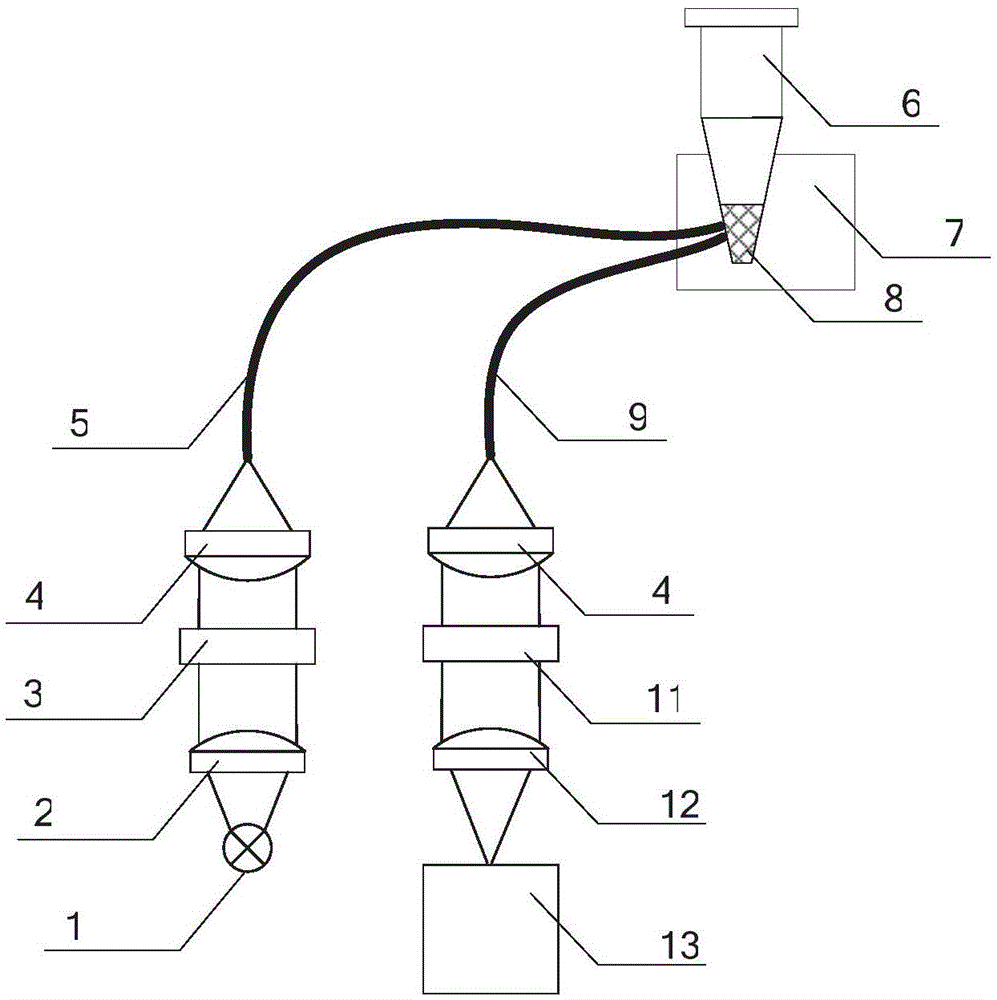
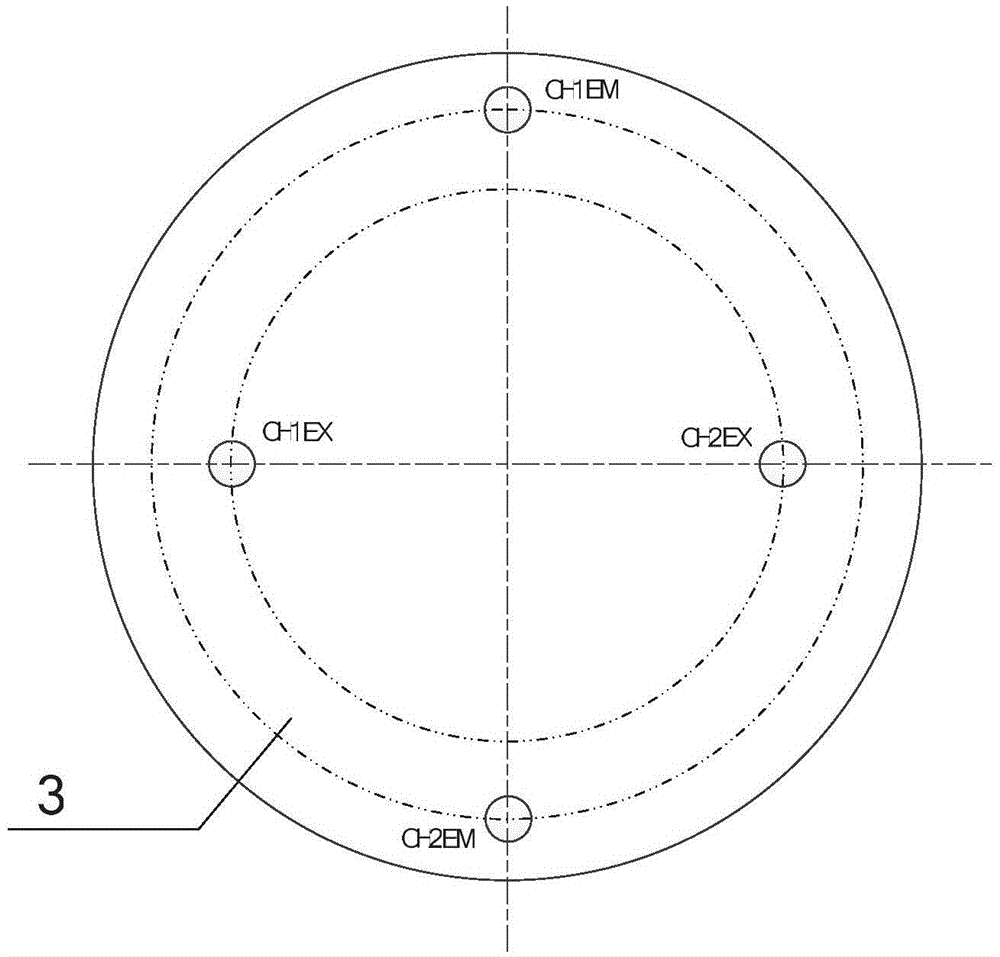
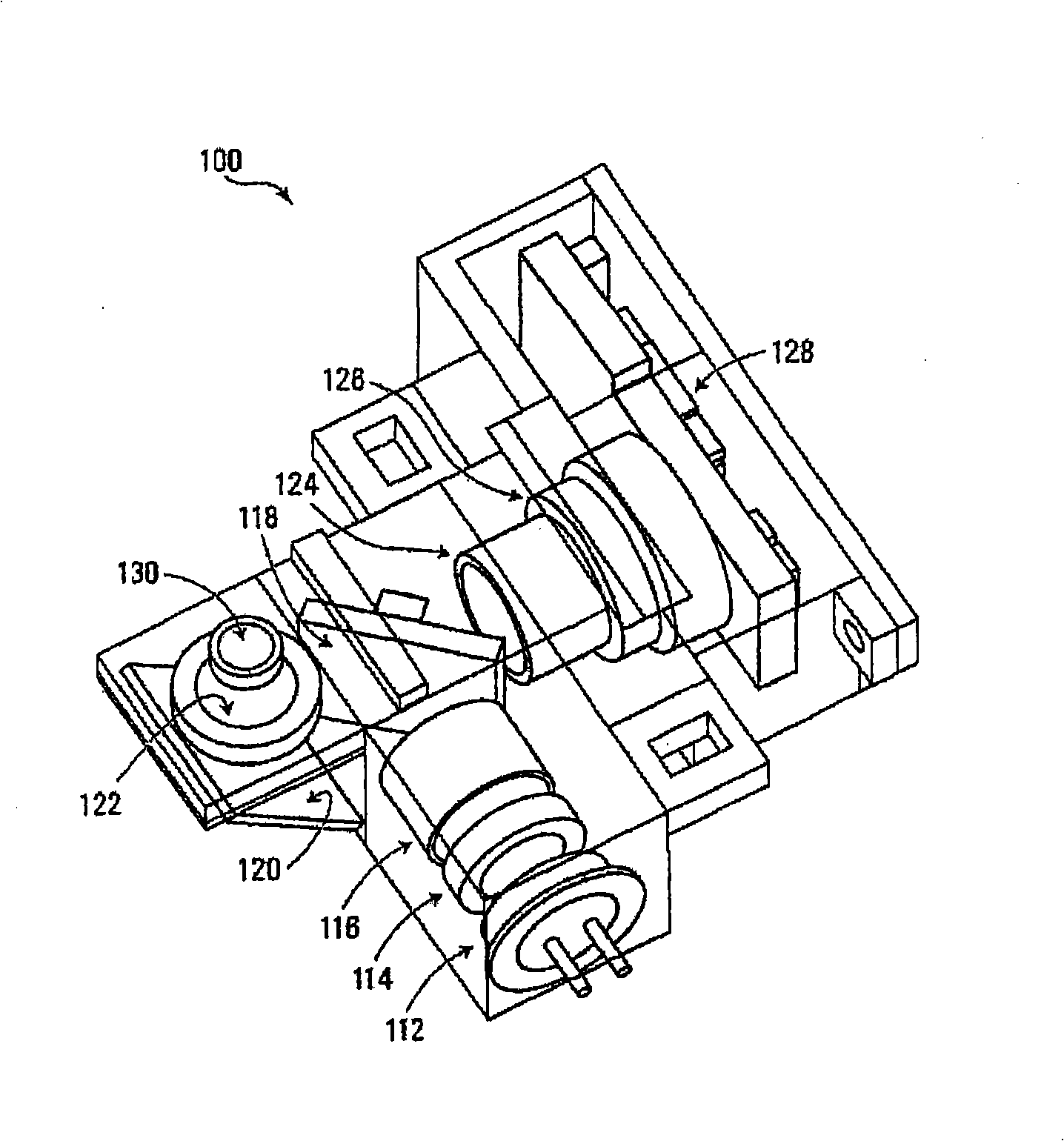
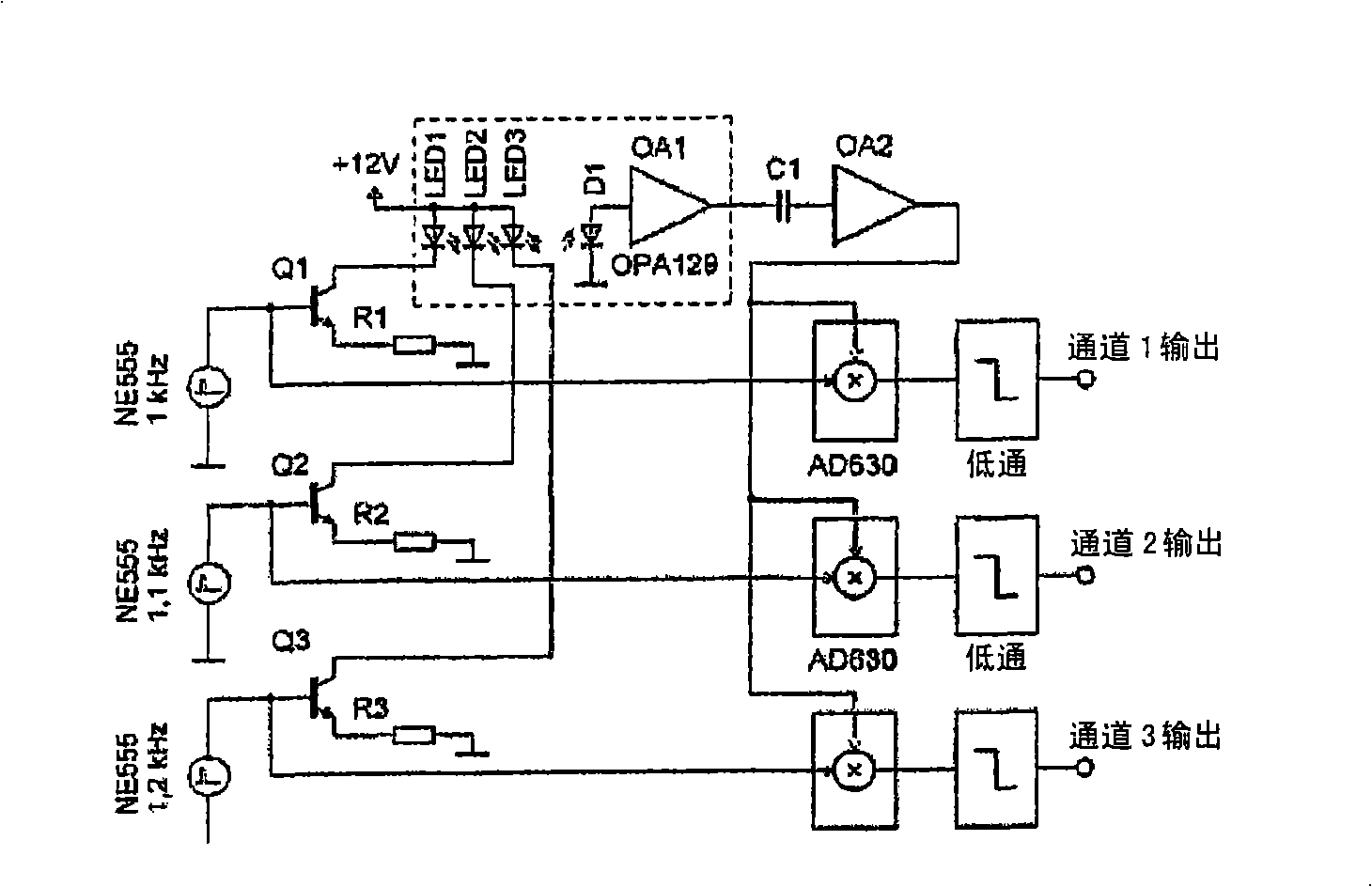
Patents
Literature
109 results about "Excitation filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
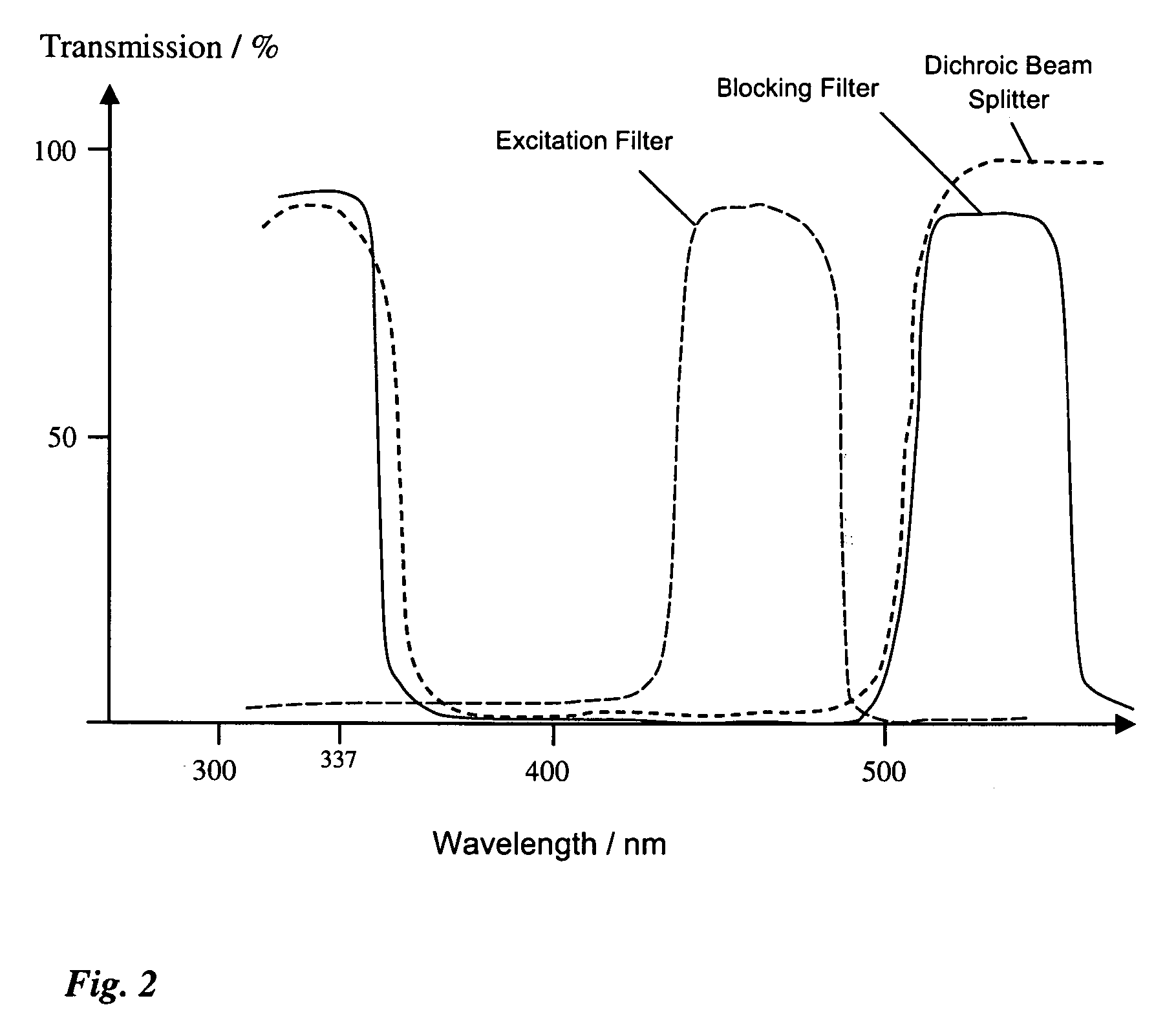
An excitation filter is a high quality optical-glass filter commonly used in fluorescence microscopy and spectroscopic applications for selection of the excitation wavelength of light from a light source. Most excitation filters select light of relatively short wavelengths from an excitation light source, as only those wavelengths would carry enough energy to cause the object the microscope is examining to fluoresce sufficiently. The excitation filters used may come in two main types — short pass filters and band pass filters. Variations of these filters exist in the form of notch filters or deep blocking filters (commonly employed as emission filters). Other forms of excitation filters include the use of monochromators, wedge prisms coupled with a narrow slit (for selection of the excitation light) and the use of holographic diffraction gratings, etc. [for beam diffraction of white laser light into the required excitation wavelength (selected for by a narrow slit)].
