Zymomonas mobilis recombination strain producing isobutanol, construction method and application thereof
A technology of Zymomonas and recombinant strains, which is applied in the field of construction and production of Zymomonas mobilis recombinant strains for producing isobutanol, which can solve the problems of unsatisfactory industrial production and low yield of isobutanol, and achieve high yield, The effect of high conversion efficiency and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 The kdcA expression module was introduced into Zymomonas mobilis to obtain the recombinant strain ZM-Q1 capable of inducing the production of isobutanol
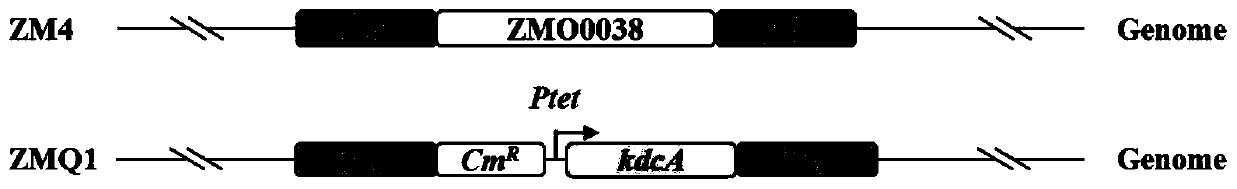
[0038] In this example, the dihydroxy-aciddehydratase (KDCA) gene derived from Lactococcus lactis was first integrated into the ZMO0038 site in the genome of the model strain Z. mobilis ZM4 by means of homologous recombination. And use the inducible promoter to control the expression of nuclease, construct the recombinant strain ZM-Q1, the recombination schematic diagram of the recombinant strain is as follows: figure 1 shown.
[0039] 1. Construction of recombinant plasmids
[0040] Use PCR to amplify the kdcA gene sequence, resistance selection marker (spectinomycin), inducible promoter gene sequence (tetracycline-inducible promoter), gene sequence upstream and downstream of the insertion site and reverse amplification of pUC57 for integration the vector sequence. The PCR amplification program was set as ...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2 Overexpression of genes in the L-valine synthesis pathway, and screening of ALS in the metabolic pathway to achieve the purpose of increasing production of isobutanol
