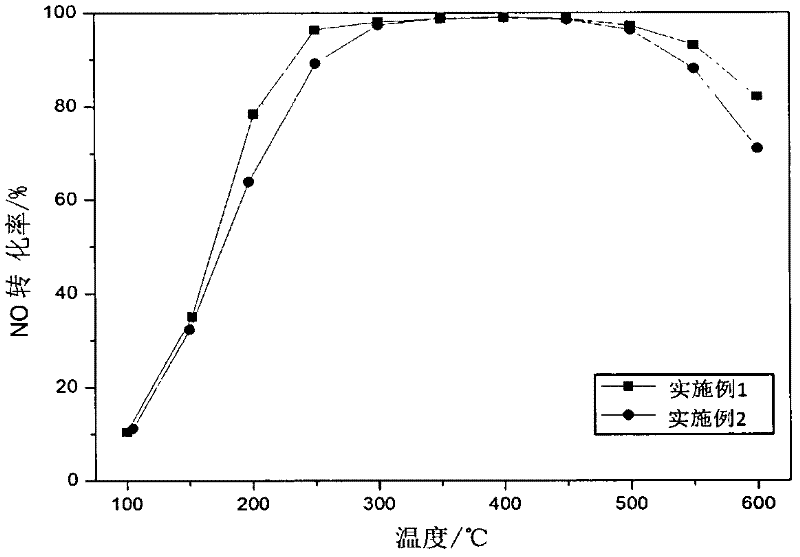
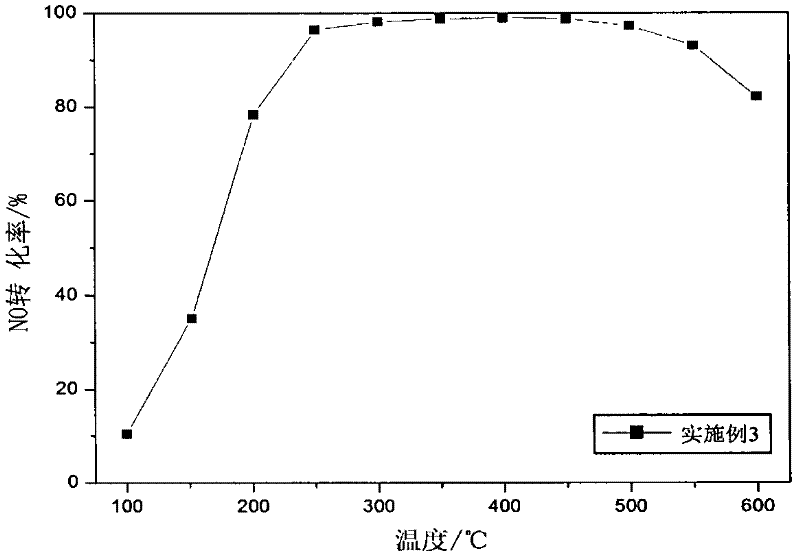
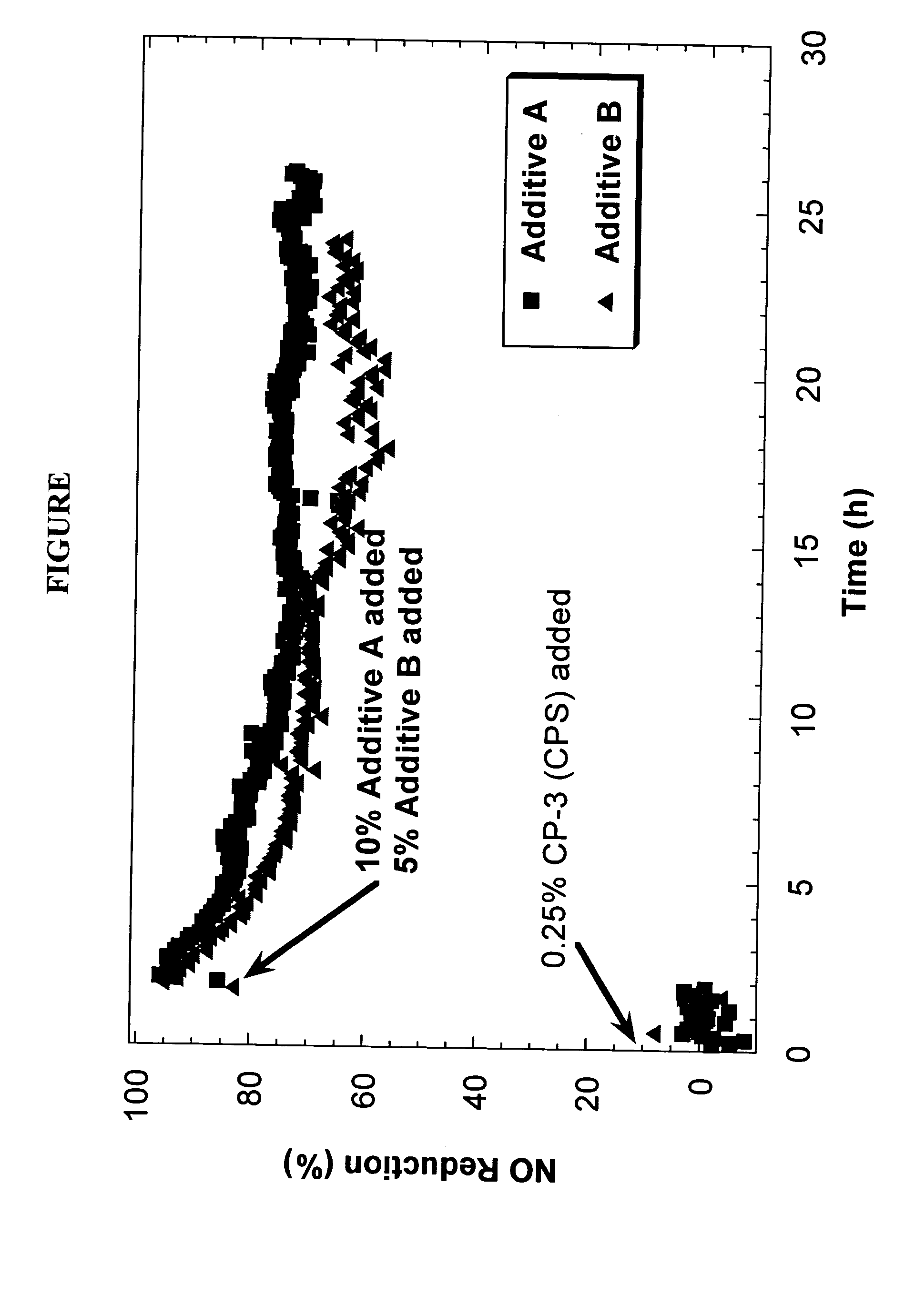
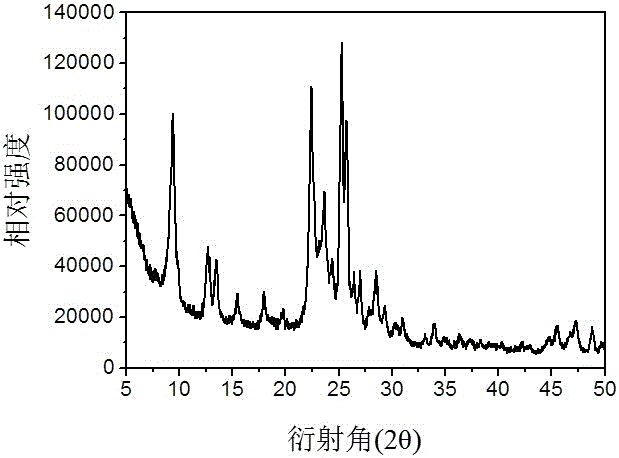
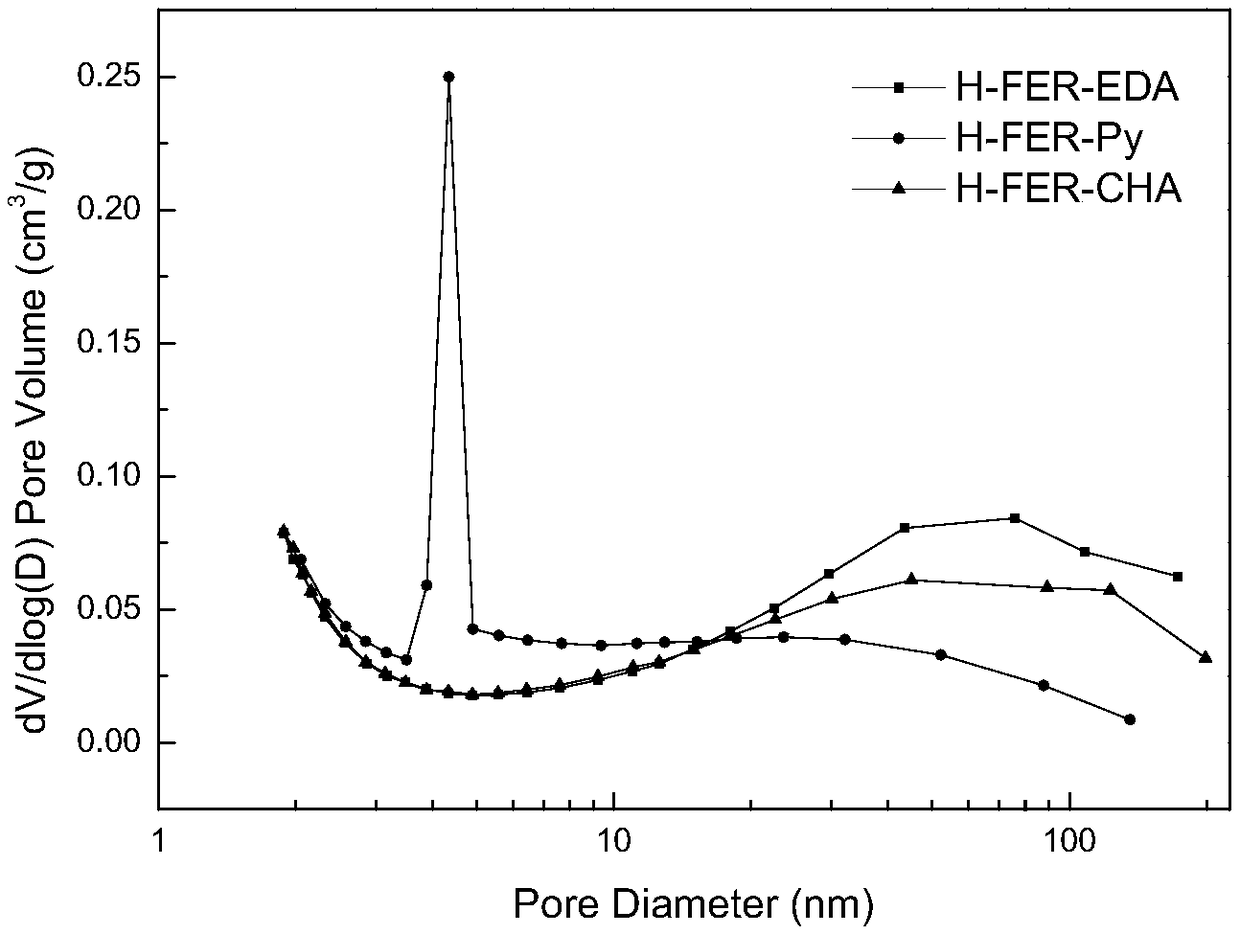
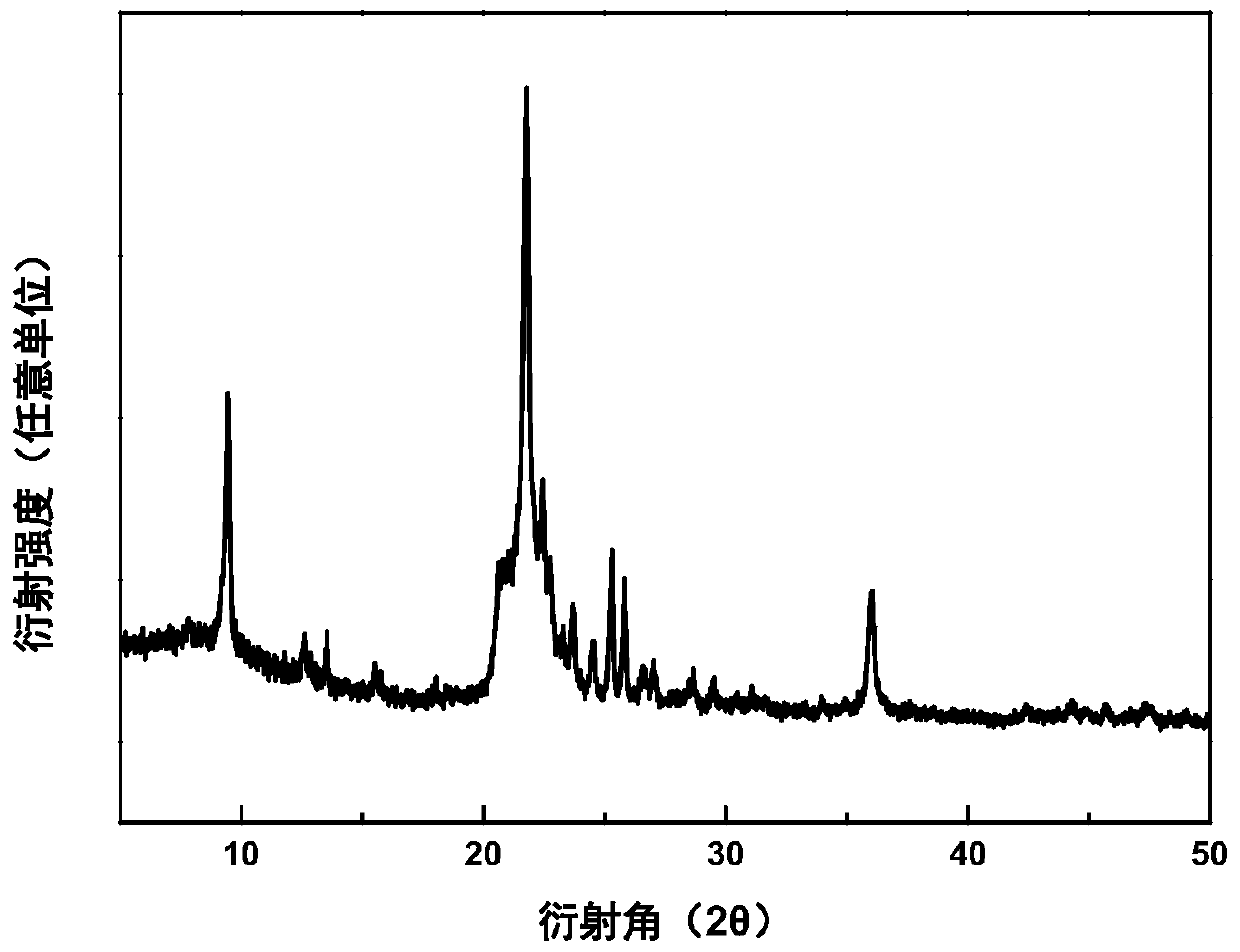
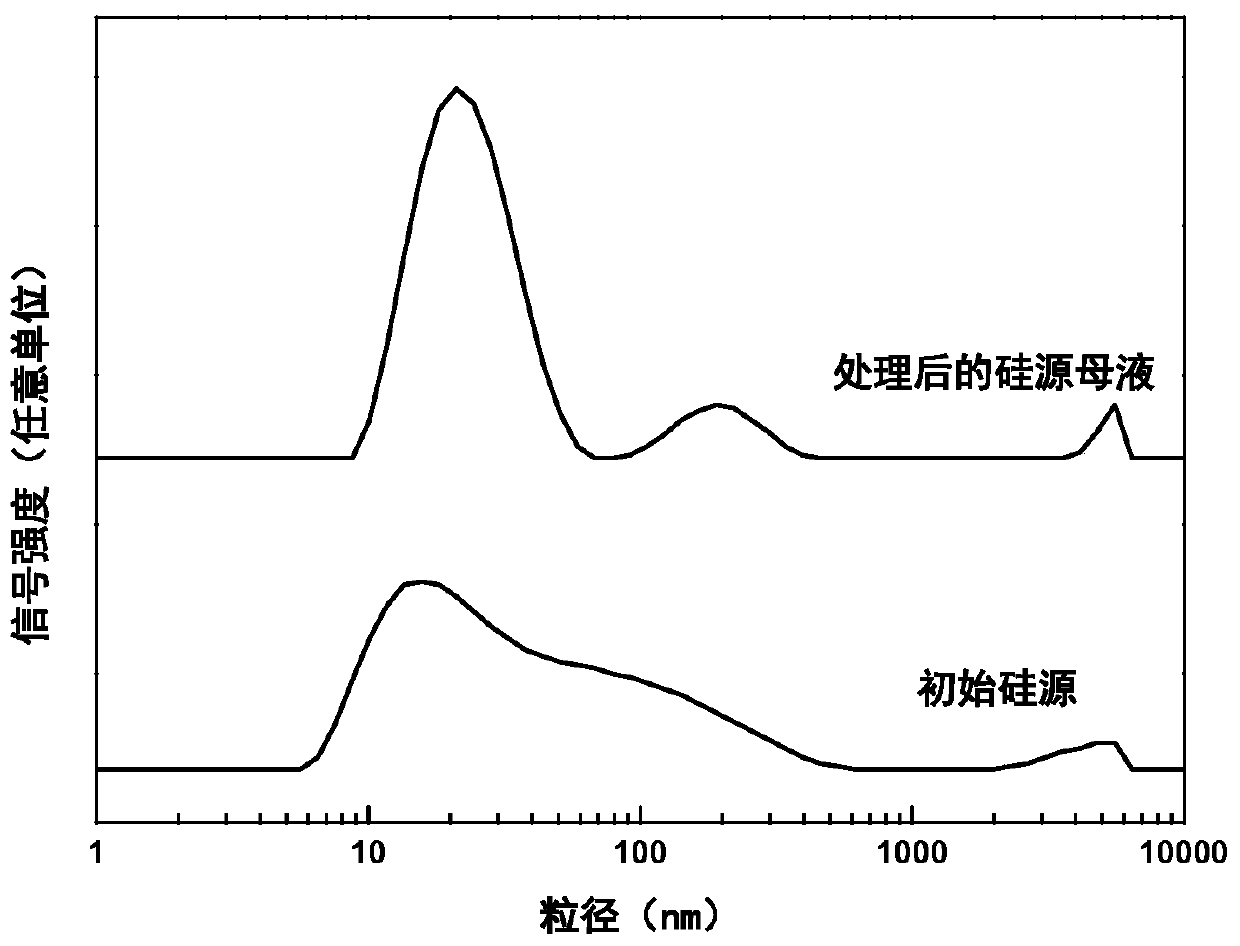
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Ferrierite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The ferrierite group of zeolite minerals (the FER structure) consists of three very similar species: ferrierite-Mg, ferrierite-Na, and ferrierite-K, based on the dominant cation in the A location. ferrierite-Mg and ferrierite-K are orthorhombic minerals and ferrierite-Na is monoclinic with highly variable cationic composition, (Na,K)₂Mg(Si,Al)₁₈O₃₆(OH)·9H₂O. Calcium and other ions are often also present. They are found in vitreous to pearly, often radiating, spherical aggregates of thin blade-shaped transparent to translucent crystals.
