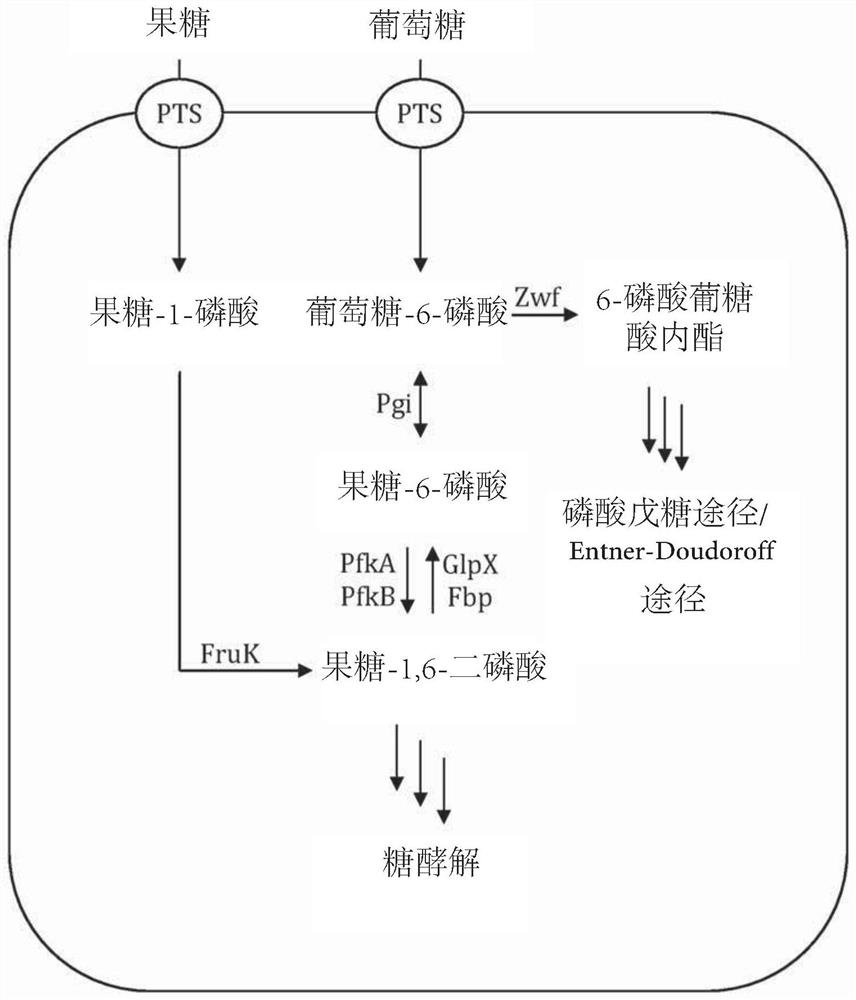
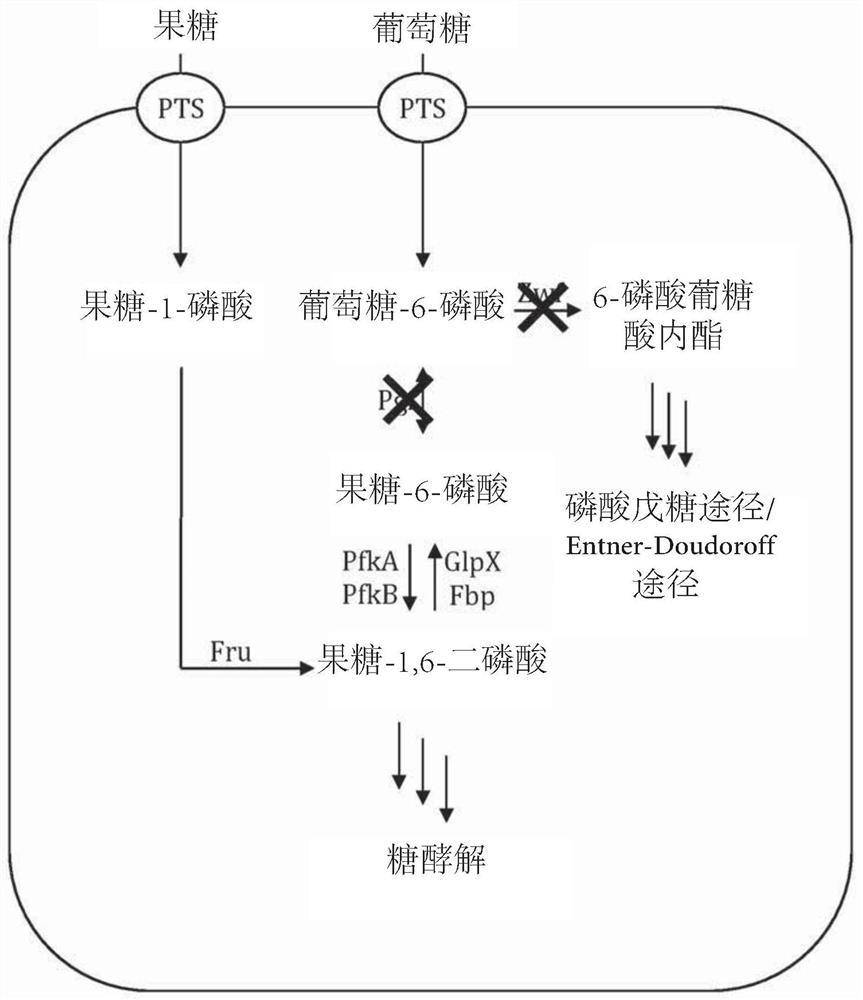
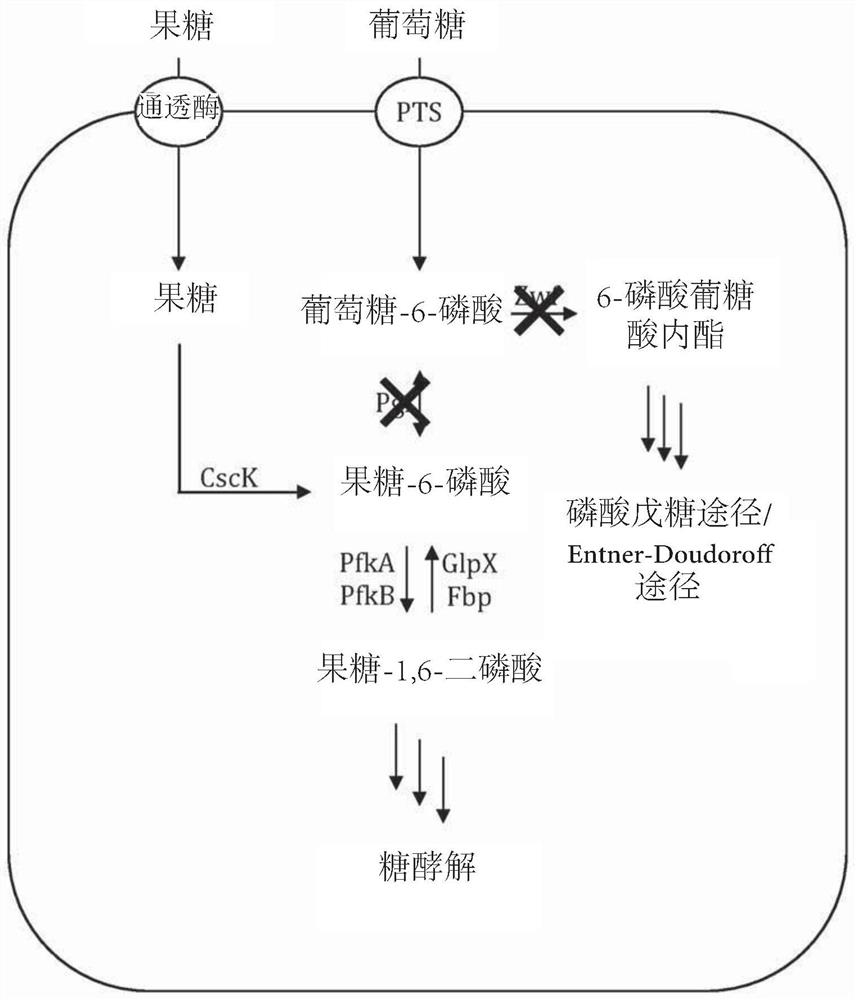
Fermentative production of carbohydrates by microbial cells utilizing mixed feedstock
A technology of microbial cells and carbohydrates, which is used in the field of fermentation and can solve the problems of offset applicability, high pollution risk of bacterial cell growth, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0142] Embodiment 1-preparation of mixed monosaccharide raw material
[0143] A 50% (w / v) sucrose solution was prepared by dissolving 500 g of sucrose in water. The final volume of the solution was 1 liter. The pH was adjusted by using 96% (v / v) sulfuric acid at a temperature of 30°C to 35°C. Then, the solution was sterilized in a vertical autoclave (Systec VX-65, Linden, Germany) at 121° C. for 45 minutes. Samples were taken before and after heat sterilization and kept frozen until high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) analysis. HPLC was performed using a RID-IOA Refractive Index Detector (Shimadzu, Germany) and a Waters XBridge Amide column 3.5 μm (250x4.6 mm) (Eschborn, Germany) connected