[0073] In the isobutanol synthesis pathway, pyruvate is first catalyzed by pyruvate synthase (ALS, EC 2.2.1.6) to generate acetolactate, and then ketoacid reductoisomerase (ILVC, EC 1.1.1.86 ) is reduced to 2,3-dihydroxyisovalerate (2,3-dihydroxyisovalerate). The intermediate 2,3-dihydroxyisovalerate is converted to 2-ketoisovalerate by dihydroxyacid dehydratase (ILVD, EC4.2.1.9). Then, 2-ketoisovalerate can be further converted to isobutyraldehyde by KDCA and then to alcohol by alcohol dehydrogenases (ADHs).
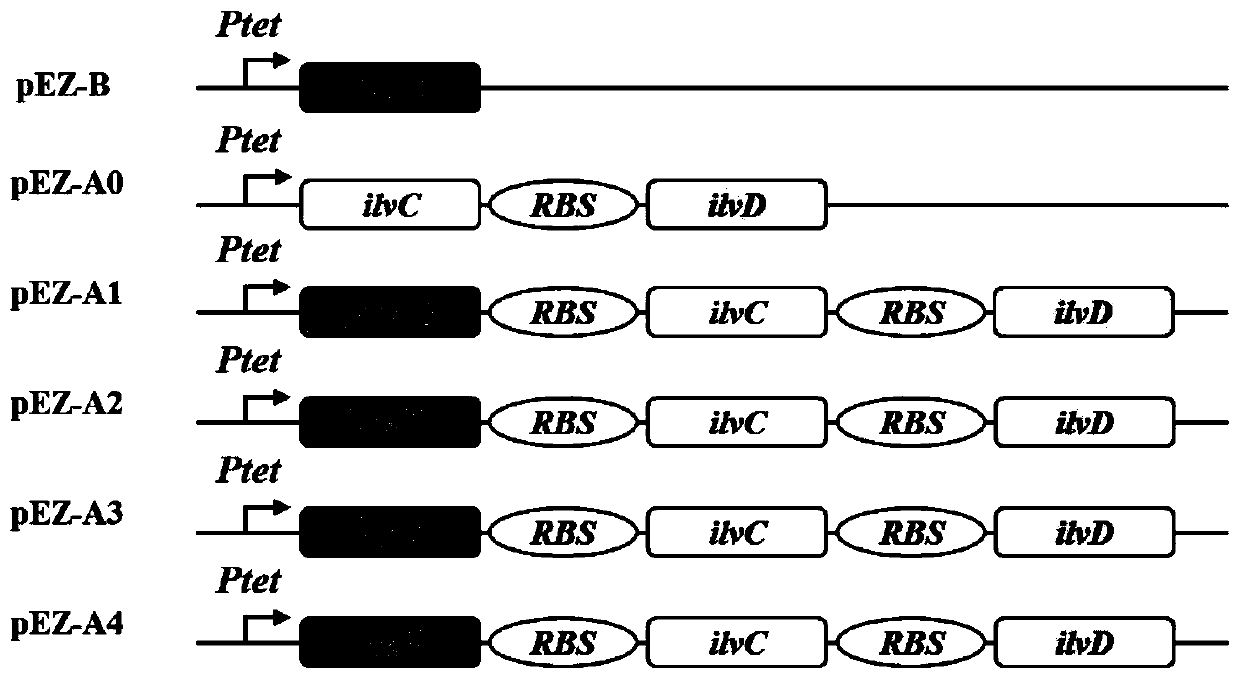
[0074] The recombinant strain ZM-Q1 can produce isobutanol, and the overexpression of Als, ilvC, ilvD in the valine synthesis pathway can transfer the carbon flow from ethanol synthesis to isobutanol production. These three genes were integrated into the shuttle plasmid pEZ15a, and the...
Embodiment 3
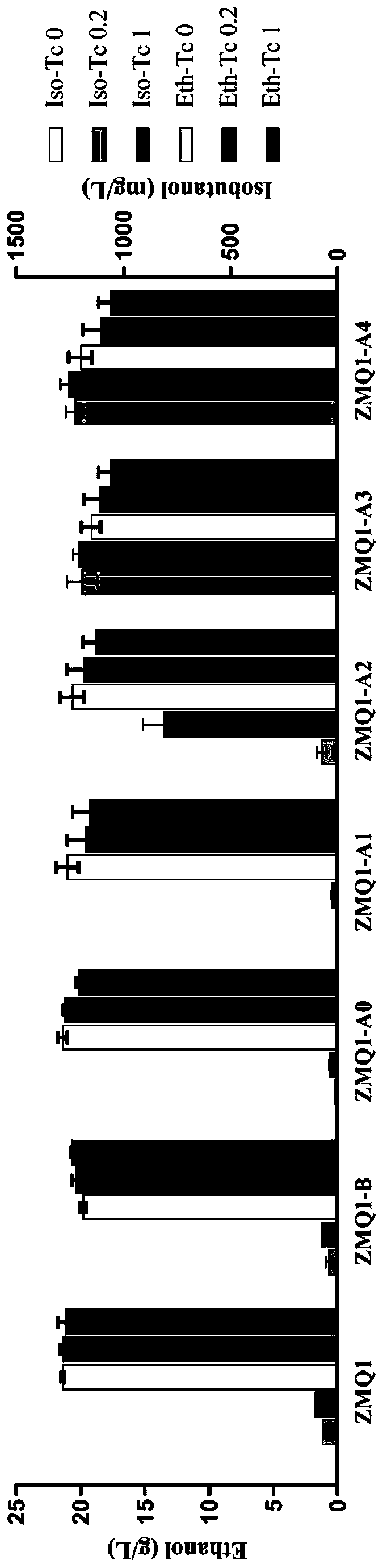
[0114] Example 3 Adjusting the expression levels of different genes in the metabolic pathway and constructing a high-yield isobutanol recombinant strain
[0115] The inventor found through experiments in the early stage that the strength of the promoter limits the production of isobutanol to a certain extent, and replaced the inducible promoter on the kdcA expression module with a constitutive promoter. The dihydroxy-acid dehydratase (KDCA) gene derived from Lactococcus lactis was integrated into the ZMO0038 site in the Z. mobilis ZM4 genome by homologous recombination, and the constitutive promoter Pgap was used to control The expression level of nuclease was used to construct the recombinant strain ZMQ3. The three genes in the valine metabolic pathway were integrated into the shuttle plasmid pEZ15a, and the expression of the genes was controlled by an inducible promoter. The recombinant plasmid was transferred into the recombinant strain of ZMQ3, and the production of isobut...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com