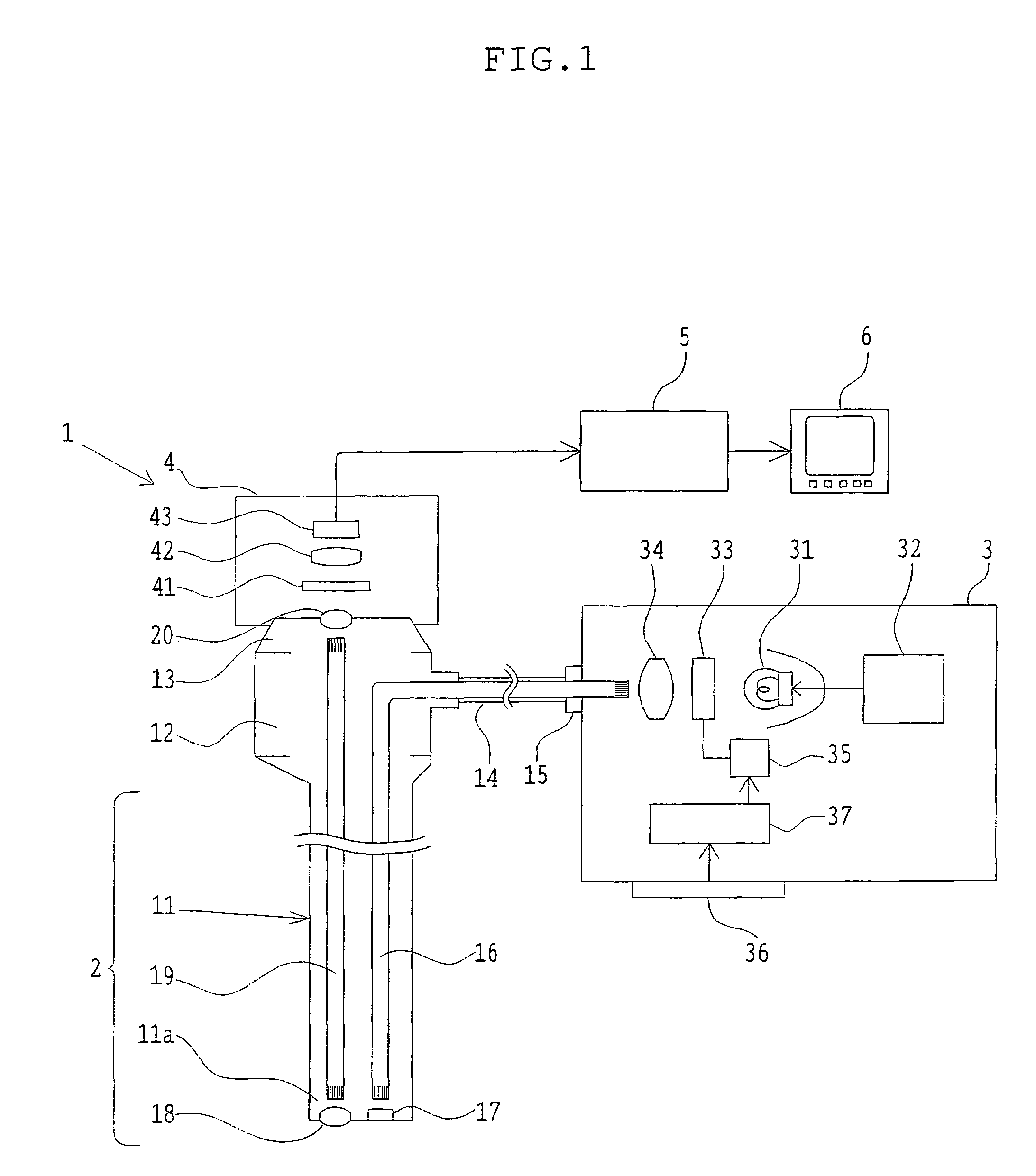
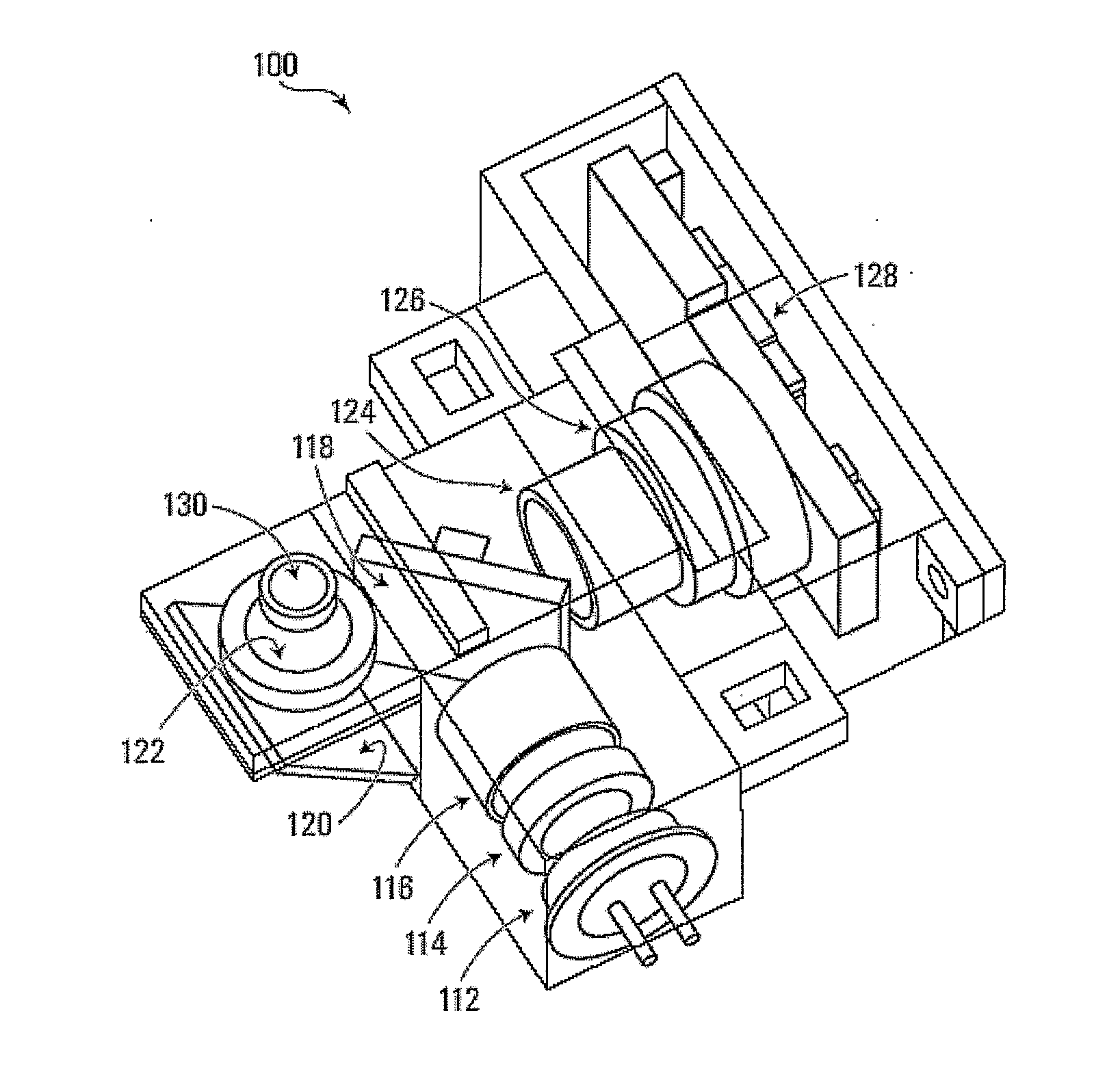
Fluorescence detector, filter device and related methods
ActiveUS20080013092A1Small sizeIncrease costSemi-permeable membranesDischarging arrangementAntigenFluorescent light
Microfluidic assay detectors and microfluidic assay detection methods are disclosed. A microfluidic chip is coupled to a light emitting device, emission filters and excitation filters. Excited fluorescent light is detected by a camera and a lens. The correspondent reading allows parallel detection of features such as antigens and biomarkers. A microfluidic filter and related methods are also disclosed. The filter can be used with on-chip fluid filtration such as whole blood filtration for microfluidic blood analysis. The filter is able to filter the necessary volume of fluid and in particular blood in an acceptable time frame.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
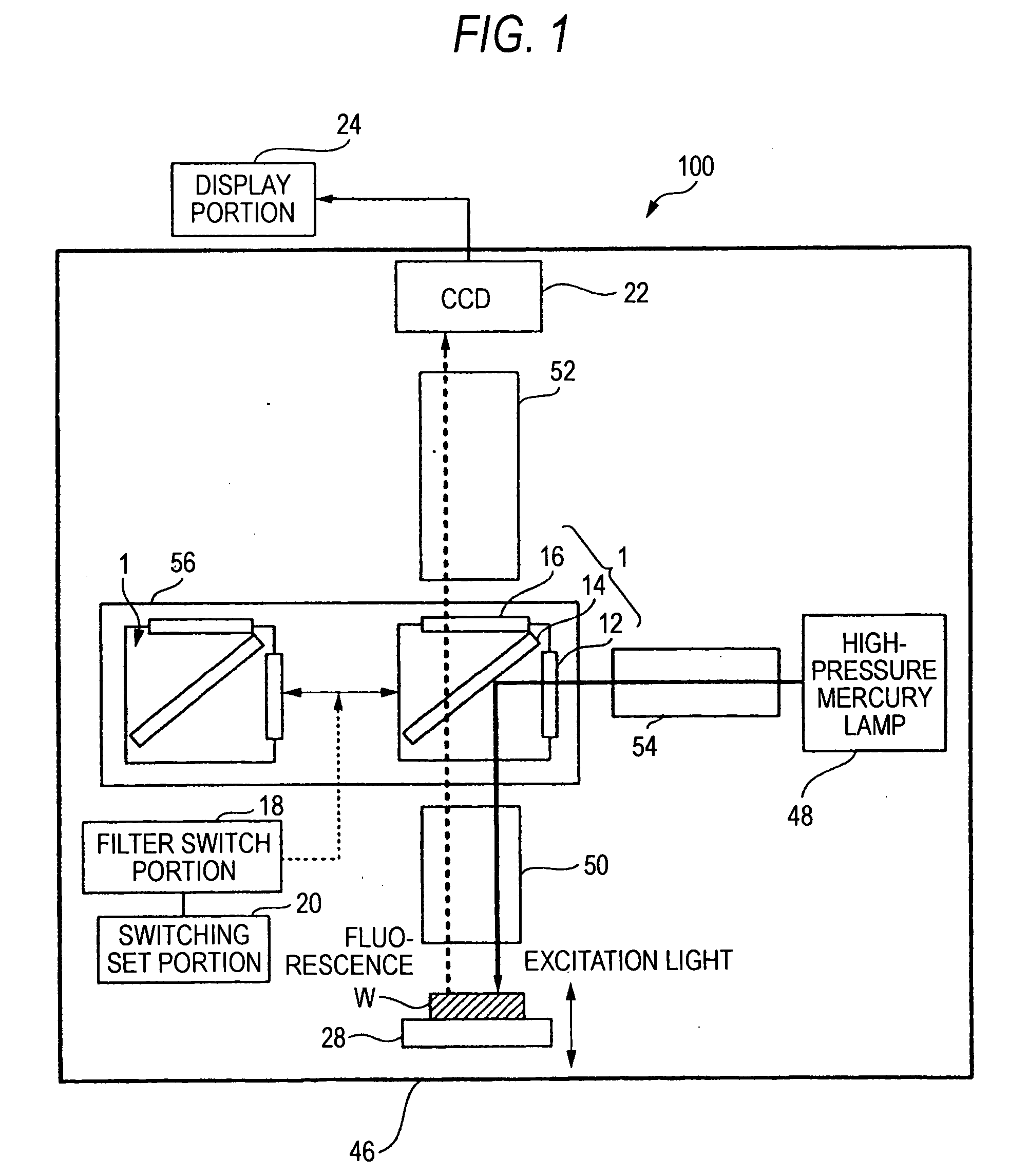
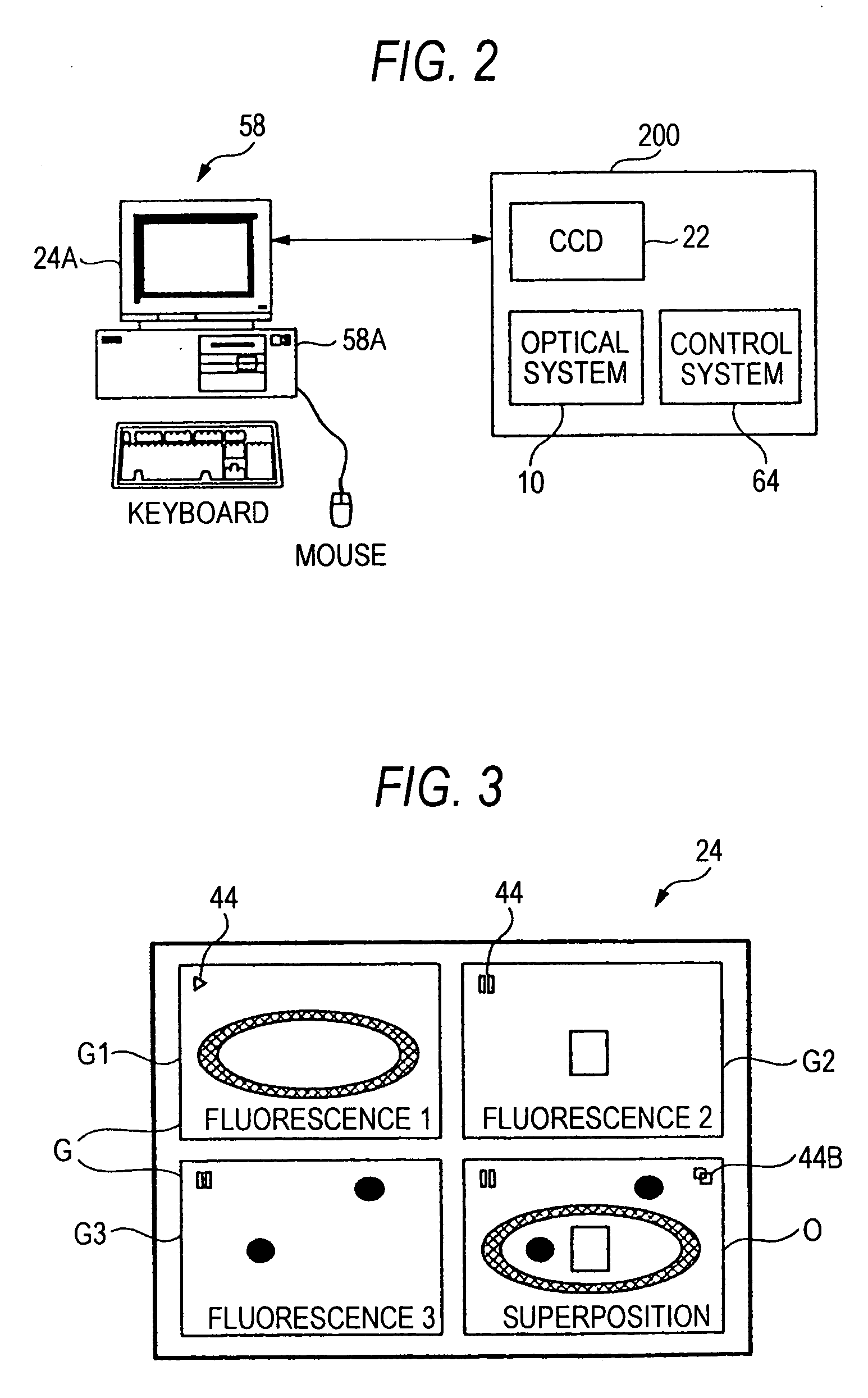
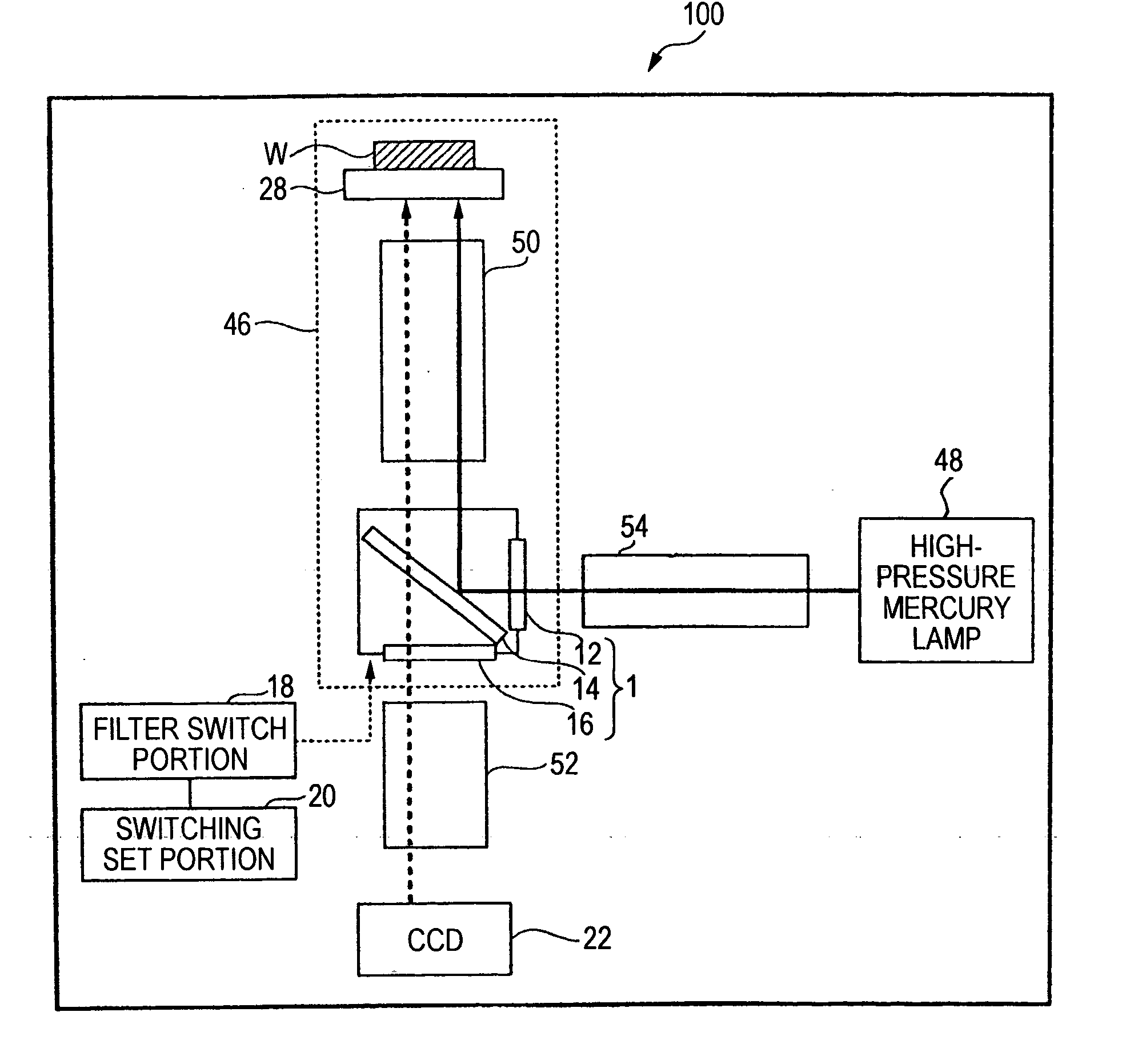
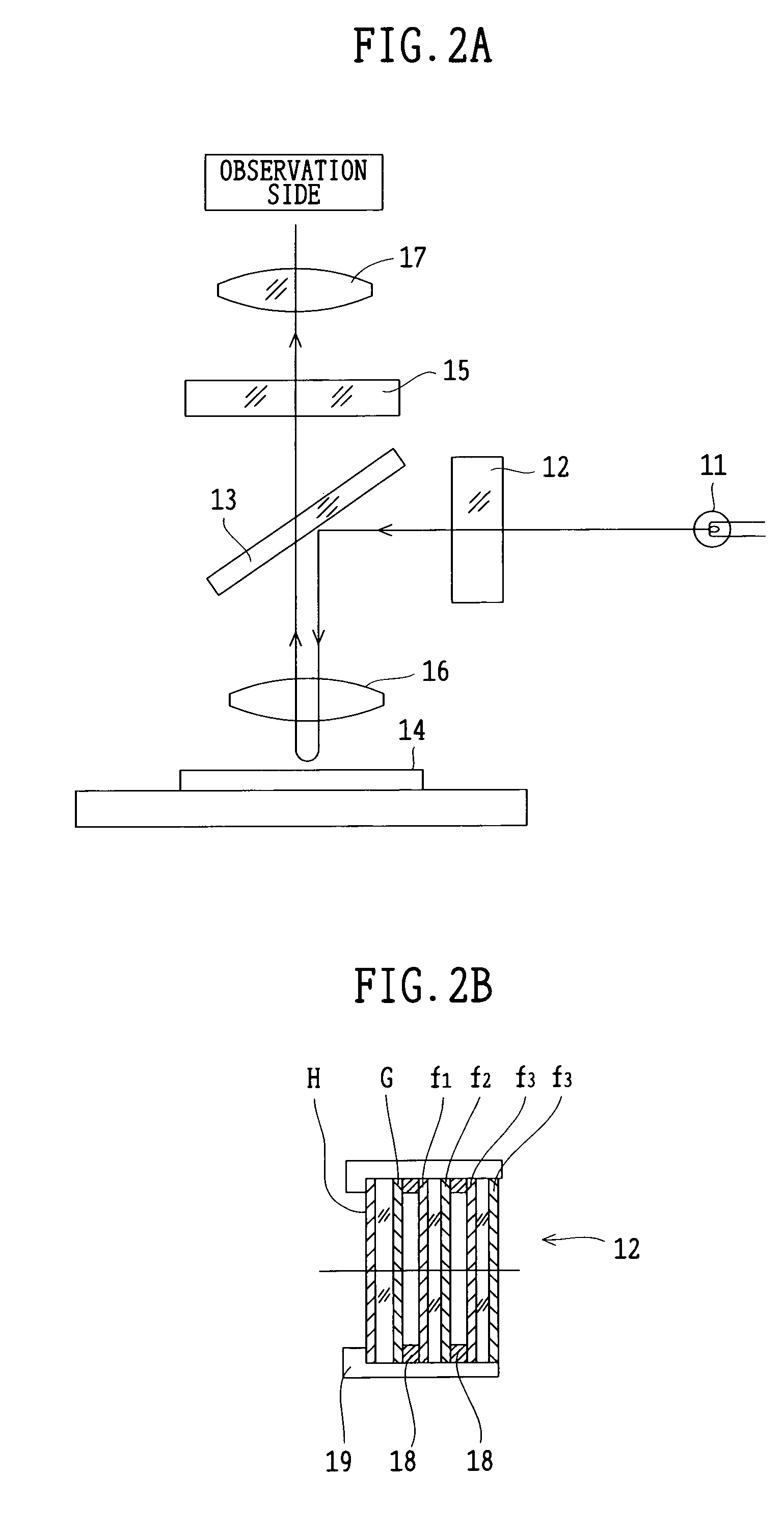
Fluorescence microscope, display method using fluorescence microscope system, and computer-readable medium
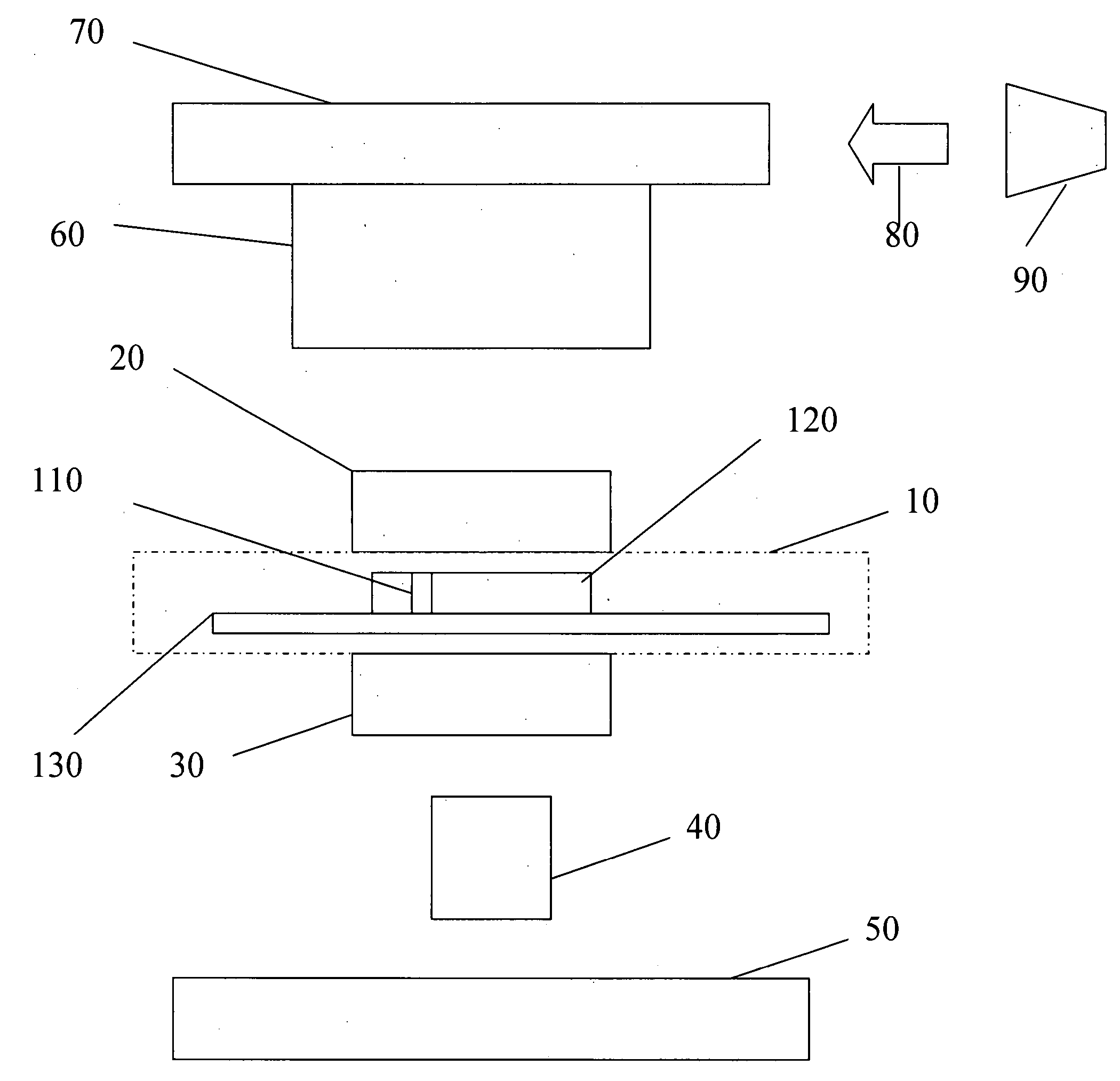
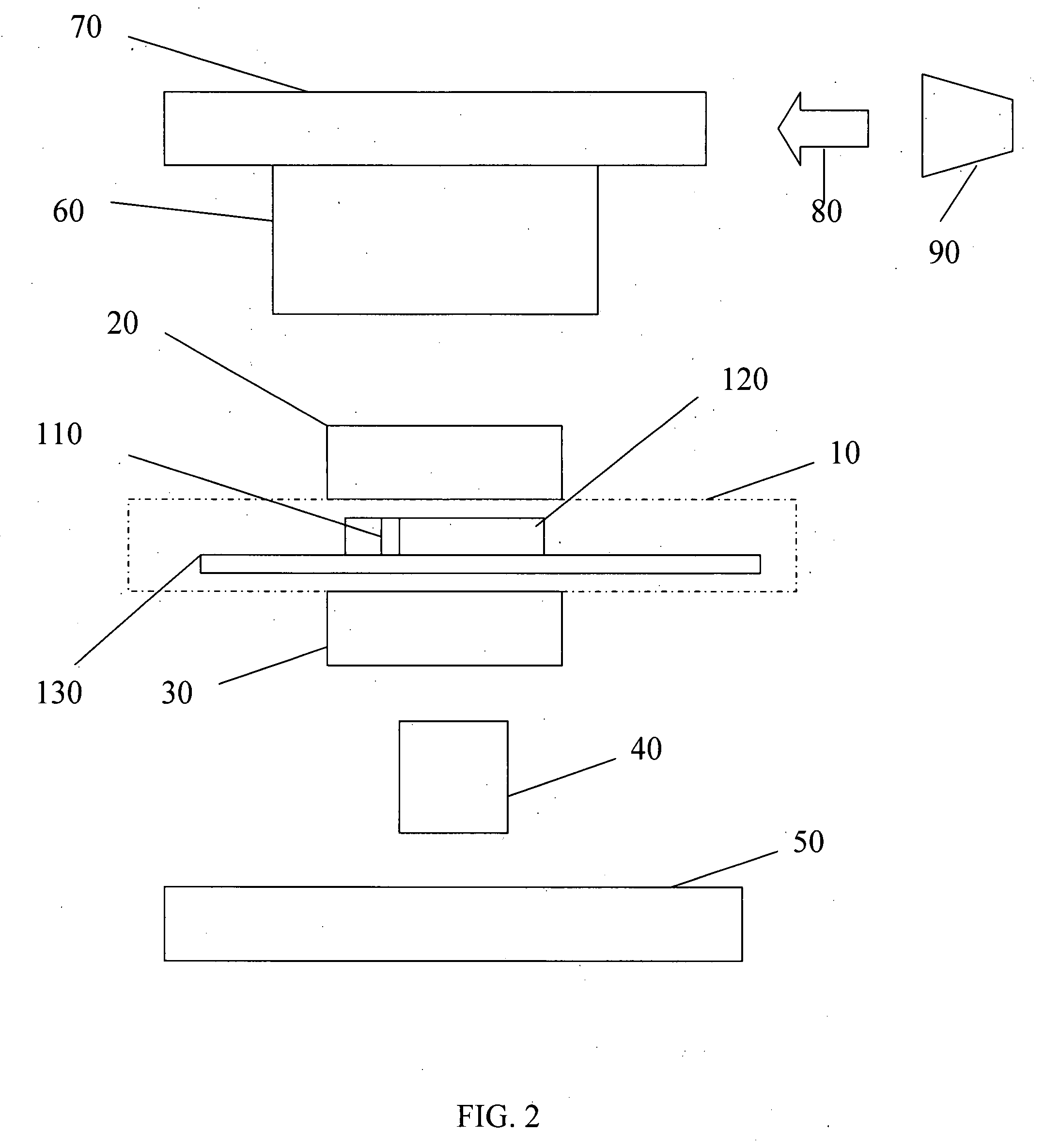
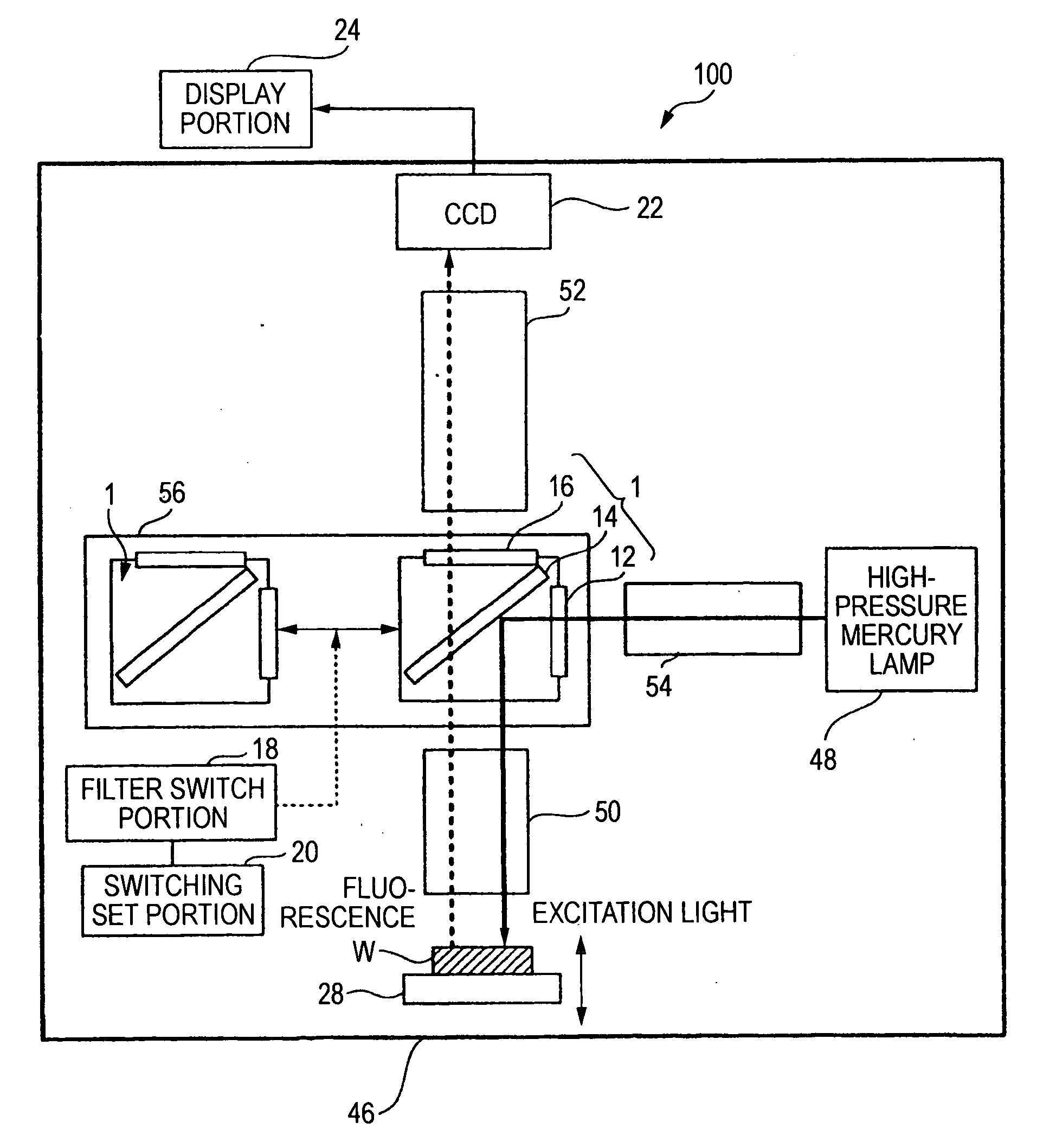
InactiveUS20050270639A1Easy to observeAvoid damageMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceAbsorption filterFluorescence microscope
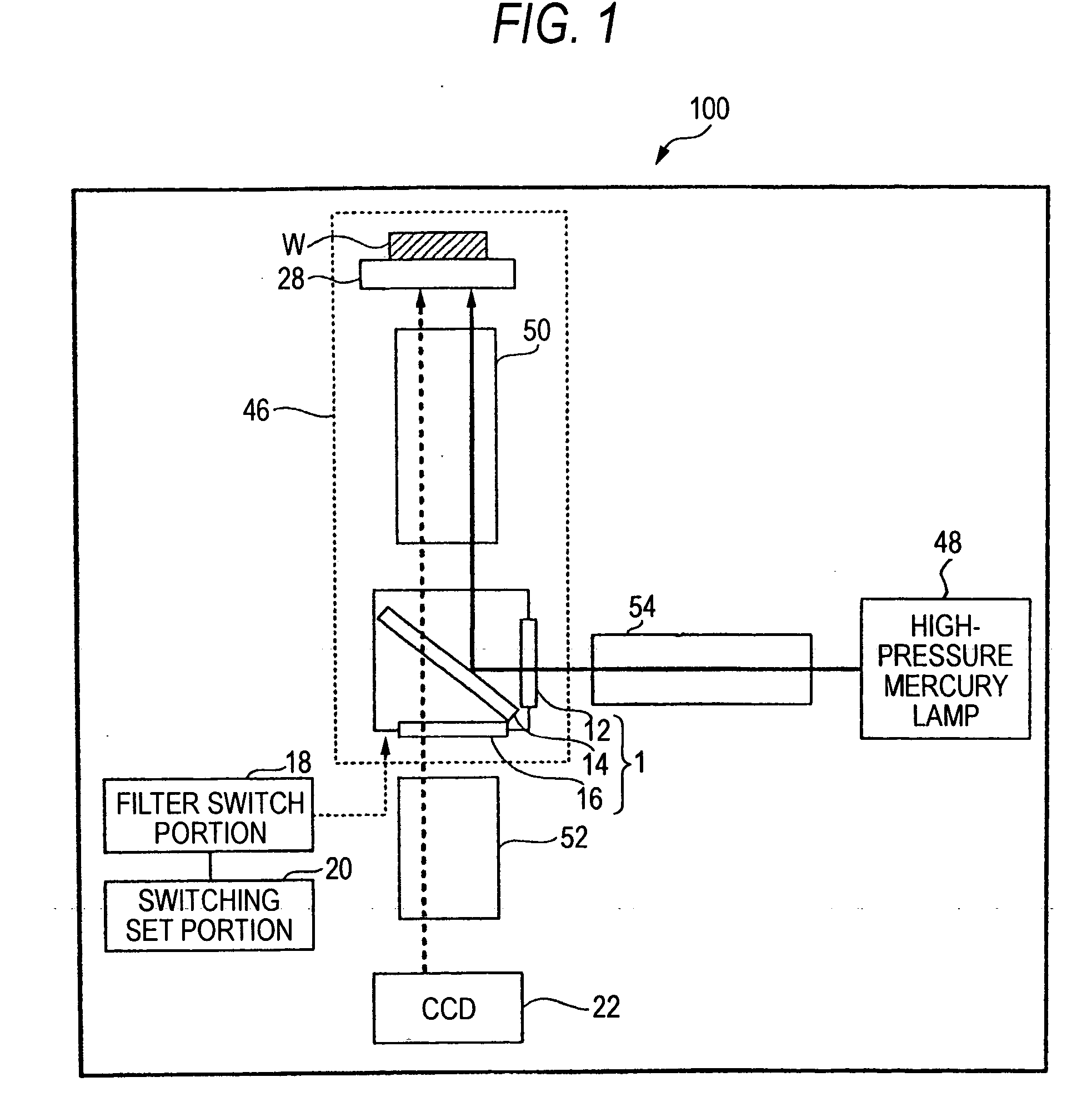
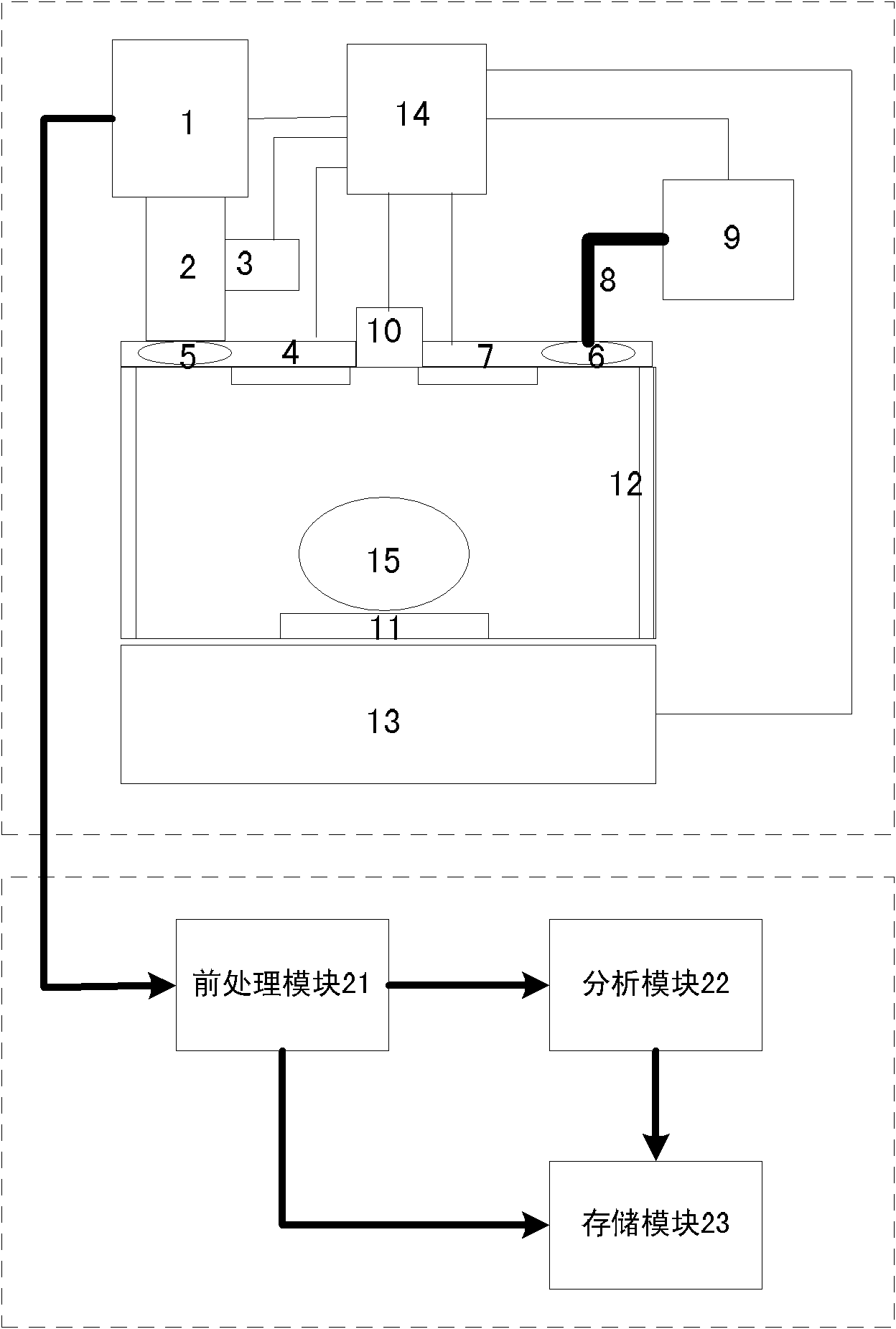
