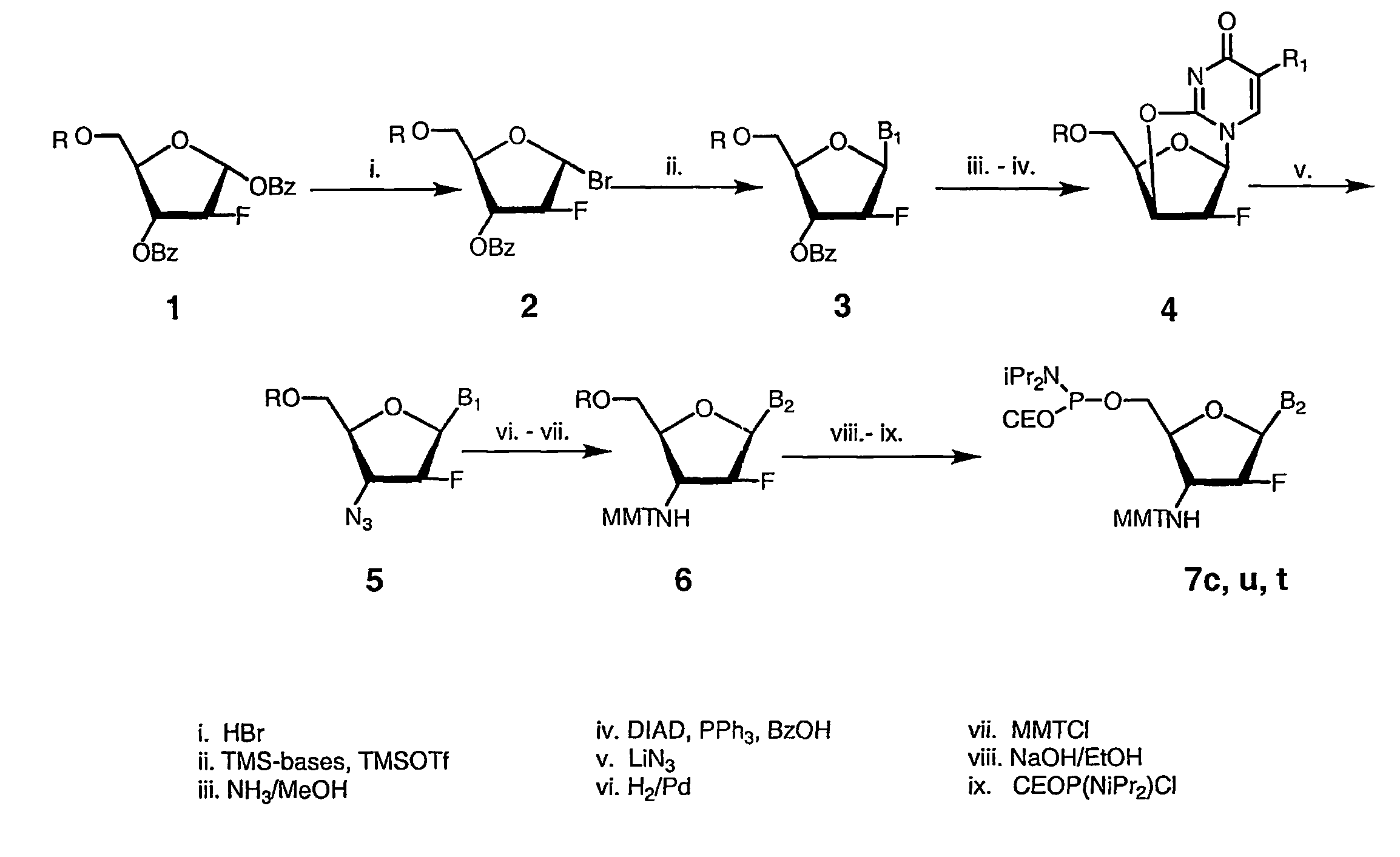
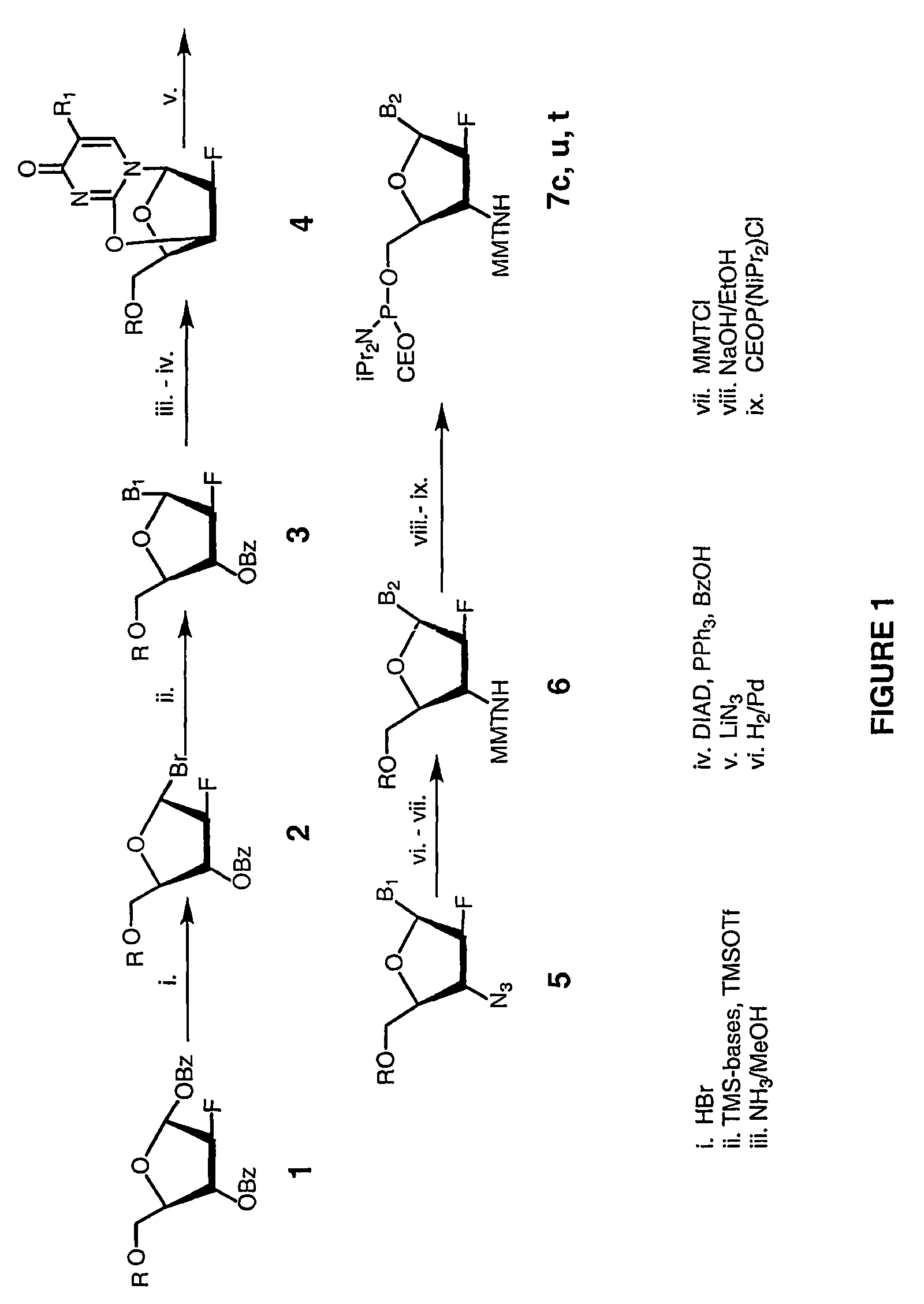
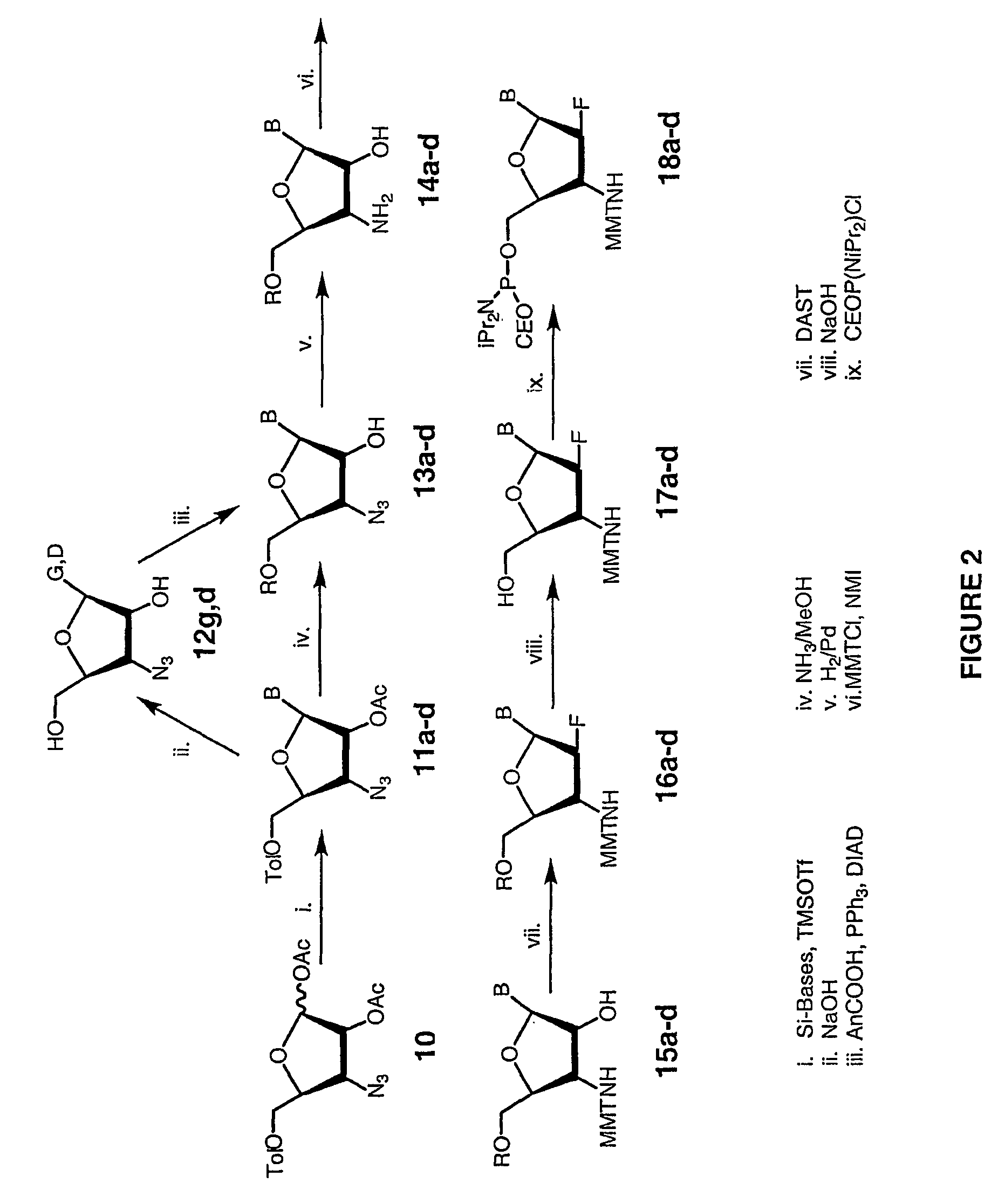
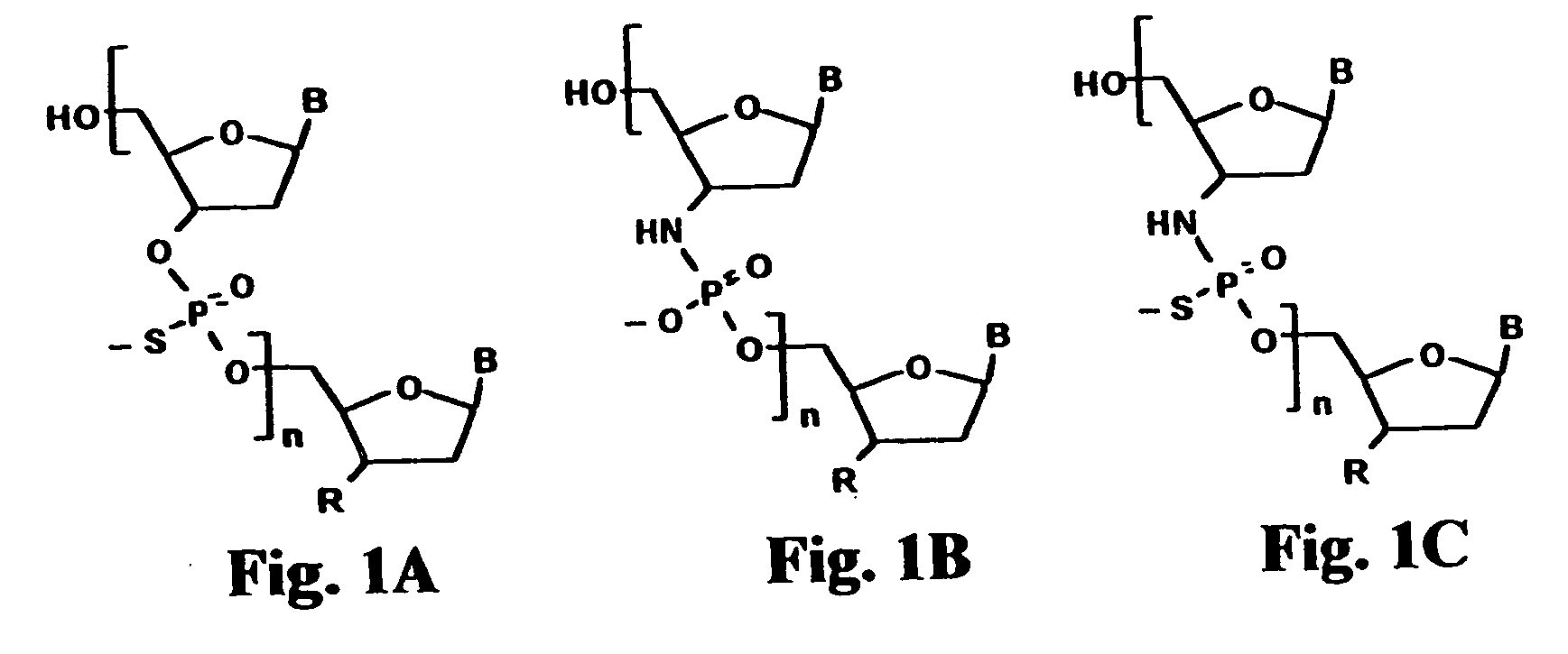
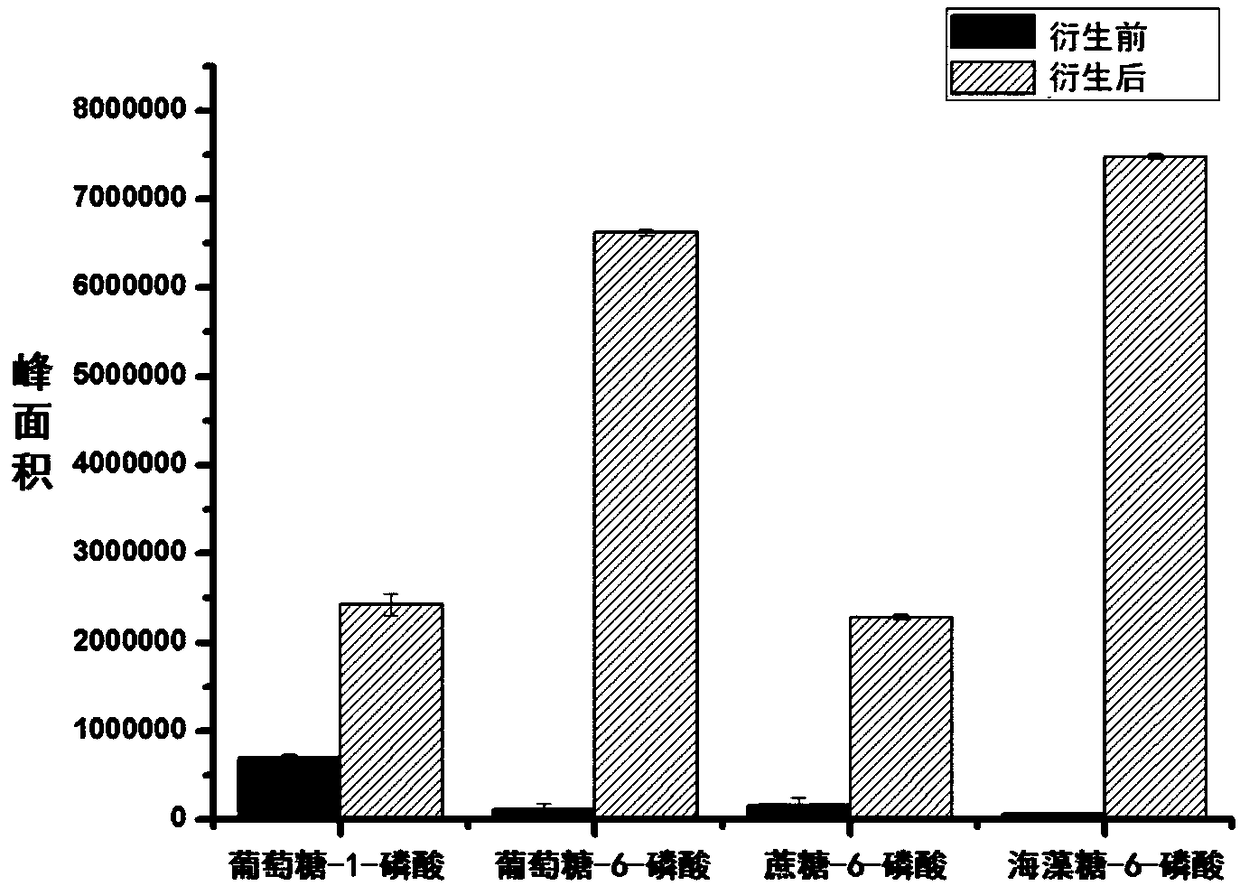
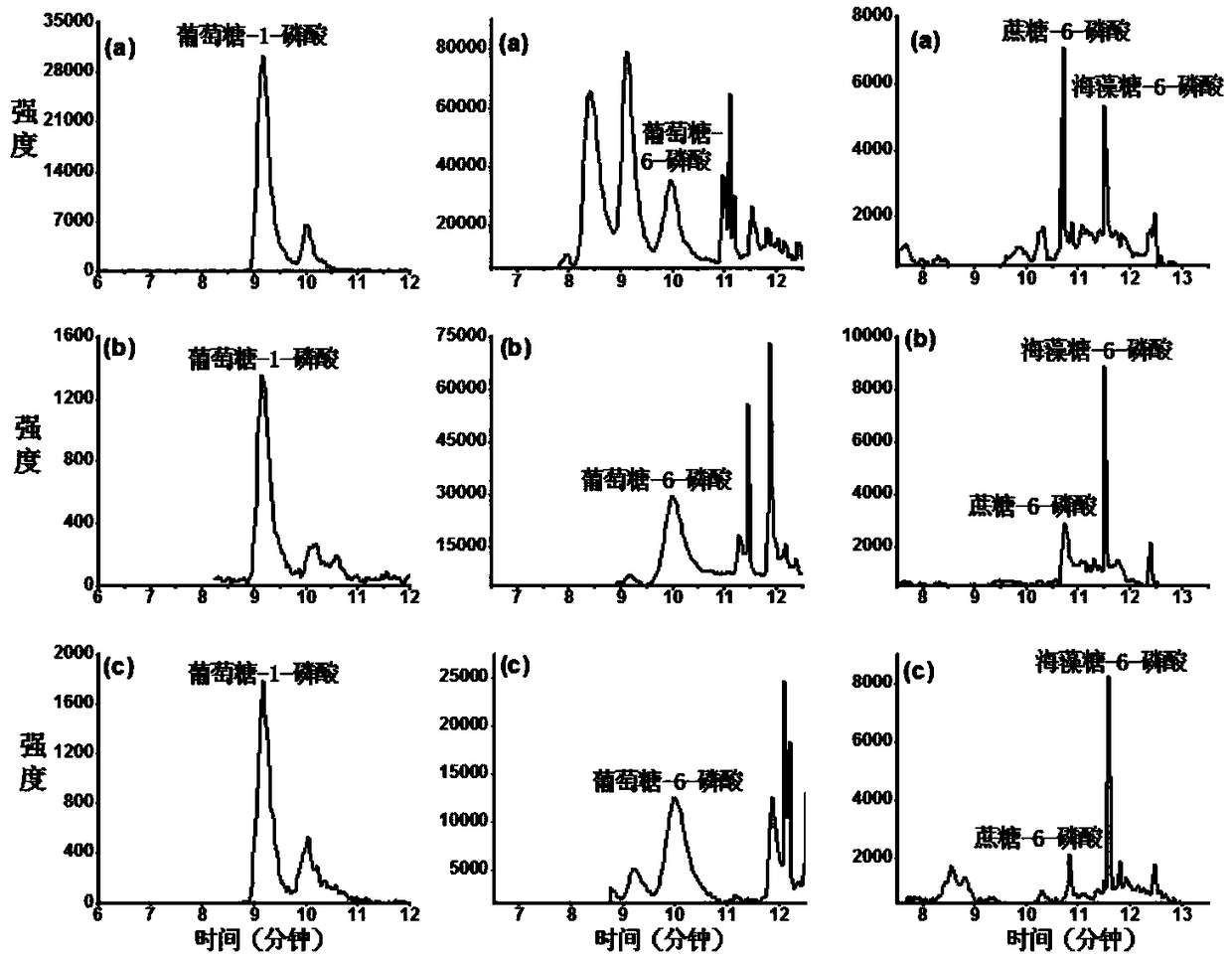
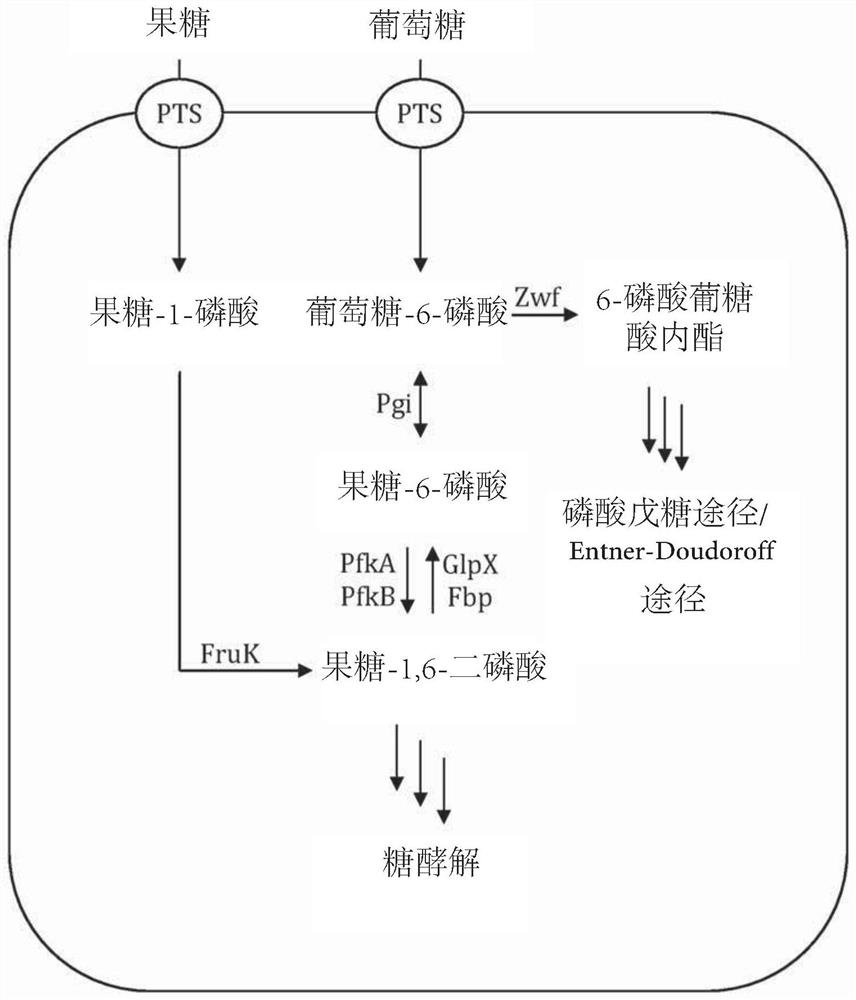
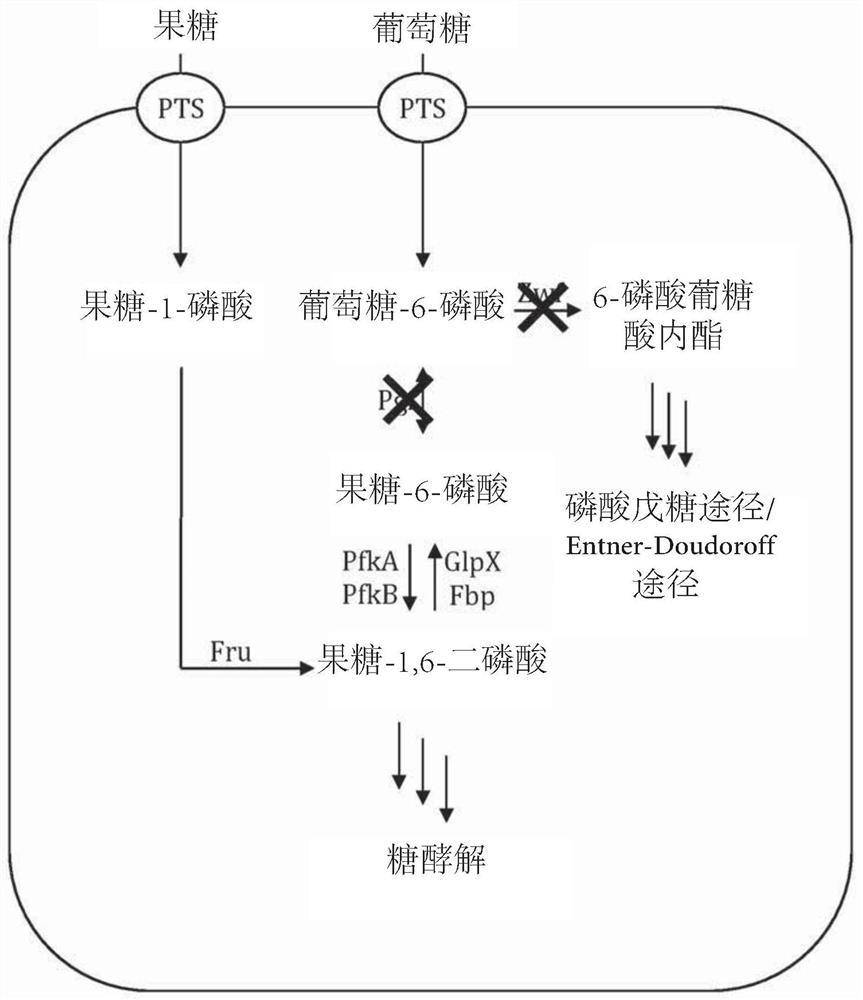
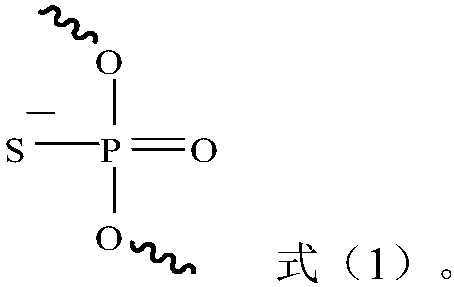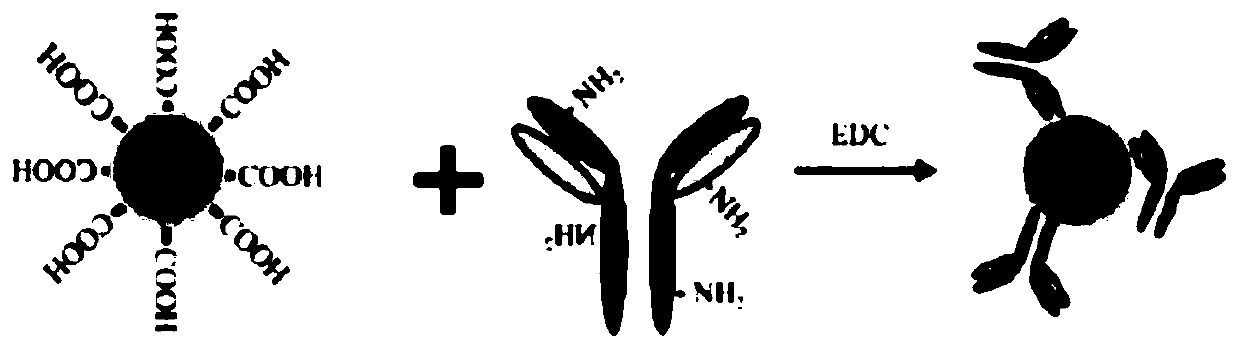Patents
Literature
45 results about "Sugar phosphates" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
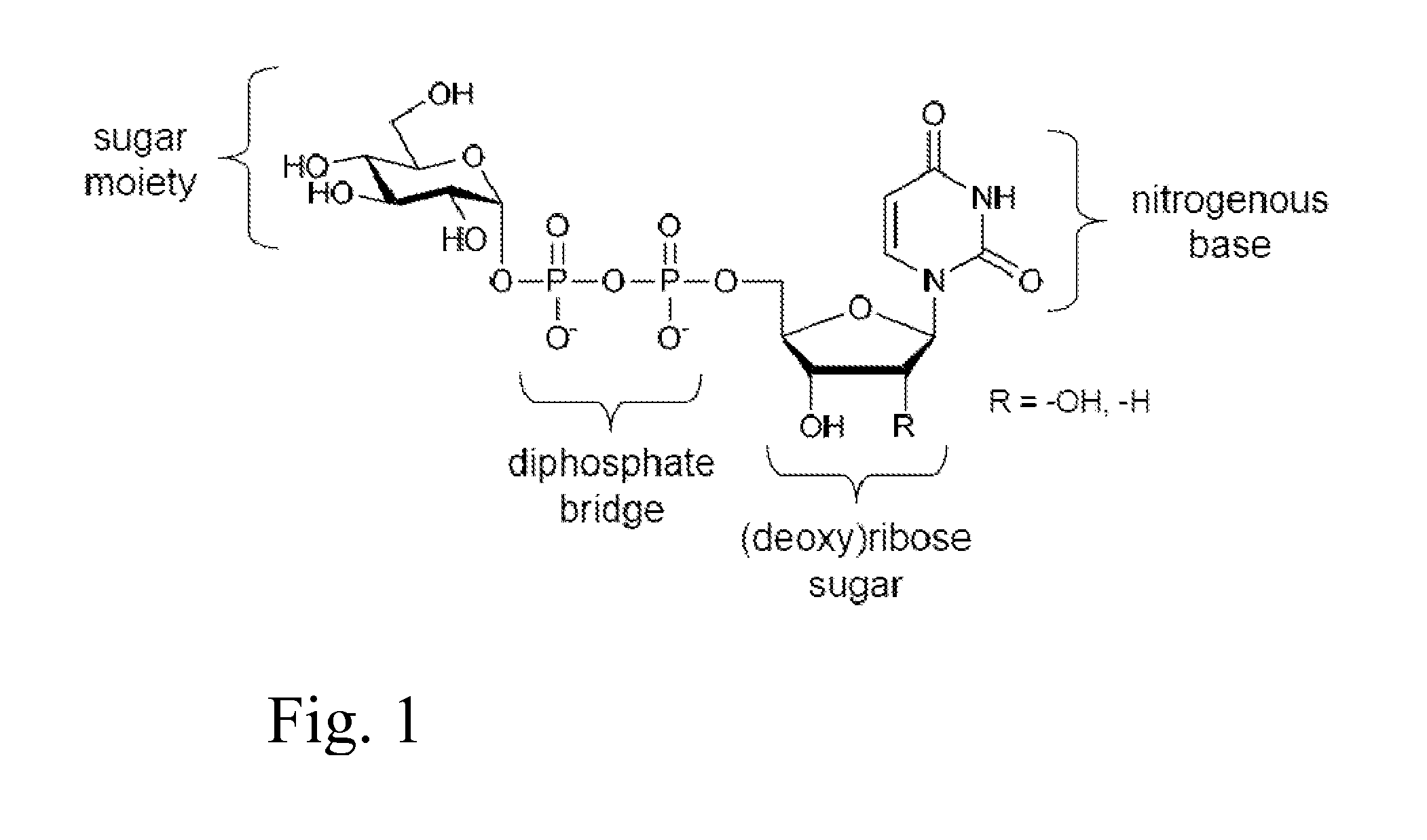
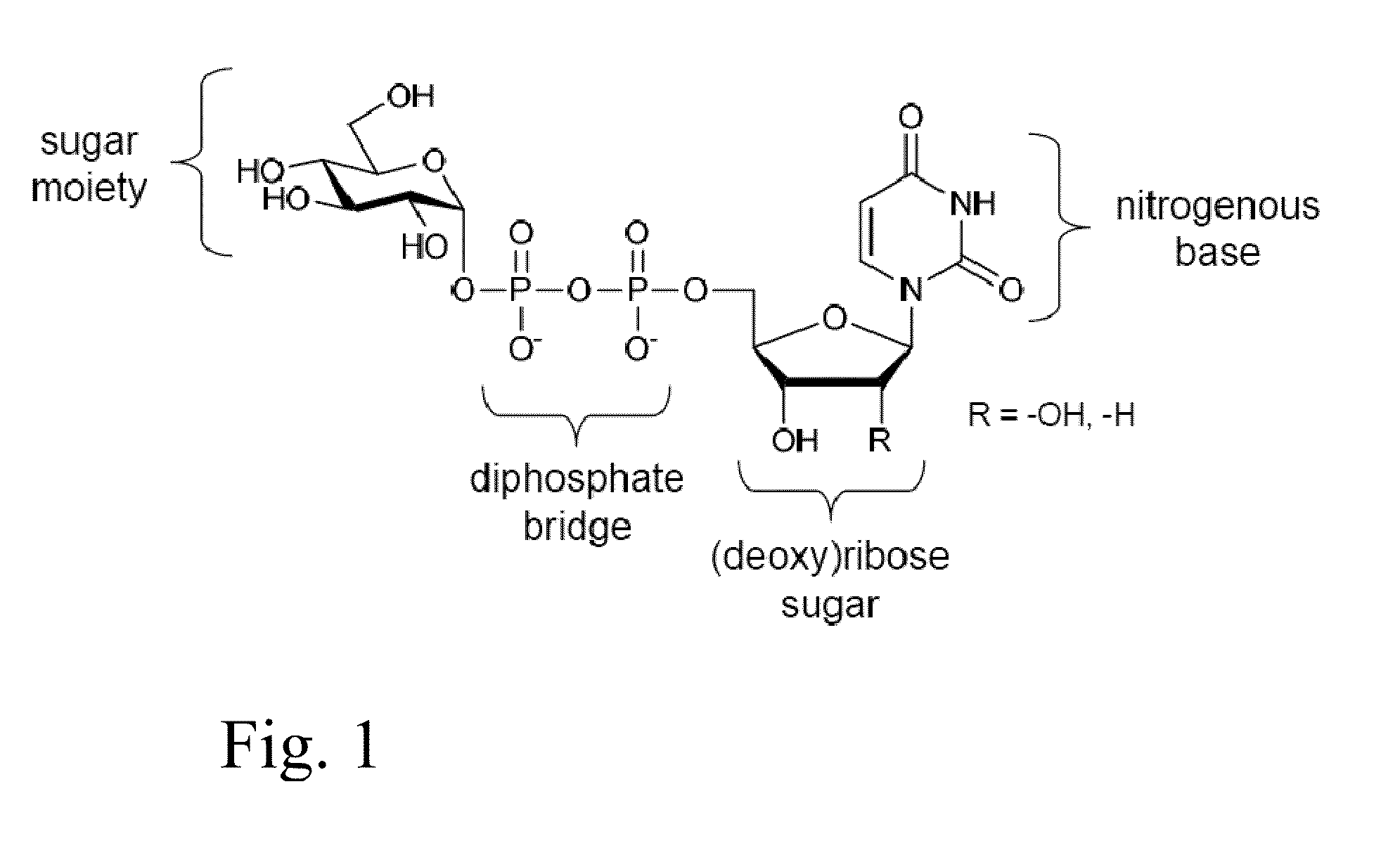
Sugar phosphates (sugars that have added or substituted phosphate groups) are often used in biological systems to store or transfer energy. They also form the backbone for DNA and RNA. Sugar phosphate backbone geometry is altered in the vicinity of the modified nucleotides.
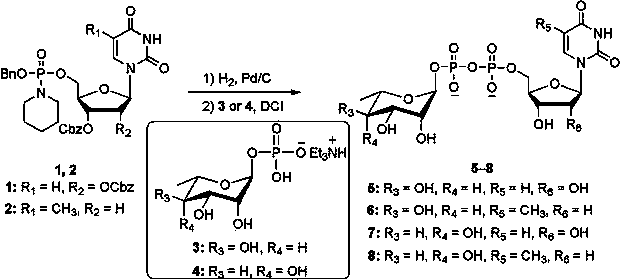
2'-arabino-fluorooligonucleotide N3'->P5' phosphoramidates: their synthesis and use
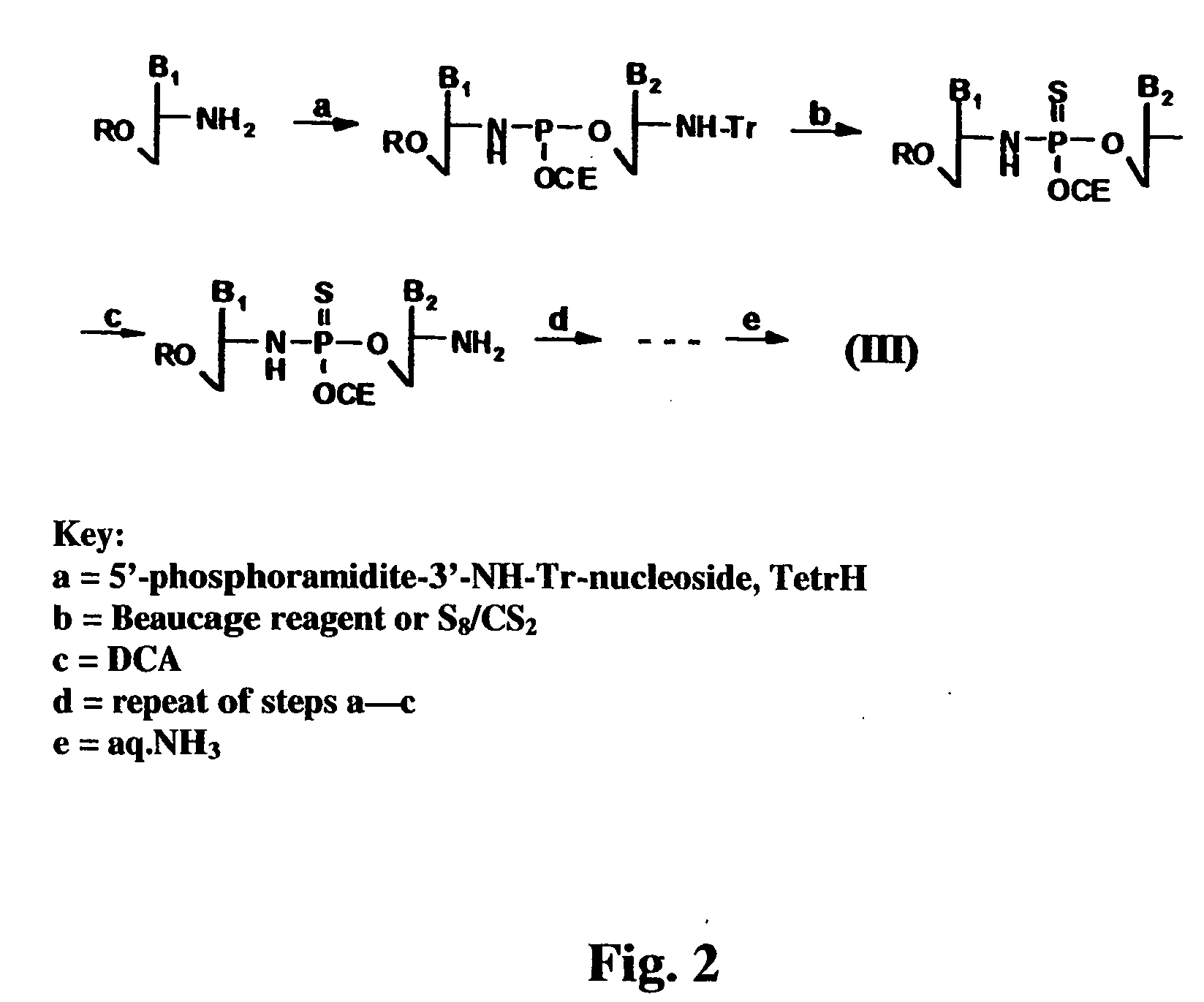
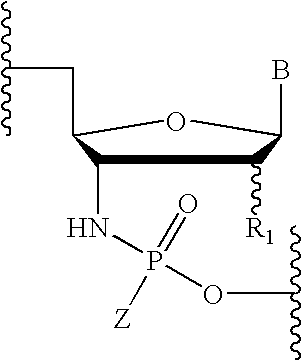
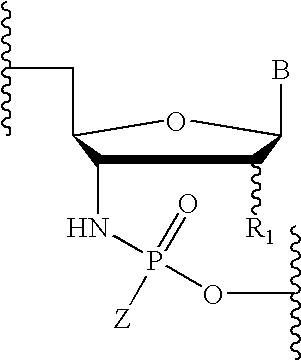
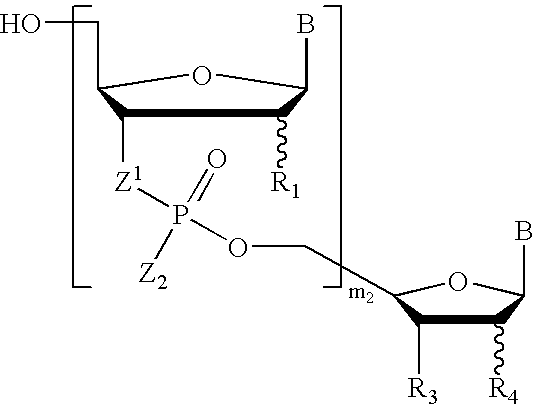
Oligonucleotides with a novel sugar-phosphate backbone containing at least one 2′-arabino-fluoronucleoside and an internucleoside 3′-NH—P(—O)(OR)—O-5′ linkage, where R is a positively charged counter ion or hydrogen, and methods of synthesizing and using the inventive oligonucleotides are provided. The inventive phosphoramidate 2′-arabino-fluorooligonucleotides have a high RNA binding affinity to complementary nucleic acids and are base and acid stable.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Oligonucleotide N3'-P5' thiophosphoramidates: their synthesis and use
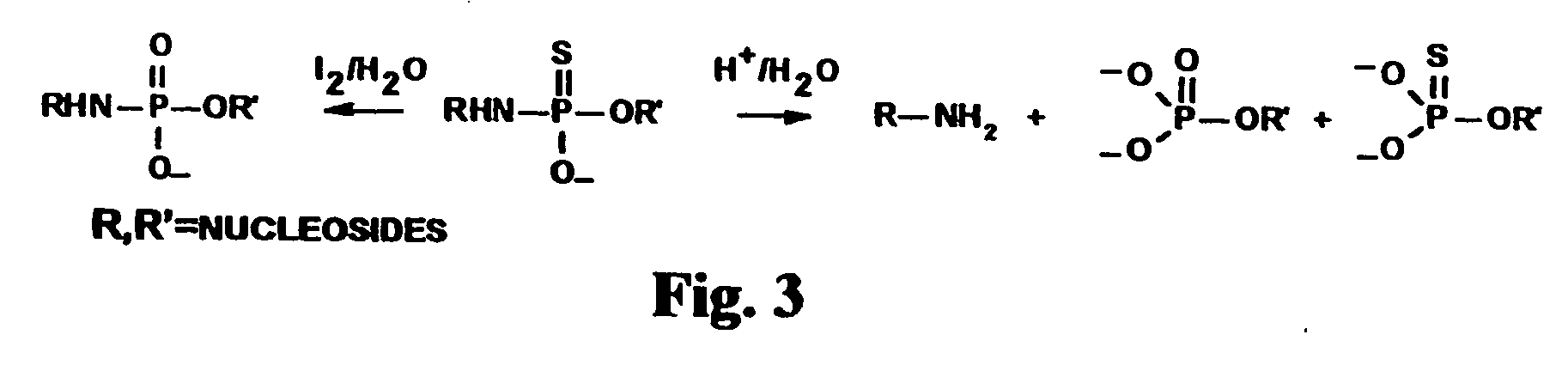
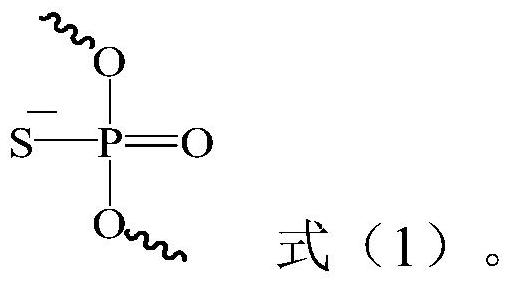
