Microfluidic chip and method for studying non-contact type cell co-cultivation by using the same
A microfluidic chip and cell culture technology, applied in the field of biomedical research, can solve the problems of large consumption of reagents, lack of biological information, and large amount of cells, and achieve the effects of less sample consumption, simple production and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
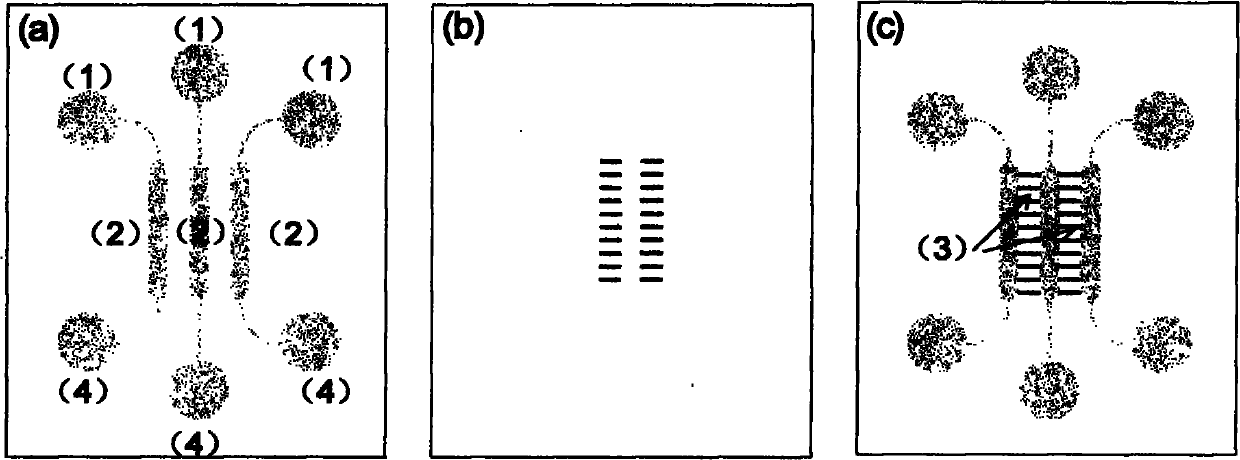
[0030] The microfluidic chip used was designed and manufactured by our laboratory. The chip is formed by reversible sealing of upper and lower layers, the upper layer material is PDMS polymer, and the lower layer material is glass. like figure 1 As shown, the dimensions of three parallel cell culture chambers are 6 mm in length, 1 mm in width, and 50 μm in height, and the dimensions of the cell migration area are 1 mm in length, 500 μm in width, and 50 μm in height. Add hepatoma cell HepG-2 into cell culture chamber C through the injection port on the right, and gently place it in 37°C CO 2 In the incubator; after the cells adhere to the wall, add the fibroblast HFL-I into the cell culture chamber B through the middle inlet; as a blank control, the left culture chamber A does not add cells, and adds the same amount of cell culture medium as B and C .
[0031] Hoechst33342 and PI were used to jointly detect the activity of three kinds of cells (HepG-2, GES-1, HFL-I), and the...
