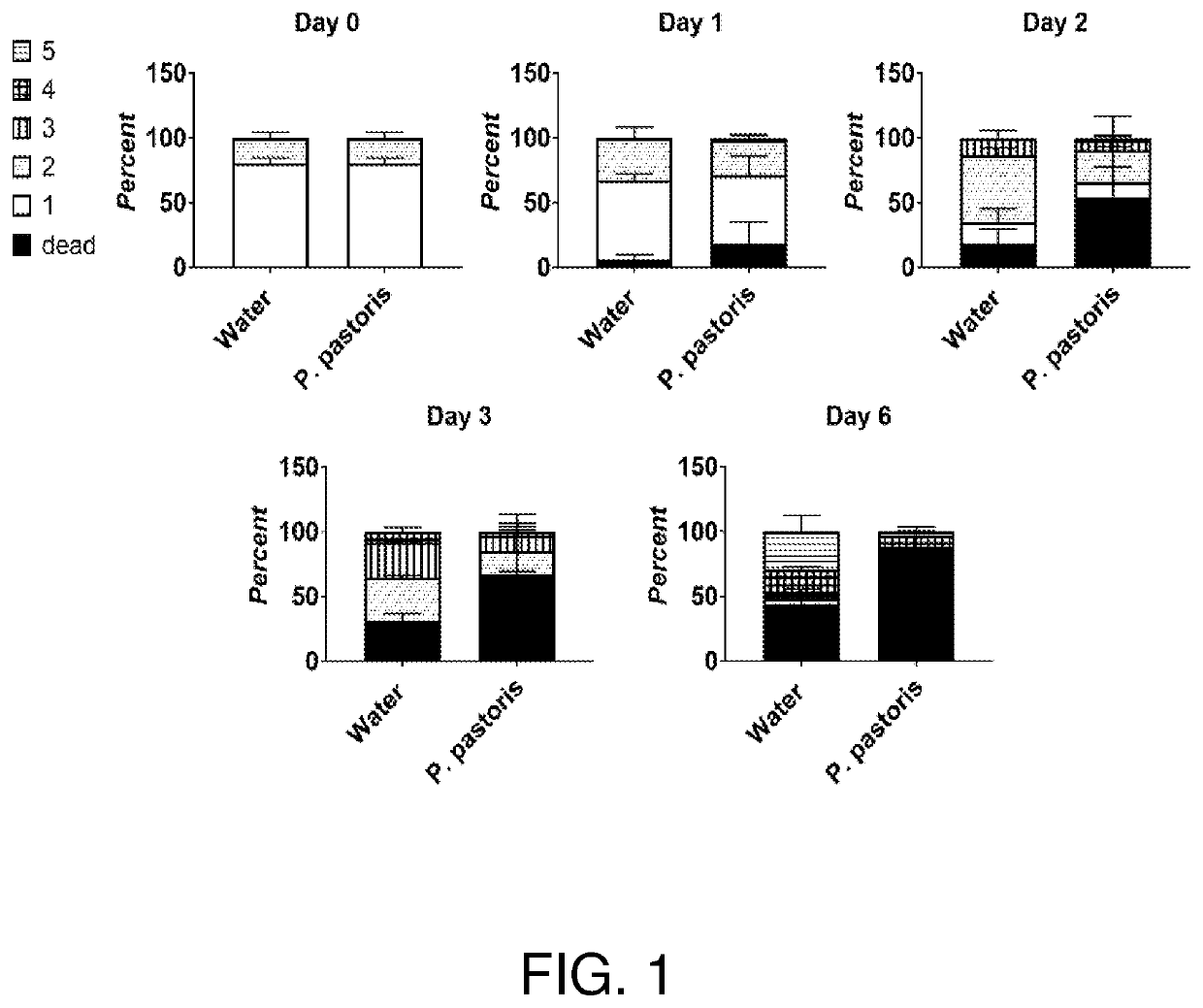
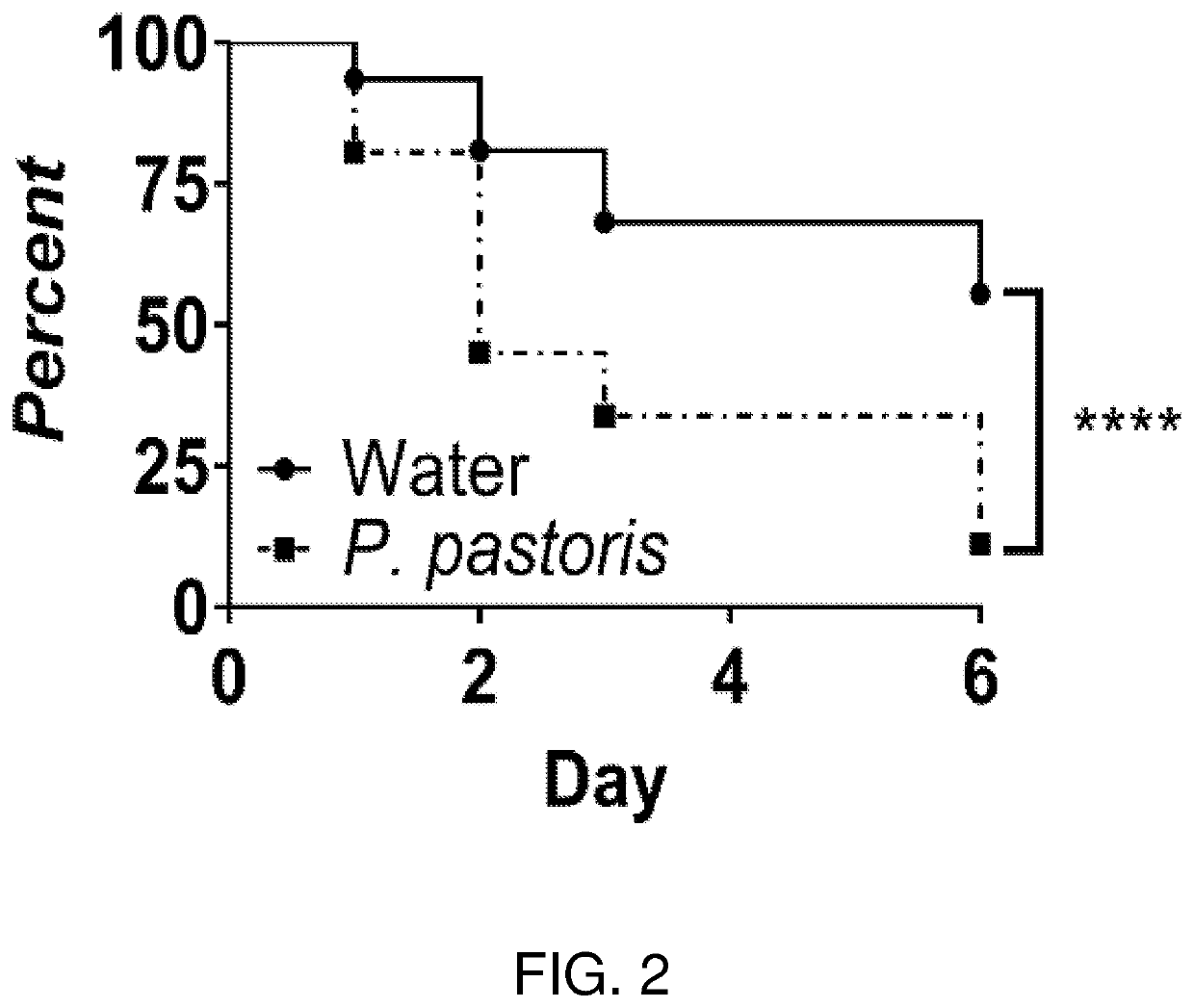
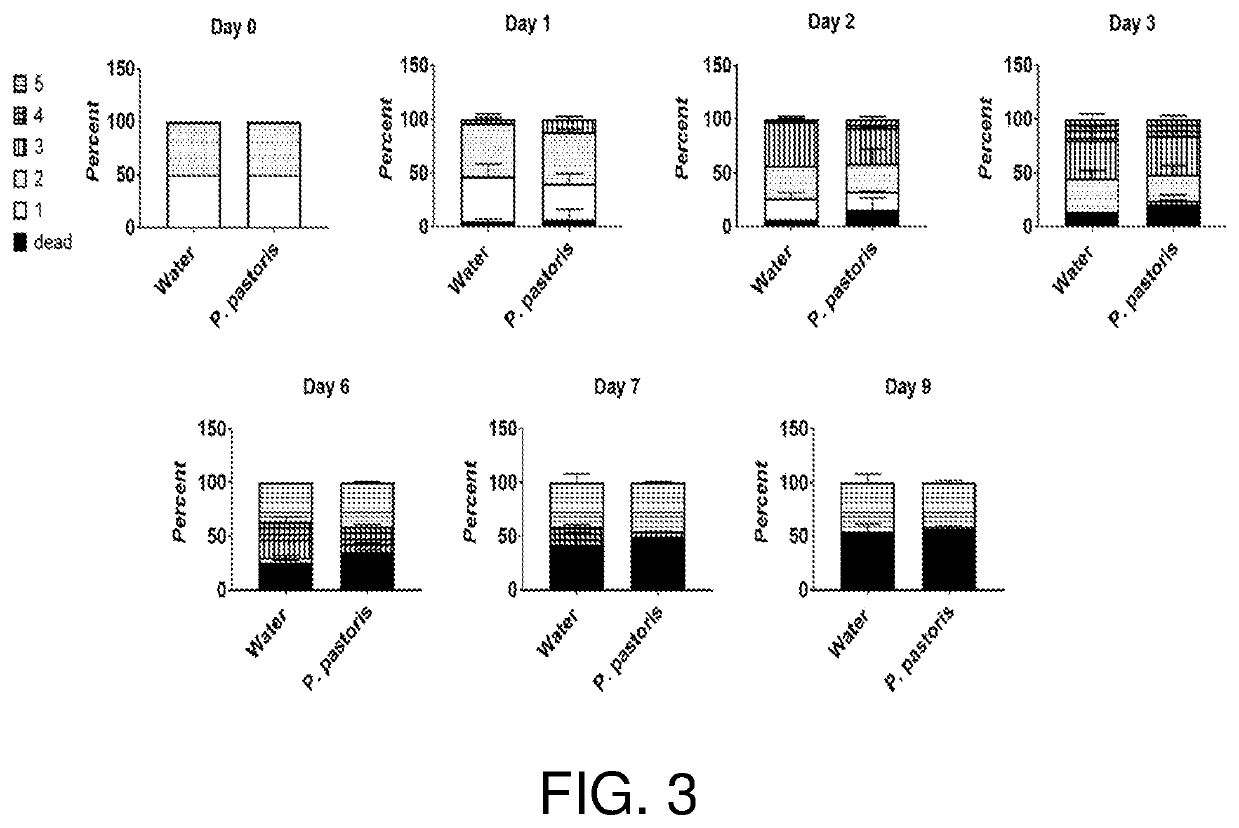
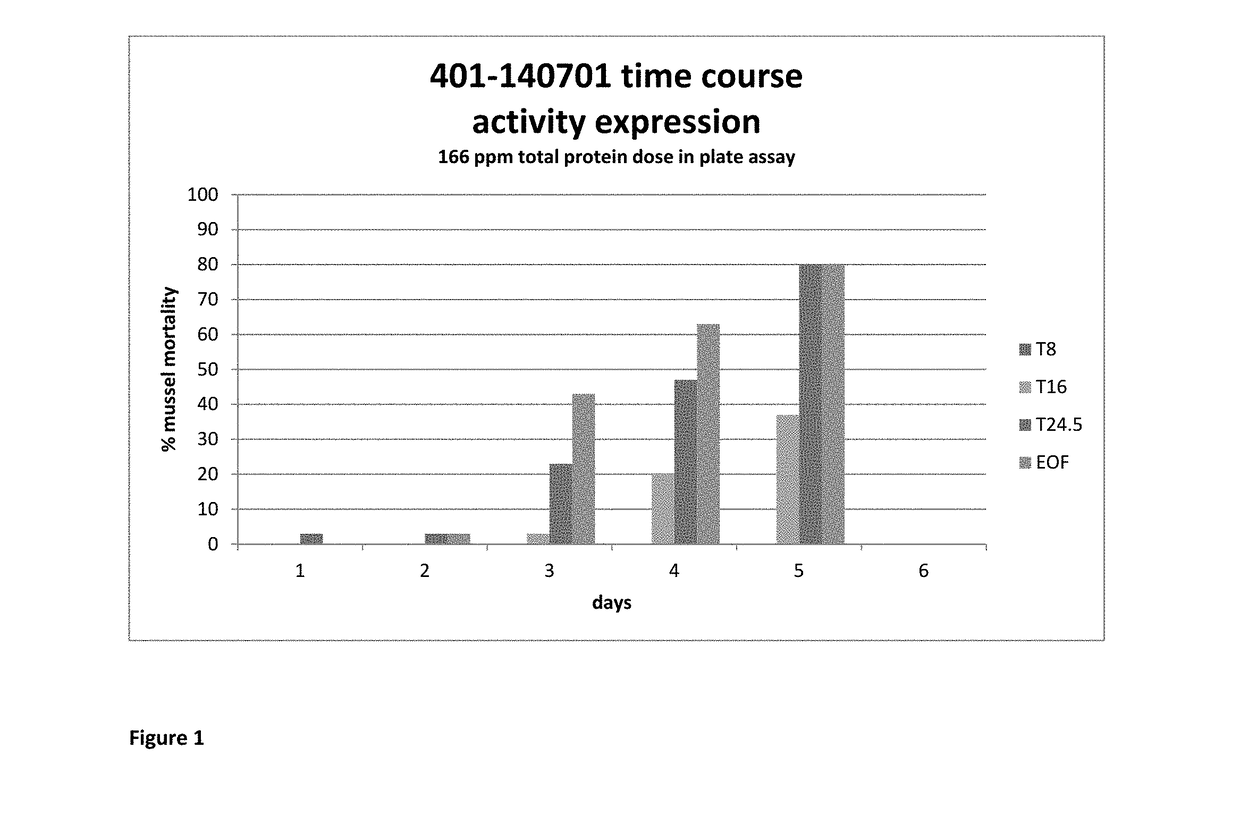
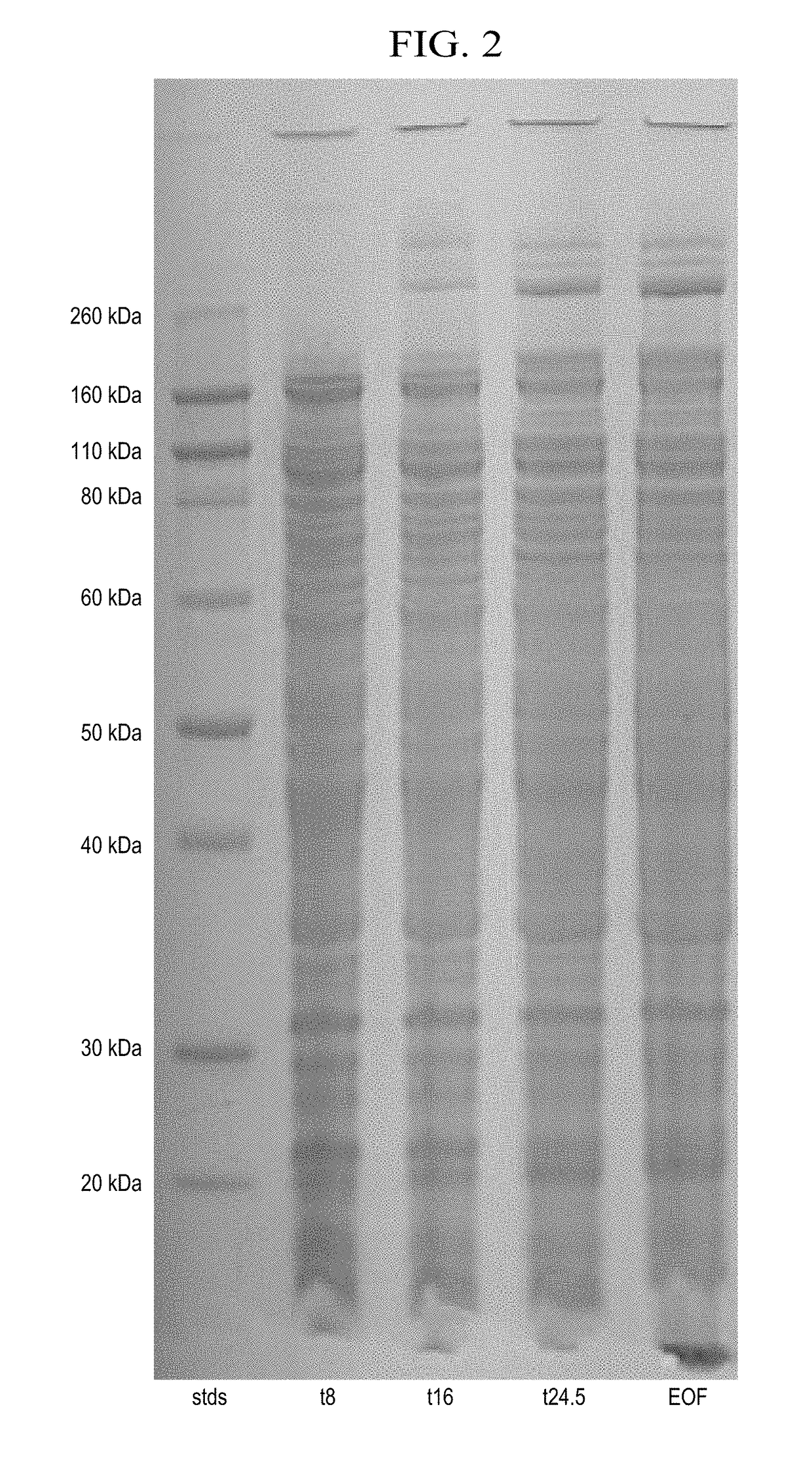
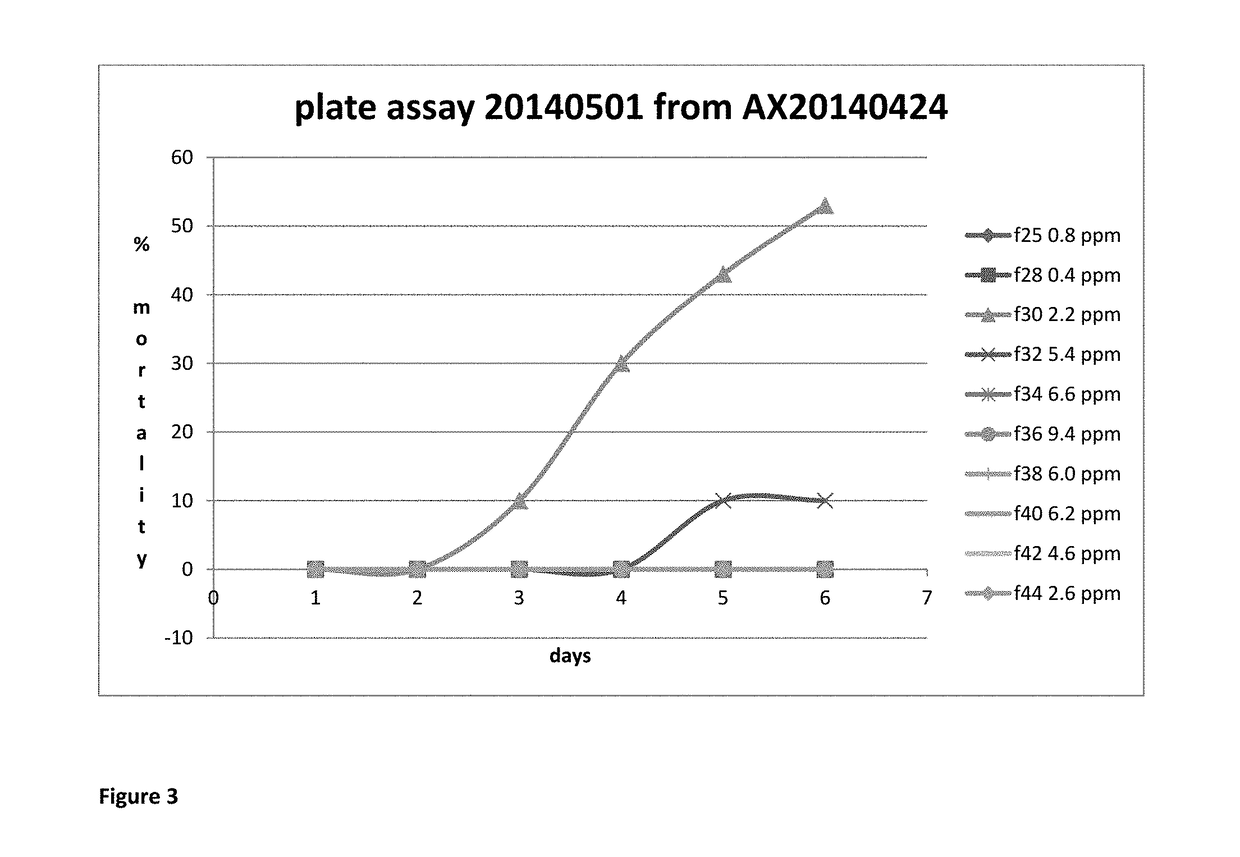
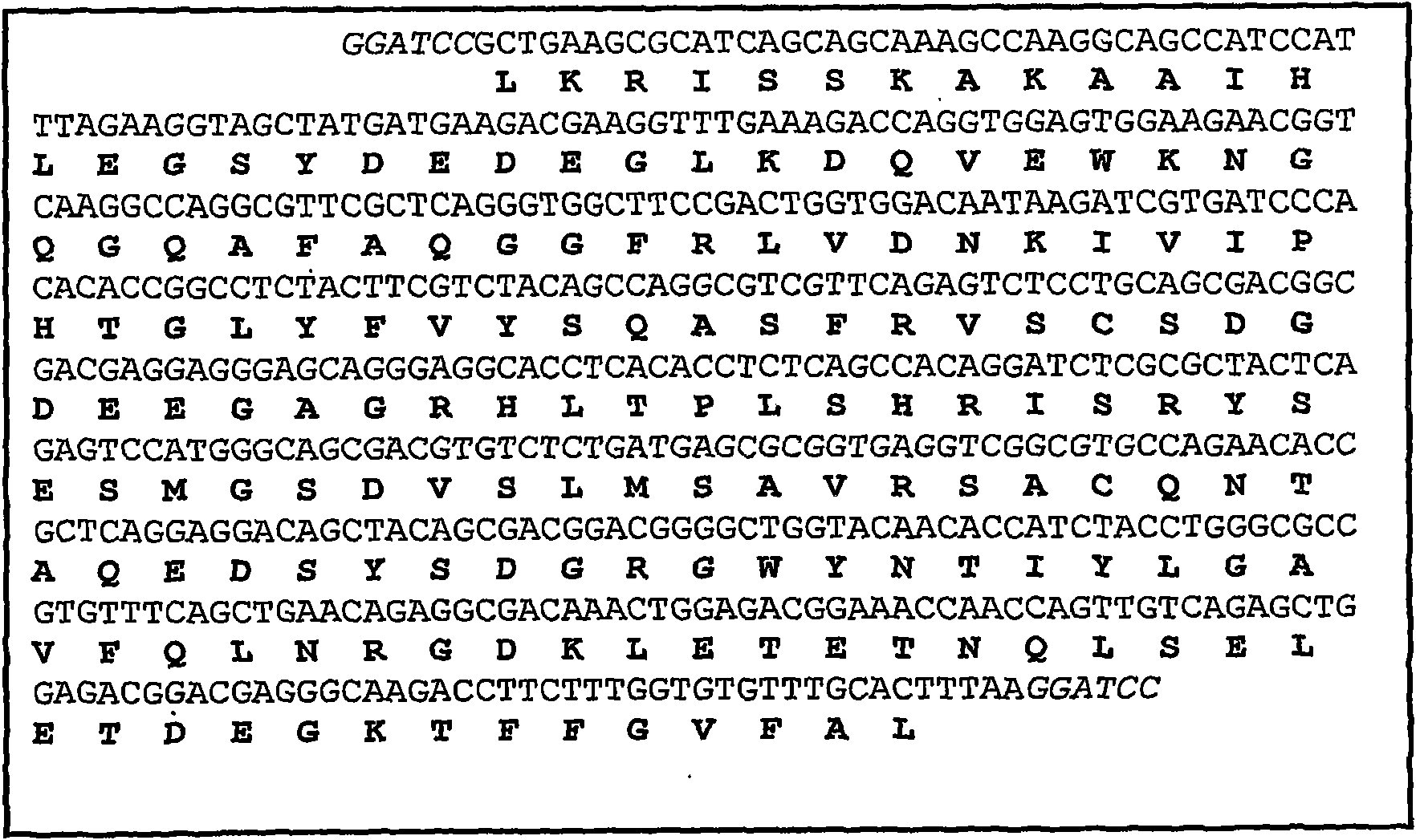
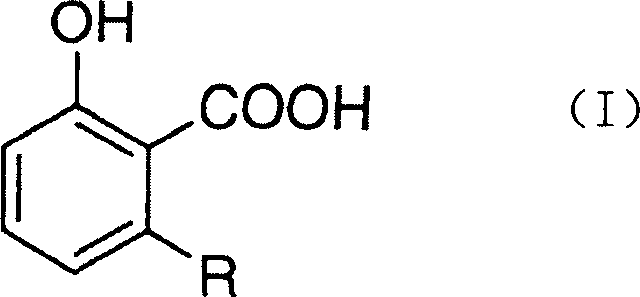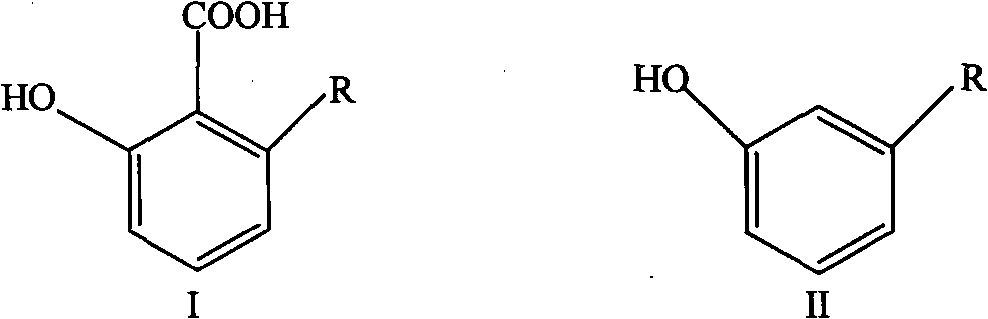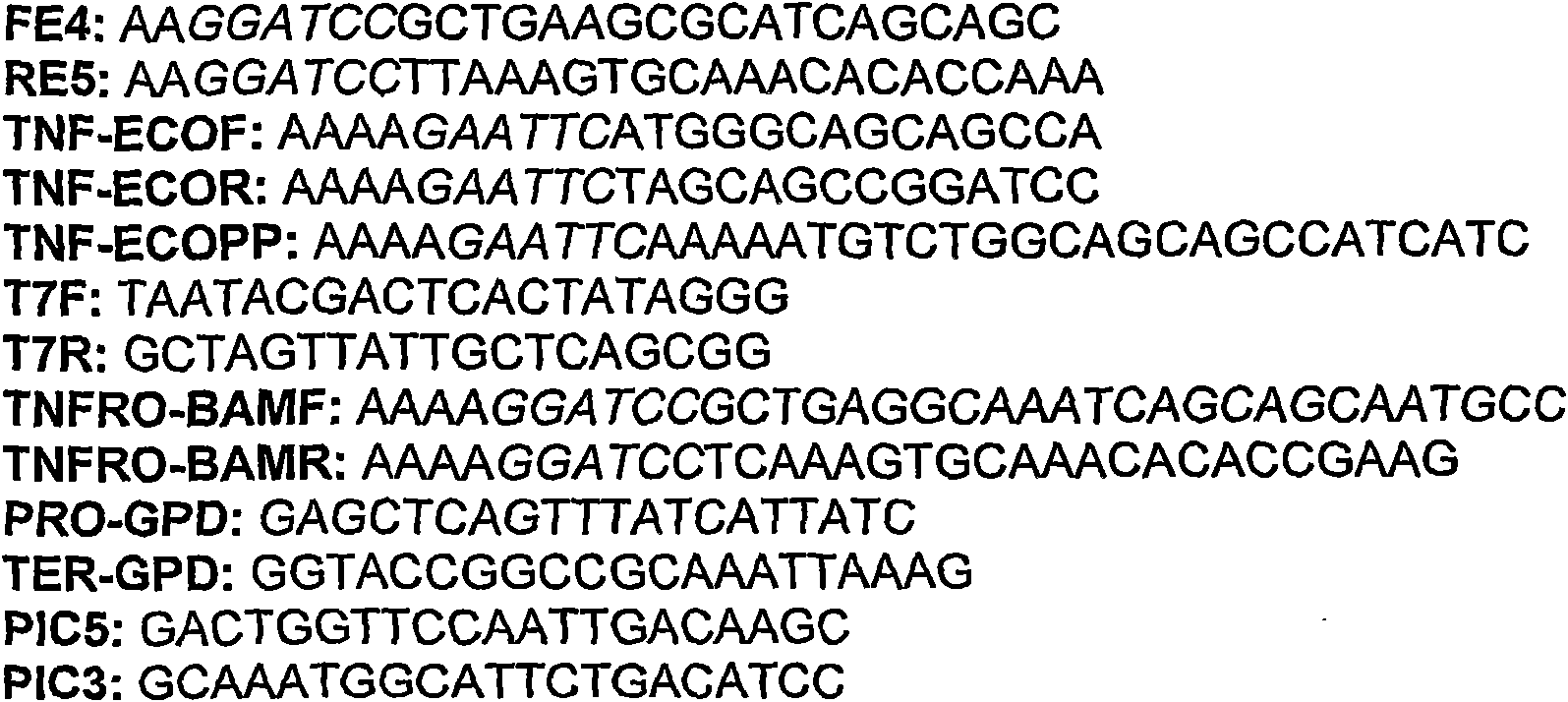Patents
Literature
37 results about "Mollicutes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mollicutes is a class of bacteria distinguished by the absence of a cell wall. The word "Mollicutes" is derived from the Latin mollis (meaning "soft" or "pliable"), and cutis (meaning "skin"). Individuals are very small, typically only 0.2–0.3 μm (200-300 nm) in size and have a very small genome size. They vary in form, although most have sterols that make the cell membrane somewhat more rigid. Many are able to move about through gliding, but members of the genus Spiroplasma are helical and move by twisting. The best-known genus in the Mollicutes is Mycoplasma.