Catalytic dewaxing with trivalent rare earth metal ion exchanged ferrierite
InactiveUS6013171AMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonCation-exchange capacityIon exchange
A process for dewaxing waxy hydrocarbonaceous materials, such as hydrocarbon fuel and lubricating oil fractions to reduce their cloud and pour points comprises reacting the material with hydrogen in the presence of a dewaxing catalyst comprising at least one metal catalytic component and ferrierite in which at least a portion of its cation exchange positions are occupied by one or more trivalent rare earth metal cations. The rare earth ion exchanged ferrierite catalyst has good selectivity for lubricating oil production, particularly when dewaxing a Fischer-Tropsch wax hydroisomerate. Preferably at least 10% and more preferably at least 15% of the ferreirite cation exchange capacity is occupied by one or more trivalent rare earth metal cations.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Flexible process for producing base stock and distillates by conversion-hydroisomerisation using a catalyst with low dispersion followed by catalytic dewaxing
InactiveUS6602402B1Facility of preparationImprove hydrogenation activityMolecular sieve catalystsRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonPtru catalystEngineering
An improved process for producing very high quality base stock and for simultaneous production of high quality middle distallates, comprising successive hydroisomerisation and catalystic dewaxing steps wherein hydroisomerisation is carried out in the presence of a catalyst containing at least one noble metal deposited on an amorphous acidic support, the dispersion of the metal being less than 20%. The support is preferably an amorphous silica-alumina. Catalytic dewaxing is carried out in the presence of a catalyst containing at least one hydrodehydrogenating element (group VIII) and at least one molecular sieve (preferably zeolite). The sieve is preferable selected from NU-10, EU-1, EU-13, zeolite and ferrierite.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
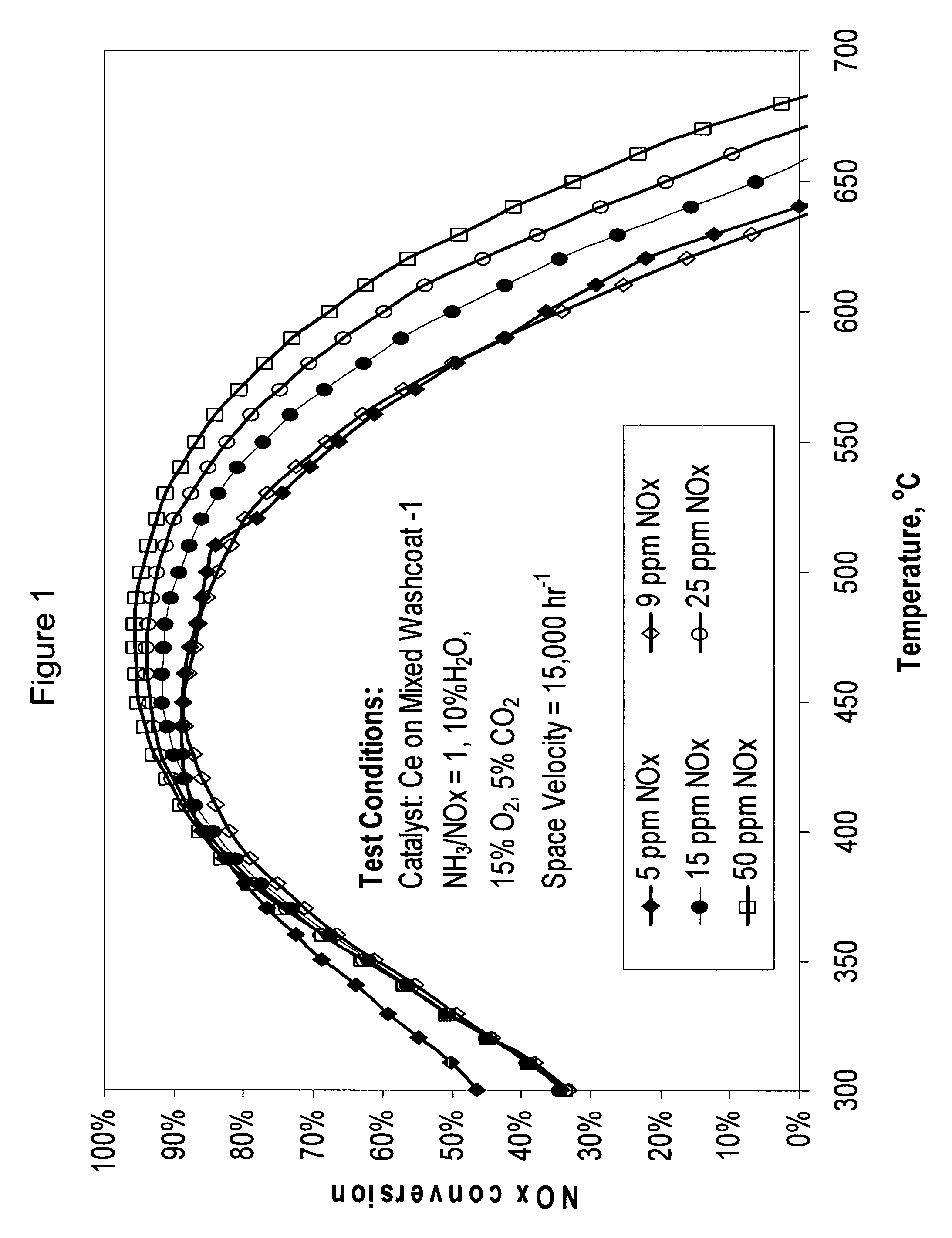
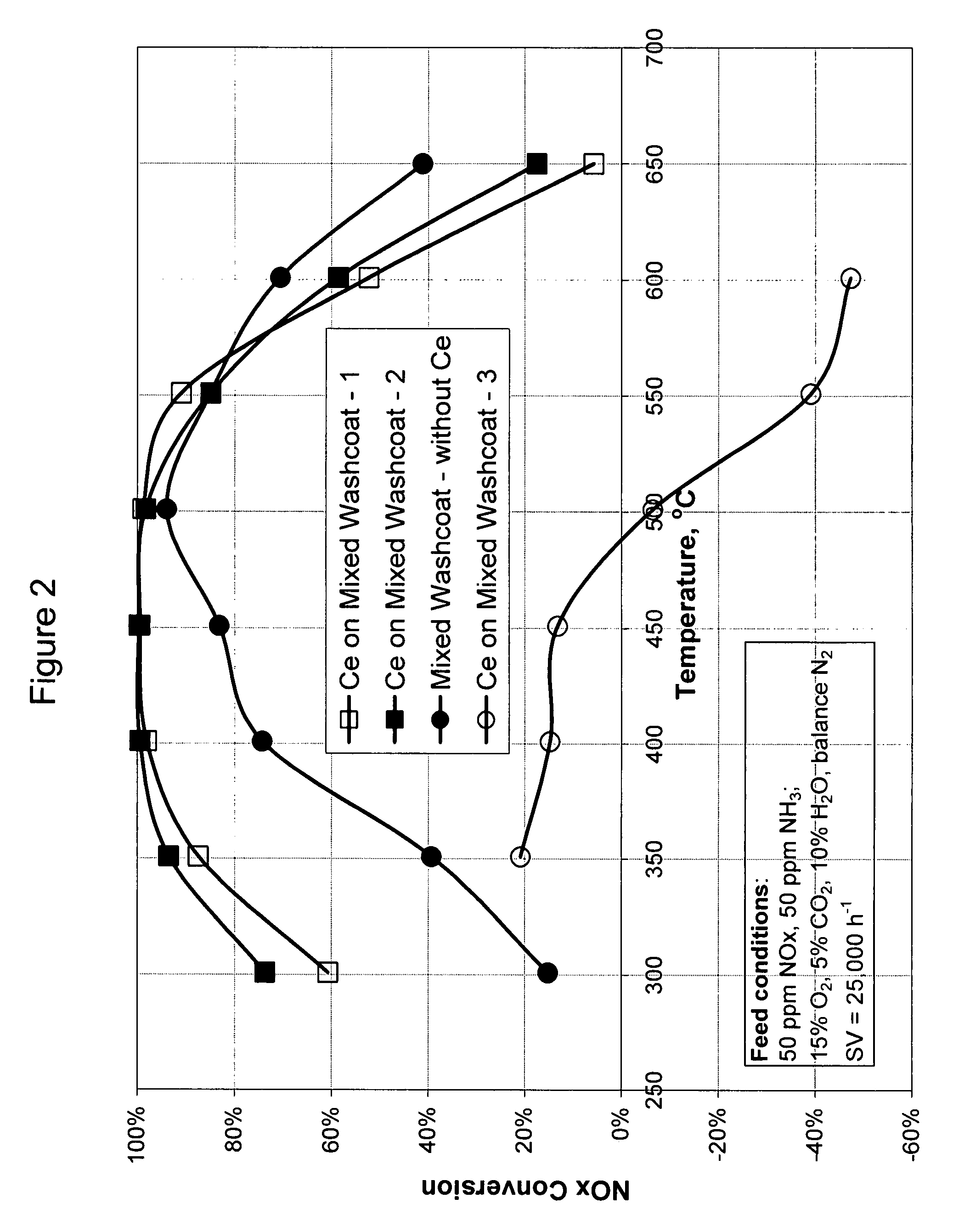
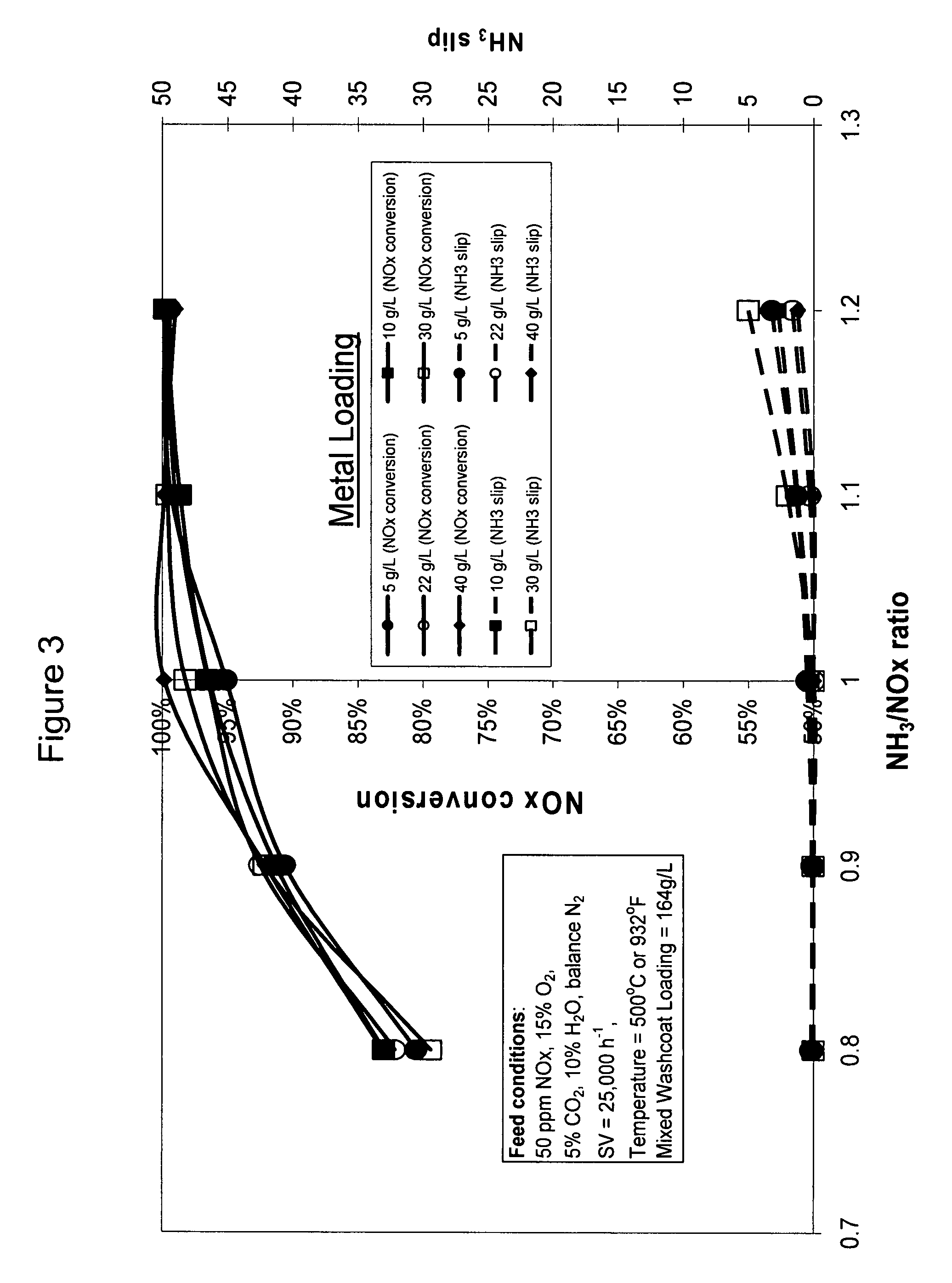
High temperature ammonia SCR catalyst and method of using the catalyst
ActiveUS20080167178A1Reduce selection requirementsMolecular sieve catalystsInternal combustion piston enginesCeriumMordenite
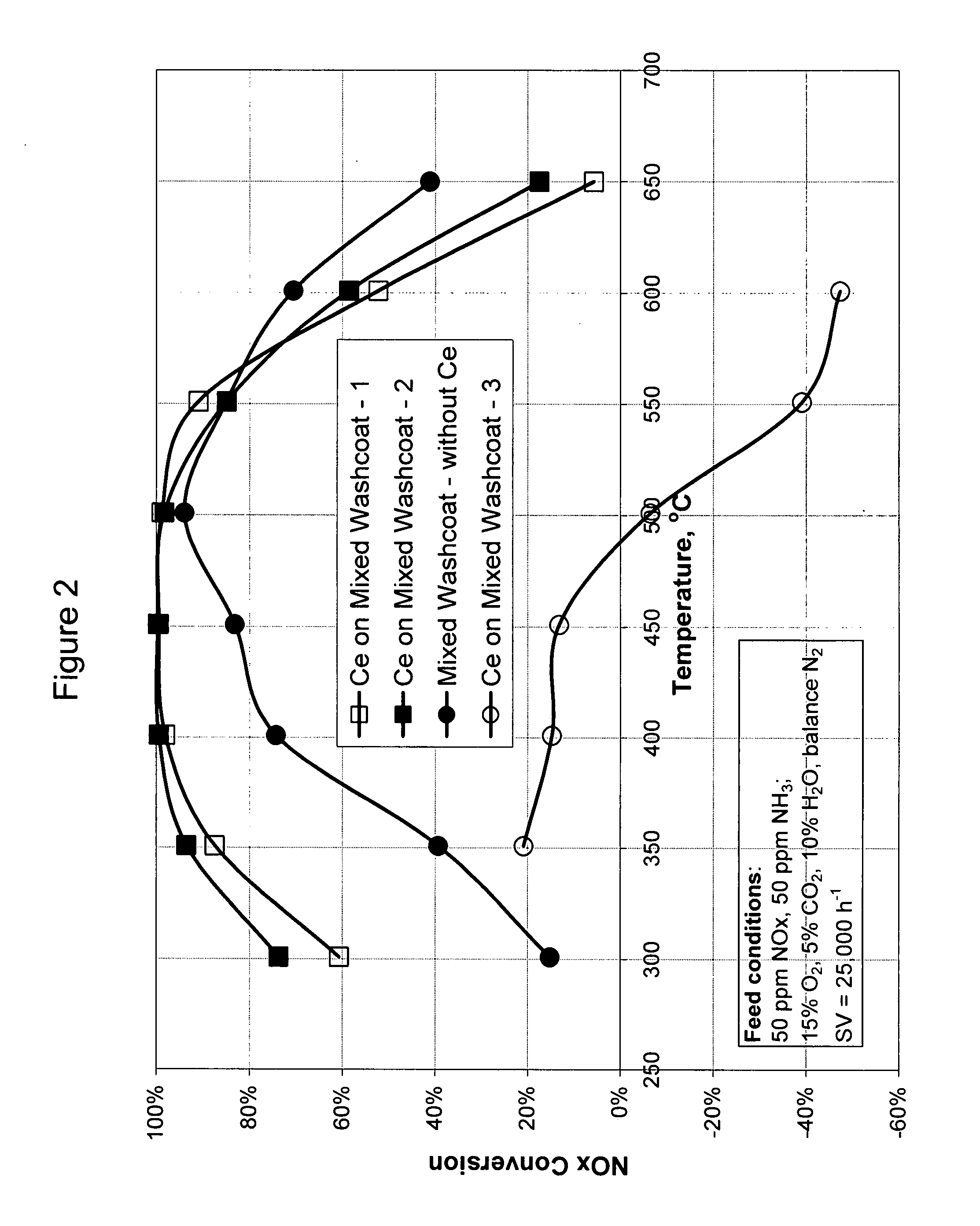
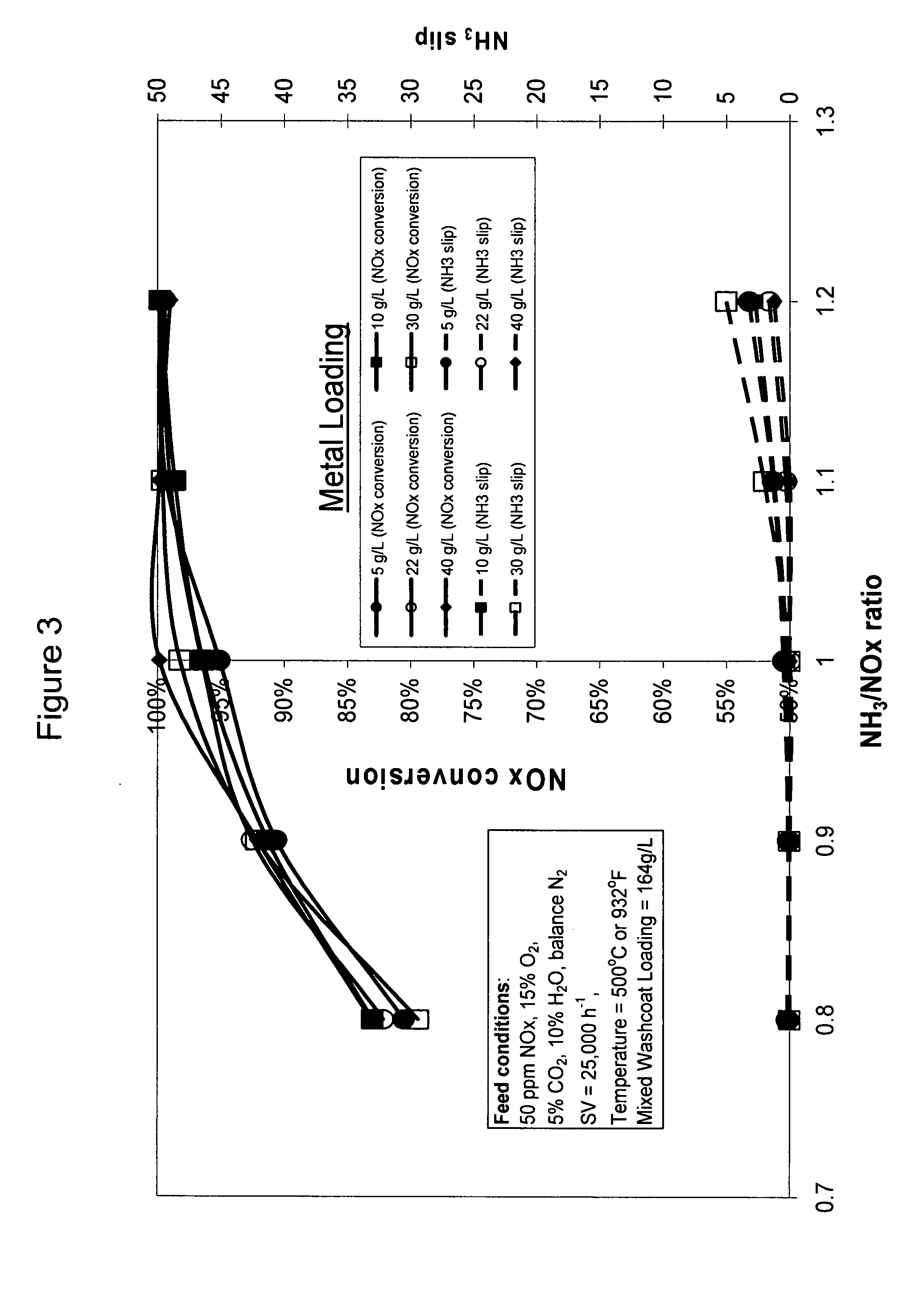
A catalyst and a method for selectively reducing nitrogen oxides (“NOx”) with ammonia are provided. The catalyst includes a first component comprising a zeolite or mixture of zeolites selected from the group consisting of ZSM-5, ZSM-11, ZSM-12, ZSM-18, ZSM-23, MCM-zeolites, mordenite, faujasite, ferrierite, zeolite beta, and mixtures thereof; a second component comprising at least one member selected from the group consisting of cerium, iron, copper, gallium, manganese, chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, tin, rhenium, tantalum, osmium, barium, boron, calcium, strontium, potassium, vanadium, nickel, tungsten, an actinide, mixtures of actinides, a lanthanide, mixtures of lanthanides, and mixtures thereof; optionally an oxygen storage material and optionally an inorganic oxide. The catalyst selectively reduces nitrogen oxides to nitrogen with ammonia at high temperatures. The catalyst has high hydrothermal stability. The catalyst has high activity for conversion of low levels of nitrogen oxides in exhaust streams. The catalyst and the method may have special application to selective reduction of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gas from gas turbines and gas engines, although the catalyst and the method have broad application to a wide range of gas streams that have excess oxygen and high temperatures. The temperature of exhaust gas from gas turbines and gas engines is high. Both the high temperature and the low levels of inlet NOx are challenging for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalysts.
