Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Improve transistor characteristics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
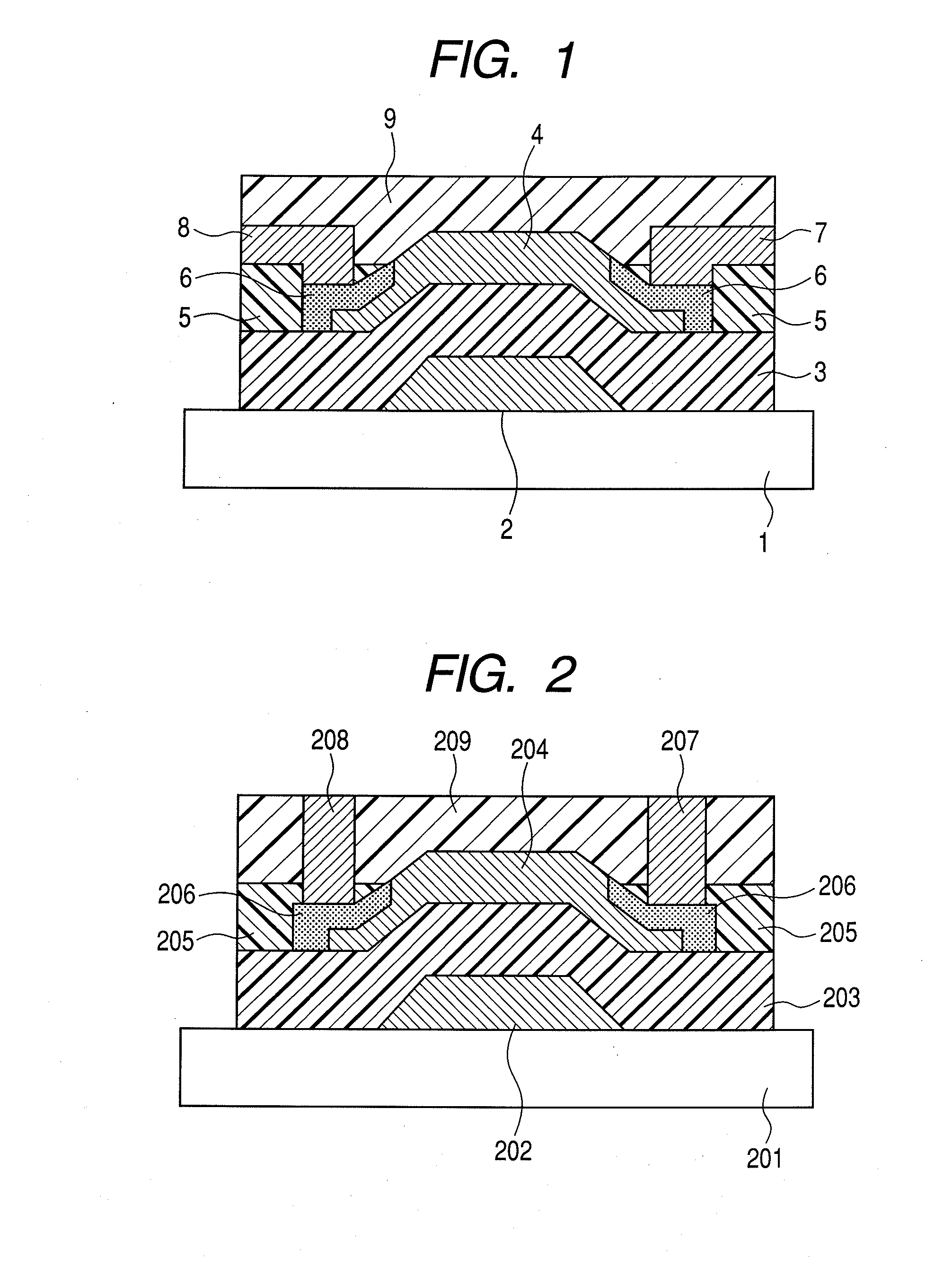
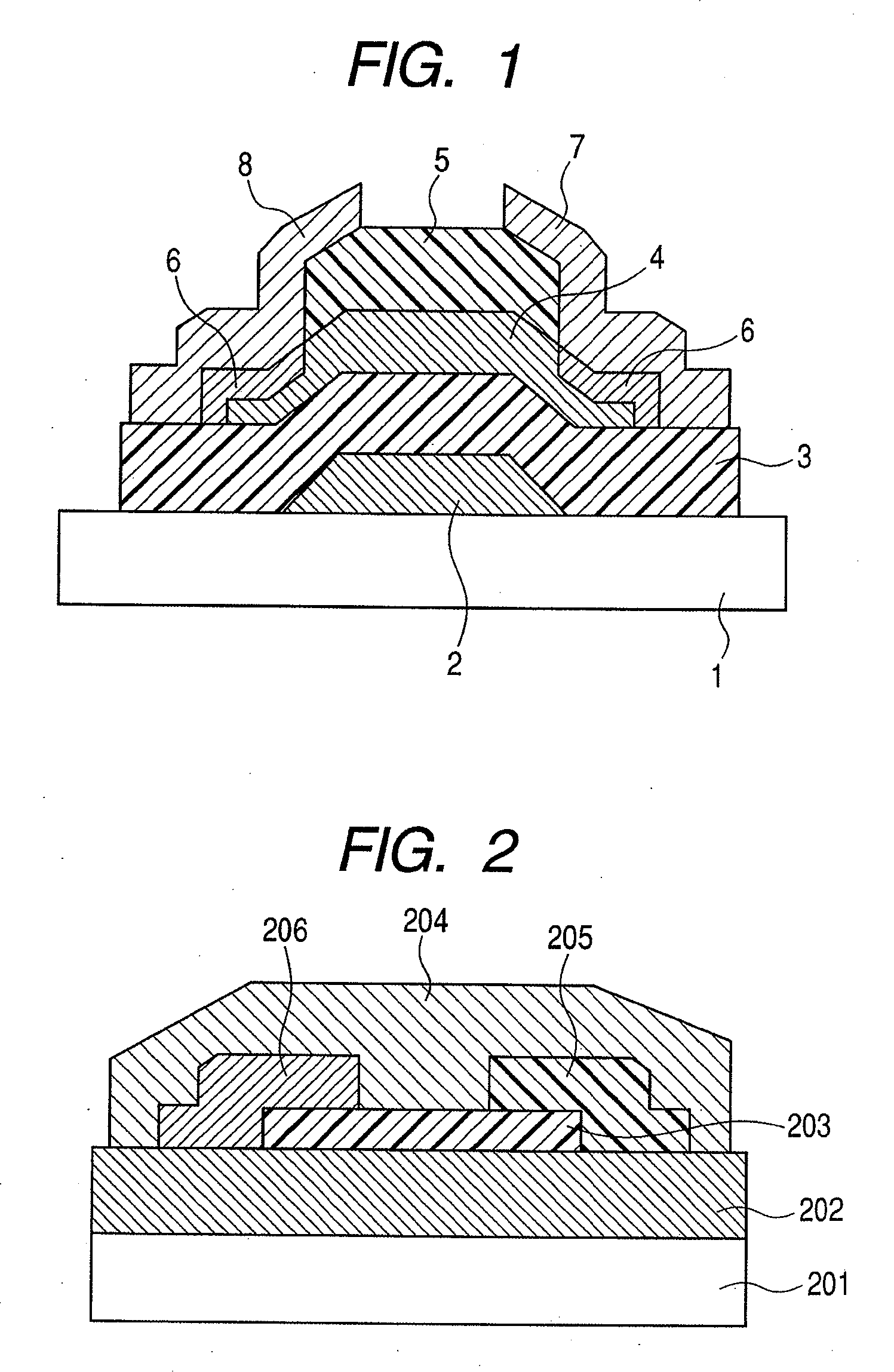
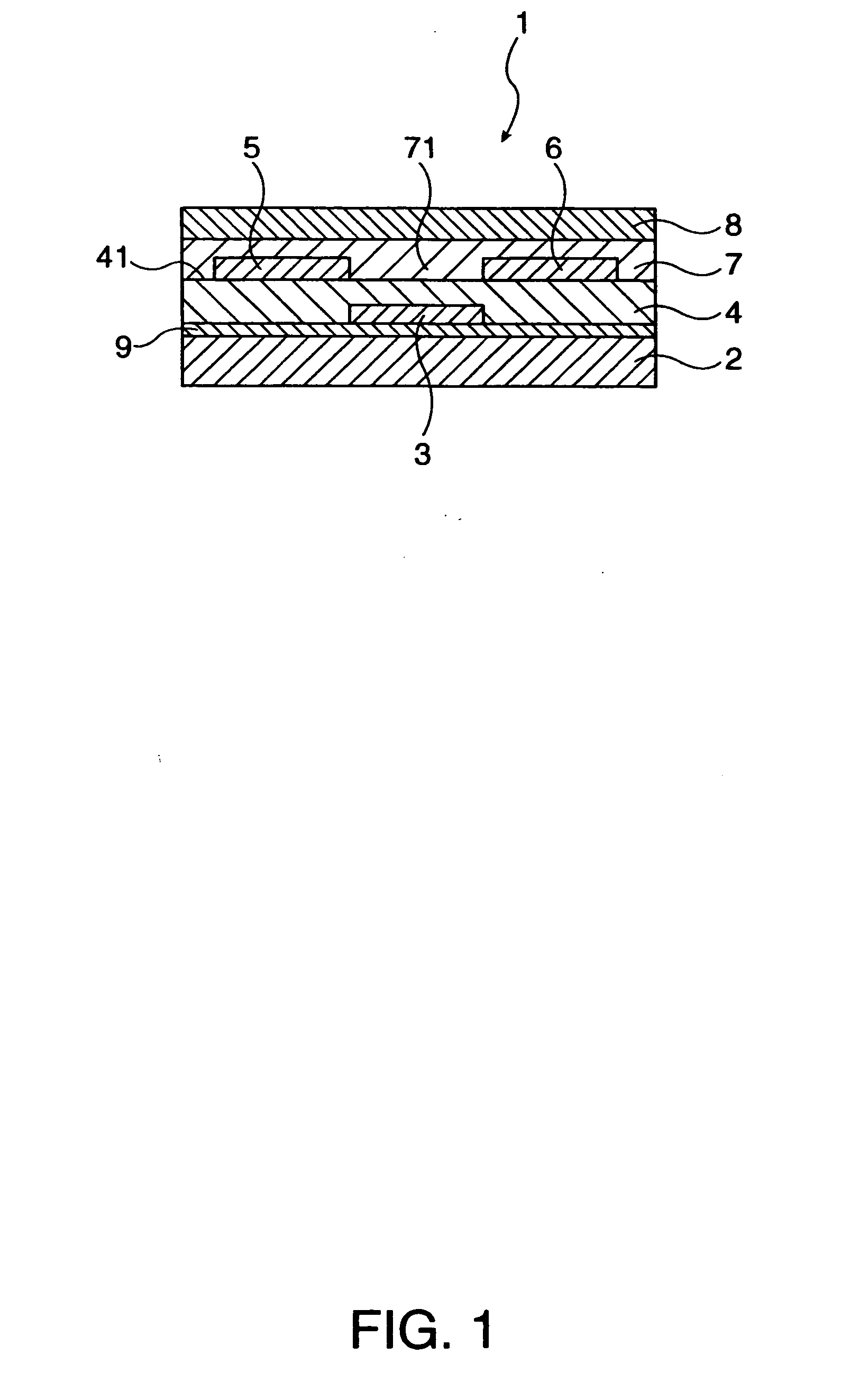
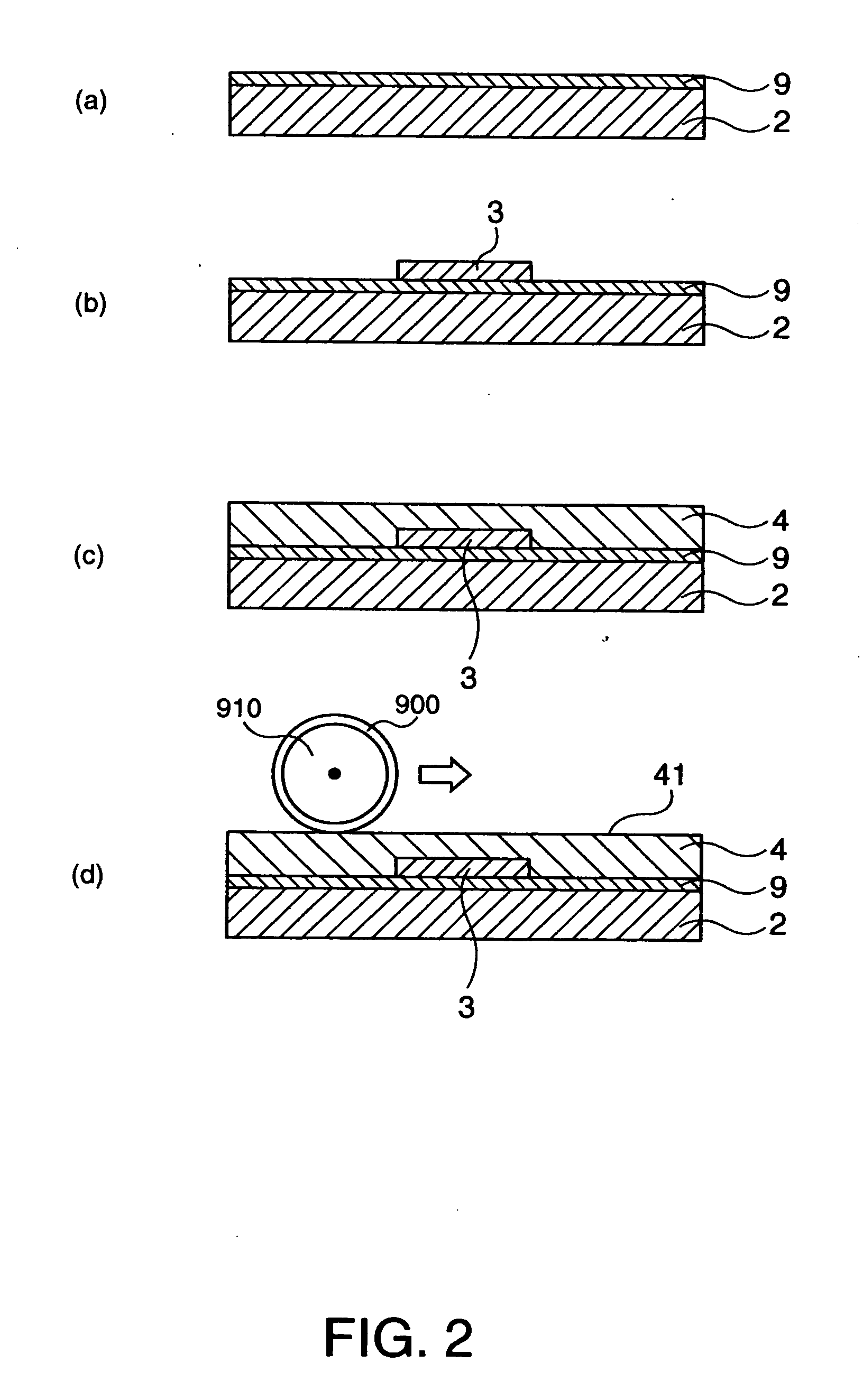
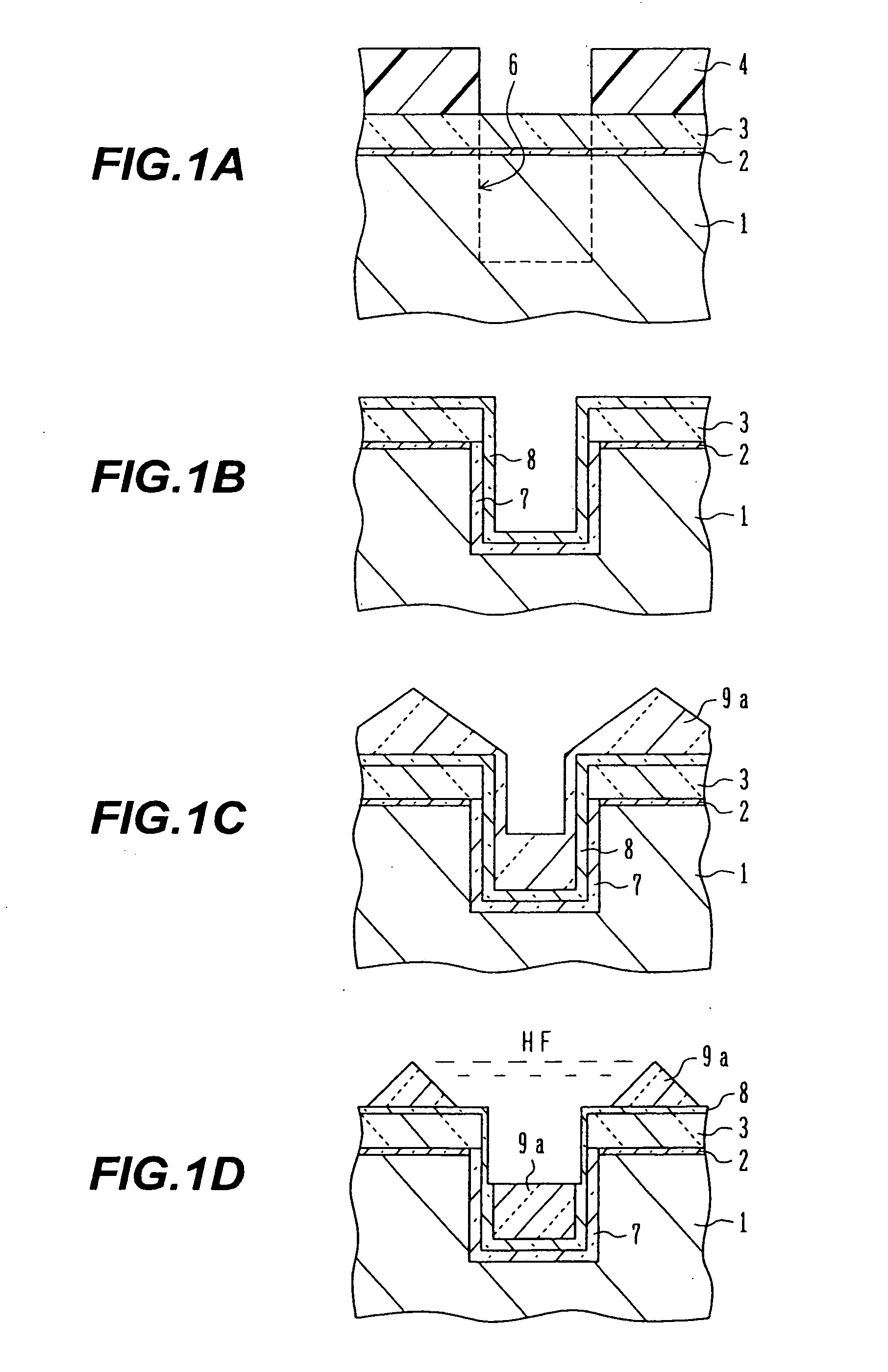
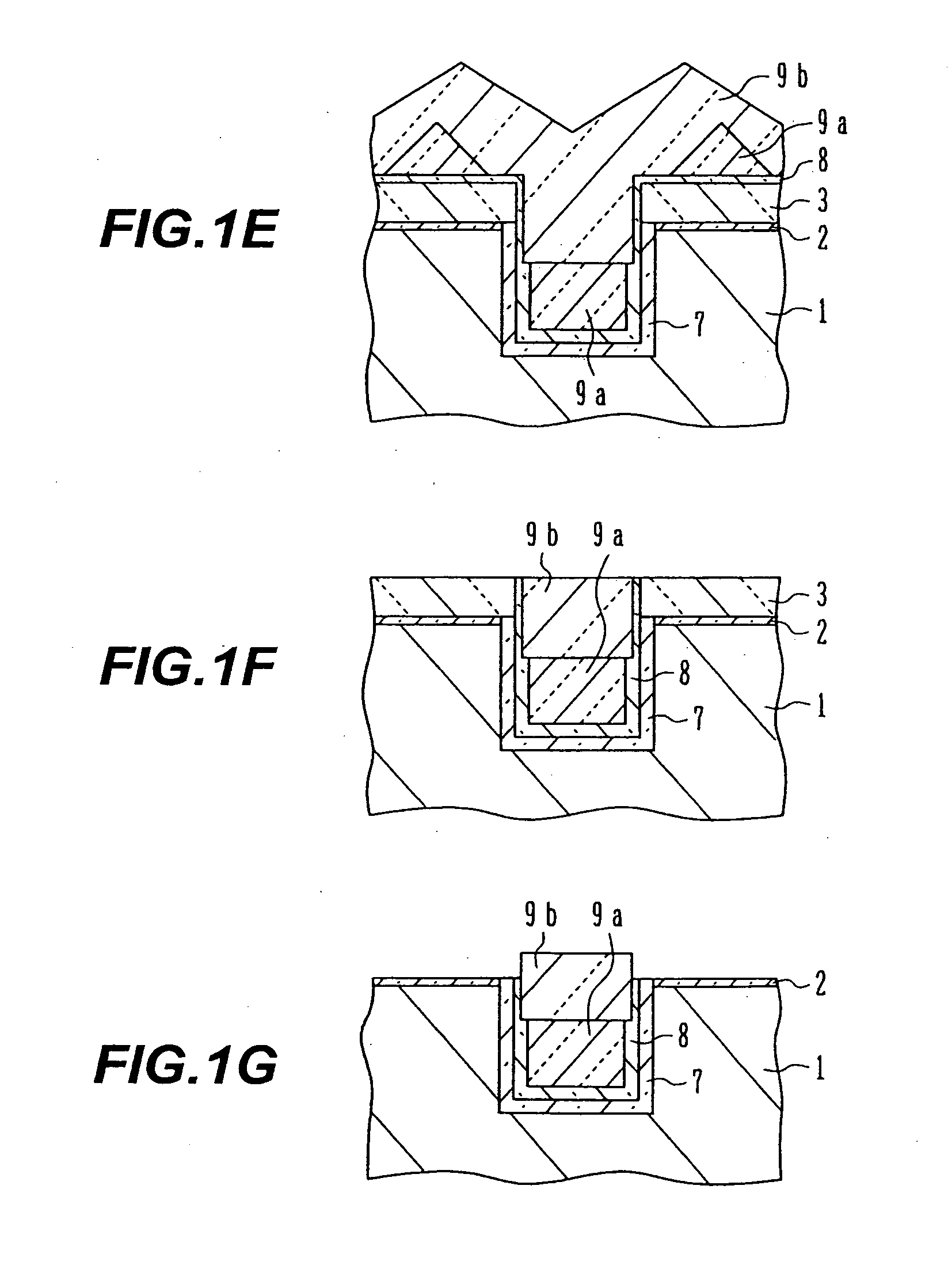
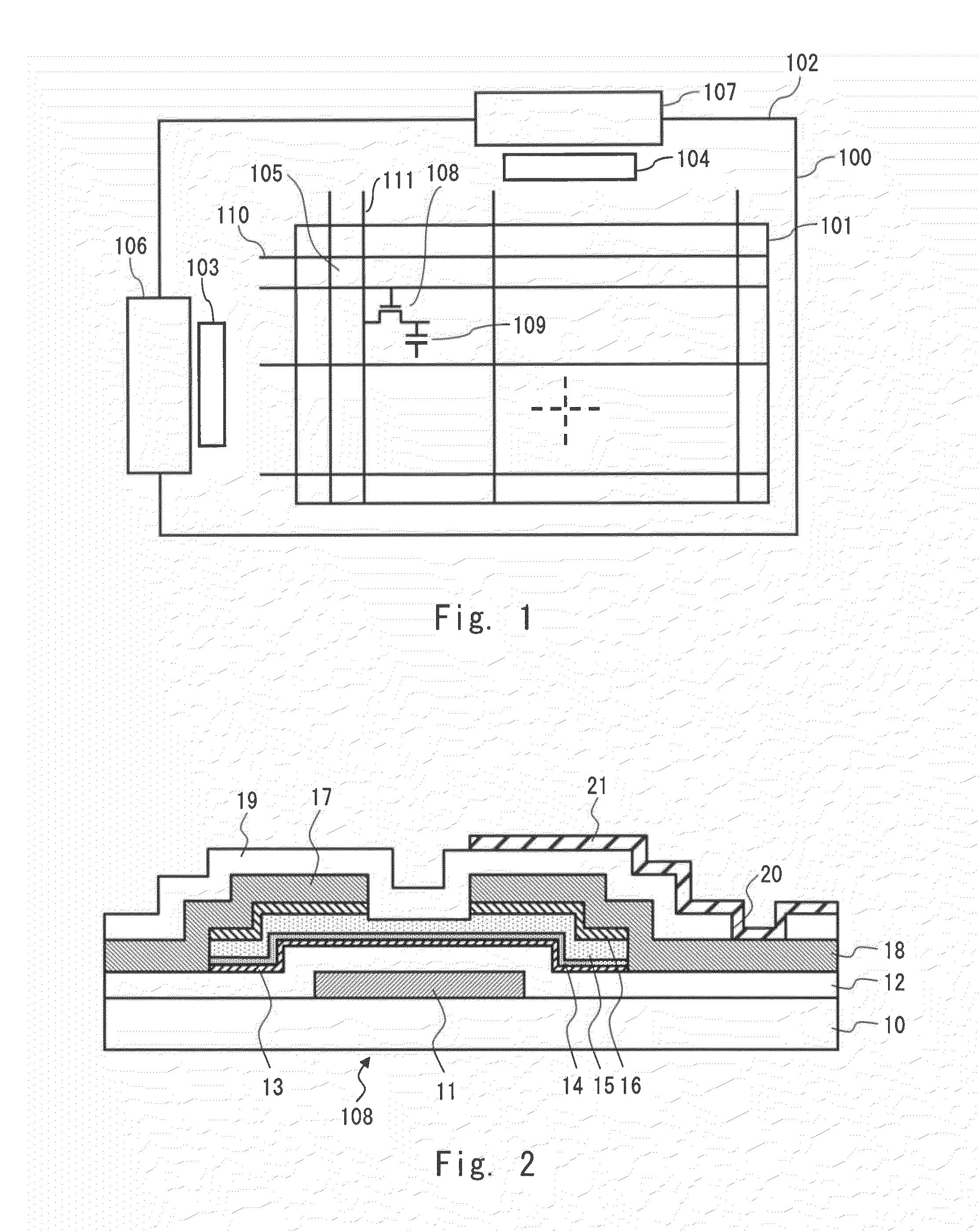
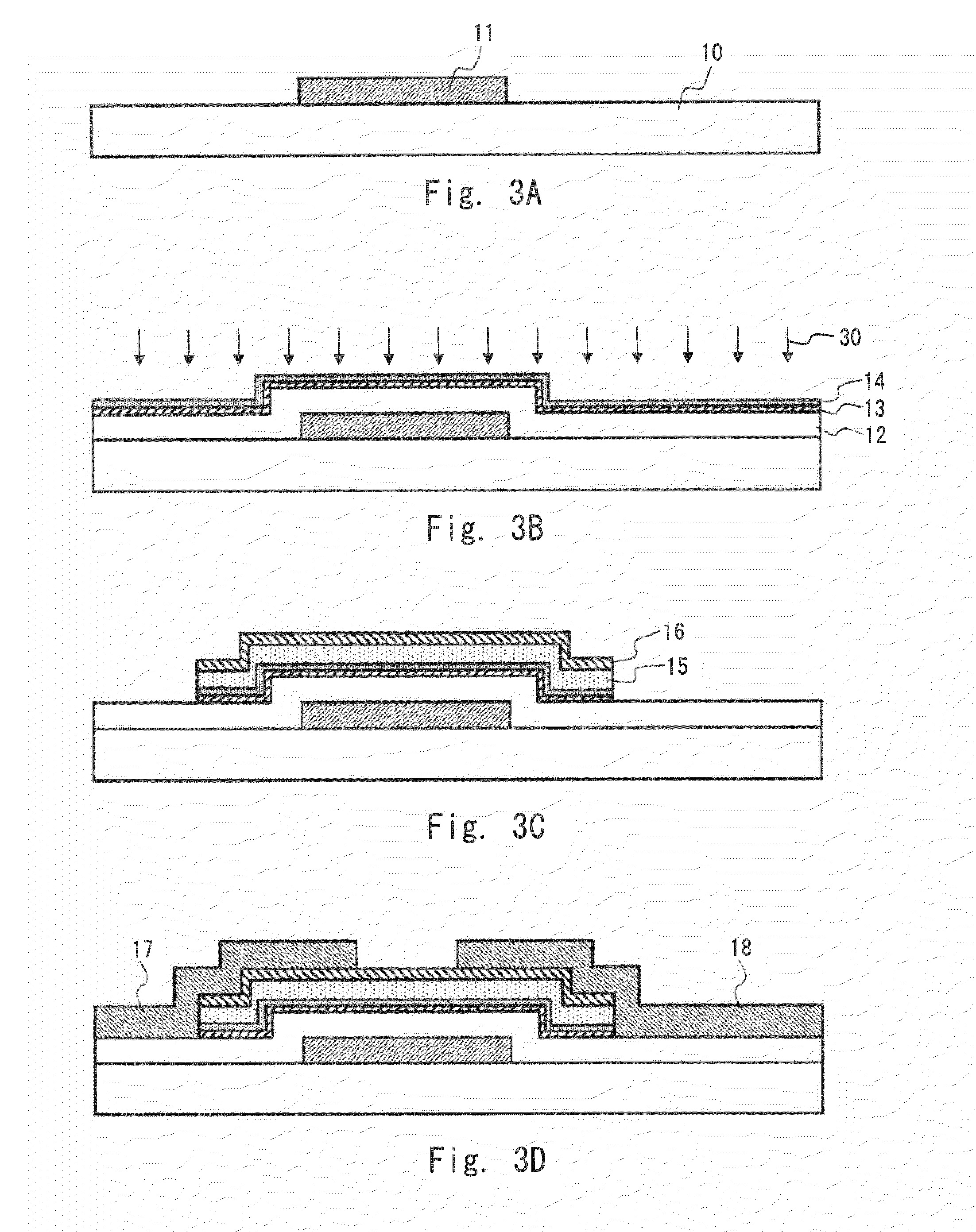
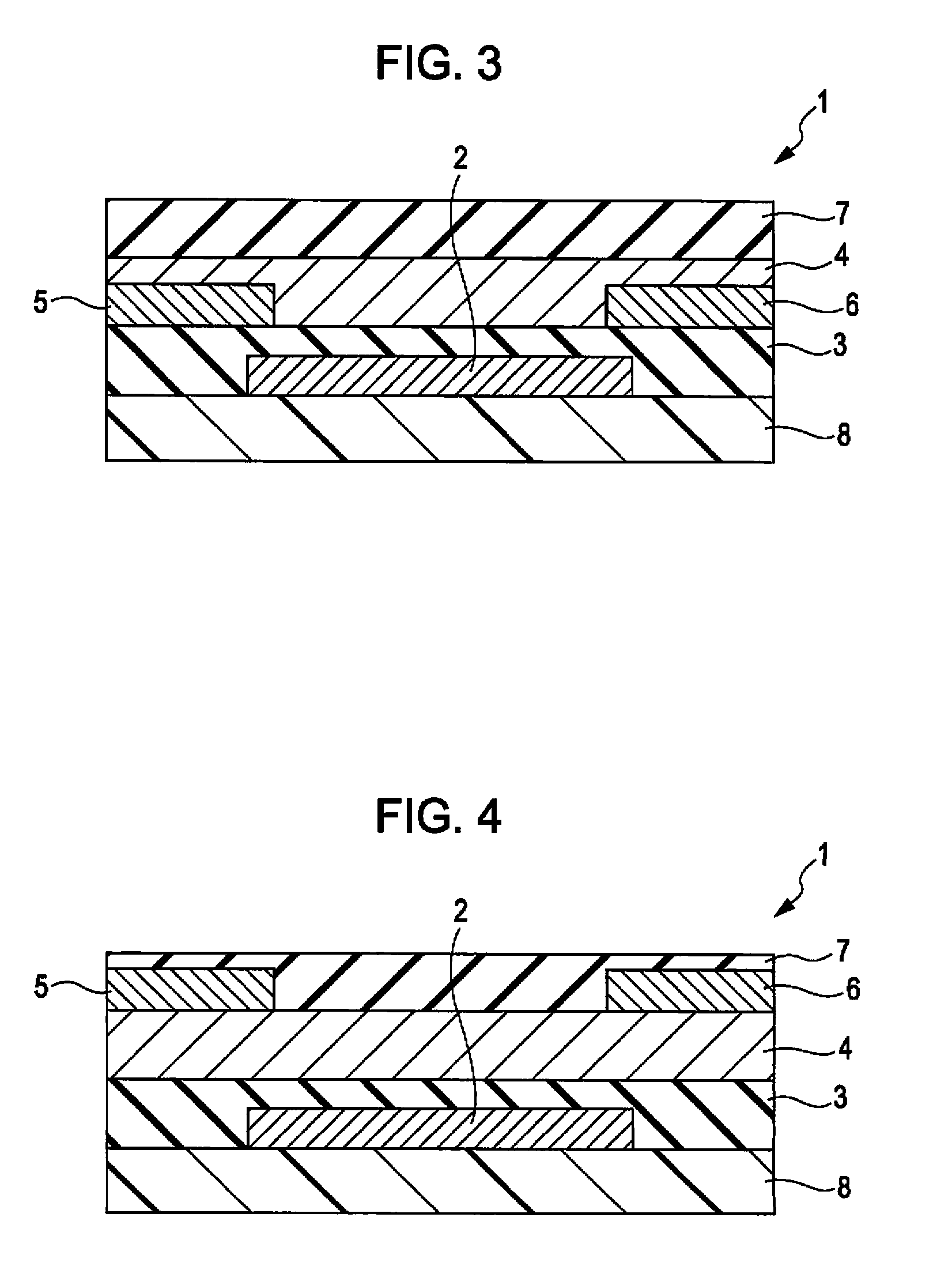
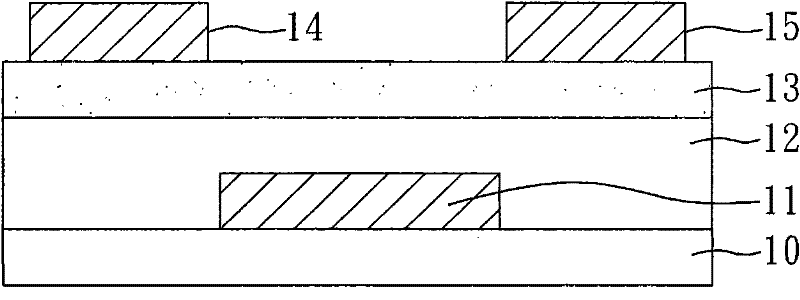
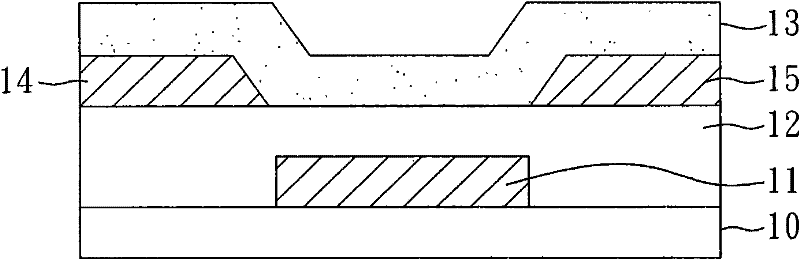
Method for manufacturing thin film transistor using oxide semiconductor and display apparatus
ActiveUS8143115B2Lower resistanceImprove transistor characteristicsTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorAtmosphere
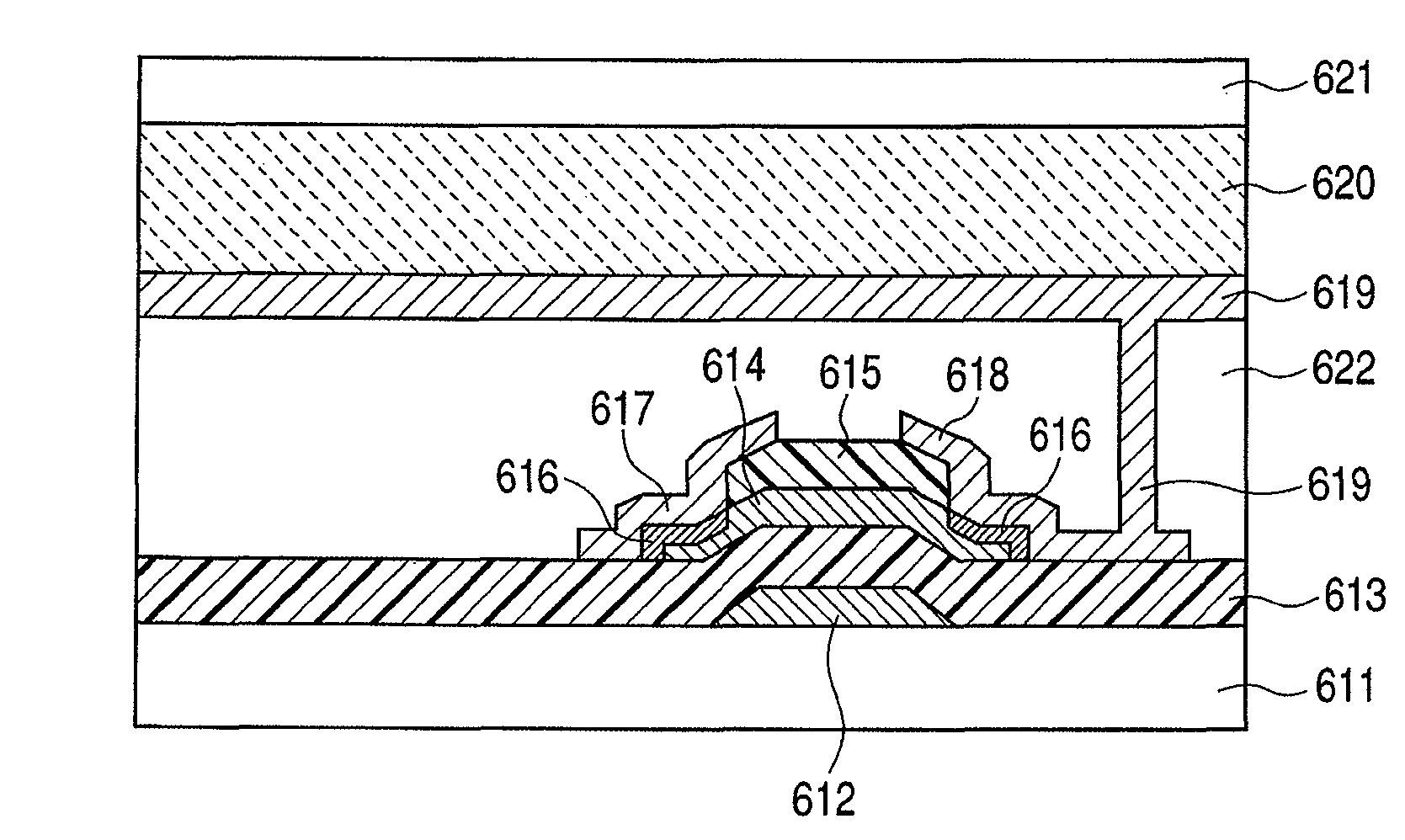
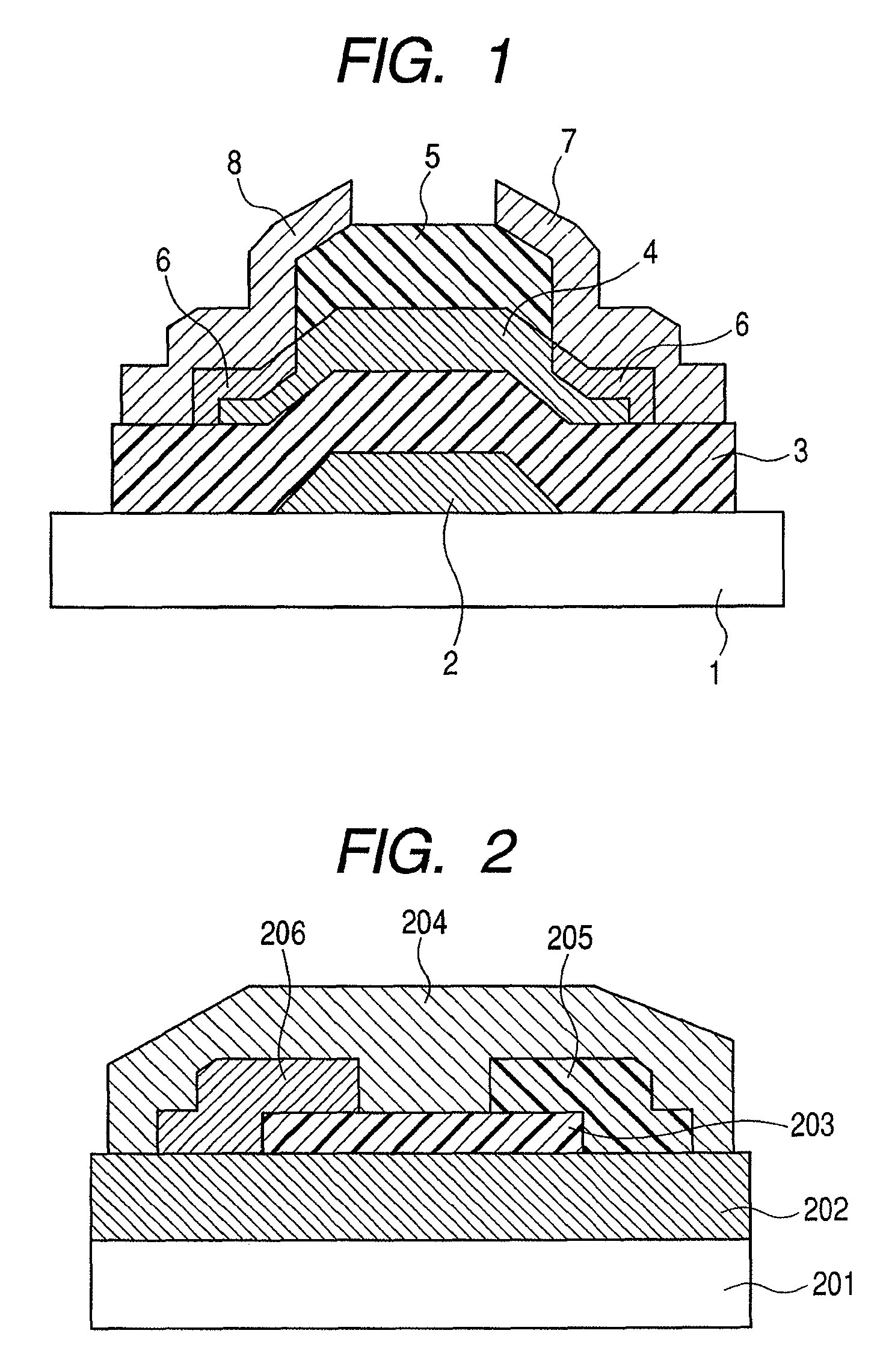
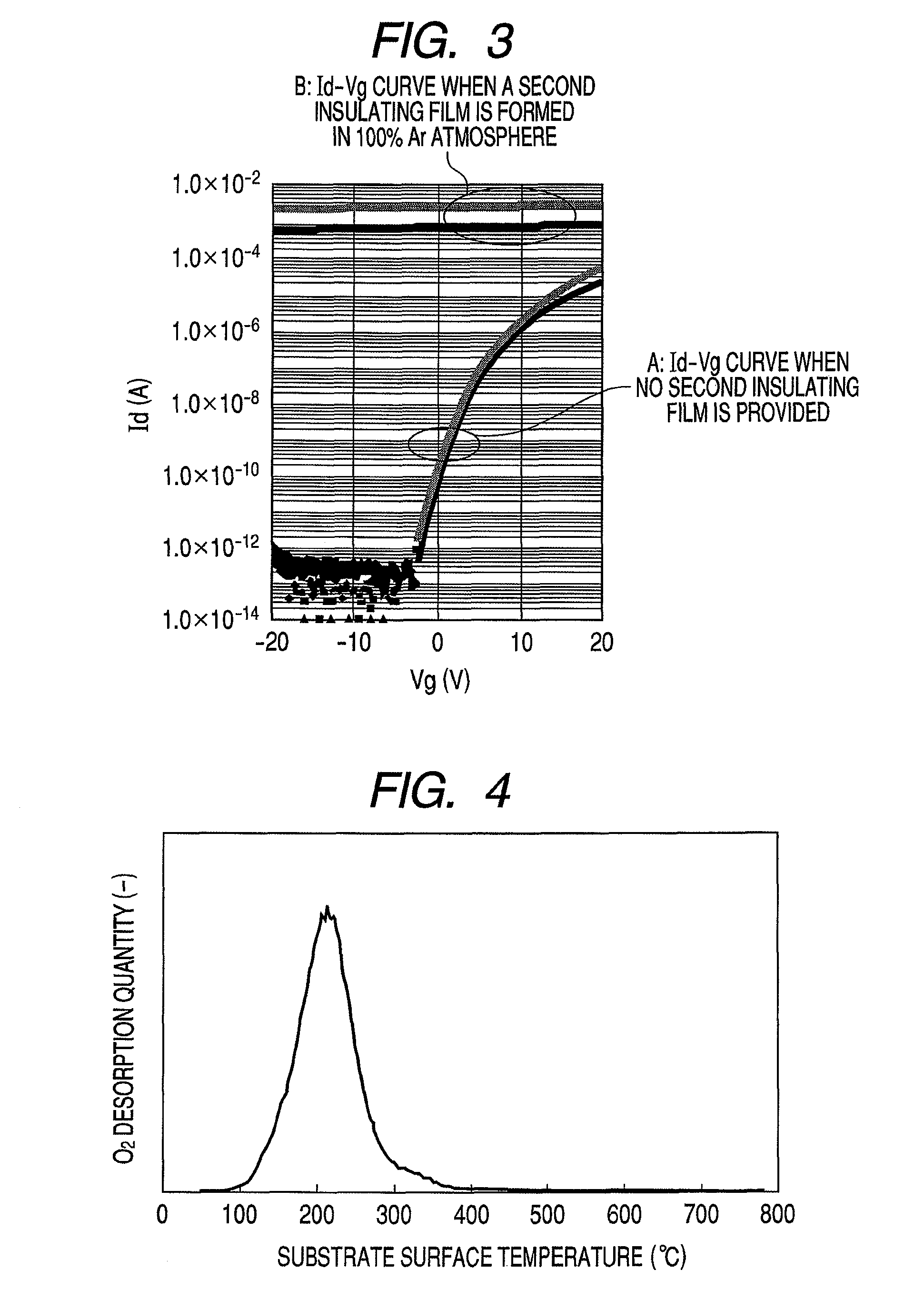
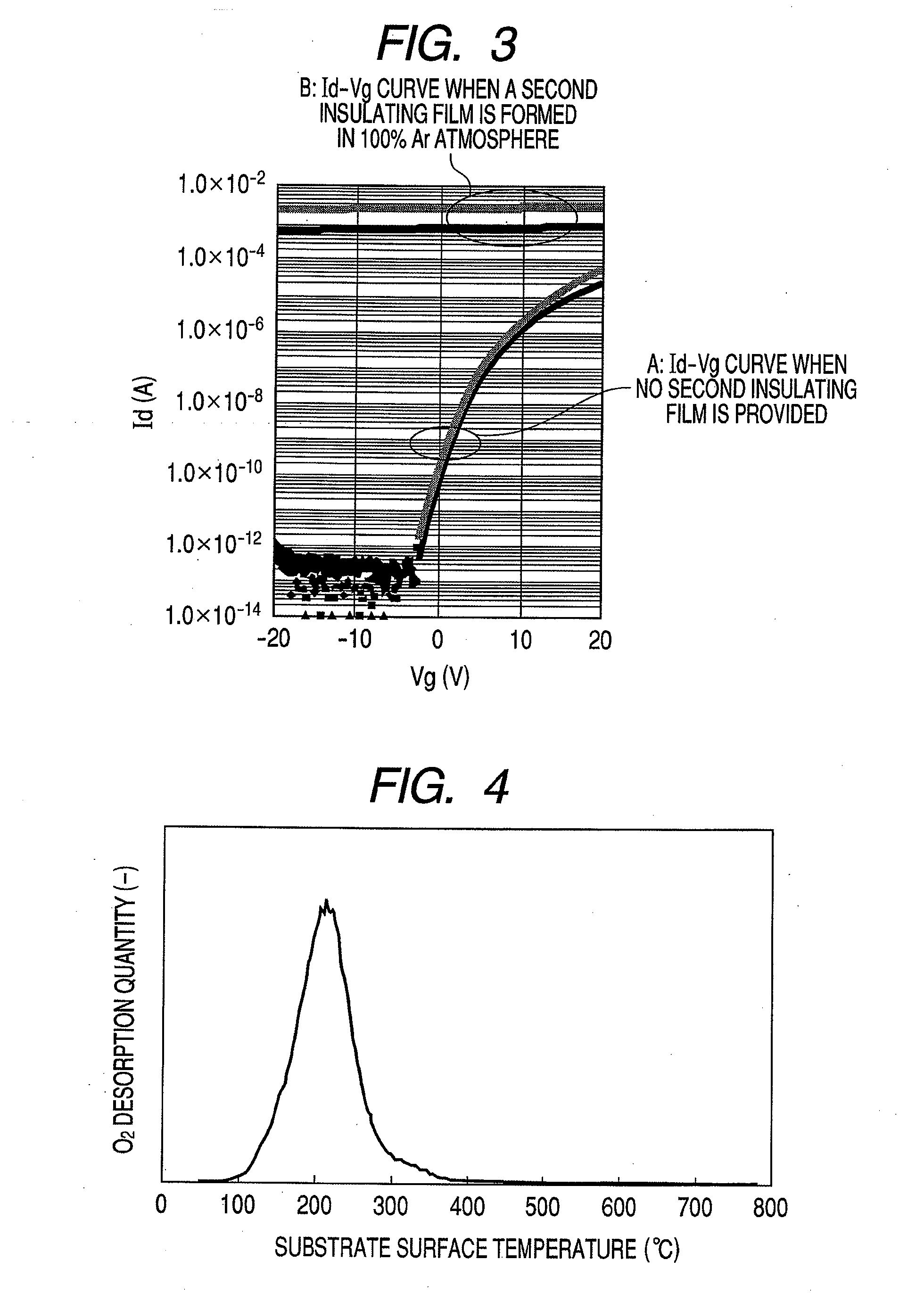
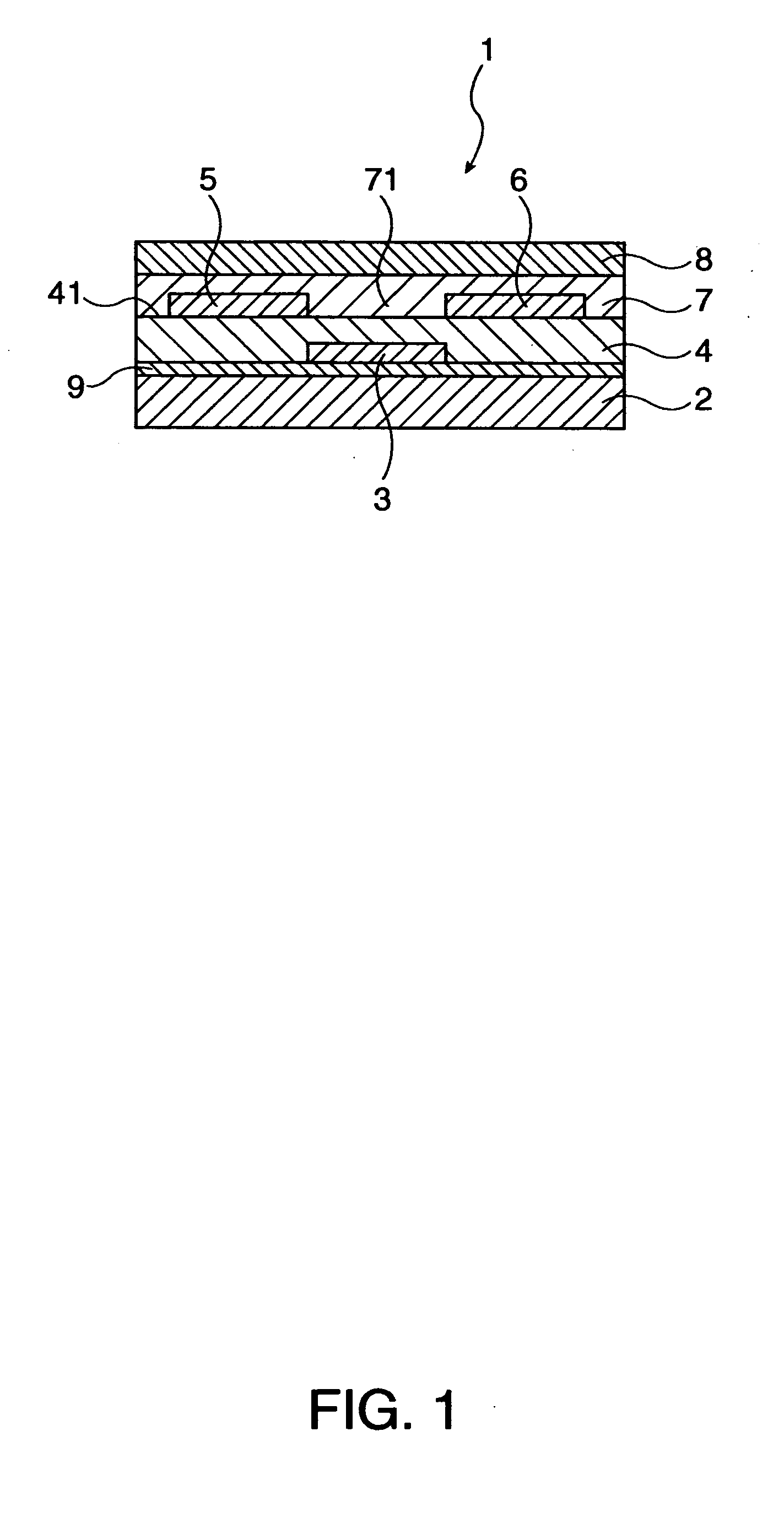
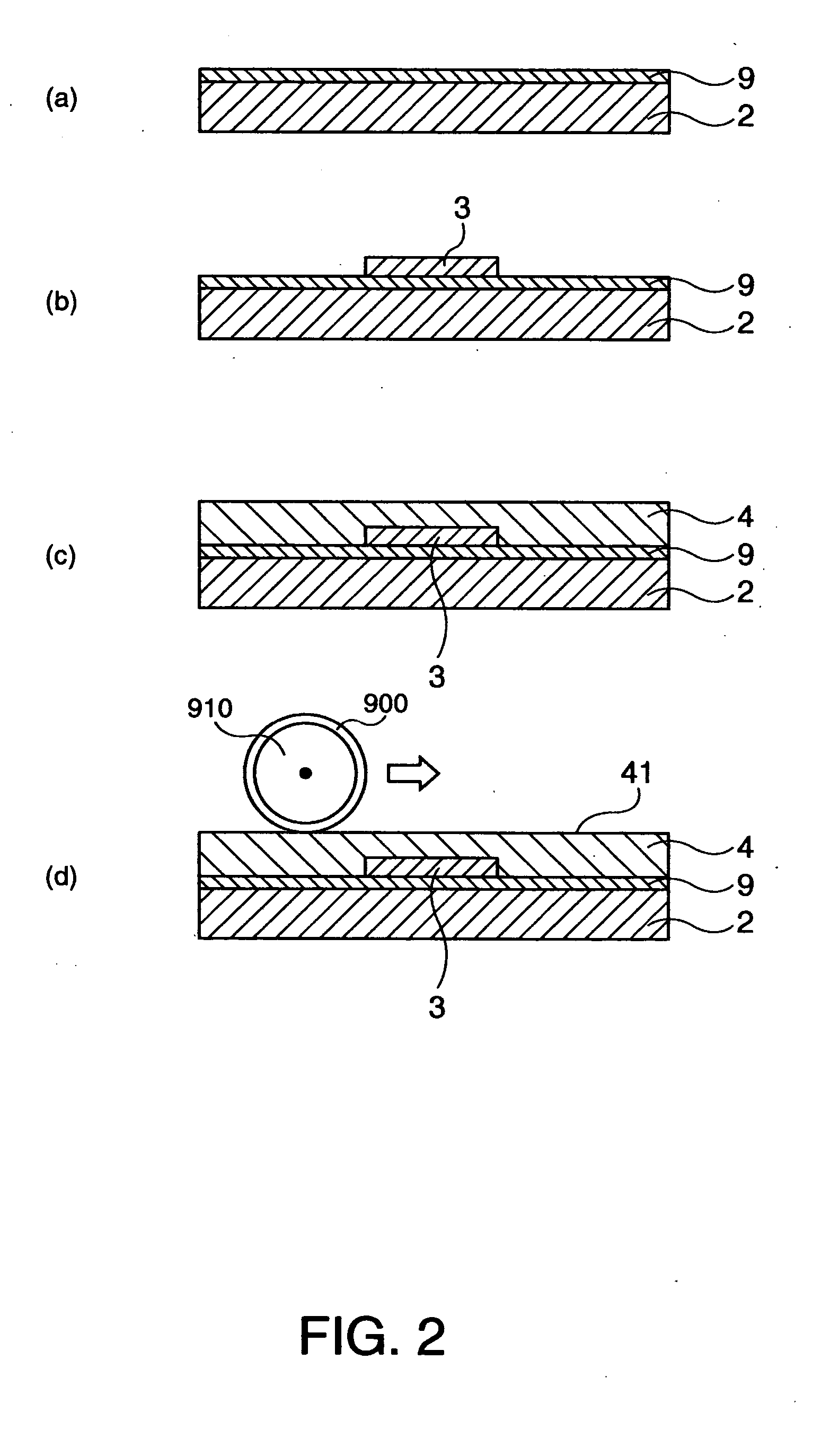
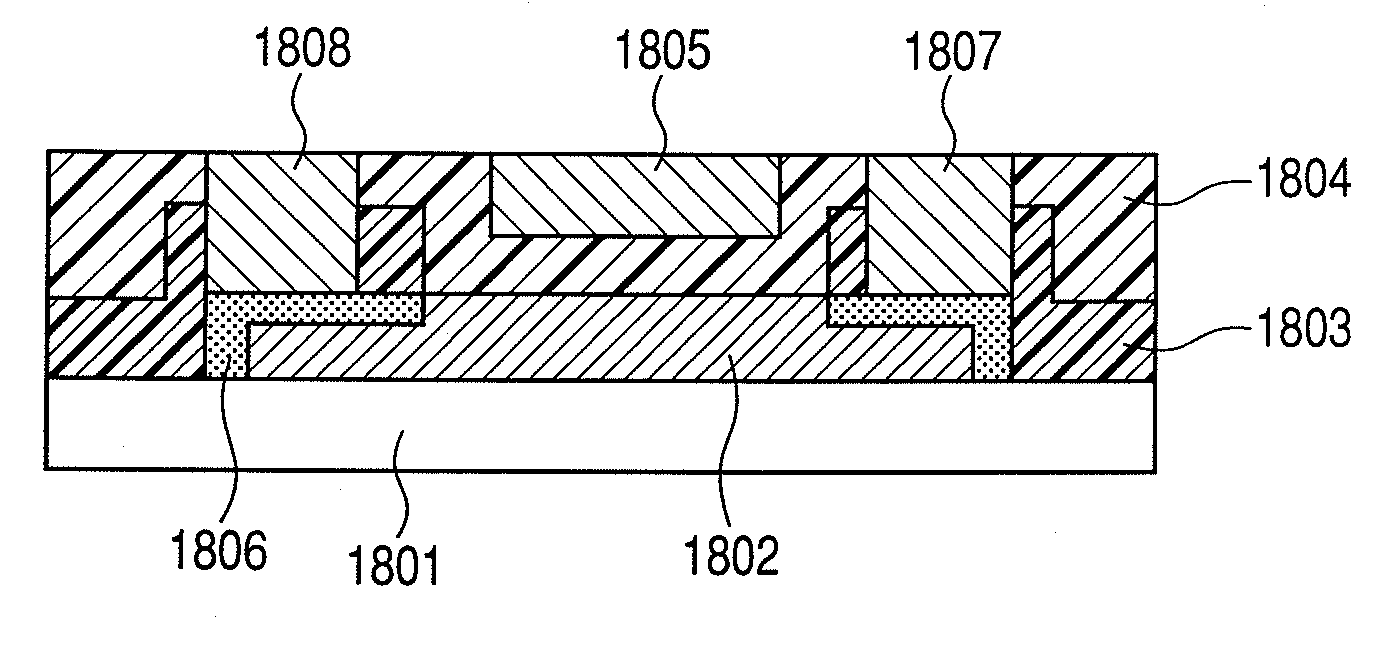
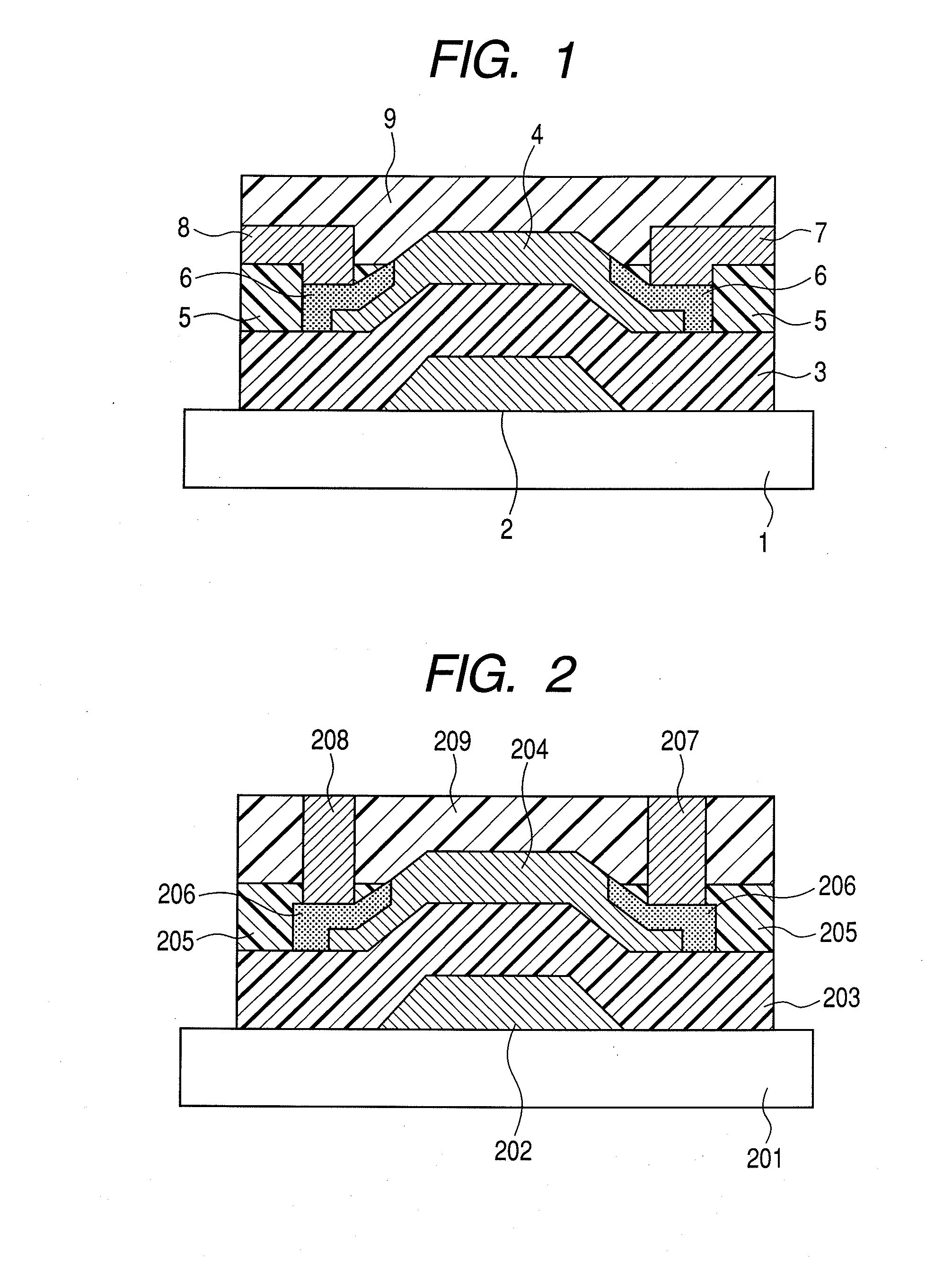
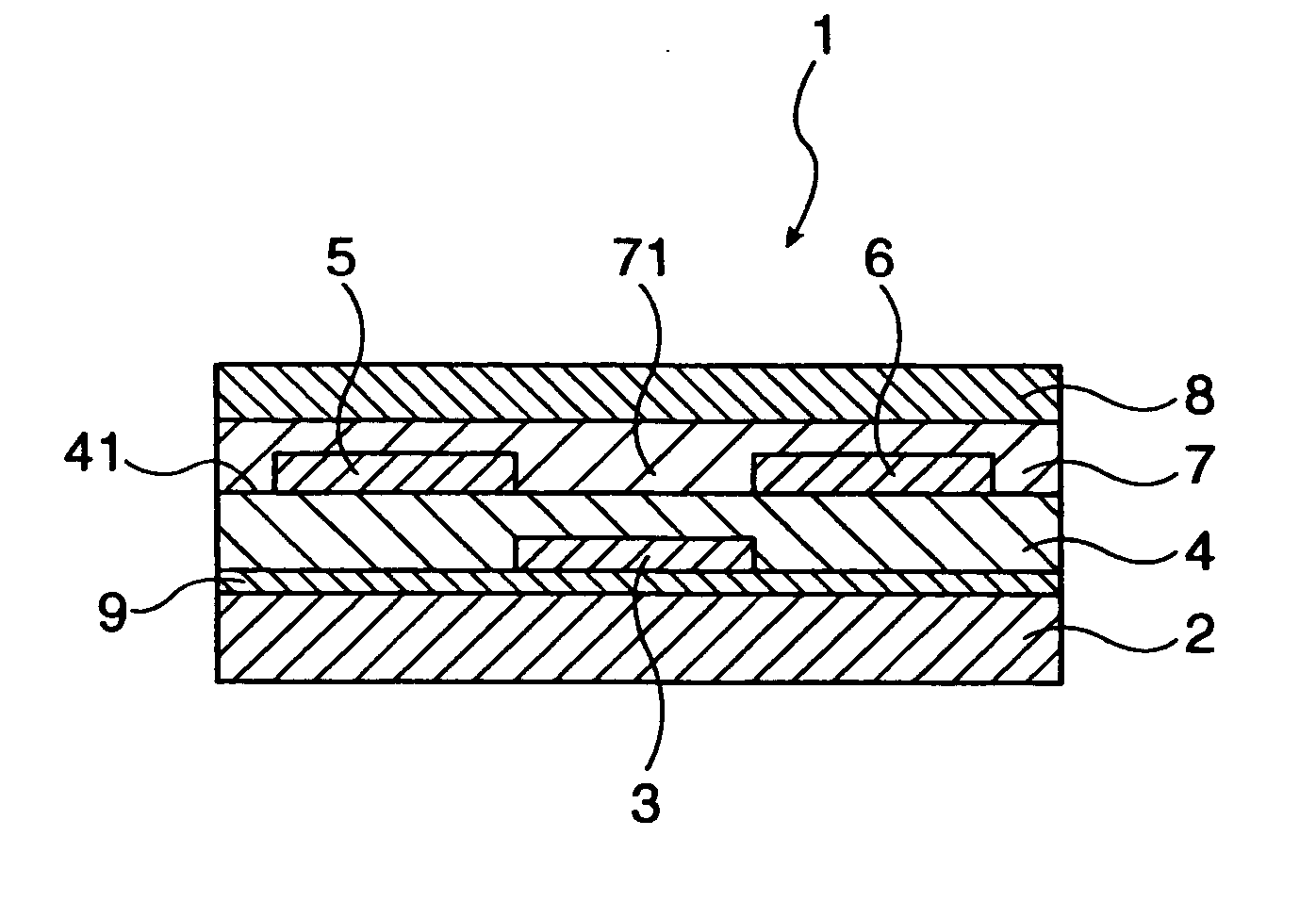
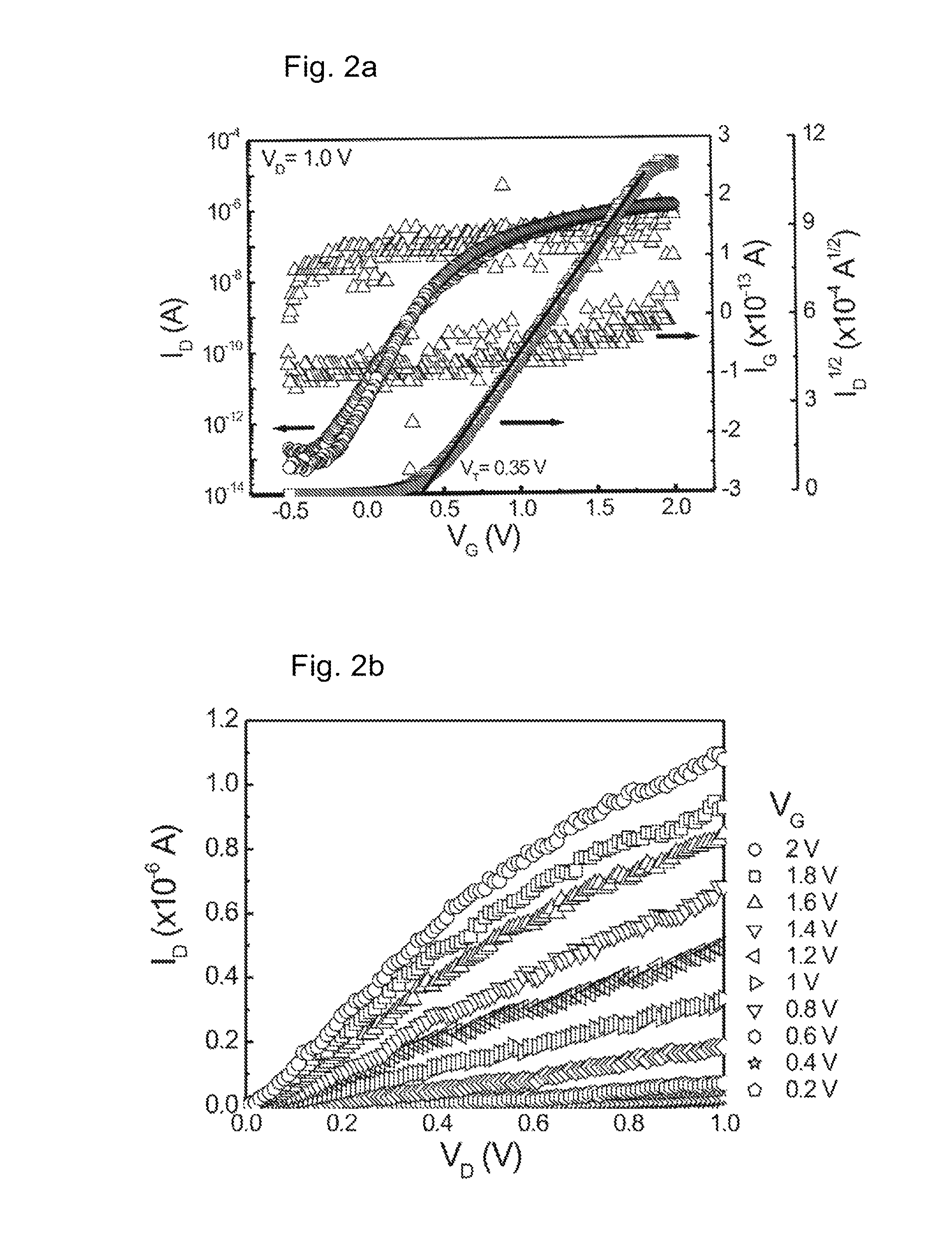
A thin film transistor is manufactured by forming a gate electrode on a substrate, forming a first insulating film on the gate electrode, forming an oxide semiconductor layer on the first insulating film with an amorphous oxide, patterning the first insulating film, patterning