Patents
Literature
180results about How to "Electrical size reduction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
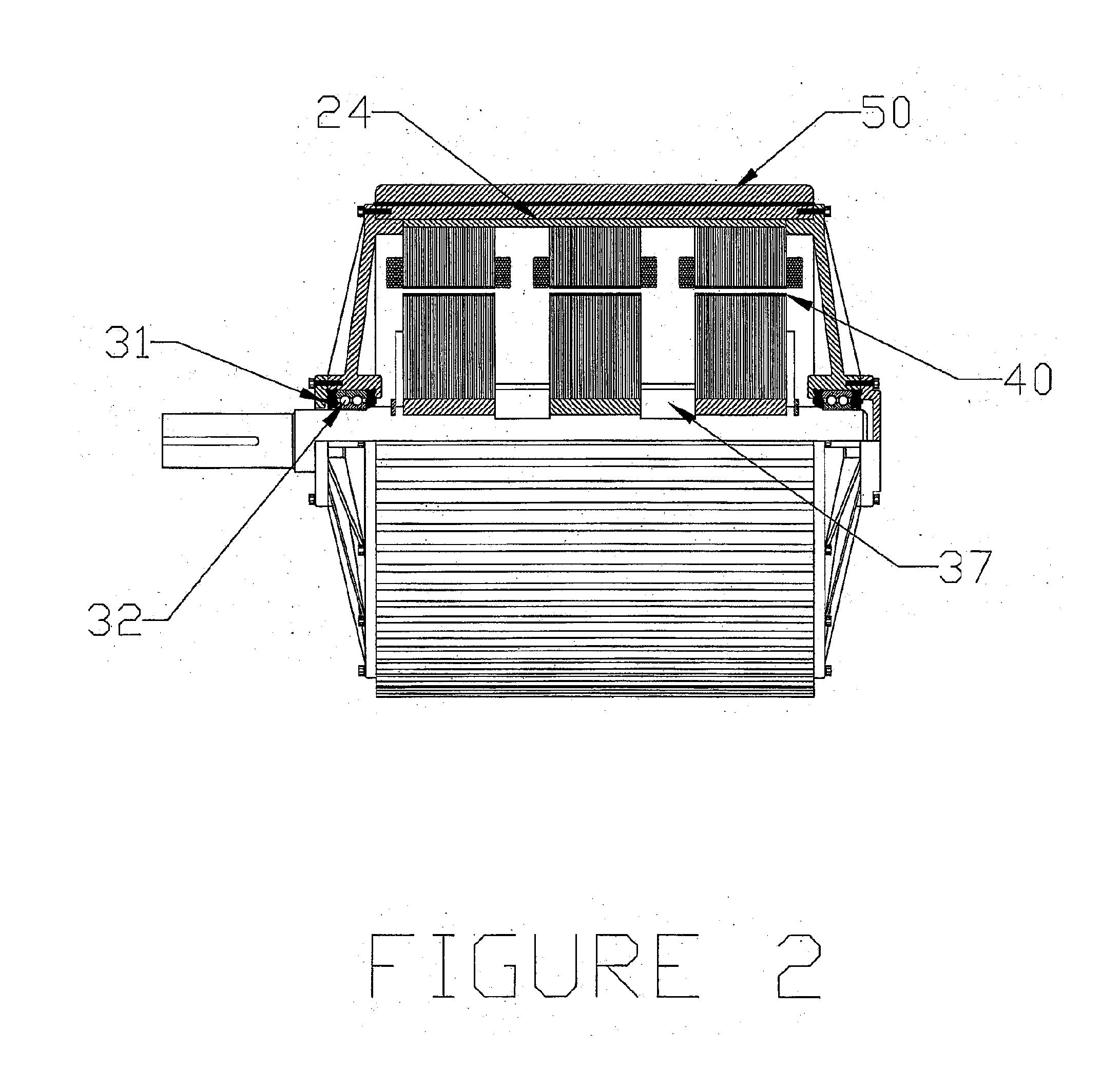
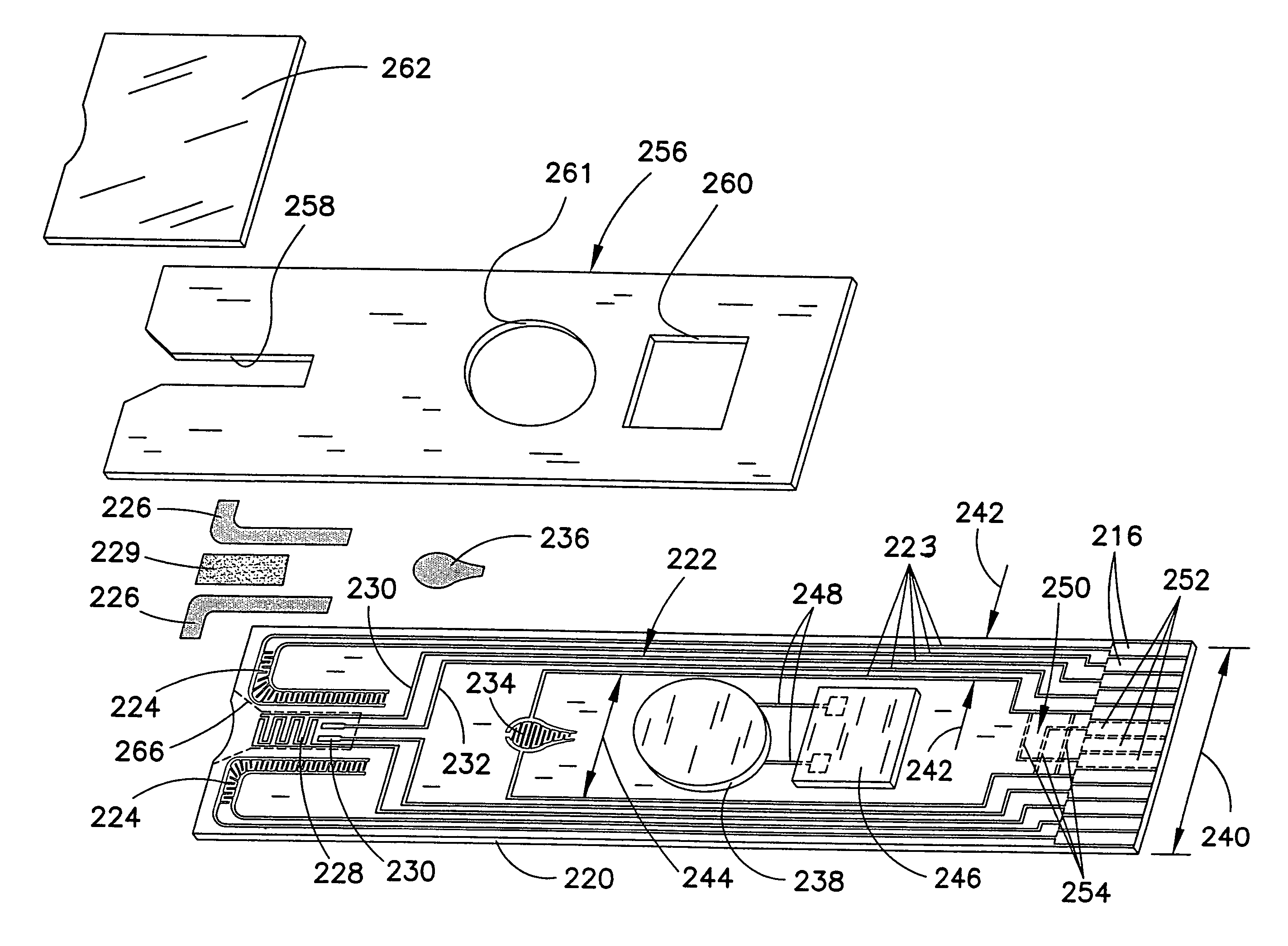
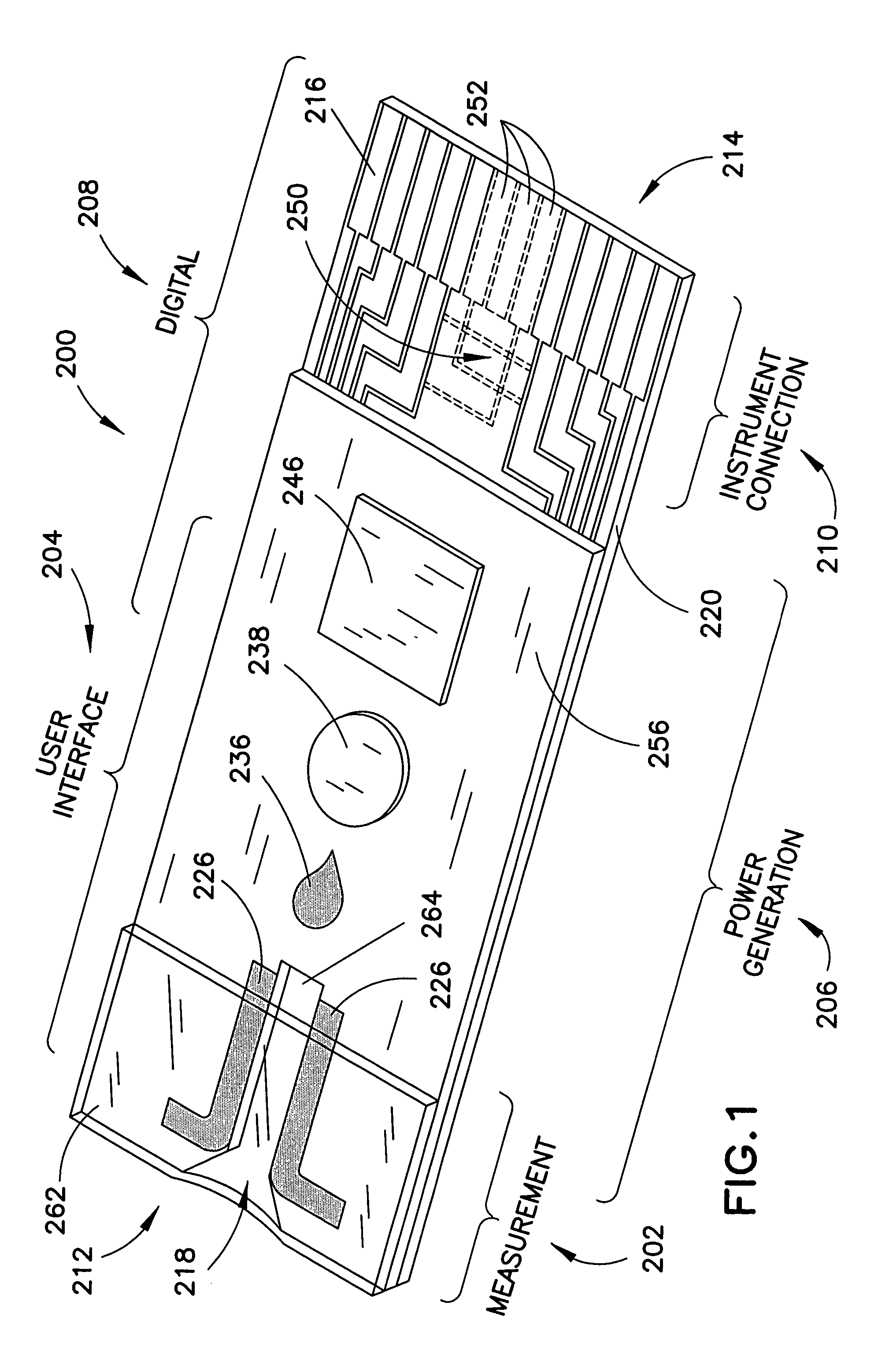
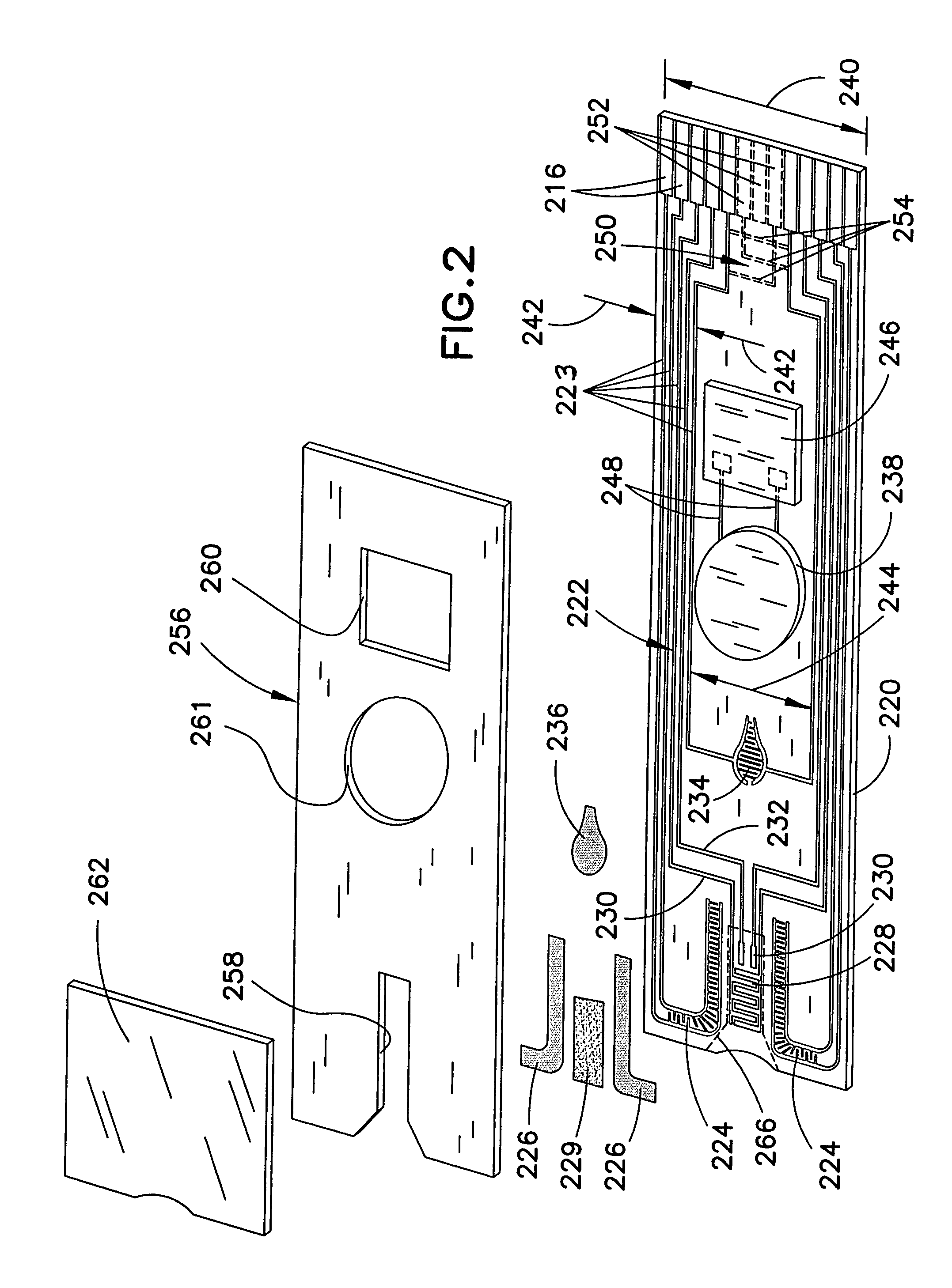
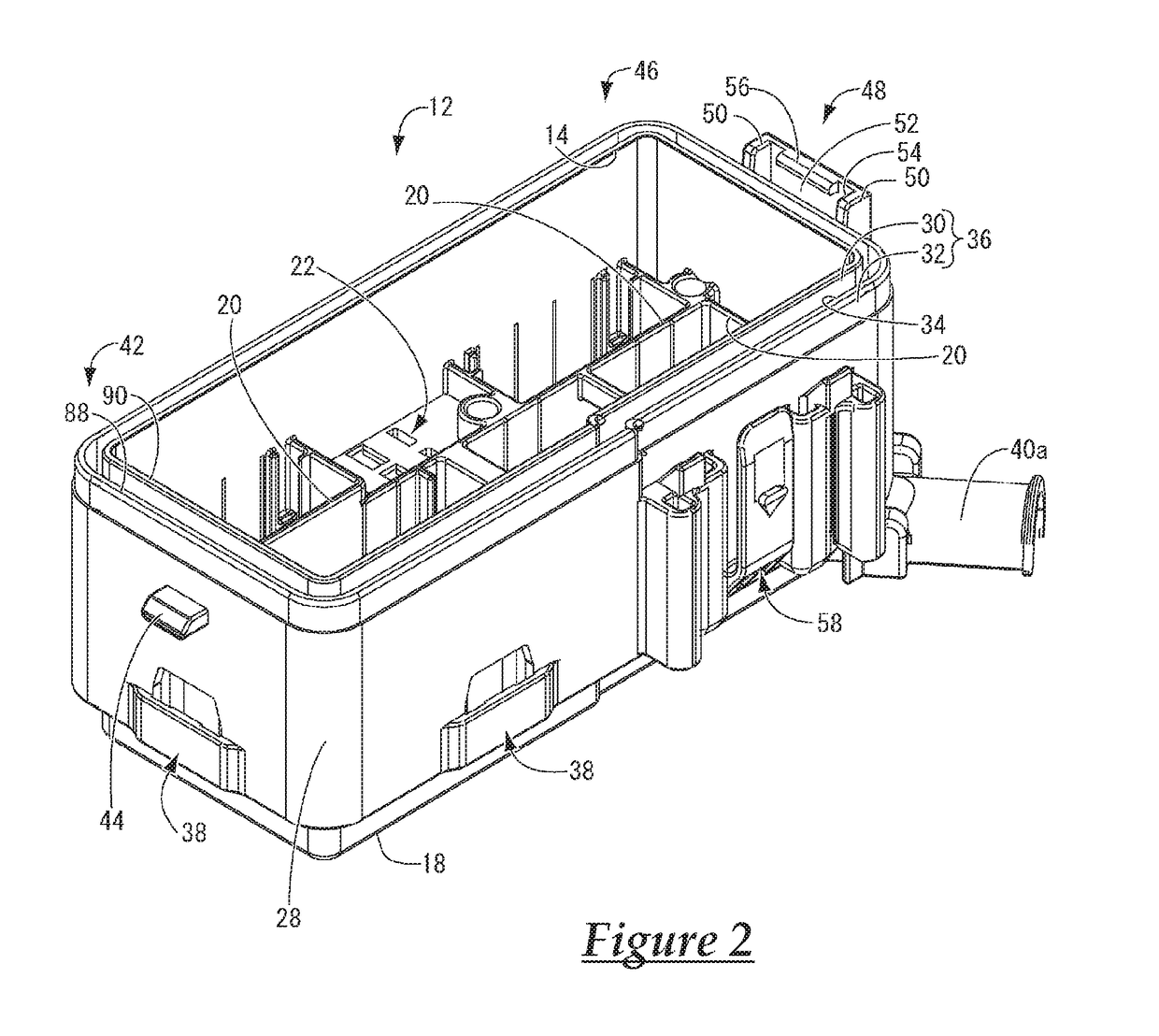
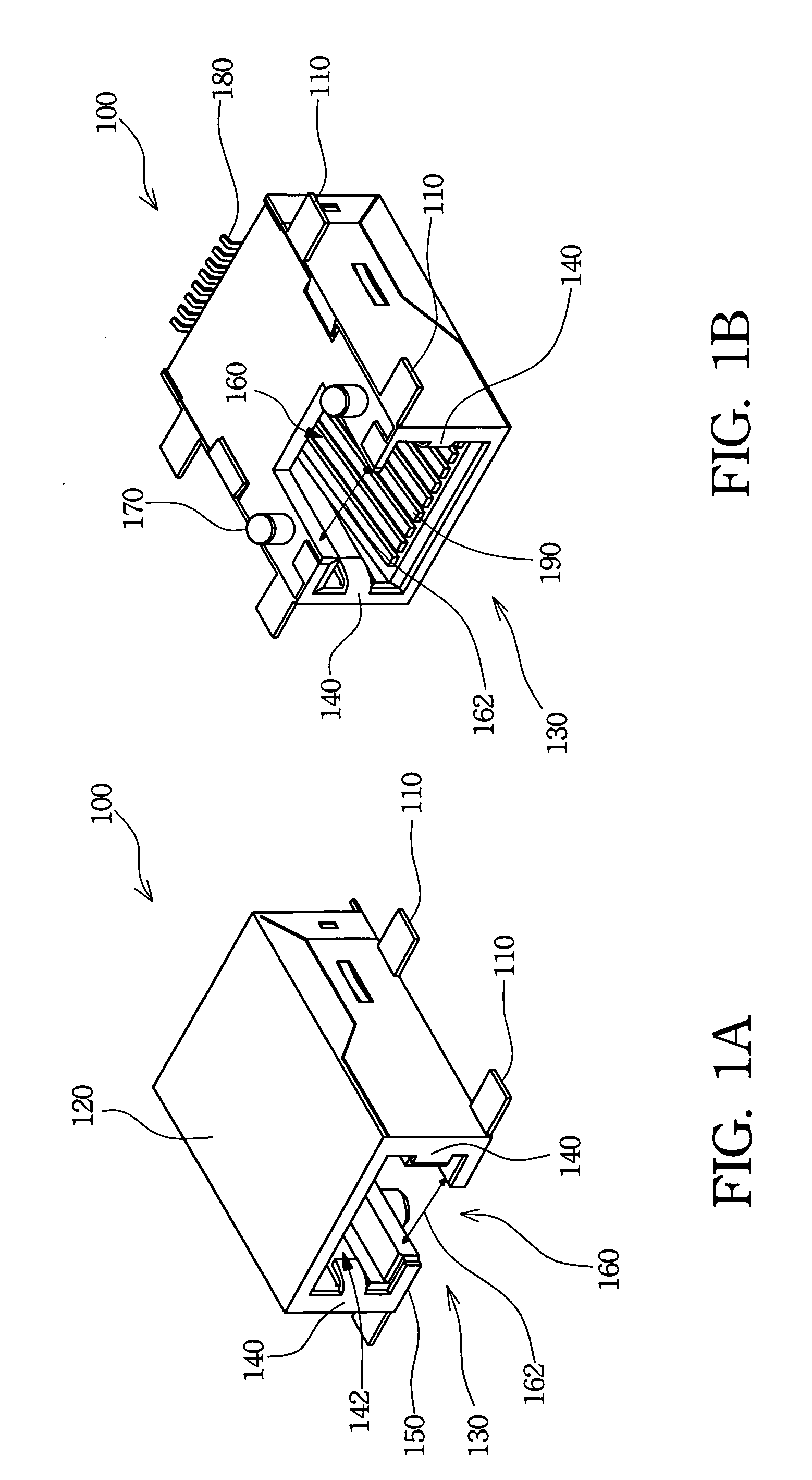
Biosensor with multiple electrical functionalities
InactiveUS20050023137A1Increase in production speedAdditional functionalityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsRelevant costInstrumentation
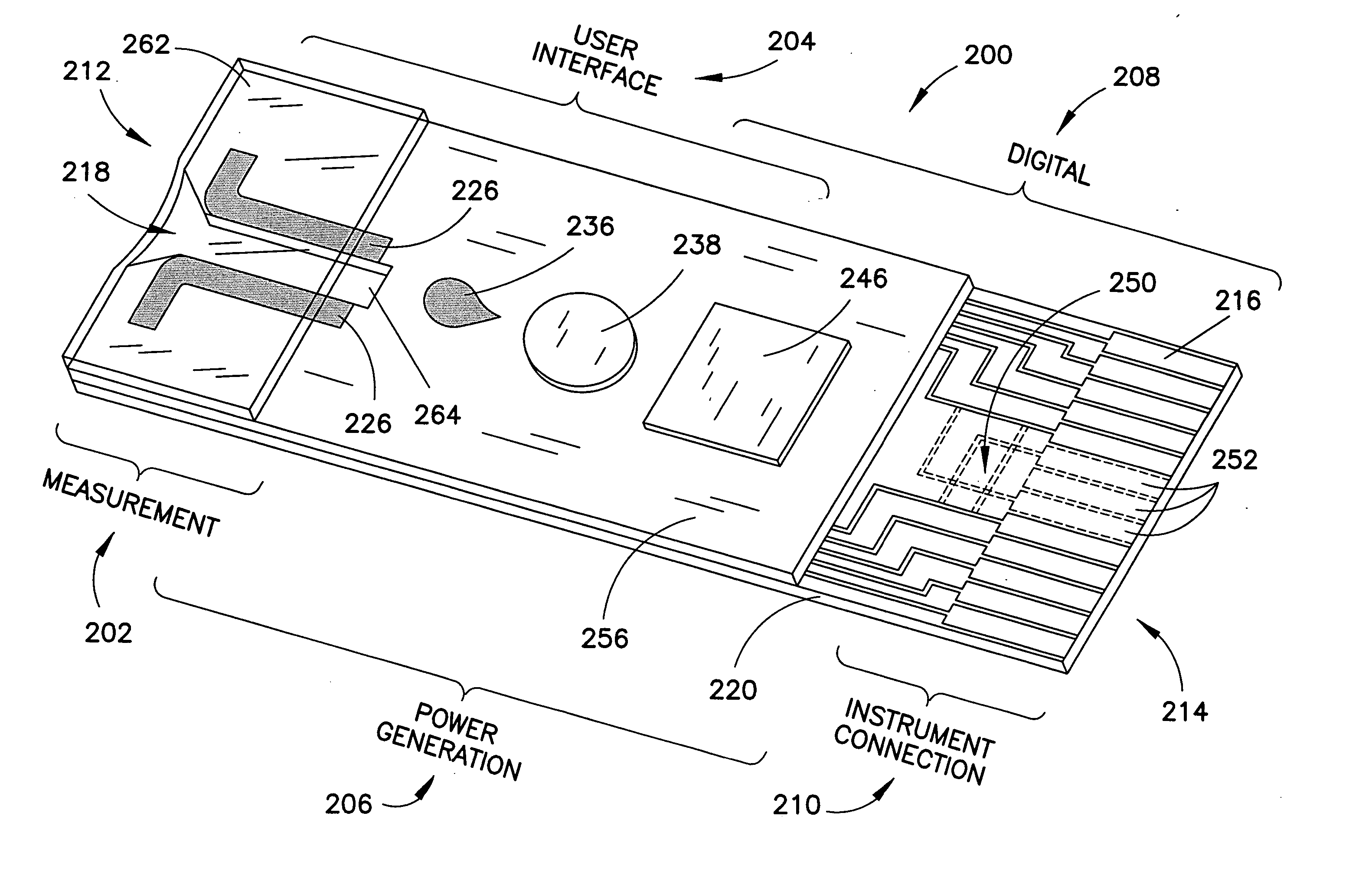
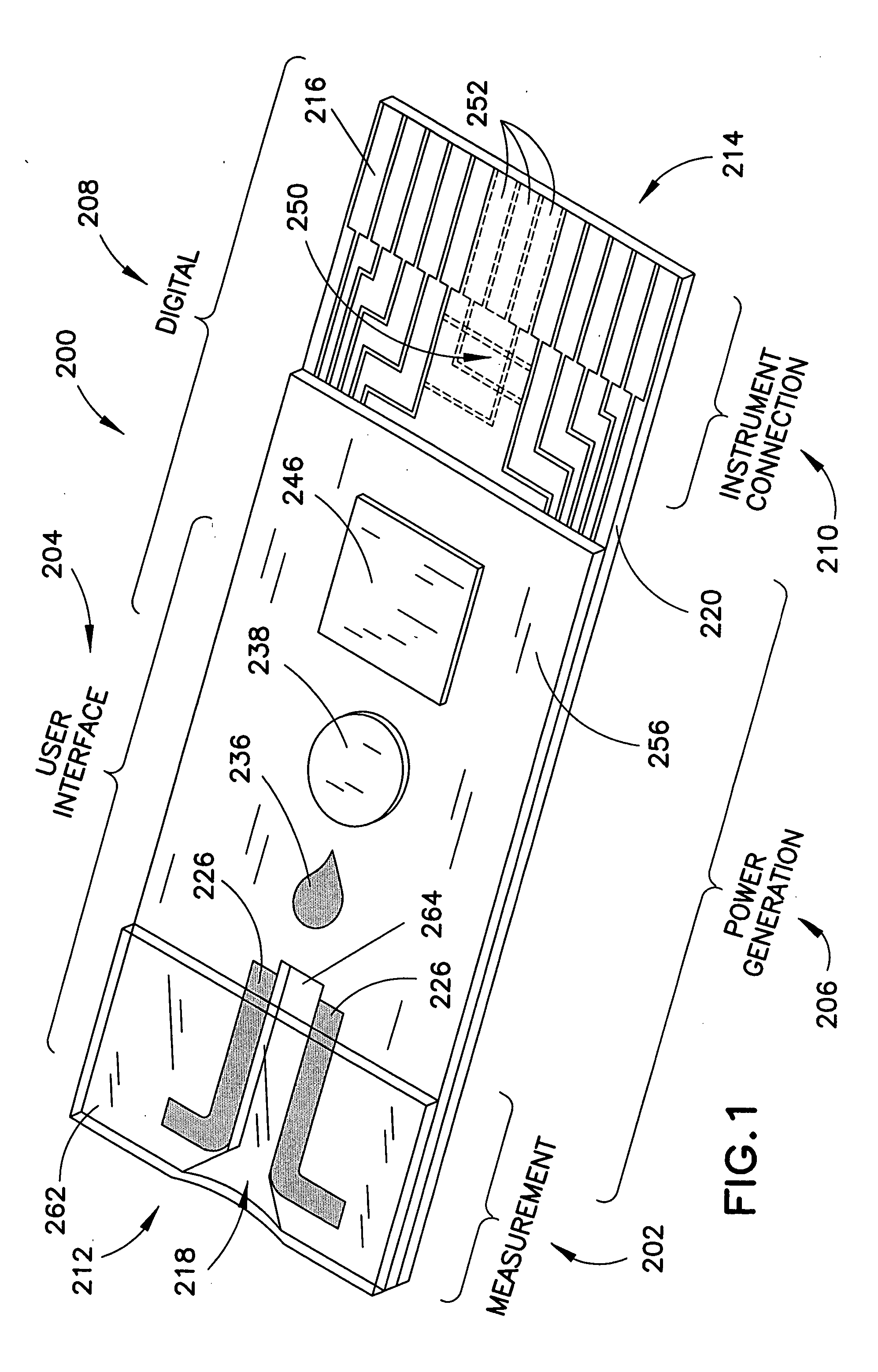
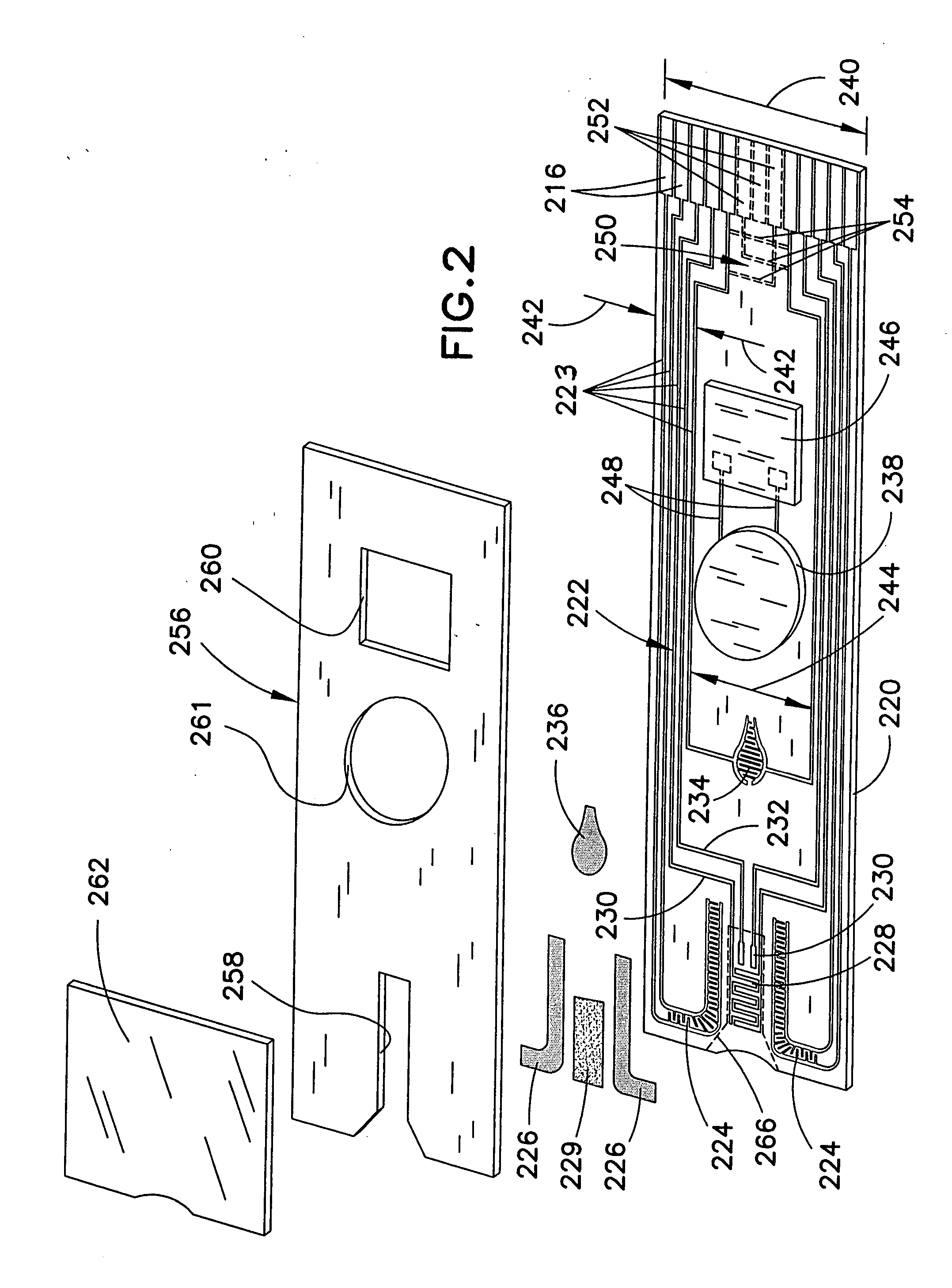
A biosensor having multiple electrical functionalities located both within and outside of the measurement zone in which a fluid sample is interrogated. Incredibly small and complex electrical patterns with high quality edges provide electrical functionalities in the biosensor and also provide the electrical wiring for the various other electrical devices provided in the inventive biosensor. In addition to a measurement zone with multiple and various electrical functionalities, biosensors of the present invention may be provided with a user interface zone, a digital device zone and / or a power generation zone. The inventive biosensors offer improved ease of use and performance, and decrease the computational burden and associated cost of the instruments that read the biosensors by adding accurate yet cost-effective functionalities to the biosensors themselves.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