to a Shimadzu HPLC system. With 30% solvent A (50% (v / v) acetonitrile in double distilled water, 0.1% (v / v) NH4OH) and 70% solvent B (80% (v / v) acetonitrile in double distilled water, 0.1 %(v / v) NH4OH) was eluted isocratically at 35°C with a flow rate of 1.4mLmin -1 . Samples...
Embodiment 2
[0146] Example 2 - Feedstock-dependent growth of various gene deletion strains
[0147] The E. coli BL21(DE3) strain (wild type) and the mutant strain E. coli pfkA were compared - (△pfkA), Escherichia coli pfkB - (△pfkB), Escherichia coli pfkA - wxya - Growth behavior of (△pfkA△pfkA). Genomic deletions were performed according to the method of Datsenko and Wanner (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:6640-6645 (2000)). All strains were cultured at 30°C in 100mL shake flasks containing 20mL of mineral salt medium containing 7g·L - 1 NH 4 h 2 PO 4 , 7g·L -1 K 2 HPO 4 , 2g·L -1 KOH, 0.3g·L -1 Citric acid, 2g·L -1 MgSO 4 ×7·H 2 O and 0.015g·L -1 CaCl 2 ×6·H 2 O, add 1mL·L -1 Trace element solution (54.4g L -1 Ferric ammonium citrate, 9.8g·L -1 MnCl 2 ×4·H 2 O, 1.6g·L -1 CoCl 2 ×6·H 2 O, 1g L -1 CuCl 2 ×2·H 2 O, 1.9g·L -1 h 3 BO 3 , 9g·L -1 ZnSO 4 ×7·H 2 O, 1.1g L -1 Na 2 MoO 4 ×2·H 2 O, 1.5g·L -1 Na 2 SeO 3 , 1.5g·L -1 NiSO 4 ×6·H 2 O) with 2...
Embodiment 3
[0148] Example 3 - Production of 2'-fucosyllactose by engineering E. coli strains
[0149] 2'-Fucosyltransferase gene wbgL from Escherichia coli: O126, from Yersinia bokwangii by overexpressing enzymes for de novo synthesis of GDP-fucose (ManB, ManC, Gmd, WcaG) (Yersinia bercovieri) ATCC 43970 sugar efflux transporter yberc0001_9420 and Escherichia coli W csc gene cluster (Accession No. CP002185.1) (including genes for sucrose permease, fructokinase, sucrose hydrolase and transcriptional repressor ( genes cscB, cscK, cscA and cscR)), further genetic engineering revealed genotype lacY + , lacZ - 、fuclK - , wcaJ - , pfkA - coli BL21(DE3) strain, enabling the strain to grow on sucrose as the sole carbon source. Genomic deletions were performed according to the method of Datsenko and Wanner (Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:6640-6645 (2000)). Genomic integration of heterologous genes by transposition. Linear DNA fragments were integrated using EZ-Tn5TM transposase (Epicentre, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com