the oxide semiconductor layer, forming a second insulating film on the oxide semiconductor layer in an oxidative-gas-containing atmosphere, patterning the second insulating film to expose a pair of contact regions, forming an electrode layer on the pair of contact regions, and patterning the electrode layer to for a source electrode and a drain electrode.
Owner:CANON KK
Manufacturing method of thin film transistor using oxide semiconductor
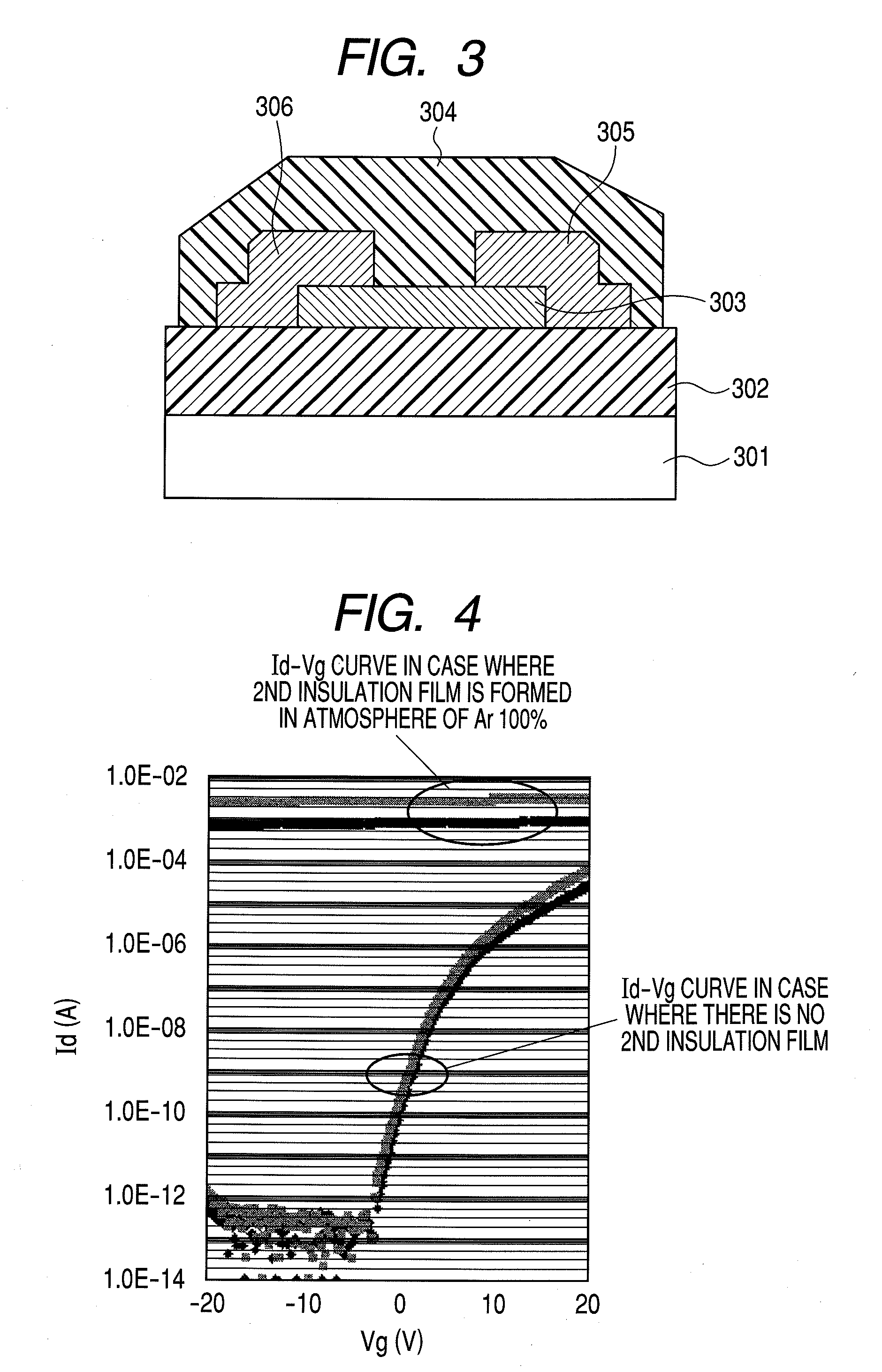
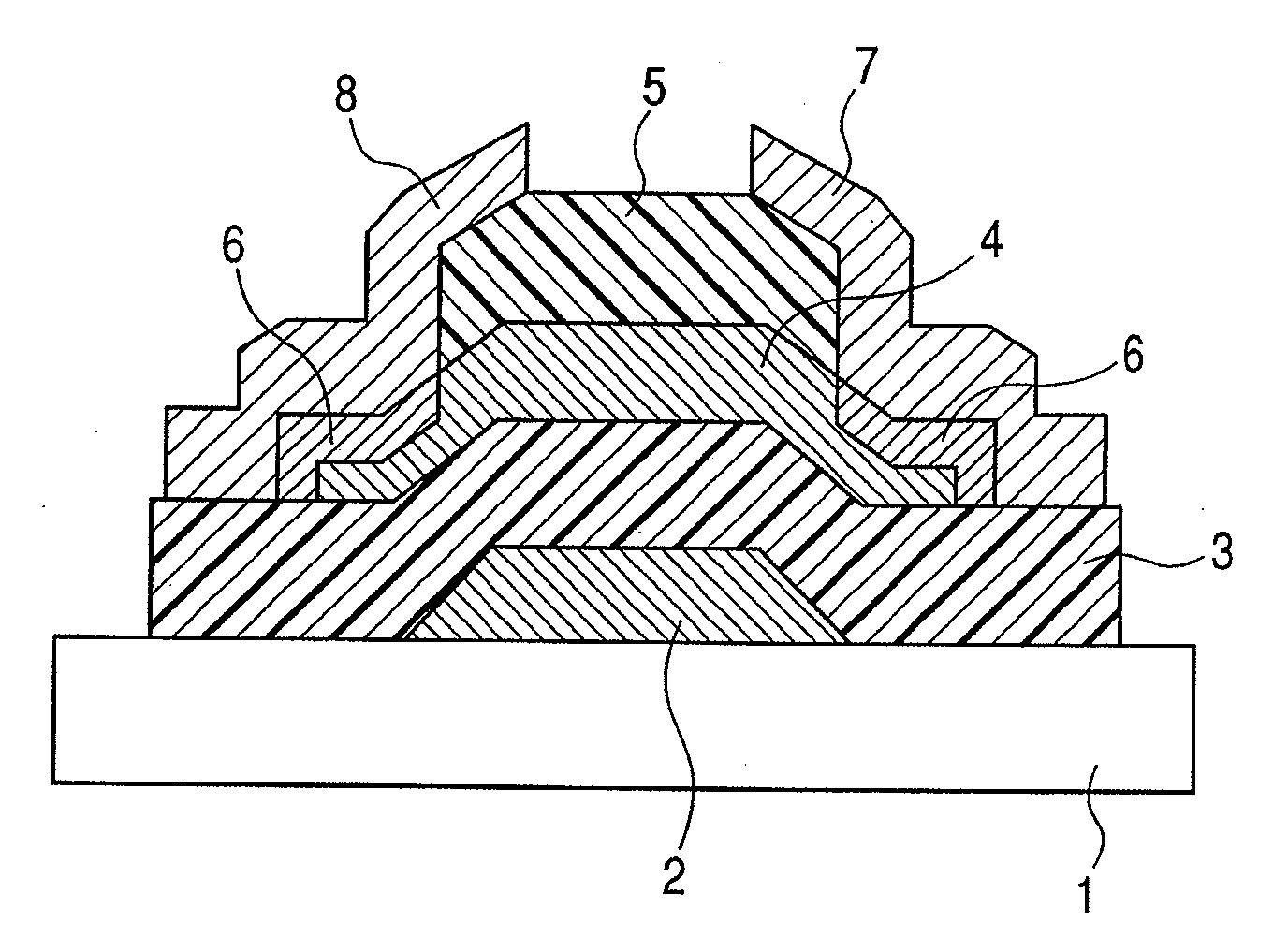
InactiveUS8193045B2Improve transistor characteristicsReduced contact areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
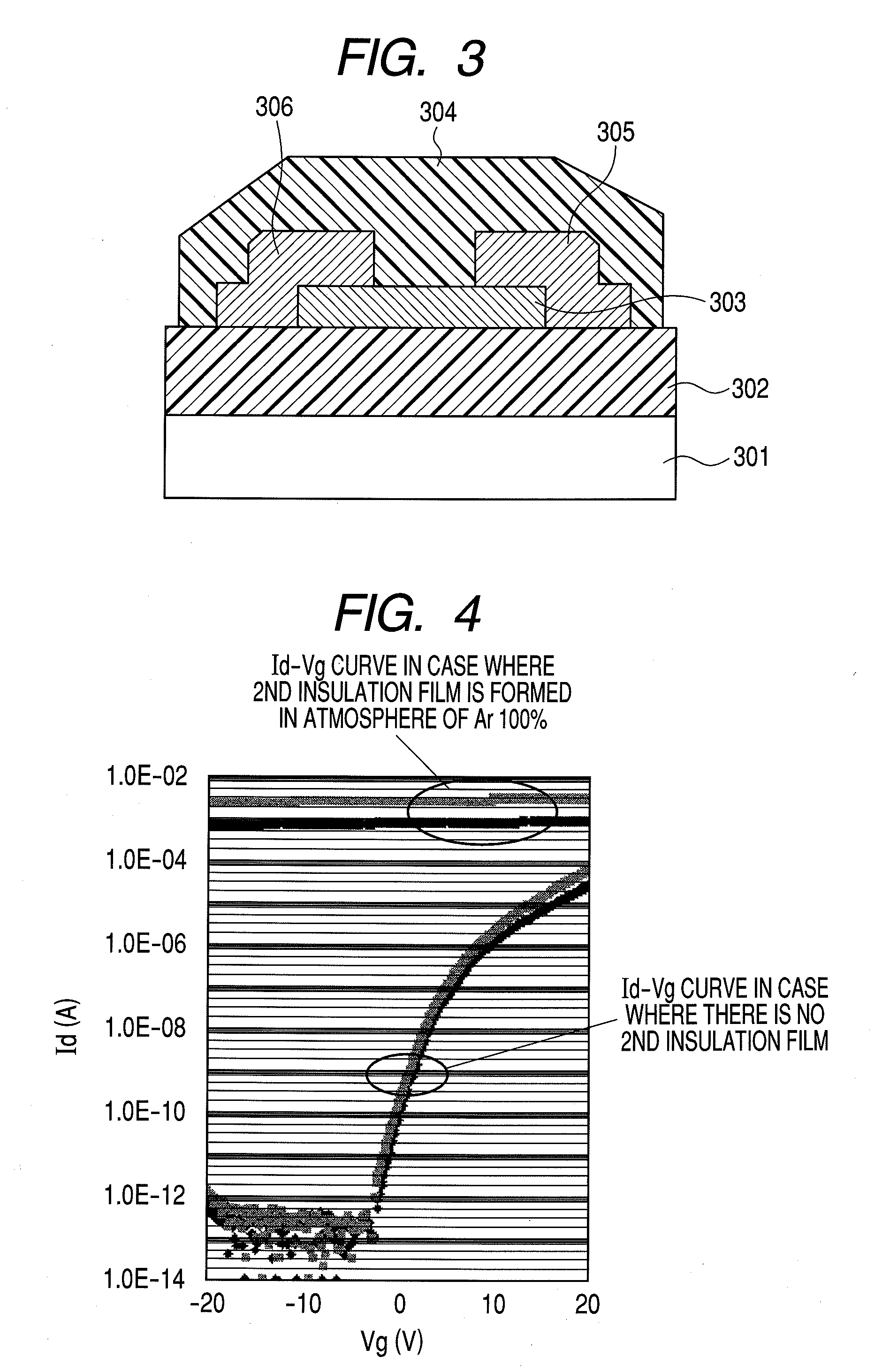
A manufacturing method of a thin film transistor having at least a gate electrode, a gate insulation film, an oxide semiconductor layer, a first insulation film, a source electrode, a drain electrode, and a second insulation film on a substrate, including: forming the gate electrode on the substrate; forming the gate insulation film on the gate electrode; forming a semiconductor layer including amorphous oxide on the gate insulation film; patterning the gate insulation film; patterning the oxide semiconductor layer; reducing the oxide semiconductor layer in resistance by forming the first insulation film on the oxide semiconductor layer in the atmosphere not including an oxidized gas; patterning the first insulation film and forming a contact hole between the source electrode and the drain electrode and the oxide semiconductor layer; forming a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer in the oxide semiconductor layer through the contact hole; forming the source electrode and the drain electrode through the contact hole and allowing the first insulation film to be exposed; patterning the exposed first insulation film and allowing a channel region of the oxide semiconductor layer to be exposed; and increasing the channel region in resistance by forming the second insulation film on the surface including the channel region of the oxide semiconductor layer in the atmosphere including an oxidized gas.
Owner:CANON KK
Method for manufacturing thin film transistor using oxide semiconductor and display apparatus
ActiveUS20100065837A1Improve transistor characteristicsLower resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorOxide semiconductor
A thin film transistor is manufactured by forming a gate electrode on a substrate, forming a first insulating film on the gate electrode, forming an oxide semiconductor layer on the first insulating film with an amorphous oxide, patterning the first insulating film, patterning the oxide semiconductor layer, forming a second insulating film on the oxide semiconductor layer in an oxidative-gas-containing atmosphere, patterning the second insulating film to expose a pair of contact regions, forming an electrode layer on the pair of contact regions, and patterning the electrode layer to for a source electrode and a drain electrode.