Oligonucleotides with a novel sugar-phosphate backbone containing at least one internucleoside 3′-NHP(O)(S−)O-5′ linkage, and methods of synthesizing and using the inventive oligonucleotides are provided. The inventive thiophosphoramidate oligonucleotides were found to retain the high RNA binding affinity of the parent oligonucleotide N3′→P5′ phosphoramidates and to exhibit a much higher acid stability.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Treating cancer using an oligonucleotide N3′->N5′ thiophosphoramidate
Oligonucleotides with a novel sugar-phosphate backbone containing at least one internucleoside 3′-NHP(O)(S−)O-5′ linkage, and methods of synthesizing and using the inventive oligonucleotides are provided. The inventive thiophosphoramidate oligonucleotides were found to retain the high RNA binding affinity of the parent oligonucleotide N3′→P5′ phosphoramidates and to exhibit a much higher acid stability.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Small interfering nucleic acid and pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
ActiveCN108239644AReduce contentPrevent and/or treat dyslipidemiaOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDyslipidemiaO-Phosphoric Acid
The invention relates to a small interfering nucleic acid and a pharmaceutical composition and an application thereof. The siRNA contains complementary positive-sense strand and antisense strand, wherein the positive-sense strand contains nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.24, SEQ ID NO.26, SEQ ID NO.28 or SEQ ID NO.30, and the antisense strand contains nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQID NO.25, SEQ ID NO.27, SEQ ID NO.29 or SEQ ID NO.31. A phosphoric acid framework and / or nucleotide pentose in a phosphoric acid-sugar framework of the siRNA has or does not have modifying groups. The invention provides a brand new efficient siRNA and a pharmaceutical composition thereof, and the siRNA can prevent and / or treat dyslipidemia effectively.