Owner:CATALYTIC SOLUTIONS INC
Method used for preparing methyl acetate via carbonylation of dimethyl ether
ActiveCN103896769AExtend your lifeControl temperature distributionPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionHydrogenReaction temperature
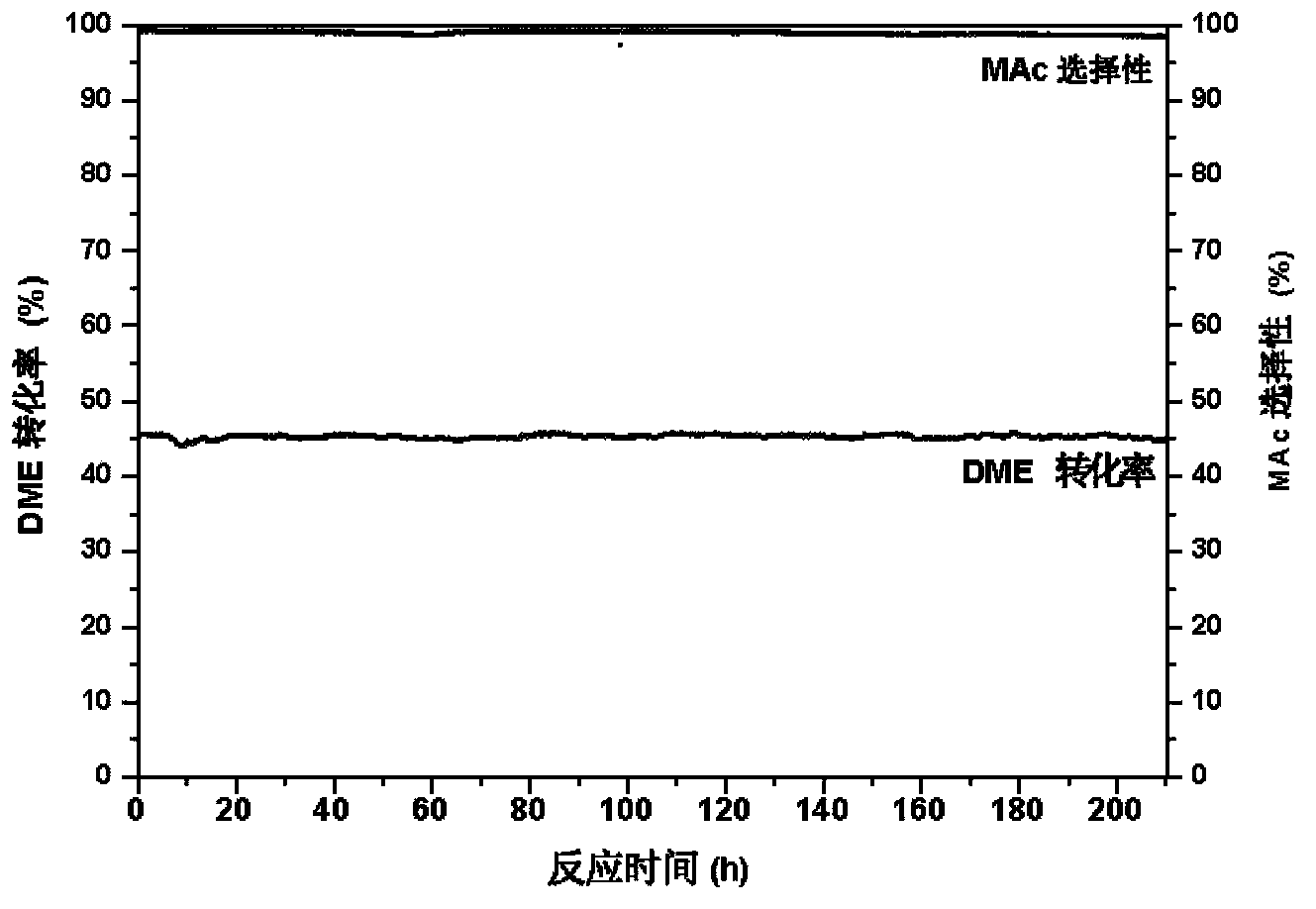
Provided is a method for preparing methyl acetate by dimethyl ether carbonylation, comprising passing a feed gas including dimethyl ether, carbon monoxide and optional hydrogen through a reactor filled with a mordenite and / or ferrierite molecular sieve based catalyst and reacting at a reaction temperature of 190-320°C, a reaction pressure of 0.5-20.0 MPa and a gas space velocity of 500-5000 h-1 so as to prepare methyl acetate, wherein the molar ratio of dimethyl ether to carbon monoxide is DME / CO=1 / 1-1 / 15, the molar ratio of hydrogen to carbon monoxide is H2 / CO=0-10 / 1, and the feed gas is distributed into each catalyst bed layer in a segmental feeding manner. A feed gas including dimethyl ether and carbon monoxide is uniformly distributed into each catalyst bed layer via a gas distributor, in a segmental feeding manner, which can remarkably improve the conversion rate of dimethyl ether, effectively control or adjust the temperature distribution of a catalyst bed layer, avoid the appearance of a hot spot, and prolong the service life of a catalyst.
Owner:YANCHANG ZHONGKE (DALIAN) ENERGY TECH CO LTD
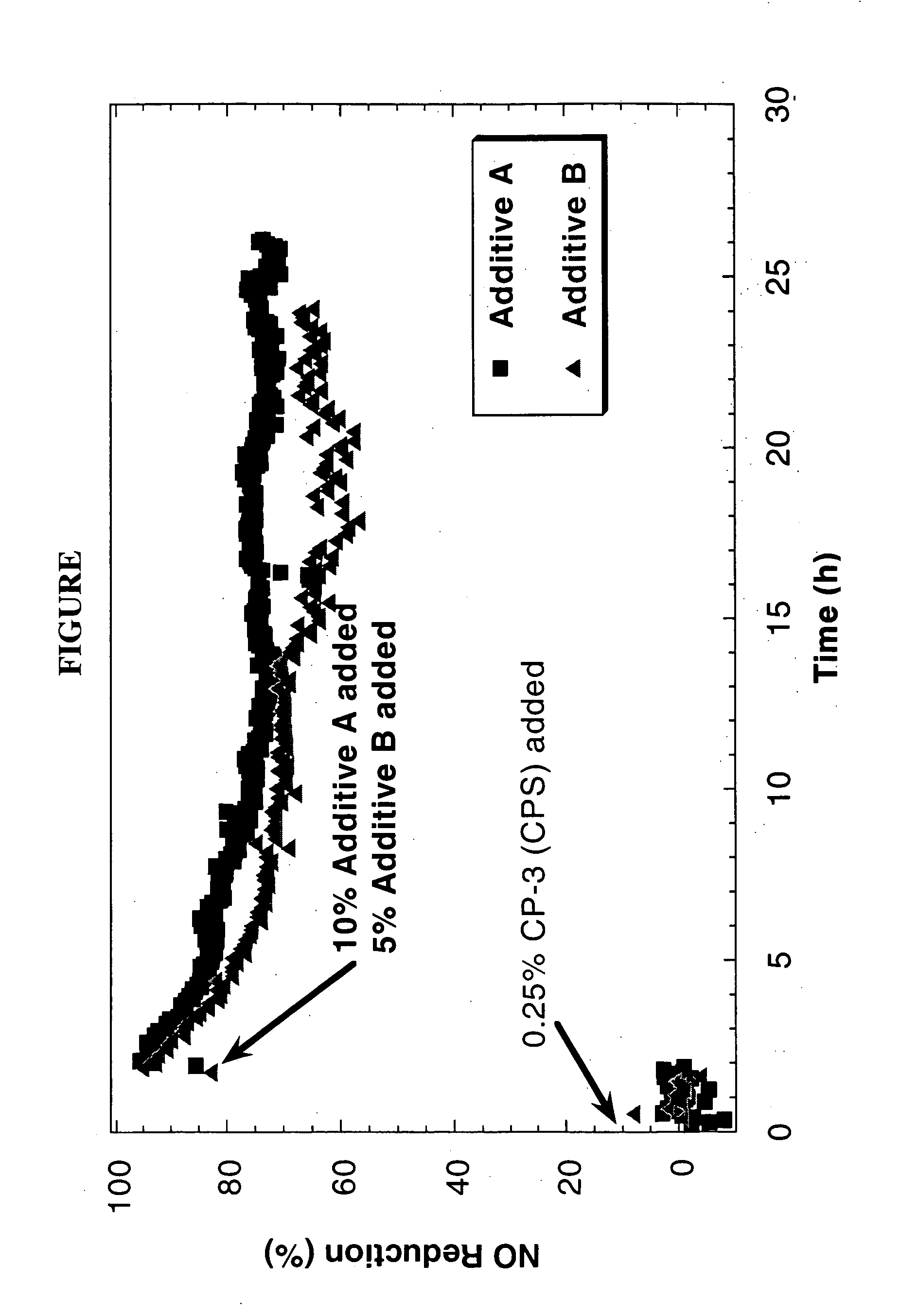
Ferrierite compositions for reducing NOx emissions during fluid catalytic cracking
InactiveUS20050100494A1Reduce contentGas treatmentCatalytic crackingPtru catalystEnvironmental engineering
Compositions for reduction of NOx generated during a catalytic cracking process, preferably, a fluid catalytic cracking process, are disclosed. The compositions comprise a fluid catalytic cracking catalyst composition, preferably containing a Y-type zeolite, and a particulate NOx reduction composition containing ferrierite zeolite particles. Preferably, the NOx reduction composition contains ferrierite zeolite particles bound with an inorganic binder. In the alternative, the ferrierite zeolite particles are incorporated into the cracking catalyst as an integral component of the catalyst. NOx reduction compositions in accordance with the invention are very effective for the reduction of NOx emissions released from the regenerator of a fluid catalytic cracking unit operating under FCC process conditions without a substantial change in conversion or yield of cracked products. Processes for the use of the compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:YALURIS GEORGE +2
Catalytic system and process for direct synthesis of dimethyl ether from synthesis gas
InactiveUS20090326281A1High acid strengthIncrease the number ofMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationSyngasPhysical form
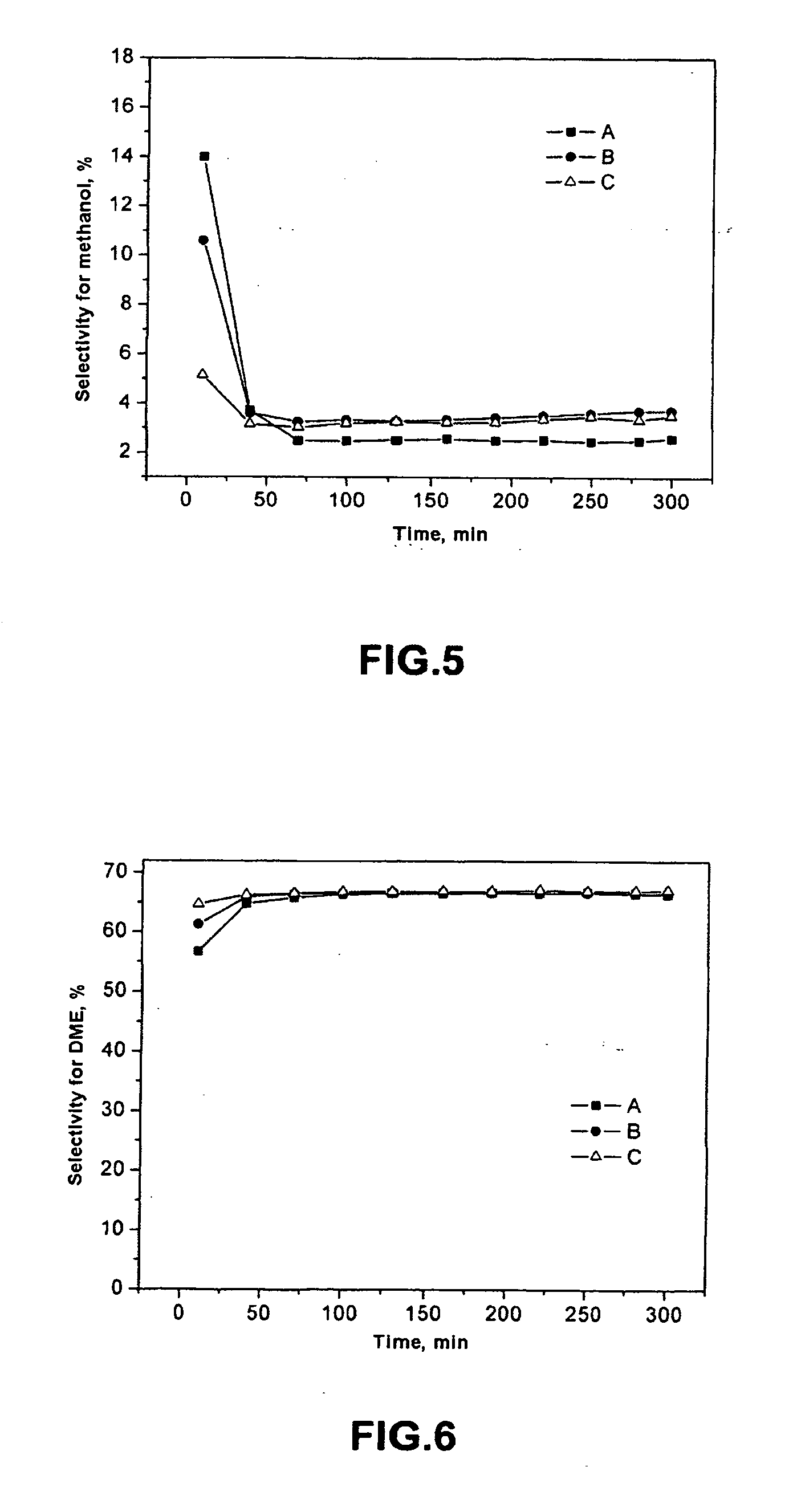
A mixed-bed catalytic system and its activation for direct synthesis of dimethyl ether from synthesis gas are described, comprising a catalyst for methanol synthesis and the zeolite ferrierite in its acid form as the methanol dehydrating component, the two being mixed physically in the form of powder of defined granulometry or as pellets. Another object of the present invention is a process for production of the acid form of the zeolite ferrierite. Another object of the present invention is a process for direct synthesis of dimethyl ether from a synthesis gas, using the catalytic system of the present invention.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS) +1
