Patents
Literature
219 results about "Artificial reefs" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
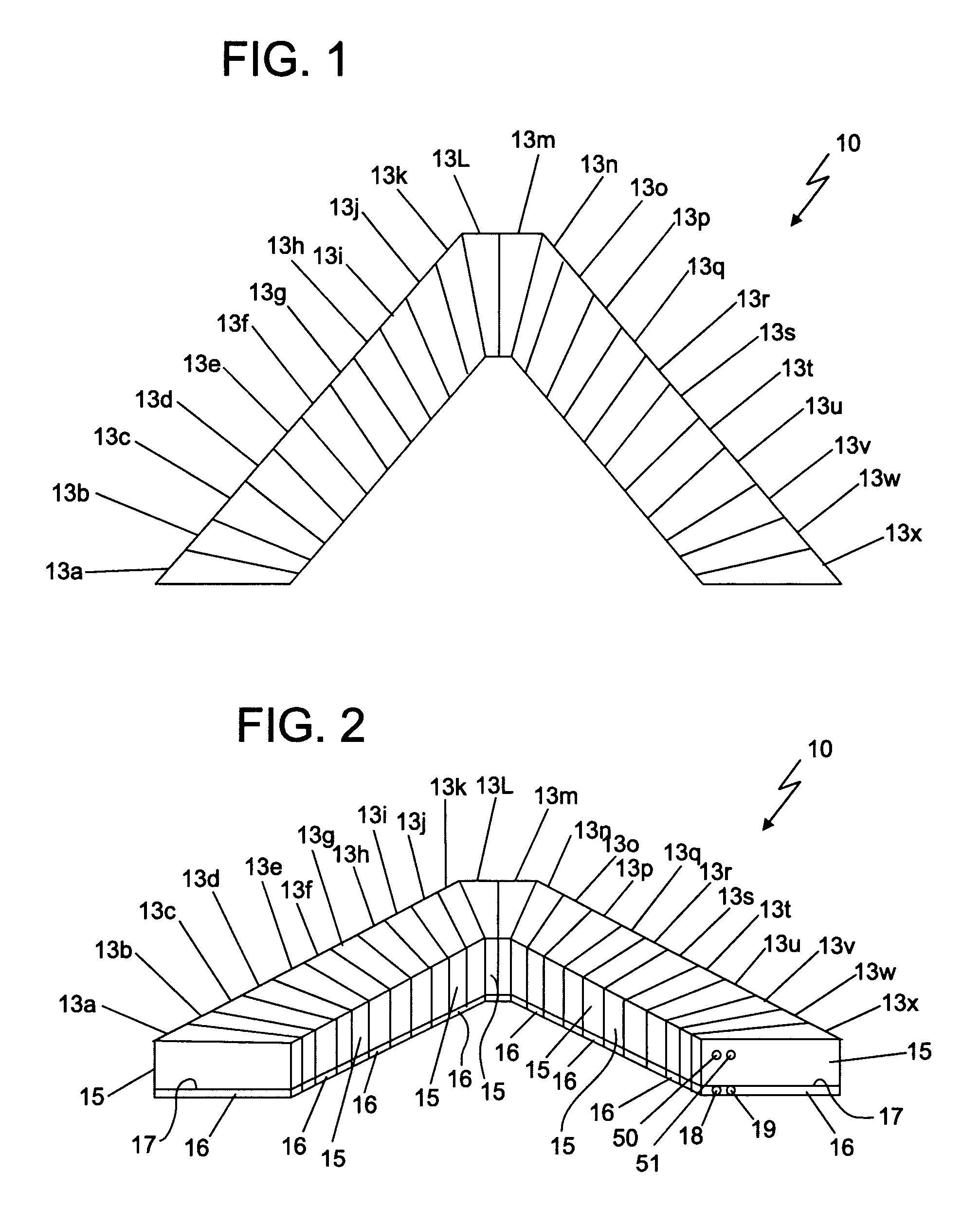
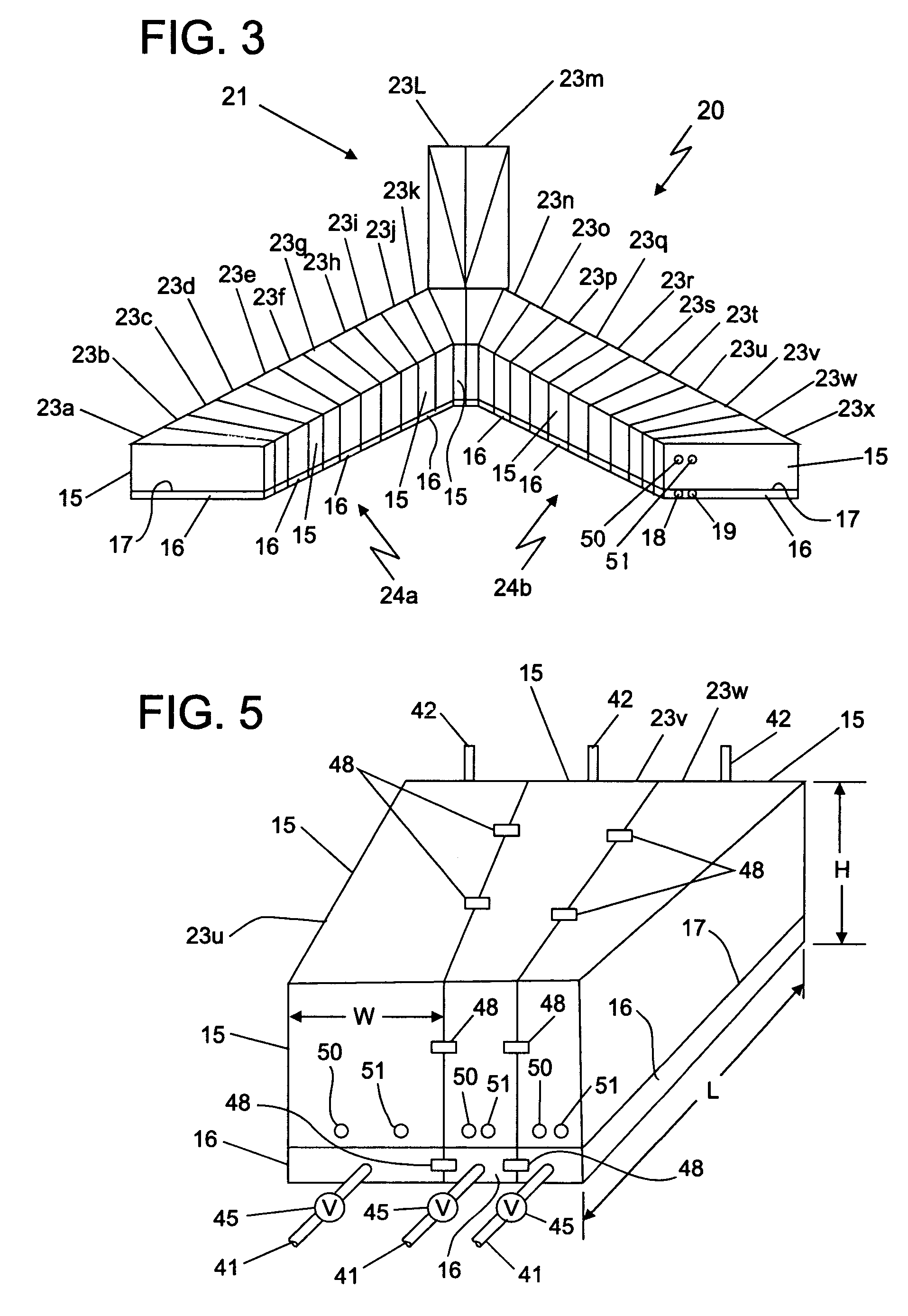
Artificial reef. An artificial reef is a man-made, underwater structure, typically built for the purpose of promoting marine life in areas of generally featureless bottom. Artificial reefs may also serve to improve hydrodynamics for surfing or to control beach erosion.
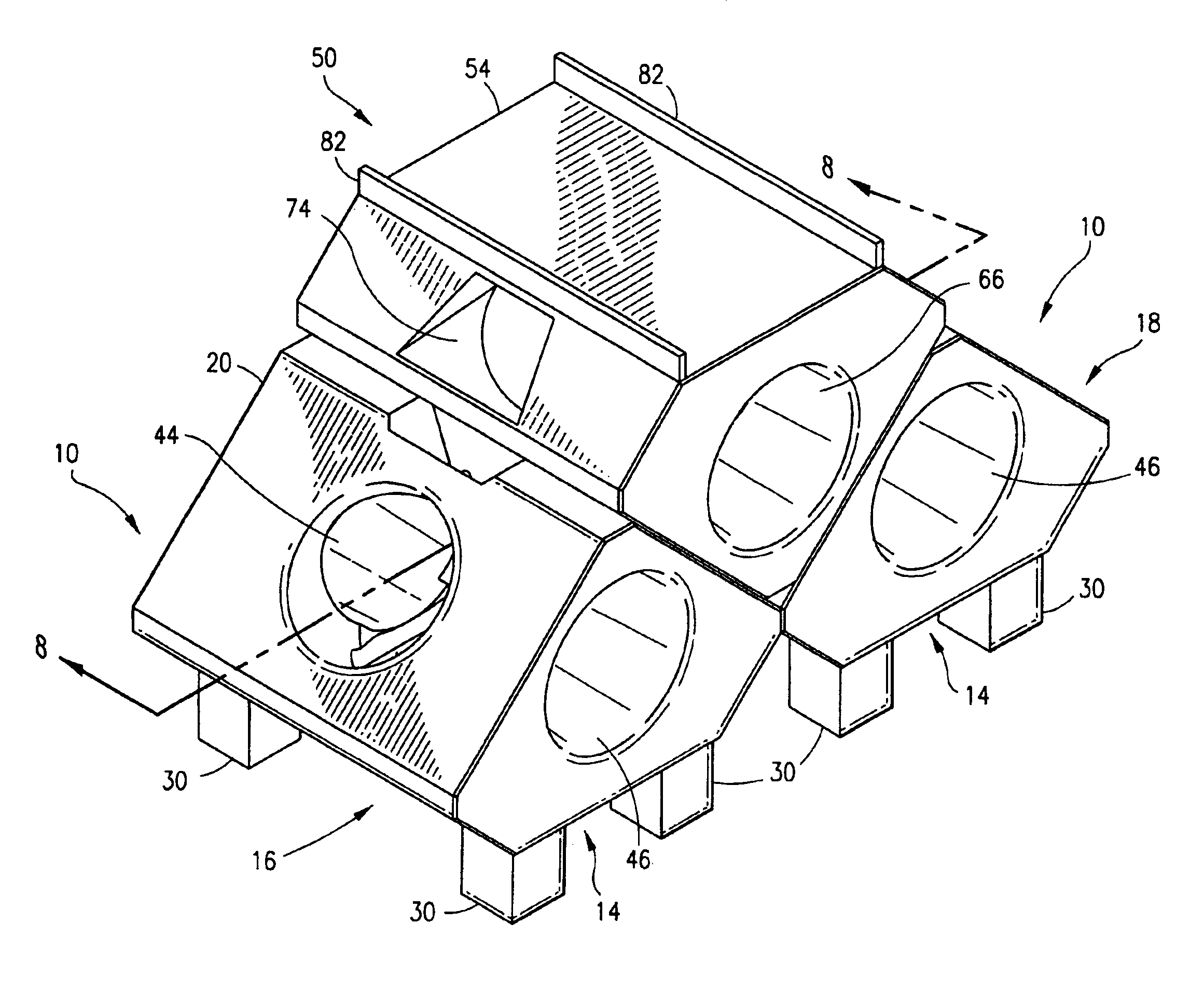
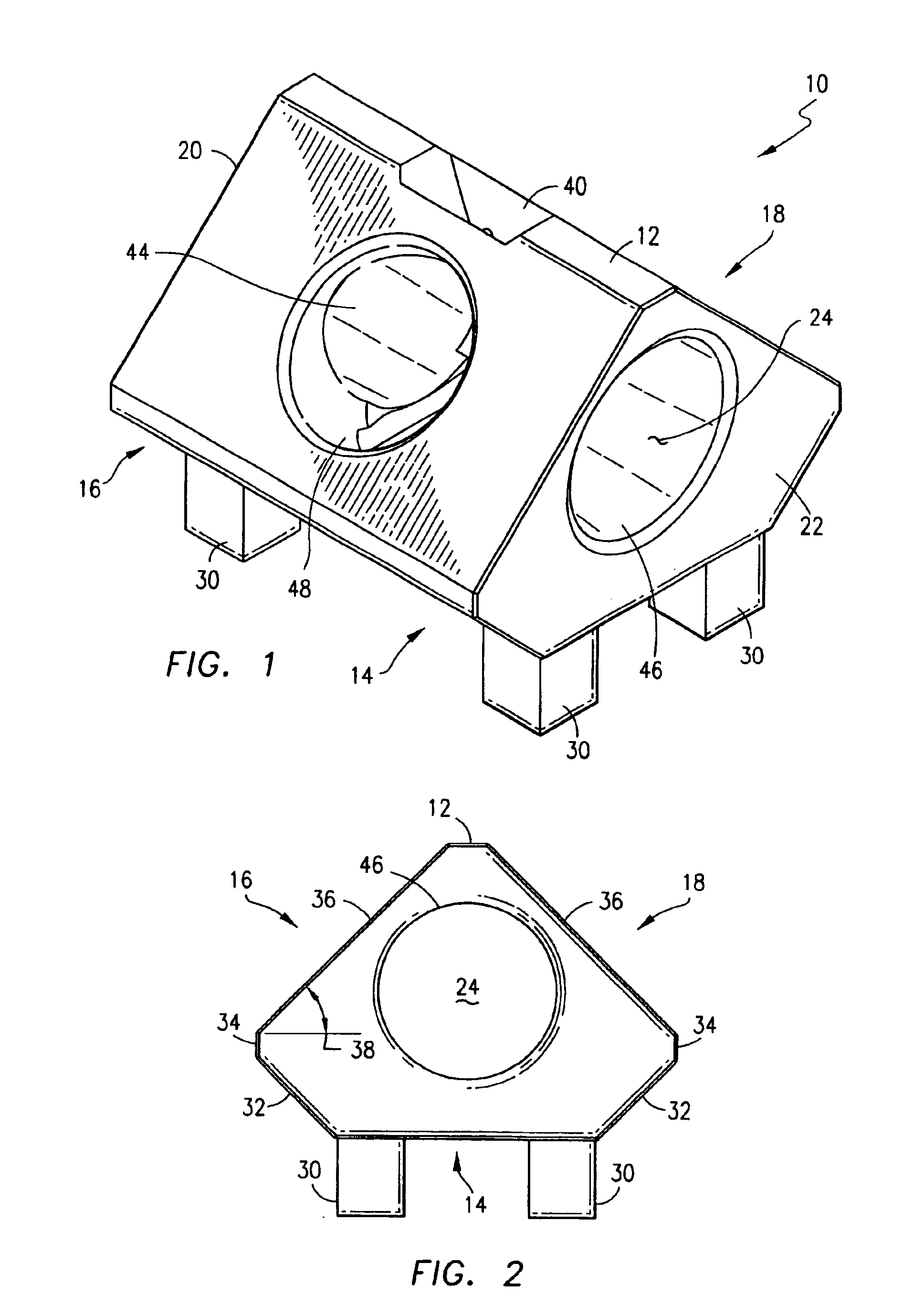
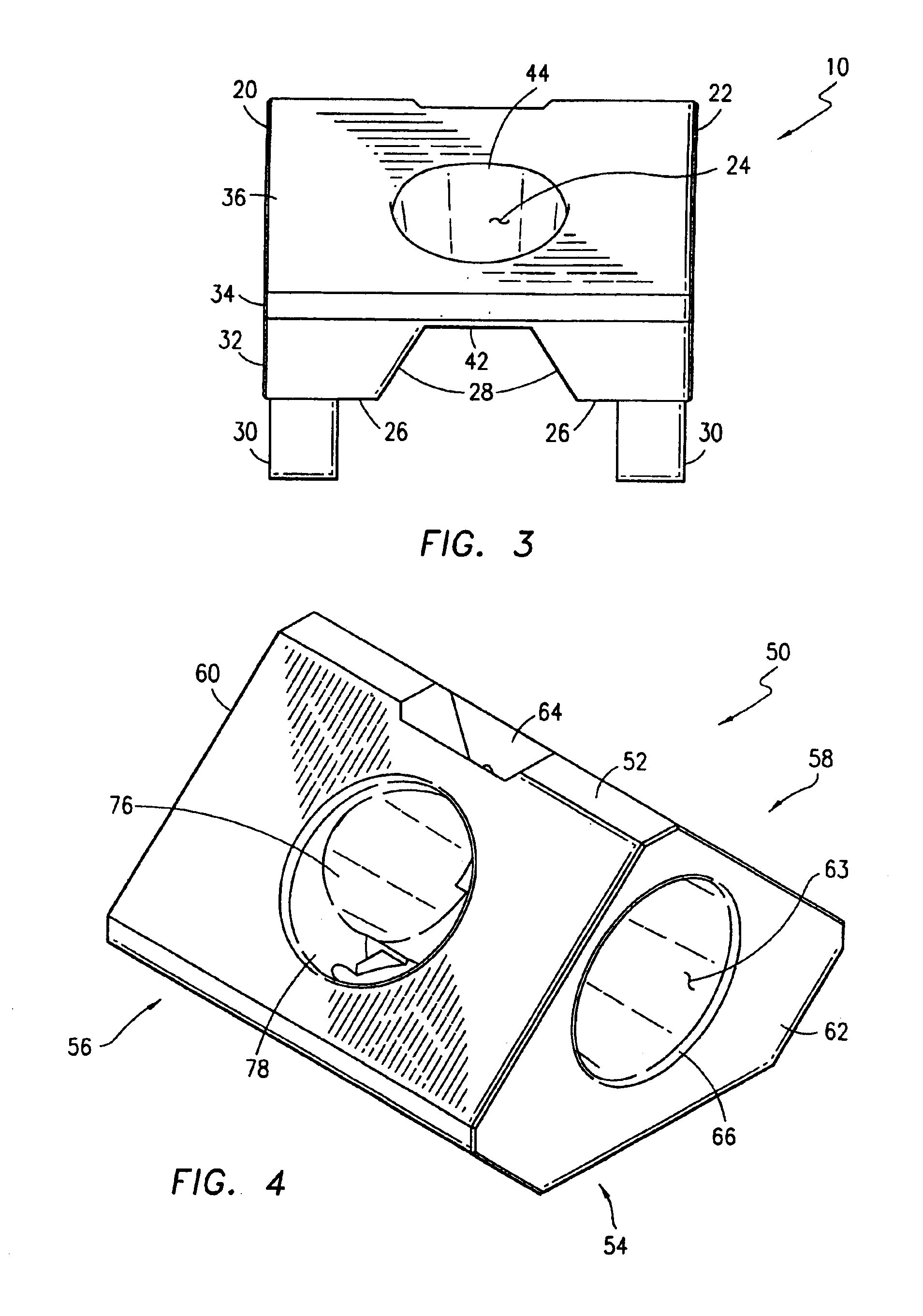