Owner:SUZHOU RIBO LIFE SCIENCE CO LTD
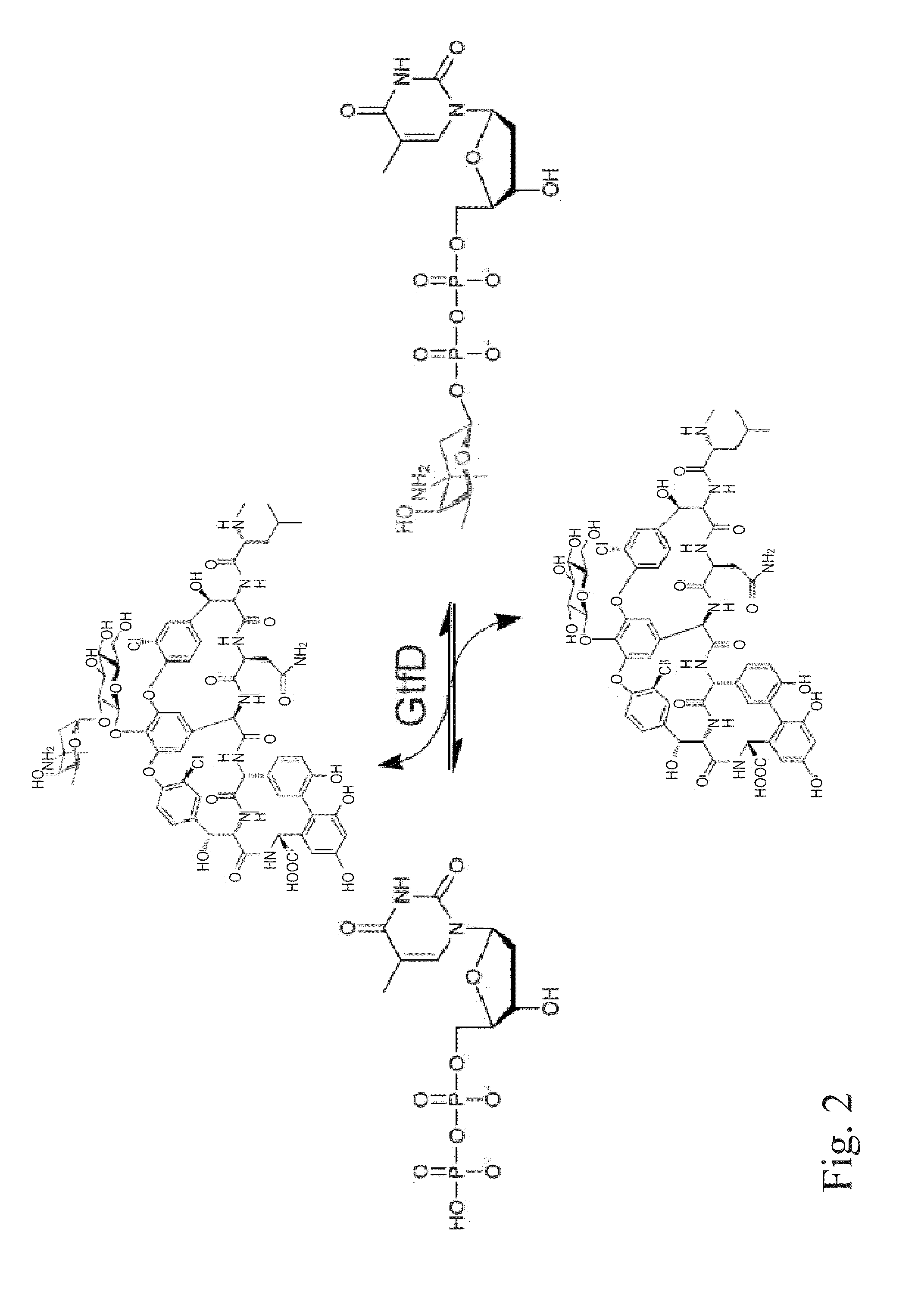
Glycosyltransferase reversibility for sugar nucleotide synthesis and microscale scanning
InactiveUS20130004979A1Simple methodEfficient synthesisBacteriaSugar derivativesNucleotideChemo enzymatic
The present invention generally relates to materials and methods for exploiting glycosyltransferase reversibility for nucleotide diphosphate (NDP) sugar synthesis. The present invention provides engineered glycosyltransferase enzymes characterized by improved reaction reversibility and expanded sugar donor specificity as compared to corresponding non-mutated glycosyltransferase enzymes. Such reagents provide advantageous routes to NDP sugars for subsequent use in a variety of biomedical applications, including enzymatic and chemo-enzymatic glycorandomization.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
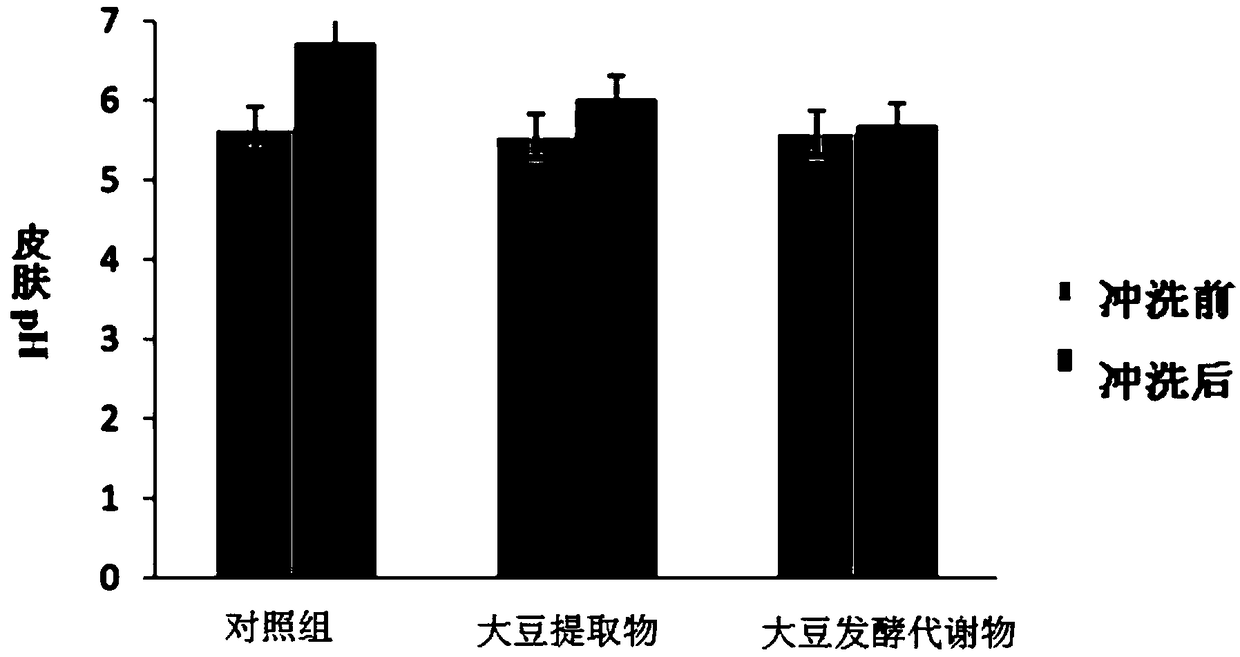
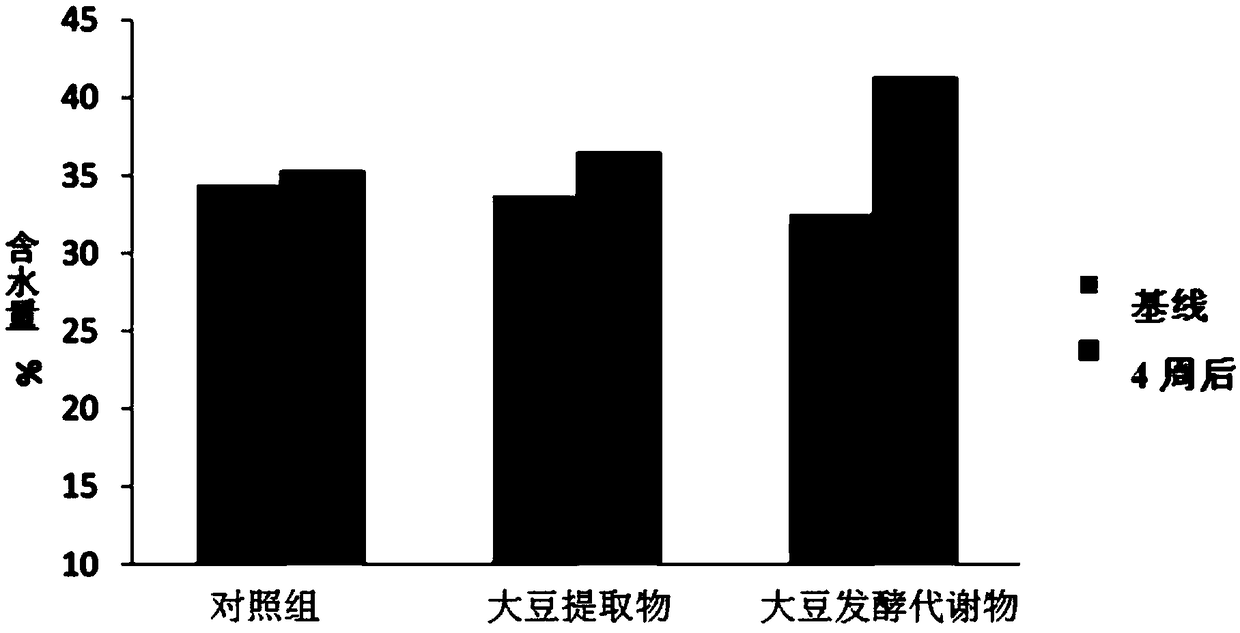
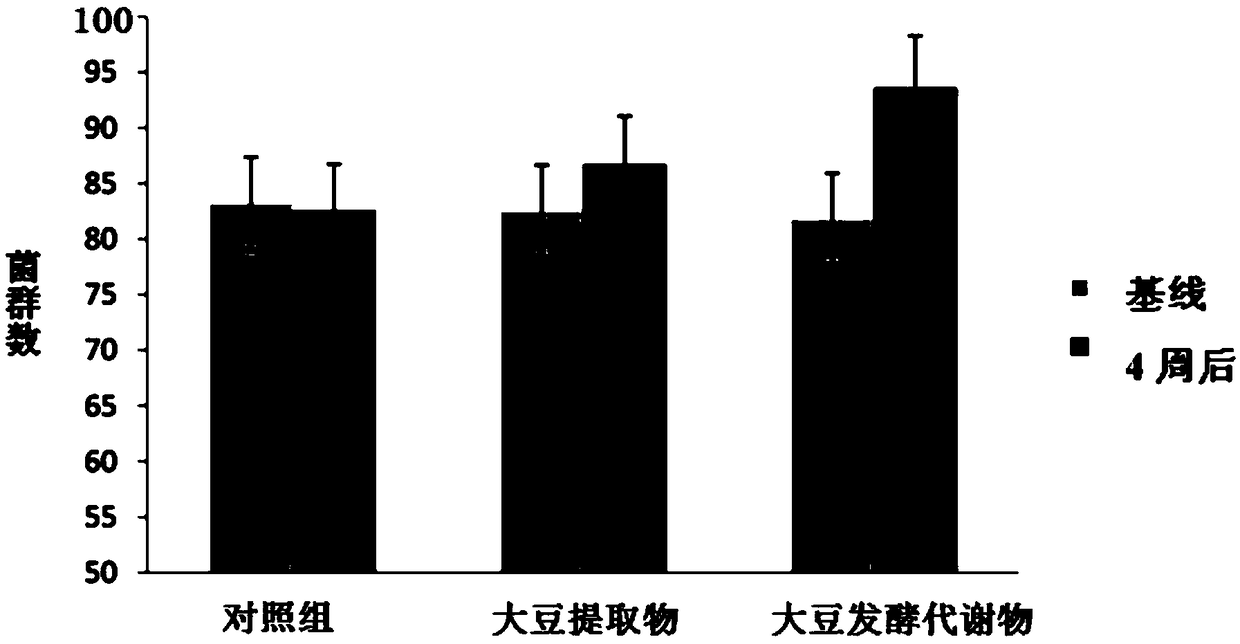
Soybean fermentation metabolin and application thereof
ActiveCN108866103AGood varietyQuality improvementCosmetic preparationsMicroorganismsSugar phosphatesFatty acid
The invention discloses a soybean fermentation metabolin. Components of the metabolin comprise amino acid and a derivative thereof, amine, sugar phosphate, nucleoside, a nucleoside derivative, organicacid and fatty acid. In addition, the invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the soybean fermentation metabolin. The soybean fermentation metabolin has the remarkable effects of improving diversity and quality of skin bacterial flora, skin water content and skin acid mantle, and is capable of avoiding loss of skin beneficial substances, maintaining balance of the skinbacterial flora, reinforcing nonspecific immune response, preventing skin infection and inflammation, and preventing skin related diseases, such as pruritus, acne, scurf, rubeosis and drying.
Owner:仙婷(广州)科技研发有限公司
Pyrimidine nucleosides preparation method and novel pyrimidine nucleoside
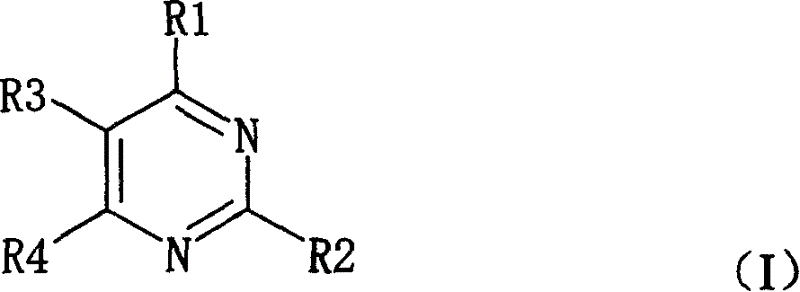
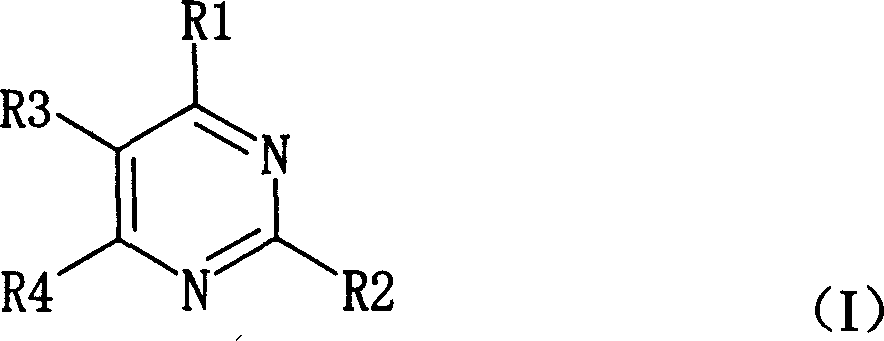
A method for producing a pyrimidine nucleoside compound includes reacting a sugar phosphate and pyrimidine base derivative using an enzyme having cytosine nucleoside phosphorylase activity, the pyrimidine base derivative being represented by general formula (I): (wherein R1 represents an amino group that may be replaced with an acyl group having an alkyl group of 1 to 3 carbon atoms or an alkyl group of 1 to 3 carbon atoms, an alkyl group of 1 to 3 carbon atoms, or a thiol group; R2 represents an amino group, a thiol group, a hydroxyl group, or a hydrogen atom; R3 represents an alkyl group of 1 to 3 carbon atoms that may be replaced with a hydroxyl group, an amino group, or a hydrogen atom; R4 represents a hydroxyl group or a hydrogen atom; when R1 is an amino group, when R2 is a hydroxyl group, and when R4 is a hydrogen atom; R3 is neither an alkyl group of 1 to 3 carbon atoms nor a hydrogen atom).
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Protein refolding agent and refolding method
InactiveUS20090111971A1Improve productivityHigh-purity proteins in large amountsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSugar phosphatesPropanoic acid
A refolding agent and refolding method which make it possible to produce high-purity proteins in high productivity. The refolding agent includes a phosphorus-containing compound (A) and an oxycarbonyl group-containing compound (B). The refolding method includes the step of treating the unfolded protein with the refolding agent. As the compound (A), there may be mentioned at least one species selected from inorganic phosphoric acids, alkyl phosphate esters, sugar phosphate esters, and salts of these, and as the compound (B), there may be mentioned at least one species selected from formic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, lactic acid, tartaric acid, and salts of these.