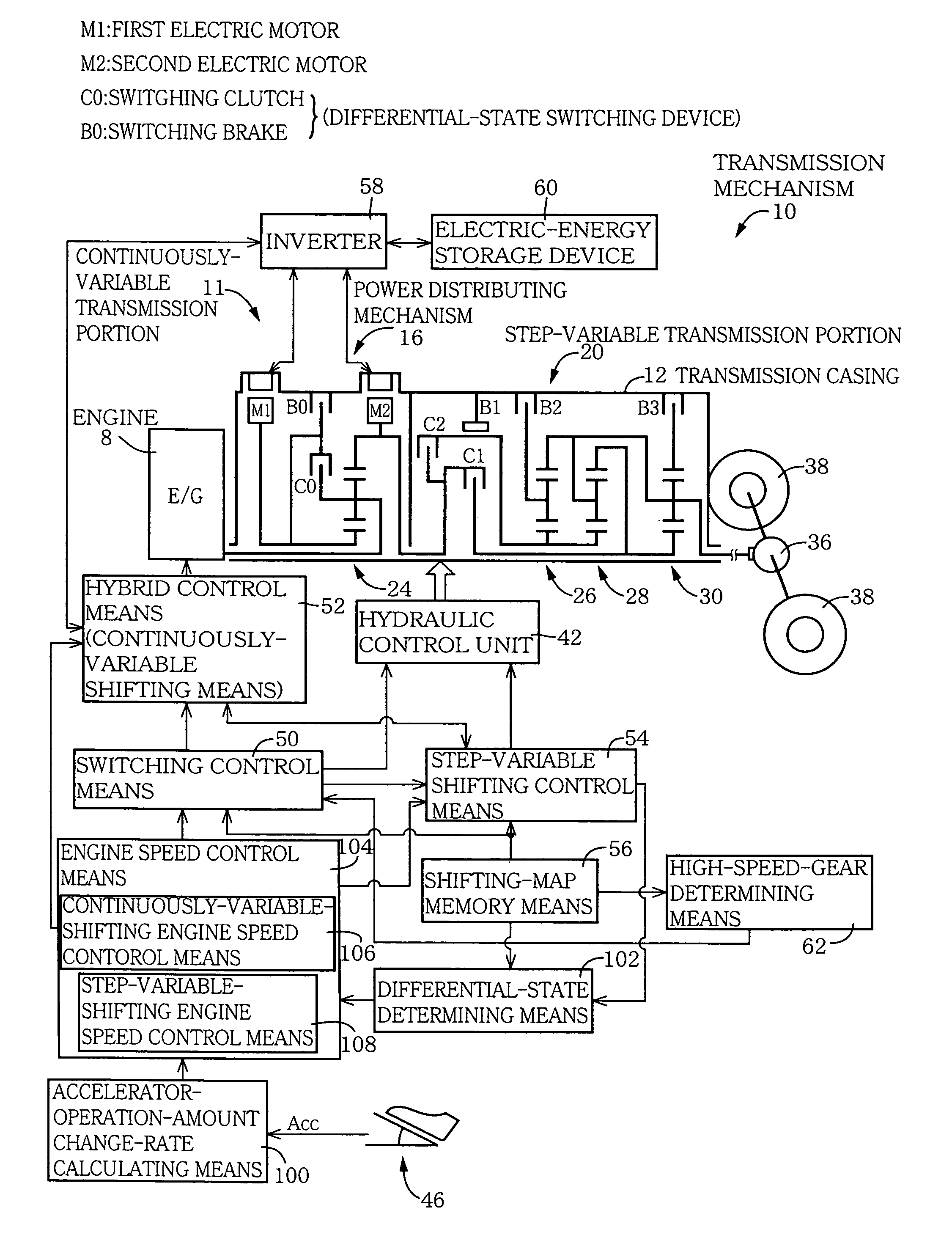
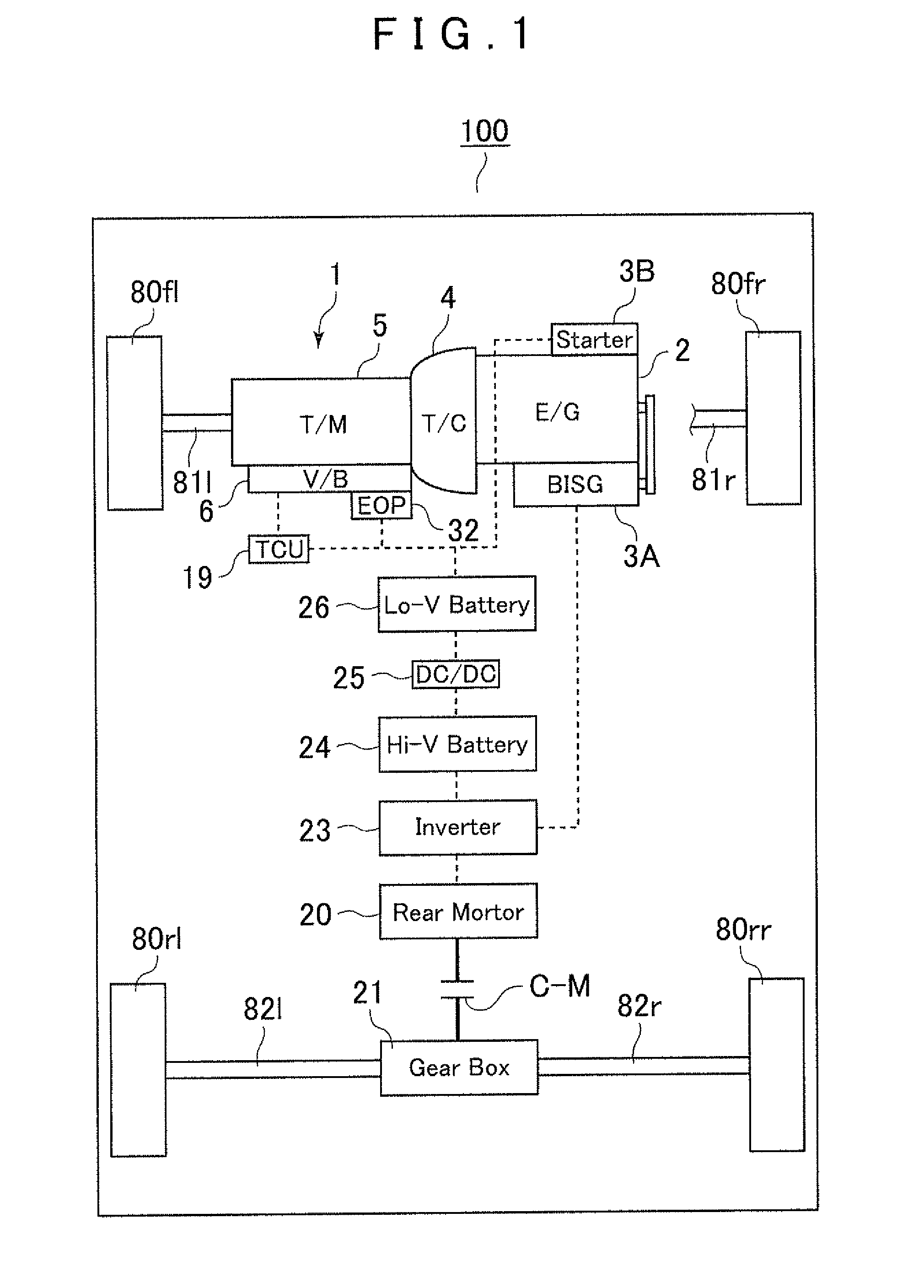
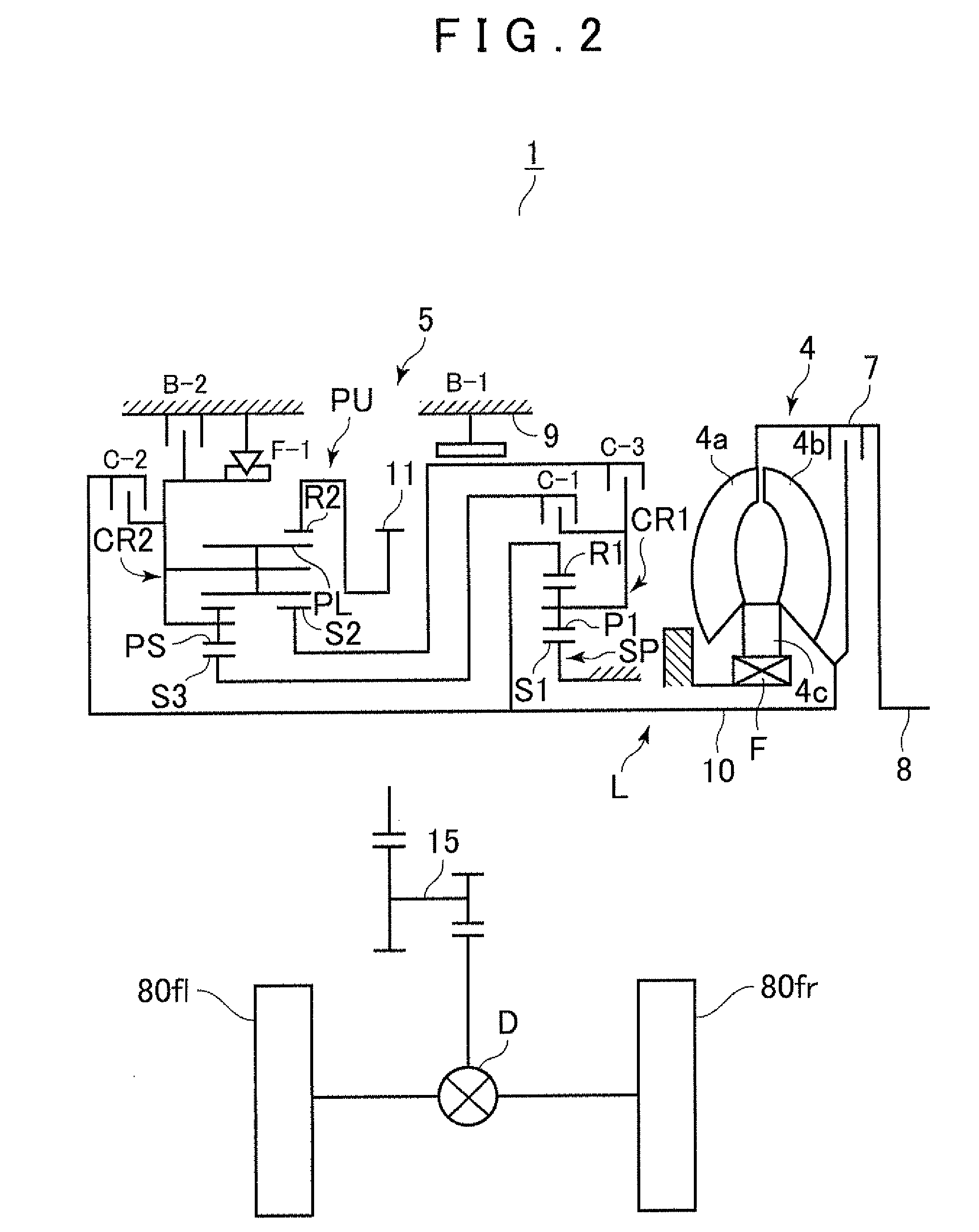
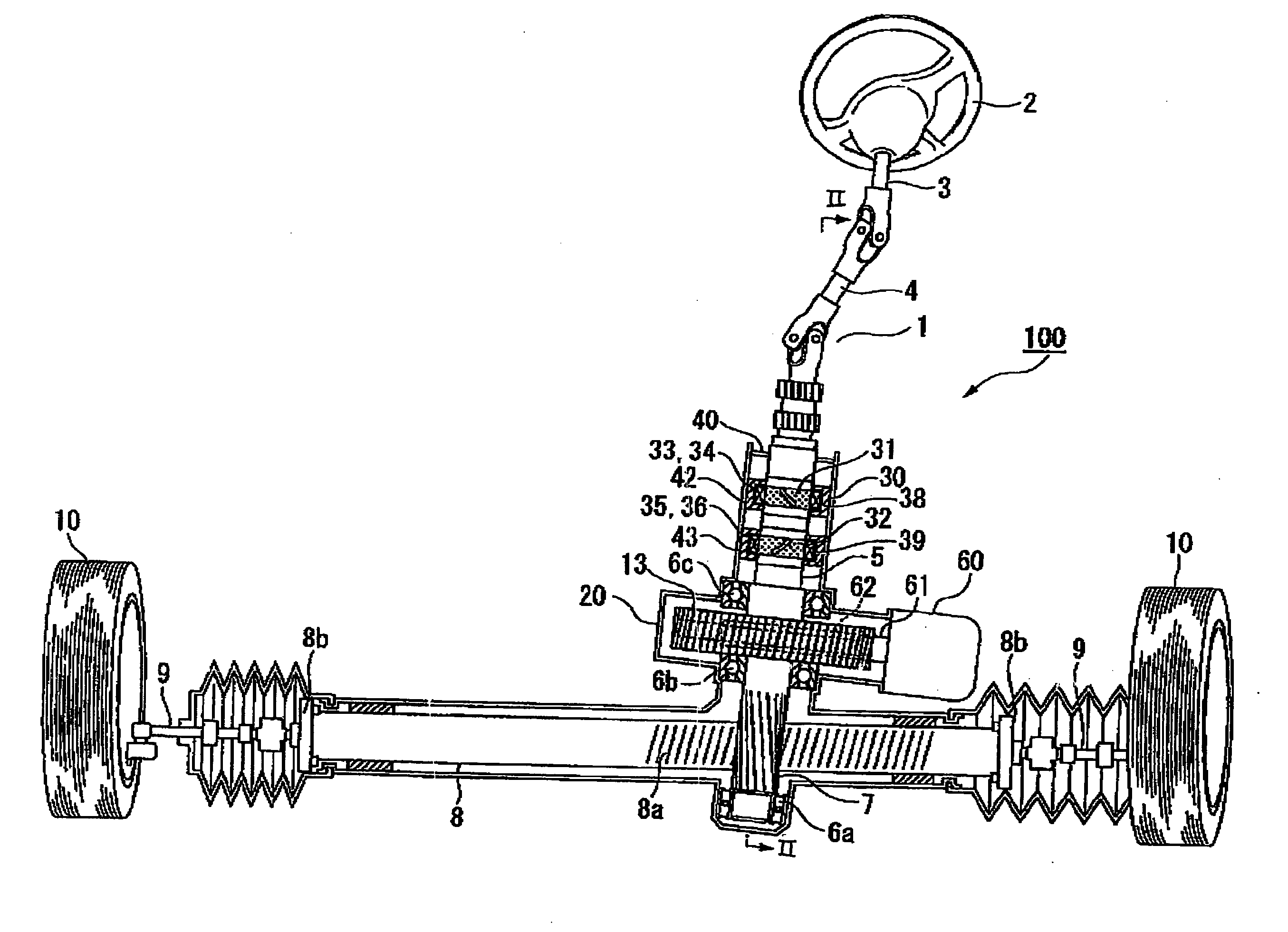
Control device for vehicular drive system
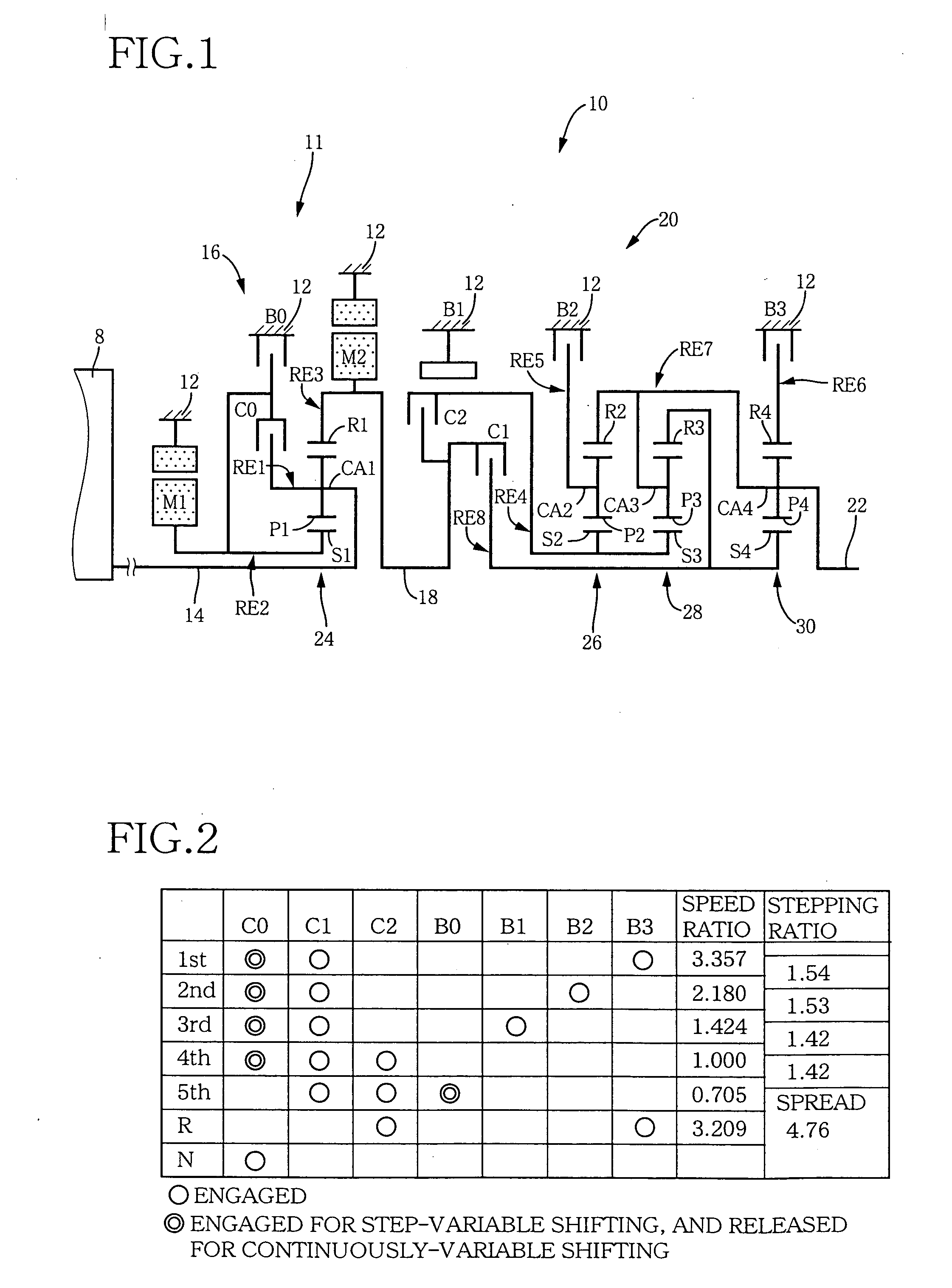
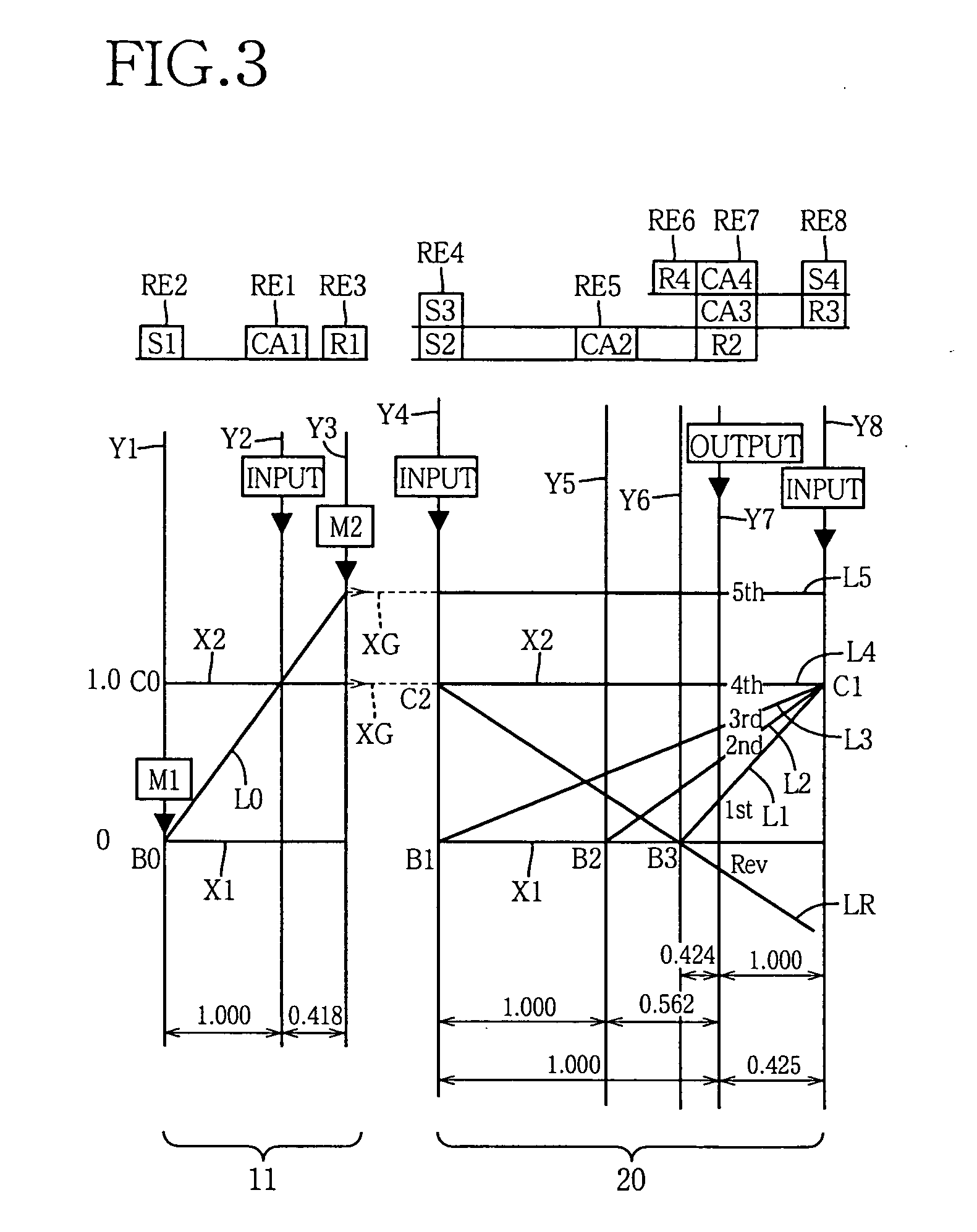
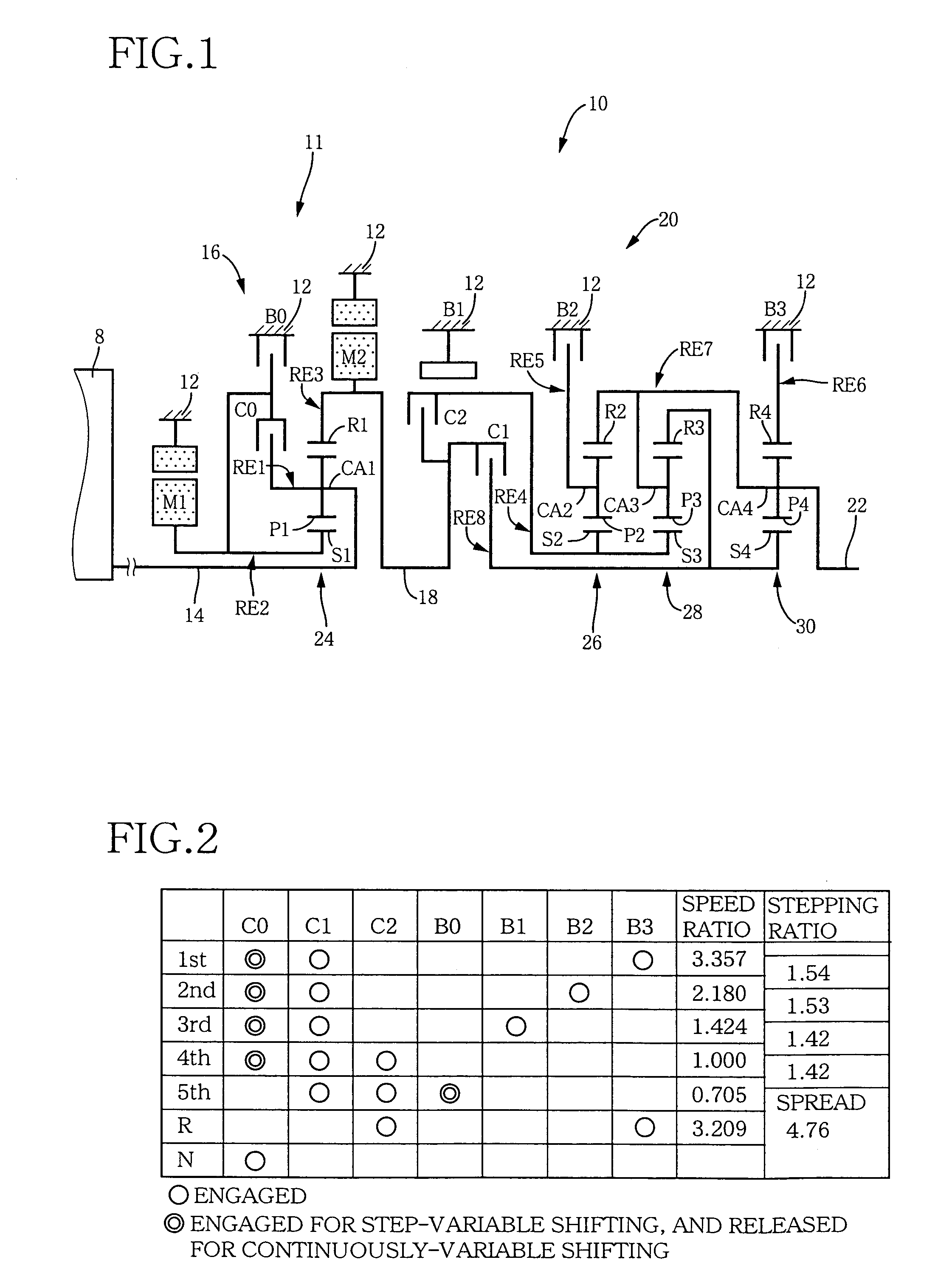
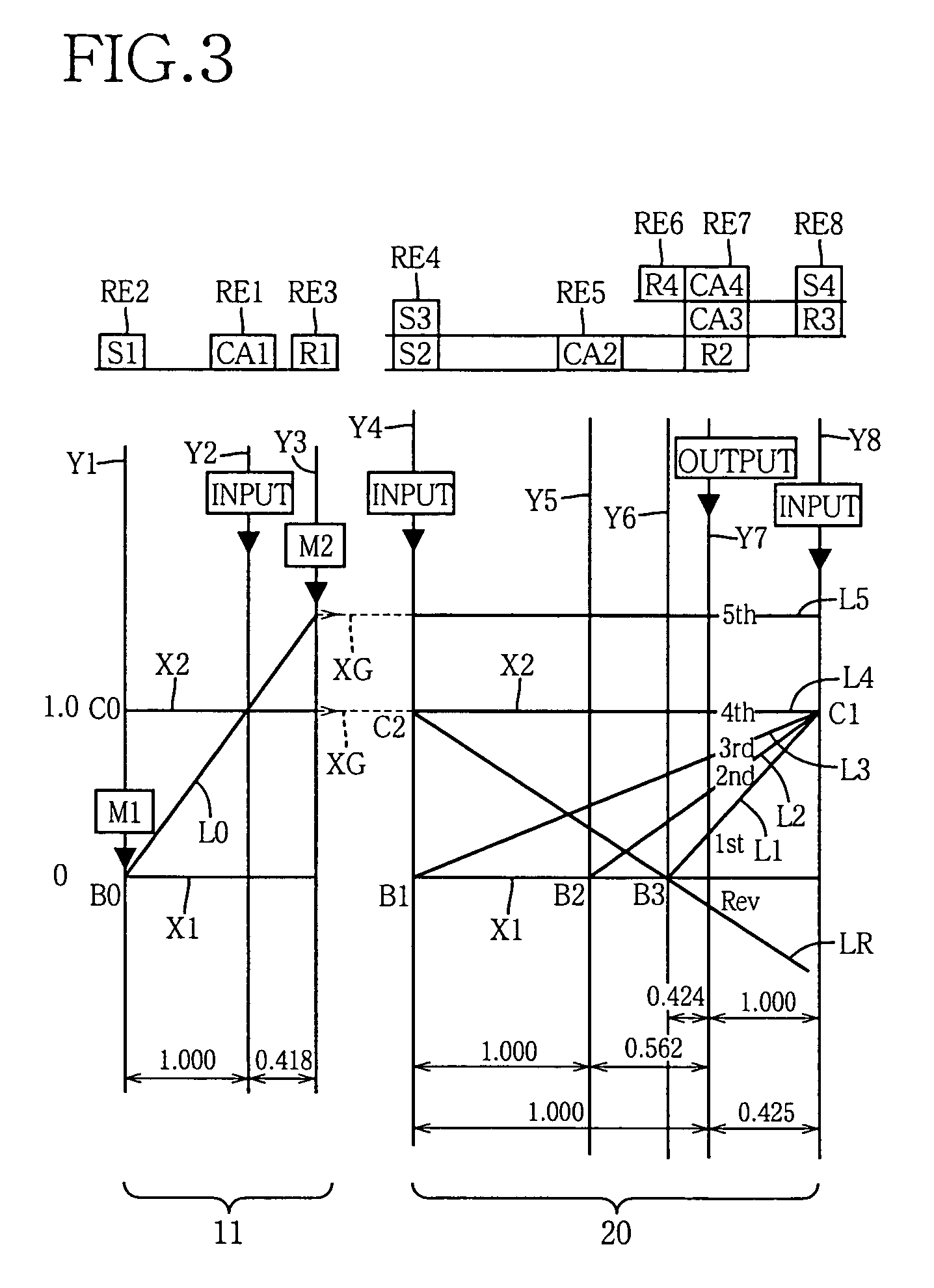
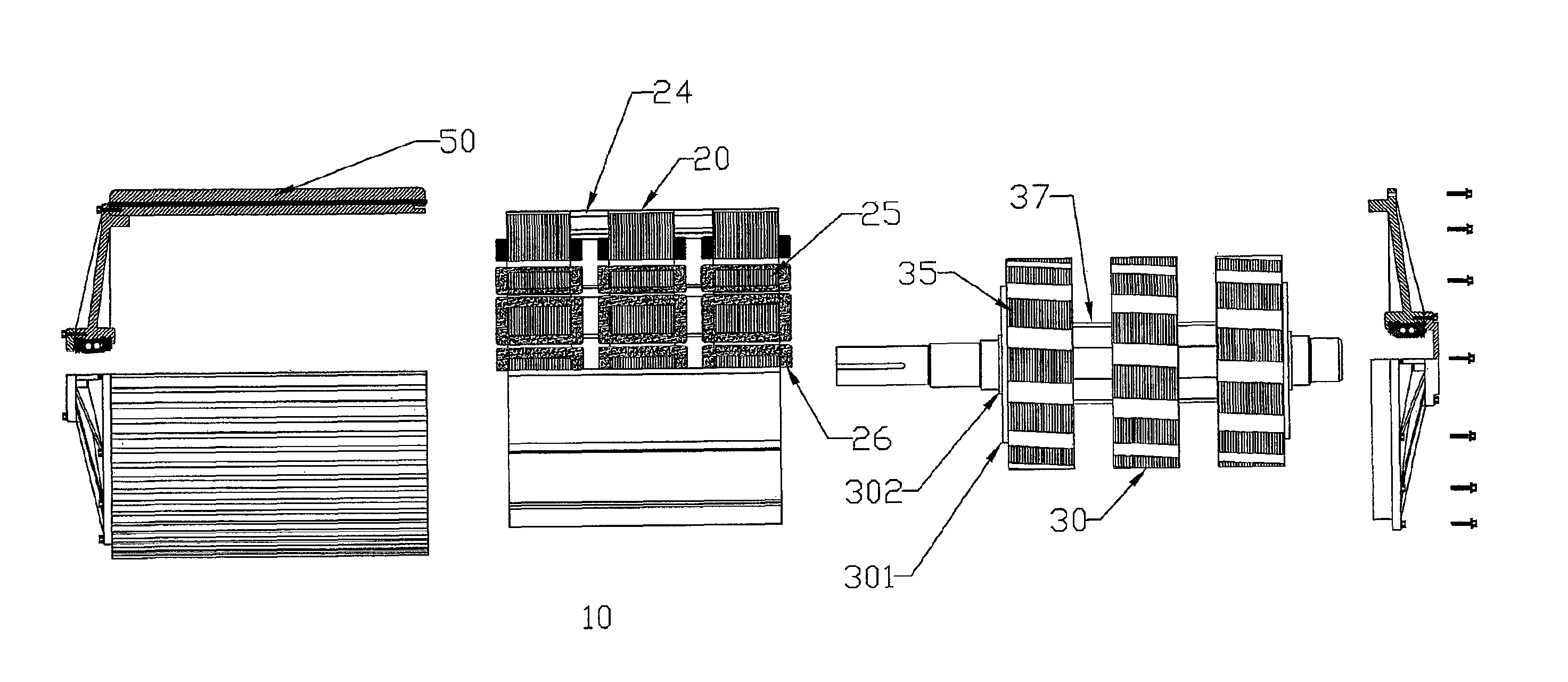
ActiveUS20060166784A1Improve fuel economyElectrical size reductionHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlContinuously variable transmissionControl theory
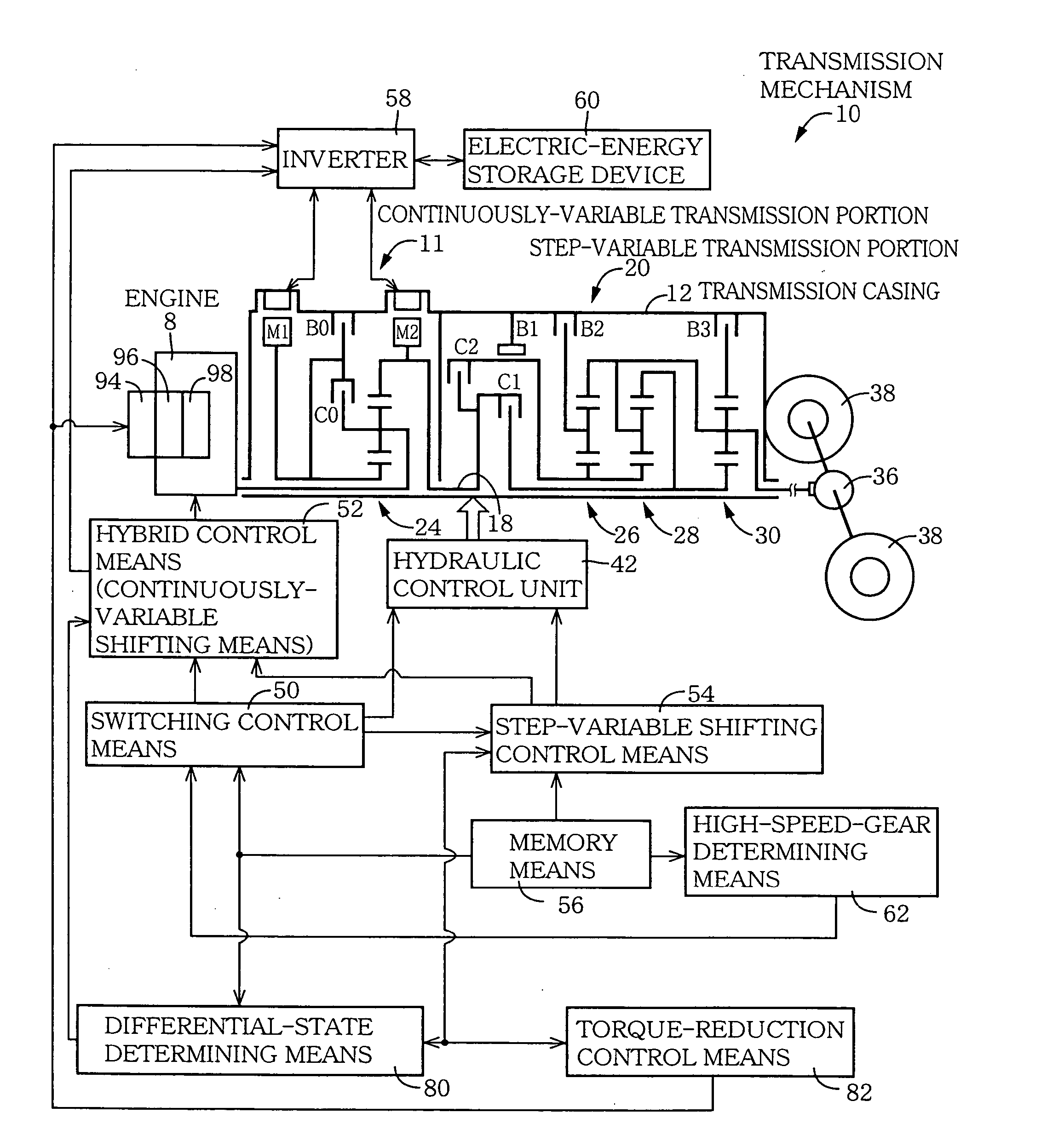
Hybrid controller 52 for a vehicular drive system is operable during a shifting control of step-variable transmission portion 20 for a stepping change of its speed ratio, for changing a speed ratio of continuously-variable transmission portion 11, such that total speed ratio γT of transmission mechanism 10 defined by the speed ratio of the continuously-variable transmission portion 11 and the speed ratio of the step-variable transmission portion 20 is continuously changed, irrespective of the stepping change of the speed ratio of the step-variable transmission portion 20, so that an amount of stepping change of engine speed NE before and after a shifting action of the step-variable transmission portion 20 is reduced, and a shifting shock