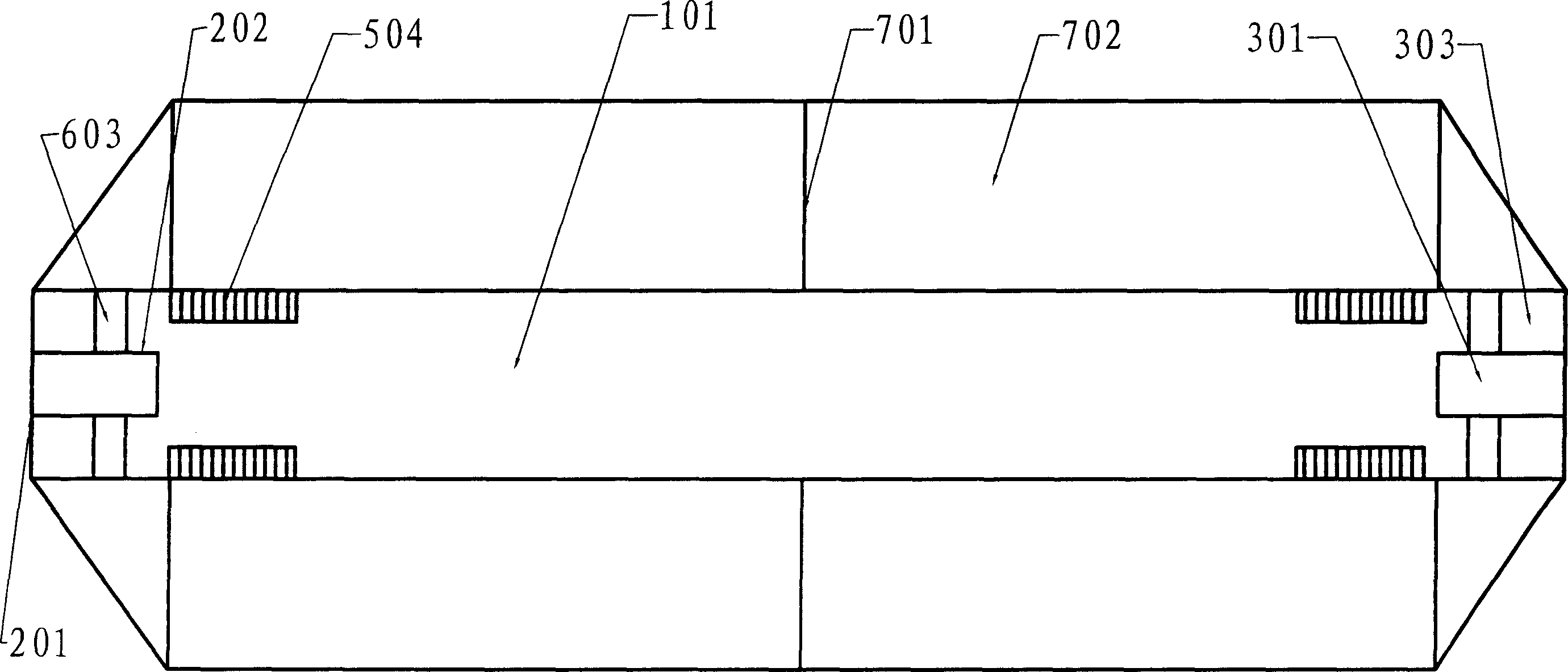
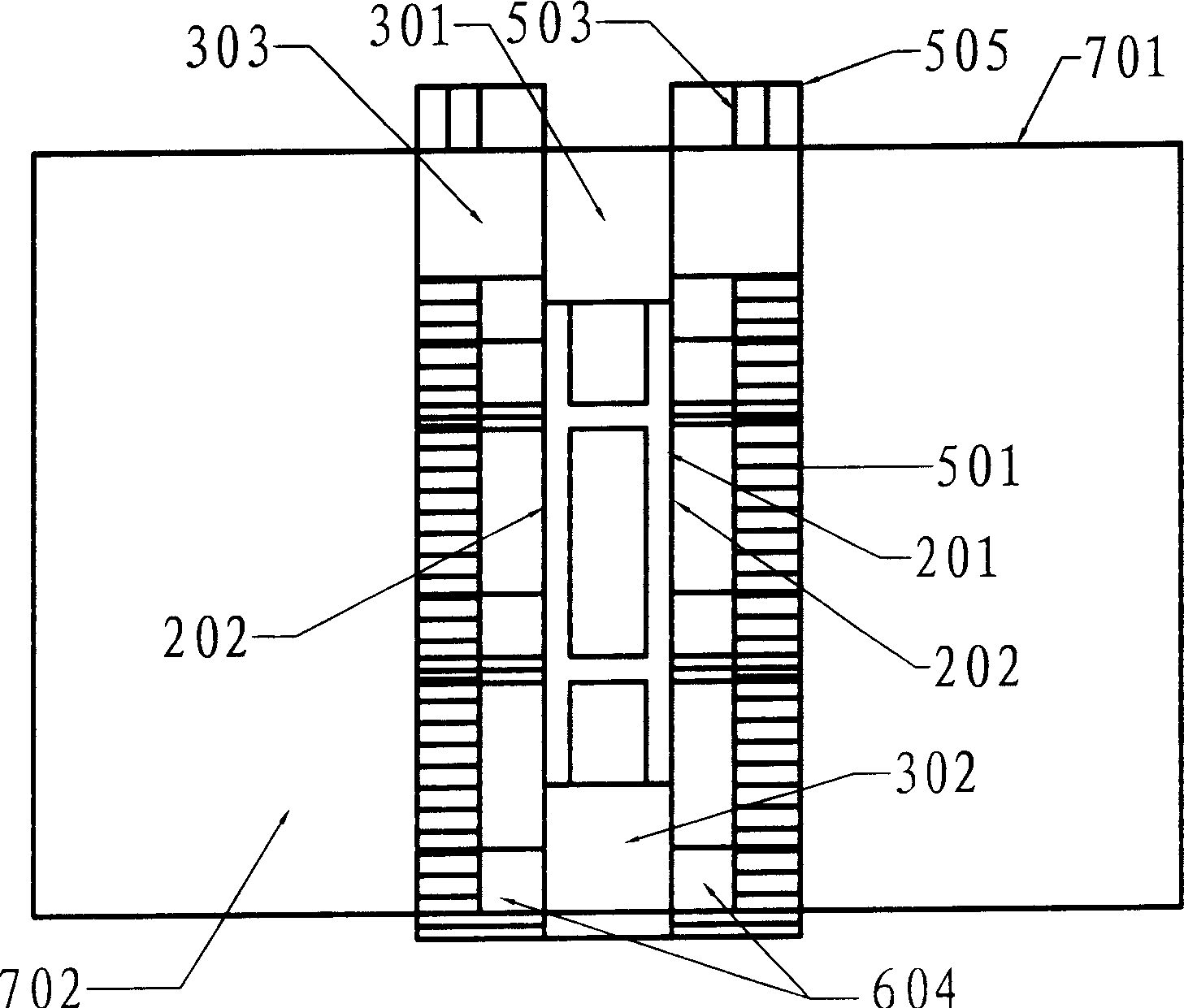
Modular artificial reef, sea wall and marine habitat
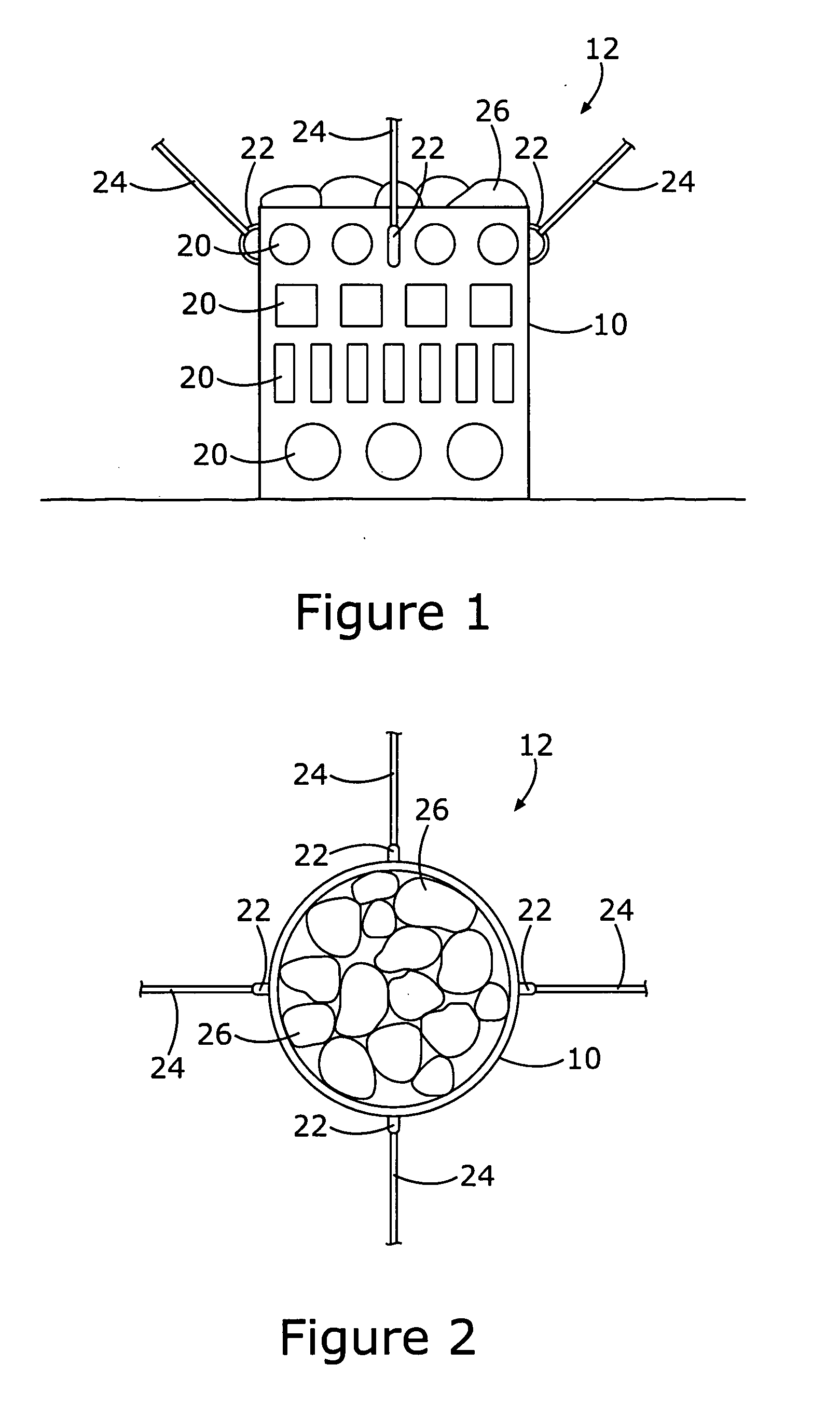
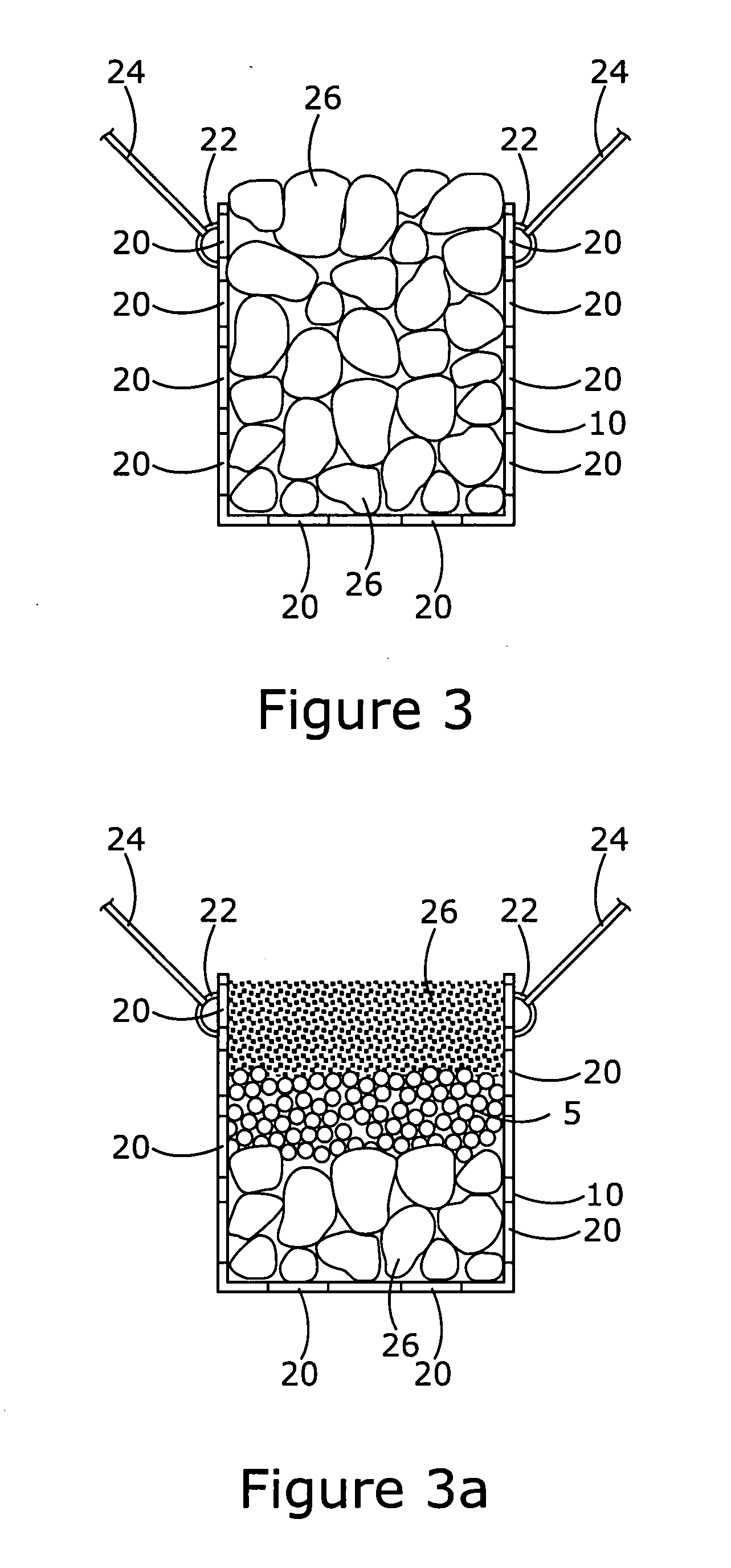
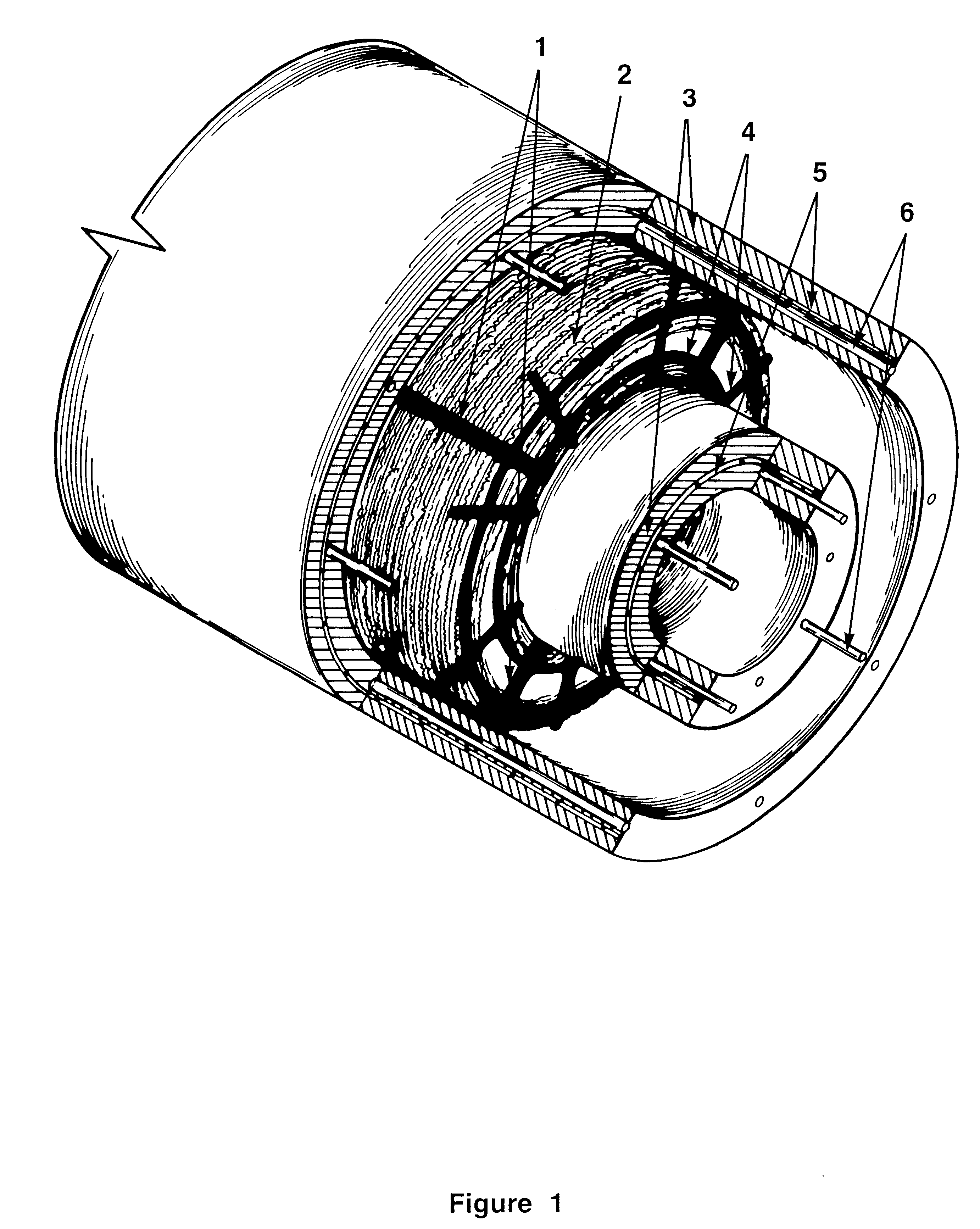
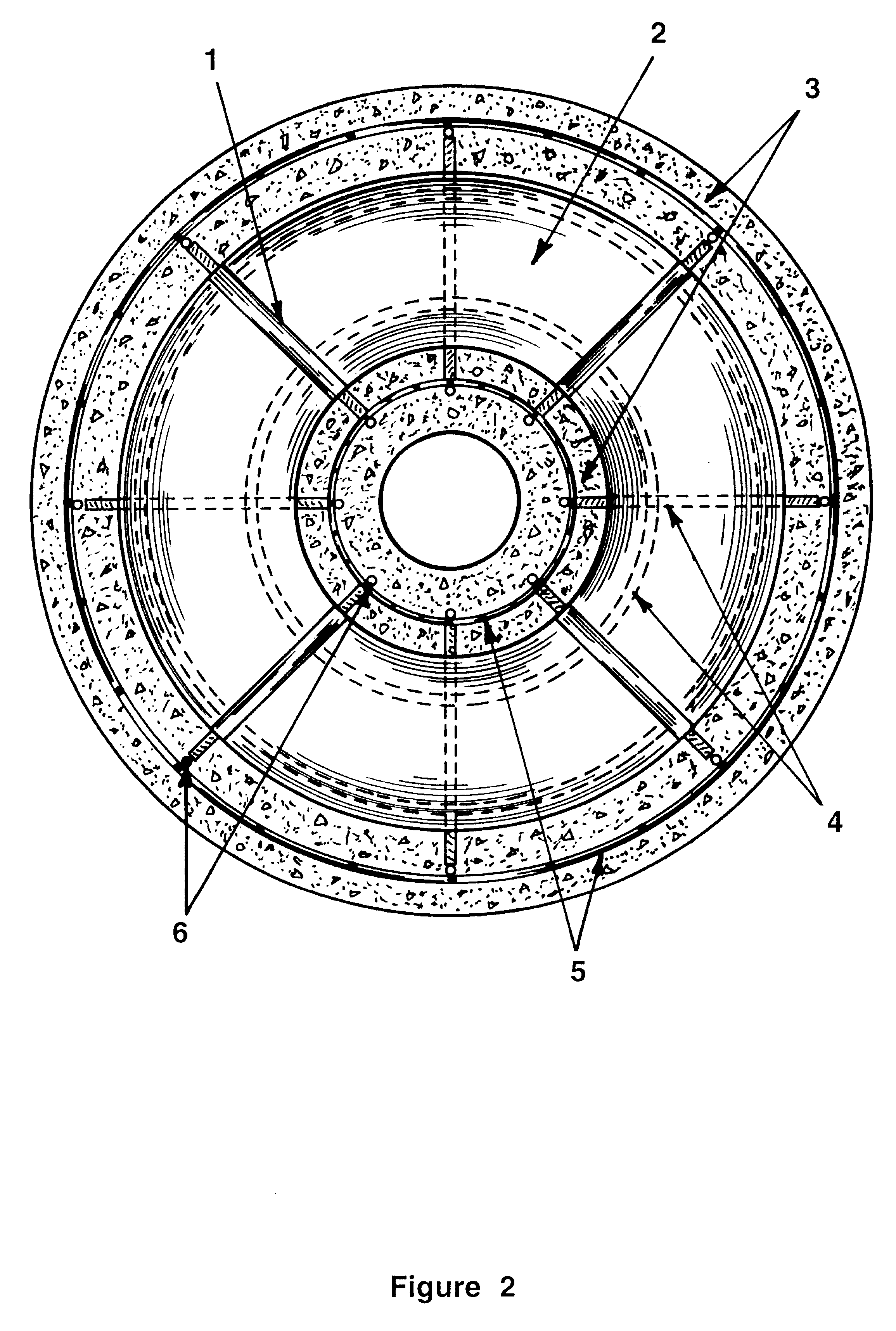
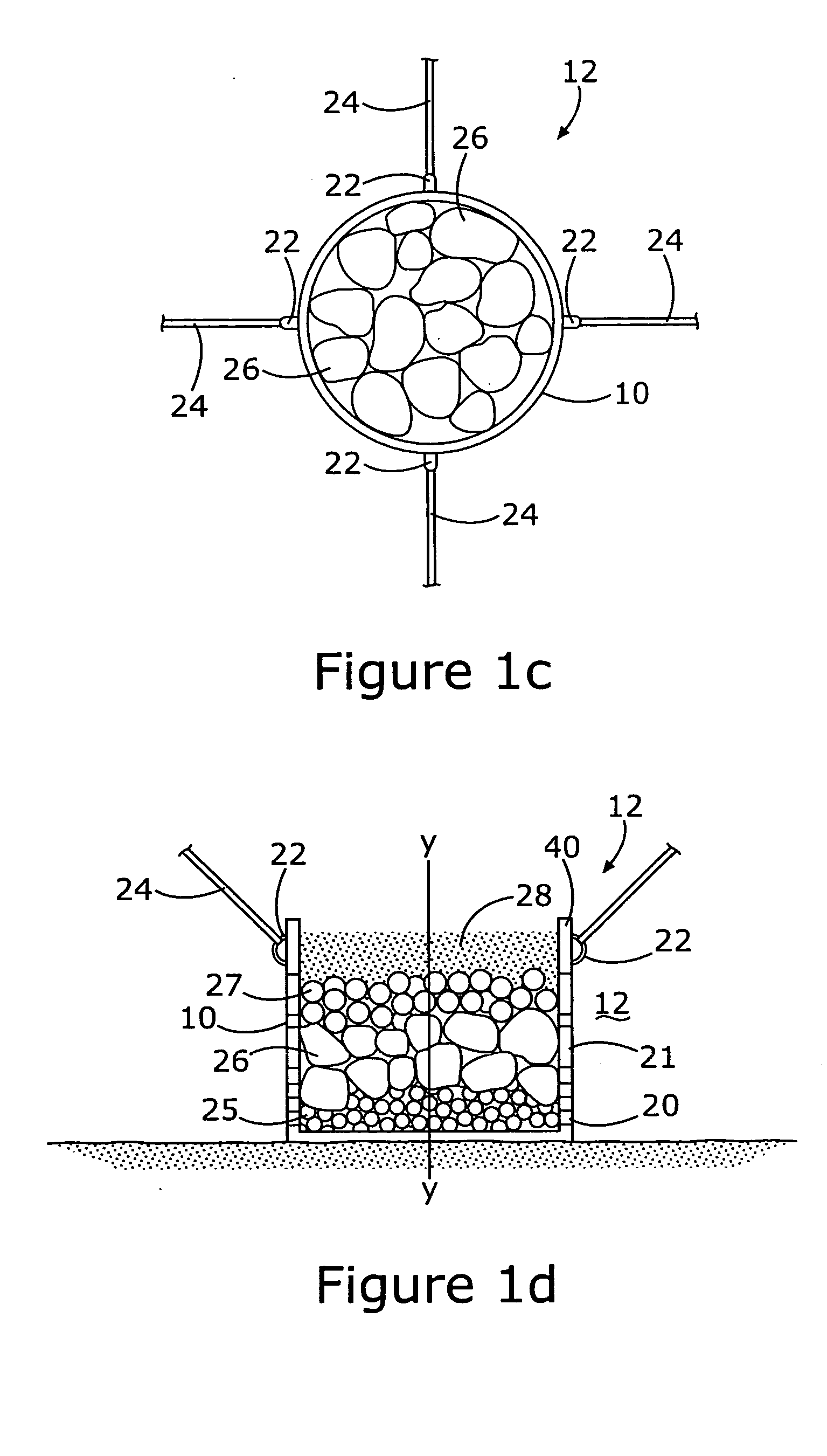
InactiveUS6896445B1Improve stabilityReduce porosity and absorptionBreakwatersQuaysSurface oceanModular unit
A modular unit intended for use as an artificial reef, marine habitat and / or sea wall which can be placed in stacked structures along the floor of an ocean, bay, or other body of water comprises a top wall, bottom wall, opposed side walls and opposed end walls which are interconnected to form a hollow interior. Each of the walls is formed with one or more openings whose position and size is designed to allow access of marine life into the interior of the units, permit the passage of sunlight therein, direct the flow of sea water into and through the units in a way which increases stability of the units when placed on the ocean floor, and permit alignment of the holes of one unit with those of another when stacked together.
