Patents
Literature
119 results about "Endoscopic Assembly" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
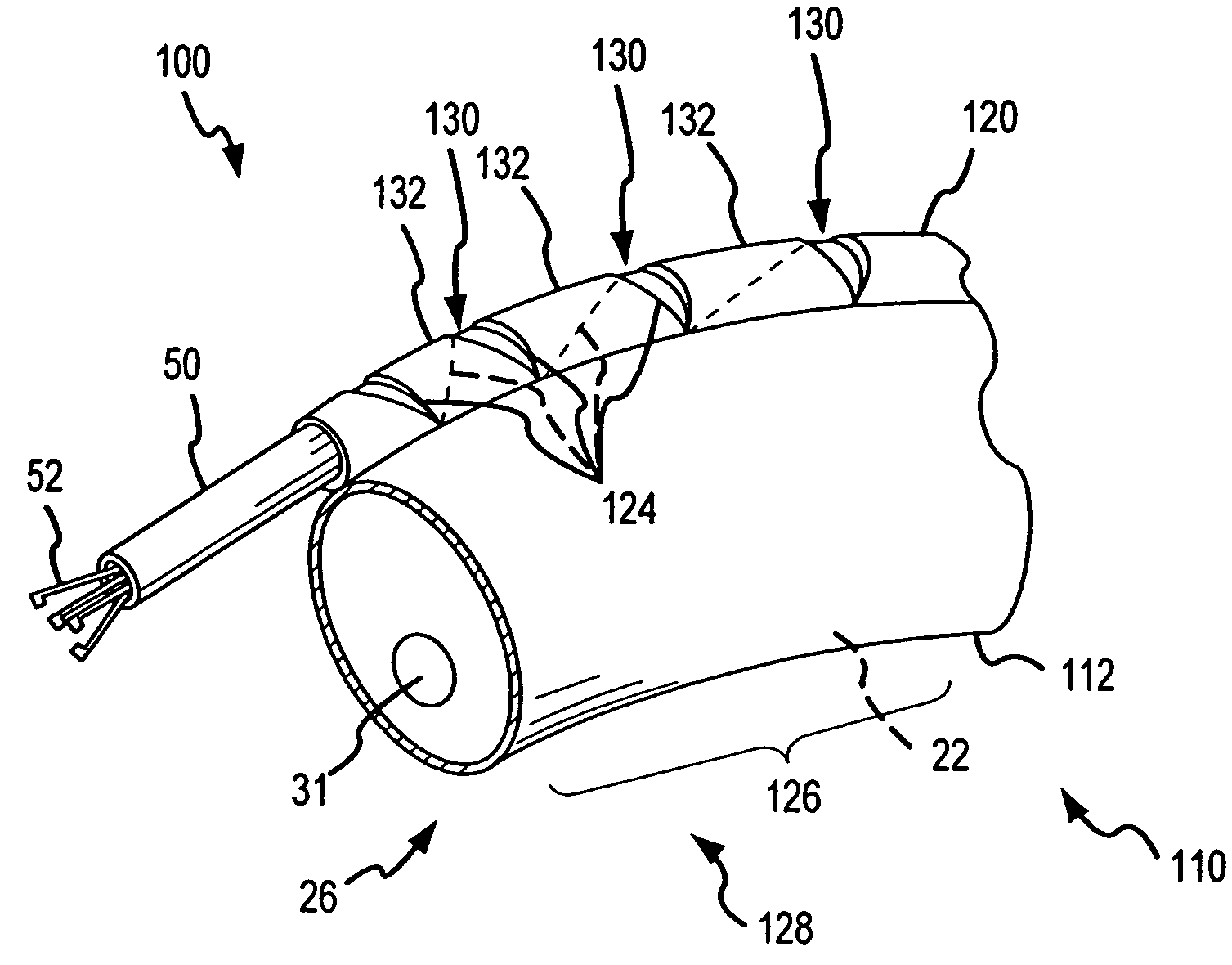
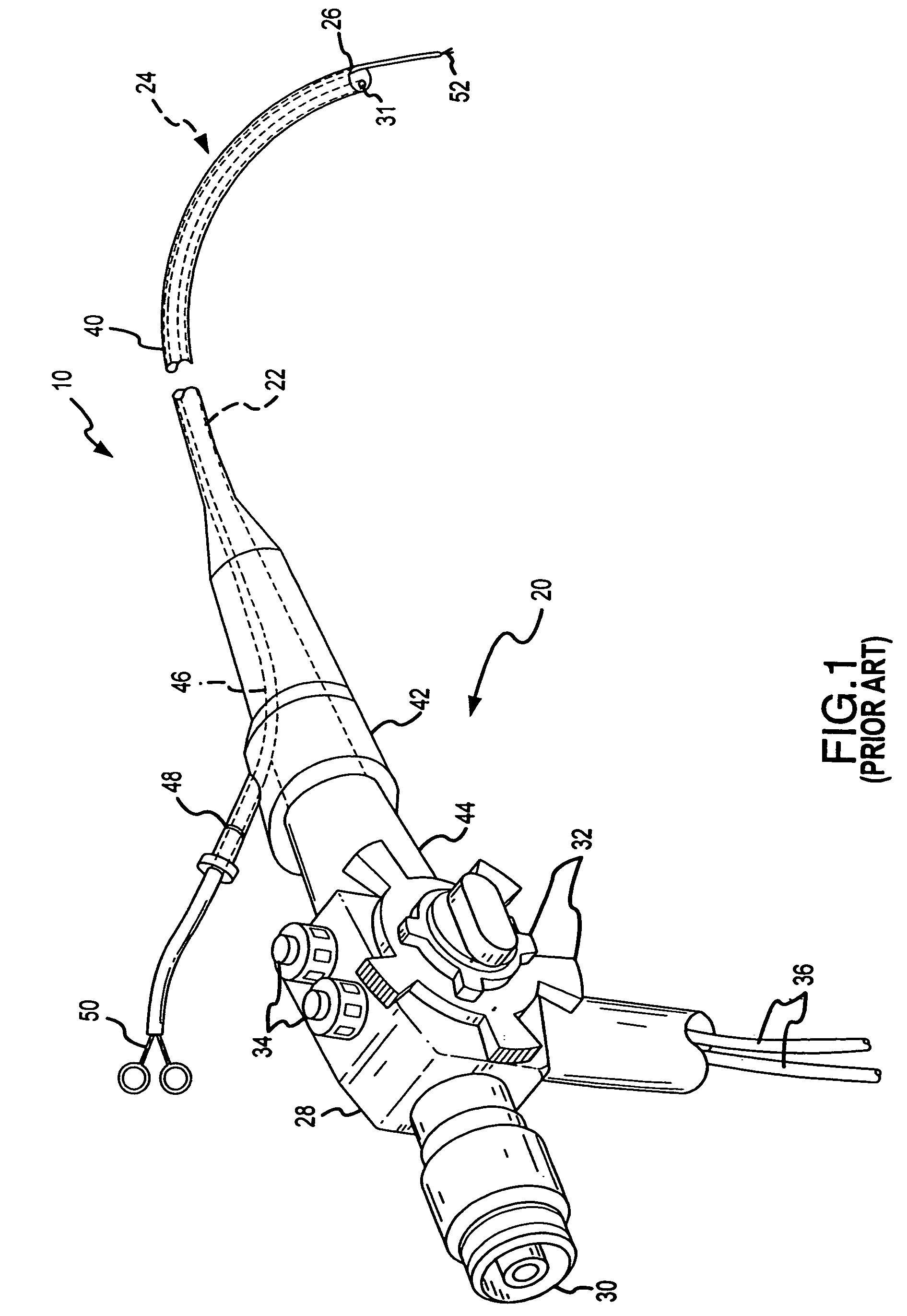
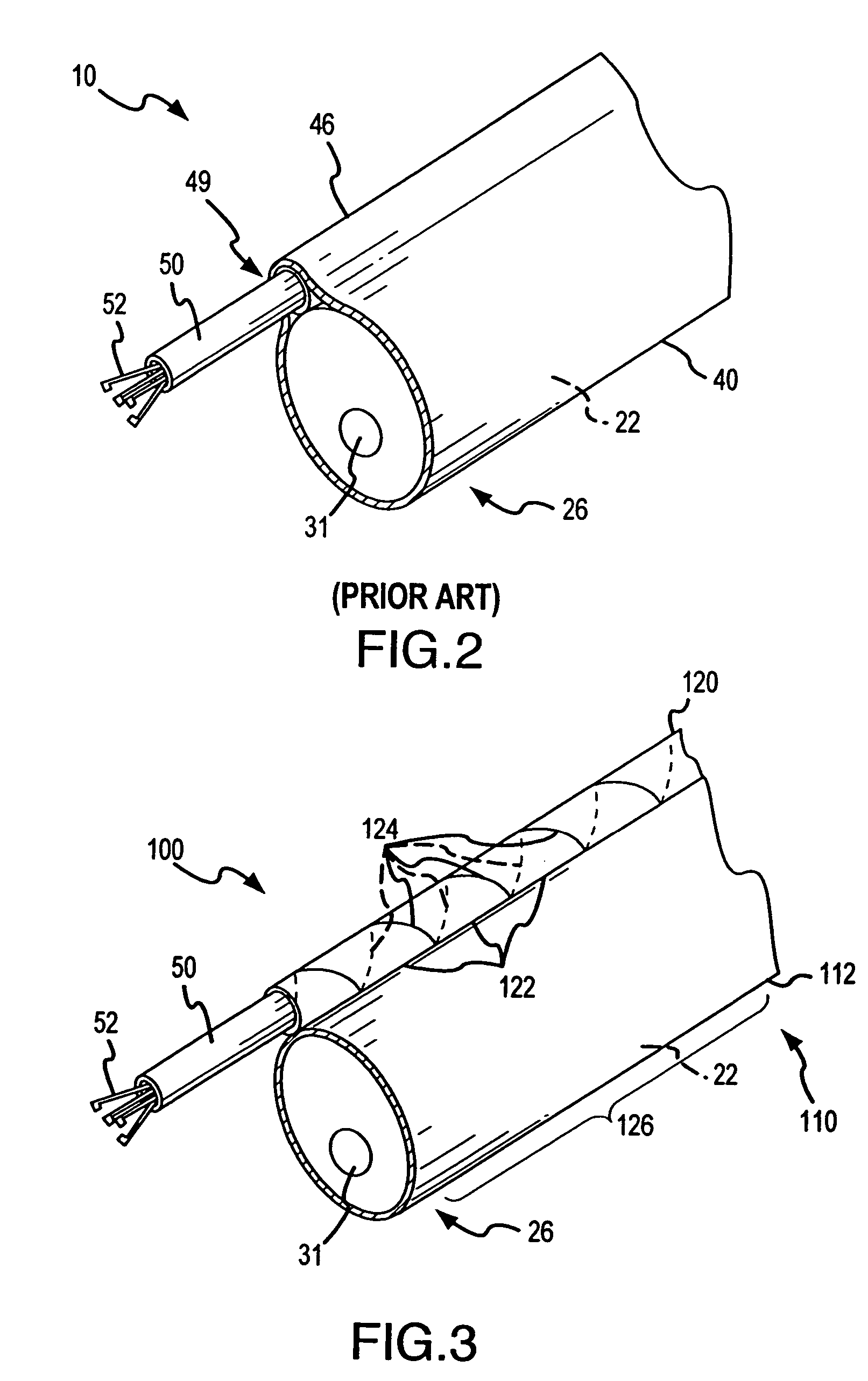
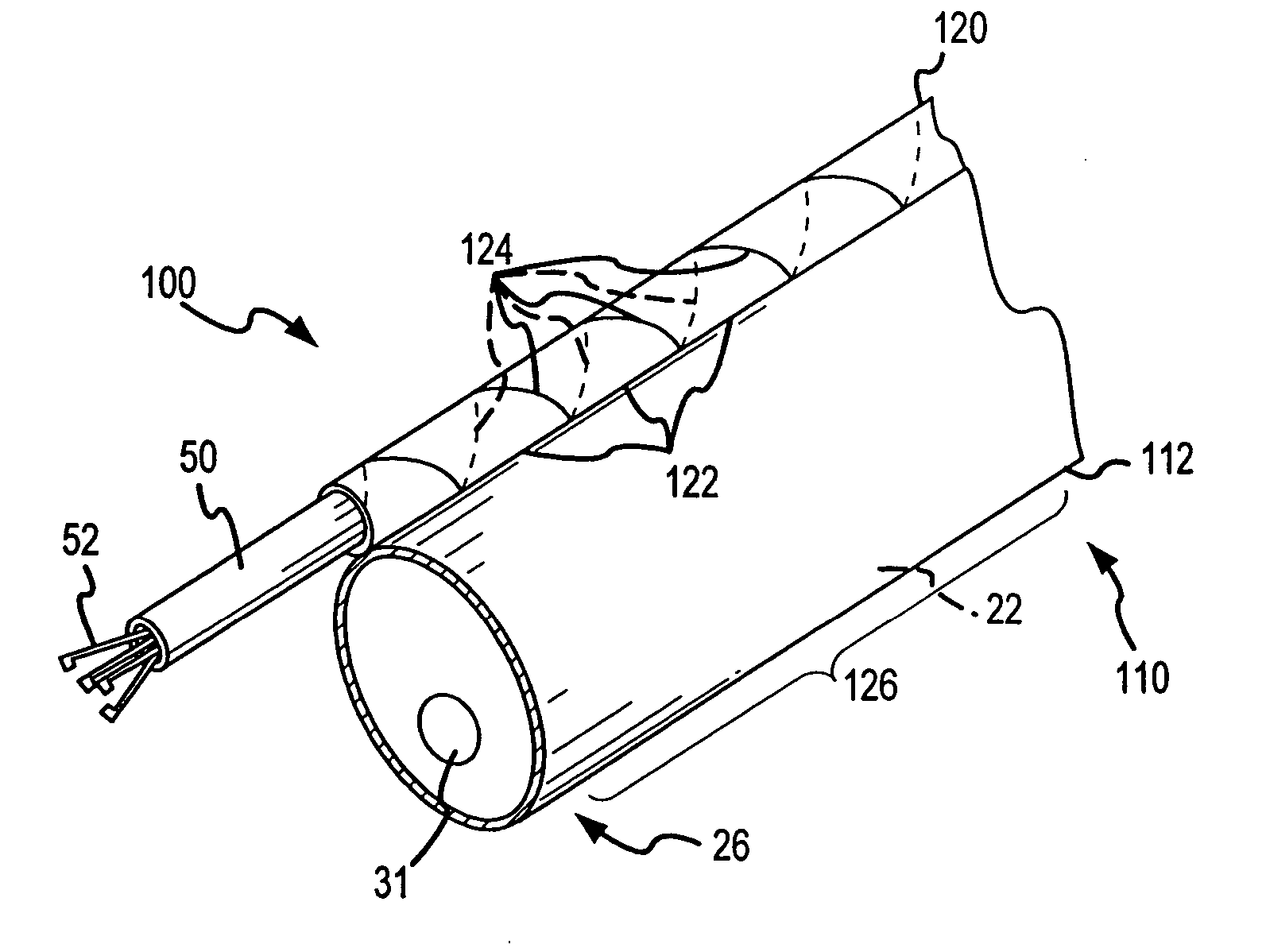
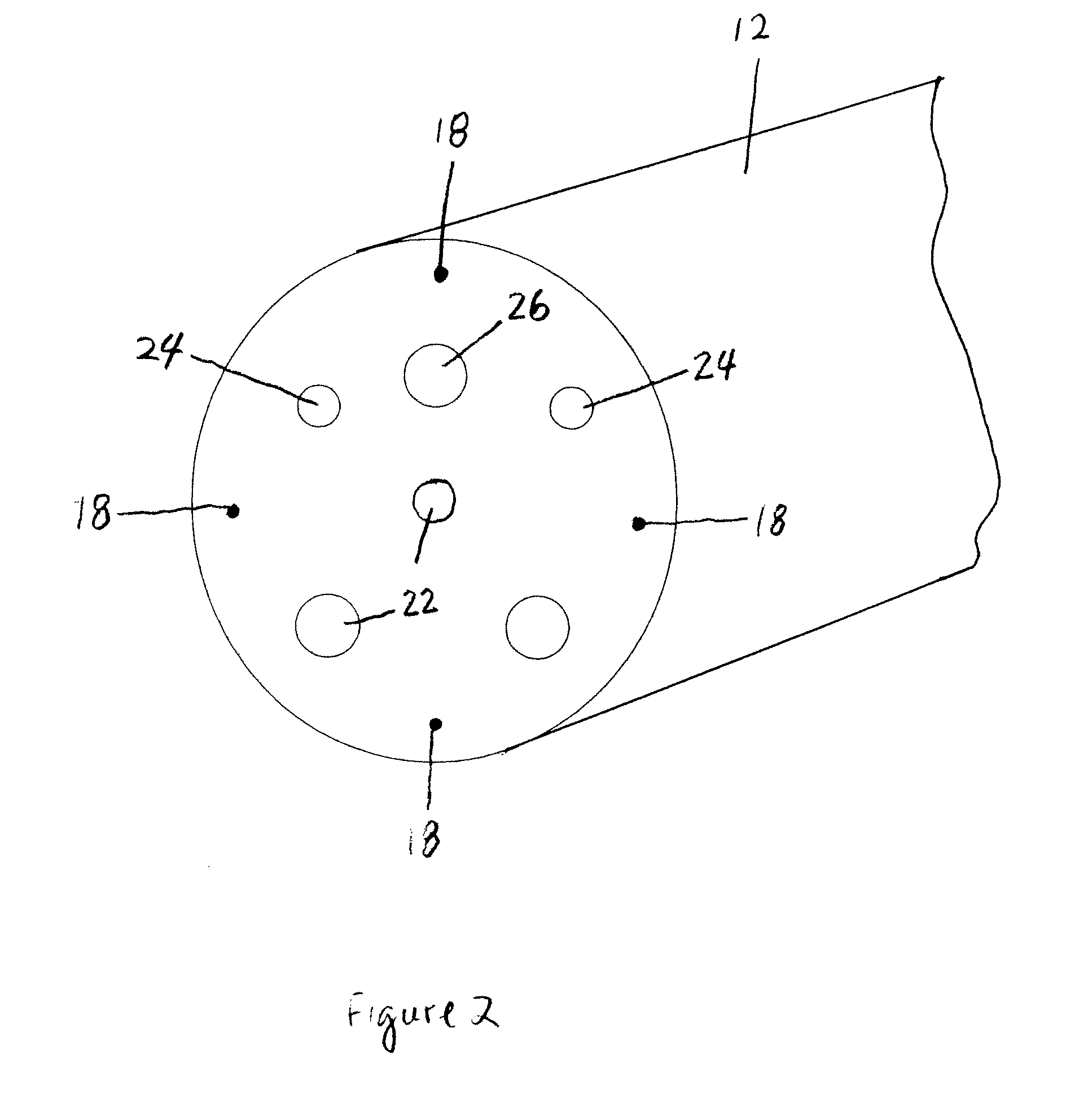
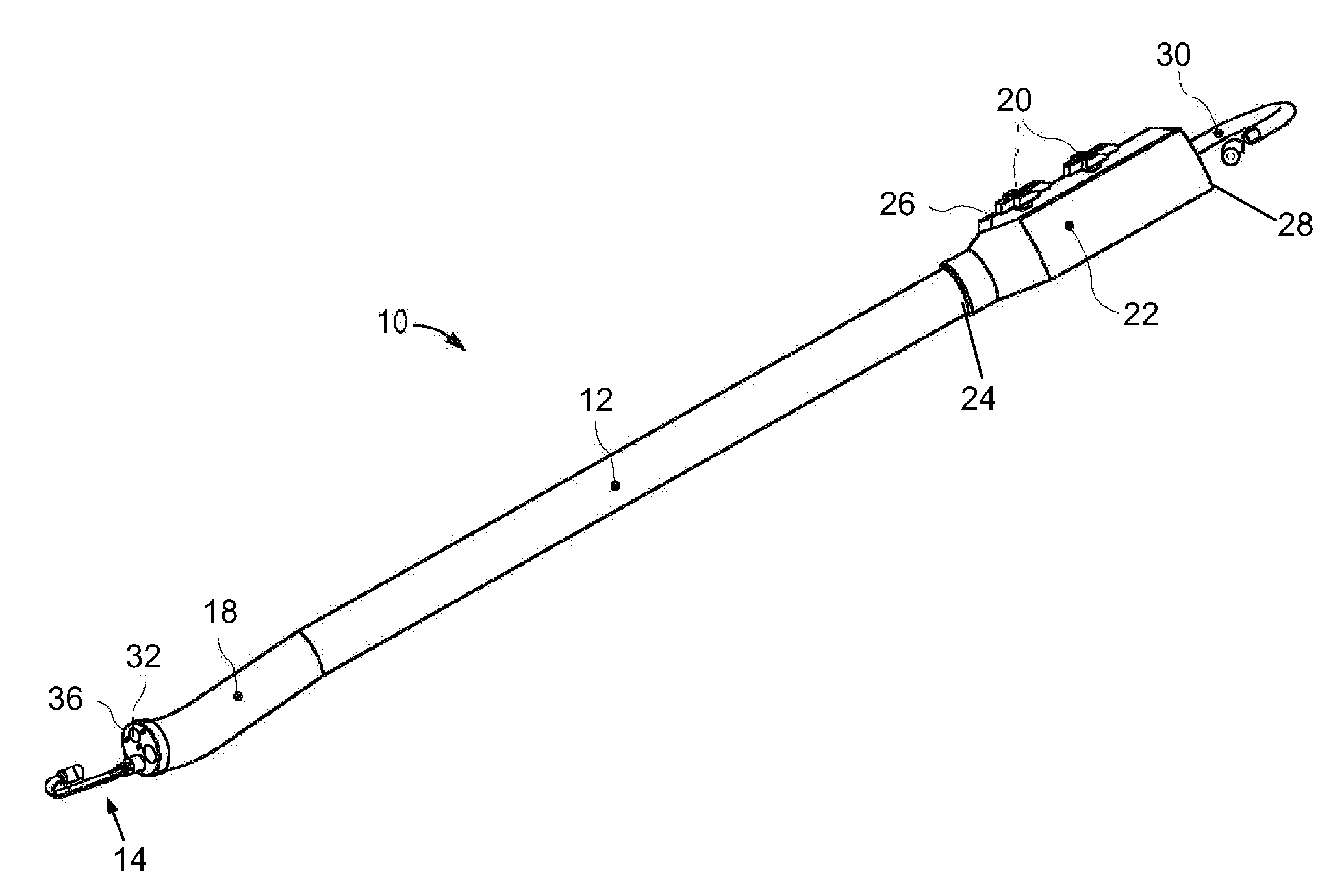
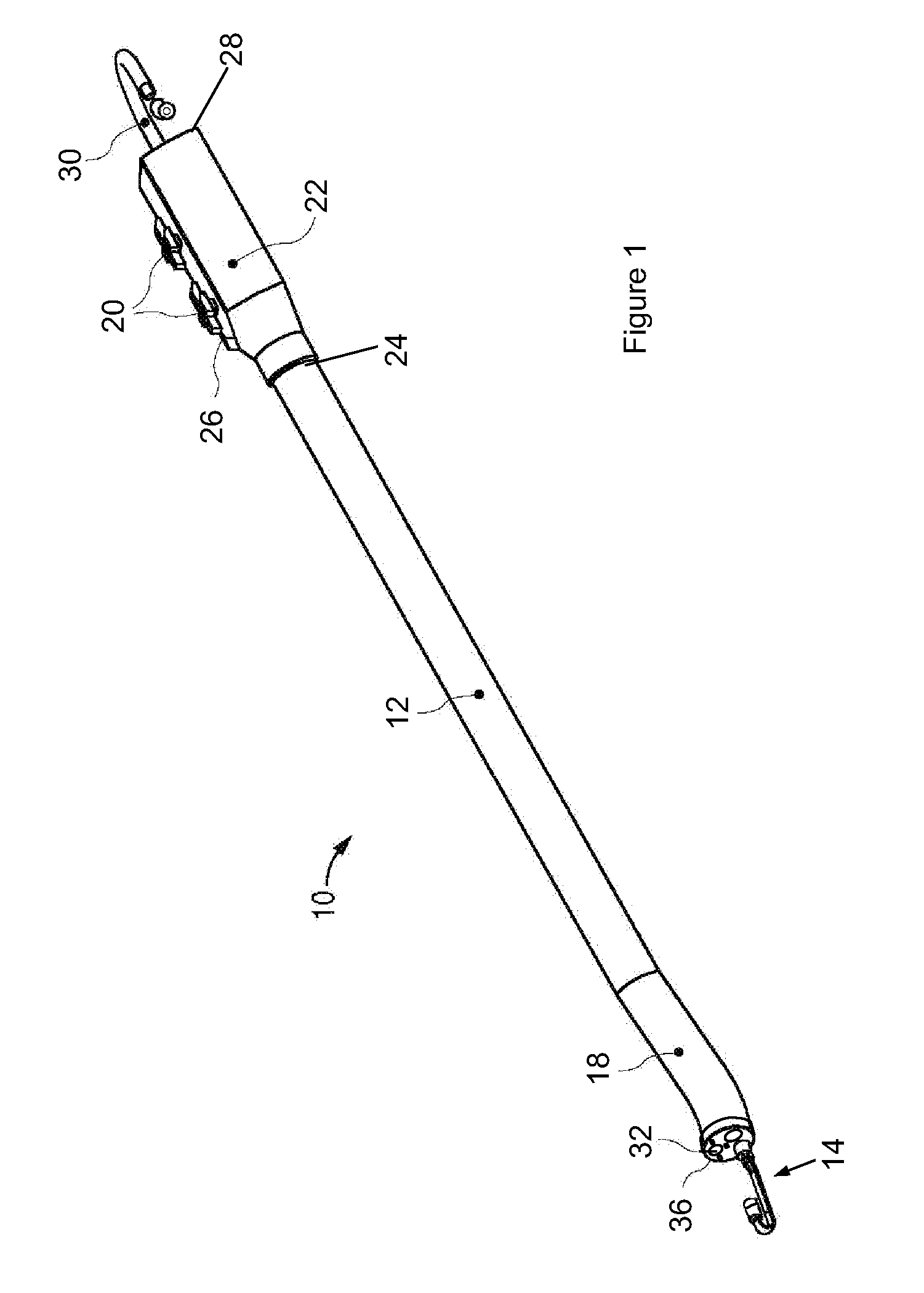
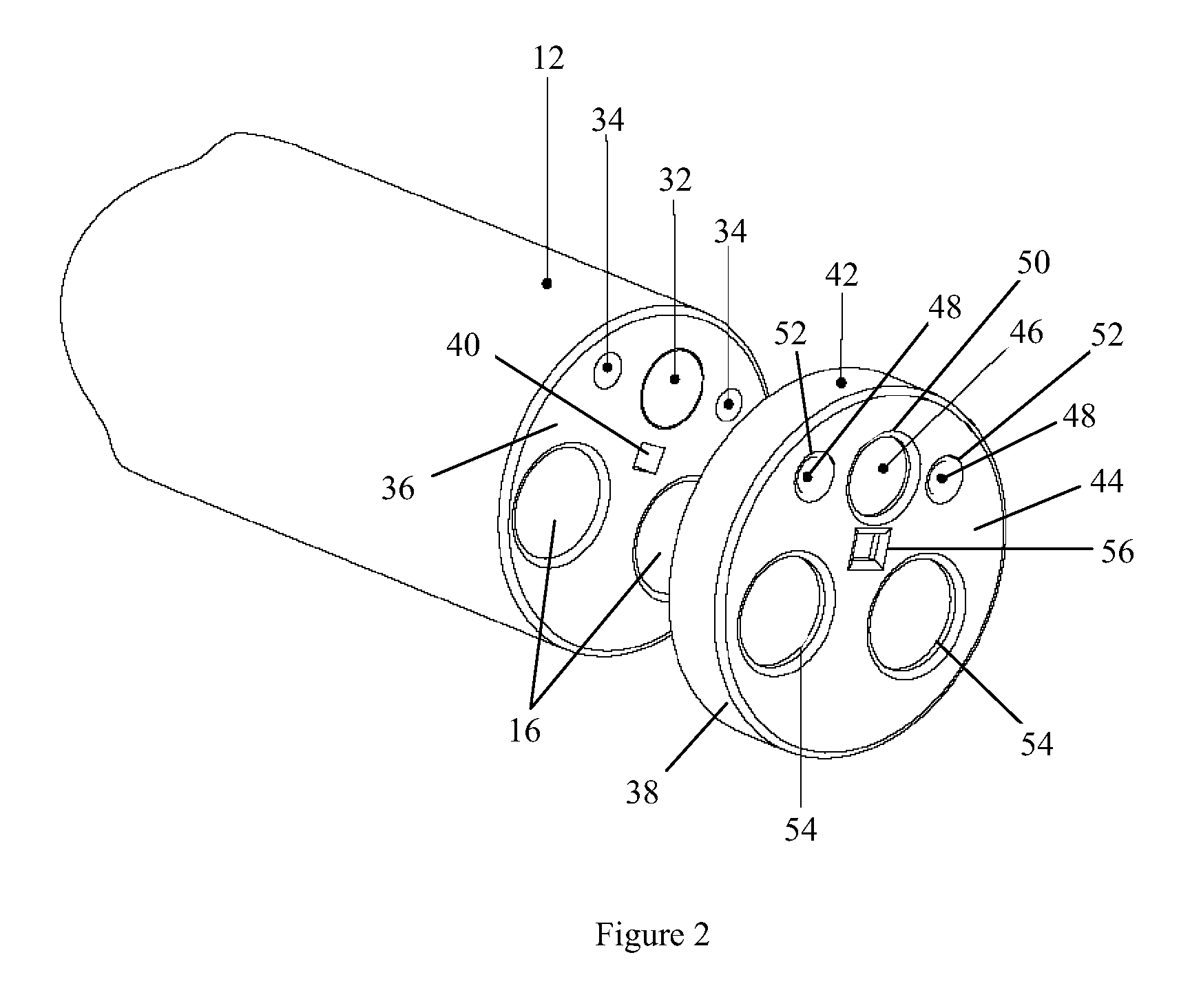
