Patents
Literature
138results about How to "High practicability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semiconductor device and manufacturing process therefor
InactiveUS20050263869A1Improve reliabilityHigh practicabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesManufacturing technologySurface layer
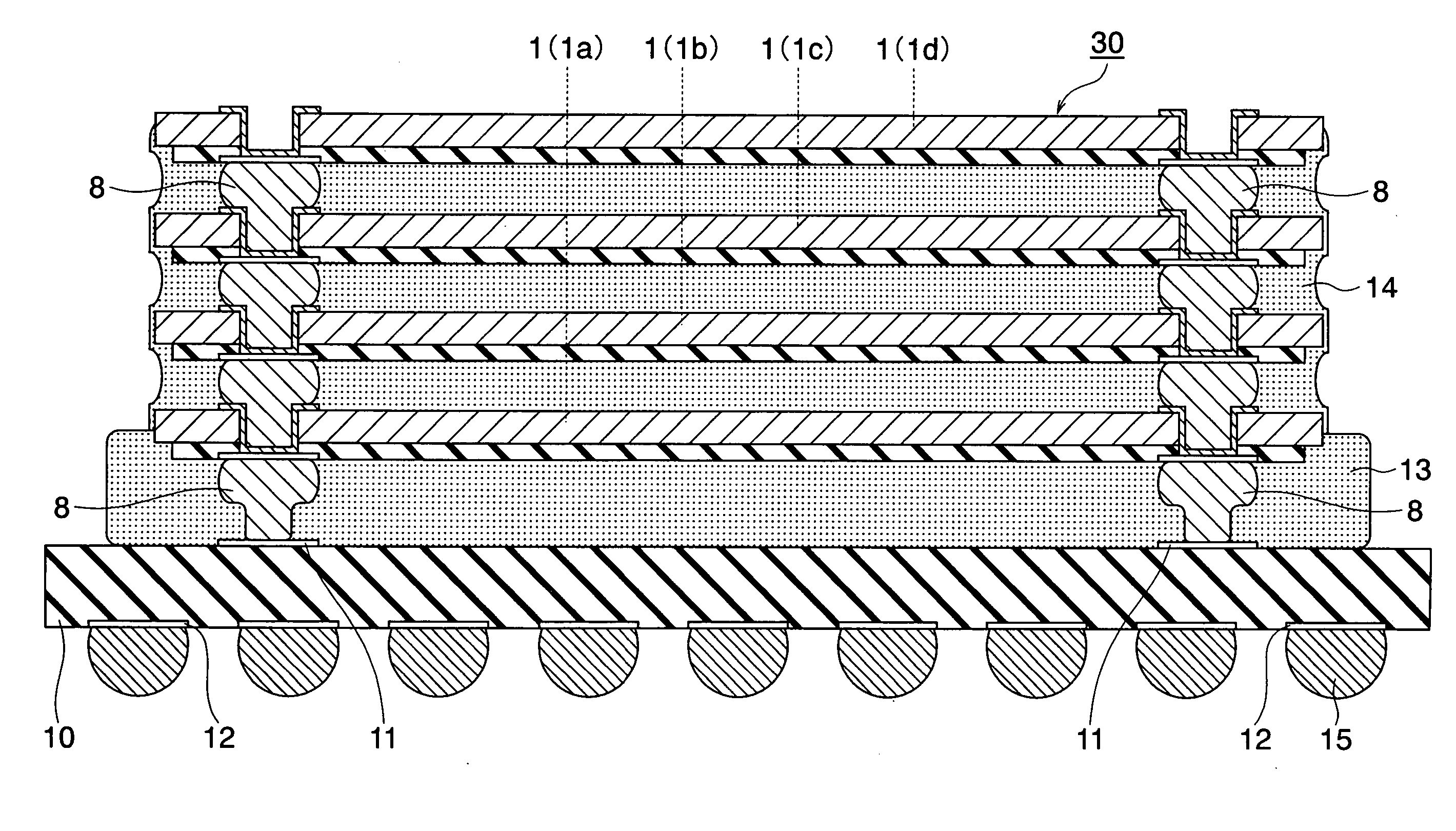
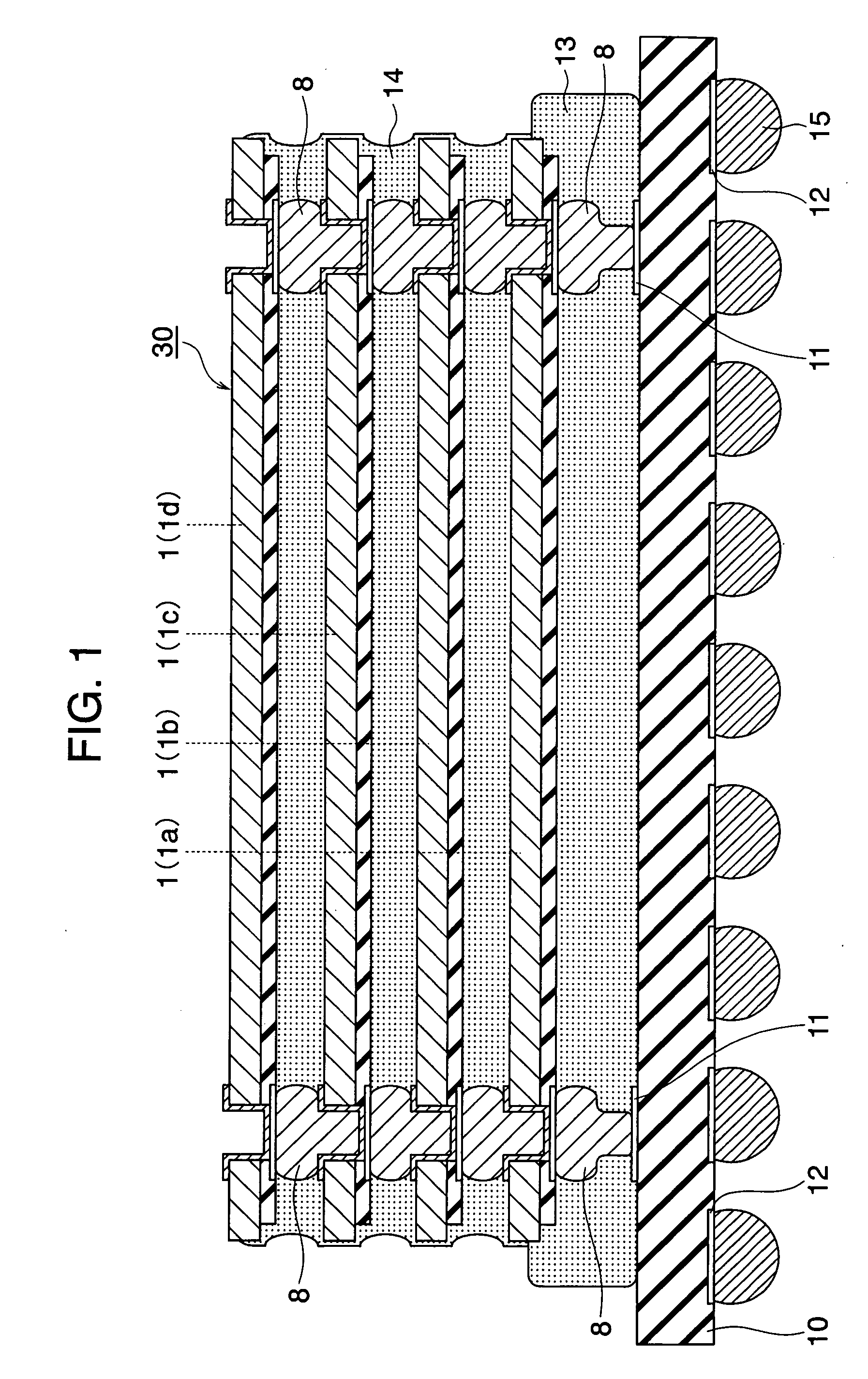
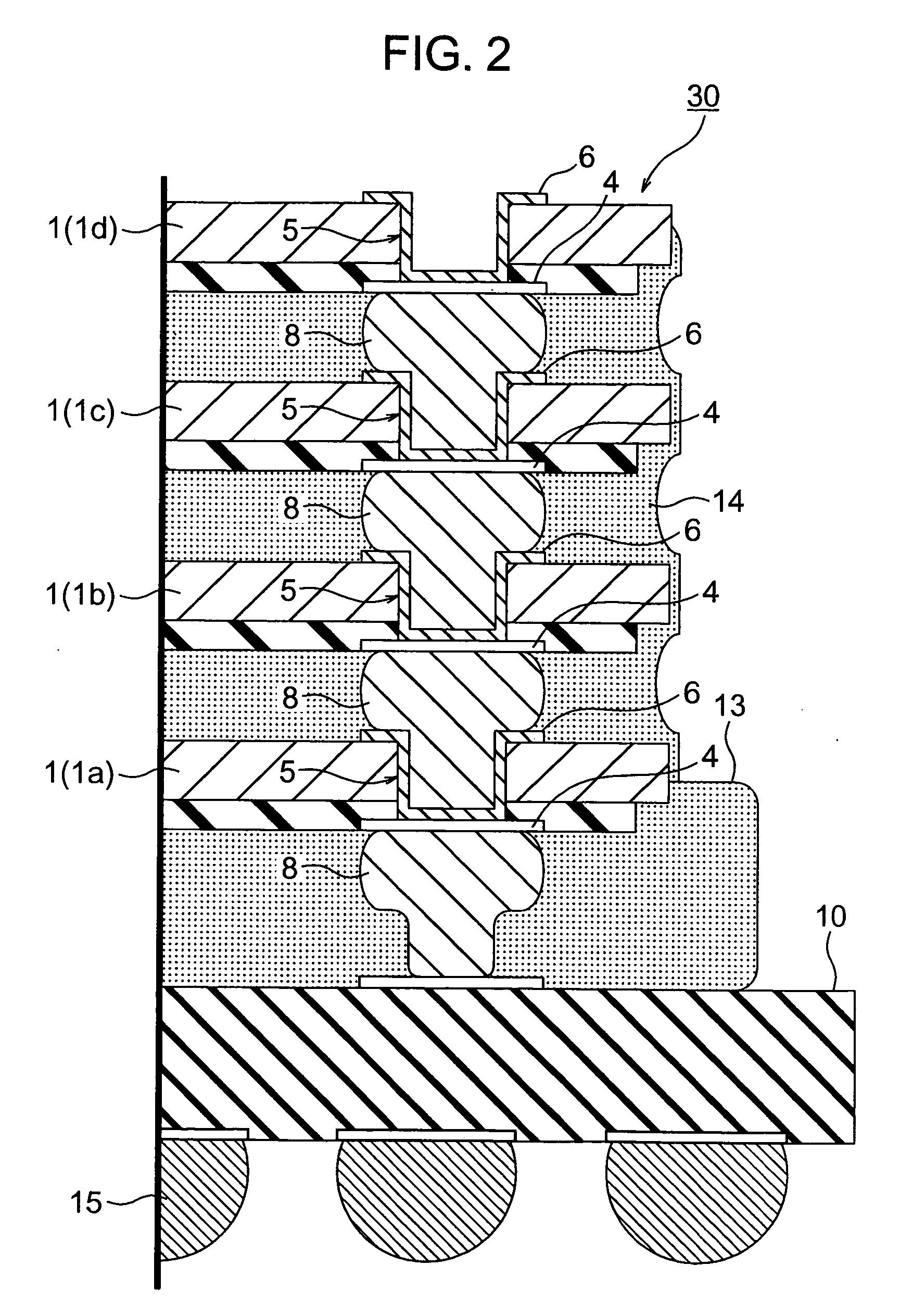
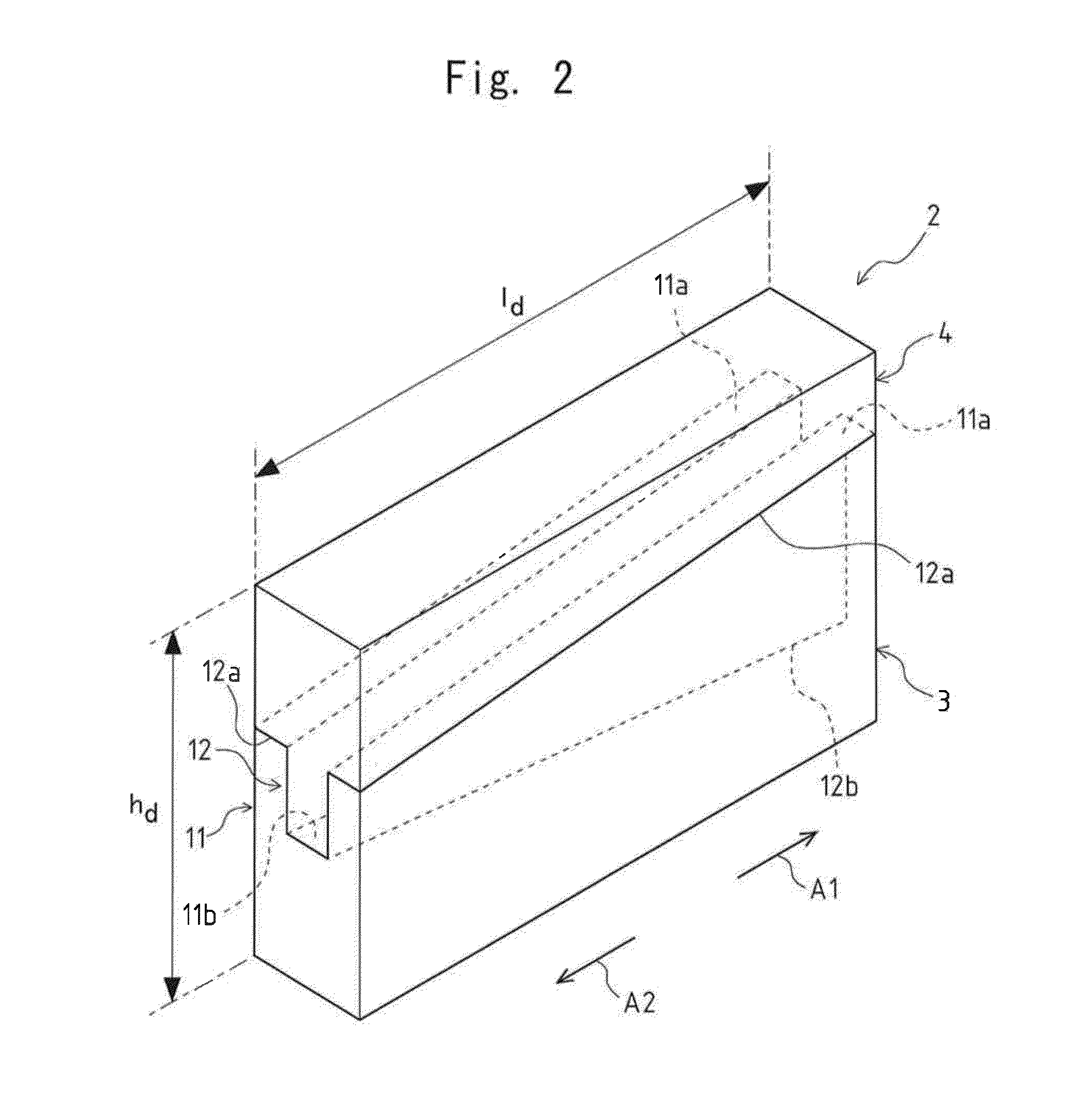
To provide a very-low-cost and short-TAT connection structure superior in connection reliability in accordance with a method for three-dimensionally connecting a plurality of semiconductor chips at a shortest wiring length by using a through-hole electrode in order to realize a compact, high-density, and high-function semiconductor system. The back of a semiconductor chip is decreased in thickness up to a predetermined thickness through back-grinding, a hole reaching a surface-layer electrode is formed at a back position corresponding to a device-side external electrode portion through dry etching, a metallic deposit is applied to the sidewall of the hole and the circumference of the back of the hole, a metallic bump (protruded electrode) of another semiconductor chip laminated on the upper side is deformation-injected into the through-hole by compression bonding, and the metallic bump is geometrically caulked and electrically connected to the inside of a through-hole formed in an LSI chip. It is possible to realize a unique connection structure having a high reliability in accordance with the caulking action using the plastic flow of a metallic bump in a very-low-cost short-TAT process and provide a three-dimensional inter-chip connection structure having a high practicability.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
White color organic electroluminescence device
InactiveUS20070063638A1Reduced chromaticity variationEfficiency of lightDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesOrganic electroluminescenceThermal stability
The present invention provides a white color organic electroluminescence device including: a cathode; an anode; and one or more organic thin film layers including at least a light emitting layer, the one or more organic thin film layers being sandwiched between the cathode and the anode, in which the light emitting layer is constituted of a laminate of a bluish color light emitting layer and a yellow-to-reddish color light emitting layer, and the light emitting layer contains an asymmetric compound containing a condensed ring. This white color organic EL device realizes reduced chromaticity changes, excels in efficiency of light emission and thermal stability, and ensures strikingly prolonged lifetime.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Thermopolymerizable composition for battery use
InactiveUS6562513B1Good storage stabilityHigh strengthCell electrodesFinal product manufactureMeth-Carbonate ester
The present invention provides (1) a thermopolymerizable composition containing a thermopolymerizable compound having (meth)acrylate having a moiety consisting of oxyalkylene, fluorocarbon, oxyfluorocarbon and / or carbonate group within the molecule, an electrolyte salt, an organic polymerization initiator having no benzene ring, and a polymerization retarder having vinyl group within the molecule, (2) a solid electrolyte obtained by heat-curing the composition, (3) a primary battery, a secondary battery and an electric double-layer capacitor each using the solid electrolyte, and processes for manufacturing the same.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