of the step-variable transmission portion 20 is reduced. The hybrid controller 52 permits the transmission mechanism 10 to function as a continuously variable transmission, thereby improving fuel economy of the vehicular drive system.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Multistage variable reluctance motor/generator
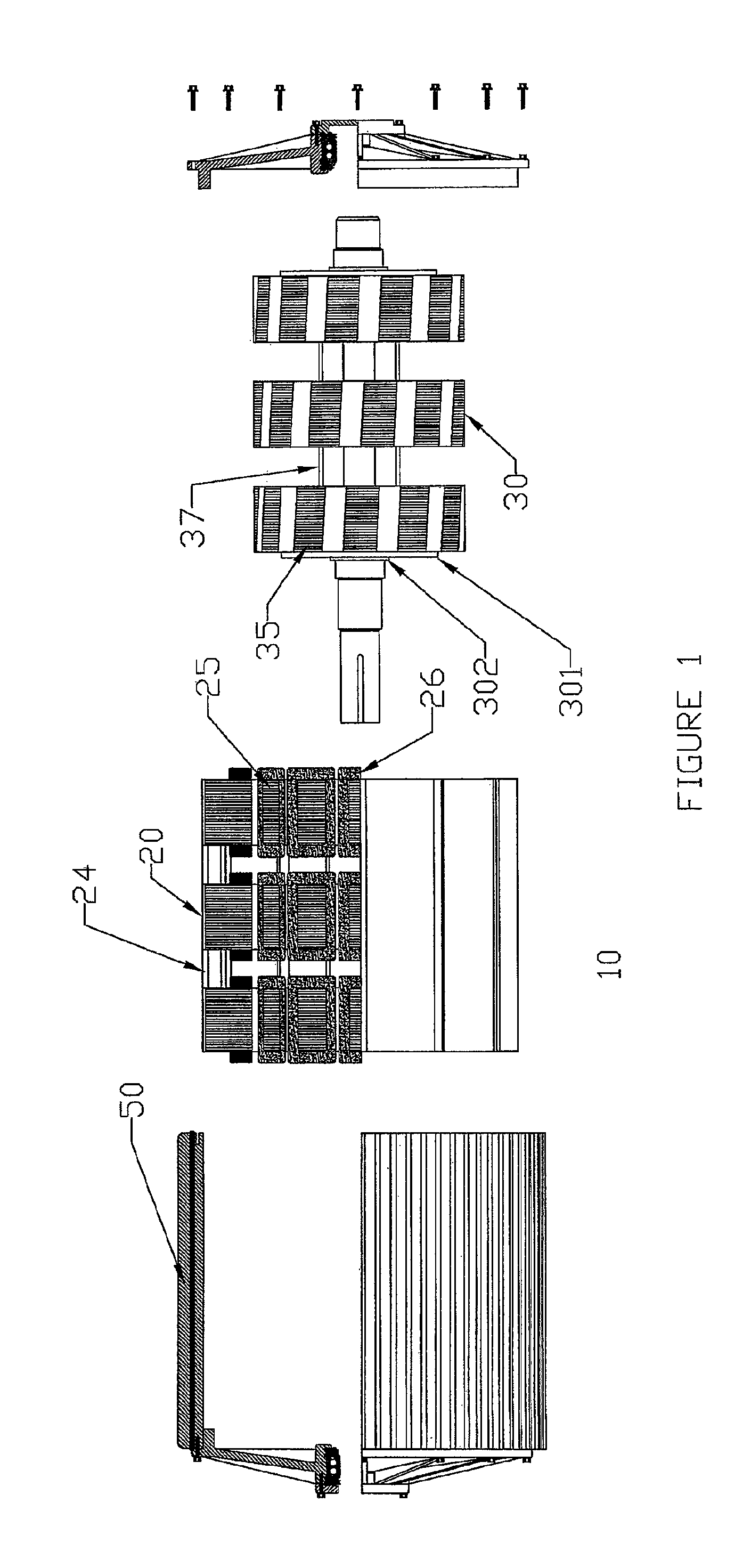
ActiveUS20100156205A1Reduce complexityImprove rendering capabilitiesSynchronous generatorsAC motor controlCopper lossMagnetic flux
A compact, rugged, variable reluctance, variable speed, electric motor capable of producing high torque at high electrical energy conversion efficiencies is provided. The present invention provides for a multi-stage motor design having a number of discreet rotor and stator elements on a common shaft. This configuration provides for the simplest of magnetic structures and produces a powerful magnetic flux modelling design technique that is used to further optimize the motor design and subsequent control logic. Thermal mapping of the magnetic mass provides for advanced cooling techniques that are used to ensure long in-service life in the most extreme of industrial applications. The electric motor inherently provides low vibration thereby greatly reducing noise; low turn to turn voltage potentials thereby eliminating costly phase to phase shorting potential; efficient motor operation through the reduction in switching and copper losses in both the machine and its control system.
