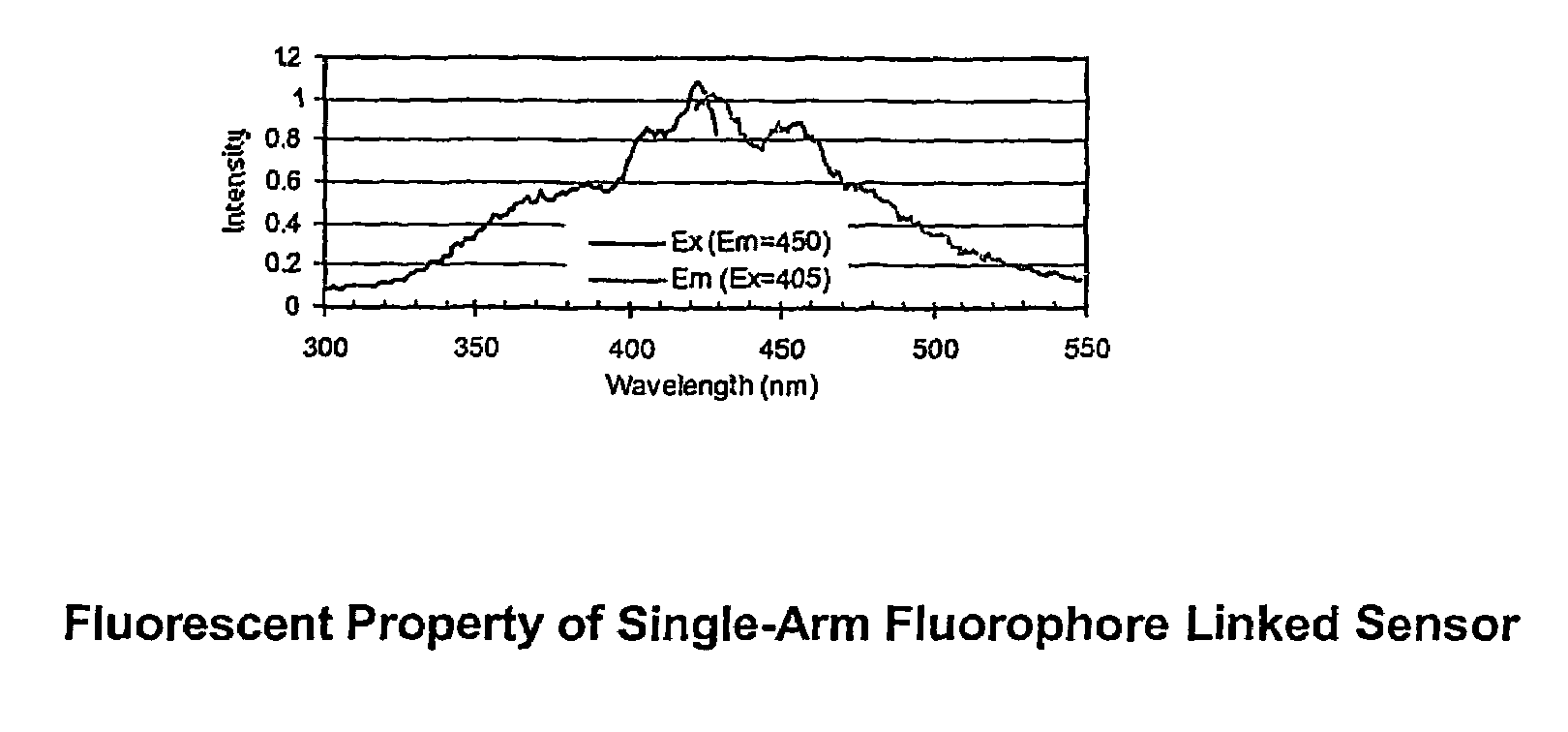
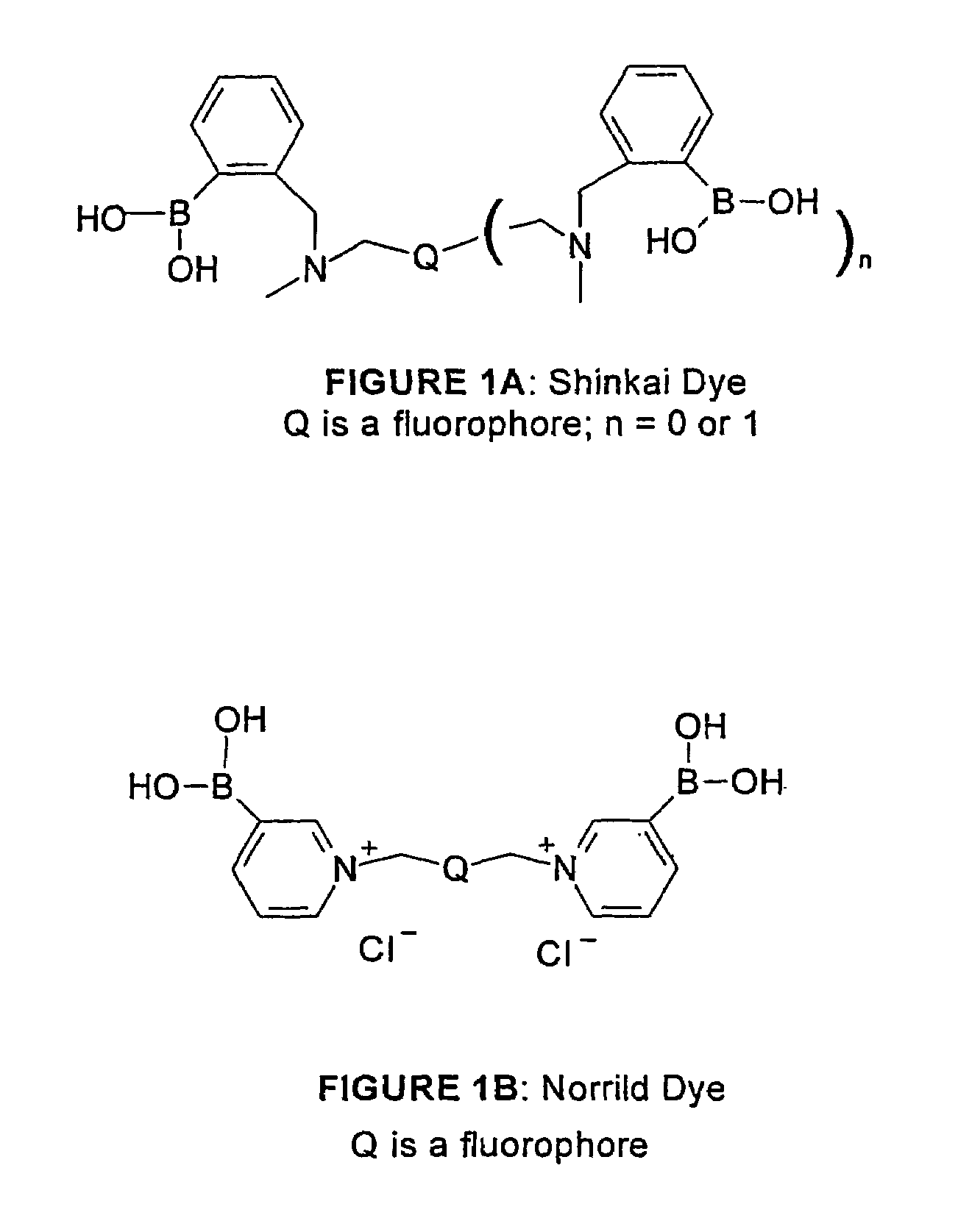
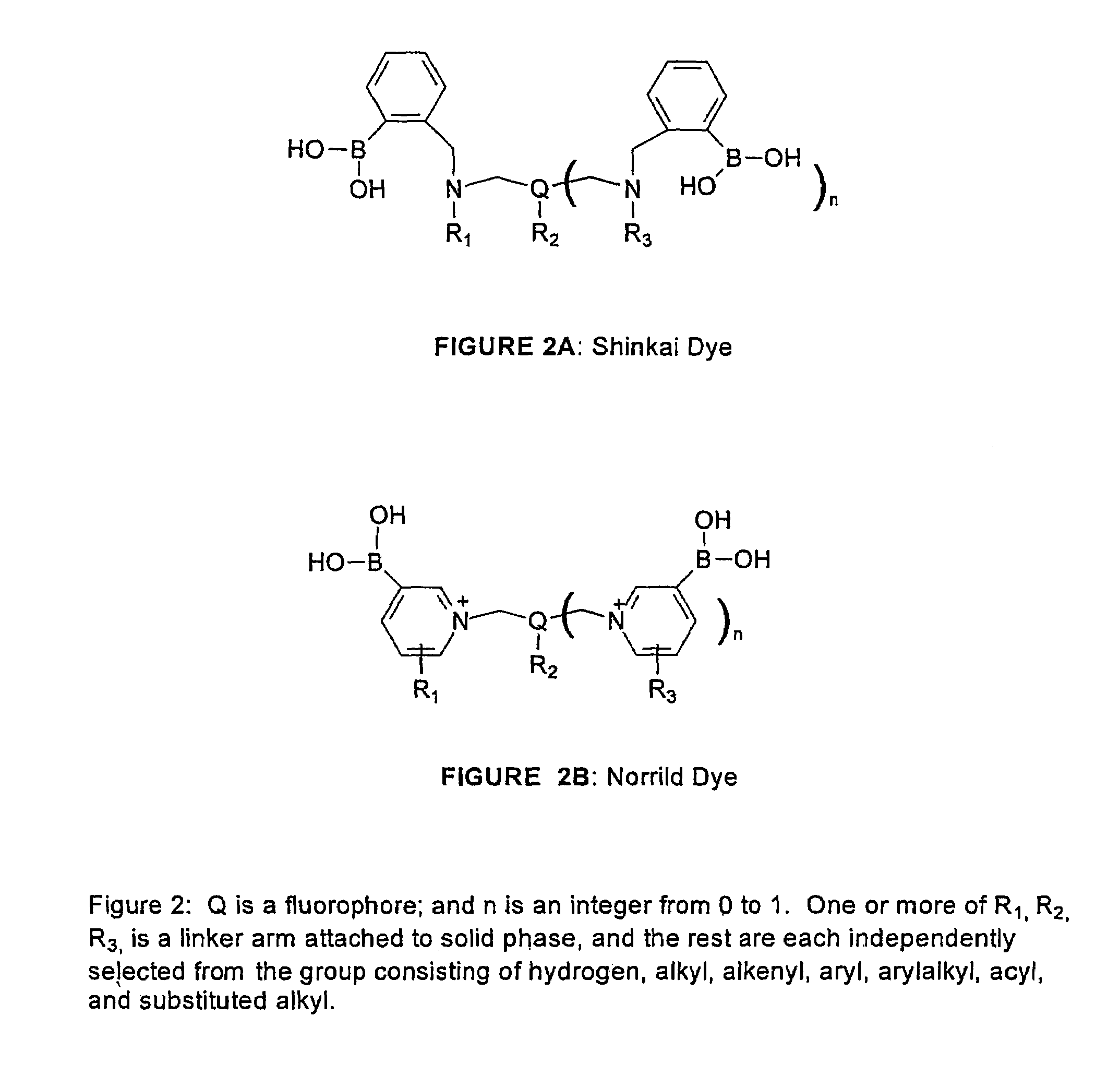
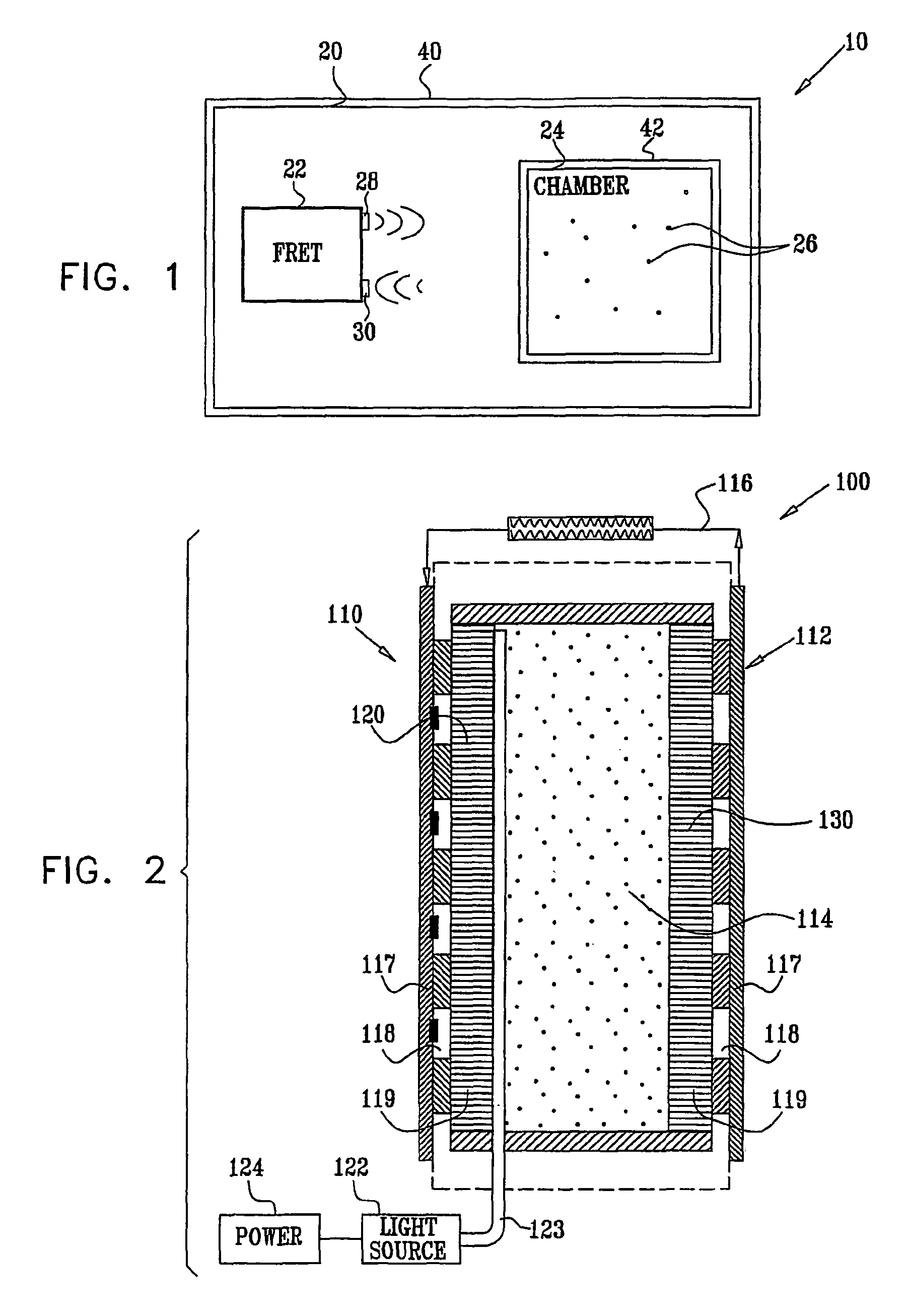
Patents
Literature
54 results about "Glucose binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interacting selectively and non-covalently with the D- or L-enantiomer of glucose. [CHEBI:17234, GOC:jl]
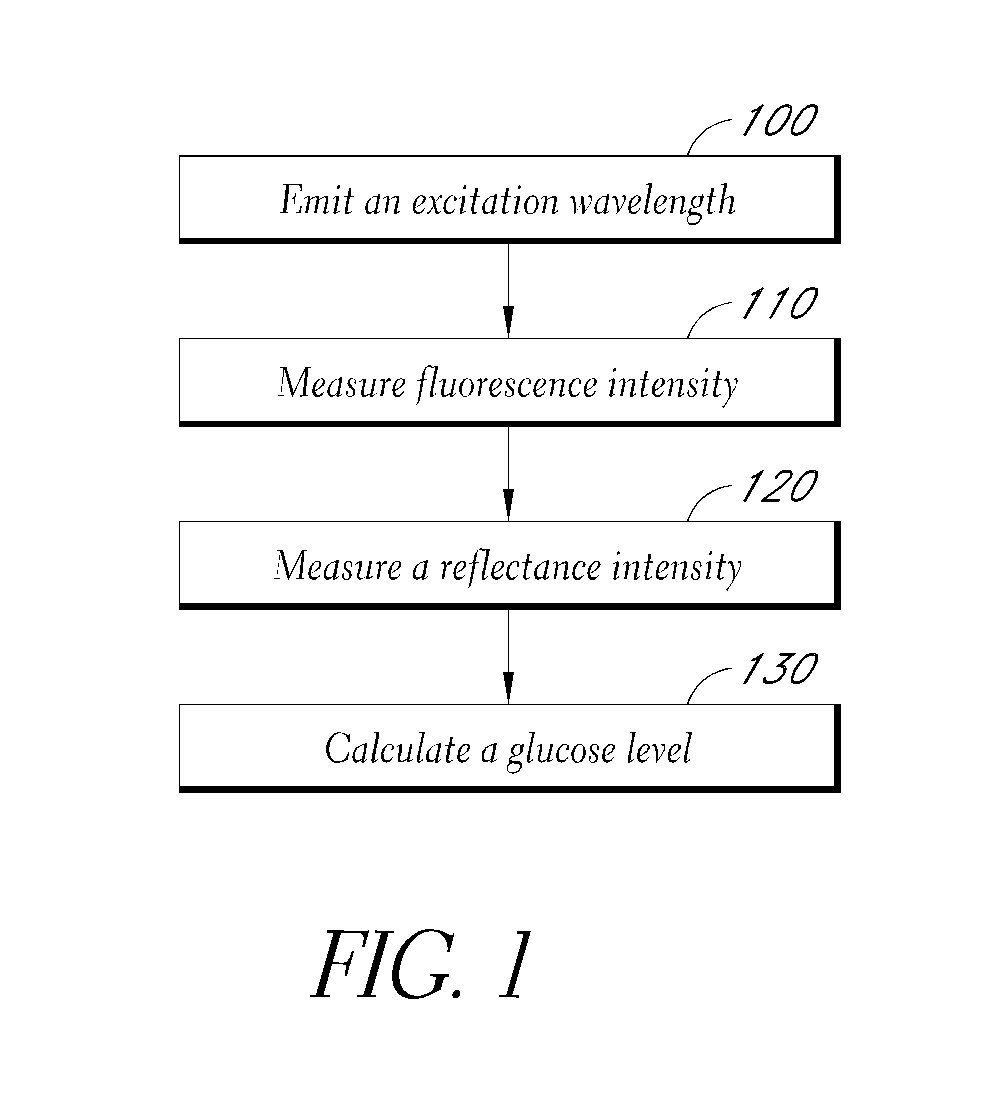
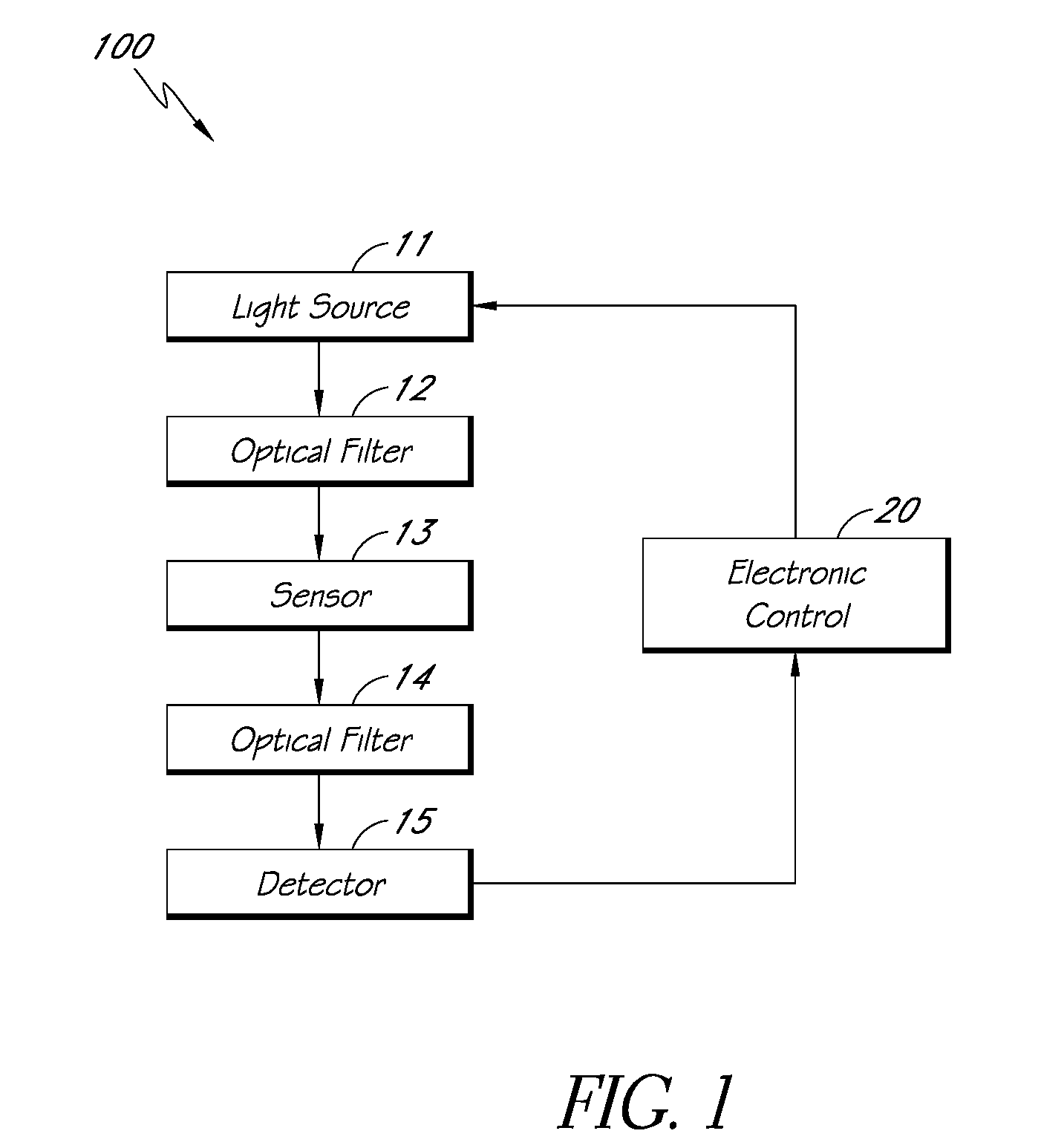
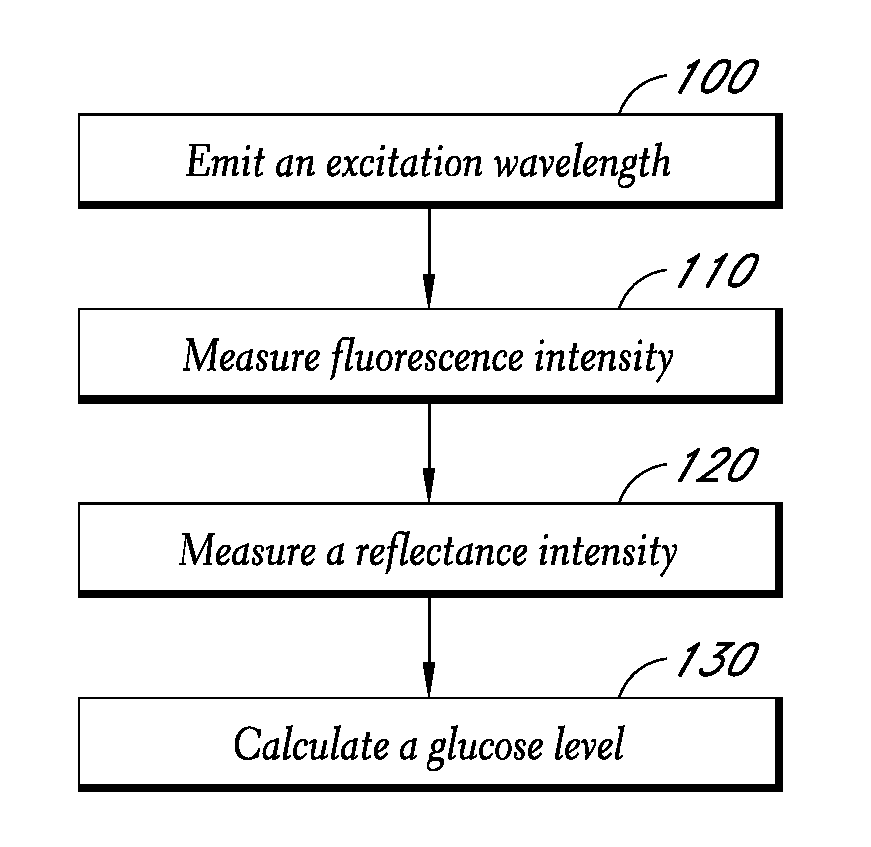
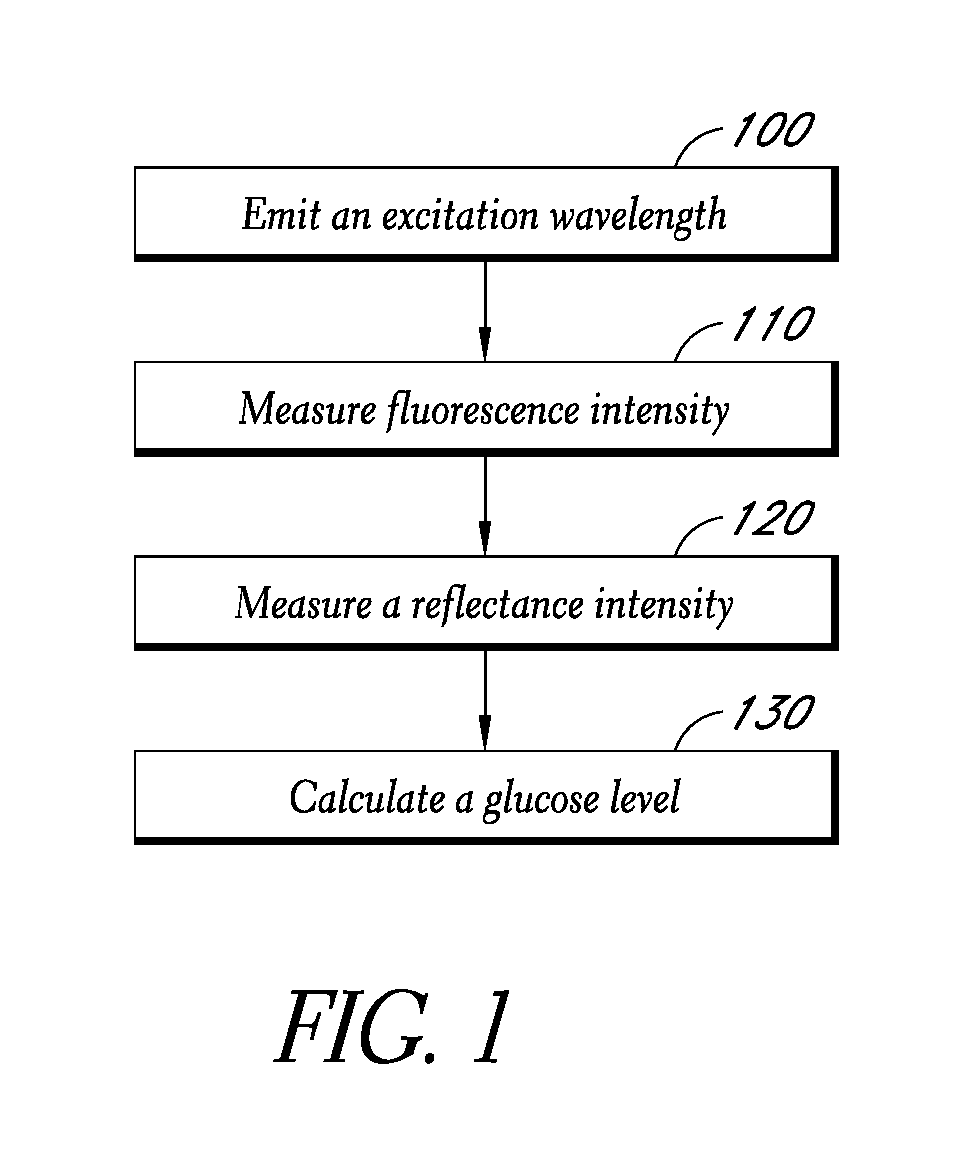
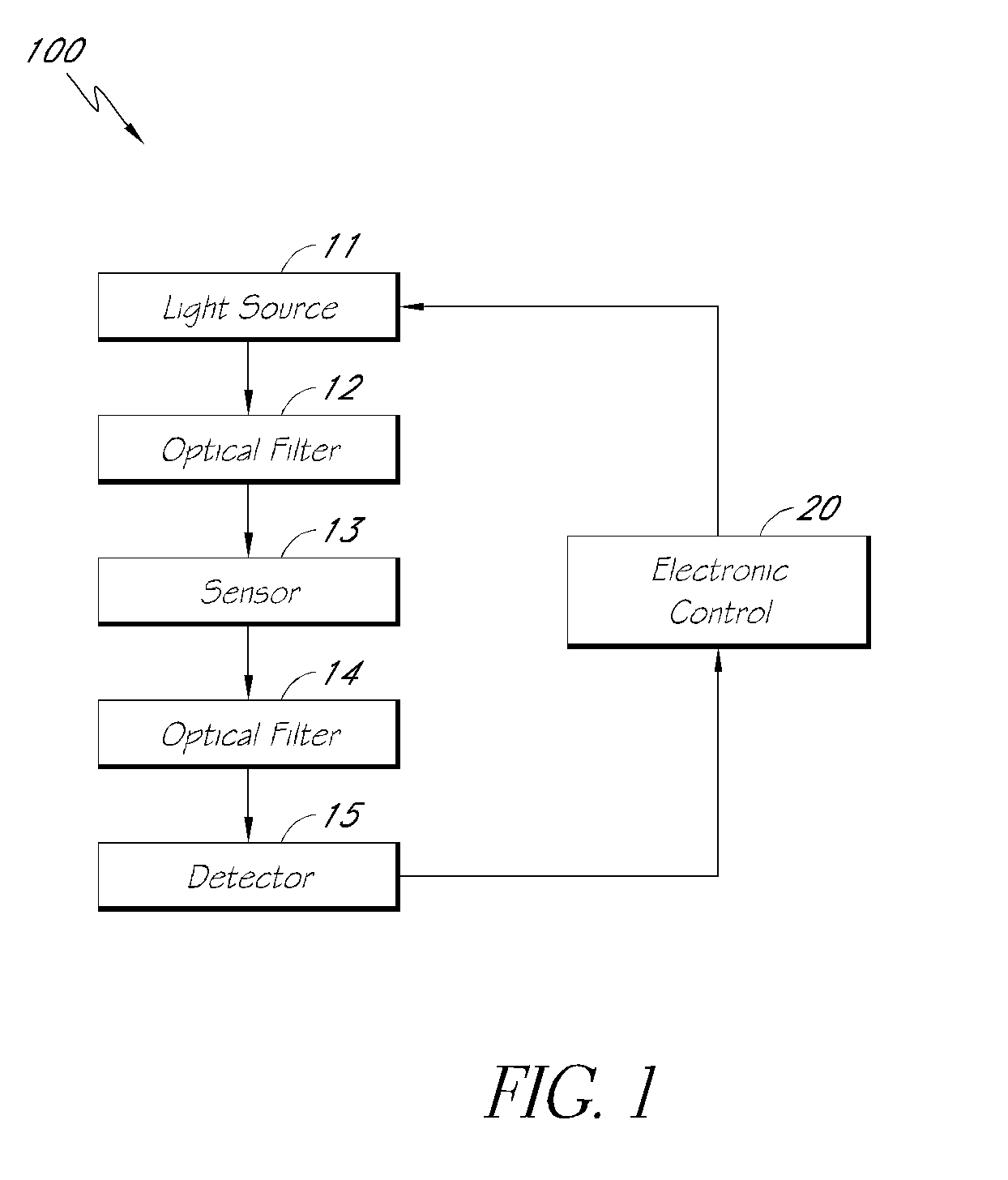
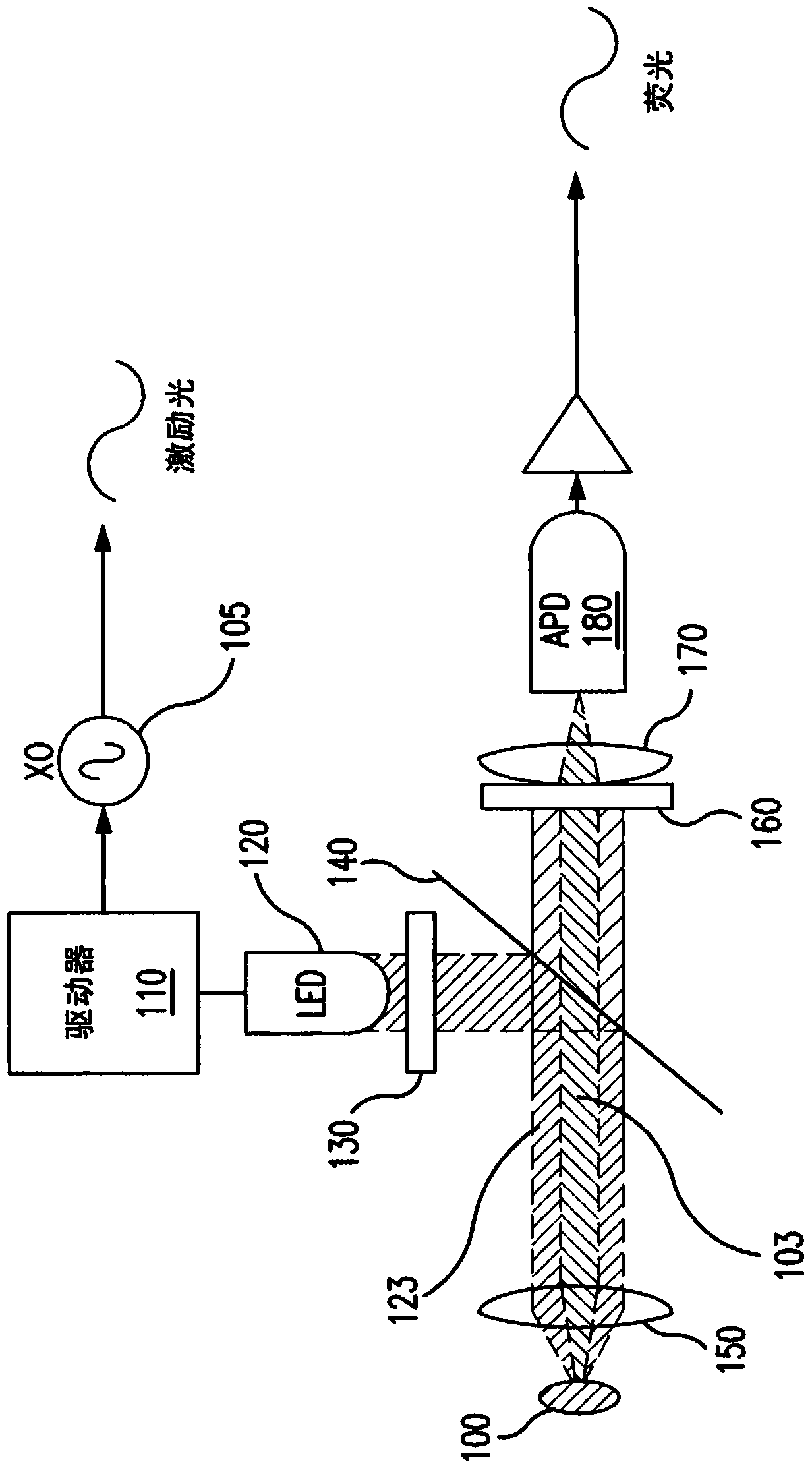
Reflectance calibration of fluorescence-based glucose measurements
InactiveUS20140330098A1Easy to detectDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMetaboliteMedicine
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Optical determination of ph and glucose
InactiveUS20080188722A1Biological material analysisAnalysis by electrical excitationAnalyteSingle indicator
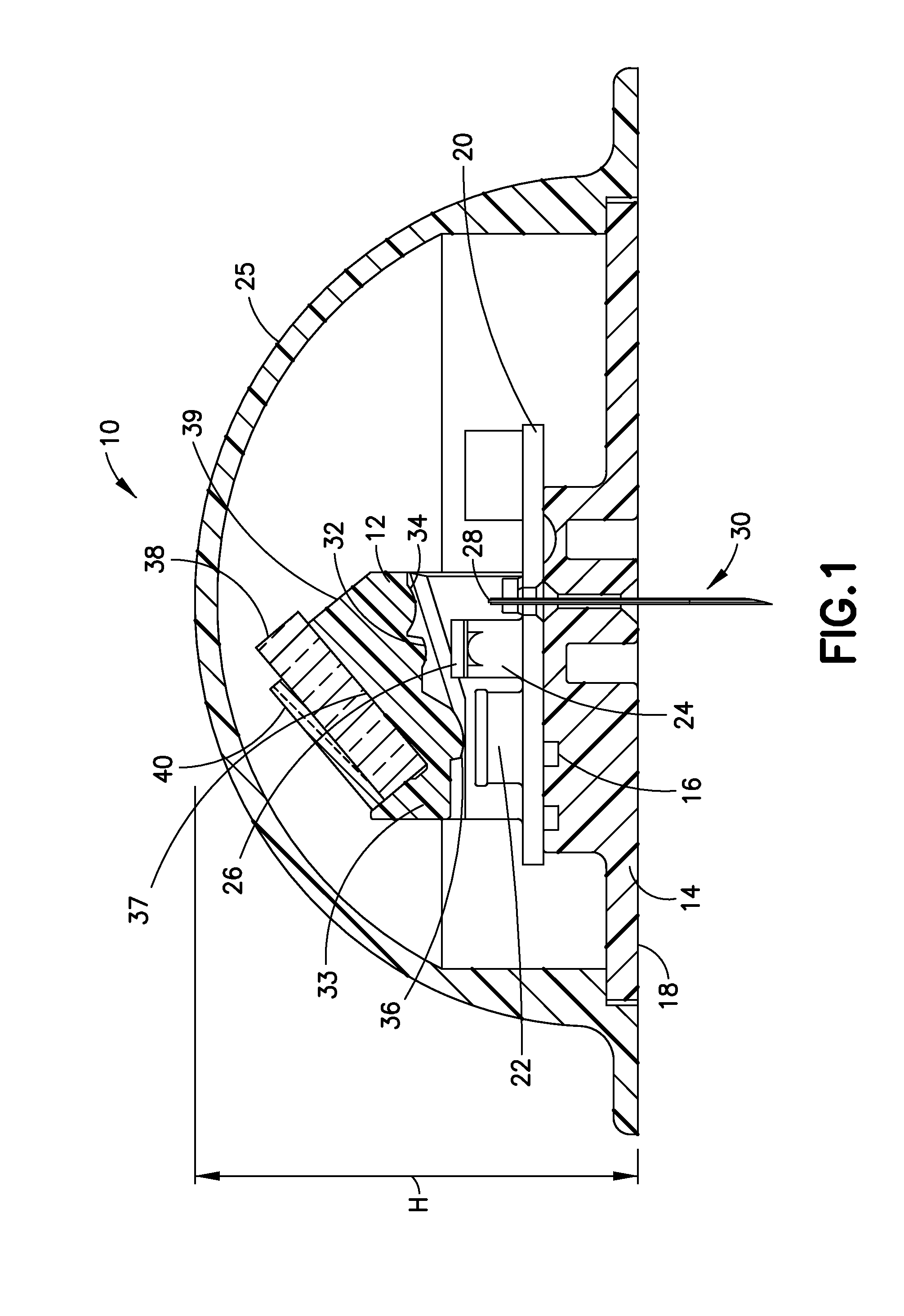
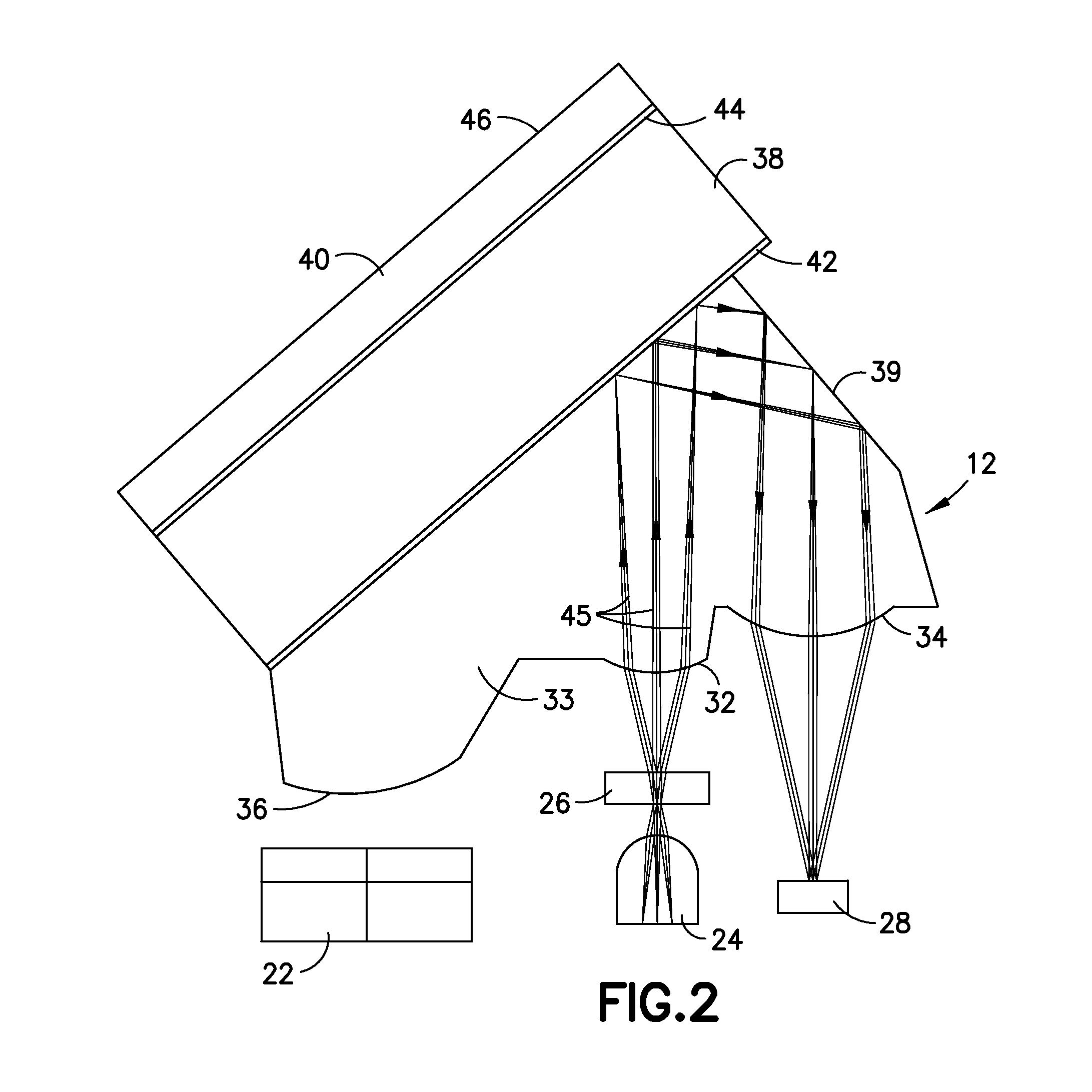
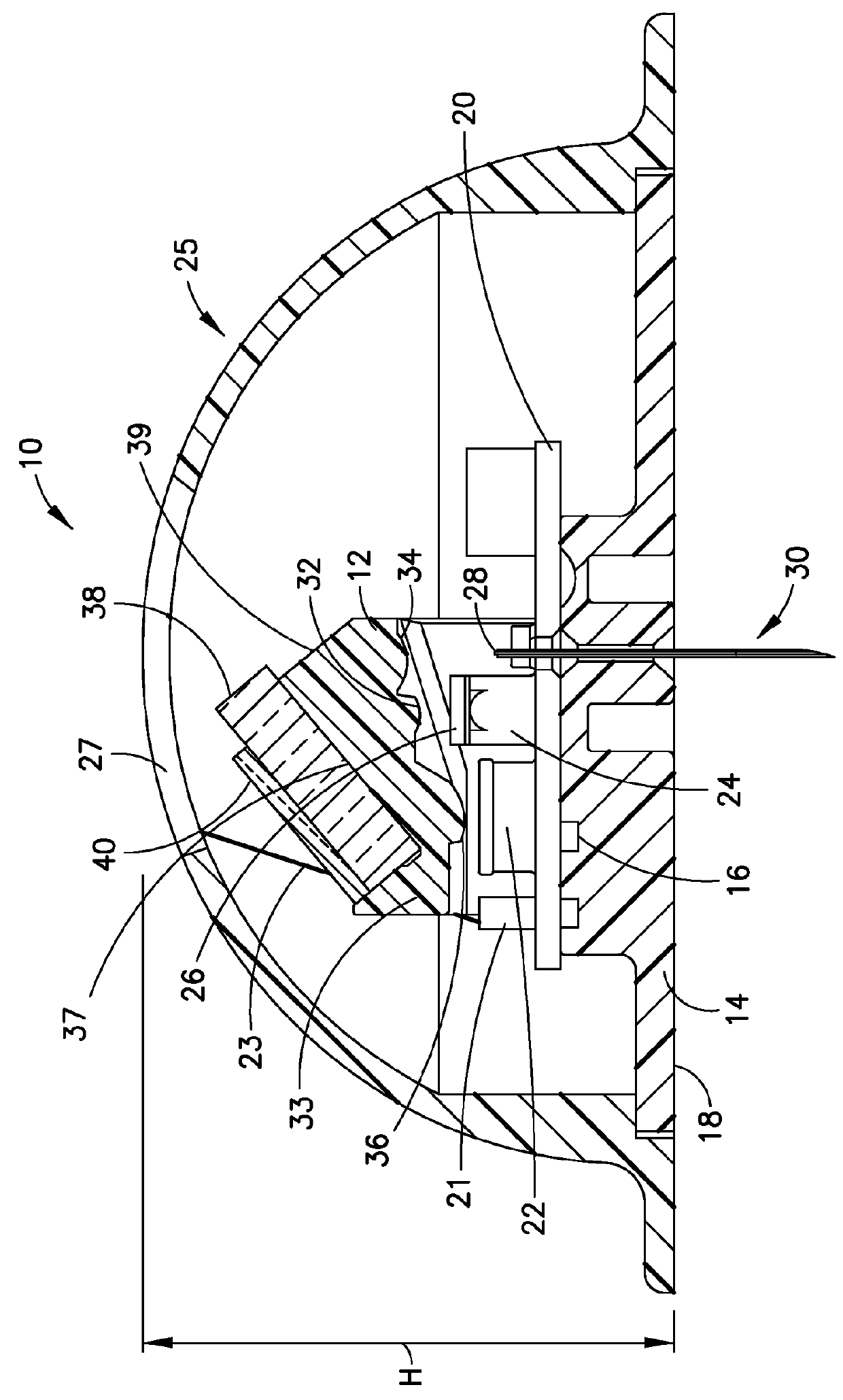
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to an optical sensor capable of measuring two analytes simultaneously with a single indicator system. In preferred embodiments, the sensor comprises a fluorescent dye having acid and base forms that facilitate ratiometric pH sensing, wherein the dye is further associated with a glucose binding moiety and configured to generate a signal that varies in intensity with the concentration of glucose.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Reflectance calibration of fluorescence-based glucose measurements