Health bed capable of adjusting the spine curve of a human body
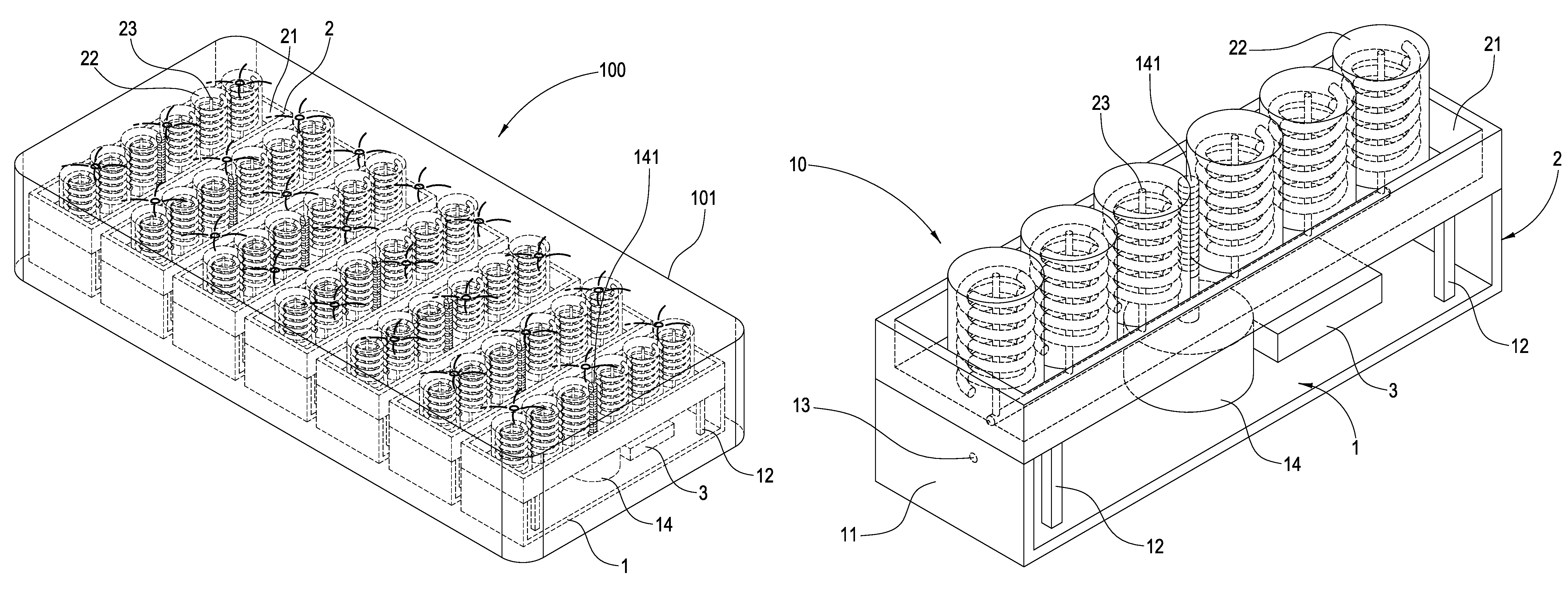
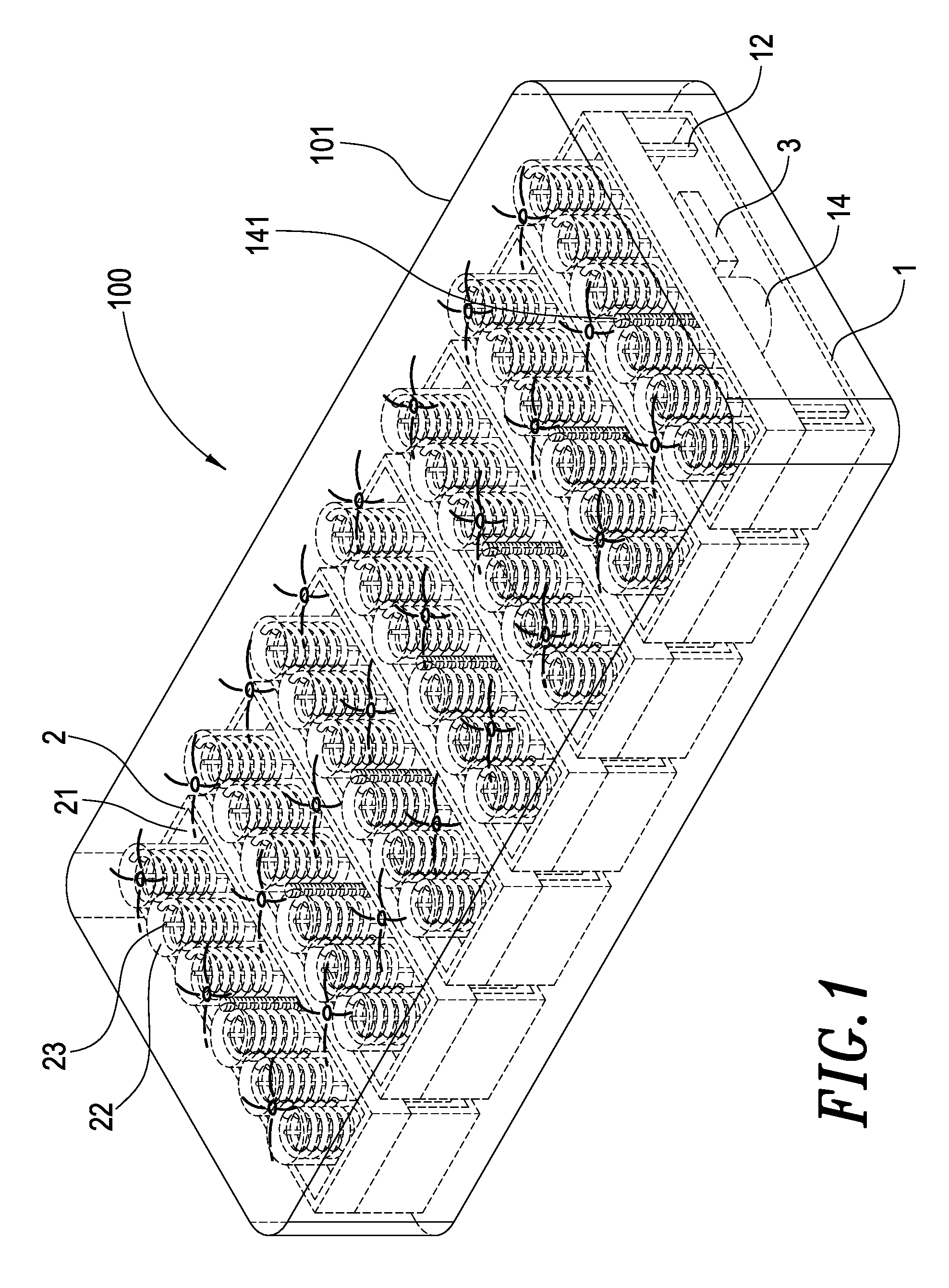
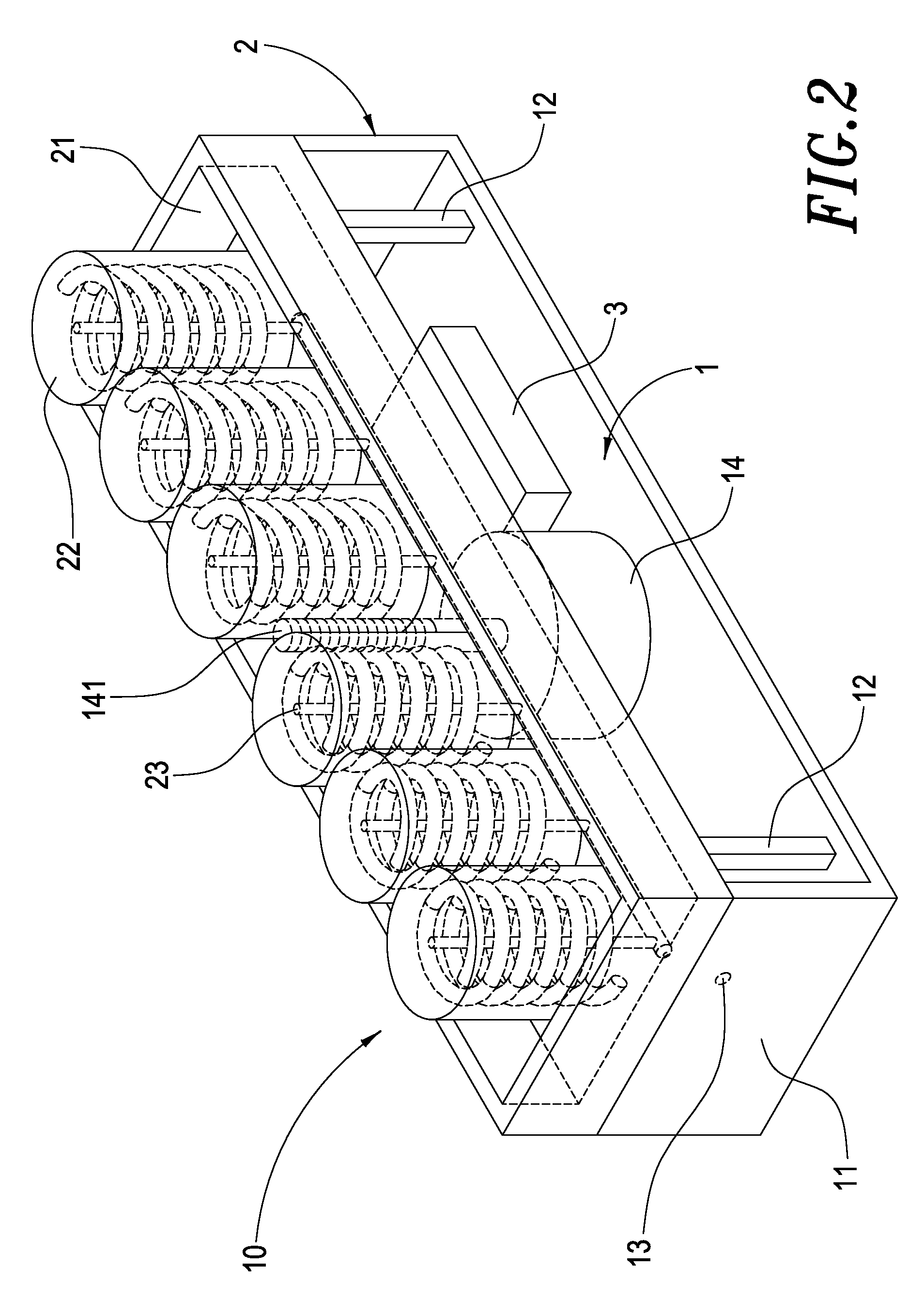
InactiveUS20080276377A1Sleep comfortablyEasy to operateStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesHuman bodyMotor drive
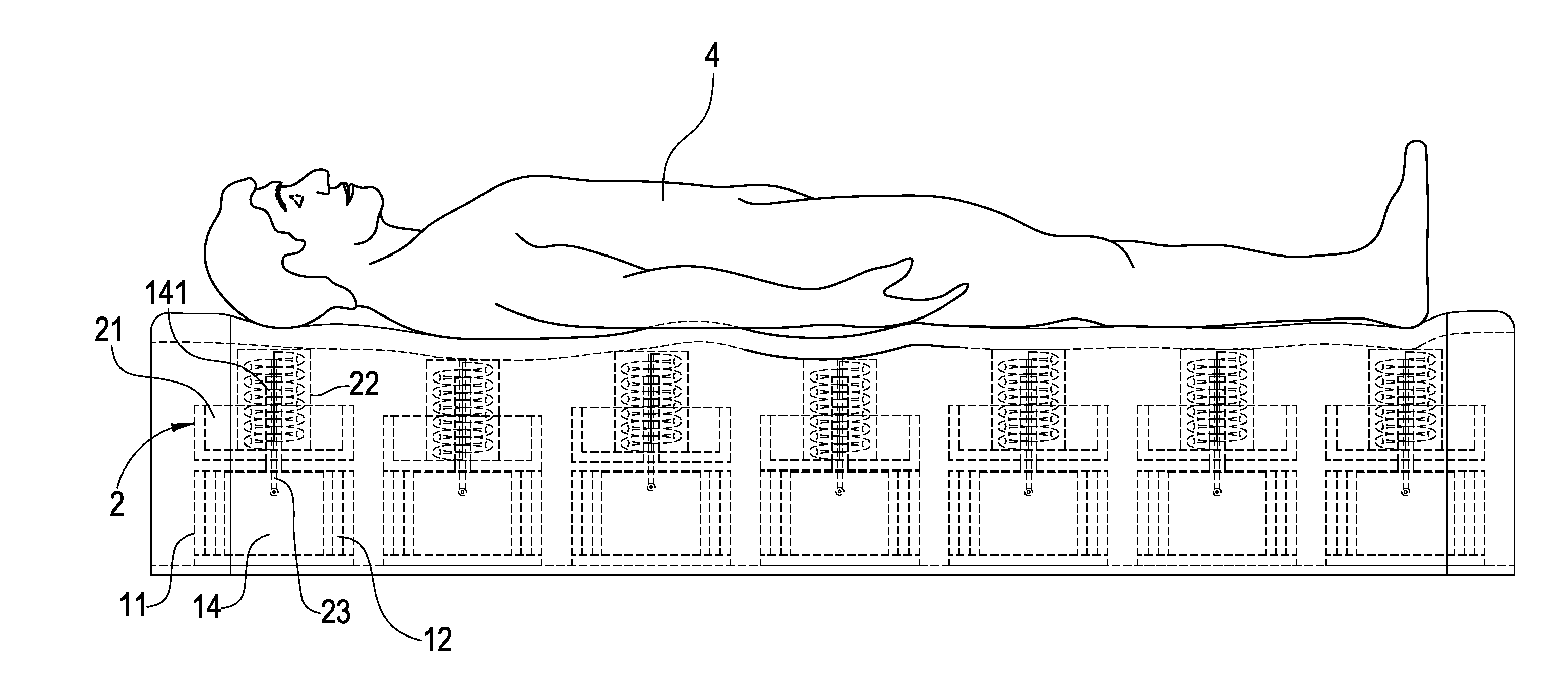
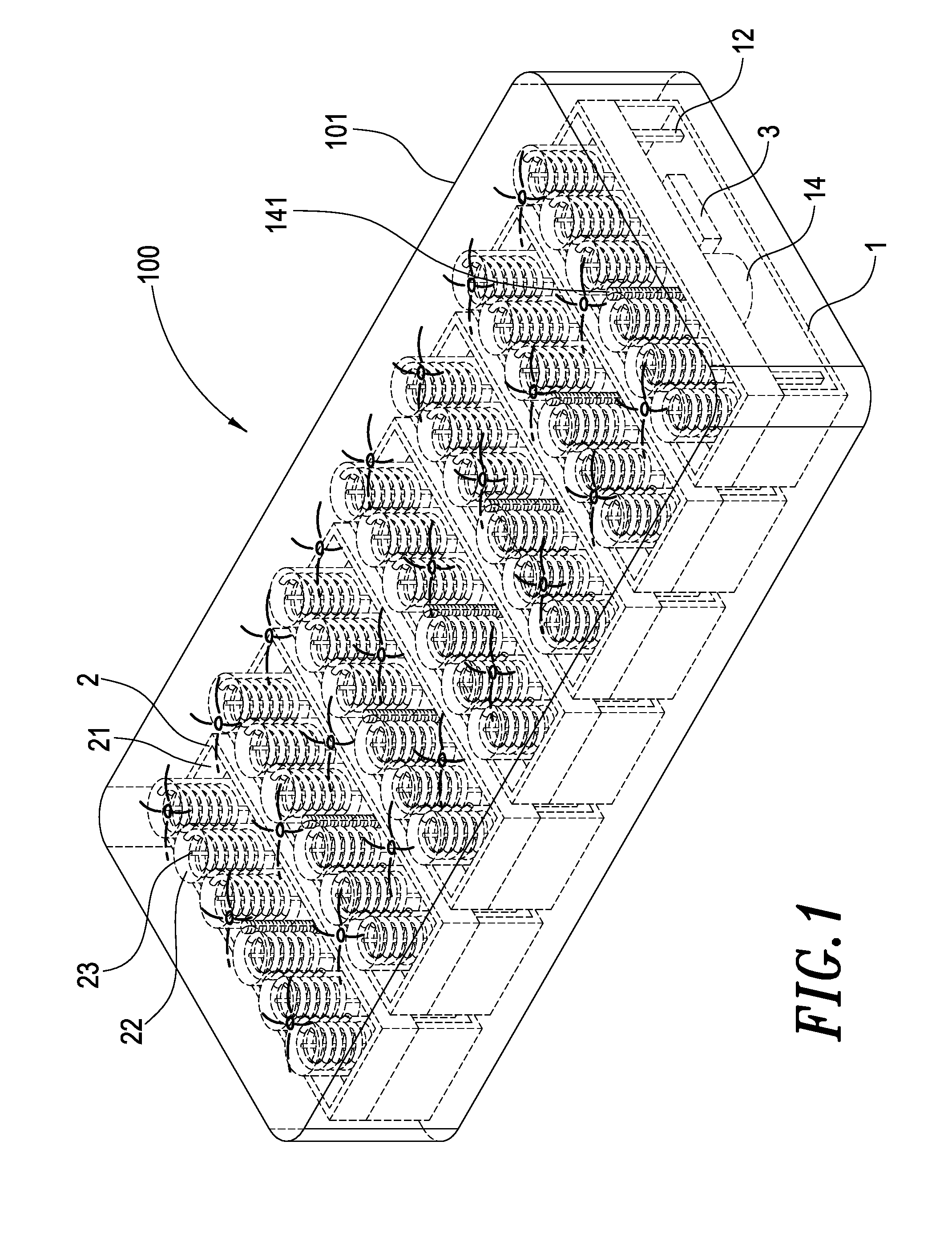
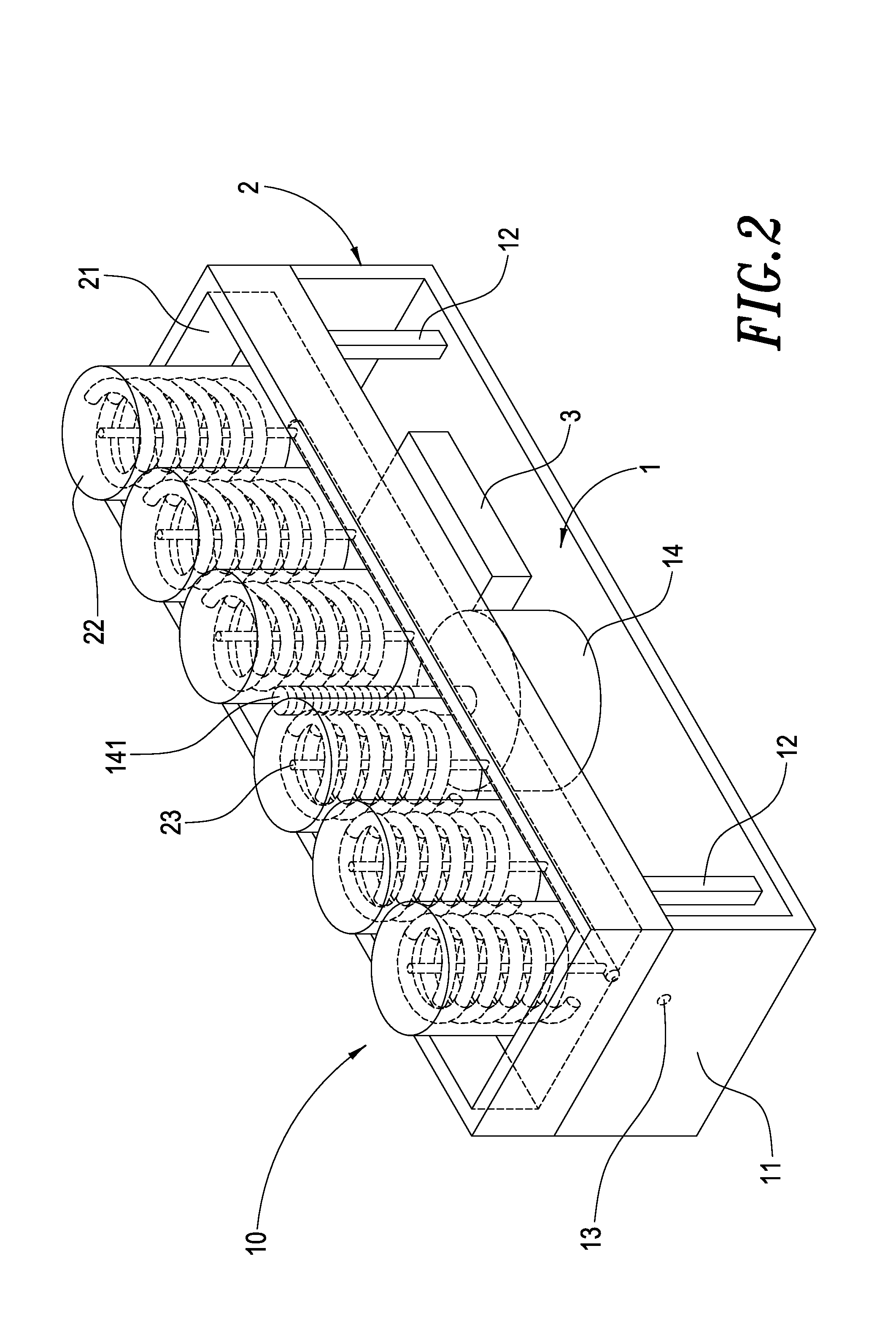
A health bed capable of adjusting the spine curve of a human body mainly comprises a plurality of elevators. Each of the elevators includes a lower plate having several upholders extending therefrom wherein a motor is fixed on the center of the lower plate and the axle of the motor is a screw engaged with the middle of a motor-driven base such that the motor-driven base can be moved upward or downward by a drive of the screw. The upholders support the motor-driven base is disposed above the lower plate and supported by upholders. A plurality of elastic objects is disposed on the motor-driven base in which the elastic object has a sense stick inside and the sense stick penetrates out of the bottom of the motor-driven base. A height sensor lateral the base may thus measure a downside movement of the elastic objects. The height sensor and the motor are connected to a control circuit that actuates the motors to drive the motor-driven bases upwardly to a desired height by receiving signals from the height sensors. When a user lies on the bed, each of the elevators actively sustains the spine curve of human body, achieving a comfortable sleep.
Owner:HUMBOLDT STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for calculating primary time constant of power grid
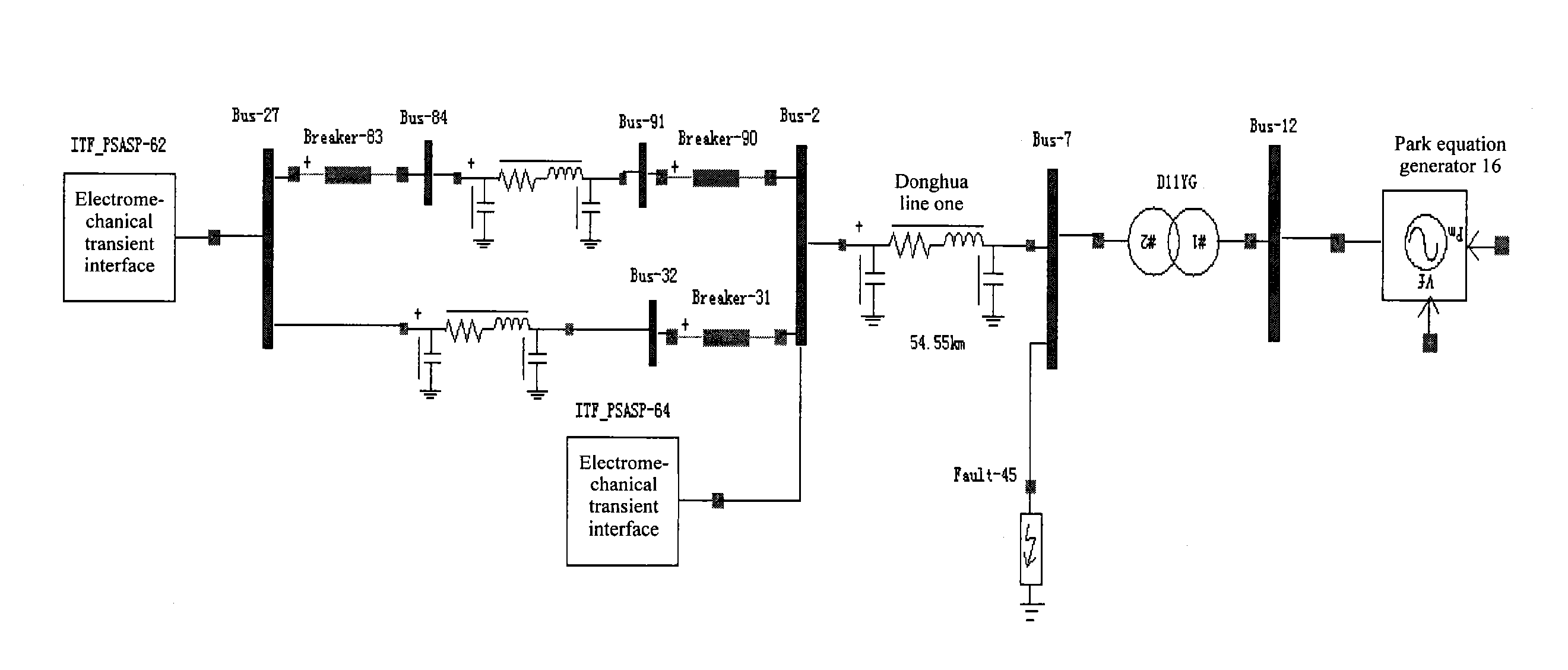
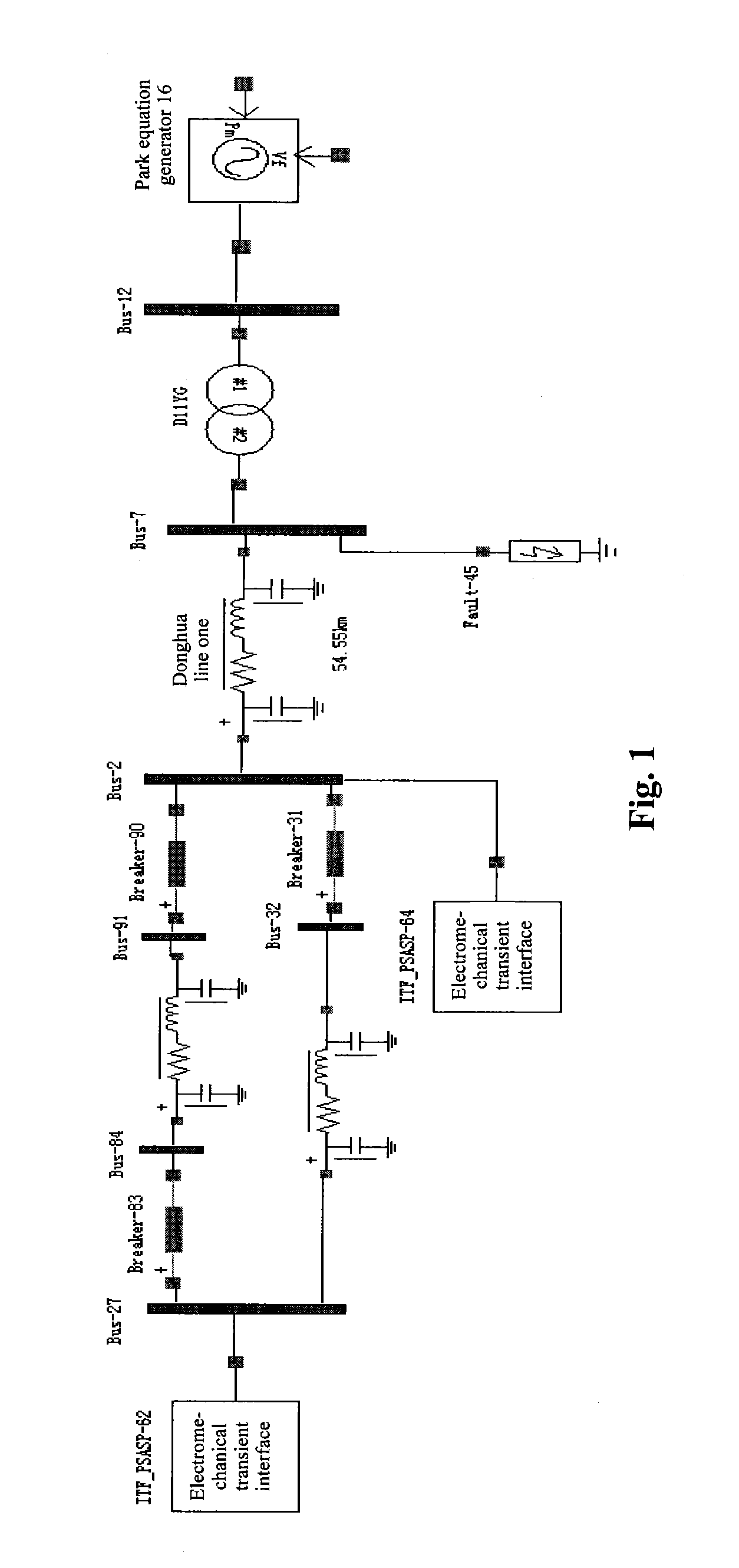
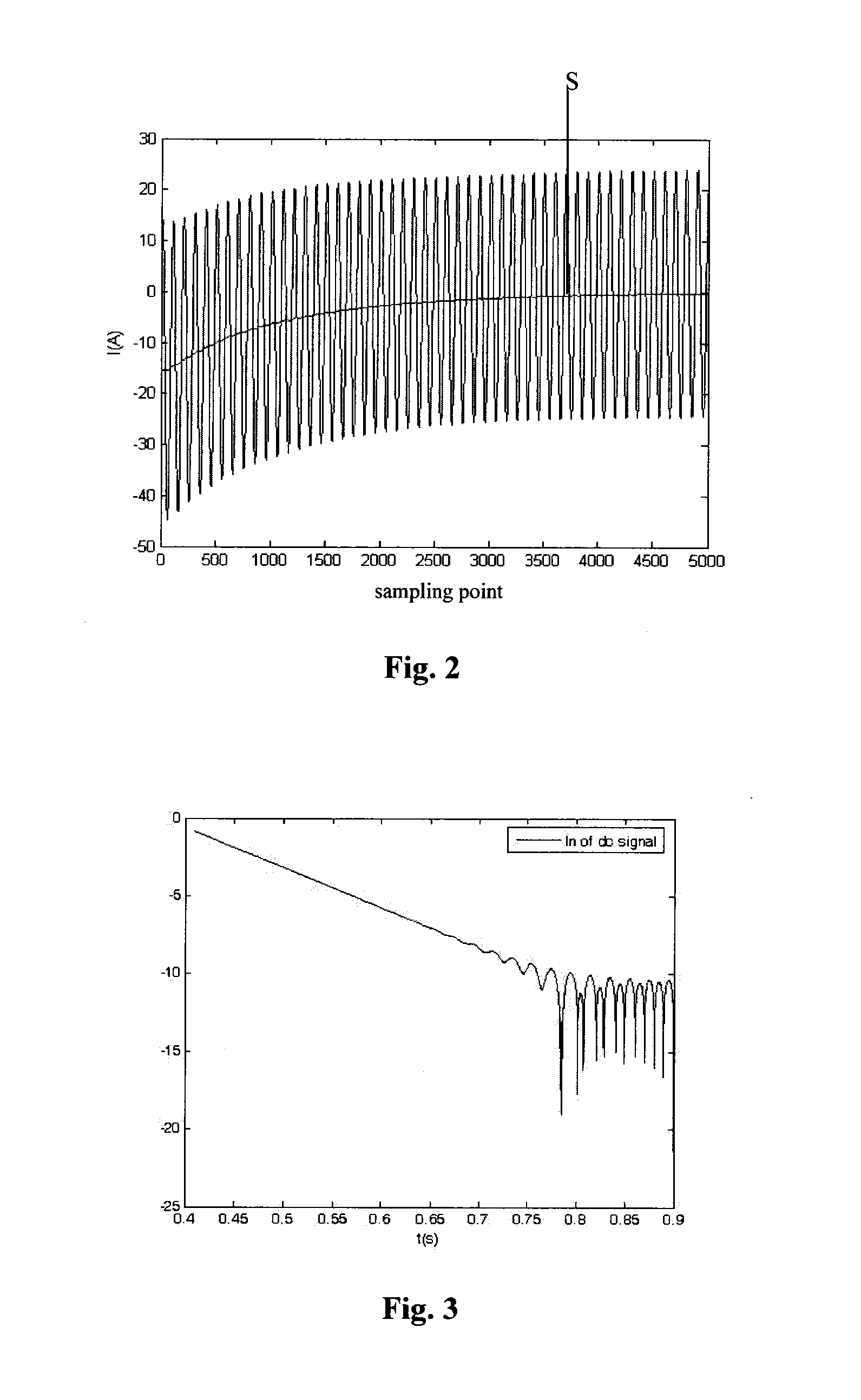
InactiveUS20130191092A1Improve analysisStrong control abilityResistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementRC time constantElectric power system
A method for calculating a primary time constant of a power grid. It comprises the steps of: establishing an electromechanical transient model of the power grid using the widely used power system analysis software package (PSASP) according to the actual power grid parameters and network topology; establishing an electromagnetic transient model under PASAP using the actual power grid parameters for a site which requires the calculation of the primary time constant of the power grid, and setting a ground short circuit fault at the site; obtaining a transient short circuit current of the short circuit point of the power grid using a hybrid simulation method of the electromechanical and electromagnetic transient models; filtering out a periodic component in the transient short circuit current to obtain a non-periodic component attenuated with time, and finding the attenuation time constant of the non-periodic component which is the primary time constant of the power grid.