Owner:SANYO CHEM IND LTD
Pretreatment method for enrichment and solid-phase derivatization of sugar phosphate substances
ActiveCN107290459AImprove retentionEasy to separateComponent separationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSugar phosphatesPretreatment method
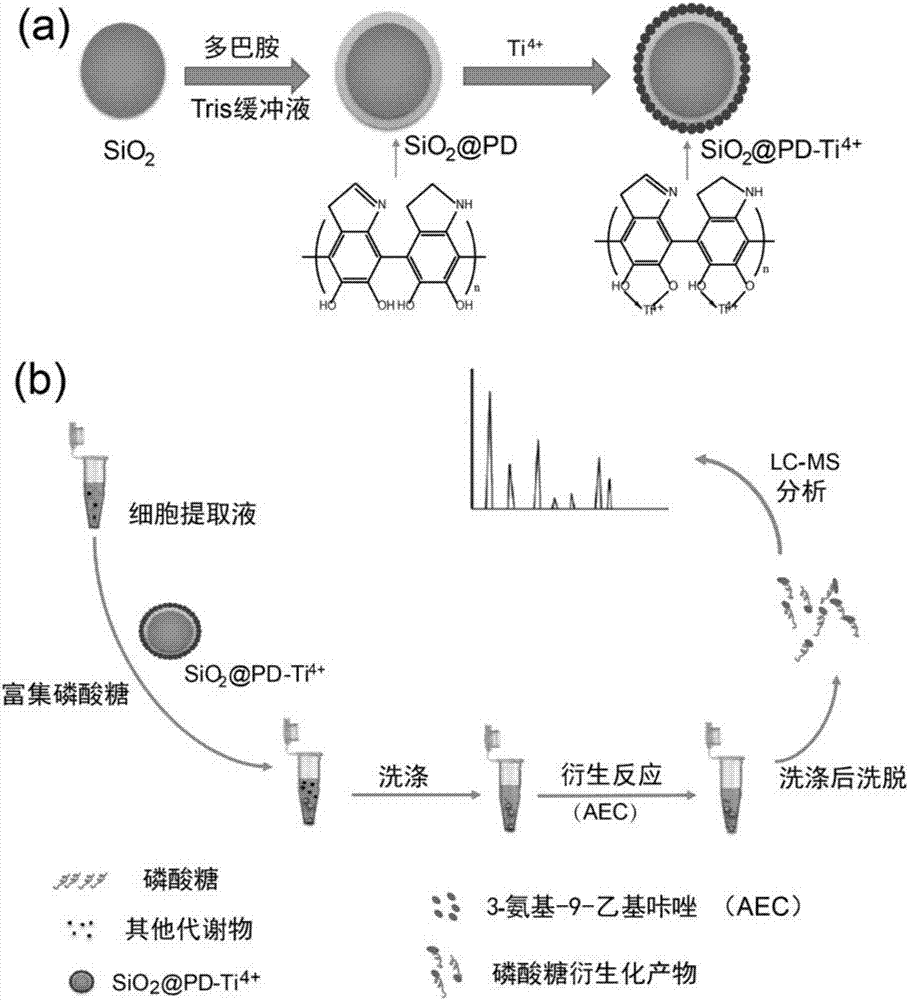
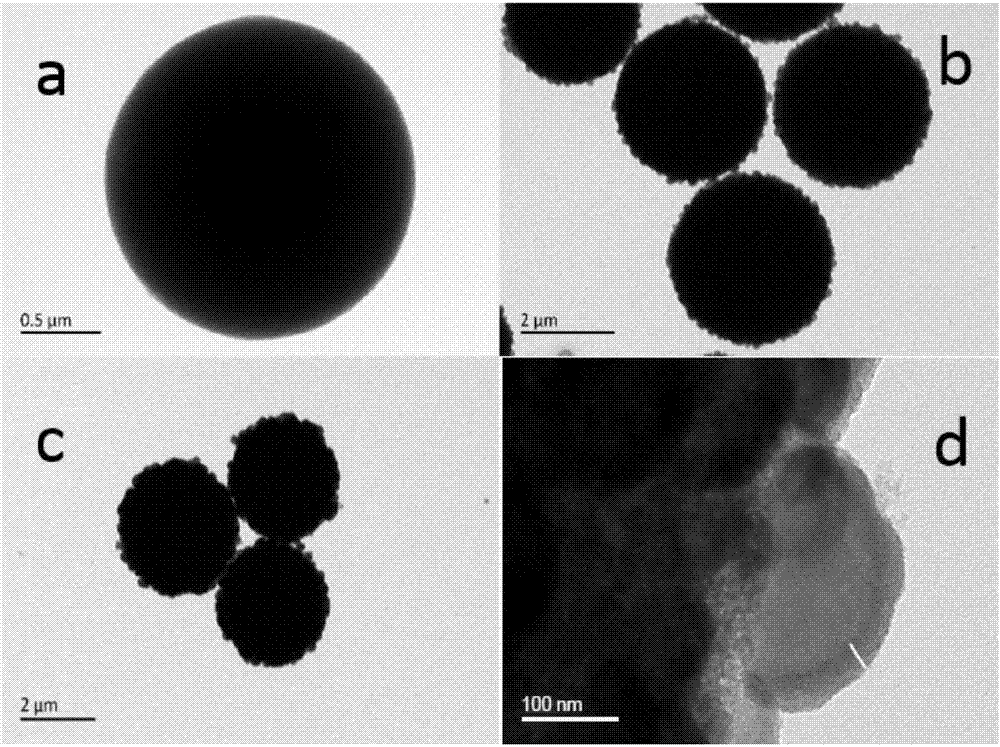
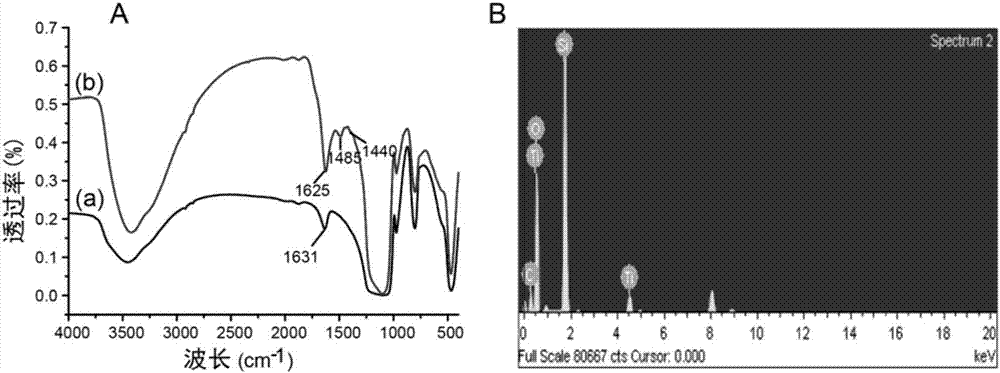
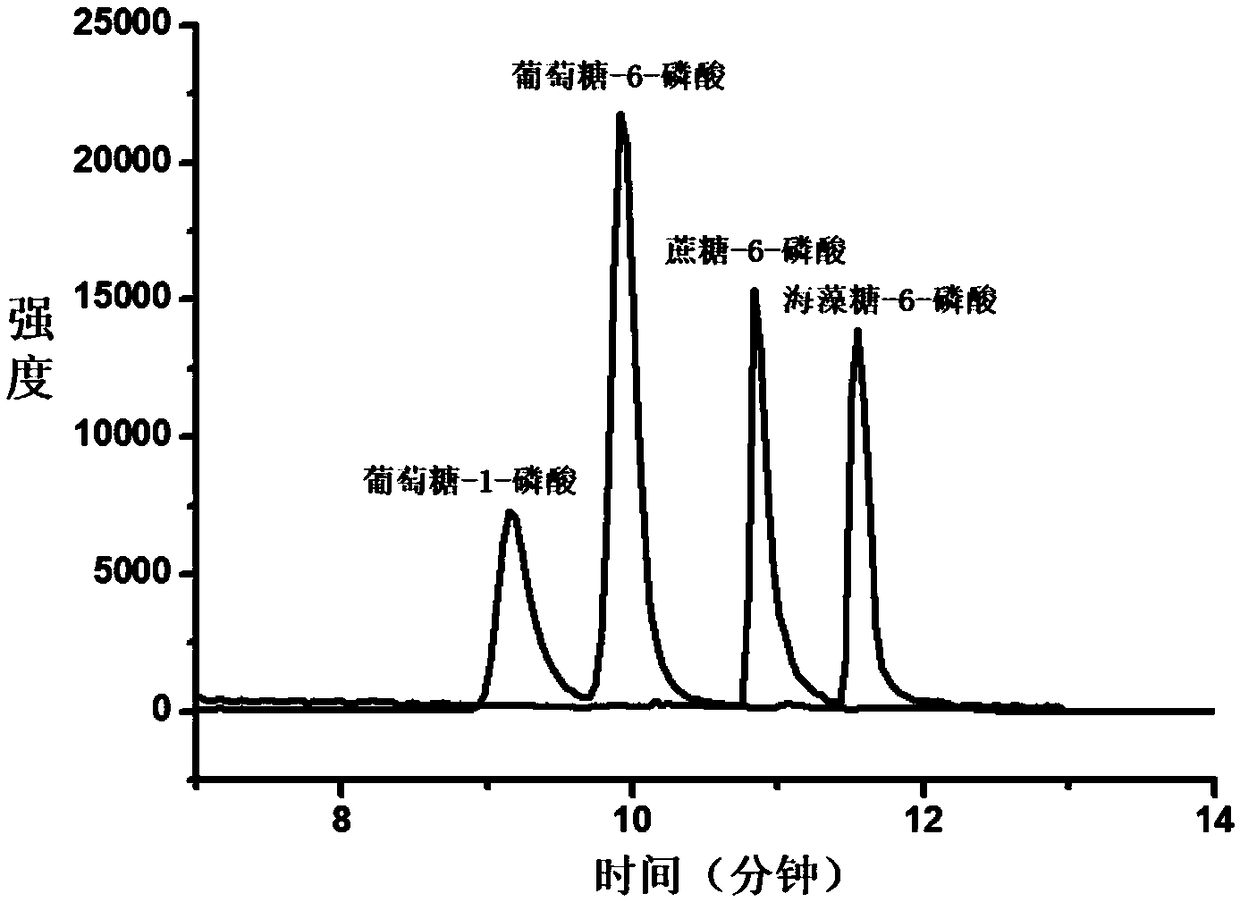
The invention belongs to the technical field of inorganic materials and analysis and particularly relates to a pretreatment method for enrichment and solid-phase derivatization of sugar phosphate substances by a metal ion affinity chromatography material (SiO2@PD-Ti<4+>). The pretreatment method comprises the following steps: firstly, enriching the sugar phosphate substances on SiO2@PD-Ti<4+> microspheres by a metal chelating action; secondly, carrying out solid-phase derivatization on enriched sugar phosphate substances. According to the method, retention and separation degree of the sugar phosphate substances on reversed phase liquid chromatography can be improved, and the mass spectrometric detection sensitivity of the sugar phosphate substances with low abundance can be improved. The pretreatment method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple and quick pretreatment process, good repeatability, low detection limit and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pretreatment method and quantitative detection method for endogenous sugar phosphate compound in plant sample
ActiveCN109358134ARealize separation detectionRealize quantitative detectionComponent separationSugar phosphatesPretreatment method
The invention discloses an analysis method for a variety of sugar phosphate compounds including endogenous trehalose-6-phosphate in a plant sample. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting the endogenous sugar phosphates through a solvent; adsorbing and removing the hydrophobic impurities in the extracted solution through a reversed-phase SPE column; using the diazo groups in a derivatization reagent to carry out derivatization reaction on the phosphate groups common to the sugar phosphate compounds; and in combination with the liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry, realizing the separation detection of the endogenous sugar phosphate isomers in the plant sample. The analysis method is simple, accurate and high in throughput, can achieve the baseline separation of the sugar phosphate isomers on a hydrophilic chromatographic column and guarantee the higher detection sensitivity, and finally can realize the separation detection of the endogenous sugar phosphates in amicroplant tissue sample.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Fermentative production of carbohydrates by microbial cells utilizing mixed feedstock
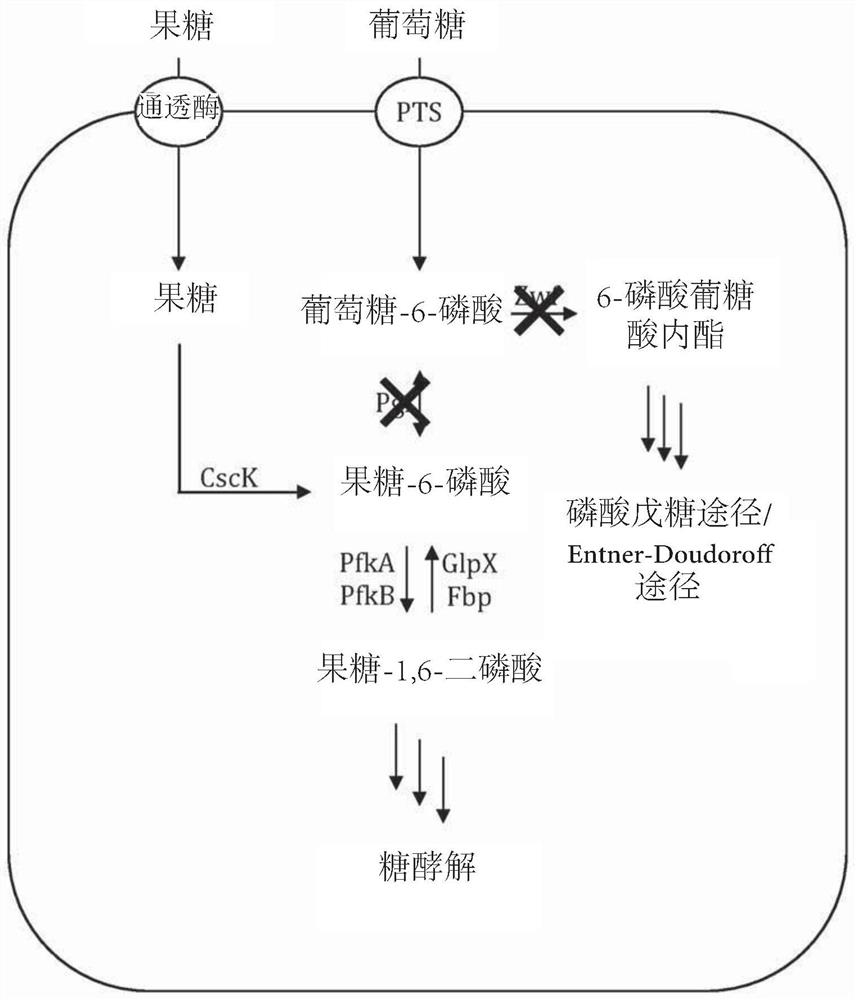
Disclosed are genetically engineered microbial cells for the production of a carbohydrate of interest, wherein the microbial cells possess an increased intracellular availability of at least one sugar phosphate, and produce the carbohydrate of interest when being cultivated in a culture medium containing a mixed monosaccharide feedstock as main carbon and energy source. Also disclosed is a fermentative method of producing a carbohydrate of interest by cultivating said genetically engineered microbial cell in the presence of a mixed monosaccharide feedstock as main carbon and energy source.
Owner:CHR HANSEN HMO GMBH
Glycoalkaloid compositions and various uses thereof
InactiveUS20050227928A1Remove the subjects ability to fall pregnantBiocideOrganic active ingredientsTagatoseGlycerol
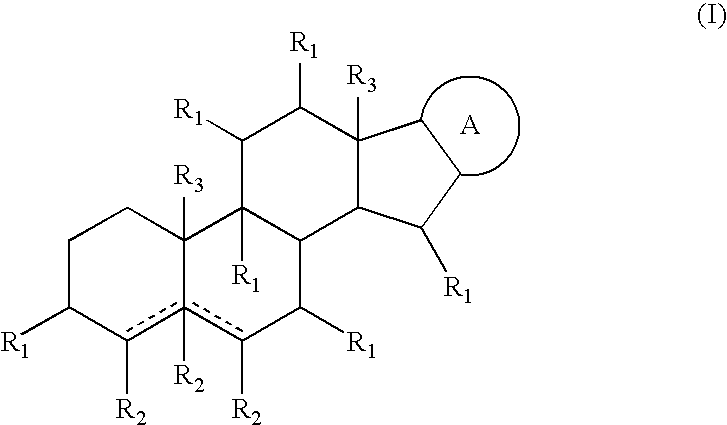
A composition comprising at least two glycoalkaloids of formula I: wherein: either one or both of the dotted lines represents a double bond, and the other a single bond, or both represent single bonds; A: represents a radical selected from the following radicals of general formulae (II) to (V): each of R1 is a radical separately selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, amino, oxo and OR4; each of R2 is a radical separately selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, amino and OR4; each of R3 is a radical separately selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, carbohydrate and a carbohydrate derivative; “X” is a radical selected from the group comprising —CH2—, —O— and —NH2—; and wherein the compound includes at least one R4 group that is a carbohydrate or a derivative thereof selected from the group comprising glyceric aldehyde, glycerose, erythrose, threose, ribose, arabinose, xylose, lyxose, altrose, allose, gulose, mannose, glucose, idose, galactose, talose, rhamnose, dihydroxyactone, erythrulose, ribulose, xylulose, psicose, fructose, sorbose, tagatose, and other hexoses, heptoses, octoses, nanoses, decoses, deoxysugars with branched chains, (e.g. apiose, hamamelose, streptose, cordycepose, mycarose and cladinose), compounds wherein the aldehyde, ketone or hydroxyl groups have been substituted (e.g. N-acetyl, acetyl, methyl, replacement of CH2OH), sugar alcohols, sugar acids, benzimidazoles, the enol salts of the carbohydrates, saccharinic acids, sugar phosphates; wherein the ratio of said glycoalkaloids is between 6:1 and 1:6 and on the proviso that when the glycoalkaloids are solamargine and solasonine and they are present in a 1:1 ratio the solamargine and solasonine are isolated.