InactiveUS20110028806A1Easily detected fluorescenceEasy to detectDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMetaboliteLight energy
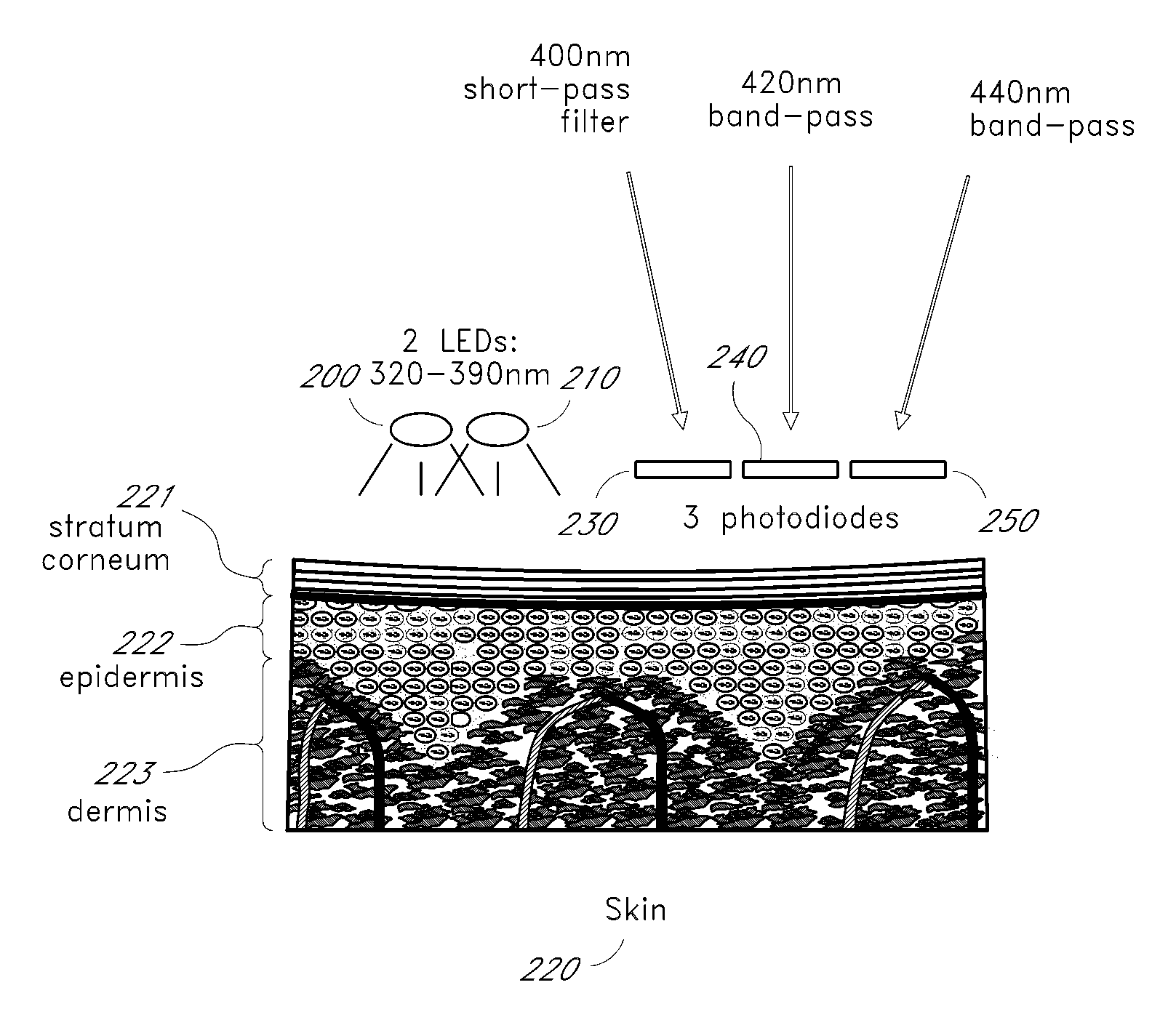
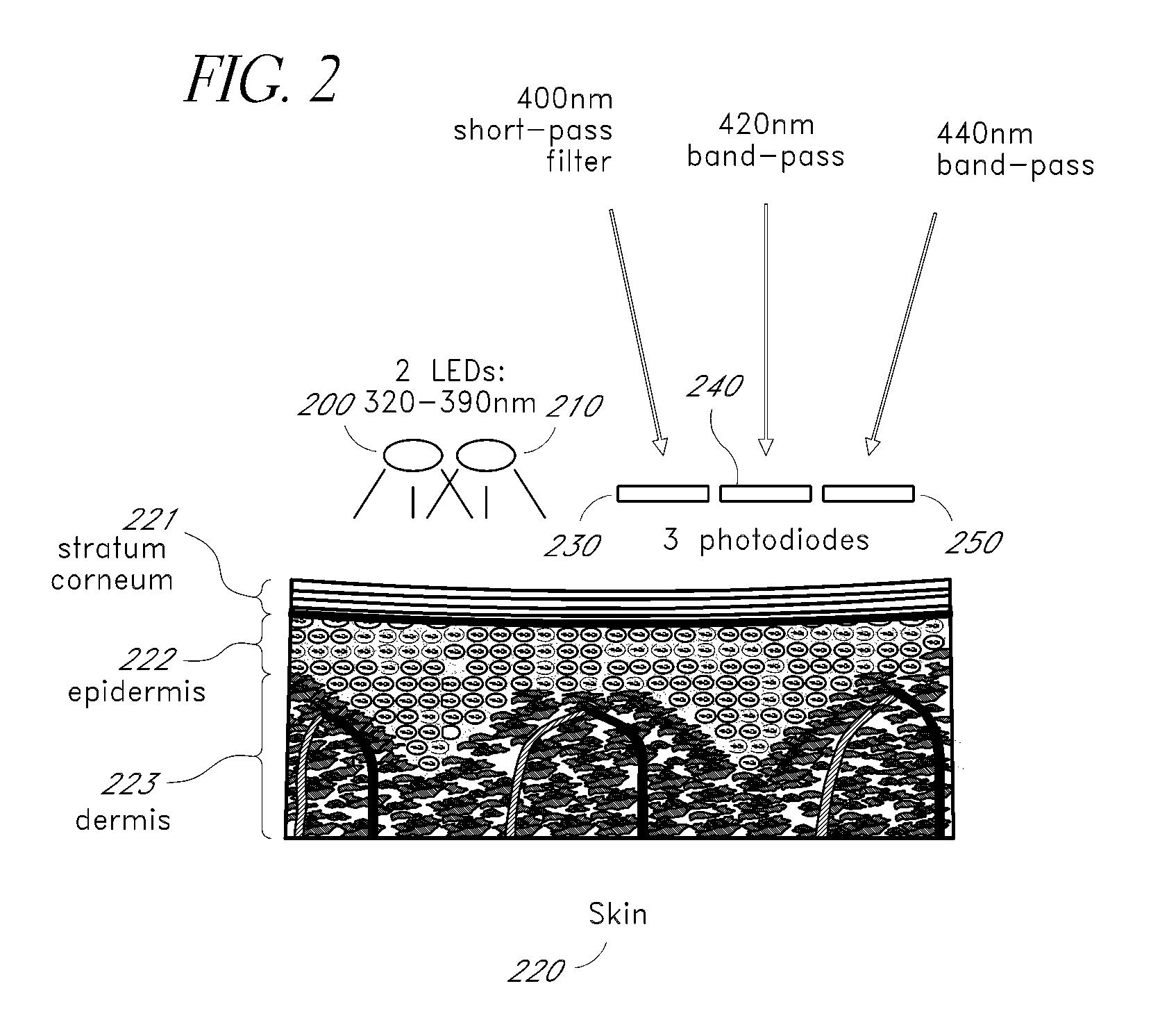
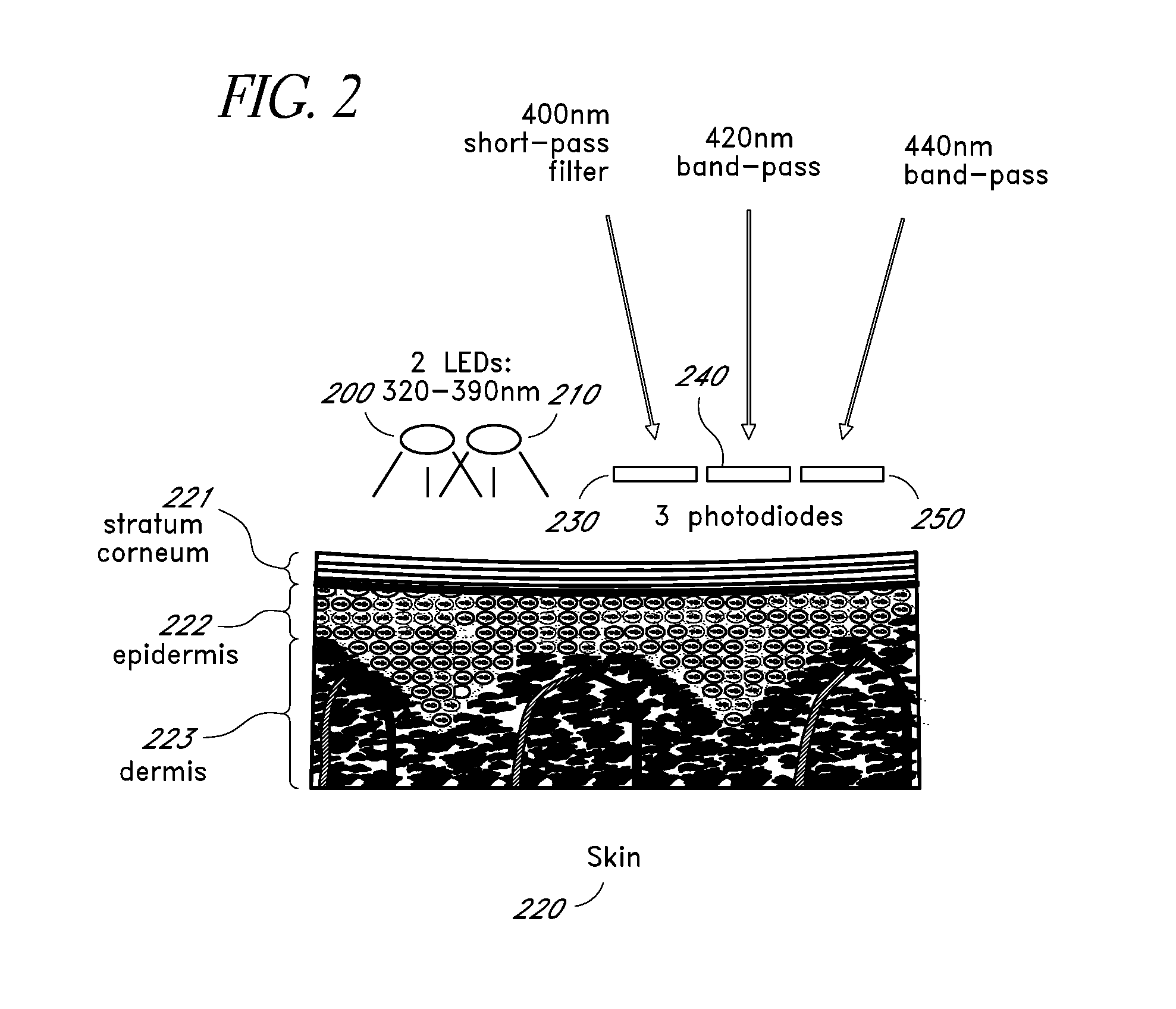
A noninvasive or minimally invasive procedure and system for measuring blood glucose levels is disclosed. A set of photodiodes detects the fluorescence and reflectance of light energy emitted from one or more emitters, such as LEDs, into a patient's skin. In an embodiment, small molecule metabolite reporters (SMMRs) that bind to glucose are introduced to the measurement area to provide more easily detected fluorescence.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Optical determination of ph and glucose
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to an optical sensor capable of measuring two analytes simultaneously with a single indicator system. In preferred embodiments, the sensor comprises a fluorescent dye having acid and base forms that facilitate ratiometric pH sensing, wherein the dye is further associated with a glucose binding moiety and configured to generate a signal that varies in intensity with the concentration of glucose.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
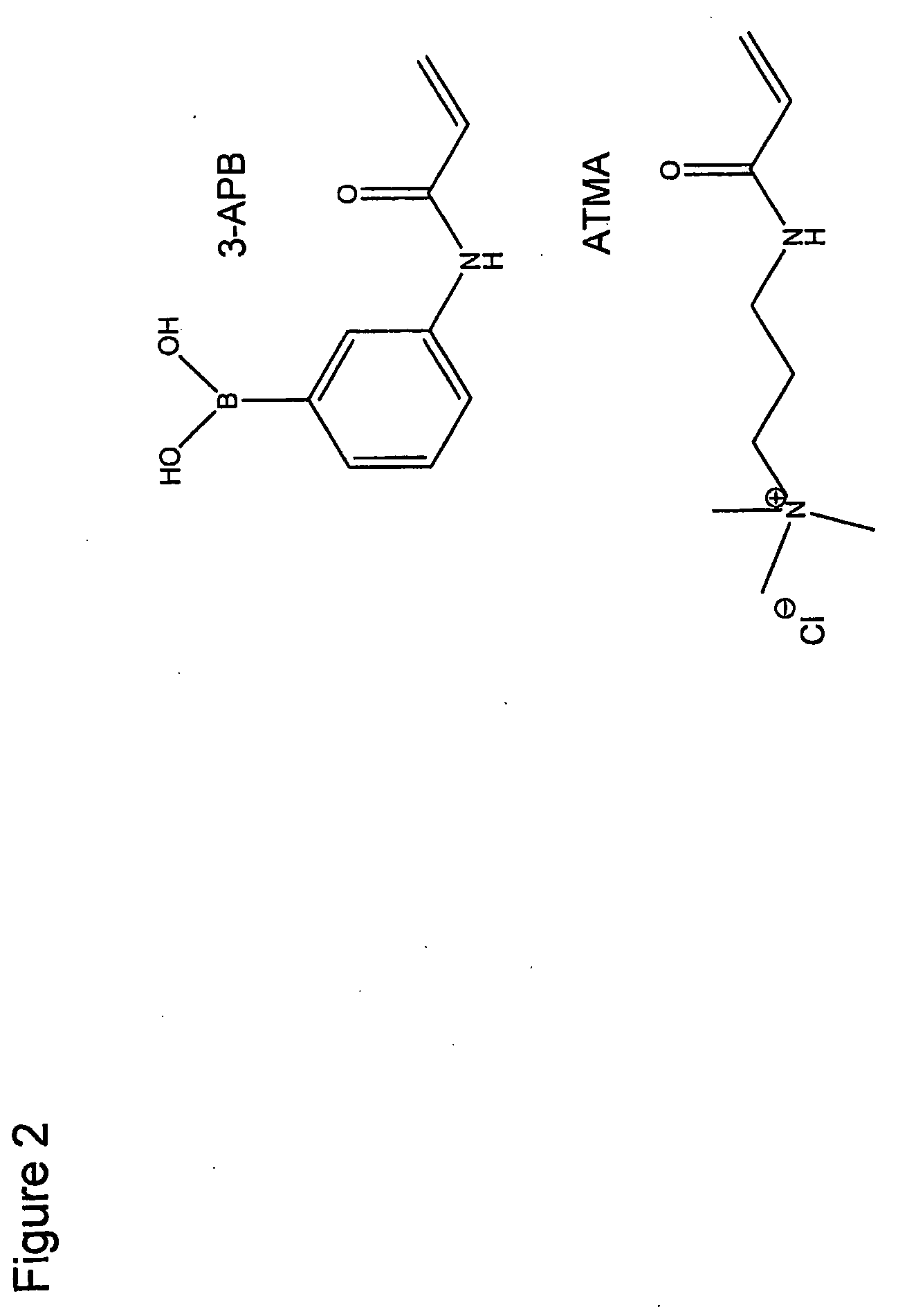
Solid-phase saccharide sensing compounds