Owner:SUNCO INVESTMENTS
Biosensor with multiple electrical functionalities
InactiveUS7867369B2Enhancing quality and complexityDecreases computational burden and associated cost of instrumentImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrical devicesUsability
A biosensor having multiple electrical functionalities located both within and outside of the measurement zone in which a fluid sample is interrogated. Incredibly small and complex electrical patterns with high quality edges provide electrical functionalities in the biosensor and also provide the electrical wiring for the various other electrical devices provided in the inventive biosensor. In addition to a measurement zone with multiple and various electrical functionalities, biosensors of the present invention may be provided with a user interface zone, a digital device zone and / or a power generation zone. The inventive biosensors offer improved ease of use and performance, and decrease the computational burden and associated cost of the instruments that read the biosensors by adding accurate yet cost-effective functionalities to the biosensors themselves.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
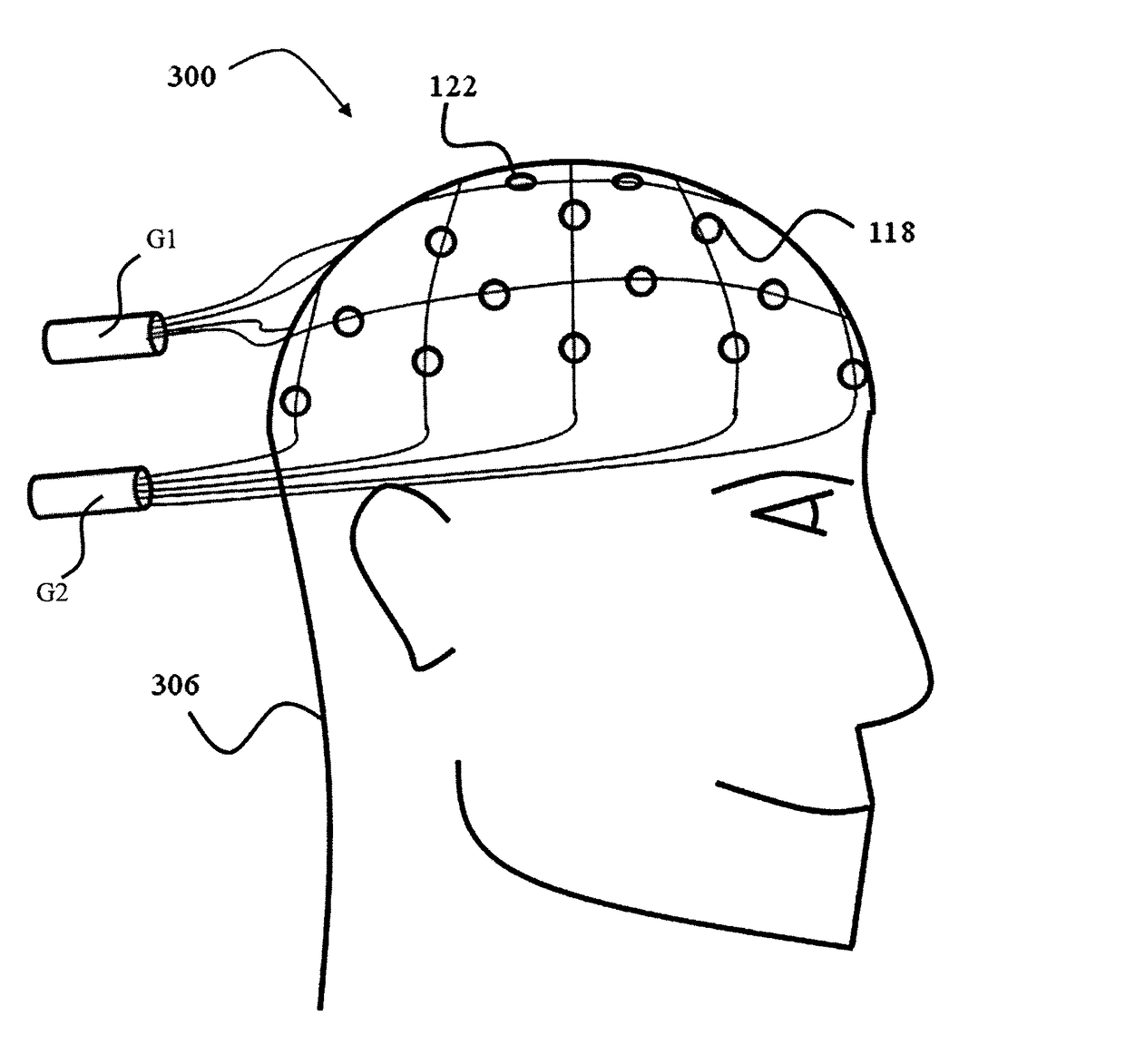
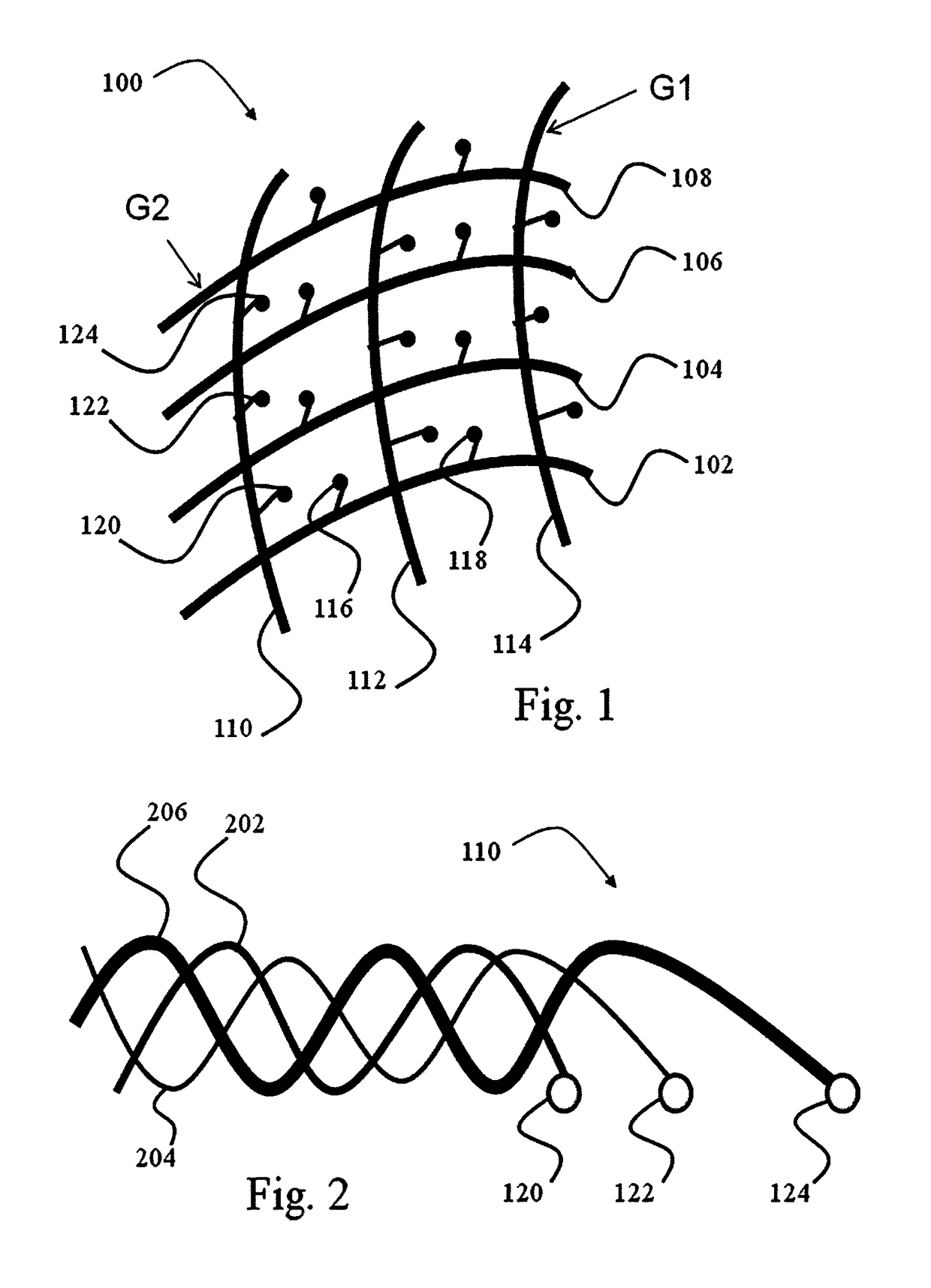
Device for use in electro-biological signal measurement in the presence of a magnetic field
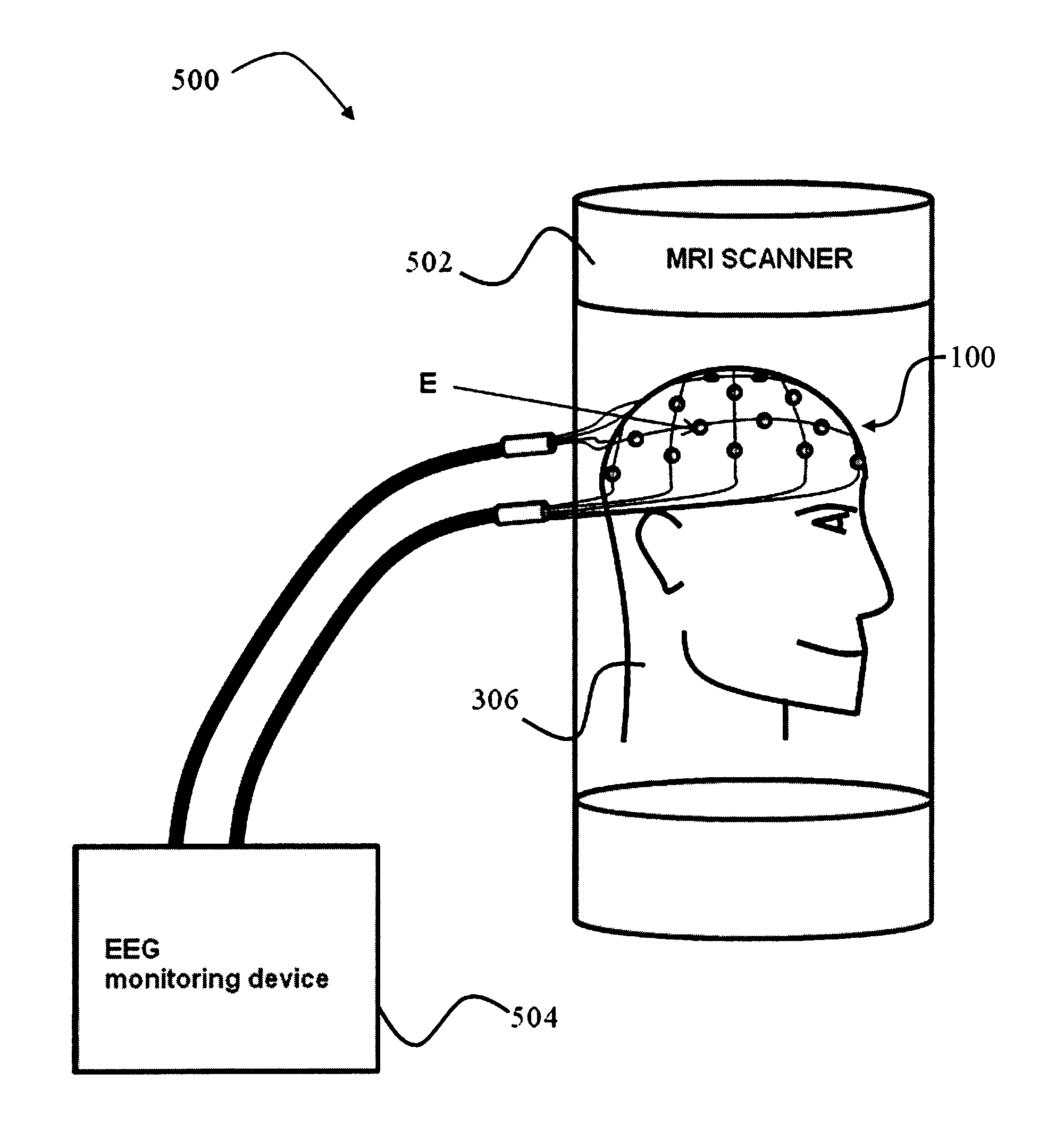
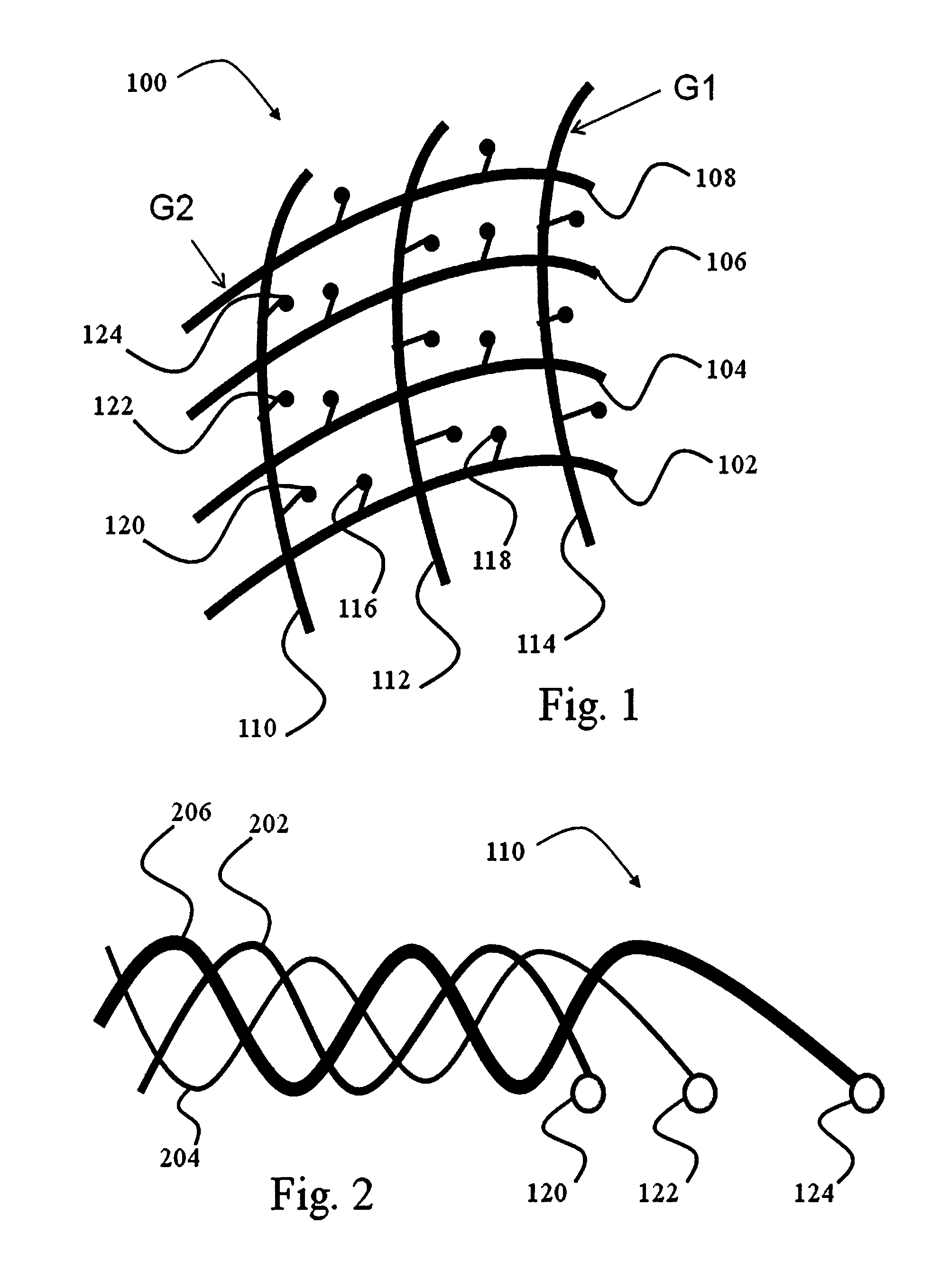
ActiveUS20130204122A1Electrical size reductionReduce Motion ArtifactsElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using suctionEeg dataMeasurement device
A measurement device is presented for use in an EEG measurement performed in the presence of a magnetic field. The device comprises a wiring array for connecting an electrodes arrangement to an electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring device. The wiring array comprises a plurality of sampling lines arranged to form a first group of sampling lines arranged in a spaced-apart substantially parallel relationship extending along a first axis, at least some of said sampling lines being wire bundles of said first group comprising a plurality of first wires for connecting to a corresponding first plurality of electrodes of said EEG electrodes arrangement; and a second group of sampling lines arranged in a spaced-apart substantially parallel relationship extending along a second axis, intersecting with said first axis, such that said second group of bundles crosses said first group of bundles to form a net structure, at least some of said sampling lines being wire bundles of said second group comprising a plurality of second wires for connecting to a corresponding second plurality of electrodes of said EEG electrodes' arrangement. The wiring array is configured and operable for transmitting a signal measured by the respective electrodes to the EEG monitoring device, enabling generation of EEG data indicative of the neural signal profile along tow directions and characterized by reduced motion artifact and / or reduced gradient artifact associated with the presence of the magnetic field during the EEG measurement.
Owner:THE MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & HEALTH SERVICES FUND OF THE TEL AVIV MEDICAL CENT
Vehicle Hybrid Energy System
ActiveUS20080245587A1Maximize cruising distanceHigh powerHybrid vehiclesElectric propulsion mountingElectrical batteryDrivetrain
A hybrid energy storage system suitable for use in a vehicle having an electrified drivetrain includes a first energy storage module and a second energy storage module that is different than the first energy storage module. The first energy storage module may have a cell configuration, a cell chemistry, a cell number, a controller or another characteristic different than a like characteristic of the second energy storage module.
Owner:THE RGT OF THE UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Miniature broadband ring-like microstrip patch antenna
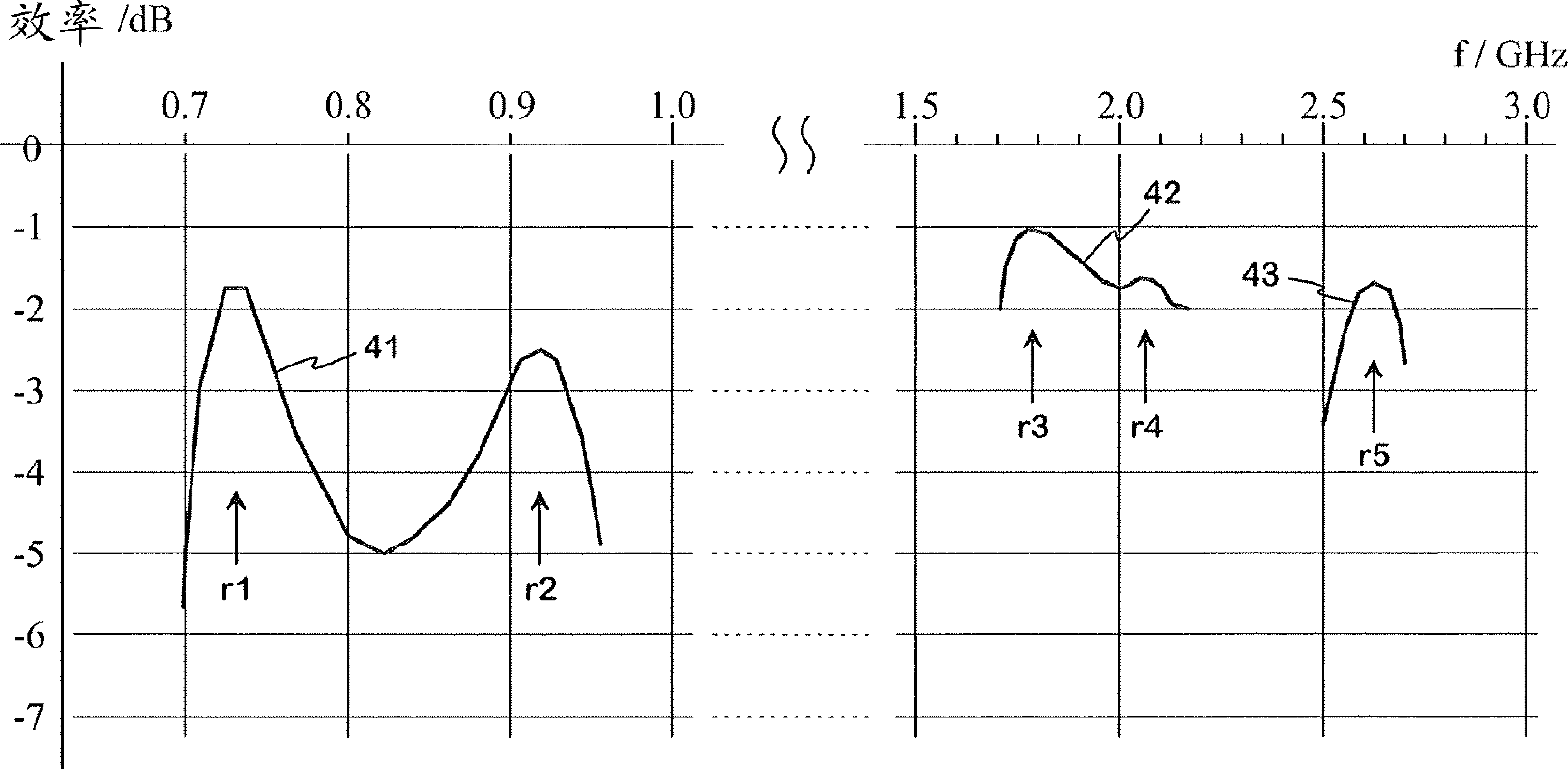
InactiveUS6870507B2Small sizeRelatively large bandwidthLogperiodic antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsMicrostrip patch antennaEngineering
A miniature broadband stacked microstrip patch antenna formed by two patches, an active and a parasitic patches, where at least one of them is defined by a Ring-Like Space-Filling Surface (RSFS) being this RSFS newly defined in the present invention. By means of this novel technique, the size of the antenna can be reduced with respect to prior art, or alternatively, given a fixed size the antenna can operate at a lower frequency with respect to a conventional microstrip patch antenna of the same size and with and enhanced bandwidth. Also, the antennas feature a high-gain when operated at a high order mode.
Owner:COMMSCOPE TECH LLC
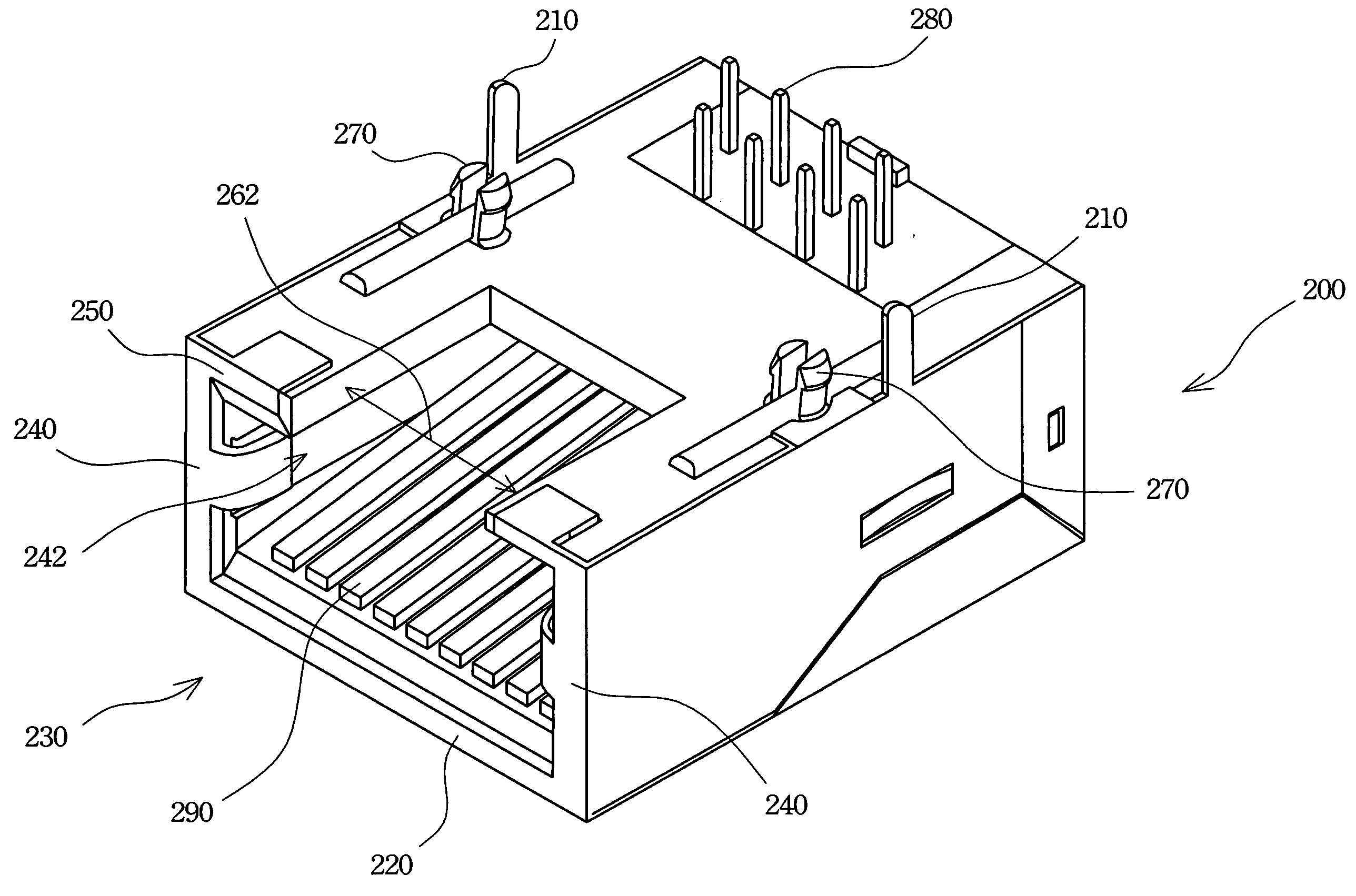
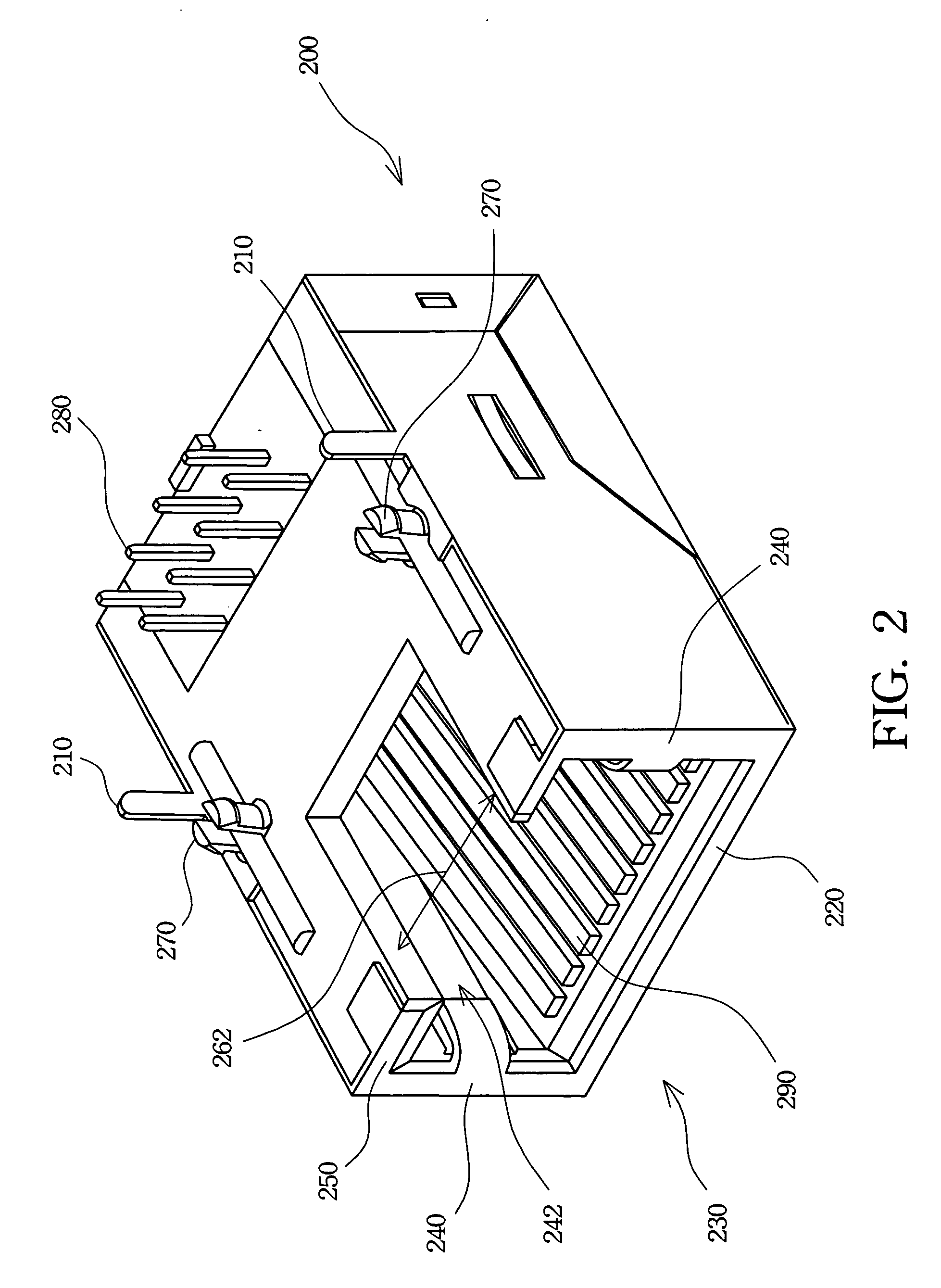
Electrical connector and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20160099526A1Simple to manufactureSmall sizeContact member manufacturingContact member assembly/disassemblyEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A electrical connector includes an insulating body having a tongue plate, a plurality of upper conductive terminals having upper contact portions, and a plurality of lower conductive terminals having lower contact portions; the upper and lower conductive terminals are buried and molded in the insulating body, the upper contact portions and the lower contact portions are vertically aligned one by one and respectively exposed on an upper surface and a lower surface of the tongue plate; the upper conductive terminals vertically corresponding to the lower conductive terminals one by one so as to form a plurality of corresponding columns, and the upper and lower conductive terminals of at least one corresponding columns are fixedly connected with each other by riveting.