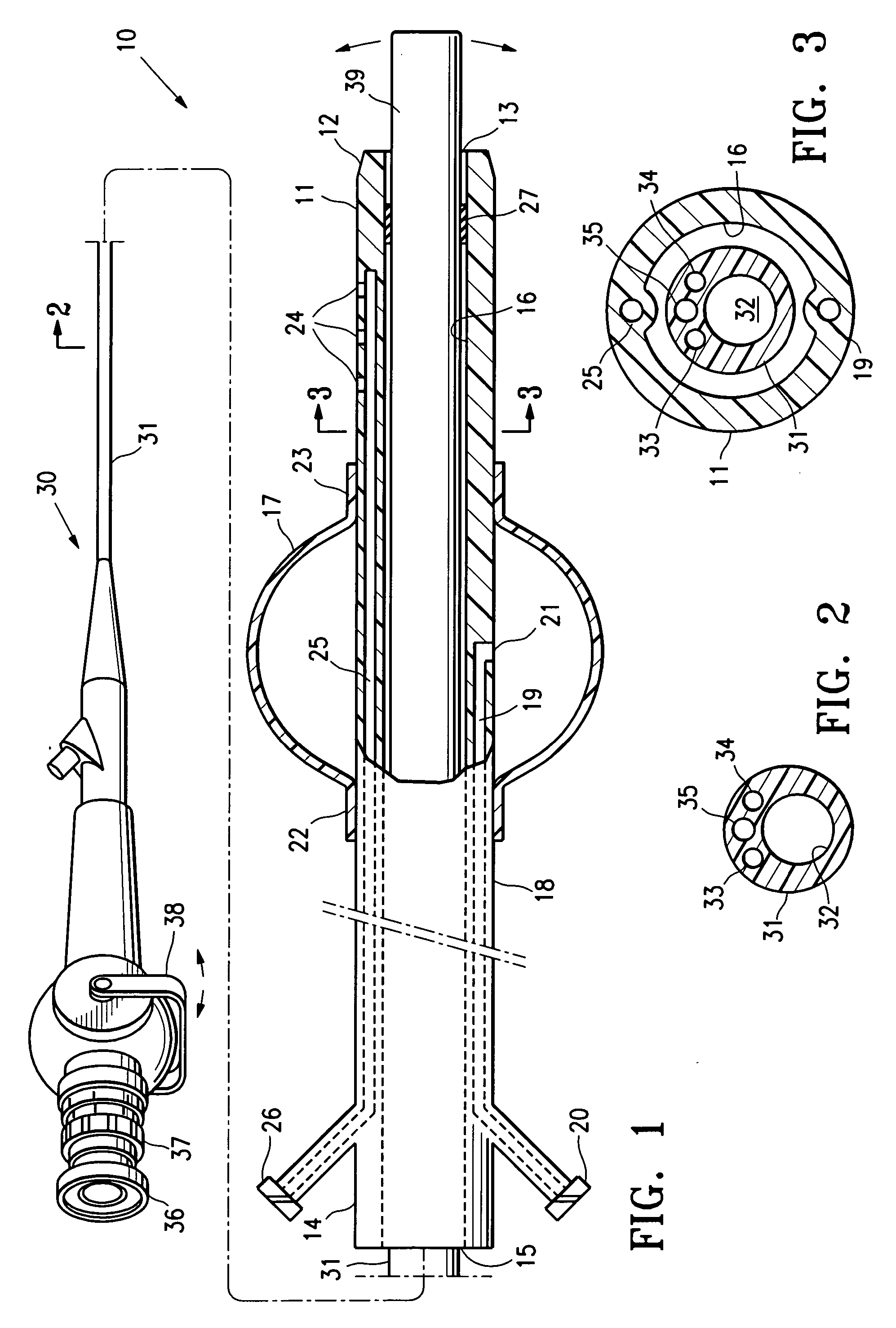
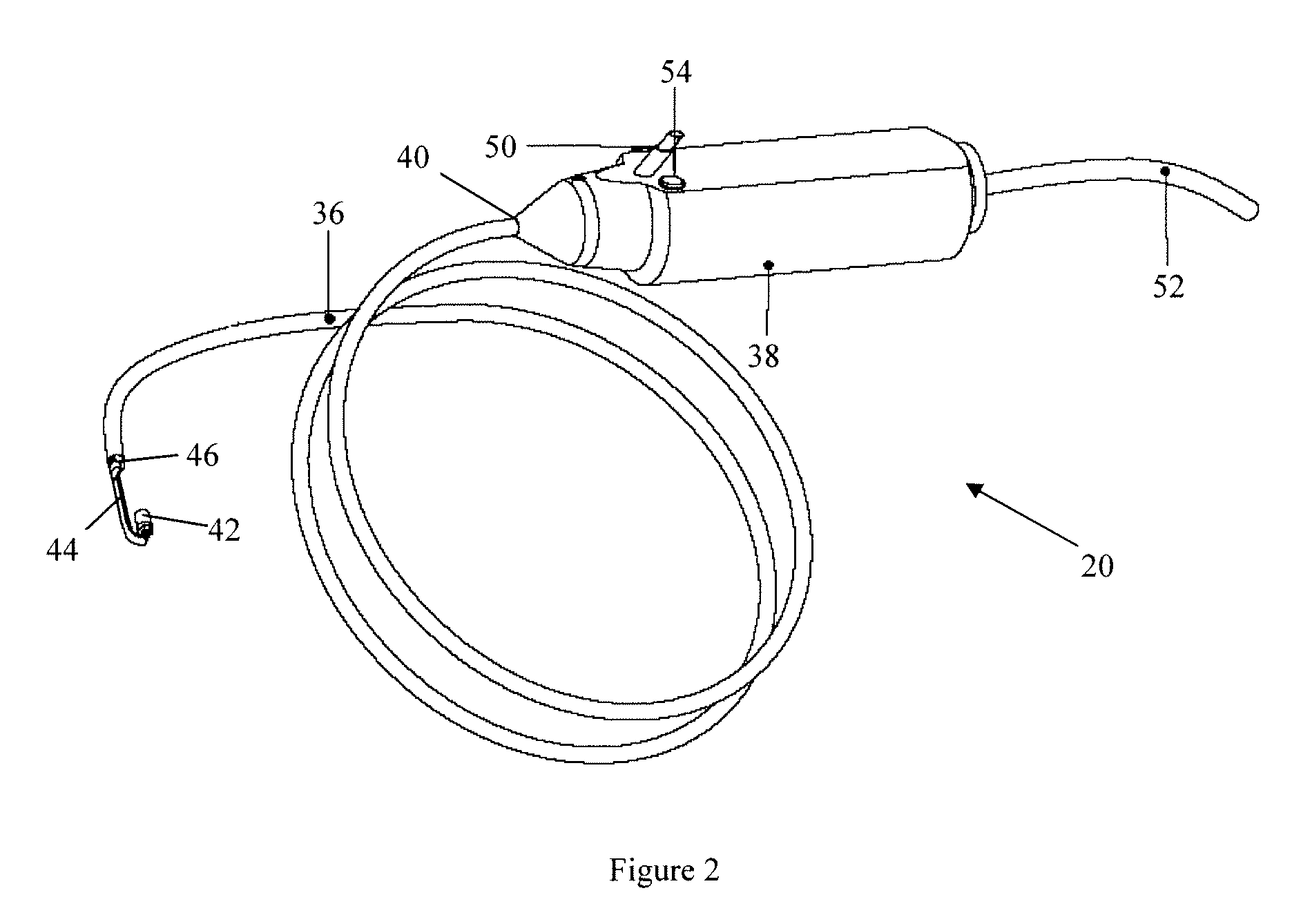
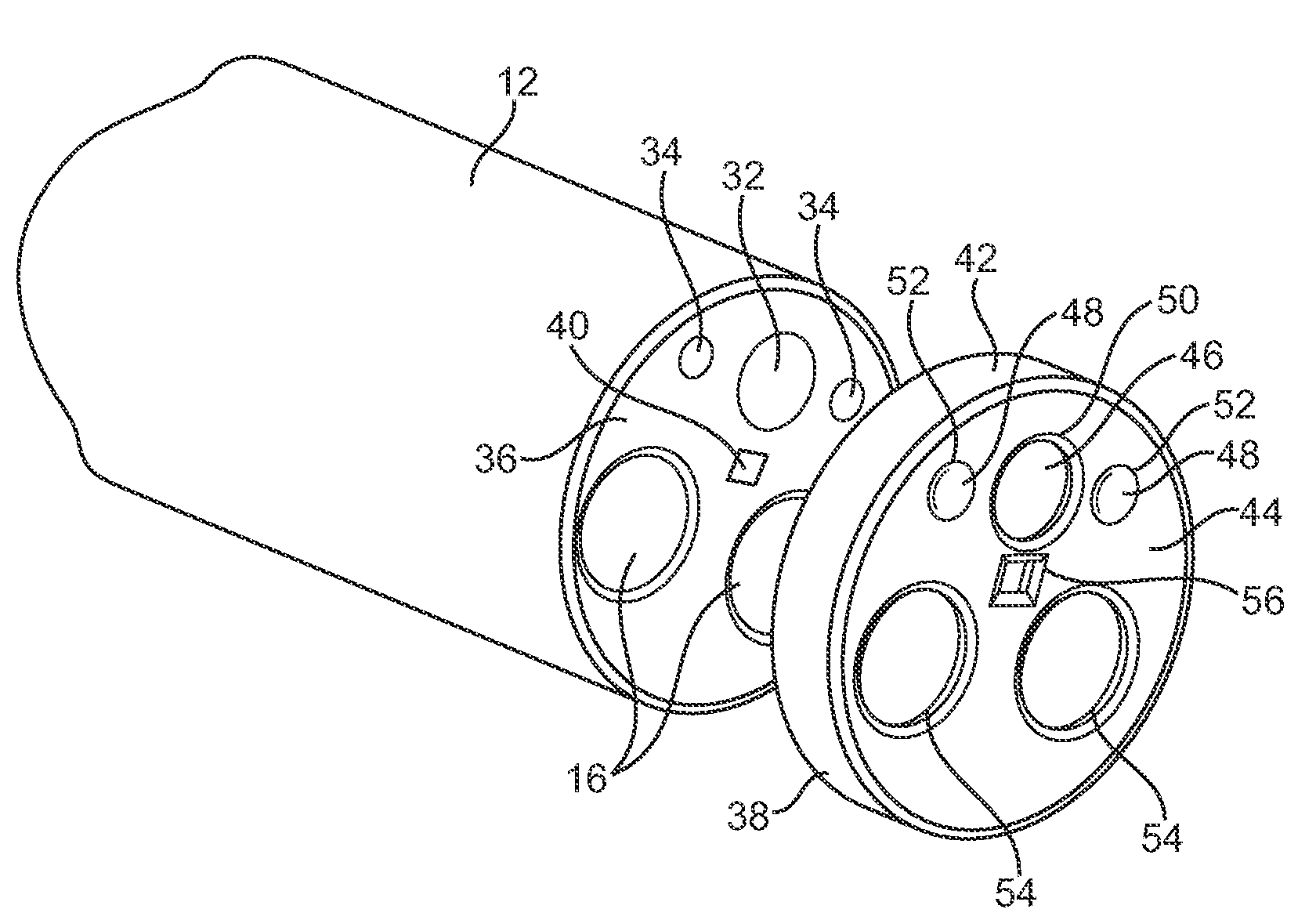
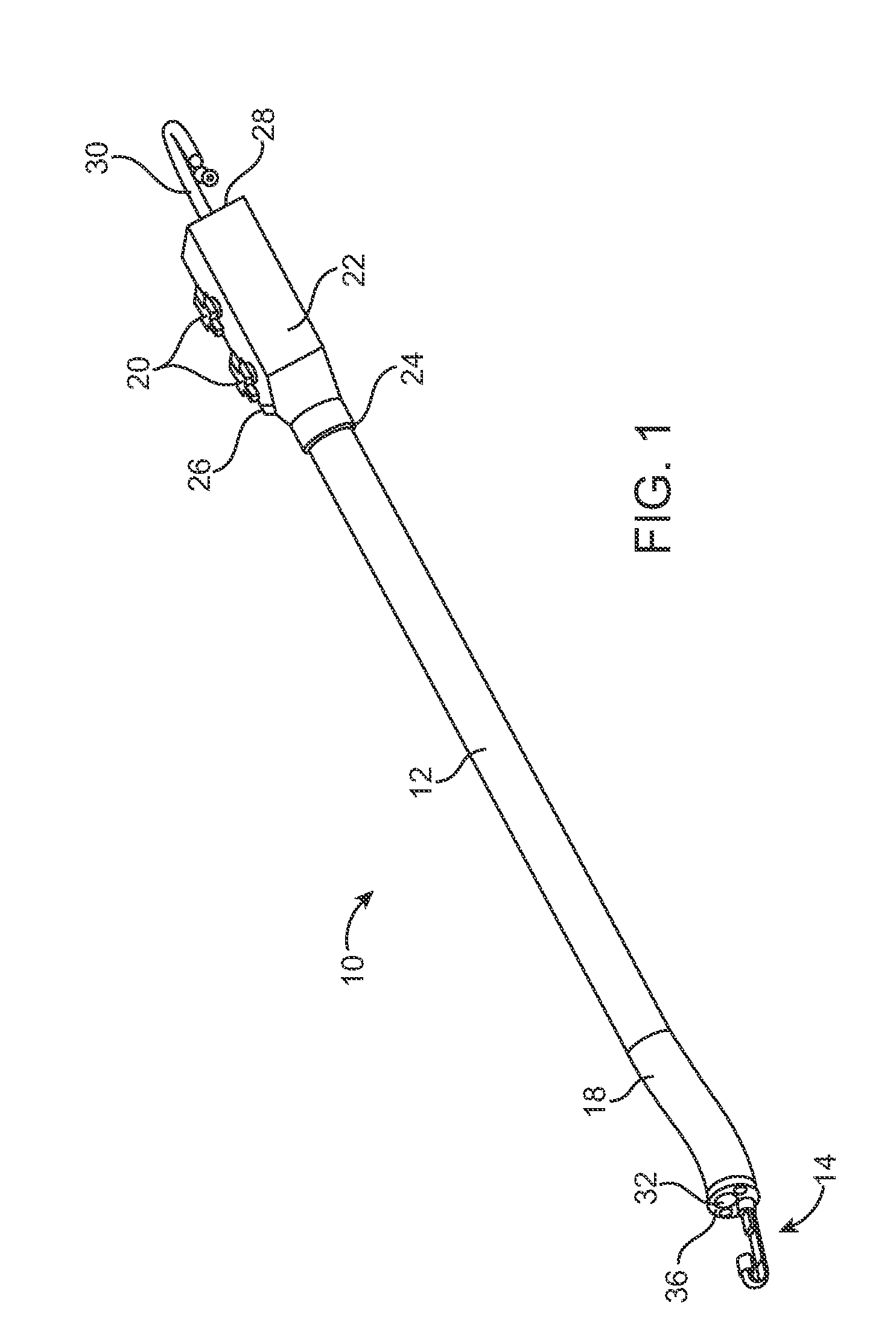
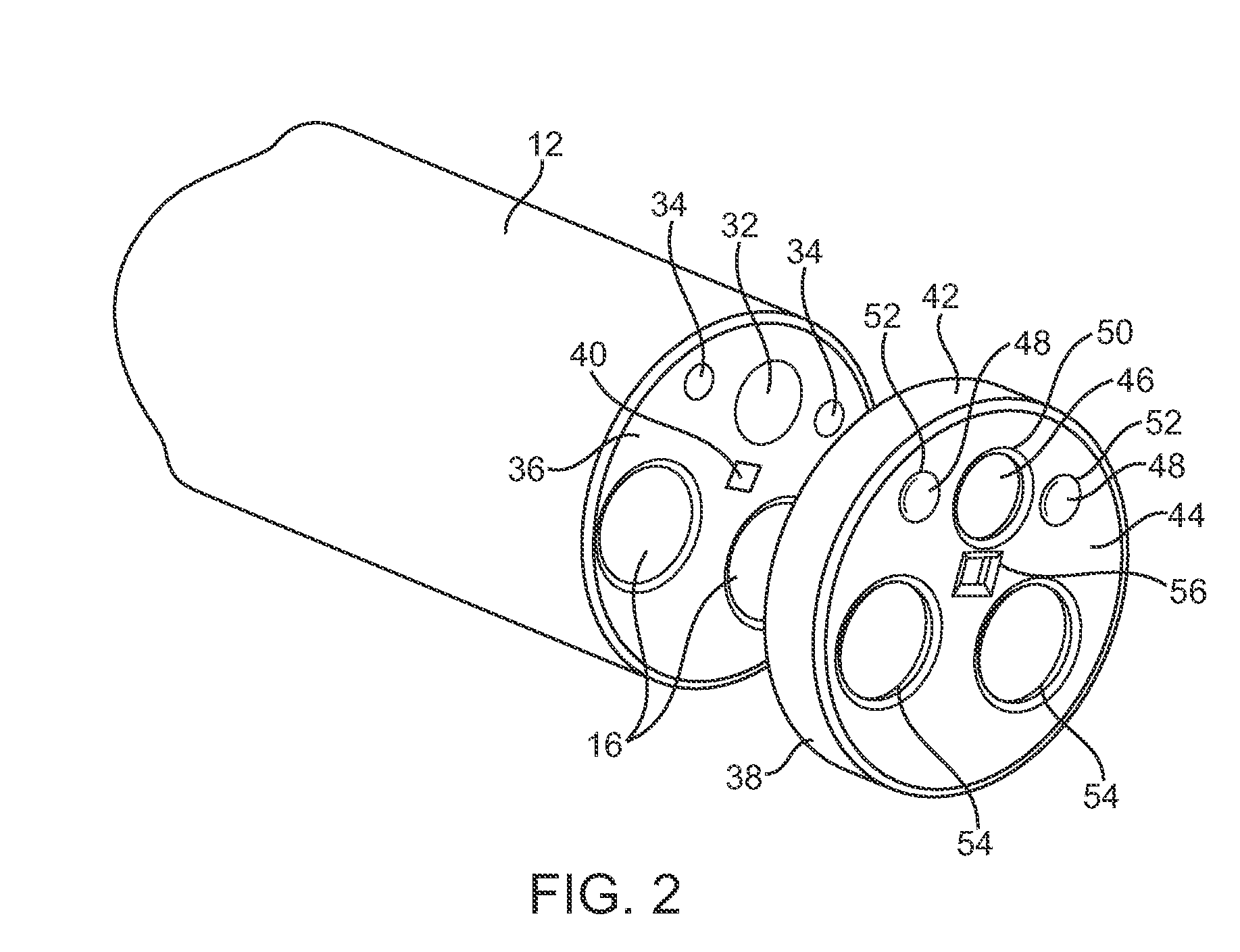
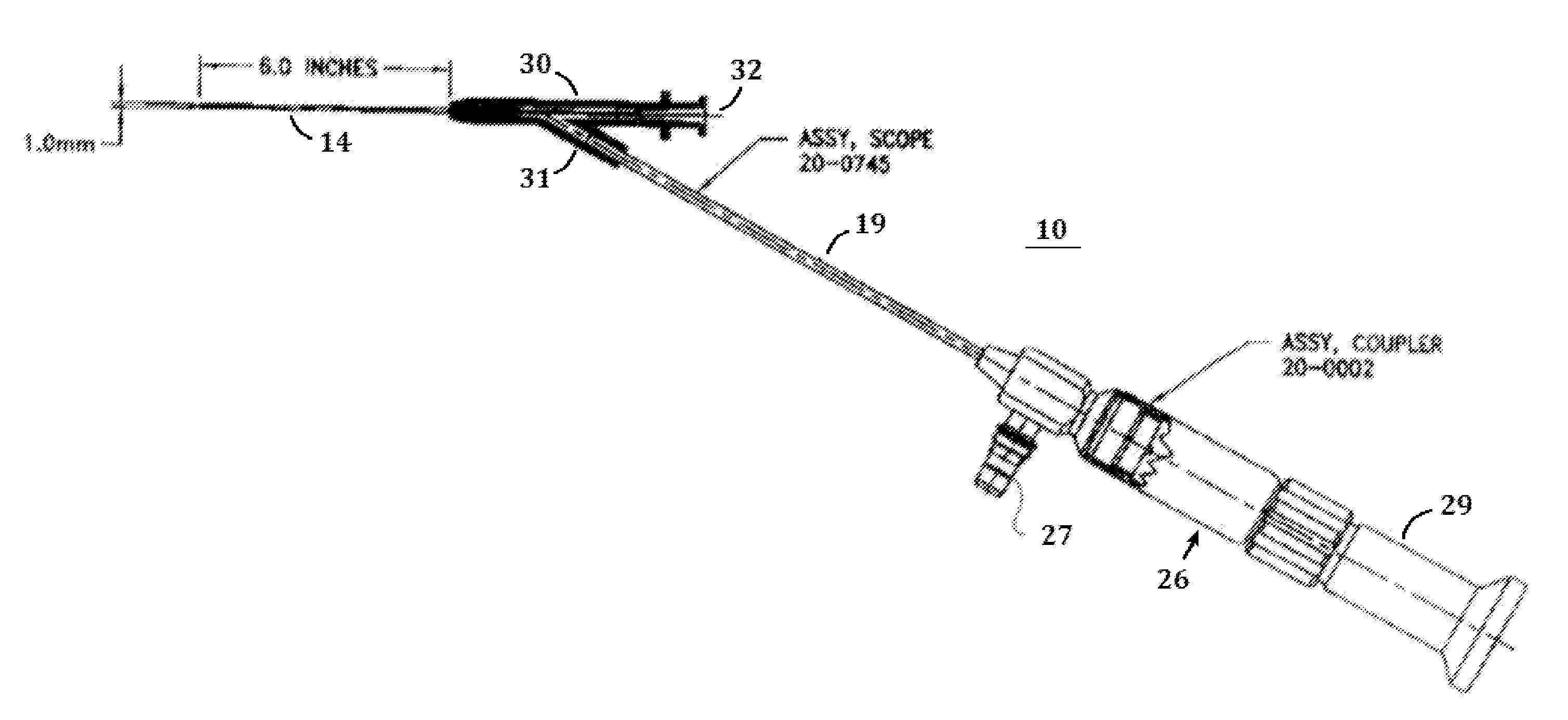
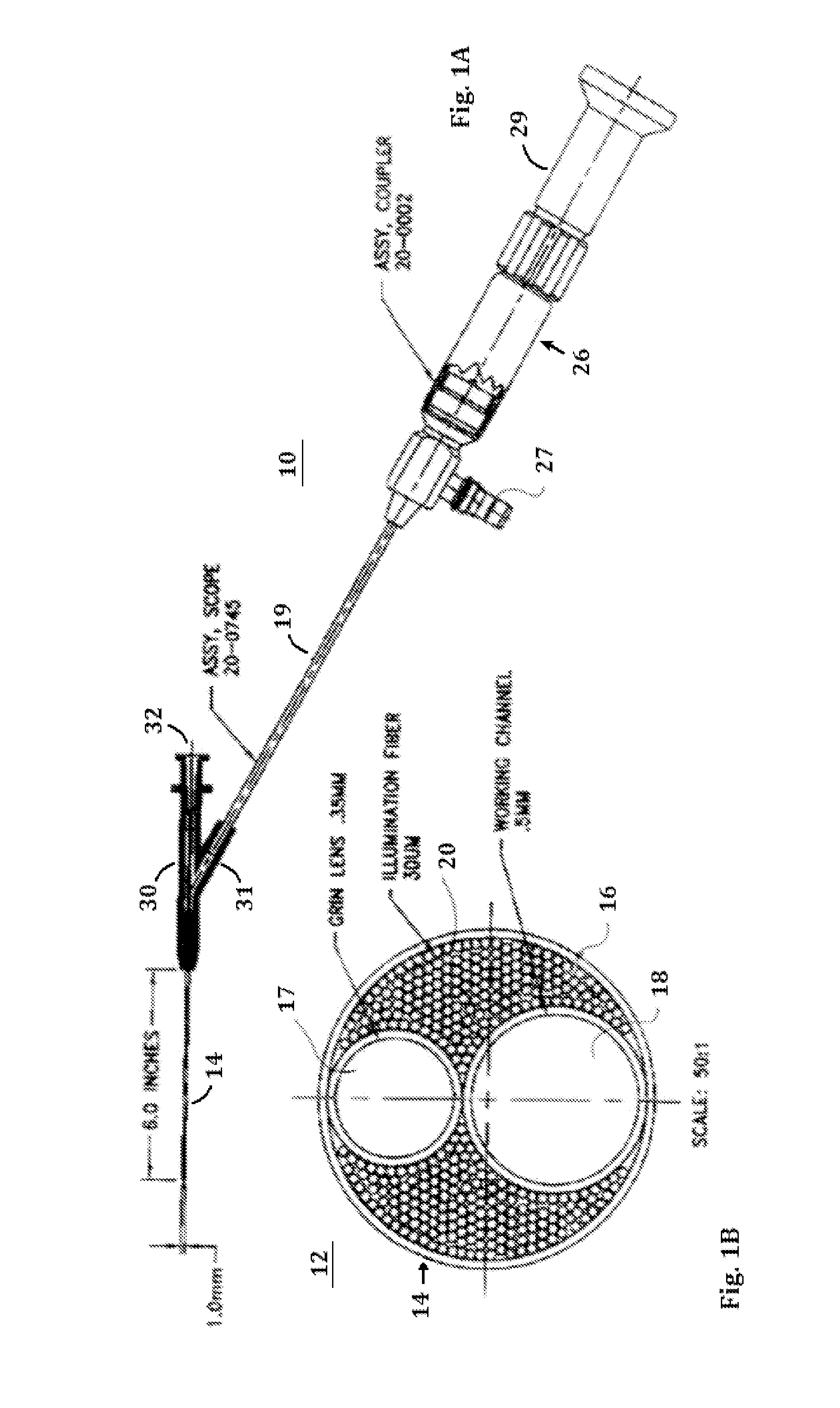
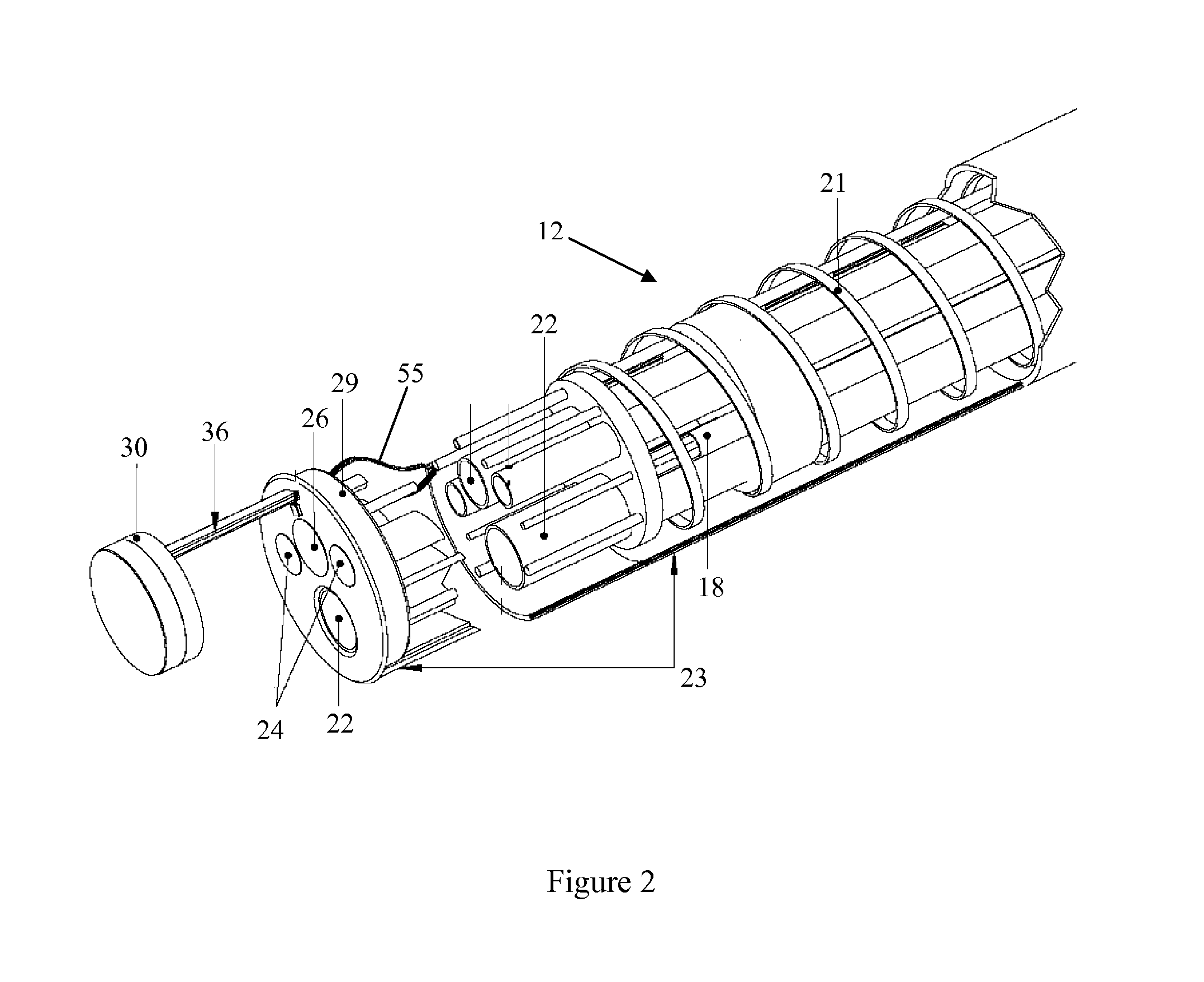
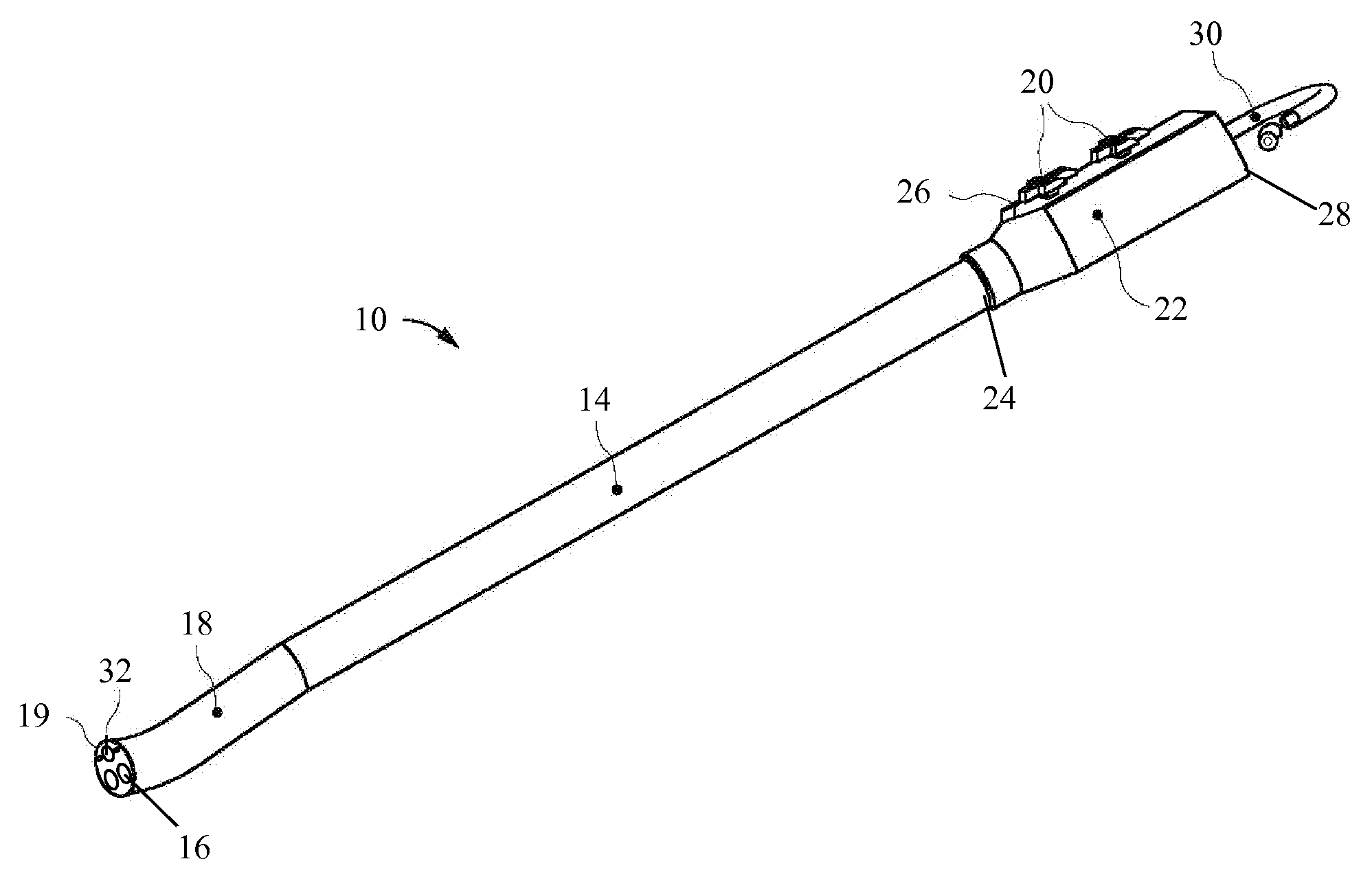
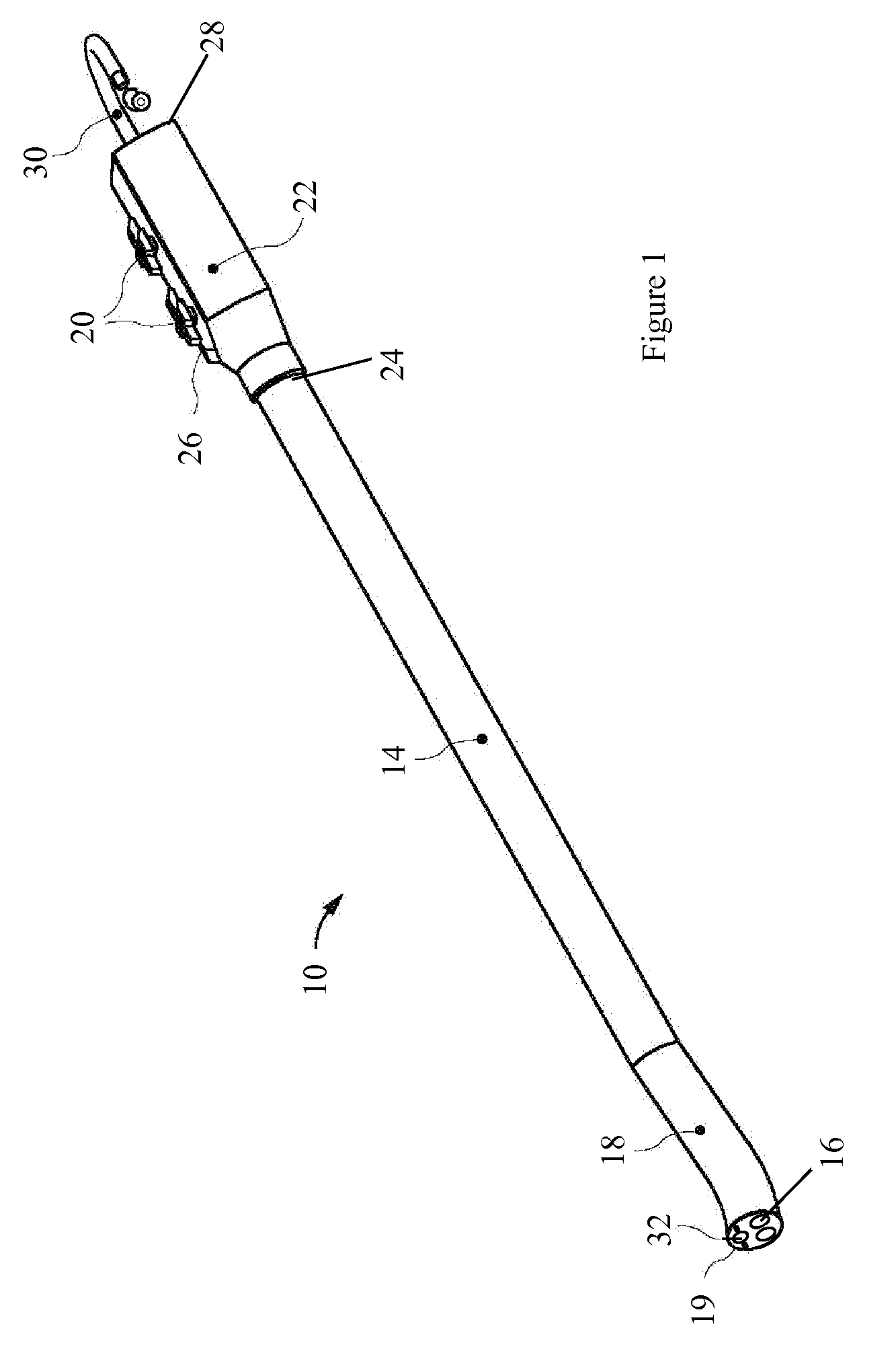