Owner:CANON KK
Thin-film transistor, method of producing thin-film transistor, electronic circuit, display, and electronic device
InactiveUS20050029514A1Easy and highly reliable mannerReduce the driving voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
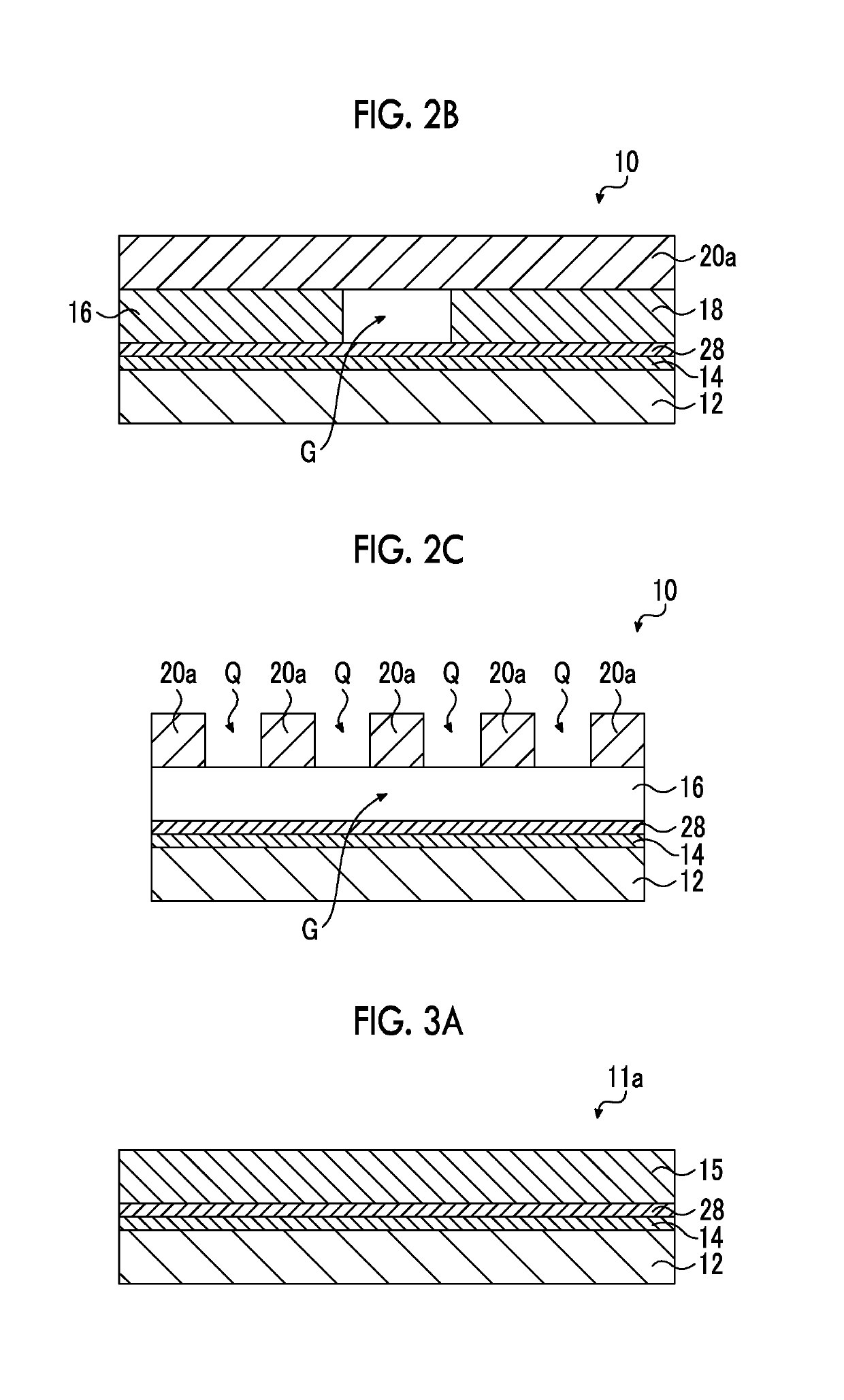
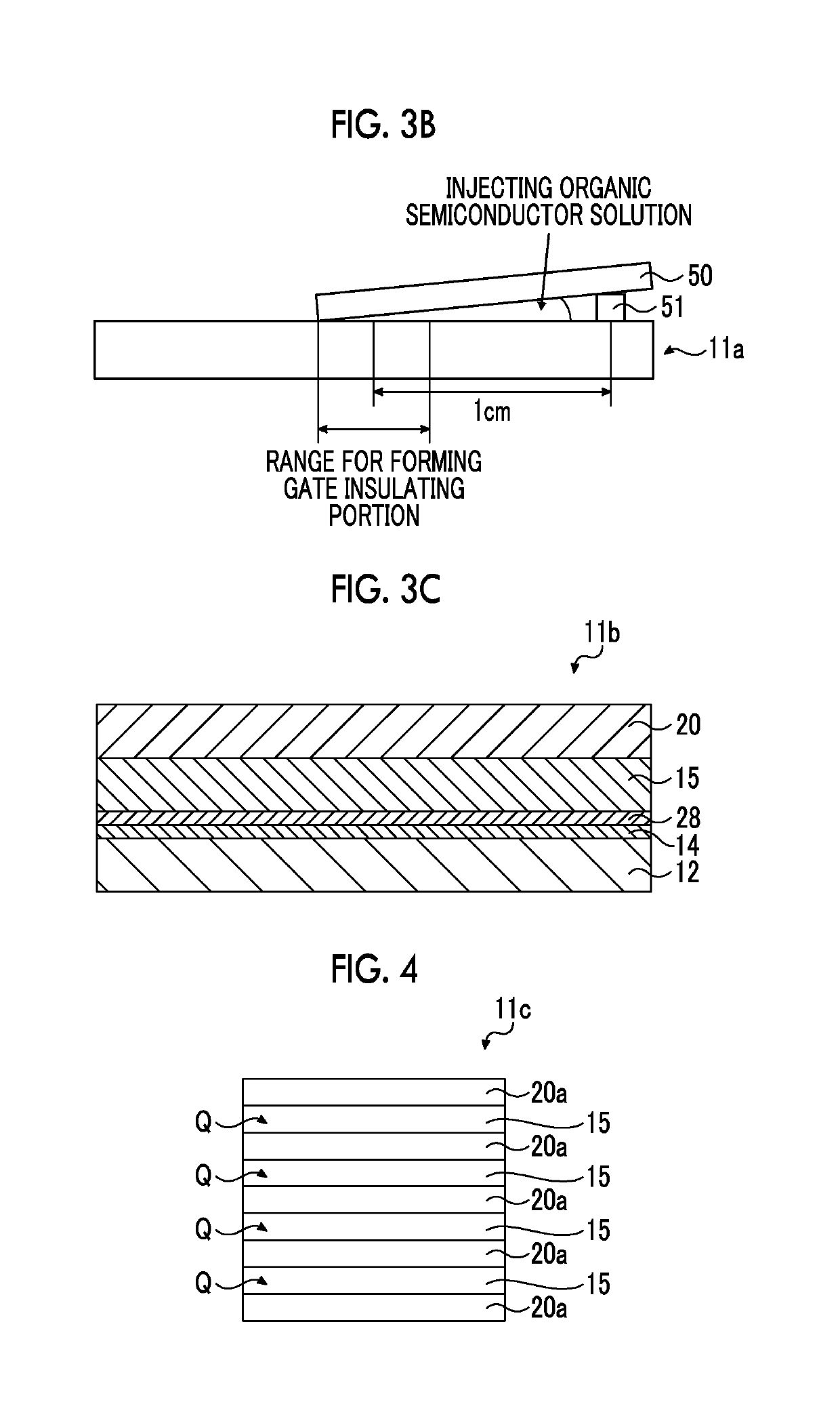
Aspects of the invention can provide a thin-film transistor having good transistor characteristics and operable with a low driving voltage, a method of producing such a thin-film transistor, a high-reliability electronic circuit, a display, and an electronic device. In an exemplary thin-film transistor according to the invention, a gate electrode can be formed on a substrate via an underlying layer, and a gate insulating layer can be formed on the substrate such that the gate electrode is covered with the gate insulating layer. A source electrode and a drain electrode are formed on the gate insulating layer such that they are separated from each other by a gap formed just above the gate electrode. An organic semiconductor layer can be formed thereon such that the electrodes are covered with the organic semiconductor layer. A region between the electrodes of the organic semiconductor layer functions as a channel region. A protective layer can be arranged on the organic semiconductor layer. This thin-film transistor is characterized in that the organic semiconductor layer is formed after the gate insulating layer is formed, and the gate insulating layer has the capability of causing the organic semiconductor layer to be aligned.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Manufacturing method of thin film transistor using oxide semiconductor
InactiveUS20100140612A1Excellent transistor characteristicReduce resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesAmorphous oxideOxide semiconductor
A manufacturing method of a thin film transistor having at least a gate electrode, a gate insulation film, an oxide semiconductor layer, a first insulation film, a source electrode, a drain electrode, and a second insulation film on a substrate, including: forming the gate electrode on the substrate; forming the gate insulation film on the gate electrode; forming a semiconductor layer including amorphous oxide on the gate insulation film; patterning the gate insulation film; patterning the oxide semiconductor layer; reducing the oxide semiconductor layer in resistance by forming the first insulation film on the oxide semiconductor layer in the atmosphere not including an oxidized gas; patterning the first insulation film and forming a contact hole between the source electrode and the drain electrode and the oxide semiconductor layer; forming a source electrode layer and a drain electrode layer in the oxide semiconductor layer through the contact hole; forming the source electrode and the drain electrode through the contact hole and allowing the first insulation film to be exposed; patterning the exposed first insulation film and allowing a channel region of the oxide semiconductor layer to be exposed; and increasing the channel region in resistance by forming the second insulation film on the surface including the channel region of the oxide semiconductor layer in the atmosphere including an oxidized gas.
Owner:CANON KK
Thin-film transistor, method of producing thin-film transistor, electronic circuit, display, and electronic device
InactiveUS20070099333A1Improve transistor characteristicsReduce the driving voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceEngineering
Aspects of the invention can provide a thin-film transistor having good transistor characteristics and operable with a low driving voltage, a method of producing such a thin-film transistor, a high-reliability electronic circuit, a display, and an electronic device. In an exemplary thin-film transistor according to the invention, a gate electrode can be formed on a substrate via an underlying layer, and a gate insulating layer can be formed on the substrate such that the gate electrode is covered with the gate insulating layer. A source electrode and a drain electrode are formed on the gate insulating layer such that they are separated from each other by a gap formed just above the gate electrode. An organic semiconductor layer can be formed thereon such that the electrodes are covered with the organic semiconductor layer. A region between the electrodes of the organic semiconductor layer functions as a channel region. A protective layer can be arranged on the organic semiconductor layer. This thin-film transistor is characterized in that the organic semiconductor layer is formed after the gate insulating layer is formed, and the gate insulating layer has the capability of causing the organic semiconductor layer to be aligned.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
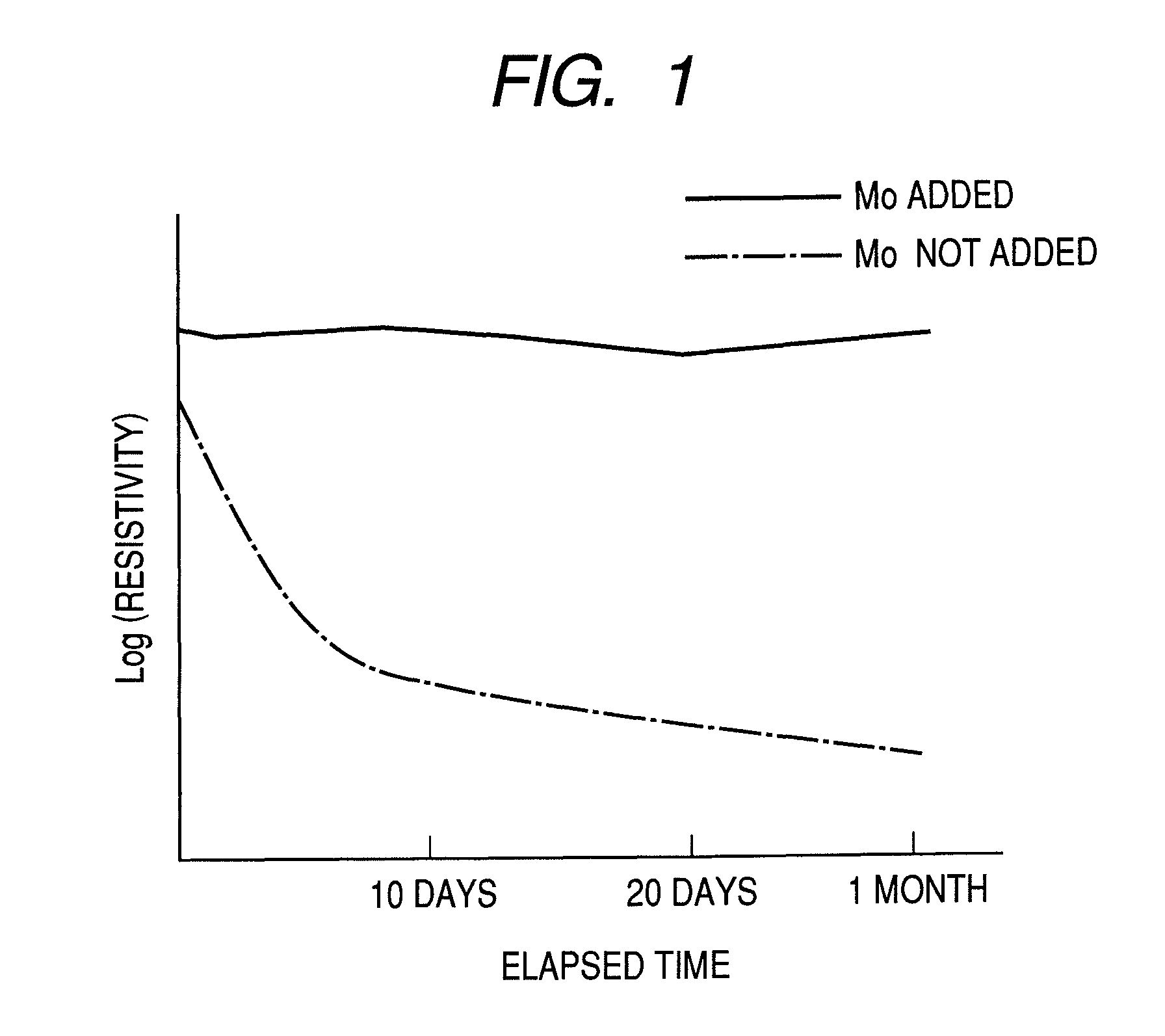
Amorphous oxide and field effect transistor
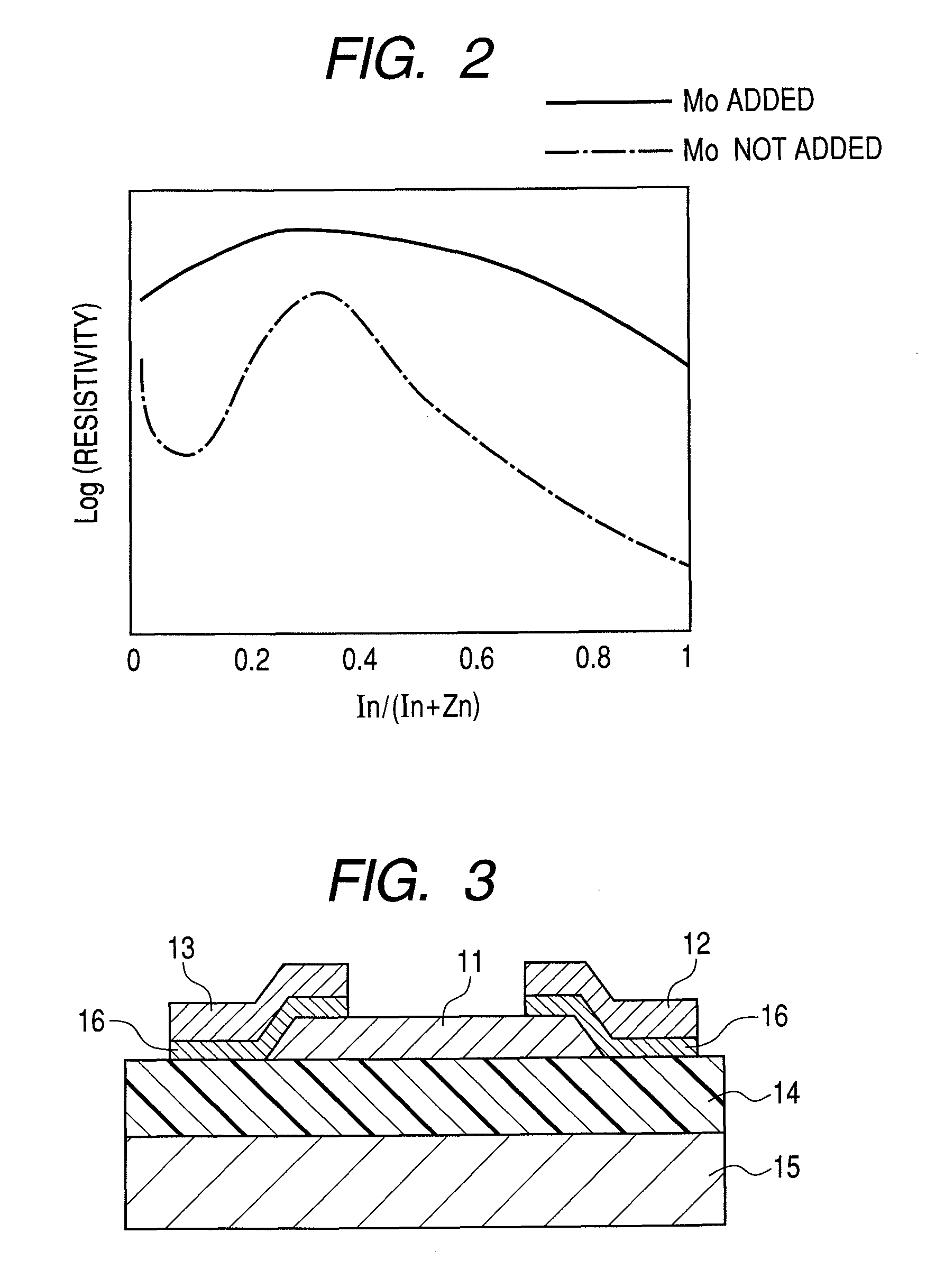
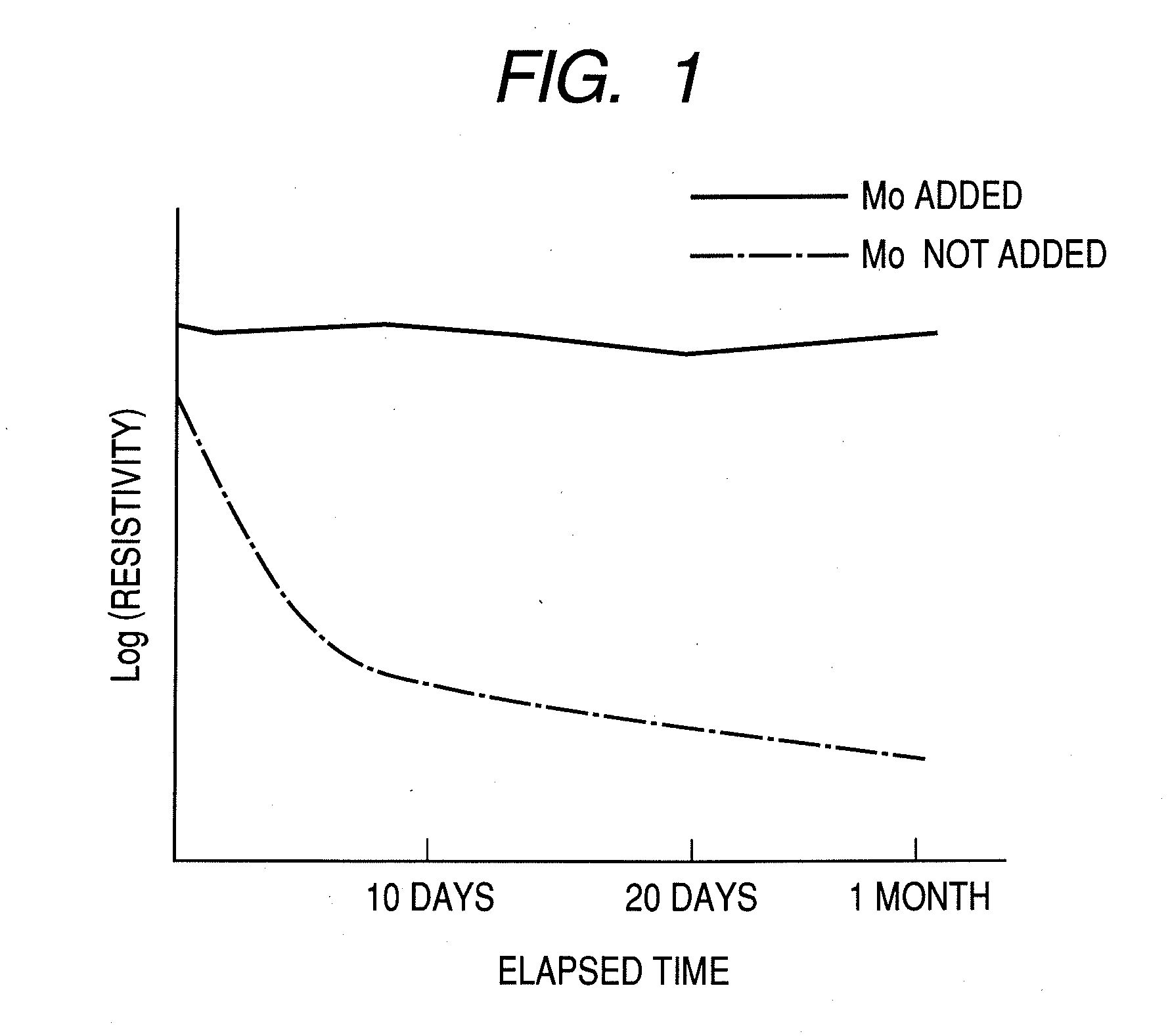
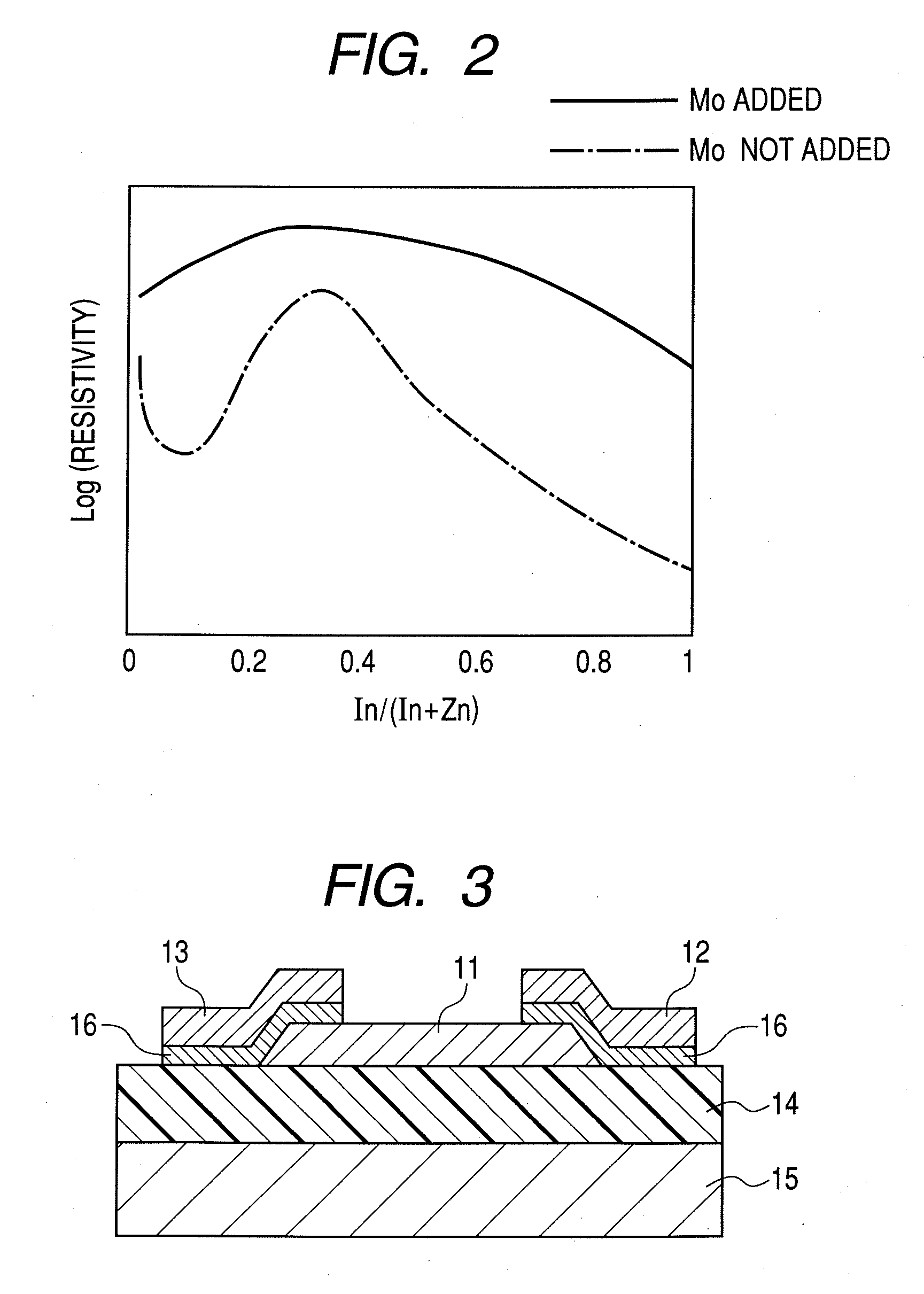
ActiveUS8212248B2Improve featuresIncrease profitSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorAtomic composition
An amorphous oxide at least includes: at least one element selected from the group consisting of In, Zn, and Sn; and Mo. An atomic composition ratio of Mo to a number of all metallic atoms in the amorphous oxide is 0.1 atom % or higher and 5 atom % or lower.
Owner:CANON KK
Amorphous oxide and field effect transistor
ActiveUS20100276685A1Improve featuresIncrease profitSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorAtomic composition
An amorphous oxide at least includes: at least one element selected from the group consisting of In, Zn, and Sn; and Mo. An atomic composition ratio of Mo to a number of all metallic atoms in the amorphous oxide is 0.1 atom % or higher and 5 atom % or lower.