Scr catalysts having improved low temperature performance, and methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20150246345A1Good dispersionIncrease resistanceFerrierite aluminosilicate zeoliteGas treatmentSimple Organic CompoundsPtru catalyst
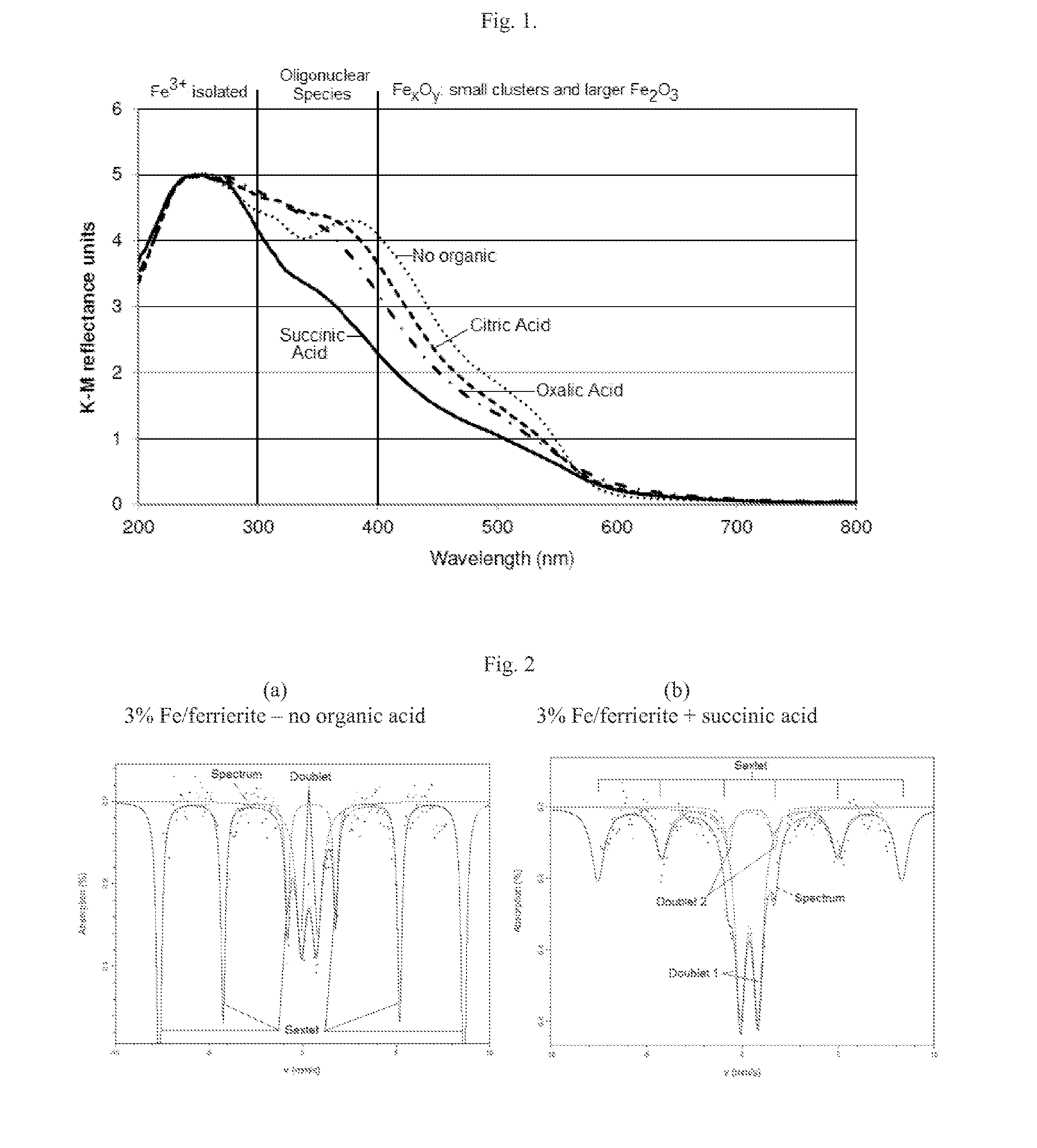
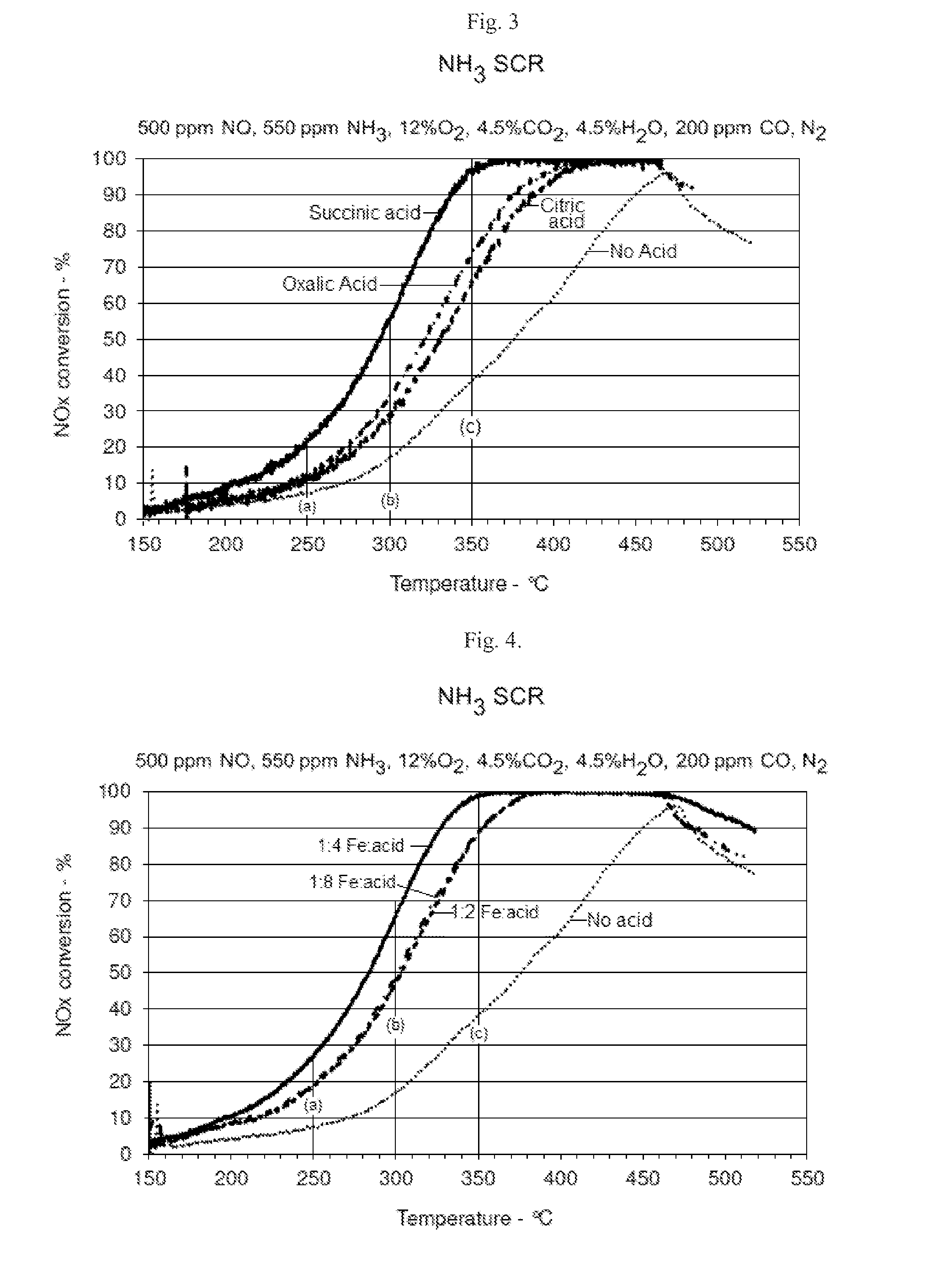
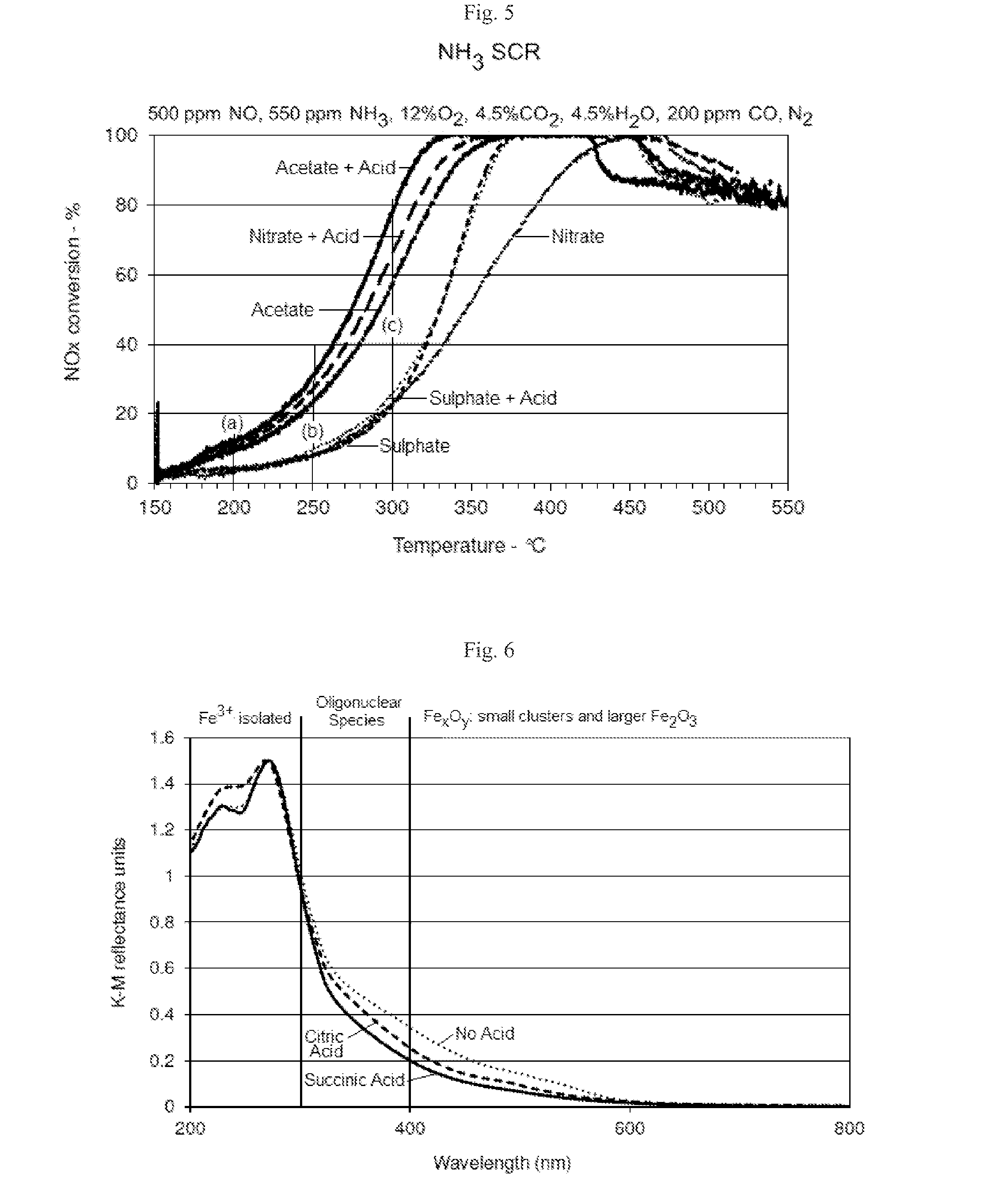
SCR-active molecular sieve based-catalysts are produced by combining a molecular sieve with at least one ionic iron species and at least one organic compound to form a mixture, then calcining the mixture to remove the at least one organic compound. This process improves the dispersion of the iron within the molecular sieve compared to an iron-containing molecular sieve that is not treated with an organic compound. Iron-containing ferrierite zeolites exhibit a selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with NH3 or urea of greater than 25% conversion at 300° C. in exhaust gases prior to ageing or exposure to steam. Iron-containing beta zeolites exhibit a selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with NH3 or urea of: (a) greater than 40% conversion at 300° C. and (b) greater than 80% conversion at 400° C., in exhaust gases after ageing for 20 hours at 700° C. in the presence of 10% H2O.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
High temperature ammonia SCR catalyst and method of using the catalyst
A catalyst and a method for selectively reducing nitrogen oxides (“NOx”) with ammonia are provided. The catalyst includes a first component comprising a zeolite or mixture of zeolites selected from the group consisting of ZSM-5, ZSM-11, ZSM-12, ZSM-18, ZSM-23, MCM-zeolites, mordenite, faujasite, ferrierite, zeolite beta, and mixtures thereof; a second component comprising at least one member selected from the group consisting of cerium, iron, copper, gallium, manganese, chromium, cobalt, molybdenum, tin, rhenium, tantalum, osmium, barium, boron, calcium, strontium, potassium, vanadium, nickel, tungsten, an actinide, mixtures of actinides, a lanthanide, mixtures of lanthanides, and mixtures thereof; optionally an oxygen storage material and optionally an inorganic oxide. The catalyst selectively reduces nitrogen oxides to nitrogen with ammonia at high temperatures. The catalyst has high hydrothermal stability. The catalyst has high activity for conversion of low levels of nitrogen oxides in exhaust streams. The catalyst and the method may have special application to selective reduction of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gas from gas turbines and gas engines, although the catalyst and the method have broad application to a wide range of gas streams that have excess oxygen and high temperatures. The temperature of exhaust gas from gas turbines and gas engines is high. Both the high temperature and the low levels of inlet NOx are challenging for selective catalytic reduction (SCR) catalysts.