Owner:HEBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Medical treating tool
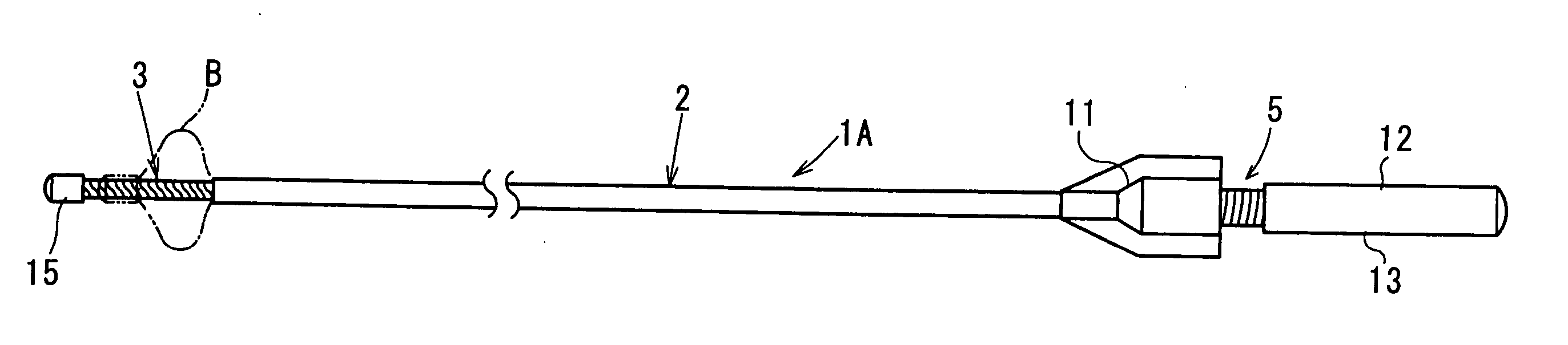
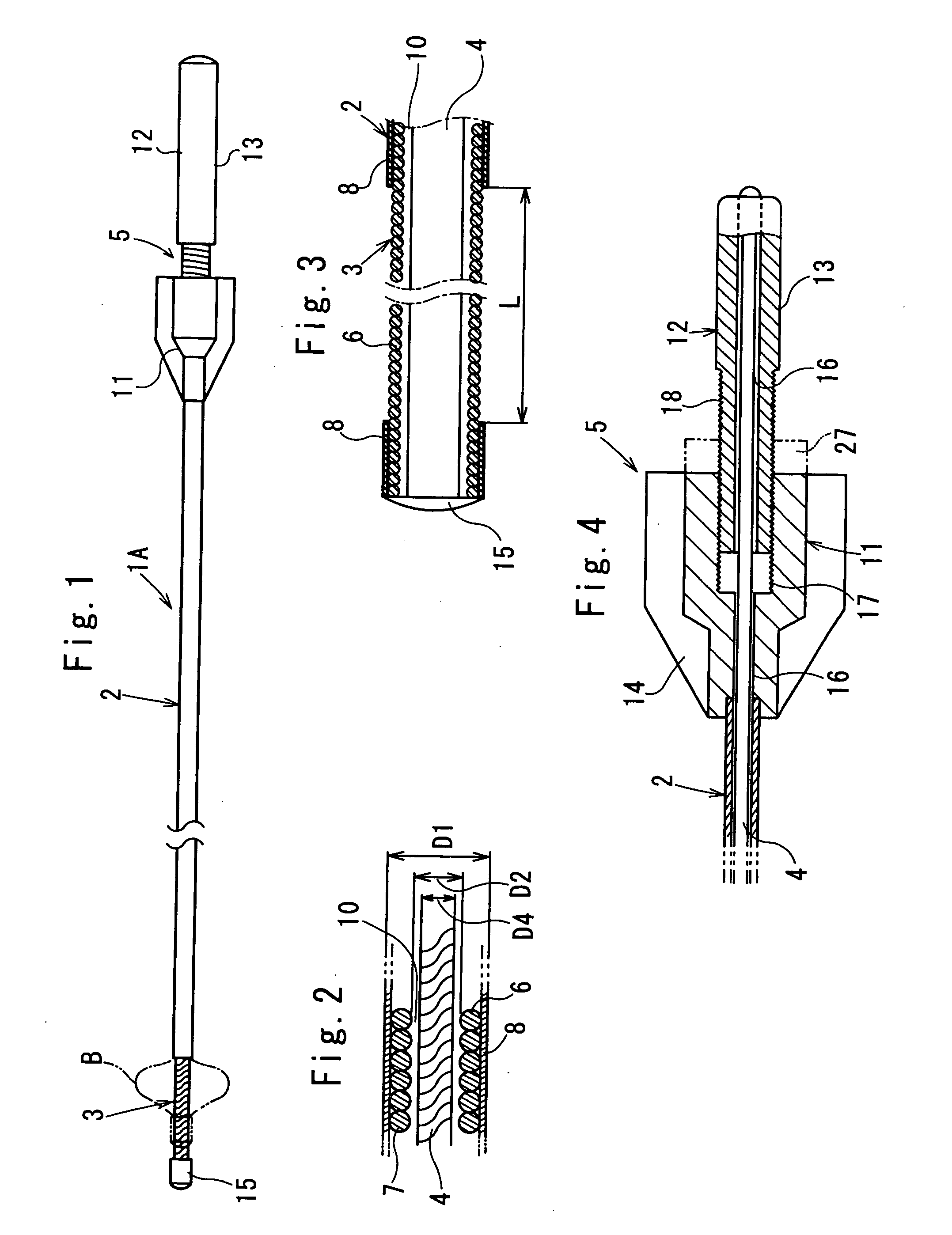
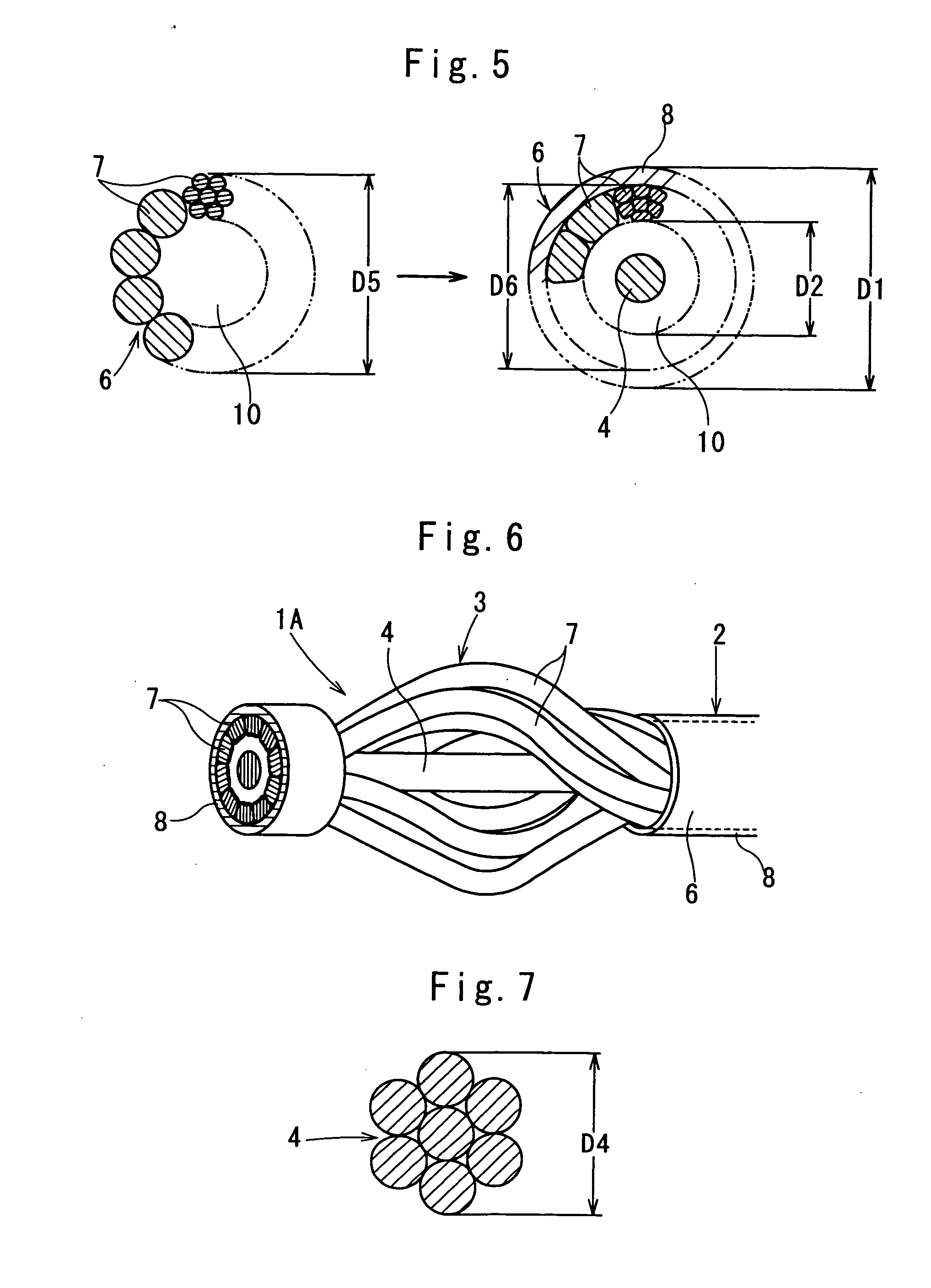
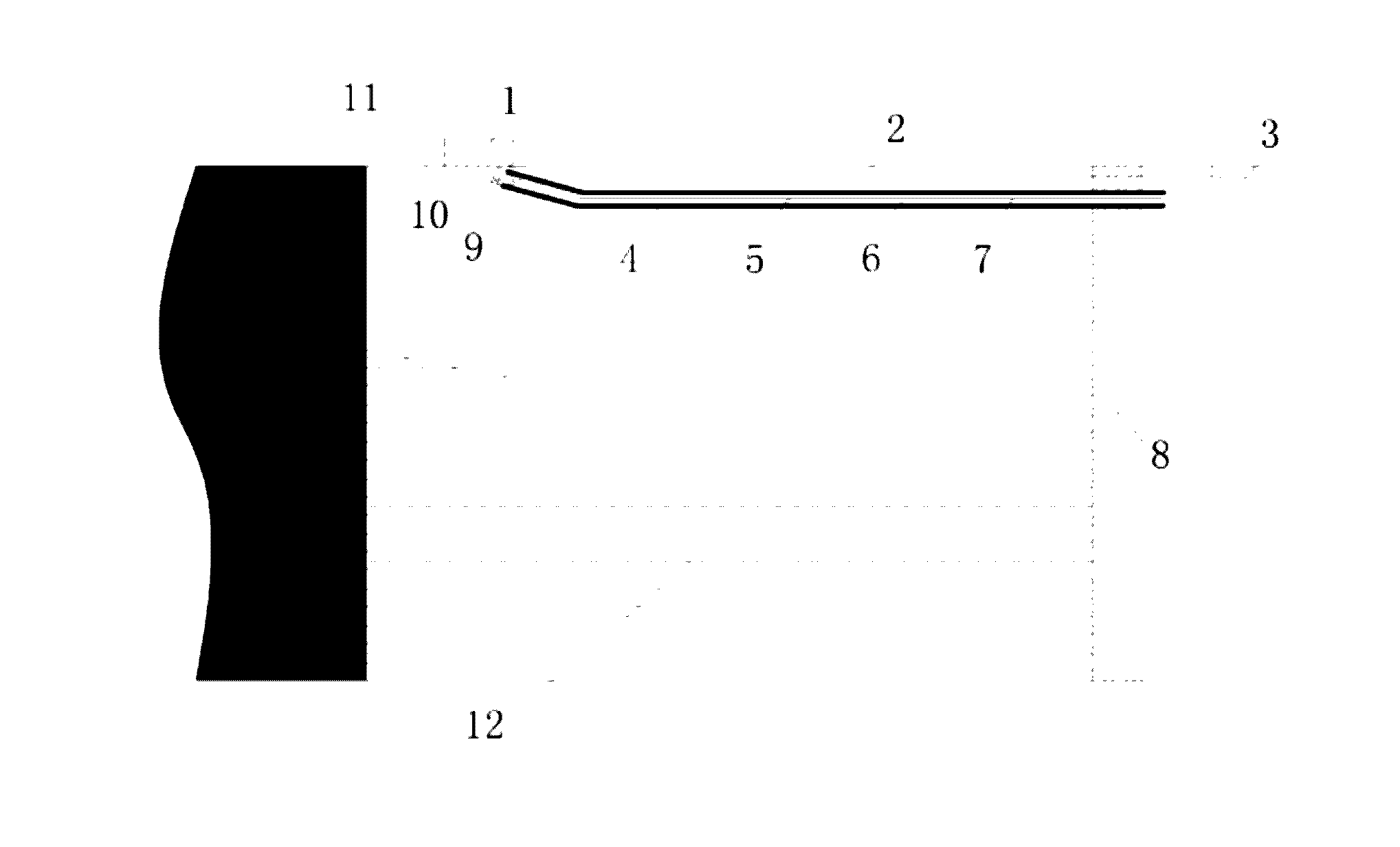
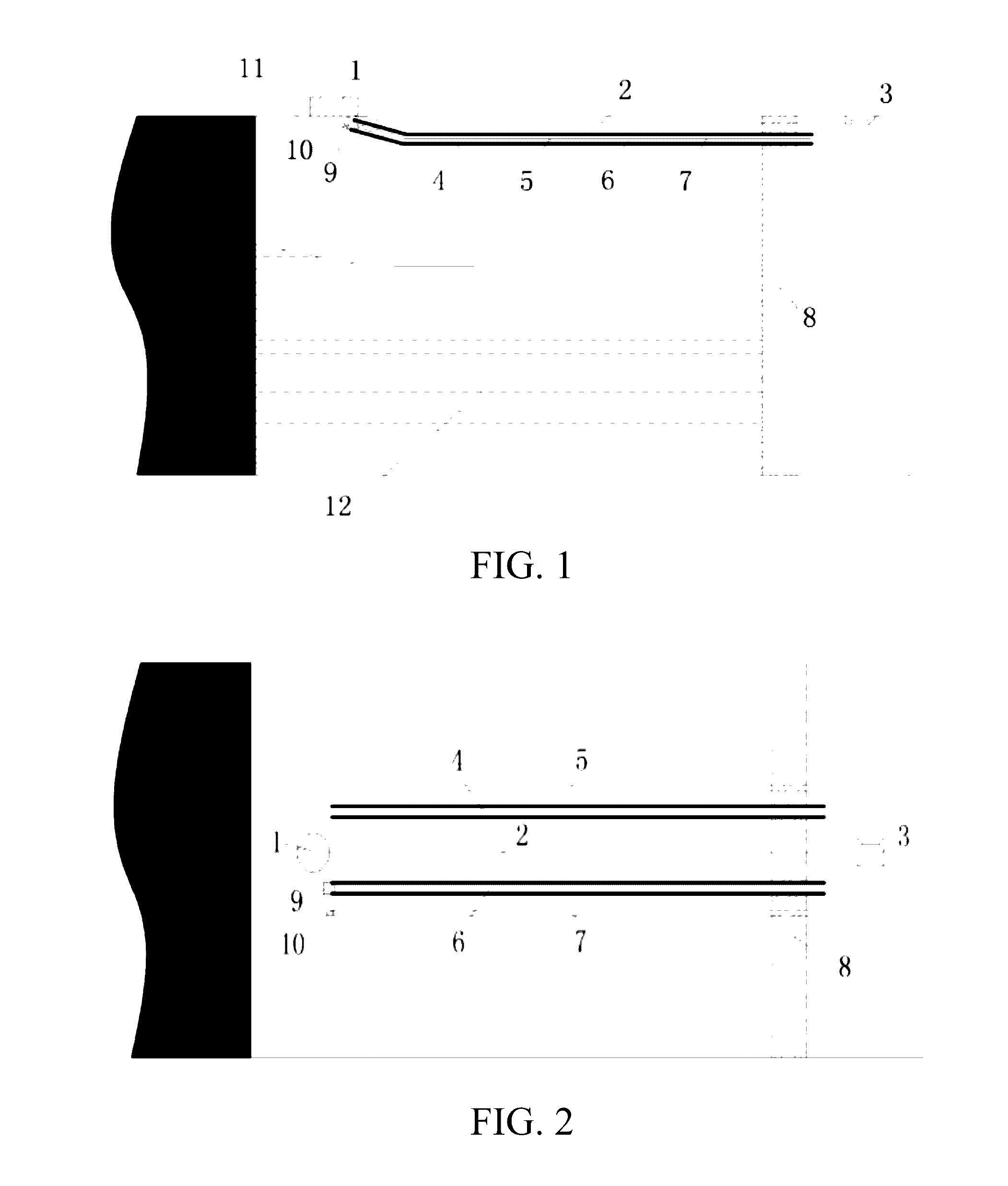
InactiveUS20050154400A1Enhance curabilityHigh practicabilityDilatorsSurgical forcepsForeign matterMedical treatment
In a medical treatment tool (1, 1A, 1B), a flexible linear wire forms a main linear wire portion (2) provided by a wire-stranded helical hollow tube (6) coated with an outer protective layer (8). An operational core elongation (4) is slidably inserted into the main linear wire portion (2) of the wire-stranded helical hollow tube (6). A front end of the main linear wire portion (2) is connected to a front end of the operational core elongation (4), and a rear end of the operational core elongation (4) is connected to a hand access portion (5) placed at a rear end of the main linear wire portion (2). A diametrically expandable portion (3) is formed at a distal end portion of the main linear wire portion (2) by exposing the wire-stranded helical hollow tube (6) outside from the outer protective layer (8). An outer surface of the wire-stranded helical hollow tube (6) of the diametrically expandable portion (3) is at least diametrically reduced, and the diametrically expandable portion (3) forms a basket-like configuration which is shiftable into a diametrically shrunken configuration due to a relative siliding displacement between the operational core elongation (4) and the main linear wire portion (2) so as to efficiently retrieve foreign matters within the human somatic cavity.
Owner:ASAHI INTECC CO LTD
Method of preventing image sticking for liquid crystal display
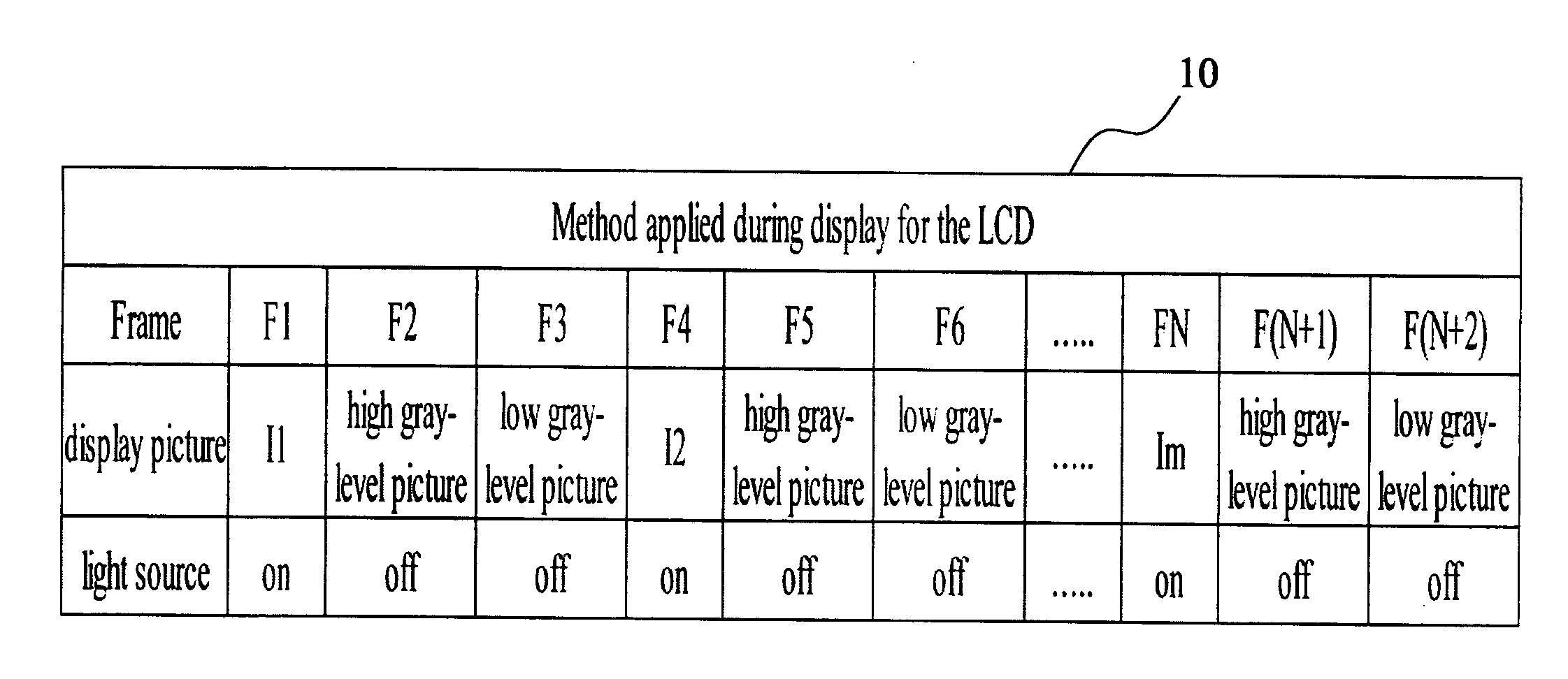
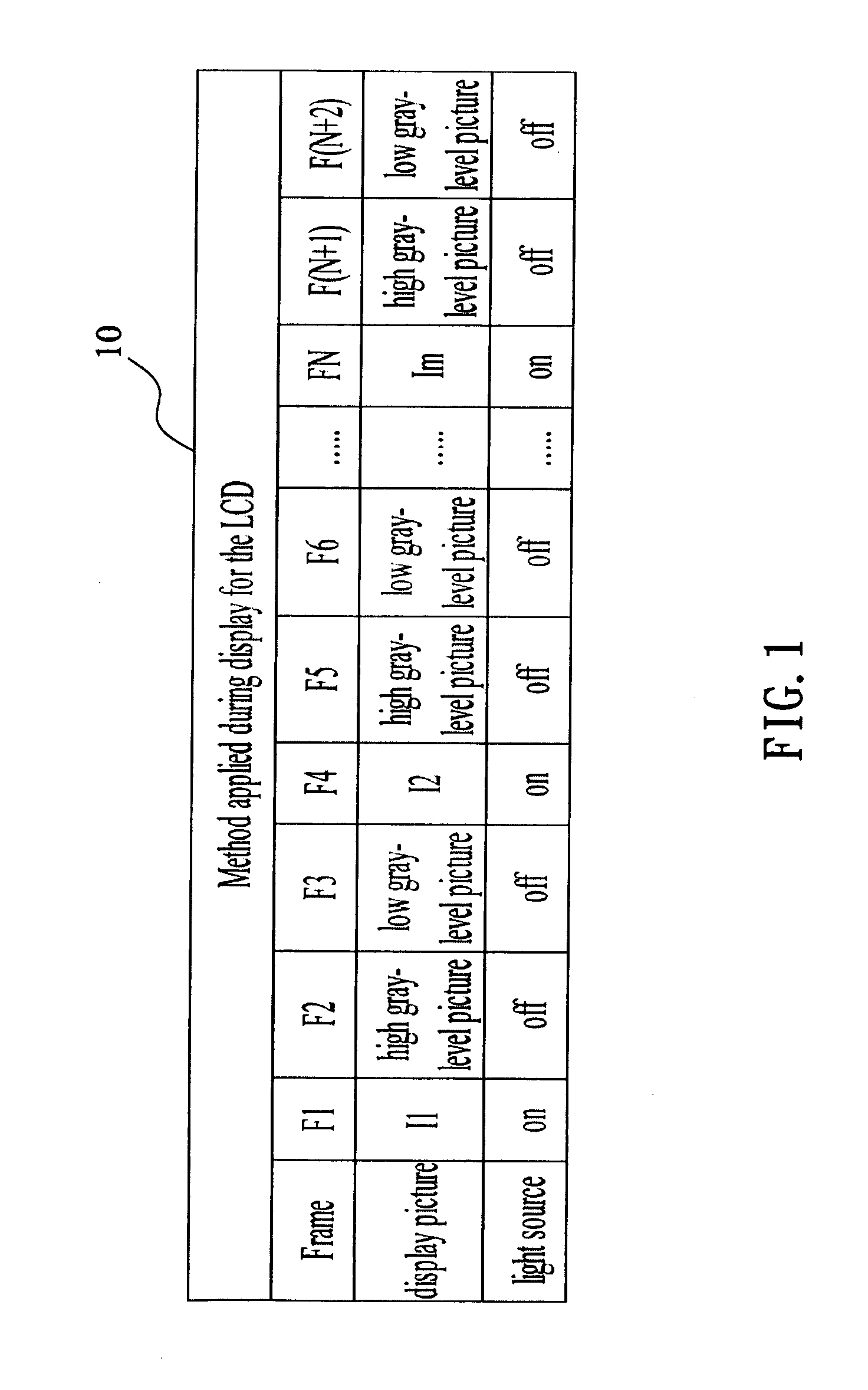
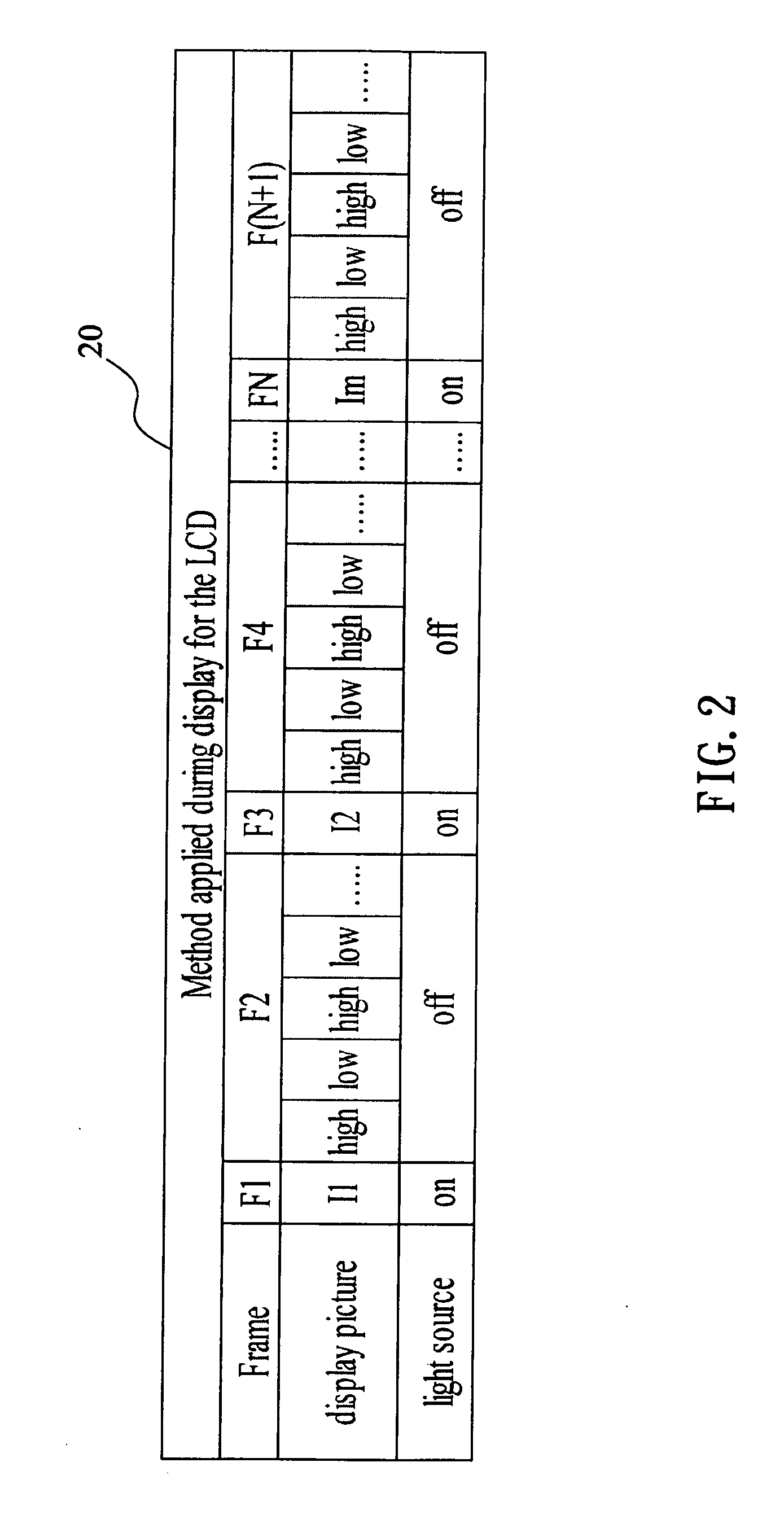
ActiveUS20080042954A1Prevent image retentionHigh practicabilityStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayGray level
A method of preventing an image sticking for a liquid crystal display includes alternately providing a high gray-level picture and a low gray-level picture between any two adjacent pictures, wherein the backlight is turned off. Or, in the turning-off process of the liquid crystal display, the high gray-level picture and low gray-level picture are provided alternately to the display panel. Therefore the ion densities of the pixels on the display panel are adjusted to the same or approximately the same to present a uniform image.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
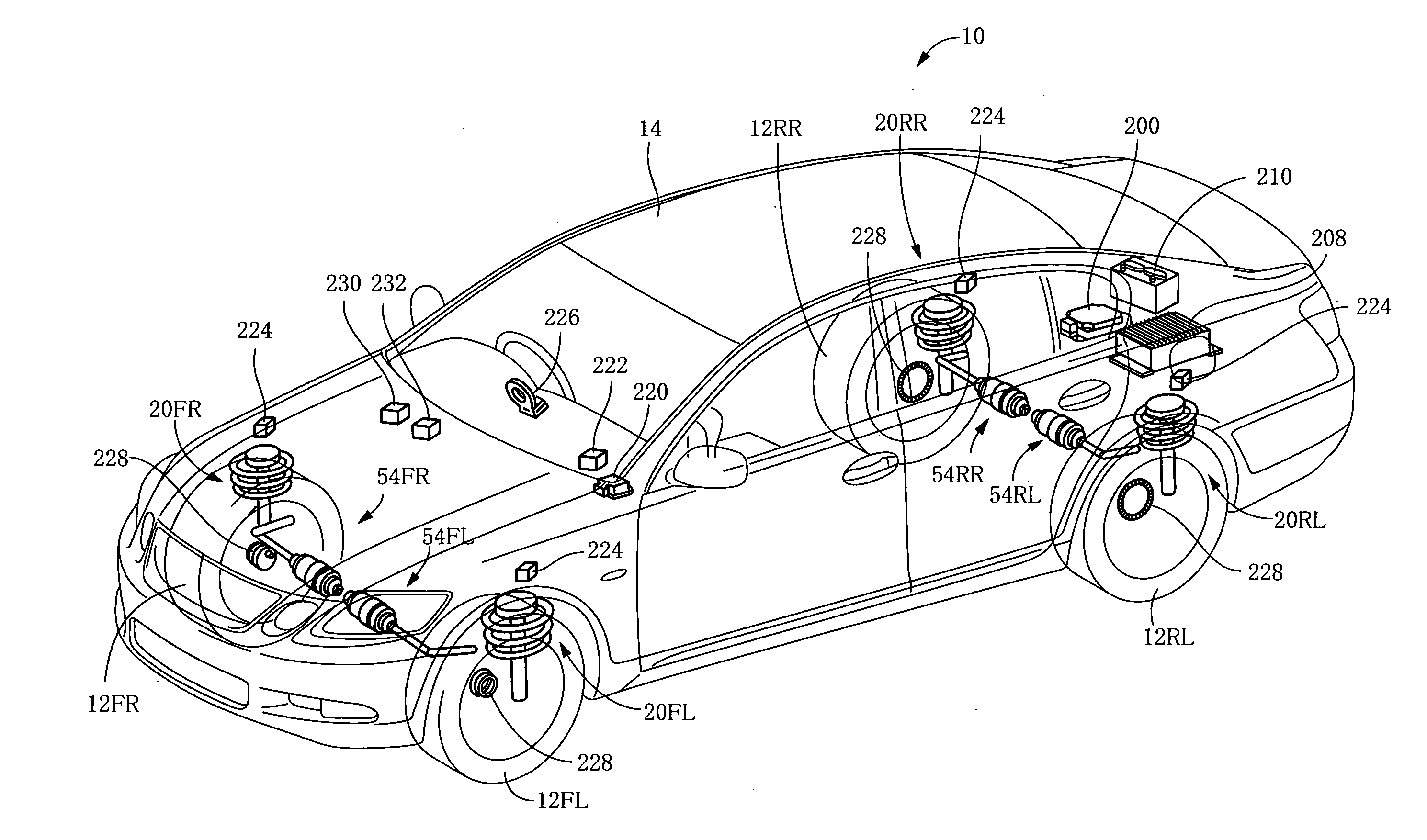
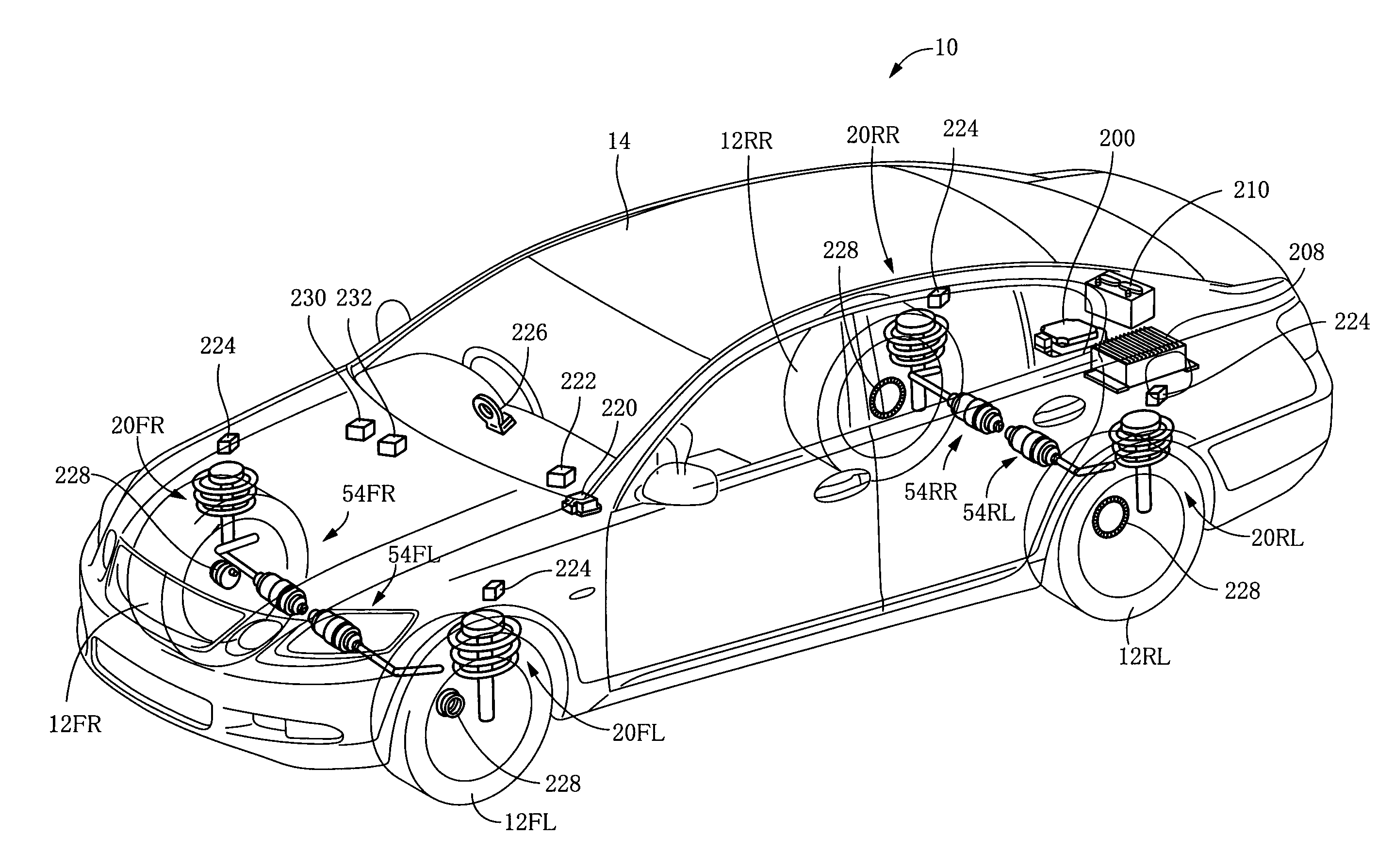
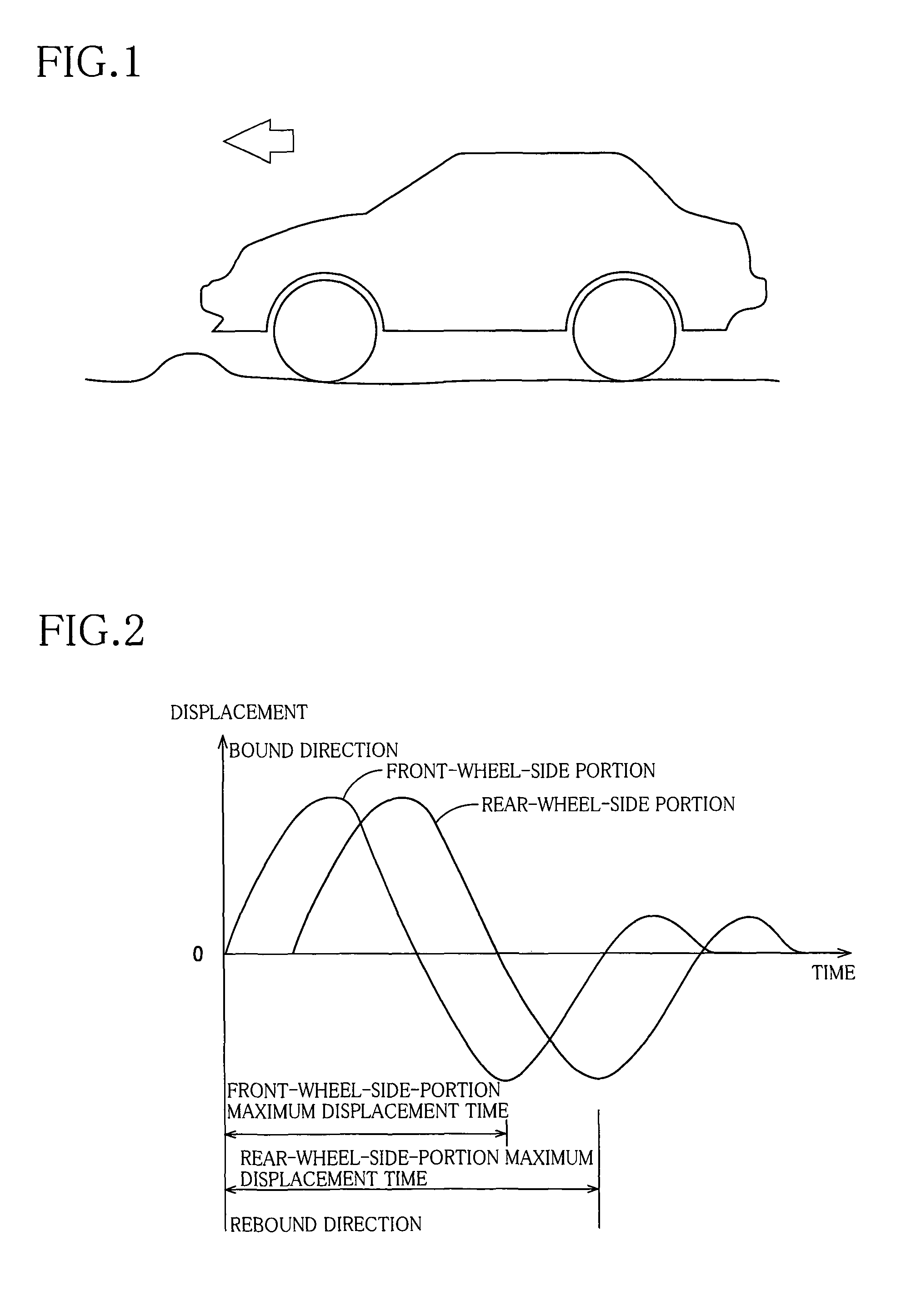
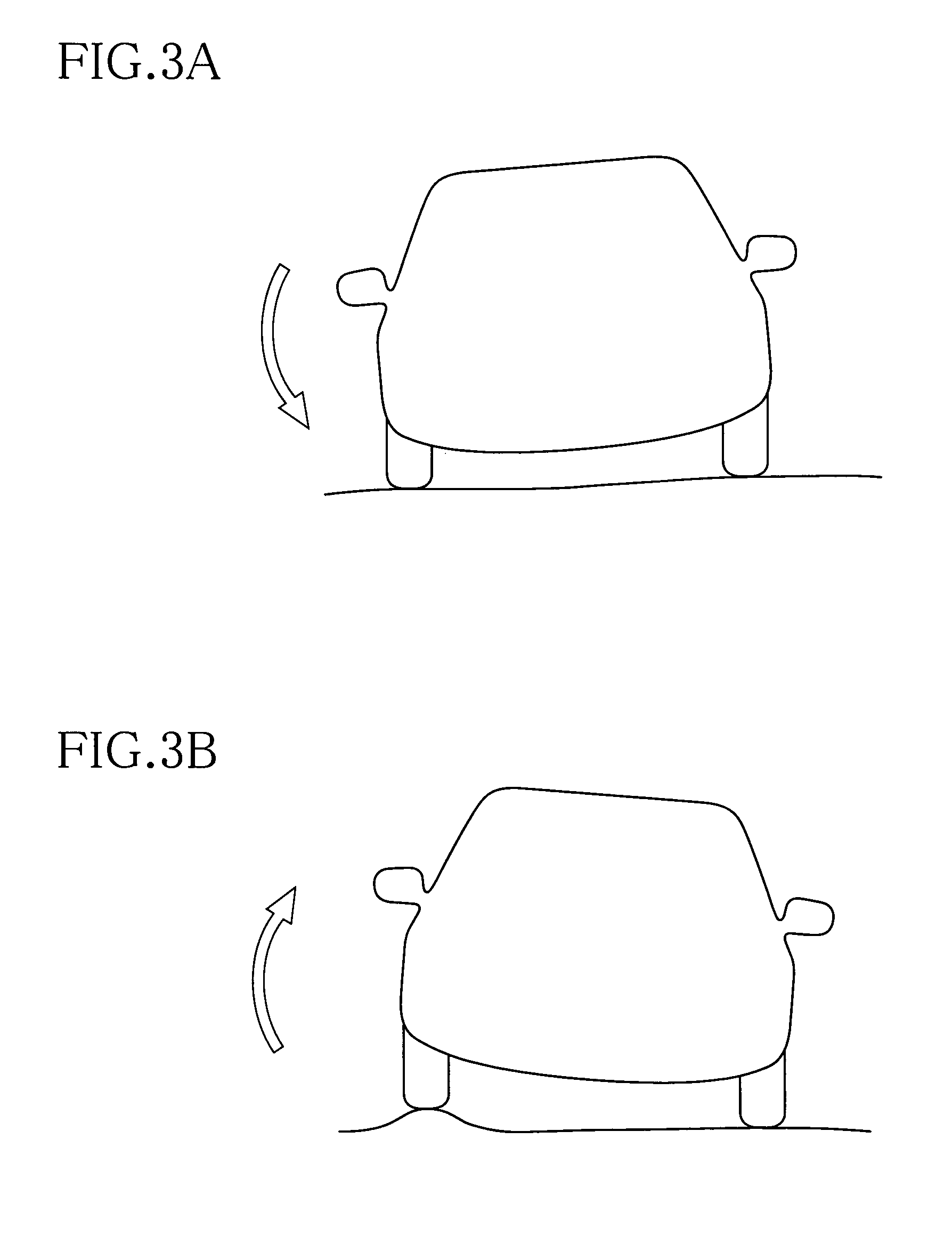
Suspension system for vehicle
ActiveUS20110160960A1Low gear ratioLow efficiencyDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesResonanceEngineering
A suspension system for a vehicle, including (a) four displacement force generators (152) each configured to generate a displacement force forcing sprung and unsprung portions of the vehicle toward or away from each other; and (b) a control unit (200) configured to control the displacement force that is to be generated by each displacement force generator. The control unit is capable of executing a plurality of vibration damping controls concurrently with each other, by controlling the displacement force, so as to damp a composite vibration containing a plurality of different vehicle-body vibrations which are to be damped by the respective vibration damping controls. The control unit is configured to refrain from executing at least one of the vibration damping controls for damping one of the vehicle-body vibrations that is not required to be damped, in a low vibration intensity situation in which intensities of sprung-portion resonance-frequency vibration components in respective four sprung portions of the vehicle are lower than a threshold intensity degree.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Suspension system for vehicle