Owner:SOLBEC PHARMA LTD
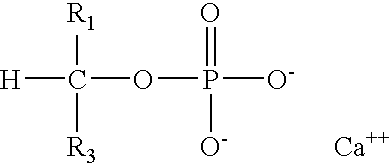
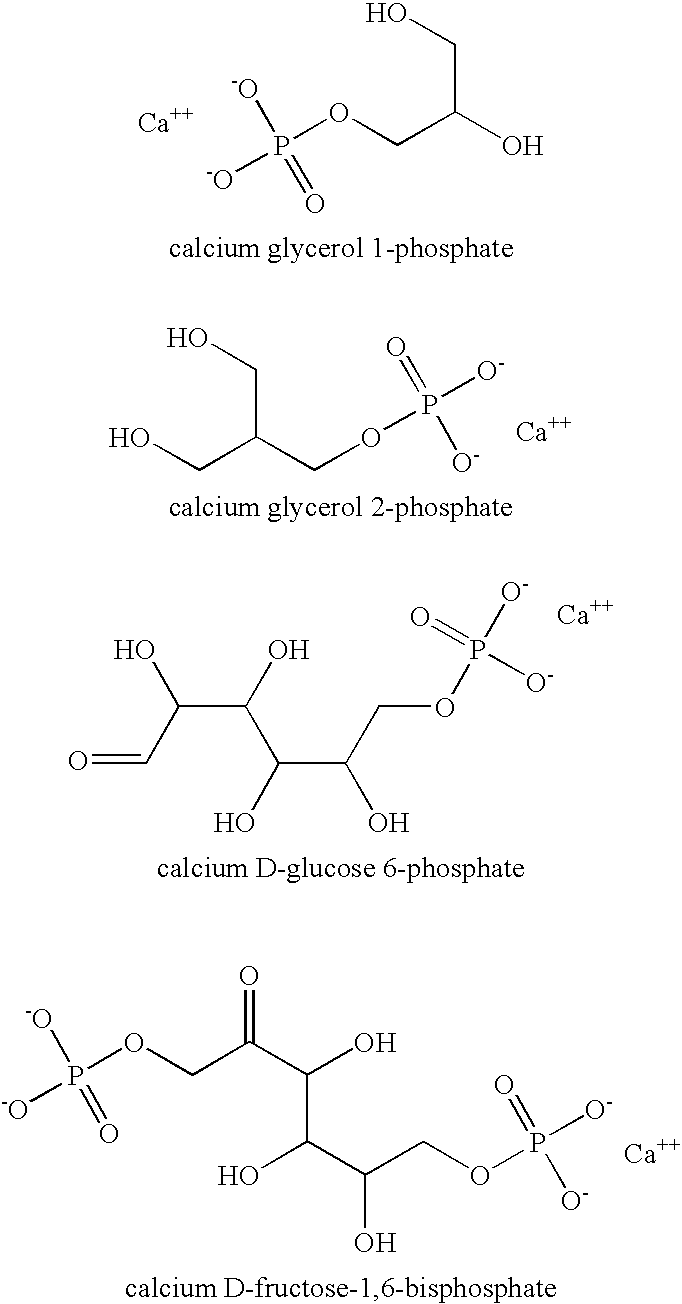
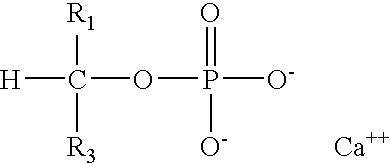
Hygiene Article Having Calcium Sugar Phosphate
A hygiene article having calcium sugar phosphate is provided. The calcium sugar phosphate reduces the production of Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1) by Staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
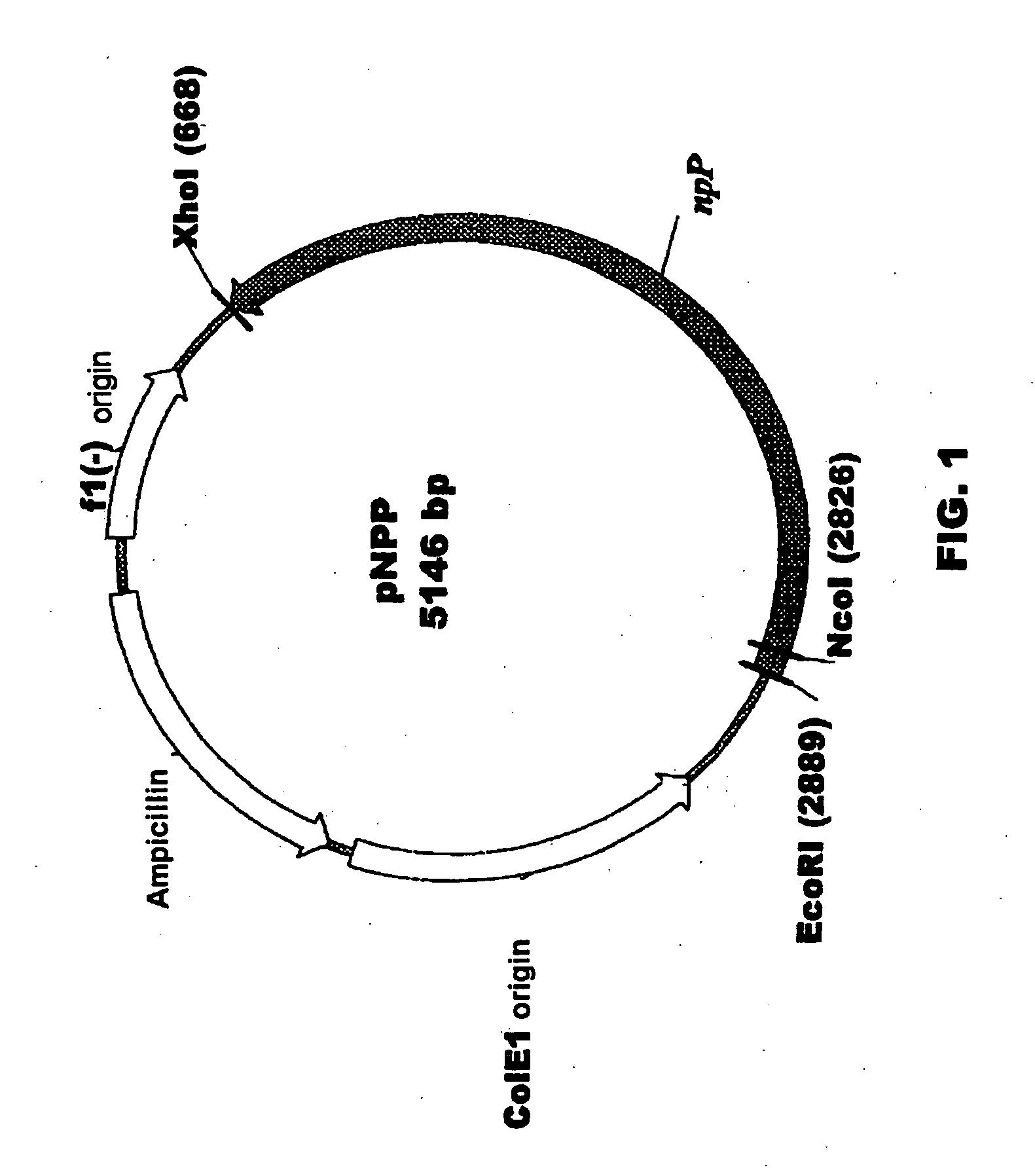
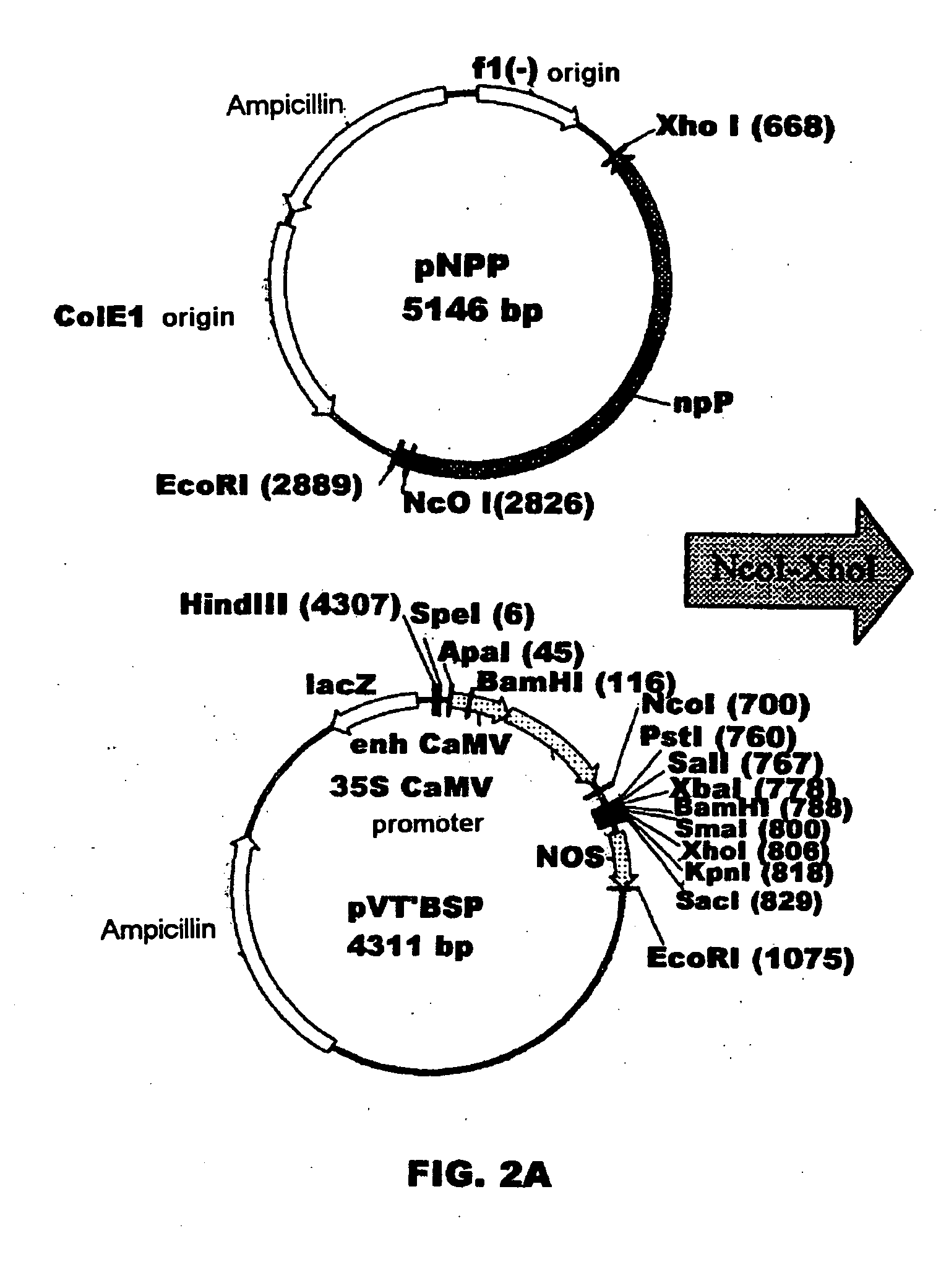
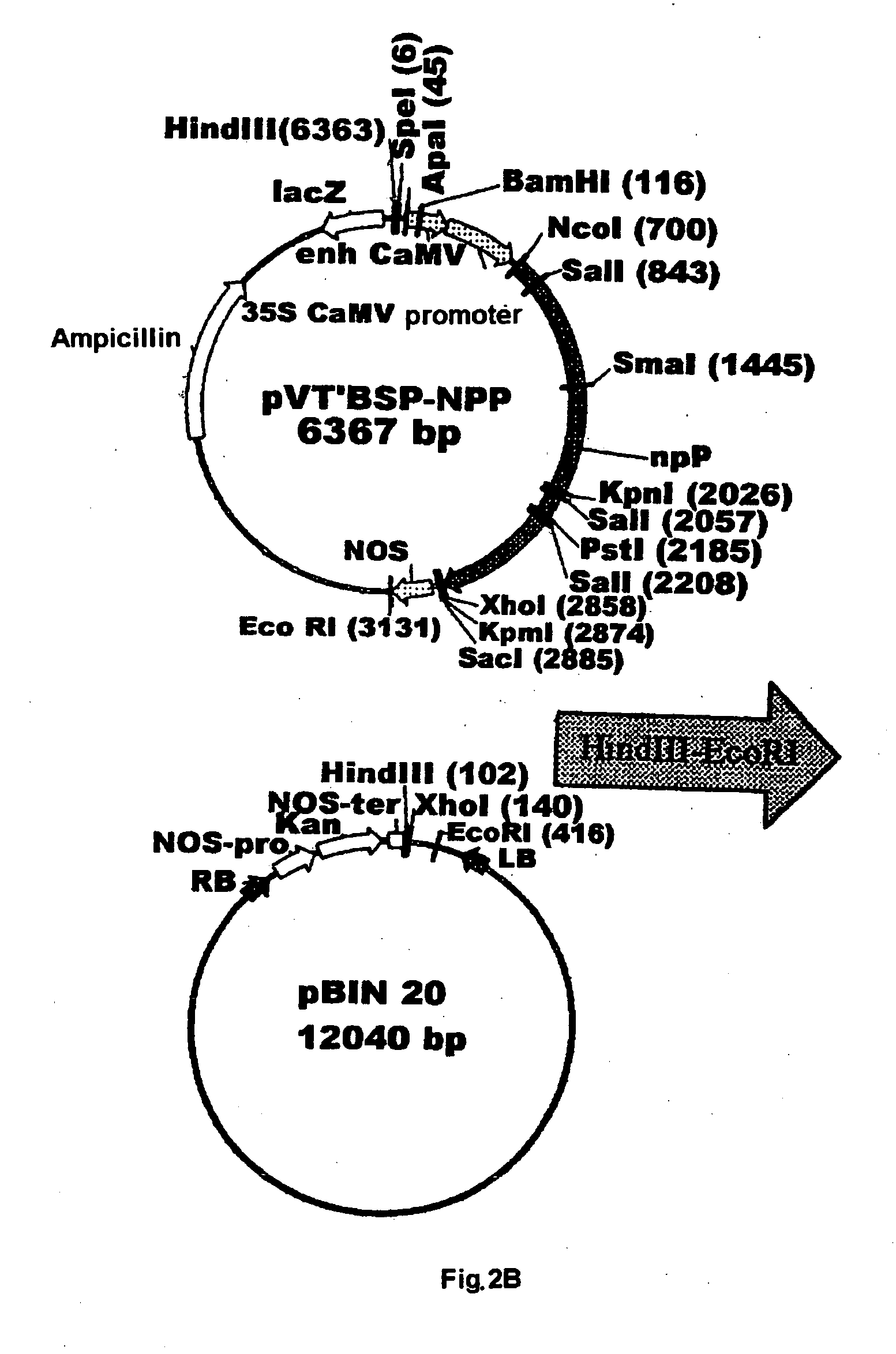
Plant nucleotide-sugar pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (nppase), method of obtaining same and use of same in the production of assay devices and in the production of transgenic plants
InactiveUS20060242739A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh resistancePhosphate
Plant nucleotide pyrophosphatase / phosphodiesterase (NPPase), method of production, use in the manufacture of testing devices and in the production of transgenic plants. NPPase is an enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of a wide range of small molecules with phosphodiester and phosphosulphate bonds, in particular ADPG (adenosine diphosphate glucose) and APS (adenosine 5′-phosphosulphate). The enzyme obtained from plant extracts is used in assay devices for determining levels of nucleoside diphosphate sugars, based either on the sugar-1-phosphate released, or on the nucleoside monophosphate, both of which are products formed by the reaction catalysed by NPPase, as well as the detection of sulphonucleotides such as 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulphate (PAPS) and APS. The amino acid sequence of the enzyme is also described, as well as the nucleotide sequence of a complete cDNA and another incomplete cDNA. Finally, it describes the production of transgenic plants that overexpress NPPase and that have a high content of sugars, low content of starch and cell-wall polysaccharides and high resistance to high concentrations of salts and high temperature.
Owner:UNIV PUBLICA DE NAVARRA PAMPLONA +1
Iron-based hydroxide-low molecular weight sugar phosphate binder as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107397760AHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsSerum phosphateSugar phosphates
The invention provides an iron-based hydroxide-low molecular weight sugar phosphate binder as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides a phosphate binder which comprises an iron-based hydroxide and low molecular weight sugar, wherein the number of monosaccharide units of the low molecular weight sugar is 3-20, and based on the total weight of the phosphate binder, the mass ratio of the iron is 2-45wt%. Experiments prove that the phosphate binder has an obvious effect of lowering the serum phosphate level. Therefore, the phosphate binder has wide application prospects.
Owner:CINKATE PHARMA INTERMEDIATES
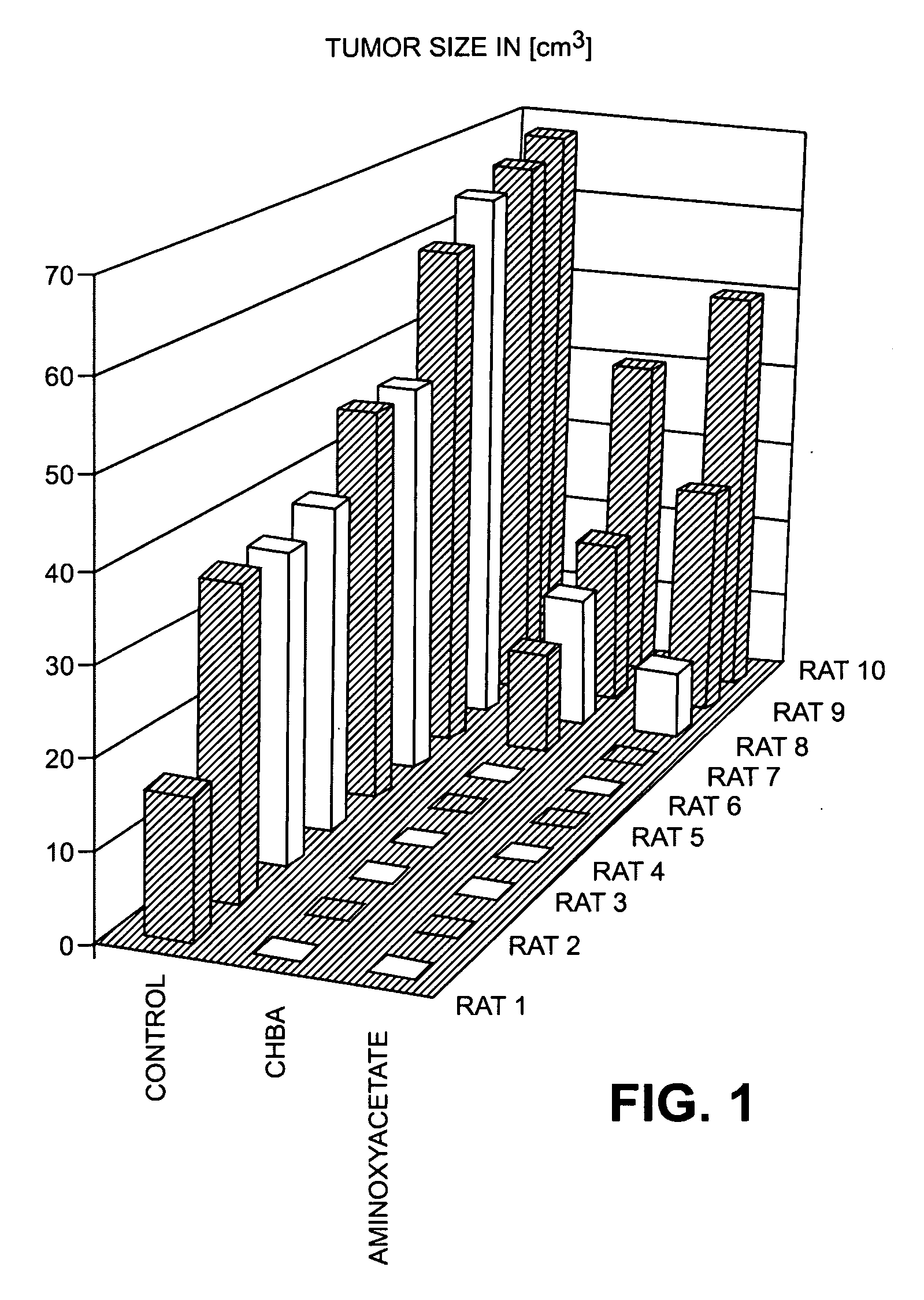
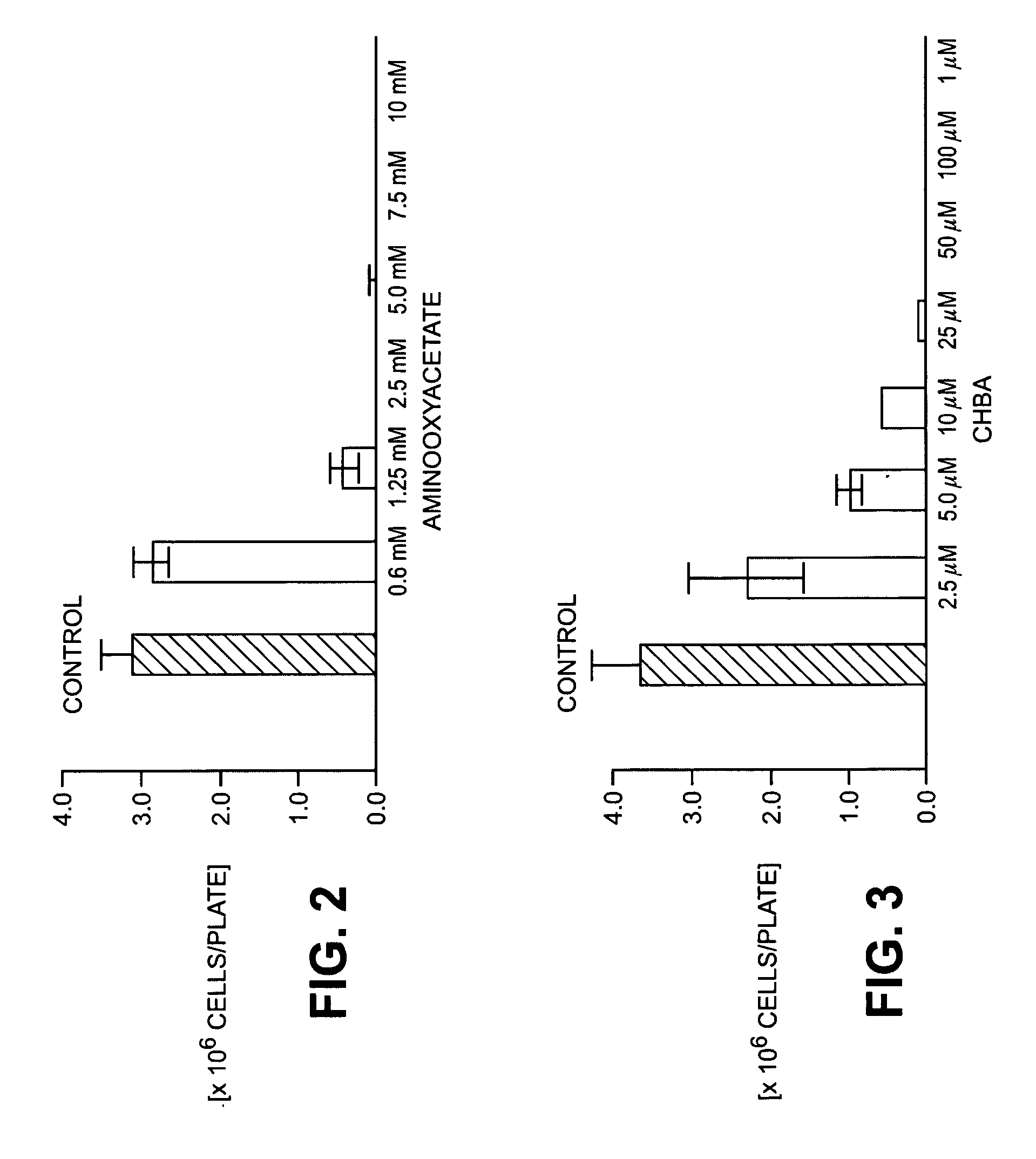
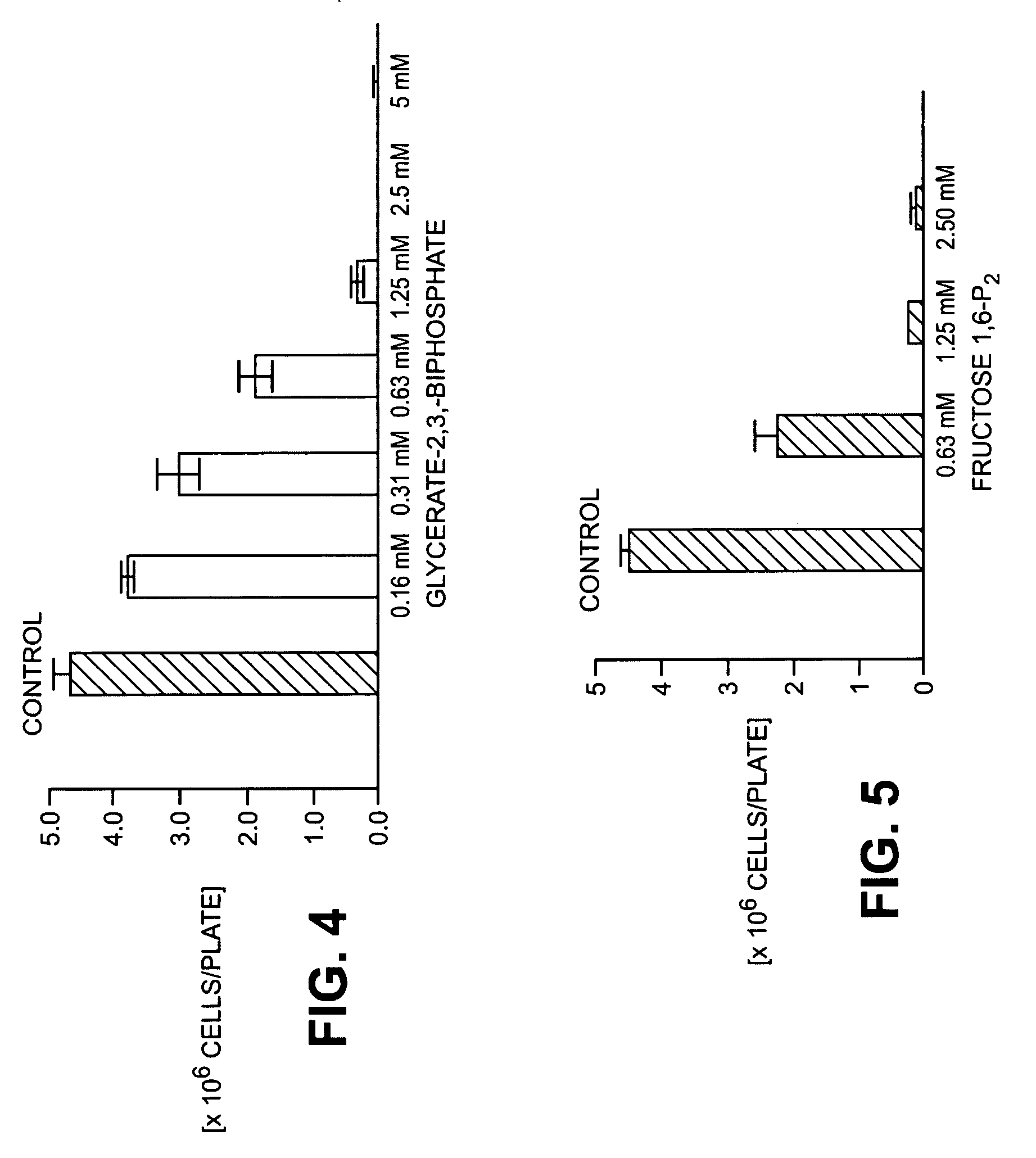
Use of sugar phosphates, sugar phosphate analogs, amino acids and/or amino acid analogs for modulating the glucolysis-enzyme complex, the malate asparate shuttle and/or the transaminases
InactiveUS20090163591A1Prevent proliferationSuppressing defensive over-reactionsBiocideAntipyreticSugar phosphatesEnzyme complex
The invention relates to methods for the treatment of tumors and / or for immune suppression and / or sepsis by modulating the association of the glycolysis enzyme complex / M2-PK and / or by inhibition of transaminases and / or separation of the binding of the malate dehydrogenase to p36 comprising administering a pharmaceutical composition comprising a substance selected from the group consisting of amino acids, amino acid analogs, sugar phosphates, sugar phosphate analogs, and mixtures of said substances.