A fluorescence microscope comprises plural types of filter sets including a combination of a excitation filter, a dichroic mirror, and an absorption filter, a filter switch portion for switching the filter sets at a predetermined timing, an imaging portion for picking up an image of a specimen as an observation object by using the filter sets, a display portion having a plurality of image display areas on which the image picked up by the imaging portion are displayed respectively, and a control portion for generating a superposed image on which the images are superposed. In this fluorescence microscope, the imaging portion picks up the image via every filter set in synchronism with a timing which is set by the switching set portion and at which the filter switch portion switches the filter sets, and then the picked-up image is automatically updated and displayed in the image display areas.
Owner:KEYENCE
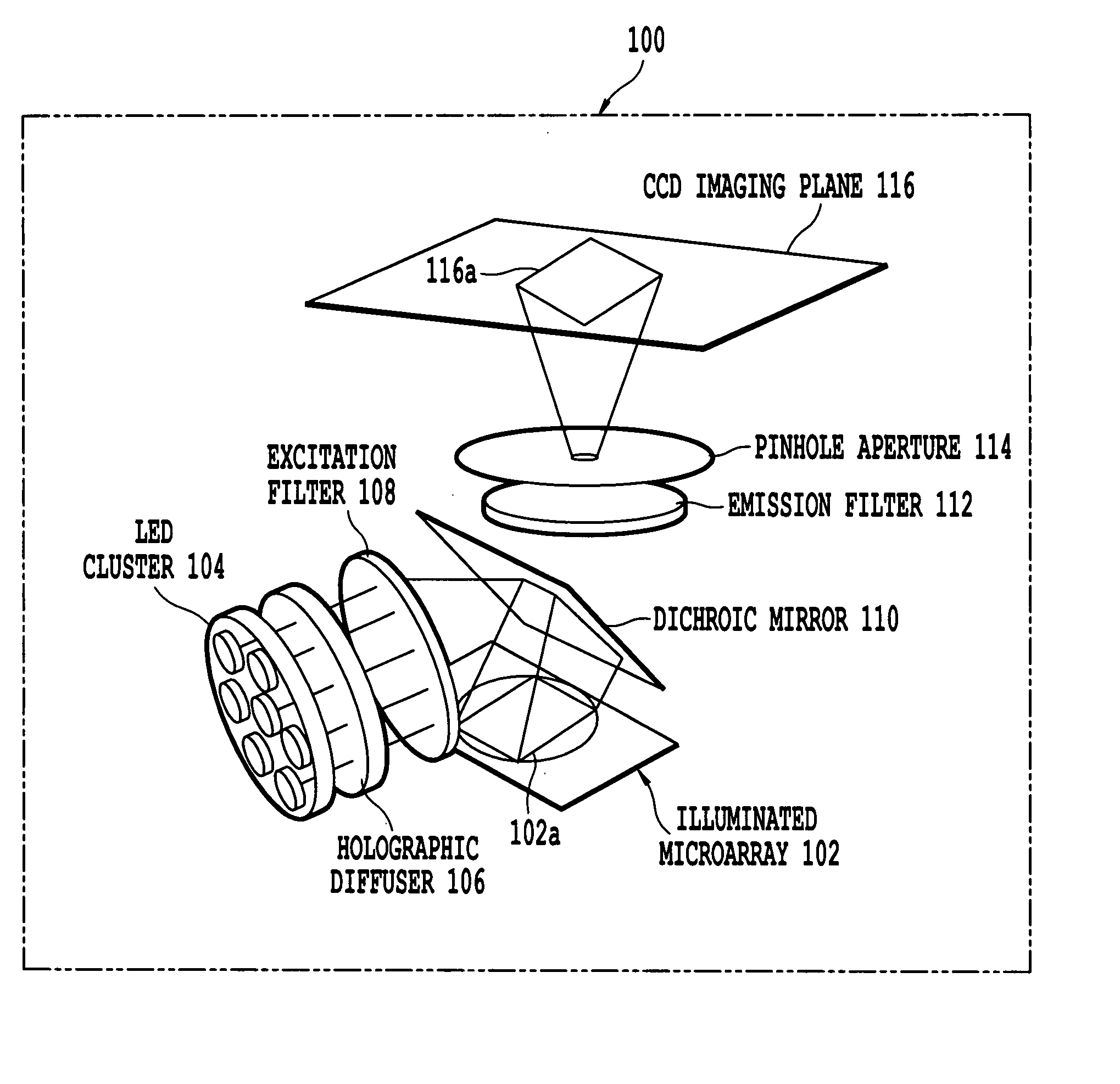
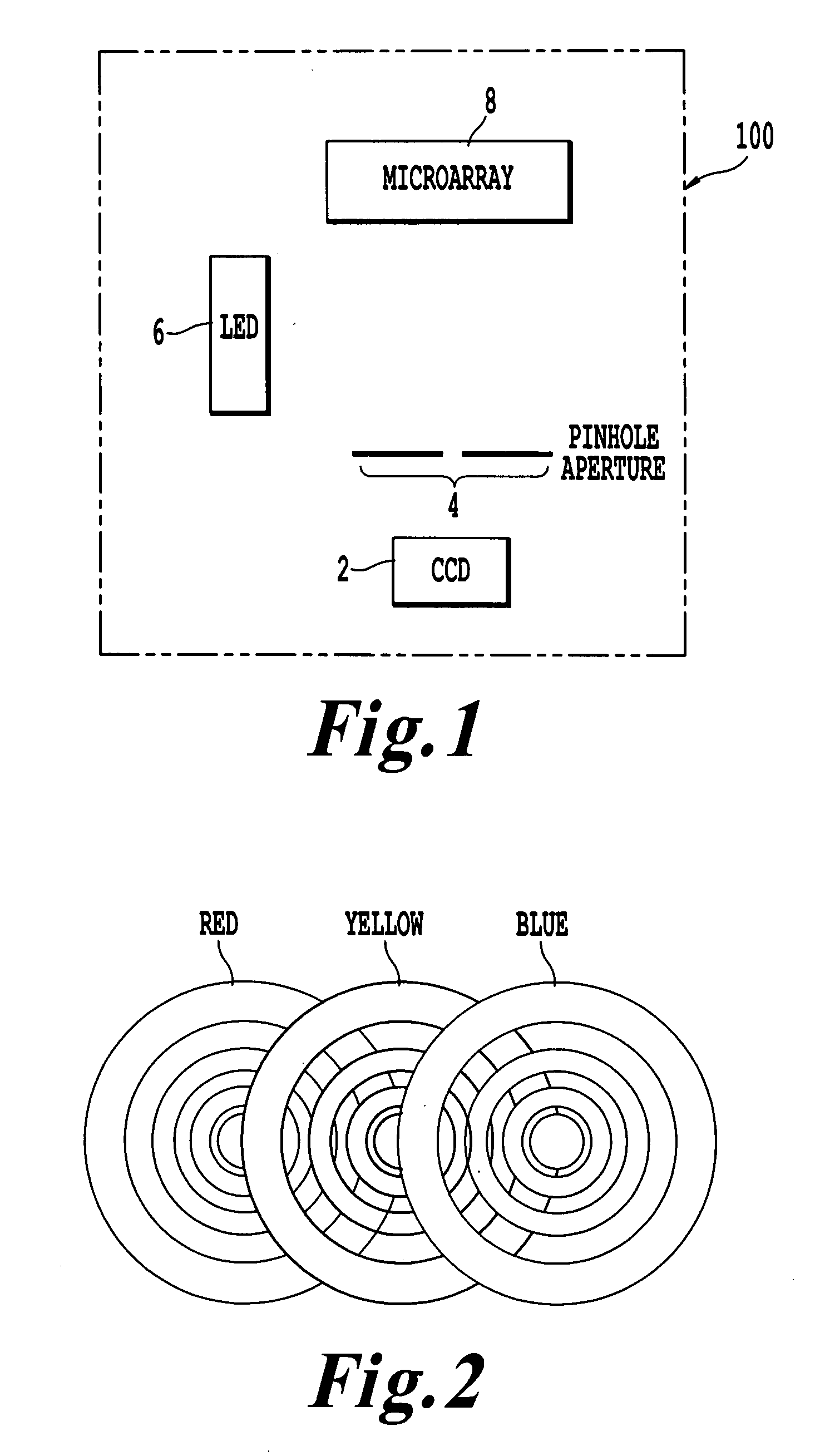
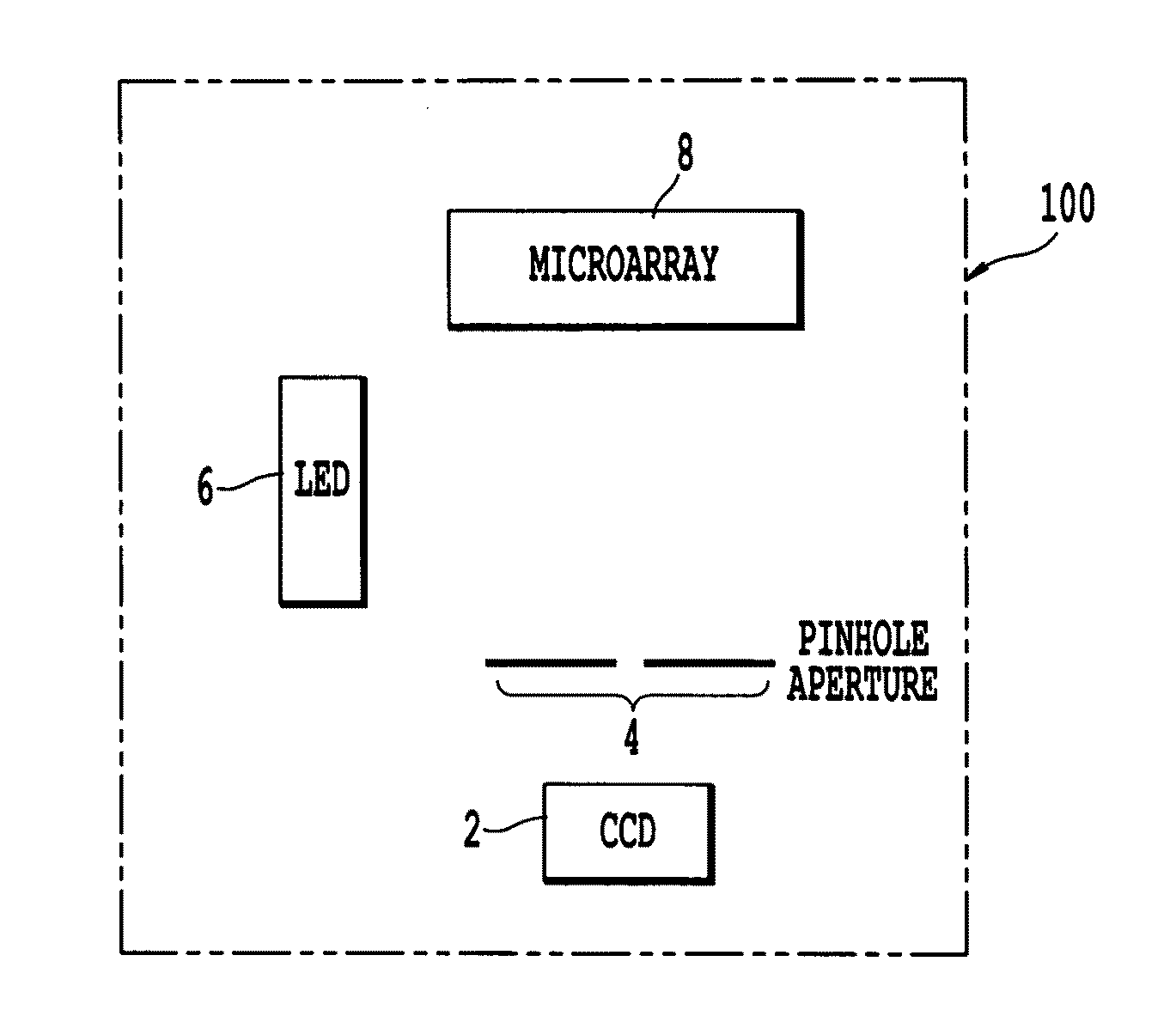
Microarray imaging system and associated methodology
InactiveUS20070263914A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionLight filterCharge couple device
An apparatus and method are provided for creating an image of a microarray. The apparatus includes at least one light source configured to direct light toward the microarray. The apparatus includes an excitation filter configured to filter the light into a first frequency band towards dichromatic mirror. The dichromatic mirror reflects light onto the microarray causing the microarray to emit electromagnetic energy. The apparatus includes emission filter configured to filter the electromagnetic energy within a second frequency band. The apparatus further includes an imaging unit having a charged coupled device (CCD), the CCD having an imaging surface masked by a pinhole blind such that when the pinhole blind receives electromagnetic energy from the emission filter, an image is created of the entire micro array.