Owner:ENGLER ERIC
Multifunctional artificial fish reef
ActiveCN104304102AImprove the primary productivity of the sea areaThe effect of gathering fish is goodClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaPrimary productivityNutrients substances
The invention discloses a multifunctional artificial fish reef, and aims to provide an artificial reef which is beneficial to formation of different flow field environments with upwelling, can raise nutrient substances deposited at the seabed, can improve the primary sea field productivity near the artificial reef and can provide sufficient feed to fishes. The multifunctional artificial fish reef comprises a reef body, an inner reef cavity and a plurality of inlets and outlets, wherein the inner reef cavity is arranged inside the reef body; the plurality of inlets and outlets are formed in the side surface of the reef body and are communicated with the inner reef cavity; the outer side surface of the reef body extends downwards from top to bottom towards the outer side of the reef body in an inclined manner; a partitioning plate which extends upwards and downwards is arranged inside the inner reef cavity.
Owner:MARINE FISHERIES RES INST OF ZHEJIANG
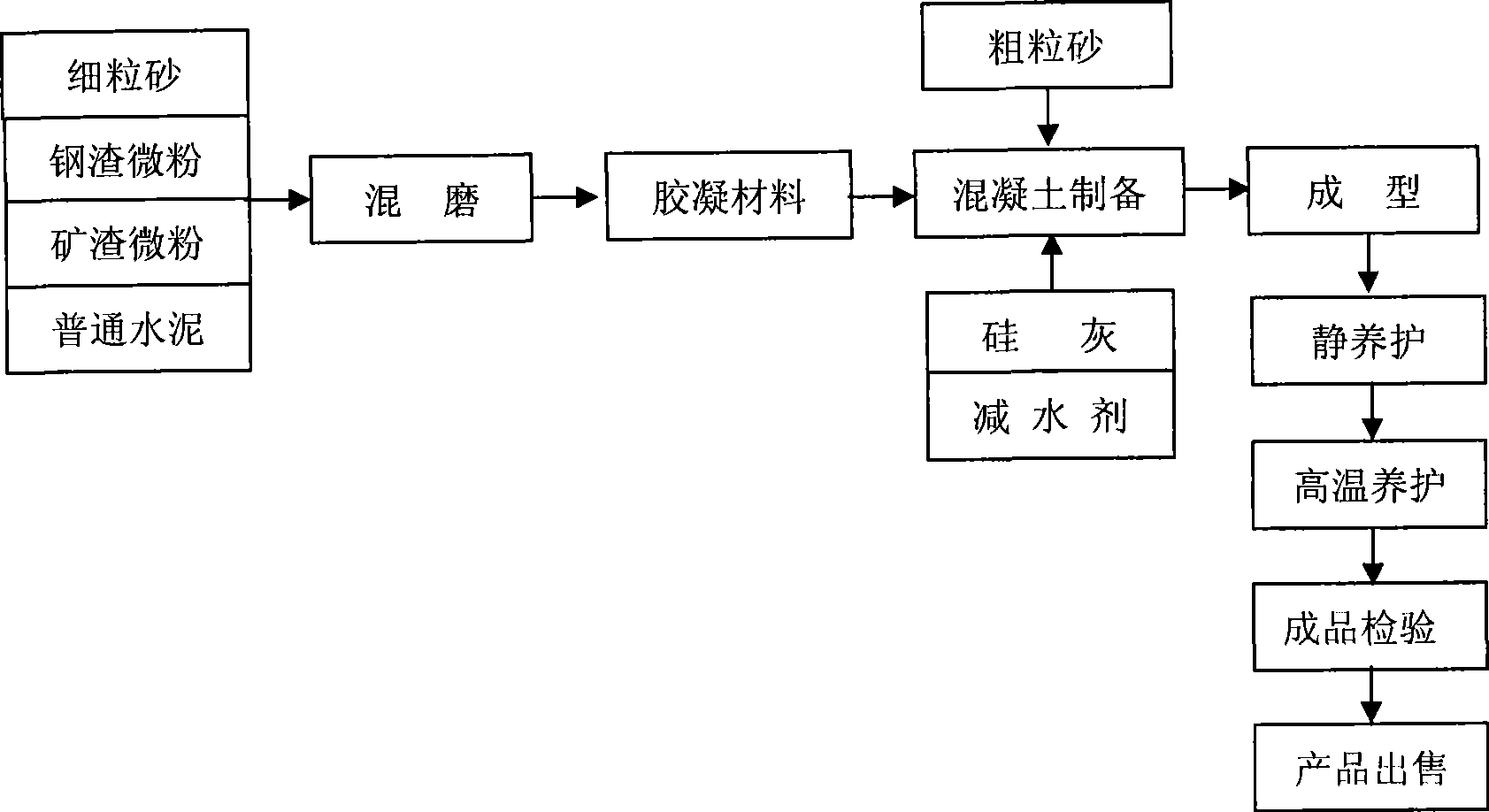
