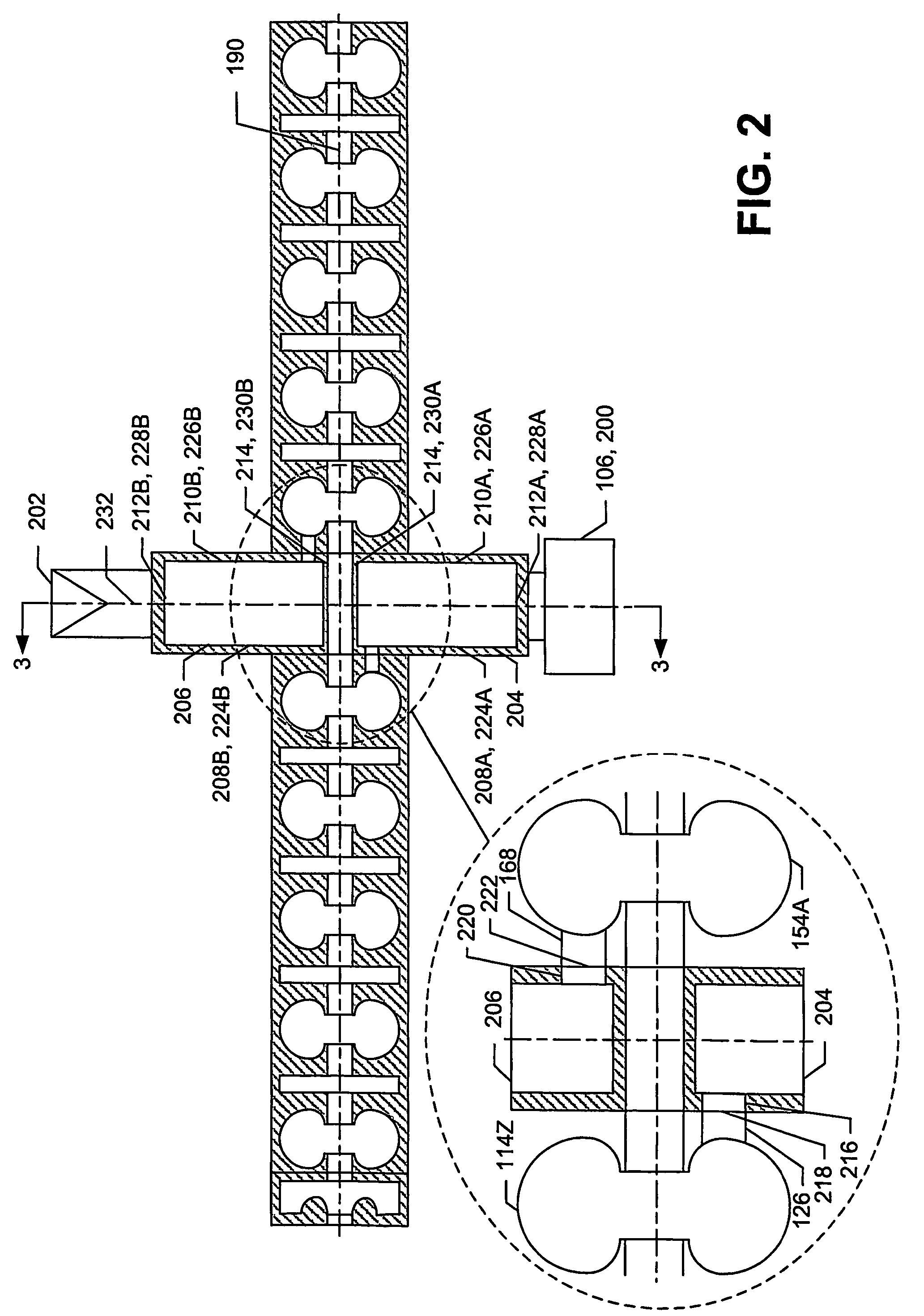
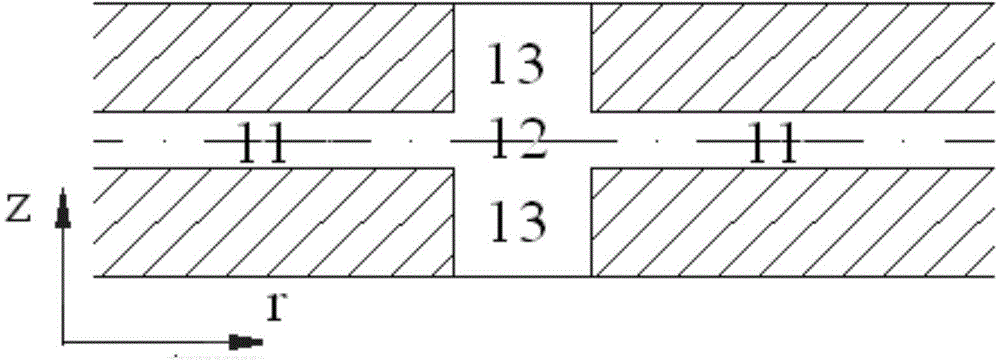
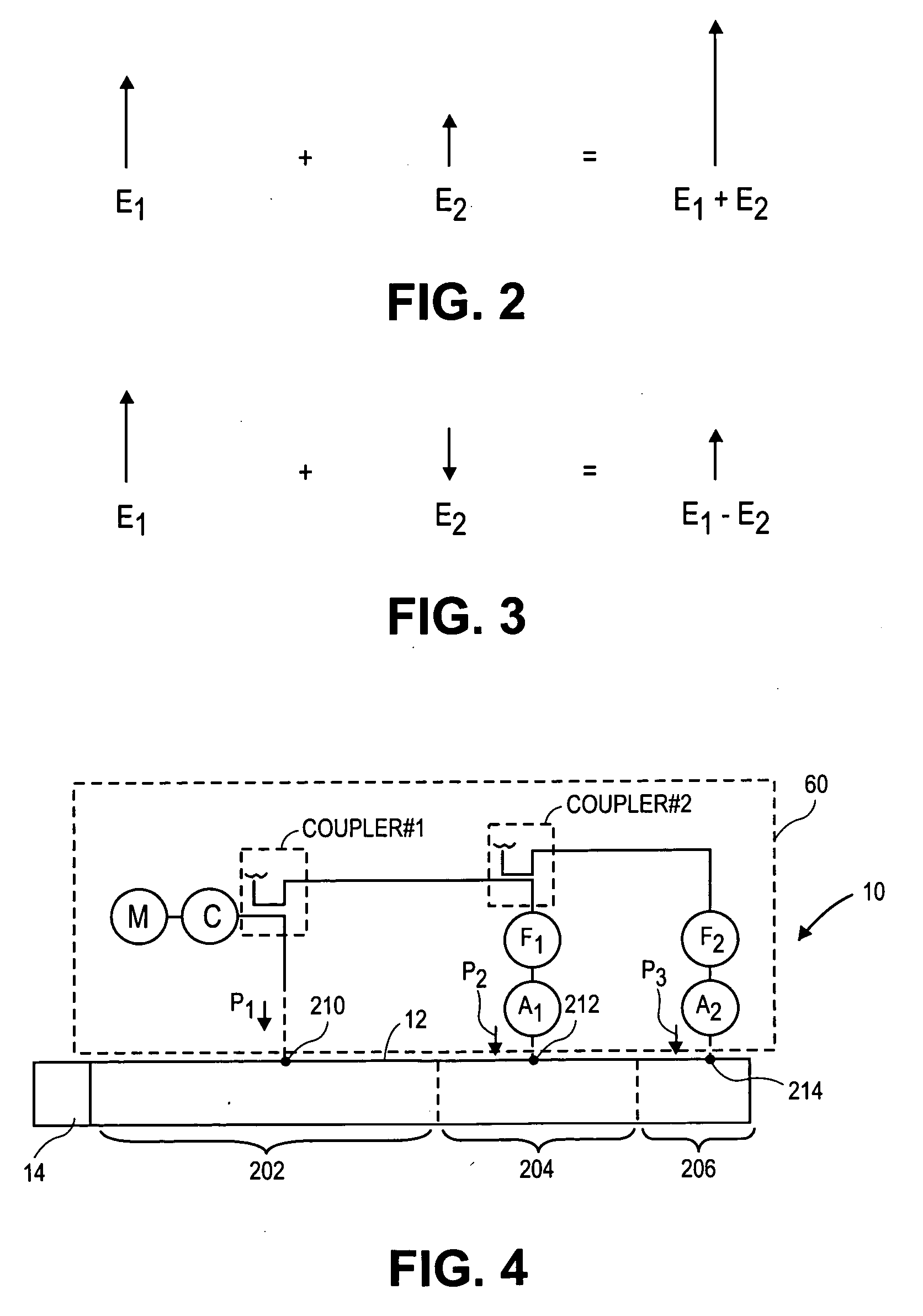
A device for generating a particle beam includes a particle source, and a structure having a first section and a second section, the first section coupled to the particle source, the first section having a first power input, and the second section having a second power input, wherein the first section is configured to produce a particle beam having a first energy E1, and the second section is configured to increase or decrease the first energy E1 by an amount E2, the absolute value of E2 being less than E1.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com