The present invention provides solid-phase saccharide dyes. The dyes are bisboronic acids covalently bonded to a solid substrate. The dyes selectively conjugate with saccharides, particularly glucose, and register a signal. The signal is proportional to the quantity of saccharide. Thus, the dyes of the present invention are useful for measuring and monitoring saccharide levels, particularly in biological fluids such as blood.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Implantable power sources and sensors
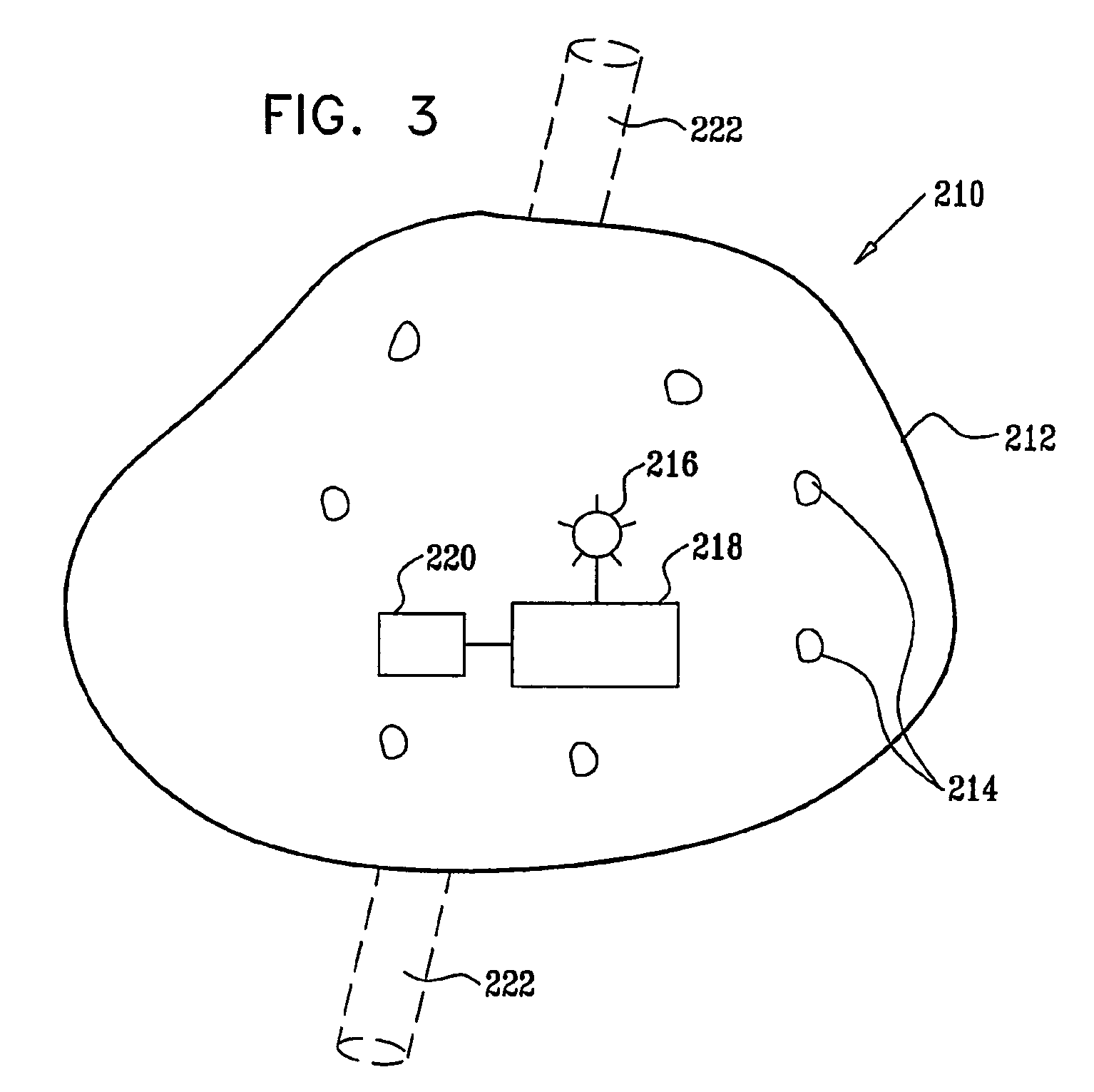
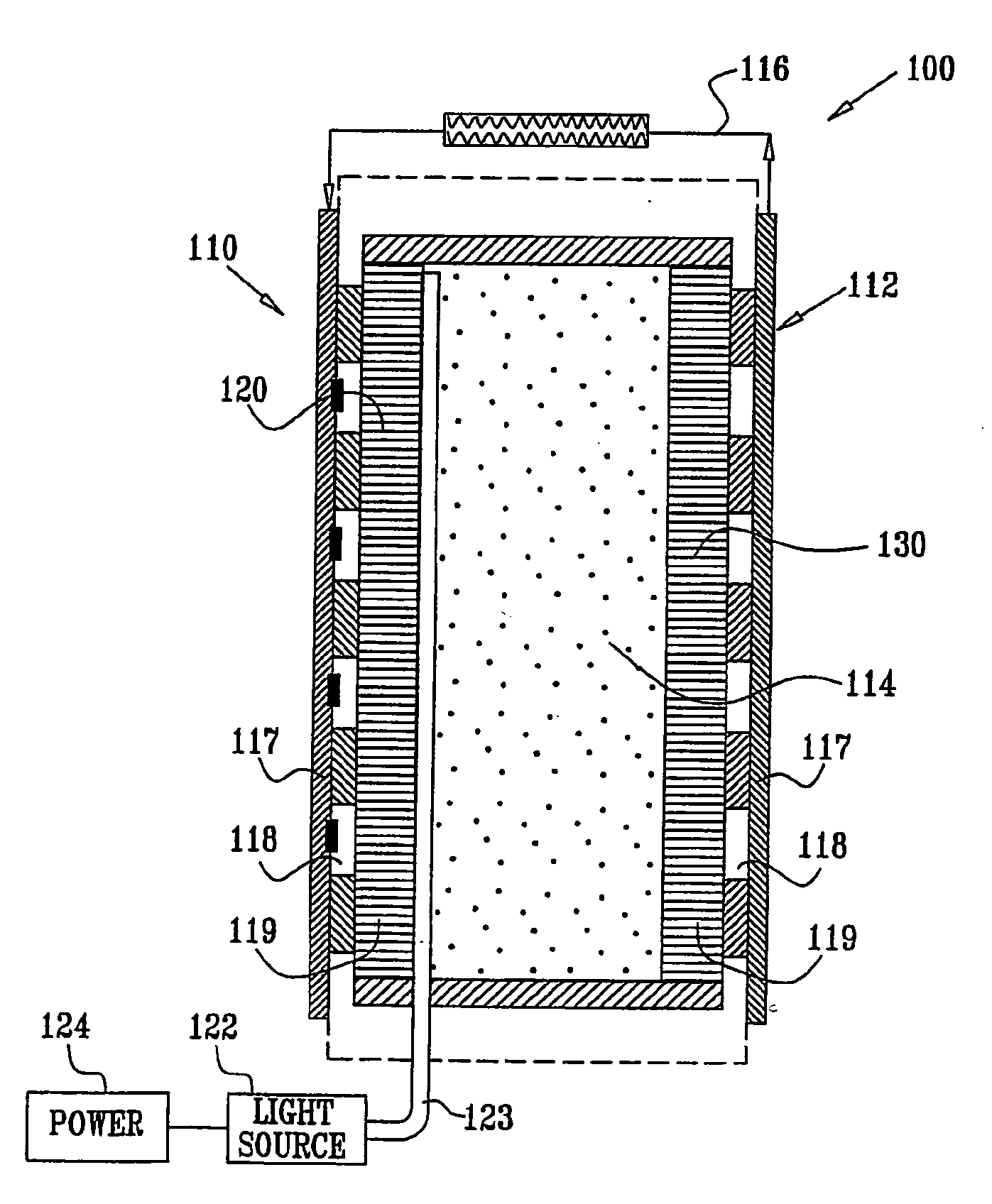
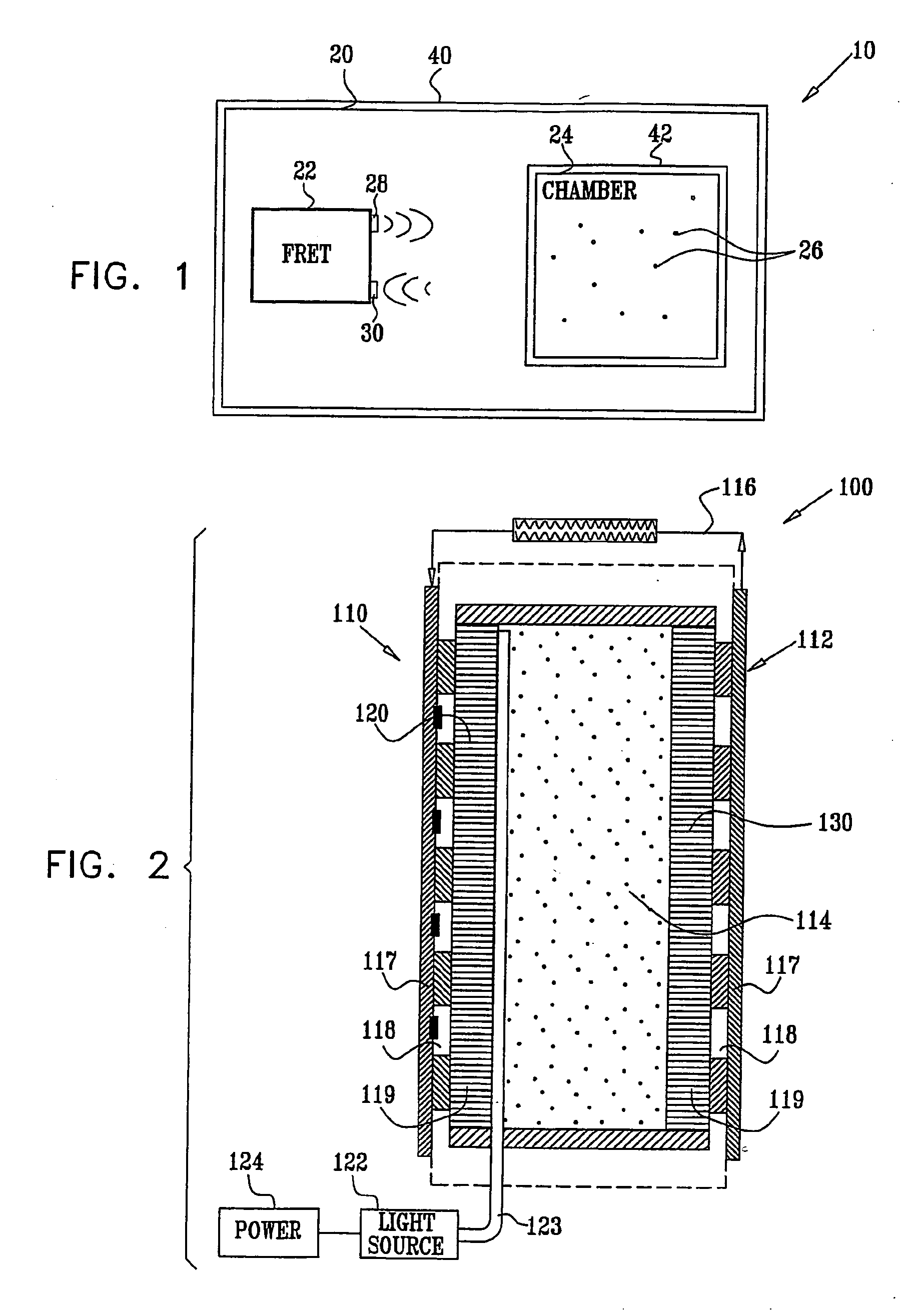
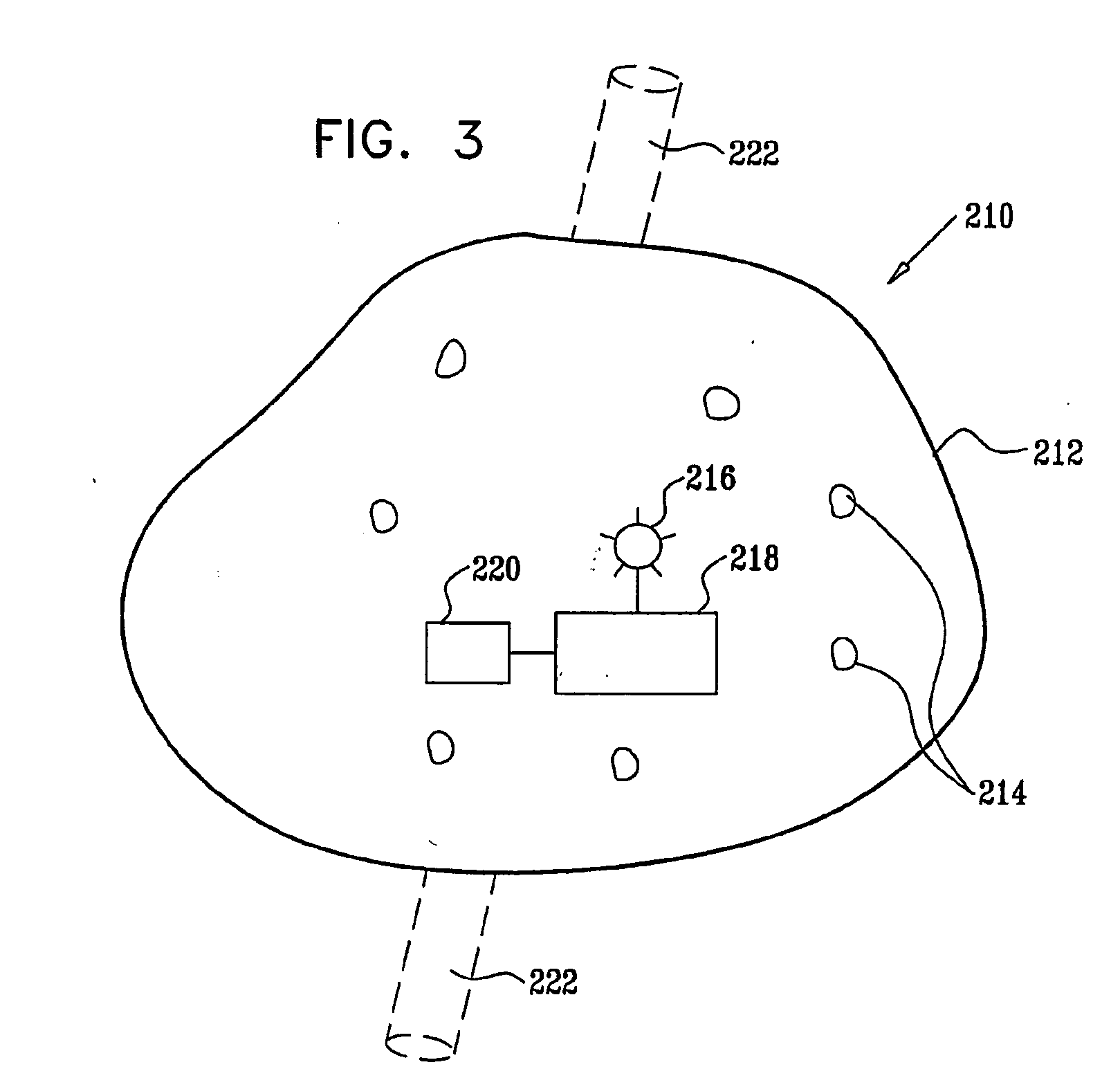
InactiveUS7951357B2Trend downObstruct passageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsD-GlucoseGlucose polymers
A protein is provided, including a glucose binding site, cyan fluorescent protein (CFP), and yellow fluorescent protein (YFP). The protein is configured such that binding of glucose to the glucose binding site causes a reduction in a distance between the CFP and the YFP. Substance monitoring apparatus (210) is also provided, including a semi-permeable barrier (212), adapted to be implanted in a body of a subject and to allow passage therethrough of a substance, while inhibiting passage therethrough of immune cells; and microorganisms (214), disposed within the semi-permeable barrier (212) so as to produce a measurable response to a level of the substance. A sensor (220) is adapted to measure the measurable response and not to measure a response of any mammalian cells that may be disposed within the semi-permeable barrier (212).