Owner:EIGENBRODT ERICH +2
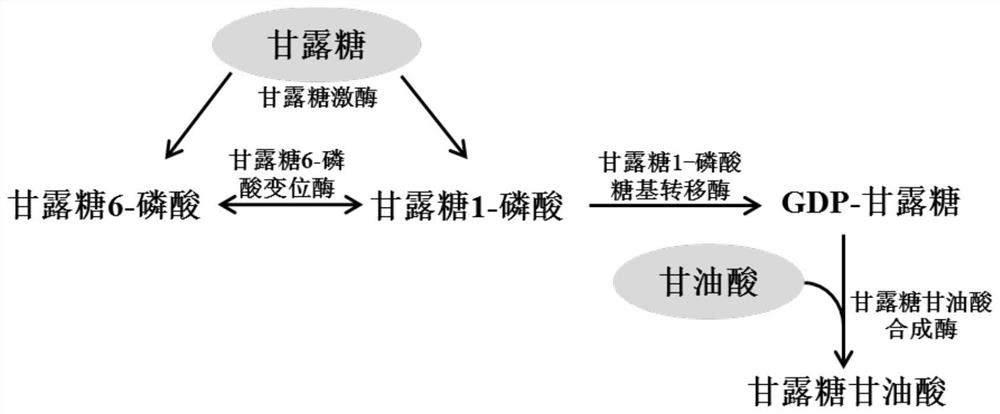
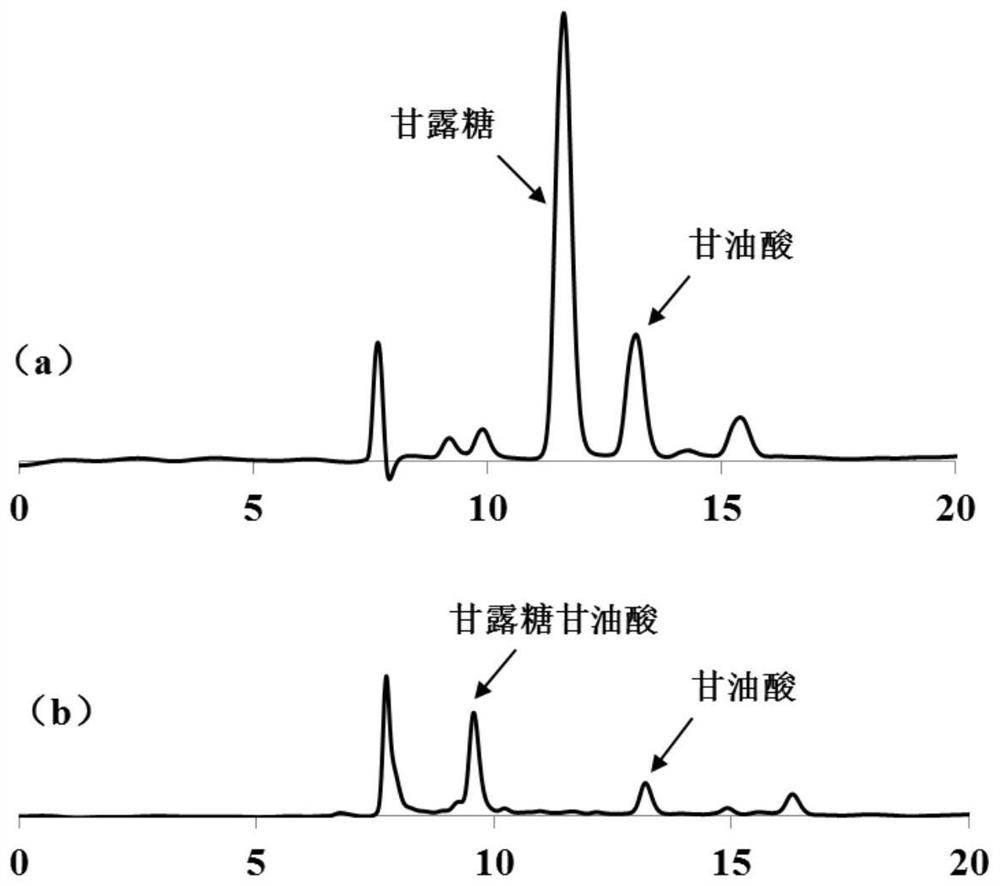
Method for biologically preparing mannoglycerate
The invention discloses a method for biologically preparing mannoglycerate, and relates to construction of an in-vitro multi-enzyme catalytic reaction system. The method comprises three enzymes, namely mannokinase, mannose-1-phosphate glycosyltransferase and mannoglycerate synthetase, and mannose and glycerate are converted to synthesize the mannoglycerate. The invention further discloses a construction method of recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum. The recombinant strain is applied to fermentation synthesis of the mannoglycerate, the mannoglycerate product is synthesized by taking the mannose and the glycerate as raw materials through a fermentation method, and the obtained mannoglycerate can be applied to the fields of foods, medicines, cosmetics and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Synthesis method of nucleoside diphosphate 6-deoxy-L-pyranose
InactiveCN103509074AShort reaction timeSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPyranoseChemical synthesis
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
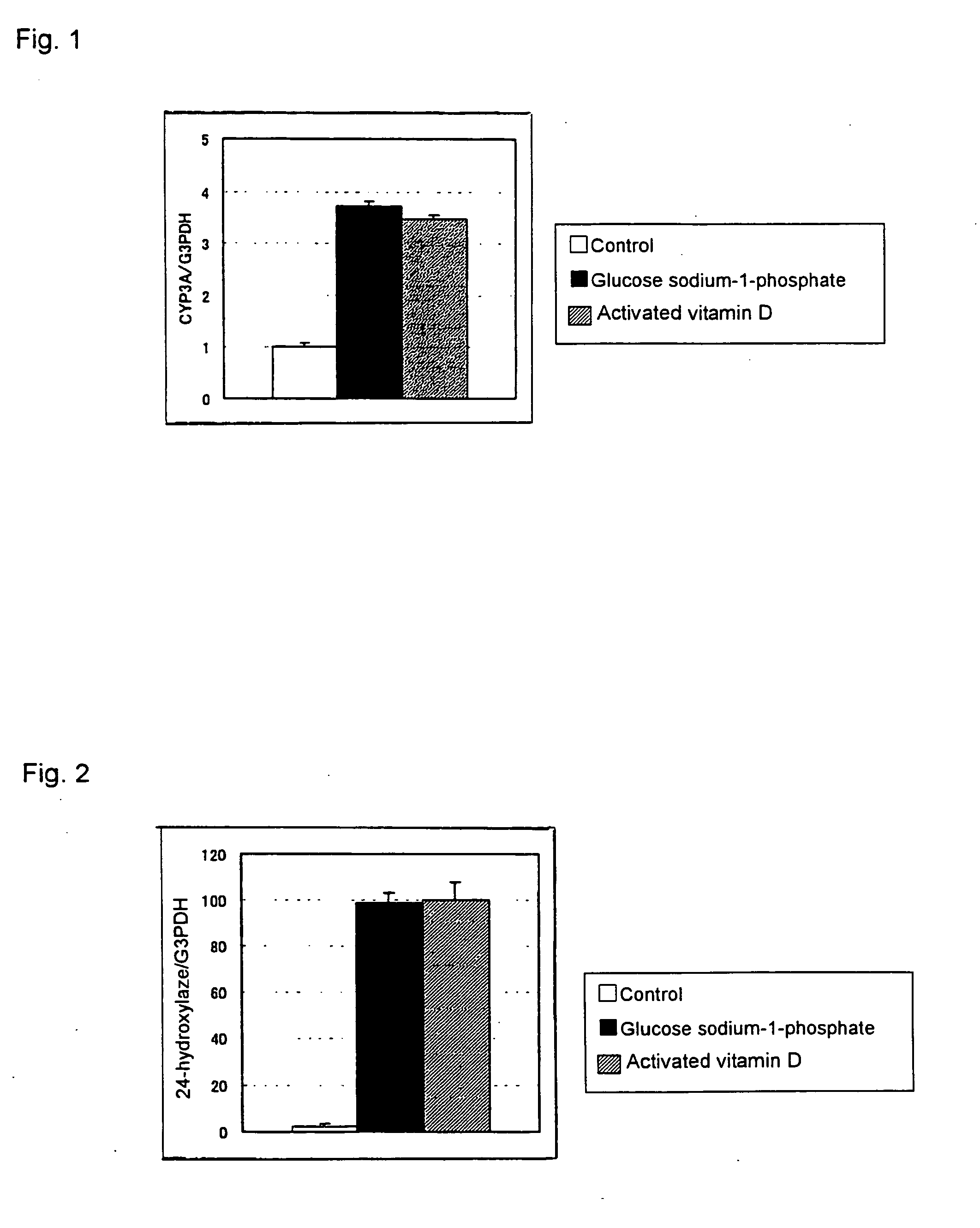
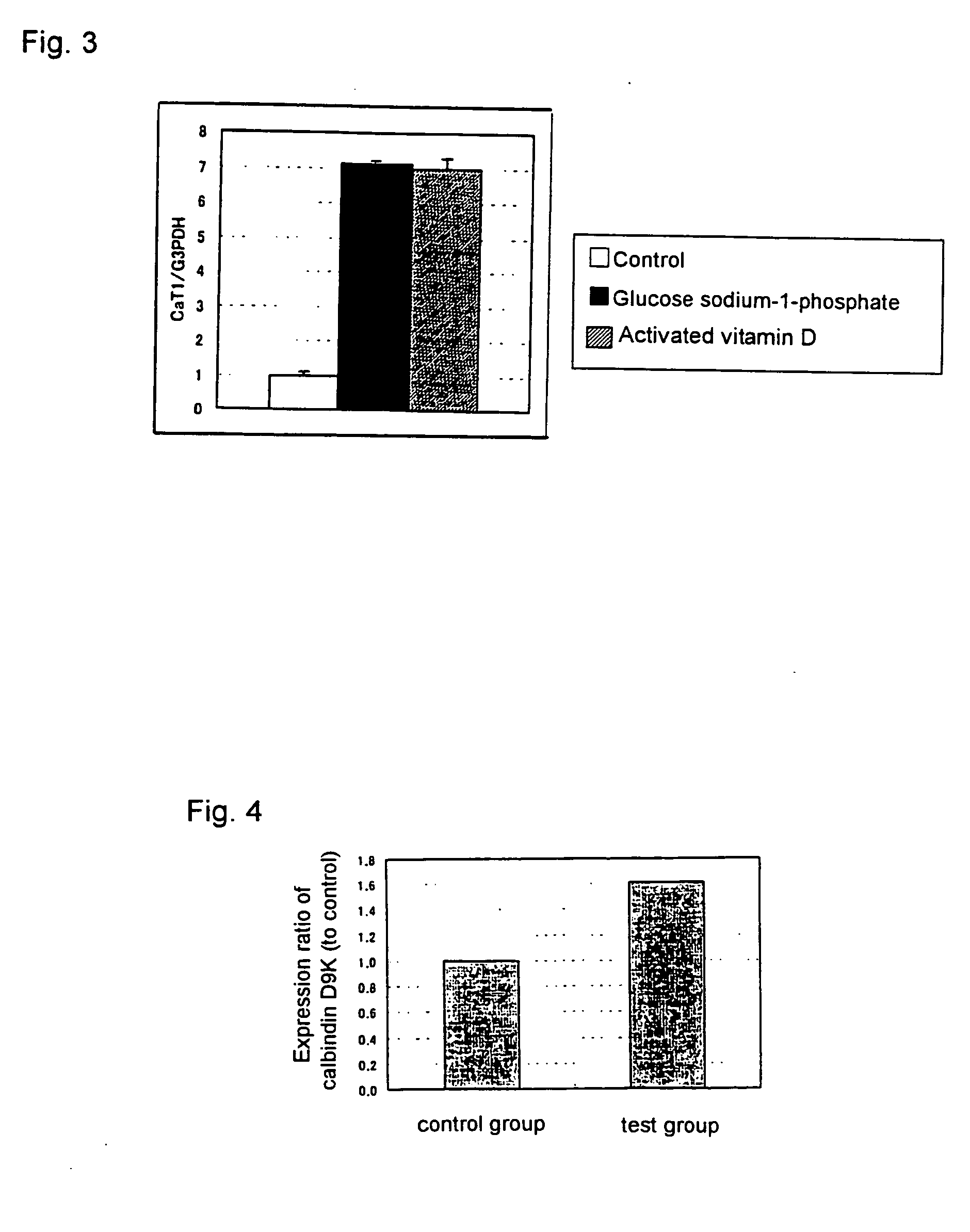
Alternative agent with vitamin D-like activity and an improving agent for intestinal function
The present invention relates to an alternative agent with vitamin D-like activity or an improving agent for age-related depression of intestinal function, comprising a sugar-phosphate ester or a salt thereof, as an active ingredient.
Owner:KAO CORP
Method for improving yield of bacillus subtilis acetylglucosamine
PendingCN111893129AReduce excess accumulationLow toxicityBacteriaHydrolasesSugar phosphatesPhosphorylation
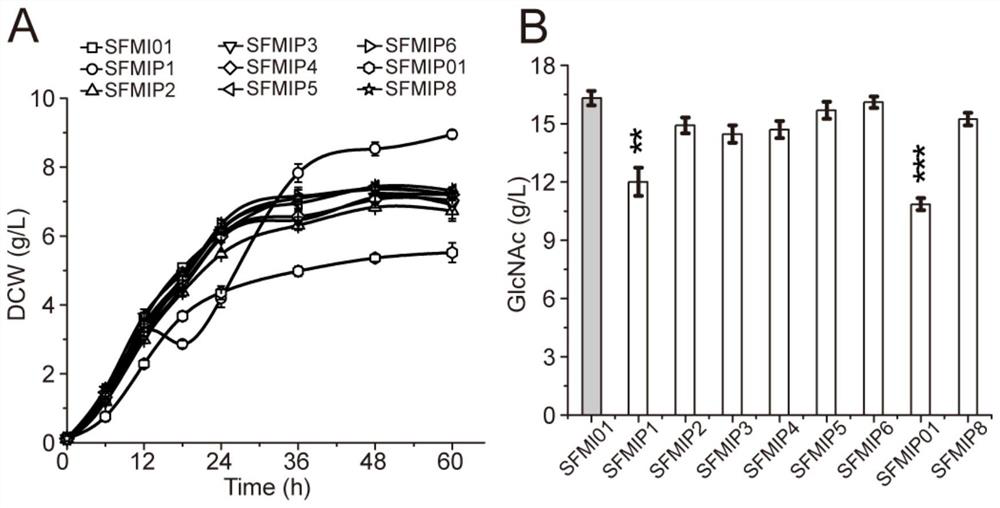
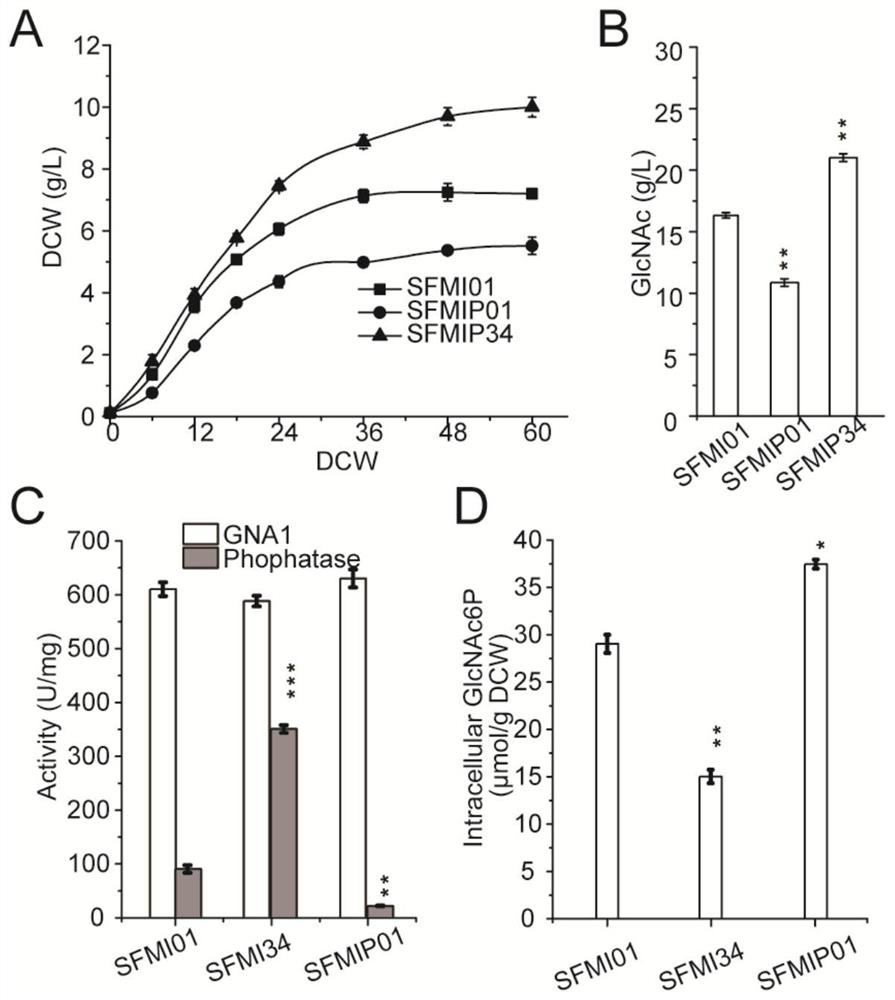
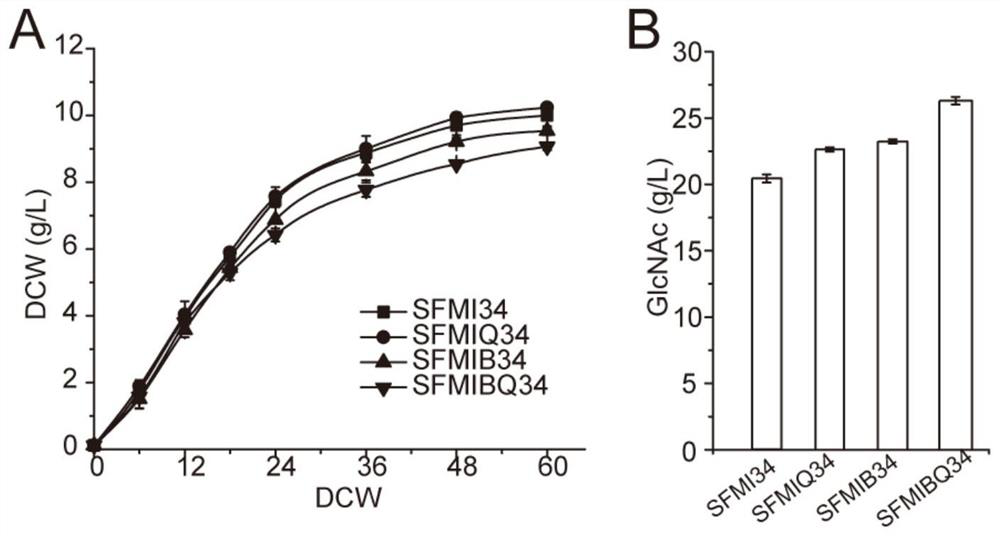
The invention discloses a method for improving yield of bacillus subtilis acetylglucosamine. According to the invention, knockout verification is carried out to obtain a result that key phosphatase YwpJ can catalyze GlcNAc-6-P to take a dephosphorylation effect to generate GlcNAc; by overexpressing the phosphatase YwpJ, excessive accumulation of intracellular sugar phosphates is reduced, a toxic effect of the excessively accumulated sugar phosphates on cells is eliminated, and the sugar phosphates are effectively secreted out of the cells, so that cell growth is improved; and GlcNAc syntheticprecursor degradation pathway key genes murQ and nagBB are further knocked out, degradation of a precusor substance is blocked, waste of carbon flow is reduced, more carbon flow is enabled to be transformed into products, a GlcNAc yield of a final recombinant strain FMIP34 reaches 26.1g / L and is increased by 61.1%, and a transformation rate of the GlcNAc reaches 0.483g per gram of glucose.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
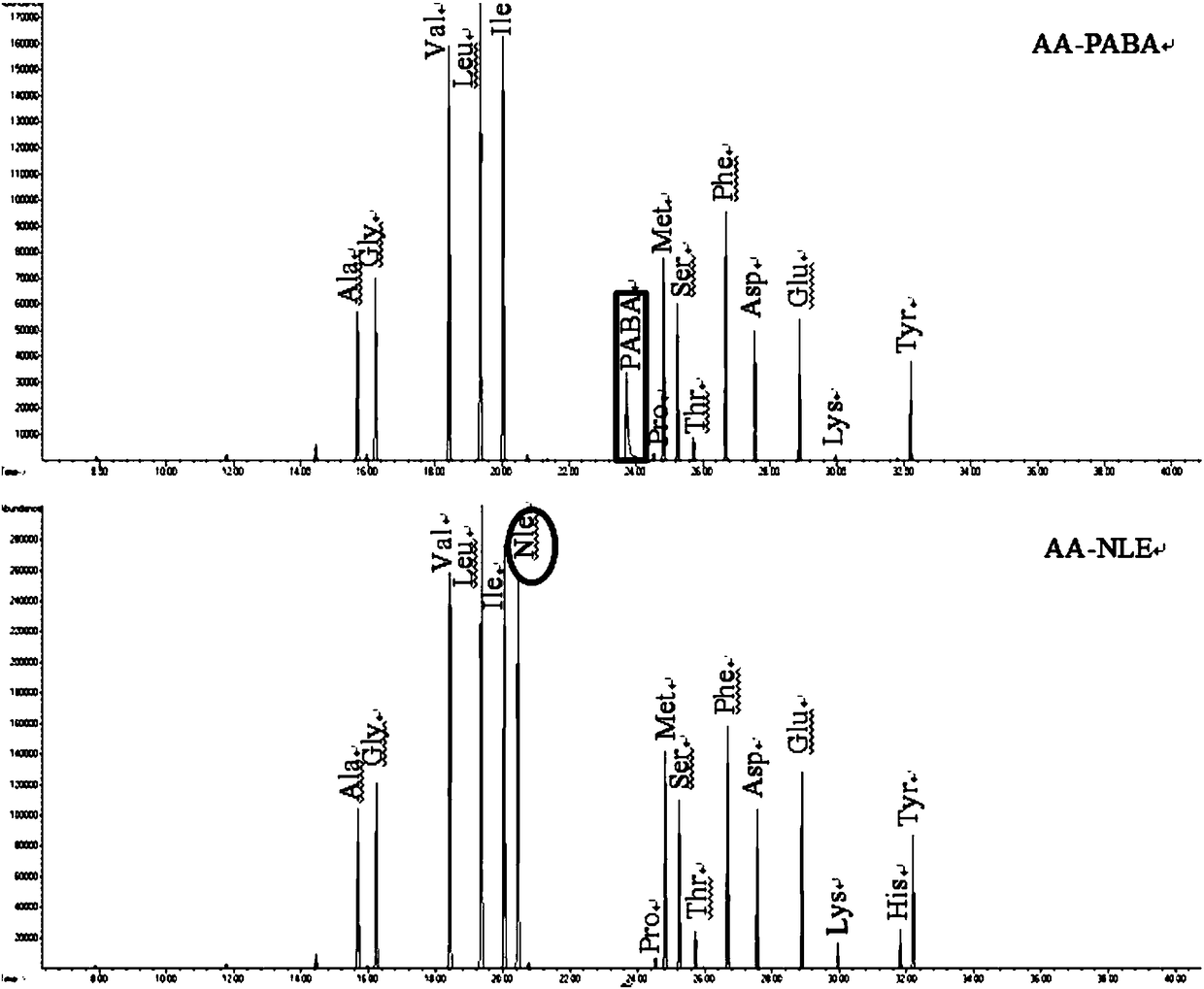
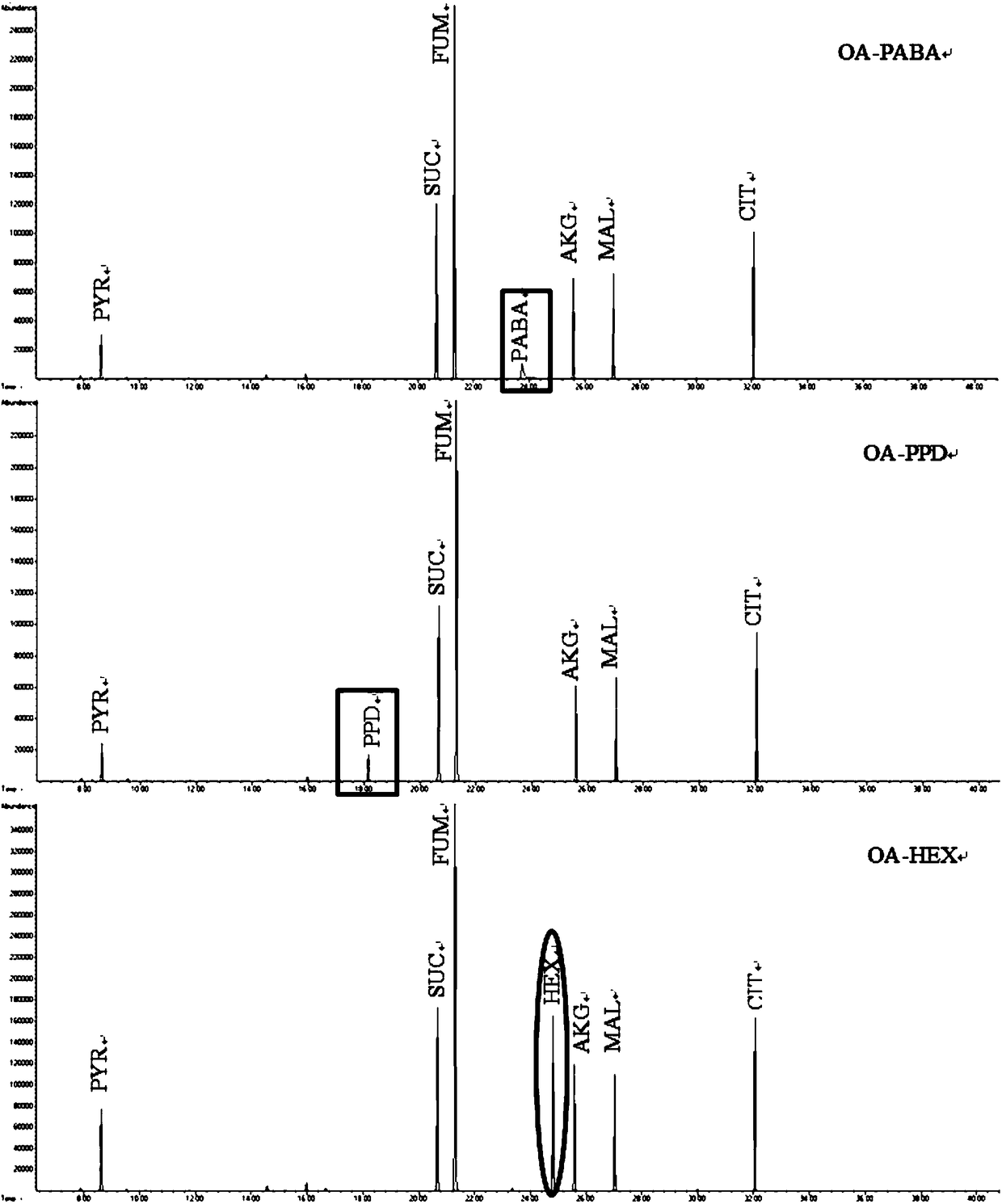
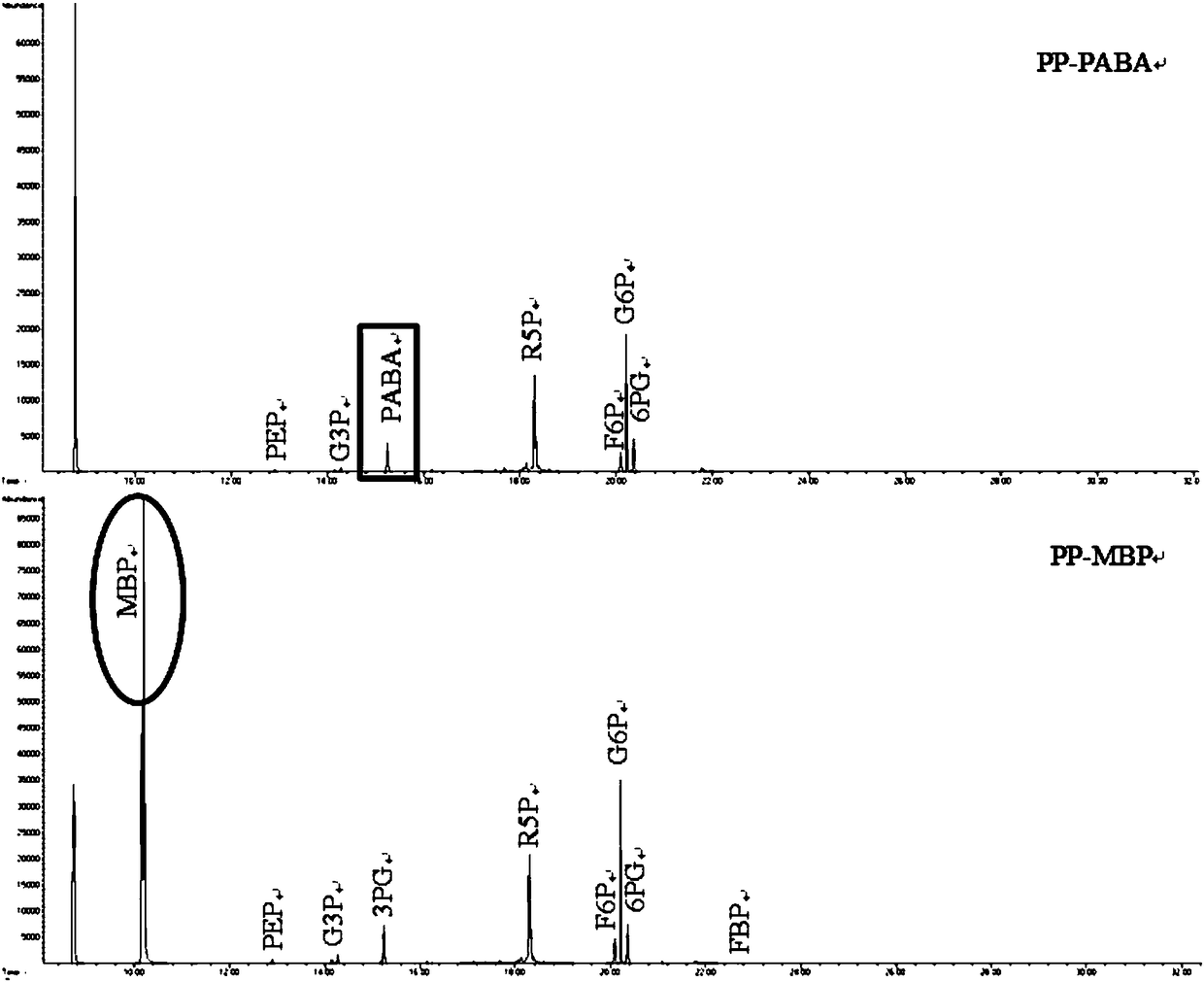
Novel internal standard substance for detecting amino acid, organic acid or sugar phosphate metabolite in sample