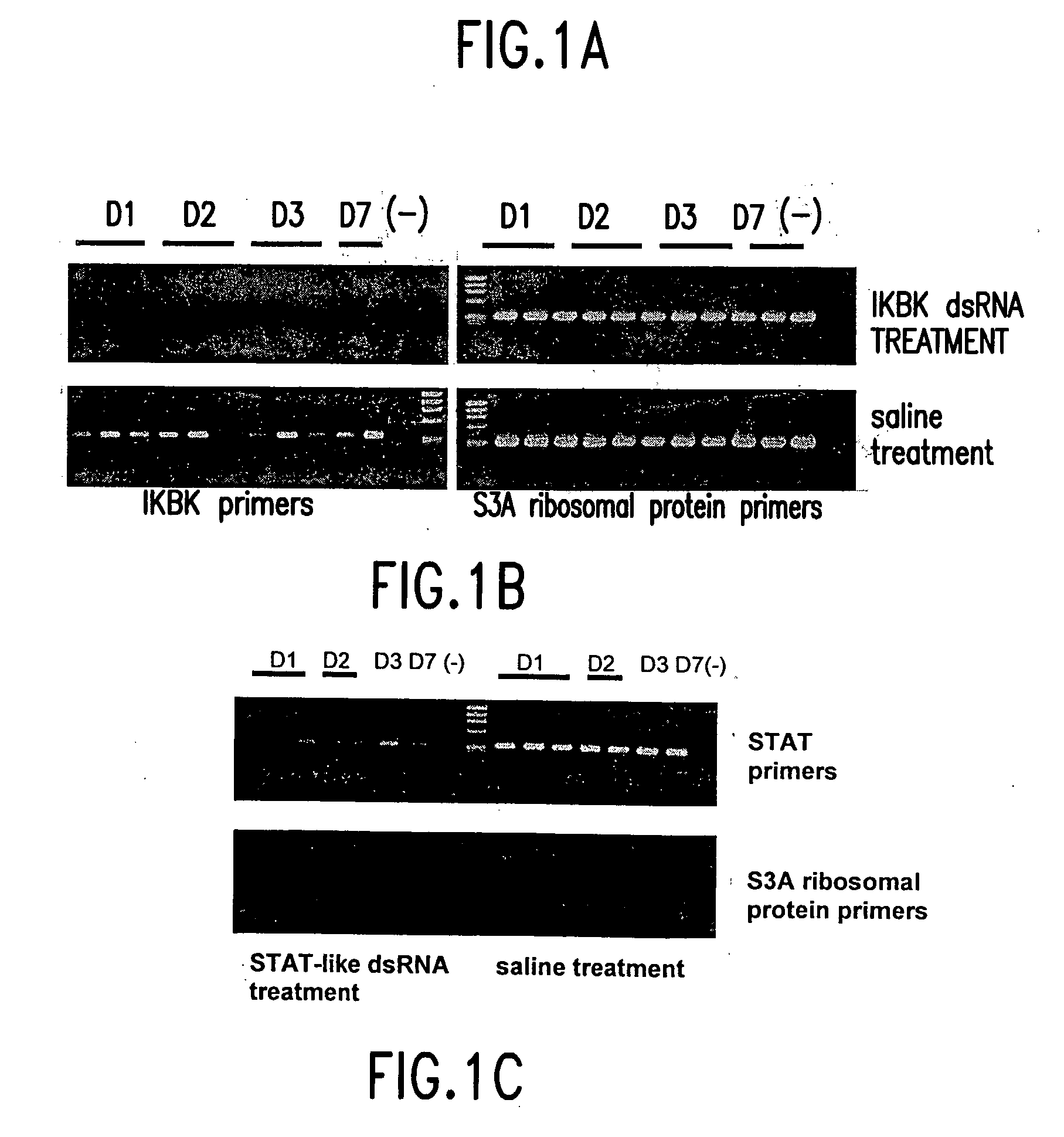
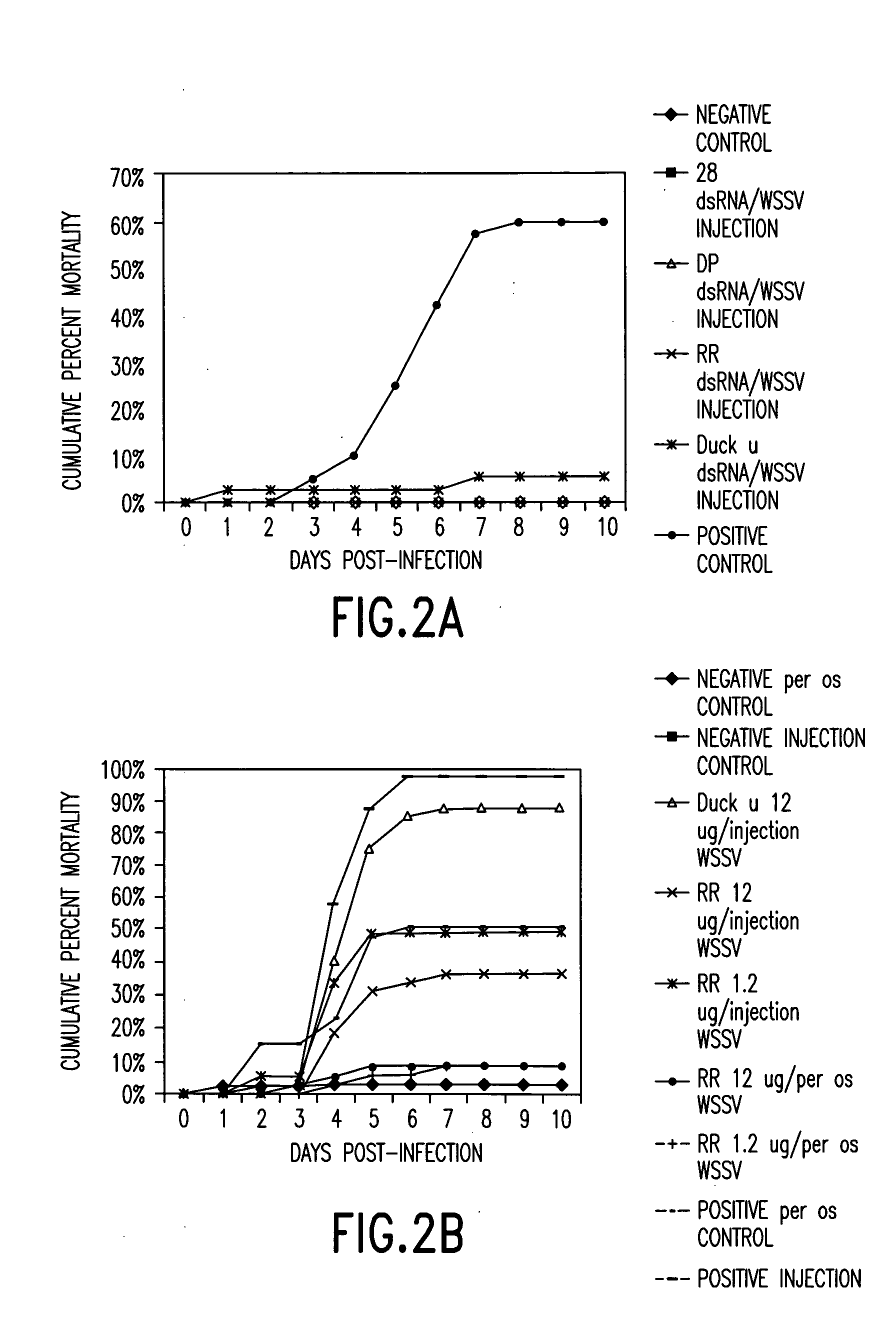
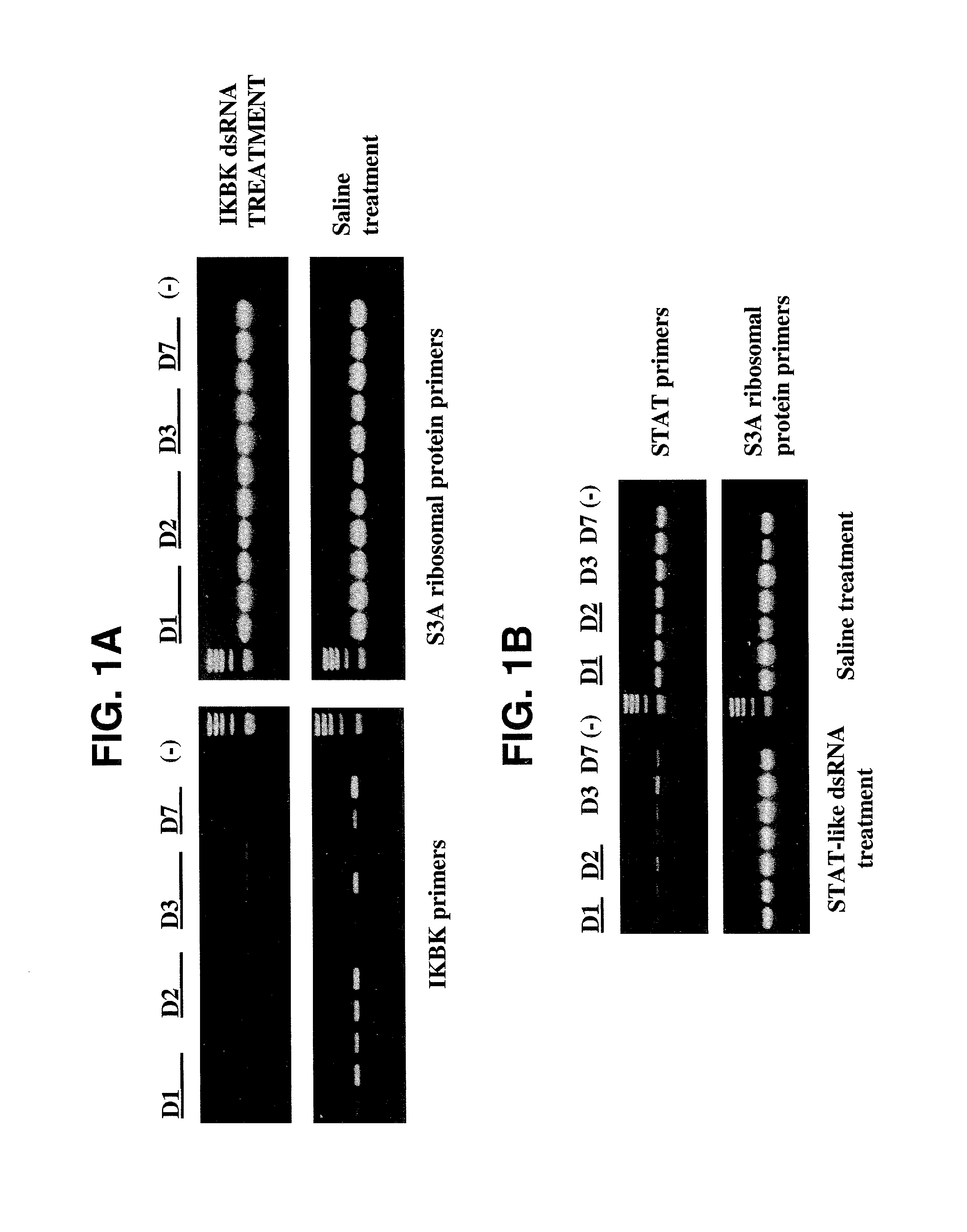
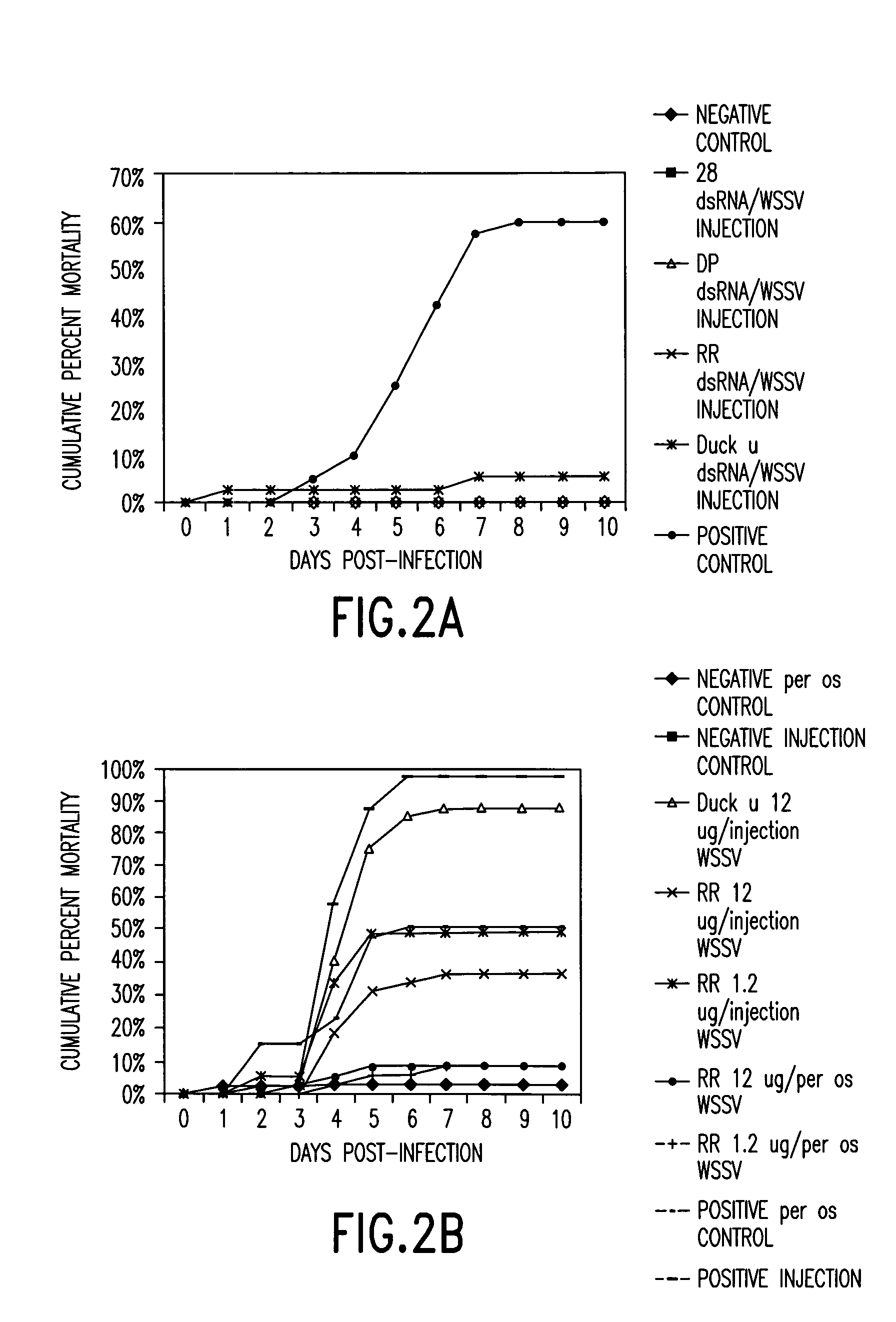
dsRNA induced specific and non-specific immunity in crustaceans and other invertebrates and biodelivery vehicles for use therein
InactiveUS20050080032A1Easy to understandGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsWhole bodyMarine invertebrates
Methods for inducing systemic, non-specific and / or sequence specific immune responses in invertebrates, e.g., marine invertebrates such as mollusks, porifera, ctenophora, echinodermas, marine worms, cnideria and preferably crustaceans, by the administration of at least one dsRNA, that confers immunity against a pathogen, or modulates expression of gene that affects growth, reproduction, and general health or "robustness" are provided. Also provided are methods of identifying invertebrate genes, e.g., crustacean genes, the expression of which is involved in the induction of non-specific (systemic) immune responses against pathogens. Also disclosed are preferred delivery systems and methods for stably administering at least one dsRNA to a crustacean whereby the dsRNA is administered via injection, immersion, in a feed or nutrient medium or comprised in a microorganism, e.g., yeast or microalgae, that expresses said dsRNA and is ingestible by said crustacean, e.g., a shrimp.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Composition for feeding prey organisms in aquaculture
InactiveUS7063855B2Increase concentrationHigh in phospholipidsBiocideAnthropod material medical ingredientsPhospholipidOrganism
A composition is for feeding aquacultural prey organisms such as Artemia and rotifiers, comprising a lipid component comprising at least 25 wt % of phospholipids and providing a DHA content of at least 30 wt %. The lipid component is preferably derived from marine organisms such as fishmeal, phytoplankton or zoo plankton biomass. The composition is used for providing prey organisms having a high content of highly-unsaturated fatty acids (HUFAs) suitable for aquaculture of fish including halibut, turbot, bass and crustaceans and molluses.