Owner:GLUSENSE LTD
Optical determination of ph and glucose
ActiveUS20100274110A1Biological material analysisAnalysis by electrical excitationAnalyteSingle indicator
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to an optical sensor capable of measuring two analytes simultaneously with a single indicator system. In preferred embodiments, the sensor comprises a fluorescent dye having acid and base forms that facilitate ratiometric pH sensing, wherein the dye is further associated with a glucose binding moiety and configured to generate a signal that varies in intensity with the concentration of glucose.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
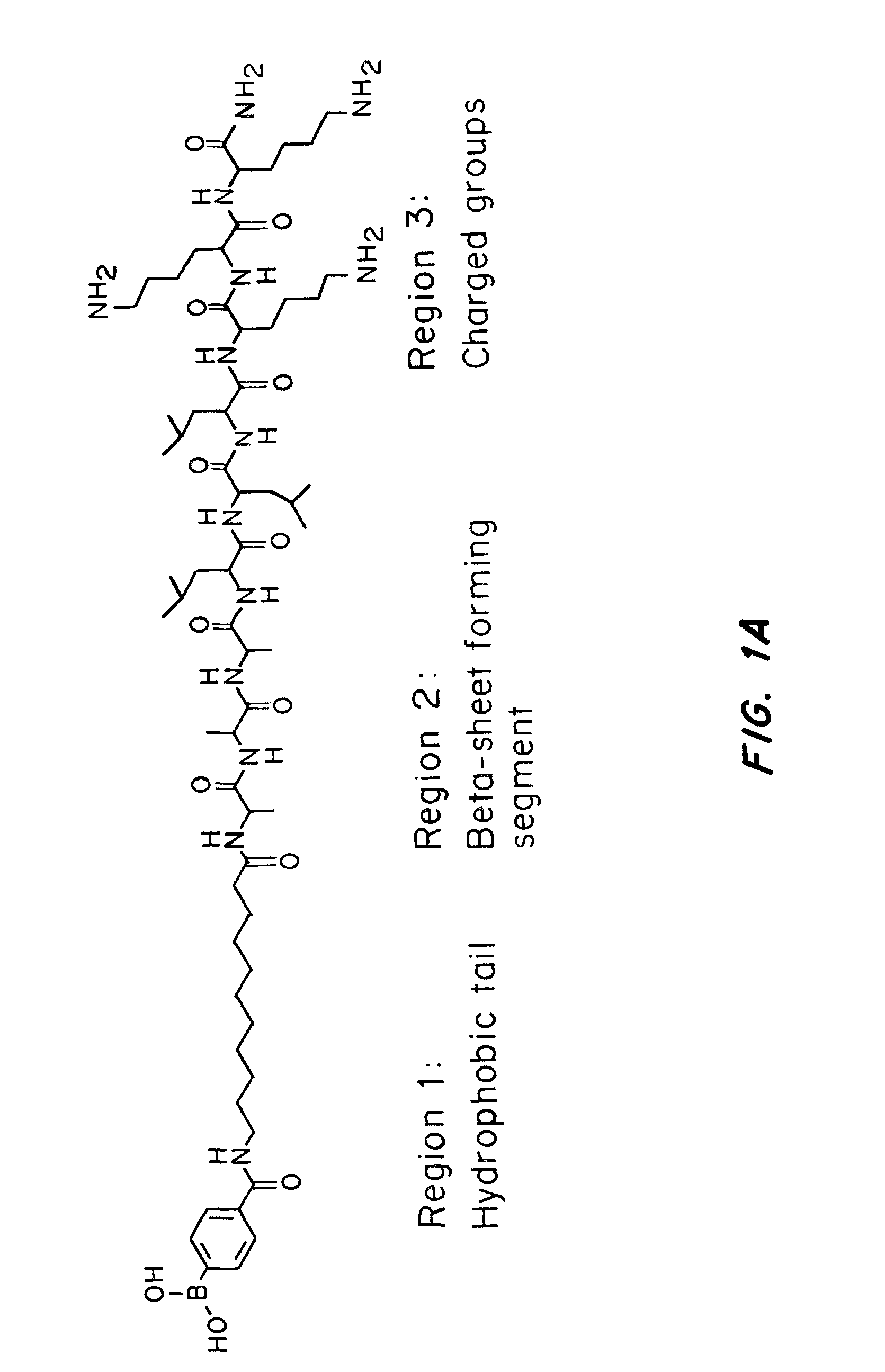
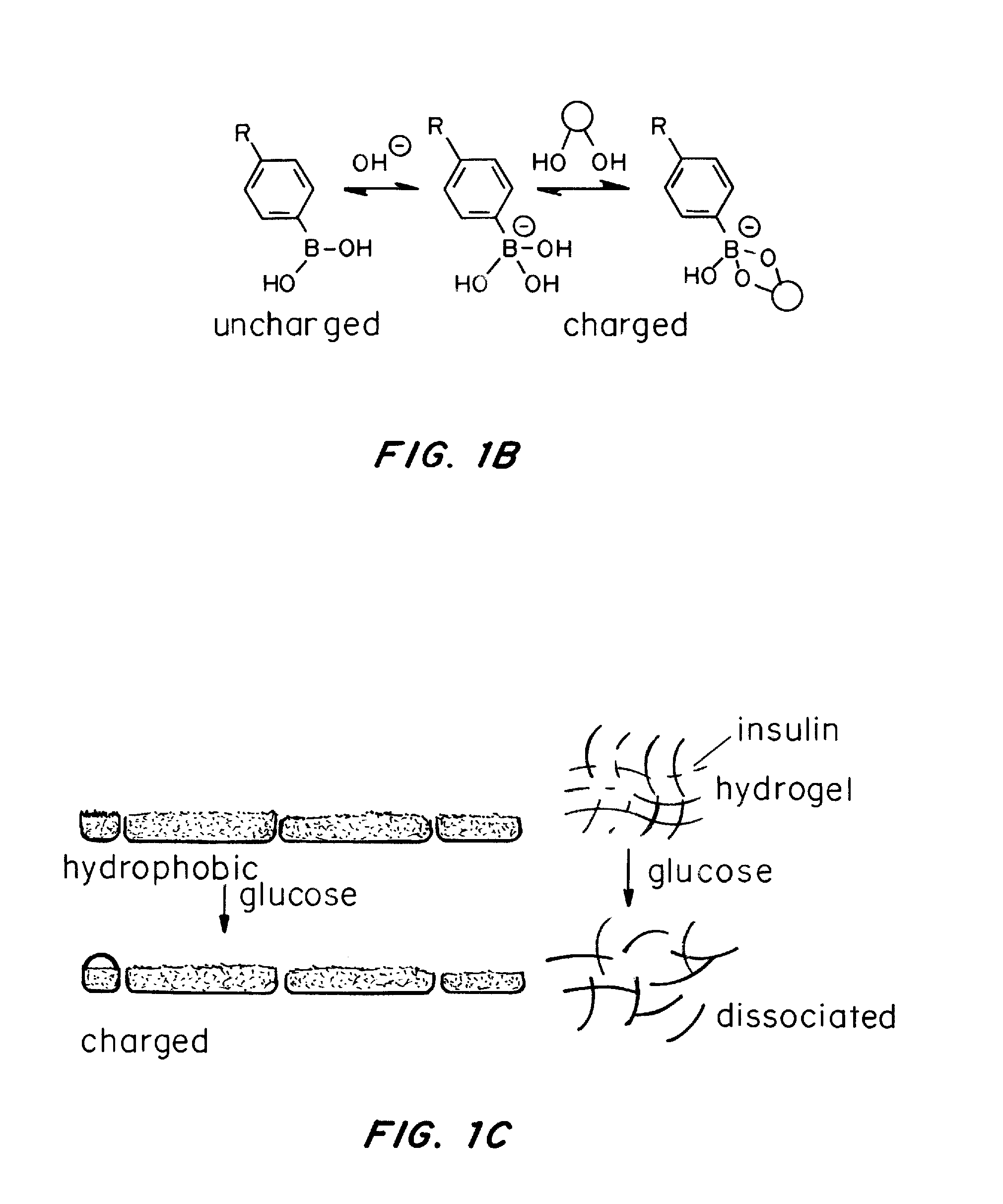
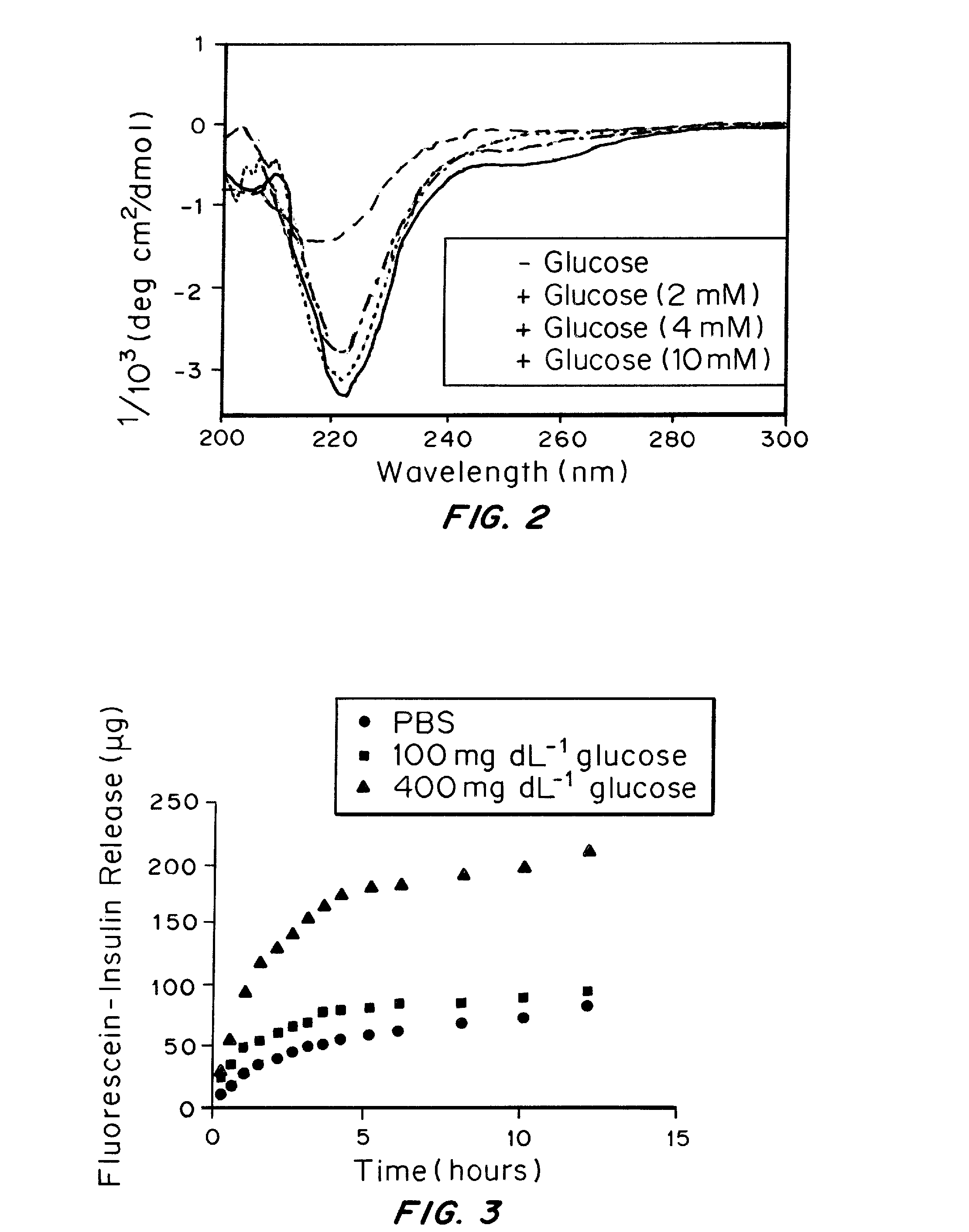
Self-regulated peptide hydrogel for insulin delivery
ActiveUS20150025005A1Avoiding both hyper- and hypoglycemiaStopping releasePeptide/protein ingredientsOintment deliveryConcentrations glucoseHypoglycemia
A glucose binding amphiphilic peptide hydrogel insulin delivery system that is responsive to glucose concentrations under physiological conditions is provided. Insulin is encapsulated in a glucose binding hydrogel, made from self-assembling amphiphilic peptides including a hydrophobic domain including a beta sheet forming region coupled to a charged hydrophilic domain modified to contain a glucose binding segment. The formulations are designed to release insulin as a function of blood glucose level, maintaining the patients' blood glucose level in an optimum range and avoiding both hyper- and hypoglycemia.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
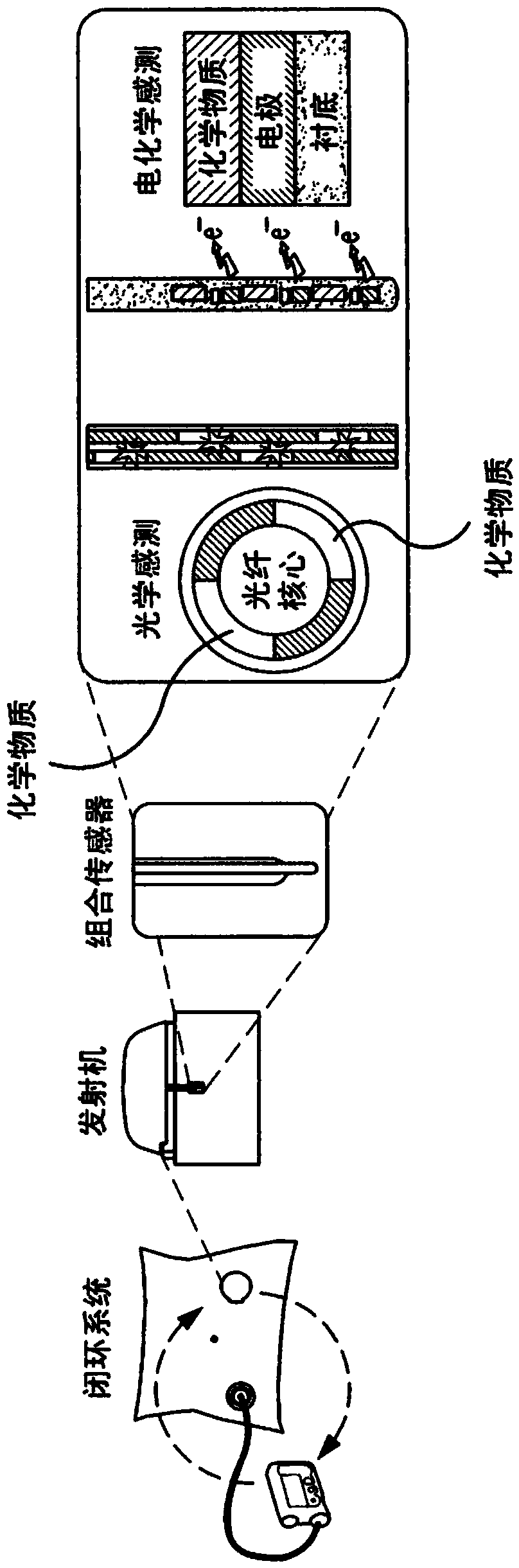
Orthogonally redundant sensor systems and methods
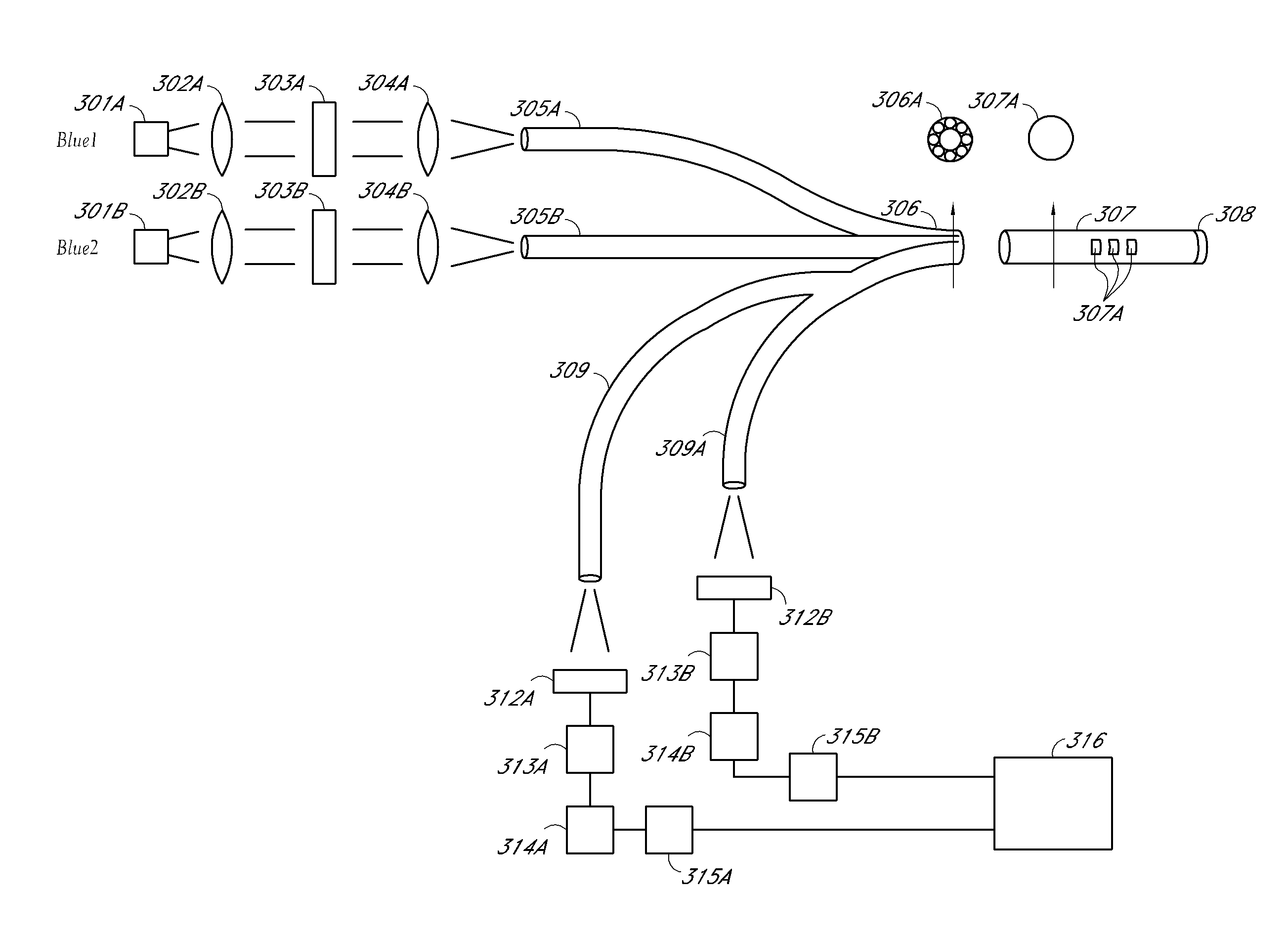
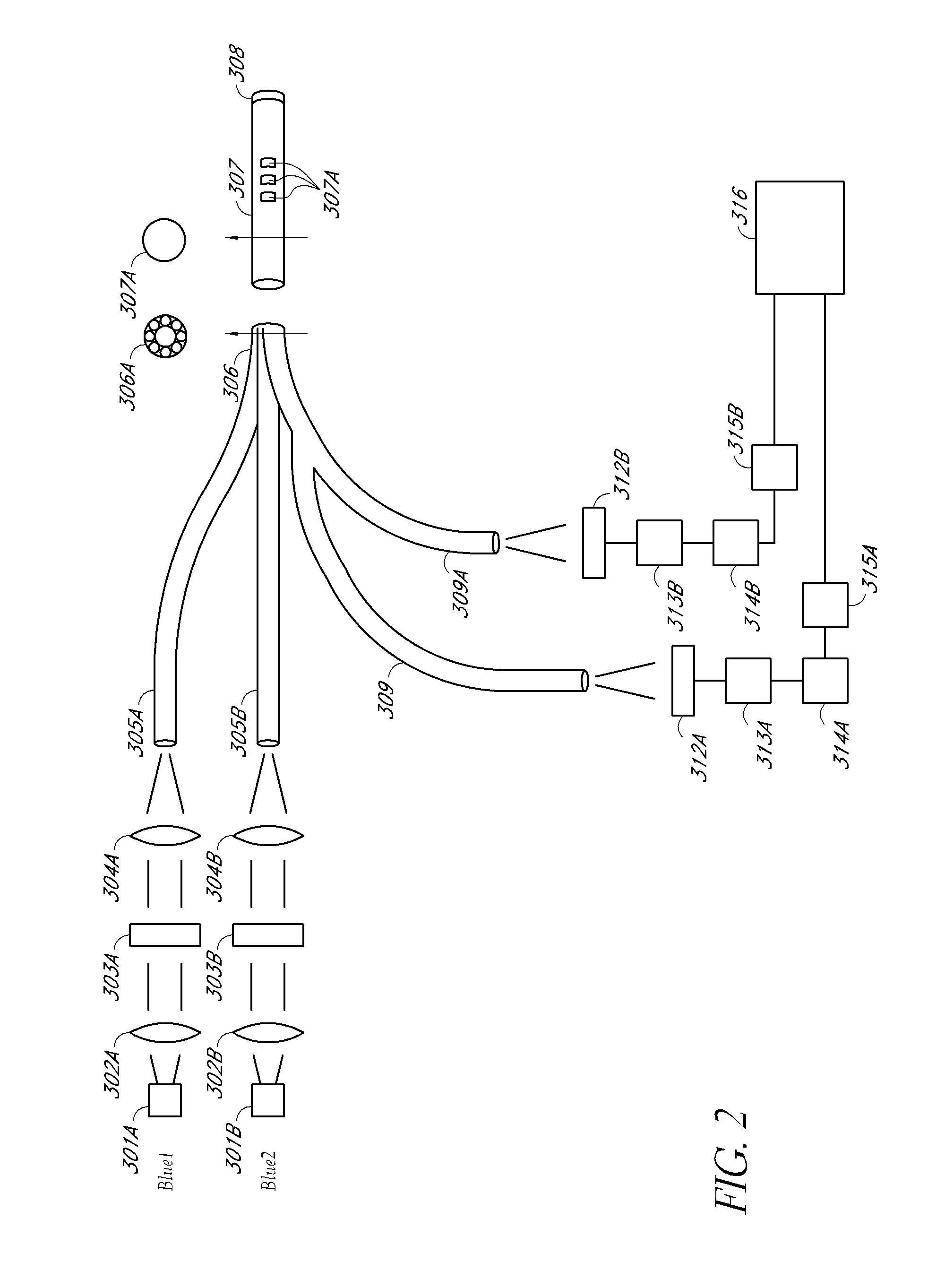
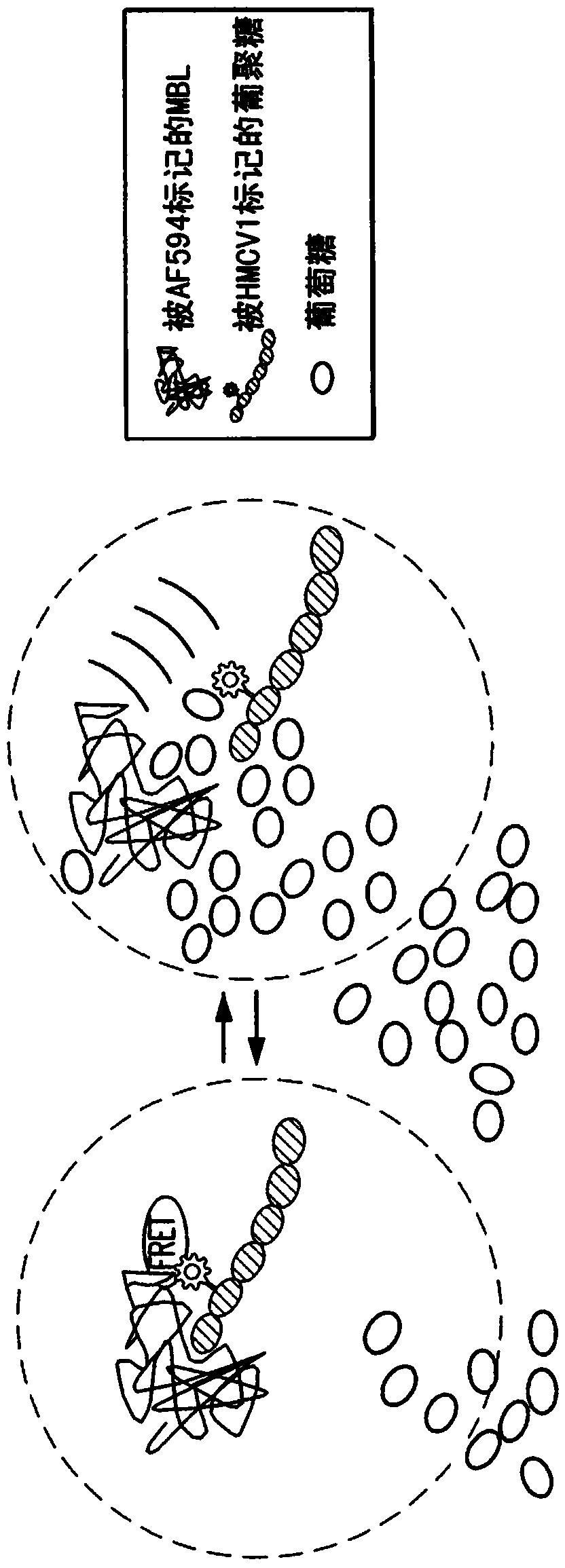
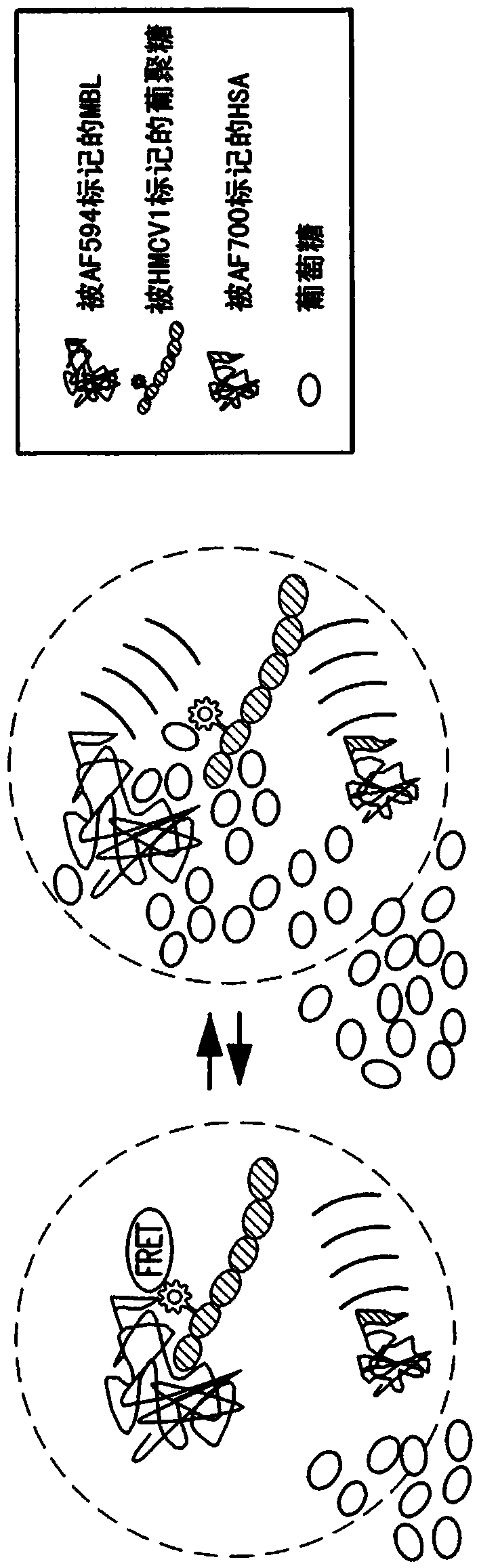
ActiveCN103917154AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological material analysisGlucose sensorsFluorescence
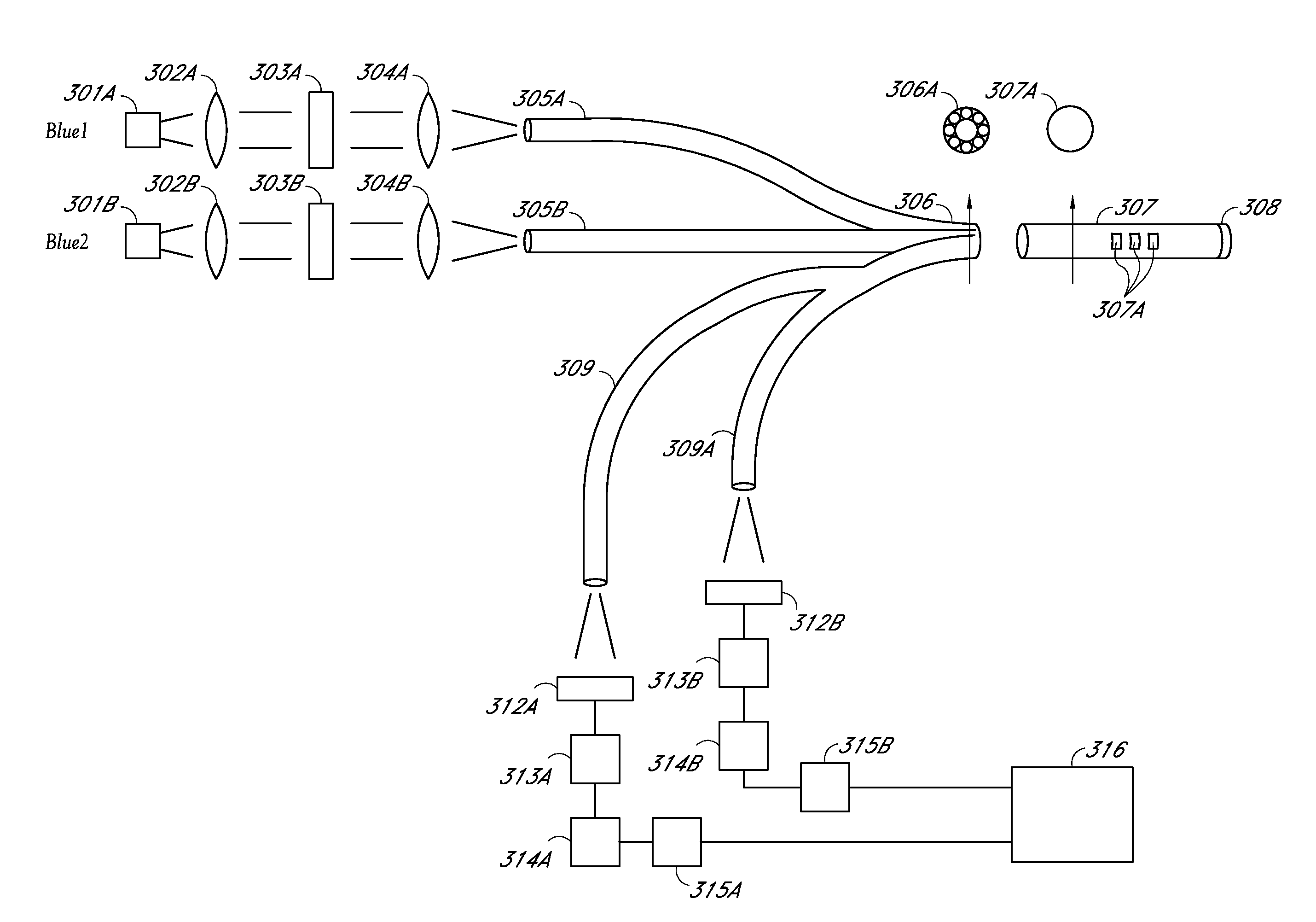
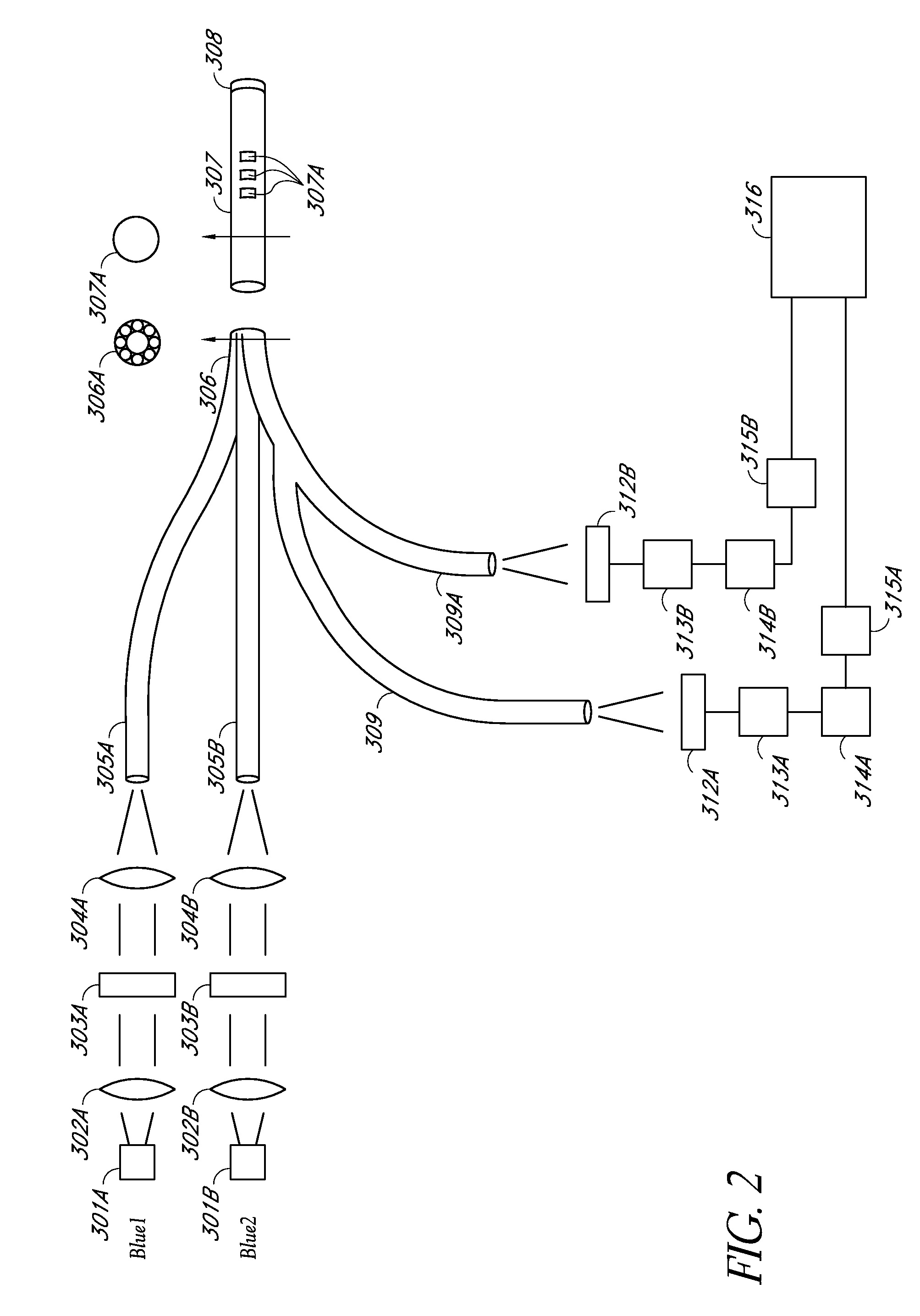
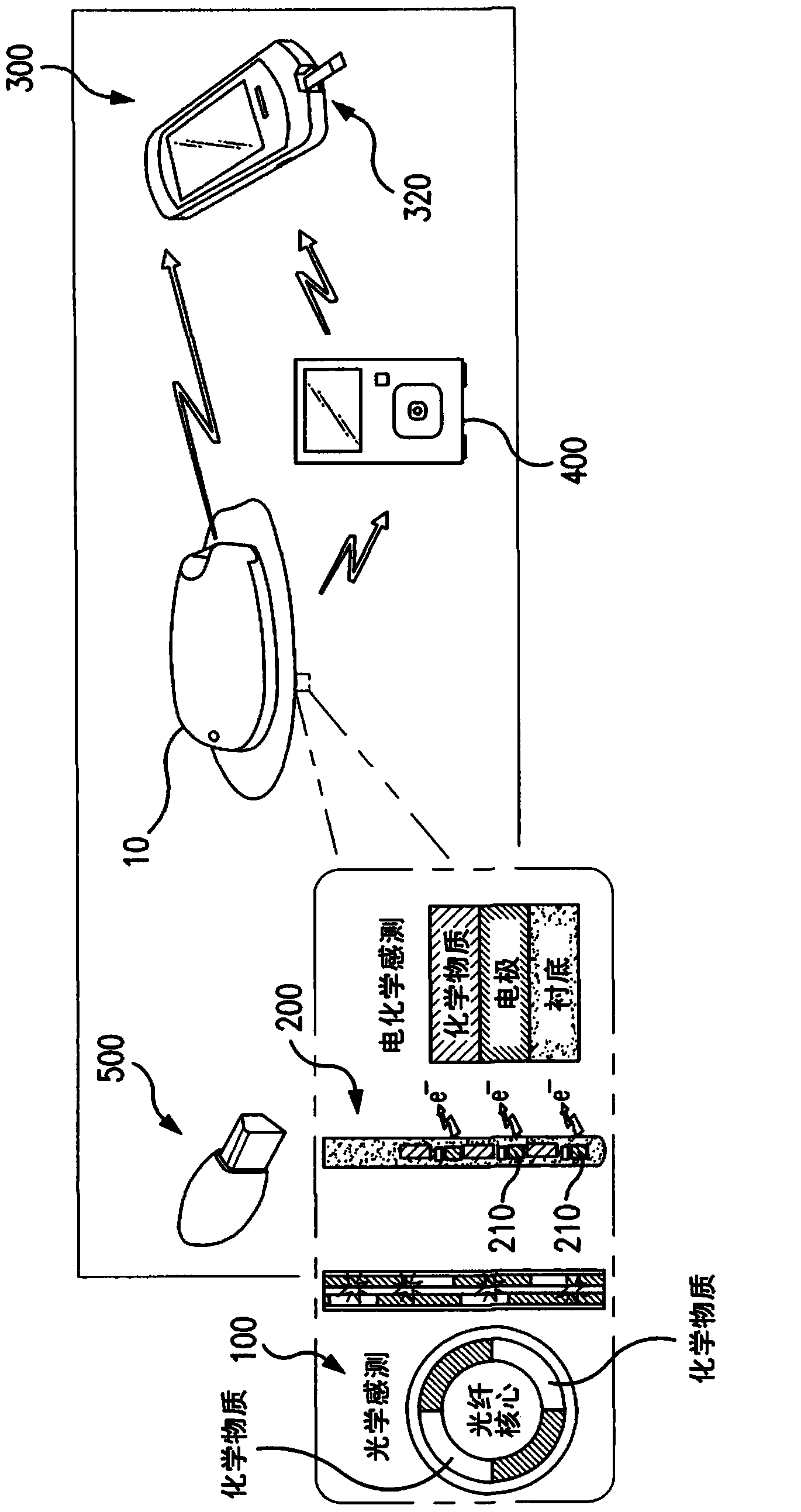
A continuous glucose monitoring system may include a hand-held monitor, a transmitter, an insulin pump, and an orthogonally redundant glucose sensor, which may comprise an optical glucose sensor and a non-optical glucose sensor. The former may be a fiber optical sensor, including a competitive glucose binding affinity assay with a glucose analog and a fluorophore-labeled glucose receptor, which is interrogated by an optical interrogating system, e.g., a stacked planar integrated optical system. The non-optical sensor may be an electrochemical sensor having a plurality of electrodes distributed along the length thereof. Proximal portions of the optical and electrochemical sensors may be housed inside the transmitter and operationally coupled with instrumentation for, e.g., receiving signals from the sensors, converting to respective glucose values, and communicating the glucose values. The sensors' distal portions may be inserted into a user's body via a single delivery needle and may be co-located inside the user's body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Novel Boronate Complex and Its Use in a Glucose Sensor
InactiveUS20100167416A1Good choiceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGlucose sensorsGlucose polymers
A sensor comprises respective acceptor and donor compounds immobilised in or on a matrix including a glucose-binding boronate and a cationic species, whereby the spacing between the acceptor and donor compounds is reduced in the presence of glucose. For example a holographic sensor comprises a glucose-binding boronate and a cationic species held within the sensor.
Owner:SMART HOLOGRAMS +1
Dry insertion and one-point in vivo calibration of an optical analyte sensor