Owner:DONGGUAN JITS IND +1
Driving apparatus having a shaft support structure
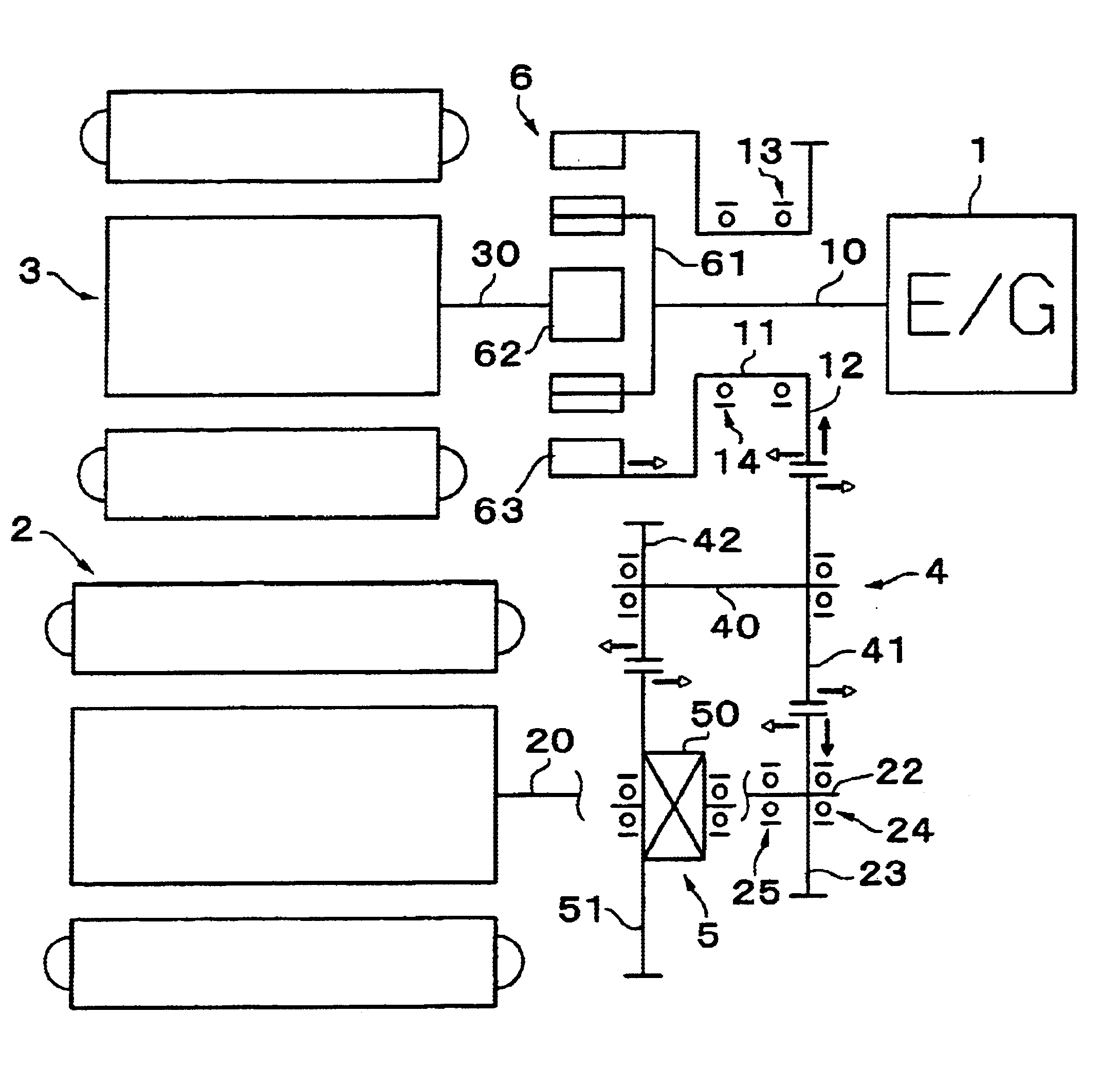
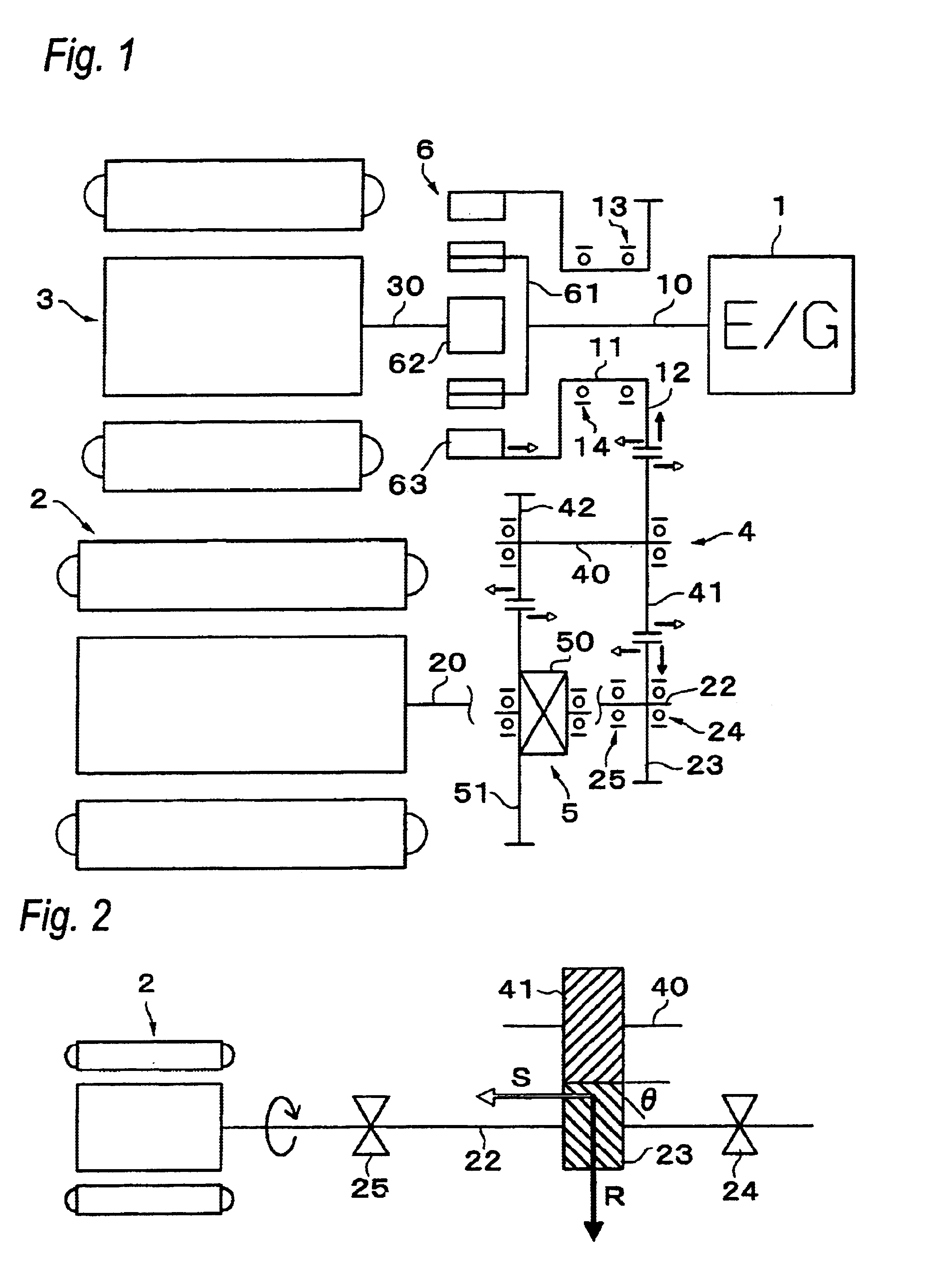
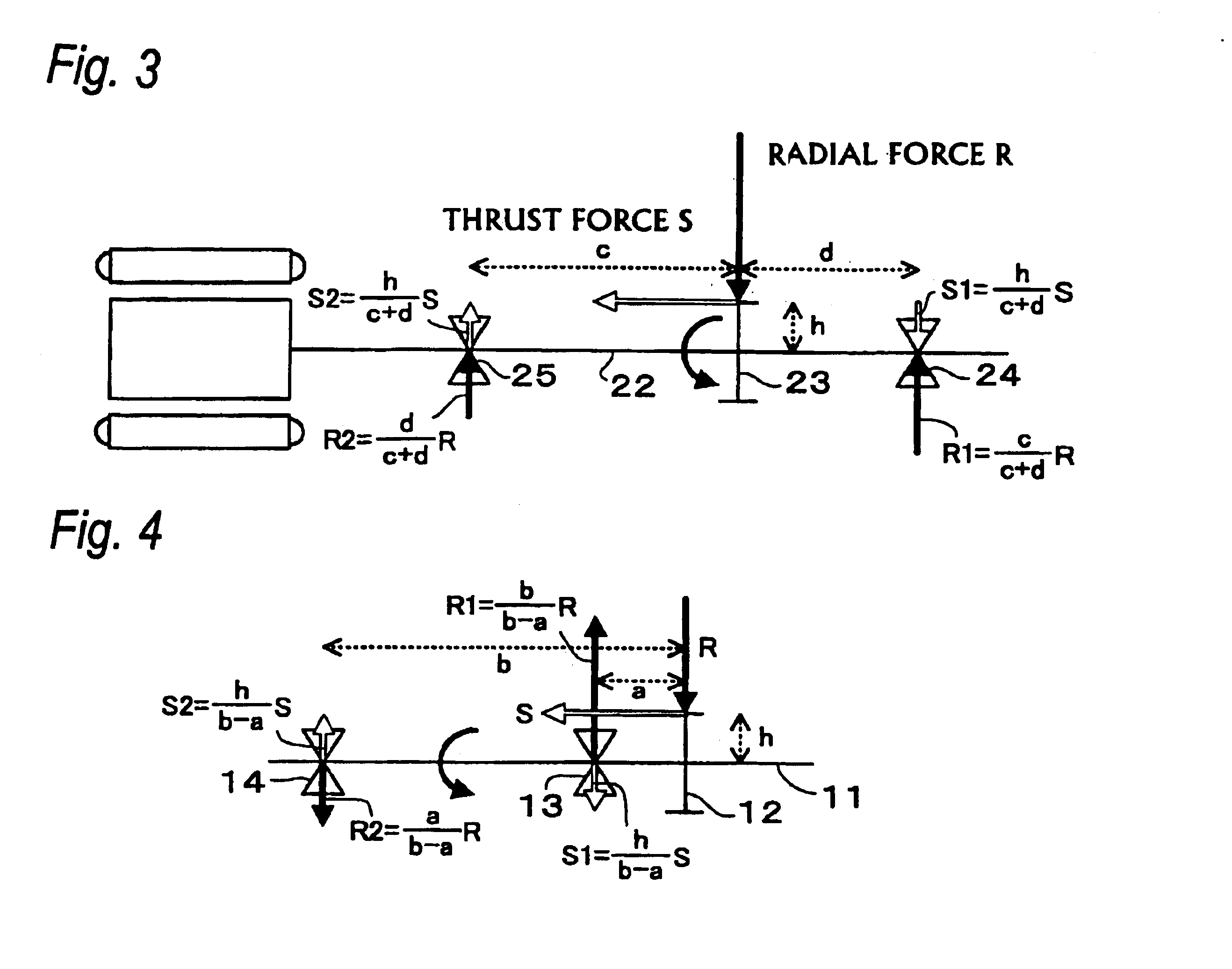
A driving apparatus having a shaft structure that reduces a load on shaft supports and enhances durability of the motor. The driving apparatus includes an electric motor, an electric motor shaft, first and second shaft supports, a counter drive gear on the electric motor shaft, and a counter driven gear to be meshed with the counter drive gear. Output of the electric motor is transmitted to wheels through both of the gears. The counter drive gear is disposed at a position closer to one of the shaft supports, a helix angle is set in a direction in which a thrust force S acts toward the second shaft support, which is farther from the gear. With this arrangement, a load caused by a radial force applied to the first shaft support, which is closer to the counter drive gear, is reduced.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Compact drive mechanism for electrically powered vehicle
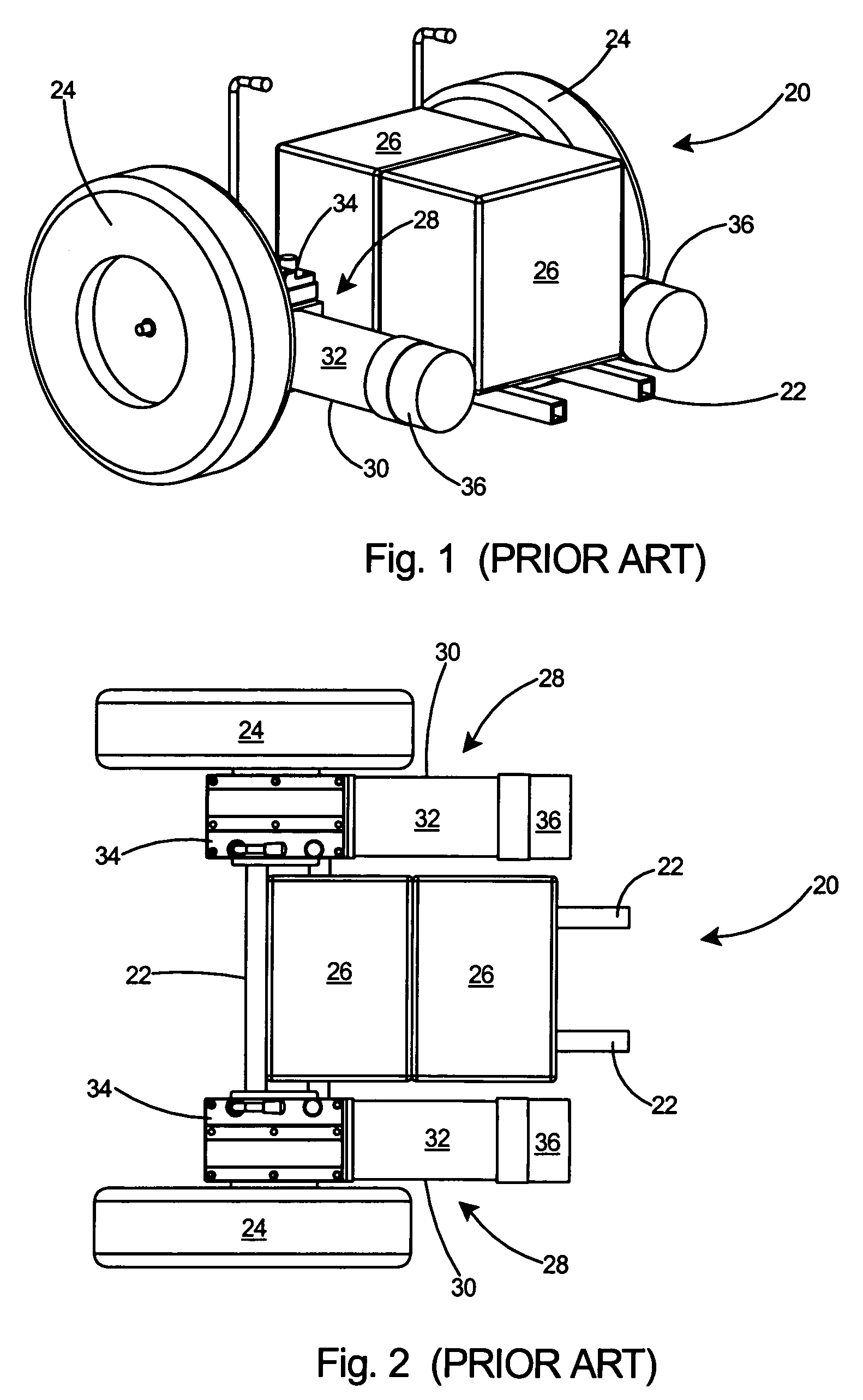
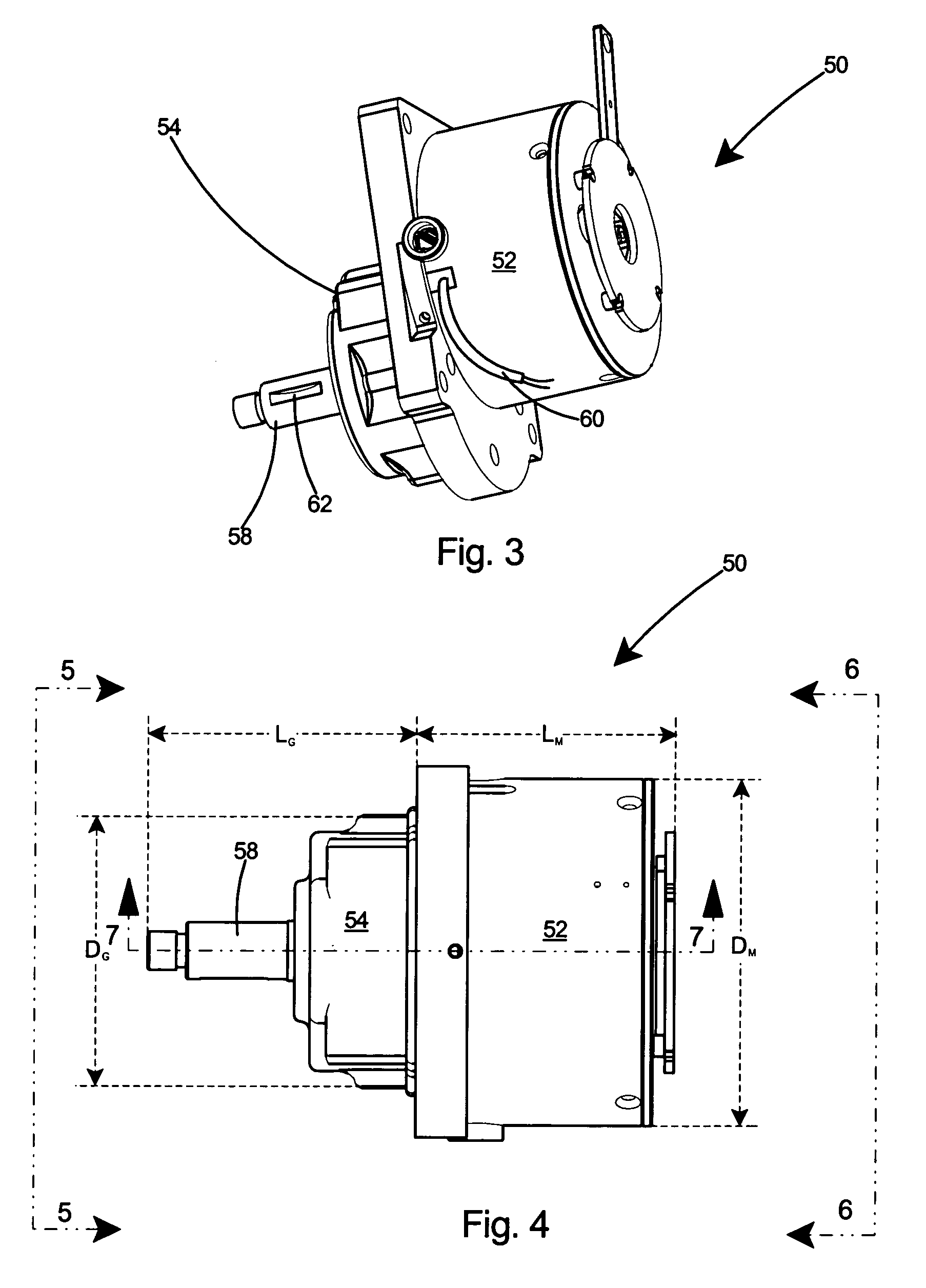
InactiveUS7159677B1Reduced footprintMore roomElectric devicesElectric propulsion mountingWheelchairElectric machine
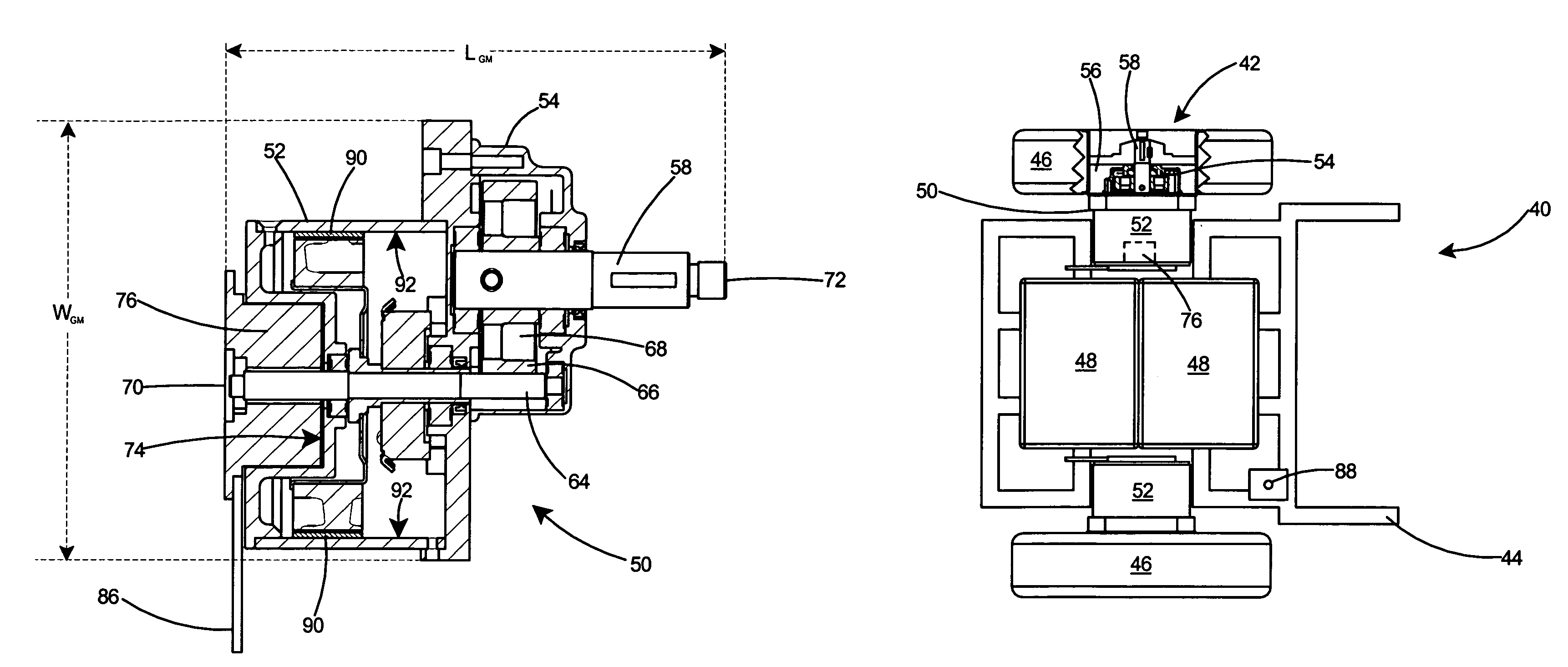
A compact and lightweight drive mechanism for an electrically powered vehicle such as a wheelchair or a scooter. The compact drive mechanism includes a gearmotor combining a motor and a gearbox. High strength rare earth magnets and a large diameter enable the motor to generate a high torque. Gearmotor efficiency is maximized by placing the motor and gearbox in a direct drive relationship, with the shafts of both motor and gearbox parallel to one another. The compact drive mechanism weighs less than conventional drive mechanisms and occupies less space. The compact drive mechanism therefore improves efficiency and lowers power requirements over conventional systems.
Owner:CCL INDAL MOTOR
Electrical junction box
ActiveUS20170207614A1Strong coverageSuppress expansionElectrical apparatusElectric/fluid circuitElectrical junctionEngineering
An electrical junction box in which the interference between an inner wall of a rotating upper cover and an outer wall of a box body can be more reliably prevented and a waterproof property can be secured, while also meeting the demand for reduction in size of the electrical junction box. In a state in which an upper cover is attached to a box body, on one end side of the box body and one end side of the upper cover, an outer wall of the box body is located on an inner side with respect to an outer wall of the upper cover, an inner wall of the upper cover is located on an inner side with respect to the outer wall of the box body, and an inner wall of the box body is located on an inner side with respect to the inner wall of the upper cover.
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Semiconductor device and method of producing the same
ActiveUS20060038245A1Reduce timeImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMagnetic layerEngineering
A semiconductor device of a wafer level chip size package type is formed by cutting a semiconductor wafer with a plurality of semiconductor elements formed thereon in pieces. The semiconductor device includes a semiconductor substrate as the semiconductor wafer having a magnetic layer formed on at least one of a front surface and a backside surface of the semiconductor wafer.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Slim phone jack
InactiveUS20050078819A1Facilitated releaseImprove signal transmission reliabilityCouplings bases/casesTwo-part coupling devicesTelephone plugEngineering
A slim phone jack is described. A height of the slim phone jack is reduced so as to reduce a height of an electric device utilized the slim phone jack. The slim phone jack has an upper cover, a lower cover and two sidewalls, and is suitable to couple to a phone plug with a spring arm. An inside of the upper cover has contact terminals. The two sidewalls form a sliding tunnel for inserting the phone plug easily. The lower cover further has a guiding slot. The slim phone jack further couples to a circuit board having a fixing slot. When the phone plug is inserted into the slim phone jack, the spring arm sticks out of the guiding slot so that a fixing edge of the spring arm couples to the fixing slot of the circuit board to fix the phone plug in the slim phone jack more strongly.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Control device for vehicular drive system
ActiveUS7396316B2Reduce transmissionImprove fuel economyHybrid vehiclesElectrical controlEngineeringControl theory
Hybrid controller 52 for a vehicular drive system is operable during a shifting control of step-variable transmission portion 20 for a stepping change of its speed ratio, for changing a speed ratio of continuously-variable transmission portion 11, such that total speed ratio γT of transmission mechanism 10 defined by the speed ratio of the continuously-variable transmission portion 11 and the speed ratio of the step-variable transmission portion 20 is continuously changed, irrespective of the stepping change of the speed ratio of the step-variable transmission portion 20, so that an amount of stepping change of engine speed NE before and after a shifting action of the step-variable transmission portion 20 is reduced, and a shifting shock of the step-variable transmission portion 20 is reduced. The hybrid controller 52 permits the transmission mechanism 10 to function as a continuously variable transmission, thereby improving fuel economy of the vehicular drive system.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Multistage variable reluctance motor/generator
ActiveUS8138652B2Optimize arrangement and construction and performance and cooling and controlOptimize design elementSynchronous generatorsAC motor controlMotor designHigh torque
A compact, rugged, variable reluctance, variable speed, electric motor capable of producing high torque at high electrical energy conversion efficiencies is provided. The present invention provides for a multi-stage motor design having a number of discreet rotor and stator elements on a common shaft. This configuration provides for the simplest of magnetic structures and produces a powerful magnetic flux modelling design technique that is used to further optimize the motor design and subsequent control logic. Thermal mapping of the magnetic mass provides for advanced cooling techniques that are used to ensure long in-service life in the most extreme of industrial applications. The electric motor inherently provides low vibration thereby greatly reducing noise; low turn to turn voltage potentials thereby eliminating costly phase to phase shorting potential; efficient motor operation through the reduction in switching and copper losses in both the machine and its control system.