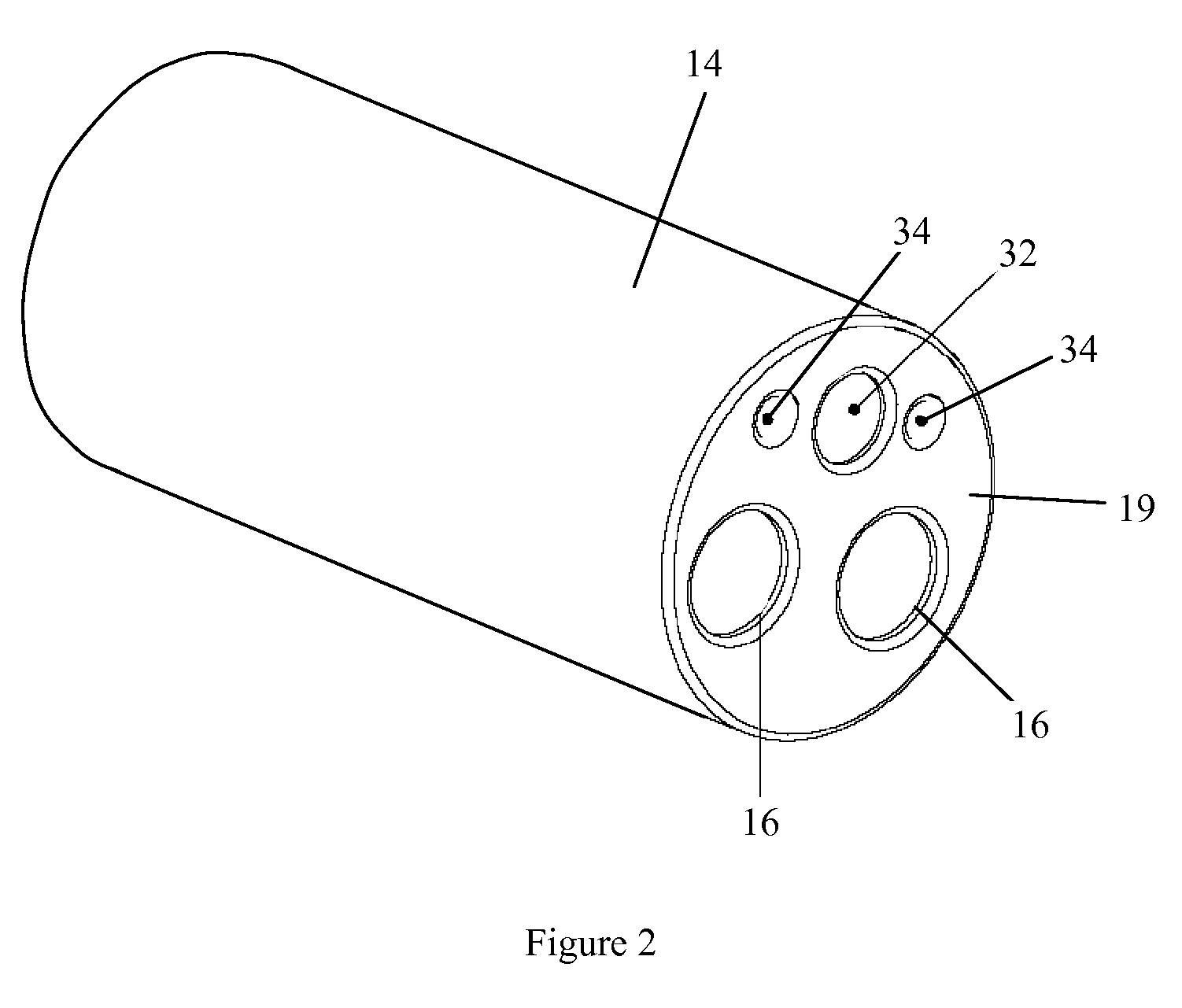
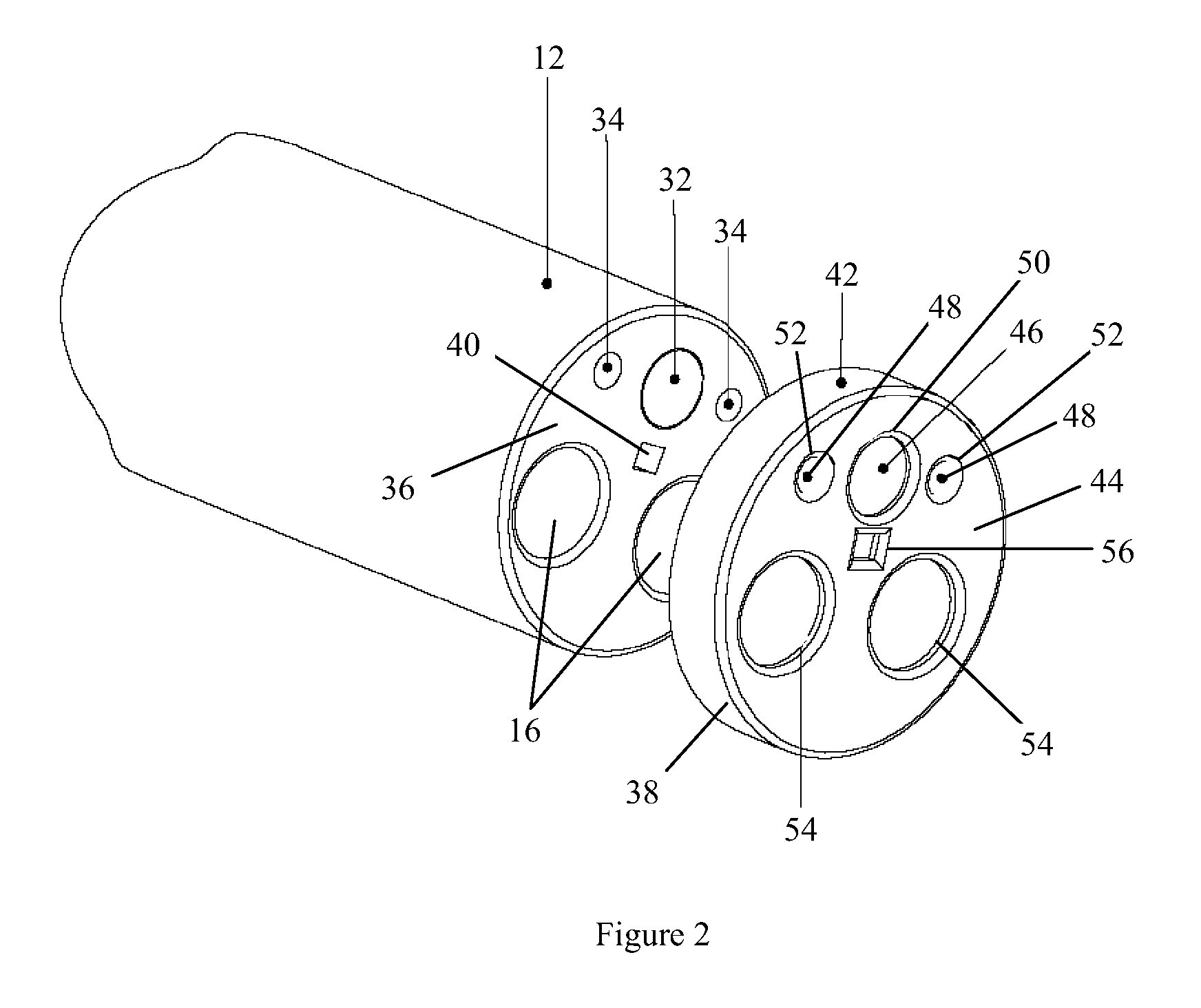
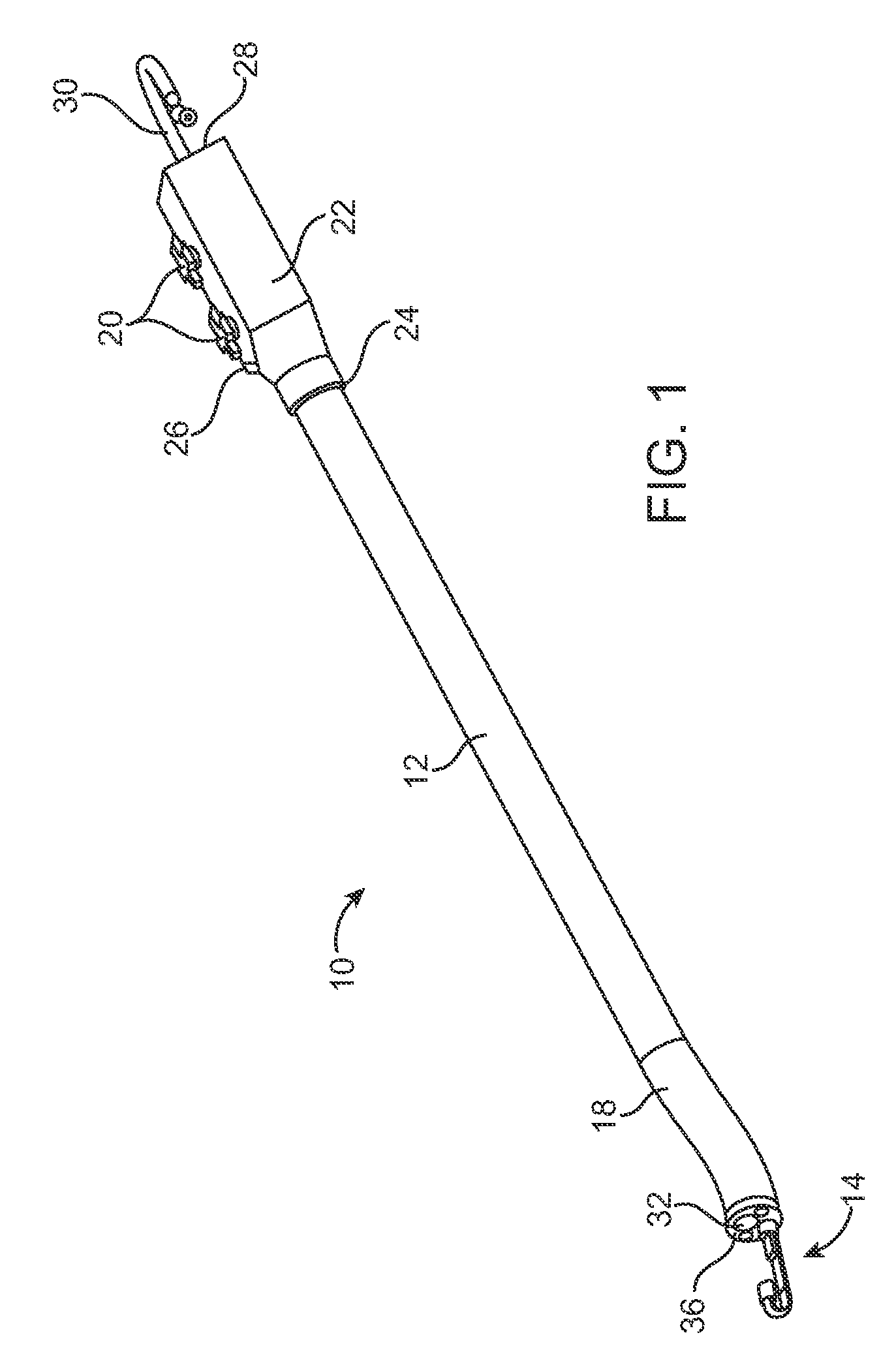
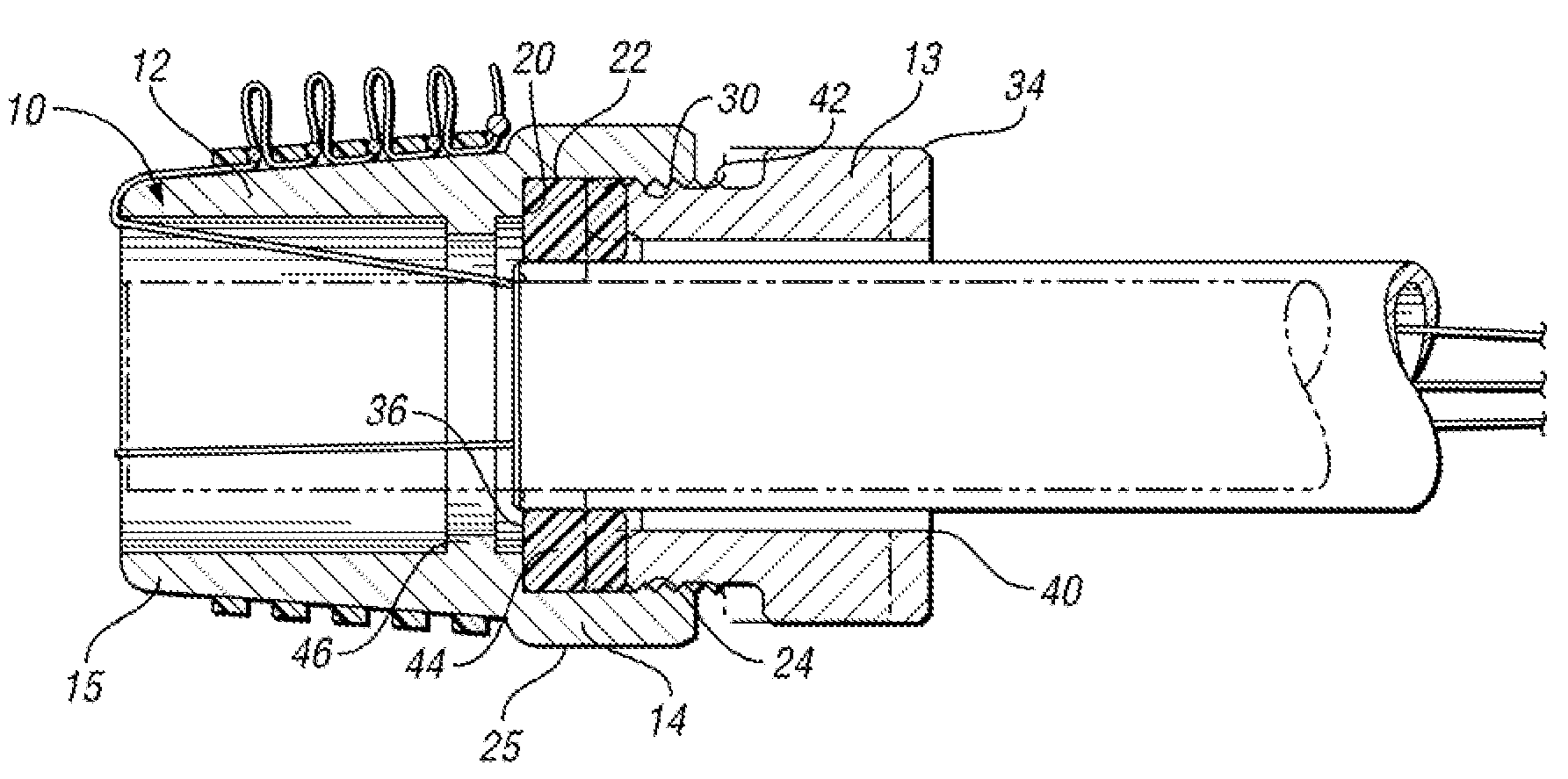
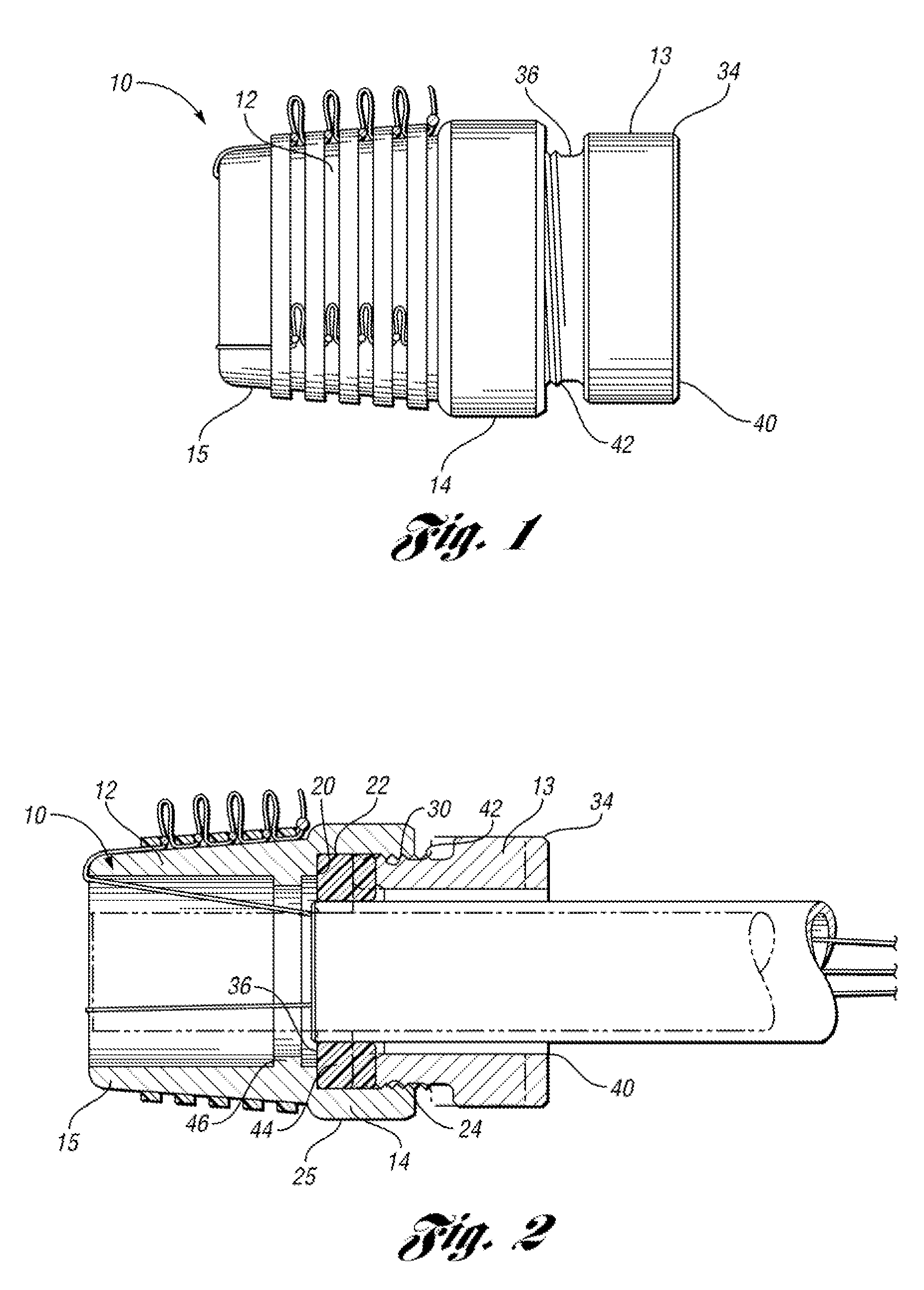
The endoscopic assembly may also include an endoscopic cap and an endoscopic sheath each including a body defining a first channel accommodating the endoscope and a plurality of second channels disposed around the first channel.