Owner:EPAX NORWAY
Cultivation of dha-rich prey organisms for aquatic species
InactiveUS6789502B2Increase successClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAquatic speciesOrganism
A method is provided for producing prey organisms such as Artermia and rotifers, for feeding aquacultural organisms in particular at the larval stage. The method comprises cultivating the prey organisms during at least part of their life cycle in an aqueous medium comprising at least one lipid component having a DHA content of at least 30 wt %. The enriched prey organisms preferably have a DHA content of at least 12 wt % of their total lipid content. The prey organisms are suitable feed for larvae of fish including halibut, turbot, bass, and flounder, and crustaceans and molluscs.
Owner:EPAX NORWAY
Crustacean Expression Vector
Methods and constructs for genetic manipulation of one or more of shrimp, shellfish, mollusks, and fish are disclosed. The nucleic acid construct includes a promoter and an internal ribosome entry site of an insect picomavirus, such as a cricket paralysis-like picomavirus. One or more open reading frames can be operably associated with one or both of the promoter and the internal ribosome entry site, and one or more proteins or protein subunits can be expressed upon introduction of the construct into a host cell, such as into a shrimp. Method for producing immortalized crustacean cell lines using enhancer elements derived from shrimp and / or shrimp viruses are also described.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Bacteriophages useful for the prophylaxis and therapy of vibrio anguillarum
InactiveUS20140105866A1Infection controlEasy to applyBiocideMicroorganismsBacteroidesVibrio anguillarum
An isolated strain of bacteriophage, specific against bacteria belonging to the Vibrio genre, particularly the anguillarum species, deposited on 3 Oct. 2012 at the Polish Collection of Microorganisms (PCM) of the Ludwik Hirszfeld Institute of Immunology and Experimental Therapy of the Polish Academy of Sciences, with access number F / 00072, characterized in that said strain is efficient in the prophylaxis, control and / or treatment of the infection caused by Vibrio anguillarum in all types of species of fish, mollusks and crustaceans that are important for aquaculture susceptible to this bacteria, genome size 48.6 Kb, it is not sensitive to chloroform and its storage temperature is −80° C.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHILE
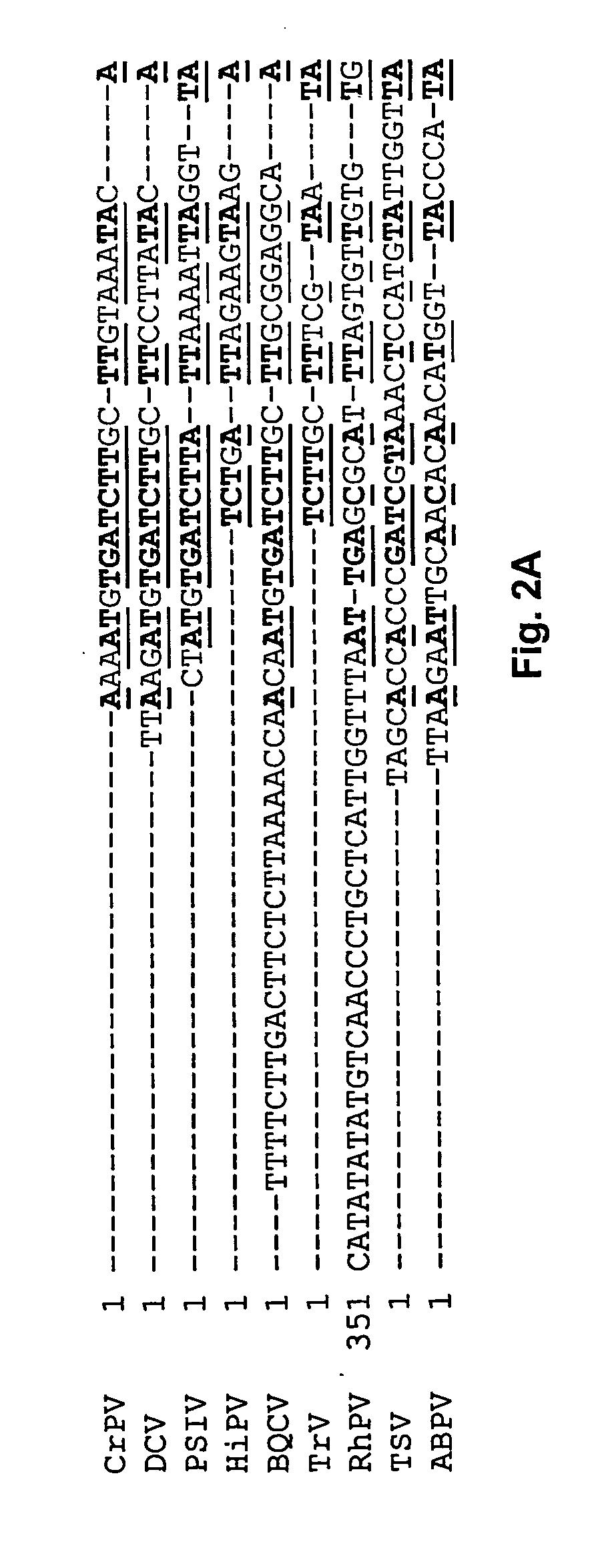
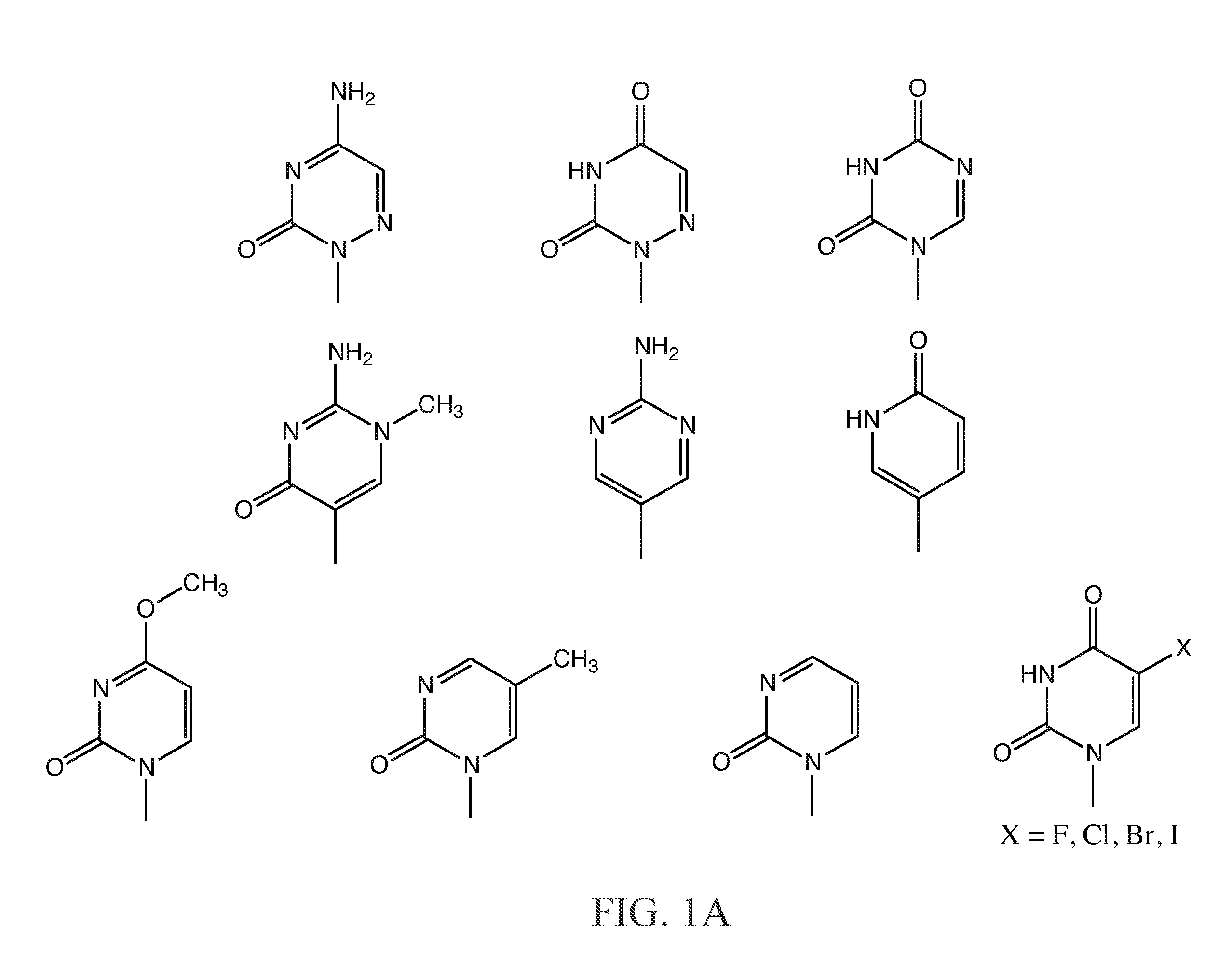
PNA probes, mixtures, methods and kits pertaining to the determination of Mycoplasma and related Mollicutes
This invention is related to PNA probes, probe sets, mixtures, methods and kits pertaining to the determination of Mycoplasma and related Mollicutes.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
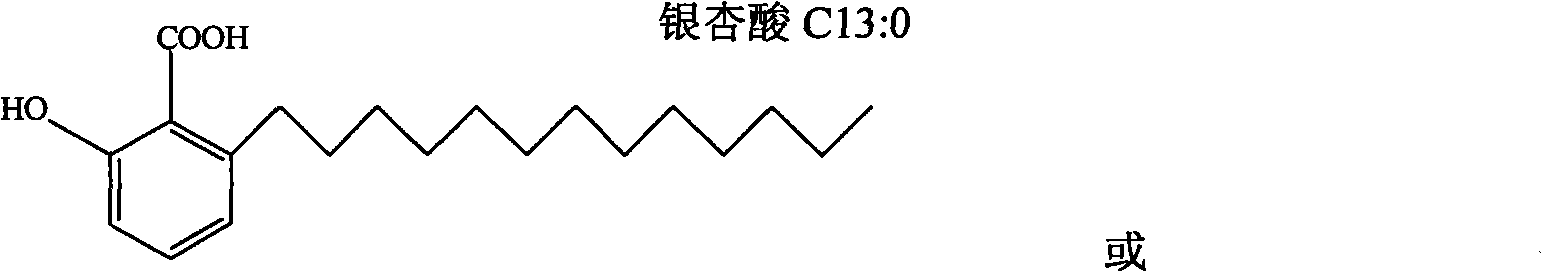
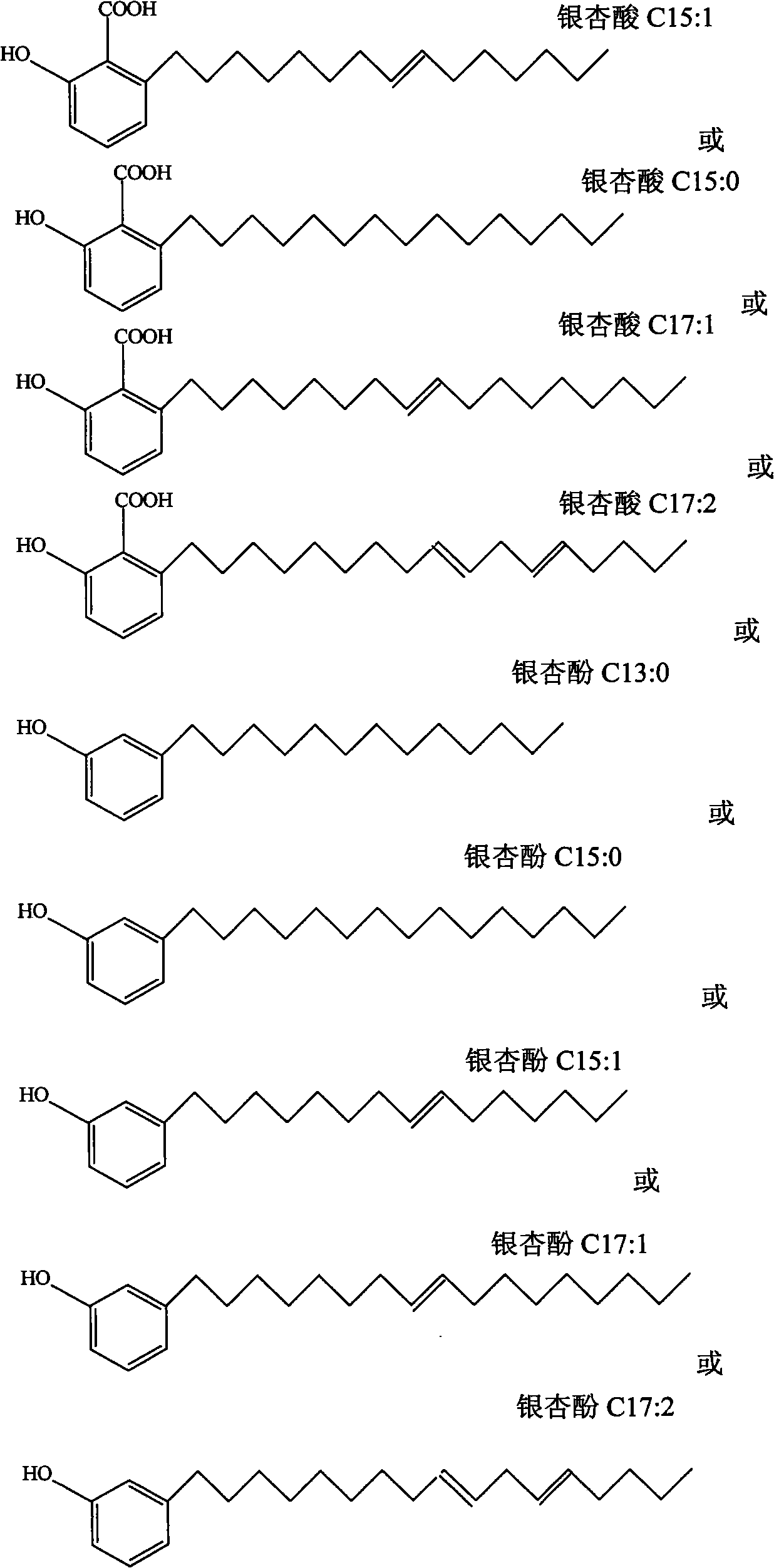
Use of ginkgoic acid in preparation of biological pesticide for killing Oncomelania snail and preventing schistosomiasis
InactiveCN1806544AEfficient killingPrevention of schistosomiasisBiocideMolluscicidesOncomelaniaPhosphorylation
The invention relates to the use of ginkgoic acid in preparation of biological pesticide for killing Oncomelania snail and preventing schistosomiasis, wherein experiment result shows that, the ginkgolic acid can effectively inhibit key enzyme and de-coupling reaction to mitochondria oxidation phosphorylation in mollusk energy supply biochemical metabolism, effectively inhibit tyrosinase during insect exuviation procedure and prostaglandin synthetase during breeding process, thus can eradicate unwanted mollusk harming agronomic crops.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Application of ginkgoic acid and ginkgol compounds to killing Ampullaria gigas
InactiveCN101911938AEfficient killingPlay a role in preventing its harmBiocideMolluscicidesAcute toxicity testingRespiratory chain
The invention belongs to the technical field of biopesticides, discloses application of ginkgoic acid and ginkgol compounds to killing agriculturally harmful mollusks, and discloses novel application of the ginkgoic acid and ginkgol to preparation of the biopesticides. The invention shows that the ginkgoic acid and ginkgol compounds can effectively inhibit the synthesis of glycogen and protein inmollusk ampullaria gigas, can simultaneously inhibit the activities of ChE, SDH and MDH in the cephalopodium and the liver of the ampullaria gigas, interfere a NADH respiratory chain and cause energymetabolic dysfunction so as to cause cell energy supply deficiency and unattainability of normal synthesis and secretion functions, and promote the lack of important proteins and enzymes in the body of the ampullaria gigas so as to cause the death of the ampullaria gigas. The ginkgoic acid and the ginkgol are readily degradable in the natural environment, and have small influence on the environment; and an acute toxicity test proves that the ginkgoic acid and the ginkgol are proved to be slightly toxic pesticides, can be developed into novel biopesticides, and can be used for preventing the ampullaria gigas for rice, vegetables and fruits.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Artificial material conducive to attract and grow oysters, mollusks or other productive and/or stablizing organisms
InactiveUS20070107663A1Easy to set upPromote growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOysterArtificial materials
Structures constructed from an artificial material facilitate the setting and growing of oysters, other mollusks, and other organisms for the purposes of food production, artificial reefs / breakwaters, and the like. The artificial material is a composite that acts as both an attractant and nutrient environment for mollusks and other aquatic organisms. The binder for the composite material includes both cement and an organic material. The organic material is selected to attract and feed the aquatic organisms.