Owner:SUNCO INVESTMENTS
Keyswitch for keyboard
InactiveUS6399909B1Small surface areaSufficiently long keystrokeCoupling device detailsContact operating partsMechanical engineeringFlexible circuits
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Method for controlling a turbocharger arrangement with an electric actuator and spring
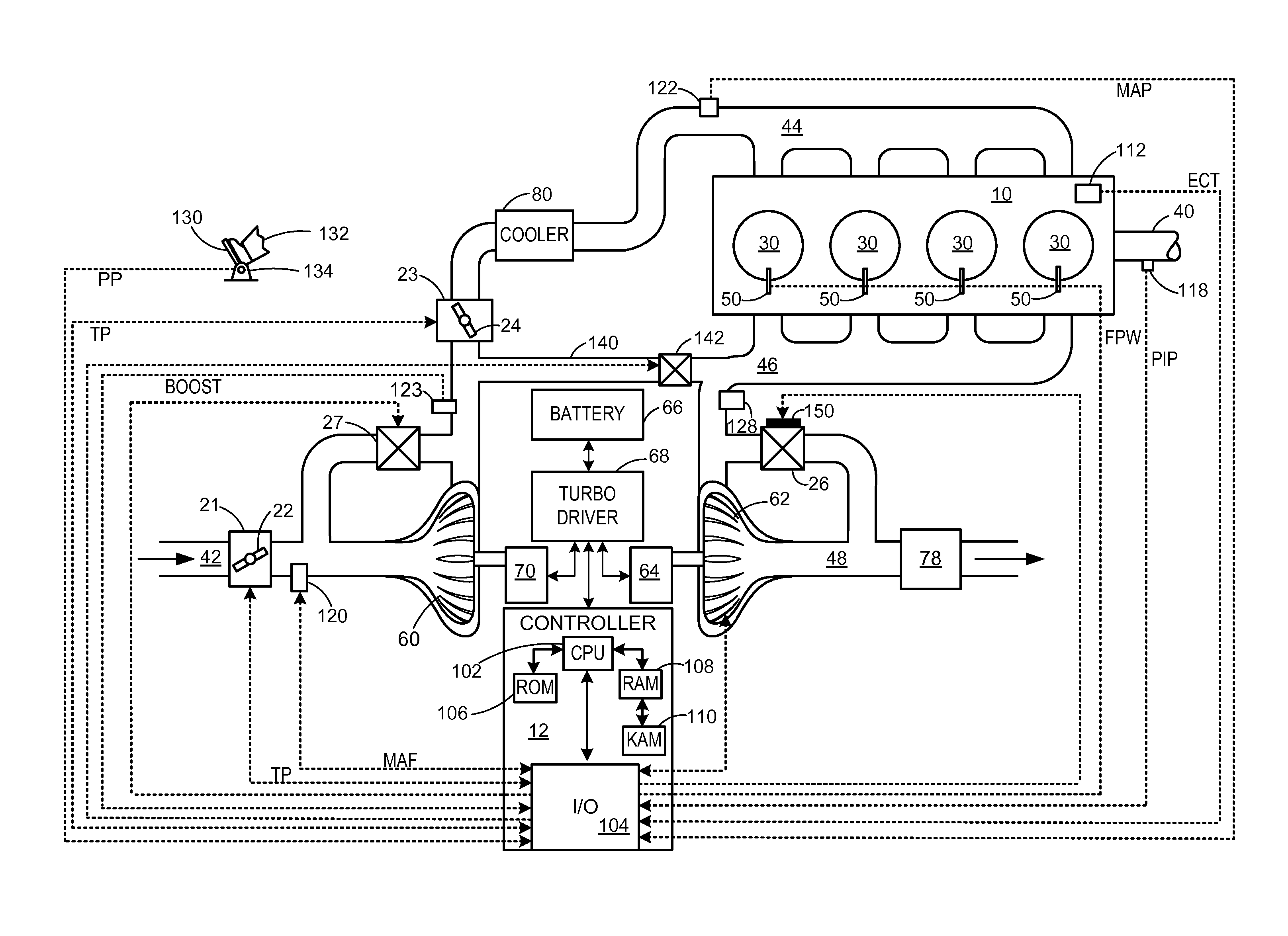
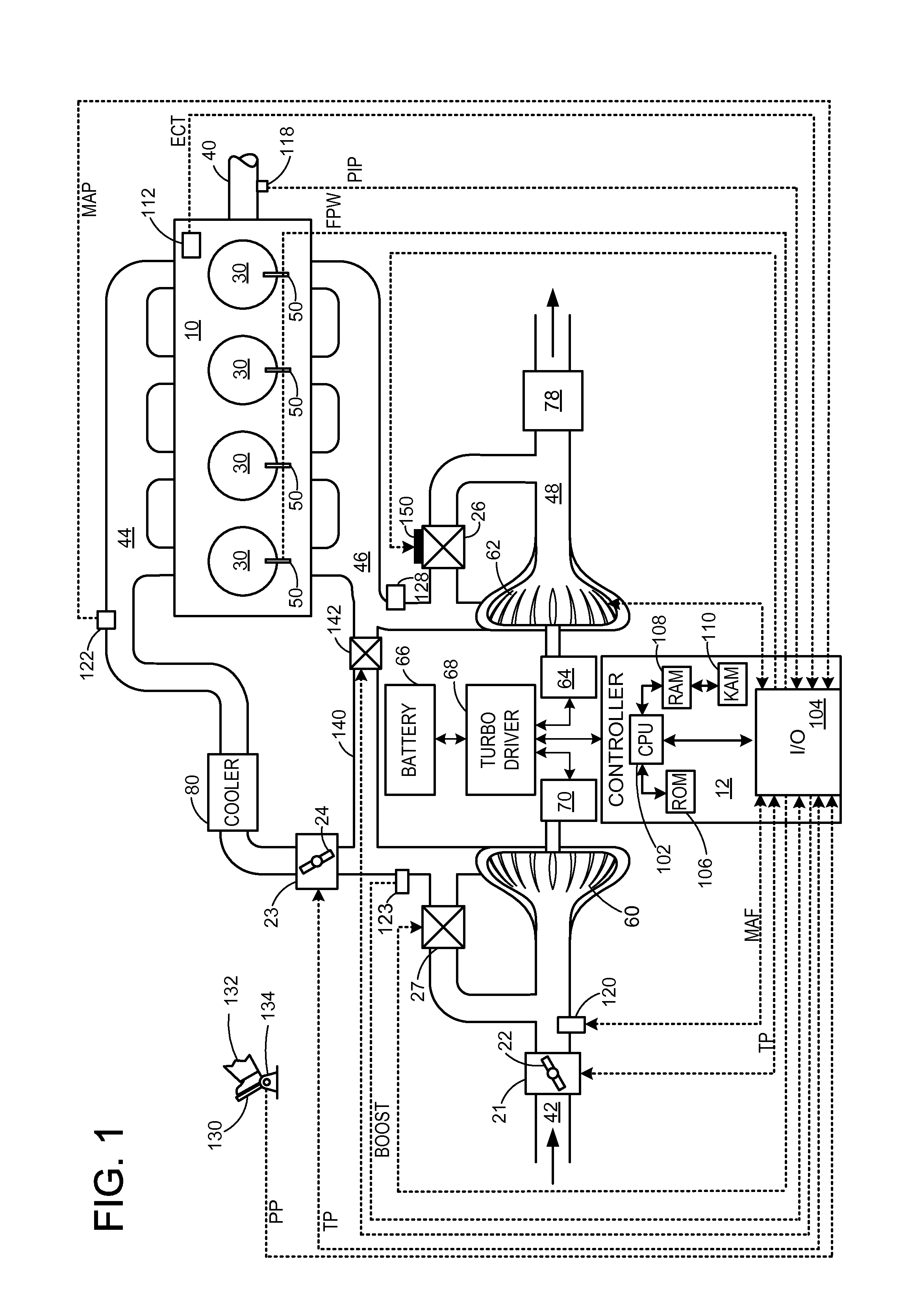
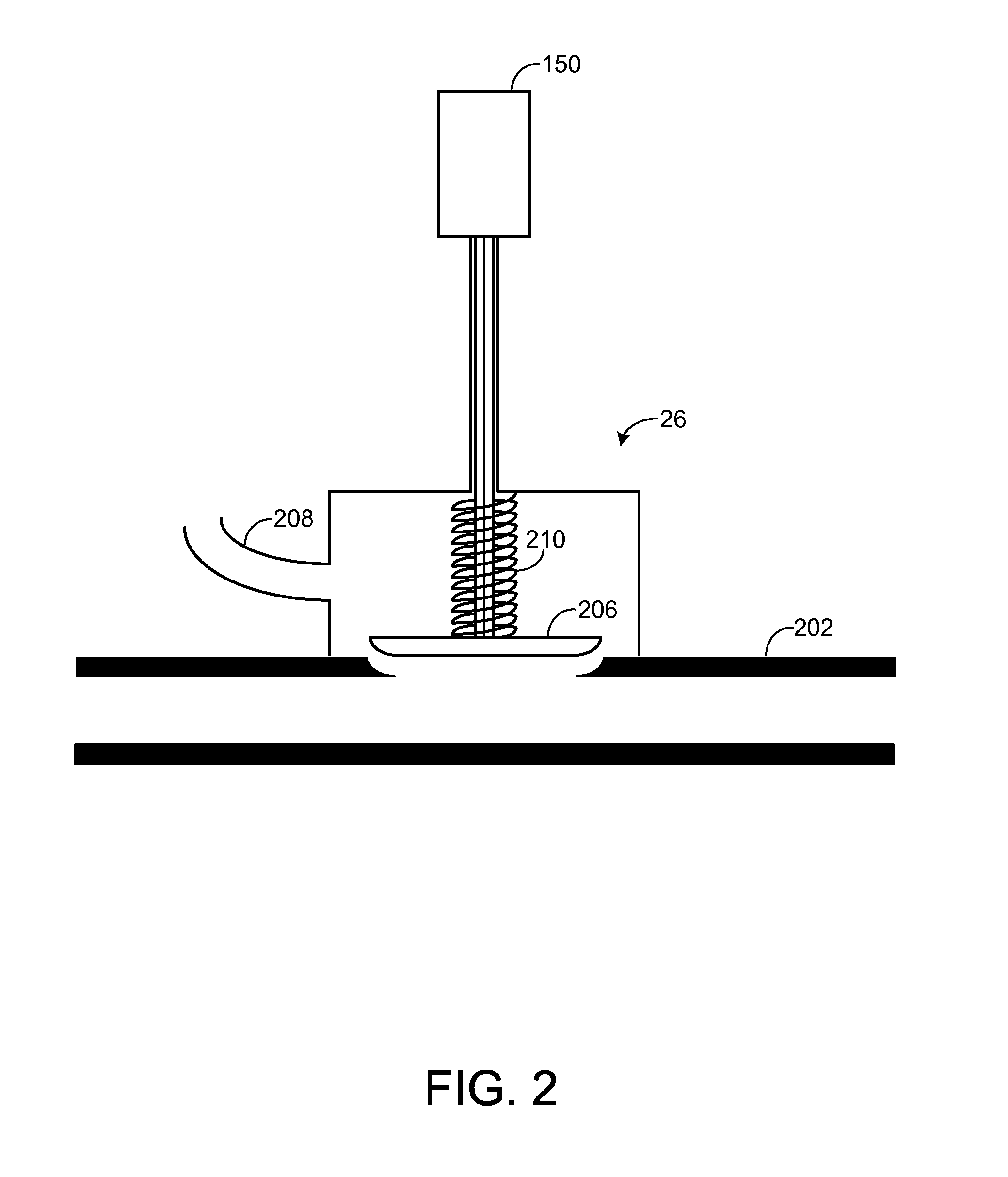
ActiveUS20140102092A1Improve engine torque/power output densityIncrease pressureInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersWastegateActuator
Various methods for controlling a wastegate with an electric actuator including a bias are provided. In one example, the actuator is supplied with a first current when moving a wastegate valve toward a fully open position, and is supplied with a second current when moving a wastegate toward a fully closed position. The methods may ensure appropriate supply of boost to an engine even in the event of wastegate degradation while enabling engine downsizing.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
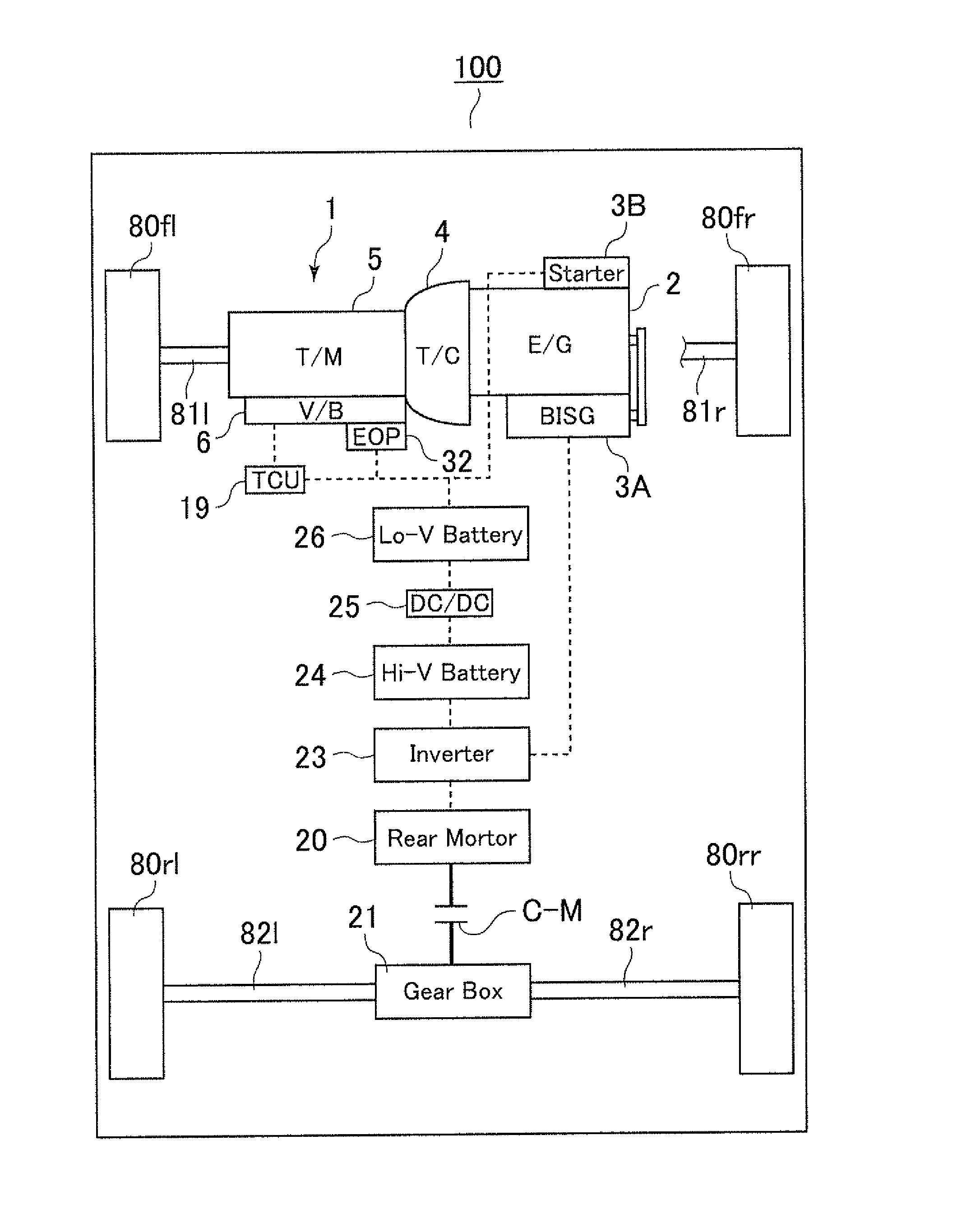
Automatic transmission for hybrid vehicle
ActiveUS8784249B2Electrical size reductionLow costFluid couplingsToothed gearingsAutomatic transmissionEngineering
An automatic transmission for a hybrid vehicle comprising a first hydraulic pressure supply source driven with an internal combustion engine; a second hydraulic pressure supply source driven independently of the first supply source; and a regulator valve regulating hydraulic pressure produced by the supply sources. A first oil passage supplying line pressure regulated by the regulator valve to a hydraulic servo operating a friction engagement element; a second oil passage supplying hydraulic pressure discharged from the regulator valve to a lubricated portion via an oil cooler; and a thud oil passage merged with the second oil passage at a point downstream of the oil cooler supplying the hydraulic pressure of the second supply source to the lubricated portion. A first reverse flow prevention mechanism is disposed between the oil cooler and the merging point to prevent reverse flow of hydraulic pressure.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
Electrical connector
InactiveUS7661972B2High strengthEasy to produceEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsCoupling contact membersElectrical connectionElectrical connector
Owner:HIROSE ELECTRIC GROUP
Electric power source device
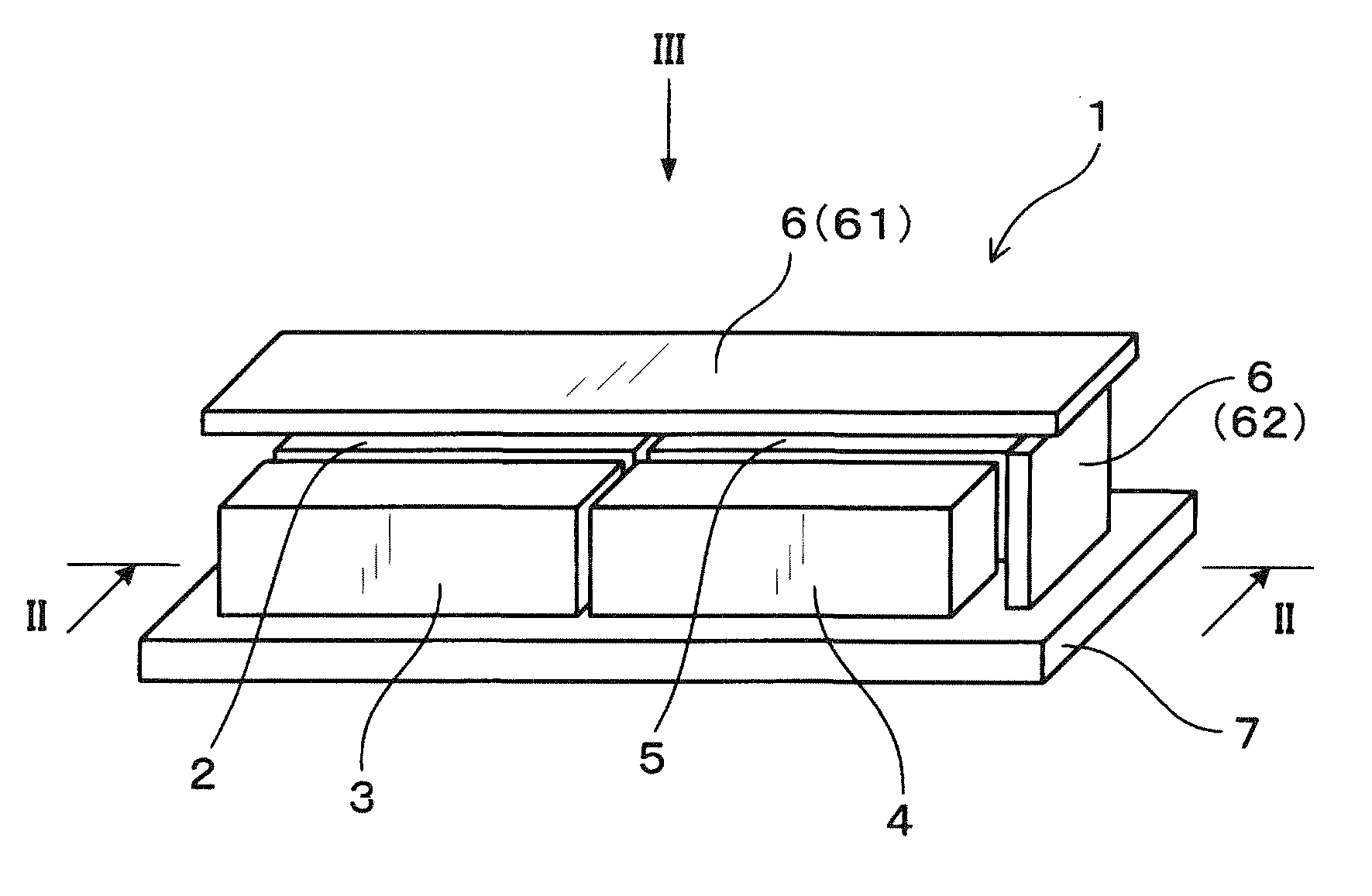
ActiveUS20150029759A1Simple structureEfficient use ofSpeed controllerPrinted circuit aspectsComputer moduleSecondary side
An electric power source device has a transformer, a primary-side semiconductor module, a secondary-side semiconductor module, a secondary-side electrical component, a base plate and a circuit substrate on which substrate-side electrical components are mounted. The primary-side semiconductor module has a larger exterior size than the secondary-side electrical component. The primary-side semiconductor module and the secondary-side electrical component form a stacked section. In the stacked section, the secondary-side electrical component is stacked, in a vertical direction, i.e. a direction of a normal line of a mounting surface of the base plate, on the primary-side semiconductor module. The primary-side semiconductor module is directly mounted on the mounting surface. At least a part of the substrate-side electrical components is arranged inside of the primary-side semiconductor module in a horizontal direction, and inside of a second surface of the stacked section toward the mounting surface along the normal line.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electrical Connector
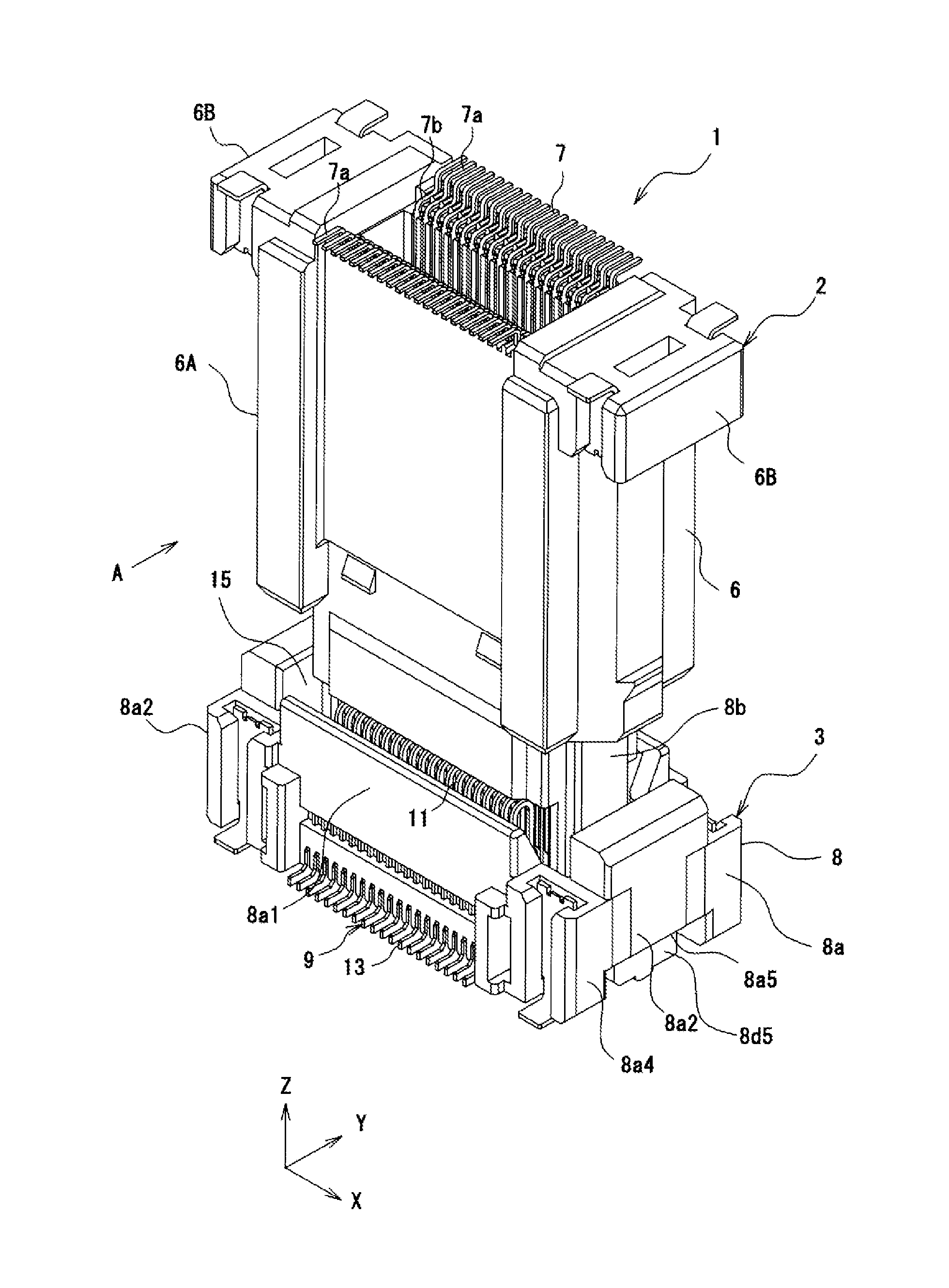
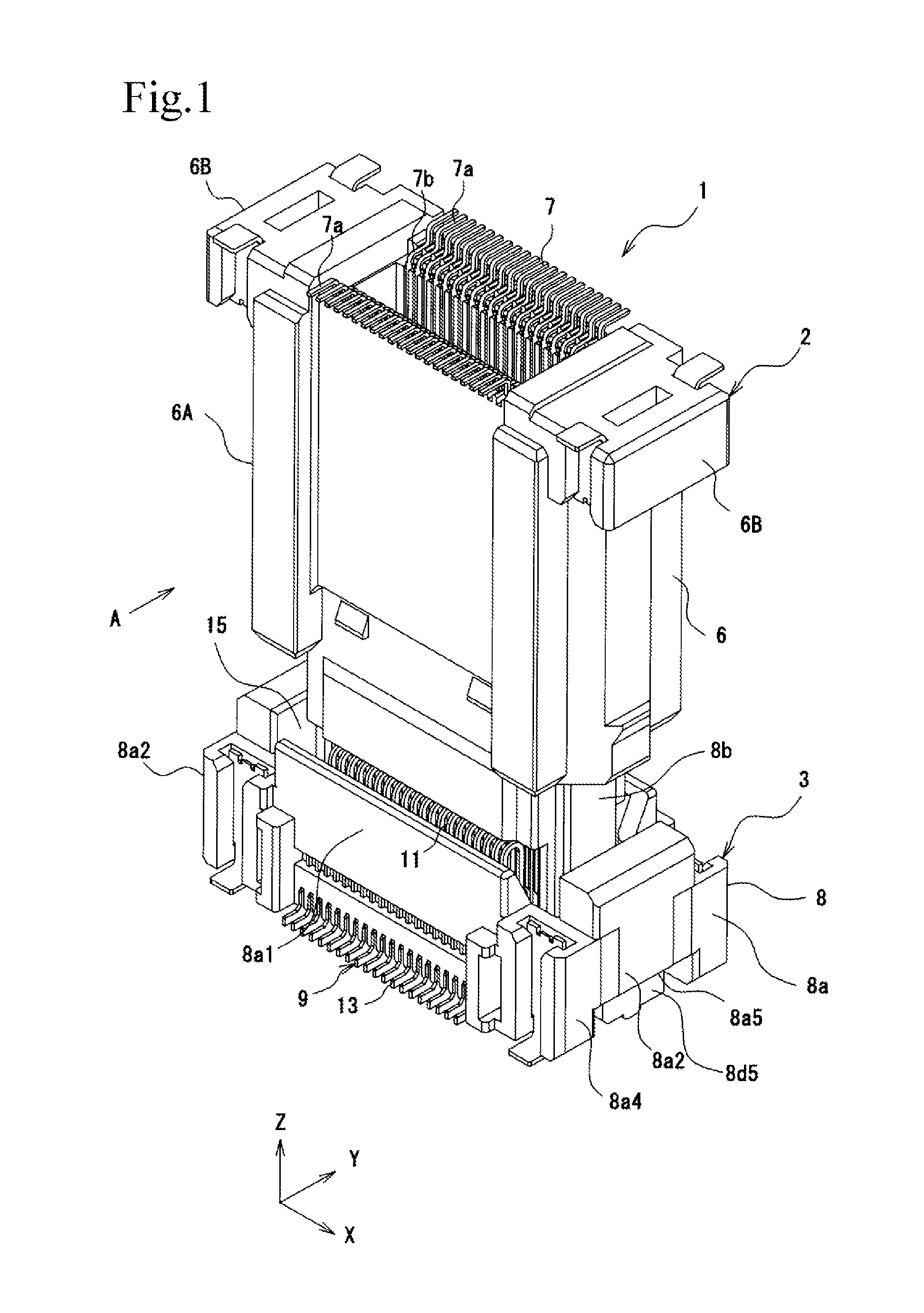
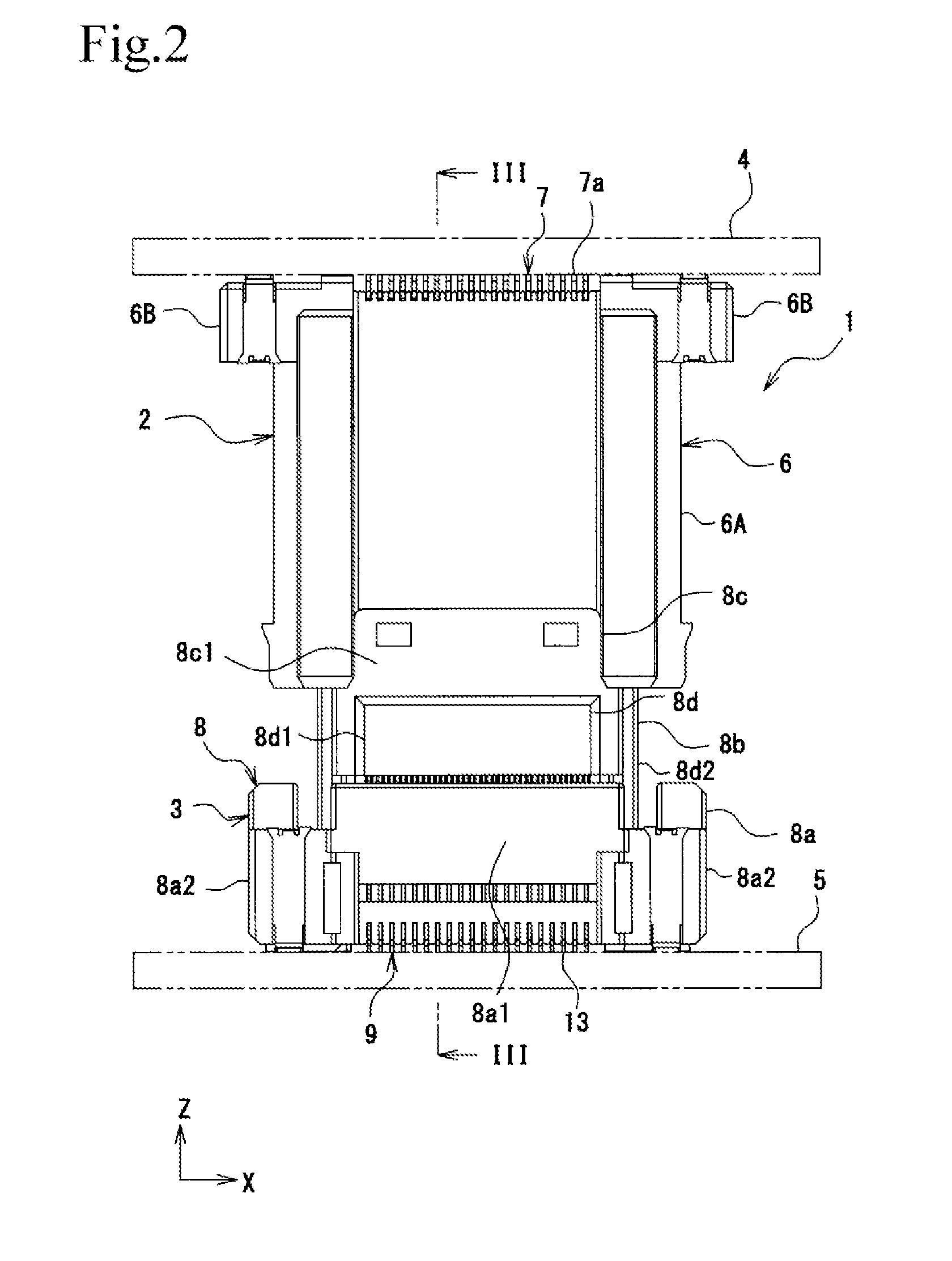
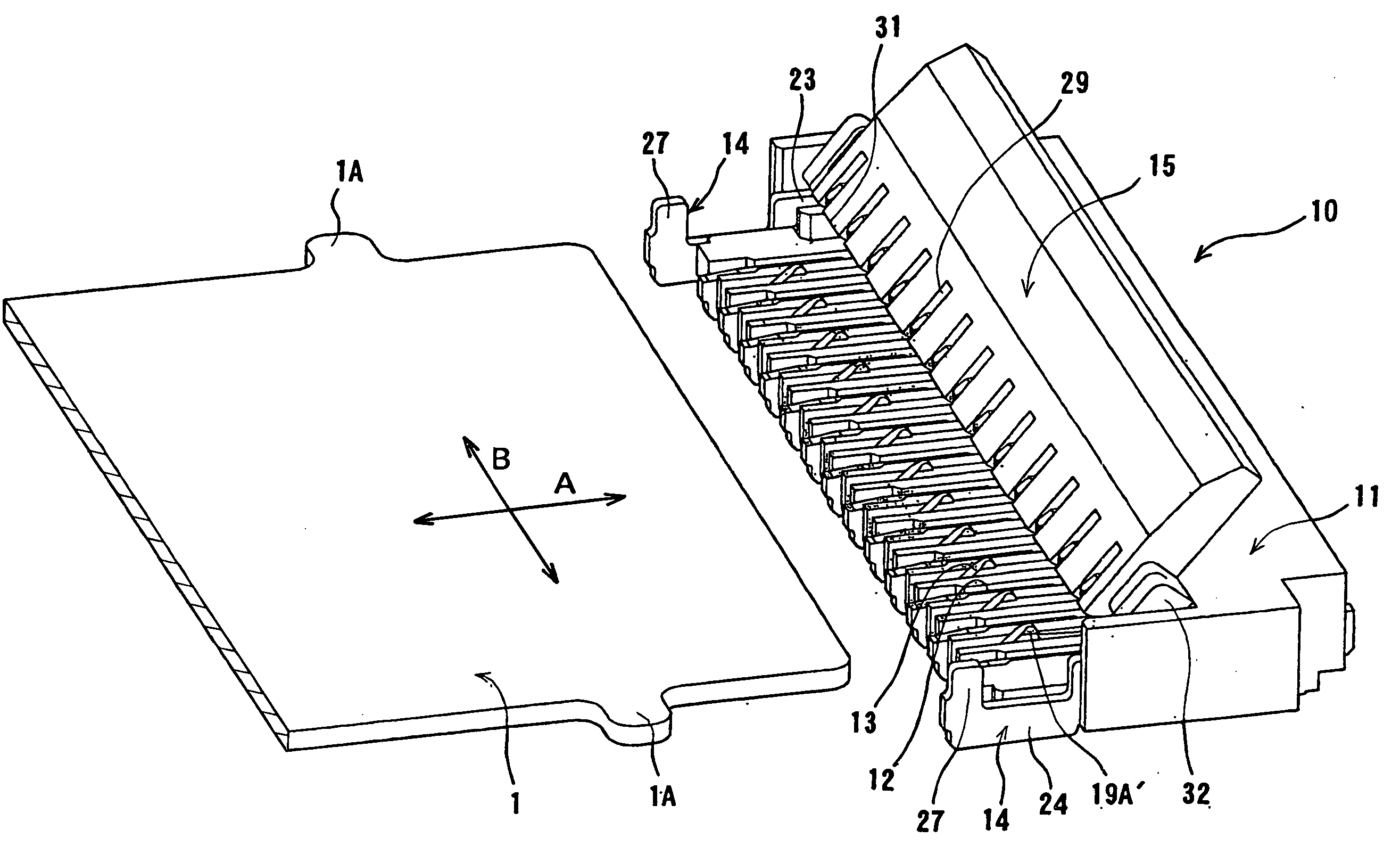
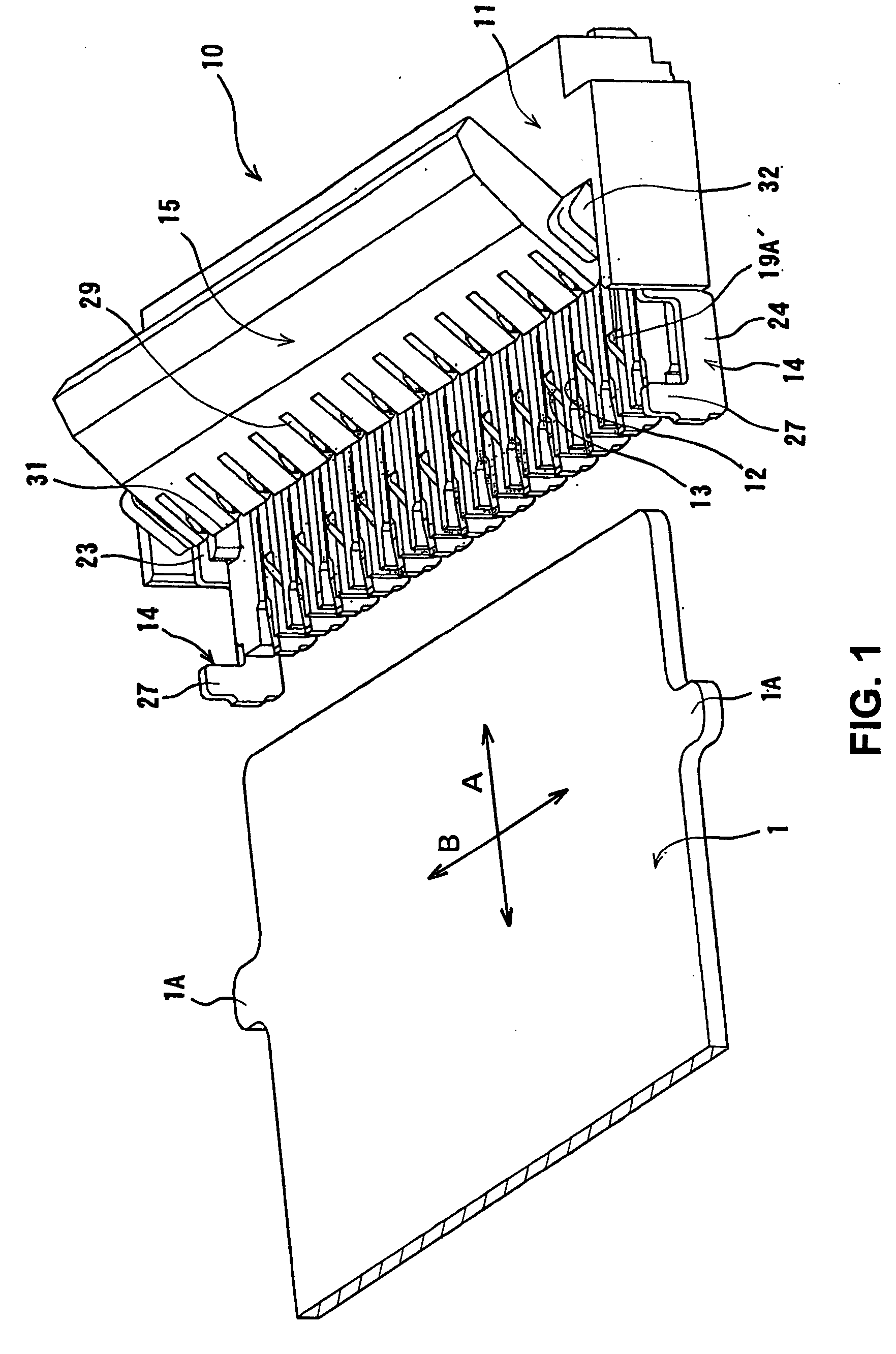
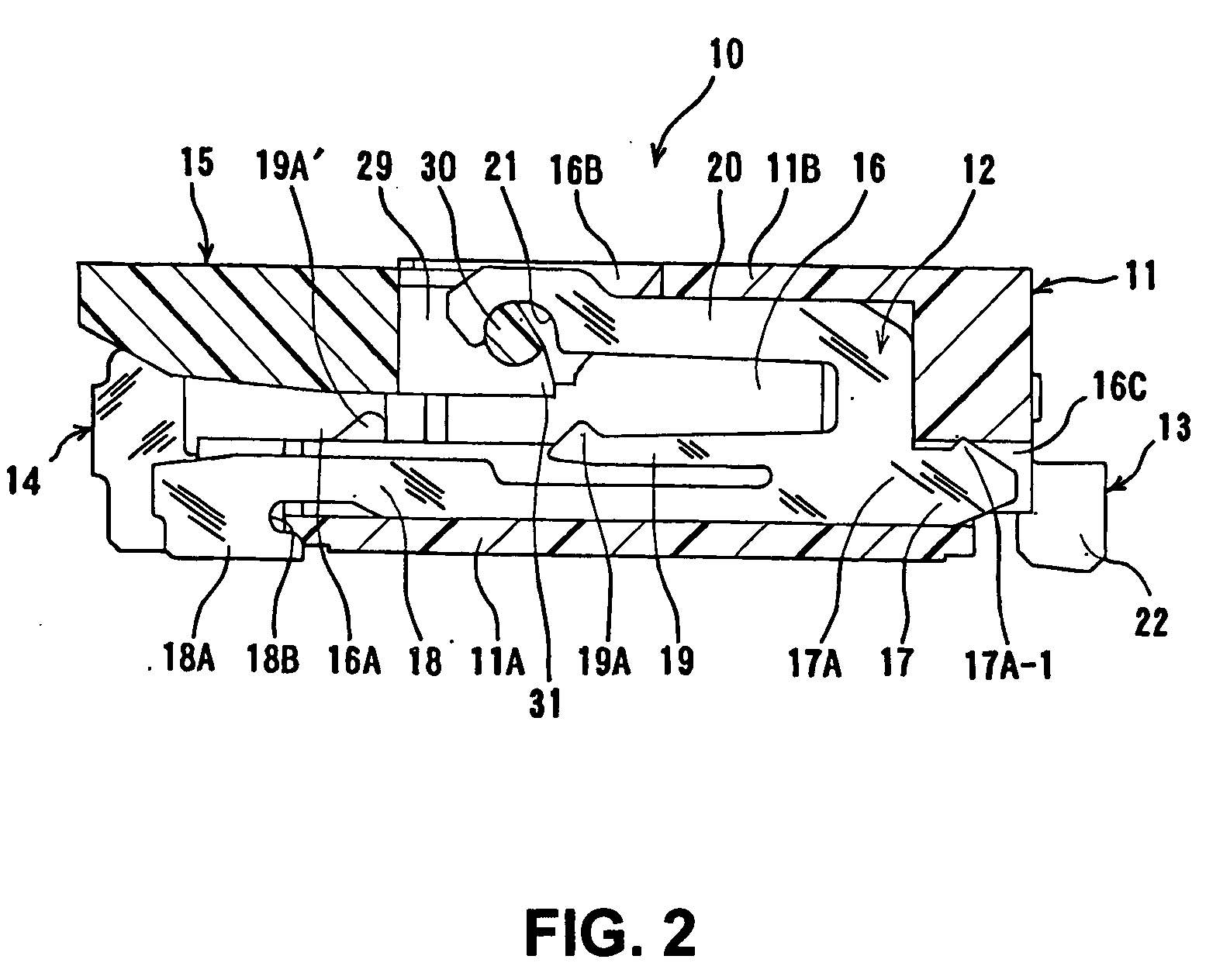
ActiveUS20150132976A1Electrical size reductionImprove reliabilityCoupling device detailsSoldered/welded conductive connectionsEngineeringElectrical connector
An electrical connector includes a socket housing and socket terminals. Each socket terminal includes a front terminal and a rear terminal. The front terminal contacts a plug connector inserted into the socket housing. The front terminal includes front contact-point portion that contacts the plug connector and an elastic piece that supports the front contact-point portion so as to be elastically displaceable. The rear terminal includes a rear contact-point portion and an elastic piece that supports the rear contact-point portion so as to be elastically displaceable. The rear contact-point portion contacts the plug connector after the front contact-point portion has contacted the plug connector. The front contact-point portion and the elastic piece, and the rear contact-point portion and the elastic piece are each formed so as to maintain a plate surface of a flat metal plate.
Owner:IRISO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electric parking brake for vehicles having operating load measuring device