Owner:CATALYTIC SOLUTIONS INC
Fe molecular sieve catalyst for purifying NOx in acrylonitrile oxidization tail gas and preparation method of Fe molecular sieve catalyst
InactiveCN102513145AEfficient removalEasy to handleMolecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationActive componentIon exchange
The invention relates to a Fe molecular sieve SCR (Selective Catalytic Reduction) catalyst for purifying NOx in acrylonitrile oxidization tail gas and a preparation method of the Fe molecular sieve SCR catalyst. A commercial ZSM-5 molecular sieve, a Y type molecular sieve, ferrierite or a beta molecular sieve is used as a carrier, 0.3-10.0 percent by mass of Fe<3+> is introduced to be used as an active component by adopting an immersion method or ion exchange method, and 0.5-8.0 percent by mass of M (lanthanum La or cobalt Co) is introduced to be used as a modification component. The SCR catalyst prepared by adopting the preparation method furthest realizes NO transformation and efficient catalysis removal of the NOx in the acrylonitrile oxidization tail gas under an oxygen enrichment condition. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple process and good repeatability, and is beneficial to industrialized production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Ferrierite compositions for reducing NOx emissions during fluid catalytic cracking
Compositions for reduction of NOx generated during a catalytic cracking process, preferably, a fluid catalytic cracking process, are disclosed. The compositions comprise a fluid catalytic cracking catalyst composition, preferably containing a Y-type zeolite, and a particulate NOx composition containing ferrierite zeolite particles. Preferably, the NOx reduction composition contains ferrierite zeolite particles bound with an inorganic binder. In the alternative, the ferrierite zeolite particles are incorporated into the cracking catalyst as an integral component of the catalyst. NOx reduction compositions in accordance with the invention are very effective for the reduction of NOx emissions released from the regenerator of a fluid catalytic cracking unit operating under FCC process conditions without a substantial change in conversion or yield of cracked products, e.g., gasoline and light olefins. Processes for the use of the compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:YALURIS GEORGE +2
Preparation method for nanometer flaky ferrierite molecular sieve
ActiveCN105129813AHigh yieldIncrease the areaCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesSynthesis PhaseTetrahydrofuran
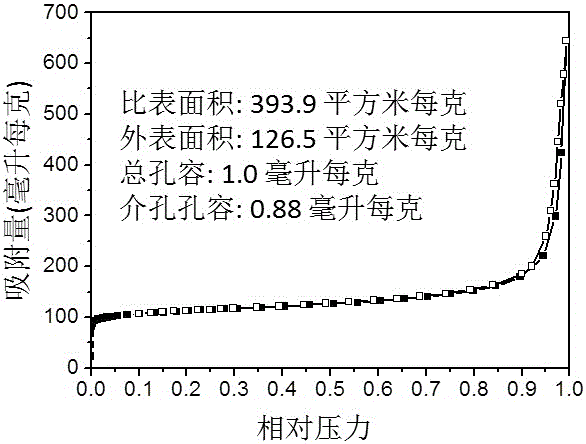
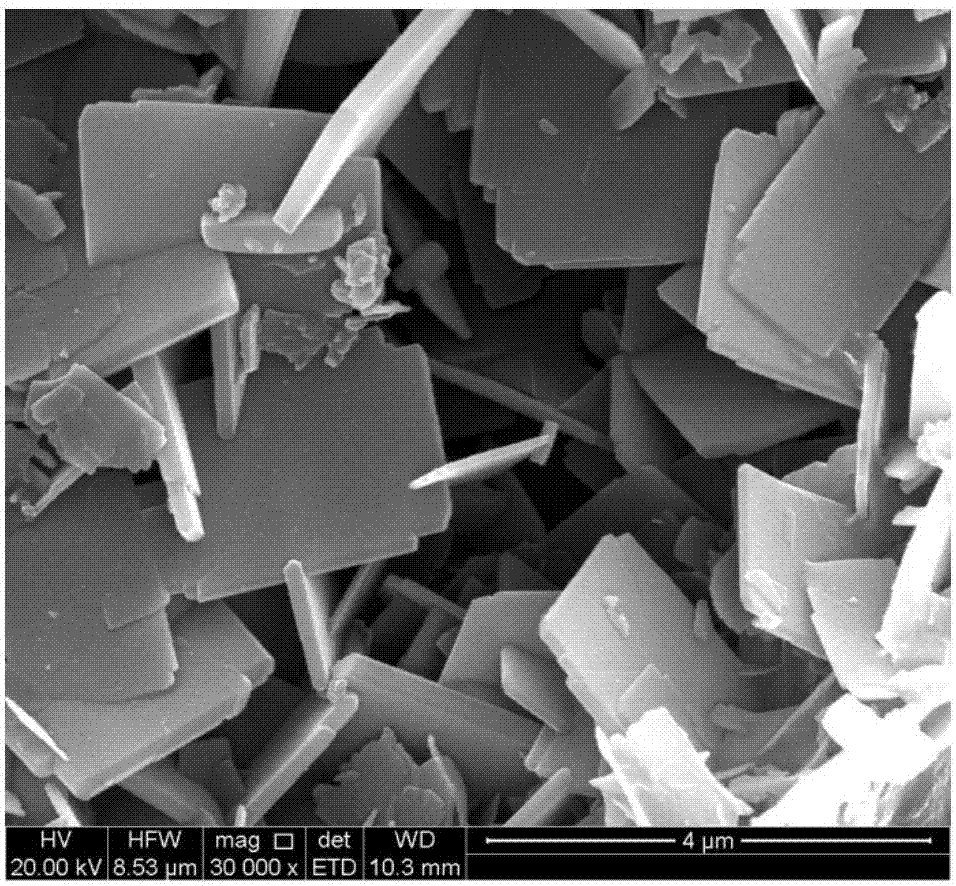
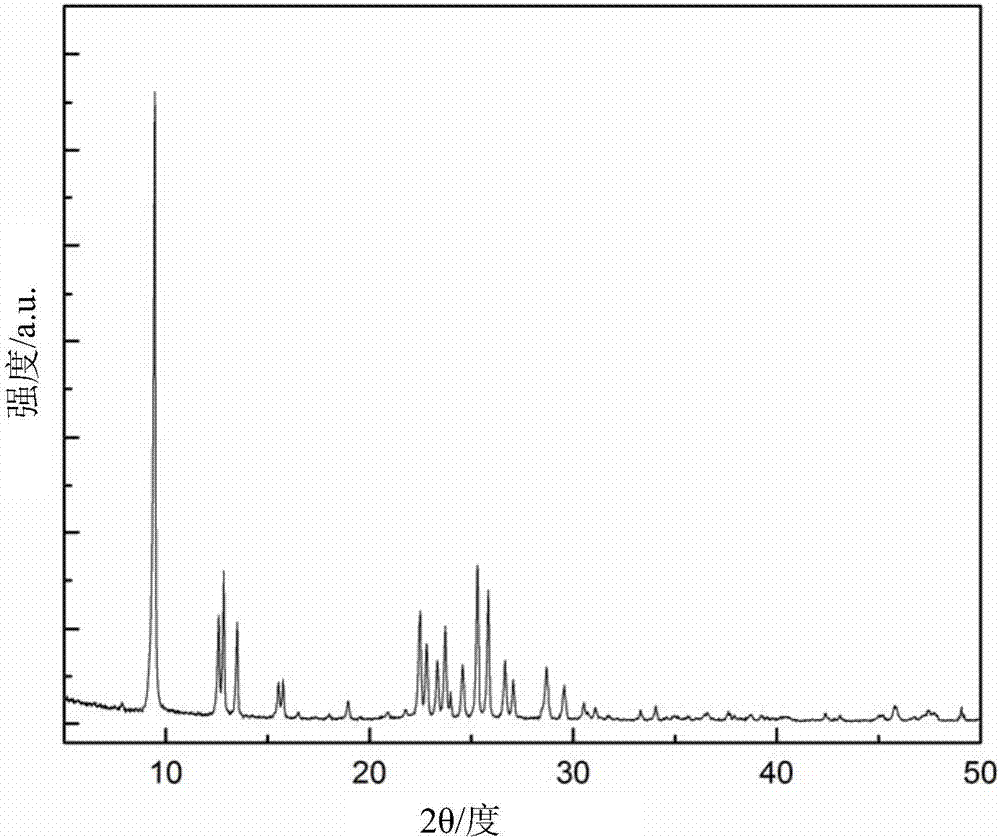
The invention discloses a preparation method for a nanometer flaky ferrierite molecular sieve. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: mixing an inorganic silicon source, an aluminum source and an alkali source with pyridine, piperidine, piperazine, tetrahydrofuran or hexylenediamine; then introducing cetyl trimethyl ammonium bromide (CTABr) and carrying out stirring at room temperature for 1 to 3 h; then carrying out a crystallization reaction at 120 to 180 DEG C for 2 and 10 d; and after completion of the reaction, carrying out filtering and drying so as to obtain the nanometer flaky ferrierite molecular sieve. Compared with the prior art, the nanometer flaky ferrierite molecular sieve prepared in the invention has a great outer specific surface area, a high accumulation mesopore volume as high as 0.88 ml / g and a flake thickness of less than 10 nanometers; and the preparation method has the advantages of easiness, mild reaction conditions, a wide synthesis phase, capacity of preparing pure-phase ferrierite in a wide range of a silica-alumina ratio, high yield of ferrierite, certain industrialization prospects and substantial economic values.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Boron-modified ferrierite molecular sieve catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107265478AHigh activityLong life one wayFerrierite aluminosilicate zeoliteHydrocarbon by isomerisationPtru catalystIon exchange
The invention provides a boron-modified ferrierite molecular sieve catalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding an alkali source, an aluminum source and a boron source into water, and stirring to form a uniform solution; adding a ferrierite molecular sieve seed crystal, a silicon source and a template agent into the uniform solution, and stirring until a sol solution is formed; crystallizing the sol solution under a hydrothermal condition, and carrying out filtration, drying and roasting, so as to obtain boron-modified sodium-type ferrierite molecular sieve raw powder; carrying out ion exchange on the boron-modified sodium-type ferrierite molecular sieve raw powder and an ammonium salt water solution or diluted hydrochloric acid, filtering, and drying, so as to obtain hydrogen-type molecular sieve raw powder; and mixing the hydrogen-type molecular sieve raw powder with a binder and water, carrying out extrusion formation, drying, and roasting, so as to obtain the boron-modified ferrierite molecular sieve catalyst. The boron-modified ferrierite molecular sieve catalyst prepared by virtue of the preparation method has the advantages of high activity, long single pass life, strong anti-carbon property and low liquid phase yield.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Preparation of Mg alkali zeolite by vapor phase self crystallization
InactiveCN1583561AReduce dosageHigh crystallinityCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesWater vaporReaction temperature
A process for preparing the magnesium-alkali zeolite (FER) by vapor phase transfer (VPT) method includes such steps as preparing the gel from the mixture of alkali metal, oxide of. 3-valence element, oxide of 4-valence element and water, dewatering to obtain dried gel, and self crystallizing in Teflon / water vapor at 100-200 deg.C.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Hierarchical pore nano ferrierite aggregate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108946764AIncrease the areaWide Si-Al Ratio RangeMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsGramCrystallinity
The invention discloses hierarchical pore nano ferrierite aggregate, characterized in that a sample of the aggregate has high degree of crystallinity; a molar ratio of SiO2 to Al2O3 is 100-1500; the particle size of particles forming the aggregate is 10-100nm; the mesoporous surface area reaches 70 square meters per gram; the mesoporous bulk volume reaches 0.12ml per gram; and the degree of crystallinity reaches 108% and is not lower than 105%. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the hierarchical pore nano ferrierite aggregate.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Fluidizing cracking catalyst and method for reducing NOx emissions during fluid catalytic cracking
InactiveCN101503632ADetailed descriptionGas treatmentCatalytic crackingALUMINUM PHOSPHATESilicon dioxide
The present invention relates to a fluid cracking catalyst and a method for reducing the discharge amount of NOx in the fluid cracking period. The catalyst composition comprises the following components: (a) an FCC cracking component which is suitable for catalyzing the cracking of hydrocarbon under FCC condition, and (b) granular composition for reducing NOx. The granular composition for reducing NOx has an average particle size larger than 45 micrometer and comprises the following components: (i) at least 10 percent of ferrierite by weight and (ii) inorganic binder which accounts for about 5-50 percent by weight. The inorganic binder is selected from aluminum oxide, silicon dioxide, aluminum oxide-silicon dioxide, aluminum phosphate and the mixture thereof. The method of the invention comprises a step of contacting the raw material of hydrocarbon with the cracking catalyst composition in a raising temperature thereby forming the hydrocarbon component with low molecular weight.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO CONN
Catalyst for preparing iso-olefins by isomerizing straight-chain olefins and preparation method of catalyst
InactiveCN102600886AHigh activityImprove stabilityHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic acidIsomerization
The invention discloses a catalyst for preparing iso-olefins by isomerizing straight-chain olefins and a preparation method of the catalyst. The catalyst uses the FER (ferrierite) zeolite raw powder as a main active body, wherein the silica-alumina ratio (SiO2 / Al2O3) (molar ratio) is less than 50. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing FER zeolite raw powder, silica sol and / or alumina sol, organic acid and water evenly; carrying out molding, drying and calcinaton, and soaking in a VIII group metal oxide solution; and carrying out drying and calcination to obtain the catalyst. For the isomerization of straight-chain olefins, the catalyst is good in activity and stability, high in both conversion rate of straight-chain olefins and selectivity to iso-olefins and can be applied to the field of industrial production of the iso-olefins, such as the industrial production of isobutene and isoamylene.
Owner:王伟跃