Disclosed are embodiments that relate to the deployment of a glucose sensor comprising an optical fiber into a physiological fluid, wherein the optical fiber has disposed along a distal region thereof a chemical indicator system comprising a fluorophore and a glucose binding moiety immobilized within a hydrogel, wherein the components of the chemical indicator system are in a dry state before deployment. Also disclosed is a one-point in vivo calibration of the chemical indicator system based on an independently measured glucose concentration.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Implantable Power Sources and Sensors
InactiveUS20080319287A1Trend downObstruct passageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismGlucose polymers
A protein is provided, including a glucose binding site, cyan fluorescent protein (CFP), and yellow fluorescent protein (YFP). The protein is configured such that binding of glucose to the glucose binding site causes a reduction in a distance between the CFP and the YFP. Substance monitoring apparatus (210) is also provided, including a semi-permeable barrier (212), adapted to be implanted in a body of a subject and to allow passage therethrough of a substance, while inhibiting passage therethrough of immune cells; and microorganisms (214), disposed within the semi-permeable barrier (212) so as to produce a measurable response to a level of the substance. A sensor (220) is adapted to measure the measurable response and not to measure a response of any mammalian cells that may be disposed within the semi-permeable barrier (212).
Owner:GLUSENSE LTD
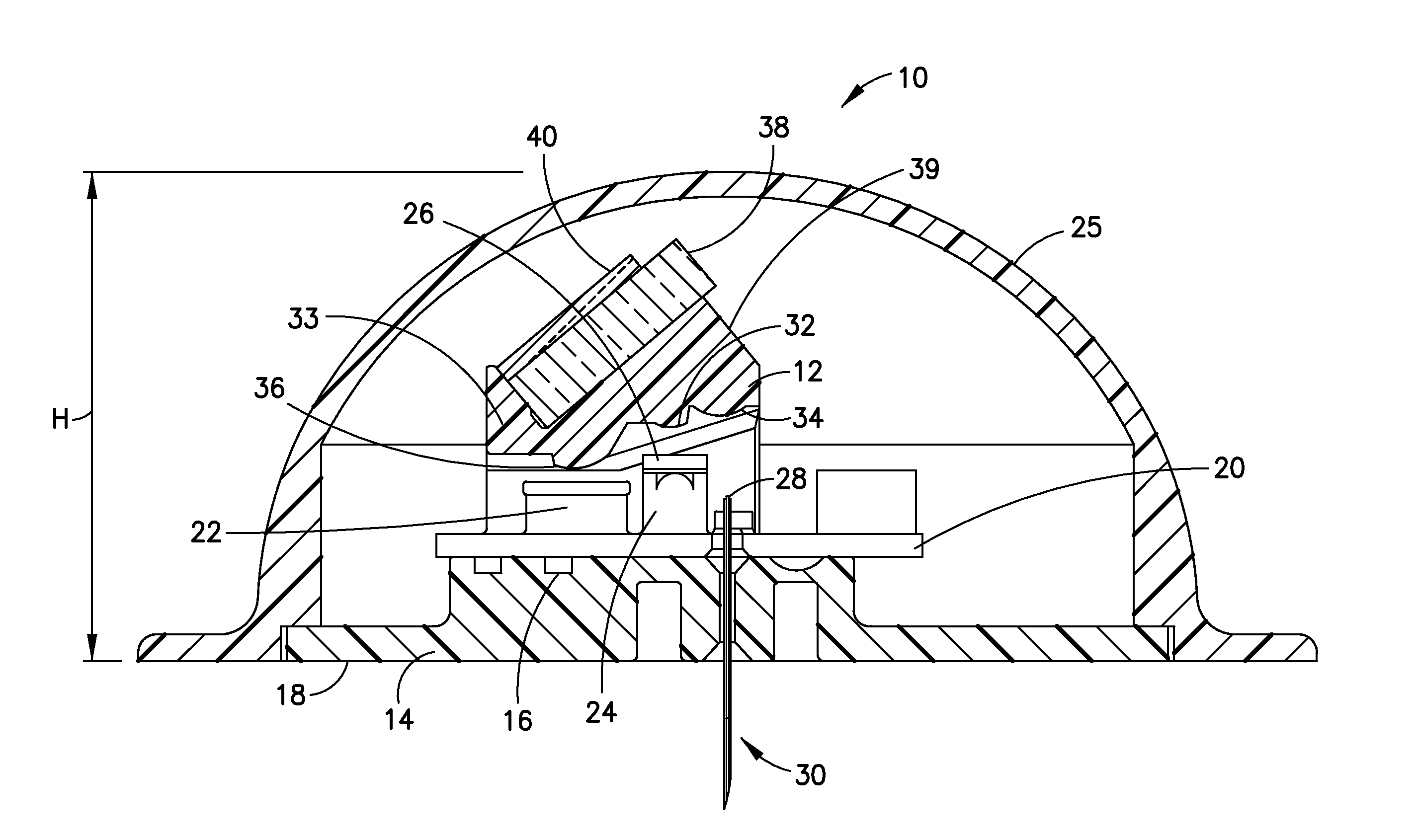
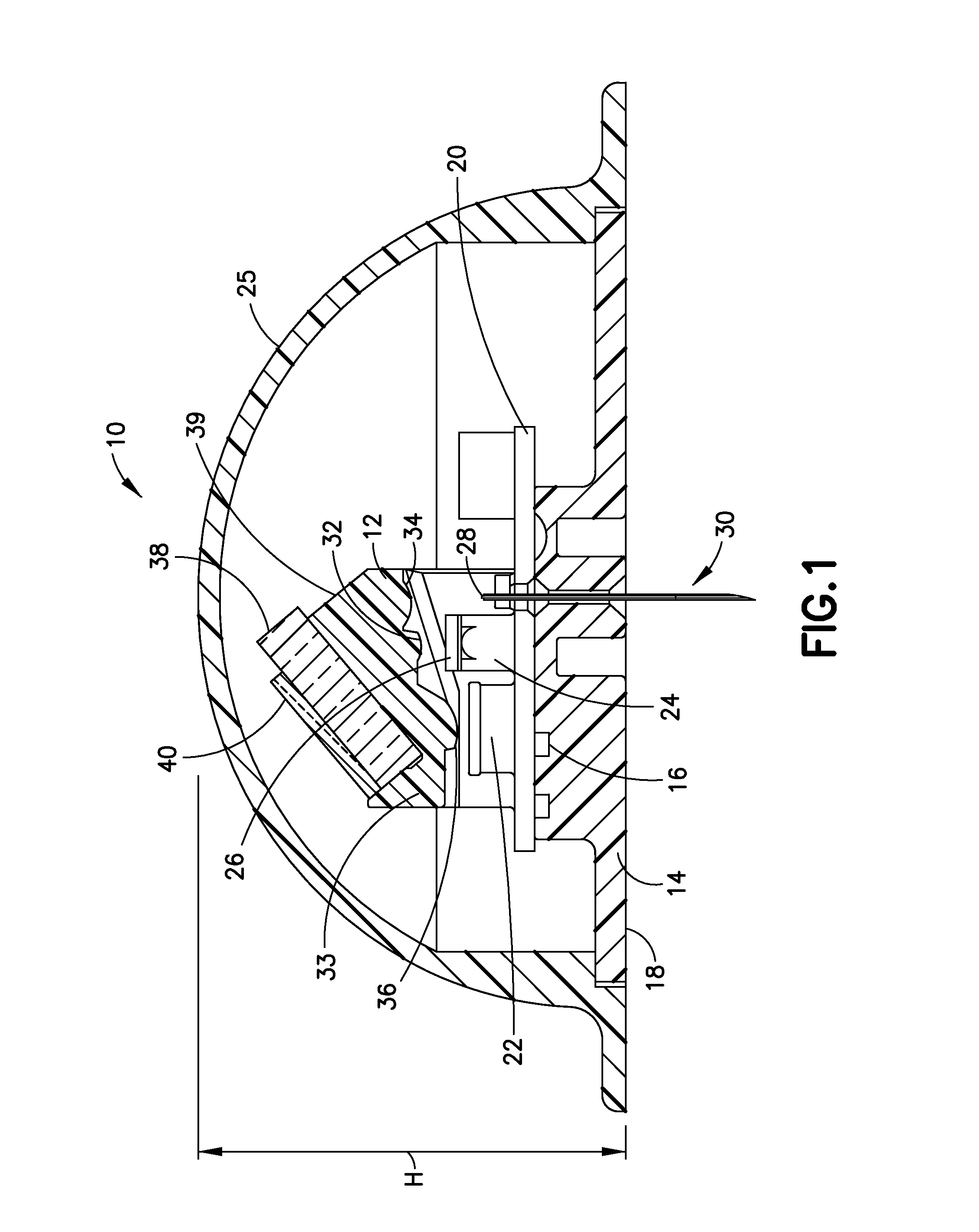
Continuous glucose monitoring on-body sensor
ActiveUS20160022179A1Improve satisfactionPrecise positioningCatheterSensorsAnalyteContinuous glucose monitoring
An on-body sensor (OBS) (5610) having a continuous monitoring (CGM) device is disclosed for use in identifying an analyte, such as glucose in blood or interstitial fluid (ISF), using a biomaterial, such as glucose binding protein (GBP), that is brought into contact with the analyte. The on-body sensor (5610) incorporating the CGM device includes a housing (5625′) which provides protection to the CGM device while providing comfort to a user wearing the device. The OBS also includes an adhesive structure that provides a comfortable, discreet and secure user experience.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Cellulose synthase encoding polynucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS7049481B1Quality improvementLow lignin contentBryophytesSugar derivativesNucleotidePlant cell
The invention relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding functional cellulose synthases and UDP-glucose binding domain thereof, transgenic plants and plant cells transformed with the polynucleotides. The invention further relates to methods of transforming plants and plant cells with cellulose synthase or UDP-encoding polynucleotides.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Continuous glucose monitoring on-body sensor having a visual display
An on-body sensor (OBS) (10) having a continuous monitoring (CGM) device is disclosed for use in identifying an analyte, such as glucose in blood or interstitial fluid (ISF), using a biomaterial, such as glucose binding protein (GBP), that is brought into contact with the analyte. The on-body sensor (10) incorporating the CGM device includes a cover (25) which provides protection to the CGM device and includes an integrated output display (27). The output display (27) can visually provide data received from the CGM device, to the user without the need for a separate data receiving device.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Novel boronate complex and its use in a glucose sensor
InactiveCN101360987AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorScattering properties measurementsGlucose sensorsD-Glucose
A sensor comprises respective acceptor and donor compounds immobilised in or on a matrix including a glucose-binding boronate and a cationic species, whereby the spacing between the acceptor and donor compounds is reduced in the presence of glucose. For example a holographic sensor comprises a glucose- binding boronate and a cationic species held within the sensor.