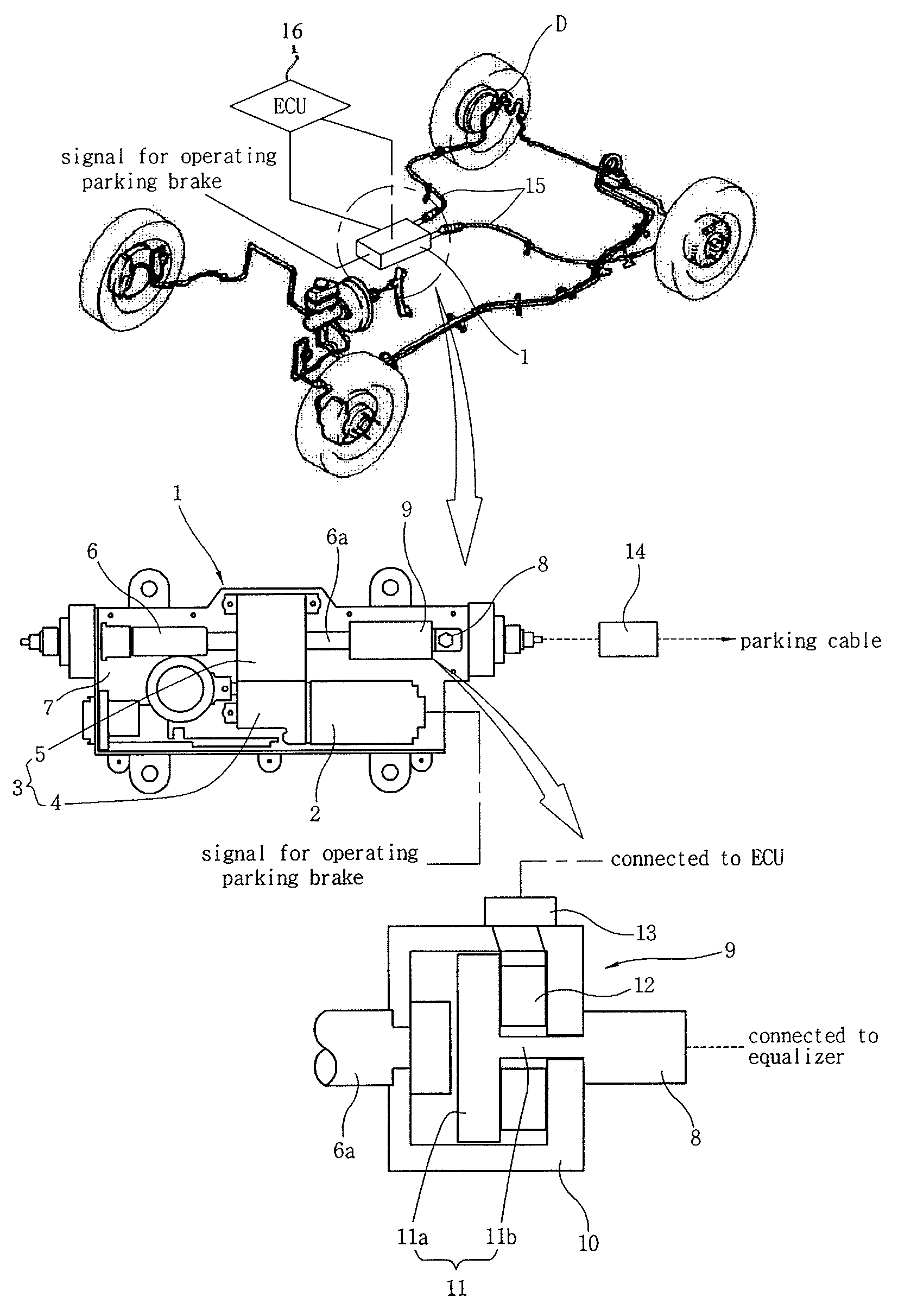
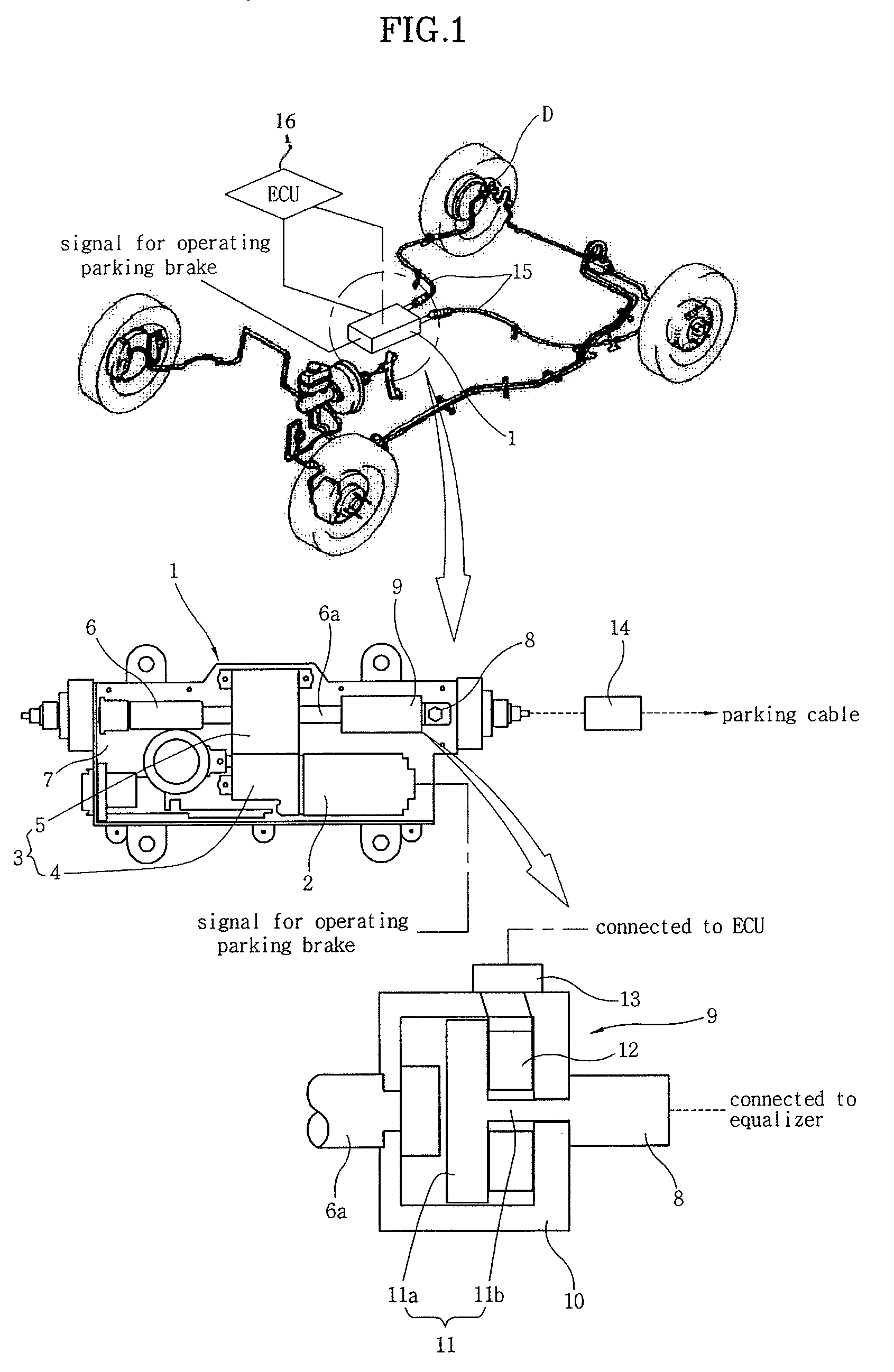
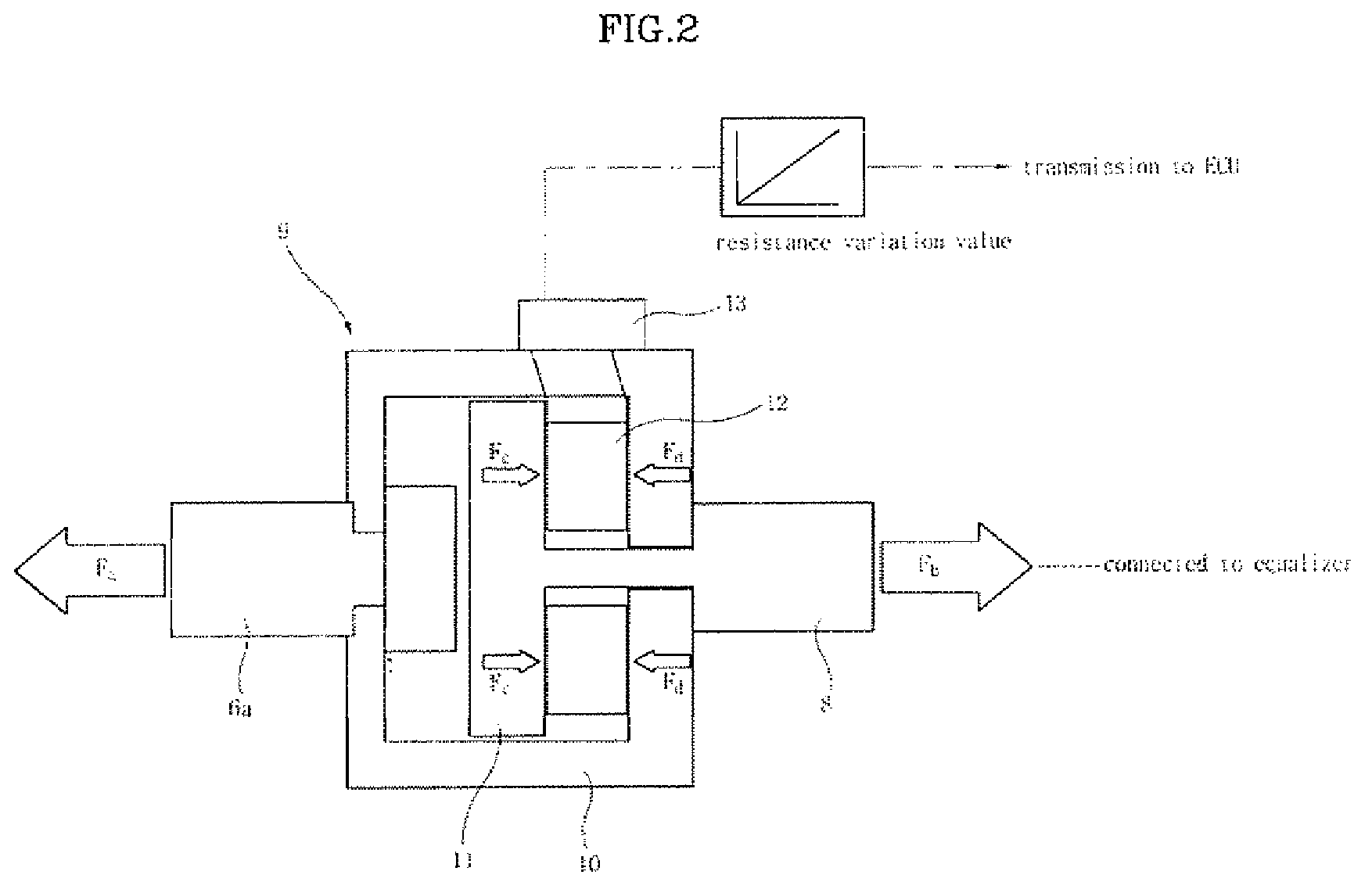
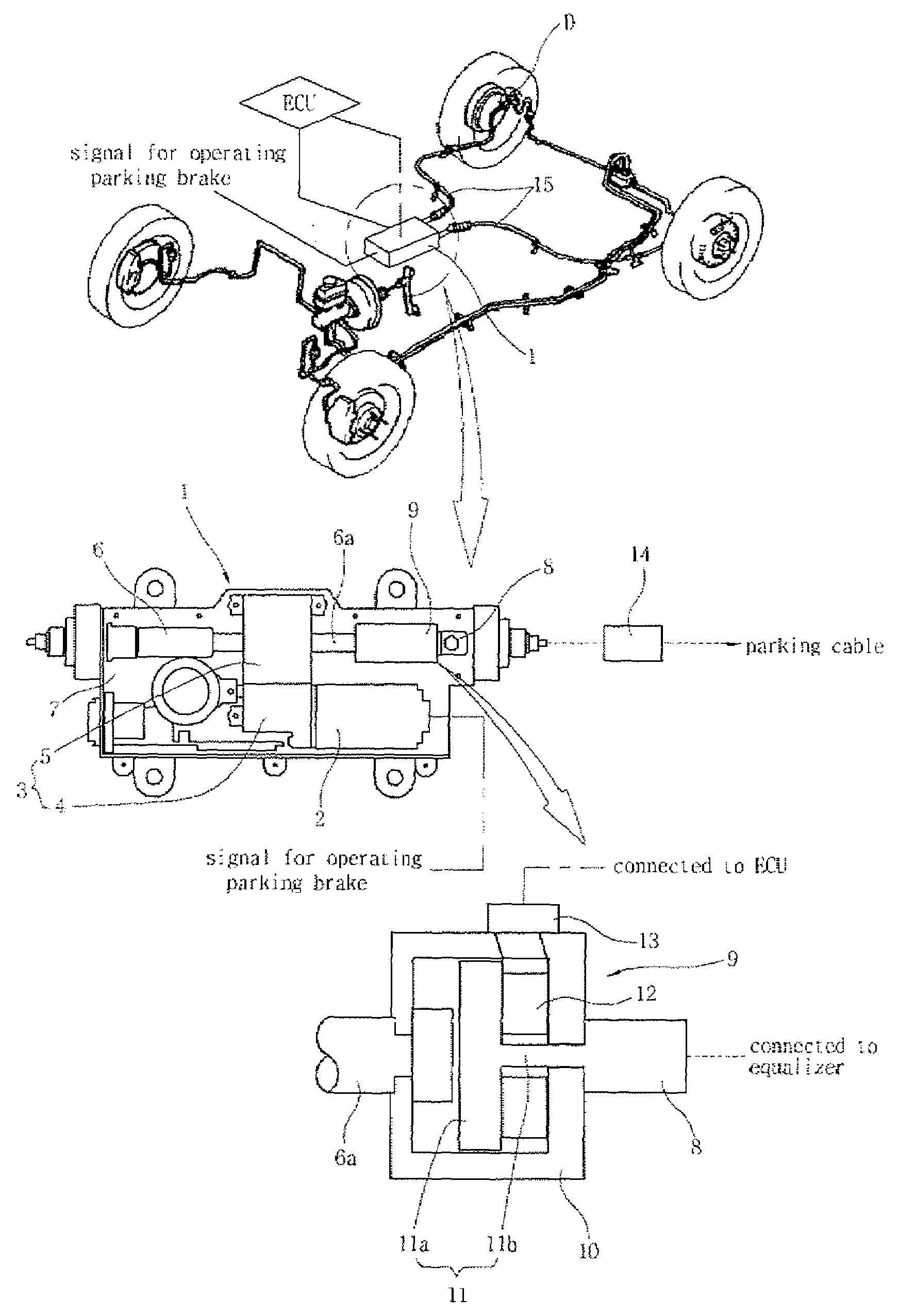
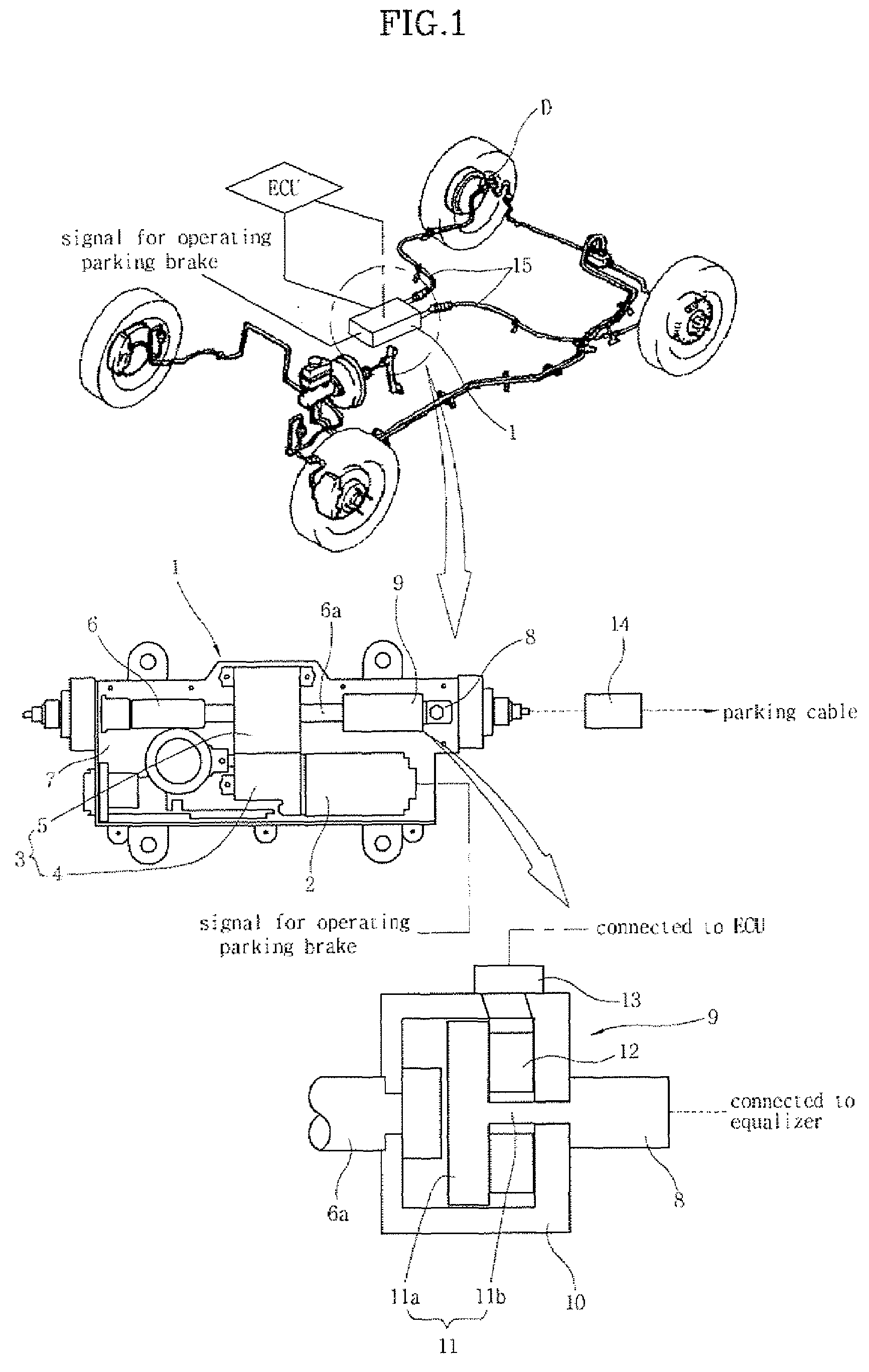
InactiveUS7458649B2Ensure reliabilityReduce in quantityBraking action transmissionElectrodynamic brake systemsElectric parking brakeAutomotive engineering
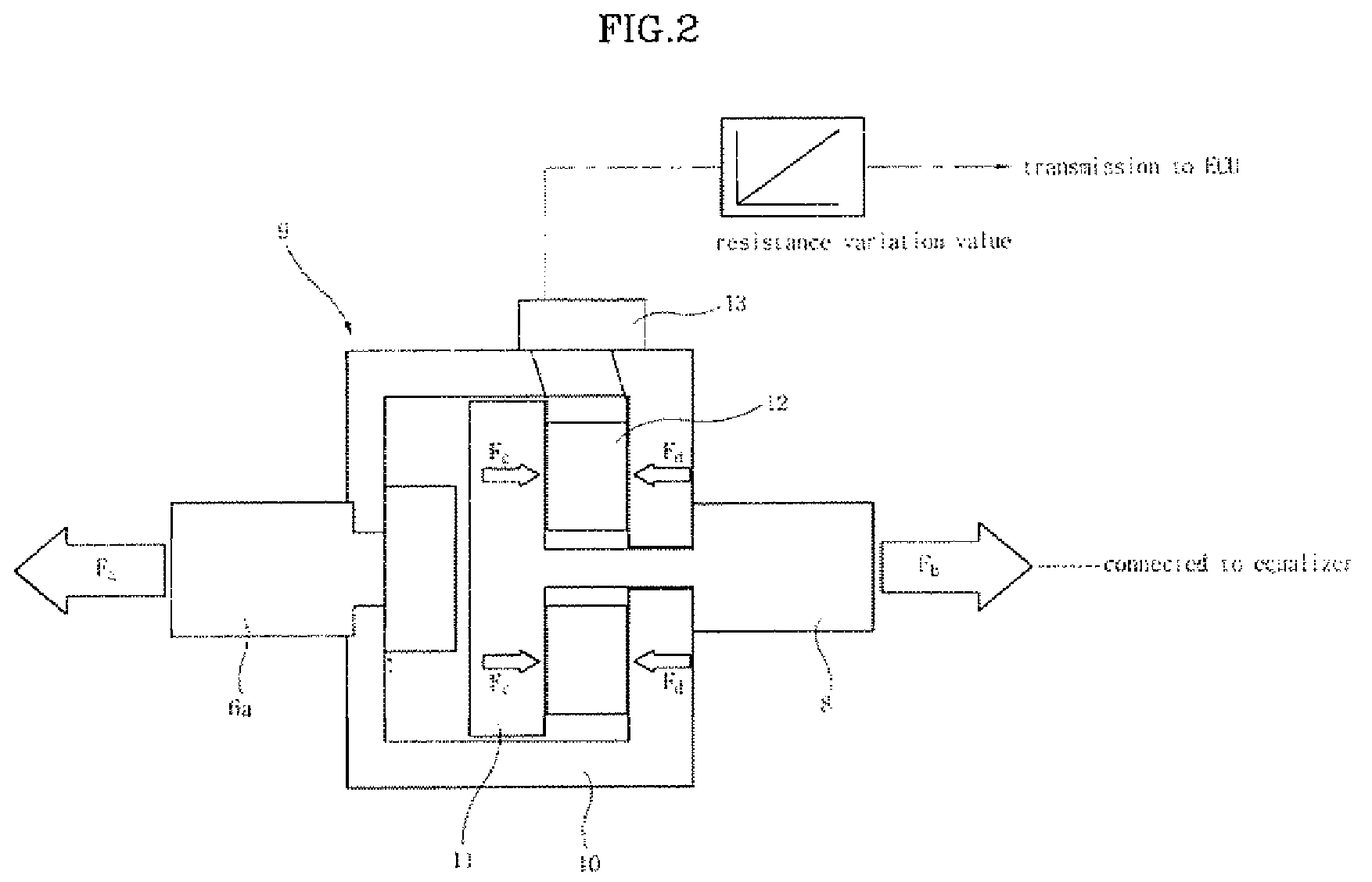
An electric parking brake includes an actuating device, which provides a force to lock and unlock the parking brake using power supplied by manipulation of a control button, and an equalizer, which is coupled at a first end thereof to the actuating device and is coupled at a second end thereof to a parking cable to pull or release the parking cable, which operates a braking device of a wheel, depending on operation of the actuating device. The electric parking brake further includes an operating load measuring unit, which measures operating load that pulls the equalizer in the parking cable and sends the measured signal to an ECU that controls the actuating device.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Multiband antenna structure
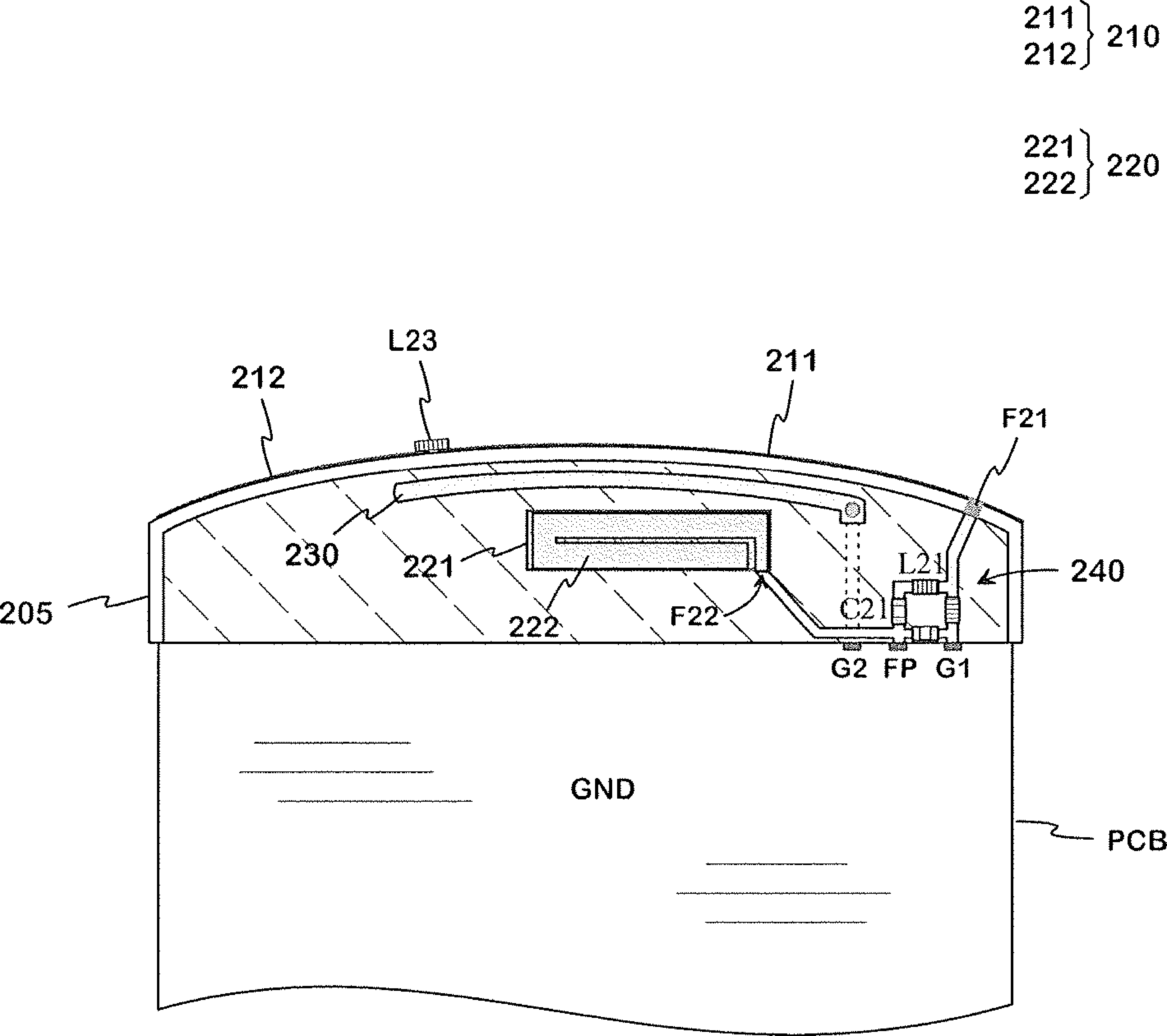
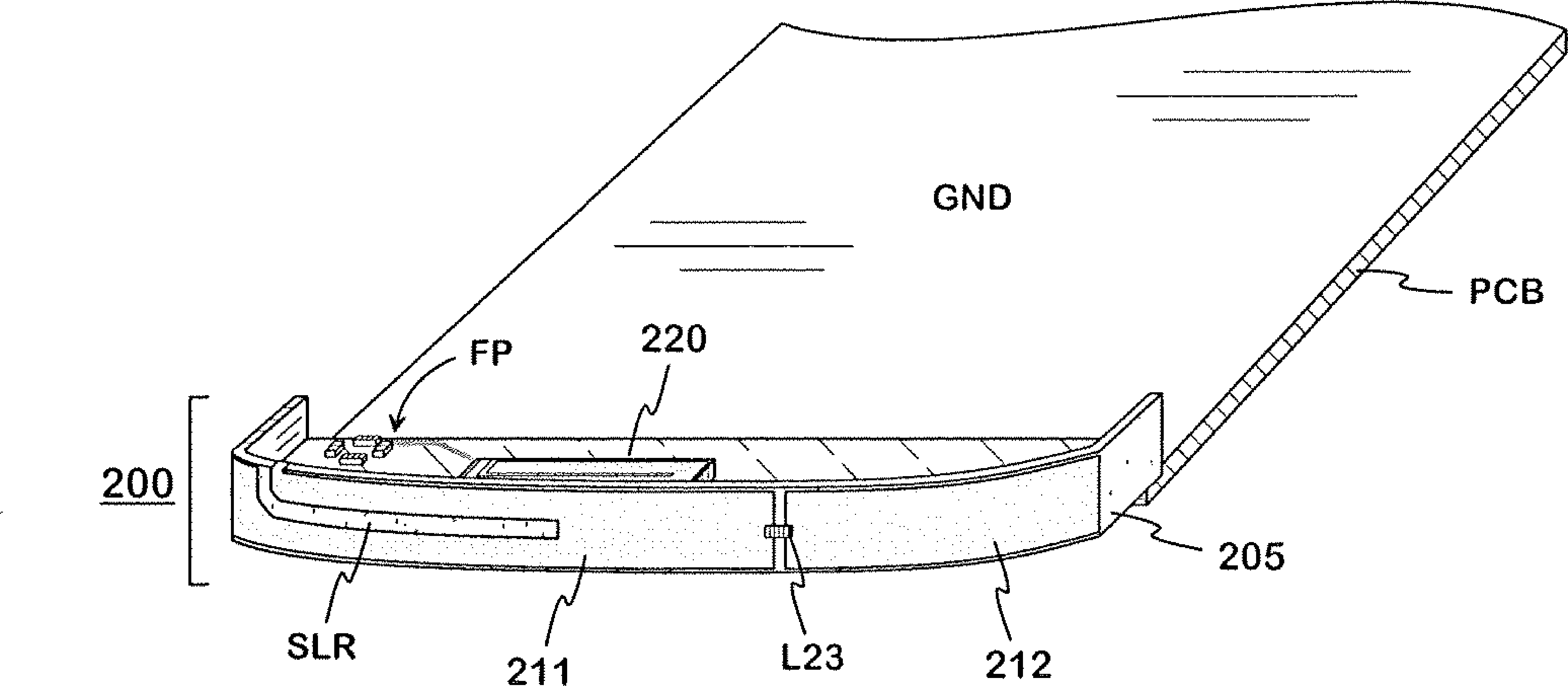
InactiveCN102742074AImprove isolationElectrical size reductionSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsElectricityEngineering
An antenna structure intended for small-sized mobile terminals. It comprises a main radiator (210) for implementing the lowest operating band and other radiators for implementing at least one operating band in the high band. The structure comprises also a matching circuit, by which a double resonance is implemented for the main radiator in the range of the lowest operating band and the isolation is improved between the main radiator and another radiator. A reactive element (L23) is joined to the main radiator so that its electric size decreases in the high band and increases in the low band. The former matter strengthens the resonances in the high band and thus results in rise in the efficiency in the high band.
Owner:PULSE FINLAND
Electric power equipment, and electronic device and power supply element inspection equipment using same
InactiveUS20110000801A1Electrical size reductionSmall sizeElectric devicesSecondary cellsElectric power equipmentPower equipment
An electric power equipment has a main body case, a plurality of power supply elements provided in the main body case, and a fire-extinguishing agent discharge space disposed facing the plurality of power supply elements. The fire-extinguishing agent discharge space includes fire-extinguishing agent spray space having a plurality of fire-extinguishing agent spray holes for spraying a fire-extinguishing agent toward the plurality of power supply elements, and a fire-extinguishing agent supply space coupled to the fire-extinguishing agent spray space via a plurality of fire-extinguishing supply holes. A fire-extinguishing agent tank is coupled to the fire-extinguishing agent supply space via a shutoff valve.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Electrical connector
InactiveUS20070254534A1Easy to produceSmall sizeEngagement/disengagement of coupling partsCoupling contact membersEngineeringElectrical connector
An electrical connector for connecting a flat conductive member includes a plurality of terminals formed of a flat metal plate arranged on a housing in a direction perpendicular to a plate direction. Each of the terminals has a contact portion disposed at a position for receiving the flat conductive member to be inserted into a receptacle portion of the housing. A metal member having an engaging portion is attached to the housing for engaging an engagement portion of the flat conductive member, so that the flat conductive member does not come off backward. A pressing member is supported on at least one of the housing and the terminals to be rotatable. The metal member further includes an attaching portion attached to the housing. The metal member is attached to the housing such that the attaching portion is situated in parallel to a plate surface of the terminals.
Owner:HIROSE ELECTRIC GROUP
Electric power source device equipped with transformer
ActiveUS20150029757A1Simple structureElectrical size reductionTransformers/reacts mounting/support/suspensionCircuit arrangements on support structuresEngineeringSmoothing circuits
An electric power source device has a transformer, primary side semiconductor components, secondary side semiconductor components, a choke coil, a base plate and first circuit substrate and one or more second circuit substrates. The transformer has a primary side coil and a secondary side coil. The primary side semiconductor components form a primary side circuit connected to the primary side coil. The secondary side semiconductor components form a secondary side circuit connected to the secondary side coil. The choke coil has a smoothing circuit for smoothing an output voltage. The transformer, the primary side semiconductor components, the secondary side semiconductor components and the choke coil are formed on the base plate. The first circuit substrate is arranged parallel to the base plate. The second circuit substrate is arranged parallel to a normal line of the first circuit substrate.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Electric parking brake for vehicles having operating load measuring device