ActiveUS8116939B2Effective dampingRestrain deterioration of ride comfortDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesResonanceEngineering
A suspension system for a vehicle, including (a) four displacement force generators (152) each configured to generate a displacement force forcing sprung and unsprung portions of the vehicle toward or away from each other; and (b) a control unit (200) configured to control the displacement force that is to be generated by each displacement force generator. The control unit is capable of executing a plurality of vibration damping controls concurrently with each other, by controlling the displacement force, so as to damp a composite vibration containing a plurality of different vehicle-body vibrations which are to be damped by the respective vibration damping controls. The control unit is configured to refrain from executing at least one of the vibration damping controls for damping one of the vehicle-body vibrations that is not required to be damped, in a low vibration intensity situation in which intensities of sprung-portion resonance-frequency vibration components in respective four sprung portions of the vehicle are lower than a threshold intensity degree.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
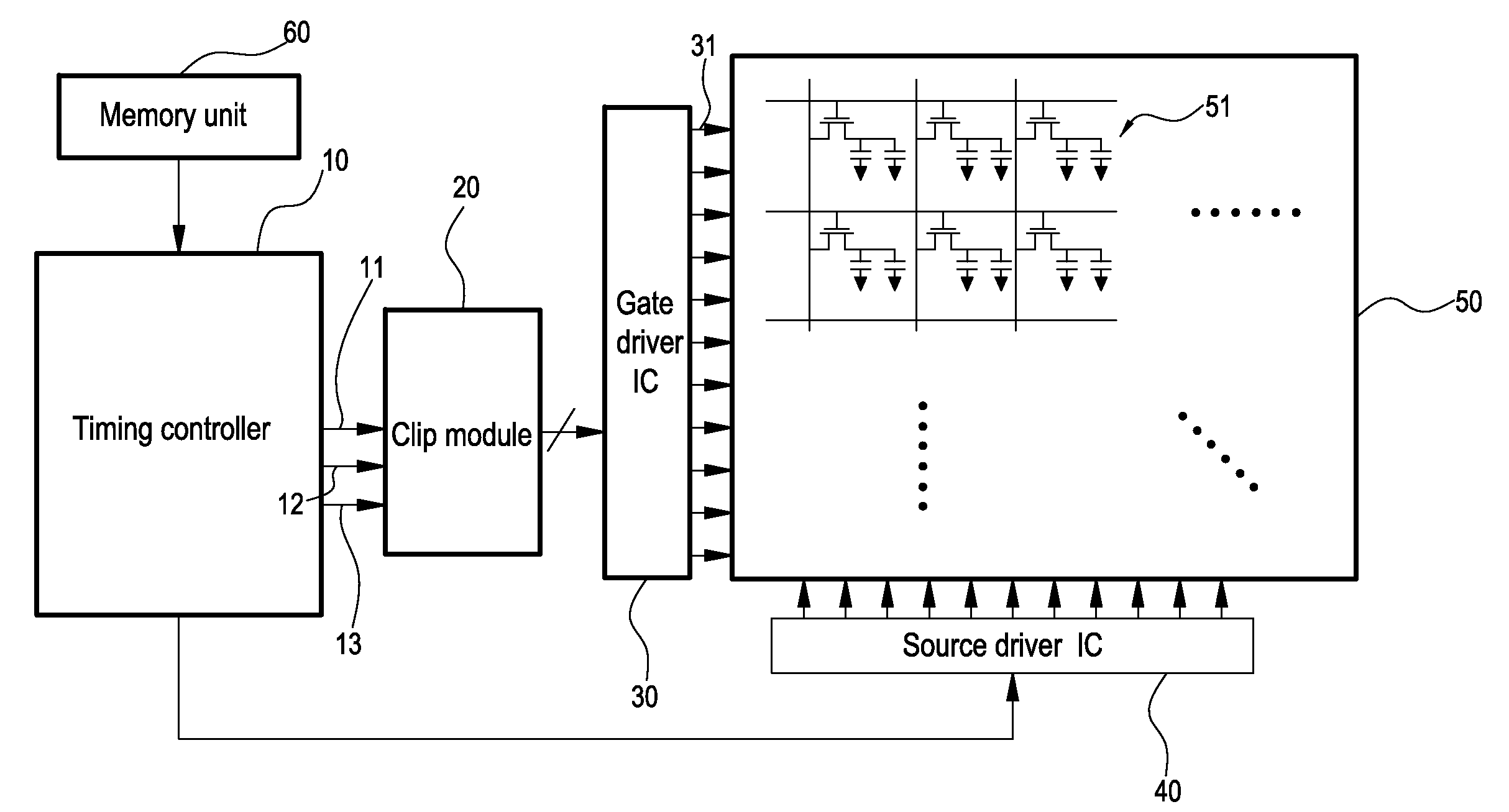
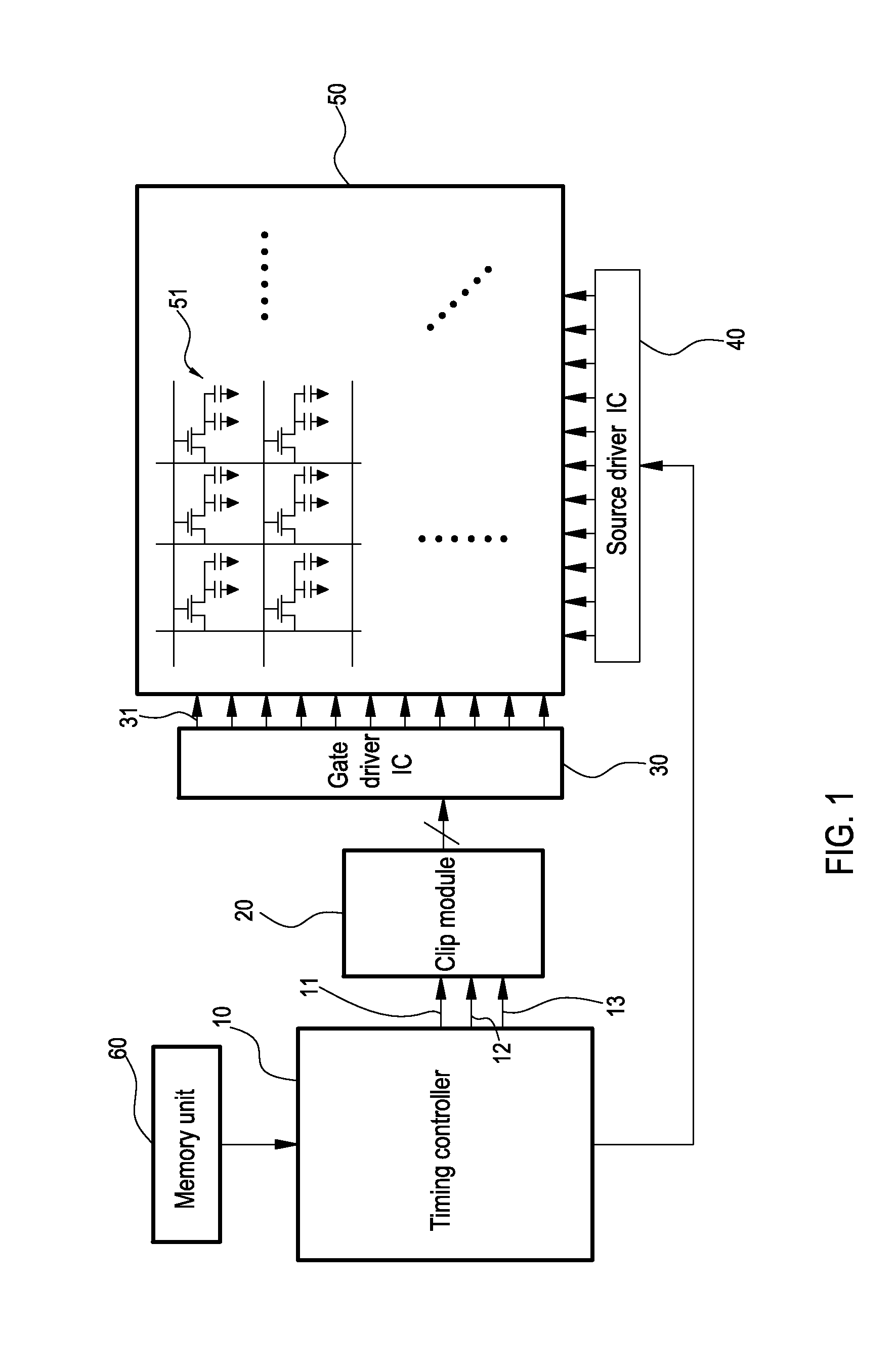
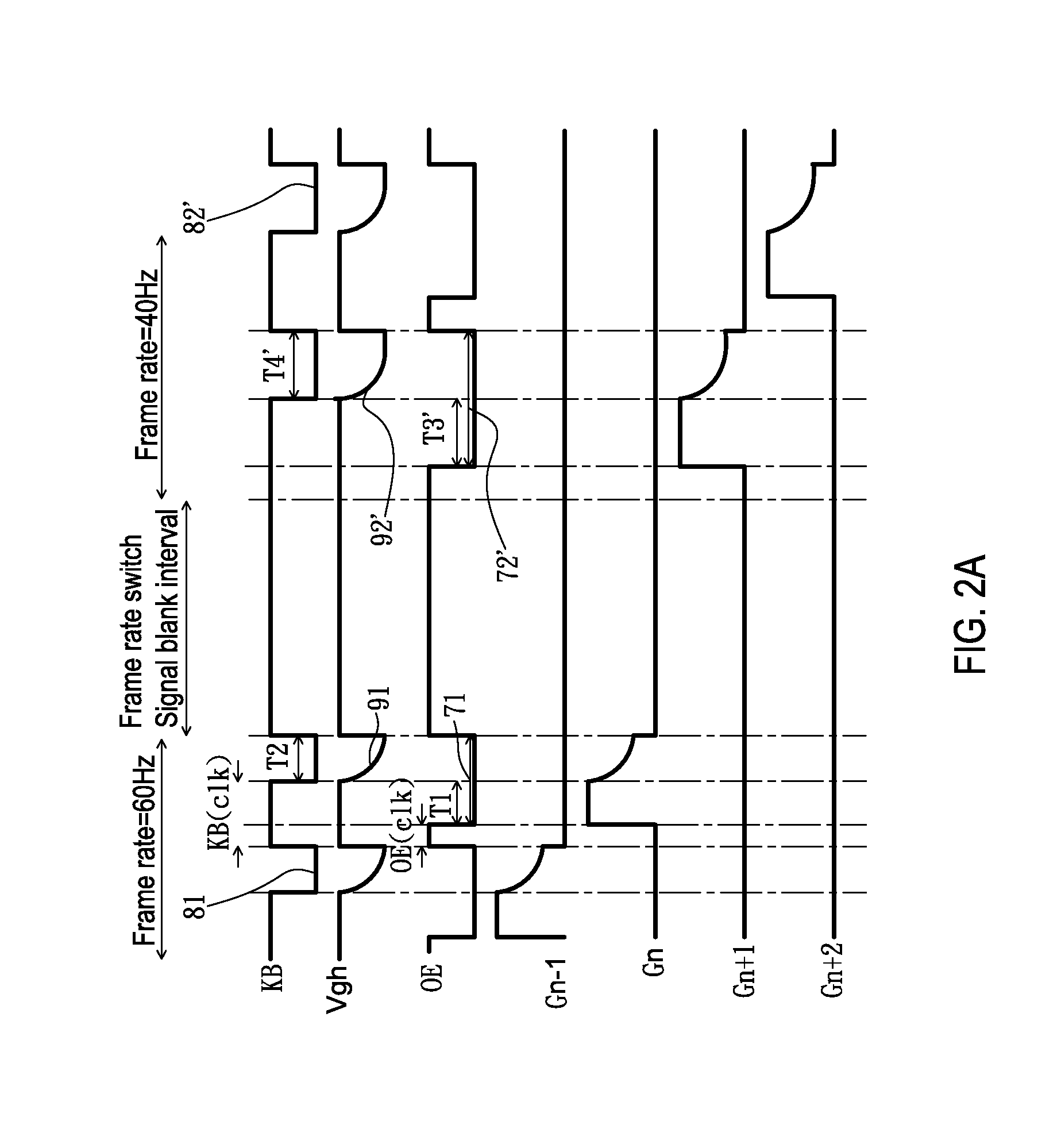
Display clip system and timing clip control method thereof
InactiveUS20120105405A1Steadying imaging luminanceAvoiding screen transient flickeringDigital data processing detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsDriver circuitComputer module
A display clip system and a timing clip control method thereof are provided. The clip system is connected to a gate driver circuit, and includes a timing controller and a clip module. According to a system input signal and it's frame rates, the timing controller generates an enable signal, a clip trigger signal, and a base working signal. The clip module adjusts the base working signal by using the enable signal and the clip trigger signal. Then, the base working signal carries a first clip voltage to output to the gate driver circuit. When the frame rate changes, the timing controller adjusts trigger points and trigger time lengths of the enable signal and the clip trigger signal, and the clip module adjusts the base working signal. Then, the base working signal carries a second clip voltage equal to the first clip voltage to output to the gate driver circuit.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Vibration damping device
InactiveUS20130104467A1Effective absorptionSimple structureProtective buildings/sheltersFriction dampersReciprocating motionNeutral position
A vibration damping device for suppressing vibrations of a structure includes: a slide body mechanism having a concave slide body and a convex slide body which are fixed to the structure and are arranged so as to be slidable relative to each other in a reciprocating manner; and a biasing means which pushes the slide bodies to each other. Each slide body has: a first slide surface having a shape which increases a height of the slide body mechanism 2 along with the increase of a displacement amount of the slide body in one sliding direction from a neutral position relative to the counterpart slide body; and a second slide surface having a shape by which the height of the slide body mechanism is increased along with the increase of the displacement of the slide body in the other sliding direction from the neutral position.