Sodium-potassium-hydrogen type ferrierite and method for preparing same
ActiveCN103043682AHigh selectivityInhibit side effectsMolecular-sieve and base-exchange compoundsIsomerizationHydrogen
The invention discloses sodium-potassium-hydrogen type ferrierite and a method for preparing the same. The sodium-potassium-hydrogen type ferrierite comprises 0.02%-0.1wt% of Na2O, 1.0%-5.0wt% of K2O, wherein the molar ratio of SiO2 to Al2O3 is 8-50. The method adopts a sodium-potassium-hydrogen type ferrierite partial ammonium exchange method. The method comprises that the sodium-potassium-hydrogen type ferrierite and an inorganic ammonium salt water solution with a certain concentration are pulped uniformly, and the exchanged pulp is filtered, eluted, dried and calcinated. After the method is adopted, the pH value of the exchange fluid does not need to be adjusted, the concentration of the inorganic ammonium salt water solution only needs to be changed, and the sodium-potassium-hydrogen type ferrierite with an appropriate total alkali metal content can be obtained through one or two times of exchange at room temperature and has good usability in straight-chain olefin isomerization reaction.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Small crystal ferrierite and method of making the same
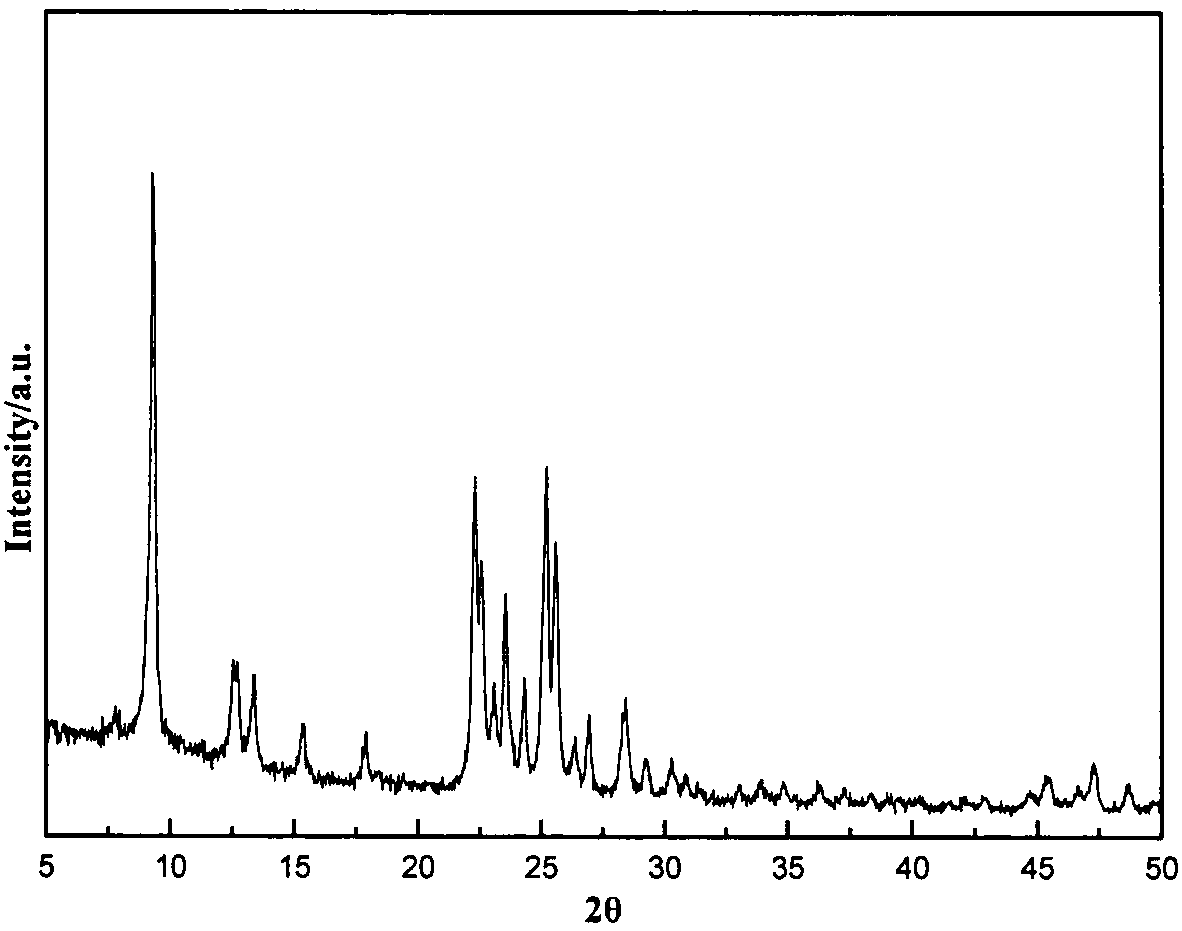
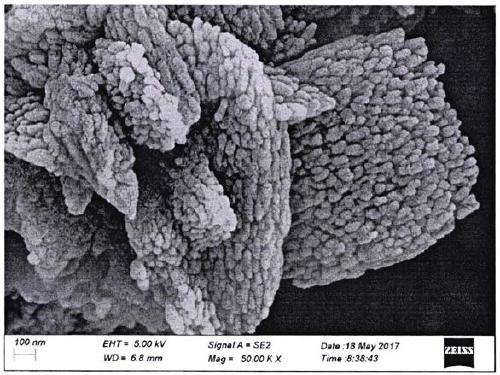
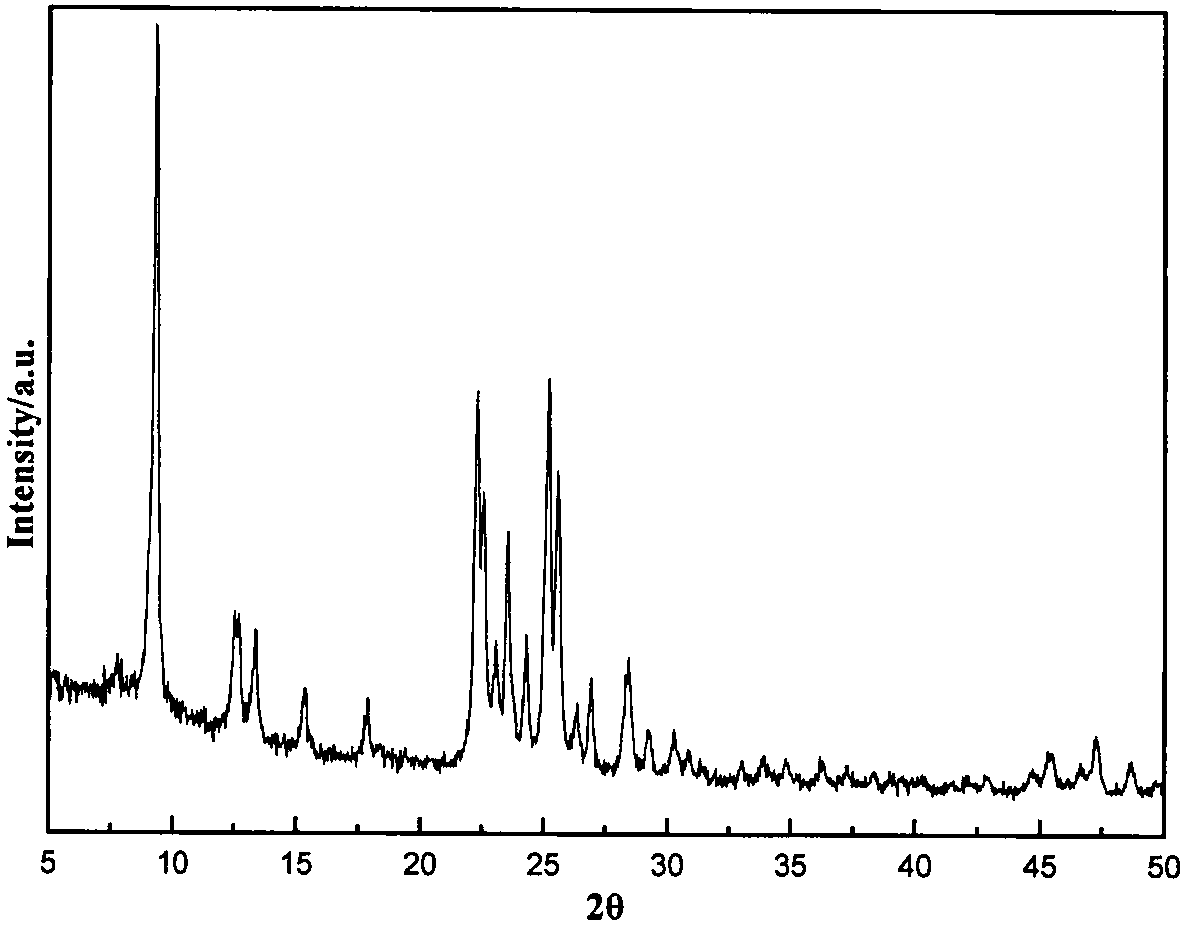
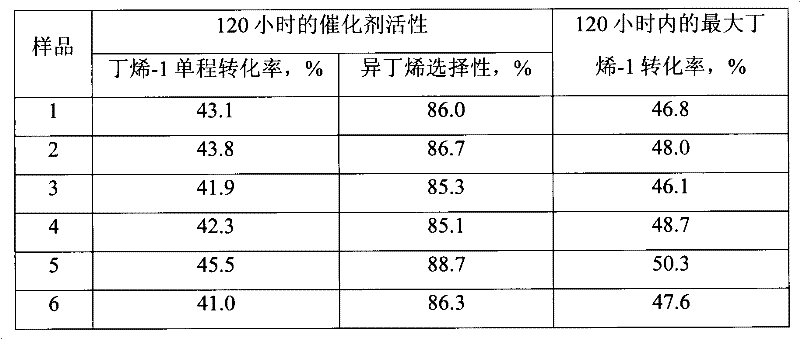
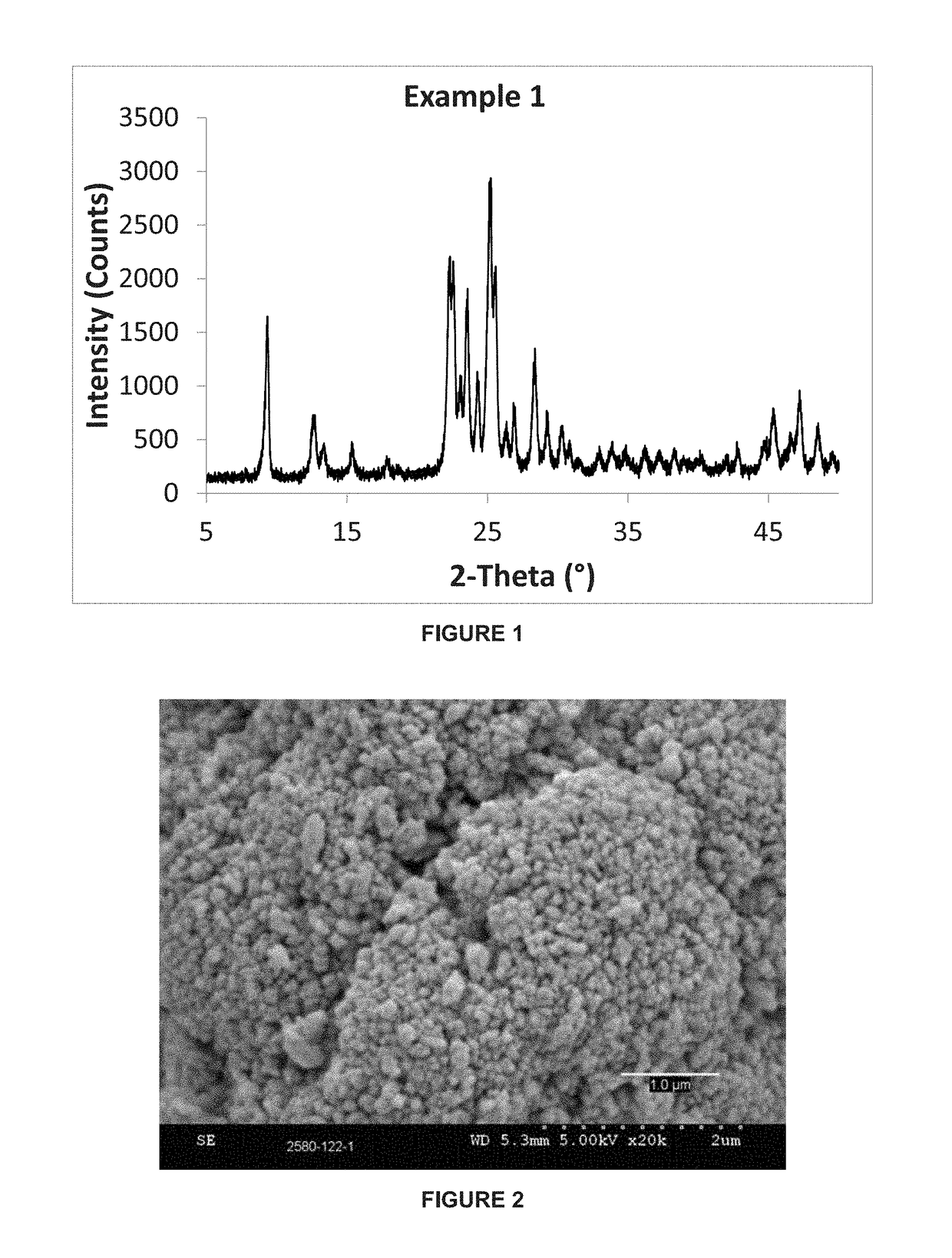
There is disclosed a highly crystalline, small crystal, ferrierite zeolite prepared from a gel containing a source of silica, alumina, alkali metal and a combination of two templating agents. The resulting material includes ferrierite crystals having a particle size of about or less than about 200 nm. The desired crystal size can be achieved by using a specific composition of the gel. The purity of the material and the crystal size was determined by using X-ray powder diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. The material has excellent surface area and micropore volume as determined by nitrogen adsorption.
Owner:ECOVYST CATALYST TECH LLC
Synthesis method of small-crystal-grain FER (Ferrierite) molecular sieve with laminar stacking structure
ActiveCN108862306AEfficient removalGood effectHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsIsomerizationSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a small-crystal-grain FER (Ferrierite) molecular sieve with a laminar stacking structure. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: taking a silicon source, an aluminum source, alkali, an organic template agent and water as raw materials, and rotating and ageing at relatively low temperature to form initial gel; then carrying out dynamic crystallization to obtain a primary product; then removing the organic template agent under a mild condition by utilizing a lot of low-temperature plasmas generated through a dielectric barrier discharge(DBD) device, so as to obtain the small-crystal-grain FER molecular sieve with the laminar stacking structure; finally, carrying out different depths of water stream coupled low-temperature plasma treatment on the prepared molecular sieve, so as to remove framework aluminum and adjust the acidic ratio of the FER molecular sieve, and further modify the shape and structure of the molecular sieve. The molecular sieve prepared by the invention not only has good stability, but also has a very strong carbon deposition resisting capability; when the molecular sieve is used for catalyzing n-butene isomerization reaction, excellent performance is obtained, and the stability of a catalyst is effectively enhanced; the service life of the catalyst is extremely improved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Ferrierite with high silica-alumina ratio and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111392745AHigh crystallinityHigh solid yieldMaterial nanotechnologyHydrocarbon by isomerisationIsomerizationCrystallinity
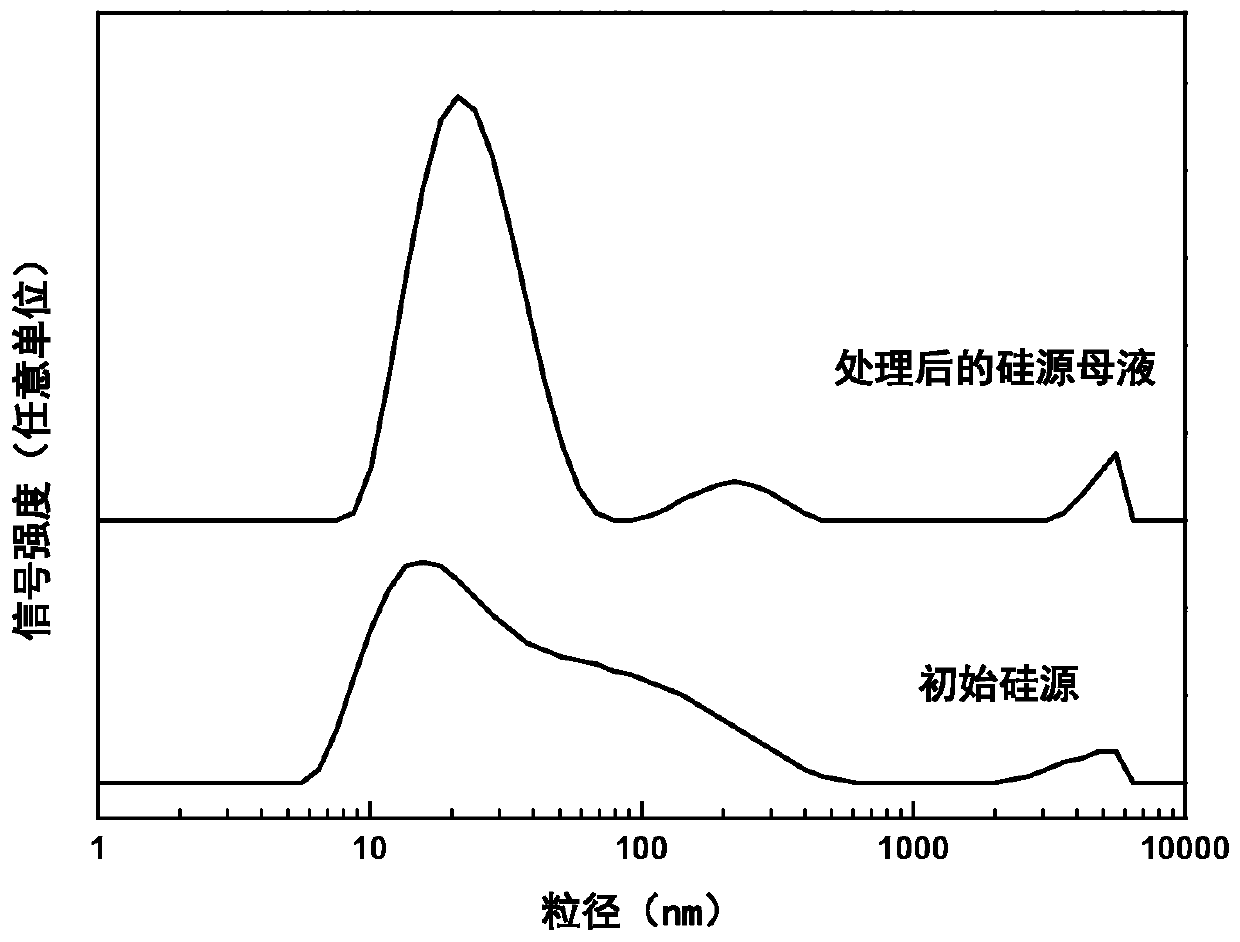
The invention provides ferrierite with a high silica-alumina ratio and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that a silicon source and an alkali metal hydroxide solution are mixed and subjected to constant-temperature treatment for 0.5-8 h at the temperature of 20-100 DEG C, silicon source mother liquor is obtained, and the average particle size of the silicon source mother liquor is 5-100 nm; water, an aluminum source, a template agent and the silicon source mother liquor are mixed to prepare silicon-aluminum gel; and the silica-alumina gel is crystallized at 140-200 DEG C for 1-5 days, and the crystallized product is washed, dried and roasted to obtain ferrierite. The ferrierite obtained by the preparation method has high crystallinity,solid yield and silica-alumina ratio and can be used for catalyzing olefin oligomerization and n-butene and n-pentene skeletal isomerization reaction.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Catalyst used for heterogeneously producing isoalkene by utilizing direct-chain olefin skeleton and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103041848AHigh selectivityInhibit side effectsHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsPtru catalystEngineering
The invention provides a catalyst used for heterogeneously producing isoalkene by utilizing a direct-chain olefin skeleton. The catalyst comprises an FER zeolite and a binder, wherein the FER zeolite is a sodium potassium hydrogen type FER zeolite, and based on the percentage by weight of zeolite, Na2O content is 0.02-0.1%, K2O content is 1.0-5.0%, and mole ratio of SiO2 to Al2O3 is 8-50. The catalyst provided by the invention is obtained by fully mixing the FER zeolite powder, the binder, sesbania powder, inorganic acid and water, moulding the obtained mixture and then drying and roasting. The ferrierite adopted by the invention is of a sodium potassium hydrogen type, and the catalyst prepared by the method provided by the invention has isoalkene selectivity compared with the hydrogen type FER zeolite containing no sodium or / and potassium.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Modified ferrierite as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103043677AHigh selectivityHigh yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsHydrogenIsomerization
The invention discloses a modified ferrierite as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The modified ferrierite is prepared from the following component in percentage by weight: 0.02-0.1% of Na2O, 1.0-5.0% of K2O and 0.05-0.5% of SiO2 in silicon introduced for surface silanization, wherein the molar ratio of the SiO2 to the Al2O3 in the modified ferrierite is 8-50. The modified ferrierite is prepared by exchanging sodium-potassium ferrierite by ammonium partially to obtain sodium-potassium-hydrogen ferrierite and silanizing the surface of the sodium-potassium-hydrogen ferrierite. Due to the adoption of the preparation method, the number of hydroxyls and acid sites on the outer surface of the ferrierite can be reduced effectively. The silanized and modified ferrierite has good use performance in the straight-chain olefin isomerization reaction.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Hollow cerium dioxide microsphere supported ferrihydrite heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110252316AEfficient activationMany active sitesWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsMicrosphereCerium
The invention discloses a hollow cerium dioxide microsphere supported ferrihydrite heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the hollow cerium dioxide microsphere supported ferrierite heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing porous cerium dioxide nanospheres by using Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a biological template in a high-temperature environment; and then, loading the porous cerium dioxide nanospheres on the surface of ferrierite by in-situ deposition. The mesoporous ceria nanospheres in the catalyst have a photosensitive effect, can generate photo-generated carriers in response to visible light, and promote the activation efficiency of the ferrihydrite on hydrogen peroxide in a Fenton system. Generated active free groups have broad-spectrum catalytic degradation effect on pollutants and have certain practical application value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Isomerization method for n-butene
ActiveCN105418353AImprove conversion rateHigh selectivityHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsButeneIsomerization
The invention discloses an isomerization method for n-butene. The method comprises the steps of: under an isomerization condition, performing a fourth contact on n-butene and an isomerization catalyst, wherein the isomerization catalyst comprises modified ferrierite and the modified ferrierite is obtained by performing a first contact on unmodified ferrierite and an ammonium-containing compound under a solution condition; the ammonium-containing compound comprises ammonium nitrate and ammonium fluosilicate. The isomerization method for n-butene disclosed by the invention can remarkably improve the conversion ratio of a reaction substrate and the selectivity of a product.