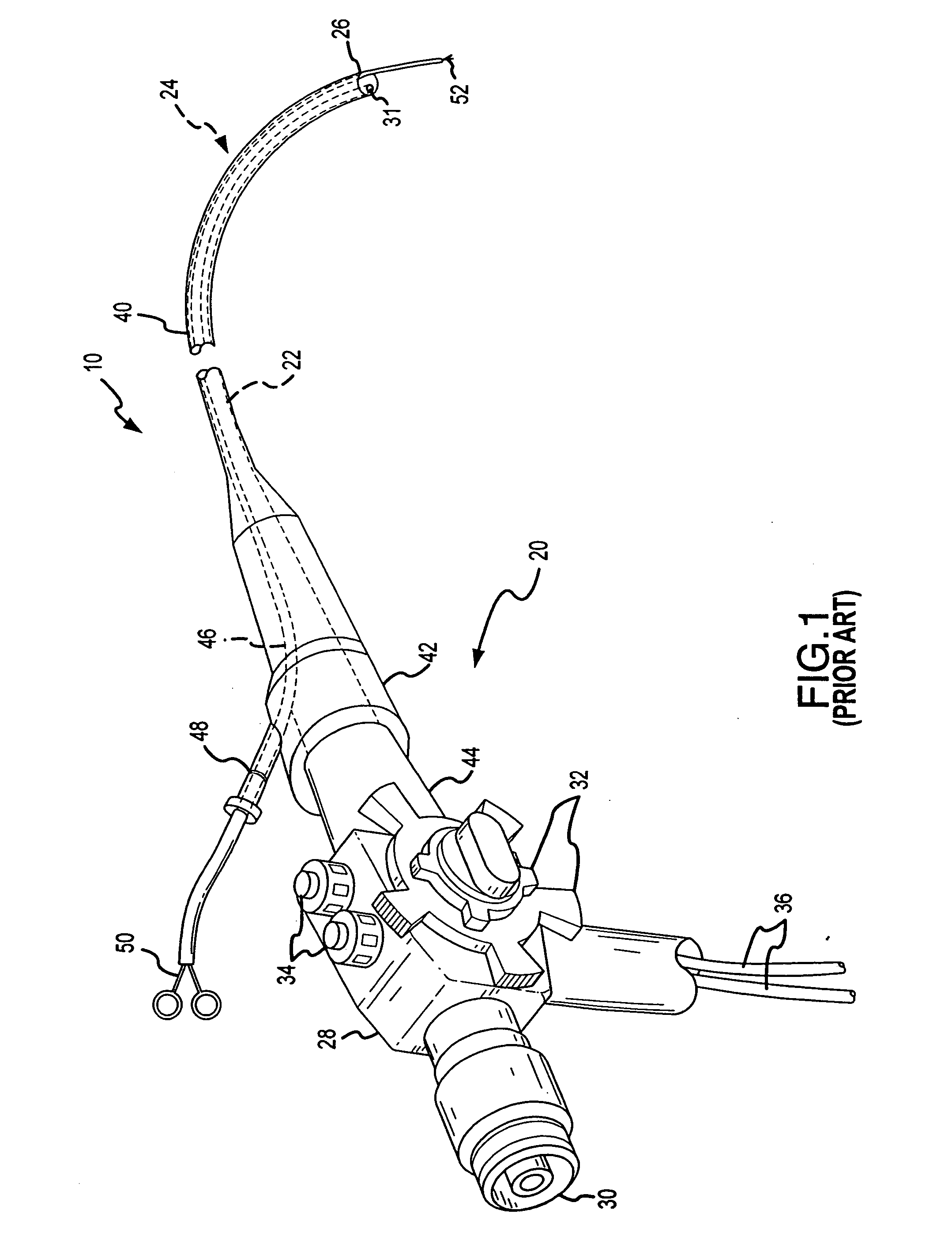
Endoscope assemblies having working channels with reduced bending and stretching resistance
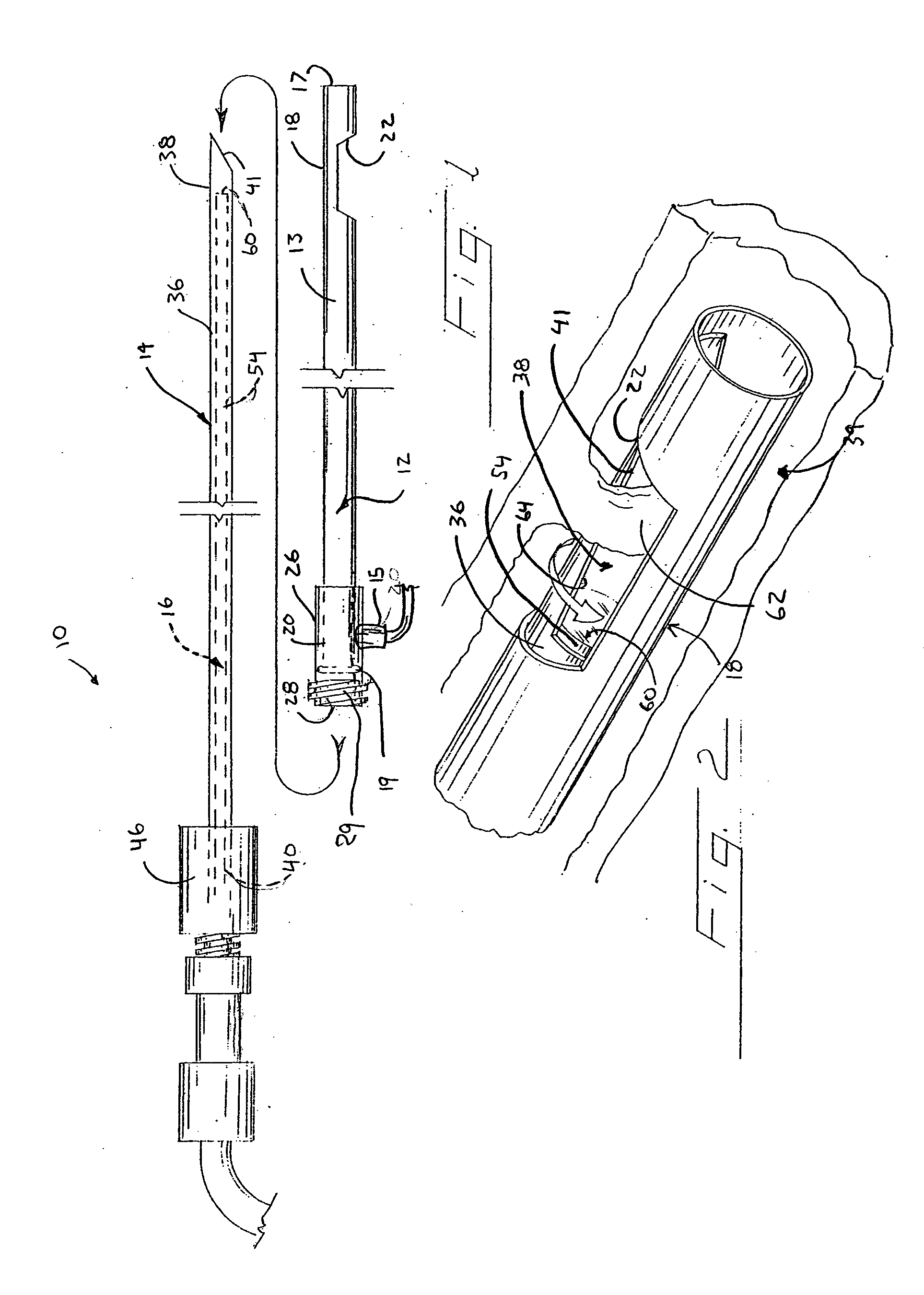
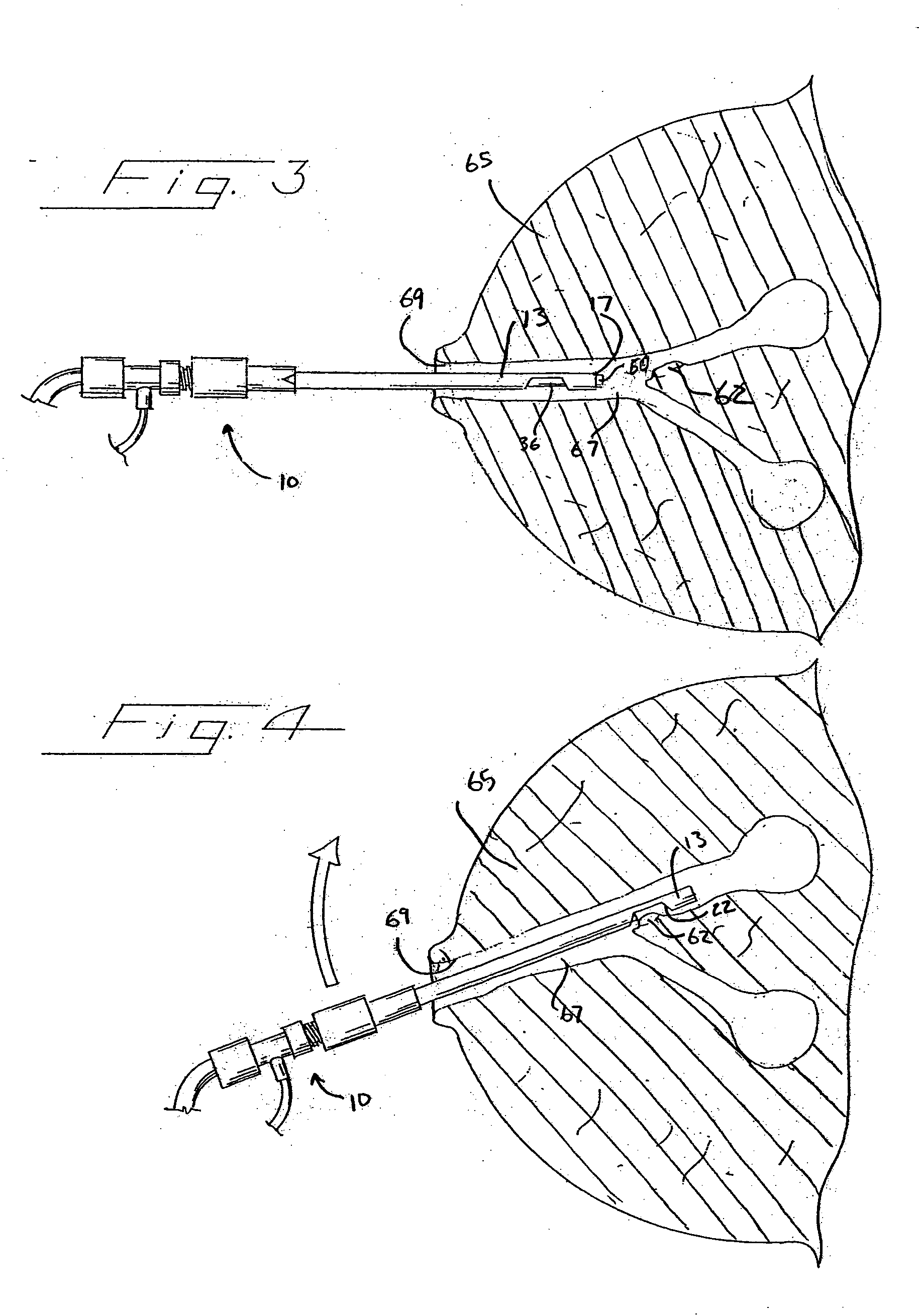
InactiveUS7056284B2Reduce bending and stretching resistanceReduce tensionSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAxial forceEngineering
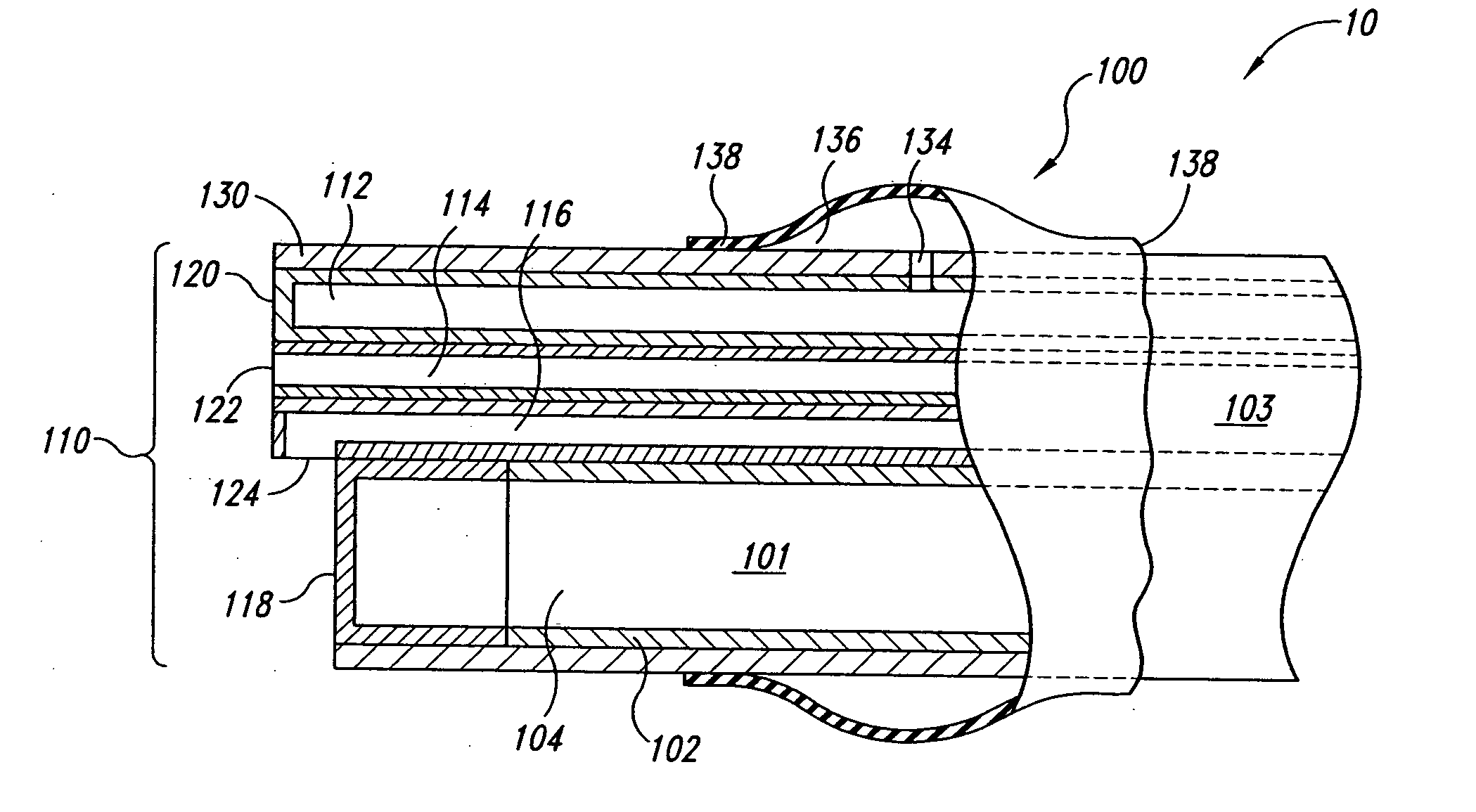
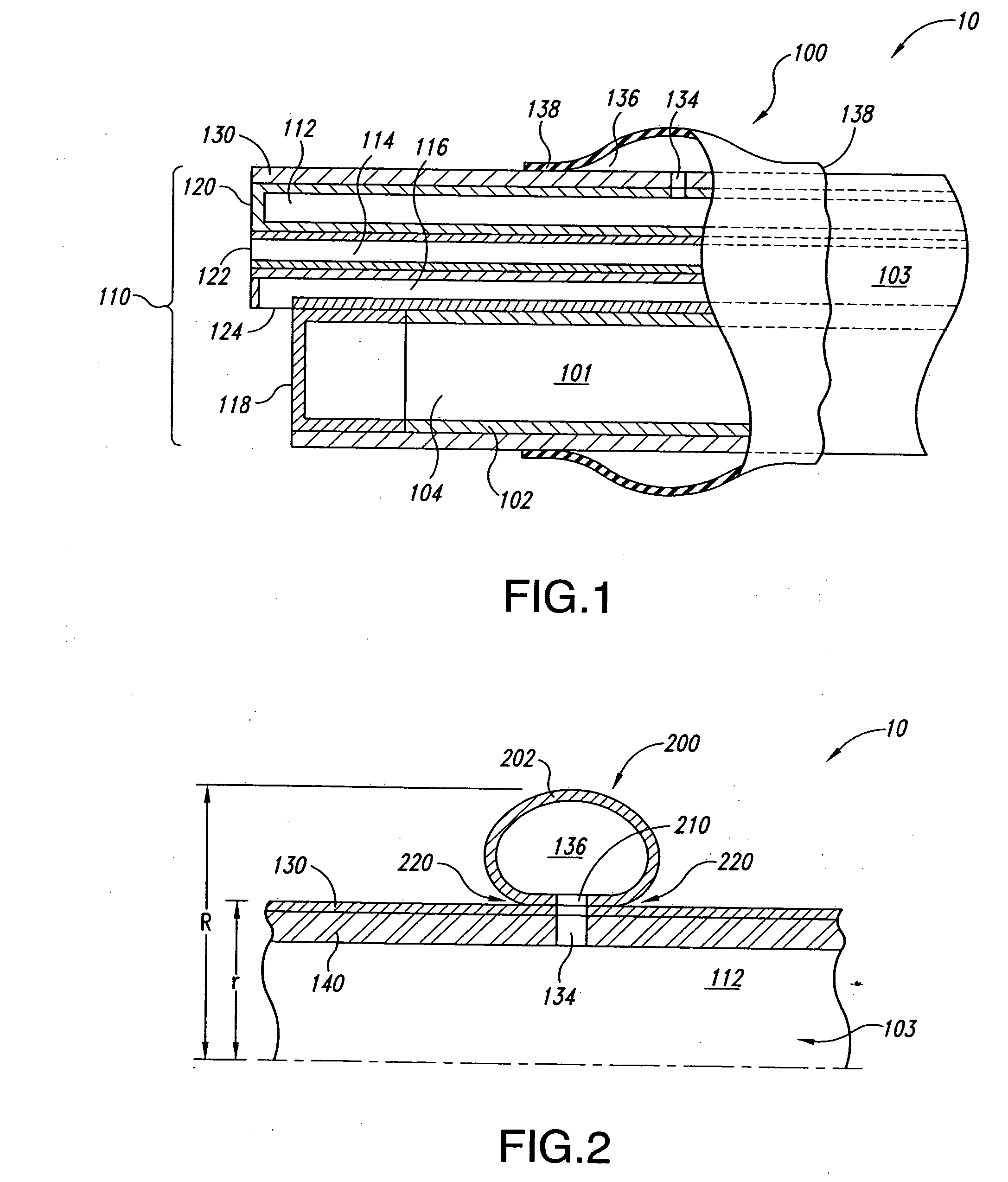
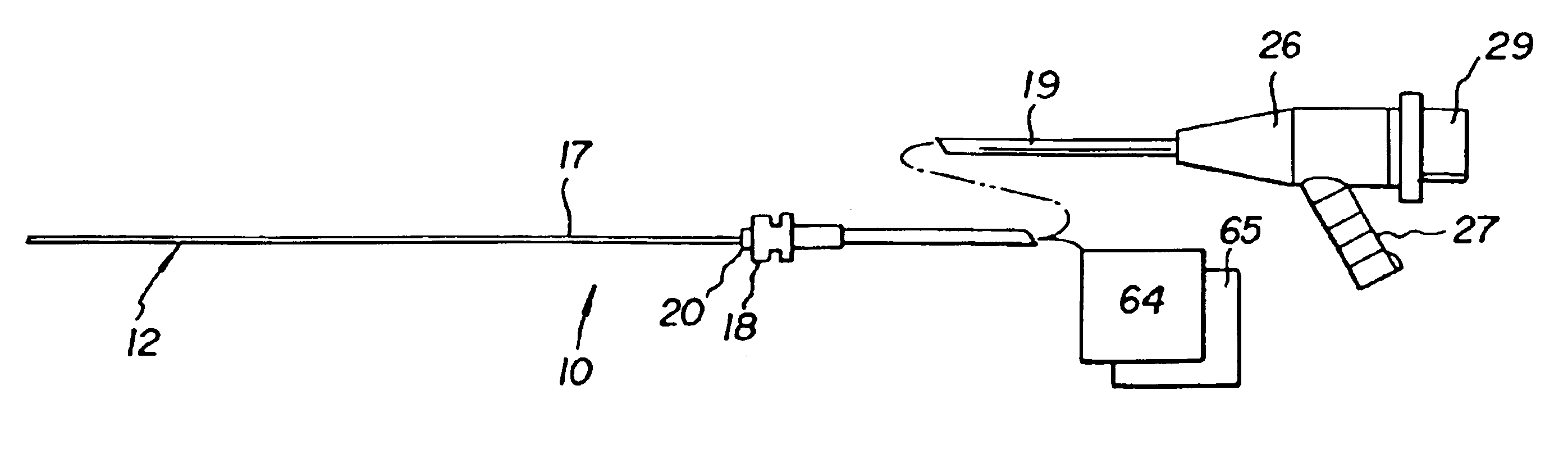
Apparatus and methods for endoscope assemblies having working channels with reduced bending and stretching resistance are disclosed. In one embodiment, an endoscope assembly includes a sheath having a body portion adapted to at least partially encapsulate an endoscopic insertion tube, and a working channel attached to the body portion and extending along at least a portion of the body portion. The working channel includes a component for reducing the resistance of the assembly to bending and stretching. In alternate aspects, the working channel may include a cut, a gap, a sliding portion, or an expansion section. Endoscope assemblies having a working channel in accordance with the invention advantageously reduce the articulation and stretching resistance of the assembly during articulation of the endoscope assembly. Also, because the axial forces (tension and compression) within the working channel are reduced, the working channel can be fabricated out of a relatively hard, inelastic material, thereby reducing the friction within the working channel and improving the physician's ability to perform a medical procedure.
Owner:COGENTIX MEDICAL
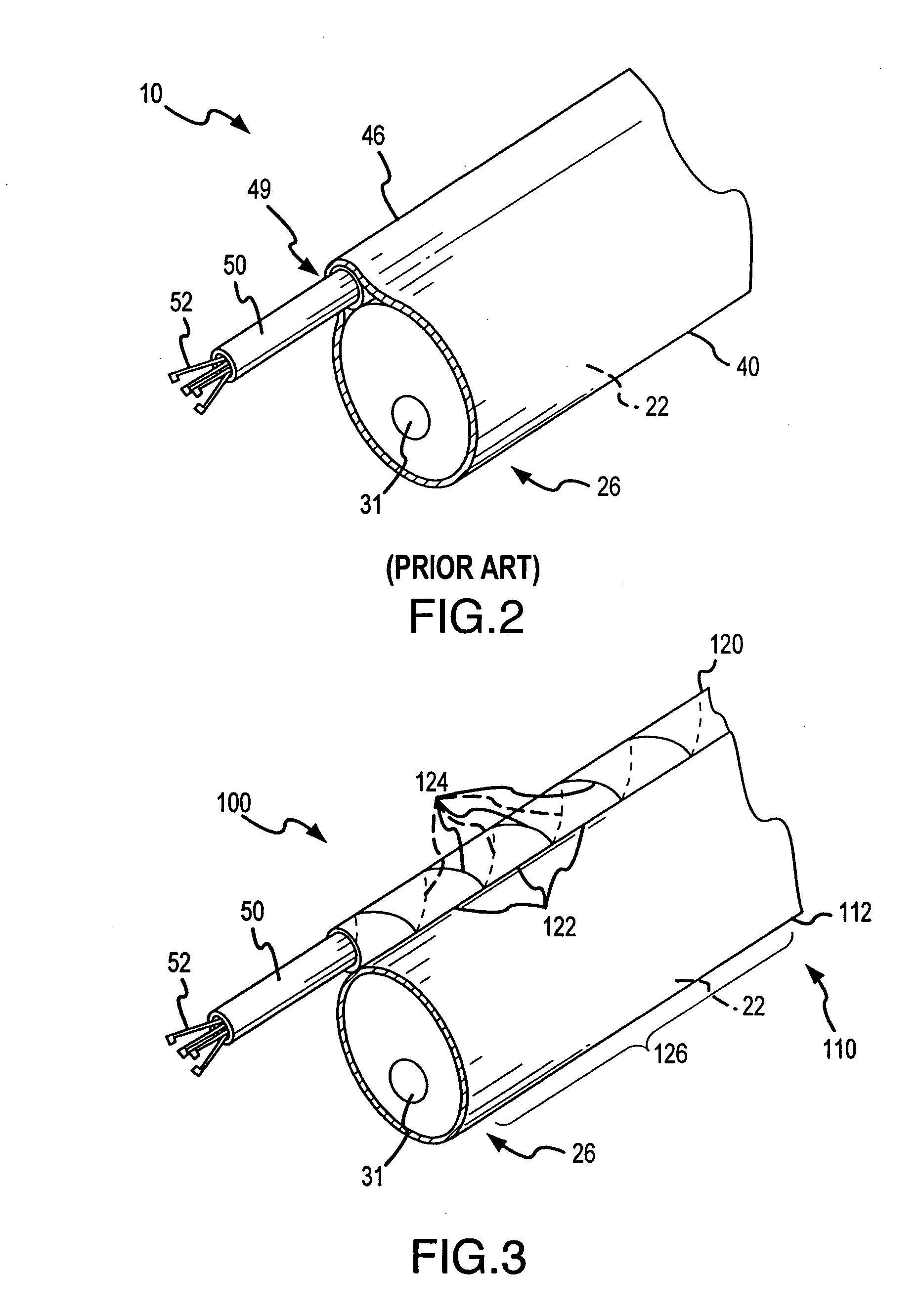
Endoscope assemblies having working channels with reduced bending and stretching resistance
InactiveUS20060079735A1Reduce bendingReduce stretch resistanceSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsElectrical resistance and conductanceAxial force
Apparatus and methods for endoscope assemblies having working channels with reduced bending and stretching resistance are disclosed. In one embodiment, an endoscope assembly includes a sheath having a body portion adapted to at least partially encapsulate an endoscopic insertion tube, and a working channel attached to the body portion and extending along at least a portion of the body portion. The working channel includes a component for reducing the resistance of the assembly to bending and stretching. In alternate aspects, the working channel may include a cut, a gap, a sliding portion, or an expansion section. Endoscope assemblies having a working channel in accordance with the invention advantageously reduce the articulation and stretching resistance of the assembly during articulation of the endoscope assembly. Also, because the axial forces (tension and compression) within the working channel are reduced, the working channel can be fabricated out of a relatively hard, inelastic material, thereby reducing the friction within the working channel and improving the physician's ability to perform a medical procedure.