Owner:ORA TECH
Methods for controlling molluscs
ActiveUS20050281854A1Easy to useWithout fear of non-target toxicityBiocidePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCelluloseCompanion animal
Novel materials for controlling molluscs, such as snails and slugs, using carbohydrates including celluloses, hemi-cellulose complexes, and / or lignin, for inducing death in molluscs. The materials are non-toxic, will not contaminate a drinking water supply, will not harm fish, birds or wild life, will not cause any harmful effects if swallowed or absorbed through the skin, will not harm children or pets, and can be safely eaten by domestic animals and livestock that may consume such dead molluscs. The materials may be applied in various formulations at various water contents. The materials do not provide nutrition to the molluscs, and disrupt normal bodily functions resulting in death. An attractant may be included to encourage ingestion by the molluscs.
Owner:VERDESIAN LIFE SCI
Application of alien invasive plant Ambrosia artemisiifolia in control of golden apple snail
ActiveCN103004892AEasy accessSimple and fast operationBiocideMolluscicidesResource utilizationPomacea canaliculata
The invention belongs to the environment-friendly technical field of snail-killing plant resource utilization, and particularly relates to a method of utilizing an alien invasive plant Ambrosia artemisiifolia to control a harmful mollusc golden apple snail which invades South China. The method comprises the step of adding dried powders of the alien invasive plant Ambrosia artemisiifolia to directly control the golden apple snail, and is characterized in that 1) the utilized plant is Ambrosia artemisiifolia (asteraceae); and 2) the dosage of the dried powders of Ambrosia artemisiifolia is 10 g / L. The method has the advantages that the plant material which is Ambrosia artemisiifolia is a common alien invasive plant in South China, so that the plant is easily obtained, and under a certain dosage, the golden apple snail can be effectively controlled.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
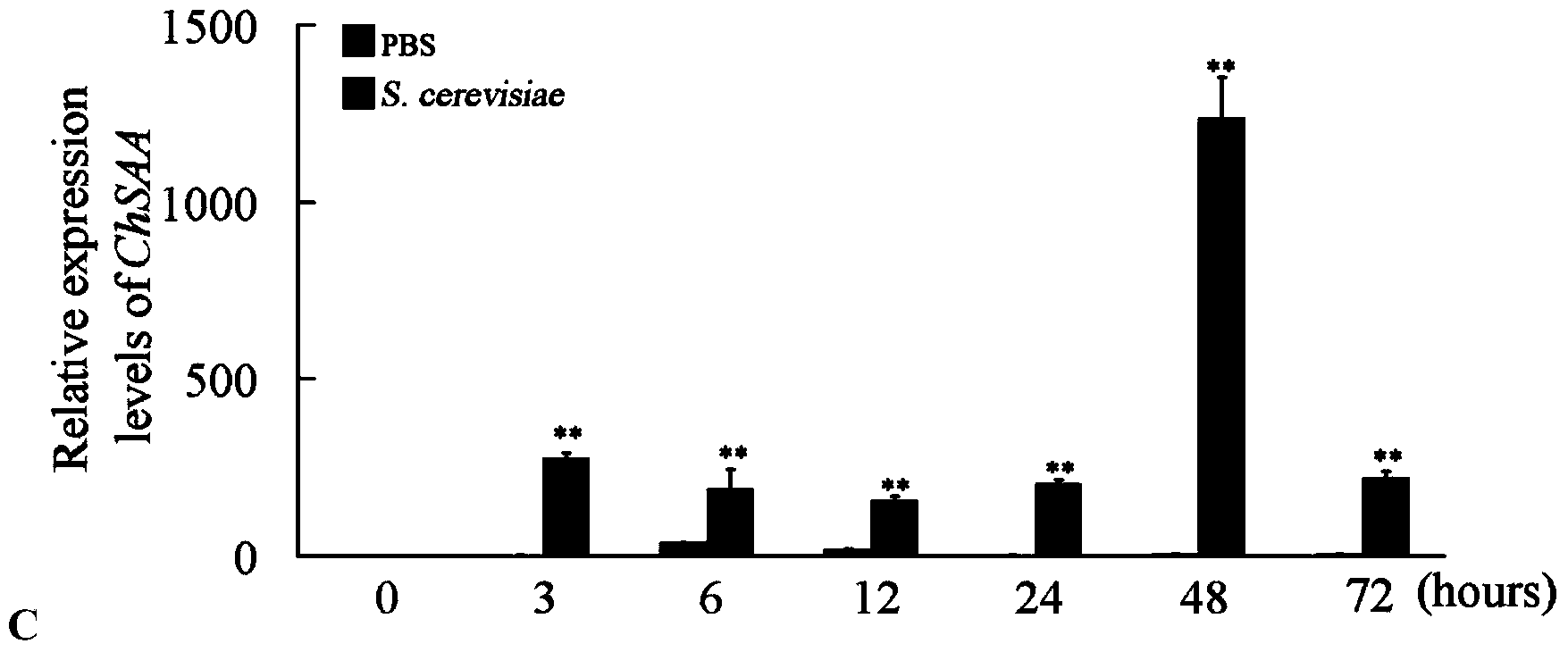
Serum amyloid A (SAA) protein and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103834663AEnhance germplasm innovation abilityPositive and Accurate Warning SignalsApolipeptidesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMammal
The invention discloses a serum amyloid A (SAA) protein and an encoding gene and an application thereof. The serum amyloid A protein is characterized in that a nucleotide sequence of the serum amyloid A protein is as showed in the 148-567th basic groups of SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the serum amyloid A protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The gene is firstly discovered in a mollusk, and at present, the gene is discovered in vertebrates and is only discovered in an echinodermata in invertebrates. The quantitative PCR experiment proves that the oyster SAA is remarkably up-regulated after bacterial infection and is similar to a mammal, and thus the gene is utilized as a gold standard for detecting the oyster physical condition. The gene can monitor the physical condition of the oyster at any time by detection, a positive accurate caution signal is provided for the oyster disease prevention, and the expansion of a disaster is prevented. The application of the technology has the advantages that the germplasm innovation capability of the cultivated shellfish is further improved, and the efficient sustainable development of an industry is supported.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anti-viral nutraceutical
A method for the prophylaxis or treatment of a viral infection in a mammal is described. The method comprises administering to the mammal an effective amount of a mollusc hemocyanin and / or an active fragment thereof. The hemocyanin may be an abalone hemocyanin.
Owner:MARINE BIOTECH AUSTRALIA
dsRNA induced specific and non-specific immunity in crustaceans and other invertebrates and biodelivery vehicles for use therein
InactiveUS8633028B2Good curative effectGood effectAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsWhole bodyMarine invertebrates
Methods for inducing systemic, non-specific and / or sequence specific immune responses in invertebrates, e.g., marine invertebrates such as mollusks, porifera, ctenophora, echinodermas, marine worms, cnideria and preferably crustaceans, by the administration of at least one dsRNA, that confers immunity against a pathogen, or modulates expression of gene that affects growth, reproduction, and general health or “robustness” are provided. Also provided are methods of identifying invertebrate genes, e.g., crustacean genes, the expression of which is involved in the induction of non-specific (systemic) immune responses against pathogens. Also disclosed are preferred delivery systems and methods for stably administering at least one dsRNA to a crustacean whereby the dsRNA is administered via injection, immersion, in a feed or nutrient medium or comprised in a microorganism, e.g., yeast or microalgae, that expresses said dsRNA and is ingestible by said crustacean, e.g., a shrimp.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
PNA Probes, Mixtures, Methods And Kits Pertaining To The Determination Of Mycoplasma and related Mollicutes
InactiveUS20110111393A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBioinformaticsMollicutes
Owner:HYLDIG NIELSEN JENS J +4
Orally administrable immunostimulant product for aquaculture
InactiveCN102209530AMaintain propertiesKeep alivePeptide/protein ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffMicroorganismRecombinant Cytokines
An orally administrable immunostimulant product comprises a microencapsulated cytokine and an enteric protection polymer to protect the cytokine, the cytokine is a fish, mollusc or crustacean cytokine, preferably a recombinant cytokine such as tumor necrosis factor a (TNFa) over-expressed in a host microorganism.
Owner:PROBELTE PHARMA
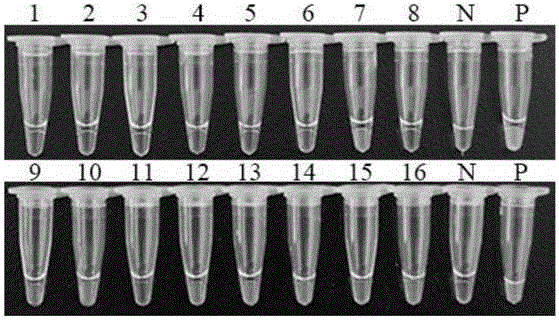
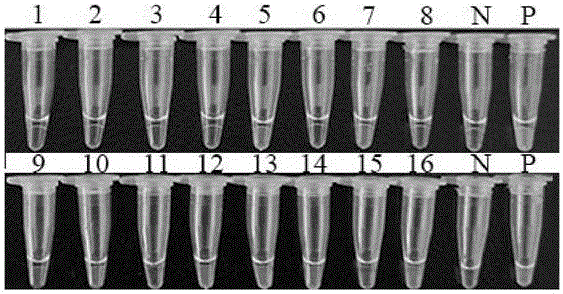
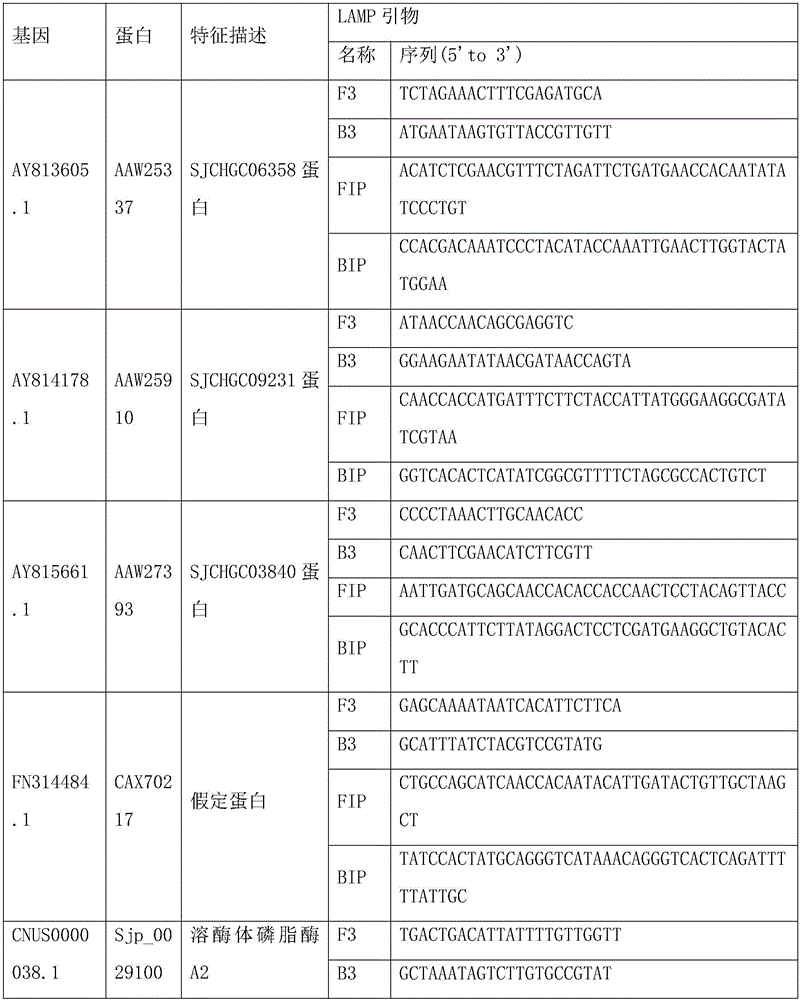
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method based on cercaria-stage gene of schistosoma japonicum katsurada
InactiveCN106636439AQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementOncomelaniaCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention belongs to the technical field of detection of cercaria-stage gene of schistosoma japonicum katsurada and particularly relates to a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method based on the cercaria-stage gene of the schistosoma japonicum katsurada. The LAMP method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a schistosoma japonicum katsurada animal model and collecting a schistosoma japonicum katsurada sample; secondly, preparing a template DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid): collecting ultrapure water subjected to oncomelania inoculation, transferring in a centrifugal pipe, and centrifuging under the condition of 1000 to 5000r / min for 5 to 20 minutes; removing supernate, extracting cercaria genome DNA from precipitation by using a blood / cell / tissue genome DNA extraction kit, pulverizing infected oncomelania, collecting oncomelania meat and internal organs, extracting oncomelania genome DNA by using a mollusk genome DNA extraction kit, and putting the extracted cercaria genome DNA and the oncomelania genome DNA at the temperature of 20 DEG C for later use; thirdly, determining a candidate gene: selecting a plurality of predicted protein genes of the cercaria stage of schistosoma japonicum katsurada as target genes; fourthly, designing and synthesizing an LAMP primer; fifthly, configuring the LAMP primer; sixthly, carrying out LAMP detection on the cercaria stage and the infected oncomelania genome DNA.