Owner:KIMIGAFUCHI GAKUEN
Identification plate having multiple information media
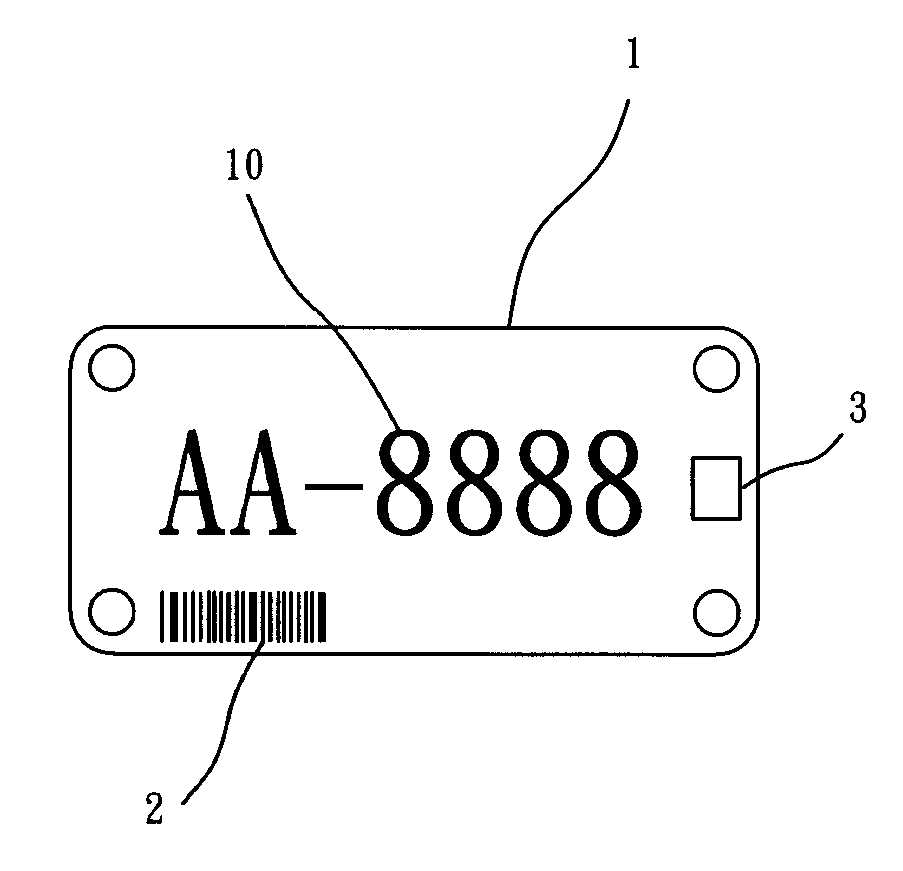
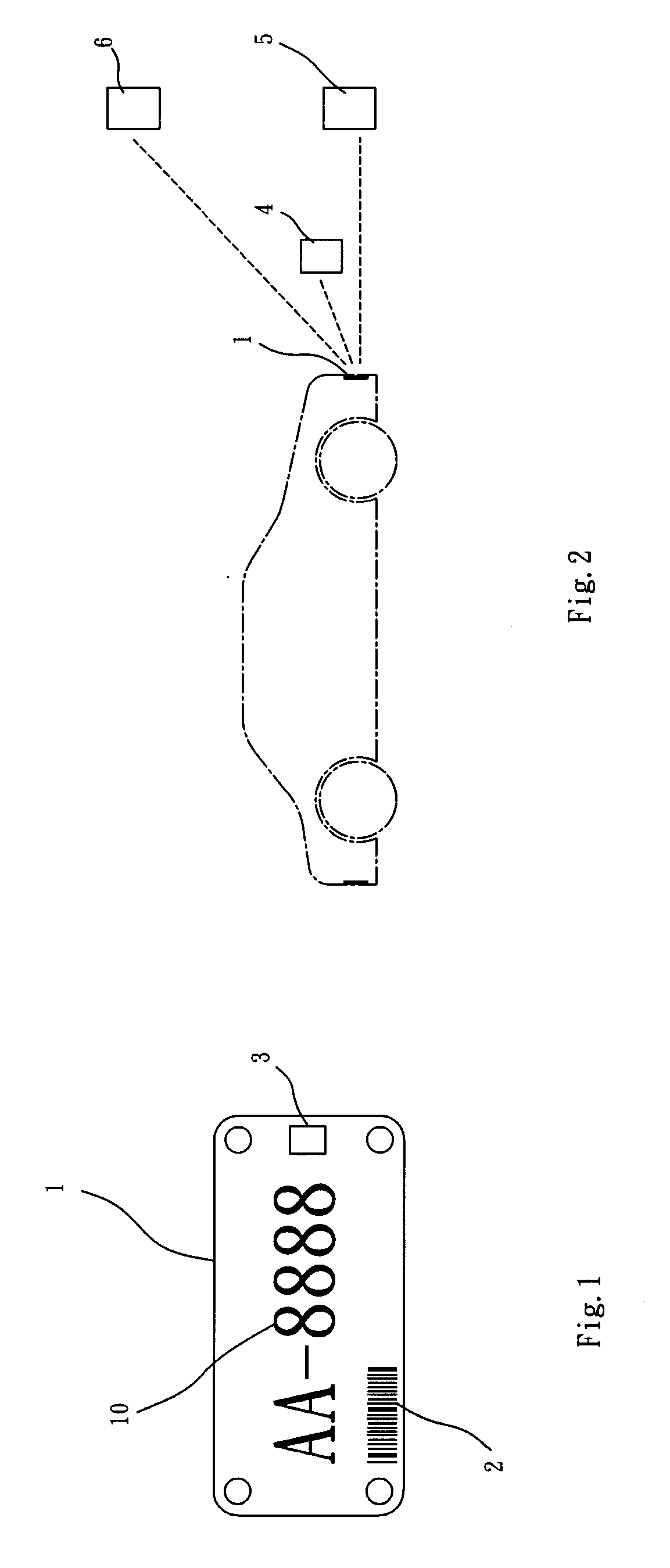
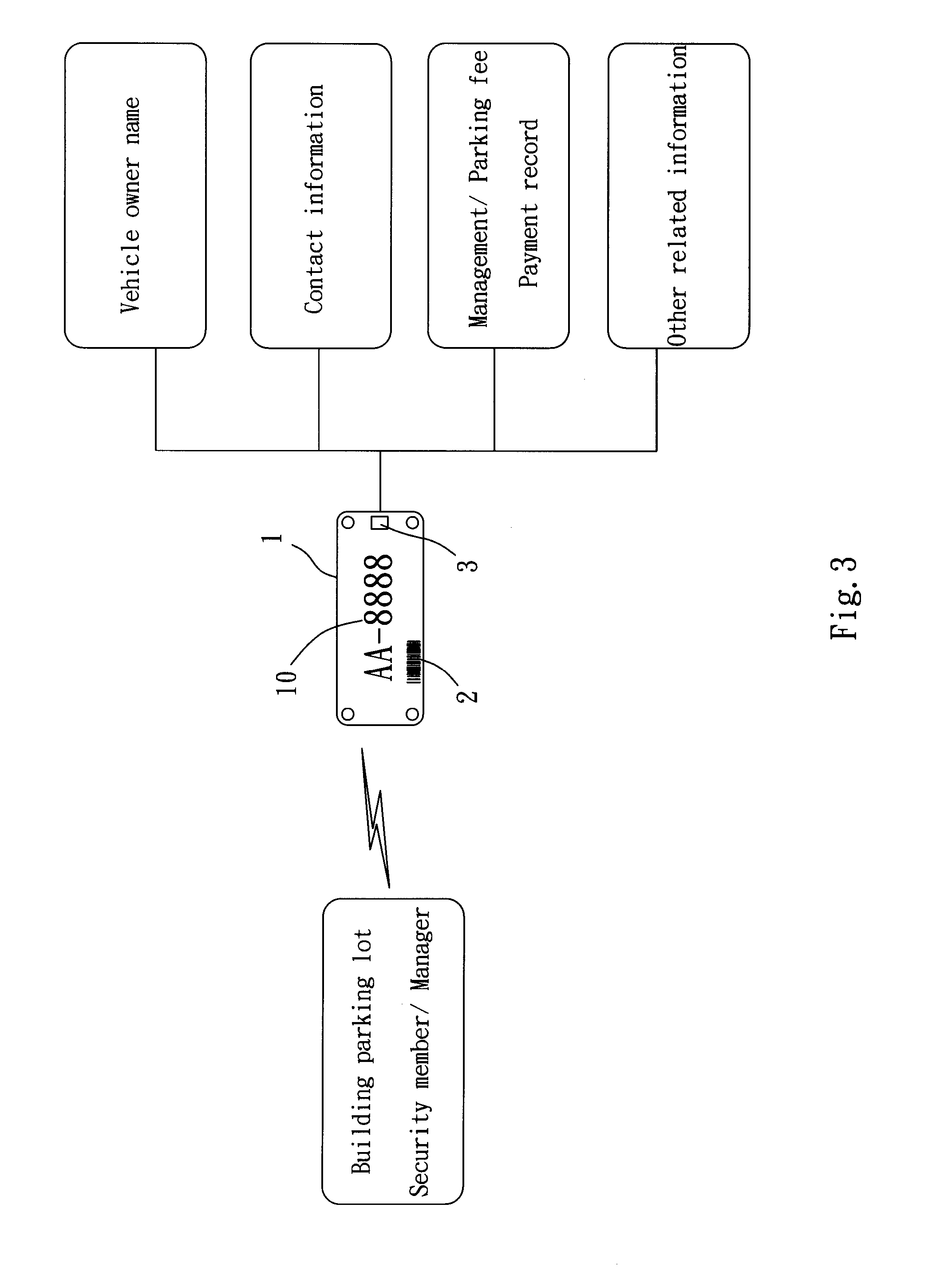
InactiveUS20120181340A1Improve management efficiencyLapse of writing and be avoidedVehicle componentsRecord carriers used with machinesPaymentRelevant information
An identification plate having multiple information media is a license plate of a motorcycle or car. Statutory words, numbers, and symbols are printed on a surface of the identification plate. A bar code containing the information of the statutory words, numbers, and symbols is arranged to the identification plate. The identification plate has a RF tag containing the same information in the bar code and other relative information such as vehicle registration, inspection record, tax record, periodic inspection record, and payment. A short ranger scanner and a long range reader are used for rapidly acquiring the information contained on the identification plate so as to improve efficiency and reduce lapse of writing. An image identification system can be used to identify the statutory symbols for matching the information of the vehicle and owner.
Owner:WEISTECH TECH CO LTD
Water-preserved-mining roof-contacted filling method for controlling fissure of overlying strata and surface subsidence
ActiveUS20160348507A1Simple and safe and reliableEasy to operateMaterial fill-upWater resourcesDisplay device
A water-preserved-mining roof-contacted filling method for controlling fissure of overlying strata and surface subsidence. The method is suitable for controlling fissure of overlying strata and surface subsidence in water-preserved-mining of a mine. A sensor is mounted at the top of a goaf of a filling working face where water-preserved-mining is carried out, and a filling body that is filled is monitored through a stress display device so as to determine whether the goaf is roof-contacted or separated. When the filling body is separated after roof-contacted, the goaf is filled for the second time so as to be roof-contacted fully, so that the purpose of controlling fissure of overlying strata and surface subsidence can be achieved, and protective mining of water resources of the mine can be realized at last. The method is simple and targeted, and has strong operability and high efficiency.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Cutter for Corn Threshing and Rotary Food Processor Therewith
InactiveUS20180184593A1Small volumeEasy to operateThreshersMetal working apparatusThreshingFood processing
The present invention provides a cutter for corn threshing. The cutter is mounted on a rotary food processor with a driving device, which comprises a cylinder with one open end; a cavity disposed in the cylinder to accommodate threshed corn cobs; a cutting member disposed at the middle of the open end of the cavity; and a locking portion disposed at the other end of the cylinder and connected to the driving device of the rotary food processor in a detachable manner. The present invention further discloses a rotary food processor with this cutter. The cutter for corn threshing and the rotary food processor both have the advantages of small volume, simple operation and high practicability.
Owner:WONG YAN KWONG
Shade Structure
InactiveUS20120103539A1Enhance variability and practicabilitySimple structureCorner/edge jointsLight protection screensEngineering
A shade structure includes a plurality of blades and a plurality of pairing units arranged in pairs such that paired ones of said pairing units are disposed at two ends of a corresponding one of the blades, respectively. The pairing units enable the shade structure to be put together or taken apart as needed, so as to enhance variability and practicability of the shade structure.
Owner:CHICOLOGY
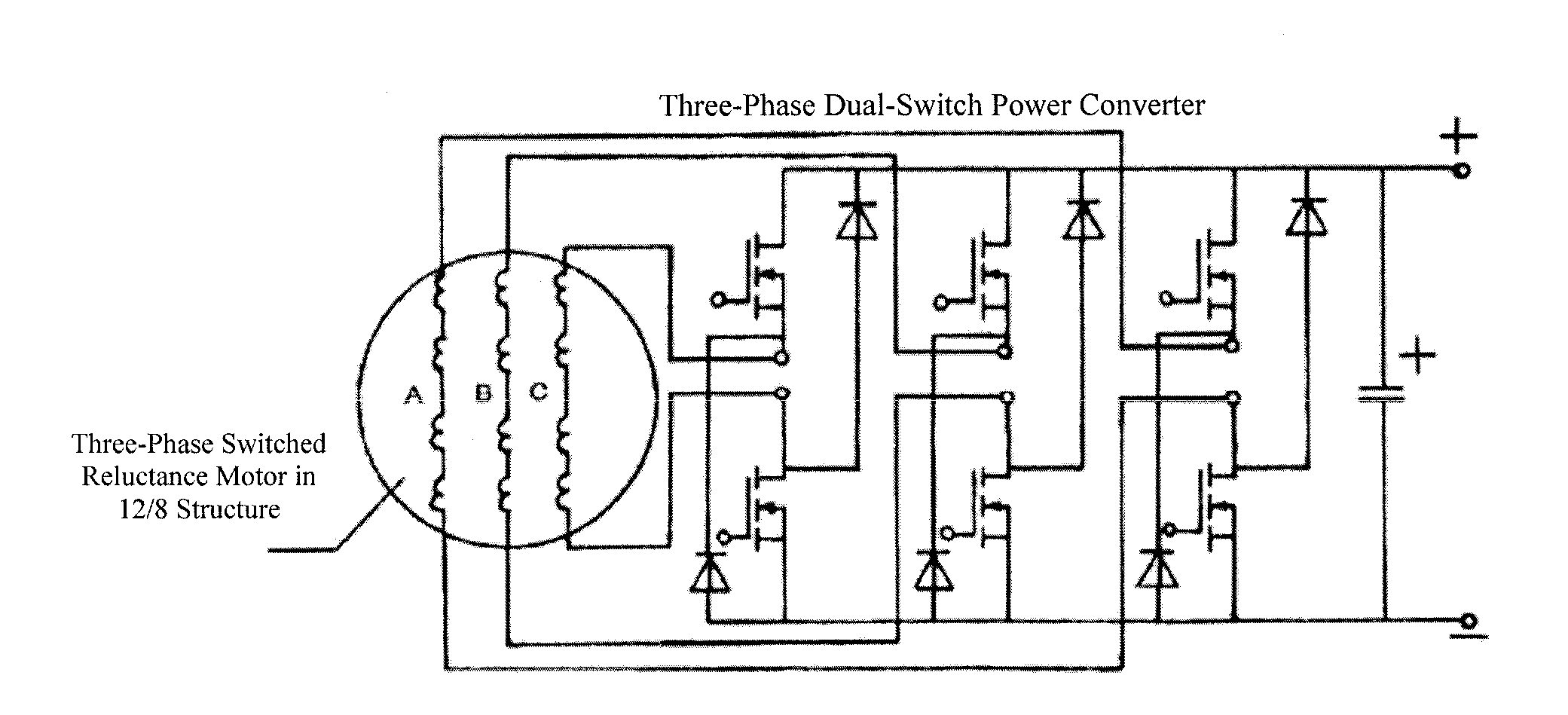
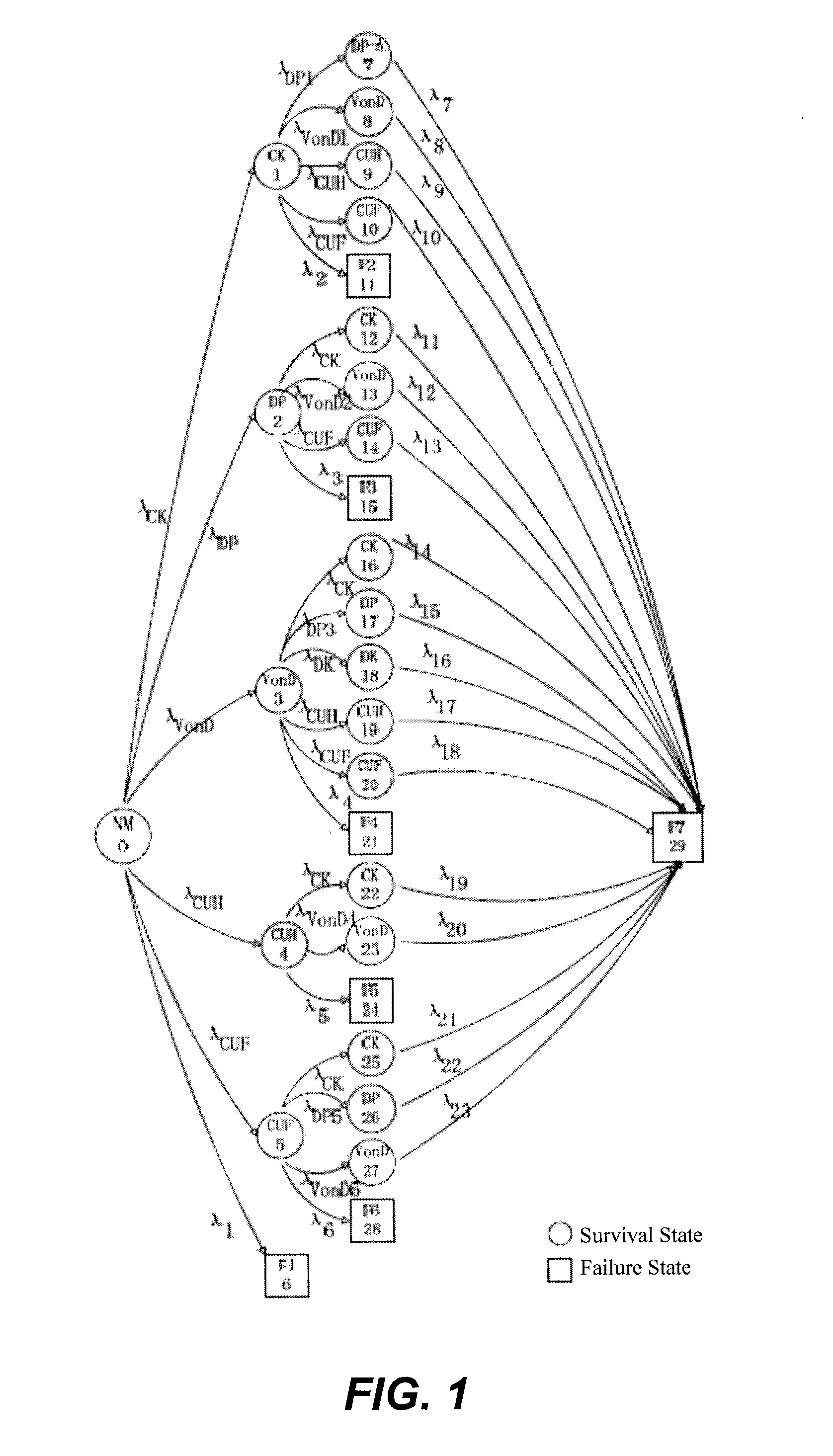
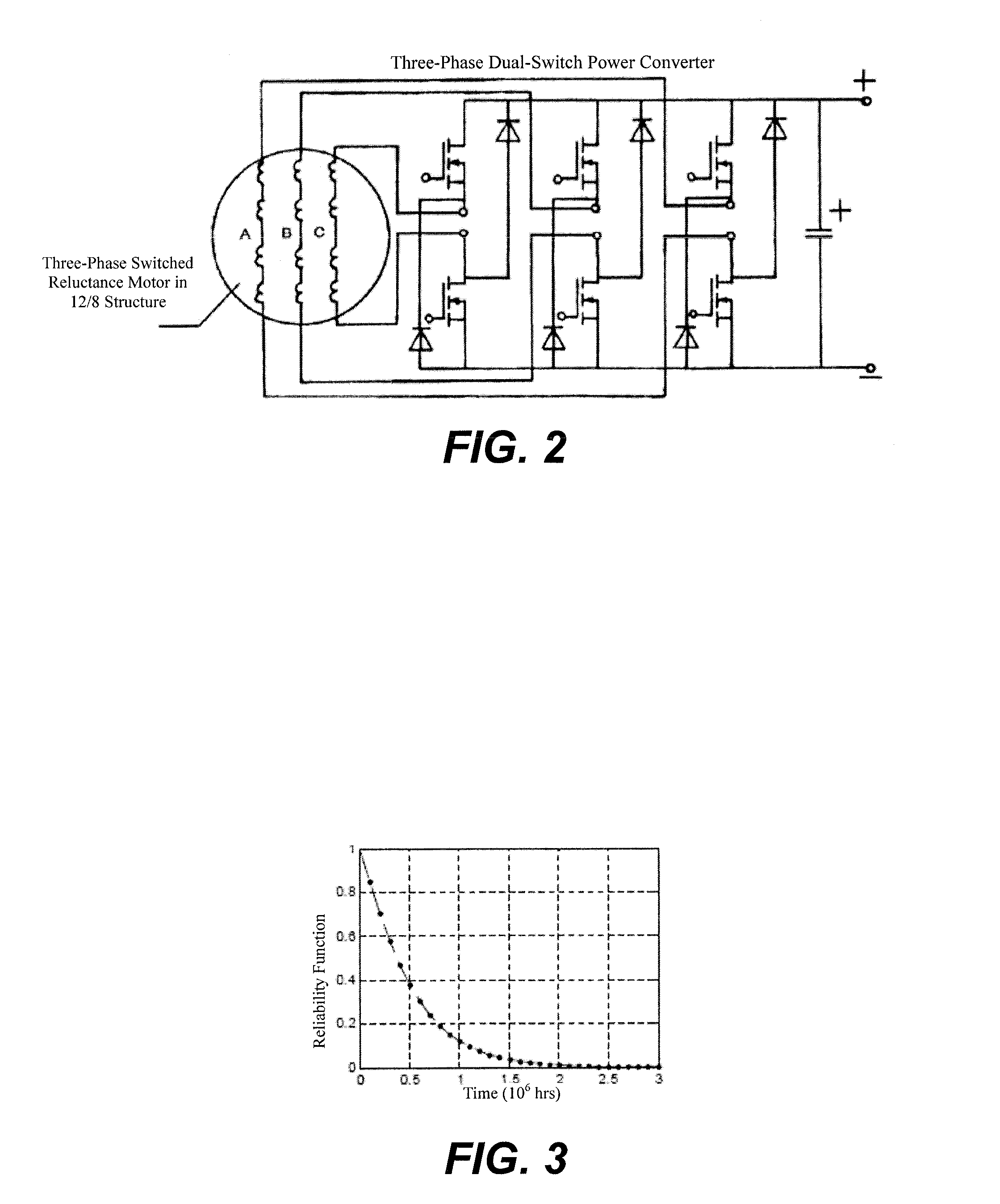
Quantitative evaluation method for reliability of markov model switch reluctance motor system
ActiveUS20160161561A1High practicabilityHigh engineering application valueNuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsState switchingSwitched reluctance motor drive
A quantitative evaluation method for the reliability of a Markov model switch reluctance motor system. The method comprises: solving a probability matrix P′T(t) of a switch reluctance motor system being in any survival state at any time t via a state conversion diagram of the switch reluctance motor system; calculating the sum of various elements of the probability matrix P′T(t) of the survival state, so that a reliability function R(t) is obtained; and thus calculating the average working time of the switch reluctance motor system before failure, thereby realizing the quantitative evaluation of the switch reluctance motor system and satisfying the requirements for the reliability analysis of a switch reluctance motor drive system. This disclosure has a good engineering application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