Owner:MARTONE STEPHEN +1
Endoscope having detachable imaging device and method of using
An endoscope assembly with a main imaging device and a first light source is configured to provide a forward view of a body cavity, and further includes a detachable imaging device with an attachment member engageable with the distal end region of the endoscope, a linking member connected to the attachment member, and an imaging element with a second light source, wherein the detachable imaging device provides a retrograde view of the body cavity and the main imaging device. Light interference is reduced by using polarizing filters or by alternating the on / off state of the main imaging device, the first light source, the imaging element and the second light source so that the main imaging device and first light source are on when the imaging element and second light source are off and the main imaging device and first light source are off when the imaging element and second light source are on.
Owner:PSIP LLC
Endoscope assembly with a polarizing filter
An endoscope includes an imaging device, a first polarizing filter disposed in front of the imaging device, a light source, and a second polarizing filter disposed in front of the light source. The planes of polarization of the first and second polarizing filters are at a substantially 90° angle.
Owner:PSIP LLC
Endoscope Assembly and Method of Performing a Medical Procedure
An endoscope assembly includes (1) an endoscope that includes a tubular body, a retrograde-viewing imaging device disposed at a distal end region of the tubular body, and a channel extending through the tubular body; and (2) an instrument extending through the channel of the endoscope and exits from a distal opening of the channel.
Owner:PSIP LLC
Endoscopic delivery of medical devices
InactiveUS20050288551A1Easy to installFallopian occludersEndoscopesEndoscopic AssemblyMedical device
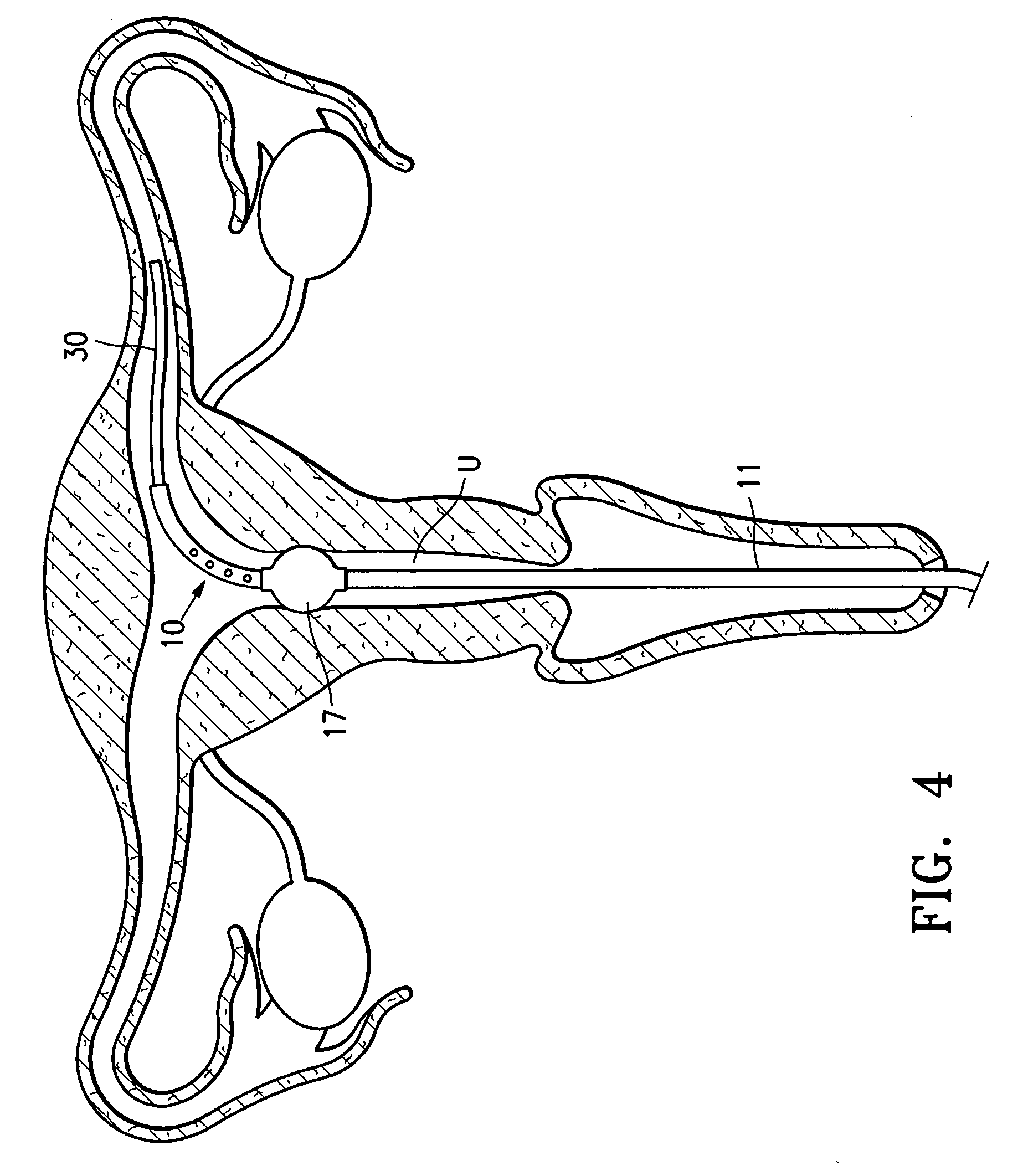
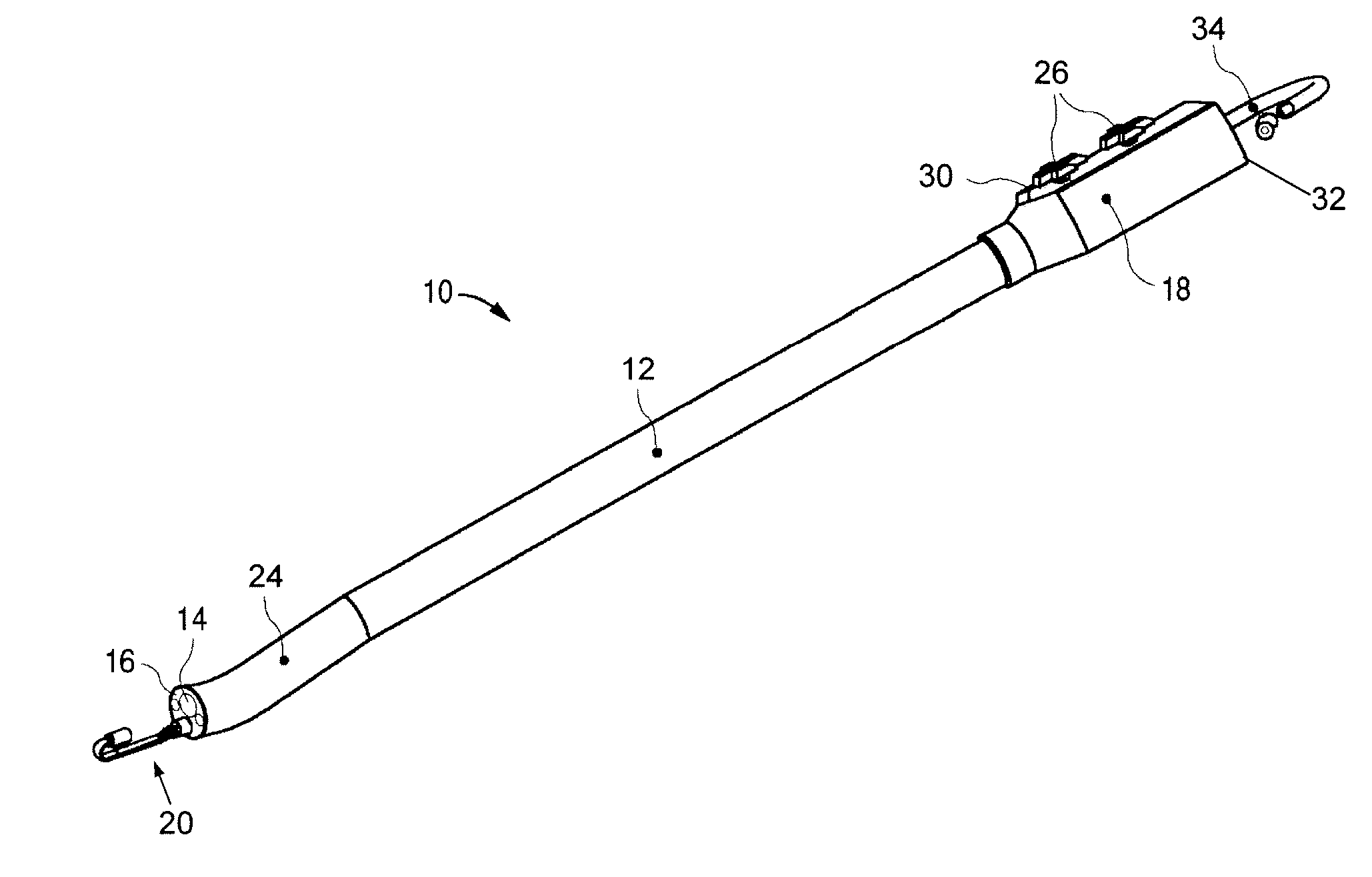
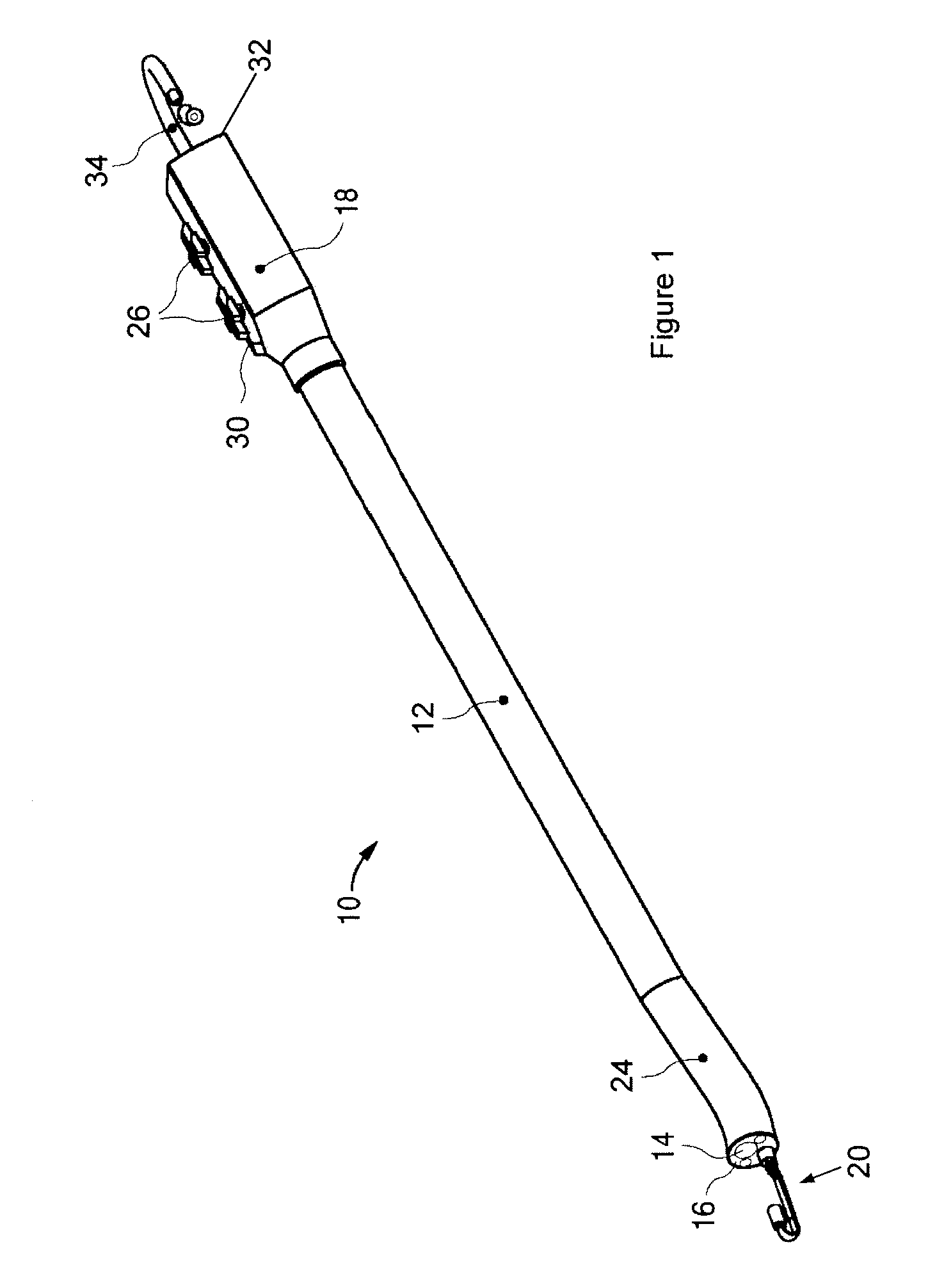
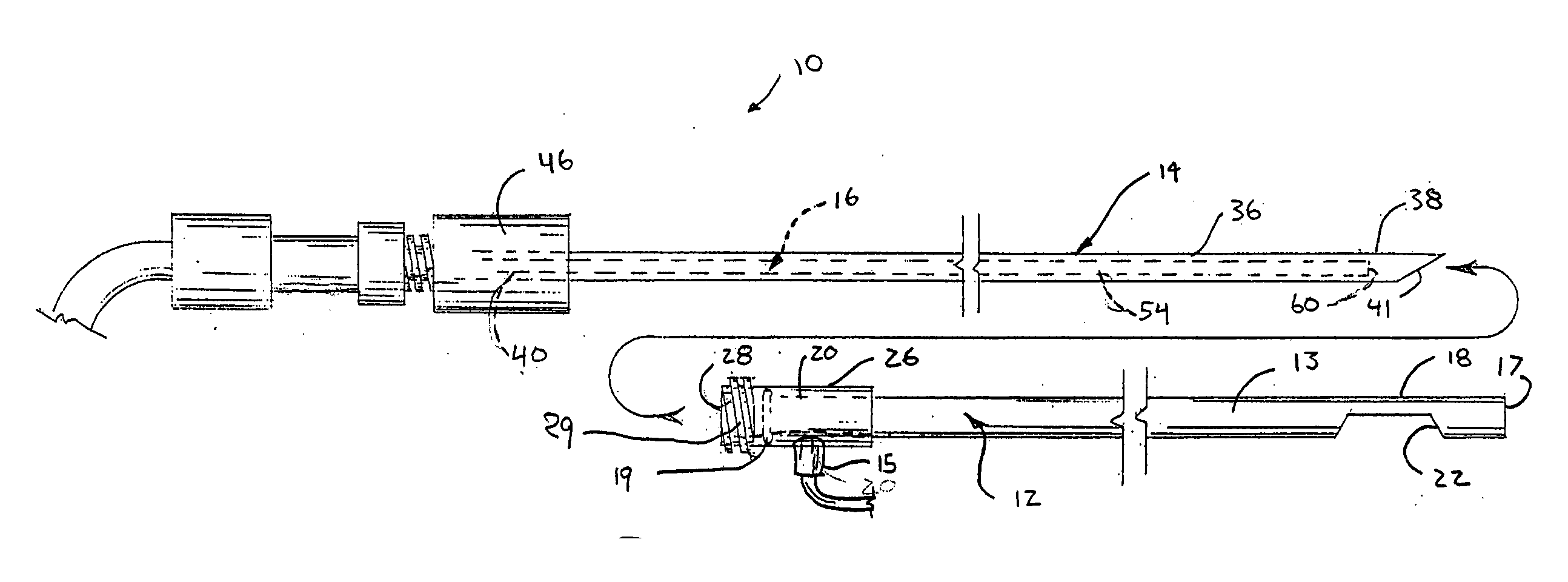
The invention is directed to an endoscopic assembly having an endoscope, particularly a flexible hysteroscope and an outer sheath disposed about a length of the shaft of the hysteroscope which has an expandable member such as an inflatable balloon for sealing the assembly within a body lumen or cavity. Specifically, the endoscope assembly is configured for delivery of an occlusive contraceptive member to the patient's fallopian tube. The invention is also directed to an endoscope having a driving member for movement of a medical device within the working lumen of an endoscope. In one embodiment the driving member is a friction wheel which engages an elongated medical device disposed within the working channel of the endoscope to effect longitudinal movement of the medical device.
Owner:BAYER ESSURE
Endoscope assembly and method of viewing an area inside a cavity
An endoscope assembly includes a first imaging device and a second imaging device, and the first and second imaging devices are positioned to provide different views of the same area at the same time. A method of viewing an area inside a cavity includes the step of using first and second imaging devices to view the same area inside a cavity at the same time.
Owner:PSIP LLC
Endoscope assembly with a polarizing filter
An endoscope includes an imaging device, a first polarizing filter disposed in front of the imaging device, a light source, and a second polarizing filter disposed in front of the light source.
Owner:PSIP LLC
Endoscope with remote control module or camera
InactiveUS20060293556A1Easy to operateImprove freedom of movementBronchoscopesDiagnostics using spectroscopyRemote controlEndoscopic Assembly
An endoscope with image-capture device remote from the probe is disclosed. The endoscope assembly has a probe, an illumination source such as one or more LEDs, and an image capture device located remotely from the probe such that the user does not have to bear the weight of the image capture device. In one embodiment the image-capture device is located in a control module with an image processor.
Owner:PERCEPTRONIX MEDICAL
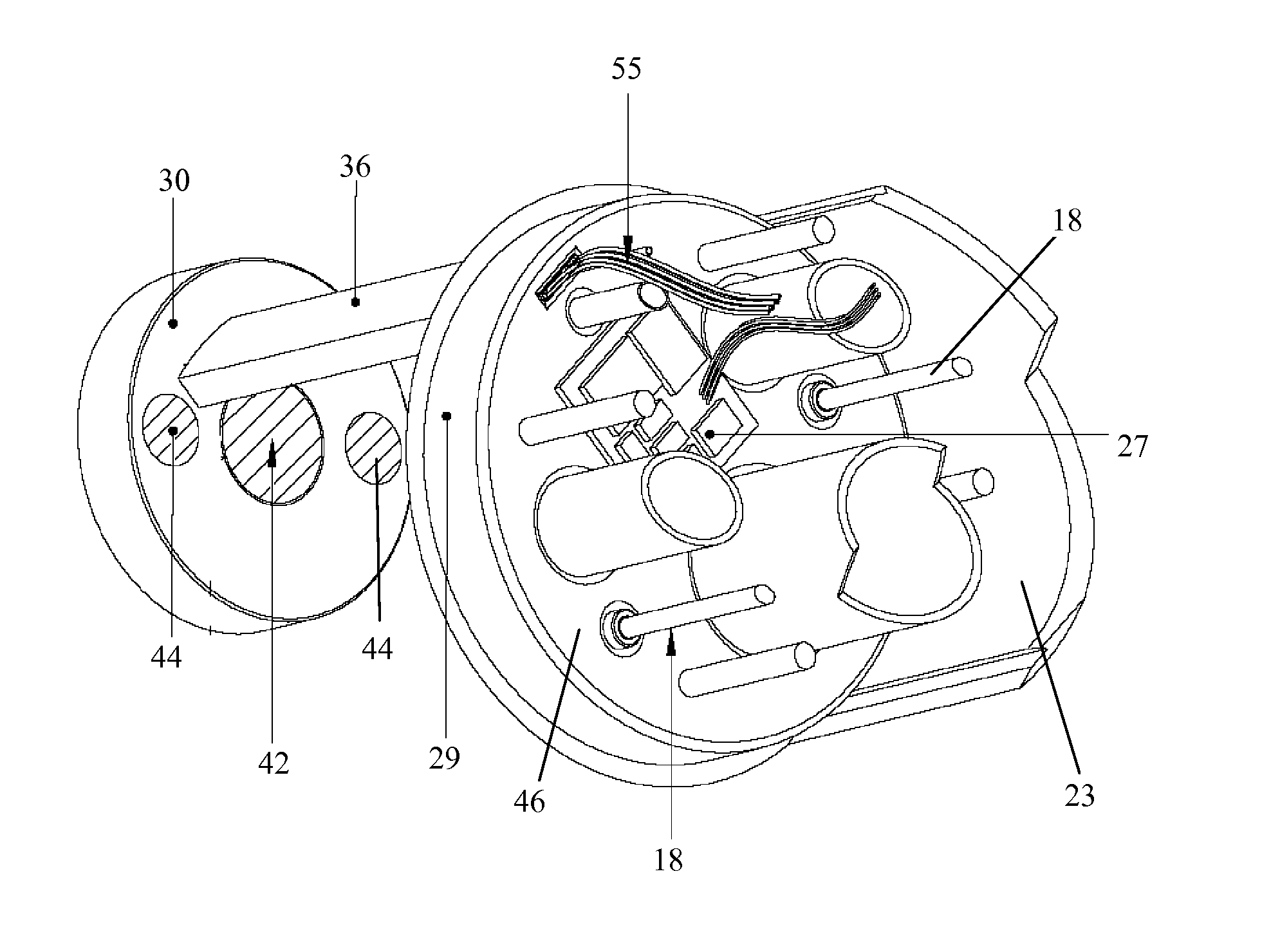
Endoscope assembly useful with a scope-sensing light cable
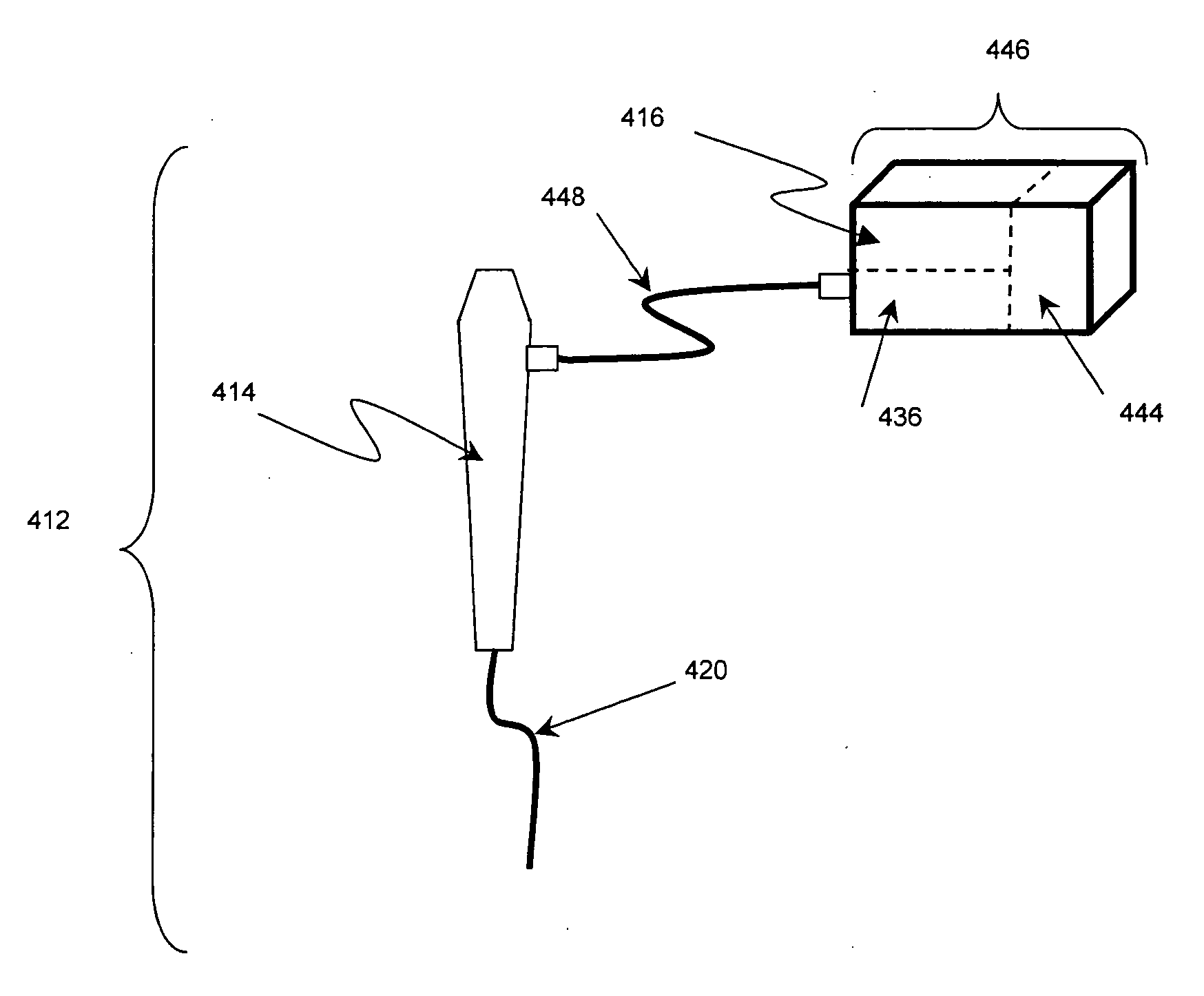
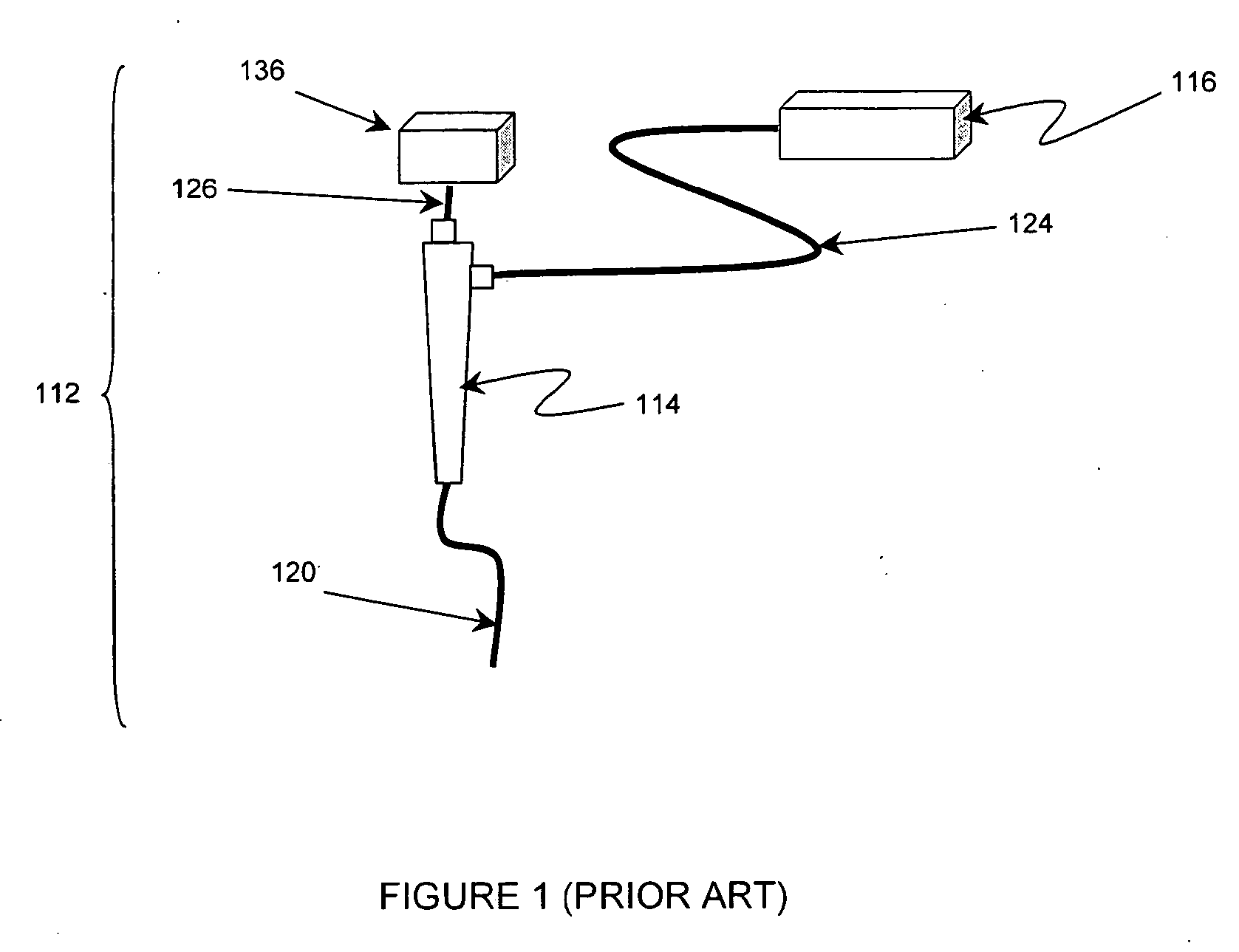
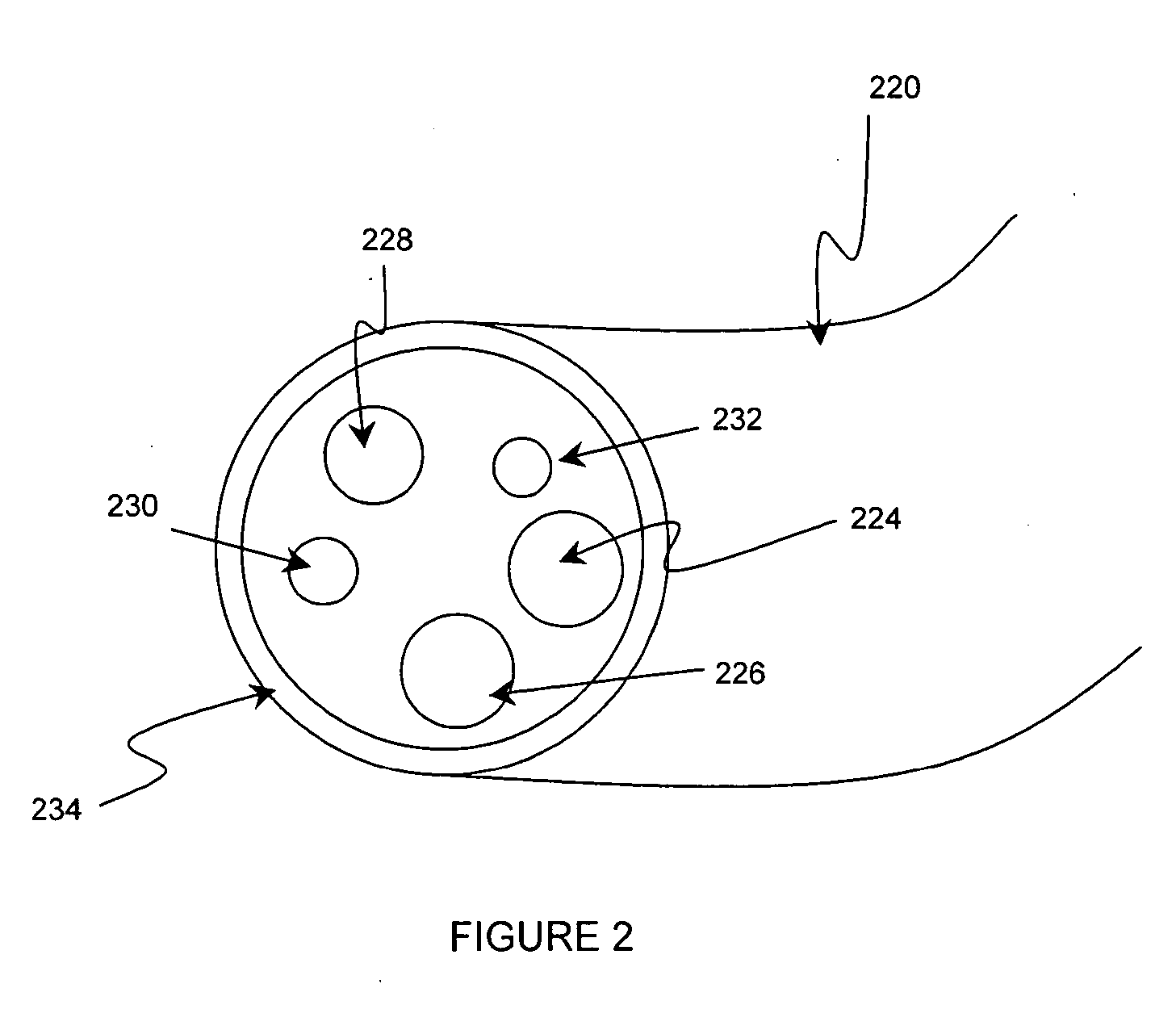
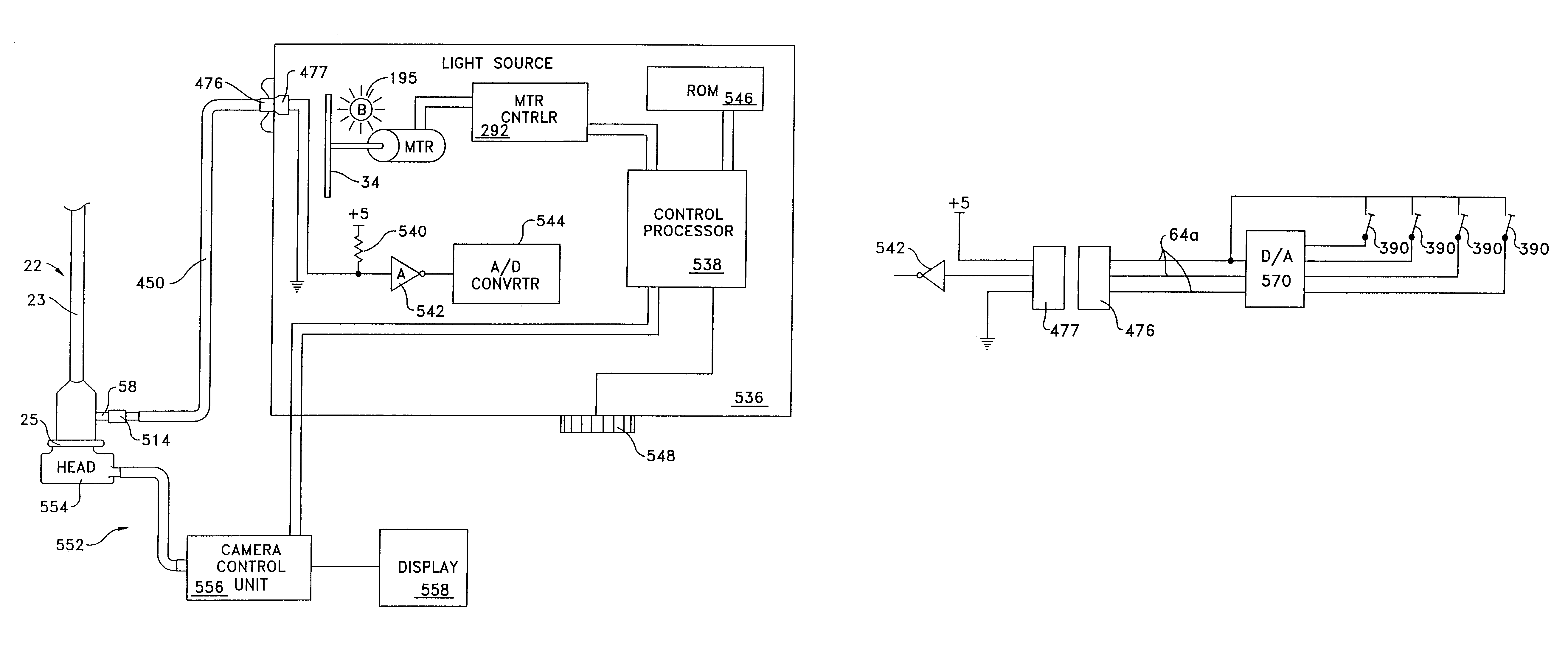