Owner:TESSARAE LLC
Lasing fluorescence scanning imaging-fluorescence correlation spectrum unimolecule detecting instrument
InactiveCN101718696AEasy to replaceEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescencePhoton detectionData acquisition
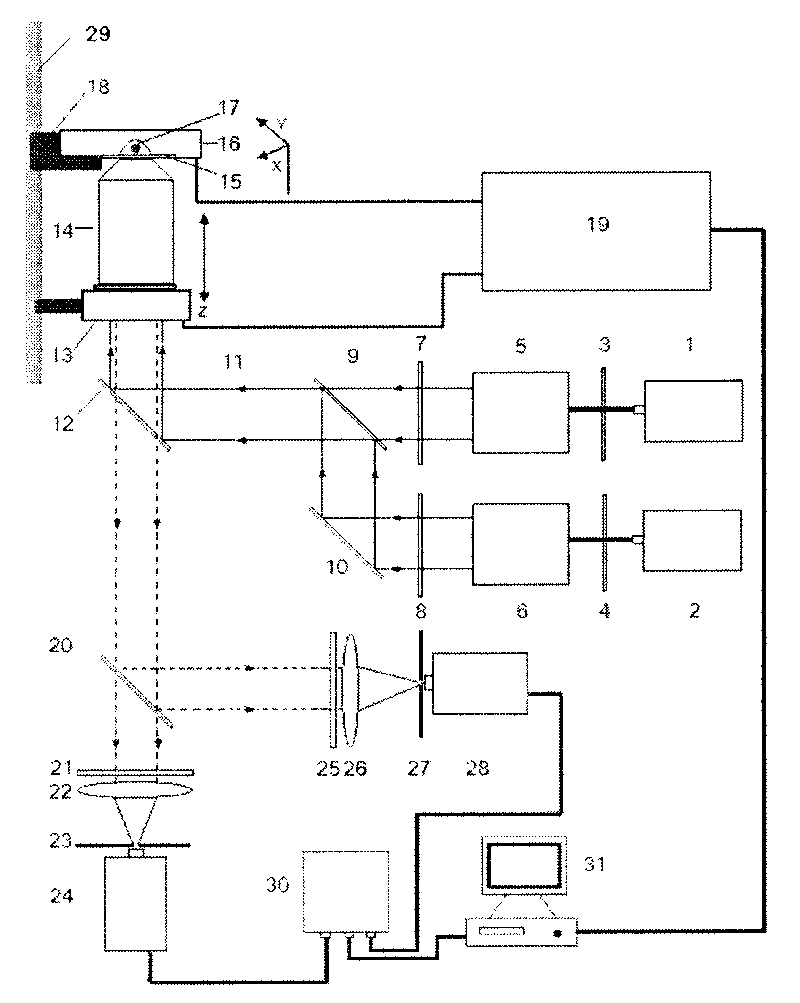
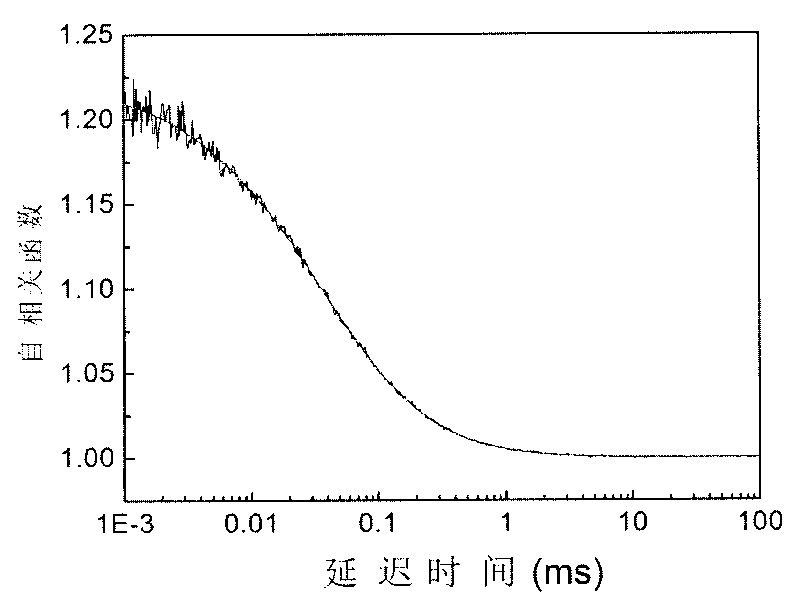
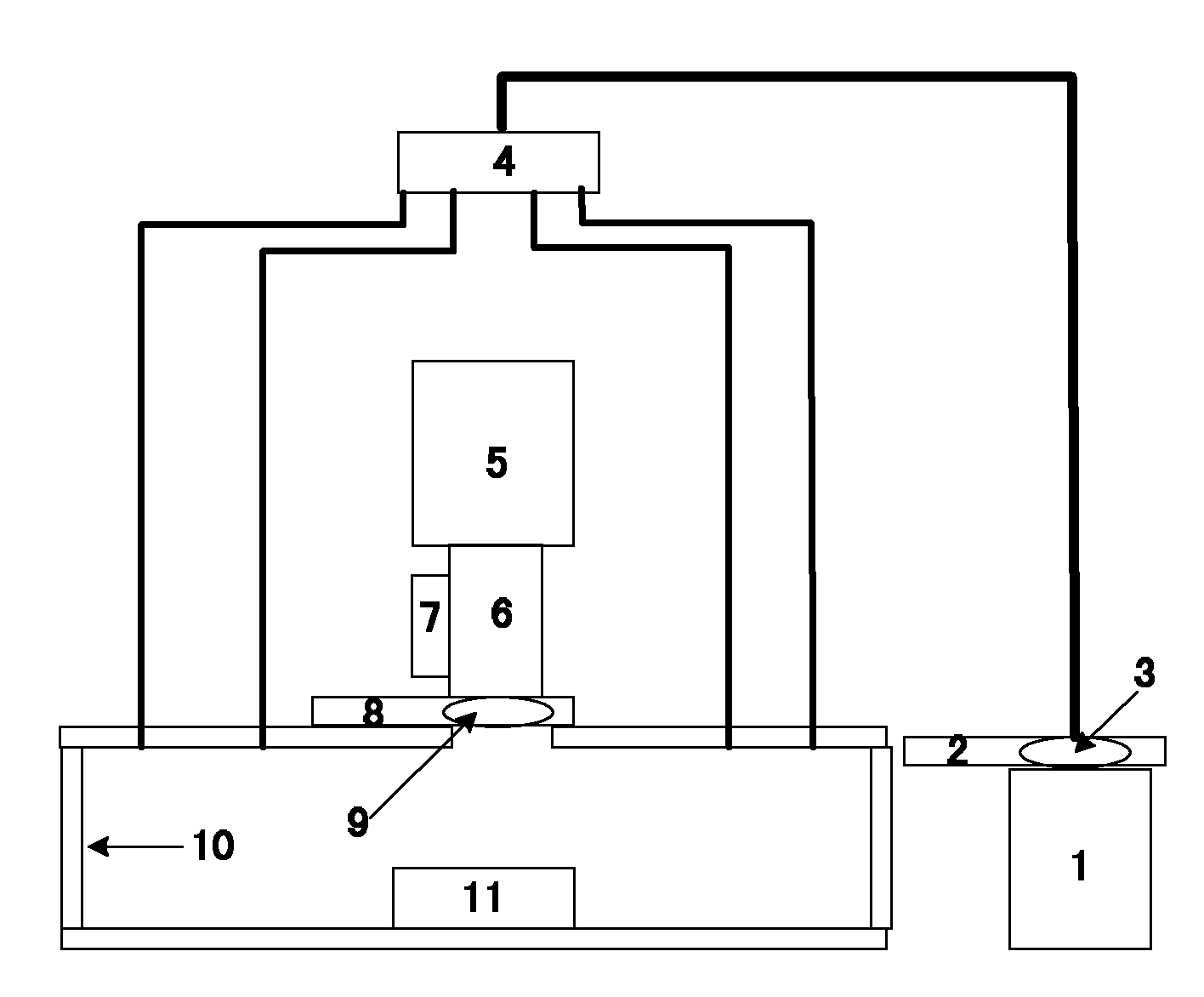
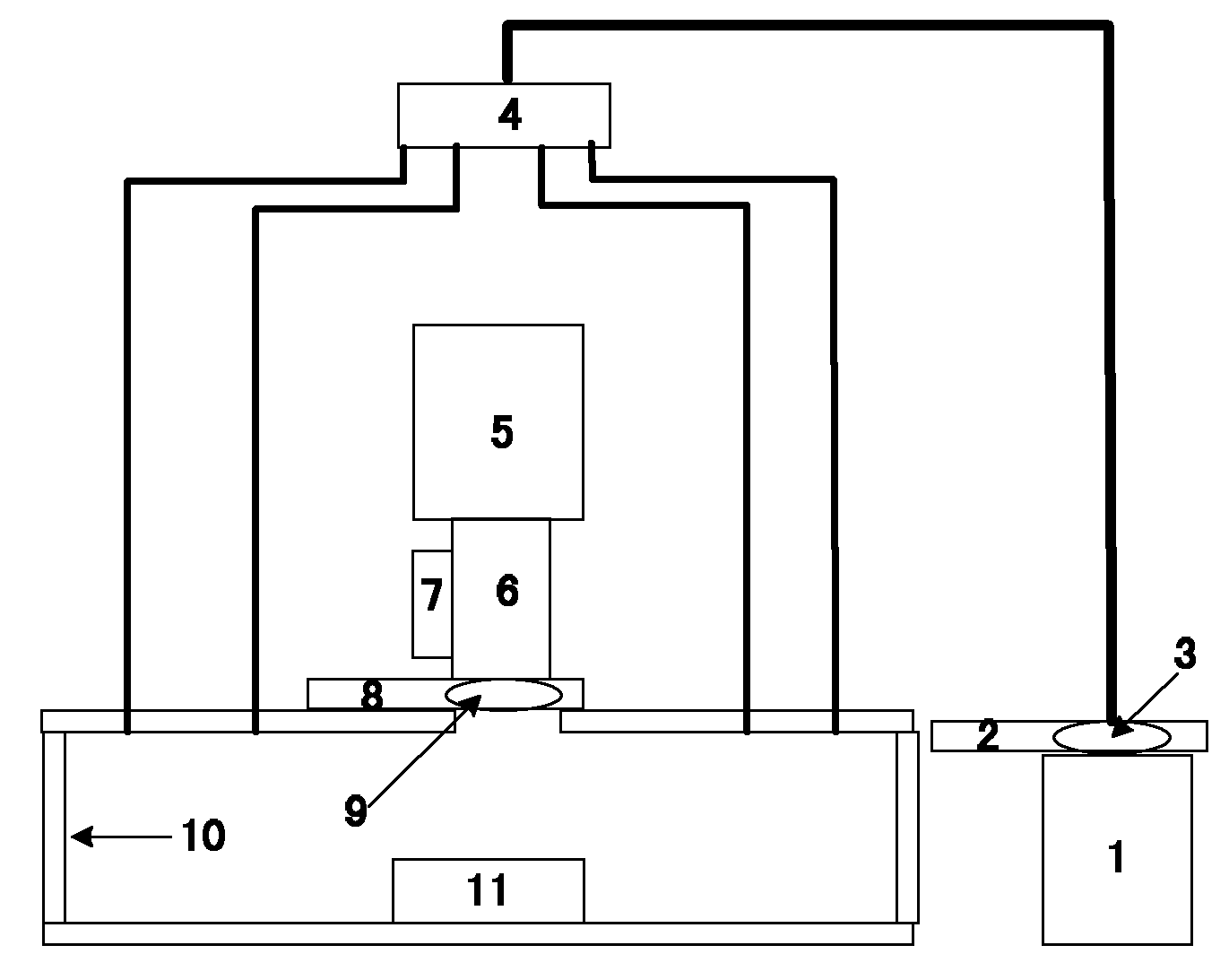
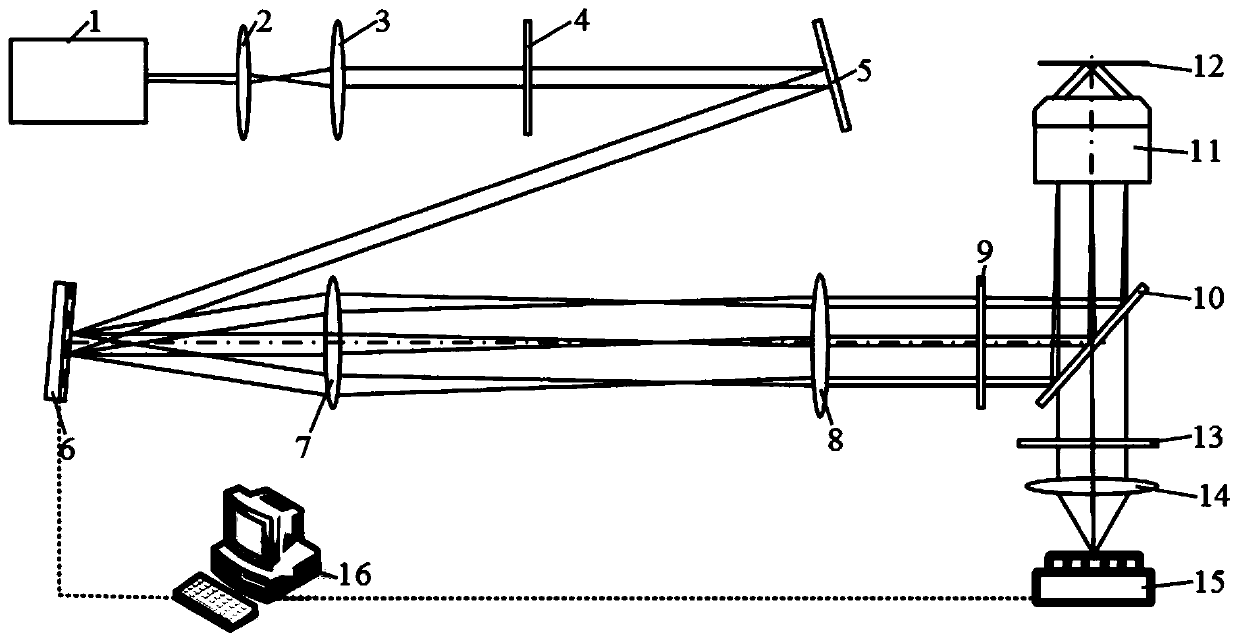
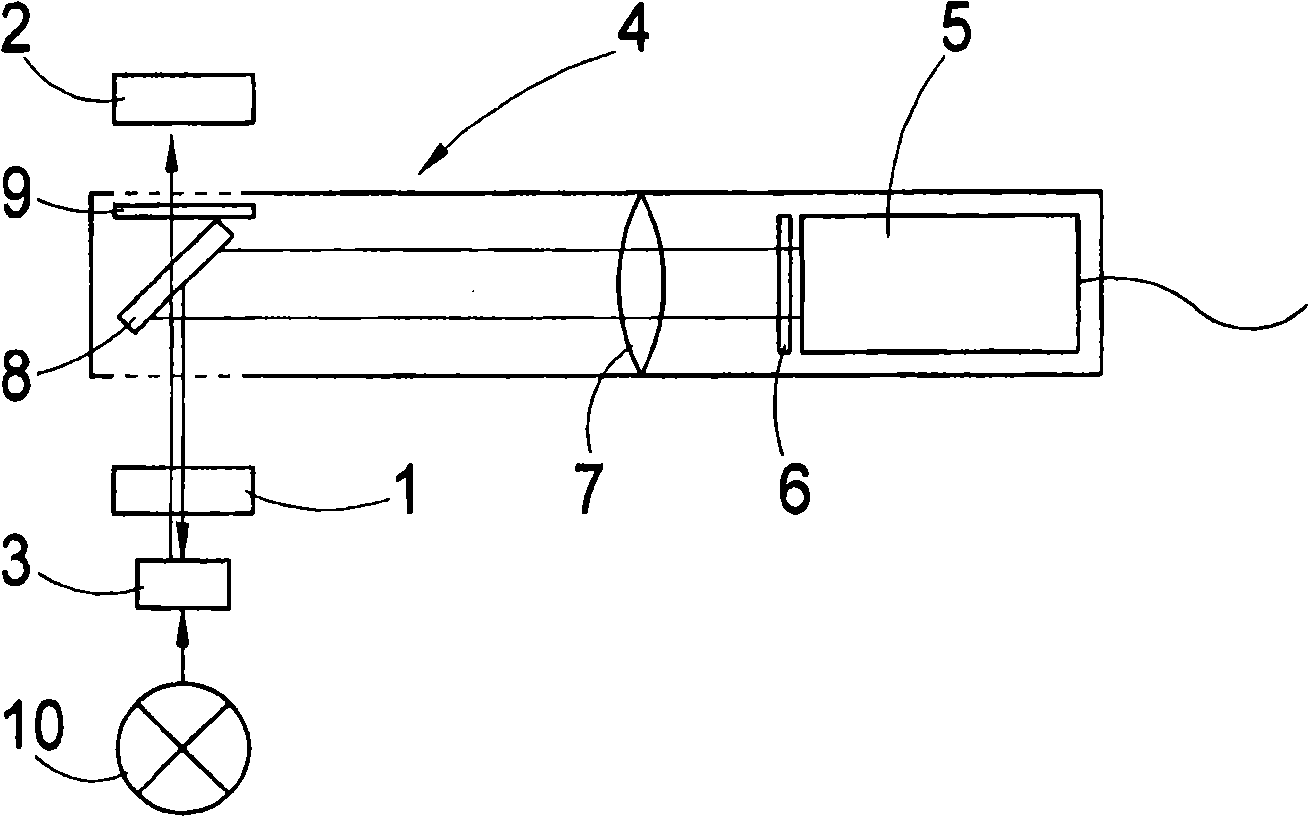
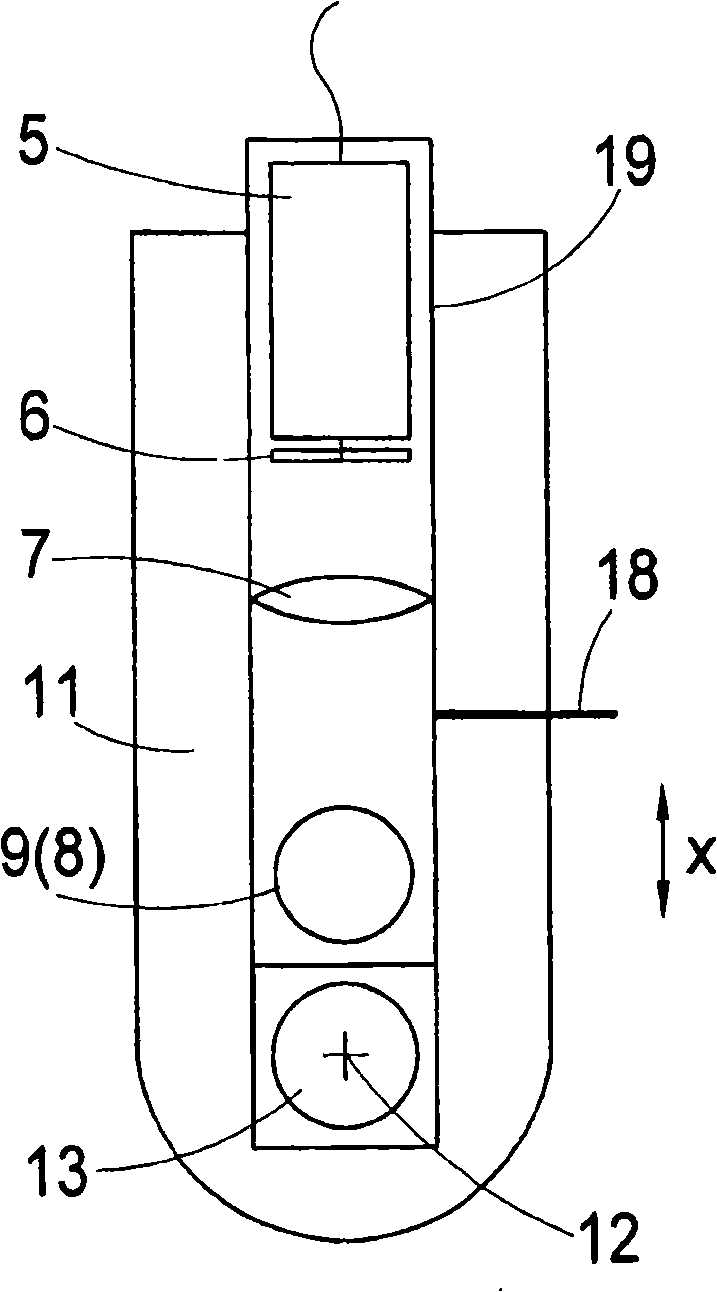
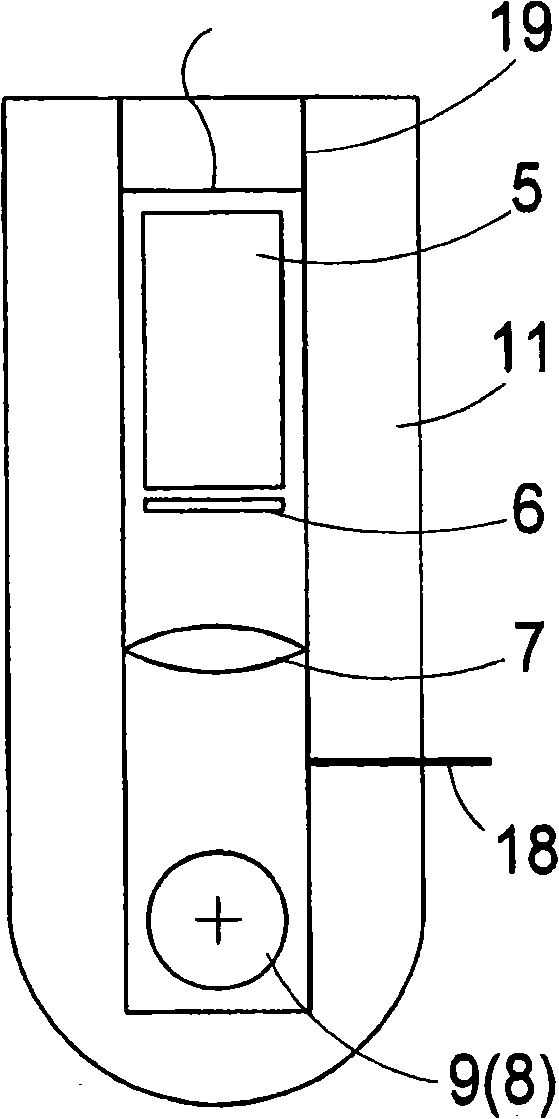
The invention relates to a lasing fluorescence scanning imaging-fluorescence correlation spectrum unimolecule detecting instrument. Cover glass or a sample cell is arranged on an X-Y scanning platform; a microscope objective is installed on a Z-direction locator. Expended laser is filtered by an excitation filter, and then reflected into the objective by a dichroic mirror, and finally radiated in a sample above the cover glass after being focused by the objective; the sample generates fluorescence; and the generated fluorescence is collected by the same objective, passes through the dichroic mirror, and stray light is filtered off by an emission filter, and finally the filtered fluorescence is focused by a focusing lens on a small hole which is coupled with a single photon detector; and a signal generated by the single photon detector enters a computer through a data acquisition card. In the computer, three-dimension displacement and positioning system control software control the X-Y scanning platform to do X-Y two-dimension movement, and the Z-direction locator controls the focus of the objective to do Z-direction movement, thereby forming the three-dimension scanning to the sample; and three-dimension space position information and the signal generated by the single photon detector construct three-dimension scanning images and fluorescence correlation spectrum curves in the computer.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Microarray imaging system and associated methodology
InactiveUS7961323B2Color/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingTissue microarrayElectromagnetic shielding
Owner:TESSARAE LLC
Fluorescence microscope
InactiveUS20050270640A1Prevents excessive fadingSafe and high-picture-quality observationMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceAbsorption filterImaging lens
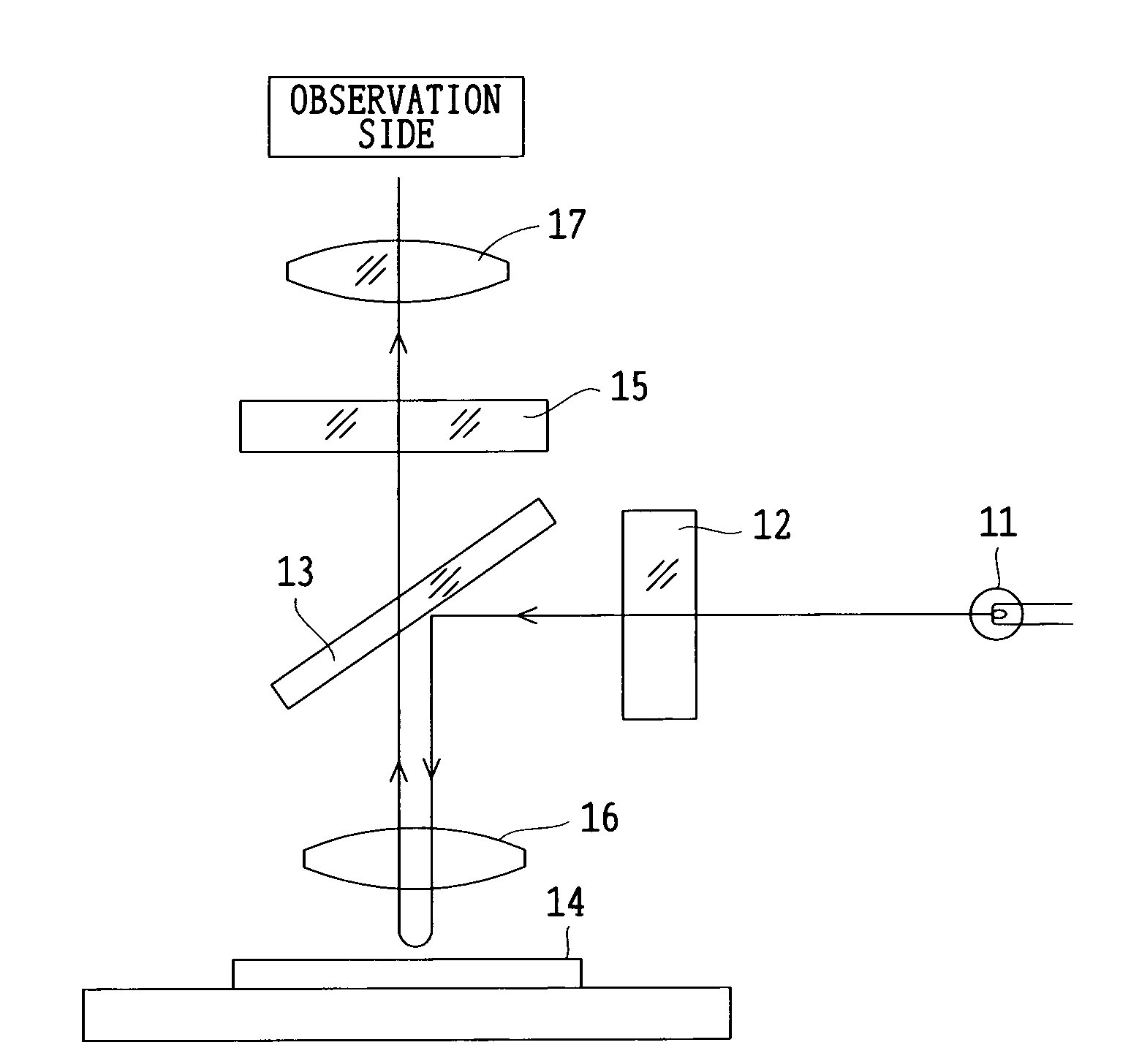
The fluorescence microscope comprises: a fixed-type objective lens placed between a filter set and a specimen loading portion; a partition that covers at least the specimen loading portion, the objective lens and the filter set to block extraneous light incident on the specimen loading portion; an imaging lens arranged on the outgoing surface of the absorption filter of the filter set, the imaging lens including a zoom lens capable of continuously changing the operation distance; and an imaging portion forms a fluorescent image from a fluorescence emitted from the specimen and received by the imaging lens via the absorption filter by irradiating an excitation light onto the specimen from the excitation light source via the excitation filter of the filter set and. This configuration avoids damage to the specimen or lens surface while allowing high-contrast fluorescence observation with reduced effect of extraneous light.
Owner:KEYENCE
Fluorescence observing apparatus
InactiveUS7050224B2Effective observationEfficiently taken outMirrorsOptical filtersAbsorption filterFluorescence