Owner:CANON KK
Amorphous oxide semiconductor and thin film transistor using the same
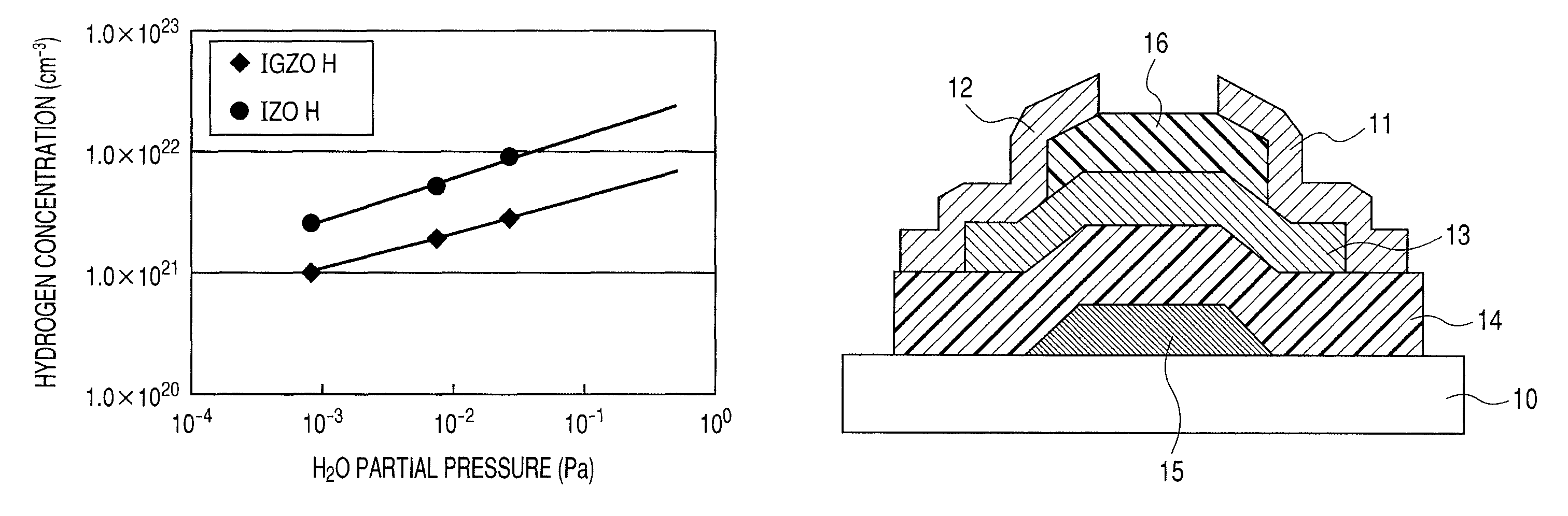
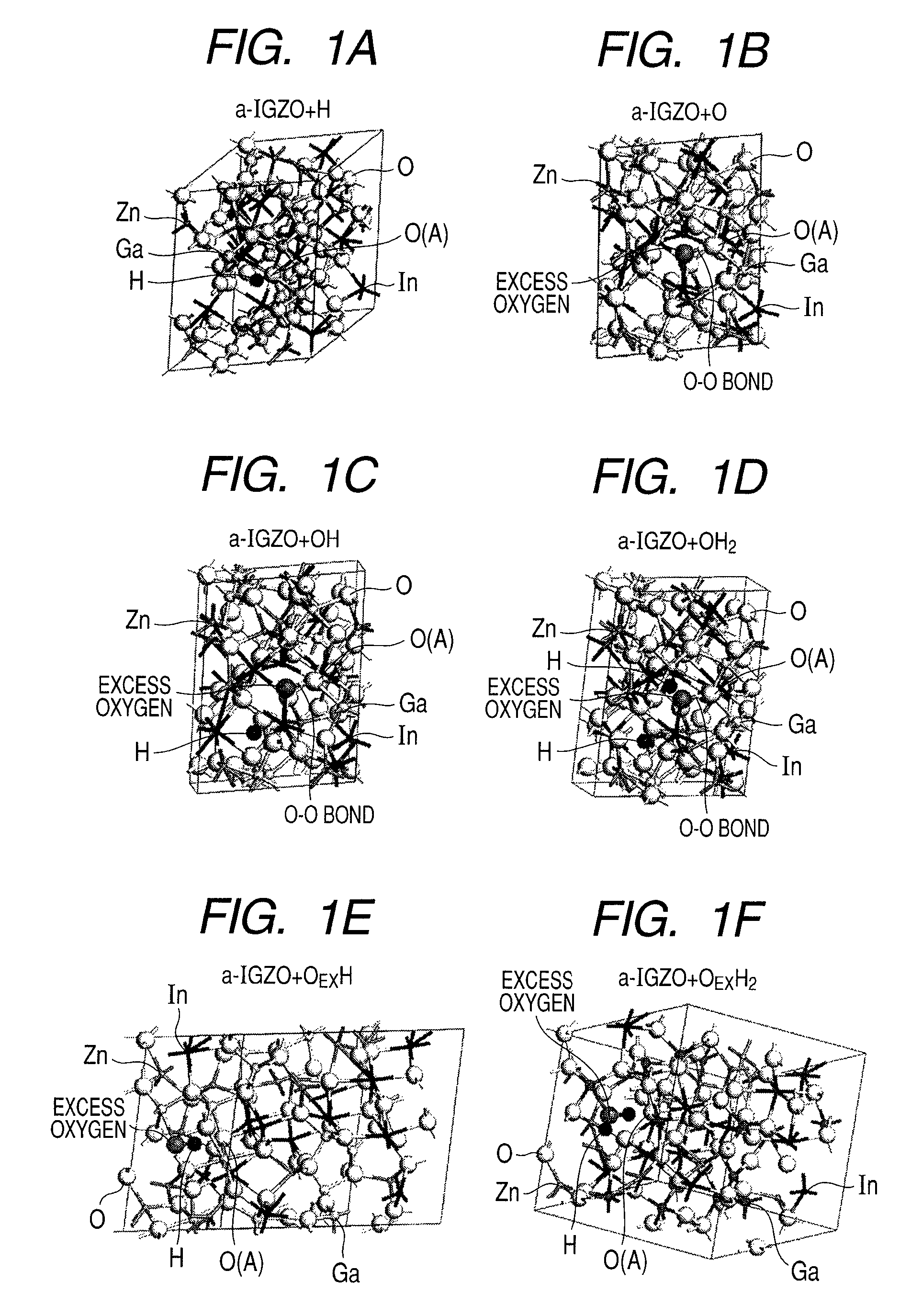
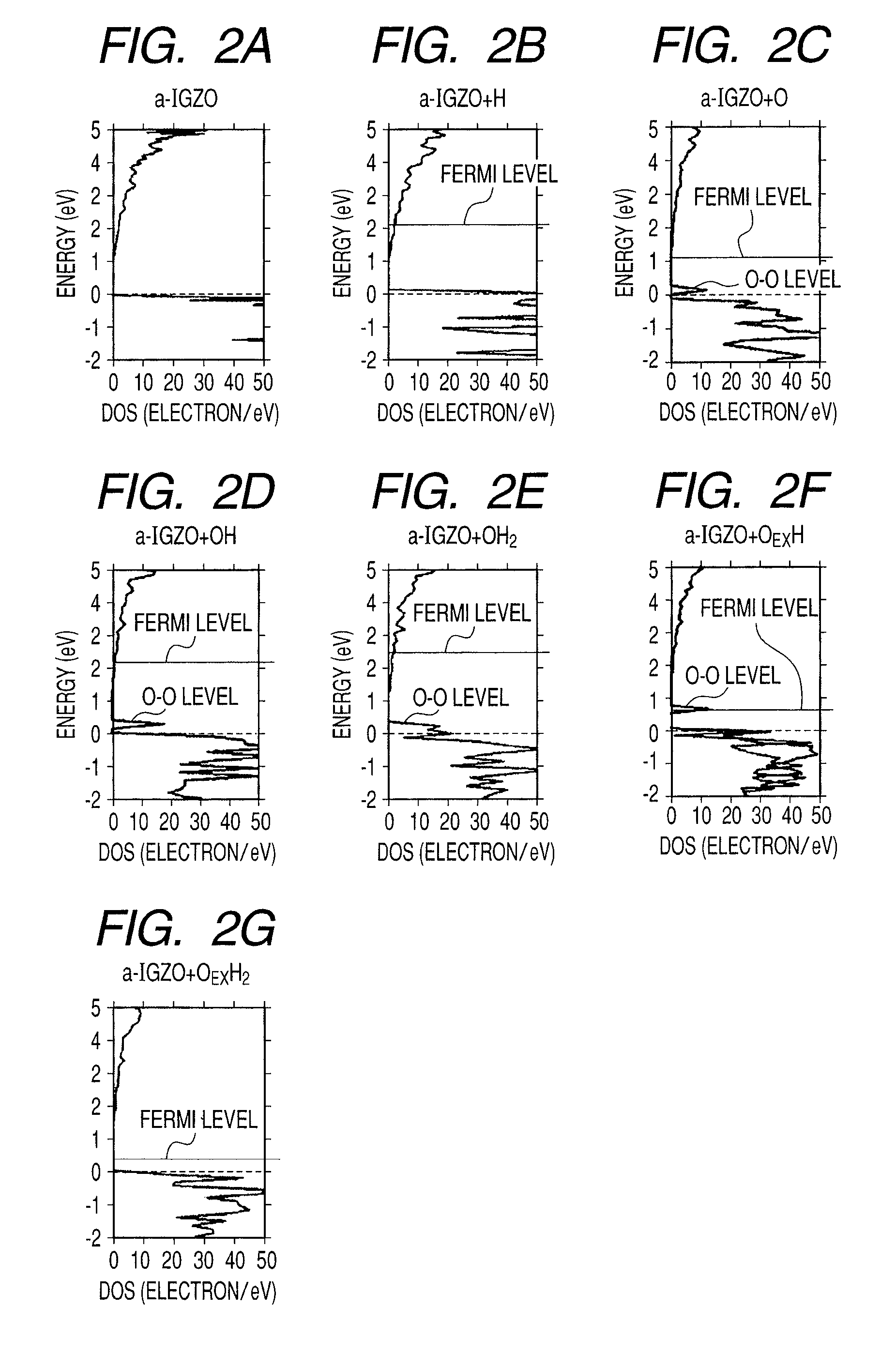
There is provided an amorphous oxide semiconductor including hydrogen and at least one element of indium (In) and zinc (Zn), the amorphous oxide semiconductor containing one of hydrogen atoms and deuterium atoms of 1×1020 cm−3 or more to 1×1022 cm−3 or less, and a density of bonds between oxygen and hydrogen except bonds between excess oxygen (OEX) and hydrogen in the amorphous oxide semiconductor being 1×1018 cm−3 or less.
Owner:CANON KK
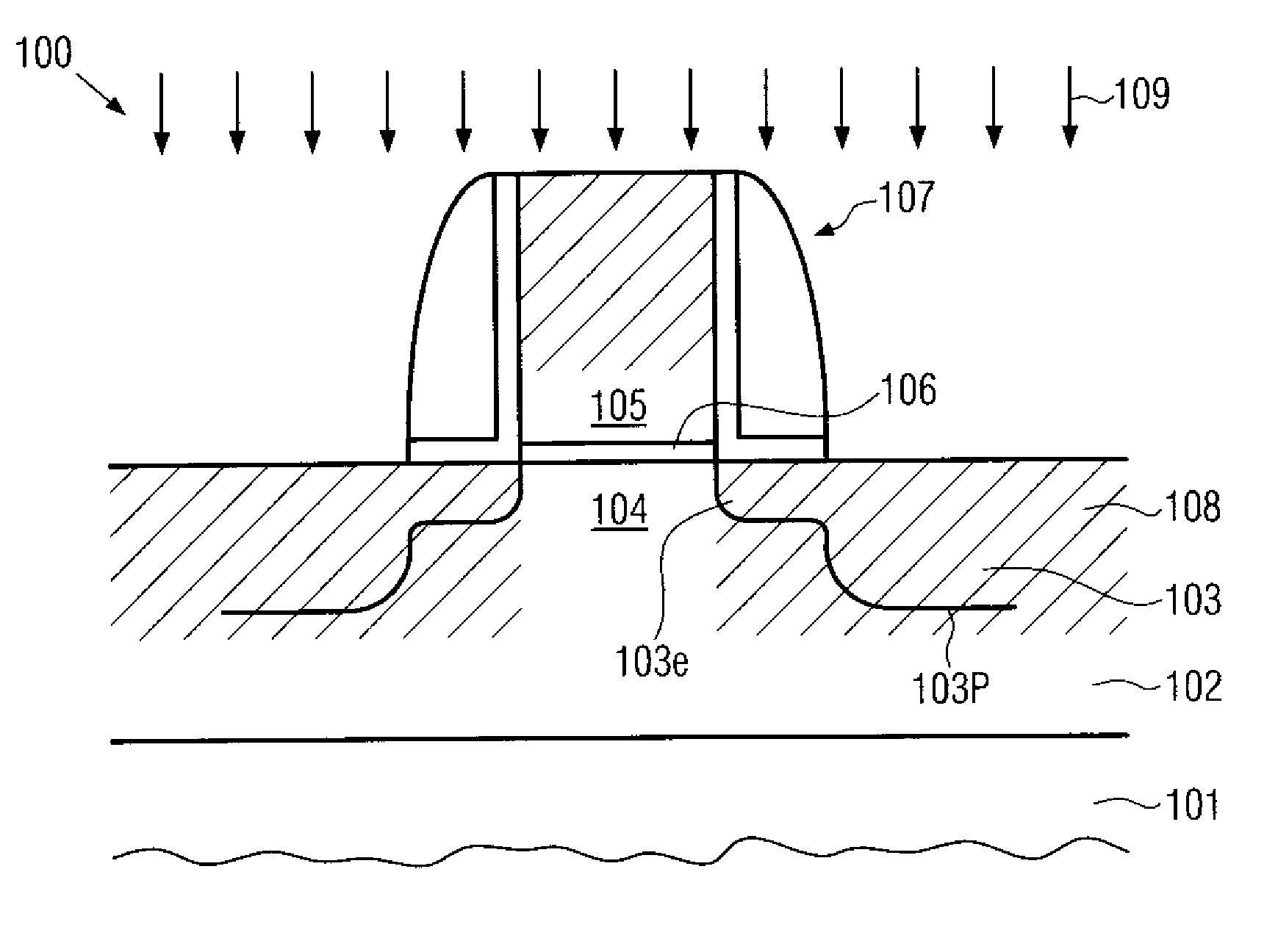
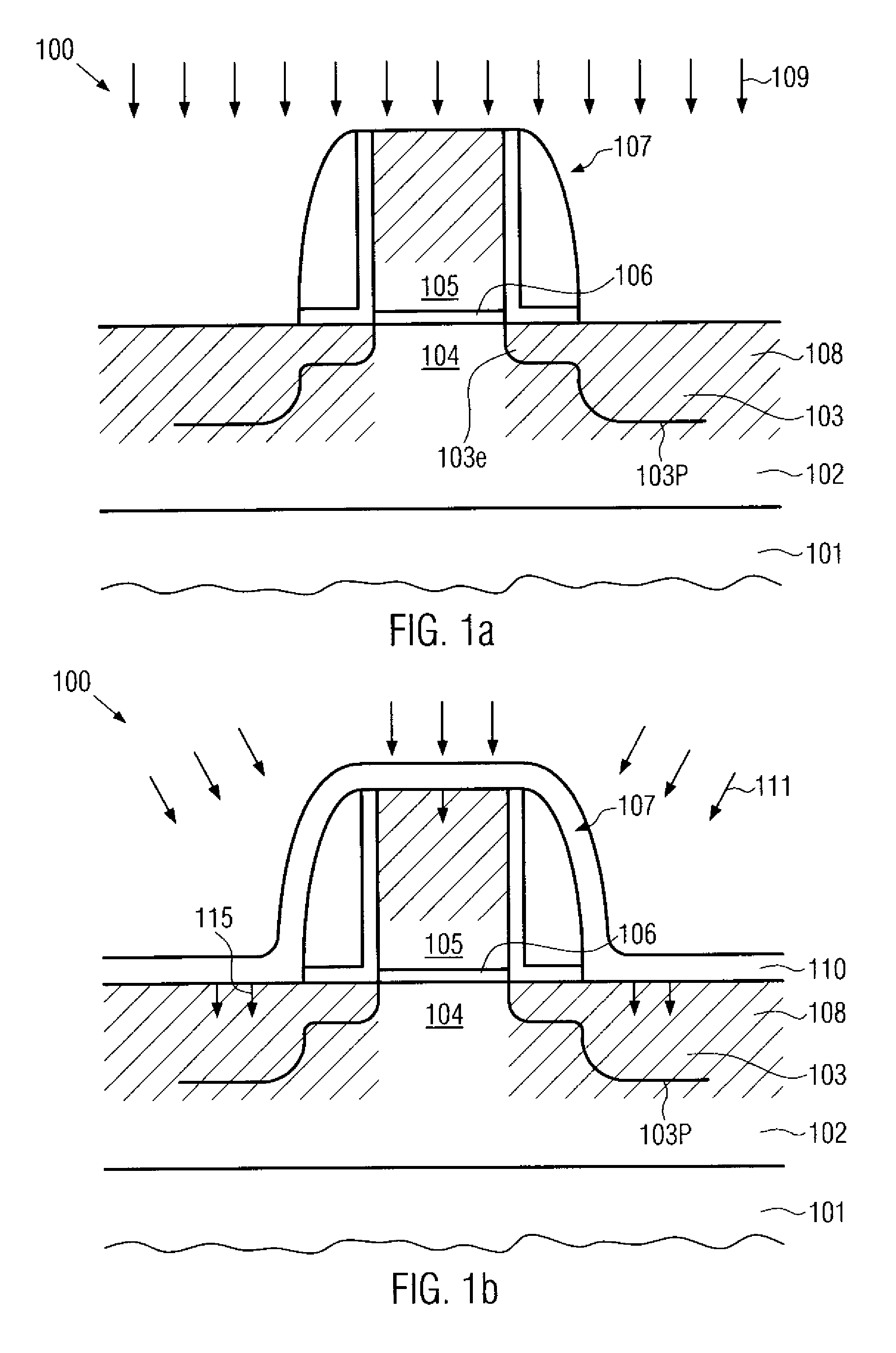
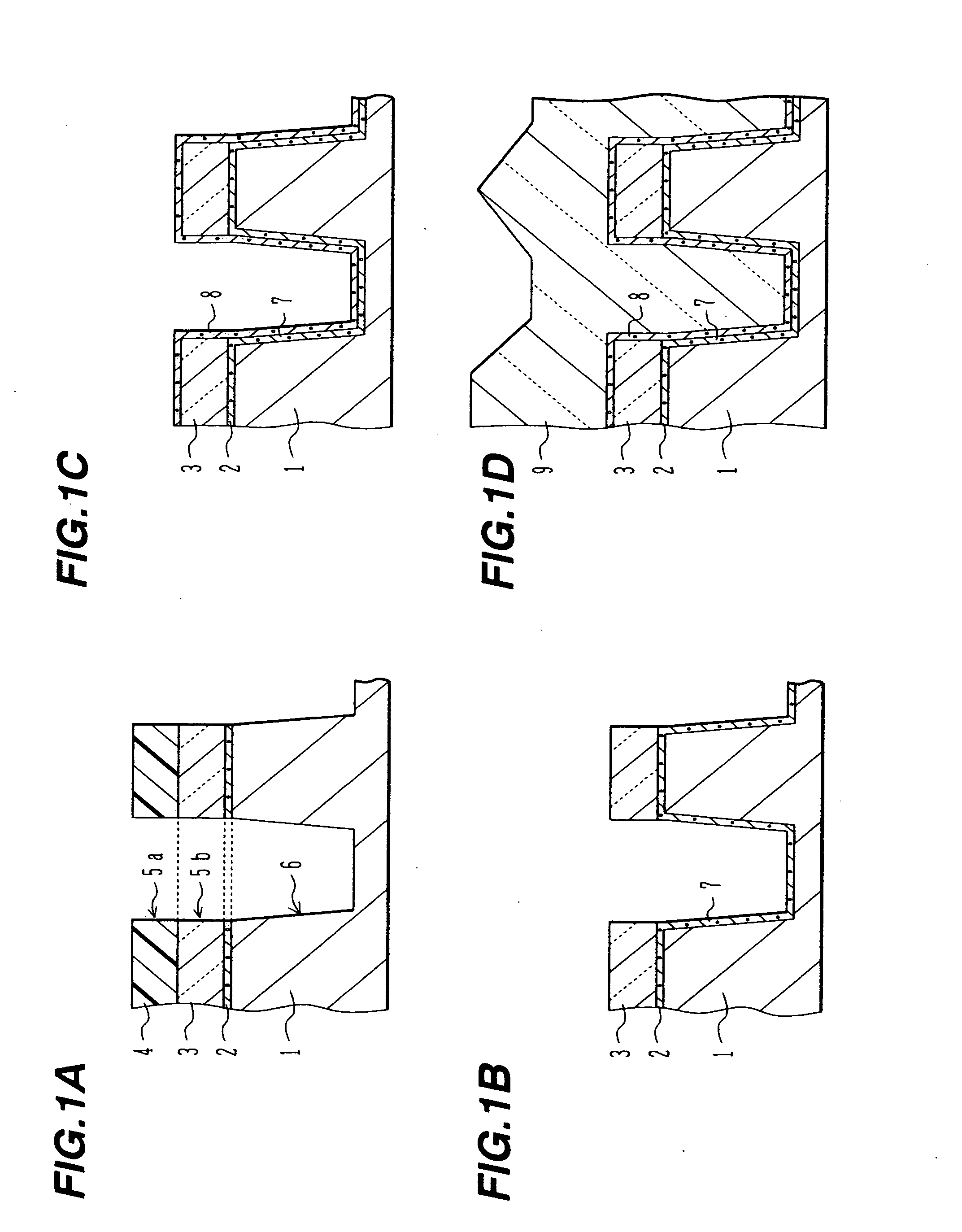
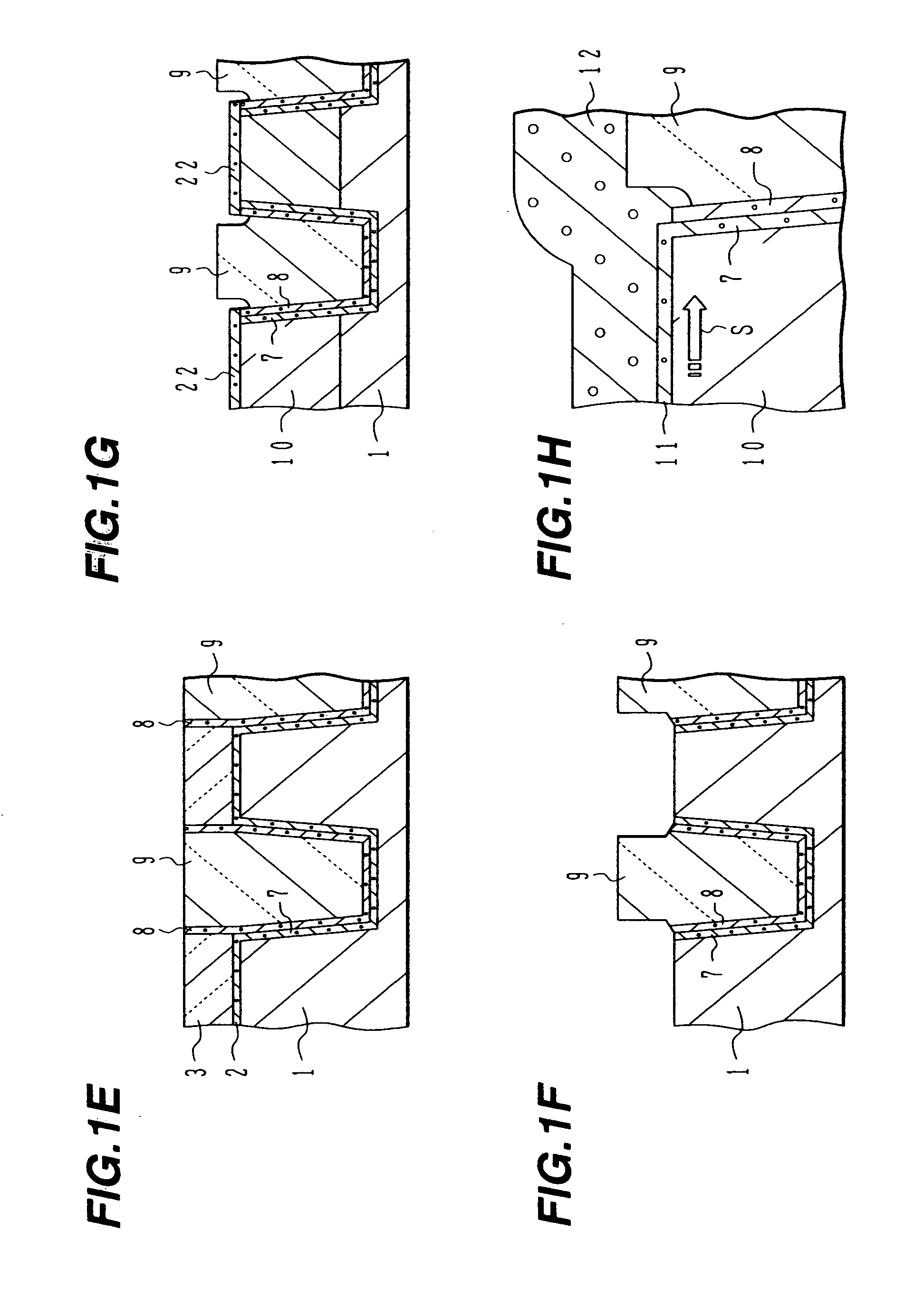
Semiconductor device with shallow trench isolation and its manufacture method
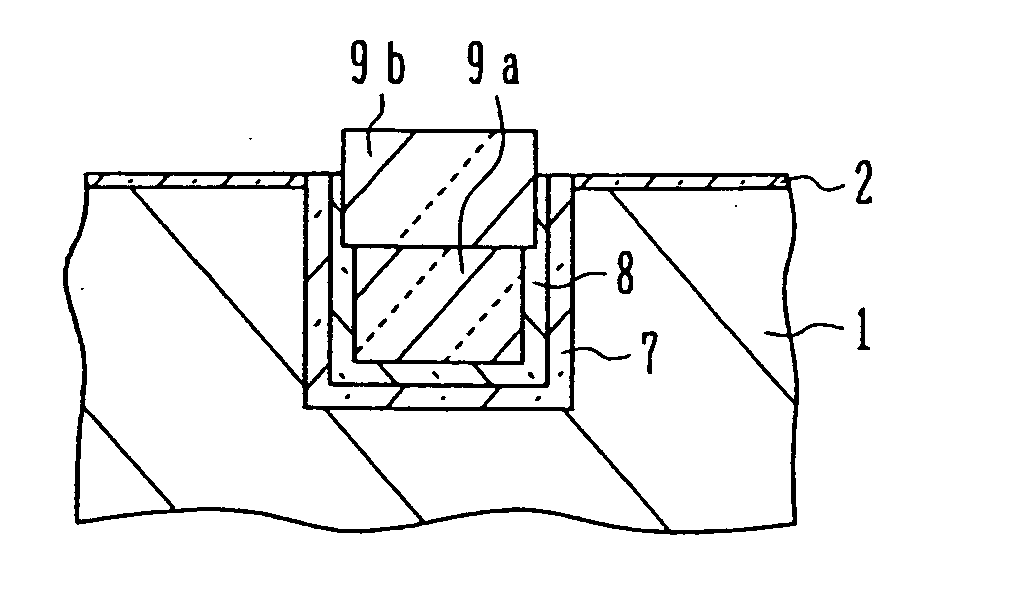
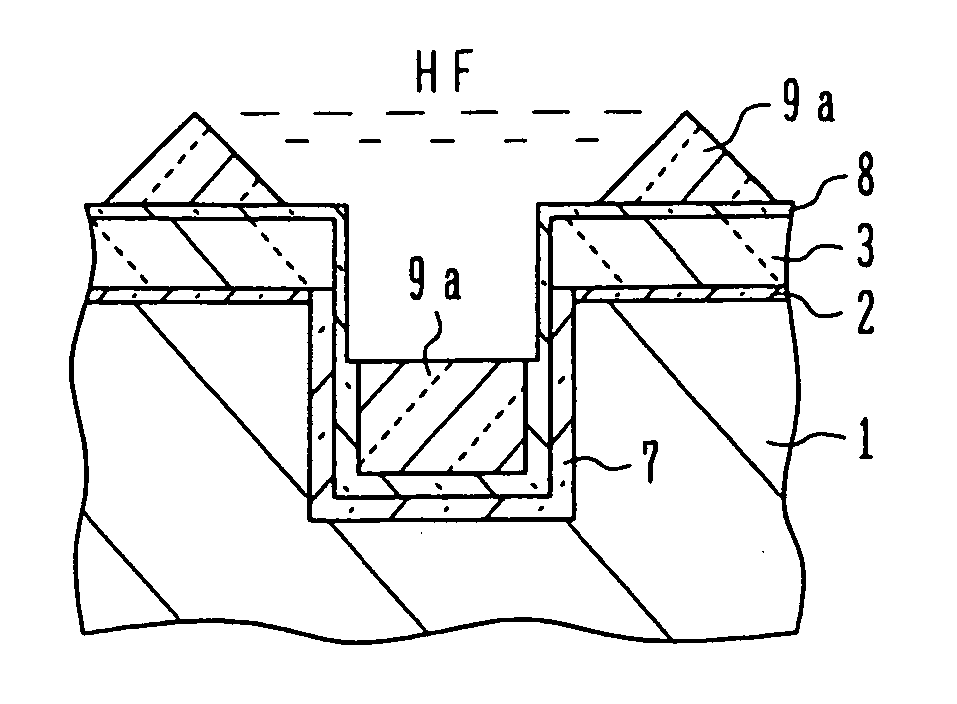
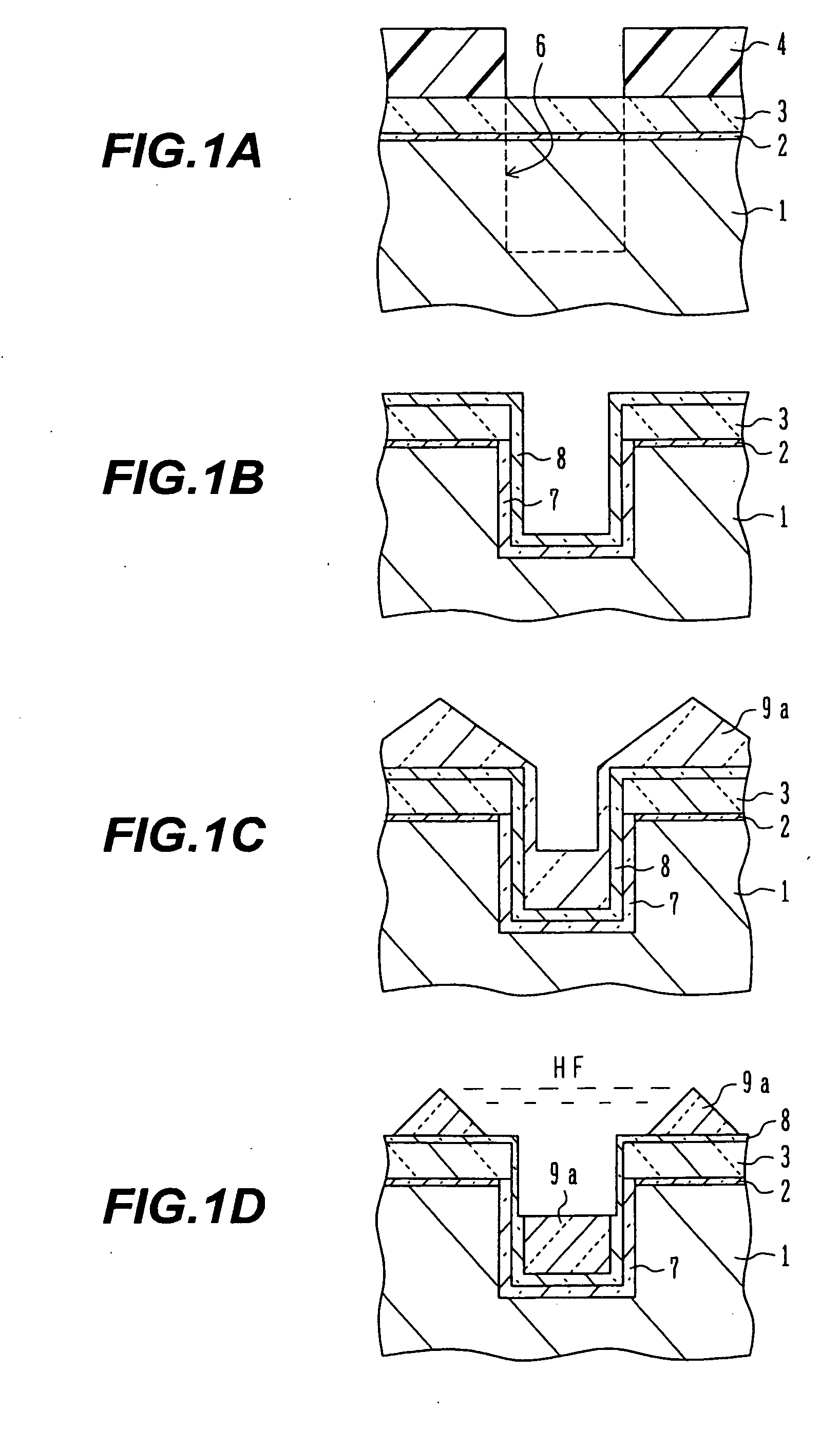
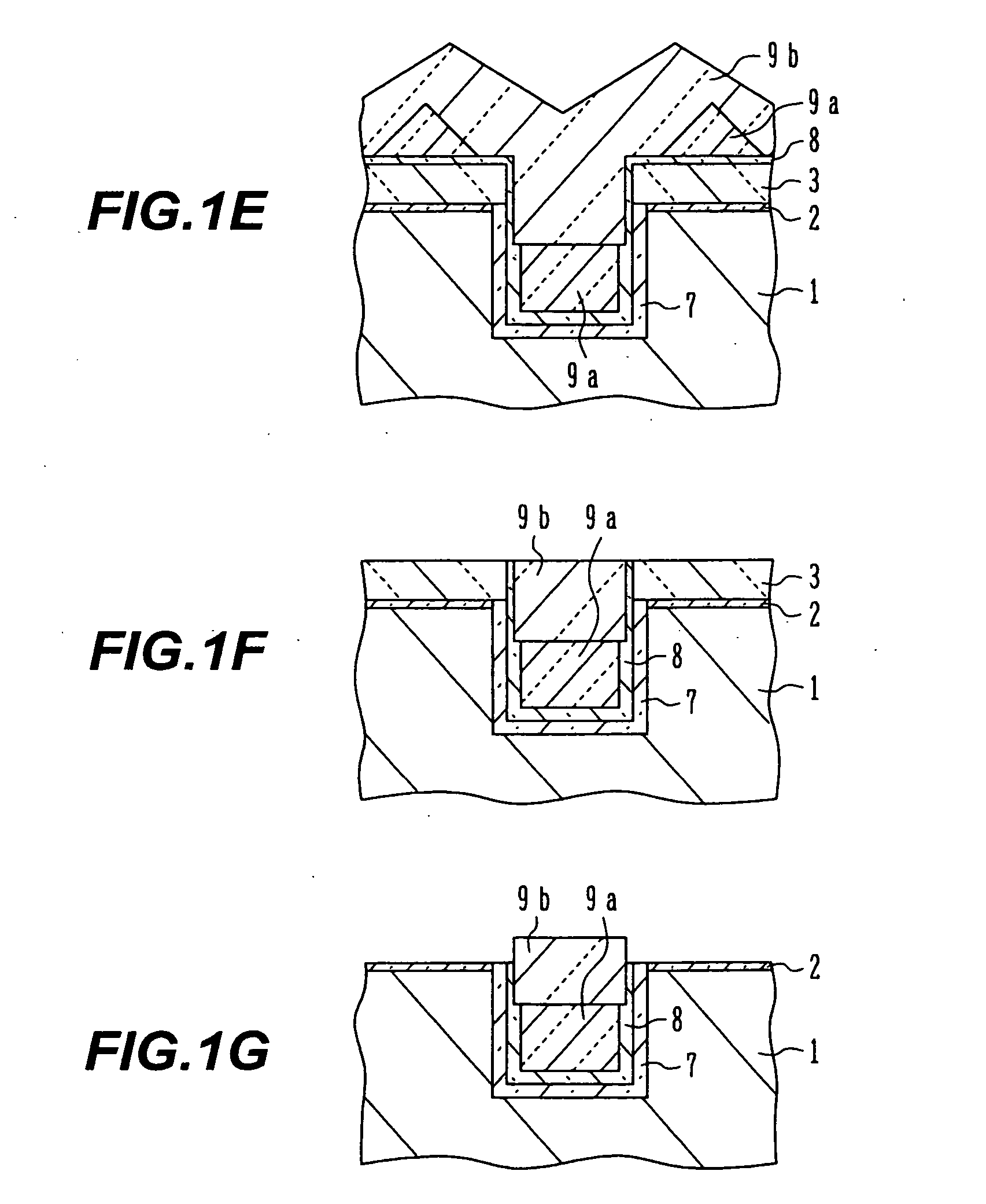
InactiveUS20060255426A1Improve transistor characteristicsIncrease currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrofluoric acidHigh density
A semiconductor device manufacturing method includes the steps of: (a) forming a stopper layer for chemical mechanical polishing on a surface of a semiconductor substrate; (b) forming an element isolation trench in the stopper layer and the semiconductor substrate; (c) depositing a nitride film covering an inner surface of the trench; (d) depositing a first oxide film through high density plasma CVD, the first oxide film burying at least a lower portion of the trench deposited with the nitride film; (e) washing out the first oxide film on a side wall of the trench by dilute hydrofluoric acid; (f) depositing a second oxide film by high density plasma CVD, the second oxide film burying the trench after the washing-out; and (g) removing the oxide films on the stopper layer by chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Method of increasing transistor performance by dopant activation after silicidation
InactiveUS20070281472A1Improve transistor characteristicsReduce process complexityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideMetal silicide
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor device with copper wirings
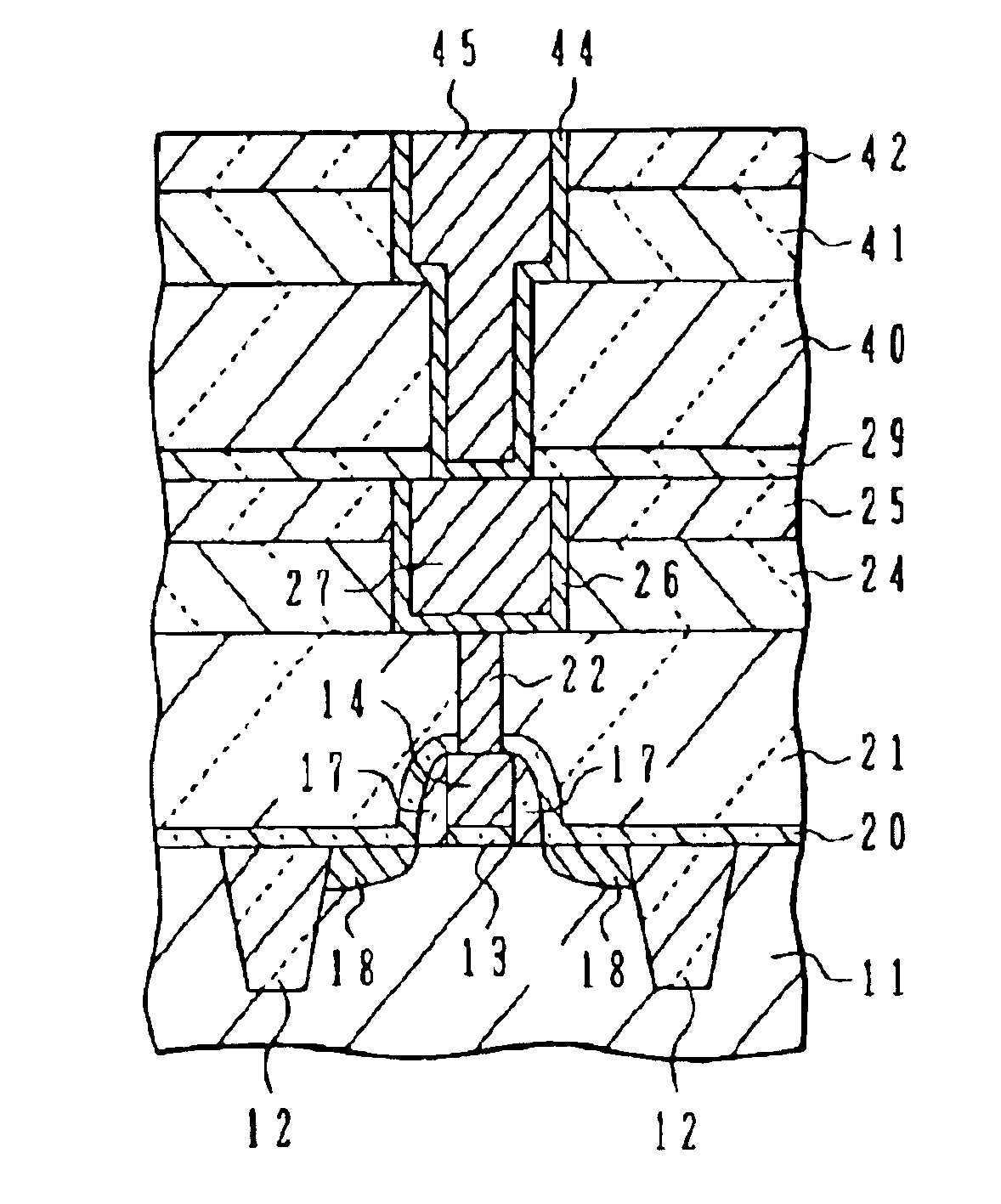
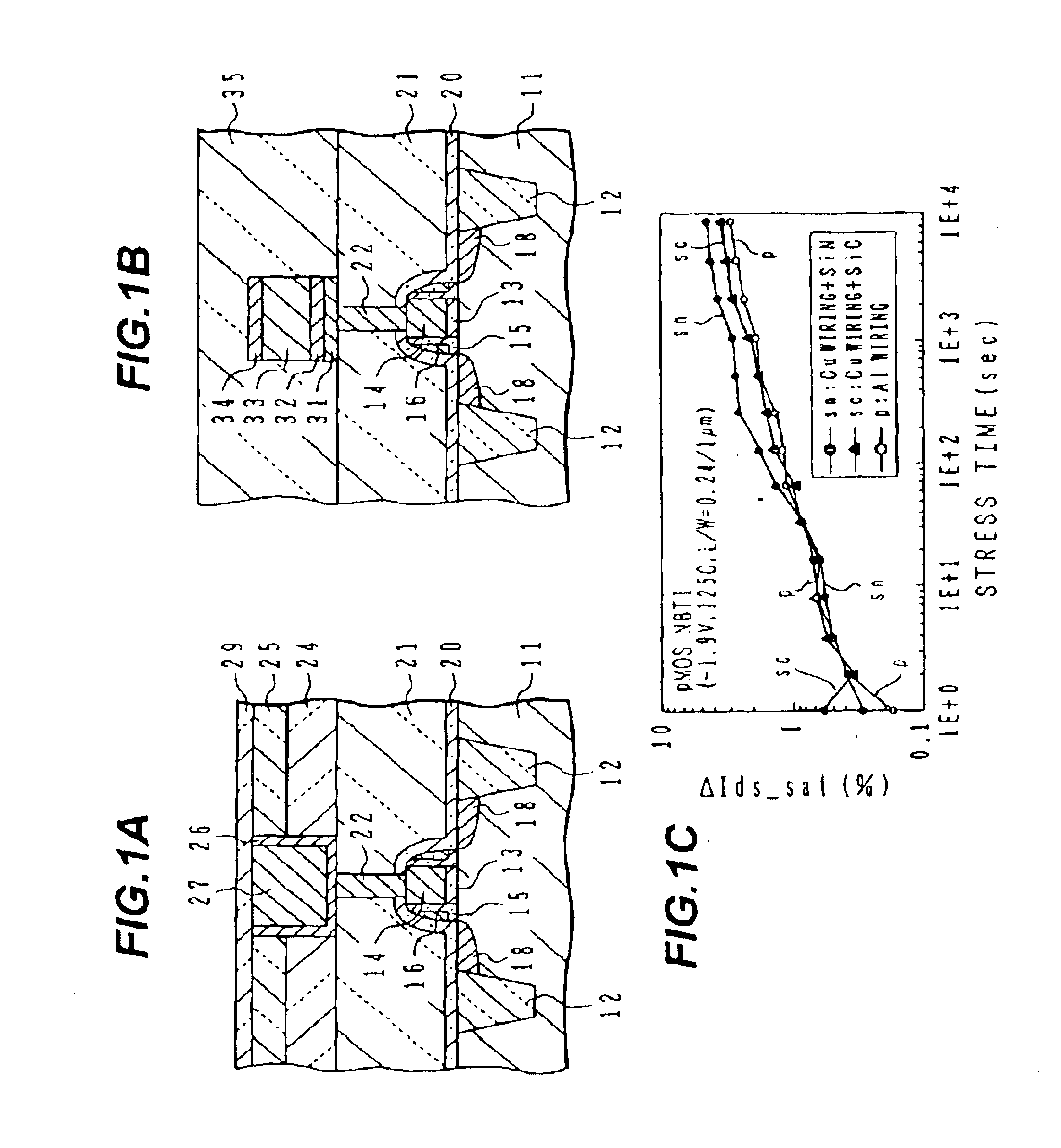
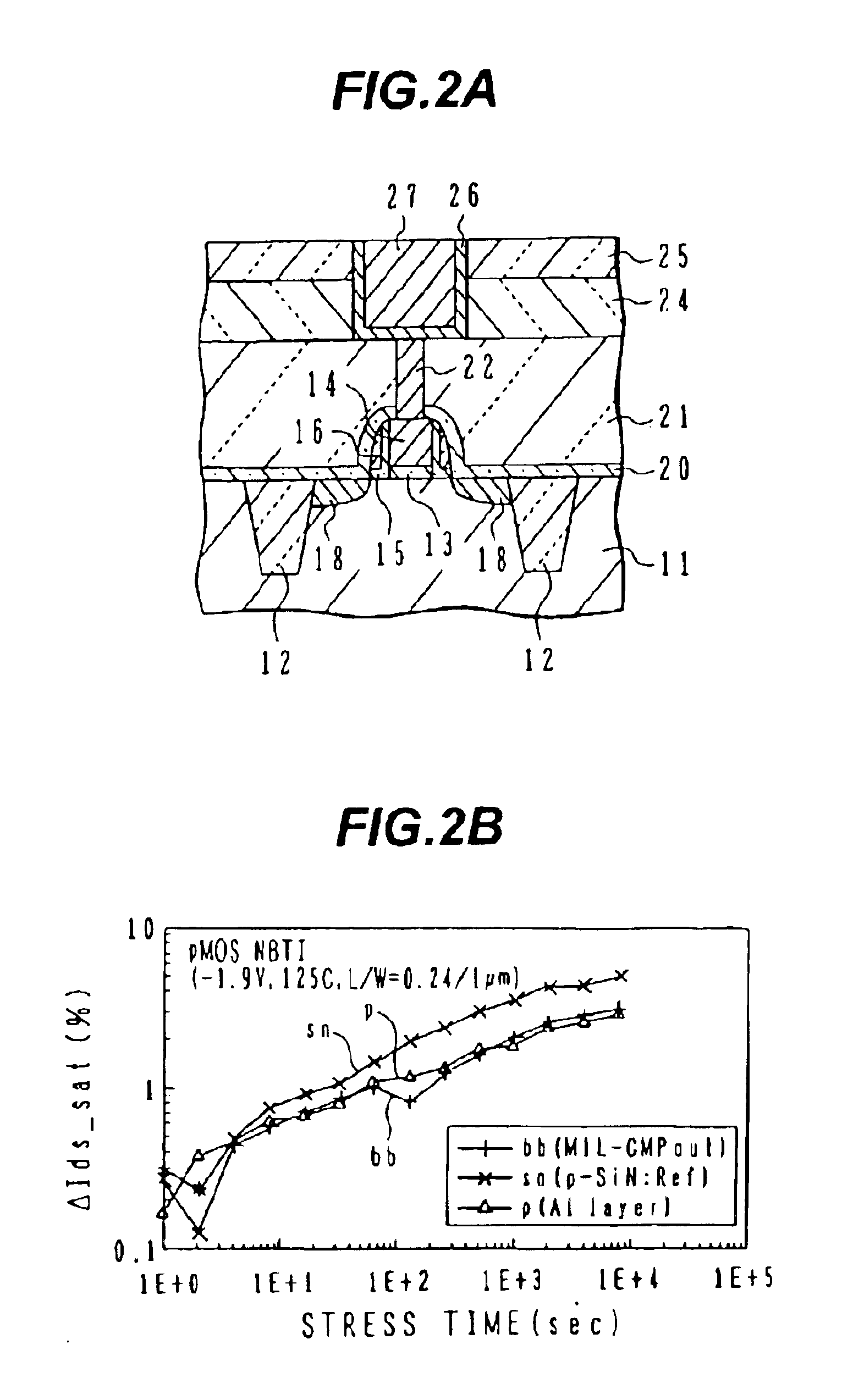
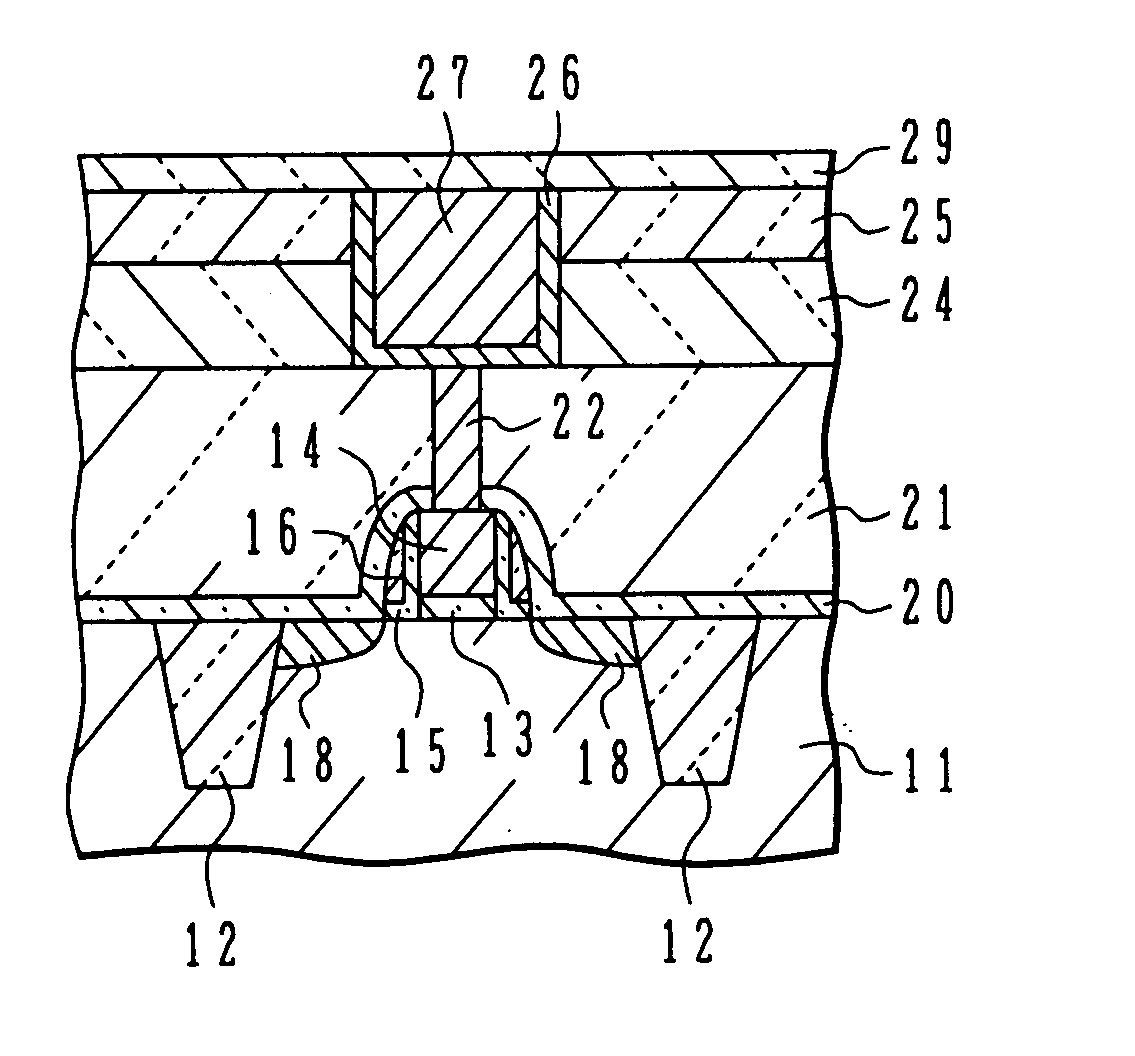
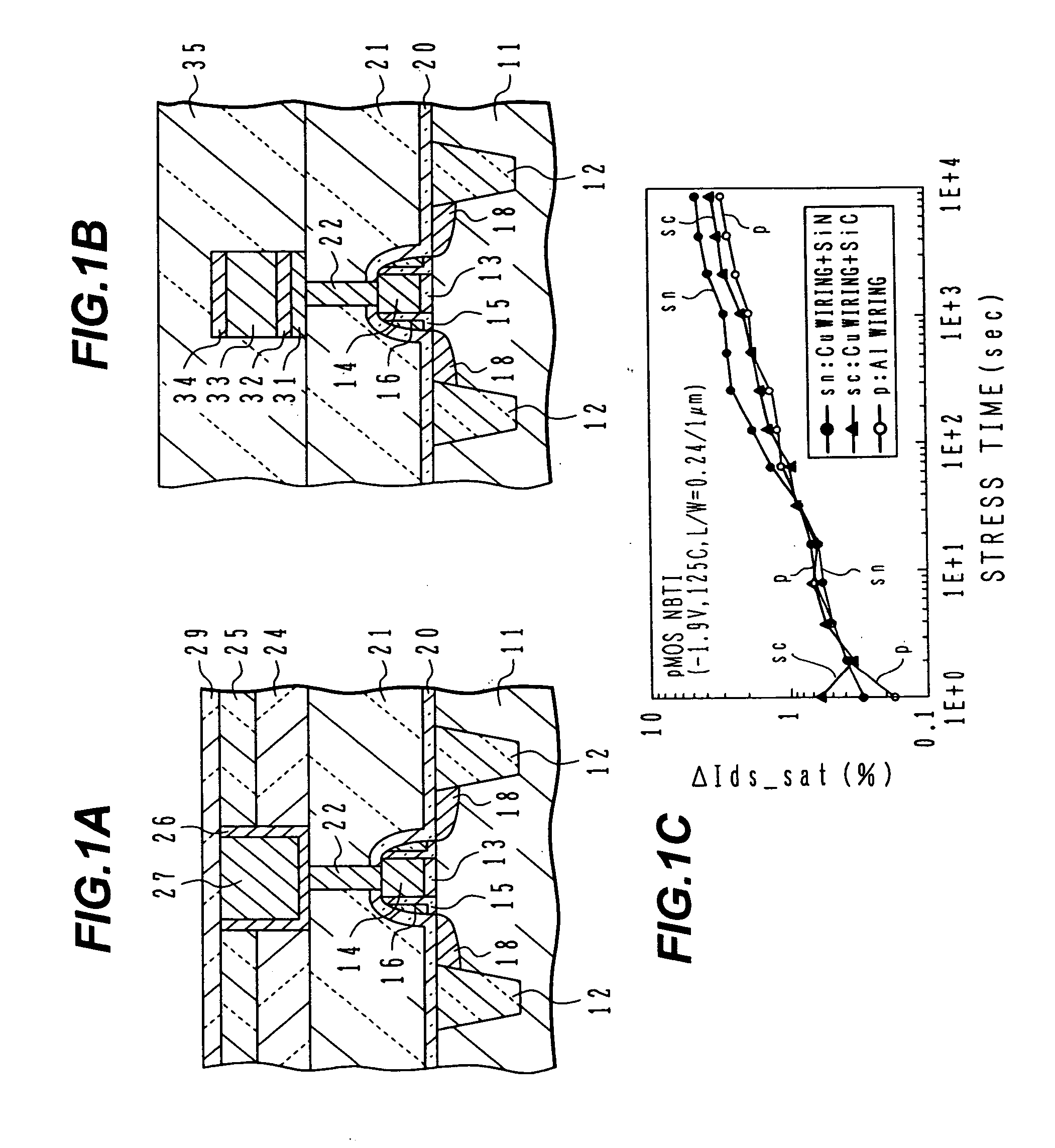
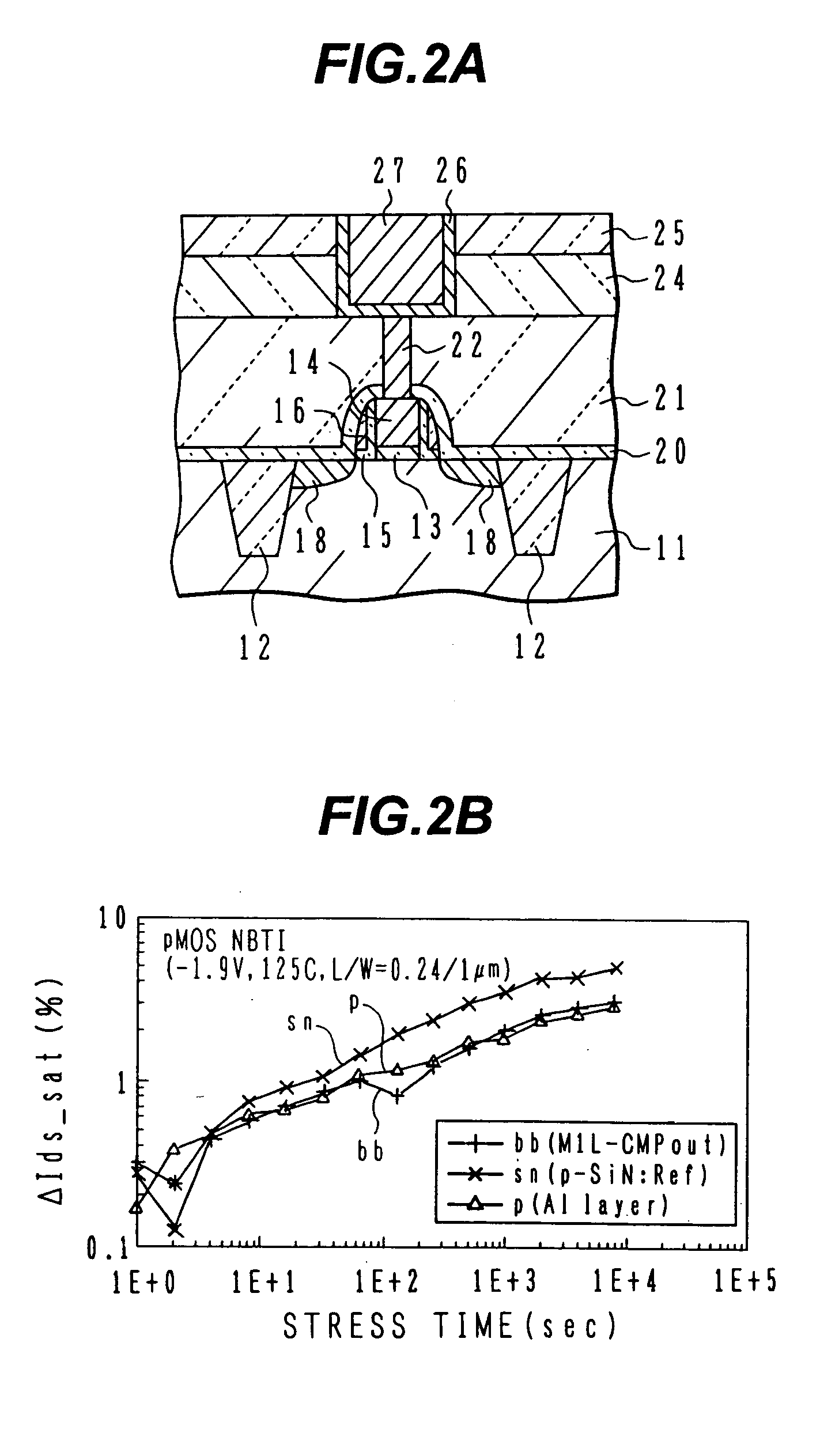
InactiveUS6885105B2Inhibit deteriorationSmall gate leak currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNitrogenBoron containing
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Semiconductor device with shallow trench isolation and its manufacture method
InactiveUS20050194646A1Increase currentGenerationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCompound (substance)Oxide
A semiconductor device manufacturing method includes the steps of: (a) forming a stopper layer for chemical mechanical polishing on a surface of a semiconductor substrate; (b) forming an element isolation trench in the stopper layer and the semiconductor substrate; (c) depositing a nitride film covering an inner surface of the trench; (d) depositing a first oxide film through high density plasma CVD, the first oxide film burying at least a lower portion of the trench deposited with the nitride film; (e) washing out the first oxide film on a side wall of the trench by dilute hydrofluoric acid; (f) depositing a second oxide film by high density plasma CVD, the second oxide film burying the trench after the washing-out; and (g) removing the oxide films on the stopper layer by chemical mechanical polishing.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