An endoscope assembly consisting of an endoscope 622, a light source, 626 and a camera 552 with display 558. The endoscope contains a memory 670 with data that describes the endoscope and its operating characteristics. When the light source is connected to the endoscope with a fiber optic cable 628, the data in the memory are read into a control processor 538a internal to the light source. The control processor, based on the endoscope data configures the light source so that it emits an appropriate amount of light for that endoscope. The light source also sends a control unit 556 of the camera data indicating the type of endoscope to which the camera is attached. Based on this endoscope type data, the control unit processes the image signals generated by the camera head in an appropriate form for the attached endoscope so as to produce appropriate signals for presenting an image on the display.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
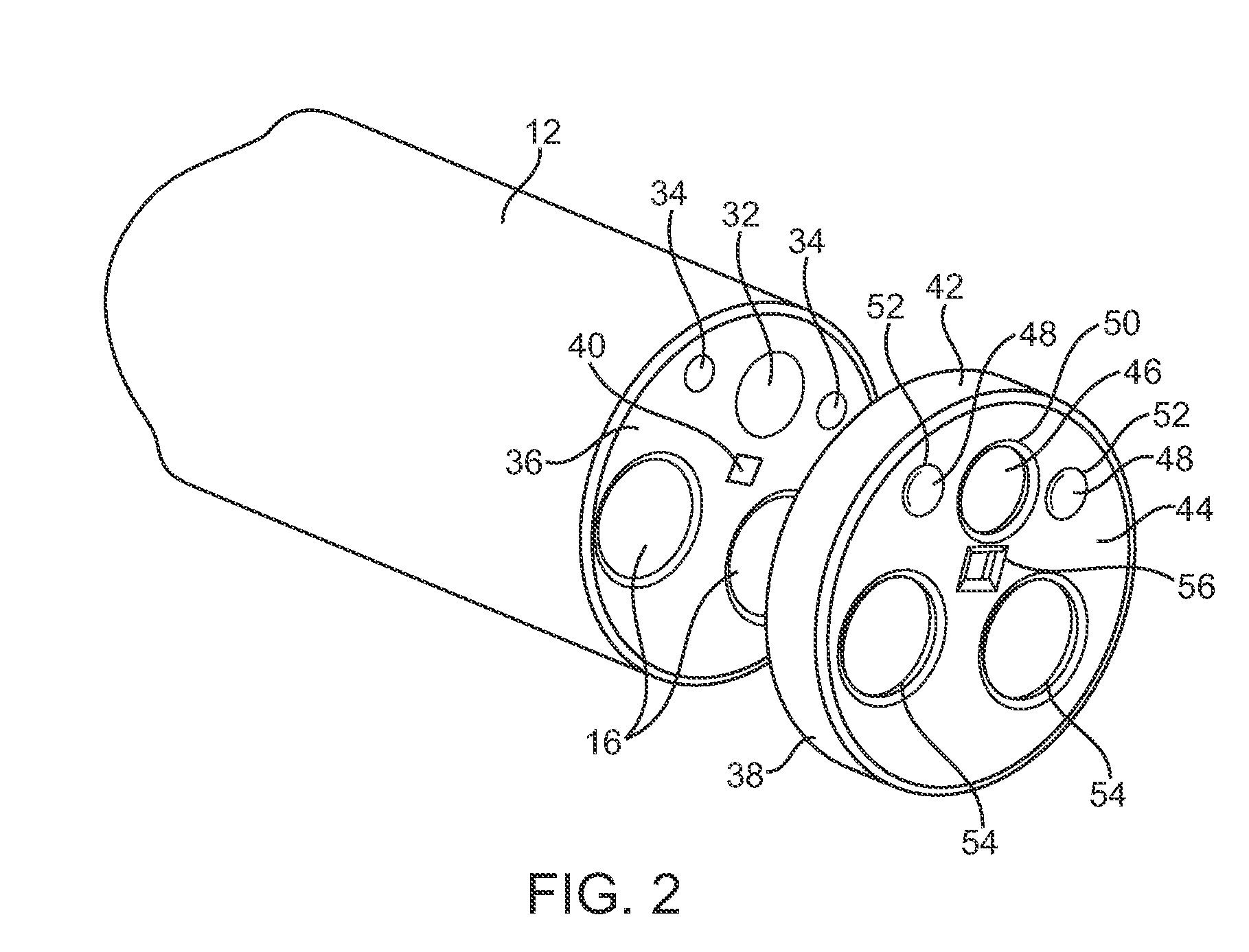
Inflatable member for an endoscope sheath
Apparatus and methods for attaching and forming enclosed inflatable members on an endoscope assembly with a disposable sheath are disclosed. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a flexible and resilient cuff member that is positioned on the outer surface of the disposable sheath and sealably and fixedly bonded to the sheath cover material at the cuff edges to form an annular space capable of being inflated. The inflatable member formed thereby is inflated through a lumen internal to the sheath that has an opening into the interior annular space. The inflatable member may be inflated to exert a longitudinal force on the insertion tube, thereby moving the endoscope assembly along a body passage. Alternately, a sheath may include a plurality of inflatable cuffs that may be inflated to create an isolated space therebetween within the body passage.
Owner:COGENTIX MEDICAL
Endoscope having microscopic and macroscopic magnification
InactiveUS6530882B1Resolving structureHigh resolutionSurgeryEndoscopesMacroscopic scaleMicroscopic exam
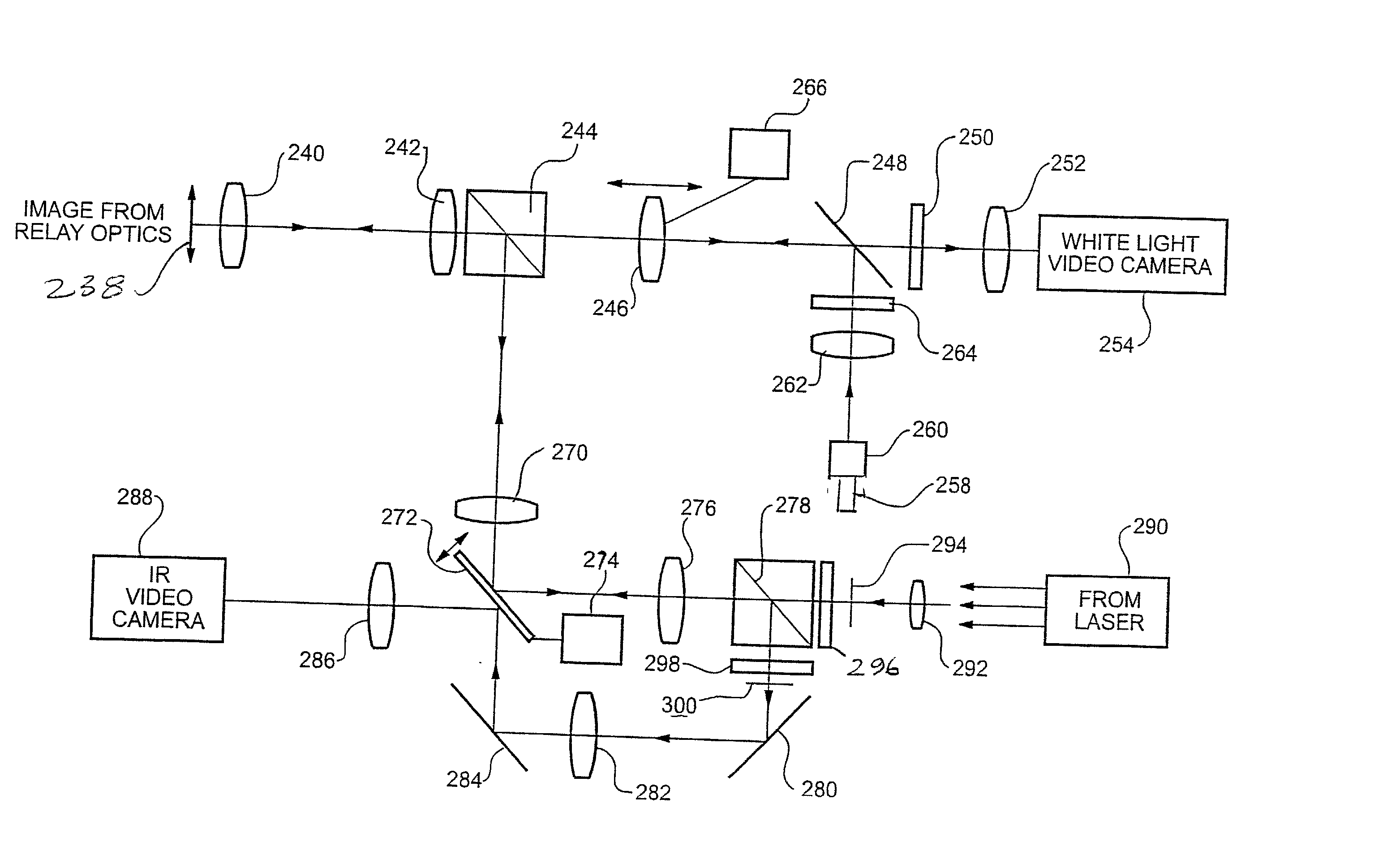
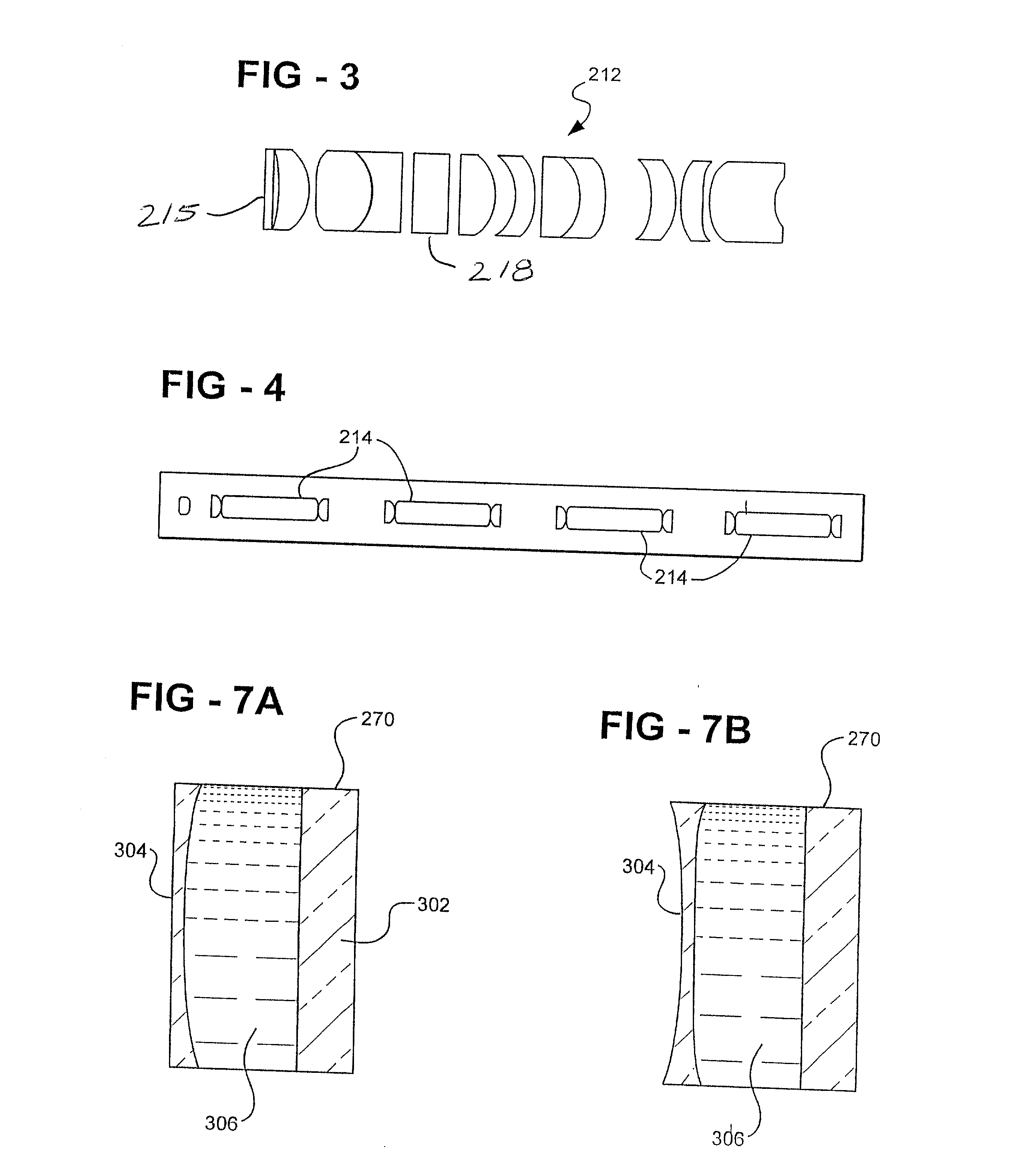
An endoscope assembly is disclosed having a housing adapted to be manipulated by medical personnel, such as a surgeon. An elongated lens tube has one end secured to the housing while an elongated stage is removably secured to the housing so that the stage encompasses and is coaxial with the tube. The stage together with the lens tube are adapted for insertion into the cavity of a body. A lens assembly provided within the lens tube relays the optical image from the free end of the stage to the housing. A lens assembly within the housing, furthermore, varies the magnification of the image between macroscopic magnification and microscopic magnification in which tissue may be examined on a cellular level. For macroscopic magnification, white light is transmitted through the lens tube as well as reflected back from the target tissue through the lens tube and to the housing. For microscopic examination, laser radiation is utilized in lieu of the white light illumination. A line scanning confocal assembly contained within the housing enables microscopic examination of the target tissue at varying levels into the tissue from the end of the stage.
Owner:INNER VISION IMAGING
Microendoscope and methods of use
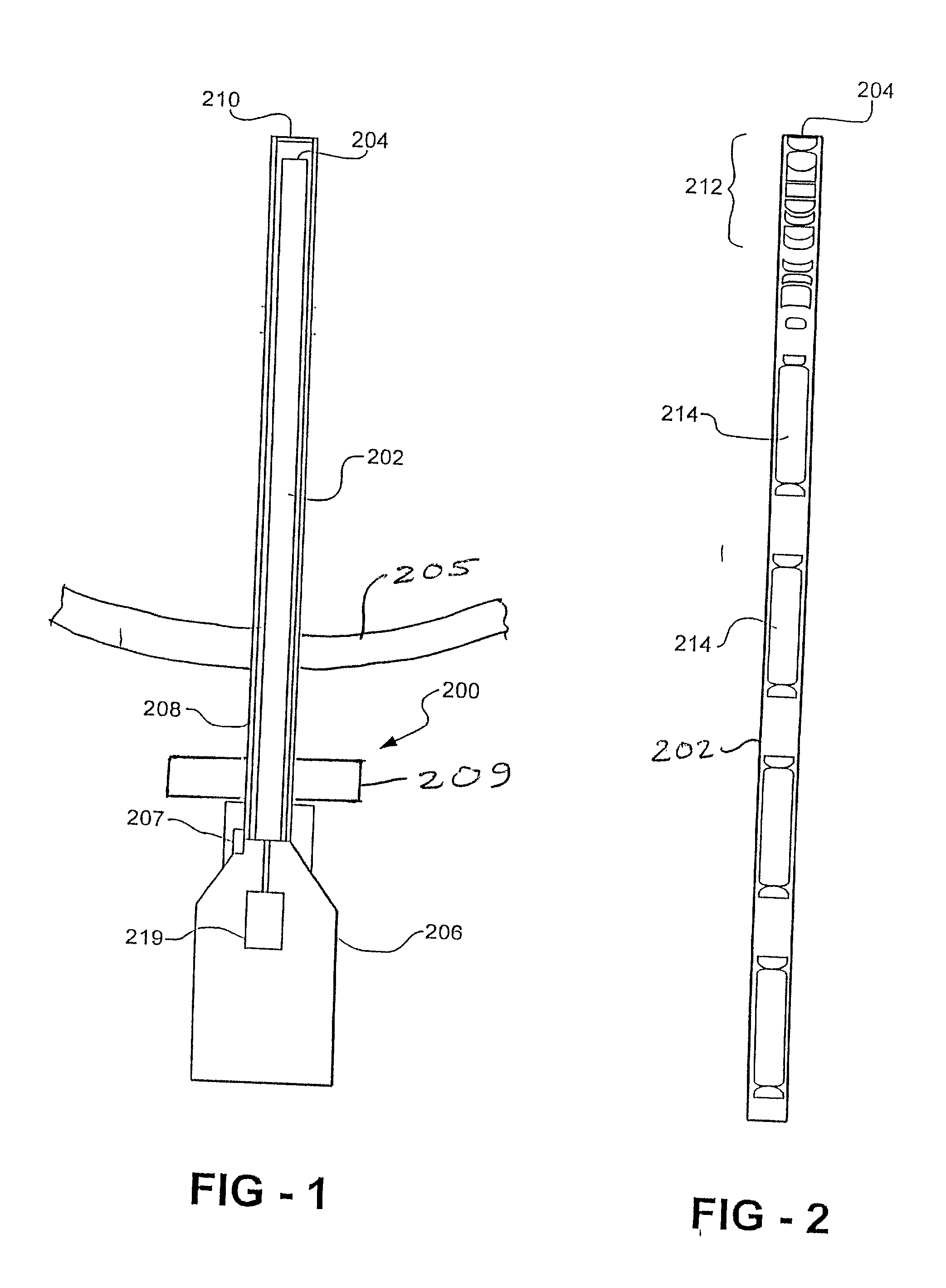
The present invention generally relates to a microendoscope assembly capable of intra-ductal use. The microendoscope generally comprises: an outer cylindrical guide tube defining an internal passageway having an exterior diameter of no greater than about 1.0 mm; a first internal cylindrical tube defining a working channel having an interior diameter of no less than about 0.5 mm; a second internal cylindrical tube defining a image guide and housing a lens; and an illumination bundle comprising optic fibers.
Owner:LUMINUS VENTURES
Endoscope assembly with retroscope
InactiveUS8235887B2Optimize locationLarge range of motionGastroscopesOesophagoscopesEndoscopic AssemblyEndoscope
An endoscope includes an insertion tube having a distal end and an imaging device with a steerable extension. The proximal end of the extension is attached to the distal end of the insertion tube. An endoscope includes an insertion tube having a distal end region and a rear-viewing imaging device at least partially disposed inside the distal end region. An endoscope includes an insertion tube having a distal end cap, an imaging device, and a link that couples the imaging device to the distal end cap of the insertion tube.