Artificial reef preparation with metallurgy slag as principal raw material
ActiveCN101475348AReduce manufacturing costImprove the living environmentSolid waste managementPisciculture and aquariaSlagSquare meter
The invention relates to a method for preparing an artificial fishing rock by using metallurgy residues as main materials, which belongs to the technical field of metallurgy residues treatment. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, sieving and grading sea sand or river sand; secondly, mixing and grinding 0 to 20 percent of the obtained sand with the particle diameter of less than 5 millimeters with 10 to 80 percent of steel slag, 0 to 80 percent of mine refuse and 10 to 70 percent of cement clinker until the specific surface area is more than 350 square meters per kilogram; thirdly, mixing 20 to 70 percent of the mixture with 20 to 50 percent of the sieved coarse sand with the particle diameter of more than 5 millimeters and 0 to 40 percent of stones; and fourthly, obtaining the concrete artificial fishing rock with high and strong performance after high temperature maintenance. The artificial fishing rock has the advantages that the artificial fishing rock with high and strong performance is prepared by using the metallurgy residues as the main materials to remarkably reduce the preparation cost of the fishing rock, and the living environment for the aquatic lives around the fishing rock is fundamentally improved because the pH value of the concrete pore solution of the prepared fishing rock is close to that of sea water.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
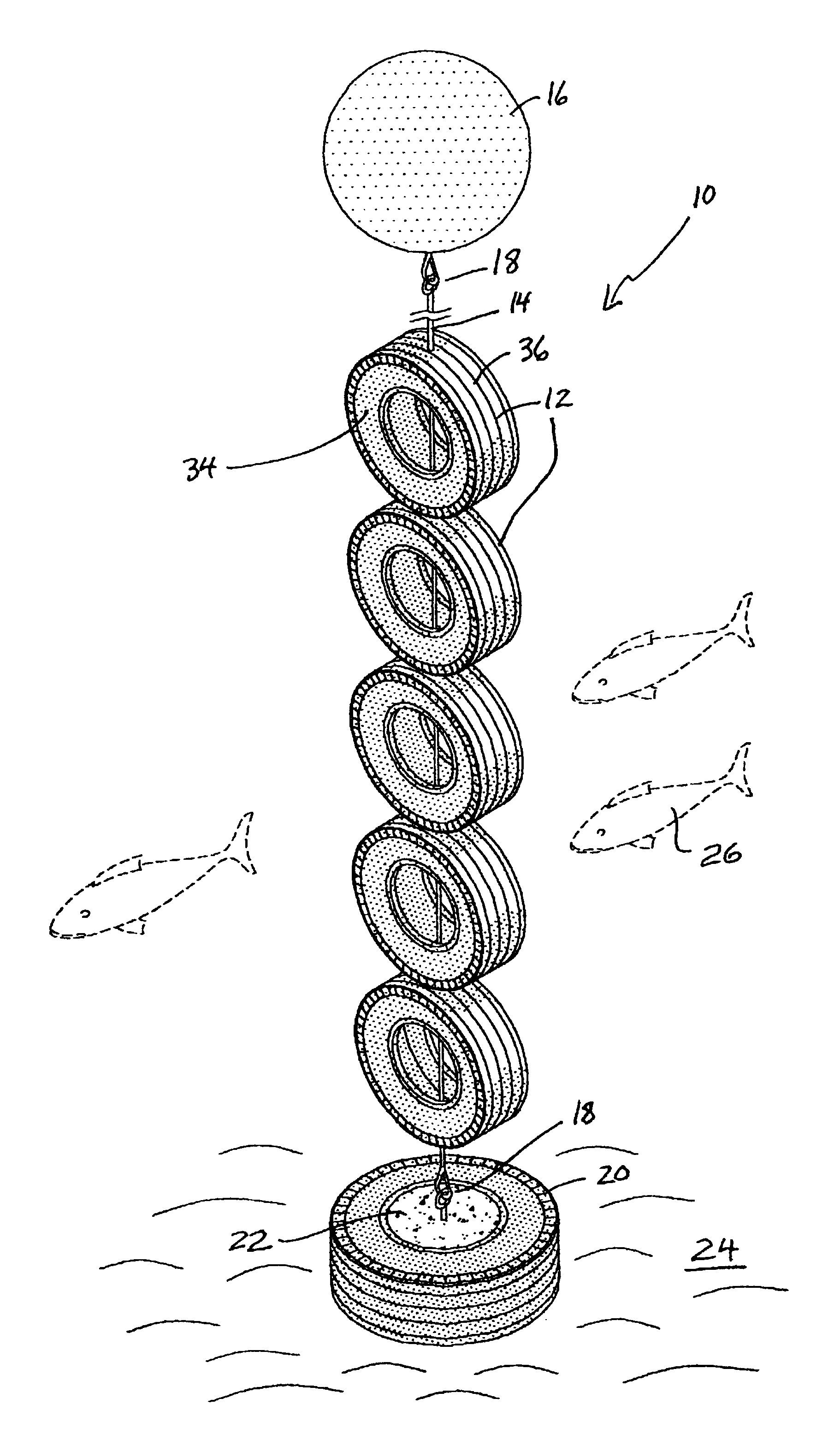
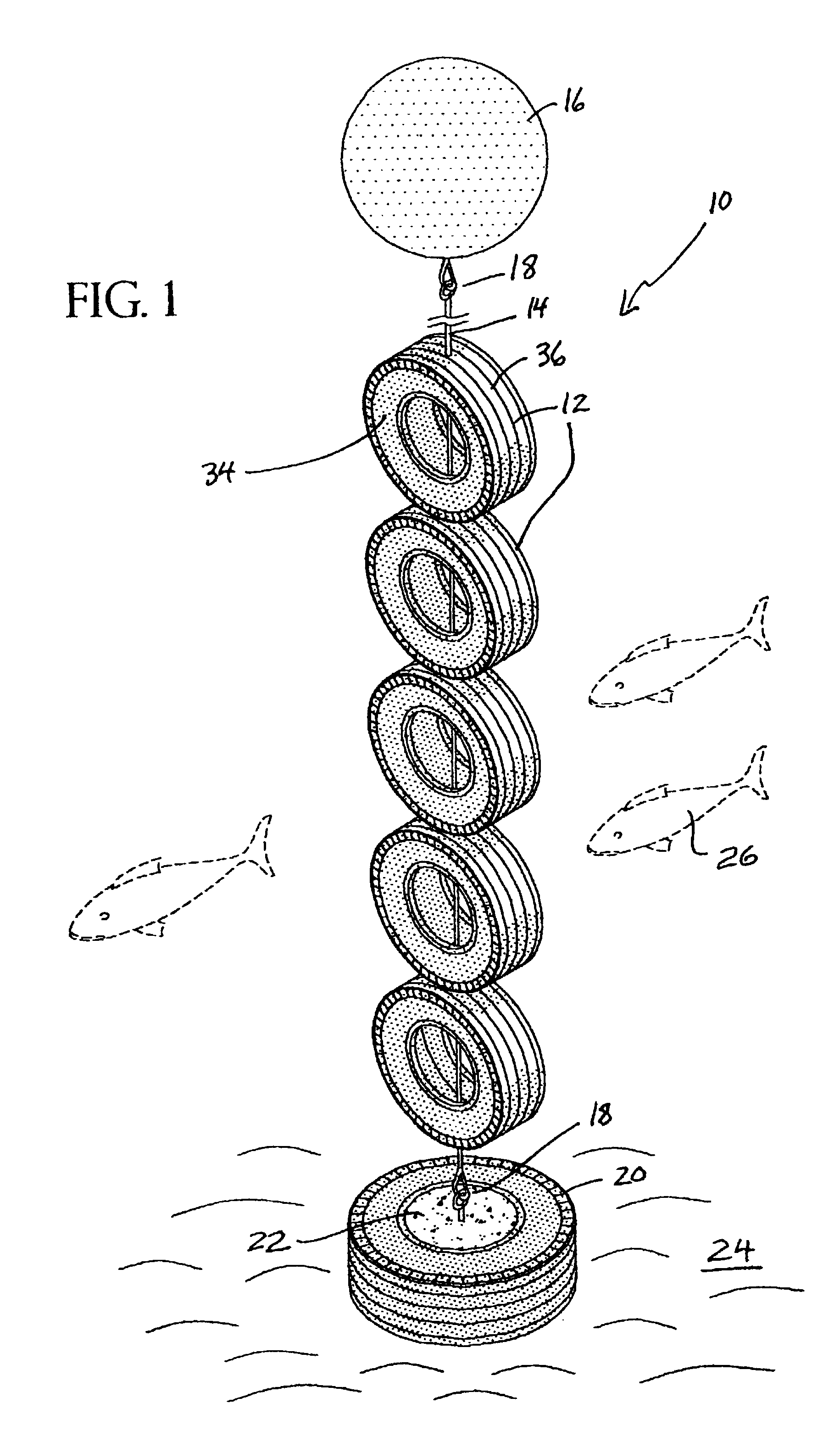
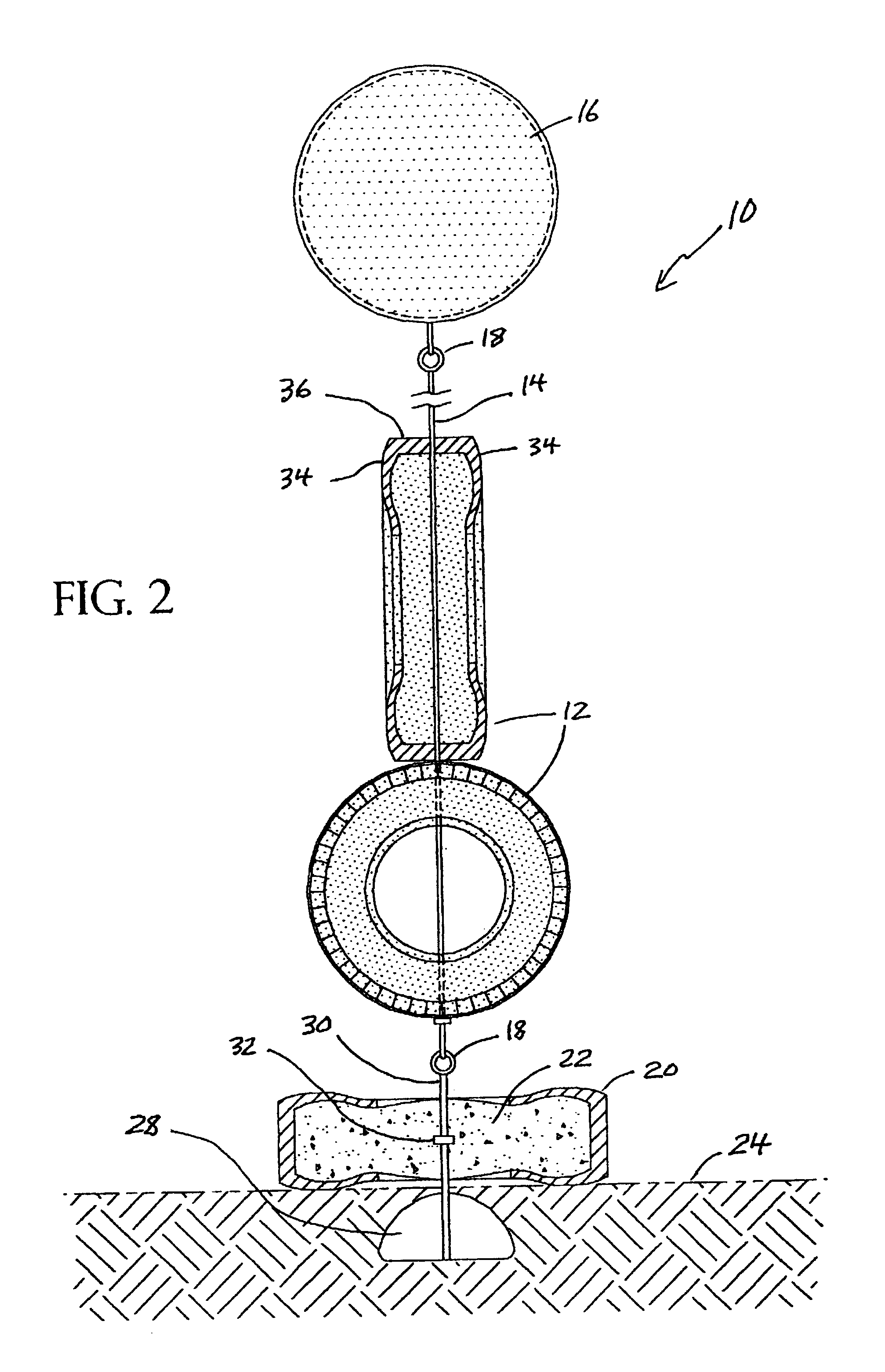
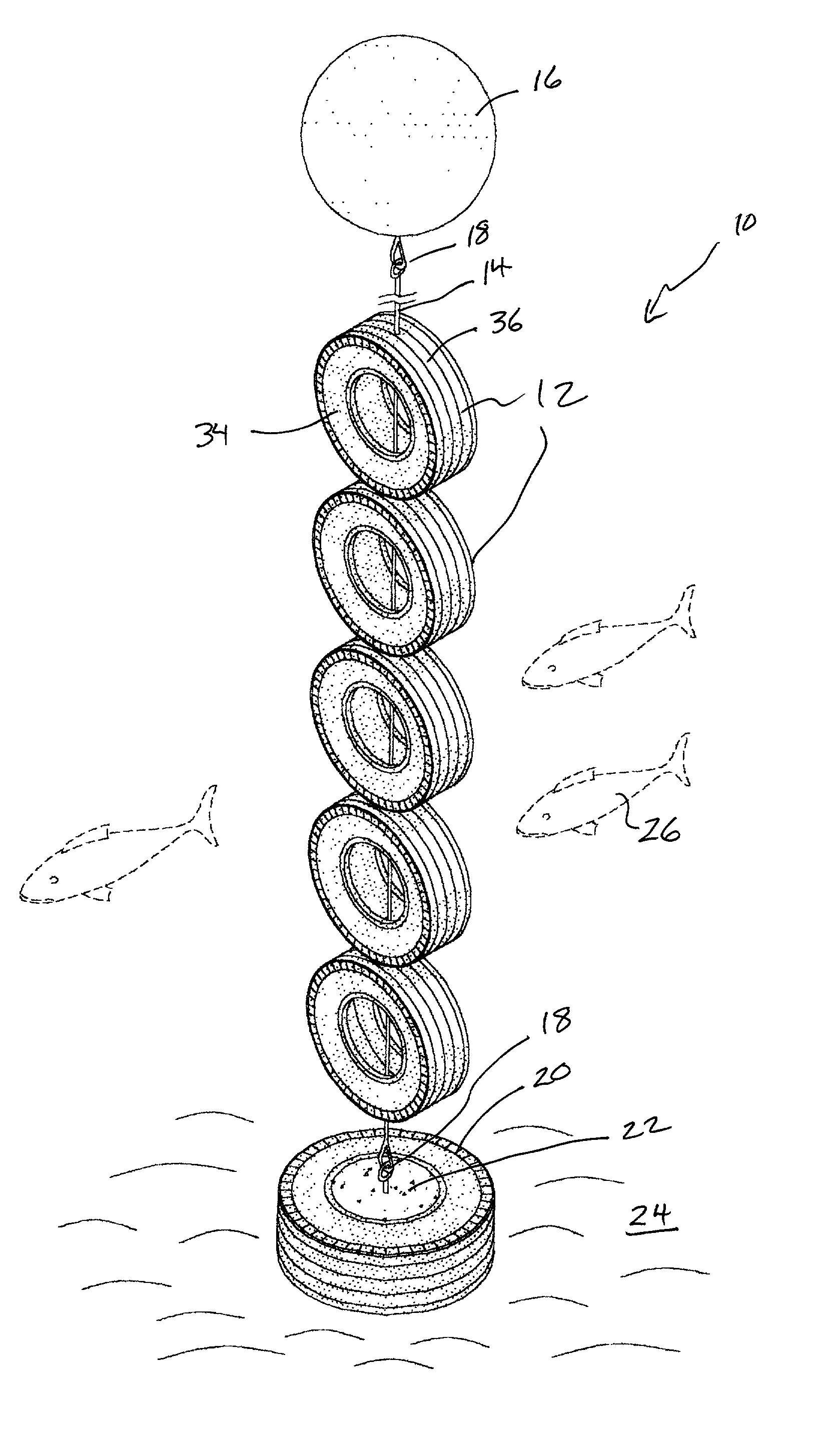
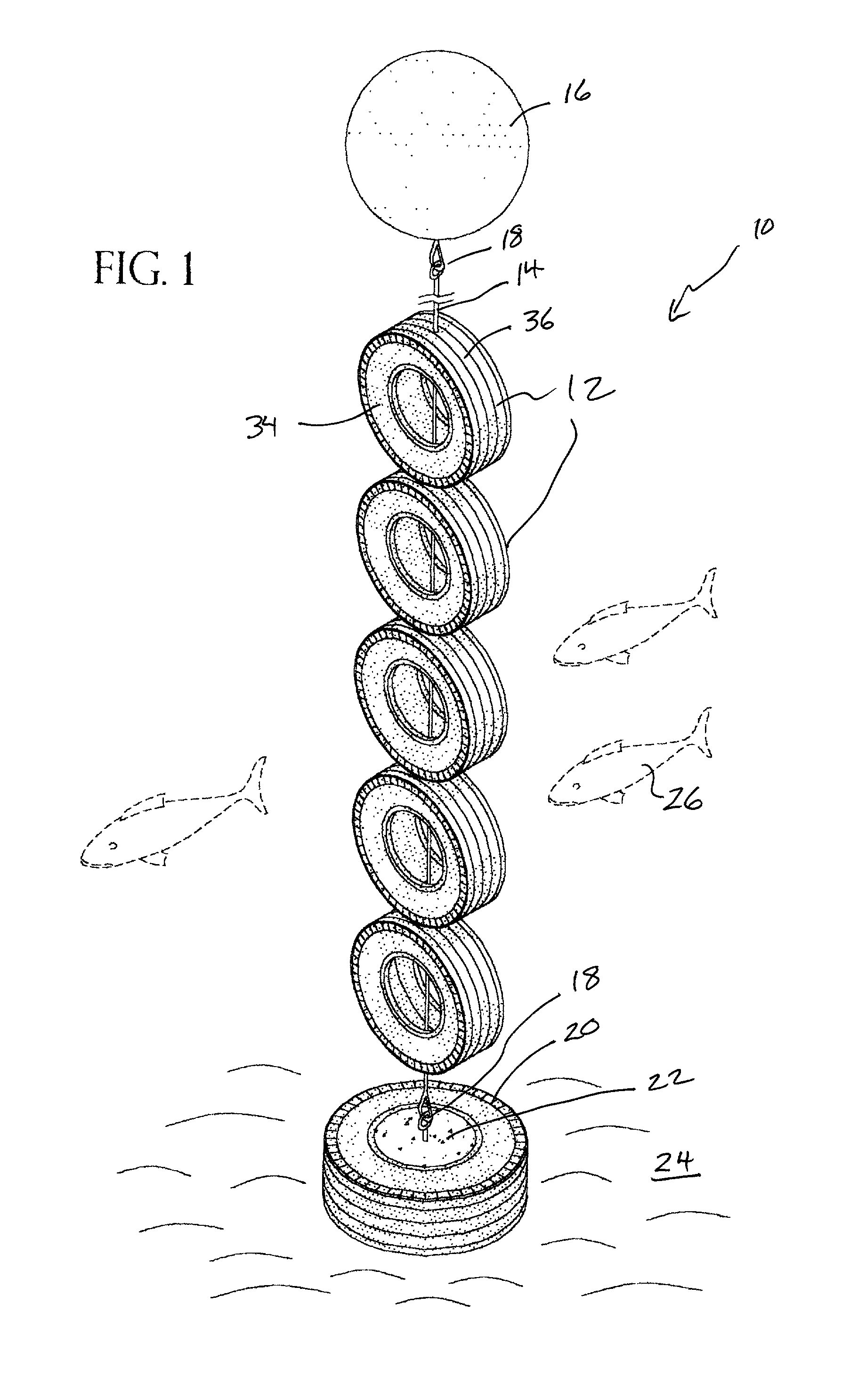
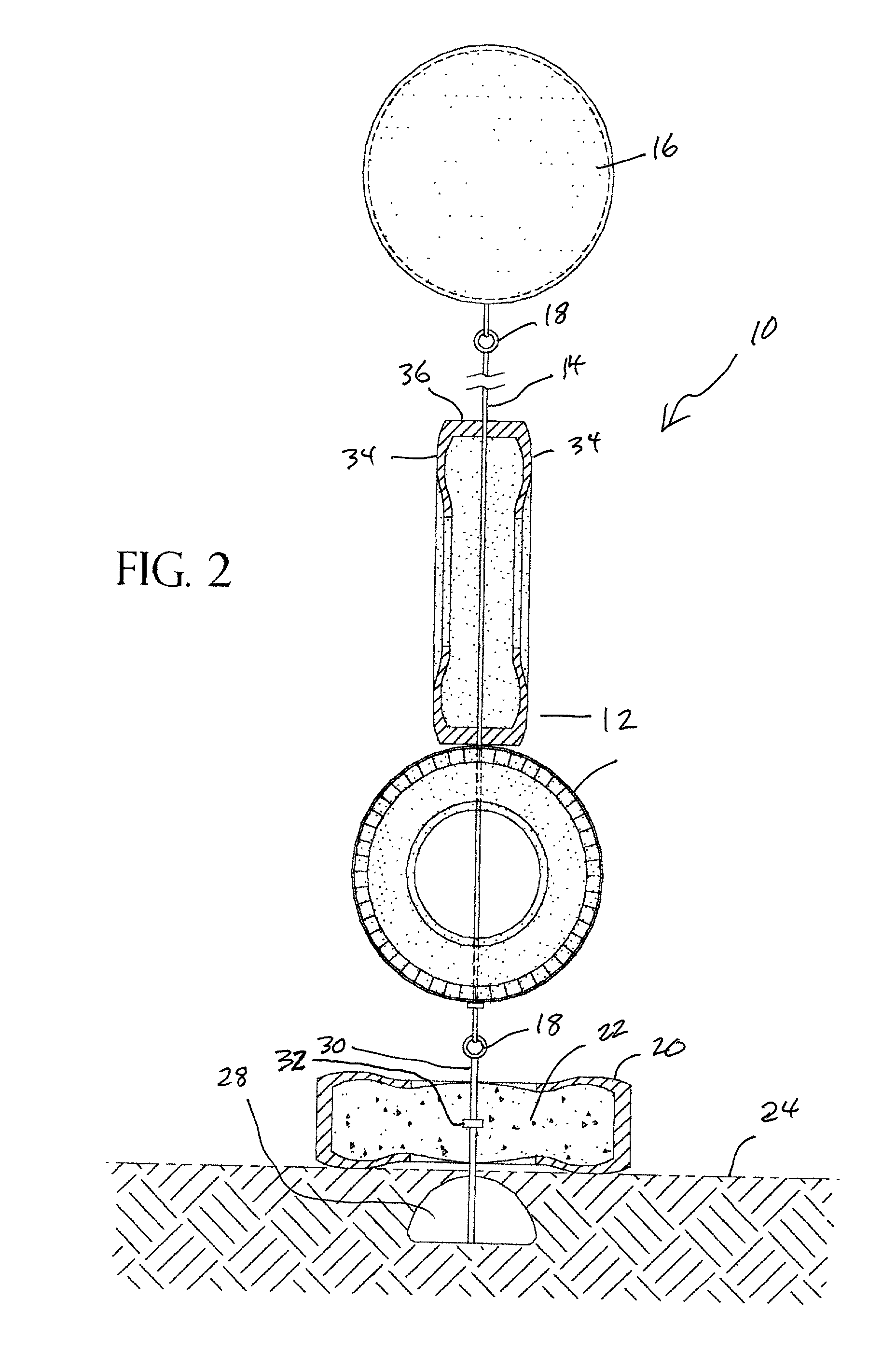
Apparatus for artificial reef
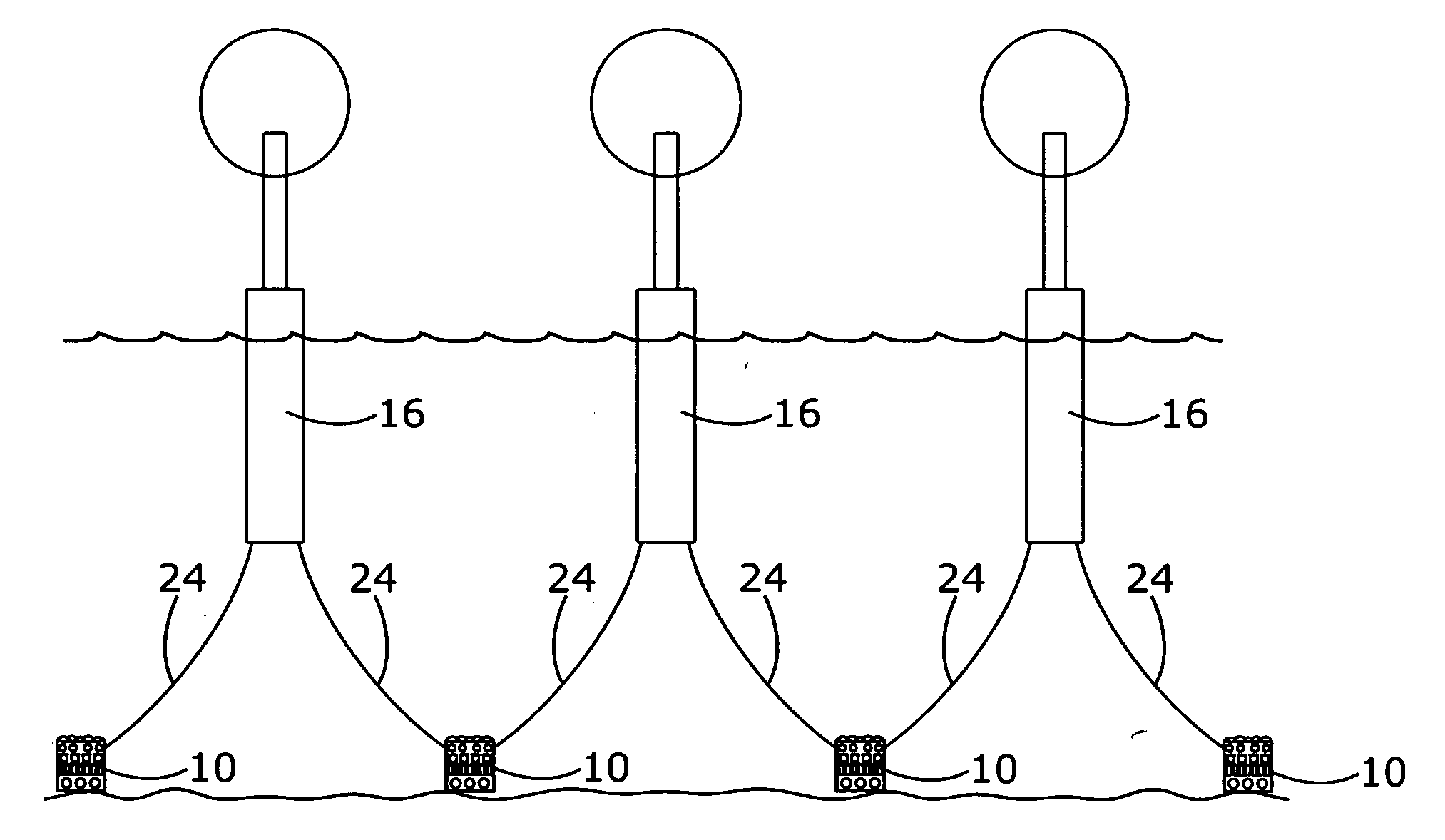
The present invention disclosed an artificial reef system having a plurality of tire casings tethered onto a cable-like line which reef system is supported in an upright position by a flotation device and which artificial reef system is anchored to the bottom of the ocean by another tire casing filled with concrete having an anchoring device disposed on its underside. The cable-like line may be monofilament. The reef system of tire casings is disposed upwardly due to the buoyancy of the flotation device and is free to move with the current in a natural manner to the extent that the cable-like allows. The flotation device may have a rigid wall so that it maintains its surface displacement when subjected to underwater pressure.