The invention relates to a novel internal standard substance for detecting amino acid, organic acid or sugar phosphate metabolite in a sample. The invention discloses a novel compound suitably used asthe internal standard substance during the detection process of the amino acid, organic acid or sugar phosphate metabolite in a to-be-detected sample, and builds a detection method. By the internal standard substance and the detection method, the detection accuracy of a fermentation metabolite can be effectively improved, and the internal standard substance is simple and convenient in process andrelatively low in cost.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of small interfering nucleic acid and pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
ActiveCN108220293BReduce cholesterolLower triglyceride levelsOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderPhosphoric Acid EstersSugar phosphates
The present disclosure relates to a small interfering nucleic acid and a pharmaceutical composition and uses thereof. The siRNA contains a sense strand and an antisense strand, the sense strand contains a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, and the antisense strand contains a sequence such as The nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.3; and the phosphate group and / or ribose group in the phosphate-sugar skeleton of the siRNA is a phosphate group and a ribose group with or without a modification group. The present disclosure provides a brand-new high-efficiency siRNA and a pharmaceutical composition thereof, which can effectively prevent and / or treat dyslipidemia.
Owner:SUZHOU RIBO LIFE SCIENCE CO LTD
High temperature selection of nucleotide-supported carbohydrate vaccines and resulting glycosylated oligonucleotides
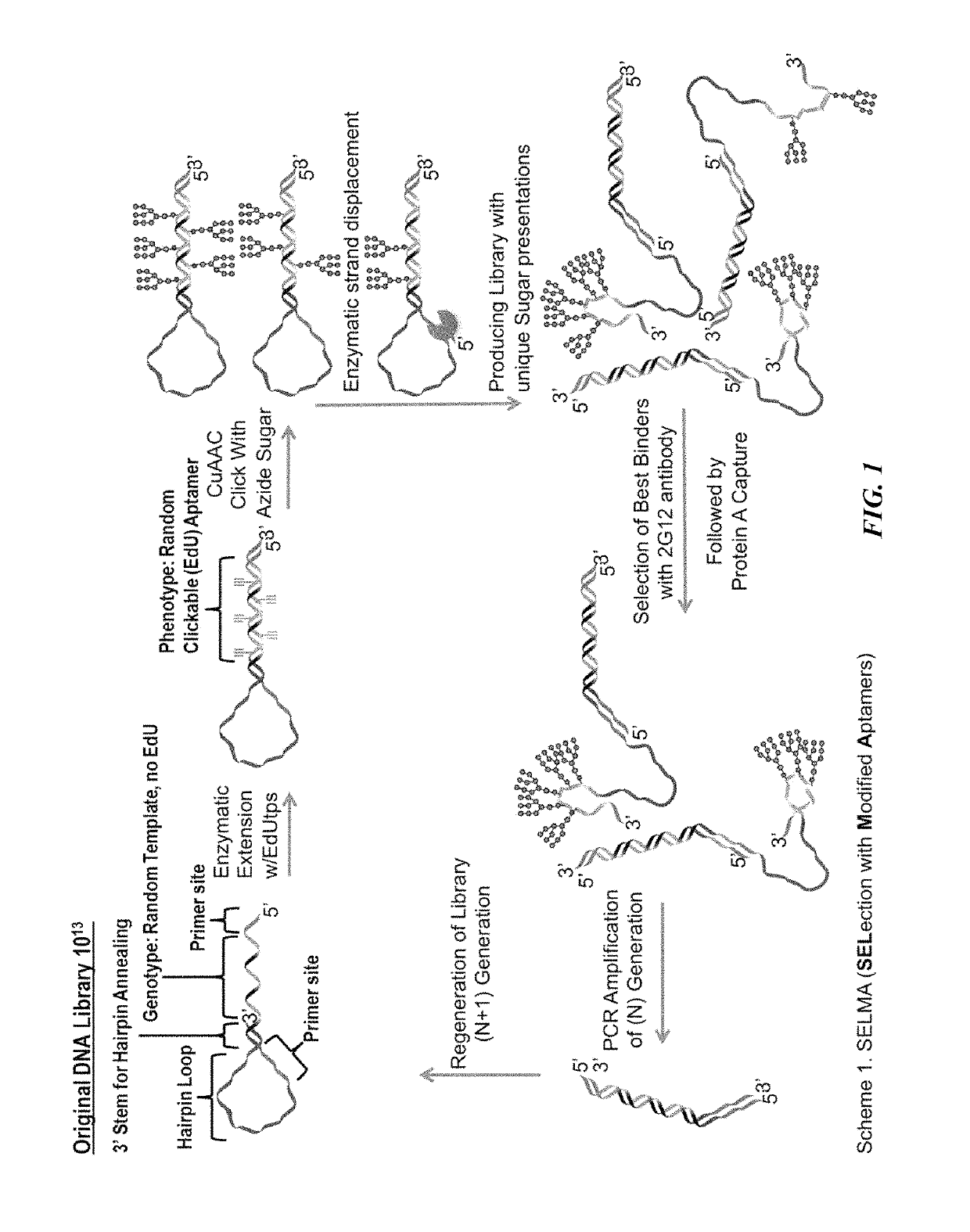
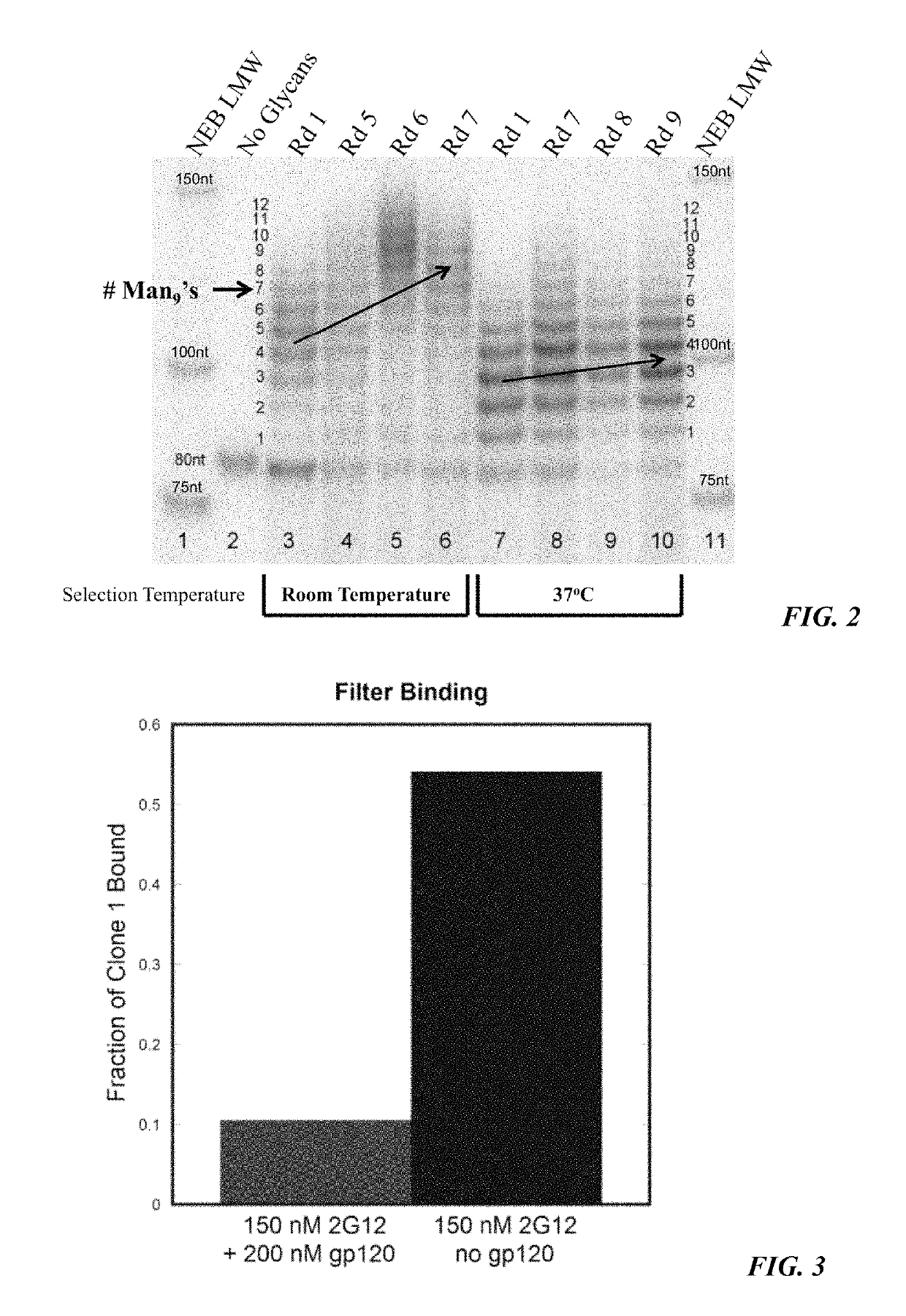
The invention relates to an oligonucleotide including one or more modified nucleoside bases having the structure -B-L-A wherein for each of the modified nucleosides A is independently a monosaccharide or oligosaccharide, L is a linker molecule, and B is independently a pyrimidine or pyridine base linked to the sugar-phosphate backbone of the oligonucleotide; and wherein the oligonucleotide binds specifically to a carbohydrate-binding monoclonal antibody with an affinity of less than 100 nM. Immunogenic conjugates that include the oligonucleotide, and pharmaceutical compositions that include the oligonucleotide or the immunogenic conjugate are also disclosed. Various method of using the oligonucleotides, immunogenic conjugates, and pharmaceutical compositions are disclosed, including inducing an immune response, inhibiting viral or bacterial infection, treating a cancerous condition, and detecting a neutralizing antibody. A method is also disclosed for selecting the oligonucleotides using an alternative Selection of Modified Aptamers (SELMA).
Owner:BRANDEIS UNIV
Protein refolding agent and refolding method
InactiveUS20100168403A1Improve productivityHigh-purity proteins in large amountsDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsSugar phosphatesPropanoic acid
A refolding agent and refolding method which makes it possible to produce high-purity proteins in high productivity. The refolding agent includes a phosphorus-containing compound (A) and an oxycarbonyl group-containing compound (B). The refolding method includes the step of treating the unfolded protein with the refolding agent. As the compound (A), there may be at least one selected from inorganic phosphoric acids, alkyl phosphate esters, sugar phosphate esters, and salts of these, and as the compound (B), there may be at least one selected from formic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, lactic acid, tartaric acid, and salts of these.