Owner:PSIP LLC
Method and apparatus for in VIVO treatment of mammary ducts by light induced fluorescence
The invention is directed toward a micro-endoscope assembly for the treatment of diseased tissue in breast ducts comprising a cylindrical guide tube with a distal end defining an internal cylindrical passageway, a first smaller cylindrical tube eccentrically formed in the cylindrical passageway of a smaller diameter than said tube internal cylindrical passageway to receive and guide an endoscope, the smaller cylindrical tube forming together with an inner wall surface of the cylindrical guide tube a second passageway. A light transmitting probe is mounted in the second passageway and is connected at the distal end of the guide tube with an energy transmitting device. The light probe is activated to generate light at a particular wavelength to cause the tissue to fluoresce and is again activated to generate light at a specific wavelength to necrose the diseased tissue.
Owner:LACHOWICZ THEODORE COLLATERAL AGENT
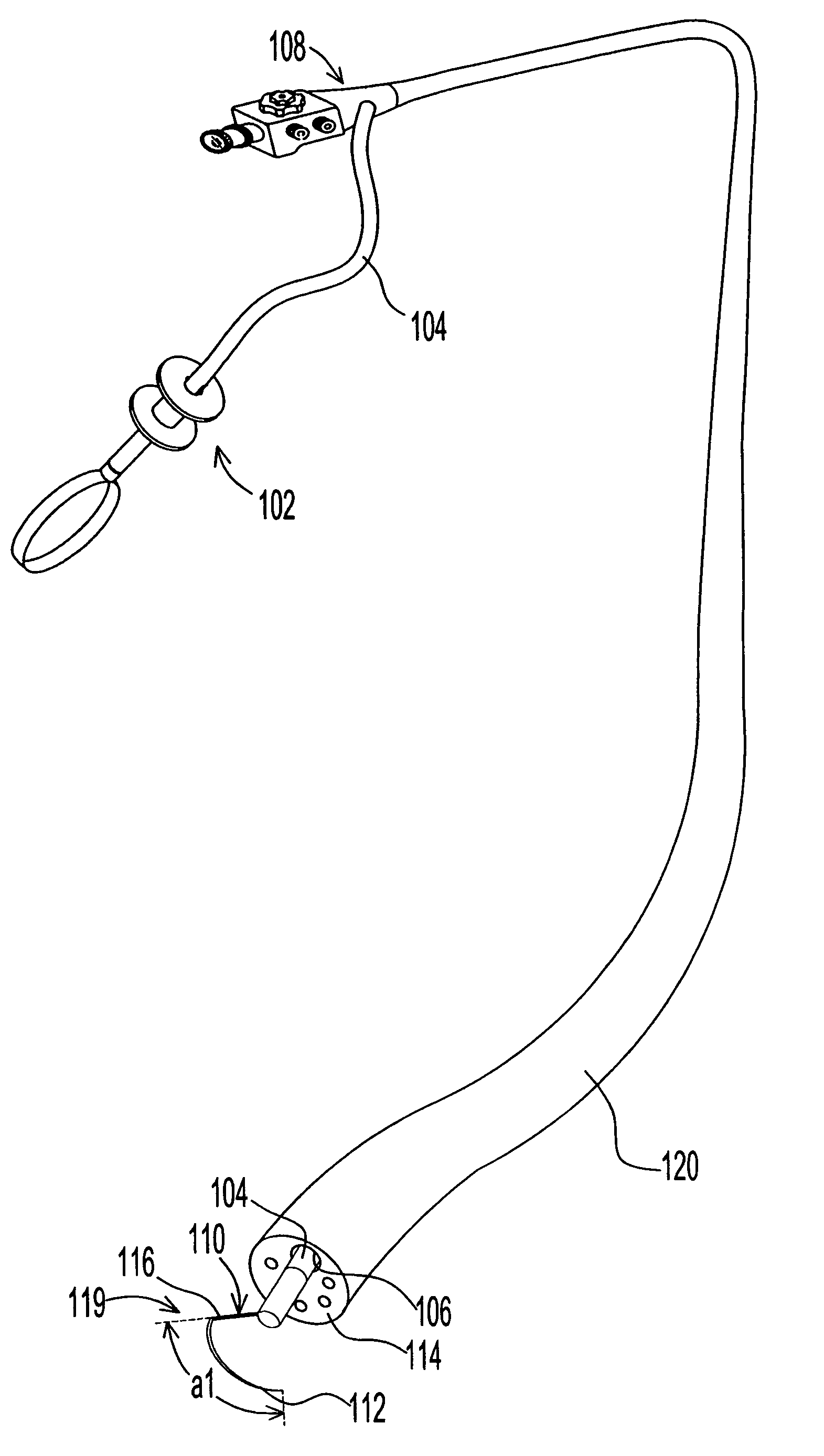
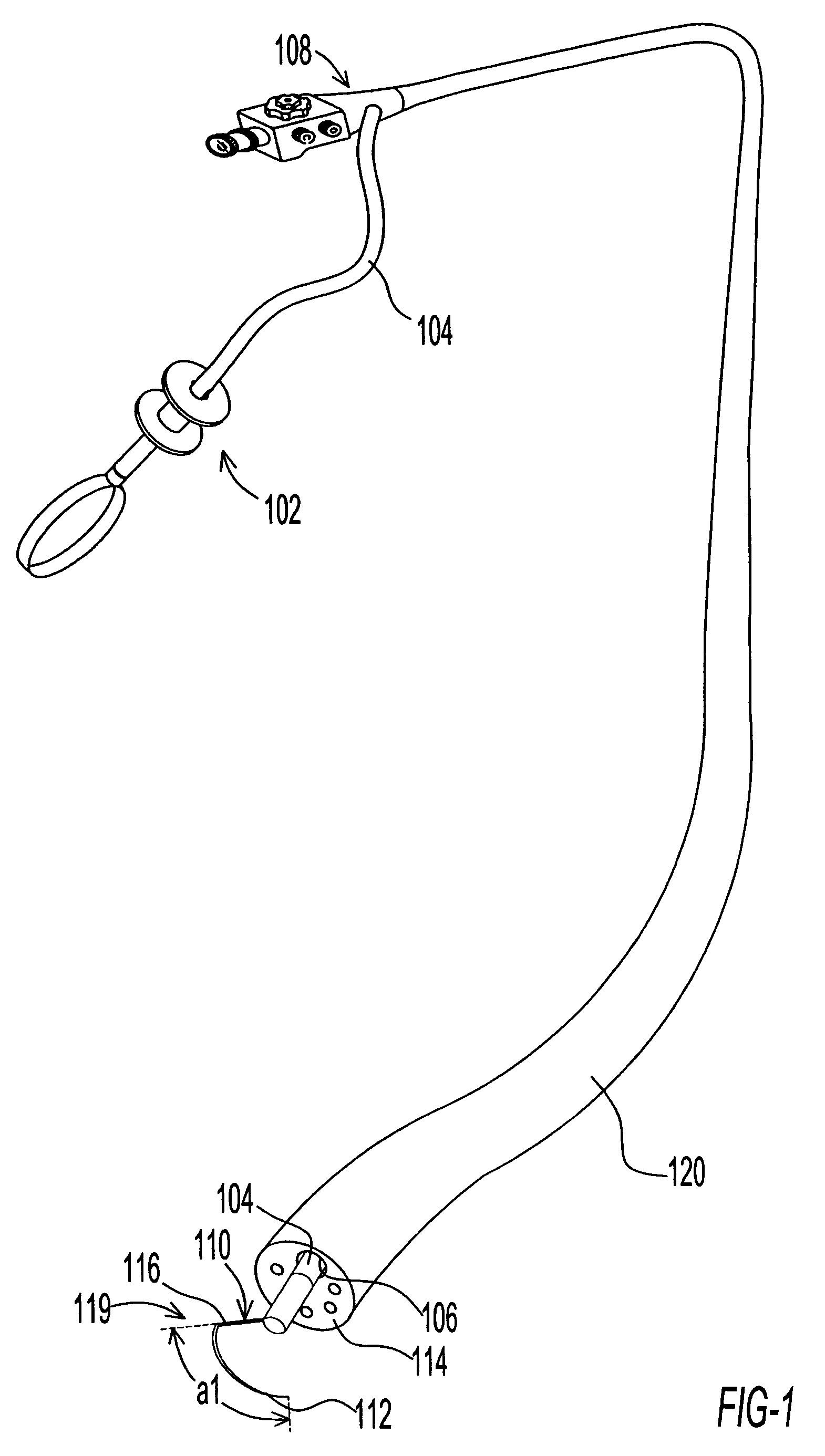
Vibratory Device, Endoscope Having Such A Device, Method For Configuring An Endoscope, And Method Of Reducing Looping Of An Endoscope.
Owner:PSIP LLC
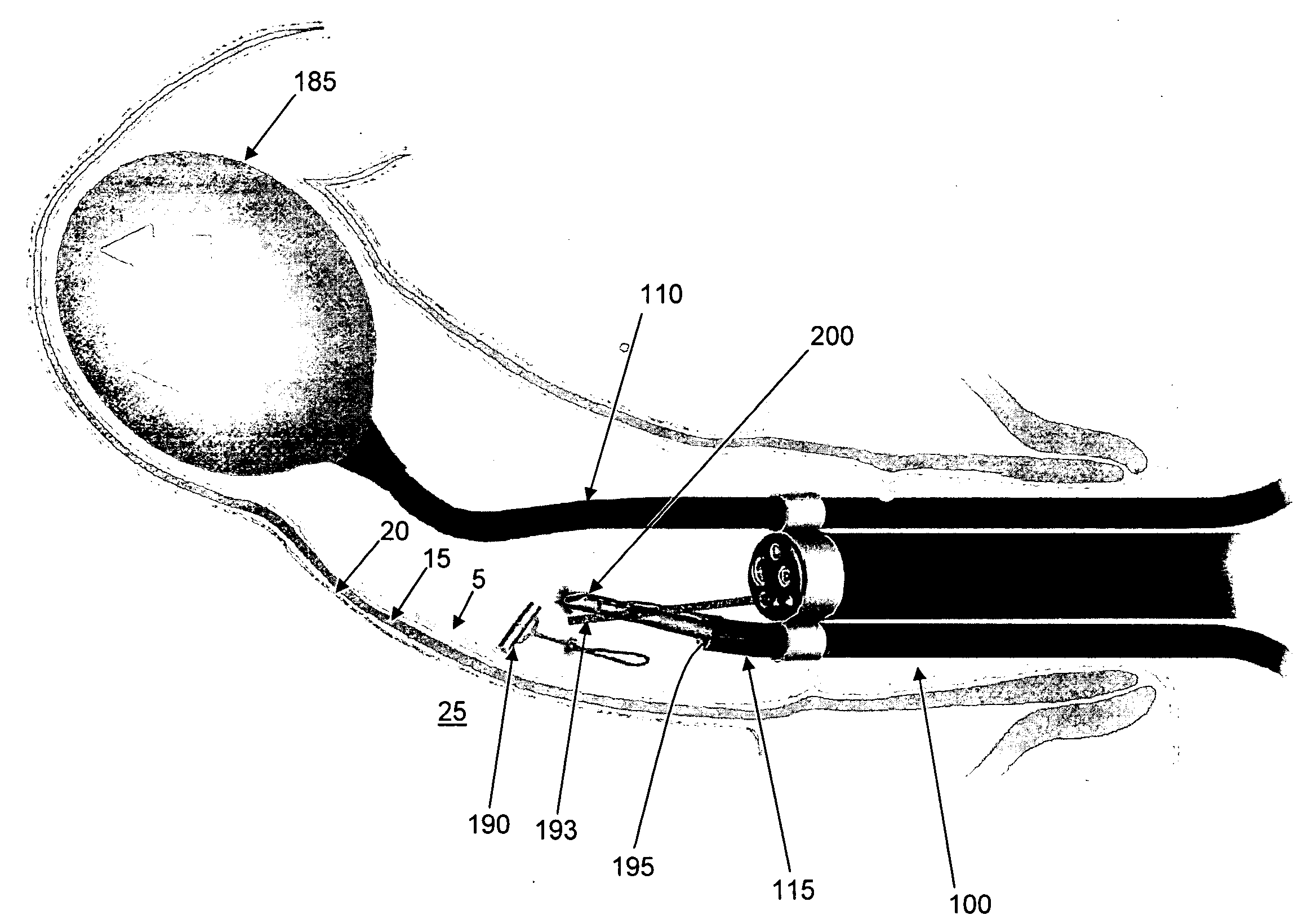
Method and apparatus for endoscopically treating rectal prolapse
InactiveUS20090156996A1Minimize traumaSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesRectal prolapseBalloon catheter
In one form of the invention, there is provided a method for treating rectal prolapse, the method comprising:inserting an expandable element into a prolapsed rectum via the anus;expanding the expandable element so that the expandable element securely engages the rectum;advancing the expanded element distally so as to return the prolapsed rectum to its normal, non-prolapsed state; andsecuring the rectum to supporting tissue whereby to retain the rectum in its normal, non-prolapsed state.In another form of the invention, there is provided an endoscope assembly for treating rectal prolapse, the endoscope assembly comprising:an endoscope;a balloon catheter; anda tacker;wherein the endoscope, balloon catheter and tacker are mounted together for insertion as a unit.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Endoscope assembly with a polarizing filter
An endoscope includes an imaging device, a first polarizing filter disposed in front of the imaging device, a light source, and a second polarizing filter disposed in front of the light source. The planes of polarization of the first and second polarizing filters are at a substantially 90° angle.
Owner:PSIP LLC
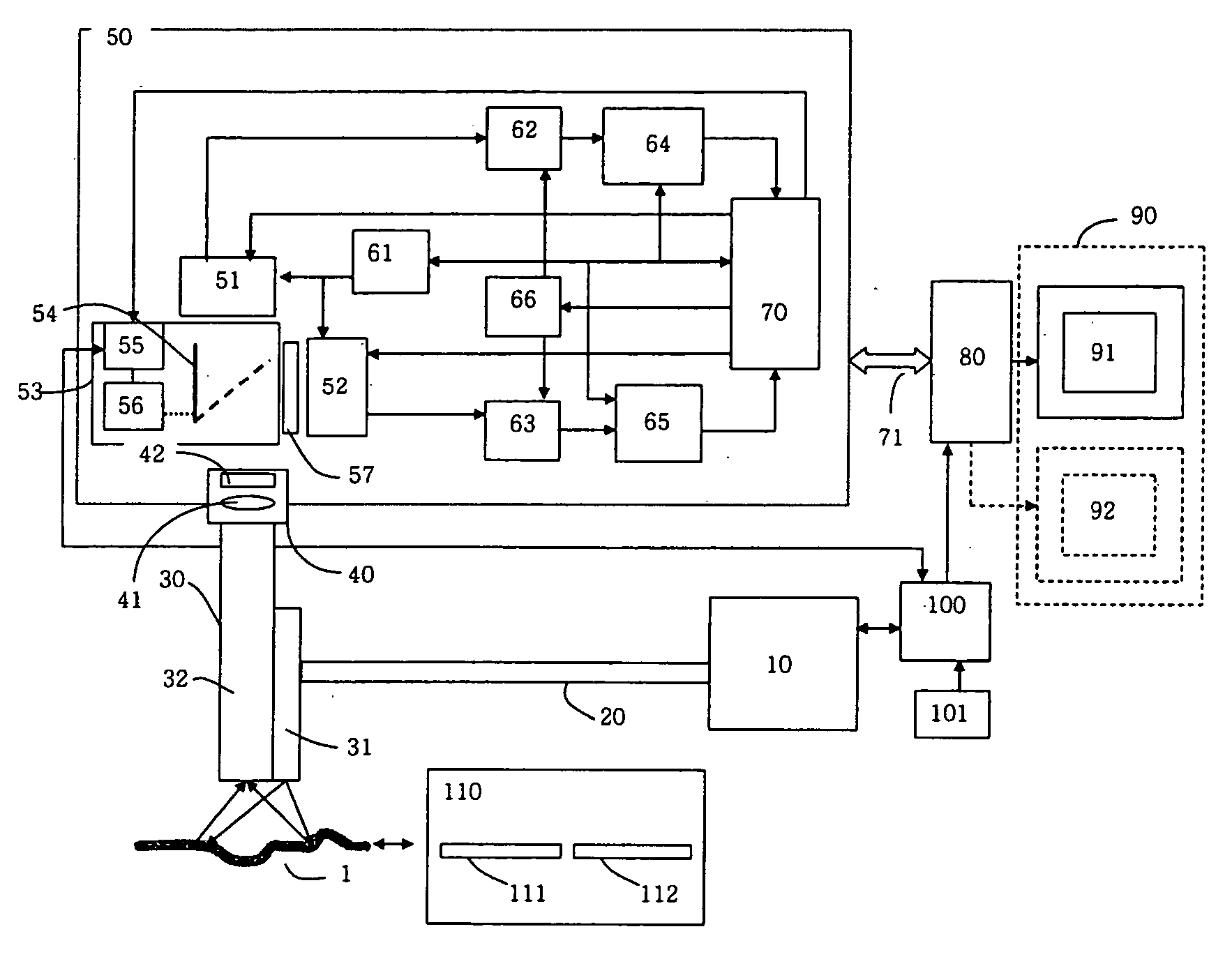
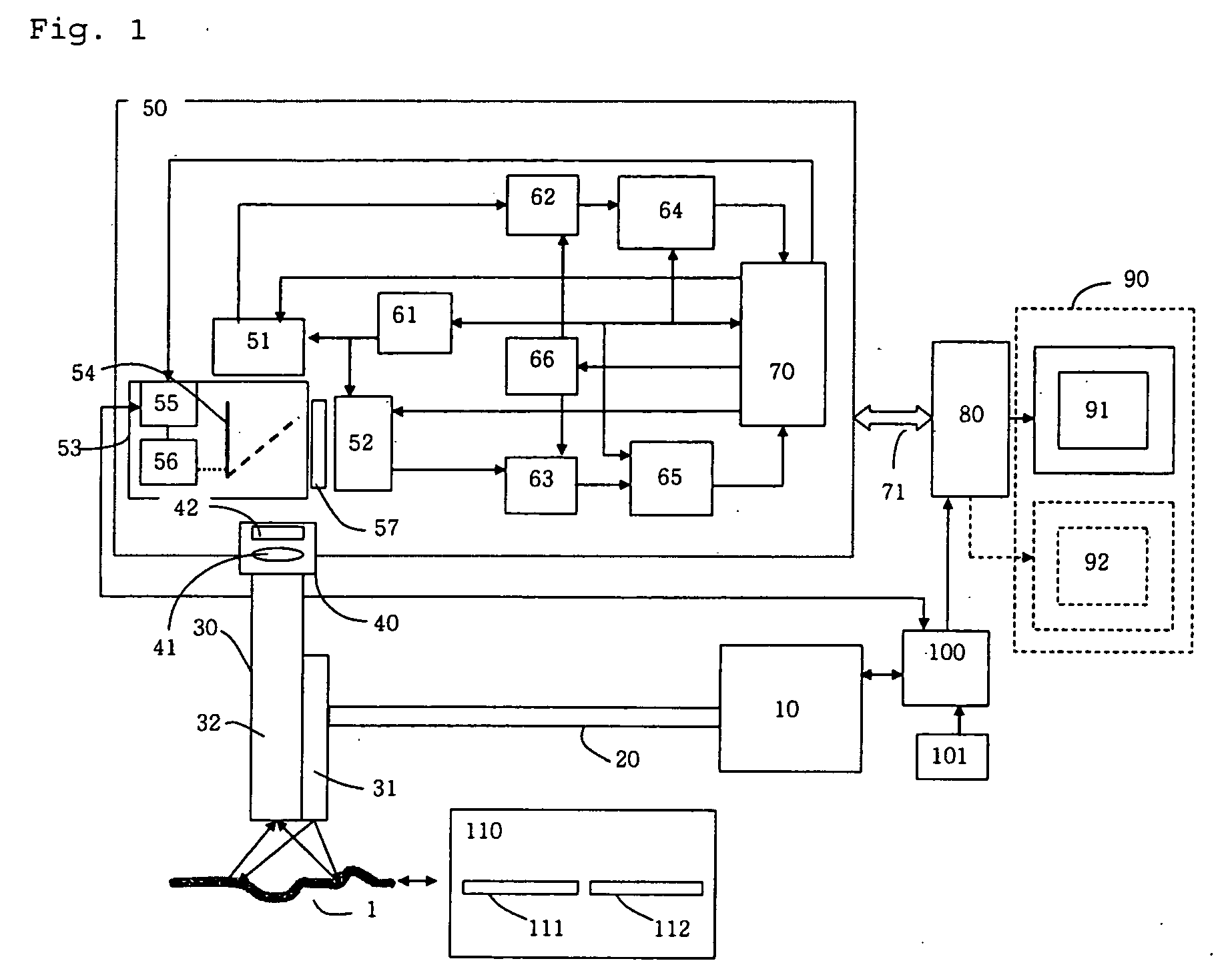
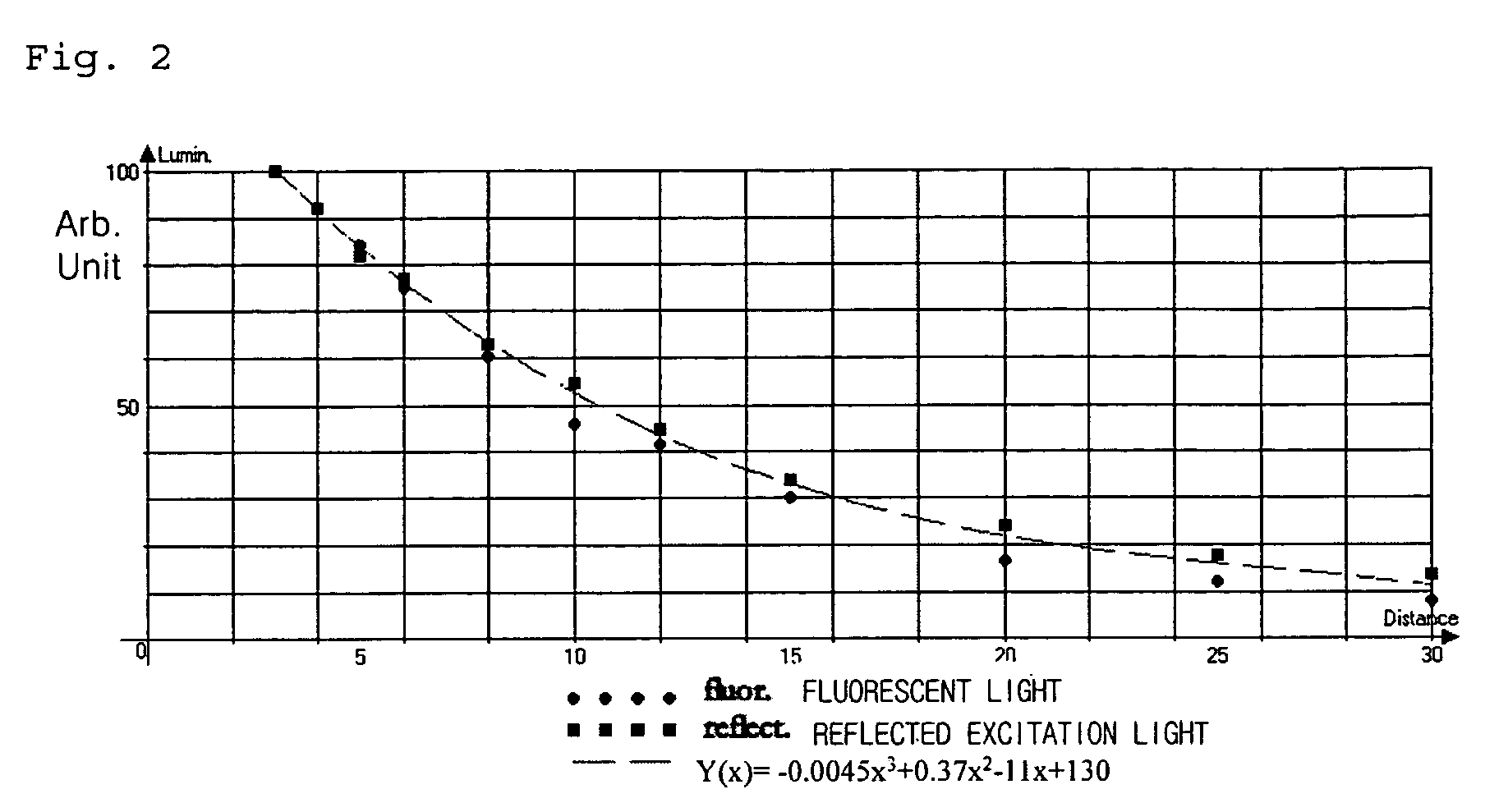
Fluorescent endoscope system having improved image detection module
ActiveUS20050203343A1Efficient compositionEffective displaySurgeryEndoscopesControl signalImage detection
Disclosed is an improved fluorescent endoscope system having reduced factors that cause errors during diagnosis based on quantitative evaluation of fluorescent intensity for improved accuracy of fluorescent endoscopic diagnosis. The fluorescent endoscope system includes an optical source module for providing white light or excitation light; an endoscope assembly having an optical transmission path for transmitting light provided from the optical source module to a diagnostic object and an optical detection module for transmitting reflection light and fluorescent light from the diagnostic object; an optical path split means for splitting the path of the reflection light and fluorescent light transmitted from the endoscope assembly; and a two-chip integration image detection module having a first optical detection chip for detecting the reflection light and outputting a first optical detection signal, a second optical detection chip for detecting the excitation light and outputting a second optical detection signal, a gain control unit for controlling a signal amplification gain value to adjust the brightness of an image detected by the first optical detection chip, a first amplification unit for amplifying the first optical detection signal according to the signal amplification gain value, and a second amplification unit for amplifying the second optical detection signal according to a changing ratio of the signal amplification gain value.
Owner:INTHESMART
Vibratory device, endoscope having such a device, method for configuring an endoscope, and method of reducing looping of an endoscope
Owner:PSIP LLC
Endoscope assembly with a polarizing filter
An endoscope includes an imaging device, a first polarizing filter disposed in front of the imaging device, a light source, and a second polarizing filter disposed in front of the light source.
Owner:PSIP LLC
Endoscopic instrument assembly with separable operative tip and associated medical method
ActiveUS7785250B2Easy to insertEasy to useSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEngineeringEndoscopic Assembly
In an insertion configuration, an endoscope assembly includes an insertion member with a distal end face and a working channel and further includes an instrument shaft extending through the working channel and an operative tip connected to the instrument shaft and extending in a plane oriented perpendicularly to the instrument shaft. The operative tip is positioned along the distal end face of the endoscope insertion member. The operative tip is separable from the distal end face of the endoscope insertion member by a distally directed motion of the instrument shaft along the working channel.
Owner:GRANIT MEDICAL INNOVATION
Endoscope
InactiveUS6450949B1Enhance the imageUnnecessary removalTelevision system detailsSurgeryMagnificationEngineering
An endoscope assembly is disclosed having a housing adapted to be manipulated by medical personnel, such as a surgeon. An elongated lens tube has one end secured to the housing while the free end of the lens tube is adapted for insertion into a cavity of a body. At least one, and preferably several, lens assemblies are longitudinally slidably mounted within the lens tube and movable between longitudinally spaced positions within the lens tube. A drive mechanism is mounted to the housing and mechanically coupled to each lens assembly to move the lens assemblies longitudinally within the lens tube independently of one another. In doing so, the lens assemblies provide varying degrees of magnification between low or macroscopic magnification and microscopic magnification at the free end of the lens tube. A stage is also detachably secured over the lens tube and has a transparent window across its end adjacent the free end of the lens tube. In use, the stage window is positioned against target tissue within a human cavity while the lens assemblies are longitudinally displaced within the lens tube to obtain the desired magnification. Strands extending through and / or connected to the lens groups are used to longitudinally displace the lens groups.