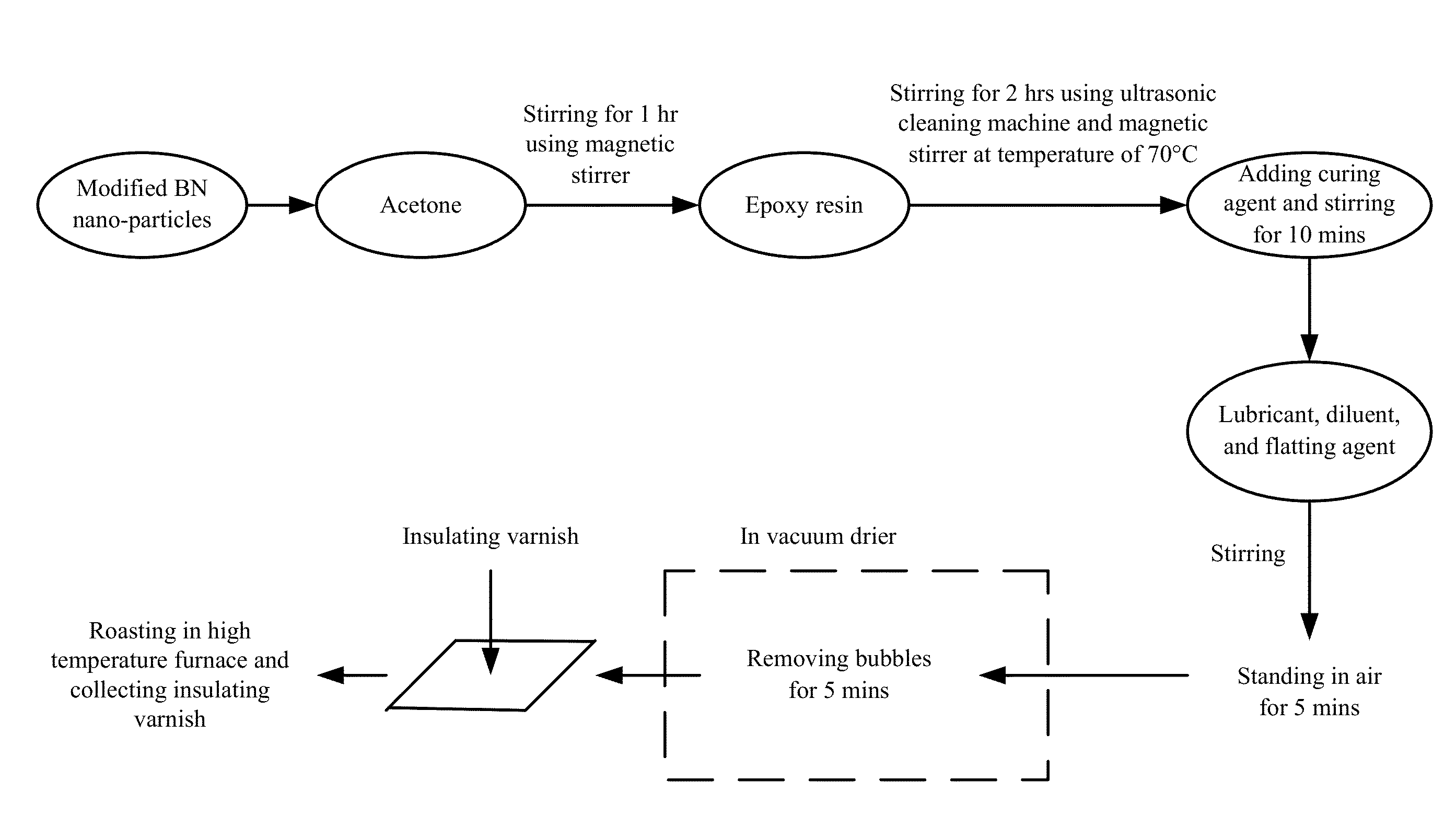
Method for preparing insulating varnish
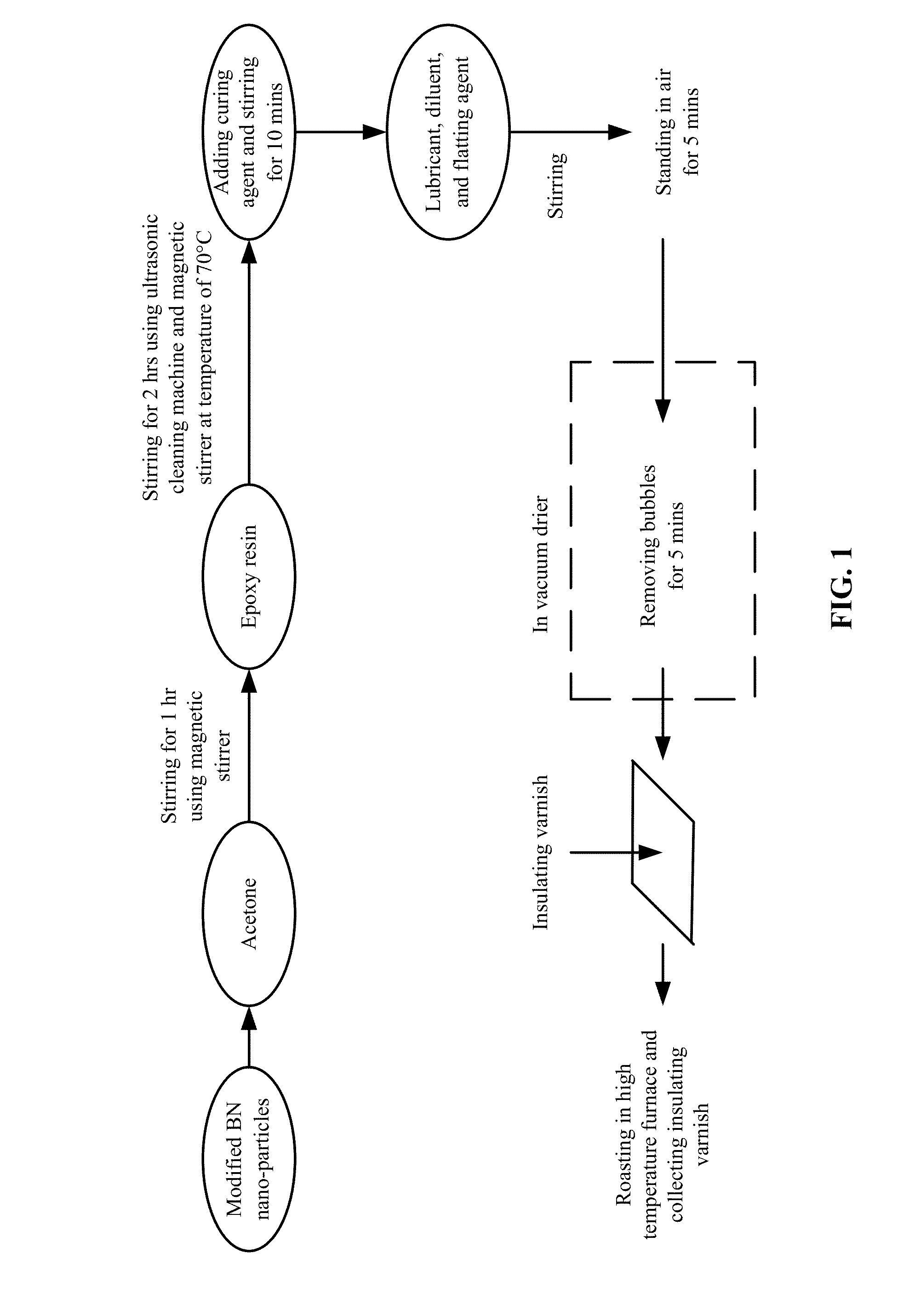
ActiveUS20140045972A1High practicabilityImprove thermal conductivityShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsEpoxyDi n butyl phthalate
A method for preparing an insulating varnish. The method includes: providing equivalence of an epoxy resin solution having a concentration exceeding 99 wt. % and acetone solution having a concentration of 40 wt. %, adding silane coupling agent-modified hexagonal boron nitride (BN) having a particle size of between 200 and 250 nm to the acetone solution and stirring; mixing the epoxy resin solution and the acetone solution and stirring, and dispersing the resulting mixture; adding to the mixture, low molecular weight polyamide resins as a curing agent, and stirring to uniformly disperse the curing agent; adding n-butane as a lubricant to the mixture and stirring, cooling the mixture to room temperature, adding di-n-butyl phthalate as a diluent to the mixture and stirring; and allowing the mixture to stand in a vacuum drier to remove bubbles to yield the insulating varnish, which is free of bubbles.
Owner:TIANJIN JINGWEI HUIKAI OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Safety cap assembly of power battery
ActiveUS20150132619A1Improve securityHigh resistivityVent arrangementsCell lids/coversPower batteryEngineering
A safety cap assembly of power battery comprises a cap plate and a first terminal unit, a second terminal unit, a vent, an electrolyte-injection hole and a safety reverse valve provided to the cap plate; the first terminal unit is electrically connected to the cap plate; the second terminal unit is insulated from and assembled to the cap plate; the safety reverse valve is electrically connected to the cap plate; a short circuit protection conducting plate is provided above the cap plate, is electrically connected to the second terminal unit, and is positioned above the safety reverse valve; the first terminal unit comprises a first terminal body, and a metal gasket and a resistance plate around the first terminal body, the resistance plate is provided below the metal gasket and comprises a substrate and a coating on a surface of the substrate.
Owner:DONGGUAN POWERAMP TECH LTD
Health bed capable of adjusting the spine curve of a human body
InactiveUS7458121B1Sleep comfortablyEasy to operateStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesHuman bodyMotor drive
A health bed capable of adjusting the spine curve of a human body mainly comprises a plurality of elevators. Each of the elevators includes a lower plate having several upholders extending therefrom wherein a motor is fixed on the center of the lower plate and the axle of the motor is a screw engaged with the middle of a motor-driven base such that the motor-driven base can be moved upward or downward by a drive of the screw. The upholders support the motor-driven base is disposed above the lower plate and supported by upholders. A plurality of elastic objects is disposed on the motor-driven base in which the elastic object has a sense stick inside and the sense stick penetrates out of the bottom of the motor-driven base. A height sensor lateral the base may thus measure a downside movement of the elastic objects. The height sensor and the motor are connected to a control circuit that actuates the motors to drive the motor-driven bases upwardly to a desired height by receiving signals from the height sensors. When a user lies on the bed, each of the elevators actively sustains the spine curve of human body, achieving a comfortable sleep.
Owner:HUMBOLDT STATE UNIVERSITY
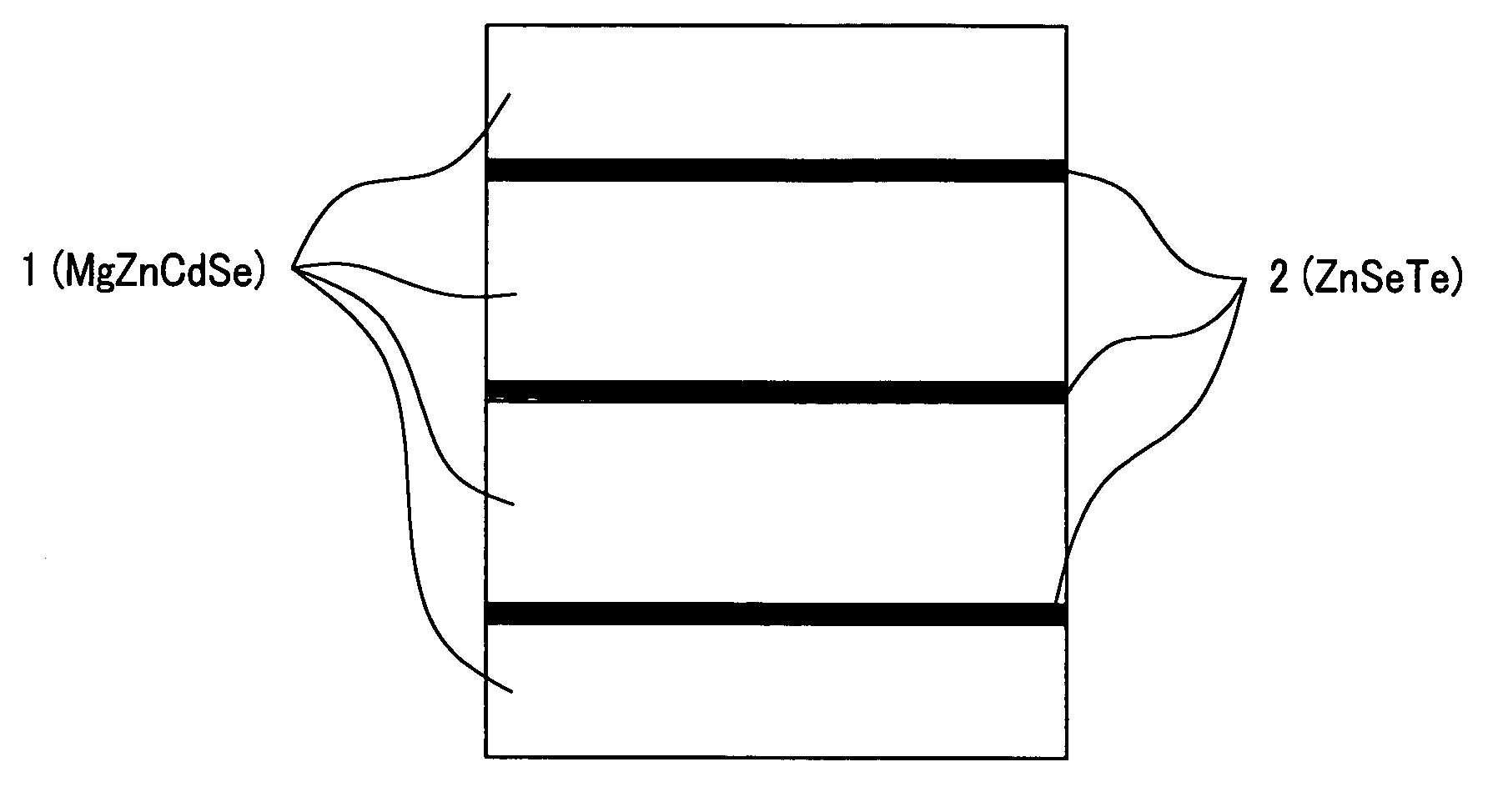
Optical semiconductor devices on InP substrate
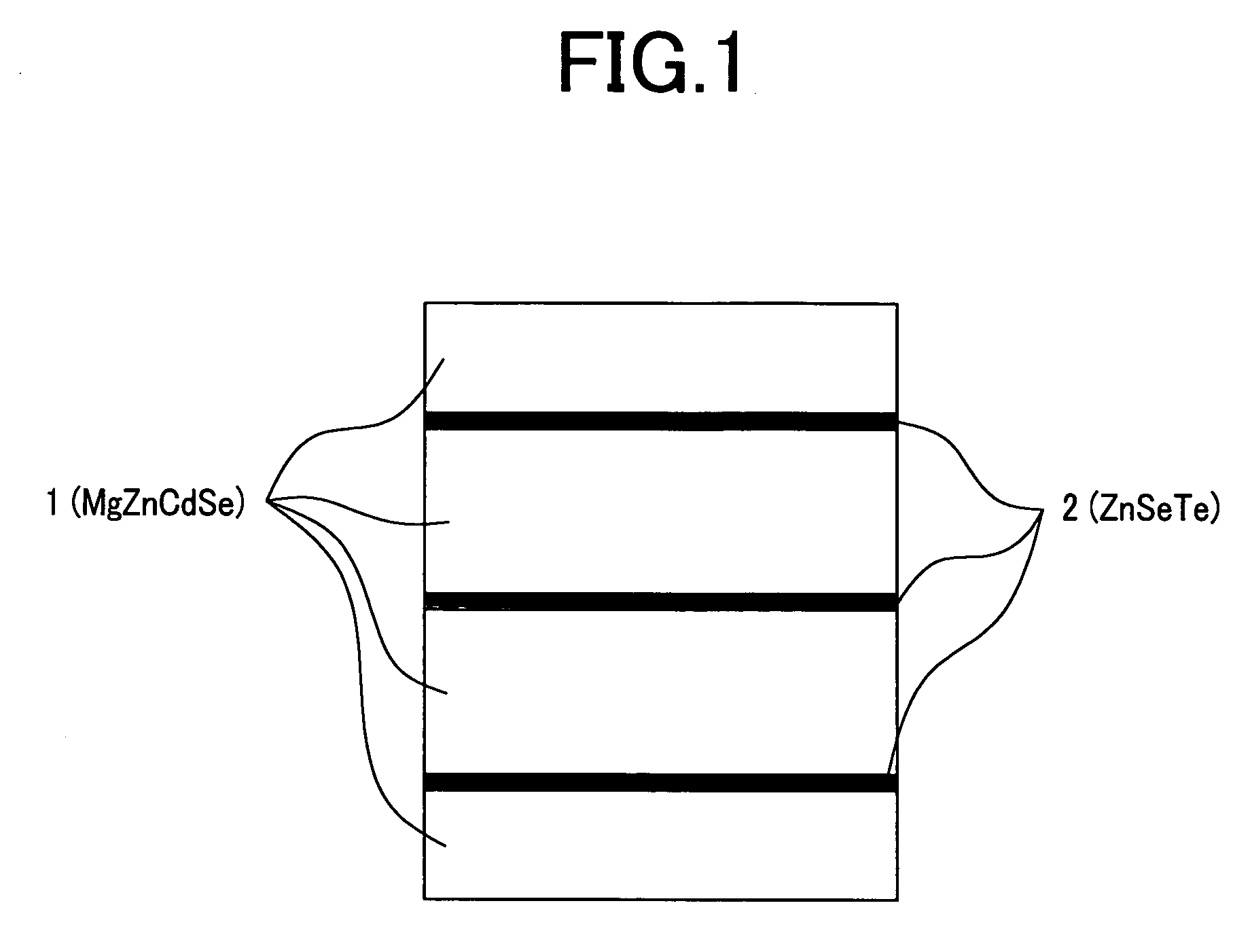
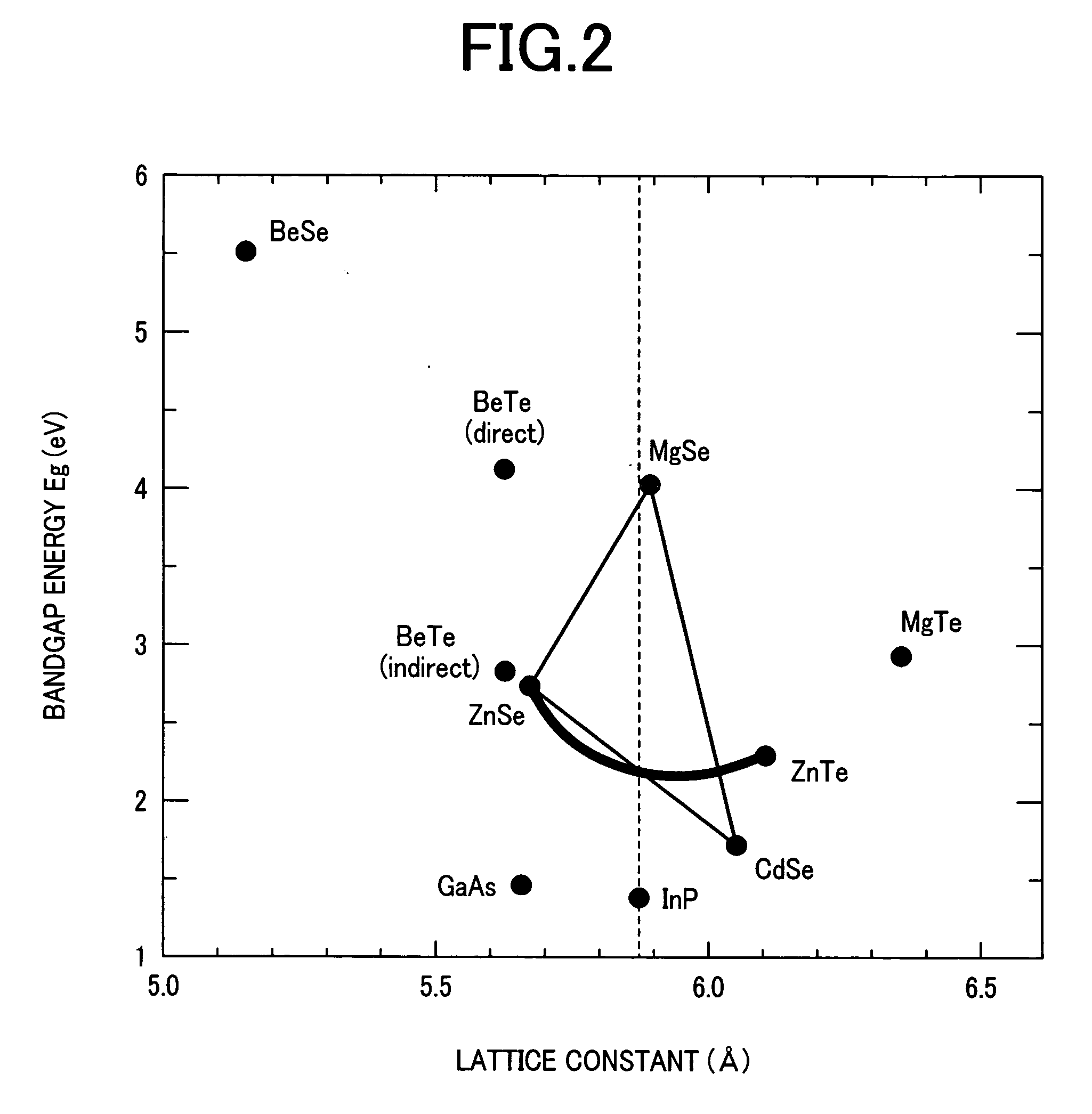
InactiveUS20070051937A1Easy to manufactureSatisfactory characteristicLaser detailsNanoopticsDevice materialMono layer
The present invention aims at providing a structure in which a high p-type carrier concentration of 1×1017 cm−3 or more is obtained in a material in which, although it shows normally p-type conductivity, a carrier concentration smaller than 1×1017 cm−3 is only obtained. Also, the present invention aims at providing highly reliable semiconductor element and device each of which has excellent characteristics such as light emitting characteristics and a long lifetime. Each specific layer, i.e., each ZnSe0.53Te0.47 layer (2ML) is inserted between host layers, i.e., Mg0.5Zn0.29Cd0.21Se layers (each having 10ML (atomic layer) thickness) each of which is lattice matched to an InP substrate. In this case, each specific layer in which a sufficient carrier concentration of 1×1018 cm−3 or more is obtained when a single layer is inserted at suitable intervals. As a result, a sufficient hole concentration of 1×1017 cm−3 or more is obtained in the overall crystal in a material in which a hole concentration smaller than 1×1017 cm−3 has been only conventionally obtained.