InactiveUS20070296269A1Ensure reliabilityReduce in quantityBraking action transmissionElectrodynamic brake systemsElectric parking brakeEngineering
An electric parking brake includes an actuating device, which provides a force to lock and unlock the parking brake using power supplied by manipulation of a control button, and an equalizer, which is coupled at a first end thereof to the actuating device and is coupled at a second end thereof to a parking cable to pull or release the parking cable, which operates a braking device of a wheel, depending on operation of the actuating device. The electric parking brake further includes an operating load measuring unit, which measures operating load that pulls the equalizer in the parking cable and sends the measured signal to an ECU that controls the actuating device.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOBIS CO LTD
Structural absorbing material
ActiveCN102291969AReduce sensitivityReduced incidence angle sensitivityMagnetic/electric field screeningEntrance angleElectromagnetic electron wave
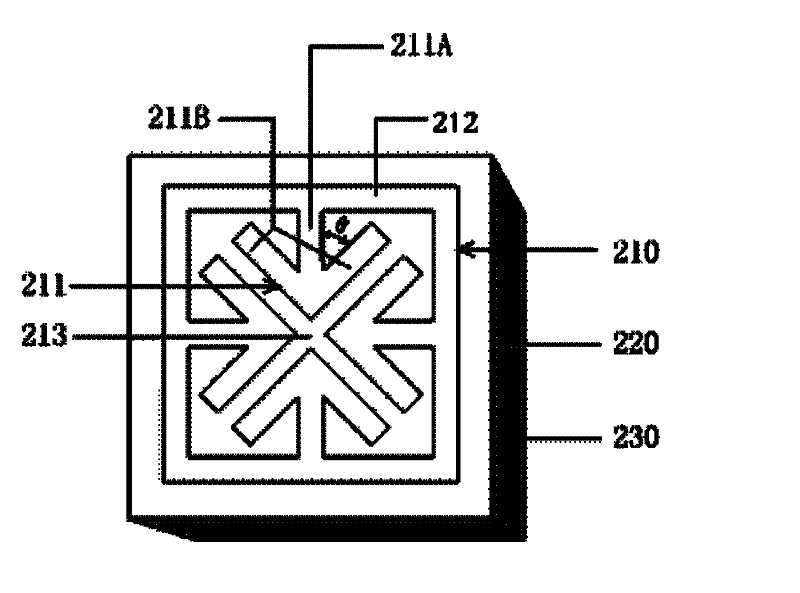
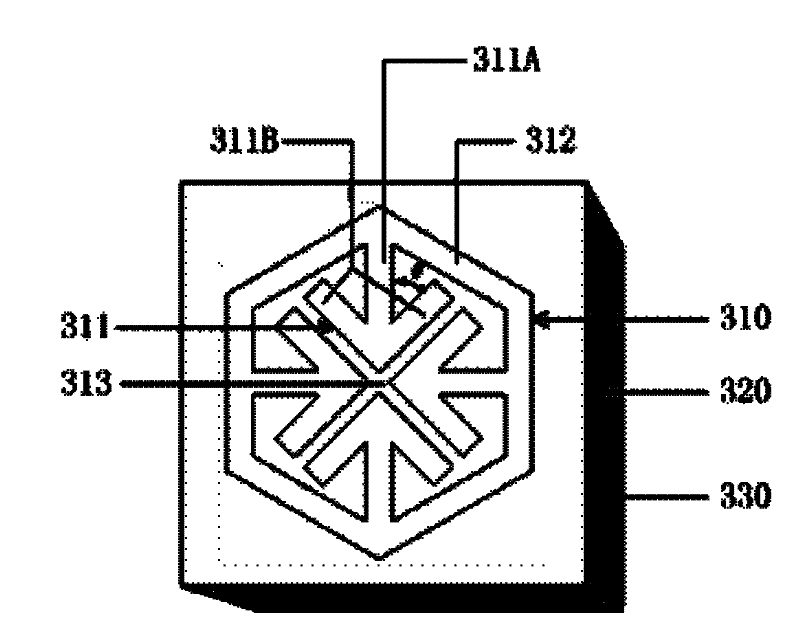
The invention discloses a structural wave-absorbing material, which mainly overcomes the defects of the prior art that only electromagnetic waves with a single polarization angle can be absorbed, the wave-absorbing entrance angle is narrow and only one wave-absorbing peak point exists. The structural wave-absorbing material is made of a medium substrate (220), the back face of the medium substrate (220) is a fully-metallic base plate (230), and the frontal face of the medium substrate (220) comprises an etched metallic pattern (210), wherein the metallic pattern (210) consists of four metallic line arrows (211) which point at the center and a regular polygonal metallic line frame (212) with sides having an even number which is more than 3 or a circular annular metallic line frame (512); two short lines (211B) at top ends of the four metallic line arrows form a symmetrical +-shaped cross structure, the middle of which is provided with a +-shaped gap (213) and the tail end of a middle bar (211A) of each metallic line arrow is connected with the metallic line frame. Compared with the prior art, the structural wave-absorbing material has the advantages of capability of absorbing electromagnetic waves with a random polarization angle, widening the wave-absorbing entrance angle and having two wave-absorbing peak points.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Device for use in electro-biological signal measurement in the presence of a magnetic field
ActiveUS9636019B2Electrical size reductionReduce Motion ArtifactsElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using suctionEeg dataEngineering
A device is presented for use in an EEG measurement performed in the presence of a magnetic field. The device includes a wiring array for connecting an electrodes arrangement to an electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring device. The wiring array includes sampling lines arranged to form first and second groups of sampling lines, arranged in a spaced-apart substantially parallel relationship extending along first and second axes respectively, at least some of the sampling lines being wire bundles including a plurality of wires for connecting to a corresponding plurality of electrodes of the EEG electrodes arrangement; the first and second groups of sampling lines intersect with each other to form a net structure when placed on area of measurement. The wiring array thereby enable generation of EEG data characterized by reduced motion artifact and / or reduced gradient artifact associated with the presence of the magnetic field during the EEG measurement.
Owner:THE MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & HEALTH SERVICES FUND OF THE TEL AVIV MEDICAL CENT
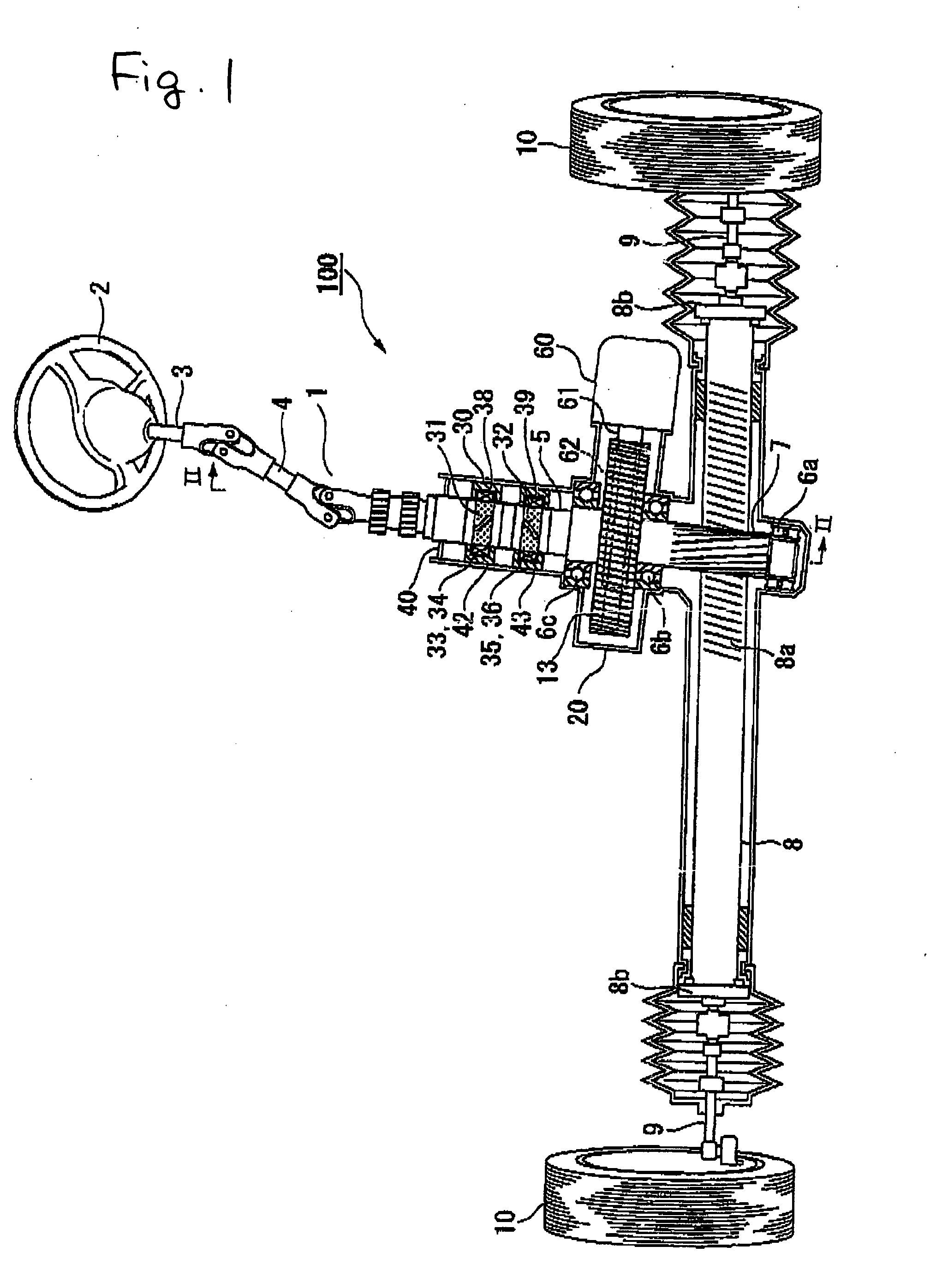
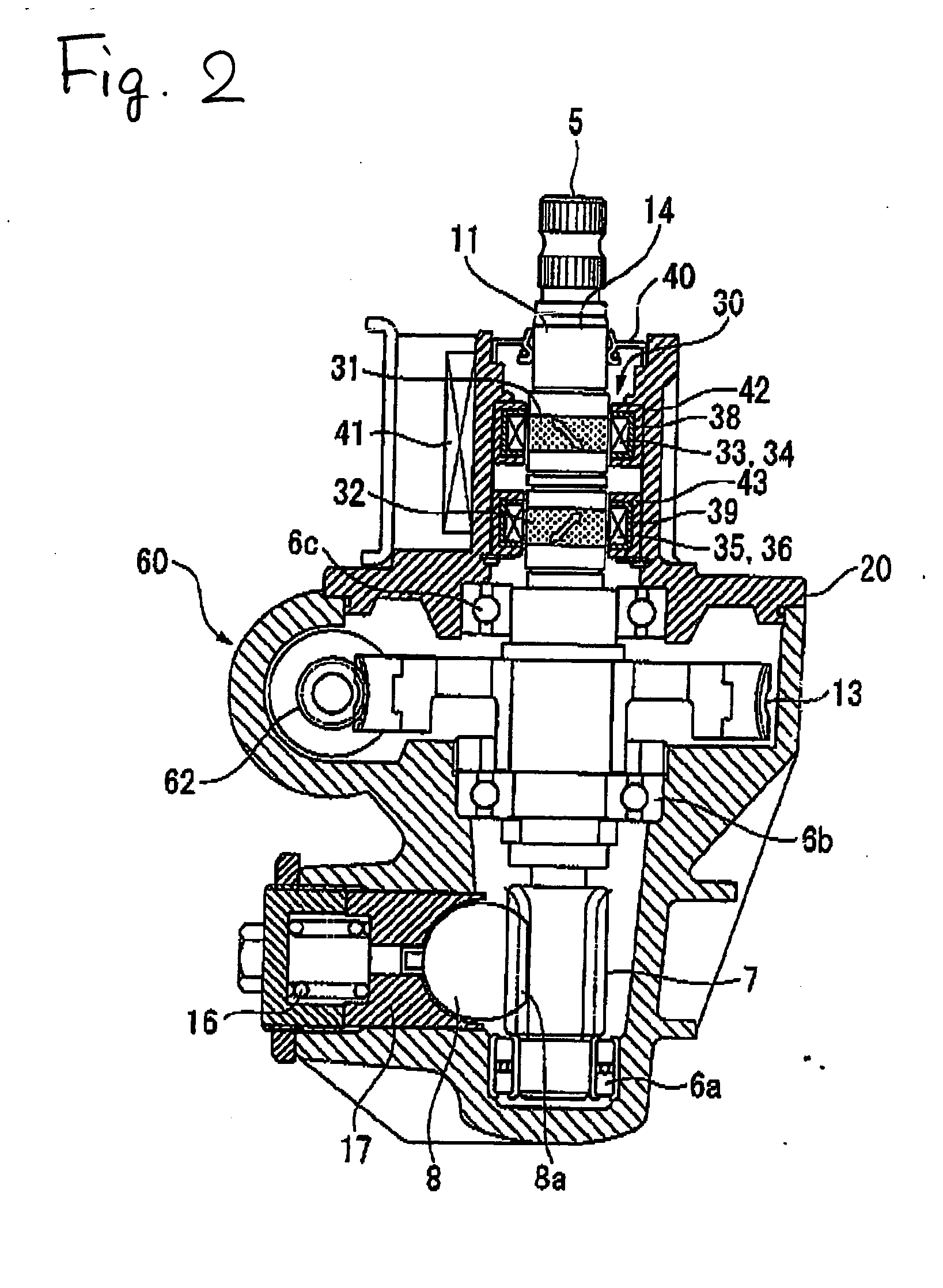
Magnetostrictive torque sensor and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20070295111A1Reduce the differenceElectrical size reductionWork measurementAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringMagnetic anisotropy
A magnetostrictive torque sensor having a first magnetostrictive film and a second magnetostrictive film, which are both provided on a shaft and have different magnetic anisotropies. A first detection coil and a second detection coil are arranged to face the first magnetostrictive film, and a third detection coil and a fourth detection coil are arranged to face the second magnetostrictive film. The first and second detection coils are wound around the same coil bobbin, while the third and fourth detection coils are wound around another common coil bobbin.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com