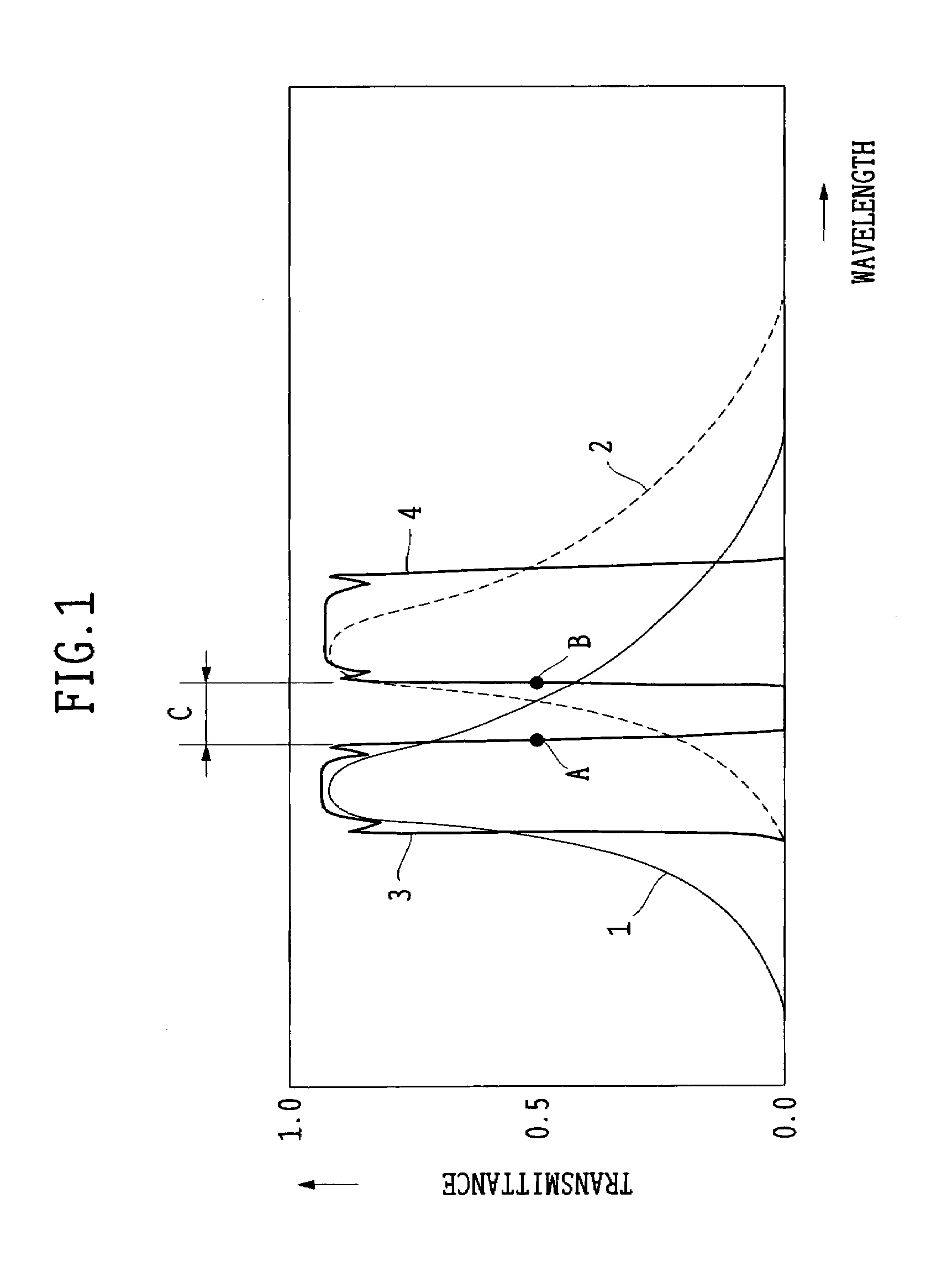
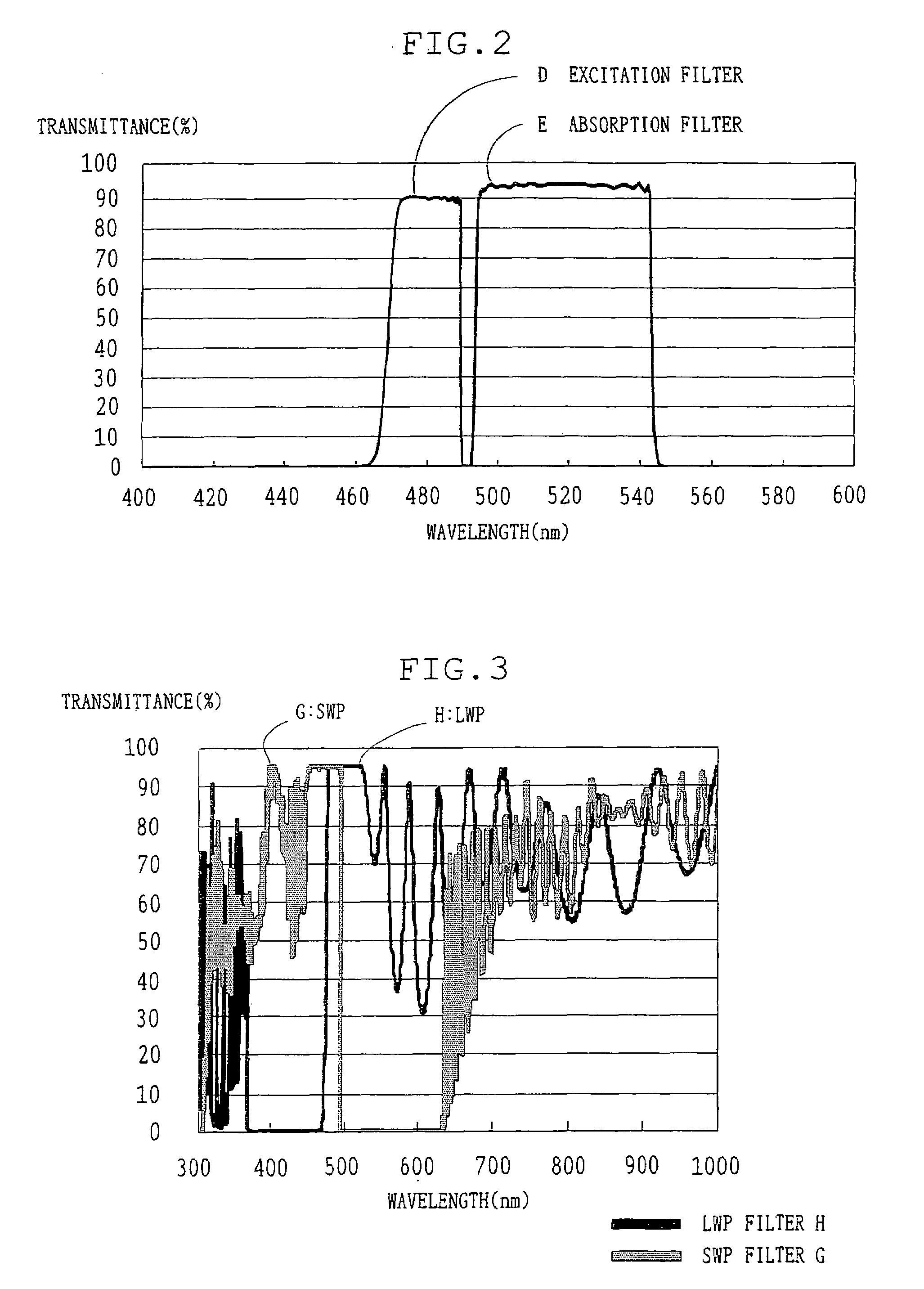
A fluorescence observing apparatus has an excitation filter unit for transmitting only exciting light with particular wavelengths, of illuminating light, and an absorption filter unit for transmitting only fluorescent light produced from a specimen by irradiating the specimen with the exciting light to block the exciting light. In this case, the space between the half-value wavelength on the long-wavelength side of the excitation filter unit and the half-value wavelength on the short-wavelength side of the absorption filter unit is in the range of 6–12 nm, and variations in the half-value wavelengths of the excitation filter unit and the absorption filter unit where humidity is changed from 10% to 95% are within 0.5 nm. Whereby, faint fluorescent light is efficiently taken out and the observation can be made.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Fluorescence observation equipment
InactiveUS7453568B2WeakHigh fluorescence intensityOptical radiation measurementForce measurement by measuring optical property variationAbsorption filterTransmission illumination
An apparatus for fluorescence observation includes an excitation filter which transmits only exciting light of an specific wavelength among illumination light, and an absorption filter which blocks the exciting light and transmits only fluorescence generated from a specimen when the exciting light is irradiated to the specimen. Here, an interval of a half-value wavelength at a long-wavelength side of the excitation filter and a half-value wavelength at a short-wavelength side of the absorption filter is in a width between 1 nm to 6 nm, and change of the half-value wavelength of the excitation filter and the absorption filter when humidity changes from 10% to 95%, is 0.5 nm or less.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Laser fluorescent molecular imaging system and an instant fluorescent imaging method
ActiveCN102151122ASimplify operabilityReasonable structureDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCamera lensLaser light
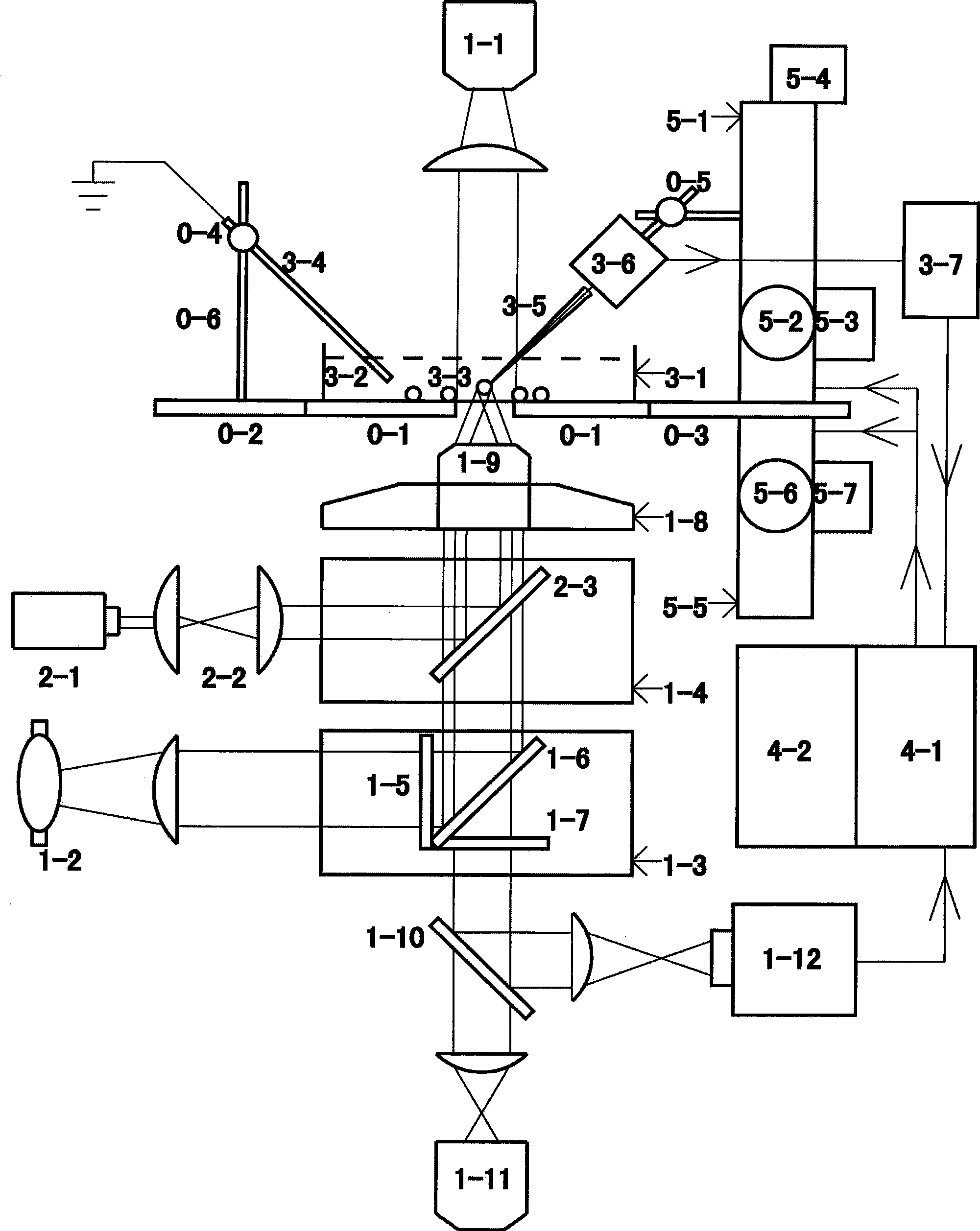
The invention provides a laser fluorescent molecular imaging system and an instant fluorescent imaging method. The system and the method comprise an image processing part and an image collecting part, wherein, in the image collecting part, a controller is connected with a camera, a lens adjusting motor, a transmission filter wheel, a laser filter wheel, a laser light source, a white lamp and electronic control translation stages in three directions, controls the lens adjusting motor to change focus length and aperture of a lens, controls the transmission filter wheel and the laser filter wheel to rotate and respectively switch a transmission filter and a laser filter to the acting position, controls opening and closing of the laser light source and the white lamp, and controls motor shafts of the electronic control translation stages in three directions to move; and the image processing part is connected with the camera in the image collecting part, receives fluorescent images and white light images, performs automatic cutting, pseudo-color addition and photon number statistic processing in the automatic cut area on fluorescent images, and overlays the processed fluorescent imagesand the white light images to obtain laser fluorescent molecular images. The system and the method can be applied in the fields of fluorescent image acquisition and analysis, medicine research and development and the like.