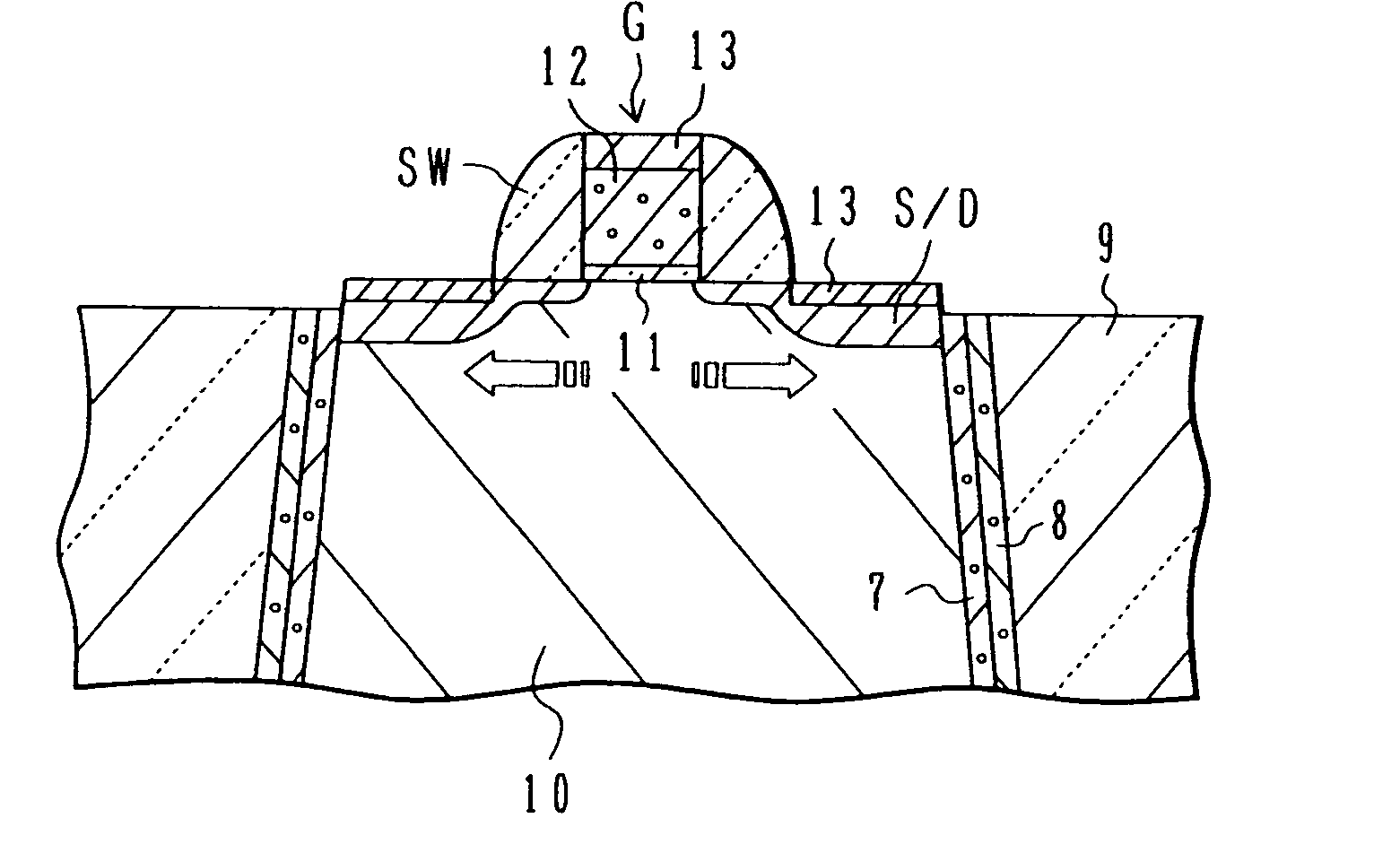
Back-channel-etch type thin-film transistor, semiconductor device and manufacturing methods thereof
InactiveUS20100176399A1Increase productivityImprove transistor characteristicsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPellicle membrane
A back-channel-etch type TFT includes a gate electrode, an SiN film that is formed on the gate electrode, and an SiO film that is formed and patterned on the SiN film. The TFT further includes an polycrystalline semiconductor film that is formed and patterned on the SiO film in contact with the SiO film in such a way that all pattern ends of the polycrystalline semiconductor film are located in close proximity to pattern ends of the SiO film.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Thin-film transistor, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20090146138A1Improve reliabilityImprove transistor characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen atomOrganic semiconductor
A thin-film transistor includes a source electrode, a drain electrode arranged apart from the source electrode, an organic semiconductor layer arranged between the source electrode and the drain electrode so as to establish connection of the source electrode and the drain electrode, a first insulating layer arranged on one surface side of the organic semiconductor layer, a gate electrode arranged on a side of the first insulating layer opposite that on which the organic semiconductor layer lie, and a second insulating layer arranged on a side of the organic semiconductor layer opposite that on which the first insulating layer lie. The organic semiconductor layer contains an organic semiconductor material having p-type semiconducting properties. The second insulating layer contains one or more compounds of the following formula (1), so that electrons are fed from the second insulating layer into the organic semiconductor layer:wherein R1 and R2 independently represent a substituted or unsubstituted alkylene group; X1, X2, X3 and X4 each represent a hydrogen atom or an electron-donating group; and n represents 100 to 100,000, wherein at least one of X1, X2, X3 and X4 represents an electron-donating group.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Semiconductor device with STI and its manufacture
InactiveUS20060202301A1Low mobilityImprove transistor characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSilicon oxide
A semiconductor device includes: a silicon substrate with semiconductor elements; an isolation trench formed in the silicon substrate for isolating active regions in the silicon substrate, the isolation trench having a trapezoidal cross sectional shape having a width gradually narrowing with a depth from the surface of the silicon substrate; a first liner insulating film formed on the surface of the trench and made of a silicon oxide film or a silicon oxynitride film having a thickness of 1 to 5 nm; a second liner insulating film formed on the first liner insulating film and made of a silicon nitride film having a thickness of 2 to 8 nm; and an isolation region burying the trench defined by the second liner insulating film.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Silk solution, organic thin film transistor prepared by using silk solution, capacitor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102208533AImprove transistor characteristicsEasy accessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceOrganic semiconductor