Owner:BEIJING ENERGY ENG TECH
Catalytic system and additive for maximisation of light olefins in fluid catalytic cracking units in operations of low severity
InactiveUS20090107885A1Quality improvementIncrease the number ofAluminium compoundsCatalytic crackingGasolineAromaticity
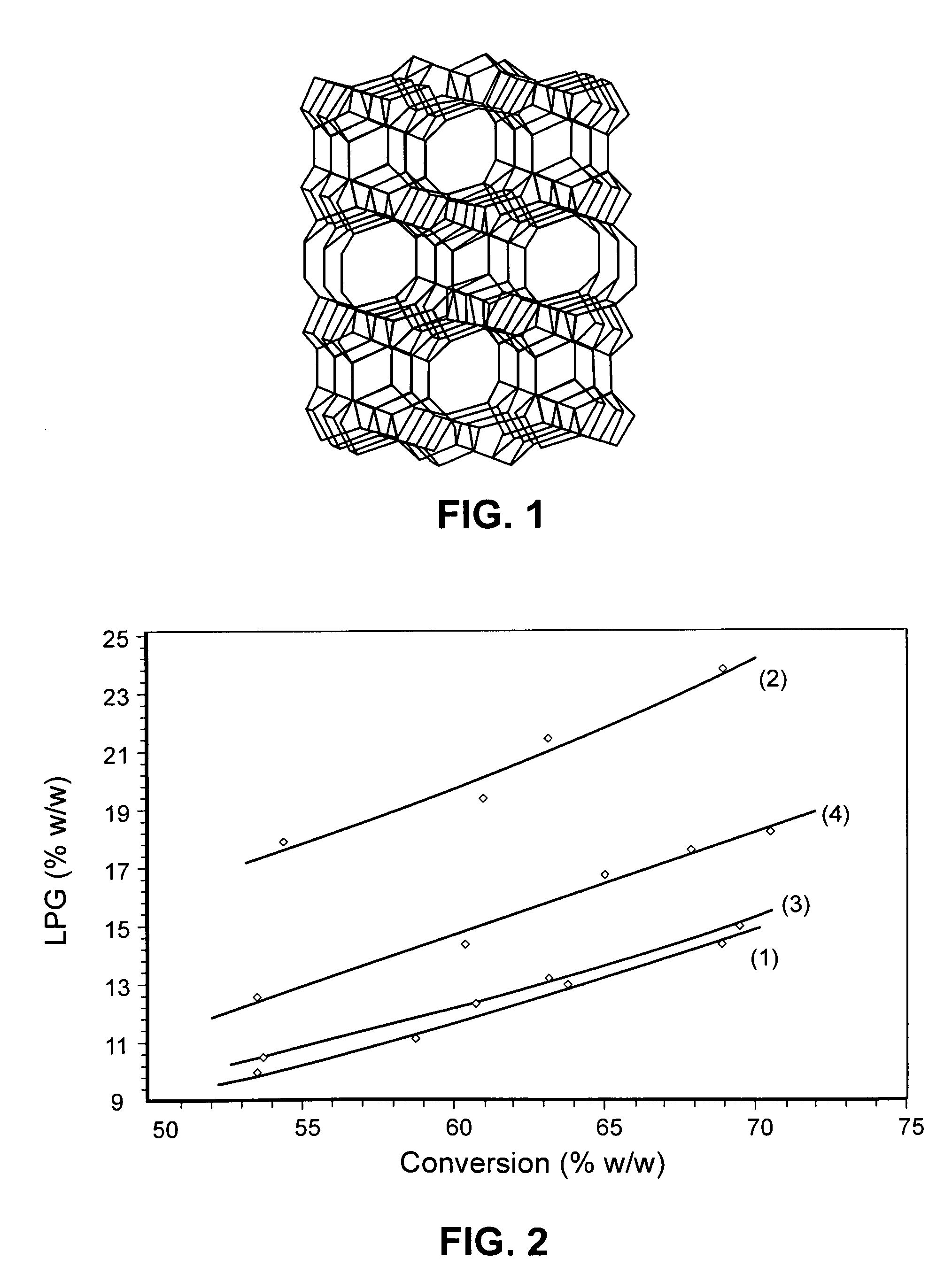
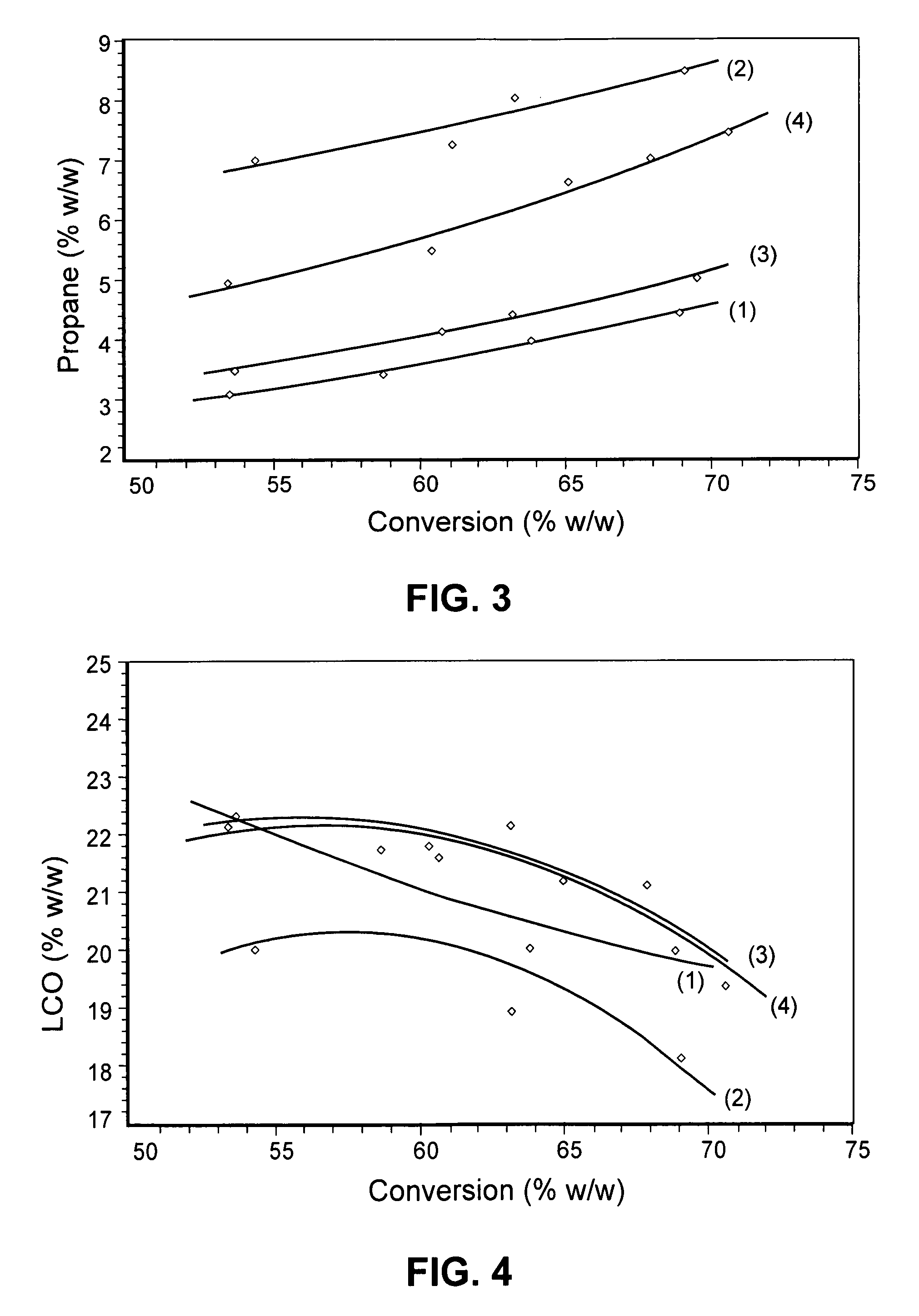
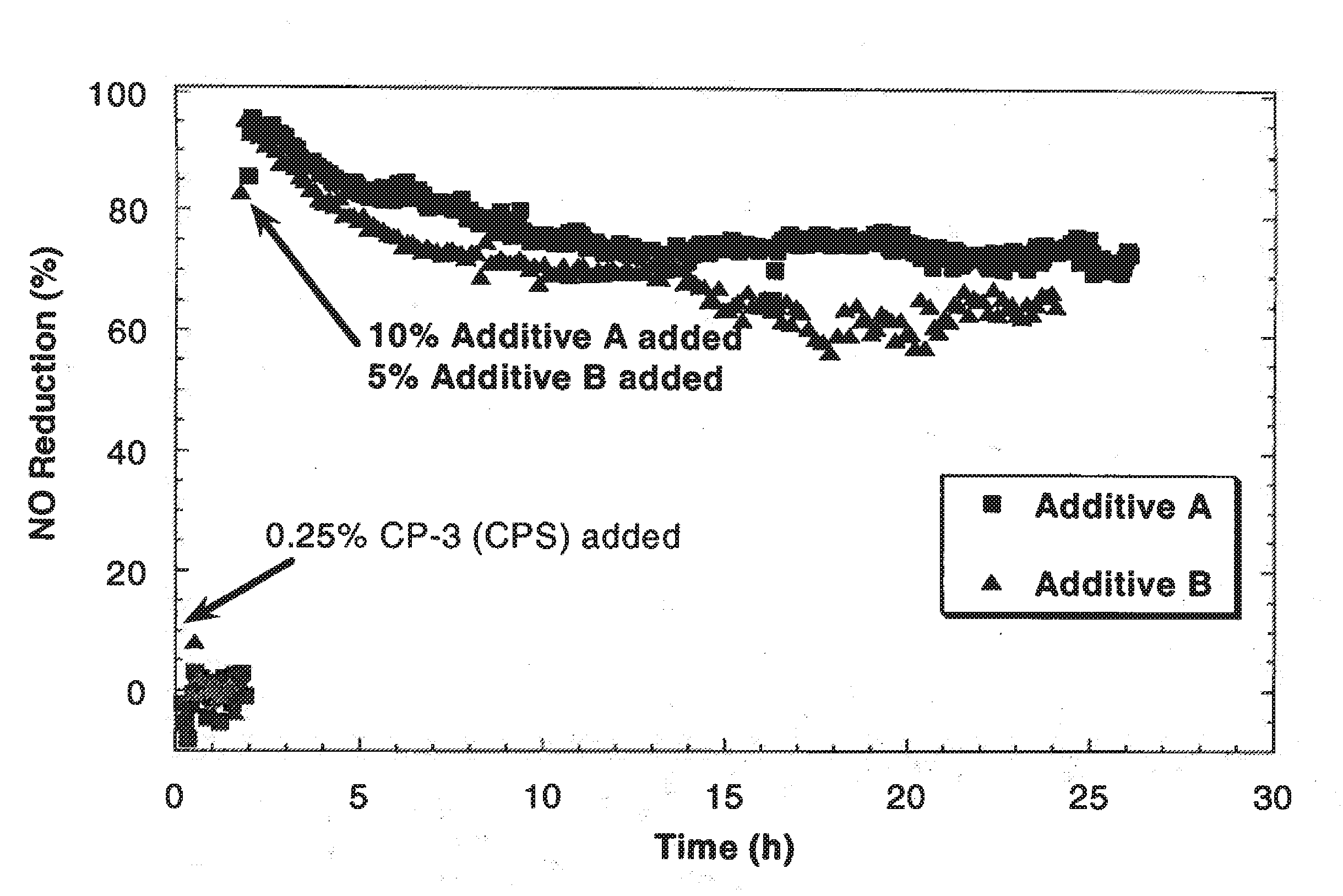
The present invention concerns the field of fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) processes. The invention provides a process increasing production of LPG and propene in FCC units operating under conditions of maximisation of middle distillates of low aromaticity, such that they may be incorporated into the diesel oil pool. The invention also relates to the preparation and employment of additives based on zeolites having small pores, such as ferrierite (FER), in catalytic systems for FCC units, wherein conditions of low severity are adopted with a view to increasing yields of LPG and light olefins whilst improving stability of petrol. The invention also provides an original catalytic system, being more efficient than catalytic systems known in the state of the art, to increase the yield of LPG and propene without prejudicing the yield and quality of LCO. Furthermore it provides a method of preparation of an additive for said process employing the zeolite ferrierite.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Ferrierite composition for reducing NOX emissions during fluid catalytic cracking
Compositions for reduction of NOx generated during a catalytic cracking process, preferably, a fluid catalytic cracking process, are disclosed. The compositions comprise a fluid catalytic cracking catalyst composition, preferably containing a Y-type zeolite, and a particulate NOx reduction composition containing ferrierite zeolite particles. Preferably, the NOx reduction composition contains ferrierite zeolite particles bound with an inorganic binder. In the alternative, the ferrierite zeolite particles are incorporated into the cracking catalyst as an integral component of the catalyst. NOx reduction compositions in accordance with the invention are very effective for the reduction of NOx emissions released from the regenerator of a fluid catalytic cracking unit operating under FCC process conditions without a substantial change in conversion or yield of cracked products. Processes for the use of the compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:WR GRACE & CO
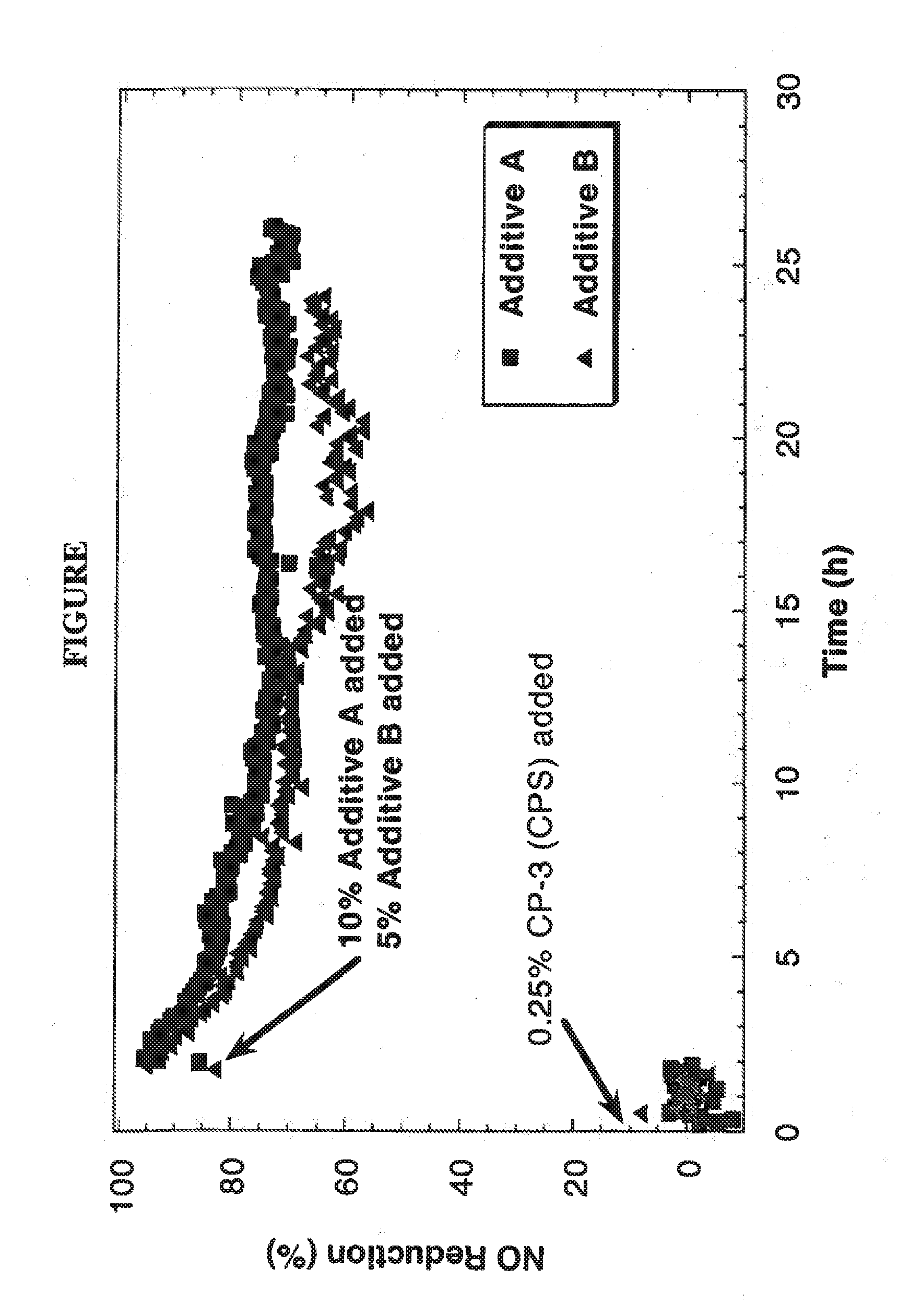
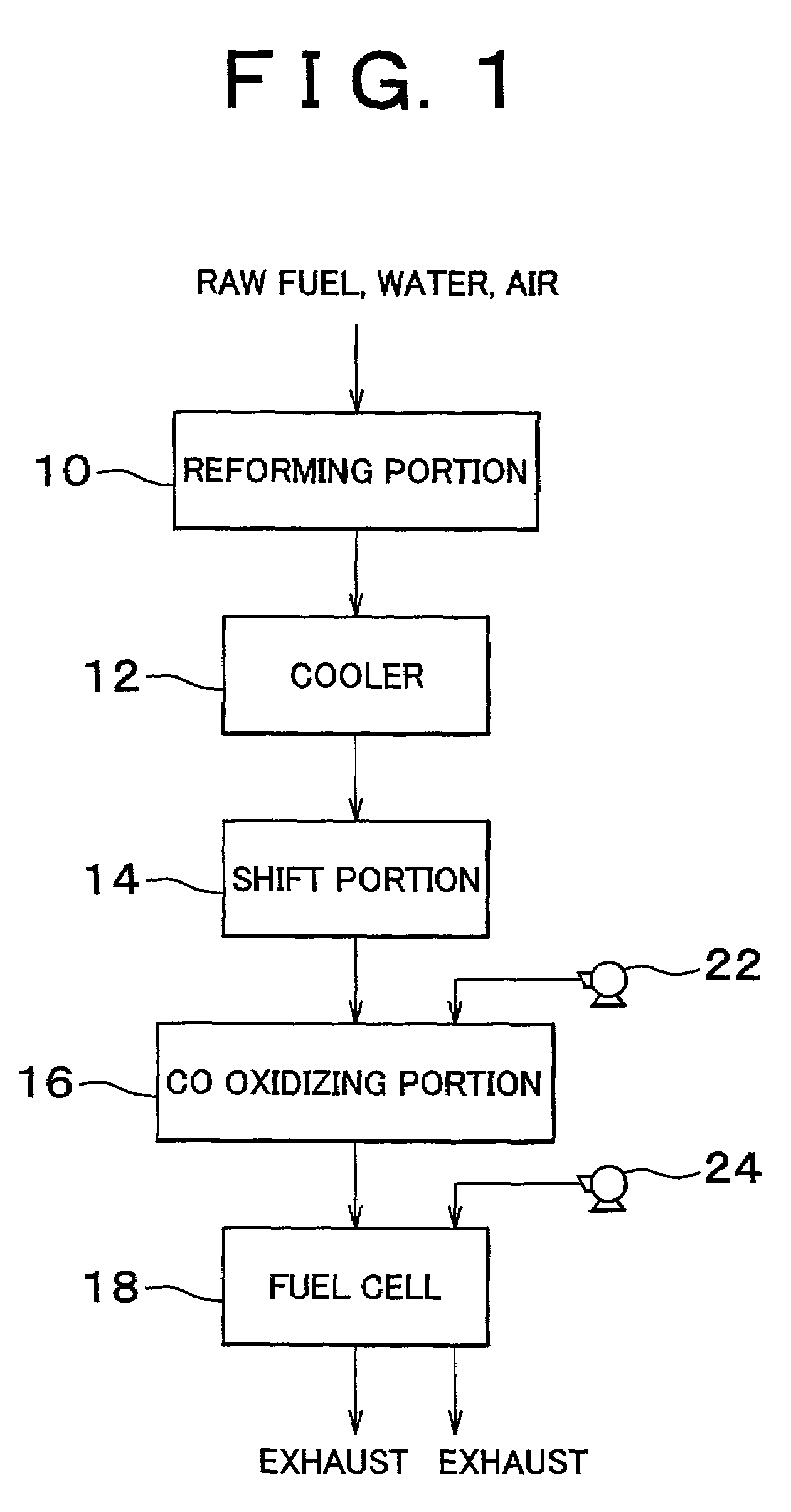
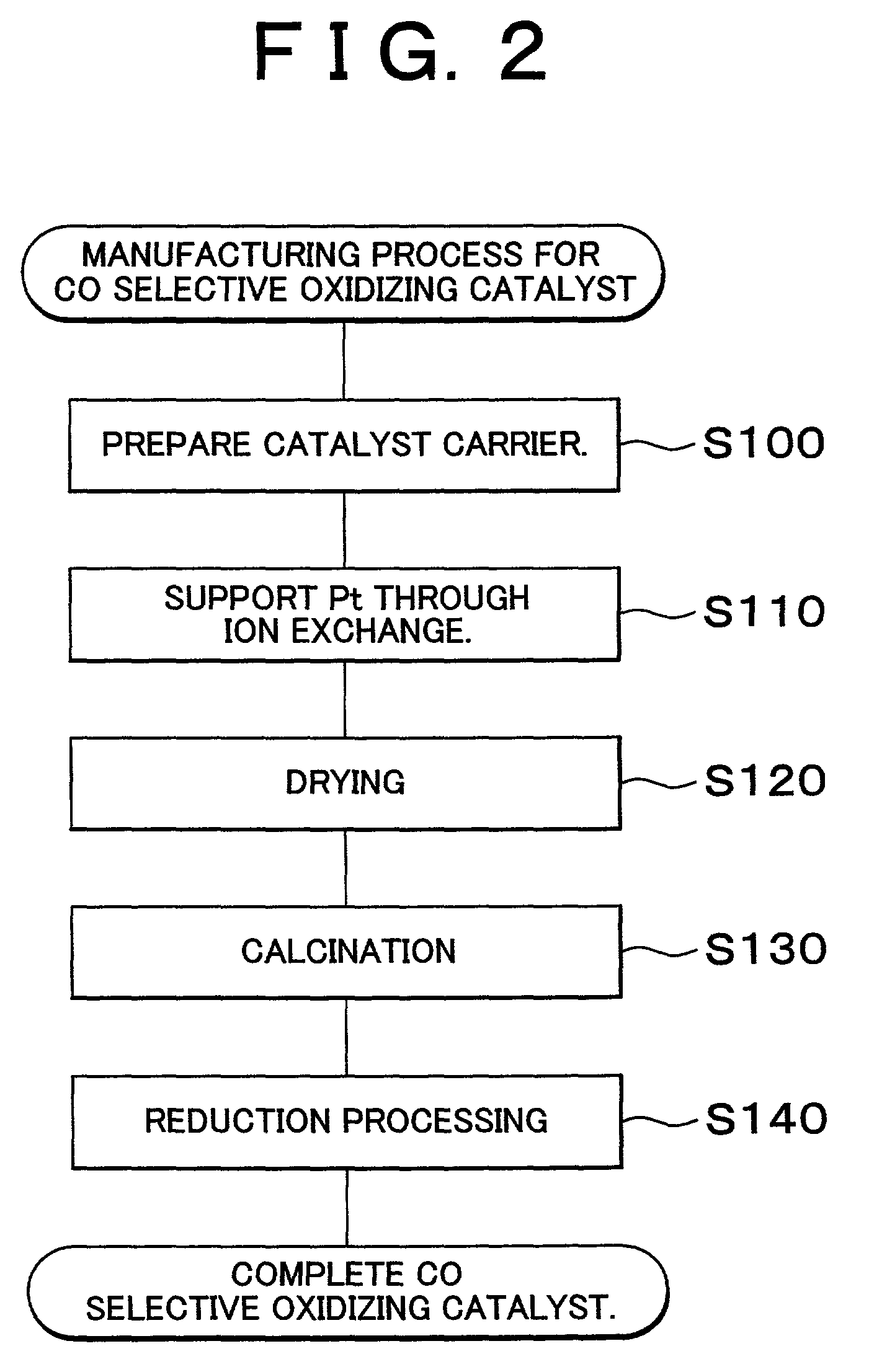
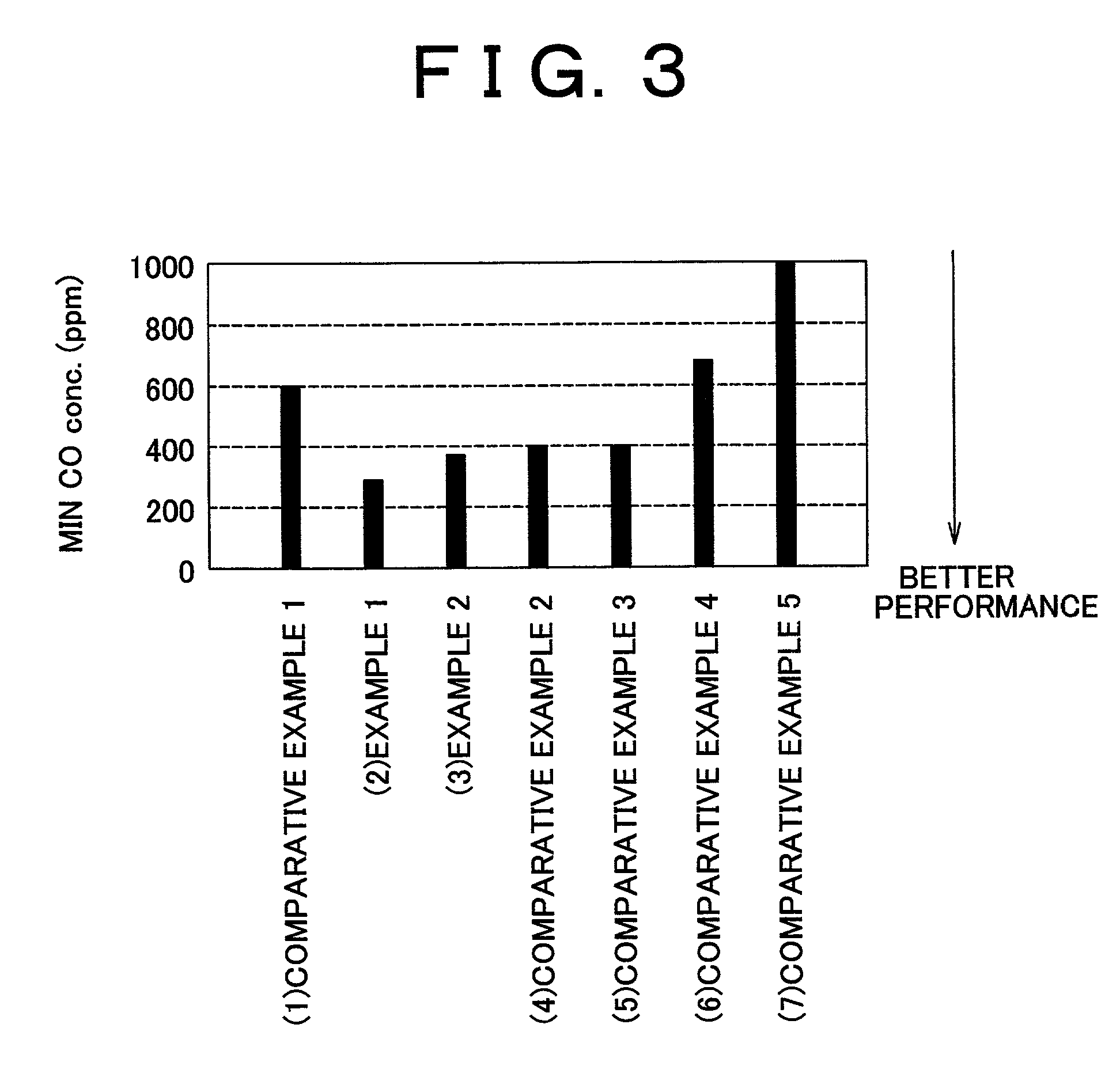
Carbon monoxide selective oxidizing catalyst and manufacturing method for the same
InactiveUS7094488B2Reduce carbon monoxide concentrationReduce probabilityCombination devicesMolecular sieve catalystsPlatinumPore diameter