Owner:SOPHIA UNIVERSITY +2
Fractional n-pll circuit, oscillator, electronic device, and moving object
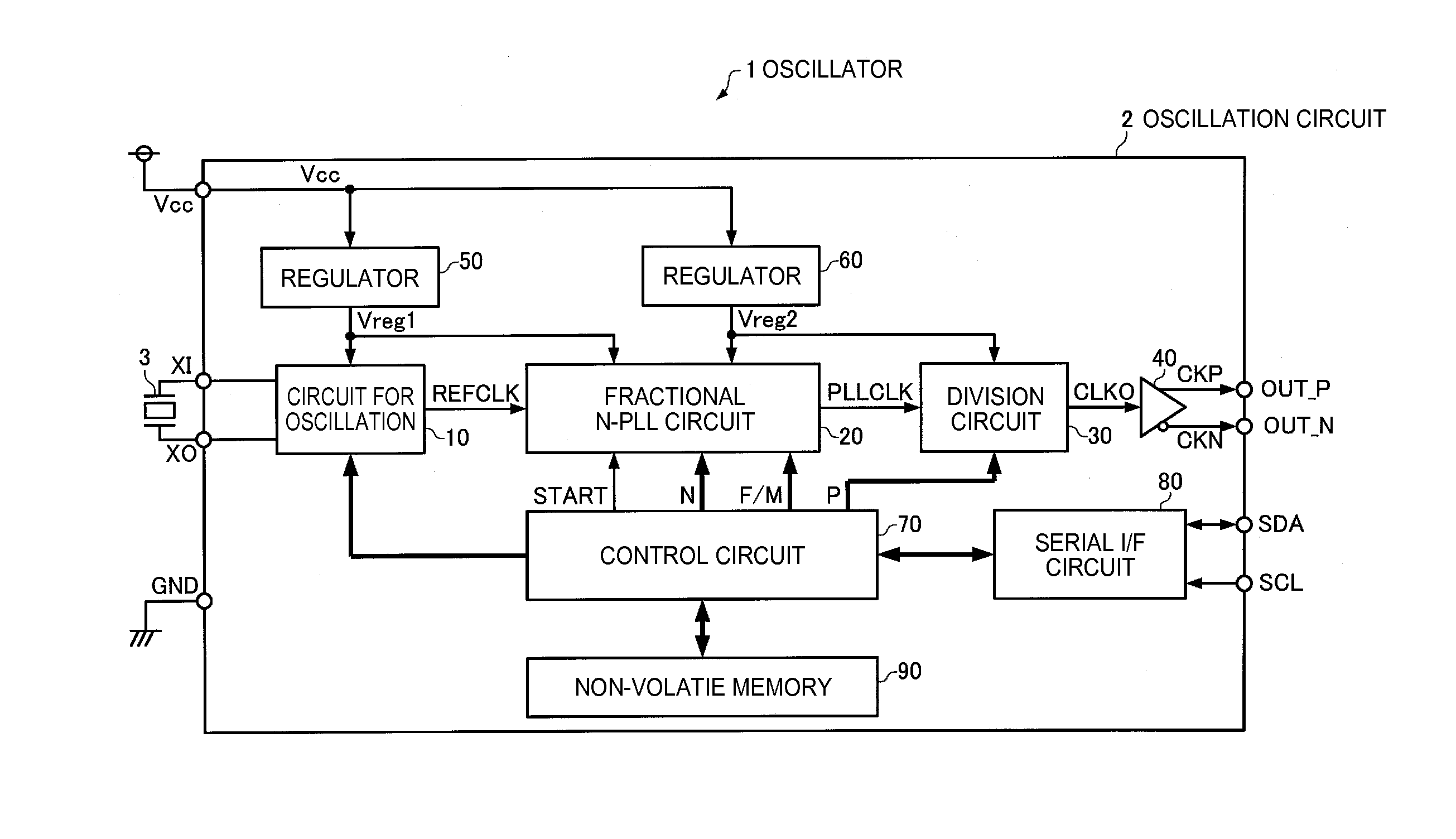
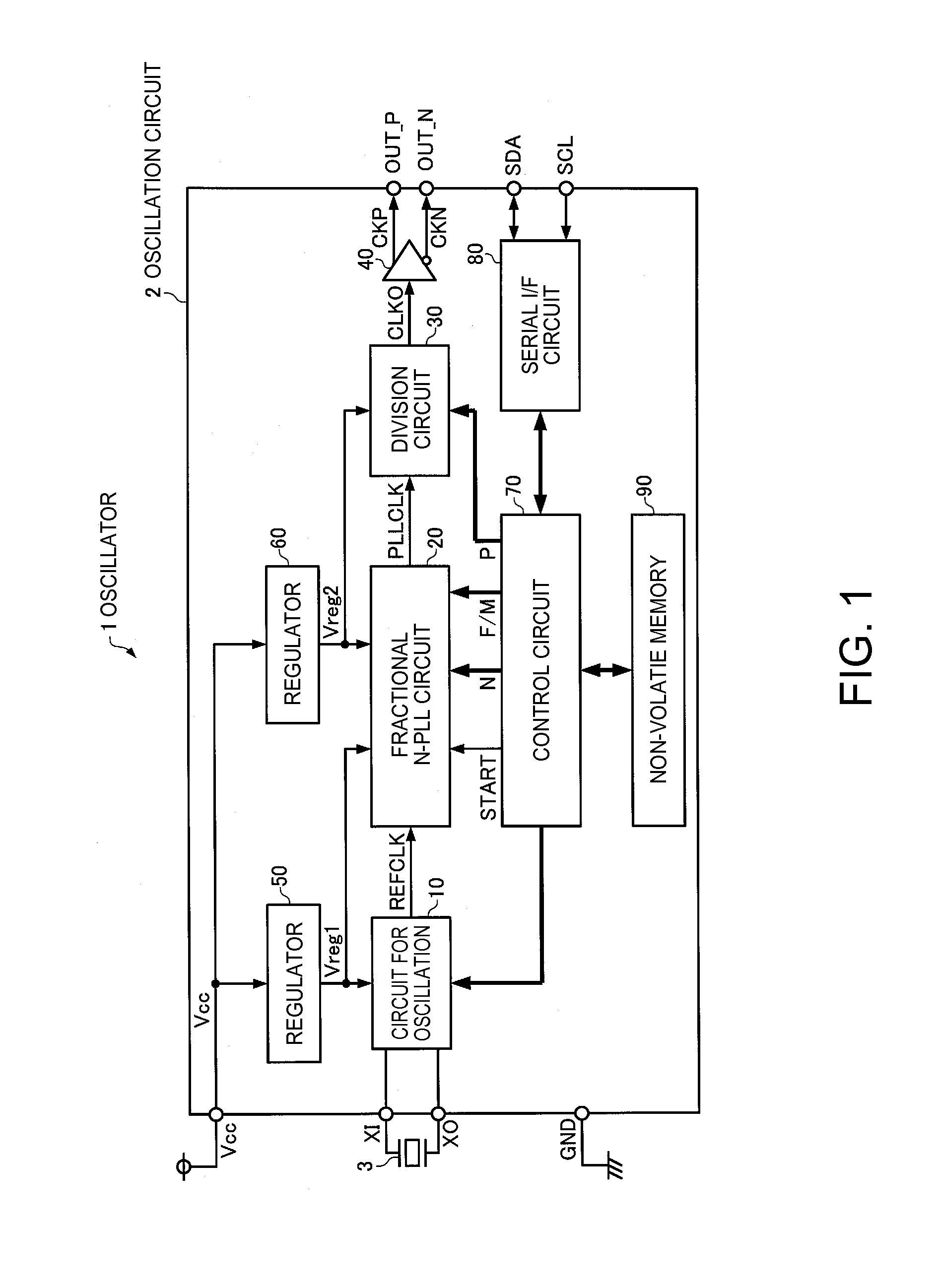
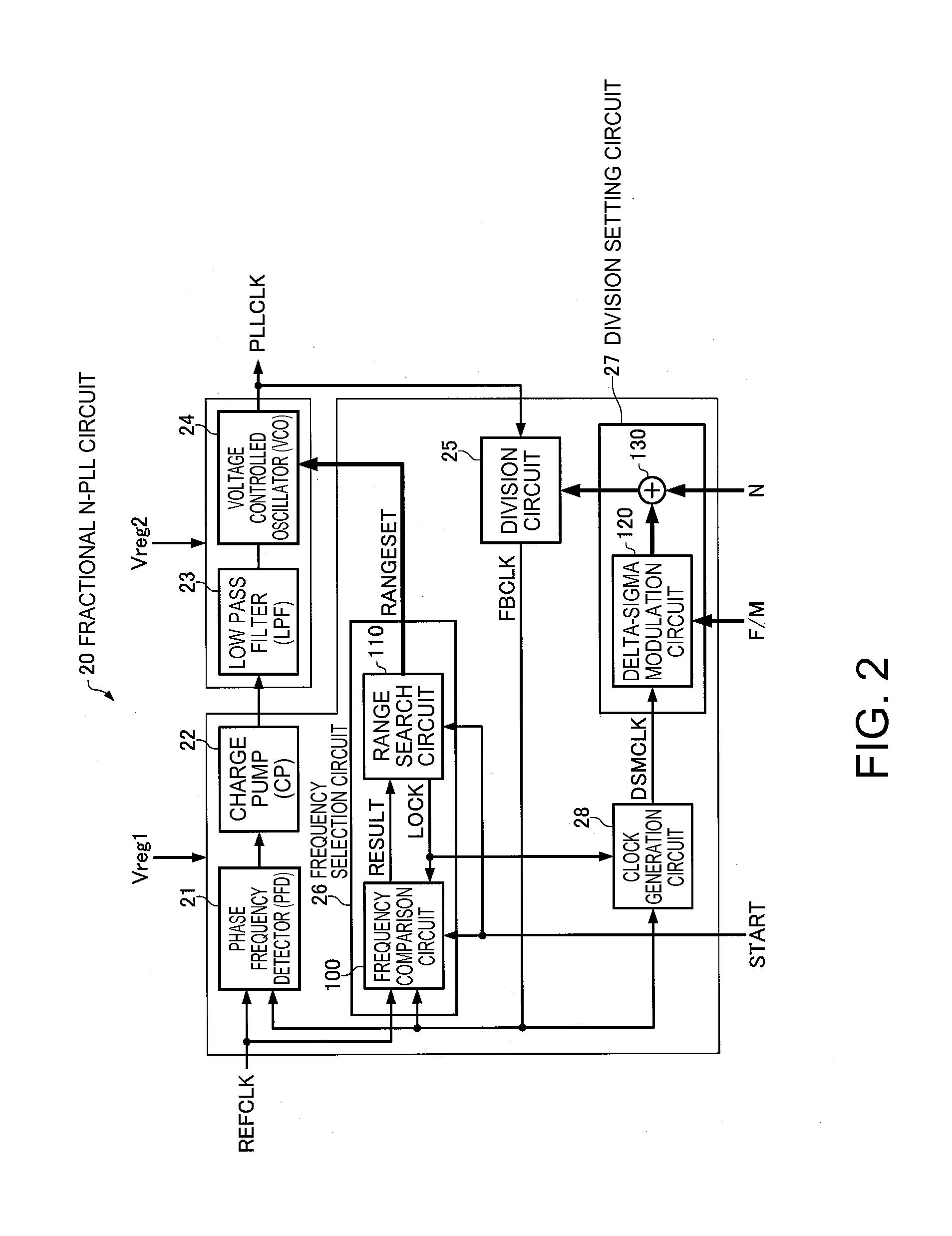
ActiveUS20160079988A1High practicabilityImprove reliabilityPulse automatic controlAnalogue conversionEngineeringDelta-sigma modulation
In order to appropriately set an operation range of a voltage controlled oscillator without excessively increasing a frequency at which delta-sigma modulation is performed, a fractional N-PLL circuit includes: a voltage controlled oscillator that is configured to set plural output frequency ranges; a frequency selection circuit that selects one output frequency range; a division circuit; and a division setting circuit that sets a division ratio of the division circuit. The division setting circuit performs, while the frequency selection circuit is searching for the plural output frequency ranges of the voltage controlled oscillator, the delta-sigma modulation at a frequency lower than a frequency after the frequency selection circuit terminates the search.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
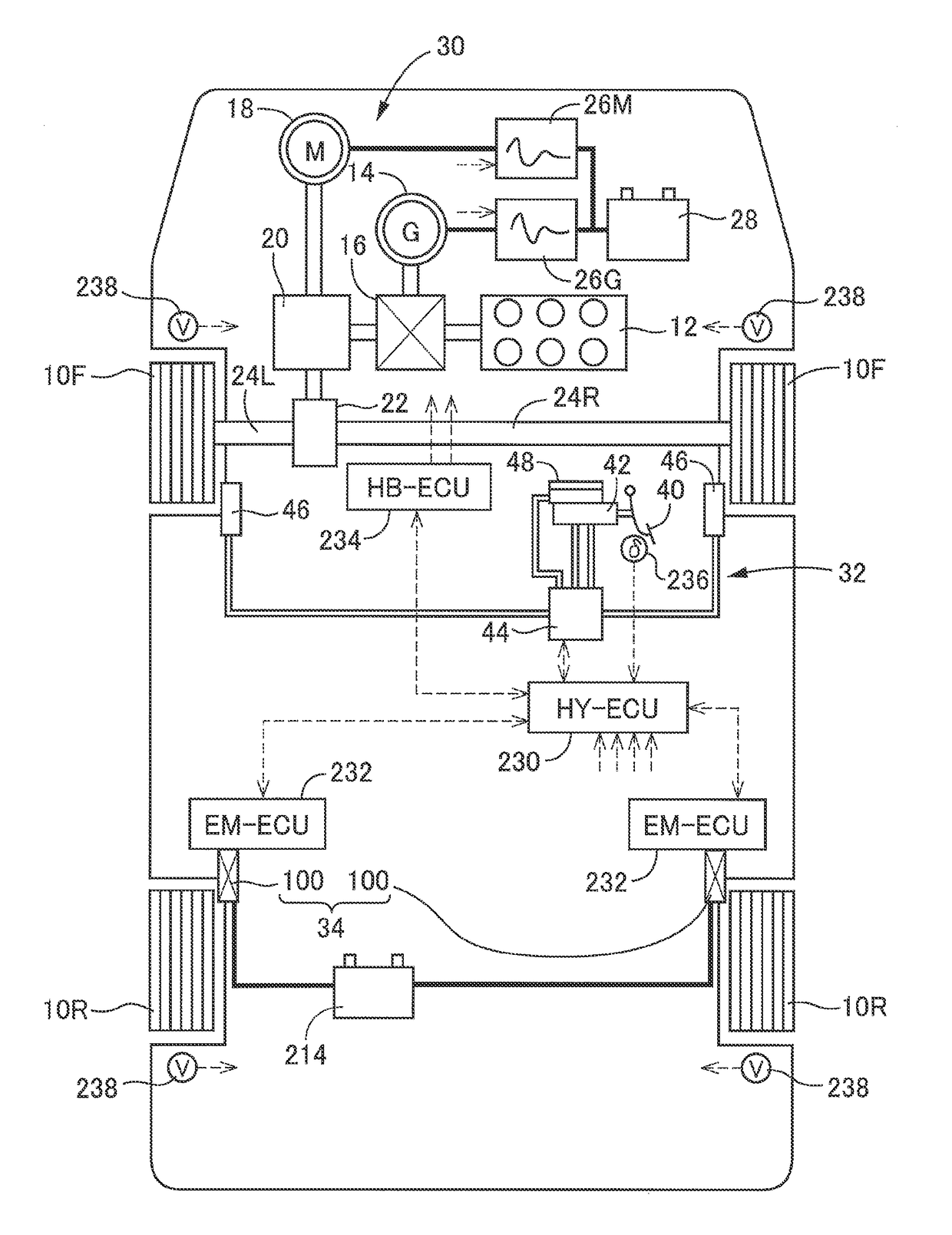
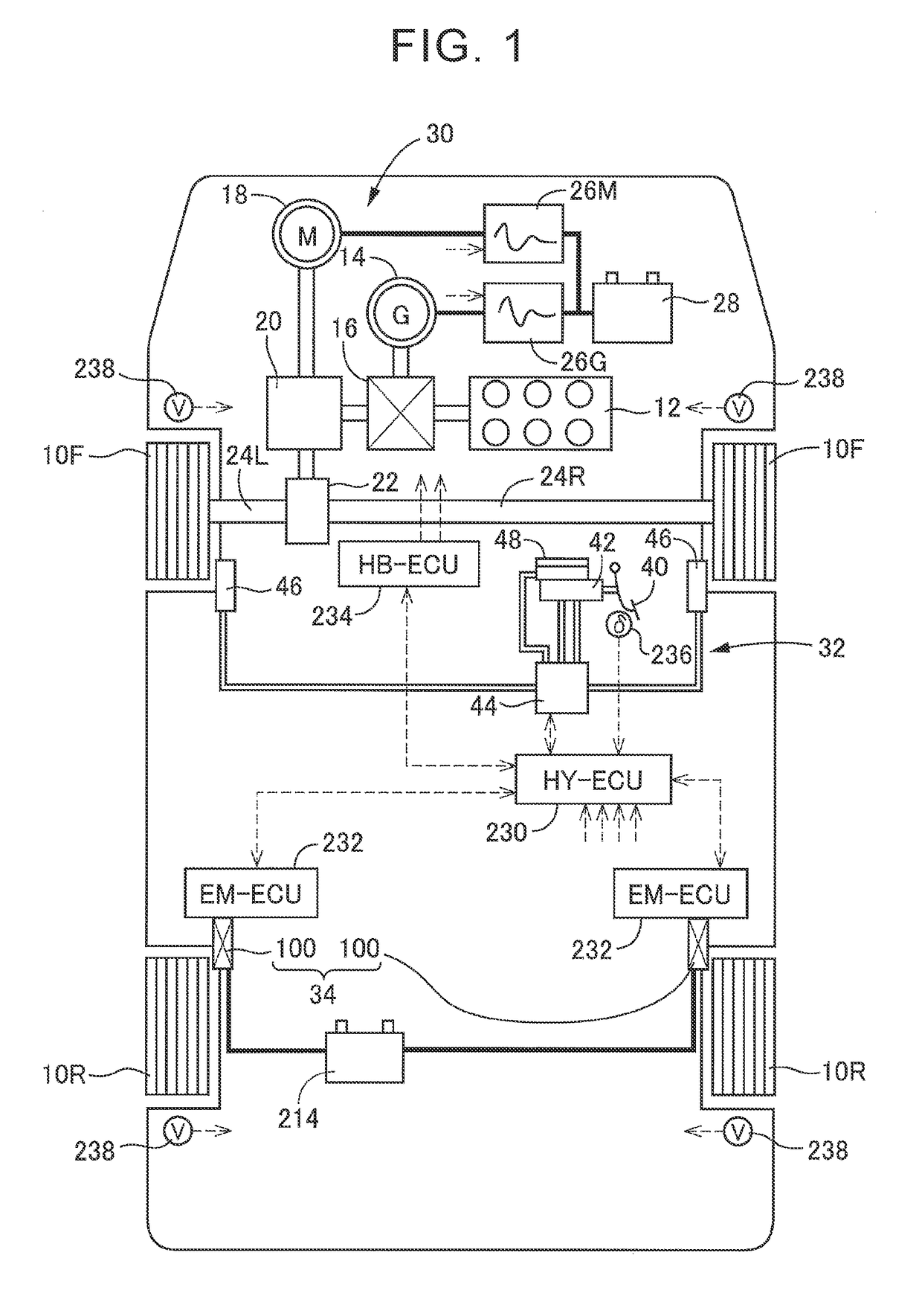
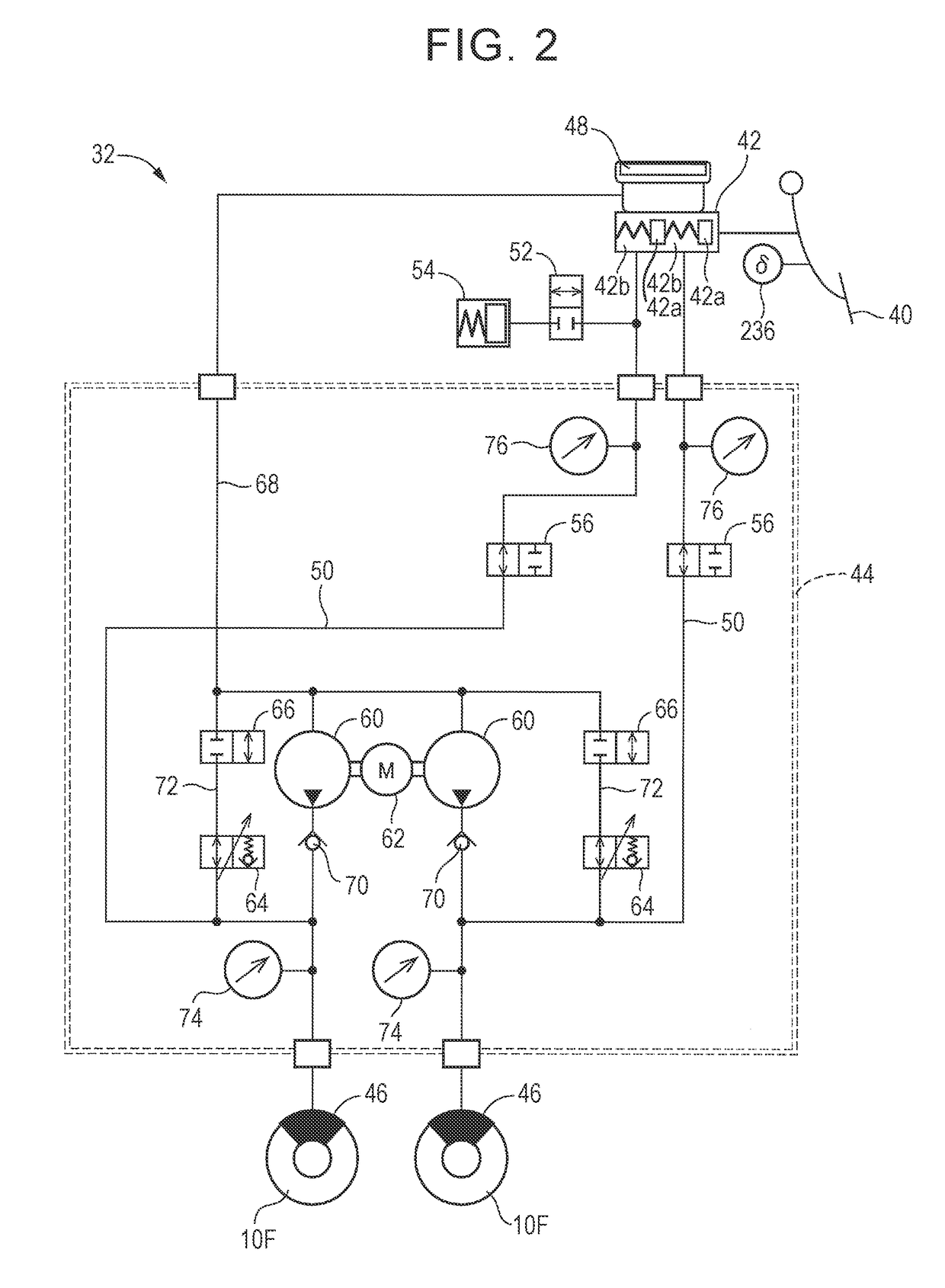
Vehicle braking system
ActiveUS20180154875A1Easy to controlControl is complicatedBraking element arrangementsAxially engaging brakesPistonVehicle braking
A brake control device is configured such that a hydraulic braking device is provided for one of a front wheel and a rear wheel, and an electric braking device is provided for the other one of them. The electric braking device is provided with a mechanism configured to prohibit retreat of a piston for pressing friction members against a rotor that rotates with the wheel. The brake control device is configured to maintain, by an operation of the mechanism, a braking force that does not depend on a force of an electric motor as a drive force and to control a braking force generated by the hydraulic braking device based on a difference between the braking force thus maintained and a braking force requested for the electric braking device.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for integrated drilling, flushing, slotting and thermal injection for coalbed gas extraction
ActiveUS20170145794A1Speed up the extraction processEasy to operateFluid removalGas removalDesorptionEngineering
A method for combining integrated drilling, flushing and slotting with thermal injection to enhance coalbed gas extraction, applicable to managing gas extraction from microporous, low-permeability, high-adsorption coalbed areas. A gas extraction borehole is drilled within a certain distance of a predetermined drilling, flushing and slotting borehole, and, once sealed, is used for gas extraction. An integrated drilling, flushing and slotting drill bit is used to sink the borehole, which is then sealed. Concentration variation in the gas extraction borehole is monitored in real time, and when concentration is below 30%, borehole is opened and high-temperature steam is injected by means of a steam generator, after which the borehole is again closed. Drilling a drilling, flushing and slotting borehole increases pressure relief space and the surface of exposed coal, relieves stress on the coal body, and increases gas permeability of the coalbed, while the injection of high-temperature steam promotes gas desorption in the coal body, promotes crack propagation around the borehole, and increases channels for gas flow, thus achieving highly efficient extraction of gas from the coalbed.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method for controlling subsidence area caused by underground mining in adjoining open-pit mine
ActiveUS20200300090A1Easy constructionLocal materialUnderground miningSurface miningGround subsidenceCoal spontaneous combustion
A method for controlling a subsidence area caused by underground mining in an adjoining open-pit mine, applied in an open-pit and underground coordinated mining process. In the method, a ground subsidence area caused by underground mining and production is directly filled and covered with overburden materials such as soil and rock discharged from an adjoining open-pit mine; small and medium fracture zones and large fracture zones caused by mining are timely backfilled, tamped, and levelled according to areas before the ground subsidence area appears, the thickness of the levelled soil layer is kept above 1 m, and the area slope is controlled within 7°. By fully using overburden materials from an adjoining open-pit mine, the method controls a subsidence area caused by underground mining and greatly shortens the discharge distance of the overburden materials from the adjoining open-pit mine, also solves the safety problems such as air leakage and spontaneous combustion of coal caused by fractures in mine subsidence, and brings significant economic and social benefits.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Device for detecting blockage of air filter mesh
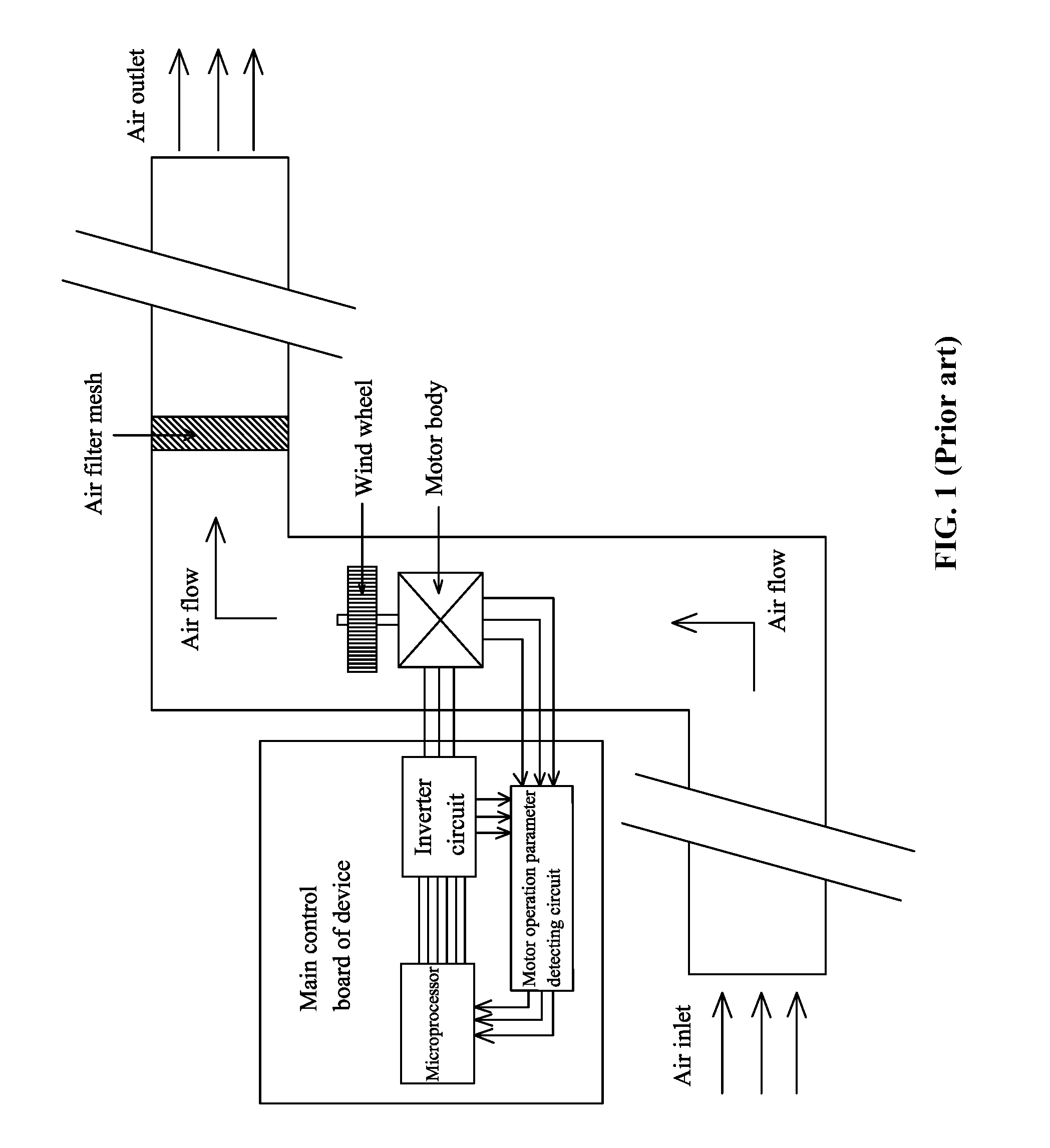
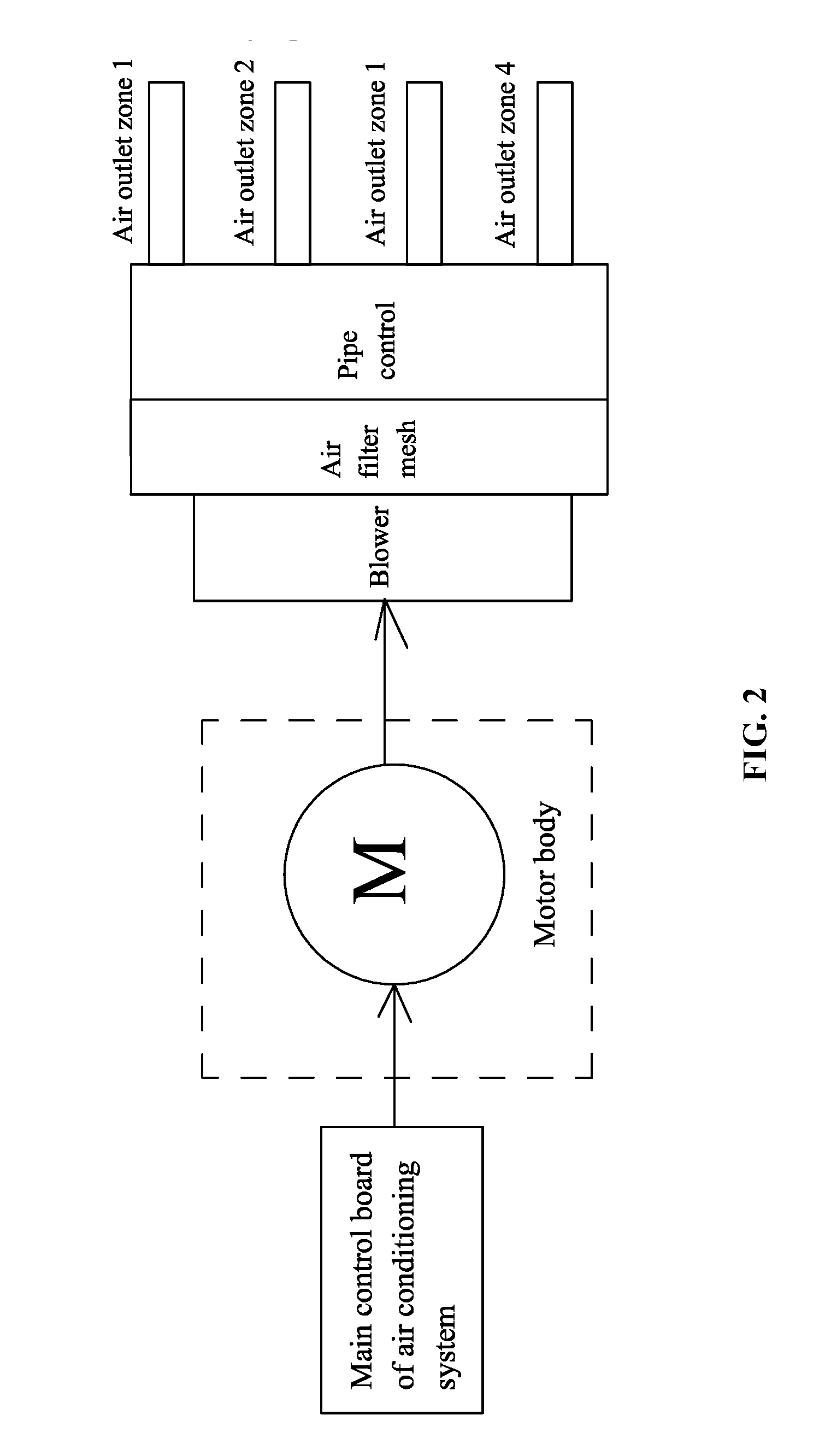
ActiveUS20160117907A1Simple and compact structureEasy to installMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsAir filtrationAir volume
A device for detecting blockage of an air filter mesh, including: an air inlet, an air outlet, an air duct, a fan or a wind wheel, a blower motor, an air filter mesh, and a controller. The controller includes a main control board including: a microprocessor, an inverter circuit, and a motor operation parameter detecting circuit. The air filter mesh is disposed in the air duct. The motor operation parameter detecting circuit inputs a real time operation parameter into the microprocessor, and the output terminal of the microprocessor controls the inverter circuit. A function module of the microprocessor calculates a detected air volume according to the real time operation parameter. When the detected air volume is smaller than a preset air volume, the microprocessor determines that the air filter mesh is obstructed and outputs a signal to an alarm circuit to trigger an alarm.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN BROAD OCEAN