Owner:BEIJING DIGITAL PRECISION MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
High-accuracy fluorescence anisotropy microscopic imaging device and method
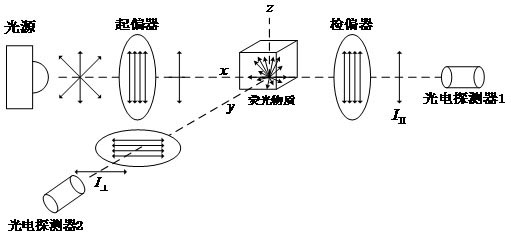
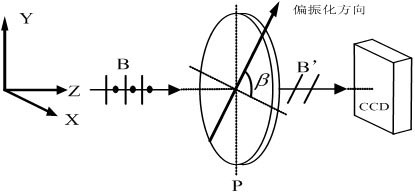
The invention relates to a high-accuracy fluorescence anisotropy microscopic imaging device and method. The imaging method comprises the following steps of: on a reflective fluorescence microscope, leading lights emitted by a light source to pass through a polarizer, an excitation filter plate and a spectroscope, and then focusing the lights on a sample; leading fluorescence reflected by the sample to pass through an objective lens, the spectroscope and an emission filter plate, and then imaging on an image plane of a CCD (Charge-Coupled Device) camera through an adjustable angle analyzer; controlling the adjustable angle analyzer to rotate around an optical axis of an imaging optical path step by step by using a computer, wherein when the adjustable angle analyzer rotates by an angle every time, the CCD camera shoots a frame of polarized fluorescence image, M images are totally shot; and finally calculating fluorescence anisotropic images from the M images by using Fourier transform.The imaging method is characterized in that the measuring resolution ratio of the fluorescence anisotropy is greatly improved by establishing a single-channel fluorescence analyzing optical path; andthe microscopic imaging system has higher stability and better anti-jamming capability.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
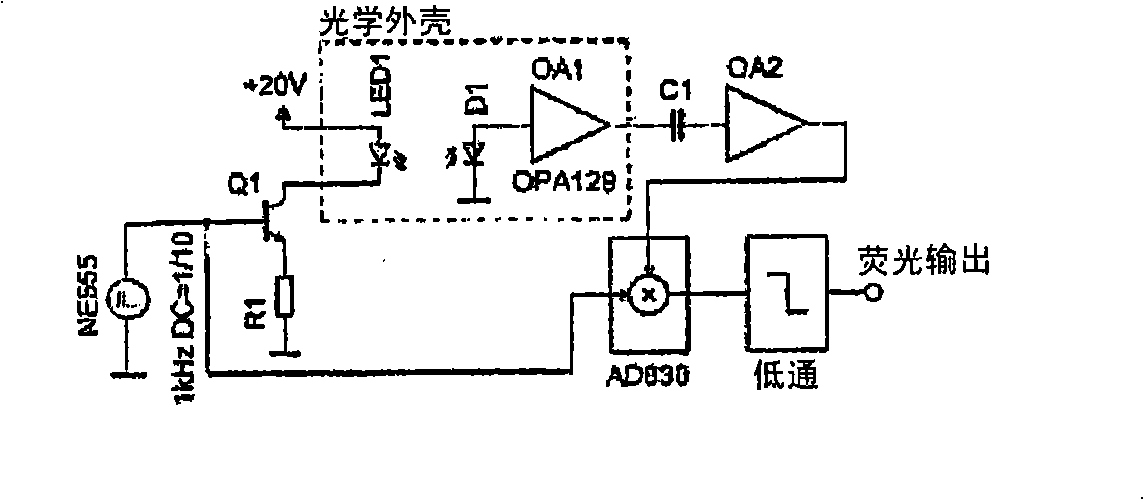
Closely attached type light emitting diode induction fluorescence detector for exciting light path
ActiveCN103134780AReduce volumeShorten the optical pathFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceDivergence angle
The invention relates to a light emitting diode induction fluorescence detector. According to the detector, a light emitting diode is adopted as an exciting light source, exciting light is filtered by an exciting light filter, and light beams are limited by small holes. After the light beams are limited, the exciting light is transferred to a capillary tube flow cell. A receiving optical fiber receives fluorescent light, and the fluorescent light is transferred to a photovoltaic conversion device to be detected after passing through an emission light filter. The light emitting diode, the light filters, the small holes and outer walls of an outer protective coating (such as polyimide) of the capillary tube flow cell are closely attached, and no condensing lens or exciting optical fibers are needed. The detector is compact in structure, convenient to use and low in cost. The fluorescent light can be received with high efficiency, the signal to noise ratio is improved and sensitivity of detection can be improved by optimizing the size of a divergence angle and the sizes of the small holes. The detector can be used for directly detecting fluorescent substances in a capillary tube running system, and can be used for detecting non-fluorescent substances when combined with a fluorescence indicator.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-fluorescence channel detection system for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR
ActiveCN105675574AReduce in quantityNo need to forkFluorescence/phosphorescencePhotoelectric conversionFluorescent light
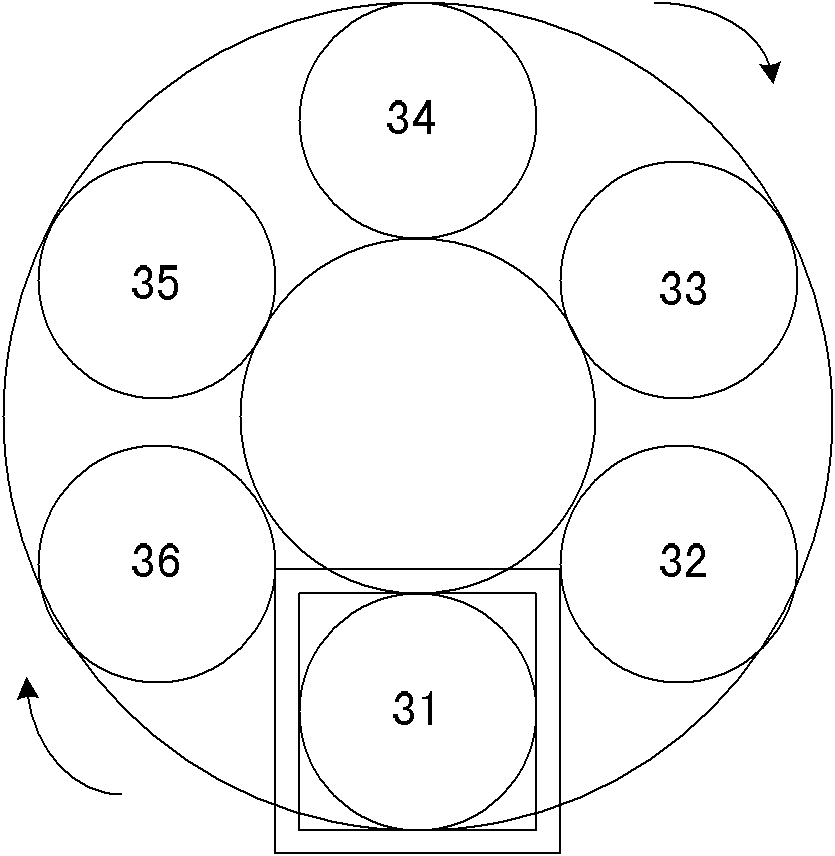
The invention discloses a multi-fluorescence channel detection system for a real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR. The multi-fluorescence channel detection system comprises fluorescence detection units, an optical fiber disc and a turntable, wherein each fluorescence detection unit comprises a light source, an excitation light filter, a dichroscope, optical fiber coupling lenses, optical fibers, a detection light filter and a photoelectric sensor, the dichroscopes enable existing excitation units and detection units to be combined to form a whole, the light emitted by the light source is sequentially subjected to filtration of the excitation light filters and coupling of the optical fiber coupling lenses and finally is emitted into a test tube through the optical fibers to excite the fluorescent substances of samples in the test tubes so as to produce fluorescent light, a part of the fluorescent light returns to the optical fiber coupling lenses through the optical fibers sequentially to be collimated, the detection light filters filter out pure fluorescent light, and the fluorescent light is finally emitted to the photoelectric sensors to perform photoelectric conversion. Multiple optical fibers are inserted into the optical fiber disc, multiple fluorescence detection units are distributed on the turntable, and fluorescence signals of multiple fluorescence channels at multiple test tube hole positions can be sequentially detected through the turntable rotating around the circle center of the optical fiber disc for one circle.
Owner:XIAN TIANLONG SCI & TECH
Compact optical detection system
InactiveCN101542273AHeating or cooling apparatusChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceBeam splitterLight reflection
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Fluorescence detector, filter device and related methods
ActiveUS8137626B2Small sizeSemi-permeable membranesDischarging arrangementTime rangeFluid filtration
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Fluorescence molecule imaging device
ActiveCN102106723AAccurate collectionReduce lossDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCamera lensFluorescence
The invention provides a fluorescence molecule imaging device, comprising an excitation module and an imaging module, wherein the excitation module consists of an exciting light source, an exciting filter wheel, an exciting optical filter and a plurality of beams of optical fibers. The imaging module consists of a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) camera, a lens, a lens adjusting unit, an emitting filter wheel, an emitting optical filter and an imaging cavity. The exciting light source generates exciting light, which passes through the exciting optical filter in the exciting filter wheel, and then the exciting light of some set wave band is irradiated to the detected object evenly via one optical fiber; the detected object is excited to generate the fluorescence signal with wavelength longer than that of the exciting light; the signal passes through the emitting optical filter of the emitting filter wheel set in front of the lens, then the specific emitting fluorescence signal is received by the CCD camera, converted into an image signal and displayed in a computer. The fluorescence molecule imaging device is simple in design and structure, convenient in operation, low in cost, and is widely applied to the fields such as medical image and the like.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-damage micrometering system for observating biological sample with fluorescent
InactiveCN101363839AKeep atraumaticNo damageMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMicro imagingEyepiece
In order to overcome the shortcomings of the optical imaging system of available non-destructive micro-measuring system on the inability to observe the fluorescence emitted from a biological sample, The invention modifies the optical imaging system based on the available non-destructive micro-measuring system so that the non-destructive micro-measuring system can observe the fluorescence emitted by the biological sample while measuring the ion / molecule flowing direction on the surface of a biomaterial to implement the screening and the state monitoring of the biomaterial to be measured. The invention belongs to the electrochemical technical field, and comprises an ion / molecule activity detection system, a micro-imaging system and a computer data processing system. The micro-imaging system includes a bright field illuminator, a stage, an objective converter, a light path switcher, an eyepiece and a digital camera, and is characterized in that an optical filter turntable converter for a fluorescence microscopic observation mode is disposed on the light path between the objective and the light path switcher, and includes an excitation optical filter, a fluorescent dichroic mirror and a blocking filter.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Compact optical detection system
InactiveUS20100227386A1Improve scalabilityMiniaturizationOptical radiation measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBeam splitterFluorophore
A detection system is provided, the detection system comprising a light source that generates excitation light having a wavelength sufficient to excite a fluorophore in a sample; an excitation filter positioned along a first line along a path of the excitation light, the excitation filter transmitting the excitation light from the light source; a beam splitter positioned along the first line, the beam splitter reflecting the excitation light transmitted by the excitation filter along a second line toward a mirror positioned on one side of the beam splitter, and passing emitted light reflected along the second line; the mirror, positioned to reflect the excitation light from the beam splitter to the fluorophore in the sample along a third line, normal to both the first and second lines, wherein the mirror further reflects emitted light emitted along the third line, along the second line toward the beam splitter; an emission filter positioned along the second line, on a second side of the beam splitter; and a detector that detects the emitted light transmitted by the emission filter.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection system
