High-temperature resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and breeding method thereof
A Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which are applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as weakening effects, and achieve the effects of strong high temperature tolerance, high genetic stability, and wide application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] Embodiment 1: Breeding of high temperature resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains
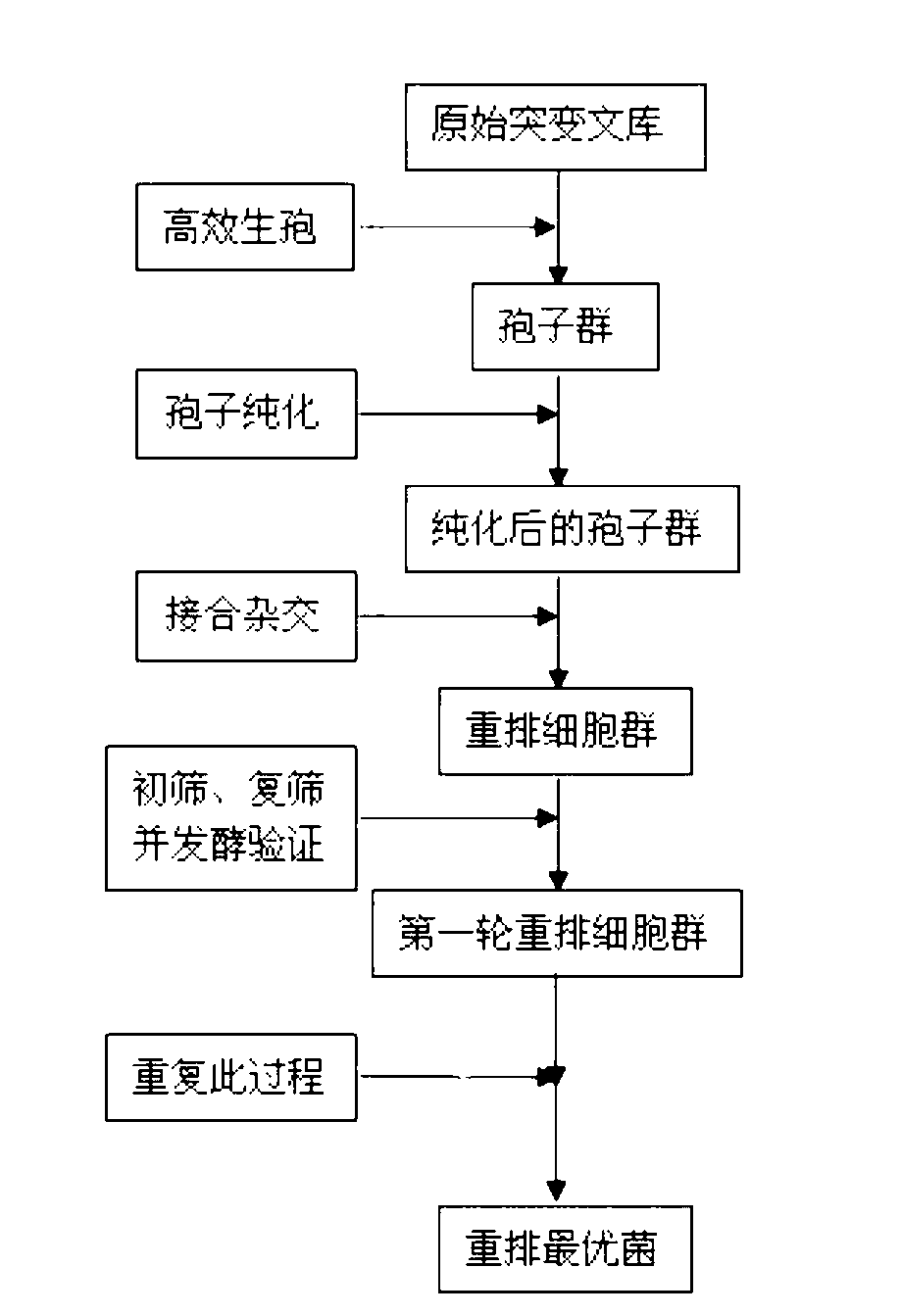
[0018] (1) Traditional mutagenesis breeding to establish a mutant strain library
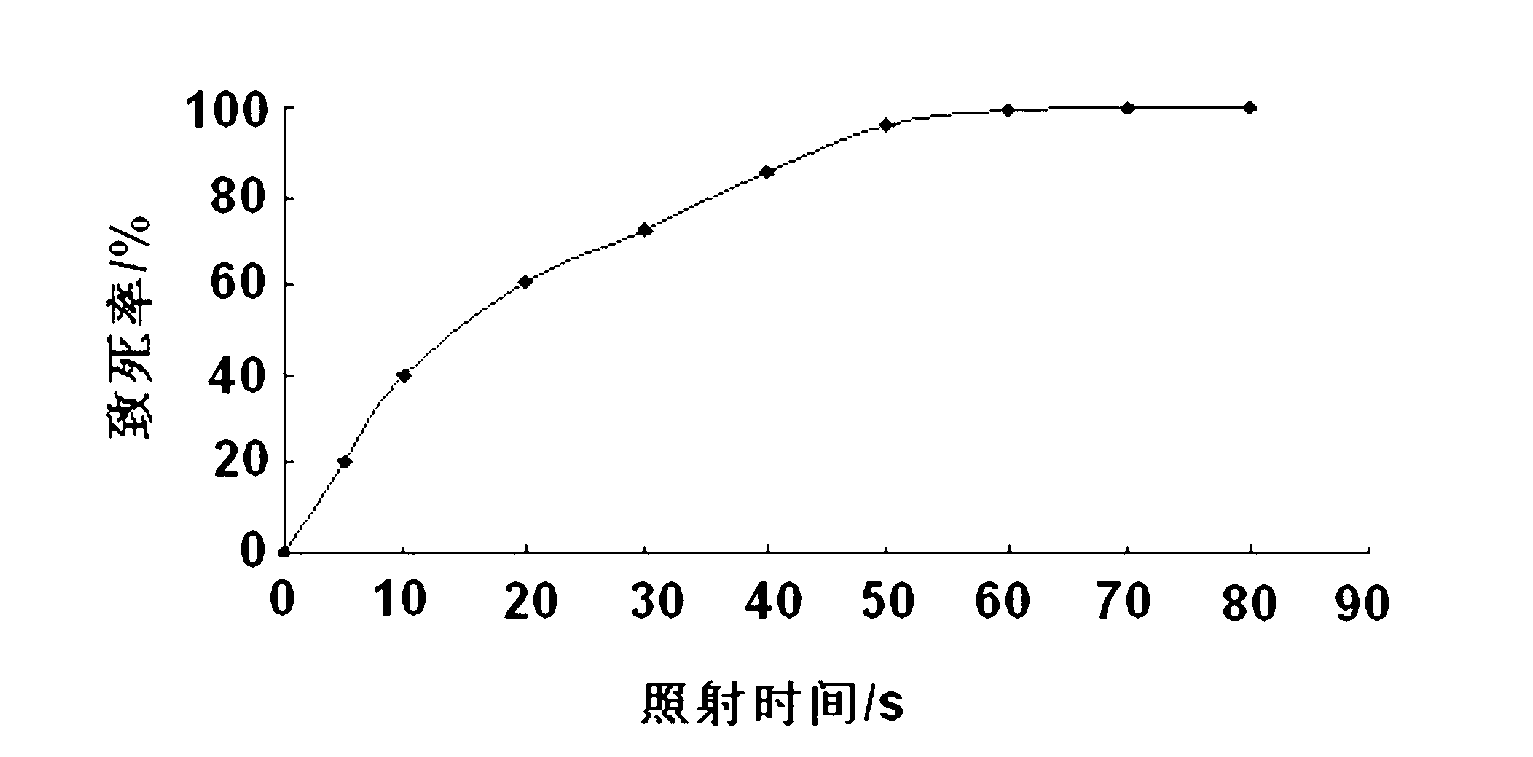
[0019] Pick a ring of yeast slant culture and inoculate it in 5mL of YPD liquid medium, cultivate it at 30°C and 100rpm until the middle and late logarithmic growth period, collect the bacteria by