Owner:HUBEI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE
Anti-cancer combination therapy
InactiveUS20110065663A1Restore cytotoxicityUseful in treatmentBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsCytosineMedicine
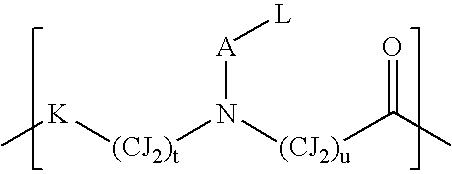
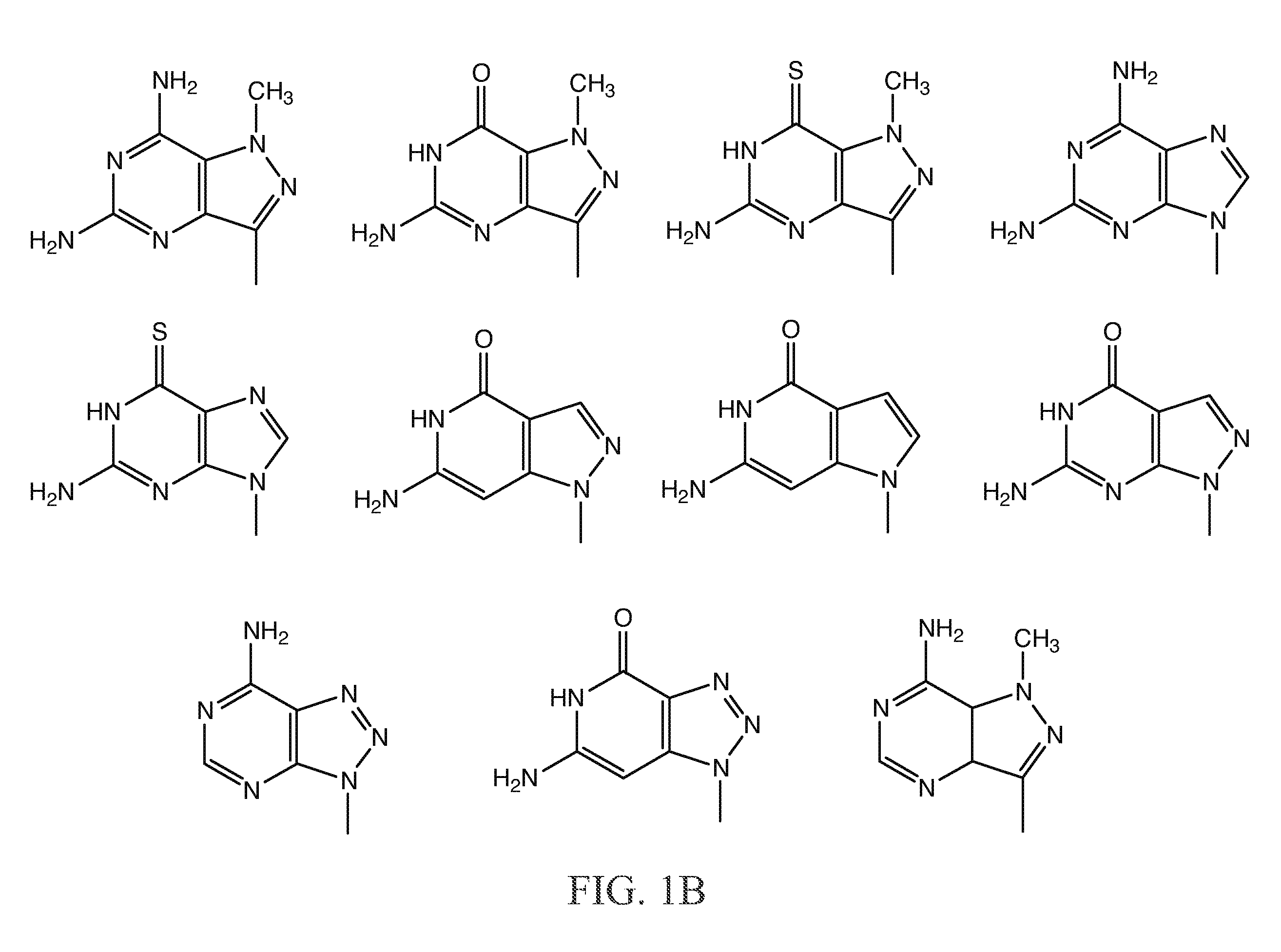
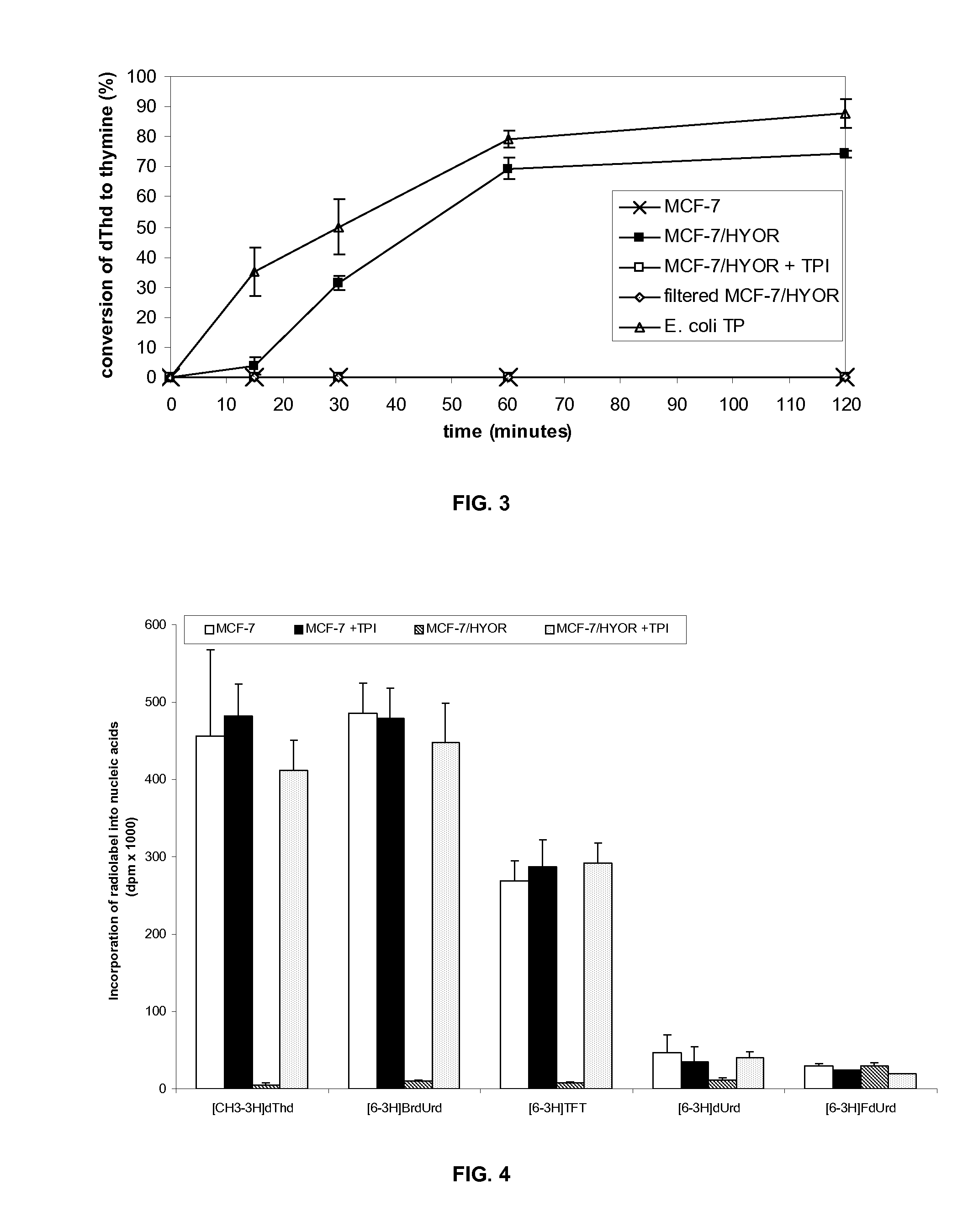
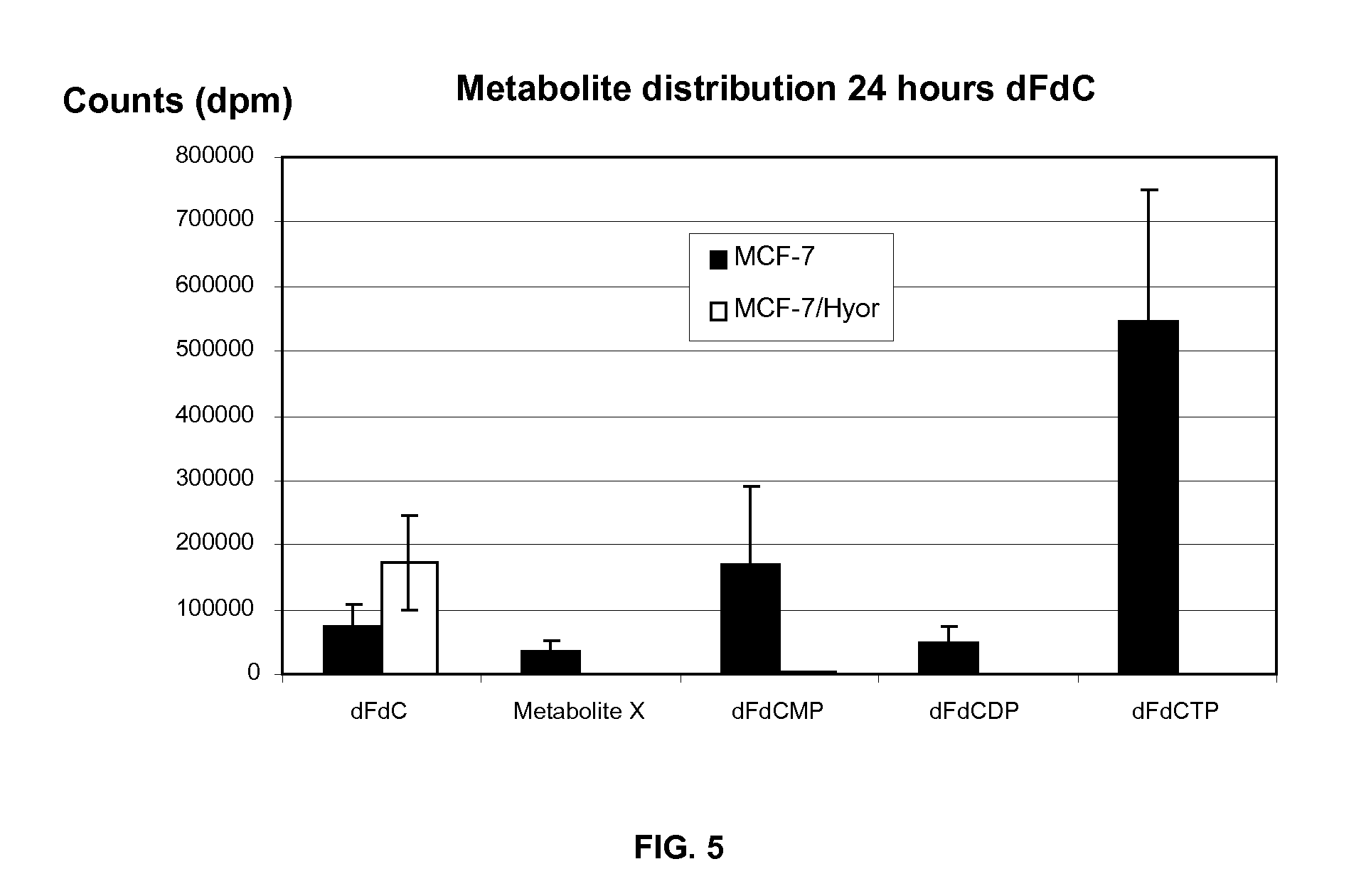
The present invention relates to a combination of therapeutic agents comprising: (a) a cytosine-based anti-cancer drug and / or a purine-based anticancer drug and (b) a therapeutic agent selected from the group consisting of thymidine phosphorylase inhibitors, and antibiotics against Mollicutes bacteria. The present invention also relates to the simultaneous, separate or sequential use of said combination for the treatment of cancer in mammals, especially in humans. The present invention also relates to methods of treatment of cancer, preferably in mammals infected with Mollicutes bacteria.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Novel retroelement found in mollusks
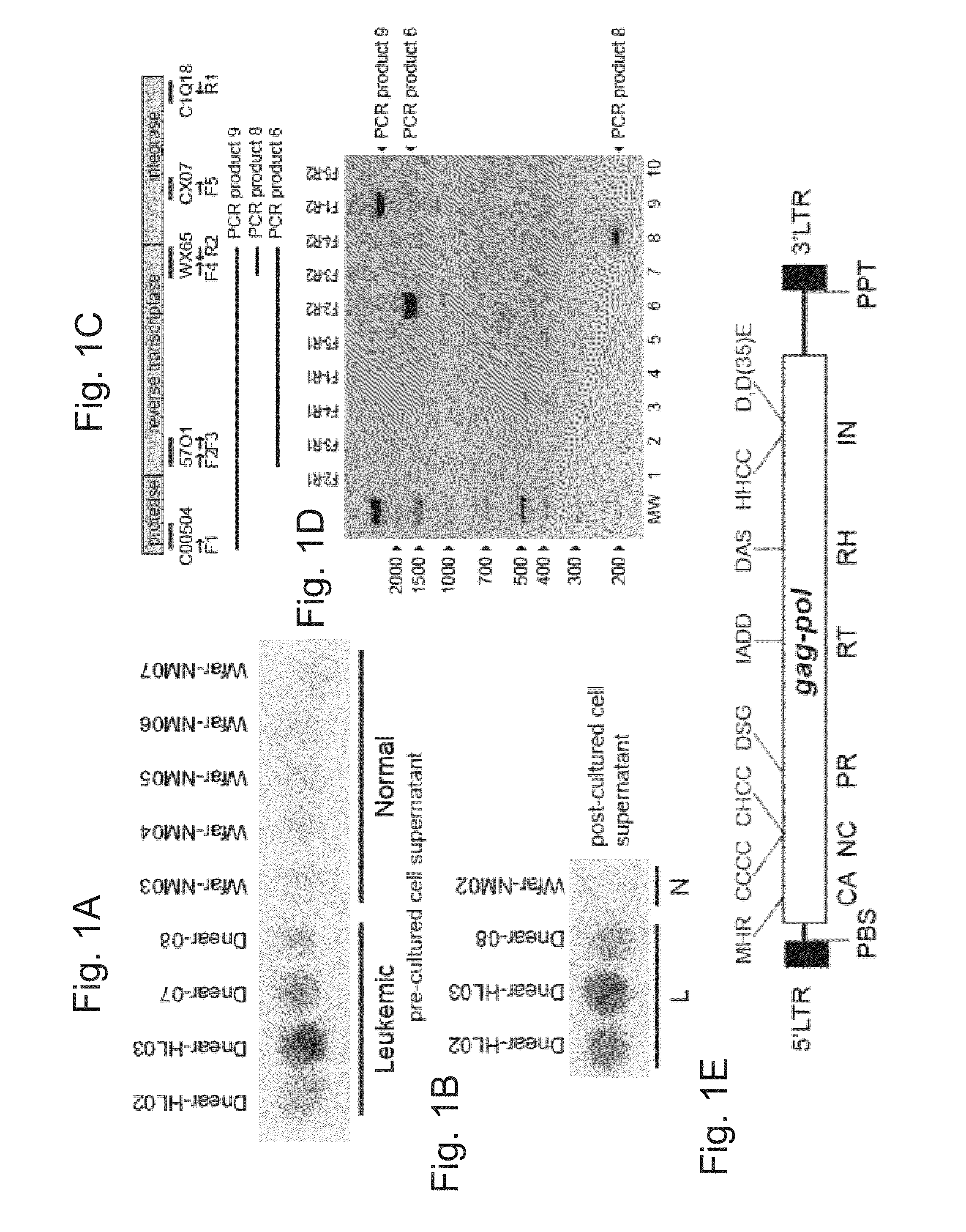
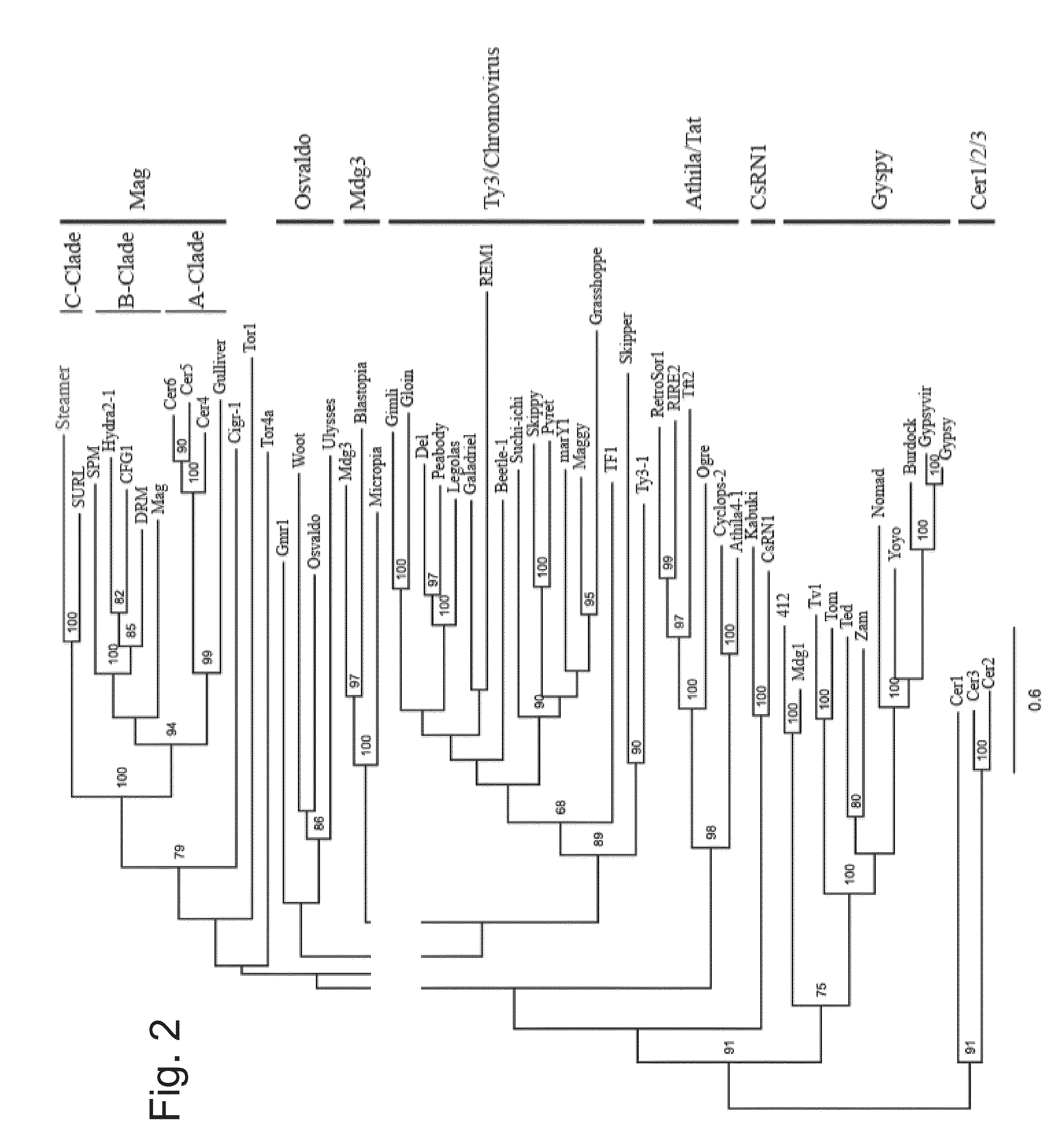
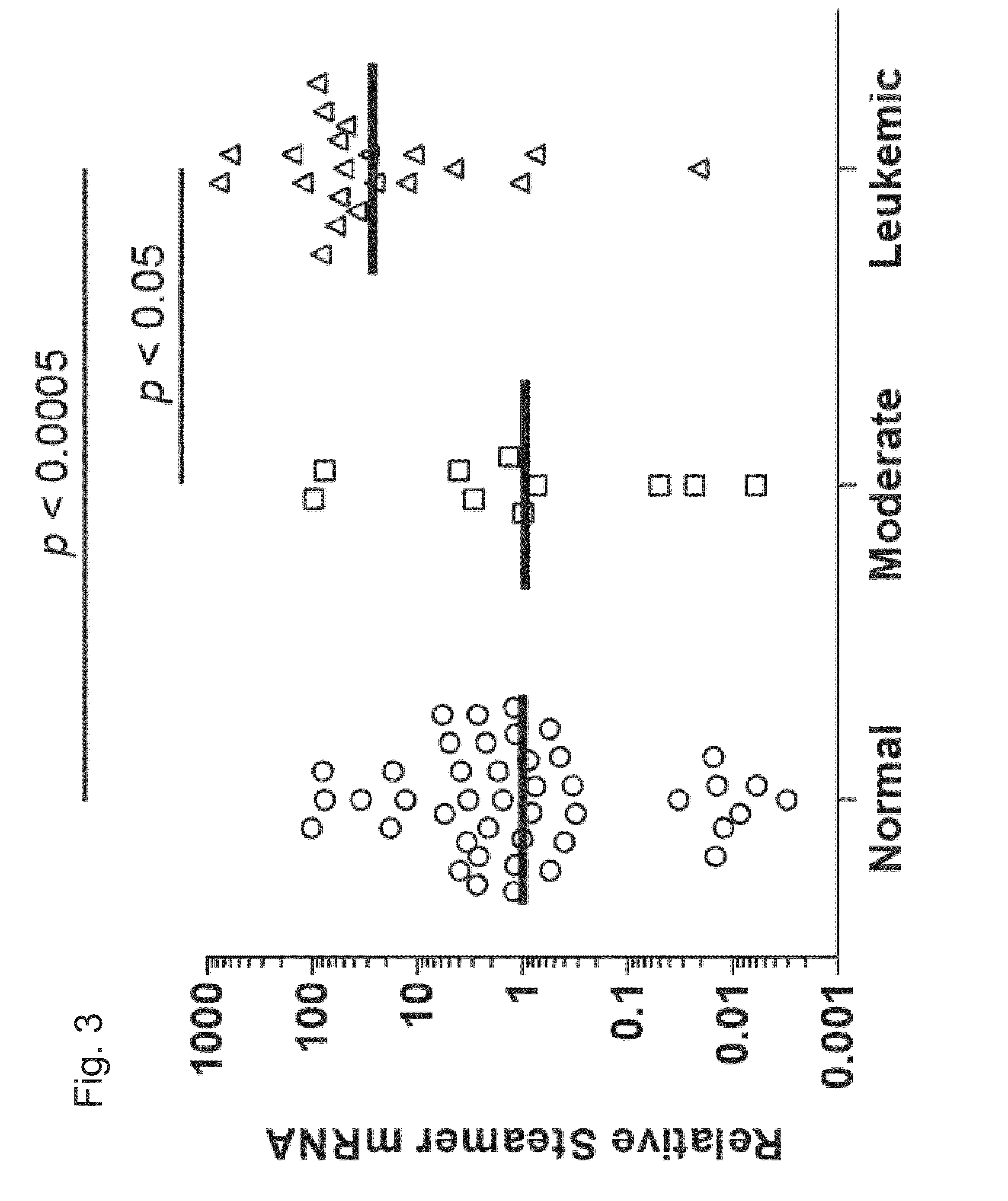
This invention relates to a novel retroelement, named “Steamer”, found in mollusks, more specifically Mya arenaria, that is associated with haemic neoplasia in these organisms. Haemic neoplasia (HN) is a recognizable leukemic-like disease.The invention provides the retroelement protein, antibodies to the protein, nucleic acids encoding the protein, probes, primer, gene constructs comprising the nucleic acids, host cells comprising the nucleic acids, and methods of using.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN IN RIGHT OF CANADA AS REPRESENTED BY ENVIRONMENT CANADA +2
Barnea dilatata mitochondrial COI gene amplification primer
InactiveCN105462995AStrong specificityHigh amplification efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention provides a barnea dilatata mitochondrial COI gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is SEQ ID NO: 1. The base sequence is used for designing an amplification primer for detecting barnea dilatata. The primer is designed for barnea dilatata mitochondrial COI gene segments. Compared with a COI gene primer universal for mollusks, the amplification primer has the advantage of absolute specificity. The amplification efficiency of the primer reaches as high as 90% or above, amplification efficiency is high, and time and cost for amplification are greatly reduced.
Owner:MARINE BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Cultivation of dha-rich prey organisms for aquatic species
InactiveUS20030097993A1Increase concentrationClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffAquatic speciesOrganism