Owner:SMART HOLOGRAMS
Glucose sensor
InactiveUS20120232251A1Easy to changeImprove responseSugar derivativesDepsipeptidesGlucose sensorsWild type
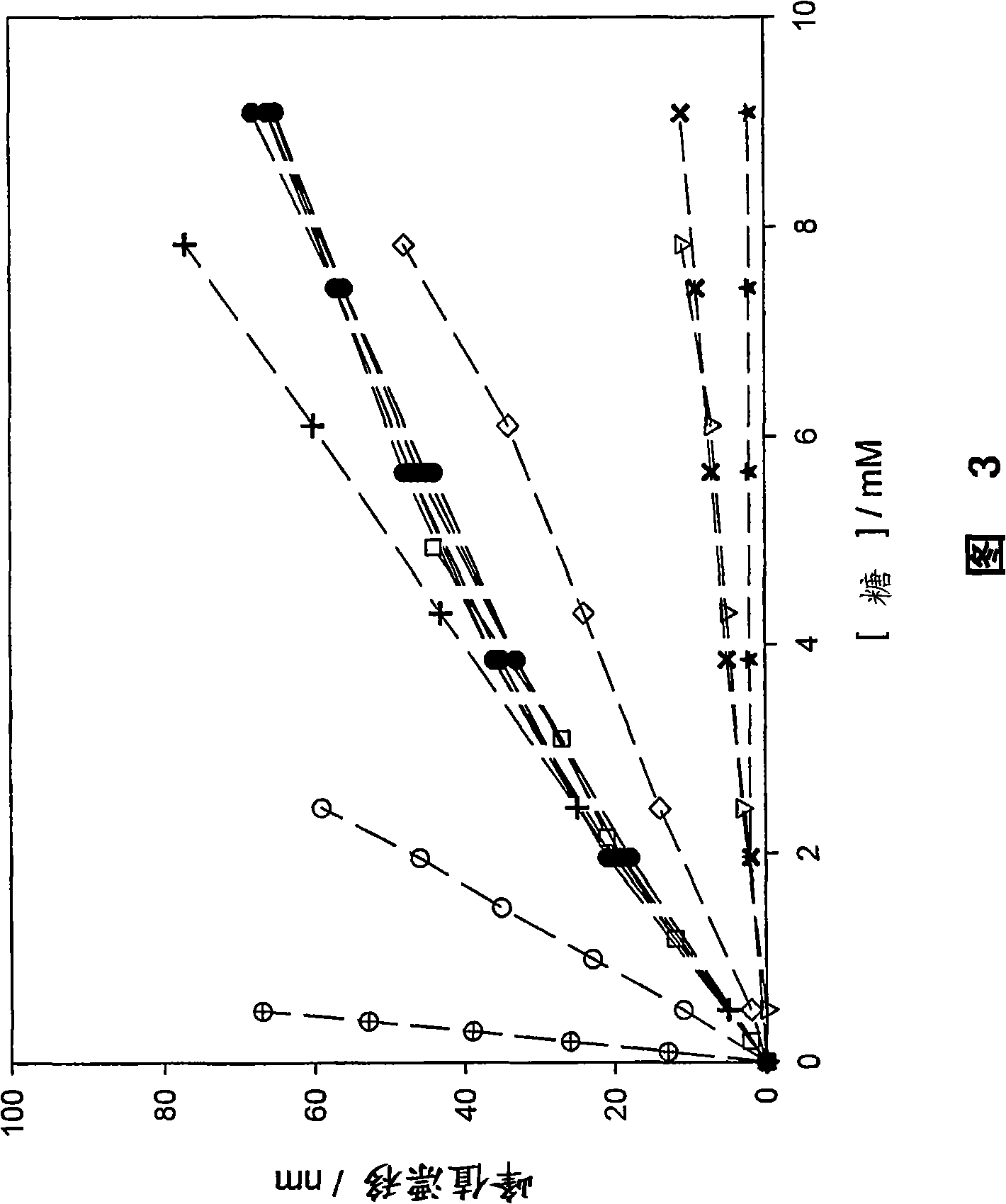
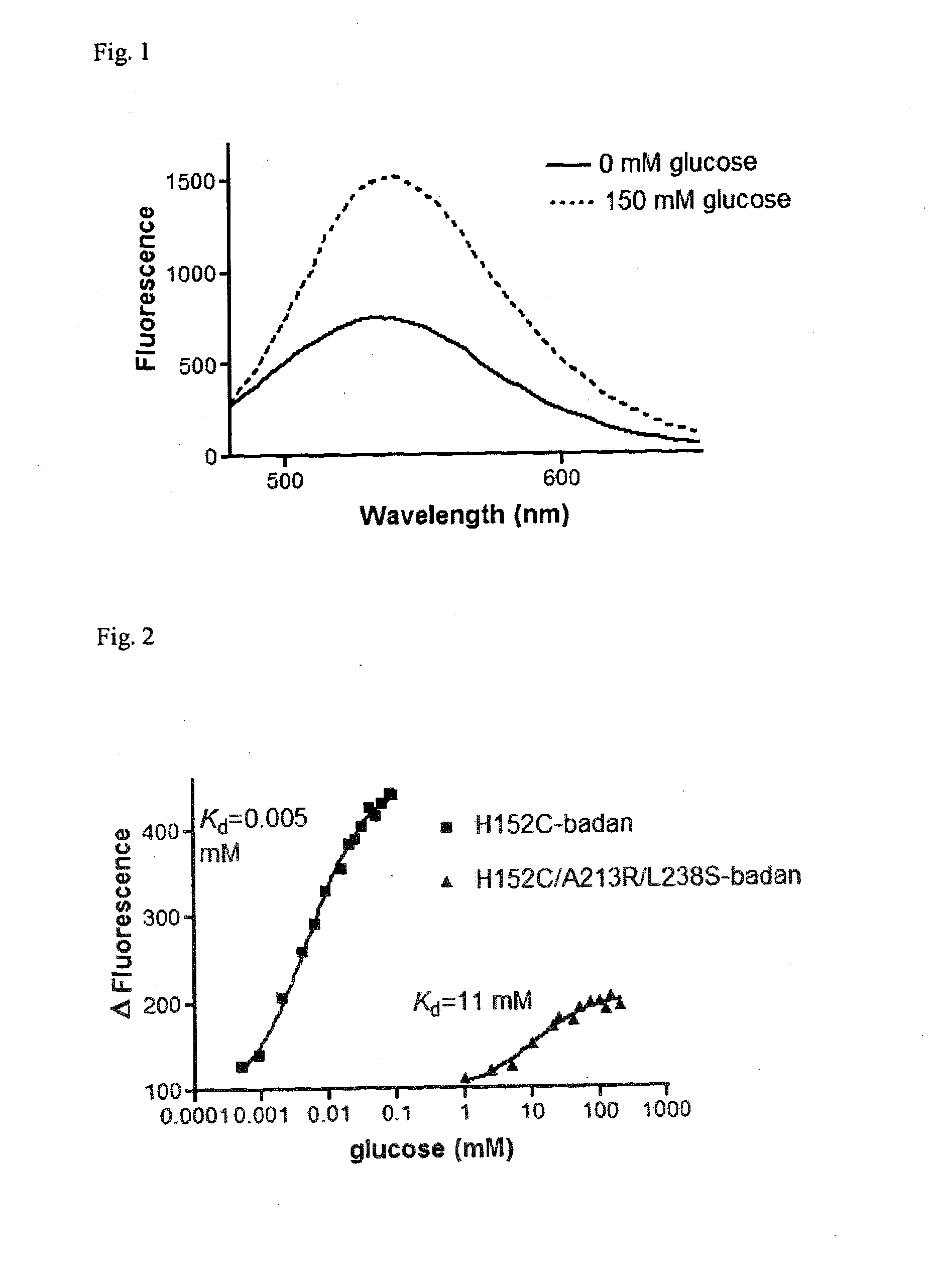
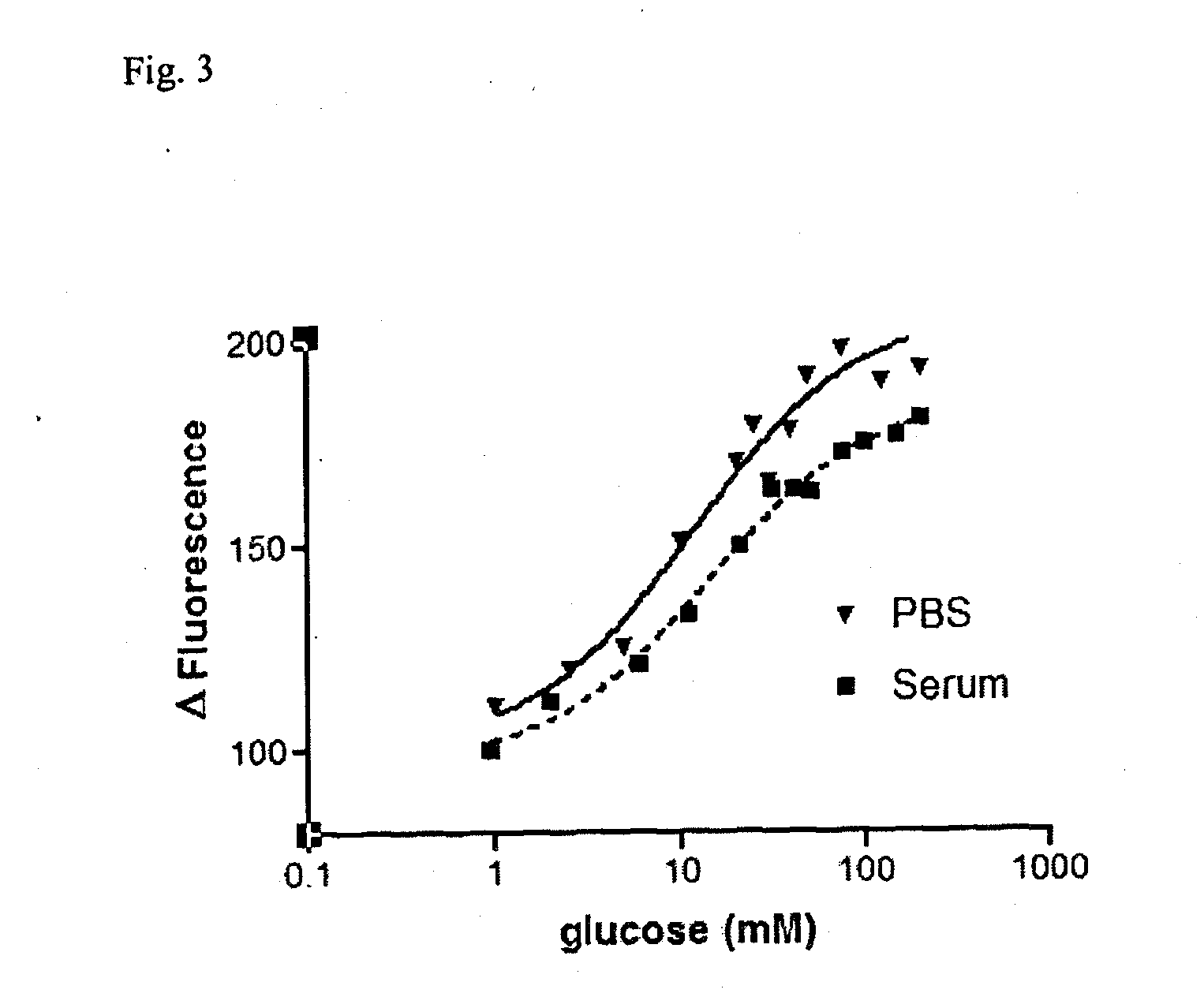
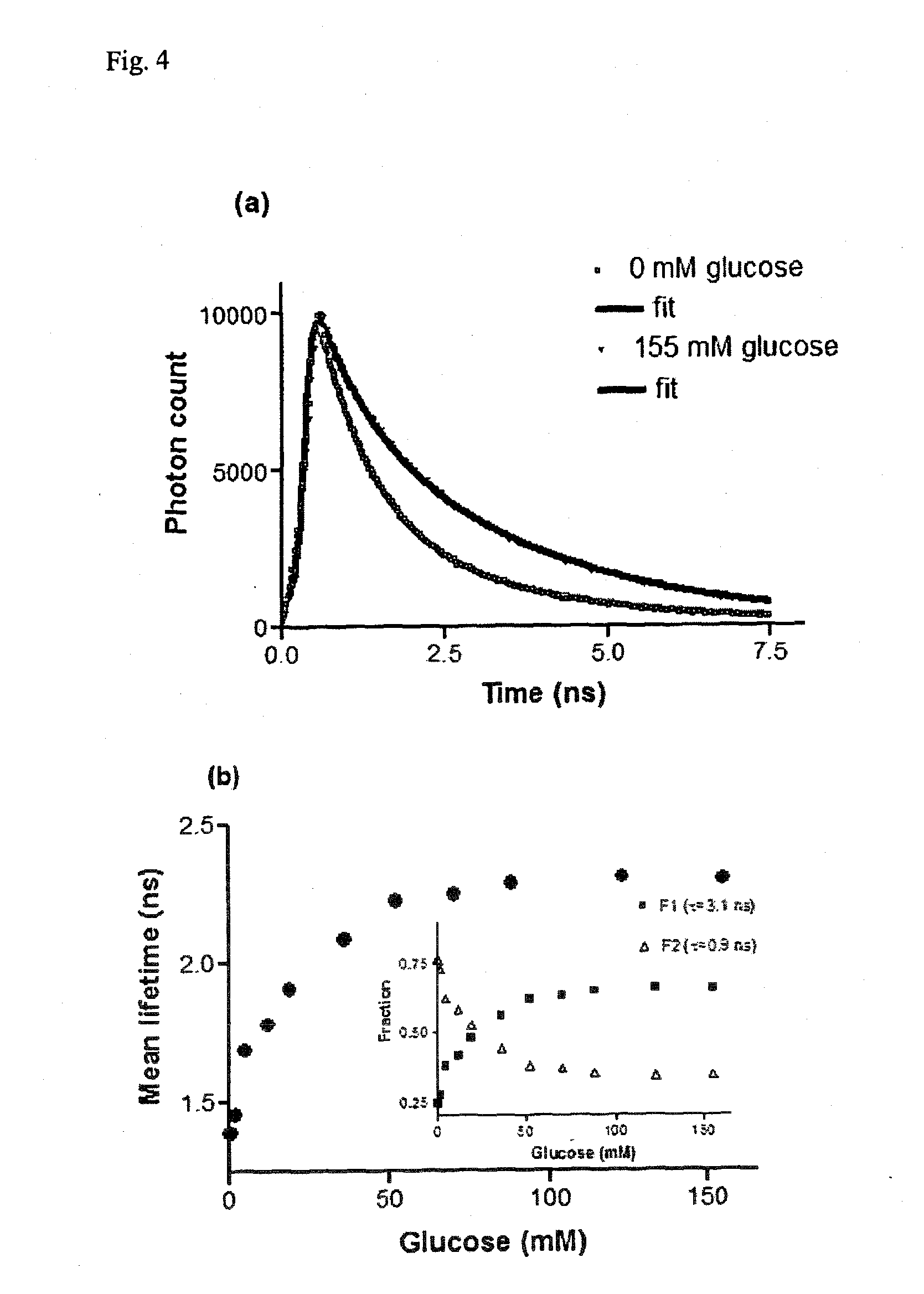
The invention relates to a glucose binding protein comprising amino acid mutations relative to the wild type sequence at the following positions: (i) H 152, (ii) A213; and (iii) L238 wherein the mutation at position H 152 is H152C. The invention further relates to such a glucose binding protein comprising the mutations H152C, A213R and L238S, in particular when linked to an environmentally sensitive dye such as badan.
Owner:KINGS COLLEGE LONDON
Method for continuously detecting glucose concentration in sample, reagent kit and method for using biosensor
The invention relates to a method for continuously detecting the glucose concentration in a sample, a reagent kit and a method for using a biosensor. The method for continuously detecting the glucose concentration in the sample comprises the following steps of: (a) providing the biosensor, wherein the biosensor comprises a converter and polysaccharide covering on the surface of the converter; (b) providing a carbohydrate-binding protein solution with specific concentration, wherein carbohydrate-binding protein is at least provided with a receptor, and the receptor has the capability of being combined with carbohydrate and glucose; (c) mixing the sample to be detected and the carbohydrate-binding protein solution with the specific concentration into a mixture; (d) contacting the mixture with the biosensor; (e) detecting the quantity of the carbohydrate-binding protein combined with the carbohydrate through the biosensor, wherein the glucose concentration of the sample to be detected and the quantity of the carbohydrate-binding protein combined with the carbohydrate form an inverse relation; and (f) recovering the surface of the biosensor through a high-concentration glucose solution.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Continuous glucose monitoring on-body sensor having a visual display
An on-body sensor (OBS) (10) having a continuous monitoring (CGM) device is disclosed for use in identifying an analyte, such as glucose in blood or interstitial fluid (ISF), using a biomaterial, such as glucose binding protein (GBP), that is brought into contact with the analyte. The on-body sensor (10) incorporating the CGM device includes a cover (25) which provides protection to the CGM device and includes an integrated output display (27). The output display (27) can visually provide data received from the CGM device, to the user without the need for a separate data receiving device.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Method for continuously detecting glucose concentration in sample, kit thereof and method for using biosensor
ActiveUS20100304399A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsHigh concentrationCarbohydrate-binding protein
The invention provides a method for continuously detecting glucose concentration in a sample, including: (a) providing a biosensor comprising a transducer and a polysaccharide covered on the surface of the transducer; (b) providing a carbohydrate binding protein solution, wherein the carbohydrate binding protein has at least one receptor, and the receptor is capable of binding to the polysaccharide and glucose; (c) mixing a sample and the carbohydrate binding protein solution to form a mixture; (d) contacting the mixture with the biosensor; (e) detecting the amount of carbohydrate binding proteins bound to the polysaccharide by the biosensor, wherein glucose concentration of the sample is inversely proportional to the amount of carbohydrate binding proteins bound to the polysaccharide; and (f) refreshing the surface of the biosensor with a high concentration glucose solution.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
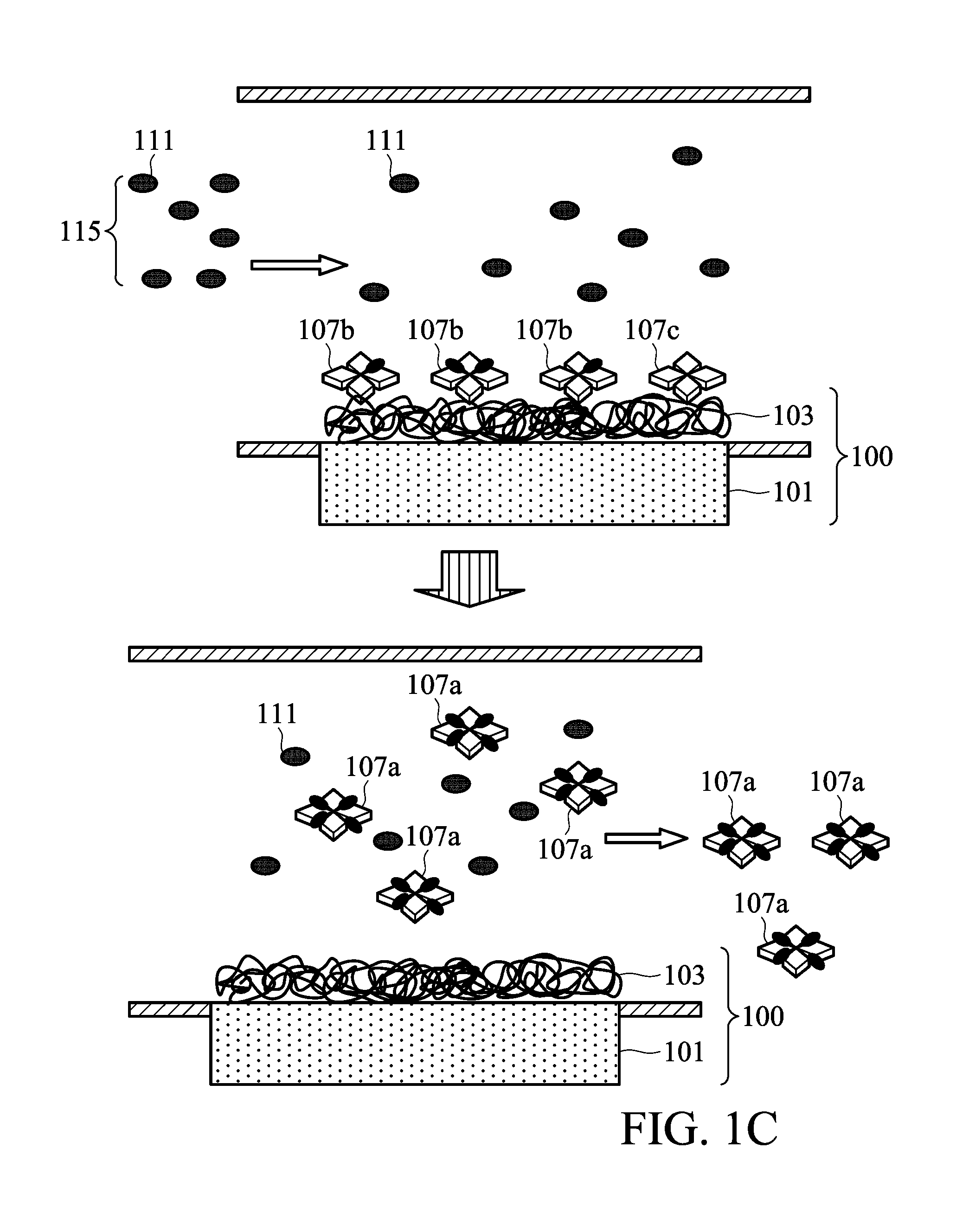
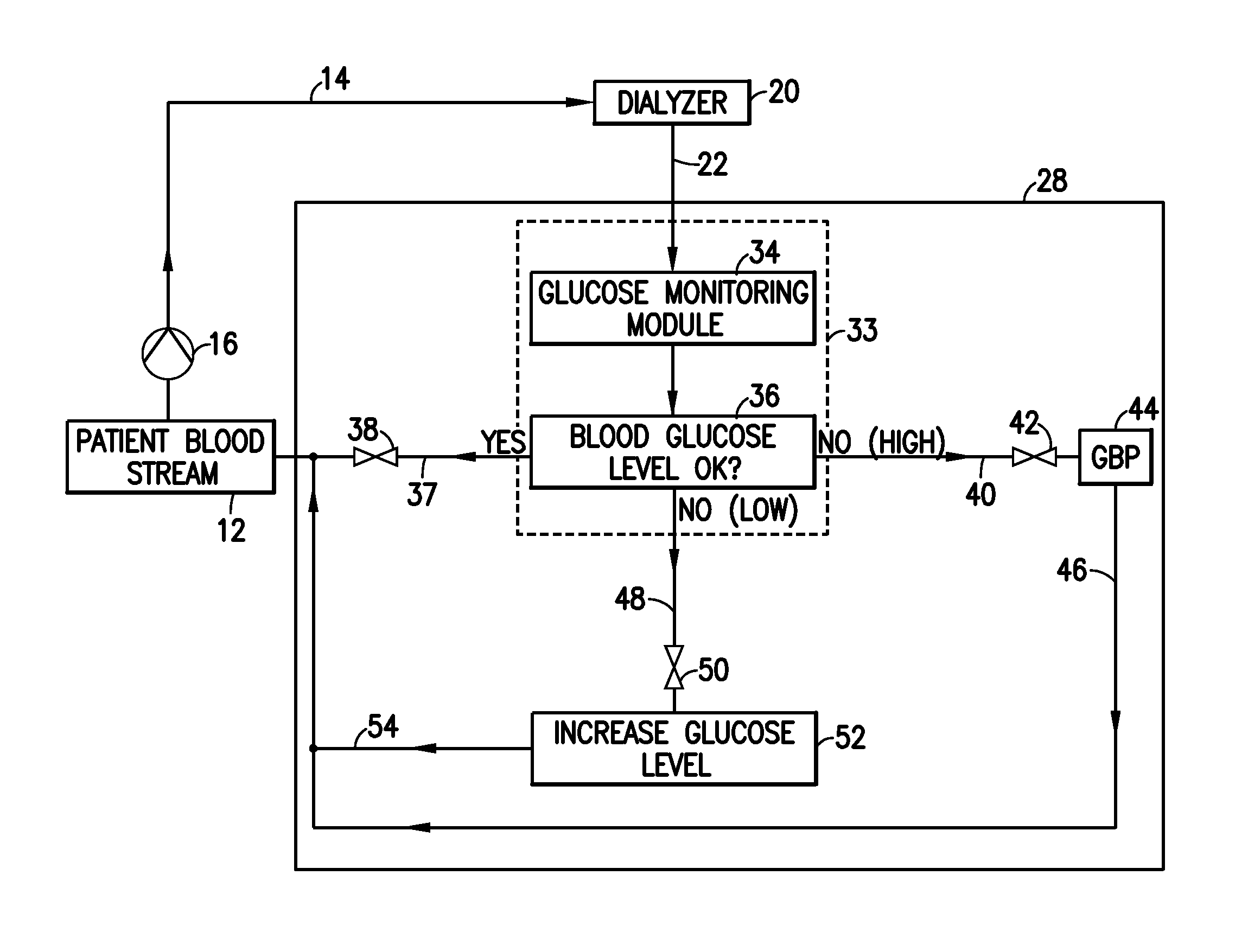
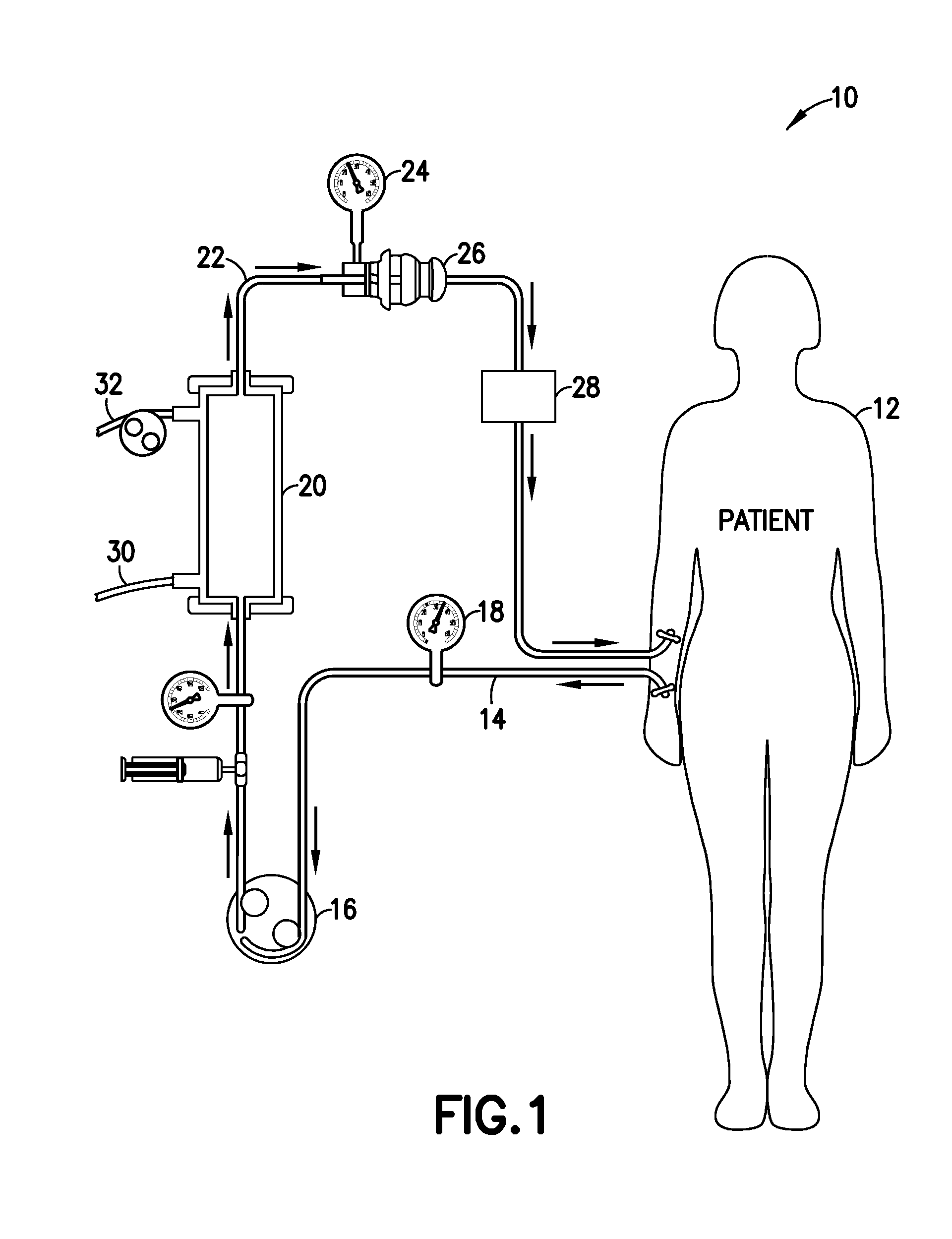
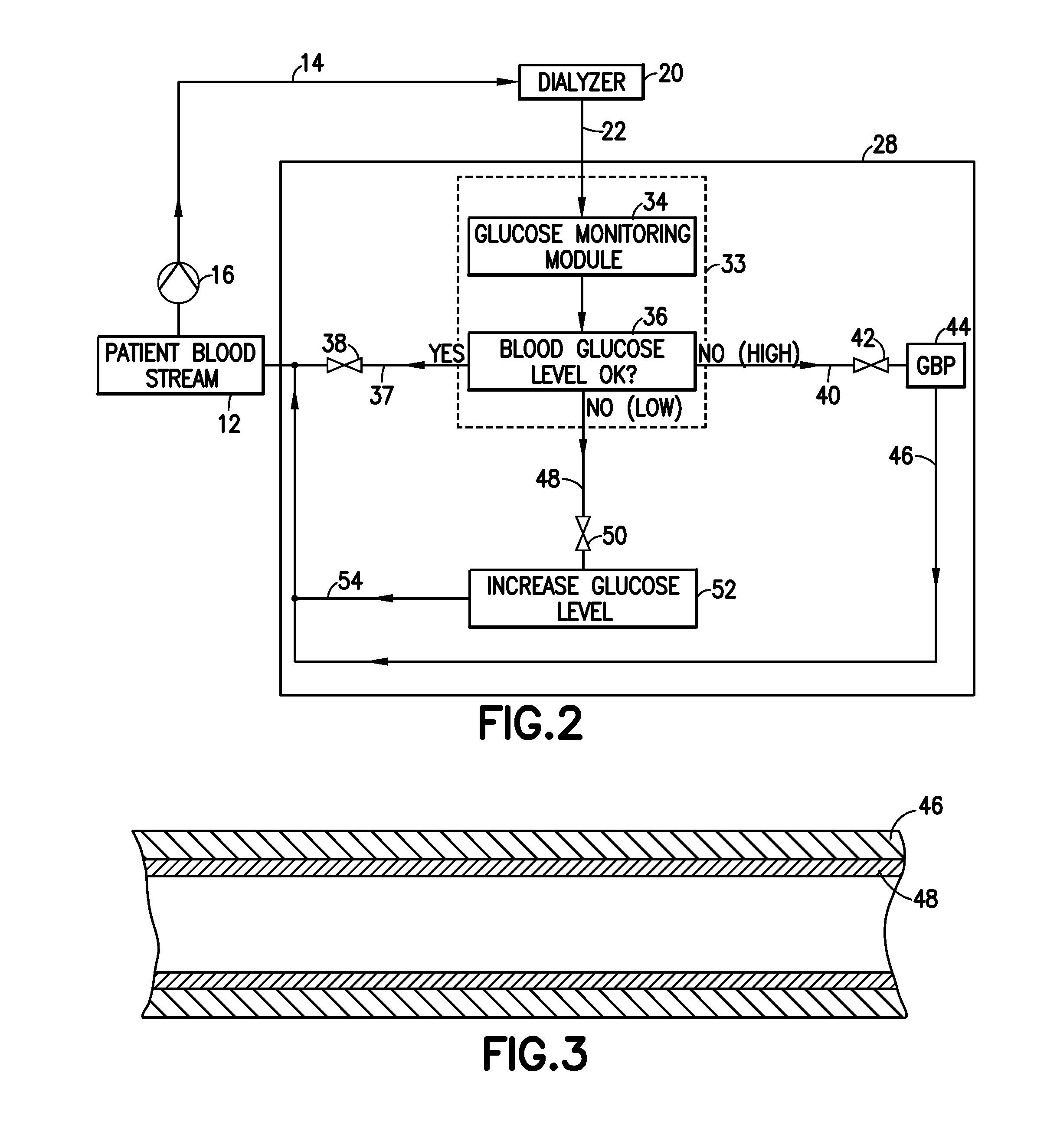
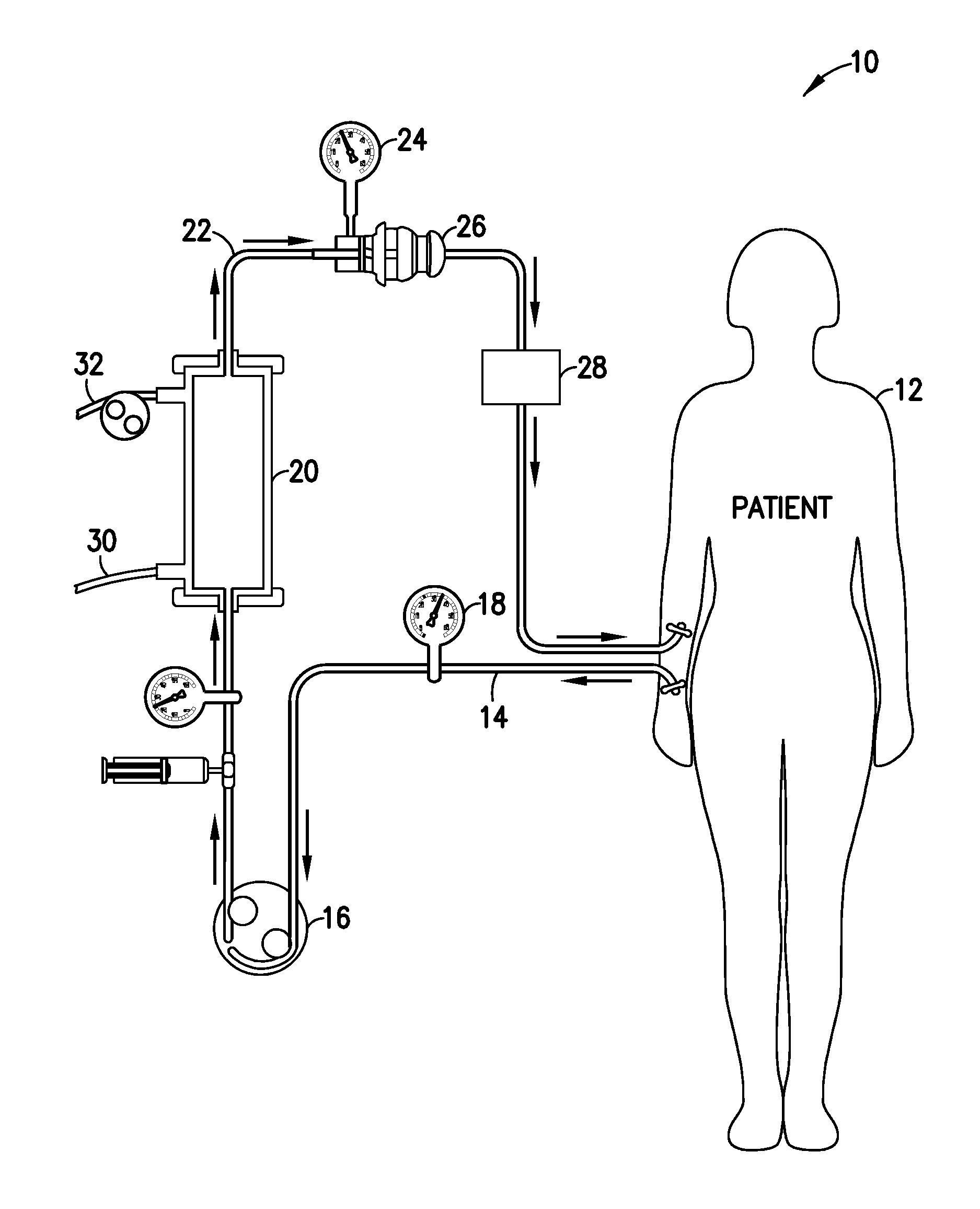
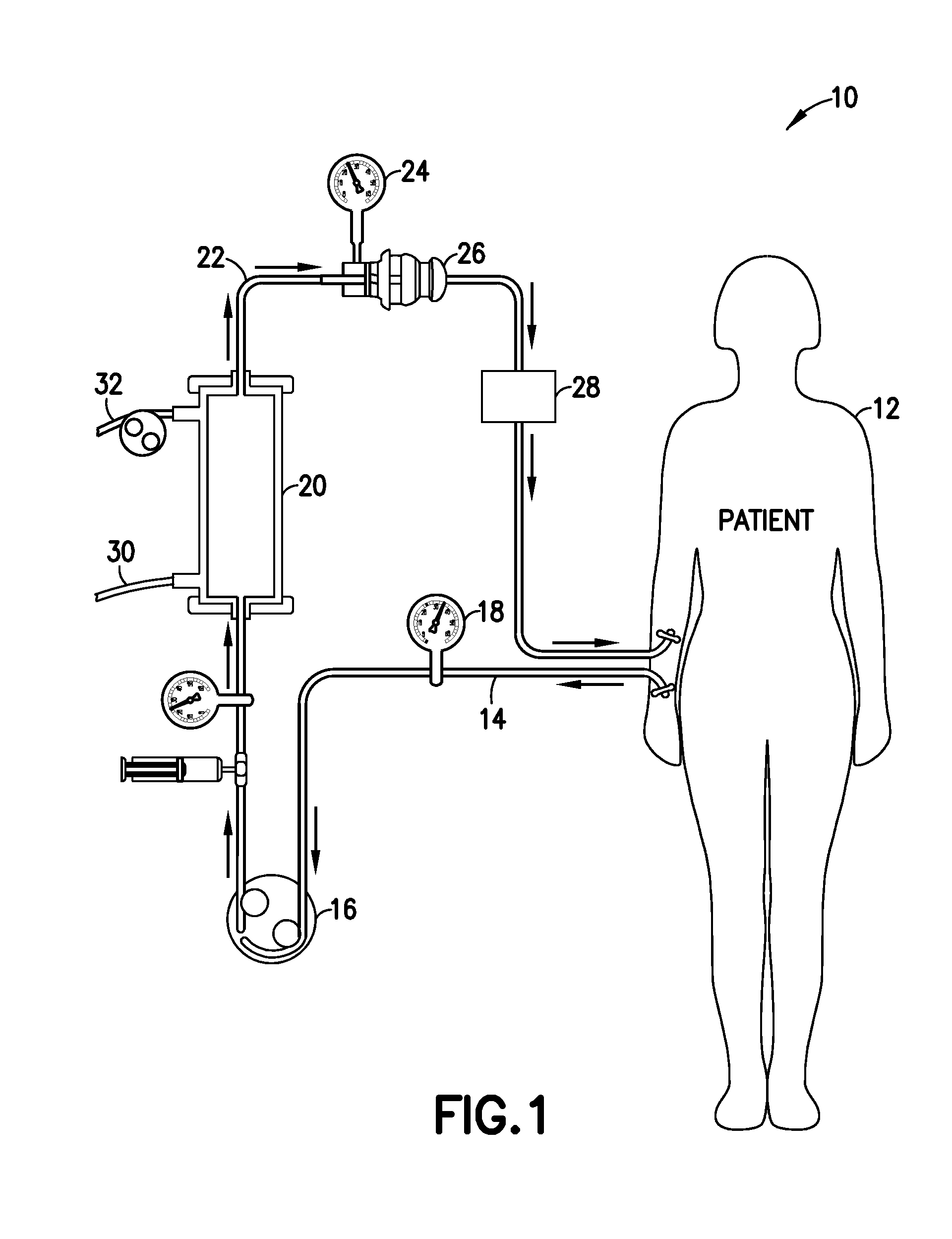
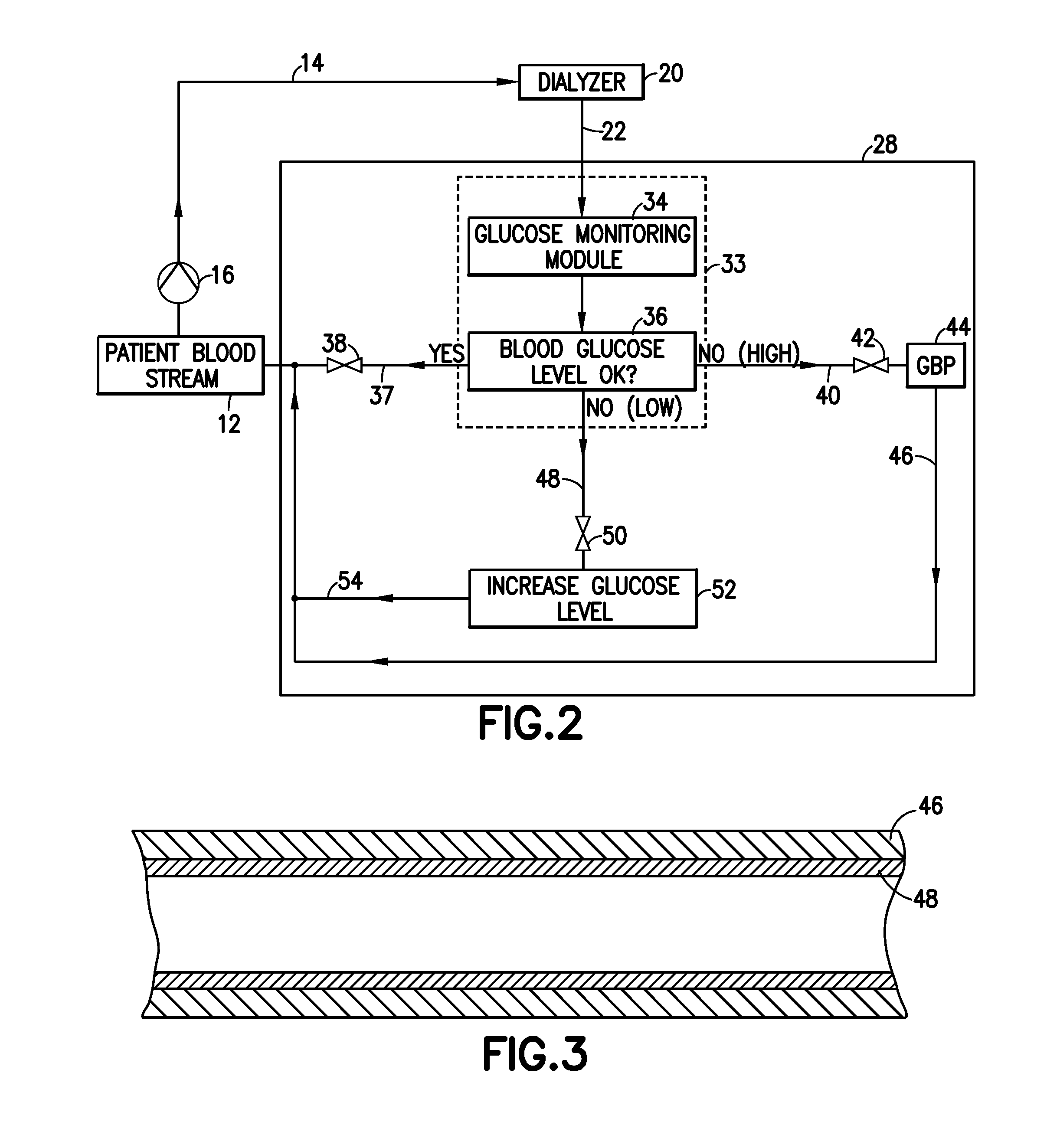
Glucose management and dialysis method and apparatus
ActiveUS8834401B2Reduce the concentration of glucoseOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsDiseaseScavenger
A process and apparatus are provided for managing and adjusting glucose levels in the blood of a patient during dialysis. The apparatus is a dialysis apparatus to treat patients with renal disease which includes a glucose scavenger to remove excess glucose from the blood before returning the blood to the patient and / or a device to increase blood glucose levels in the blood when the glucose level is below a threshold level. The glucose scavenger can include a glucose binding protein, boronic acid derivative, boronic ester derivative or mixture thereof bonded to the surface of a support such as a fiber bundle in a cartridge or the inner surface of tubing used in the apparatus.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Glucose management and dialysis method and apparatus
ActiveUS20140148749A1Reduce the concentration of glucoseDialysis systemsMedical devicesGlucose ClearanceGlucose management
A process and apparatus are provided for managing and adjusting glucose levels in the blood of a patient during dialysis. The apparatus is a dialysis apparatus to treat patients with renal disease which includes a glucose scavenger to remove excess glucose from the blood before returning the blood to the patient and / or a device to increase blood glucose levels in the blood when the glucose level is below a threshold level. The glucose scavenger can include a glucose binding protein, boronic acid derivative, boronic ester derivative or mixture thereof bonded to the surface of a support such as a fiber bundle in a cartridge or the inner surface of tubing used in the apparatus.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