The invention discloses silk solution, an organic thin film transistor prepared by using the silk solution, a capacitor and a manufacturing method thereof. The organic thin film transistor device comprises a substrate, a grid, a grid dielectric layer, an organic semiconductor layer, a source and a drain, wherein the grid is deployed on the substrate; the grid dielectric layer is deployed on the substrate and covers the grid, and the material of the grid dielectric layer contains a silk protein; and the organic semiconductor layer, the source and the drain are deployed above the grid dielectric layer.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
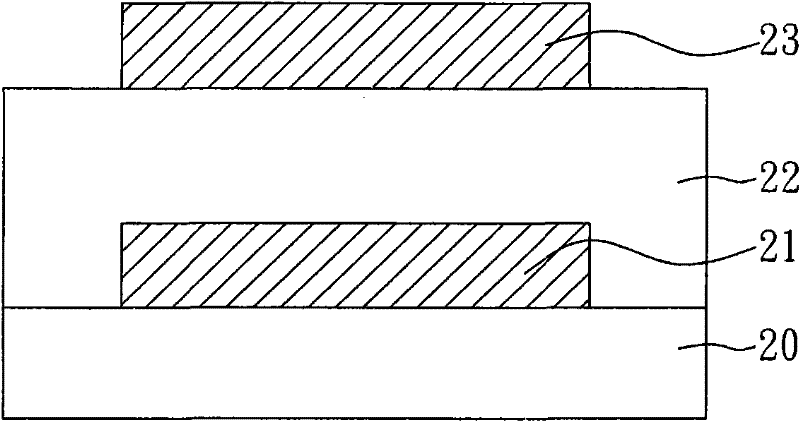
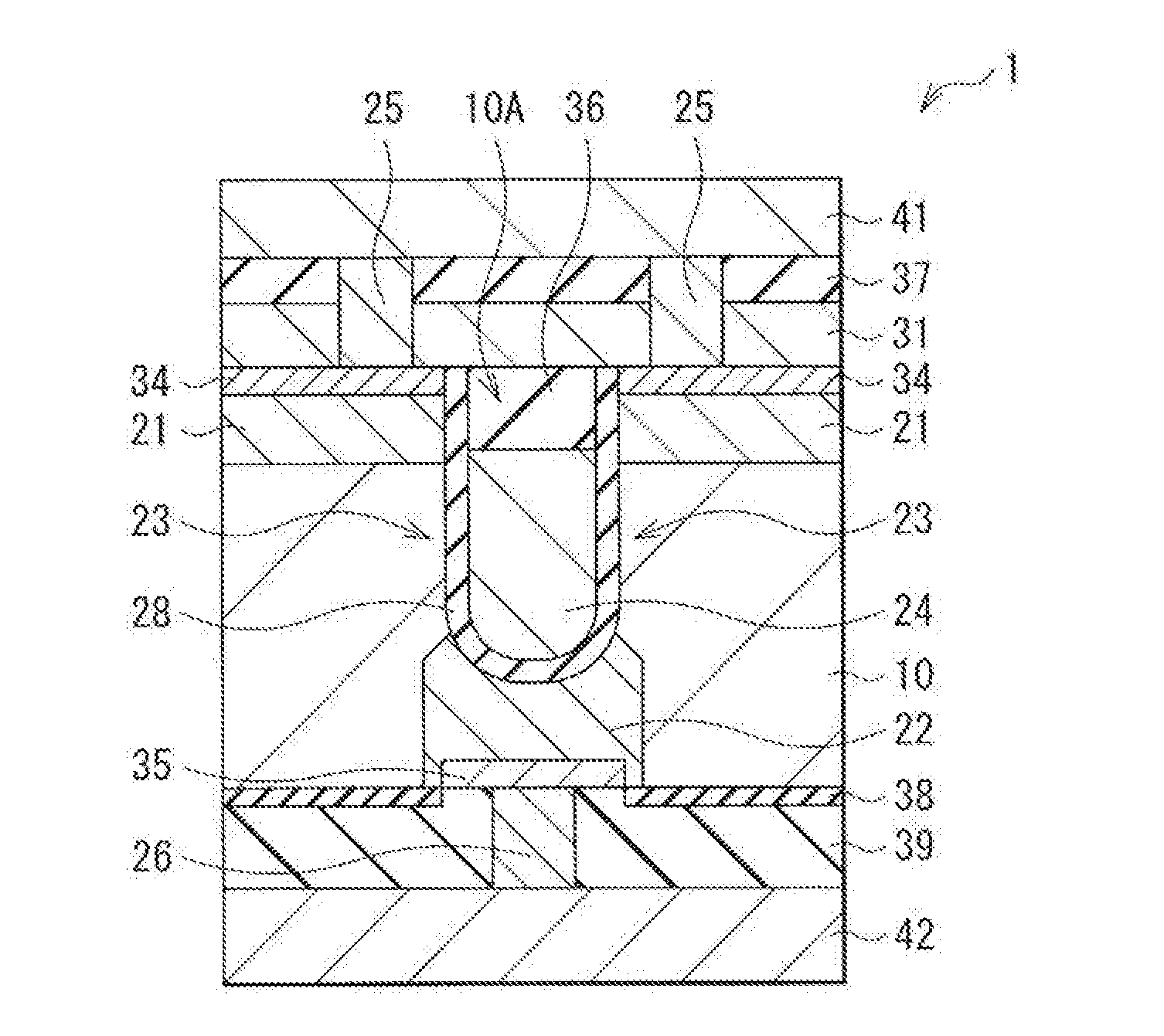
Semiconductor device, memory circuit, method of manufacturing semiconductor device
ActiveUS20160322422A1Improve transistor characteristicsReduced footprintSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialMemory circuits
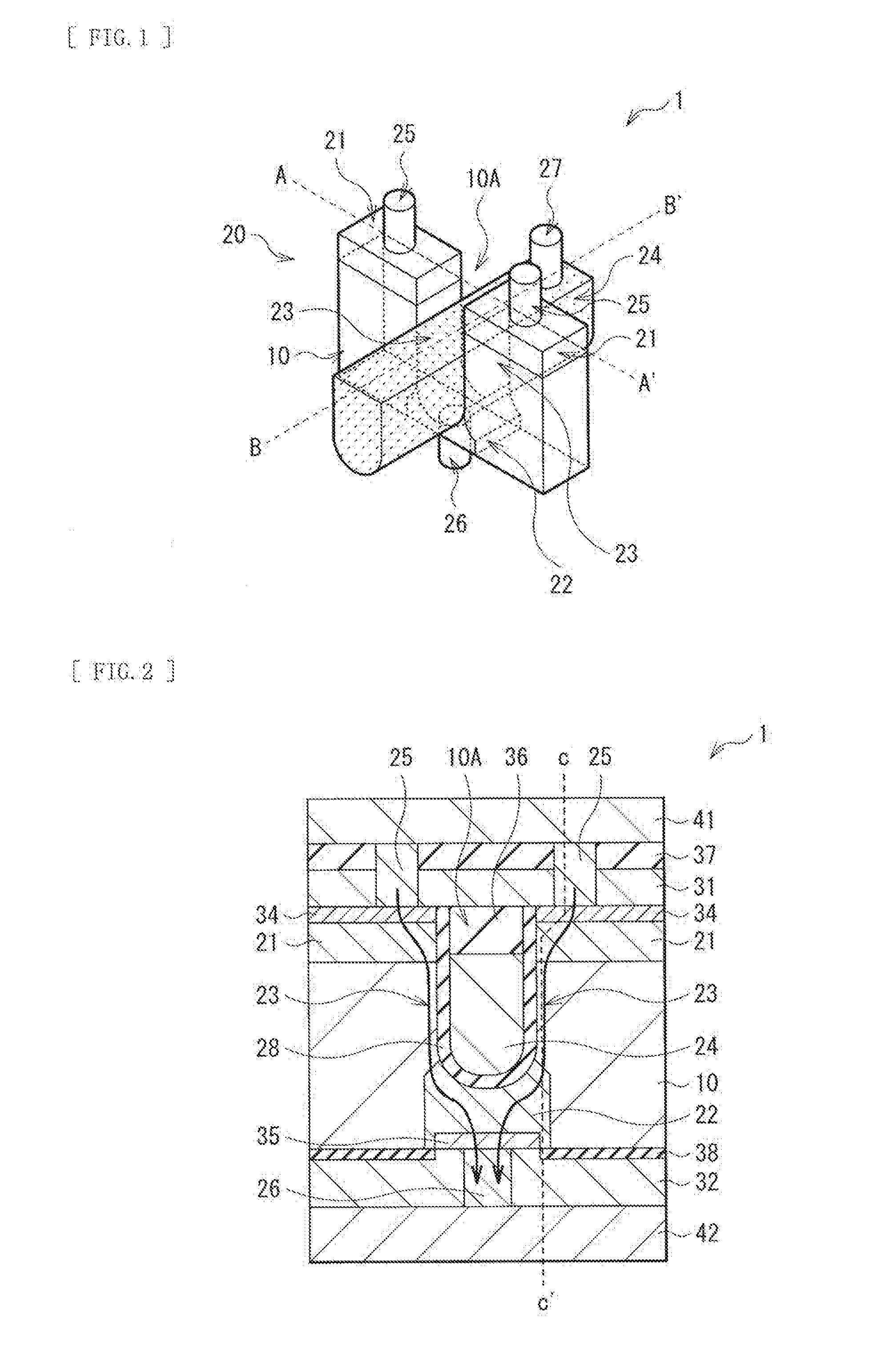
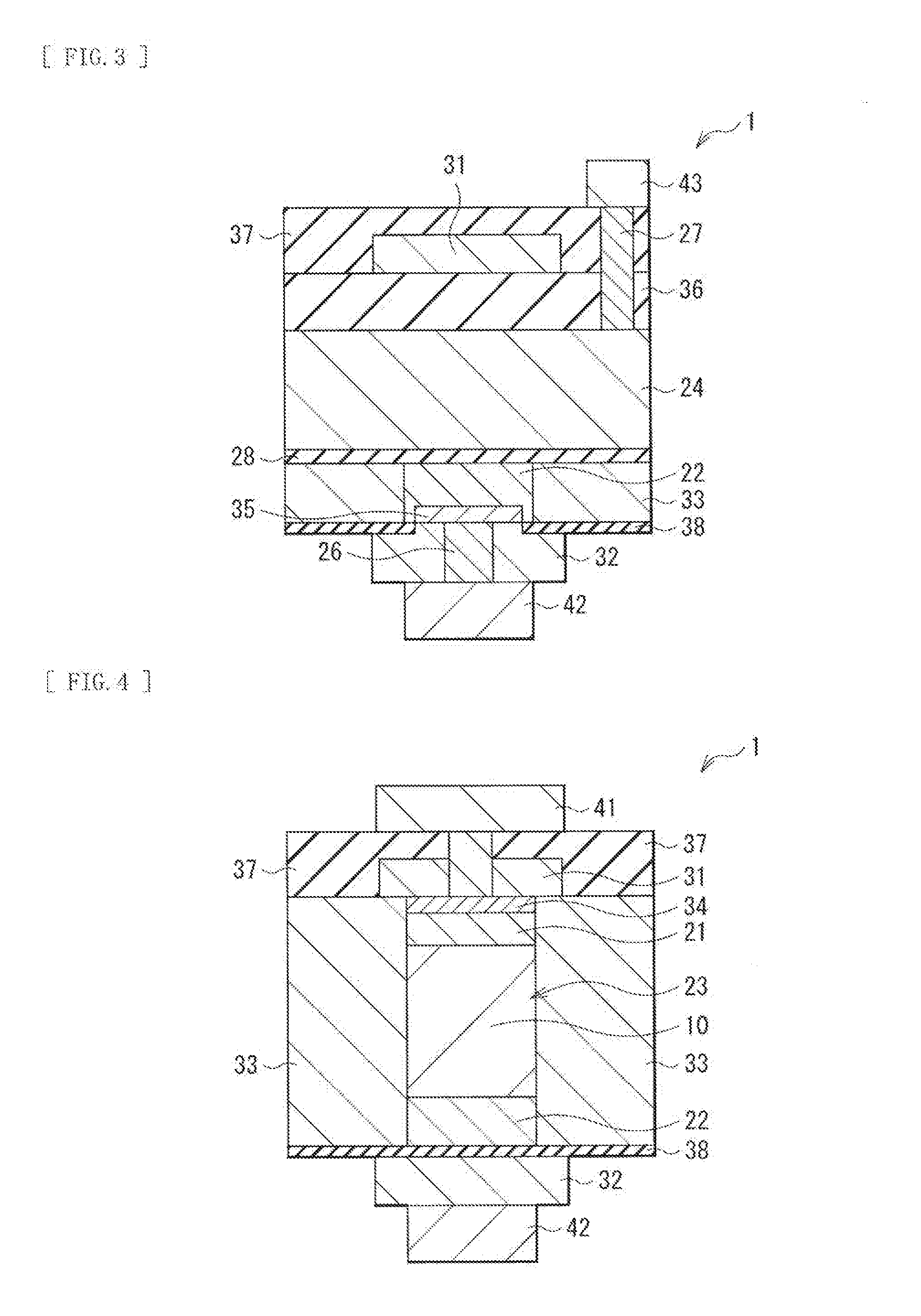
A semiconductor device of the technology includes a first diffusion section (22), a second diffusion section (21), a channel section (23), a gate section (24), and a stress application section (31, 32, or 33). In a semiconductor layer (10) having a groove (10A), the first diffusion section (22) is formed at or in the vicinity of a bottom of the groove (10A), the second diffusion section (21) is formed at an upper end of the groove (10A), and the channel section (23) is formed between the first diffusion section (22) and the second diffusion section (21). The gate section (24) is buried in the groove (10A) at a position opposing the channel section (23). The stress application section (31, 32, or 33) applies one of compressive stress and tensile stress to the channel section (23) in a normal direction to the semiconductor layer (10).
Owner:SONY CORP
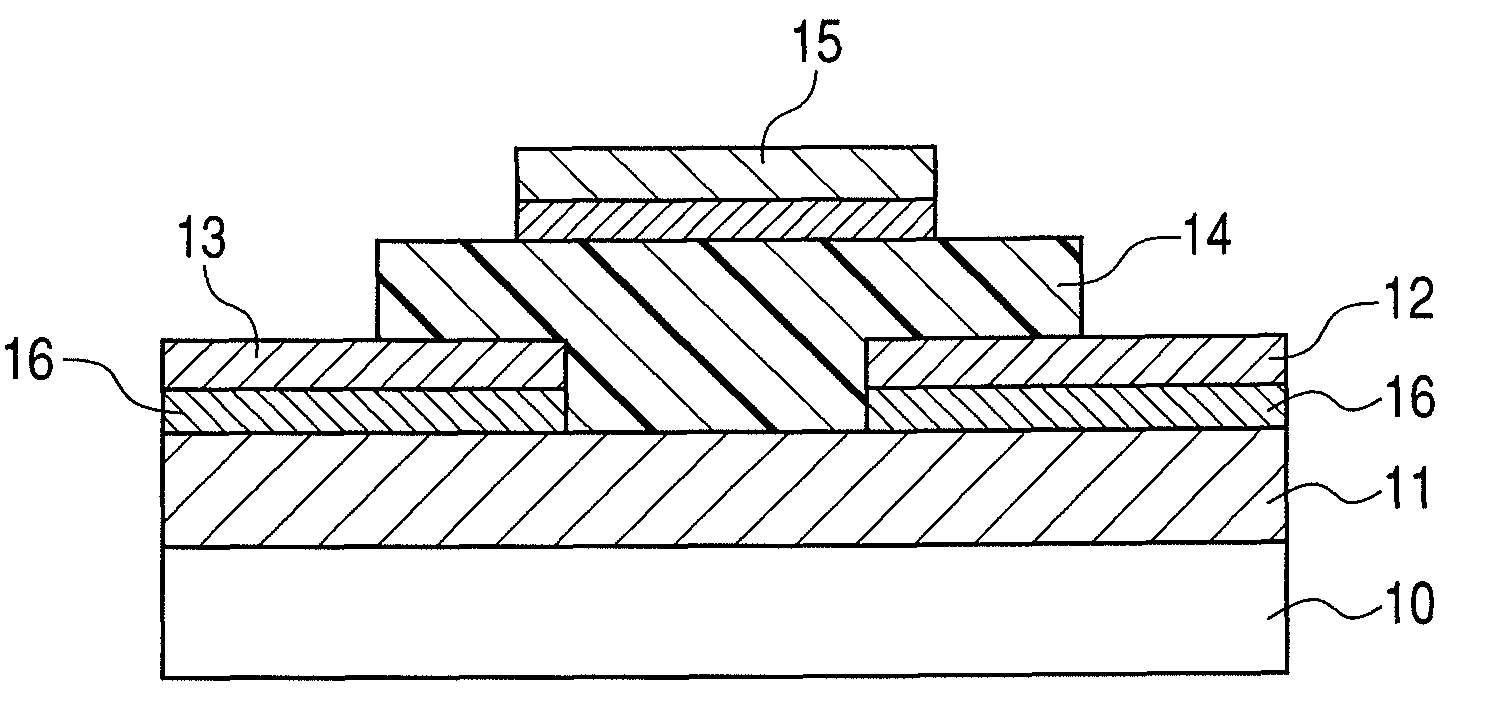
Active matrix substrate, display device, and television receiver
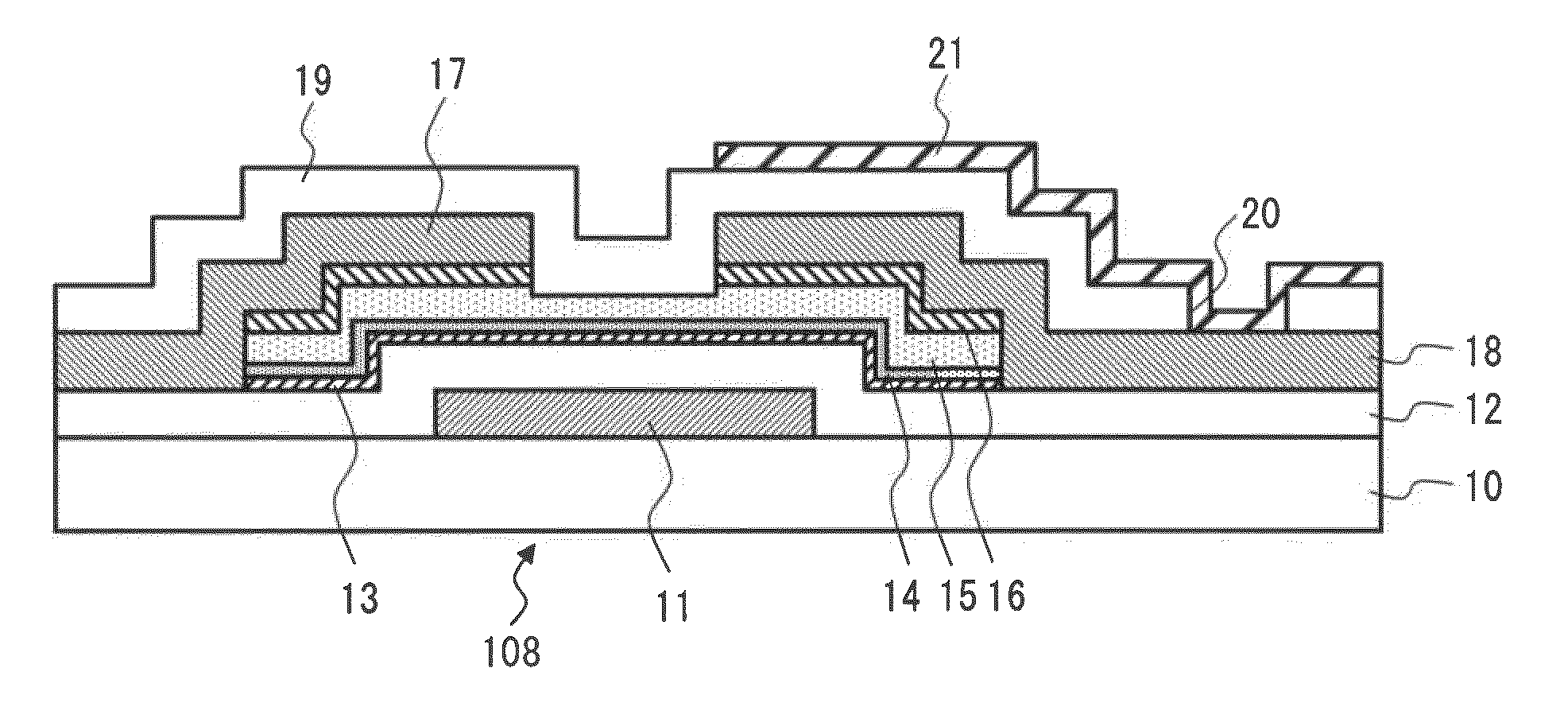
ActiveUS20090091676A1Improve transistor characteristicsPrevent short-circuitingSolid-state devicesNon-linear opticsTelevision receiversActive matrix
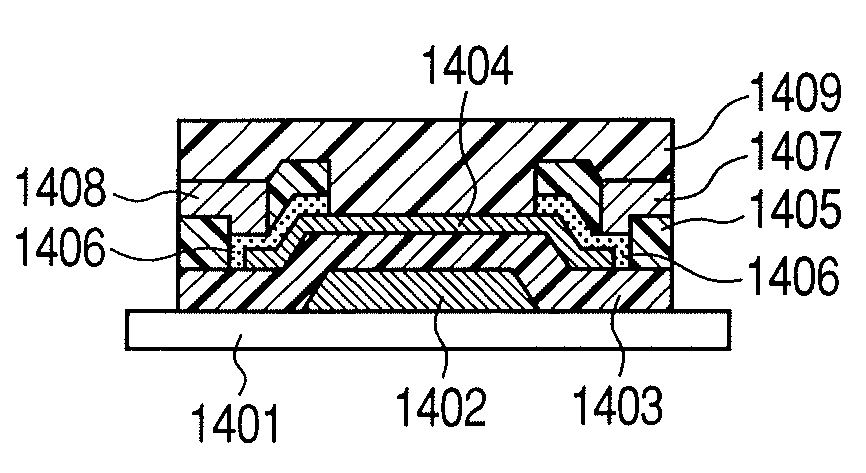
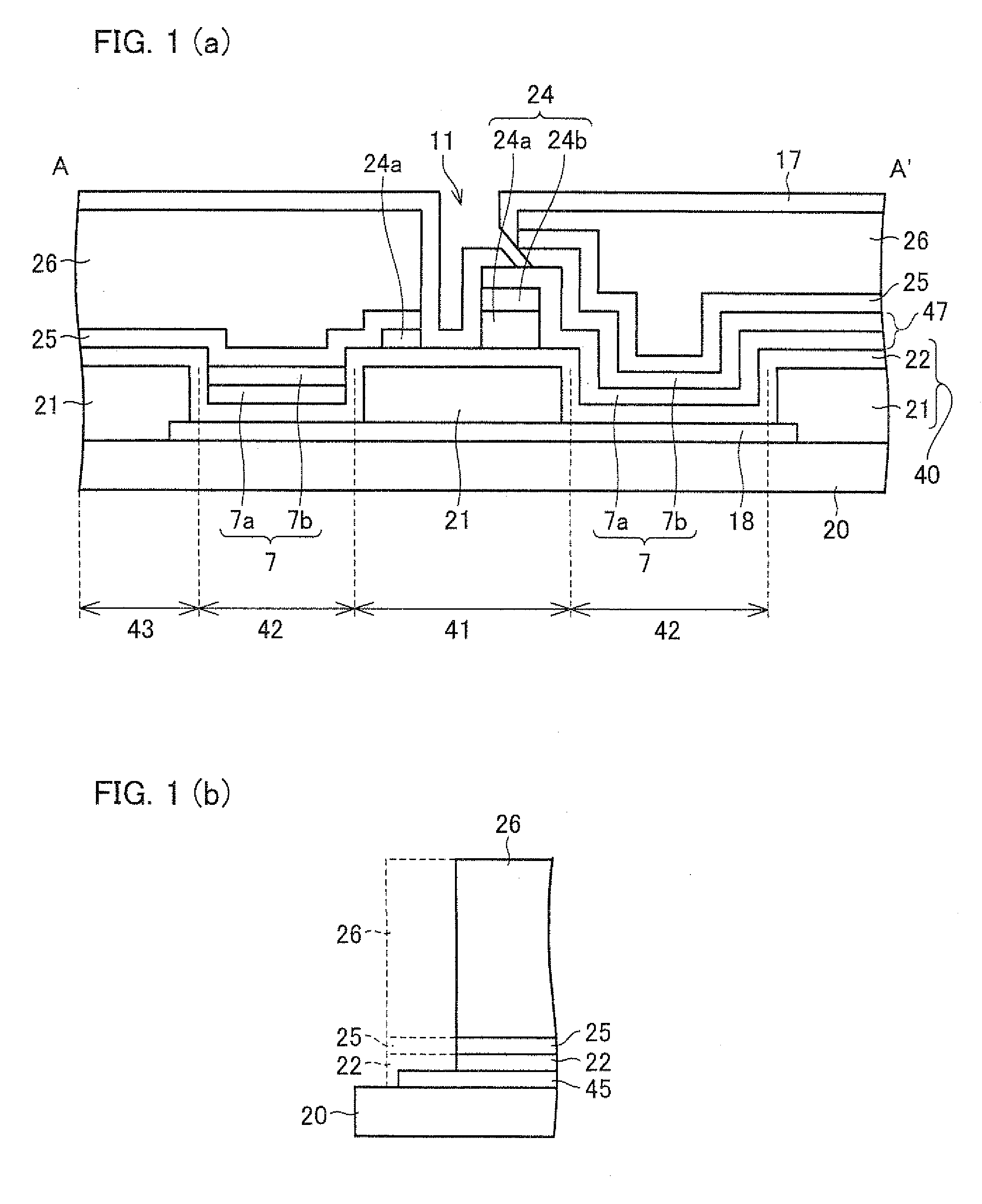
An active matrix substrate including, in each pixel area, a transistor, a pixel electrode (17), a conductive member (18) functioning as one of electrodes of a storage capacitor, a drain lead-out (7) electrode connected to a drain electrode of the transistor, and overlapping with the conductive member (18), and a contact hole for connecting the drain lead-out electrode (7) to the pixel electrode (17), includes a gate insulating film (40) covering a gate electrode of each transistor, the gate insulating film including a first thickness portion (41) overlapping with at least part of the contact hole, and a second thickness portion (42) formed adjacent to the first thickness portion, and overlapping with the drain lead-out electrode, the first thickness portion (41) having a greater thickness than the second thickness portion (42). This makes it possible to provide the active matrix substrate in which a short-circuit between the conductive member functioning as one of the electrodes of the storage capacitor, and the drain lead-out electrode (or the pixel electrode) is successfully prevented.