Owner:HALL JOHN W
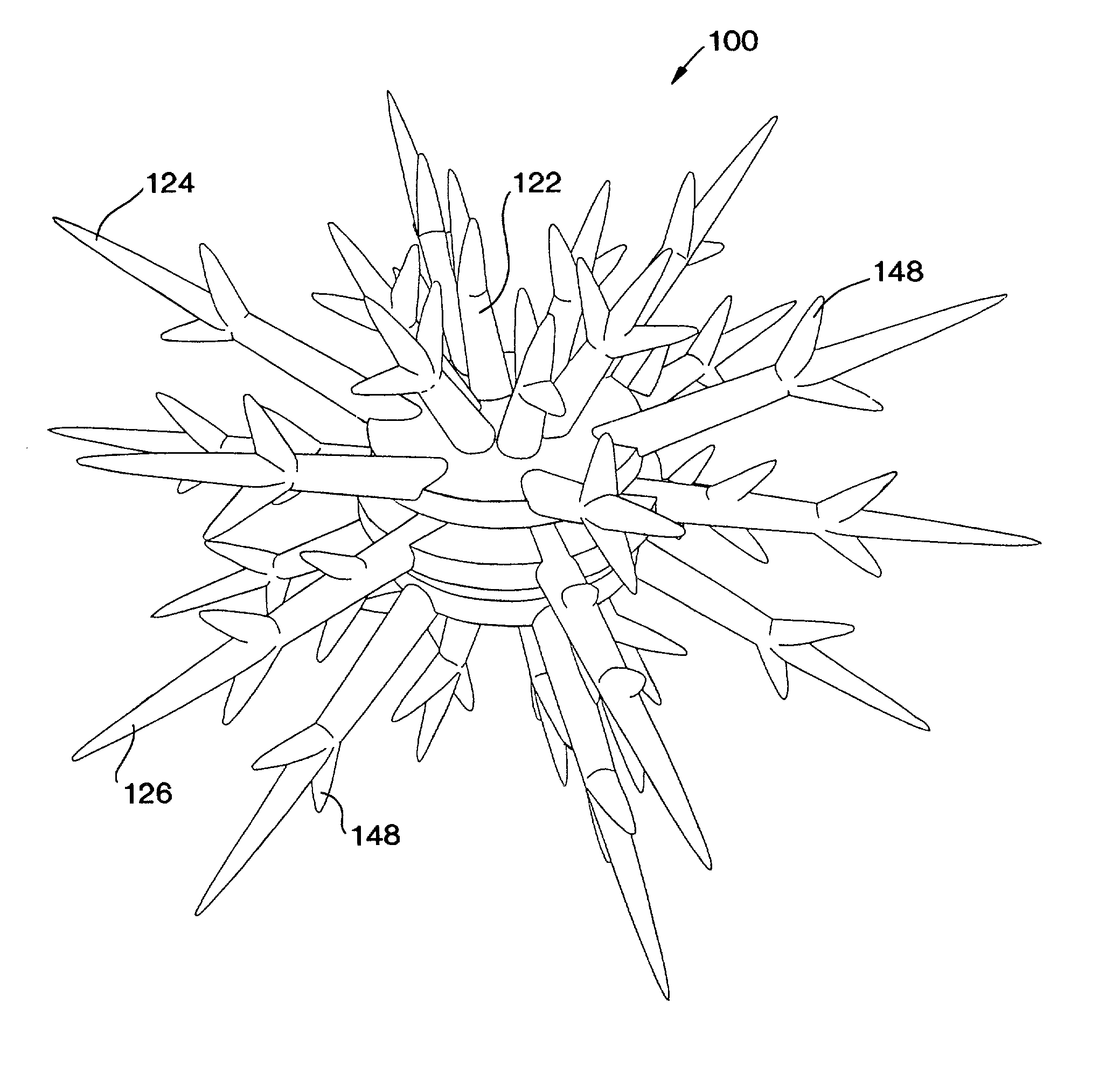
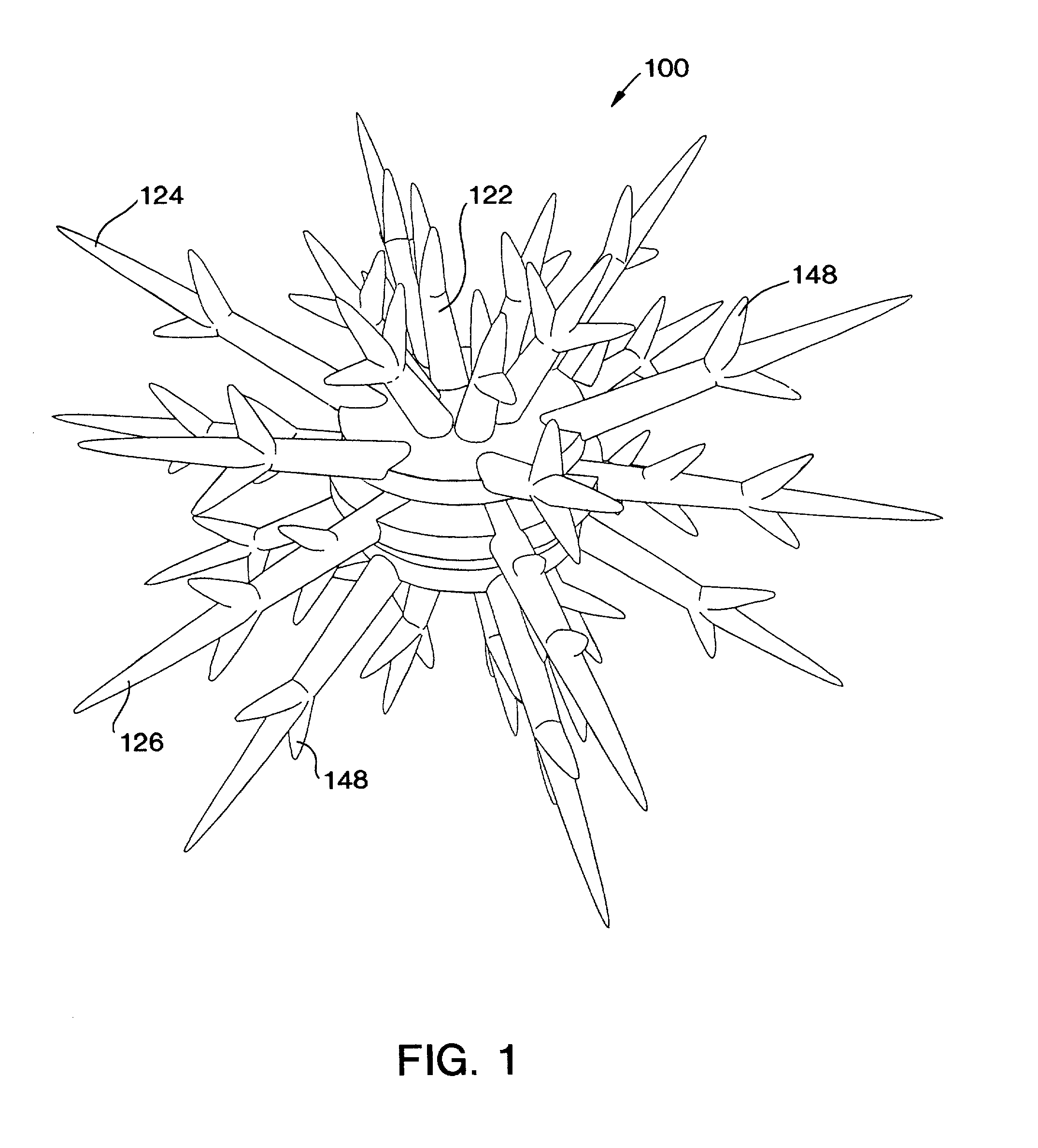
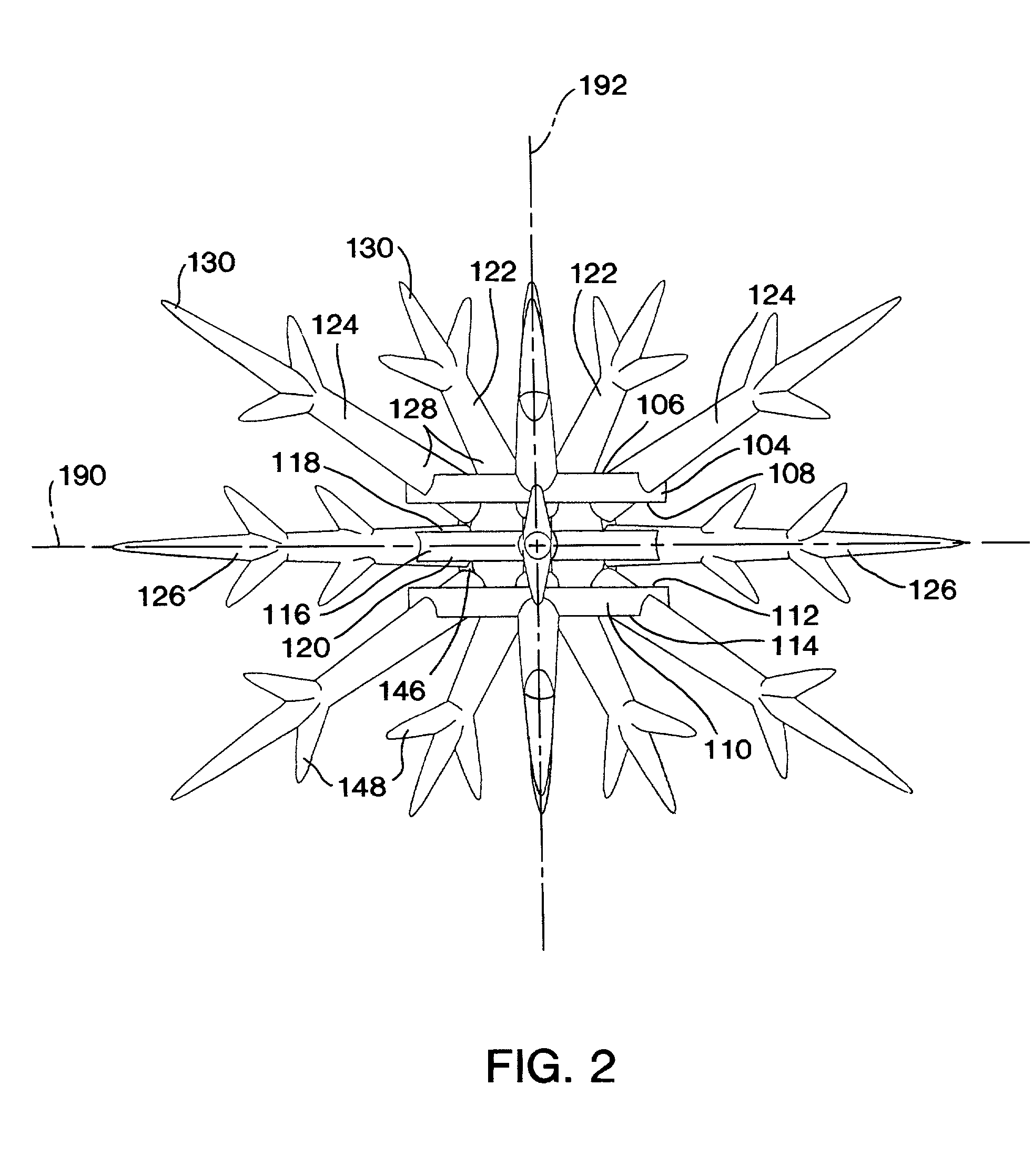
Artificial reef module for coral reef remediation
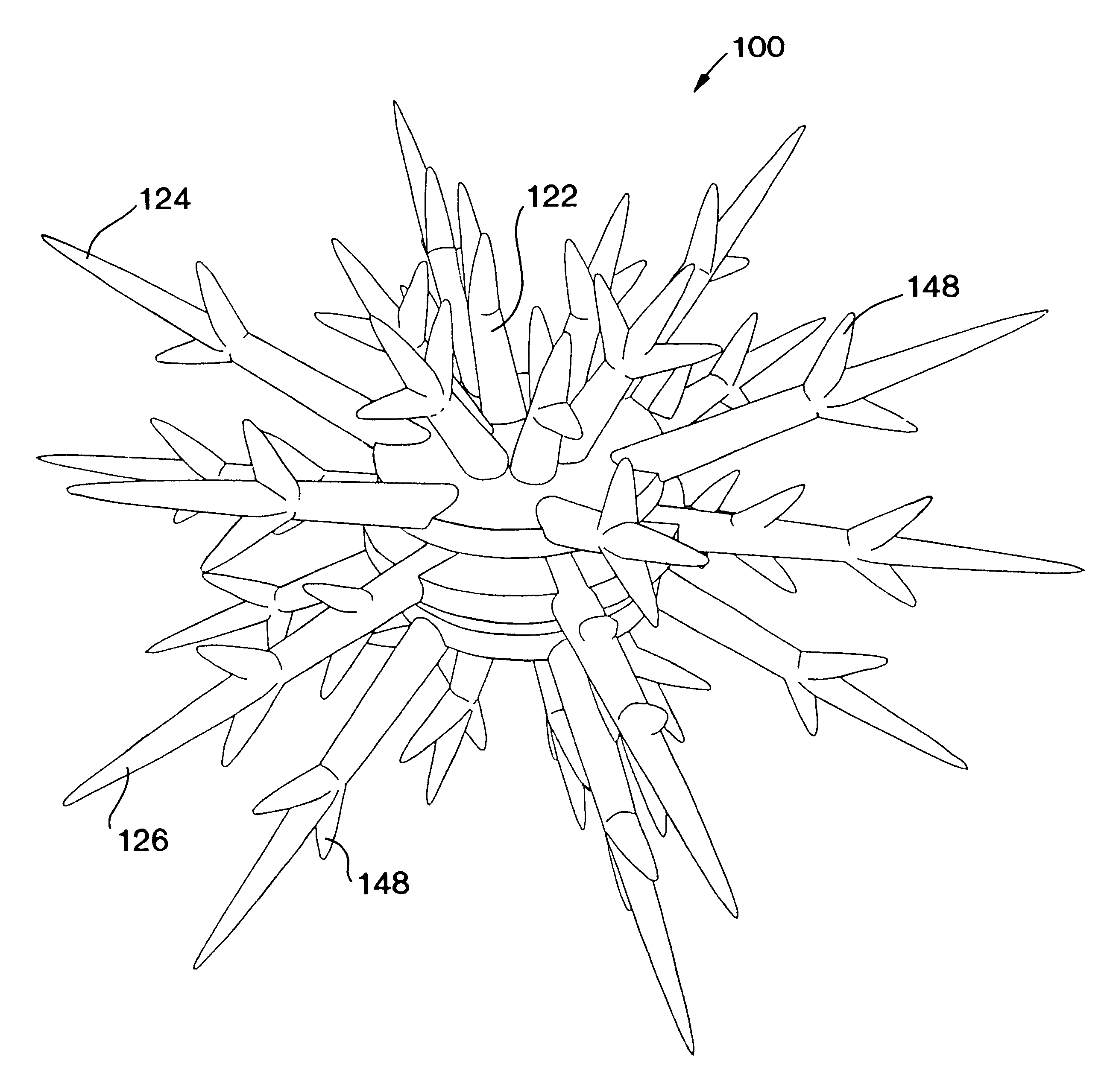
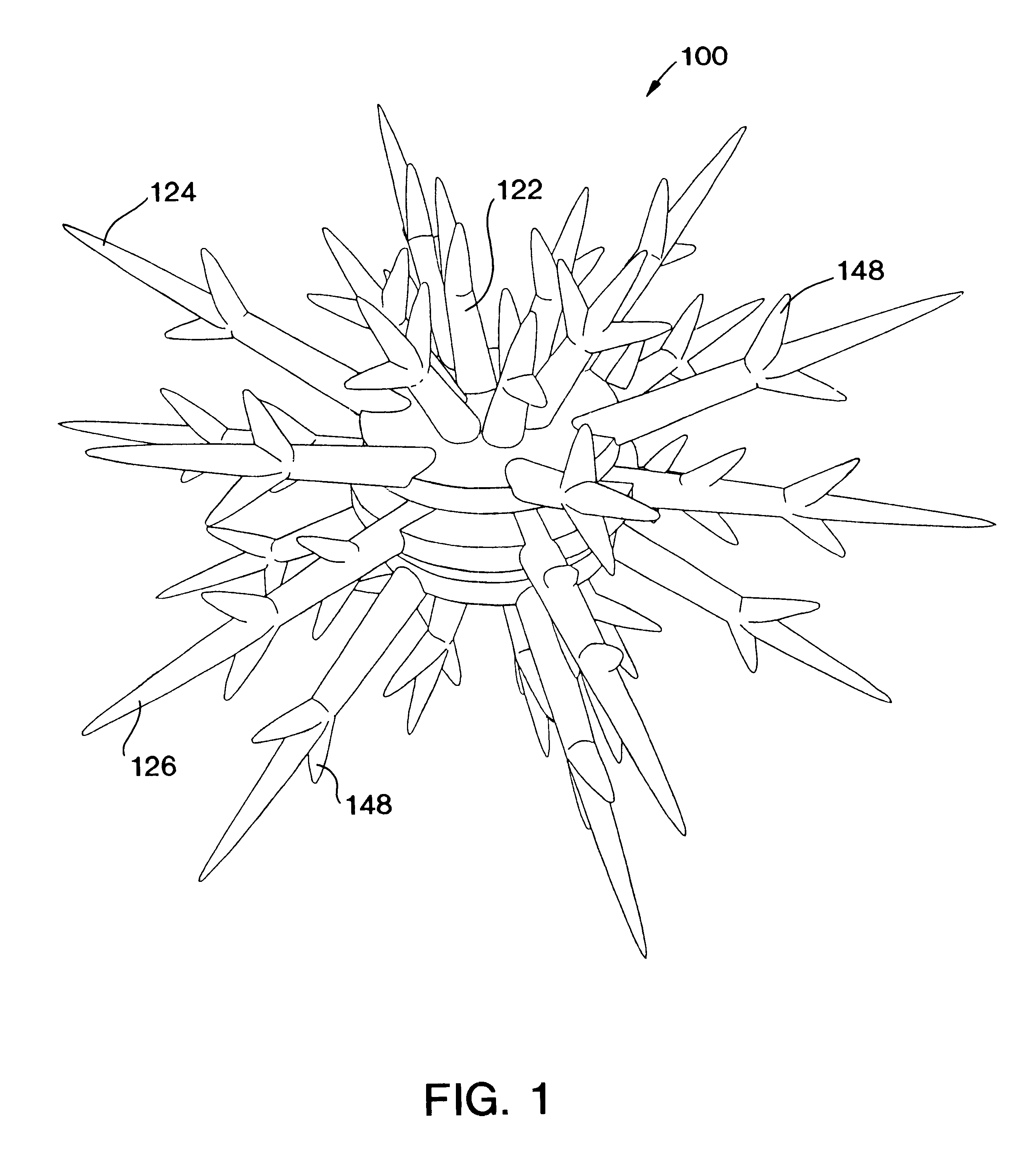
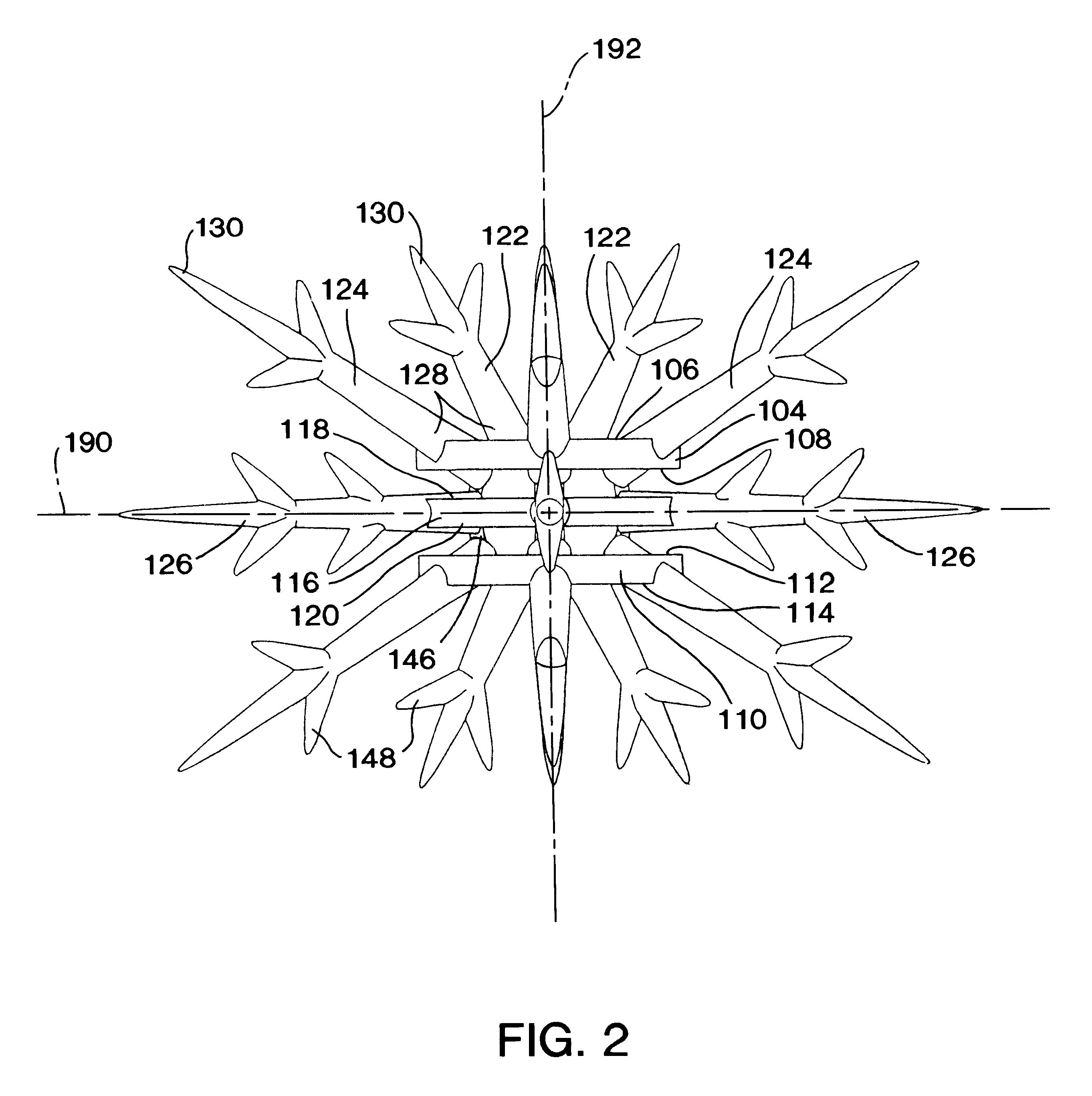
InactiveUS6464429B2Aid in disseminationPromote reproductionBreakwatersQuaysEngineeringArtificial reef
The artificial reef module for coral reef remediation of the present invention includes a central body having an upper settling plate, a middle settling plate, and a lower settling plate. Extending from the central body is a plurality of primary tines which further include a plurality of secondary tines extending from them. The primary tines include the supporting tines, the stabilizing tines, and the space filling tines. The branching of the tines closely replicates the appearance of natural branching coral. Over time the individual artificial reef modules for coral reef remediation would slowly degrade and allow the tines to break off. This degradation closely approximates the fragmentation that occurs with natural branching coral.
