Method for constructing genetic engineering strains for producing (R)-acetoin and application of genetic engineering strains
A technology of genetically engineered strains and construction methods, which is applied to the construction of highly optically pure-acetoin genetically engineered strains and the application field of producing highly optically pure-acetoin, which can solve the problem of ineffective regeneration of oxidized coenzyme NAD, Low yield of acetoin, pathogenicity of strains and other problems, to achieve the effect of releasing transcription inhibition, low cost and stable properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] The construction of (R)-acetoin genetically engineered strain ECRA1:
[0035] The nucleotide sequences of the α-acetolactate synthase gene budB, the α-acetolactate decarboxylase gene budA derived from Enterobacter cloacae and the NADH oxidase gene noxE derived from Lactobacillus brevis were codon optimized, adding Containing the nucleotide sequence TAAGGAGGATATACA of the ribosome binding site, and then using the method of artificial synthesis to obtain the gene cluster budB-budA-noxE, the nucleotide sequence length is 3849 bases, and the nucleotide sequence is as SEQ ID NO.1 mentioned. The gene cluster budB-budA-noxE was inserted behind the promoter of the plasmid pTrc99A by double enzyme digestion and ligation to obtain the polycistronic recombinant plasmid pTrc99A-budB-budA-noxE, and then the recombinant plasmid pTrc99A-budB-budA- noxE was introduced into the host strain E.coli MG1655 to obtain (R)-acetoin-producing genetically engineered strain ECRA1.
Embodiment 2
[0037] Construction of the production (R)-acetoin genetic engineering strain ECRA2:
[0038] The genome sequence of Paenibacillus polymyxa DSM 365 was analyzed, and the nucleotide sequences of the α-acetolactate synthase gene alsS and α-acetolactate decarboxylase gene alsD of the strain were obtained. The length of the alsS gene nucleotide sequence is 1701 bases, and the nucleotide sequence is as described in SEQ ID NO.2; the length of the alsD gene nucleotide sequence is 747 bases, and the nucleotide sequence is as described in SEQ ID NO.3 stated. Codon optimization was performed on the nucleotide sequences of alsS, alsD and noxE, and the nucleotide sequence TAAGGAGGATATACA containing a ribosome binding site was added in front of each gene, and then the gene cluster alsS-alsD-noxE was obtained by artificial synthesis. The length of its nucleotide sequence is 3837 bases, and the nucleotide sequence is as described in SEQID NO.4. Then the gene cluster alsS-alsD-noxE was inser...
Embodiment 3
[0040] The construction of (R)-acetoin genetically engineered strain ECRA3:
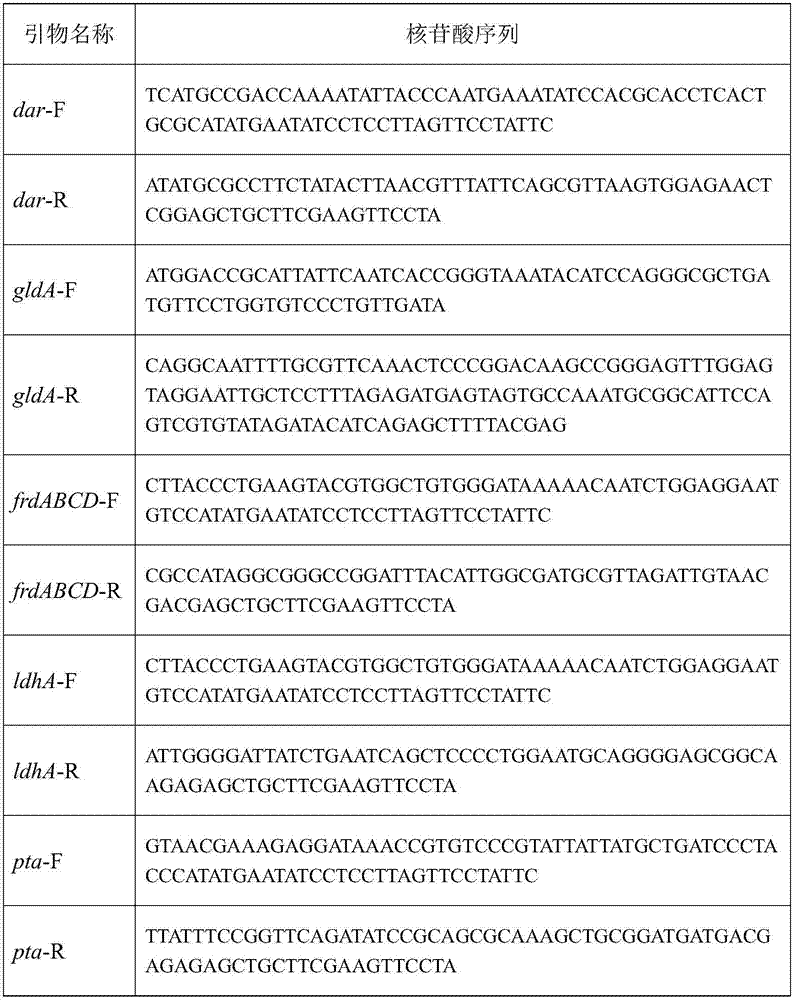
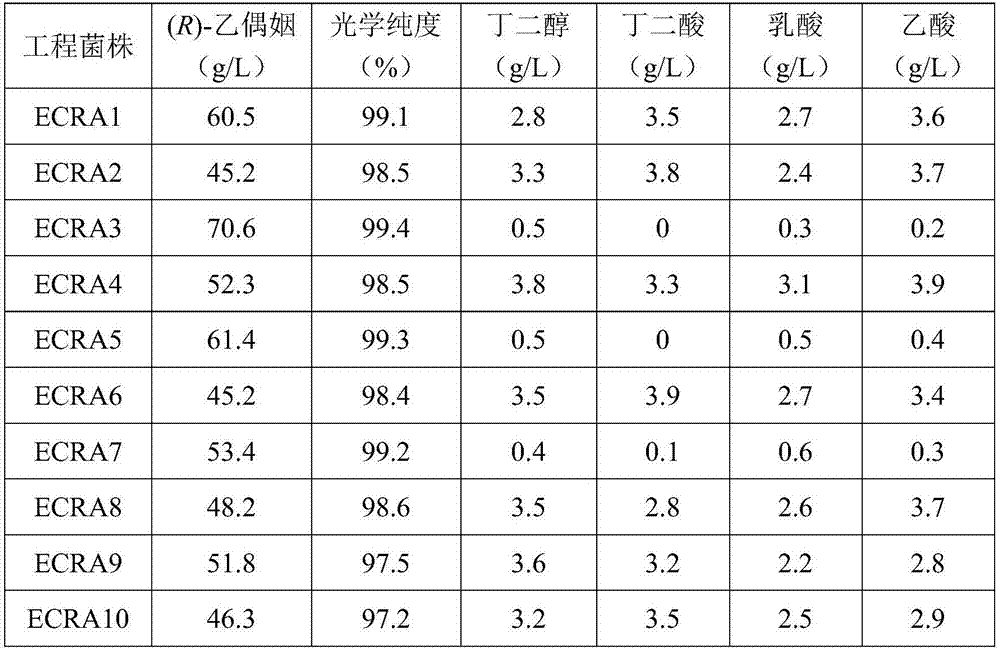
[0041] Through analysis, it was found that the by-products of the fermentation of engineering strains ECRA1 and ECRA2 were (S)-acetoin, 2,3-butanediol, succinic acid, lactic acid, and acetic acid, and the key genes of the synthesis pathway were dar, gldA, frdABCD, ldhA and pta. Using the principle that the Red recombination system derived from Escherichia coli λ phage can efficiently mediate homologous recombination events in bacteria, first replace the above target gene with an antibiotic resistance gene with FRT sites on both sides, and then induce exogenous temperature The sensitive plasmid expresses FLP recombinase to delete the antibiotic resistance gene to achieve the purpose of knocking out the target gene. The specific steps are as follows:
[0042] Transform the pKD46 plasmid into host cells to prepare electroporation-competent cells; use primers to carry out PCR to construct the targeting ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com