A carbon monoxide selective oxidizing catalyst includes a carrier of ferrierite or ZSM-5 that supports a metal component of platinum (Pt) alone or platinum and at least one type of transition metal. Alternatively, a carbon monoxide selective oxidizing catalyst includes a carrier whose maximum pore diameter ranges from 0.55 to 0.65 nanometers (nm) that supports a metal component of platinum (Pt) alone or platinum and at least one type of transition metal.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Small crystal ferrierite and method of making the same
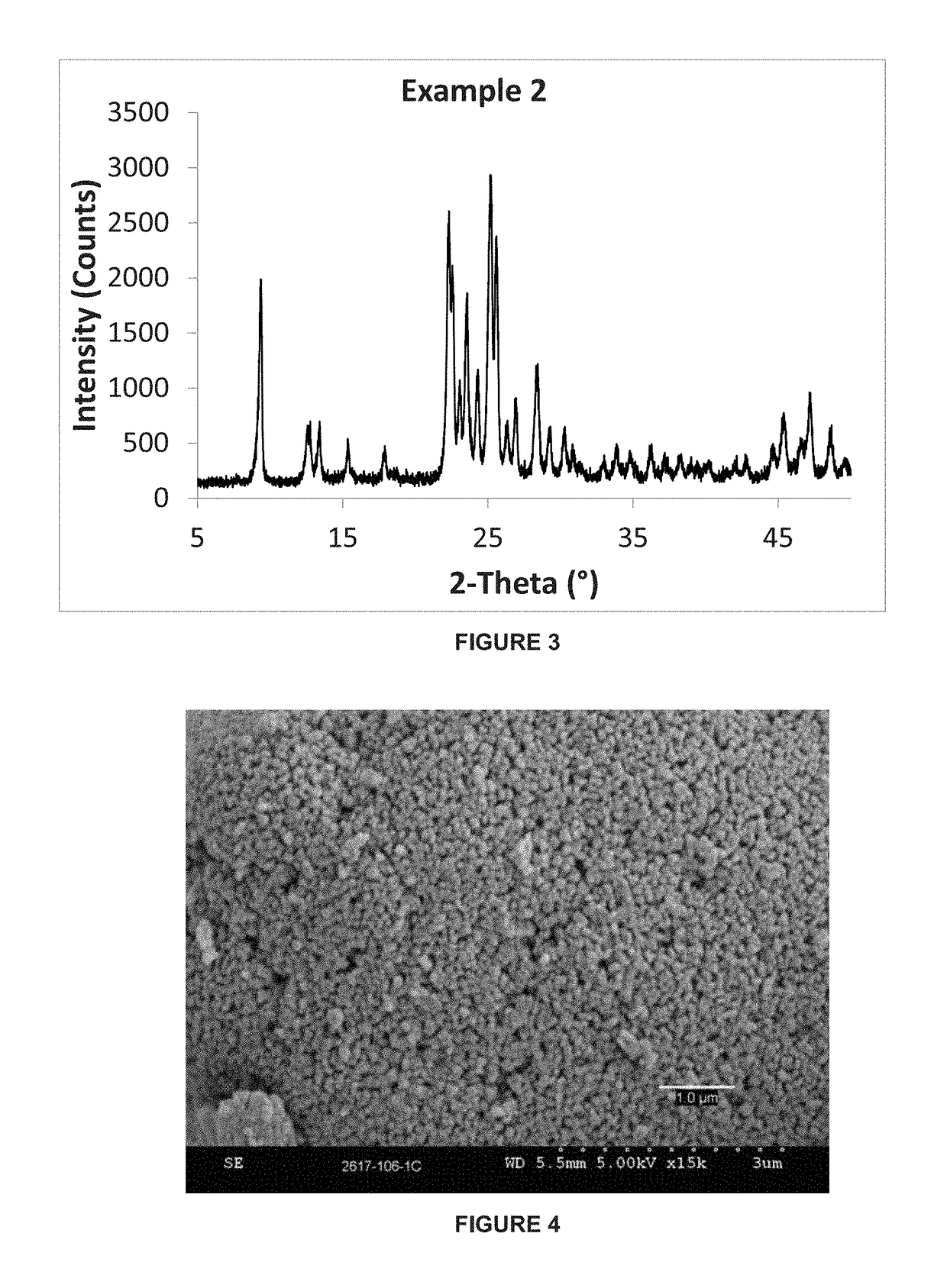
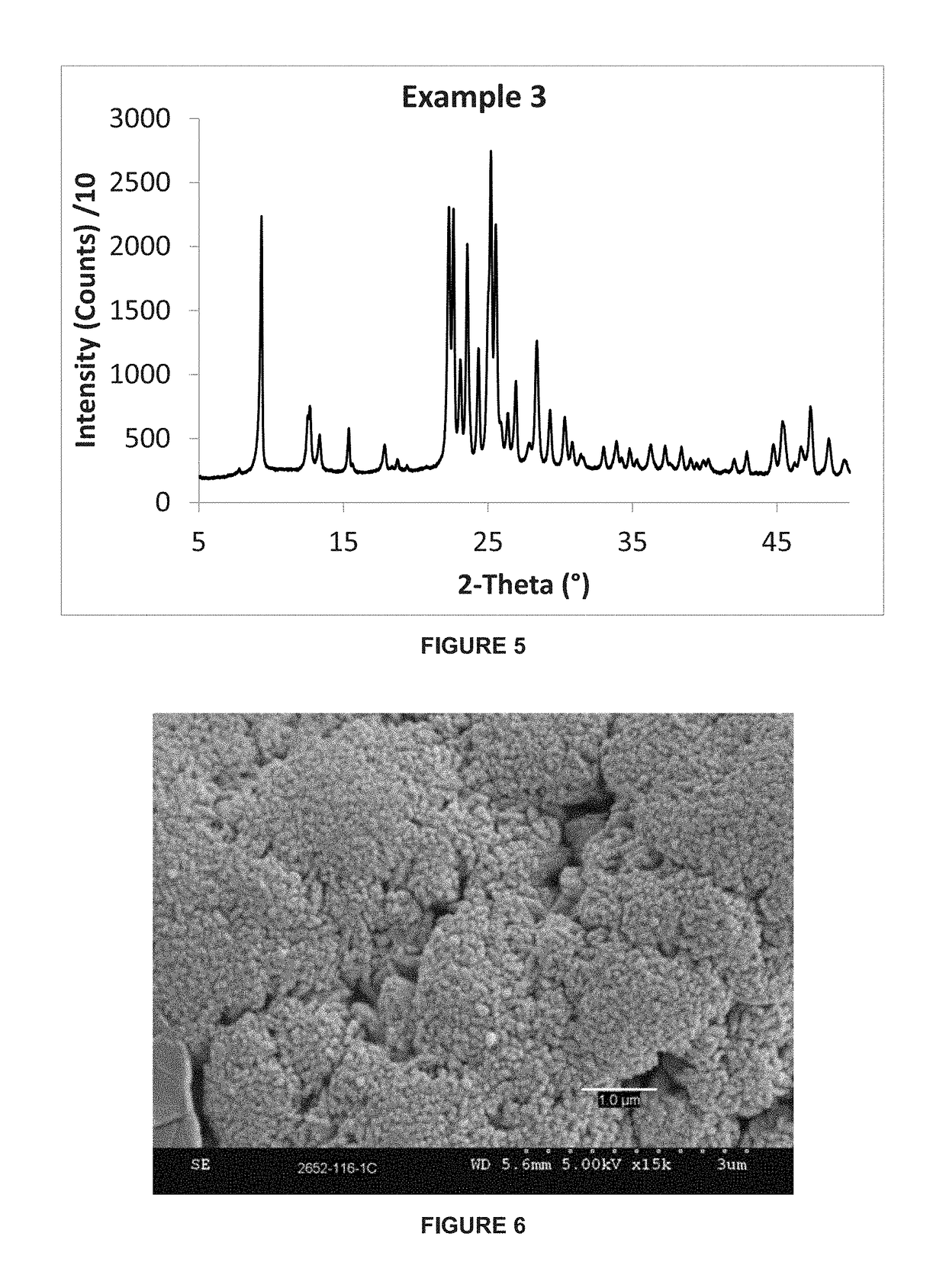
There is disclosed a highly crystalline, small crystal, ferrierite zeolite prepared from a gel containing a source of silica, alumina, alkali metal and a combination of two templating agents. The resulting material includes ferrierite crystals having a particle size of about or less than about 200 nm. The desired crystal size can be achieved by using a specific composition of the gel. The purity of the material and the crystal size was determined by using X-ray powder diffraction and scanning electron microscopy. The material has excellent surface area and micropore volume as determined by nitrogen adsorption.
Owner:ECOVYST CATALYST TECH LLC
Alkali earth metal modified ferrierite, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103041849BSuitable degree of exchangeHigh isobutene yieldHydrocarbon by isomerisationMolecular sieve catalystsIsomerizationAlkaline earth metal
The invention discloses an alkali earth metal modified ferrierite, and a preparation method and application thereof. Based on the weight percent of zeolite, the modified ferrierite comprises 0.1-1.5% of alkali earth metal based on Me<2+>; and the SiO2 / Al2O3 mol ratio is 8-50. The modified ferrierite is prepared from hydrogen ferrierite through an alkali earth metal ion exchange method; and the method comprises the following steps: uniformly pulping the hydrogen ferrierite and an alkali earth metal solution, and exchanging at 20-95 DEG C for 1-8 hours, wherein the exchange is performed 1-10 times; and then, filtering the pulp, leaching, drying, and roasting. The modified ferrierite prepared by the method disclosed by the invention can achieve higher isobutylene yield in isobutylene preparation reaction based on n-butylene skeleton isomerization in comparison with unmodified hydrogen ferrierite.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for producing monobranched fatty acids or alkyl esters thereof
ActiveUS20150291912A1Fatty acid hydrogenationFatty acid isomerisationBranched chain fatty acidsIsomerization
A process for producing a composition having a ratio by weight of C10-C26 monobranched fatty acids or alkyl esters thereof to C10-C26 polybranched fatty acids or alkyl esters thereof of greater than 6 using a zeolite, preferably ferrierite, isomerisation catalyst. The zeolite catalyst is preferably the only isomerisation catalyst used. The zeolite catalyst can be reused many times after simple separation from the reaction products without having to be regenerated.
Owner:CRODA INT PLC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com