InactiveCN103091298AOvercome the effects of decay and degradationShorten the total inspection timeFluorescence/phosphorescenceMulti bandPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention relates to PCR detection, and concretely relates to a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection system. The real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection system has a simple structure, is simple to operate and can simultaneously realize the fluorescent detection imaging of all samples. The real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR detection system comprises a light source, a multi-band-pass excitation optical filter, a multi-band-pass dichroscope, a lens assembly, a heat cycle system, a multi-band-pass fluorescent optical filter, a color plane array detector and an information analysis processing unit; the light source and the excitation optical filter are arranged on the horizontal axis of the dichroscope having an angle of 45DEG with a horizontal direction, and light emitted by the light source passes through the excitation optical filter reaches the dichroscope; and the lens assembly, the fluorescent optical filter and the color plane array detector are arranged on the vertical axis of the dichroscope having an angle of 45DEG with the horizontal direction from bottom to top, and the color plane array detector is connected with the information analysis processing unit.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Biodiagnosis Apparatus
InactiveUS20090234234A1Good enough color contrastSolve lack of contrastMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionImage transferFluorescence
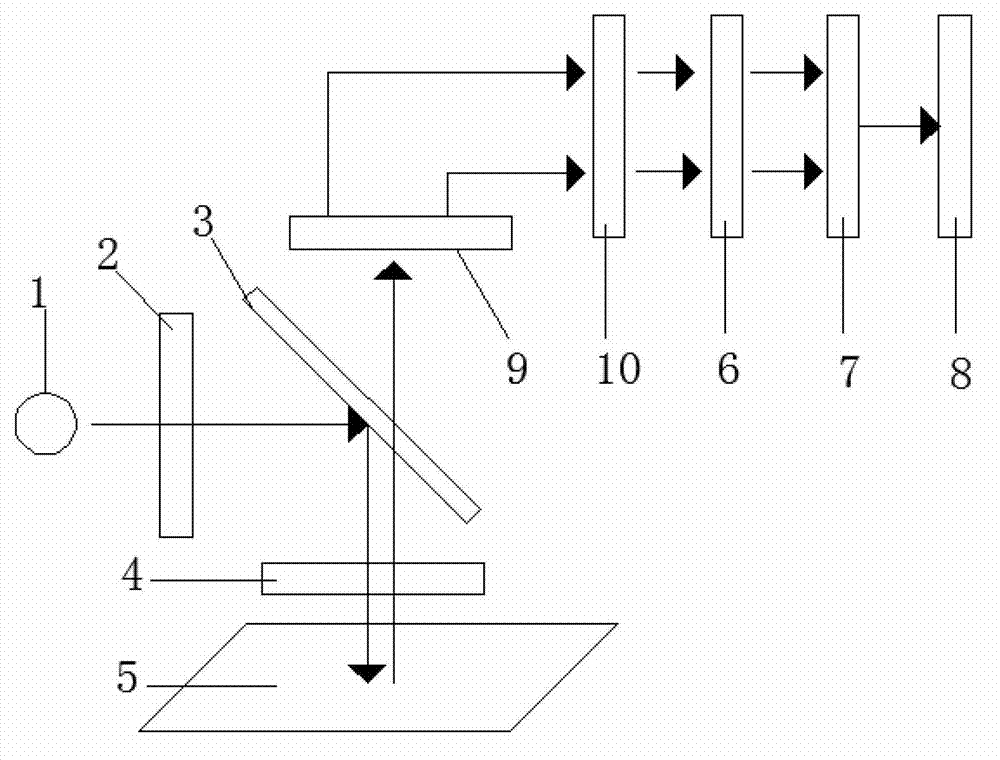
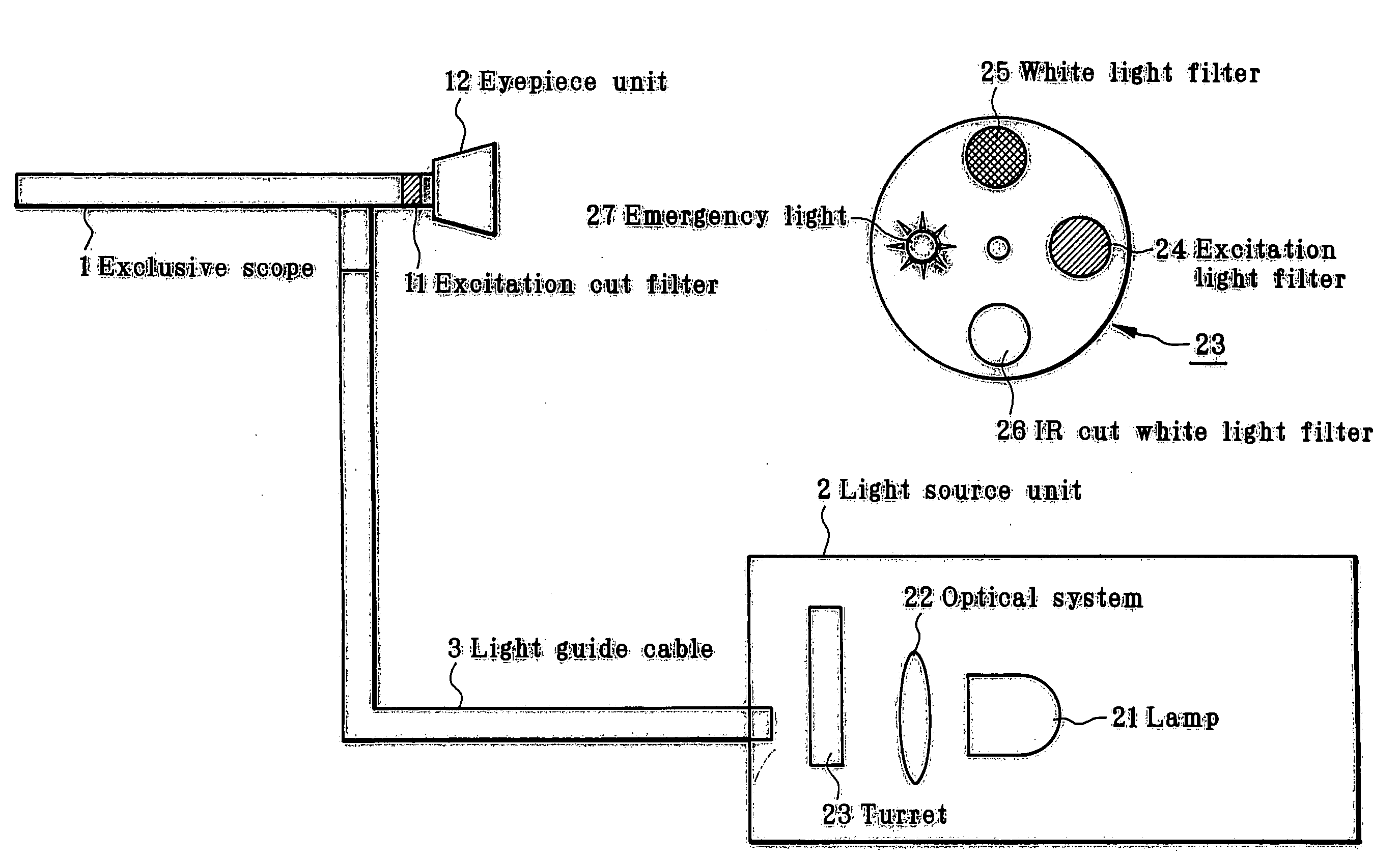
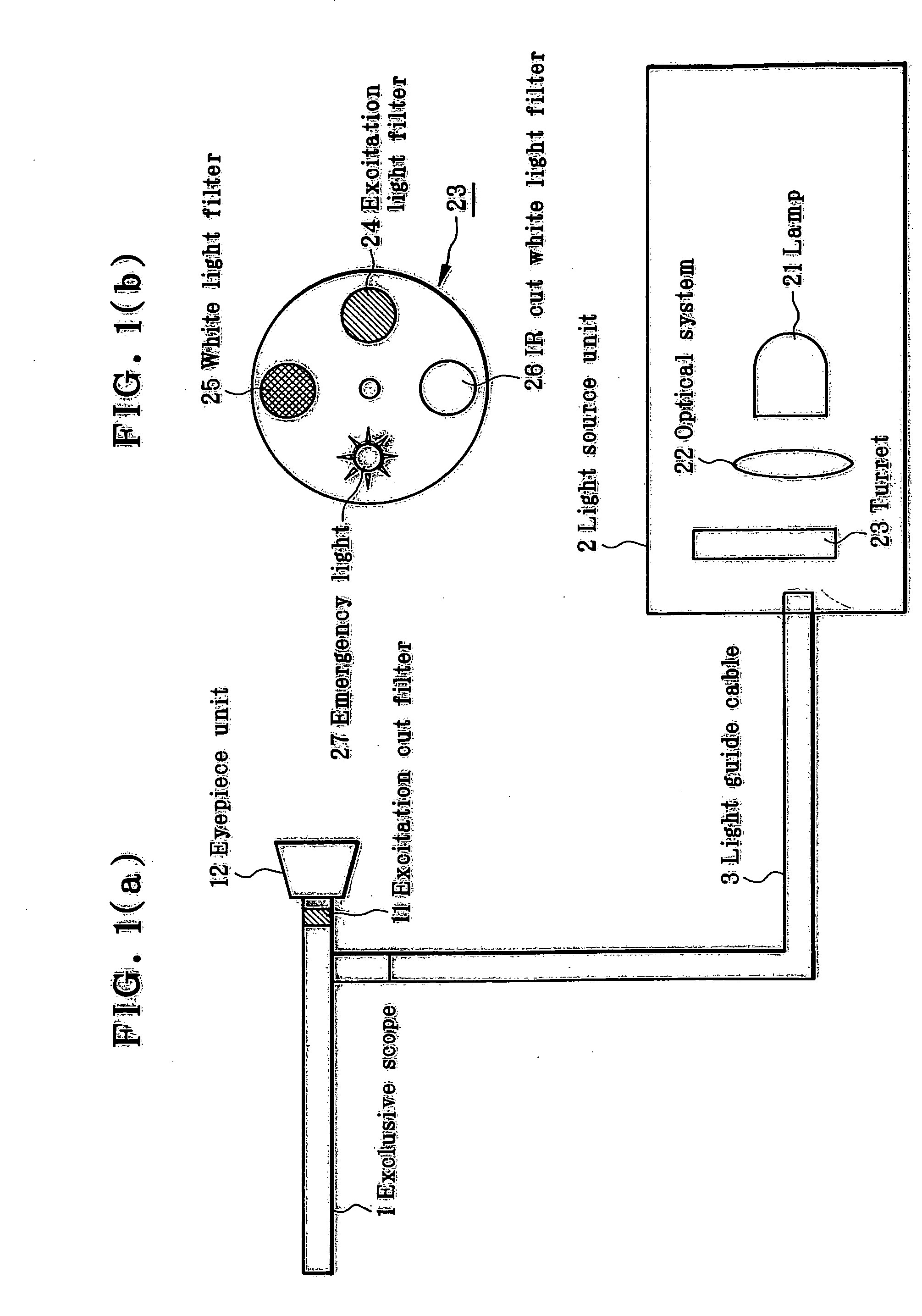
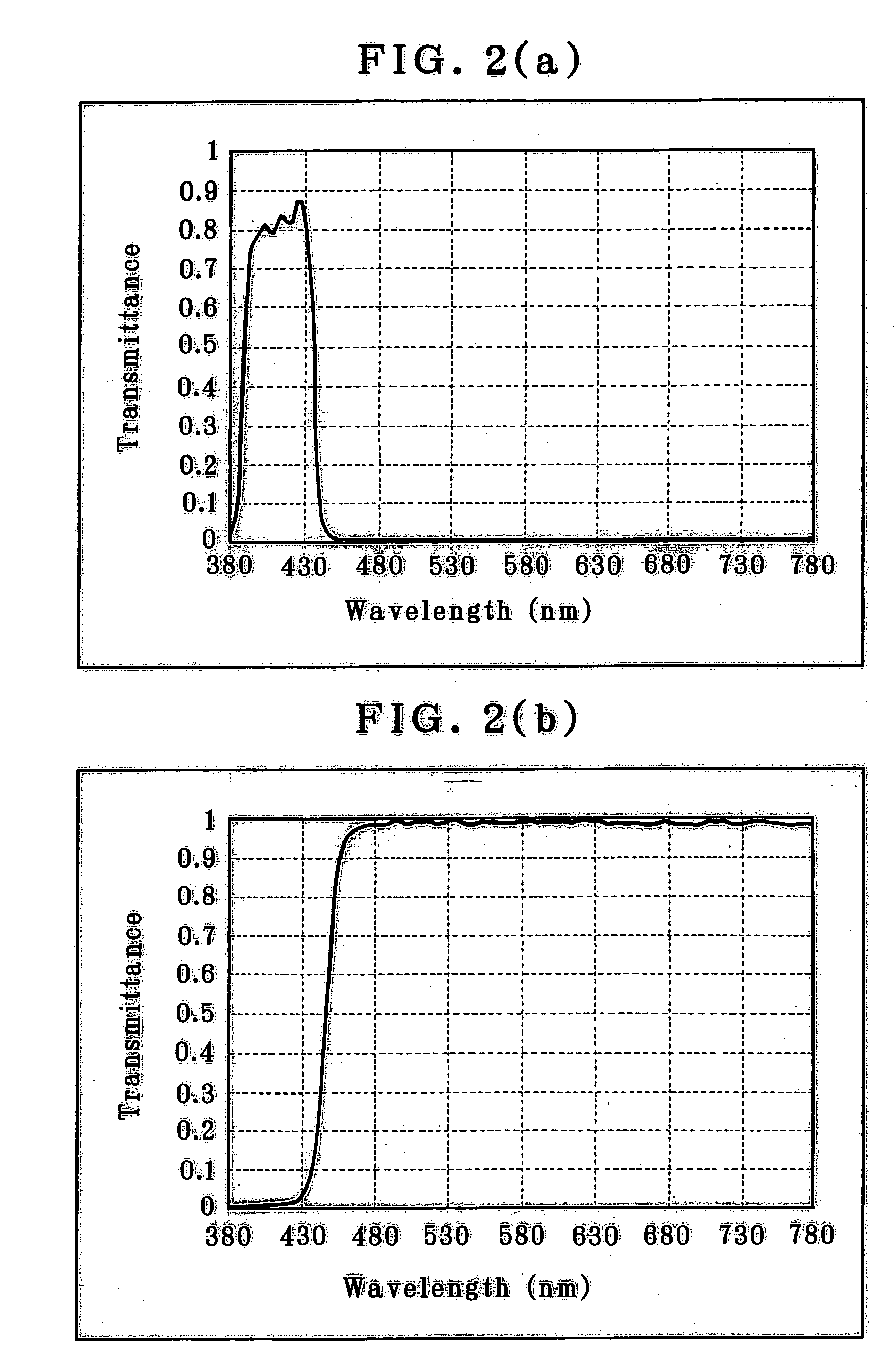
The invention provides a biodiagnosis apparatus capable of observing a reflection image of a site other than a fluorescent site through excitation light taken in an observation system so that fluorescence observation can be implemented in good enough color contrast. The apparatus a light source (21), a light source optical system (22), a light transfer system (3) for guiding illumination light from the light source (21) to the living body, an excitation light filter (24) interposed between the light source (21) and the light transfer system (3), an image transfer system for guiding light from the living body to an image plane, and an excitation cut filter (11) located in said image transfer system. The spectral characteristics of illumination light transmitting through the excitation filter (24) and the transmittance characteristics of the excitation cut filter (11) have an overlapping portion. Upon observation of a subject under the biodiagnosis apparatus, the spectral characteristics of a site of the image plane other than a fluorescent site satisfy the following condition:0.005≦I(λp+Δ) / I(λp)≦0.5provided that 40≦Δ≦80 nm, where λp is the wavelength (nm) at which the spectral intensity reaches a maximum, and I(λp) is indicative of the then spectral intensity.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Optical apparatus
InactiveUS20050231799A1Minimize autofluorescenceIncrease contrastPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersEyepieceOptical axis
An optical apparatus minimizes autofluorescence and stray light as well as leakage of excitation light and efficiently utilizes illuminating light from a fluorescence illumination optical system to allow observation of a bright fluorescence image. An observation apparatus has an objective, an observation optical system unit including a variable magnification optical system, and an imaging optical system unit including an imaging lens and an eyepiece. A fluorescence illumination apparatus, which is provided separately, is removably attached to the observation apparatus. The fluorescence illumination apparatus has a light source, a collector lens unit, and a reflecting member placed between the objective and the observation optical system unit at a position displaced from the optical axis of the objective to make light from the light source incident on the objective. An excitation filter is provided between the light source and the reflecting member. An optical member for selectively transmitting fluorescent light emitted from a sample is placed between the objective and the observation optical system unit.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Throwing-into type fluorescence method water quality on-line analyzer
InactiveCN102253018AOvercome volumeOvercoming energy consumptionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceUltraviolet lights
The invention relates to a throwing-into type fluorescence method water quality on-line analyzer, and belongs to the technical field of water quality monitoring device. The analyzer is used for water body in situ detection. A technical scheme of the analyzer is characterized in that: the analyzer comprises a sealed metal housing and a detection section; the metal housing comprises two chambers; the detection section is arranged in one chamber; the housing wall of the other chamber is provided with a plurality of drain holes to communicate with the outside environment; two light-through holes are arranged on the wall between the two chambers; the light-through holes are provided with sealed quartz lenses; axial lines of the two light-through holes intersect and form a angle of 90 DEG; ultraviolet light source of the detection section, a lens and an excitation filter are arranged on the axial line of the one light-through hole, an emission filter is arranged on the axial line of the other light-through hole; the emission filter is connected with a photoelectric detector; a signal treatment and control unit is respectively connected with the ultraviolet light source and the photoelectric detector. The analyzer provided by the present invention has characteristics of small volume, light weight, simple and reasonable structure, easy use, rapid and exact detection and waterproof design, and can be thrown into the water to perform the in situ detection for the water body.
Owner:HEBEI SAILHERO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION HIGH TECH
Laser microdissection unit
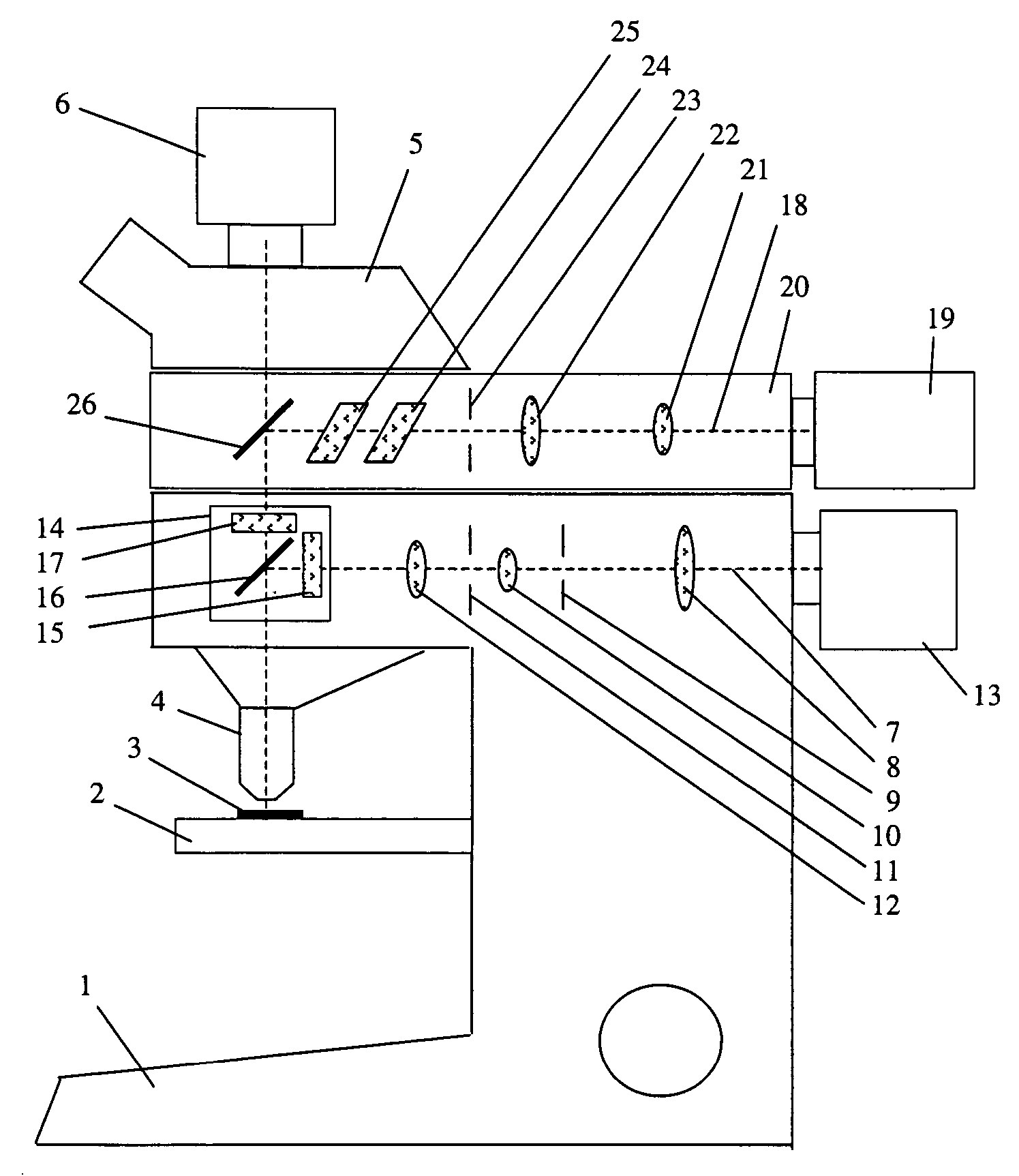
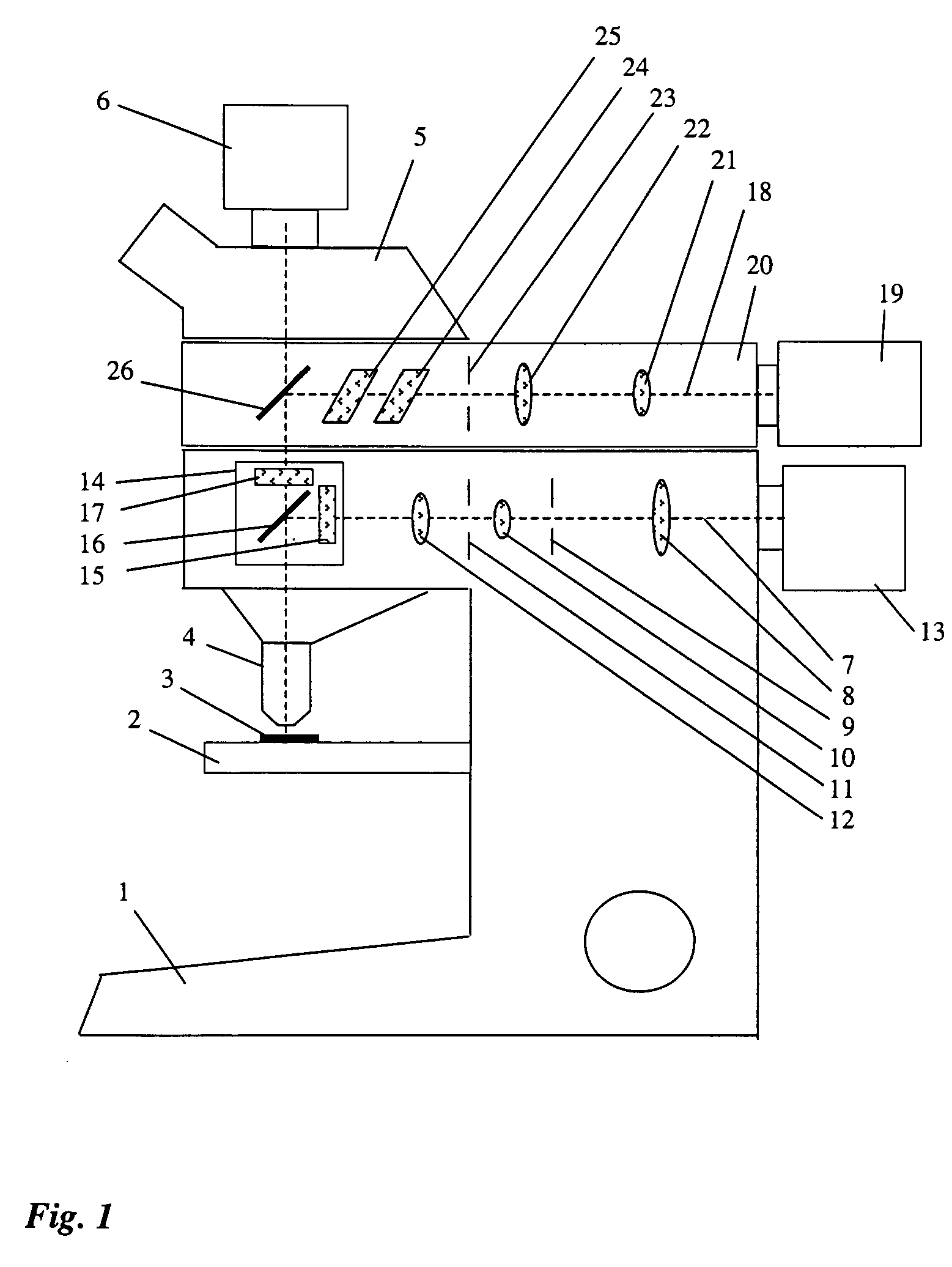
A laser microdissection unit for cutting a microscopic sample using a laser beam of a laser includes a microscope and a fluorescence device. The microscope includes an illumination beam path directed onto the sample, and an imaging beam path configured to image the sample. The fluorescence device includes an excitation filter, a dichroic beam splitter, and a blocking filter. The dichroic beam splitter and the blocking filter are spectrally transparent to the laser beam, and the laser beam is directable through the dichroic beam splitter and the blocking filter onto the sample.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Multi-channel fluorescent light filter cubic box and fluorescence microscopy imaging system
InactiveCN102621119AEasy to storeHigh resolutionOptical filtersTransmissivity measurementsMicro imagingBeam splitter
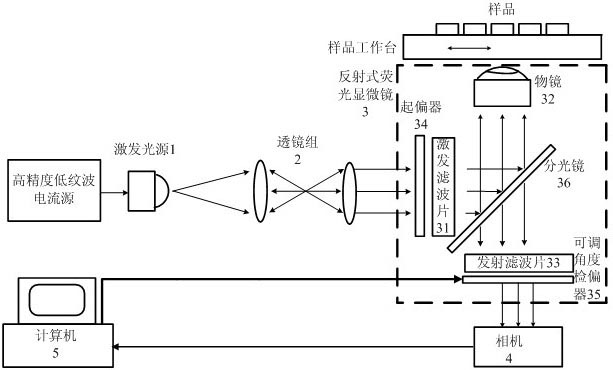
The invention discloses a multi-channel fluorescent light filter cubic box. The multi-channel fluorescent light filter cubic box comprises an excitation light filter pack, a transmission light filter pack and a dichroscope or a spectroscope, wherein the excitation light filter pack and the transmission light filter pack are respectively fixed on two adjacent vertical planes on the cubic box, the dichroscope or the spectroscope is positioned at a 45-degree included angle surface between the excitation light filter pack and the transmission light filter pack, and the surface on the cubic box, opposite to the transmission light filter pack, is provided with holes. The invention has the key points that the excitation light filter pack is formed by embedding at least two excitation light filters on one bottom liner equidistantly, and two ends of the bottom liner are fixedly arranged on a turning wheel; and the transmission light filter pack is formed by embedding at least two transmission light filters on the other bottom liner equidistantly, and the two ends of the bottom liner are fixedly arranged on a turning wheel. According to the multi-channel fluorescent light filter cubic box disclosed by the invention, the storage of a large amount of filters can be easily realized in a smaller volume, and more than 10 types of fluorophores can be observed; and a fluorescence imaging device employing the multi-channel fluorescent light filter cubic box can perform high-resolution imaging on both the space and the spectrum.