centrifugation and wash twice with sterile saline, resuspend the cells to adjust the concentration to 10 6 individual / mL. Take 4mL of bacterial suspension in a Ф70mm petri dish, and irradiate it with a 15W ultraviolet lamp at a height of 30cm from the bacterial liquid in the petri dish. Then spread on the YPD medium plate. Irradiate the bacterial solution for different times (0s, 5s, 10s, 20s, 30s, 40s, 50s, 60s, 70s, 80s), respectively, dilute and plate for two days, wait for the colonies to grow out, count the colonies on the plate, and Calculate the lethality rate and draw the lethality rate curve base...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Embodiment 2: Fermentation performance of genome rearrangement bacterial strain
[0026] (1) High temperature tolerance of genome rearranged strains
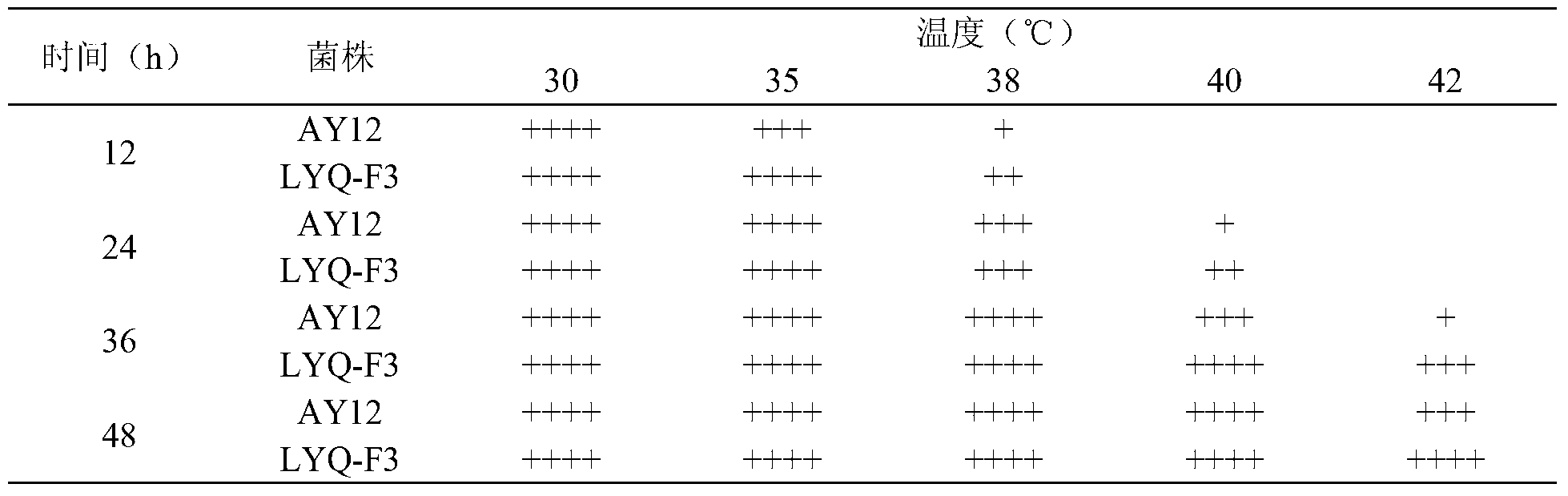
[0027]The starting strain AY12 and the genome rearrangement strain LYQ-F3 were cultured to the logarithmic growth phase, respectively inoculated into Duchenne tubes containing wort medium (6°Brix), respectively, at set temperatures (30°C, 35°C, 38°C, 40°C, 42°C) for static culture, observe the gas production every 12 hours and record the results (as shown in Table 1). As shown in the results, after genome rearrangement, the gas production of the strain under high temperature conditions was significantly improved compared with the original strain, indicating that the high temperature tolerance of the genome rearranged strain was higher than that of the original strain.
[0028] Table 1 High temperature tolerance of starting strains and genome rearrangement strains
[0029]
[0030] Note: The data shown are representat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com