Owner:YAMAGUCHI SHUNICHLRO +1
Glycosyltransferase reversibility for sugar nucleotide synthesis
ActiveUS20110306074A1Simple methodEfficient synthesisSugar derivativesBacteriaNucleotideGlycorandomization
The present invention generally relates to materials and methods for exploiting glycosyltransferase reversibility for nucleotide diphosphate (NDP) sugar synthesis. The present invention provides engineered glycosyltransferase enzymes characterized by improved reaction reversibility and expanded sugar donor specificity as compared to corresponding non-mutated glycosyltransferase enzymes. Such reagents provide advantageous routes to NDP sugars for subsequent use in a variety of biomedical applications, including enzymatic and chemoenzymatic glycorandomization.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
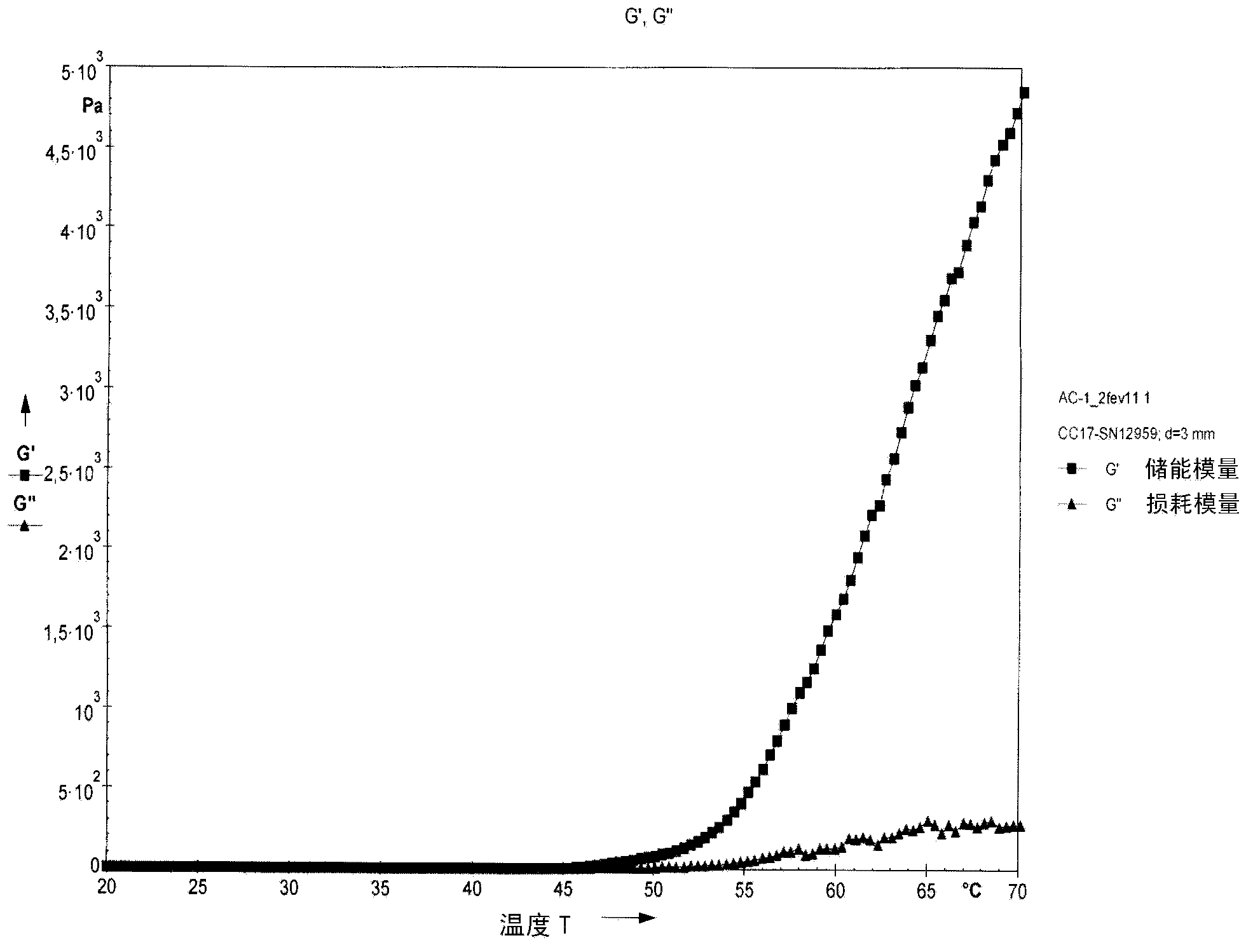
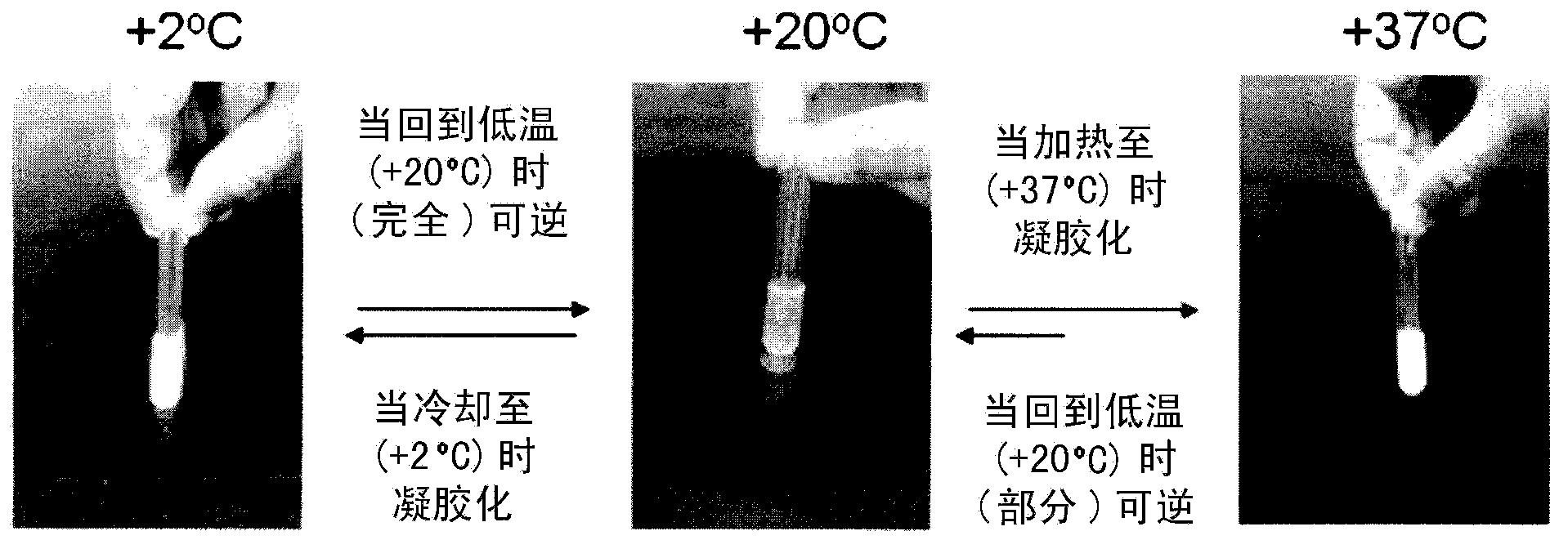
Highly biocompatible dual thermogelling chitosan/glucosamine salt compositions
The present disclosure relates to a chitosan solution neutralized with amino-sugar carbonate buffering solution or amino-sugar phosphate buffering solution or phosphorylated aminosugar buffering solution. The resulting themogelling chitosan composition is highly biocompatible, isotonic and has the ability to rapidly turn into gel upon heating to the body temperature. It provides a novel chitosan-based composition to suitable for drug delivery, cell delivery and repair or regeneration of tissues and organs as well as other clinical treatment.
Owner:OLIGO MEDIC
A kind of small interfering nucleic acid and pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
ActiveCN108239644BReduce contentPrevent and/or treat dyslipidemiaOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDyslipidemiaSugar phosphates
The present disclosure relates to a small interfering nucleic acid and a pharmaceutical composition and uses thereof. The siRNA contains a complementary sense strand and an antisense strand, and the sense strand contains such as SEQ ID NO.24, SEQ ID NO.26, SEQ ID NO. 28 or the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.30, the antisense strand contains the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.25, SEQ ID NO.27, SEQ ID NO.29 or SEQ ID NO.31 and the phosphate backbone and / or nucleotide pentose in the phosphate-sugar backbone of the siRNA may or may not have a modification group. The present disclosure provides a brand-new high-efficiency siRNA and a pharmaceutical composition thereof, which can effectively prevent and / or treat dyslipidemia.
Owner:SUZHOU RIBO LIFE SCIENCE CO LTD
A kind of small interfering nucleic acid and pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
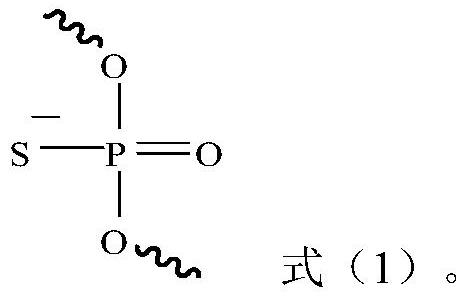
ActiveCN108431224BReduce dosageExtended dosing intervalOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBase JSugar phosphates
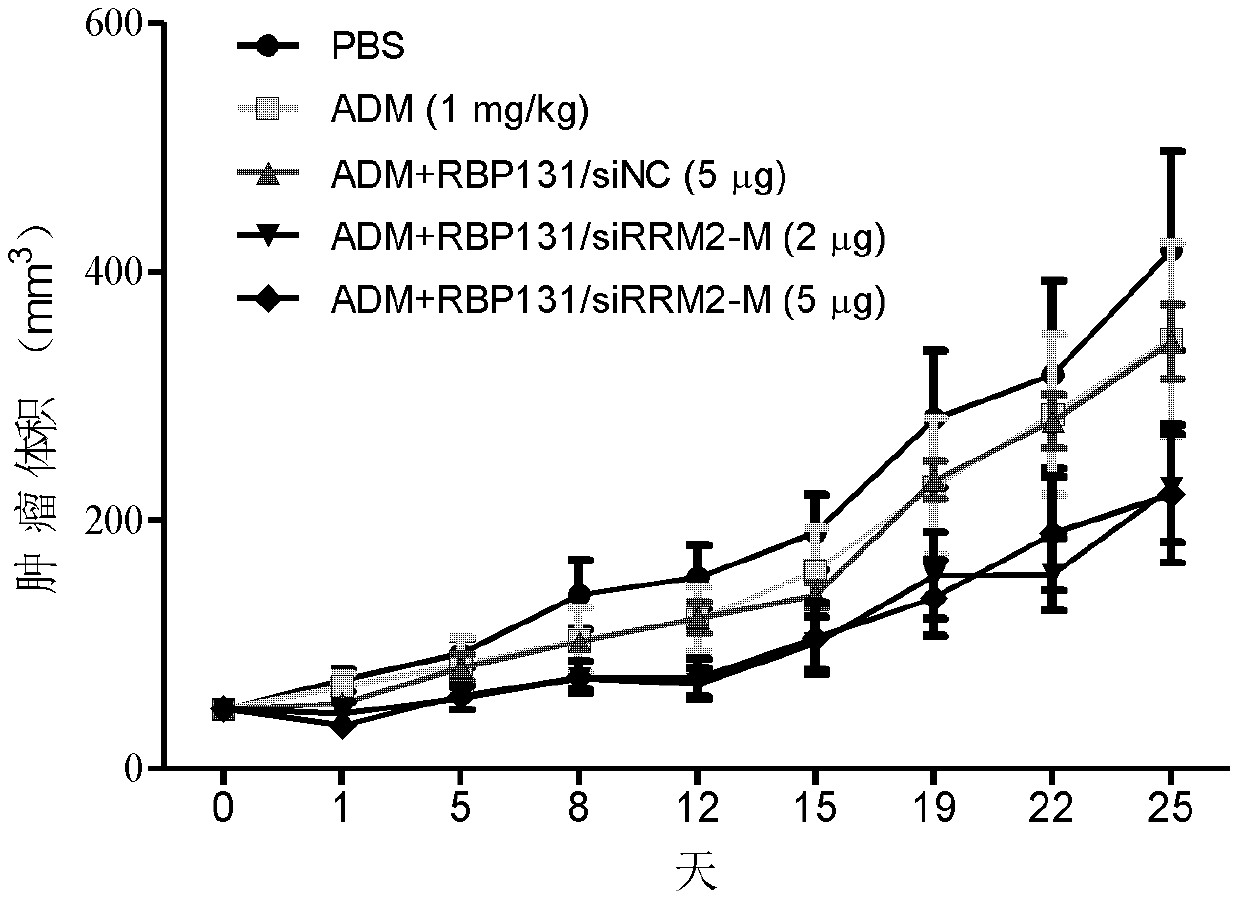
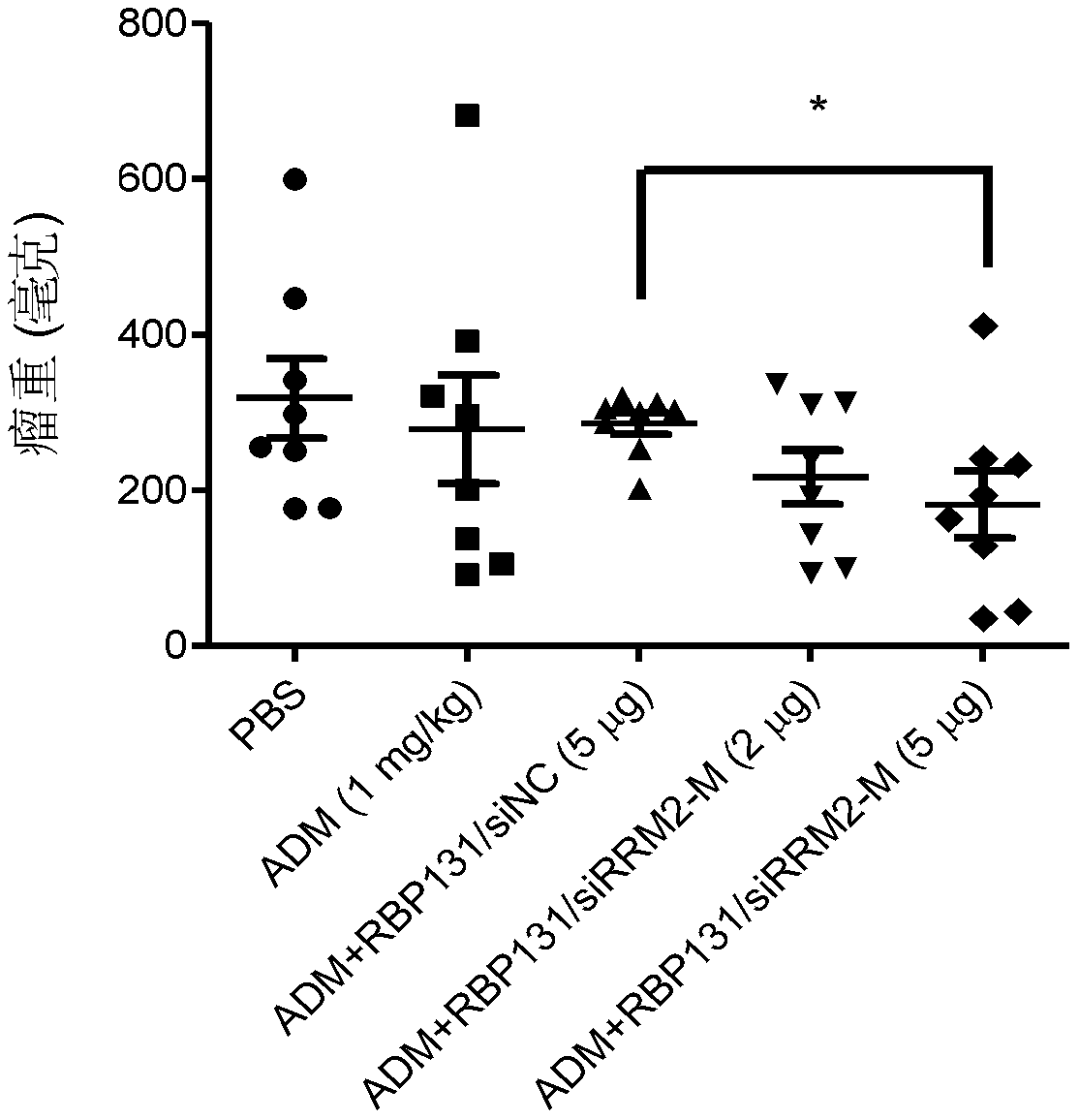
Provided is a siRNA that inhibits RRM2 gene expression. A sense-strand base sequence of the siRNA is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2, an antisense-strand base sequence of the siRNA is as shown in SEQ ID NO:3, and a phosphate-sugar backbone of the siRNA may further have a modified group; also provided is a pharmaceutical composition comprising the siRNA, which can inhibit tumor cell proliferation and facilitate tumor cell apoptosis, thereby inhibiting growth of tumor tissues.
Owner:SUZHOU RIBO LIFE SCIENCE CO LTD
Novel internal standard for the detection of amino acids, organic acids, or sugar phosphate metabolites in samples
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kit for detecting tumor m2-type pyruvate kinase and its preparation method
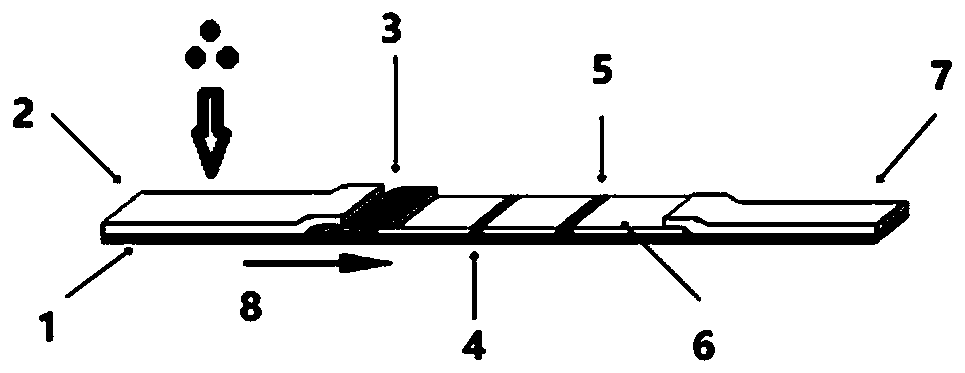
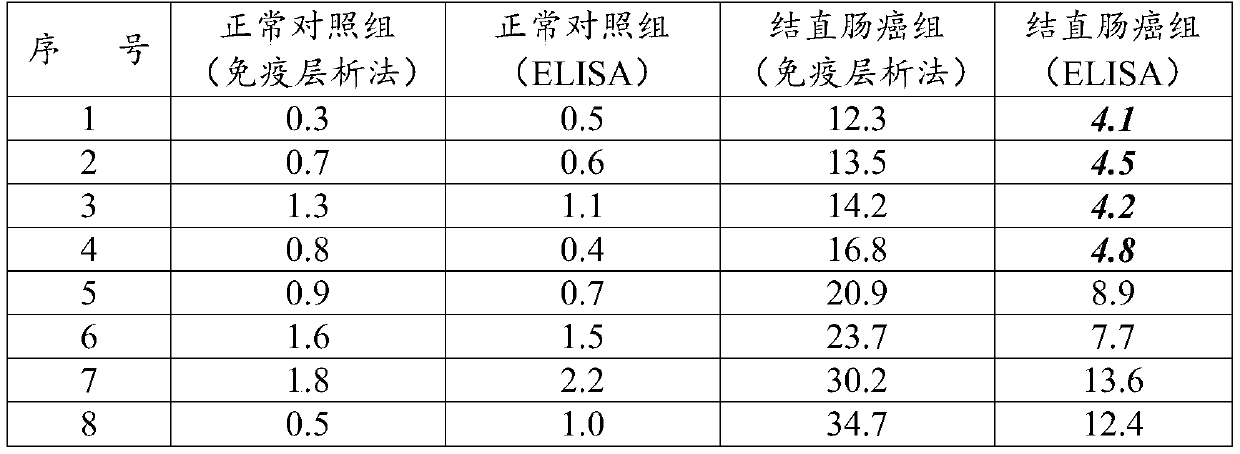
ActiveCN109884316BRealize quantitative detectionHigh fluorescence intensityBiological testingEpitopeSugar phosphates
The invention discloses a kit for inspecting tumour M2 type pyruvate kinase and a preparation method of the kit. The kit comprises a test paper card. The test paper card comprises a bottom plate, thebottom plate is provided with a sample pad, a combination pad, a nitrocellulose membrane and an absorbent pad which are sequentially connected at the ends in the sample flowing direction, capture antibodies marked by quantum dots are adsorbed by the combination pad, the nitrocellulose membrane is successively provided with an inspection belt and a quality control belt in the sample flowing direction, the inspection belt is covered with inspection antibodies, and the quality control belt is covered with IgG; the capture antibodies and the inspection antibodies are anti-tumour M2 type pyruvate kinase antibodies, and the capture antibodies and the inspection antibodies are combined with different epitopes of the tumour M2 type pyruvate kinase; and before the capture antibodies are marked by the quantum dots, the capture antibodies are modified with monophosphate sugar. The kit has the advantages that high sensitivity and specificity are achieved, operation is fast, simple and convenient,the result is accurate, and affordability is achieved.
Owner:广州春康生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com