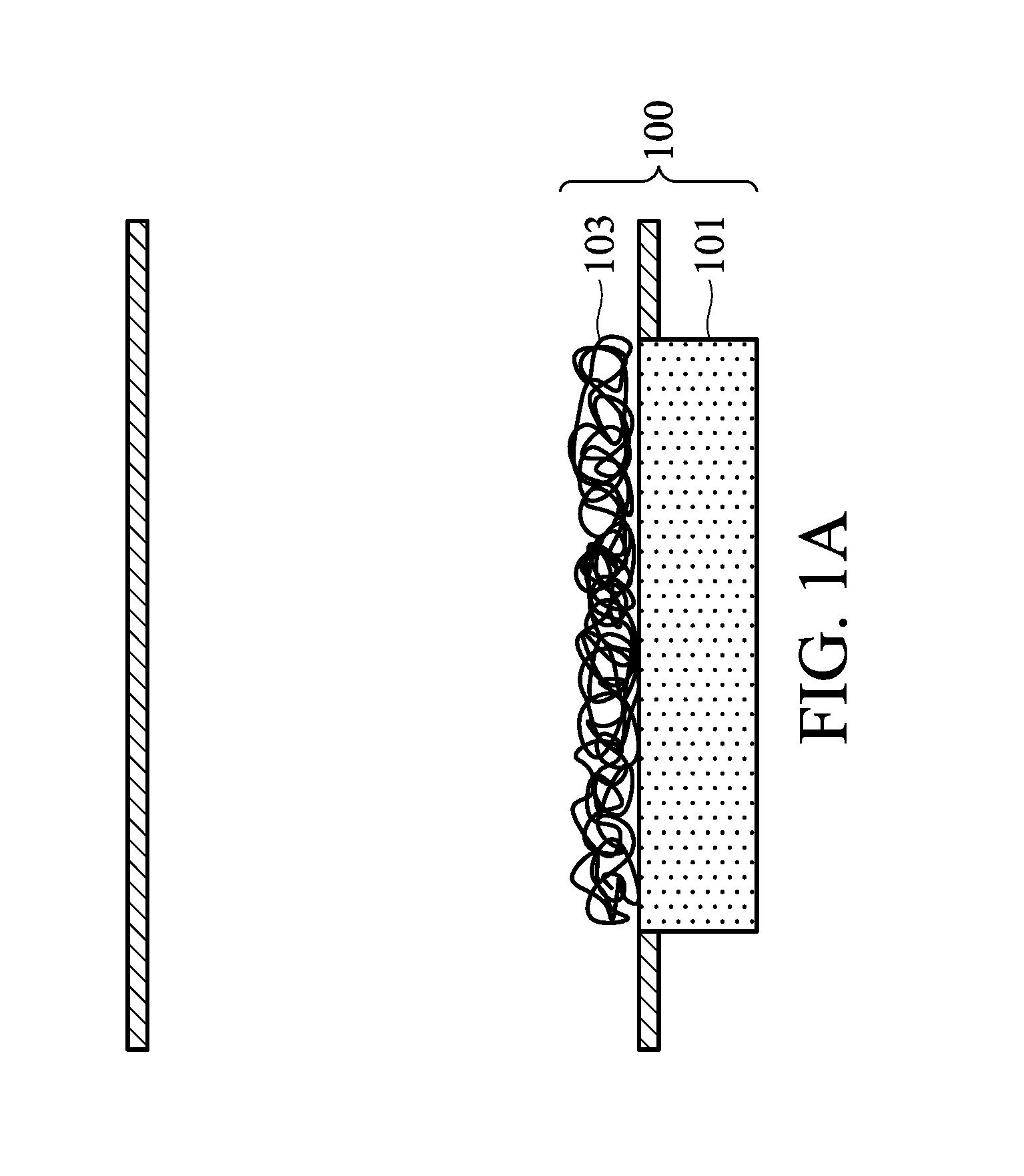
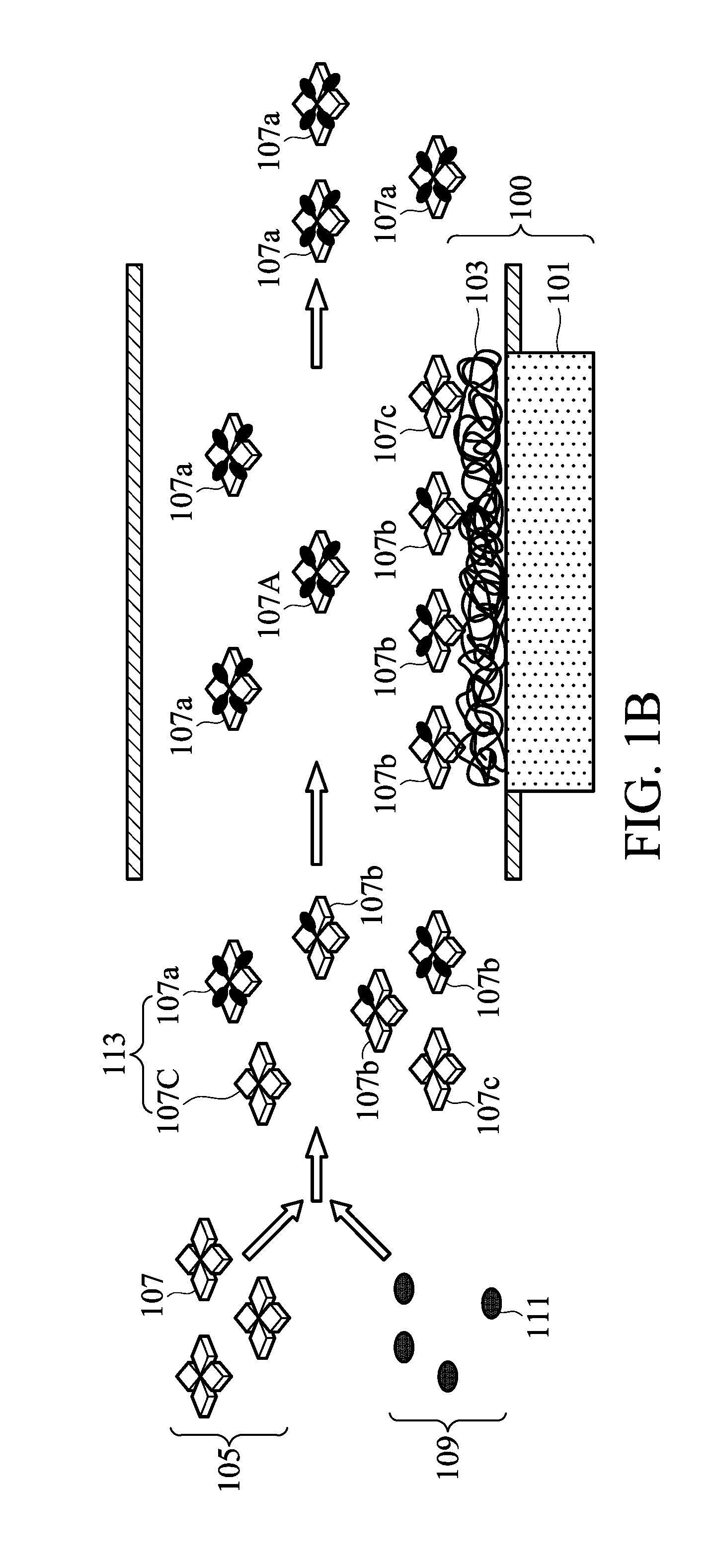
Implantable glucose sensors having a biostable surface
PendingUS20190142317A1Reduce the differenceReduced protein and cell depositionSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGlucose sensorsBiointerface
Disclosed are implantable glucose sensors having a biostable surface. The implantable glucose sensor includes a glucose detector and an enclosure defining a boundary between an internal space and an external space. The enclosure includes a semipermeable biointerface film containing a base polymer and a biostabilizing additive. The semipermeable biointerface film has a biostable surface and is permeable to glucose. The working electrode is disposed inside the internal space, and the biostable surface faces the external space or faces both the internal and the external spaces. Also disclosed are methods of preparation of the semipermeable biointerface films adapted for use in the implantable glucose sensors. Further, disclosed are methods of monitoring glucose levels in a subject through the use of an implantable glucose sensor. The implantable glucose sensor may be an implantable electrochemical glucose sensor, in which the glucose detector is a working electrode. Alternatively, the implantable glucose sensor may be an implantable optical glucose sensor, in which the glucose detector is a glucose recognition element including a glucose-binding fluorophore.
Owner:EVONIK CANADA INC
Preparation method of drug for hyperphosphatemia
ActiveCN105125575AEasy to compressEvenly filledHeavy metal active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSilicon dioxidePharmacology
The invention relates to a drug composition for hyperphosphatemia and a preparation method of the drug composition. The drug composition, as chewable tablets, comprises 477-954g of lanthanum carbonate hydrate, 5-10g of polylactic acid, 500-1000g of dextrates, 20-40g of colloidal silicon dioxide and 10-20g of magnesium stearate.
Owner:CONSUN PHARML NEI MENG GU
Insulin analogues with a glucose-regulated conformational switch
ActiveUS20180057559A1Reduce rateLoss of affinityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsC-terminusDouble strand
A two-chain insulin analogue contains an A chain modified by (i) a monomeric glucose-binding element at or near its N terminus and (ii) a B chain modified by at or near its C terminus by an element that reversibly binds to the monomeric glucose-binding element such that this linkage is displaceable by glucose. The monomeric glucose-binding element may be phenylboronic acid derivative (optionally halogenated). The B chain may be modified by a diol-containing element derived from a monosaccharide, disaccharide or oligosaccharide, a non-saccharide diol-containing moiety or a α-hydroxycarboxylate-containing moiety. The analogue can be manufactured by trypsin-mediated semi-synthesis. Formulations can be at strengths U-10 to U-1000 in soluble solutions at pH 7.0-8.0 with or without zinc ions at a molar ratio of 0.0-3.0 ions per insulin analogue monomer. A patient with diabetes mellitus may be treated with subcutaneous, intraperitoneal, or oral administration of a physiologically effective amount of the insulin analogue.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Preparation method of glucose combined magnesia carbon brick
Belonging to the technical field of refractory material preparation, the invention relates to a preparation method of a glucose combined magnesia carbon brick. The method adopts magnesite (fused magnesite or sintered magnesite) and a carbon raw material (flake graphite, carbon black or electrode chip) as the main raw materials, glucose is added as a binding agent and other additives are added, and by means of compounding, mixing, aging, molding, drying and other technological processes are carried out to obtain a non-fired magnesia carbon brick. The refractory material provides low temperature strength through the glucose binding agent, and the glucose binding agent undergoes thermal decomposition and carbonization to form a carbon structure so as to provide medium and high temperature strength. Compared with the traditional phenolic resin combined magnesia carbon brick, the glucose combined magnesia carbon brick has the advantages of environmental friendliness and low cost. The preparation method also provides the technical and theoretical basis for application of glucose binding agent to other high-temperature resistant materials.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (BEIJING)
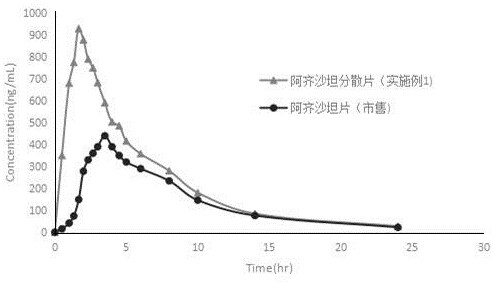
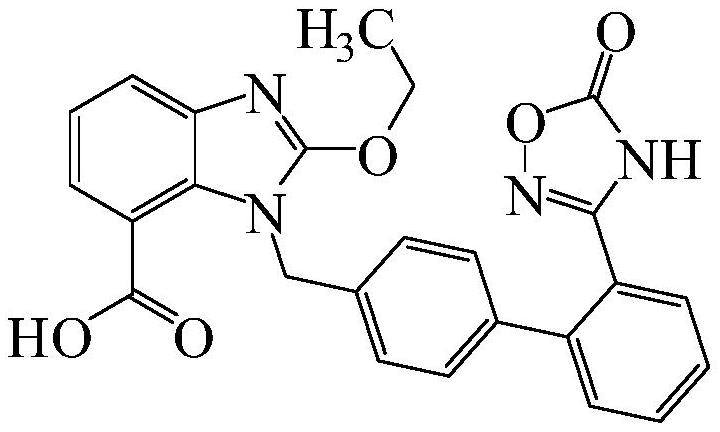
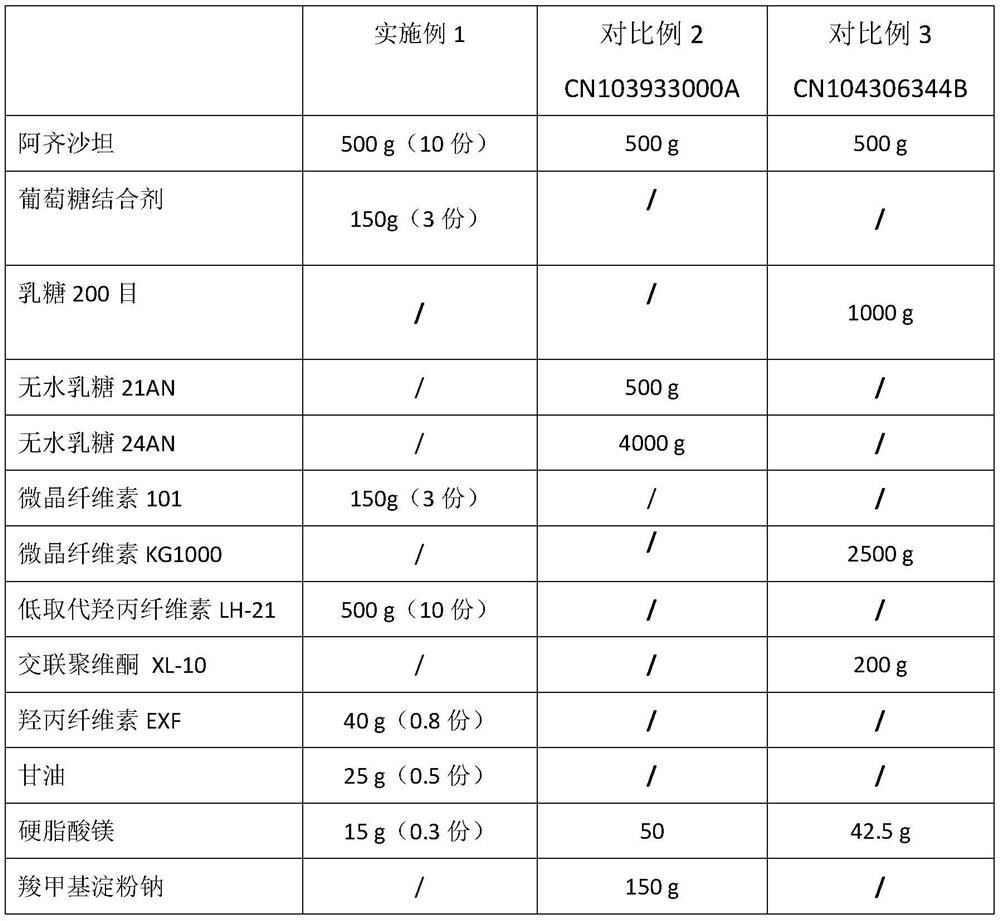
Azilsartan dispersible tablet and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN111617046AFully combinedDissolution rate is fastOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEngineeringPharmaceutical Substances
The invention provides an azilsartan dispersible tablet and a preparation process thereof. The preparation process comprises the following steps of mixing micronized azilsartan with a glucose bindingagent as a filling agent and partial disintegrating agent, performing wet-method granulation by adopting a stabilizer-added adhesive solution, then adding other fillers, the remaining disintegrating agent and a lubricant, and performing tabletting, wherein micronization of an azilsartan raw material is to more effectively increase the dissolution rate with the glucose binding agent together. For the azilsartan dispersible tablet and the preparation process, by using the glucose binding agent, the hydrophilicity of a drug is improved, so that the azilsartan dispersible tablet still has a relatively high dissolution rate under relatively high hardness, and the bioavailability is improved. Moreover, the process is simple and is suitable for industrial mass production.