A method is provided for producing prey organisms such as Artermia and rotifers, for feeding aquacultural organisms in particular at the larval stage. The method comprises cultivating the prey organisms during at least part of their life cycle in an aqueous medium comprising at least one lipid component having a DHA content of at least 30 wt %. The enriched prey organisms preferably have a DHA content of at least 12 wt % of their total lipid content. The prey organisms are suitable feed for larvae of fish including halibut, turbot, bass, and flounder, and crustaceans and molluscs.
Owner:EPAX NORWAY
Transgenic mollusk and method for producing the same
A transgenic mollusk which can express a desired foreign gene, and a method for producing the same are disclosed. The mollusk is a transgenic mollusk into which a desired foreign gene (excluding a gene giving resistance to a virus) is introduced, which expresses the foreign gene. This transgenic mollusk can be produced by microinjecting into gonad of male and / or female of mollusk a recombinant vector into which a desired foreign gene to be introduced or a nucleic acid containing the foreign gene is inserted; crossing the male and female to produce individuals of first generation; and selecting therefrom (an) individual(s) which express(es) the desired gene.
Owner:MIKI KEIZABURO +2
Crustacean expression vector
Methods and constructs for genetic manipulation of one or more of shrimp, shellfish, mollusks, and fish are disclosed. The nucleic acid construct includes a promoter and an internal ribosome entry site of an insect picomavirus, such as a cricket paralysis-like picomavirus. One or more open reading frames can be operably associated with one or both of the promoter and the internal ribosome entry site, and one or more proteins or protein subunits can be expressed upon introduction of the construct into a host cell, such as into a shrimp. Method for producing immortalized crustacean cell lines using enhancer elements derived from shrimp and / or shrimp viruses are also described.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Compositions and related methods for modulating endosymbionts
PendingUS20190367943A1Reduce diversityReduce functionBiocideElcosanoid active ingredientsNematodeBiology
Provided herein are methods and compositions for modulating the fitness of a host invertebrate (e.g., insect, mollusk, or nematode) by altering interactions between the host and one or more micoorganisms resident in the host. The invention features a composition including a modulating agent (e.g., a polypeptide, nucleic acid, small molecule, or combinations thereof) that can induce changes in the host's microbiota in a manner that modulates (e.g., increases or decreases) host fitness. The modulating agent described herein may modulate the fitness of a variety of invertebrates that are important for agriculture, commerce, and / or public health.
Owner:FLAGSHIP PIONEERING INNOVATIONS V INC
Use of Proteins to Control Molluscs
The present disclosure includes proteins toxic to Zebra mussels, its method of production, and uses thereof. The protein was isolated from whole cell broth of Pseudomonas protegens CL145A via anion exchange chromatographic fractionation. The protein was found to be a secondary metabolite with highest expression at the fermentative production harvest stage.