Owner:INNER VISION IMAGING
Endoscope
InactiveUS20020115908A1Resolving structureHigh resolutionSurgeryEndoscopesEngineeringMicroscopic exam
An endoscope assembly is disclosed having a housing adapted to be manipulated by medical personnel, such as a surgeon. An elongated lens tube has one end secured to the housing while an elongated stage is removably secured to the housing so that the stage encompasses and is coaxial with the tube. The stage together with the lens tube are adapted for insertion into the cavity of a body. A lens assembly provided within the lens tube relays the optical image from the free end of the stage to the housing. A lens assembly within the housing, furthermore, varies the magnification of the image between macroscopic magnification and microscopic magnification in which tissue may be examined on a cellular level. For macroscopic magnification, white light is transmitted through the lens tube as well as reflected back from the target tissue through the lens tube and to the housing. For microscopic examination, laser radiation is utilized in lieu of the white light illumination. A line scanning confocal assembly contained within the housing enables microscopic examination of the target tissue at varying levels into the tissue from the end of the stage.
Owner:INNER VISION IMAGING
Biopsy device with viewing assembly
A biopsy device suitable for collection of a tissue sample from a biopsy site in a body lumen is provided. The biopsy device comprises a combination of an introducer assembly, a cutter assembly, and an endoscope assembly that coact with one another. The introducer assembly includes a hollow sheath having a distal end portion defining an aperture suitable for receiving a tissue mass therein. The cutter assembly includes a cutter tube having a distal end portion with a cutting edge. The cutter tube is sized to fit axially within the introducer sheath. The endoscope assembly includes a bundle of optical fibers sized to fit axially within the cutter tube. In use, the fiber optic bundle of the endoscope is nested within the cutter tube, which in turn is nested within the introducer sheath to form a co-axial structure.
Owner:LACHOWICZ THEODORE COLLATERAL AGENT
Endoscope Tip Protector
The invention provides an endoscope tip protector for protecting the distal tip of an endoscope and an endoscope assembly including the tip protector affixed thereto. The endoscope tip protector can include a main body with an opening through the main body sized to accept an endoscope sheath and a white surface arranged to face a distal end of an endoscope sheath when the sheath is placed in the endoscope tip protector. Methods of making and using the tip protector and assembly are also provided.
Owner:MD IDIZ
Apparatus and method for intraductal cytology
InactiveUS6840909B2Easy to handleReliable diagnosisSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCytologyAnatomy
The invention is directed toward a micro-endoscope assembly for the removal of tissue and cells from breast ducts comprising a cylindrical guide tube with a beveled distal end defining an internal cylindrical passageway and a first smaller cylindrical tube eccentrically formed in the cylindrical passageway of a smaller diameter than the tube internal cylindrical passageway and adapted to receive and guide an endoscope with a handle assembly wherein the smaller cylindrical tube together with an inner wall surface of the cylindrical guide tube forms a second passageway. A second conduit of a smaller diameter than the smaller cylindrical tube is mounted in the second passageway to divide the second passageway into two separate divided sections and is of sufficient diameter to receive a laser fiber and a micro-endoscope is mounted in the smaller cylindrical tube and a laser is mounted in the second cylindrical tube in the second passageway. The assembly is inserted into a mammary duct and the interior of the duct is viewed until an abnormality is determined in the duct. The tissue and cells from the abnormality area are dislodged, irrigated and aspirated through a suction channel to a removable collection device.
Owner:LACHOWICZ THEODORE COLLATERAL AGENT
Endoscopic barrel with connector
An endoscopic assembly for an endoscope is disclosed. The assembly comprises a ligator barrel having proximal and distal portions. The proximal portion has a seat and a receiving wall extending to a proximal end. The receiving wall has a first threaded portion formed thereon. The assembly further comprises a connector for connecting the ligator barrel about the endoscope. The connector has a scope portion and a tip portion. The scope portion has a receiving end through which the endoscope is disposed to engage the seat for connecting the ligator barrel about the endoscope. The tip portion has a second threaded portion formed thereon and are configured to cooperate with the first threaded portion to receive the receiving wall and attach the connector with the ligator barrel. The first and second threaded portions are configured to cooperate with each other to tighten the connection of the ligator barrel about the endoscope as the threads increase surface area contact therebetween.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
Endoscopic instrument assembly with separable operative tip and associated medical method
ActiveUS20070038022A1Easy to insertEasy to useSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEngineeringEndoscopic Assembly
In an insertion configuration, an endoscope assembly includes an insertion member with a distal end face and a working channel and further includes an instrument shaft extending through the working channel and an operative tip connected to the instrument shaft and extending in a plane oriented perpendicularly to the instrument shaft. The operative tip is positioned along the distal end face of the endoscope insertion member. The operative tip is separable from the distal end face of the endoscope insertion member by a distally directed motion of the instrument shaft along the working channel.
Owner:GRANIT MEDICAL INNOVATION
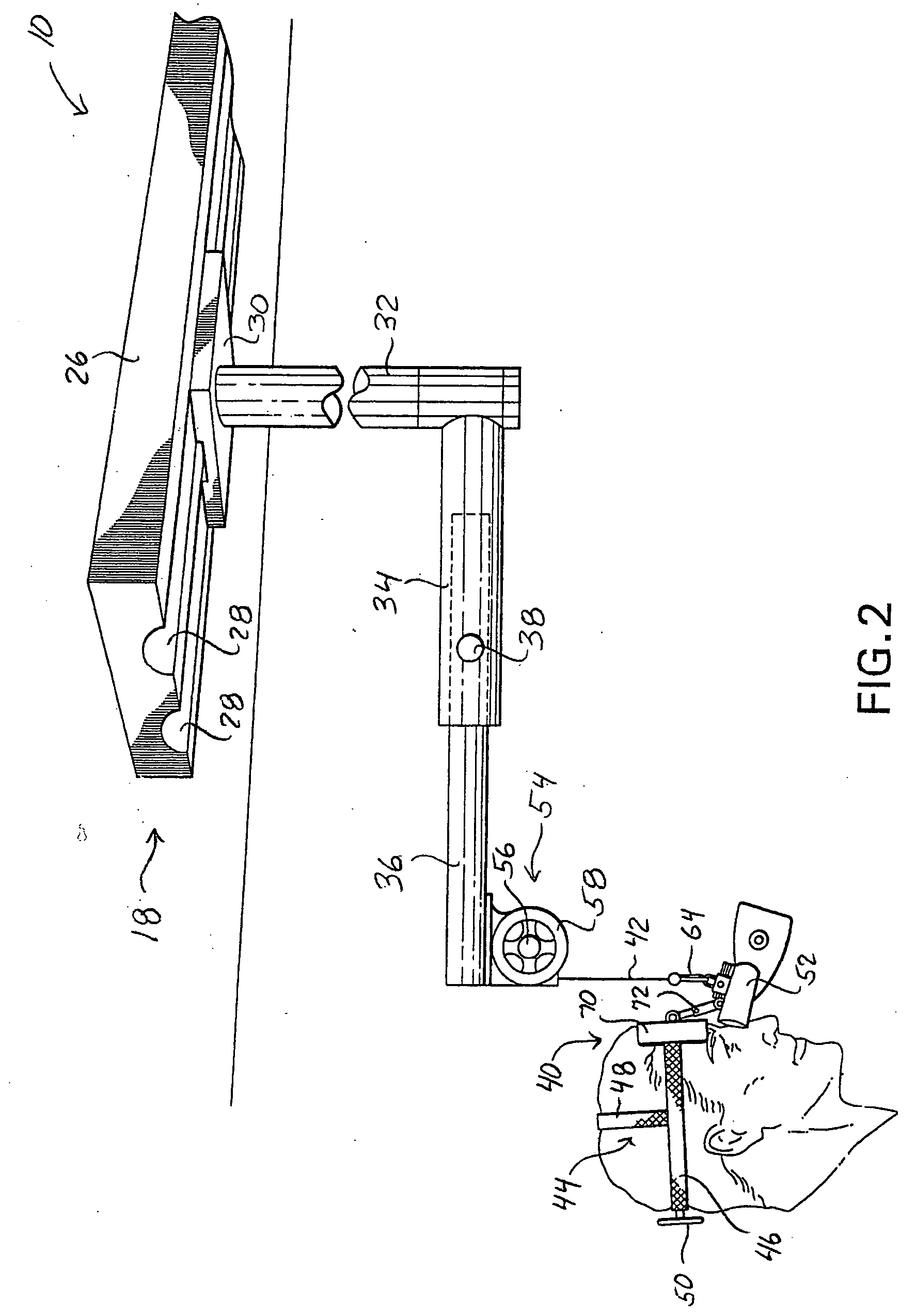
Surgical microscope support system
InactiveUS20060126167A1Eliminate relative motionPrevent movementDiagnosticsStands/trestlesSupporting systemSurgical microscope
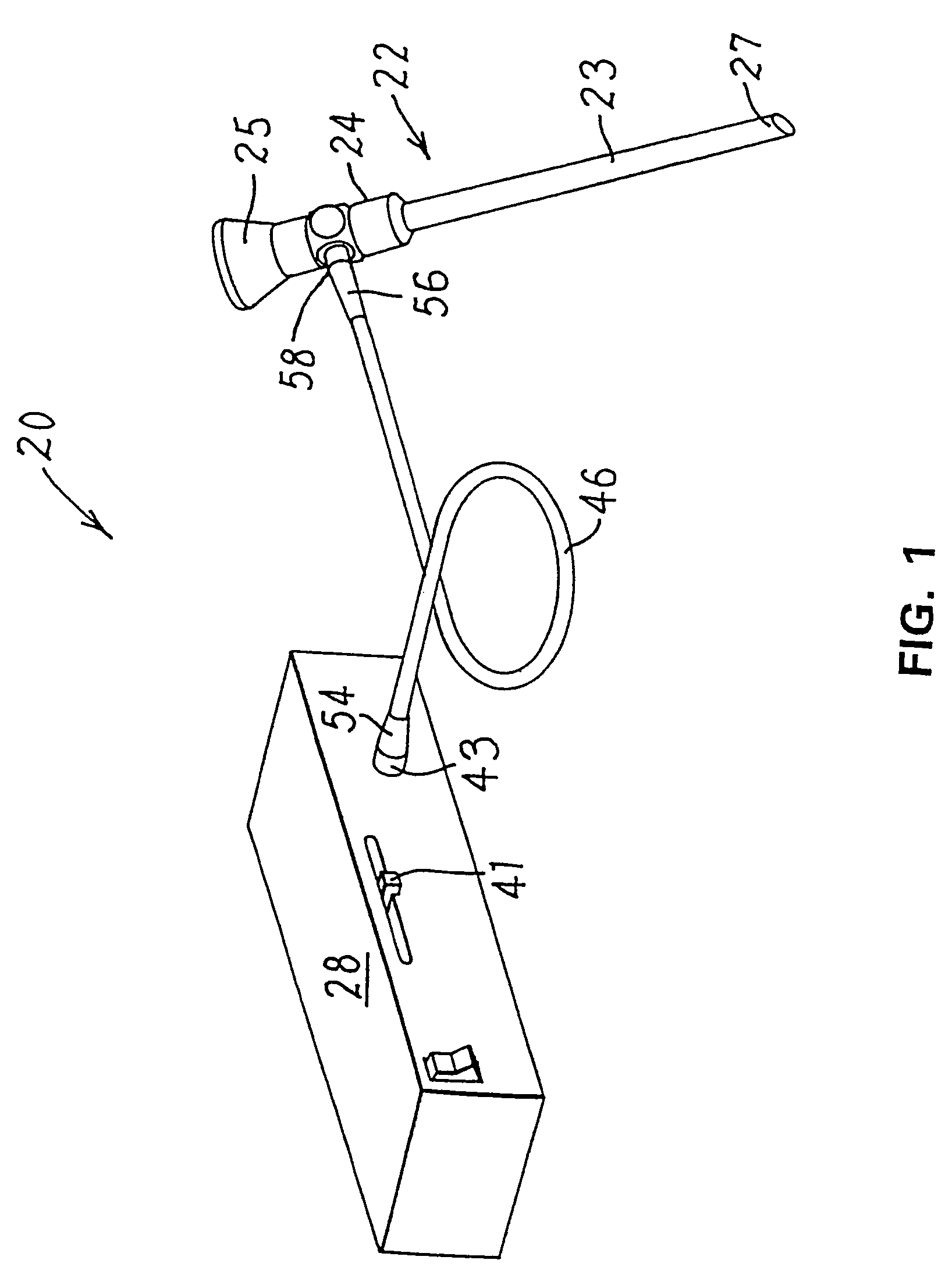
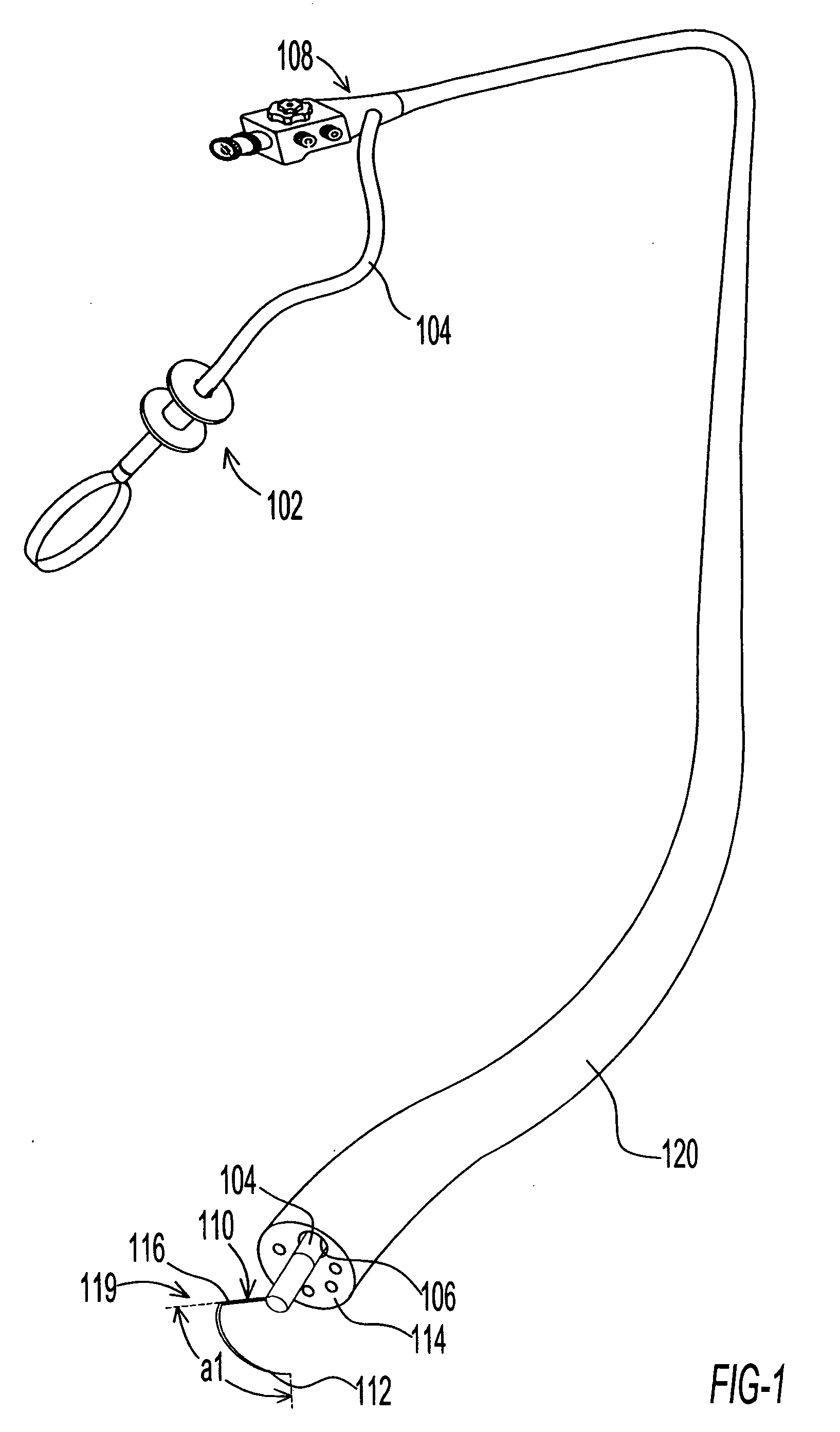
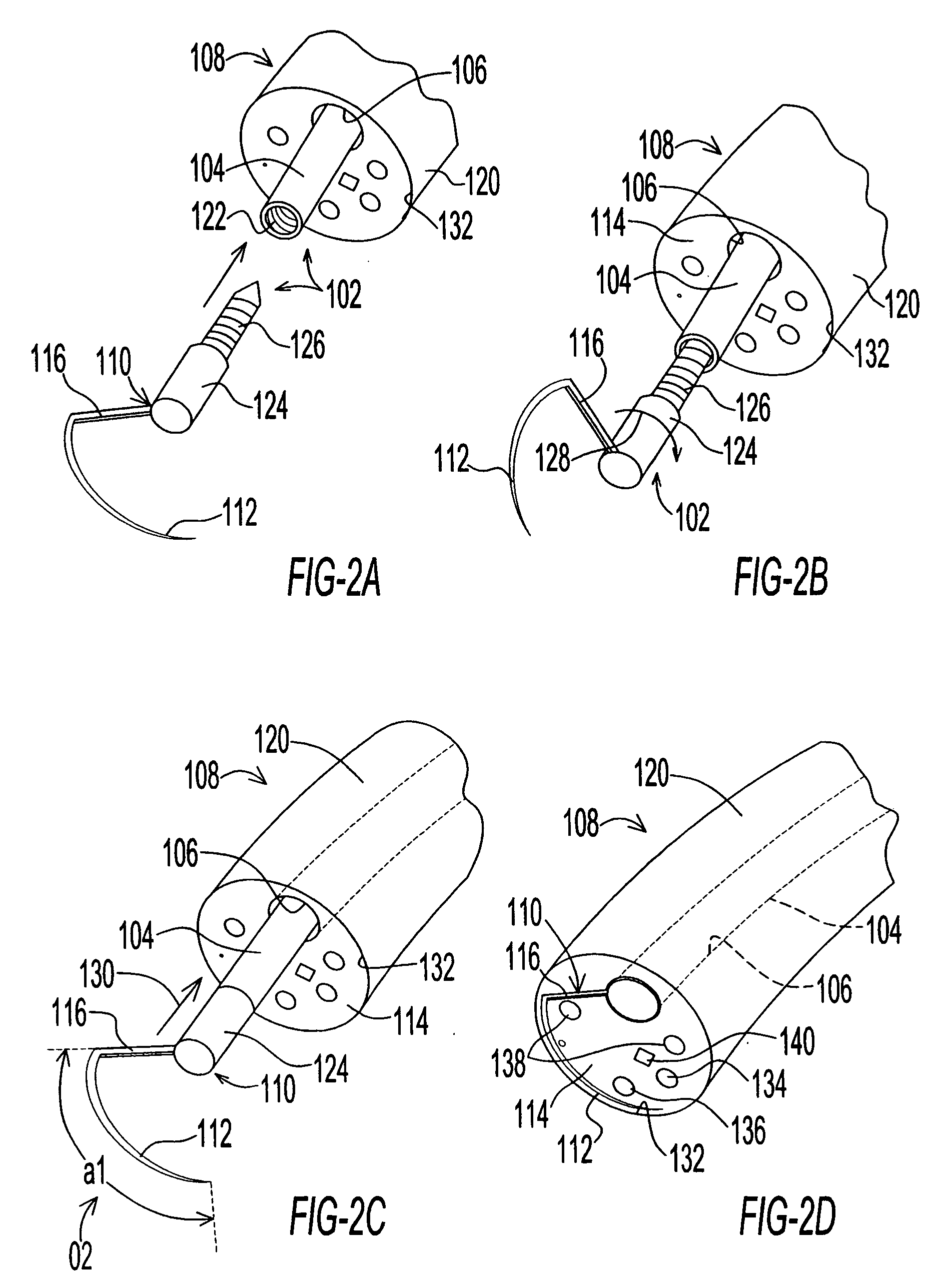
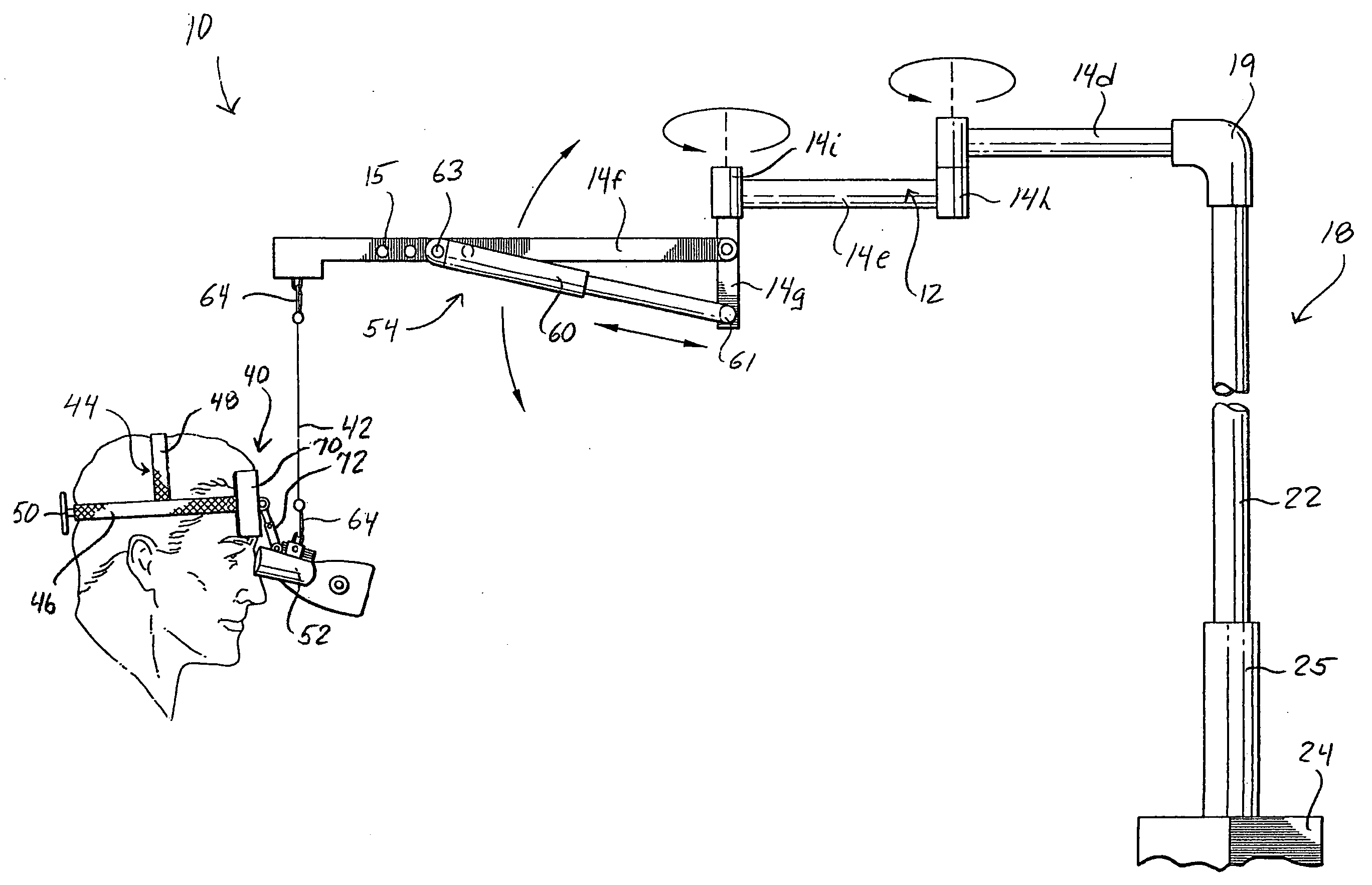
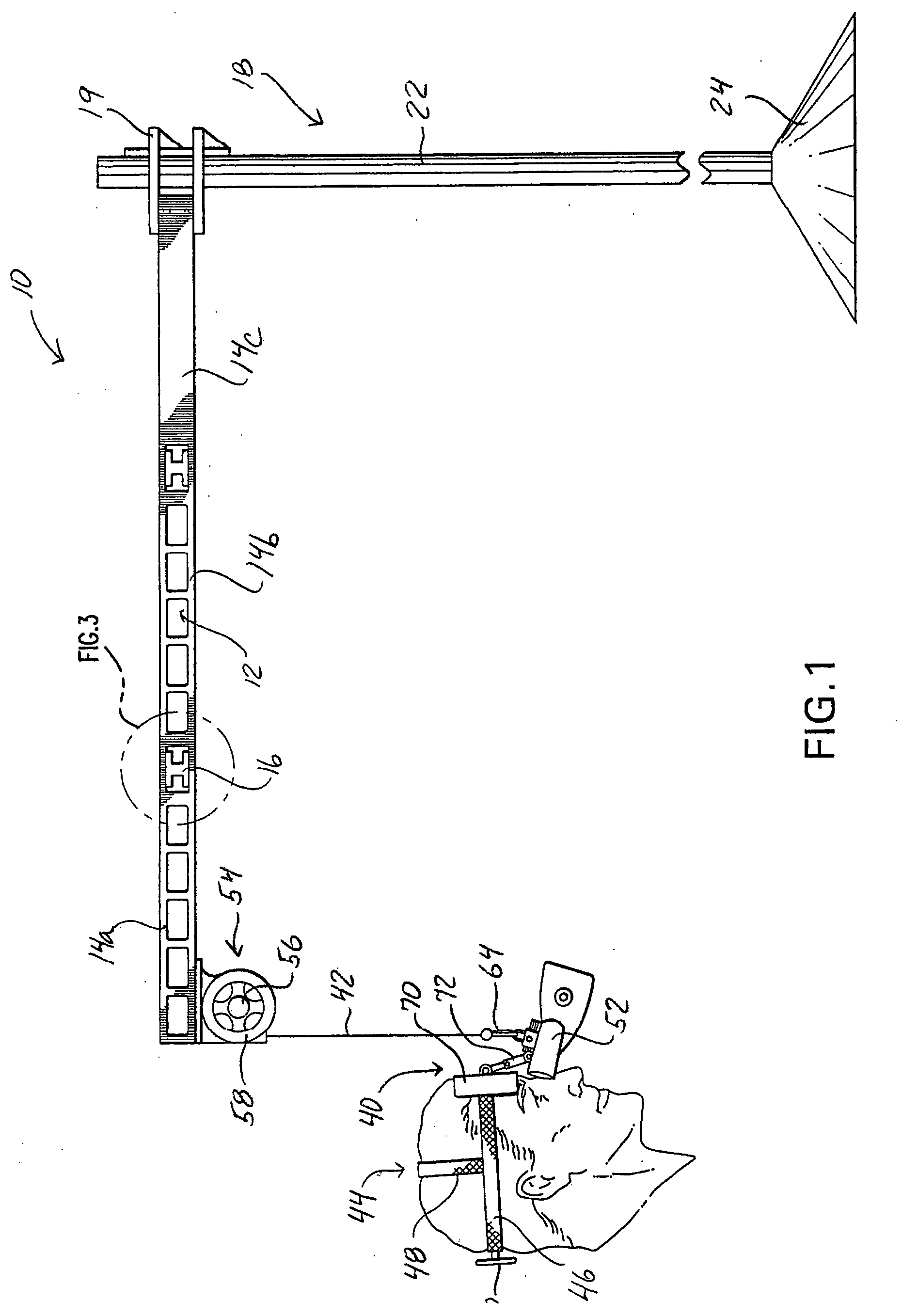
A microscope system includes an adjustable arm attached at one end to a support mount. A suspension member is configured at an opposite end of the adjustable arm and supports a scope assembly. The scope assembly includes a head harness and a microscope adjustably connected to the harness such that the microscope is disposed along an operator's line of site upon the operator donning the head harness. A weight compensator device is configured on the arm to compensate for the weight of the scope assembly hanging on the suspension member.
Owner:PIONTKOWSKI PAUL K
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com