Owner:SHARP KK
Semiconductor device having a gettering layer
InactiveUS20050245052A1High mechanical strengthImprove transistor characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor chipActive layer
A multi-chip-package (MCP) module includes a plurality of semiconductor chips layered one on another. The lower semiconductor chip includes a semiconductor substrate having a top active layer and a bottom heavily-doped layer. The bottom of the heavily-doped layer is polished twice by a rough-polishing treatment and a mirror-polishing treatment. The thickness of the impurity-doped layer is not less than 50% of the thickness of the semiconductor substrate which is not larger than 130 μm.
Owner:ELPIDA MEMORY INC
Semiconductor device with STI and its manufacture
InactiveUS7589391B2Improve transistor characteristicsLow mobilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device includes: a silicon substrate with semiconductor elements; an isolation trench formed in the silicon substrate for isolating active regions in the silicon substrate, the isolation trench having a trapezoidal cross sectional shape having a width gradually narrowing with a depth from the surface of the silicon substrate; a first liner insulating film formed on the surface of the trench and made of a silicon oxide film or a silicon oxynitride film having a thickness of 1 to 5 nm; a second liner insulating film formed on the first liner insulating film and made of a silicon nitride film having a thickness of 2 to 8 nm; and an isolation region burying the trench defined by the second liner insulating film.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Compound semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same
ActiveCN102487079AImprove transistor characteristicsReduce dangling bondsHigh frequency amplifiersSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringDry etching
The present invention relates to a compound semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same, wherein on a surface of a compound semiconductor layer including inner wall surfaces of an electrode trench, an etching residue 12a and an altered substance 12b which are produced due to dry etching for forming the electrode trench are removed, and a compound semiconductor is terminated with fluorine. Gate metal is buried in the electrode trench via a gate insulating film, or the gate metal is directly buried in the electrode trench, whereby a gate electrode is formed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Organic thin film transistor using paper substrate and silk dielectric layer and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN102270743AImprove transistor characteristicsEasy accessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
The invention relates to an organic thin film transistor using a paper substrate and a silk dielectric layer and a manufacturing method thereof. Wherein, the organic thin film transistor device includes: a paper substrate; a gate, which is arranged on the paper substrate; a gate dielectric layer, which is arranged on the paper substrate and covers the gate, wherein the material of the gate dielectric layer is It includes a fibroin; an organic semiconductor layer; and a source and a drain, wherein the organic semiconductor layer, the source and the drain are arranged on the gate dielectric layer.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Thin-film transistor, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS7902547B2Improve transistor characteristicsImprove reliabilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogen atomOrganic semiconductor
A thin-film transistor includes a source electrode, a drain electrode arranged apart from the source electrode, an organic semiconductor layer arranged between the source electrode and the drain electrode so as to establish connection of the source electrode and the drain electrode, a first insulating layer arranged on one surface side of the organic semiconductor layer, a gate electrode arranged on a side of the first insulating layer opposite that on which the organic semiconductor layer lie, and a second insulating layer arranged on a side of the organic semiconductor layer opposite that on which the first insulating layer lie. The organic semiconductor layer contains an organic semiconductor material having p-type semiconducting properties. The second insulating layer contains one or more compounds of the following formula (1), so that electrons are fed from the second insulating layer into the organic semiconductor layer:wherein R1 and R2 independently represent a substituted or unsubstituted alkylene group; X1, X2, X3 and X4 each represent a hydrogen atom or an electron-donating group; and n represents 100 to 100,000, wherein at least one of X1, X2, X3 and X4 represents an electron-donating group.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Semiconductor device with copper wirings
InactiveUS20050029671A1Inhibit deteriorationSmall gate leak currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialNitrogen
A semiconductor device with p-channel MOS transistor having: a gate insulating film of nitrogen-containing silicon oxide; a gate electrode of boron-containing silicon; side wall spacers on side walls of the gate electrode, comprising silicon oxide; an interlayer insulating film having a planarized surface; a wiring trench and a contact via hole formed in the interlayer insulating film; a copper wiring pattern including an underlying barrier layer and an upper level copper region, and filled in the wiring trench; and a silicon carbide layer covering the copper wiring pattern. A semiconductor device has the transistor structure capable of suppressing NBTI deterioration.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
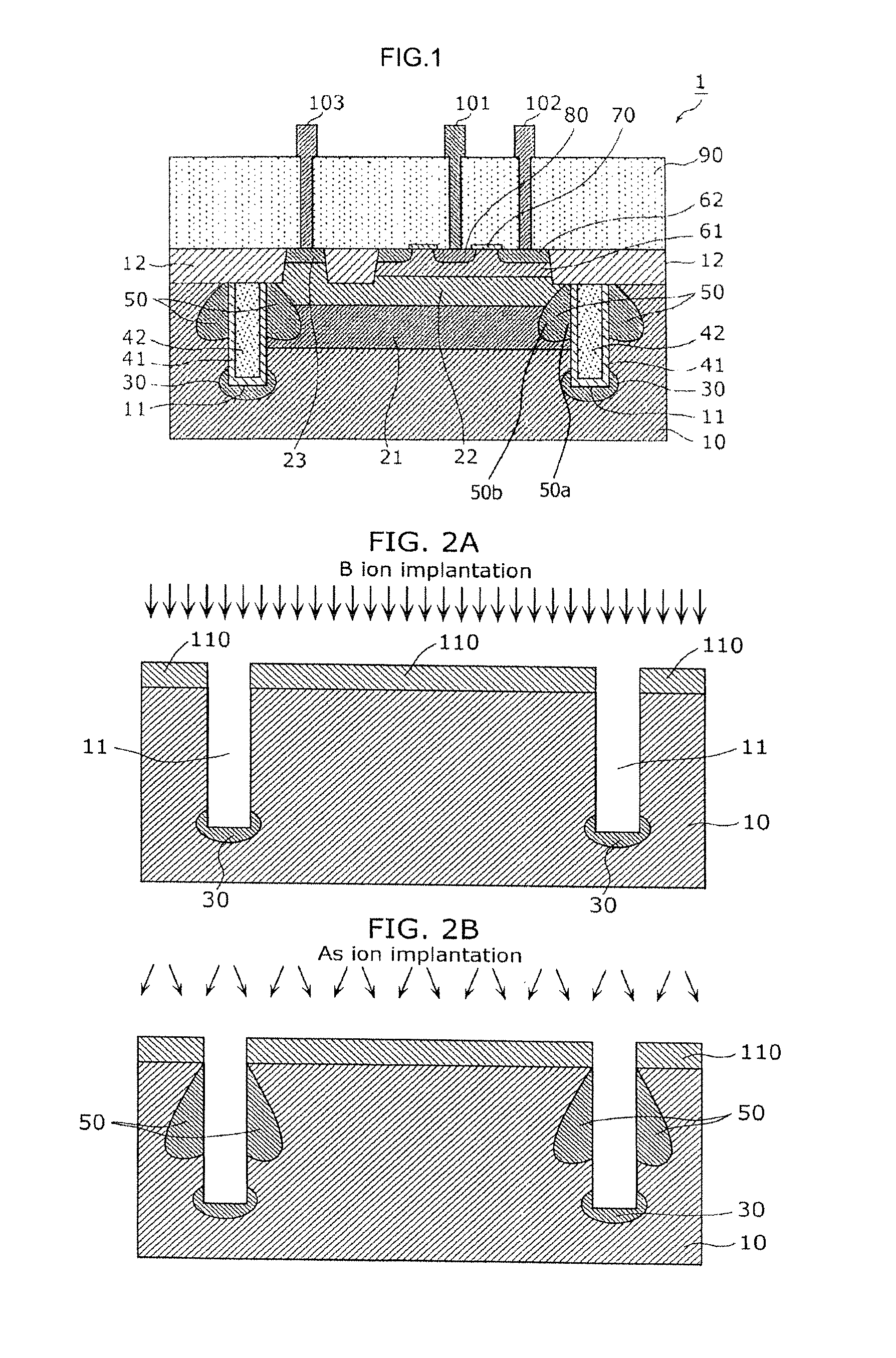
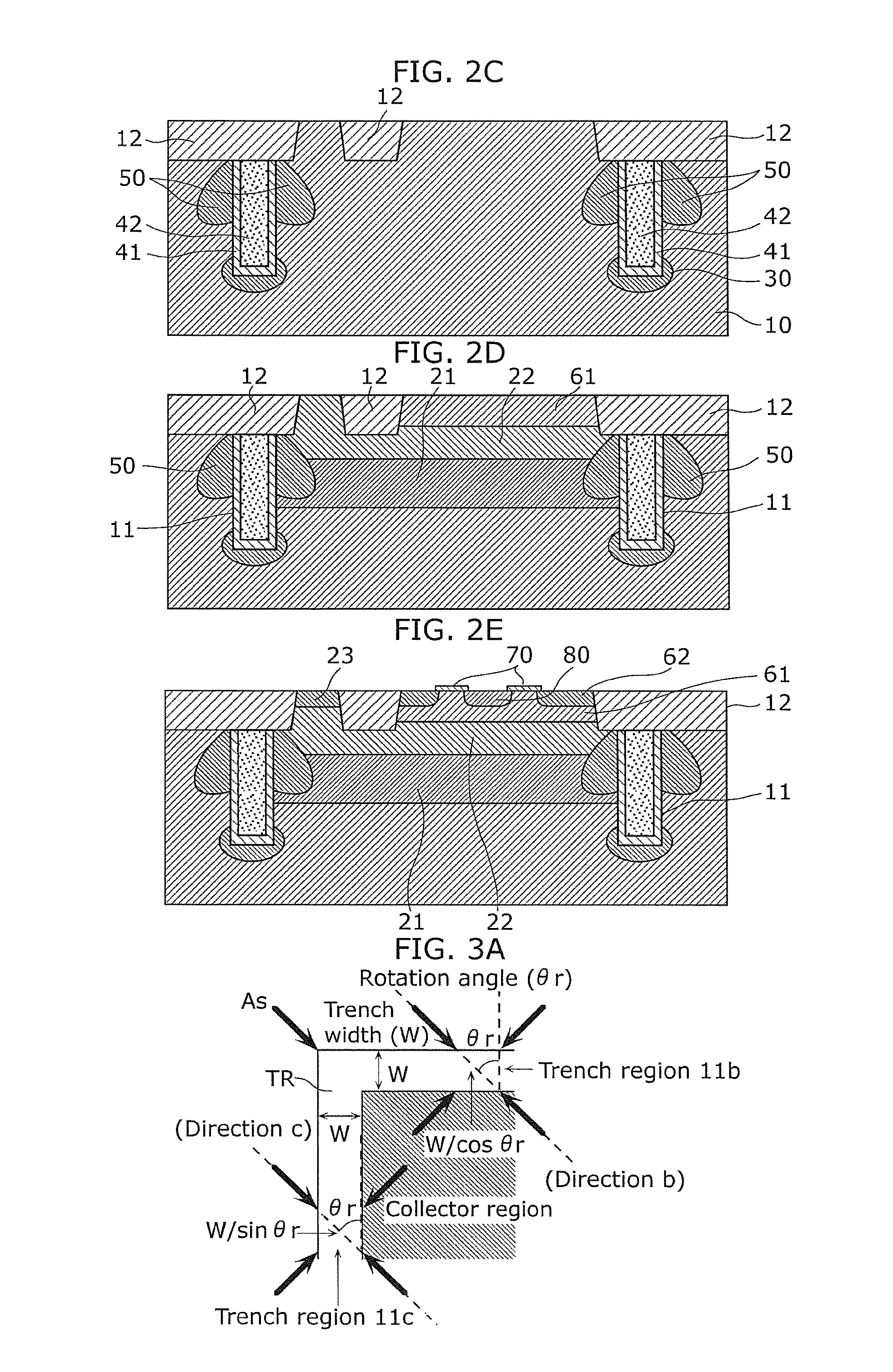
Bipolar transistor with diffused layer between deep trench sidewall and collector diffused layer
InactiveUS8710621B2Improve featuresReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesChannel-stopperDiffusion layer
A semiconductor device according to the present invention includes a p-type semiconductor substrate, a first n-type collector diffusion layer formed in the p-type semiconductor substrate, a deep trench formed in the p-type semiconductor substrate so as to surround the first n-type collector diffusion layer, a p-type channel stopper layer formed beneath the deep trench, and an n-type diffusion layer formed between a sidewall of the deep trench and the first n-type collector diffusion layer.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Electrochemically-gated field-effect transistor, methods for its manufacture and use thereof
InactiveUS8927967B2High performanceEasily obtainElectrolytic capacitorsMagnetic bodiesTransistor channelEngineering
An electrochemically-gated field-effect transistor includes a source electrode, a drain electrode, a gate electrode, a transistor channel and an electrolyte. The transistor channel is located between the source electrode and the drain electrode. The electrolyte completely covers the transistor channel and has a one-dimensional nanostructure and a solid polymer-based electrolyte that is employed as the electrolyte.
Owner:KARLSRUHER INST FUR TECH
Manufacturing method of organic semiconductor device
InactiveUS8202759B2Improve transistor characteristicsHighly-productiveSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid crystallineInsulation layer
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of an organic semiconductor device comprising a step of transferring an organic semiconductor layer to a gate insulation layer by a thermal transfer at a liquid crystal phase transition temperature of a liquid crystalline organic semiconductor material, and the step uses: an organic semiconductor layer-transferring substrate comprising a parting substrate having parting properties, and the organic semiconductor layer formed on the parting substrate and containing the liquid crystalline organic semiconductor material; and a substrate for forming an organic semiconductor device comprising a substrate, a gate electrode formed on the substrate, and the gate insulation layer formed to cover the gate electrode and having alignment properties which are capable of aligning the liquid crystalline organic semiconductor material on a surface of the gate insulation layer.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Compound semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN102487079BImprove transistor characteristicsReduce dangling bondsHigh frequency amplifiersConversion without intermediate conversion to dcEngineeringDry etching
On a surface of a compound semiconductor layer including inner wall surfaces of an electrode trench, an etching residue 12a and an altered substance 12b which are produced due to dry etching for forming the electrode trench are removed, and a compound semiconductor is terminated with fluorine. Gate metal is buried in the electrode trench via a gate insulating film, or the gate metal is directly buried in the electrode trench, whereby a gate electrode is formed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Transistor and manufacturing method of transistor
InactiveUS10249733B2Reliable electrical connectionImprove transistor characteristicsTransistorSolid-state devicesMicrofabricationElectrical connection
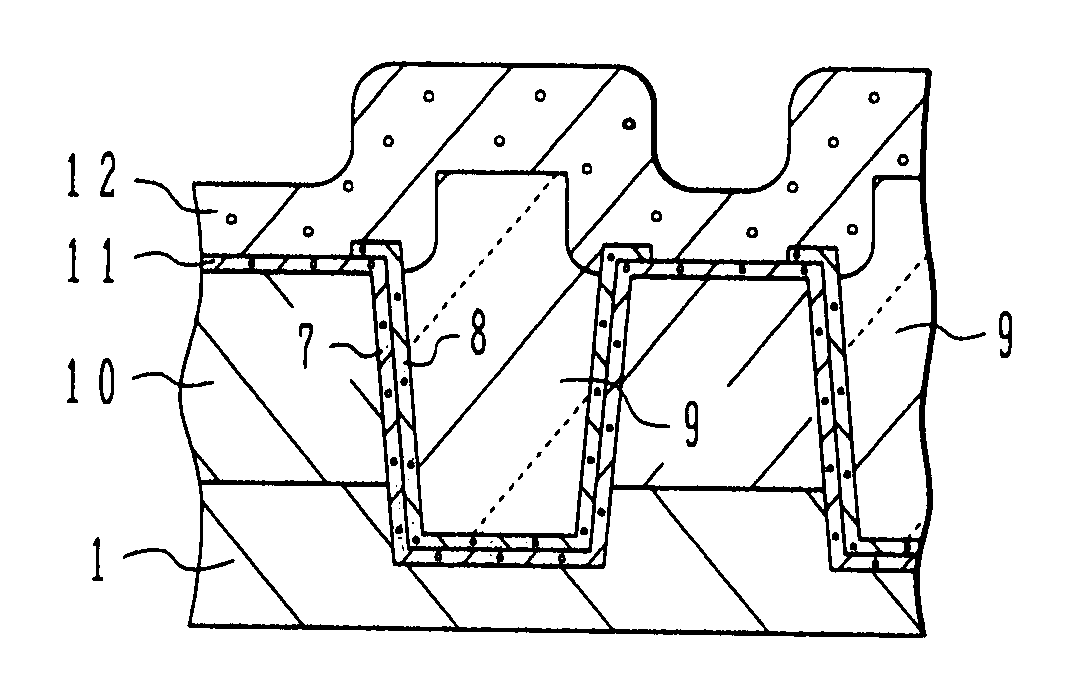
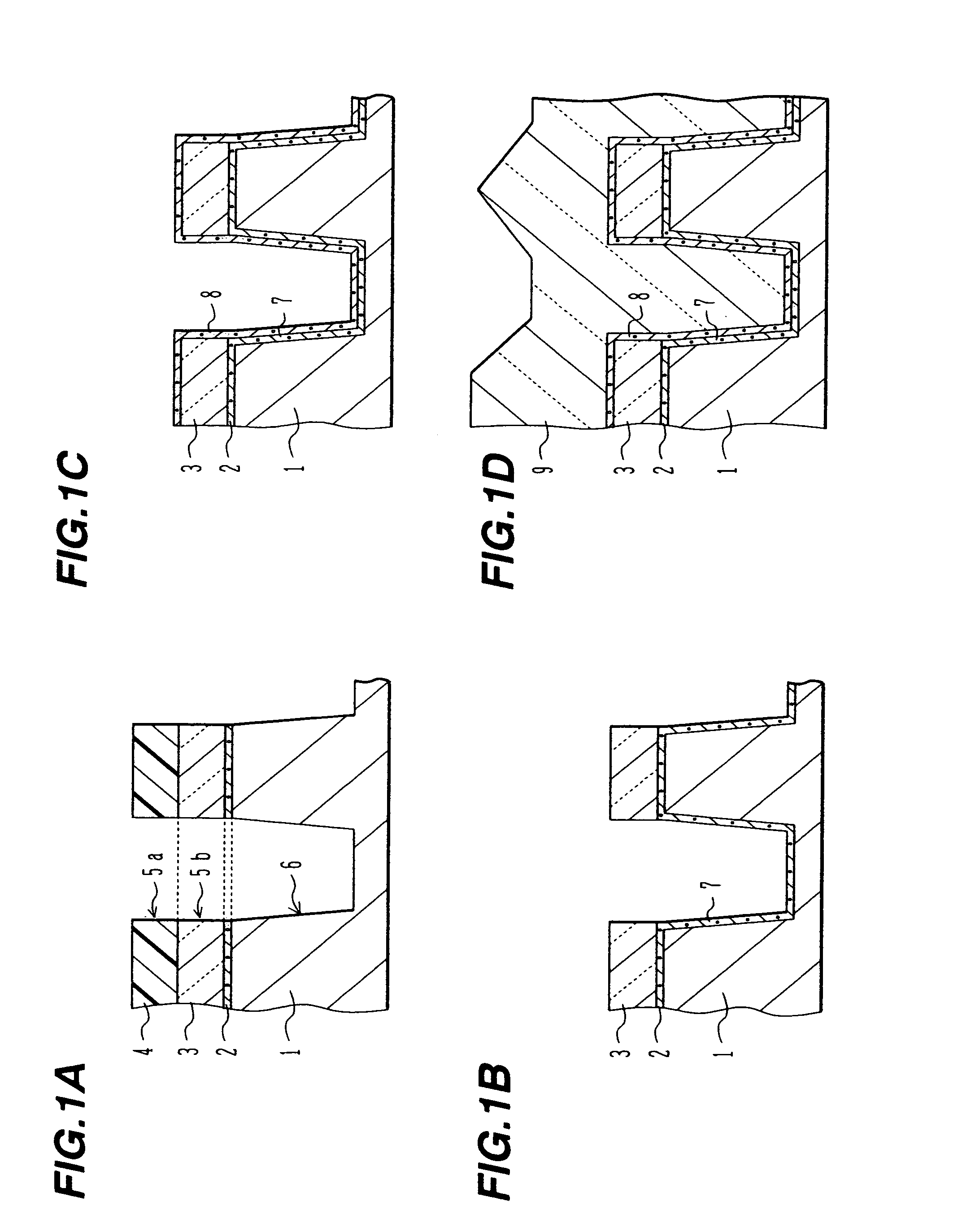
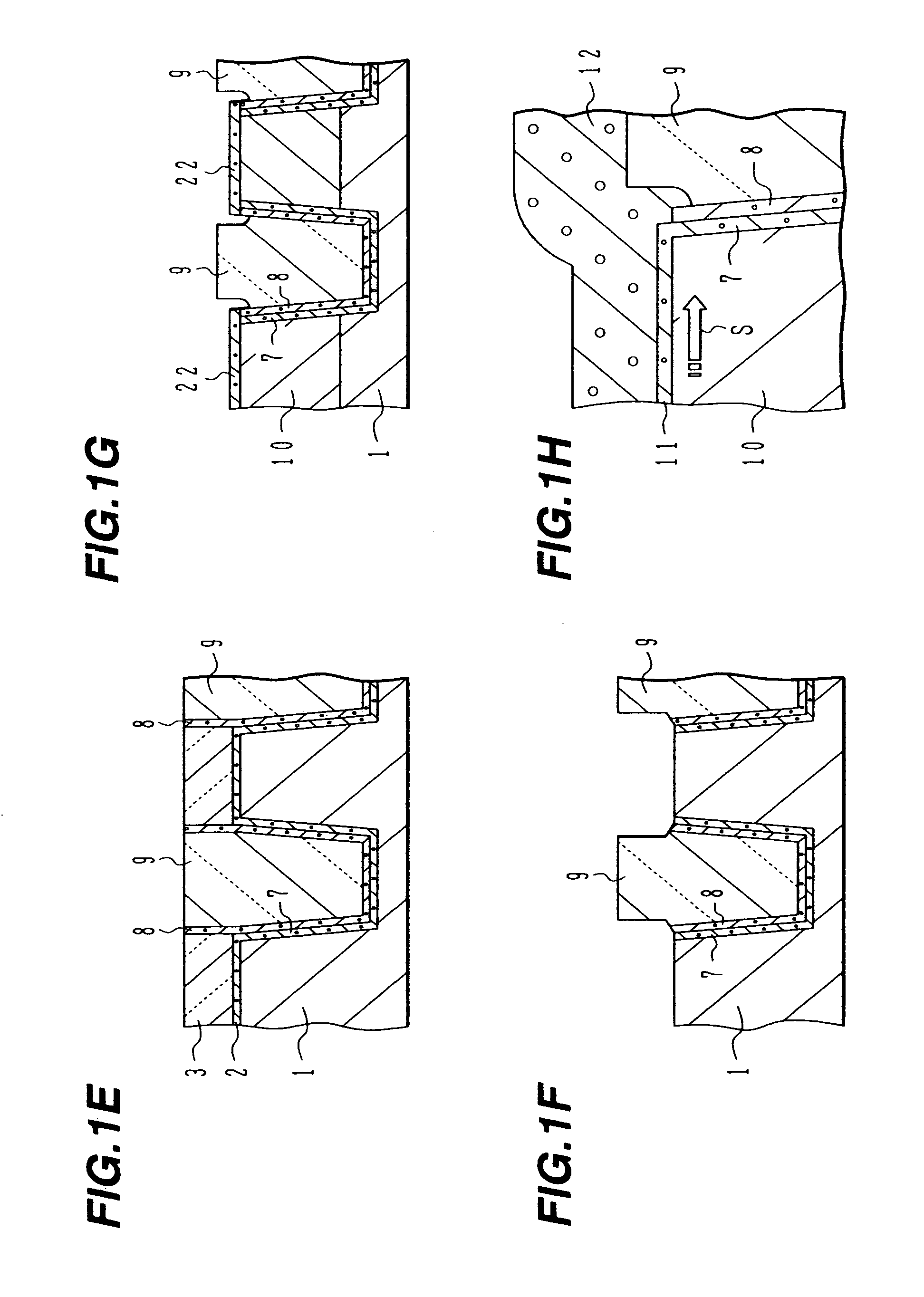
Provided are an air up type transistor which has high electrical connection reliability and high productivity, and is capable of exhibiting good transistor characteristics while achieving microfabrication, and a manufacturing method of a transistor. A semiconductor layer is formed on an upper surface of a support precursor layer which becomes a semiconductor layer support and then a part of the semiconductor layer is removed to form one or more opening portions from which the support precursor layer is exposed. Two etching protective layers are formed on the semiconductor layer such that the two etching protective layers are separated from each other and at least a part of the opening portion is positioned in a region between the two etching protective layers. A part of the support precursor layer is removed by bringing an etchant into contact with the support precursor layer through the plurality of opening portions, thereby forming a space at a position corresponding to a region between the two etching protective layers so as to form two semiconductor layer supports that are arranged with the space interposed therebetween.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com