Owner:孔令华
Laser fluorescence correlation spectrum unimolecular analyzer
InactiveCN1605856AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceData acquisitionBasic research
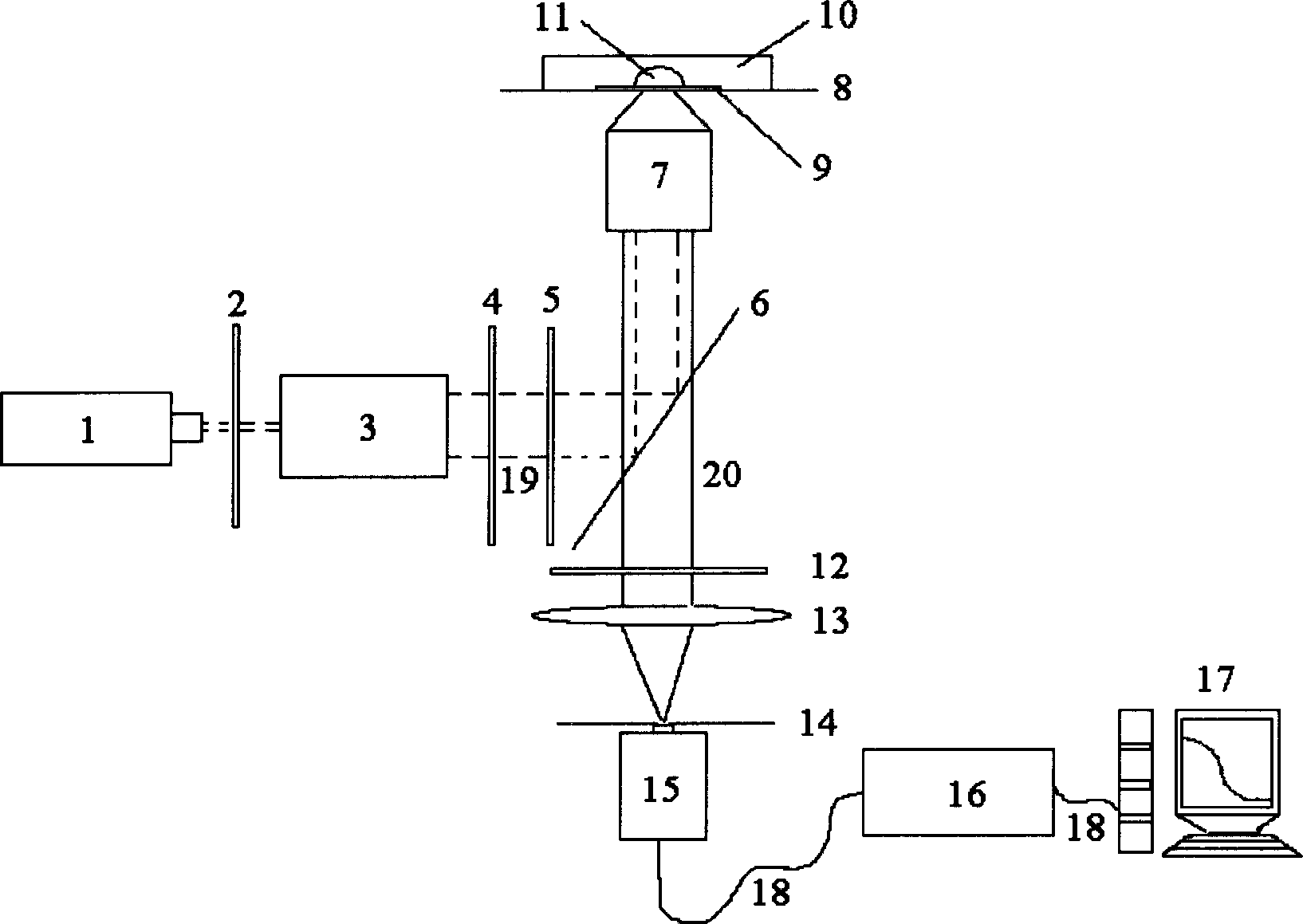
The laser fluorescent correlating spectrum single molecular analyzer is used in the research of single molecule inside solution in life science, chemistry, physics and other fields. The sample solution is set on cover glass or sample pond; the laser beam, after being beam expanded, filtered in exciting filter, reflected in the dichromatic mirror and focused in the objective of microscope, irradiates the sample solution to excite the molecule under research; the fluorescence the sample solution emits is made to pass through the same objective, the dichromatic mirror, emitting filter to eliminate hybrid light, lens to focus and pinhole coupled to reach the single photon detector; and the signal the single photon detector generates is acquired with the data acquisition card and processed in the computer. The present invention has the features of simple operation, high stability, less light loss, high sensitivity, etc. and may be used in various basic researches.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Wide-field super-resolution microscopic imaging method and system thereof
ActiveCN110954521AMotivating realizationAvoid damageMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicro imagingBeam splitter
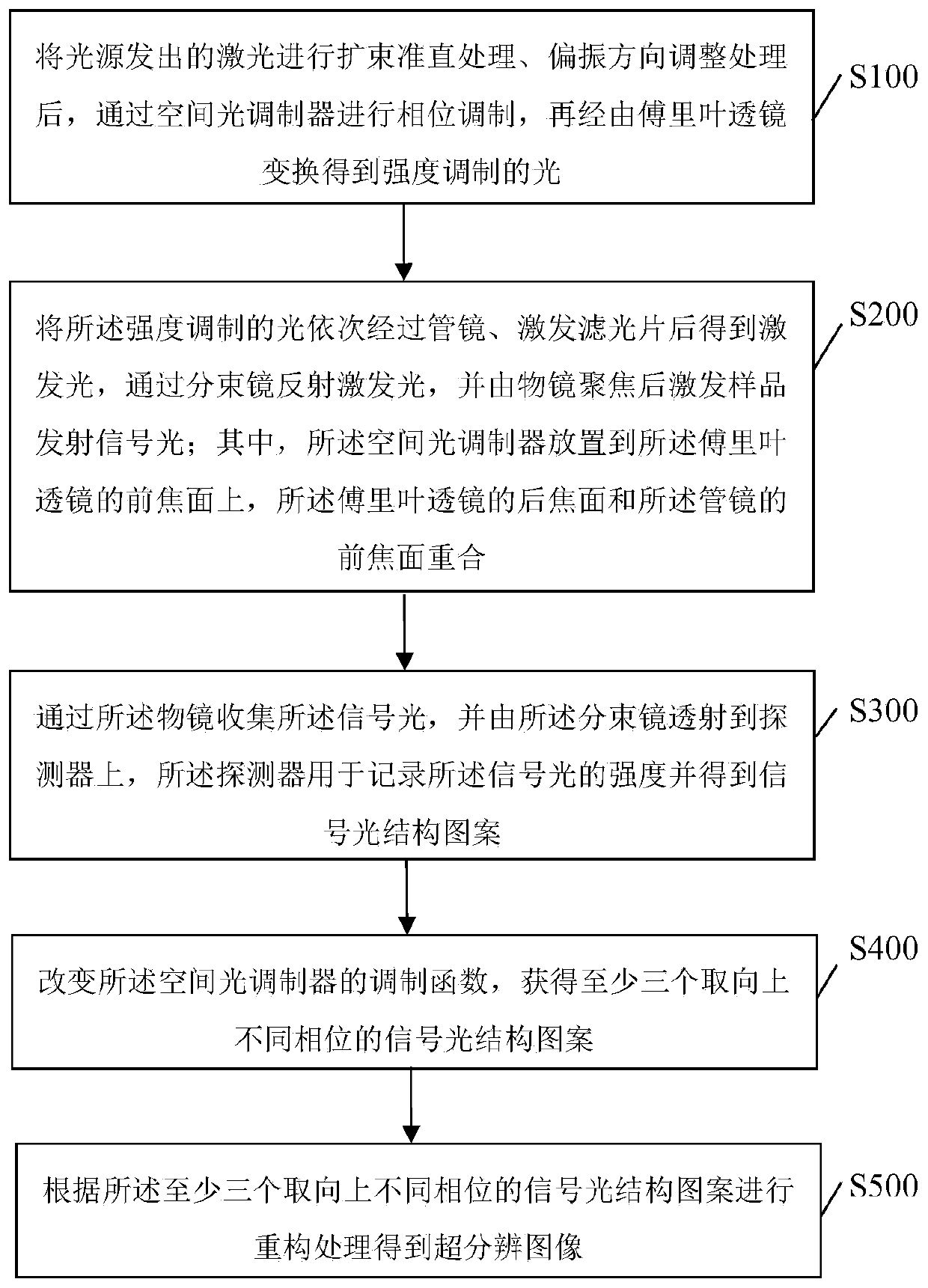
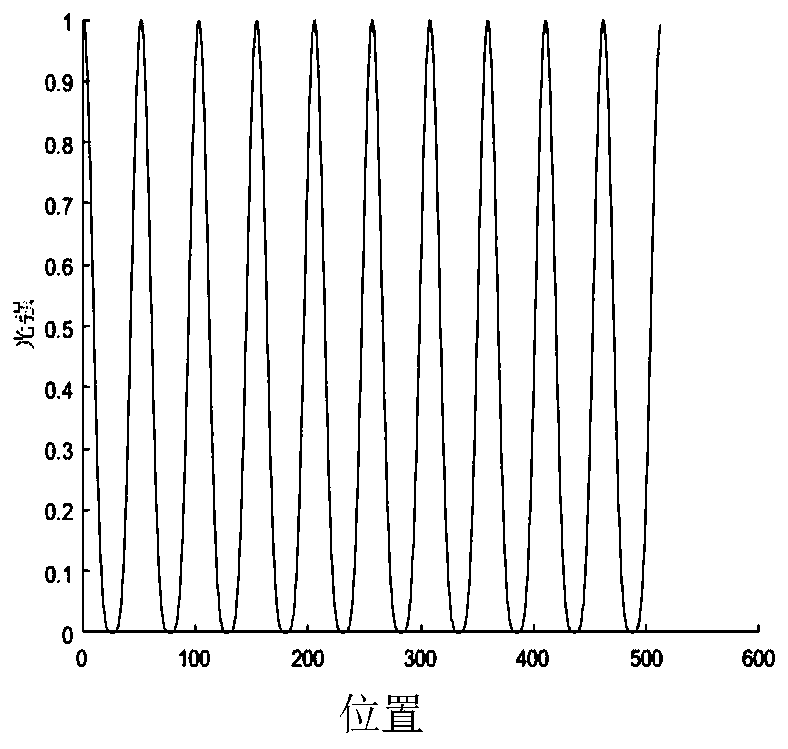
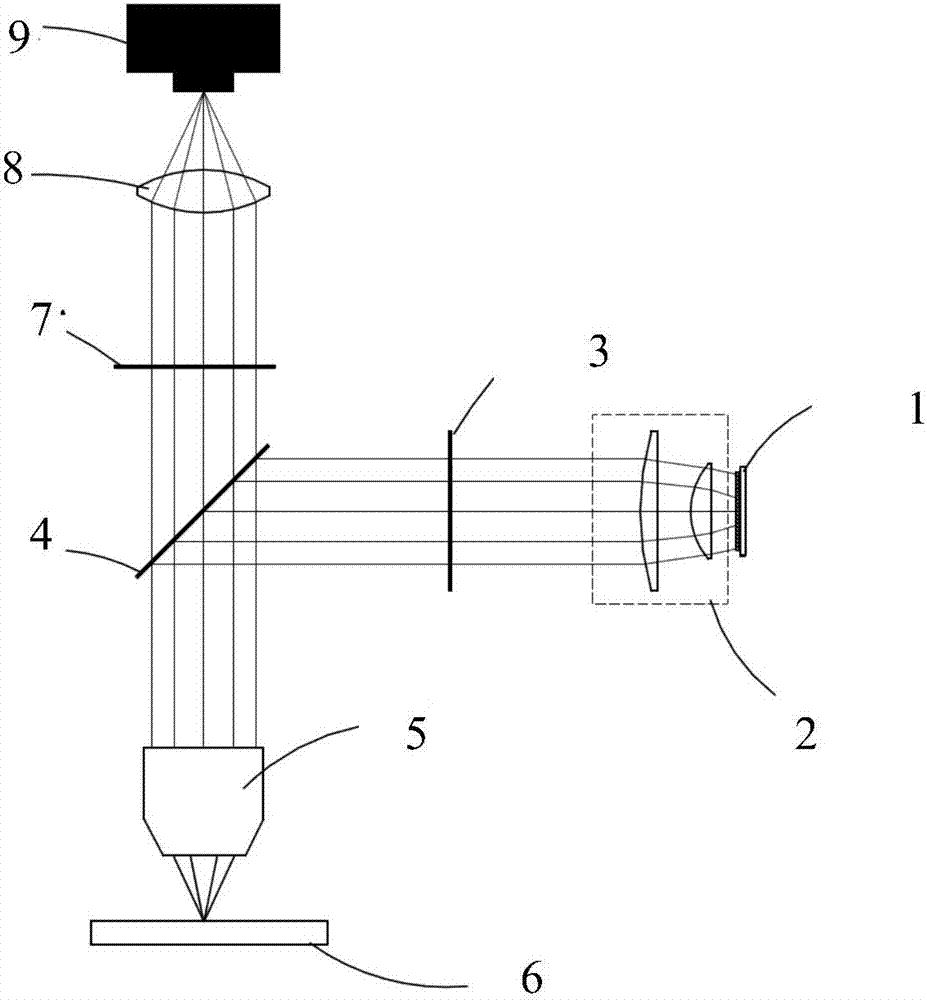
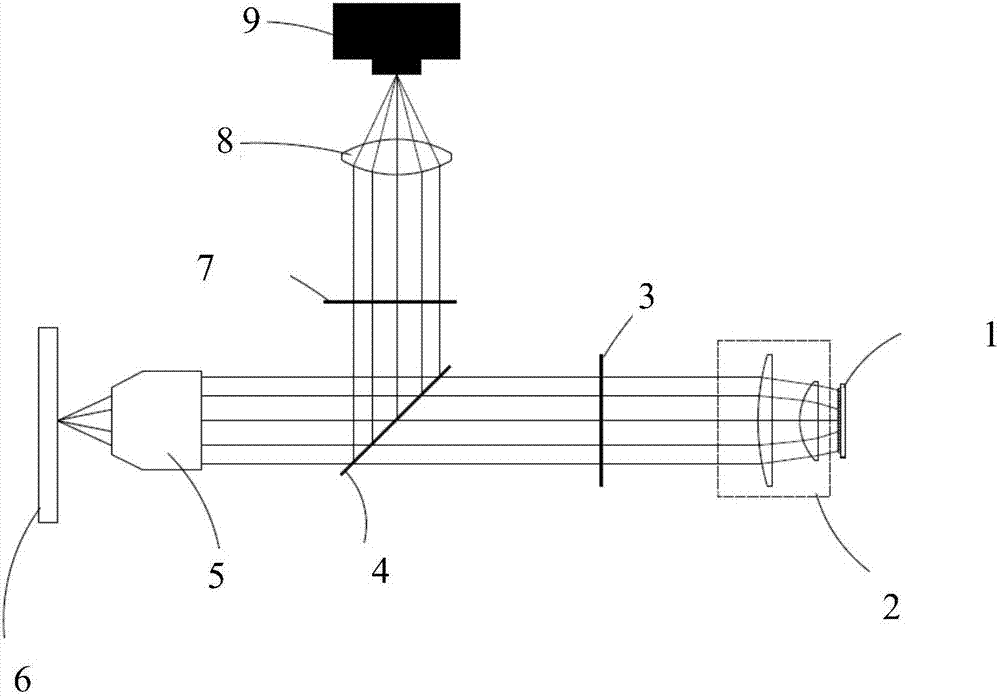
The invention discloses a wide-field super-resolution microscopic imaging method and system. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the phase modulation of laser emitted by a light source through a spatial light modulator, and obtaining intensity-modulated light through a Fourier lens; enabling the intensity-modulated light to sequentially pass through a tube mirror, an excitation light filter, a beam splitter and an objective lens, and then exciting a sample to emit signal light; collecting the signal light through the objective lens, and transmitting the signal light to a detector through the beam splitter; and performing reconstruction processing according to the signal light structure patterns of different phases in at least three orientations to obtain a super-resolution image.The spatial light modulator modulates the laser into an excitation light pattern whose intensity satisfies sinusoidal power distribution and excites a fluorescence pattern so as to generate multistagefrequency spectrum aliasing. And higher-frequency sample information is obtained by demodulating and resetting the aliasing frequency spectrum. Under an unsaturated excitation condition, super-resolution structured light illumination obvious micro-imaging is realized, and the spatial resolution is determined by the harmonic order of stripe structured light.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Structured light illumination microscopic imaging system
The objective of the invention is to provide a structured light illumination microscopic imaging system. According to the invention, a light beam shaping lens, an excitation filtering sheet and a dichroscope are successively arranged on an emission light path of a structured-light light source; an objective lens and a sample are arranged on a first optical path of the dichroscope successively; and an emission filtering sheet, a cylinder mirror and a detector are successively arranged on a second optical path of the dichroscope. Compared with a structured light illumination microscopic imaging system with a compound eye lens, under the premise of reducing installation and processing precision of the structured light illumination microscopic imaging system, super-resolution microscopic images with quite high signal to noise ratios and contrast degrees can be obtained. Compared with a structured light illumination microscopic imaging system based on a digital micro-lens array or an optical grating, the system cost is greatly reduced and system stability is quite high.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Microscope for observing a sample in the bright field illumination by transmitted light or in fluorescence-contrast epi-illumination
The invention relates to a microscope for observing a sample in bright-field transmitted light contrast procedure or the incident-light fluorescence contrast procedure. The microscope is used for observing an object selectably using the bright-field transmitted light contrast procedure or the incident-light fluorescence contrast procedure. During the bright-field transmitted light contrast procedure, an illumination beam path is directed from a bright-field light source to the object and an imaging beam path is directed from the object through the microscope objective into the microscope tube, wherein a fluorescence unit is composed of a fluorescence excitation light source, an illumination optical system, a filter set having at least one excitation filter and at least one emission filter, as well as a beamsplitter. The fluorescence unit is mounted movably, so that in a first end position of movement, the beamsplitter and the emission filter are out of the imaging beam path of the microscope and in a second end position of movement, the beamsplitter and the emission filter are in the imaging beam path between the microscope objective and the microscope tube.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MIKROLMAGING
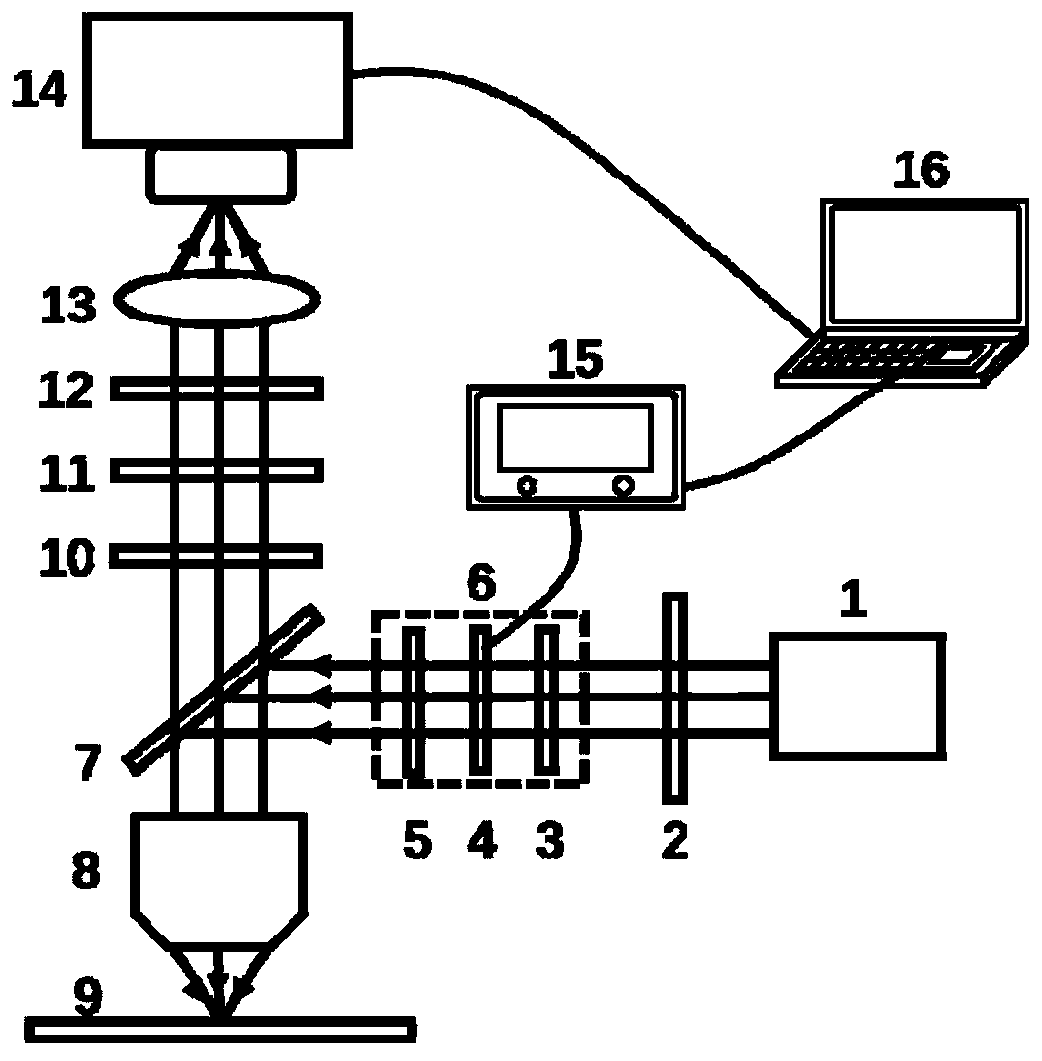
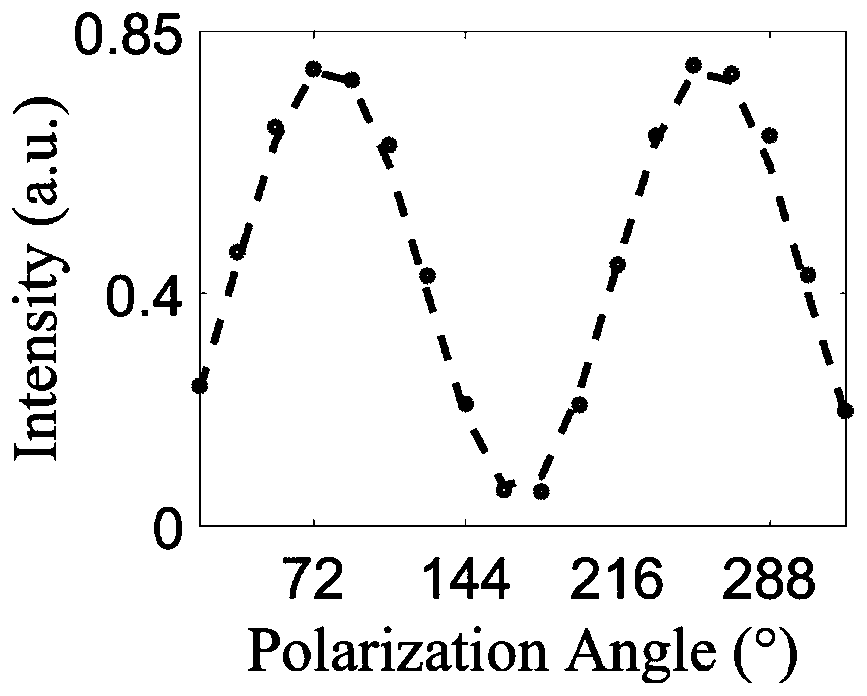
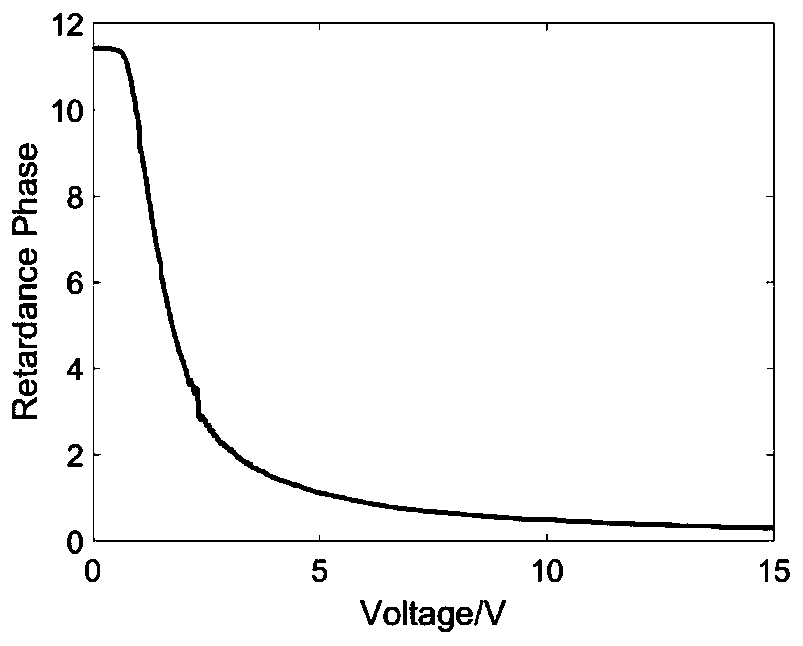
Rapid modulation fluorescence polarization microscopic imaging device and method based on liquid crystal
PendingCN110849849ASimple structureHigh modulation accuracyMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageLiquid crystalline
The invention discloses a rapid modulation fluorescence polarization microscopic imaging device and method based on liquid crystal, and relates to the technical field of optical imaging. The device comprises a light source, an excitation filter, a liquid crystal polarization rotator, a dichroscope, an objective lens, an emission filter, a wave plate, an analyzer, an imaging lens, a camera, a liquid crystal controller and a computer. The method comprises the following steps: converting an emergent light beam of the light source into linearly polarized light through a liquid crystal polarizationrotator; after the linear polarization exciting light enters a sample, exciting the fluorescent light; enabling the fluorescent light to pass through the objective lens, the emission filter, the waveplate and the analyzer and then enter the camera target surface for imaging; in the process, enabling the computer to control the liquid crystal controller to drive the liquid crystal polarization rotator to modulate the polarization angle of the incident exciting light, controlling the camera to acquire a series of fluorescence polarization images, and then performing calculating according to the series of fluorescence polarization images to obtain each fluorescence parameter image. The device has the advantages of high imaging speed, high resolution, wide field of view, high modulation precision and the like, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Portable mineral age determinator
InactiveCN102207461AImprove sealingReduce volumeFluorescence/phosphorescenceControl linePulse shaping
The invention relates to a portable mineral age determinator specifically applied to age determination of geological mineral samples. The age determinator includes a detection machine and a host machine that are connected through a control line. The darkroom comprises a darkroom housing, a top cover of the darkroom, a darkroom base plate, a photomultiplier fixed on the top cover of the darkroom, an optical filter for detection fixed in front of the photomultiplier, an excitation light source installed on the darkroom base plate and controlled by the host machine, an excitation optical filter fixed in front of the excitation light source, and a detachable box type sample wafer holder positioned at the center of the darkroom base plate. The host machine comprises an ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) machine, a liquid crystal screen, a high pressure control module, a high pressure module, a pulse shaping module, a counting module and a light source control module. The darkroom is configured with a double-housing structure, in other words, another housing exists outside the darkroom. And each interface of the detection machine is provided with a sealed structure. The present invention has the advantages of small volume, light weight and portability.
Owner:河北地质大学
Fluorescence detection system
A fluorescence detection system capable of detecting fluorescence with a high sensitivity even if a sample generating fluorescence is small in amount includes a light source emitting excitation light, a probe arranged in opposition to a sample unit, an optical multiplexer / demultiplexer, a detector, a first optical fiber connecting the light source to the optical multiplexer / demultiplexer, a second optical fiber connecting the probe to the optical multiplexer / demultiplexer, and a third optical fiber connecting the detector to the optical multiplexer / demultiplexer. An excitation filter, serving as a short-pass filter, is arranged on the first optical fiber and a detection filter serving as a long-pass filter is arranged on the third optical fiber. The optical multiplexer / demultiplexer includes a multiplexing / demultiplexing filter serving as a long-pass filter.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com