Owner:MARRONE BIO INNOVATIONS
Orally administrable immunostimulant product for aquaculture
InactiveCN102209530BMaintain propertiesKeep alivePeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory food factorsMicroorganismWilms' tumor
The present invention relates to an orally administrable immunostimulatory product comprising microencapsulated cytokines, which are cells of fish, molluscs or crustaceans, and an enteroprotective polymer for protecting said cytokines Factors, preferably recombinant cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα) overexpressed in the host microorganism.
Owner:PROBELTE PHARMA
Methods for controlling molluscs
ActiveUS7566461B2Reduced food intake, bleachingReduce productionBiocidePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCompanion animalDomestic animal
Novel materials for controlling molluscs, such as snails and slugs, using carbohydrates including celluloses, hemicellulose complexes, and / or lignin, for inducing death in molluscs. The materials are non-toxic, will not contaminate a drinking water supply, will not harm fish, birds or wild life, will not cause any harmful effects if swallowed or absorbed through the skin, will not harm children or pets, and can be safely eaten by domestic animals and livestock that may consume such dead molluscs. The materials may be applied in various formulations at various water contents. The materials do not provide nutrition to the molluscs, and disrupt normal bodily functions resulting in death. An attractant may be included to encourage ingestion by the molluscs.
Owner:VERDESIAN LIFE SCI
Detection of bacterial (mollicutes) contamination
InactiveUS20150086990A1Optimization orderHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementTrue positive rateGenomic DNA
The present disclosure provides a method and system for the PCR amplification of a target sequence which suppresses non-specific amplification products. The disclosure concerns the use of a primer pair optimized to amplify a nucleic acid of a contaminant in the background of genomic DNA of a first organism. When DNA from a second organism suspected for comprising the contaminant is subjected to the same PCR-based amplification reaction, detection sensitivity and specificity of the contaminant is enhanced when an amount of genomic DNA of the first organism is present in the amplification reaction.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Application of alien invasive plant Ambrosia artemisiifolia in control of golden apple snail
ActiveCN103004892BEasy accessSimple and fast operationBiocideMolluscicidesResource utilizationPomacea canaliculata
The invention belongs to the environment-friendly technical field of snail-killing plant resource utilization, and particularly relates to a method of utilizing an alien invasive plant Ambrosia artemisiifolia to control a harmful mollusc golden apple snail which invades South China. The method comprises the step of adding dried powders of the alien invasive plant Ambrosia artemisiifolia to directly control the golden apple snail, and is characterized in that 1) the utilized plant is Ambrosia artemisiifolia (asteraceae); and 2) the dosage of the dried powders of Ambrosia artemisiifolia is 10 g / L. The method has the advantages that the plant material which is Ambrosia artemisiifolia is a common alien invasive plant in South China, so that the plant is easily obtained, and under a certain dosage, the golden apple snail can be effectively controlled.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
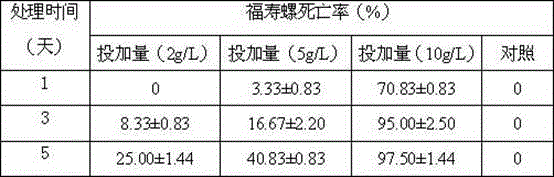
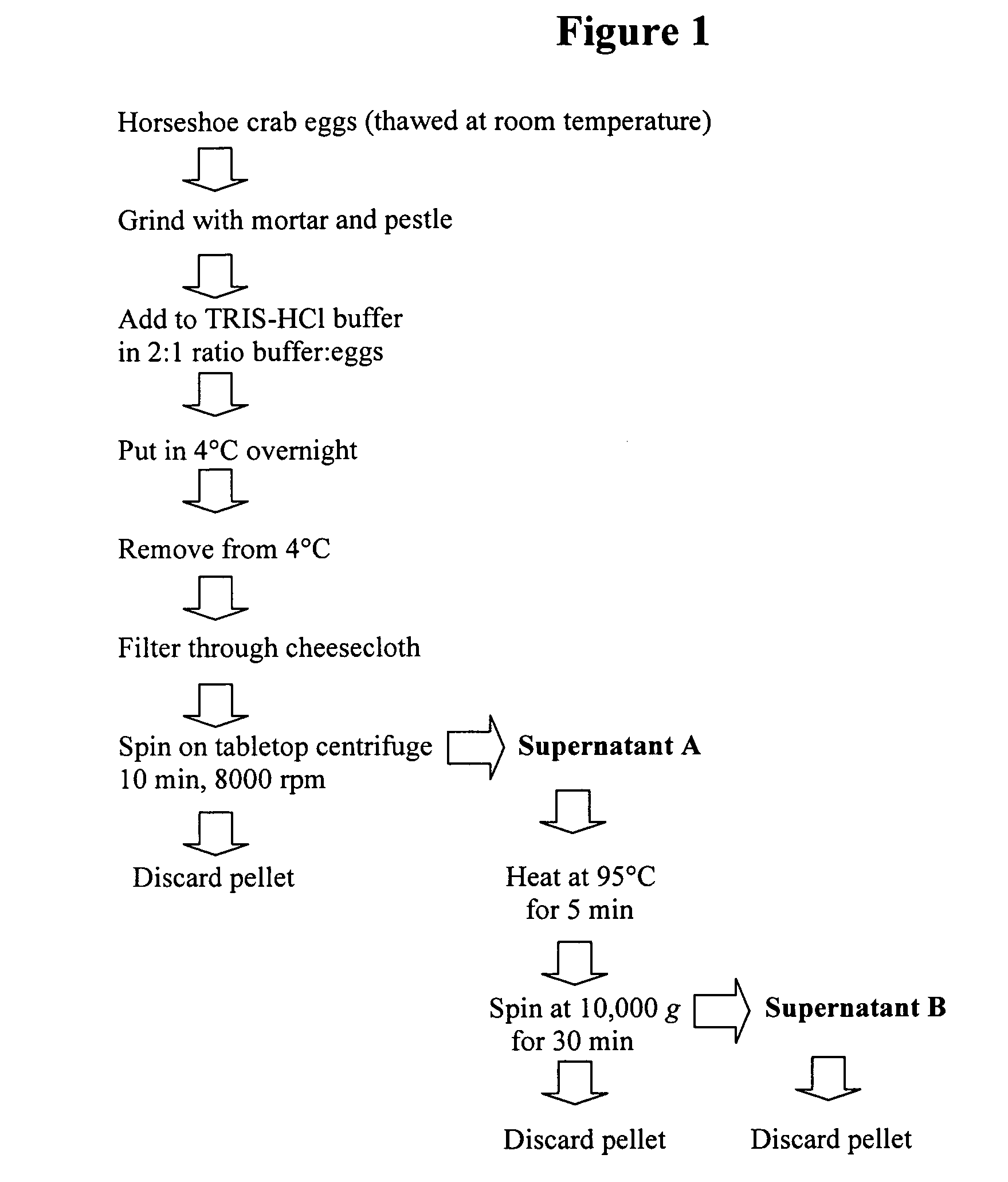
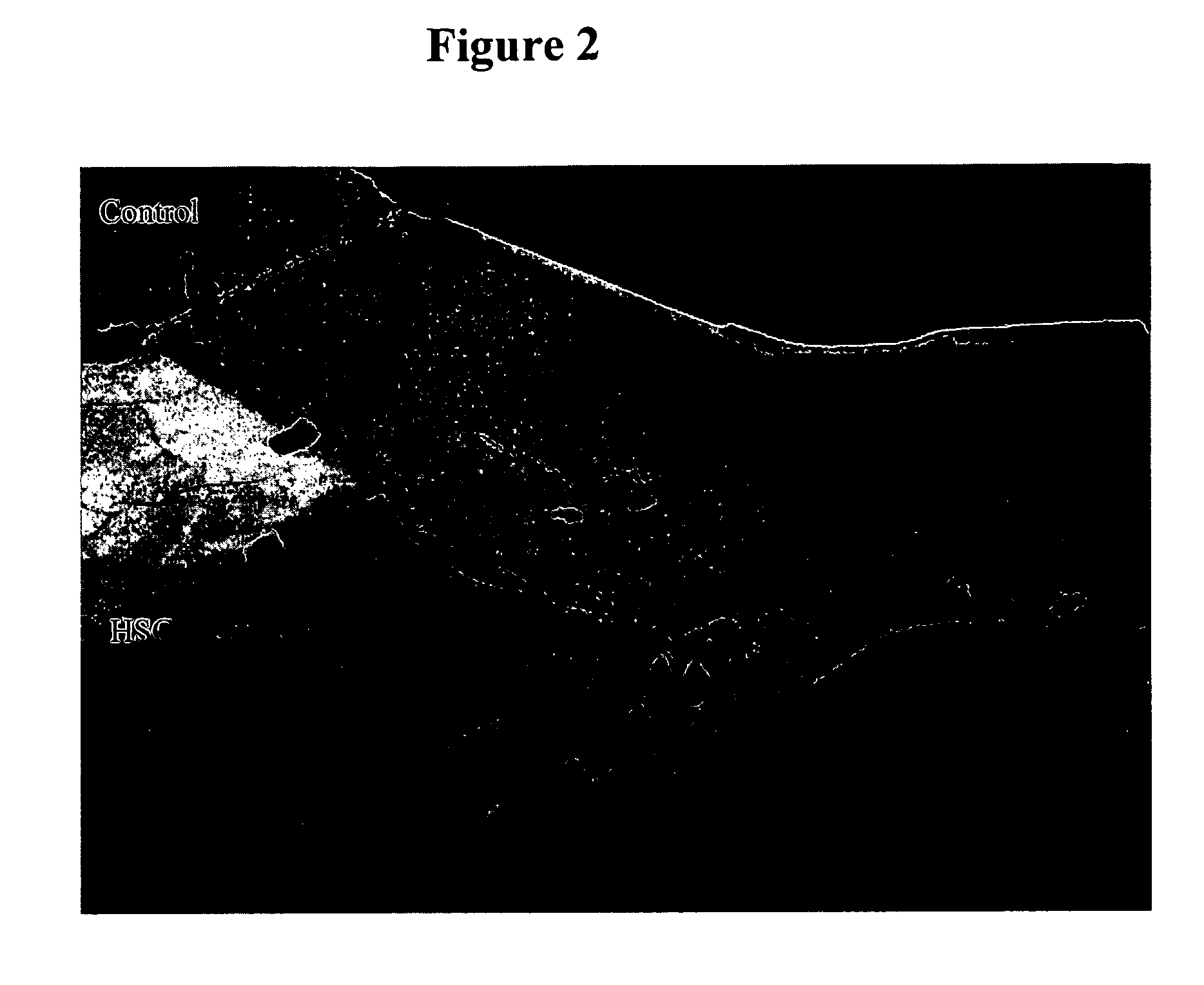
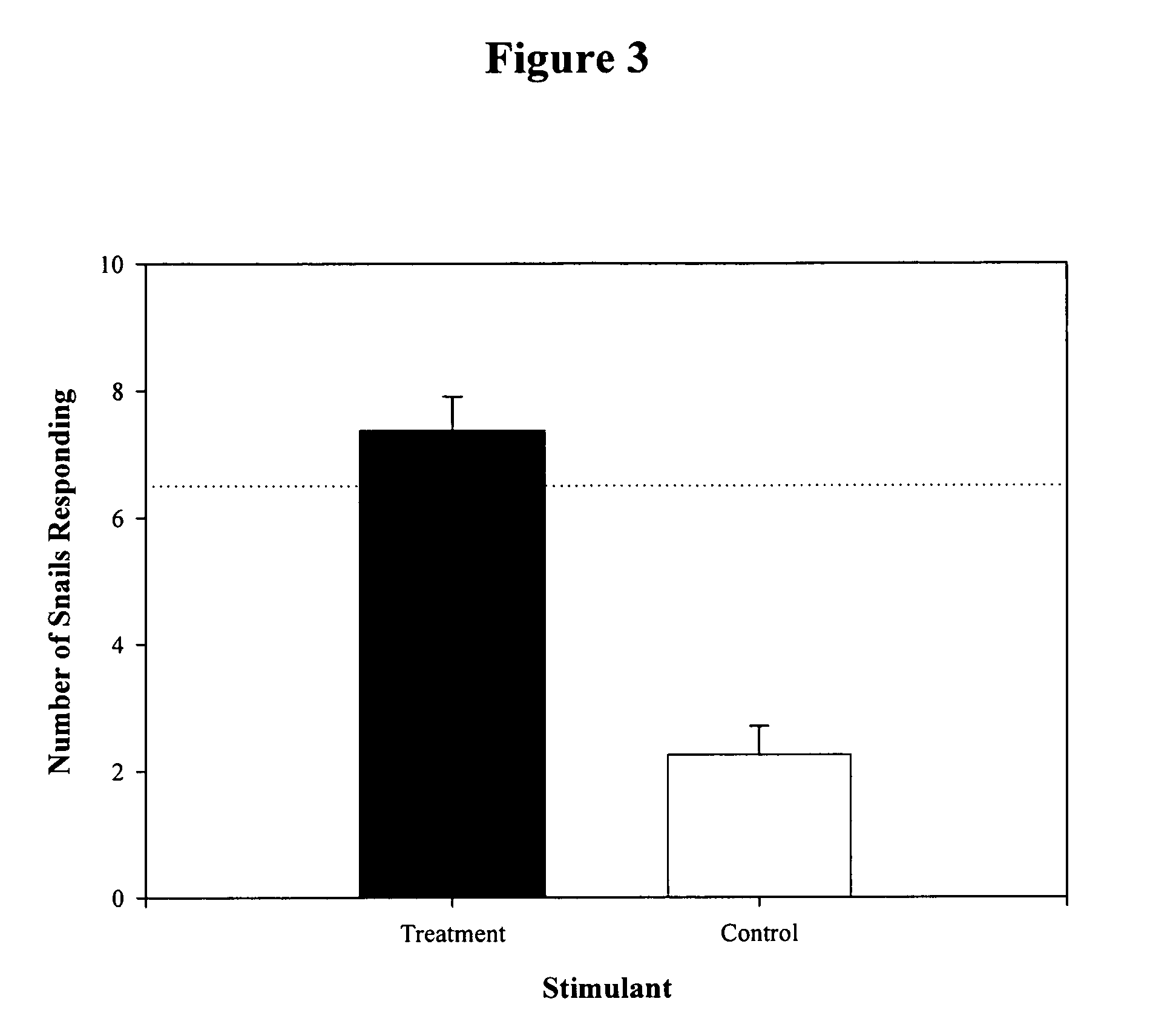
Artificial bait based on a peptide attractant found in horseshoe crab eggs
The present invention relates to a novel attractant for fish and mollusks isolated from the eggs of the horseshoe crab, Limulus polyphemus. The invention also relates to a method for attractant peptide extraction, separation, purification, quantitation, and characterization of function. In other aspects, the invention provides for the isolation of the attractant peptide from horseshoe crab eggs for use as “bait” for attracting fish and mollusks. More particularly, the invention relates to the use of biochemical approaches to characterize a peptide attractant, and provides for the creation of recombinant or synthetic attractant peptides, and their use.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF DELAWARE
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com