Method for integrated drilling, slotting and oscillating thermal injection for coal seam gas extraction
ActiveUS20180209255A1Easy to operateRemarkable improvement effectLiquid/gas jet drillingFluid removalEngineeringHigh pressure
A method for combining integrated drilling and slotting with oscillating thermal injection to enhance coalbed gas extraction, applicable to managing gas extraction from microporous, low-permeability, high-adsorption coal seam areas. A number of slots are formed within a thermal injection / extraction borehole by means of integrated drilling and slotting technology; a steam generator, is then used to three high-pressure, cyclically temperature-changing steam into said borehole; the steam passing through a spinning, oscillating-pulse jet nozzle forms an oscillating superheated steam, heating the coal body. The present method overcomes the limitations of simple permeability-increasing techniques, the slotting by means of hydraulic. pressure significantly increasing the pressure relief range of a single borehole and forming a fracture network that provides channels for passage of the superheated steam, while oscillating variation in steam temperature and pressure also promote crack propagation and perforation of the coal body; the combined effect of the two enhances the efficiency of gas desorption and extraction.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Pluripotent Stem Cell Cloned From Single Cell Derived From Skeletal Muscle Tissue
InactiveUS20080213231A1Low purityMinimize contaminationBiocideMuscular disorderPluripotential stem cellInduced pluripotent stem cell
Techniques are provided which can isolate pluripotent stem cells at high purity capable of differentiation into at least a myocardial cell to regenerate the cardiac muscle. The pluripotent stem cells at high purity capable of differentiation into at least a myocardial cell to regenerate the cardiac muscle can be isolated through the following steps: (i) collecting a skeletal muscle tissue from a mammal and enzymatically treating the obtained skeletal muscle tissue to prepare a skeletal muscle tissue-derived cell; (ii) culturing the obtained skeletal muscle tissue-derived cell in a culture medium containing an epidermal growth factor and a fibroblast growth factor; (iii) selecting and separating a colony that is floating in the culture medium.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Secondary battery and electrolyte used therefor
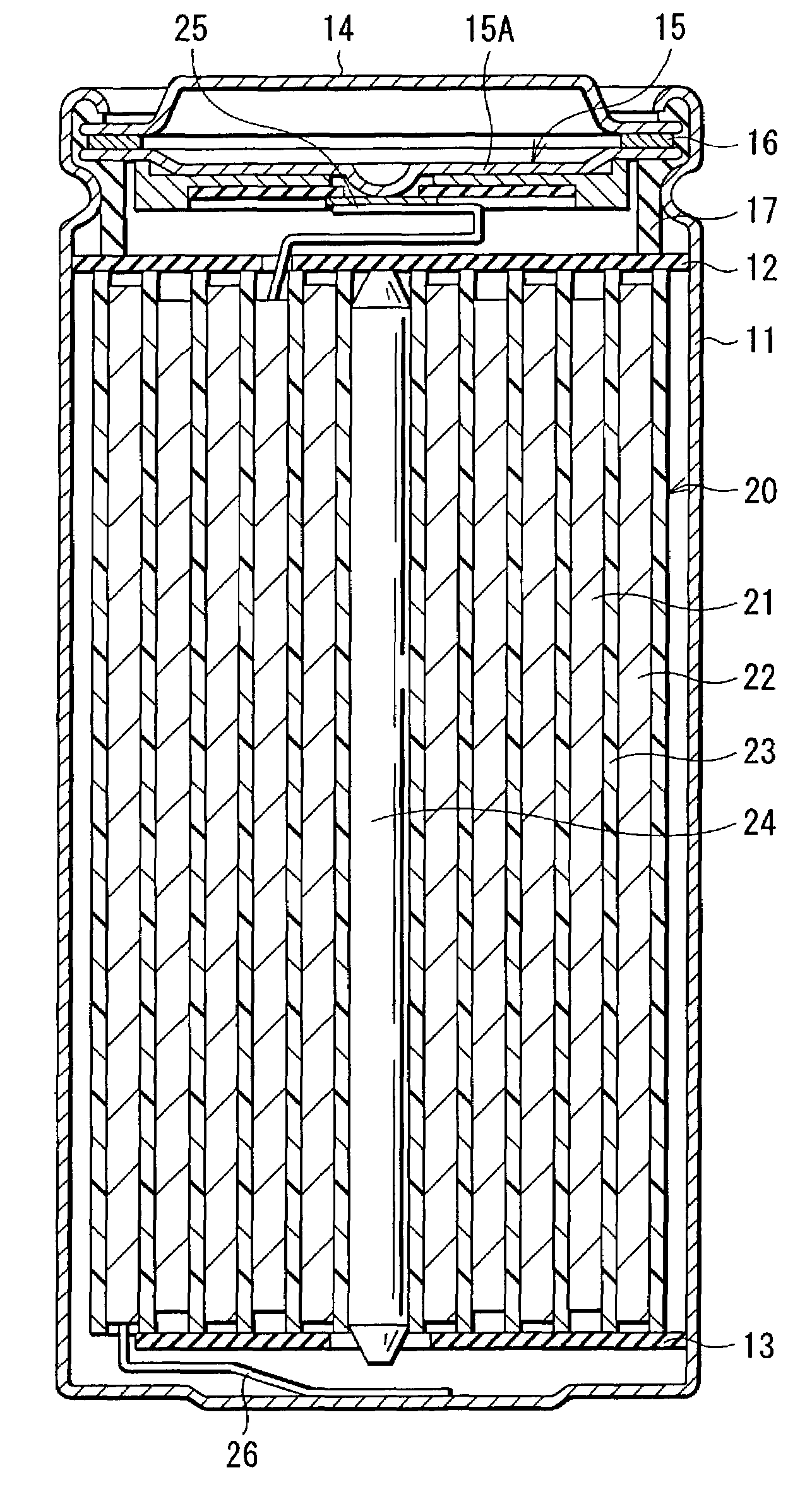
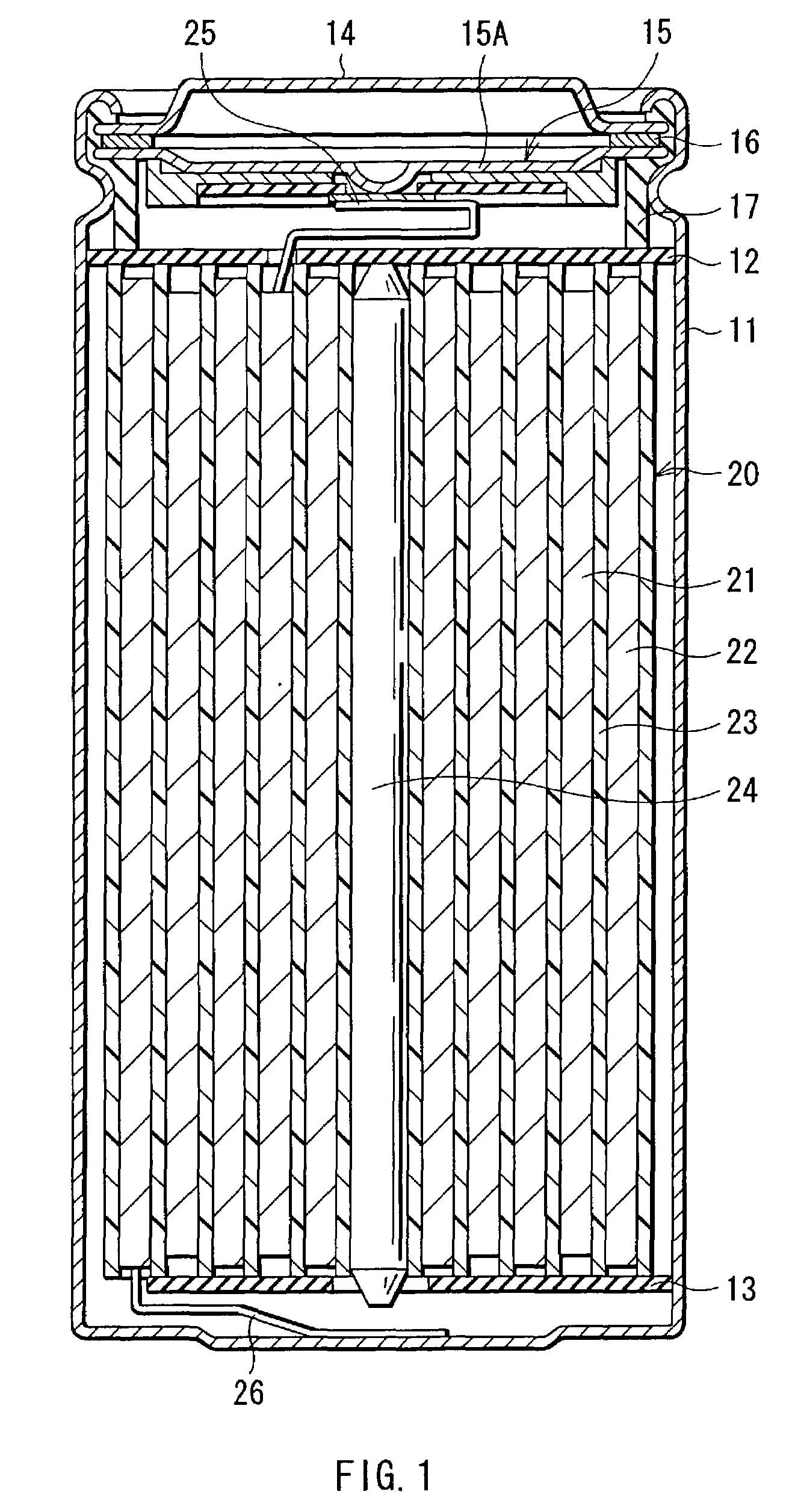
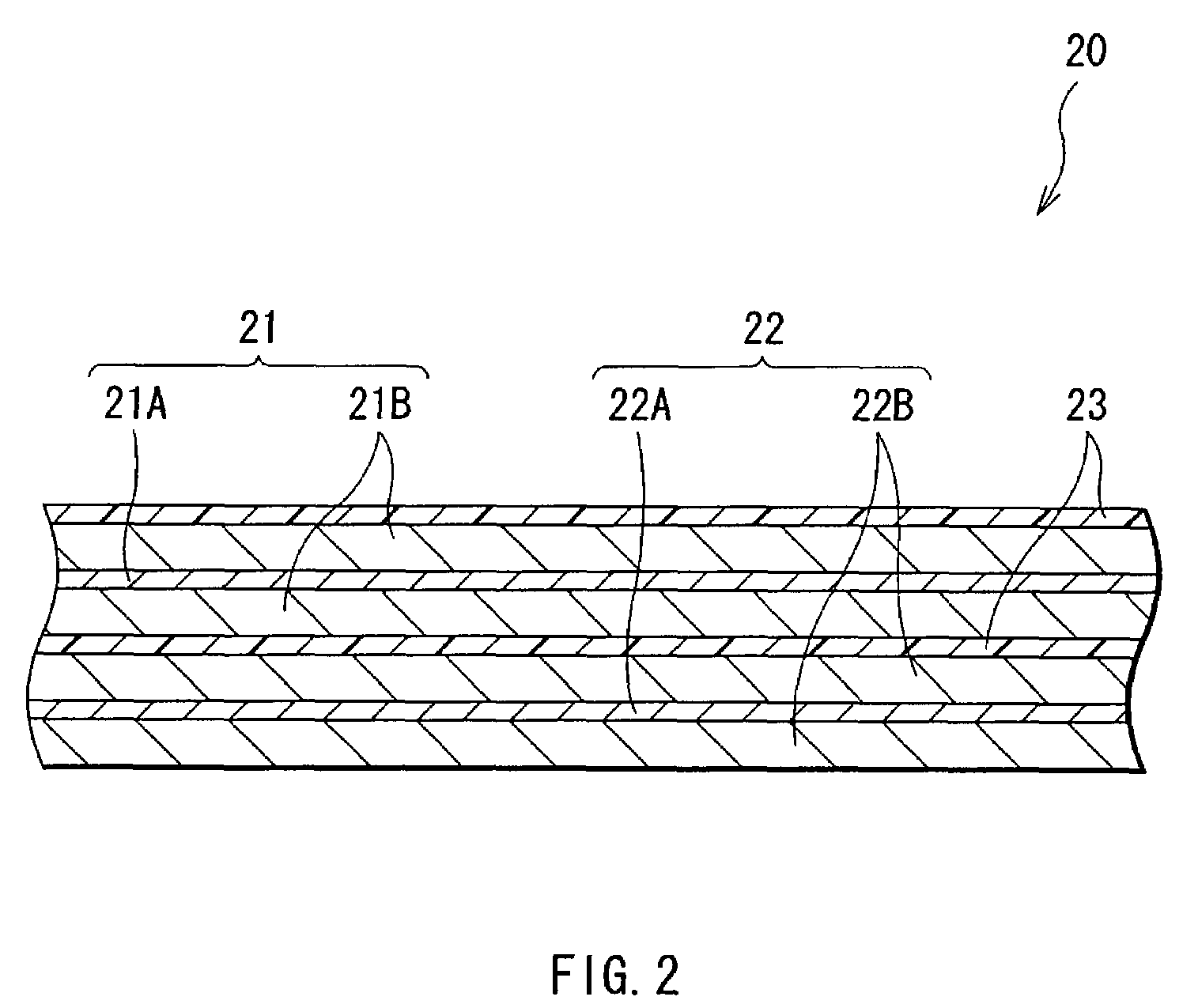
InactiveUS7220518B2Excellent capacity storage characteristicHigh practicabilityCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersOrganic electrolyte cellsElectrolytic agentChemical physics
A secondary battery which exhibits less deterioration of capacity, can maintain high energy densities in high temperature atmospheres, and has high practicality, and an electrolyte used therefor, are provided. The electrolyte contains an anion expressed by (PFaQbRc)−, so degradation of the electrolyte can be prevented. In the formula, Q expresses at least one of CF3, C2F5, and C3F7, and R expresses SO2CF3 and / or SO2C2F5. a, b and c satisfy 1≦a≦5, 0≦b≦5, and, 0≦c≦5, respectively. Furthermore, an anion expressed by N(CnF2n+1SO2)2− is contained, which can further prevent the degradation of the electrolyte. In the formula, n satisfies 1≦n≦2. Therefore, the capacity recovery rate after storage and heavy load discharge maintenance rate are high even in high temperature atmospheres, and high reliability can be obtained.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
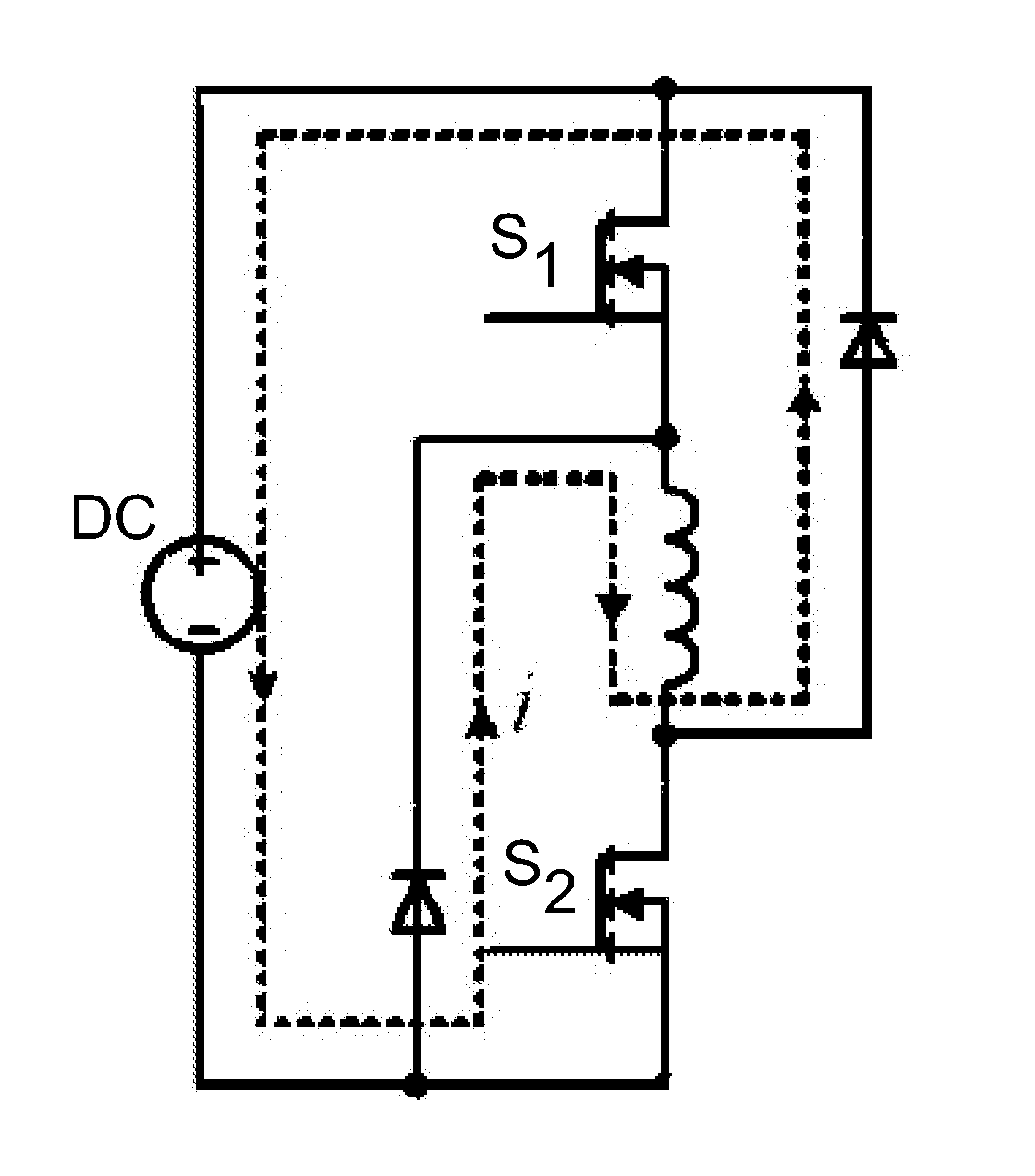
Position Sensorless Step-Wise Freewheeling Control Method for Switched Reluctance Motor
ActiveUS20140340006A1Operational reliability is increasedHigh dynamic responseAC motor controlPhase currentsPeak value
A position sensorless step-wise freewheeling control method for a switched reluctance motor having dual switched-mode power converters for each phase doesn't require any additional external hardware, any rotor-position sensor, or storage of flux linkage data of the motor. After the upper and lower tubes of the main switch are switched off, and the phase of the switched reluctance motor enters into a negative voltage forced freewheeling state, the phase current is detected. When the phase current falls to a preset threshold, one of the upper or lower tubes is switched on and the phase enters into a zero voltage natural freewheeling state. When the phase current reaches a peak value, the rotor position becomes the start position of the minimum phase inductance and the rotor position is used as the switch-on position of the main switch. The upper and lower tubes are then switched on.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Skip-mining type wangeviry stope branch roadway filling and coal mining method
ActiveUS20160305245A1High recovery rateGood control effectUnderground miningSurface miningMining engineeringCoal pillar
A transportation main roadway and stope branch roadways are arranged by adopting a wangeviry coal mining method. A plurality of stope branch roadways are divided into multiple mining stages, based on which the stope branch roadways are skip-mined; and coal pillars are not reserved among the stope branch roadways. The transportation main roadway is a main transportation channel, and the stope branch roadways are coal mining roadways. All the stope branch roadways are sequentially stoped in a skip-mining manner according to the designed mining sequence and are sequentially and timely filled. The coal never stoped or the filled stope branch roadways is / are used as supports for controlling roofs at the two sides of the stope branch roadways, and the stope branch roadways are sequentially stoped according to a plurality of mining stages, and finally the coal pillar-free mining is realized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com