Embodiment 2
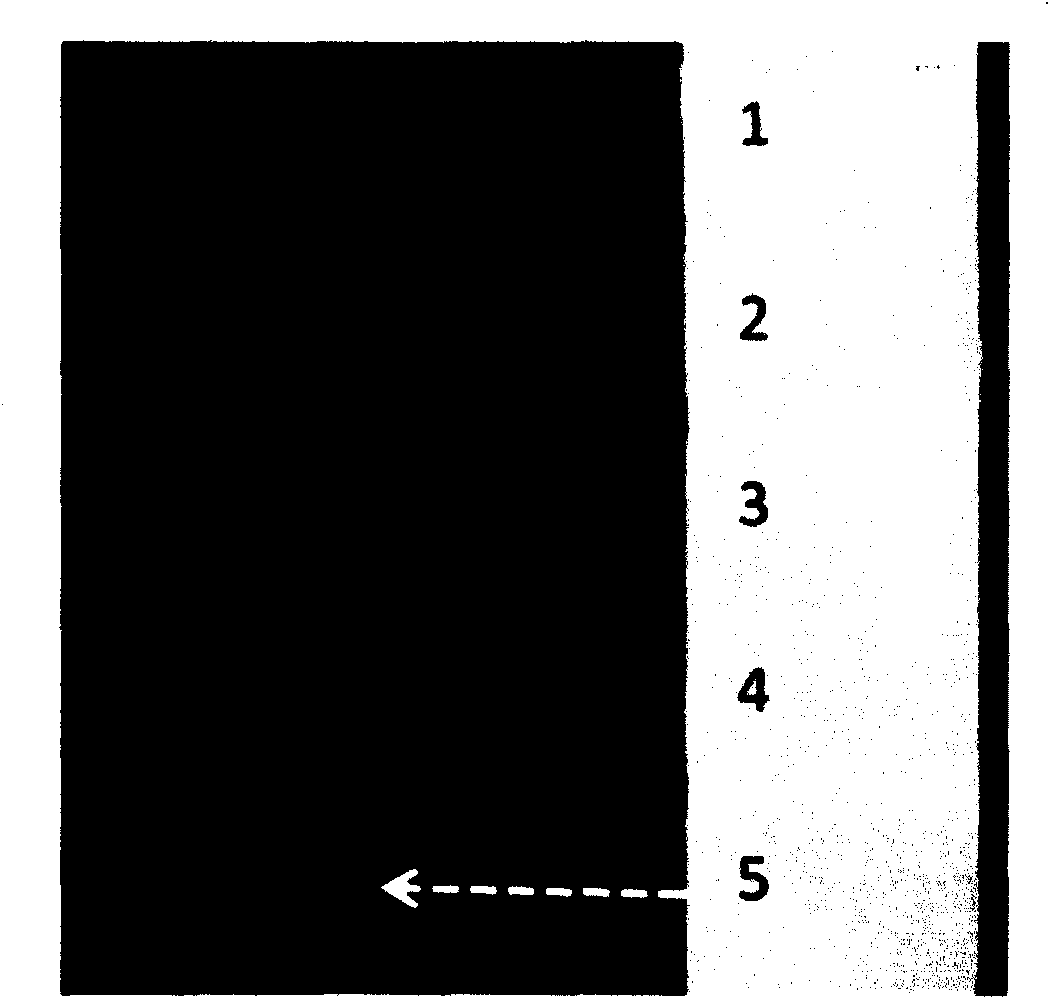
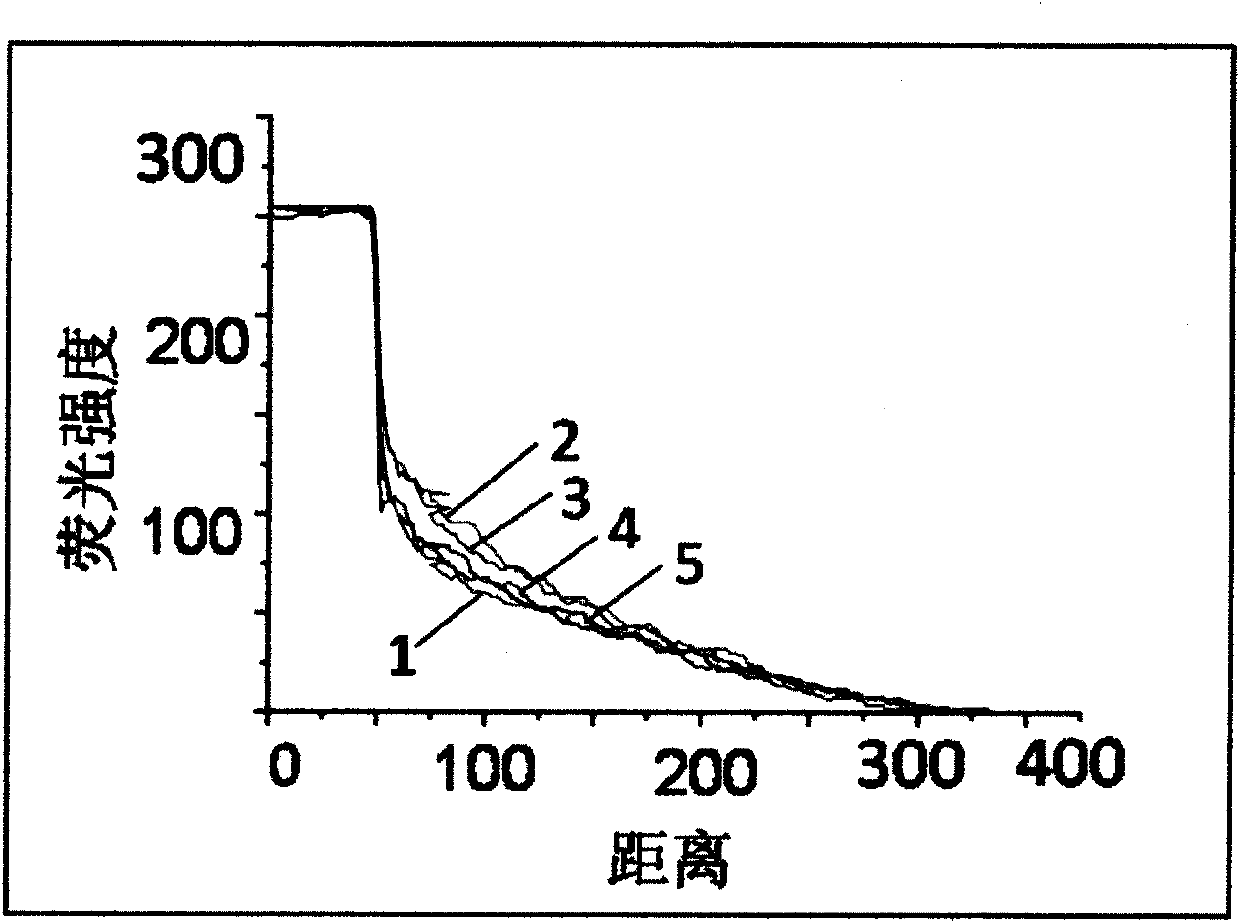
[0034] Embed fluorescent dye labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) in BME, add it into cell culture chamber C through the injection port, and add an equal amount of α-MEM culture solution to the rest of the cell culture chambers. After a period of time, the cells A fluorescent signal appeared in the migration area ( figure 2 ), data analysis shows that the cell migration area forms a stable fluorescence concentration gradient ( image 3 ).
[0035] Add the normal cell GES-1 into the cell culture chamber C through the injection port on the right, and gently place it in the CO at 37°C. 2 In the incubator; after the cells adhere to the wall, add the fibroblast HFL-I into the cell culture chamber B through the middle inlet; as a blank control, the left culture chamber A does not add cells, and adds the same amount of cell culture medium as B and C . Compared with the migration of HFL-I cells on the blank control side, at 6h and 48h, the migration number and area of ...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Add oral cancer cells ACC-2 / ACC-M into cell culture chamber C through the injection port on the right, and gently place it in 37°C CO 2 In the incubator; after the cells adhere to the wall, add the fibroblast HFL-I into the cell culture chamber B through the middle inlet; as a blank control, the left culture chamber A does not add cells, and adds the same amount of cell culture medium as B and C . Compared with the HFL-I cell migration on the blank control side, there was no significant difference in the HFL-I cell migration area on the experimental side and the control side under the induction of oral cancer cell ACC-2 / ACC-M ( Figure 8 , Figure 9 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com