Owner:浙江诺得药业有限公司
Dry insertion and one-point in vivo calibration of an optical analyte sensor
Disclosed are embodiments that relate to the deployment of a glucose sensor comprising an optical fiber into a physiological fluid, wherein the optical fiber has disposed along a distal region thereof a chemical indicator system comprising a fluorophore and a glucose binding moiety immobilized within a hydrogel, wherein the components of the chemical indicator system are in a dry state before deployment. Also disclosed is a one-point in vivo calibration of the chemical indicator system based on an independently measured glucose concentration.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Glucose sensor
ActiveCN103917858AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological material analysisGlucose sensorsFluorophore
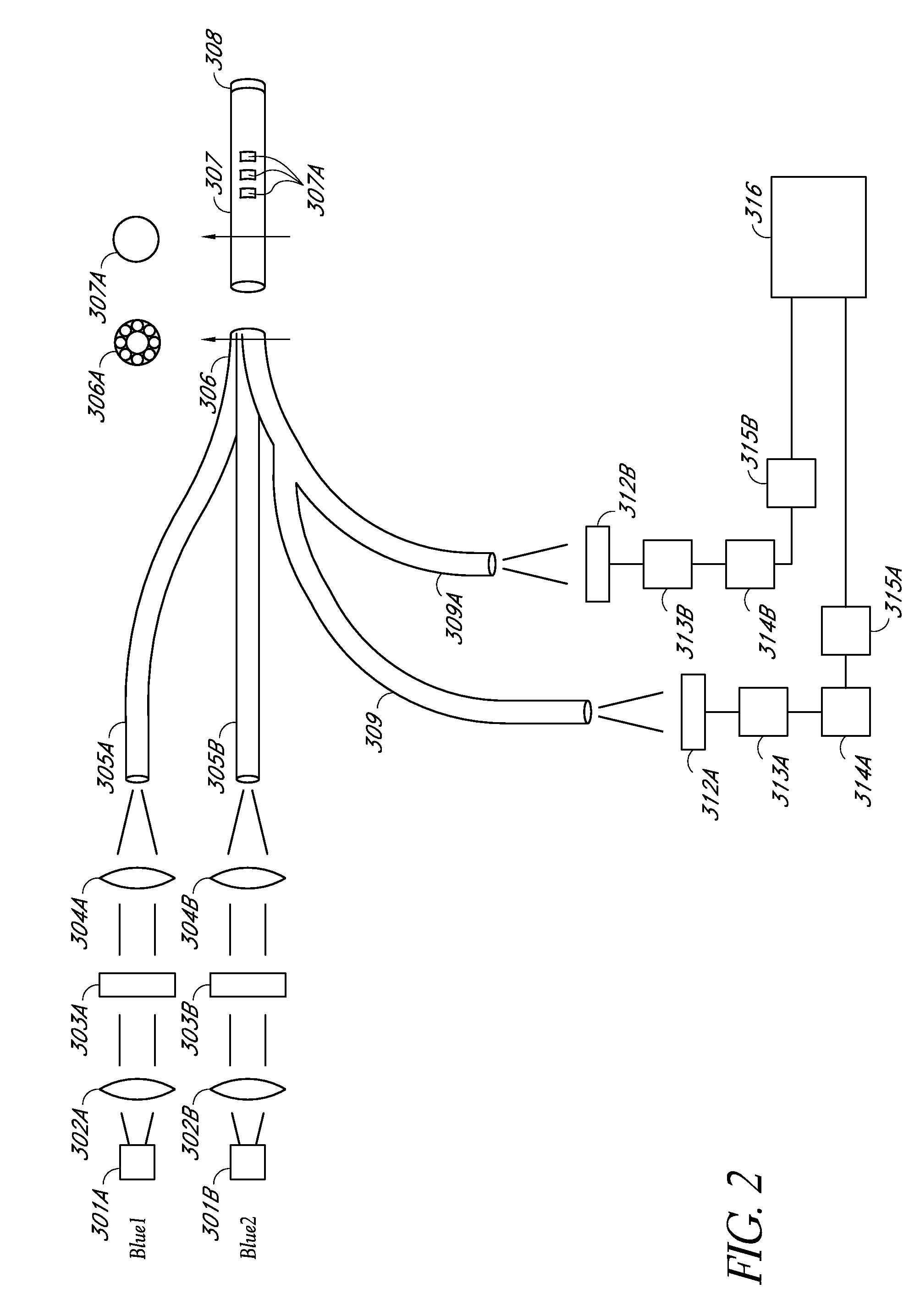
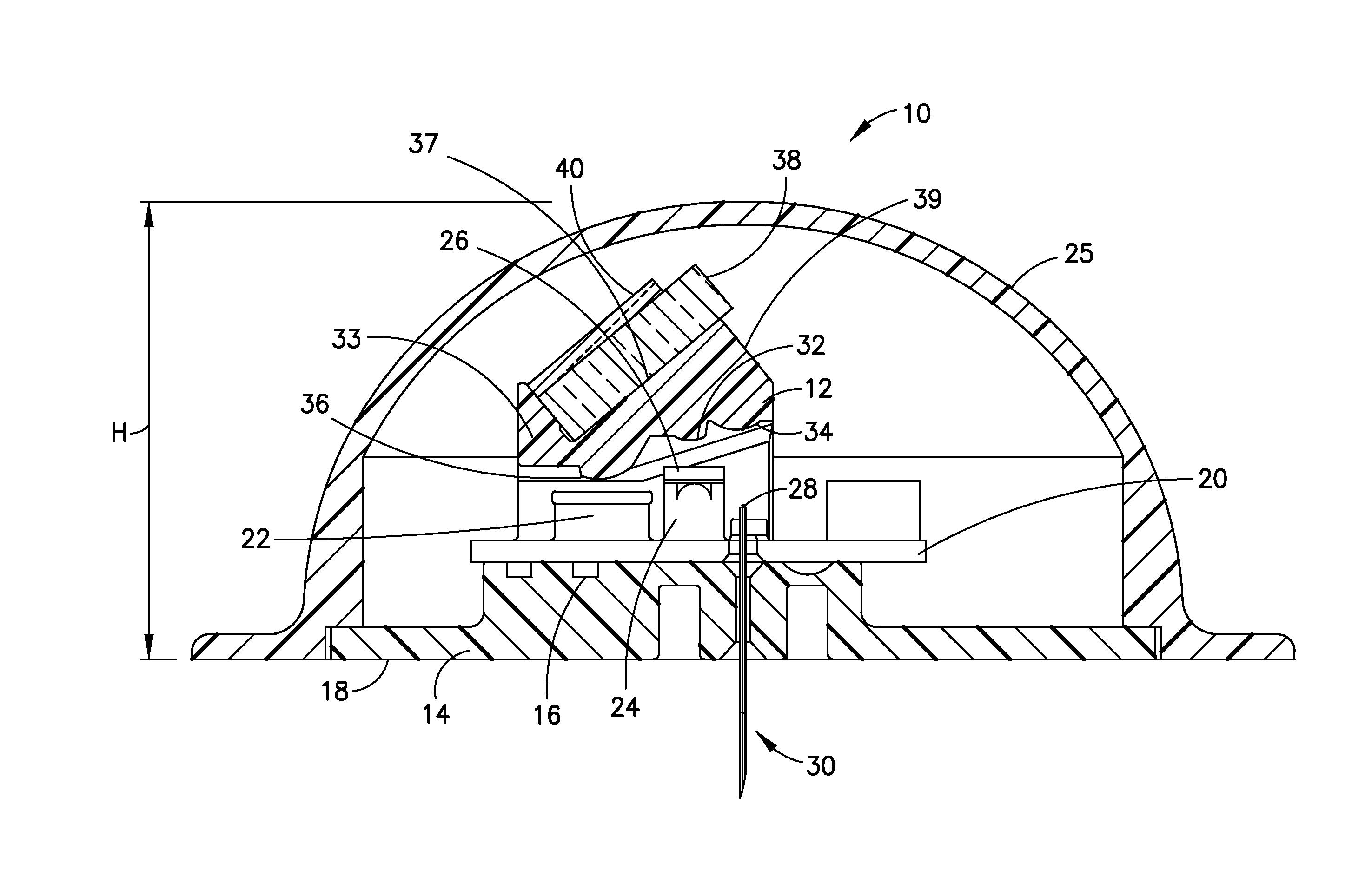
An optical glucose sensor may include an optical fiber and a glucose-permeable membrane having a hollow interior and being coupled to the optical fiber's distal end. The membrane's hollow interior provides a compartment to house a competitive glucose binding affinity assay. The assay may include a glucose analog that may be labeled with a dye, and a glucose receptor that may be labeled with a fluorophore. The optical fiber may include a compound parabolic concentrator tip, and the compartment may additionally house a reflector disposed so as to face the optical fiber's tip. A fluorophore-labeled assay may be interrogated by an optical interrogating system including a light source and a filter substrate having one or more coatings to effect, e.g., an excitation filter and / or an emission filter. The interrogating system may be manufactured as a stacked planar integrated optical system and diced into smaller units.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
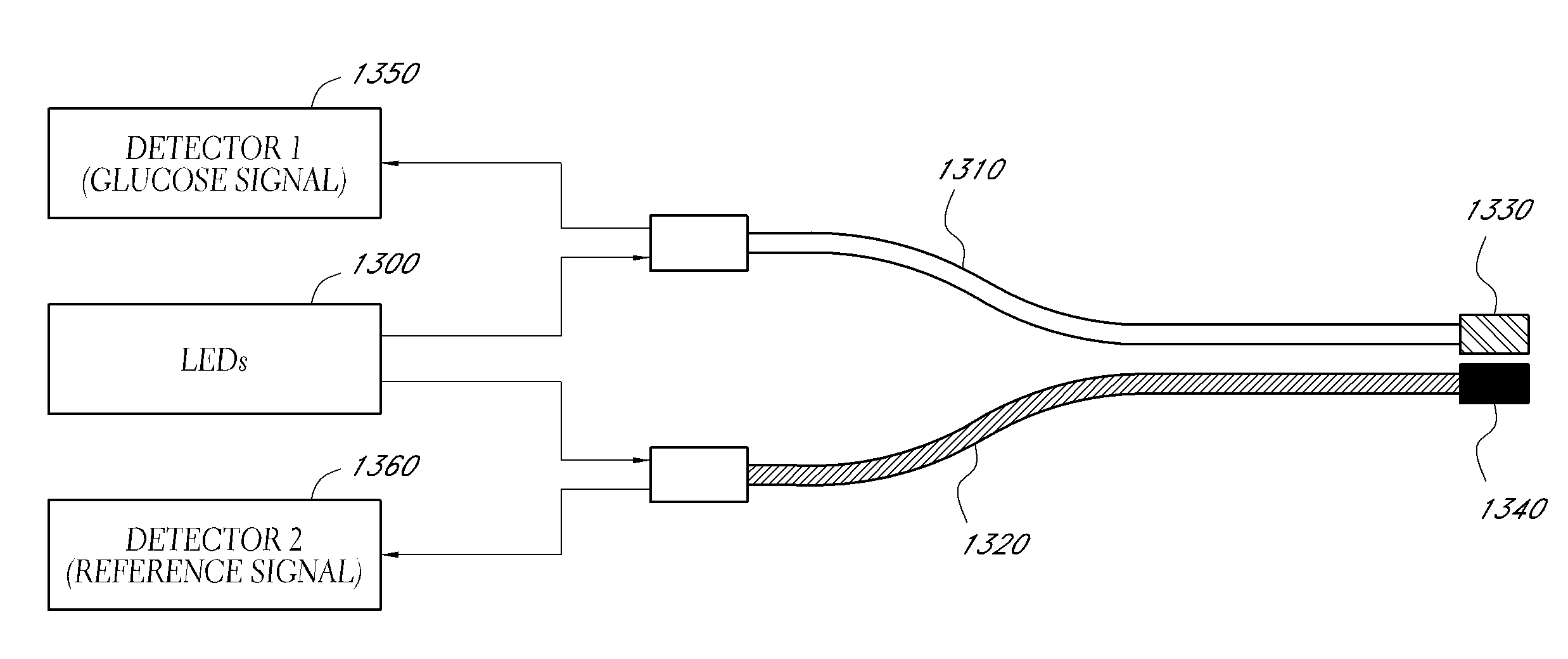
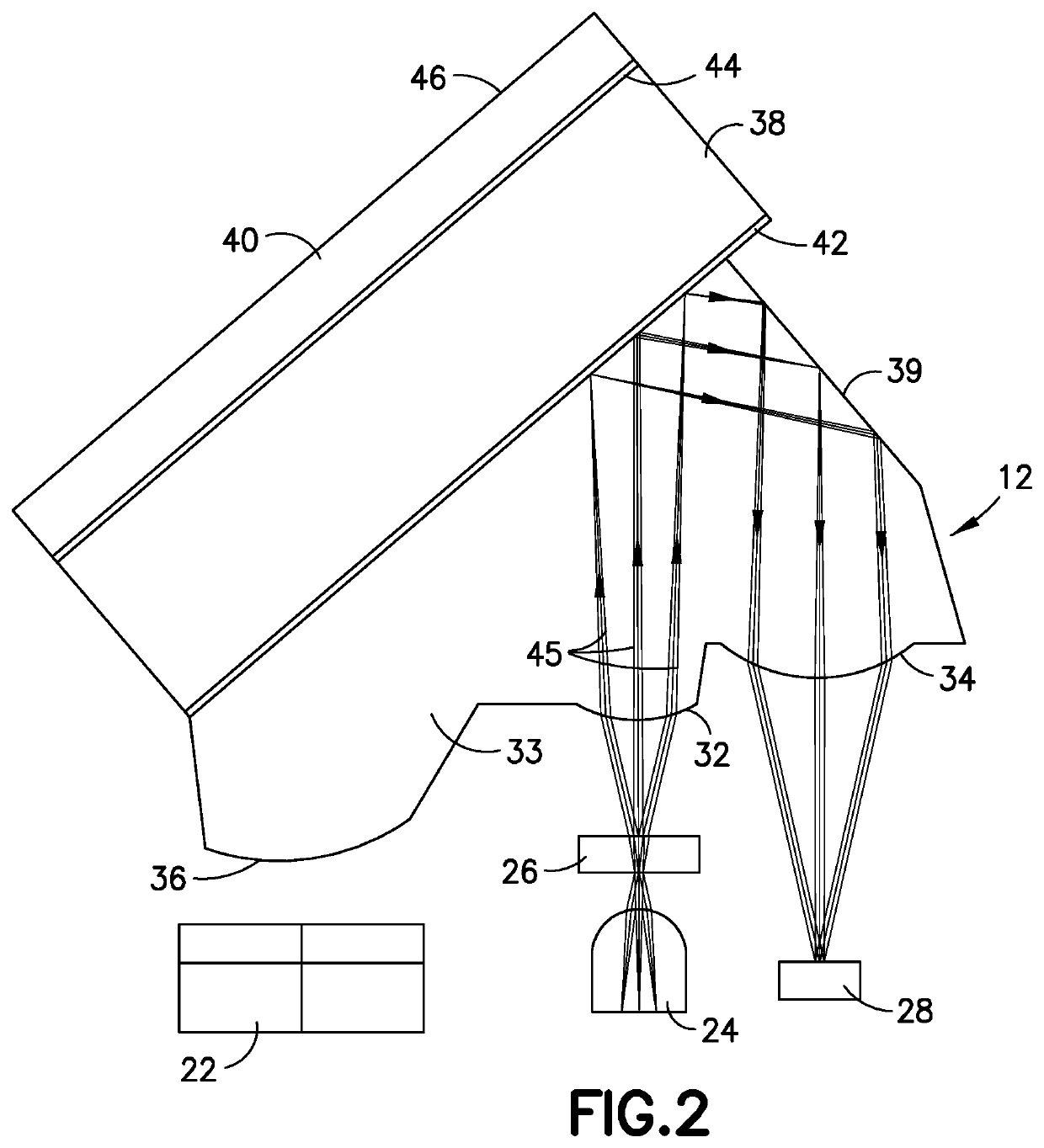
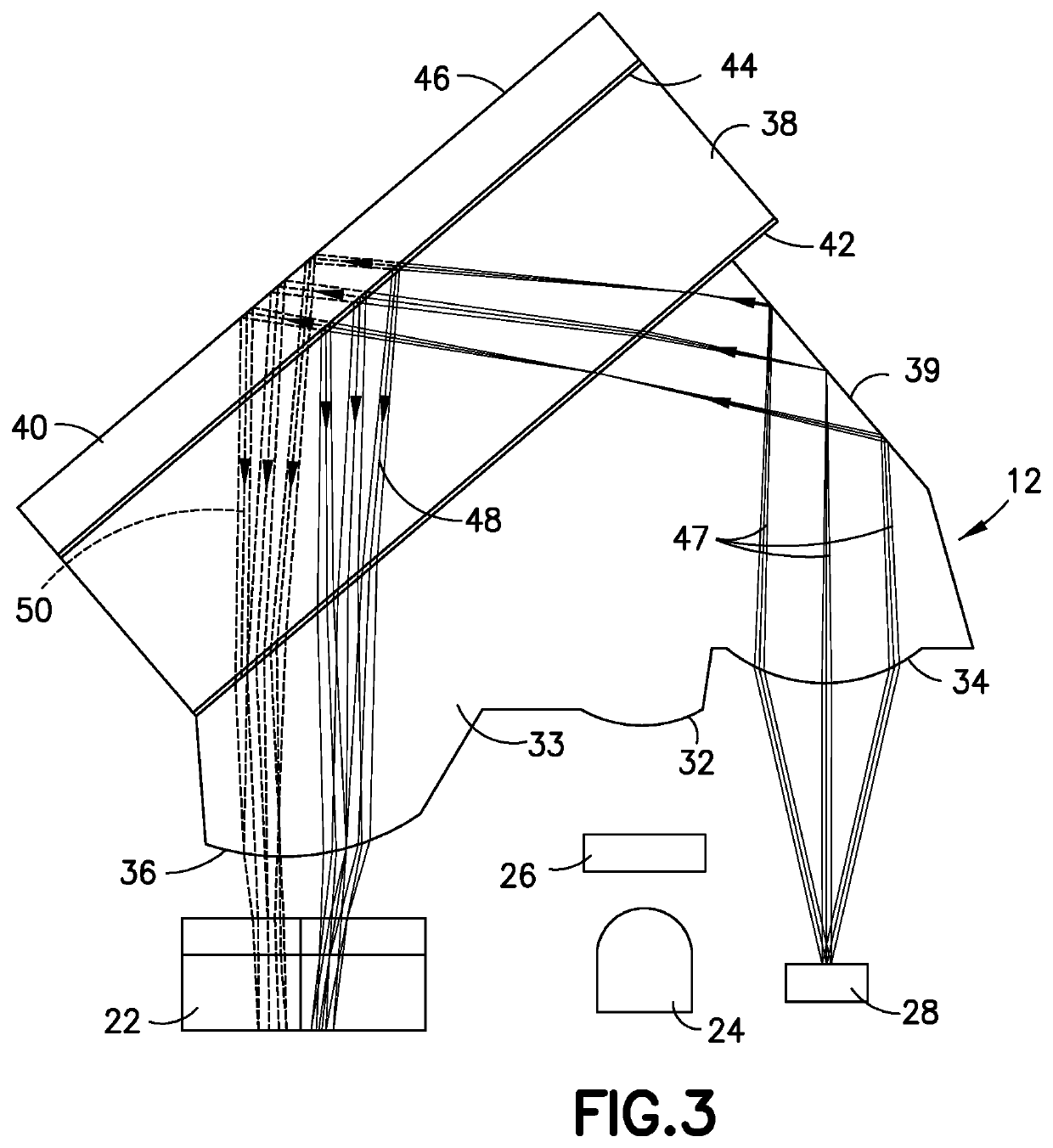
Reduced Size Optical Coupler for Fluorescence Detection
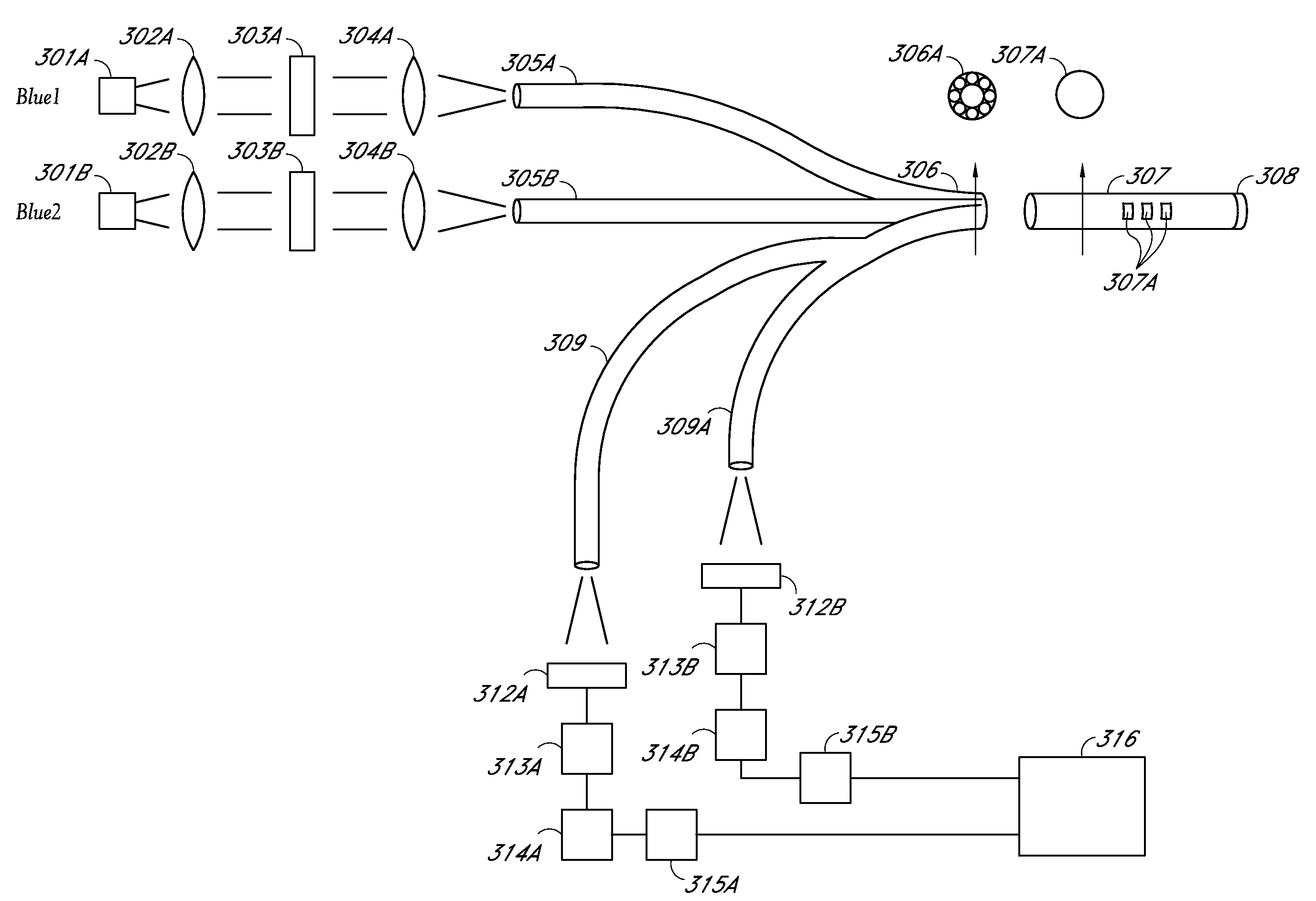
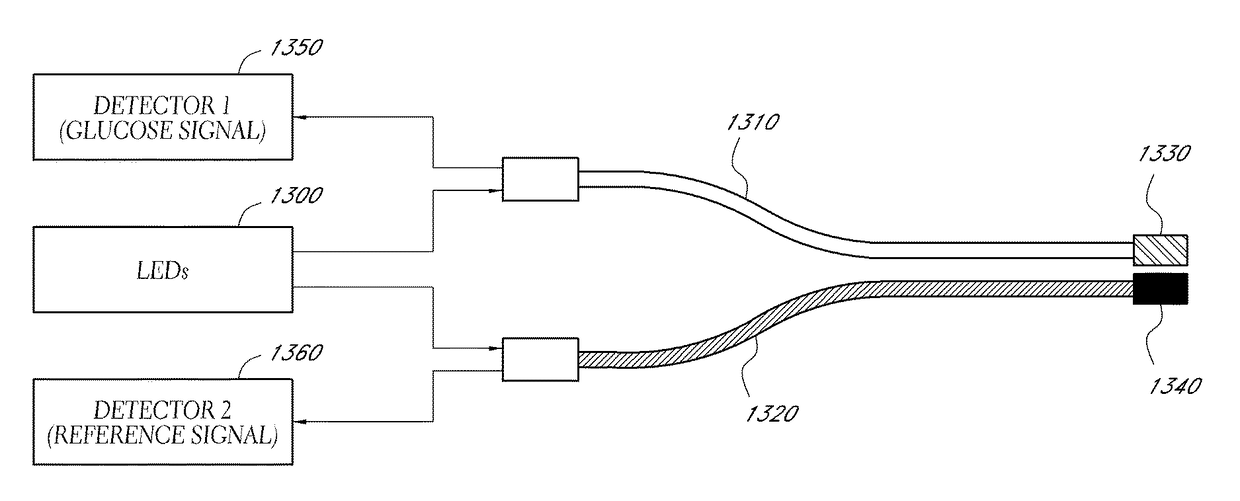
ActiveUS20150351669A1Low costSmall sizeCatheterDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionFluorescenceBiological materials
Optical systems are disclosed for use in identifying an analyte, such as glucose in blood or interstitial fluid (ISF), using a biomaterial, such as glucose binding protein (GBP), that is brought into contact with the analyte. An optical system includes a first filter adapted to reflect light emitted from a light-emitting diode to illuminate a fluorescent body, and further adapted to transmit light emitted from the fluorescent body, and a second filter adapted to separate light transmitted by the first filter into signal band light and reference band light.
Owner:EMBECTA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com