Owner:MOORE MICHAEL D
Artificial reef anchor structure
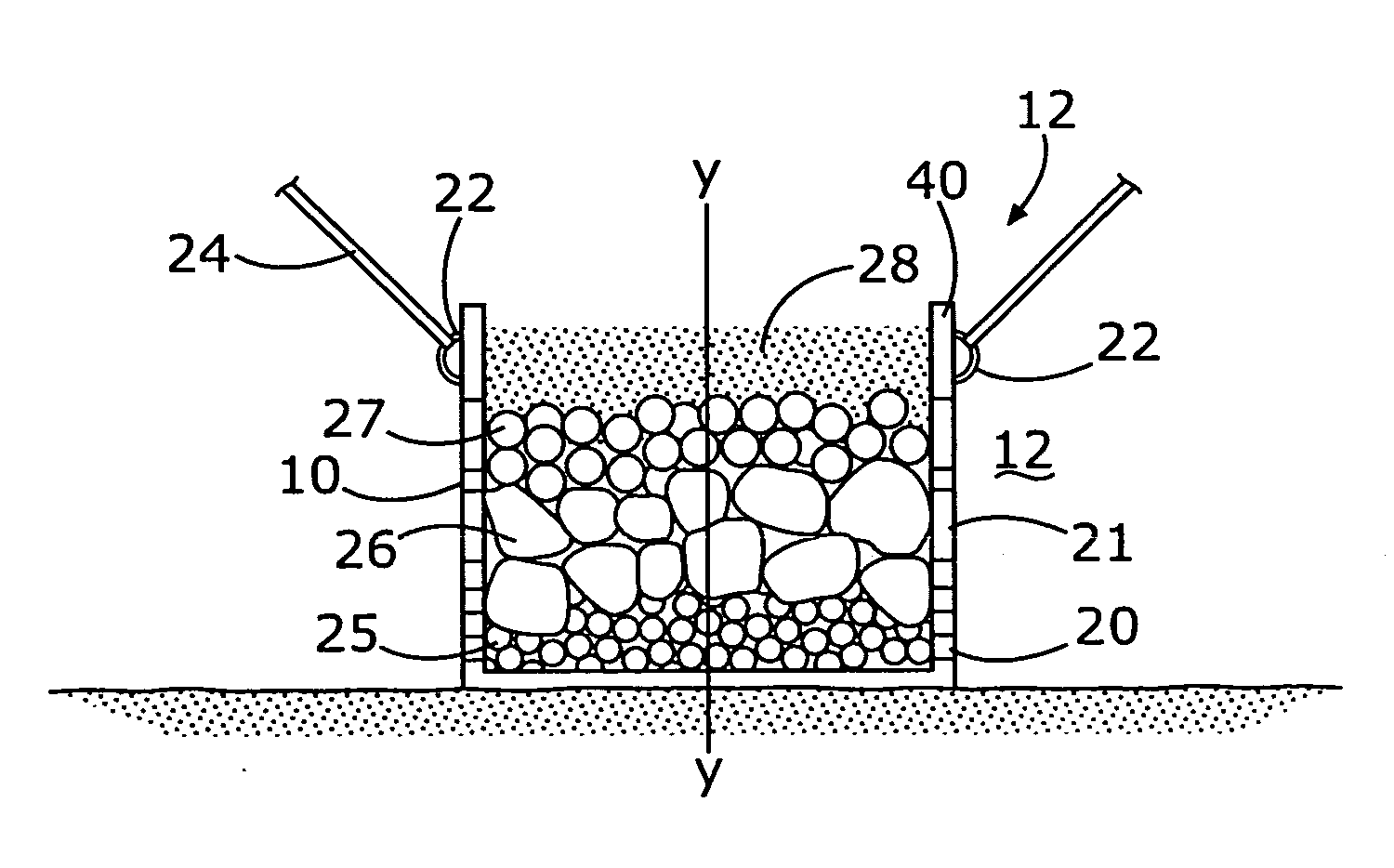
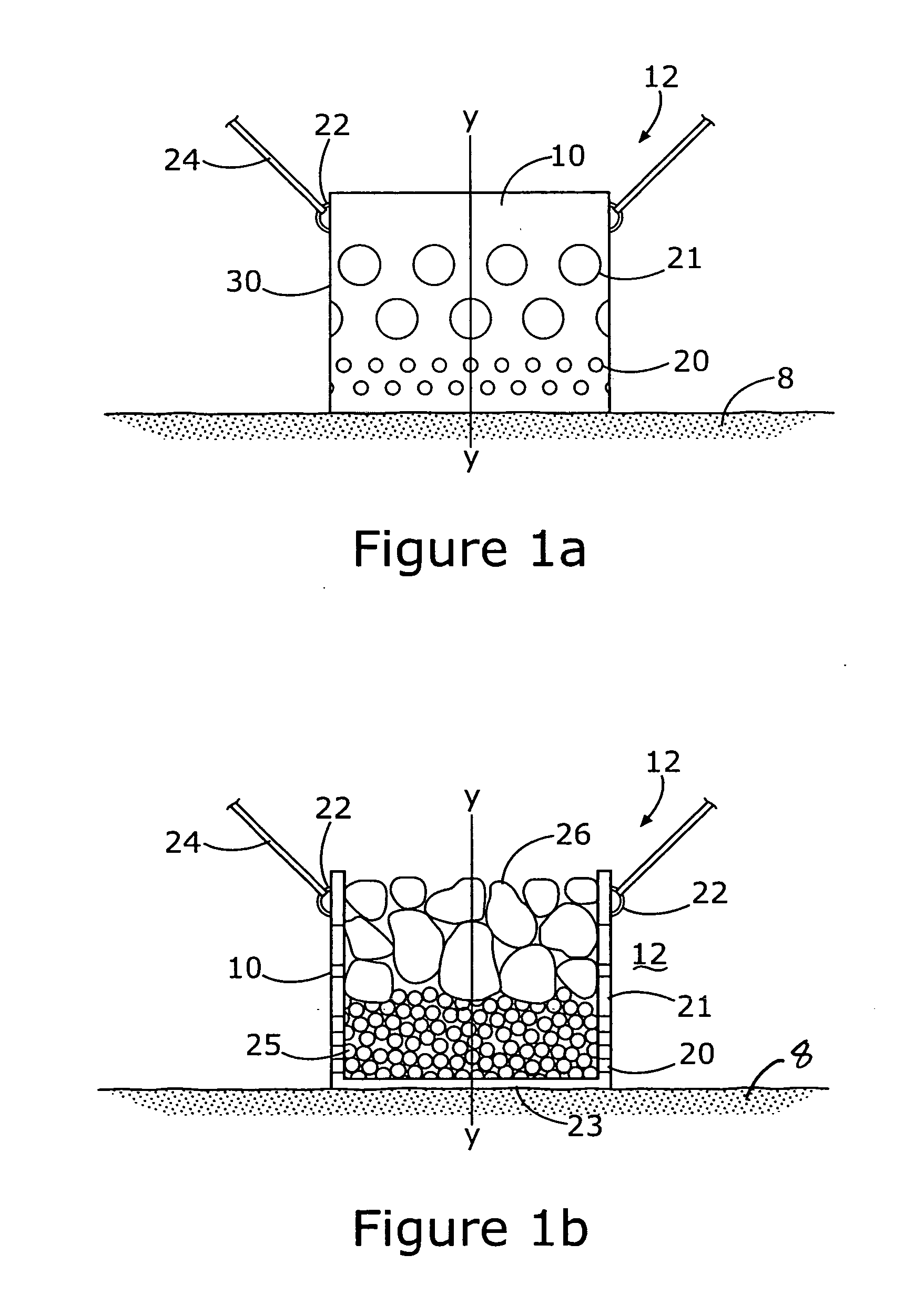
A container for underwater placement on a sea, lake or river bottom. The container has openings in the sides, top and bottom and is filled with ballast of large boulders, cobble, crushed coral, cast concrete modules or other materials. The openings allow water and water currents, as well as marine organisms, to pass freely therethrough. Over time, a wide assortment of marine organisms infiltrate and colonize the nooks, crevices and cavities of the ballast, thus utilizing the habitat as they would an artificial reef. One or more hitch points are provided on the container for attaching mooring lines for ships, boats, floating wind turbines or other floating structures, thereby allowing the artificial reef to anchor such structures.
Owner:HARDISON STEWART
Method for planting salvia officinalis in hardness adherance
InactiveCN102524041ASolve resource problemsSolve the problem of breeding year after yearClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsSalvia officinalisCladodes
The invention discloses a method for planting salvia officinalis in hardness adherance, which belongs to the technical field of algae propagation. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-processing the adherance, preparing a seedling collection pond, preparing to plant algae, collecting seedlings, cultivating young seedlings, putting in a sea area and managing on the sea. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the salvia officinalis are directly planted on artificial reefs, stones or cement components, can be firmly combined on the surfaces of the artificial reefs, the stones or the cement components through adhesion accentuation trainings in stages and then can be put into sea water in a appropriate time, new branches of the salvia officinalis can be grown on the adherance year by year, the problems that the salvia officinalis are in resource exhaustion due to man-made damage and the year-to-year propagation for maintaining algae resources in the sea area are solved, the method plays a great role in environment modification, resource recovery and the like, and simultaneously, the operation is simple and convenient.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Real-time fish stock monitoring and fish amount estimating system based on wireless communication network
InactiveCN105116414AAchievement distanceRealize the display effectAcoustic wave reradiationFish stockingReflection mapping
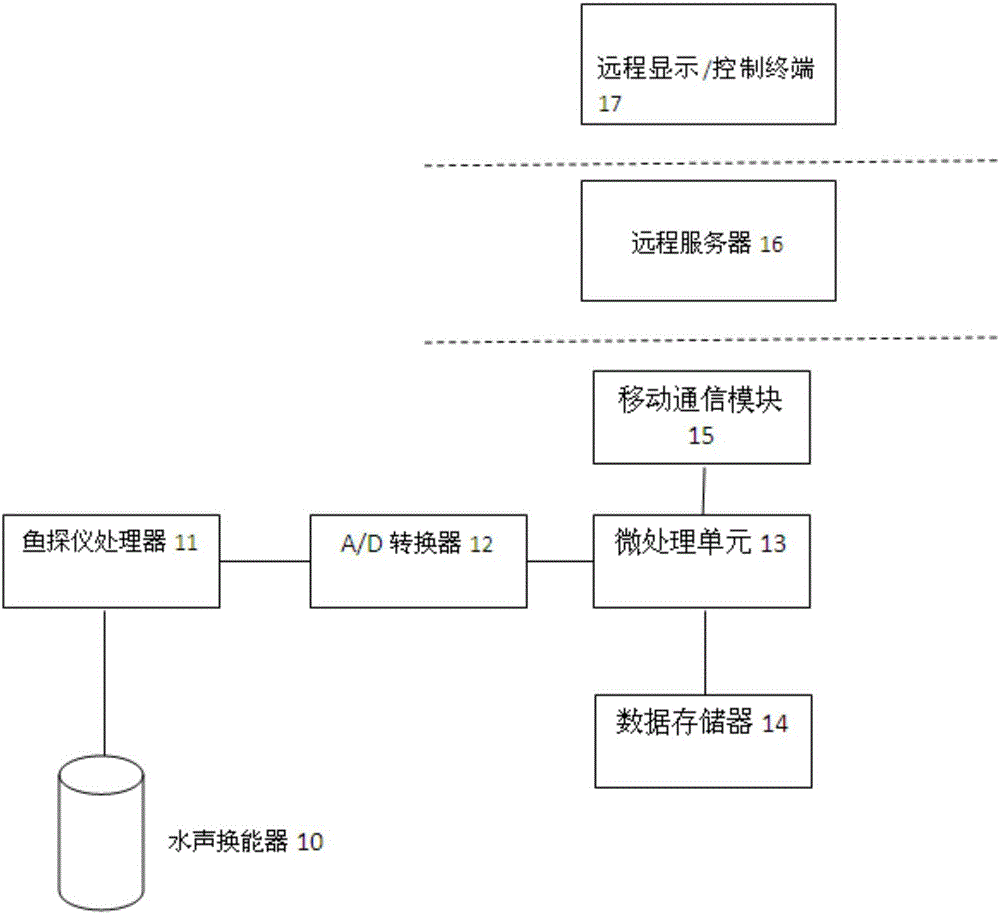
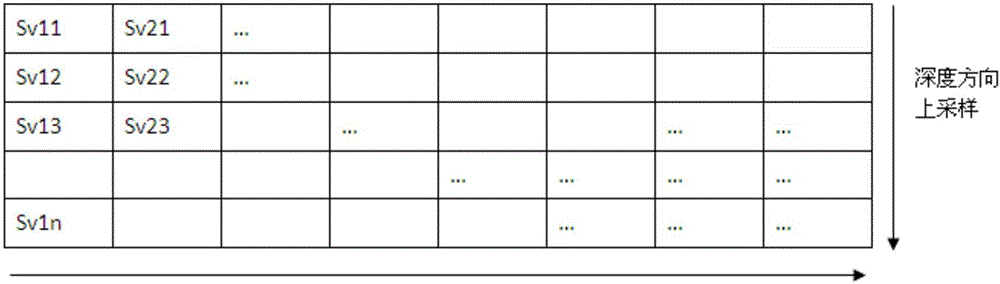
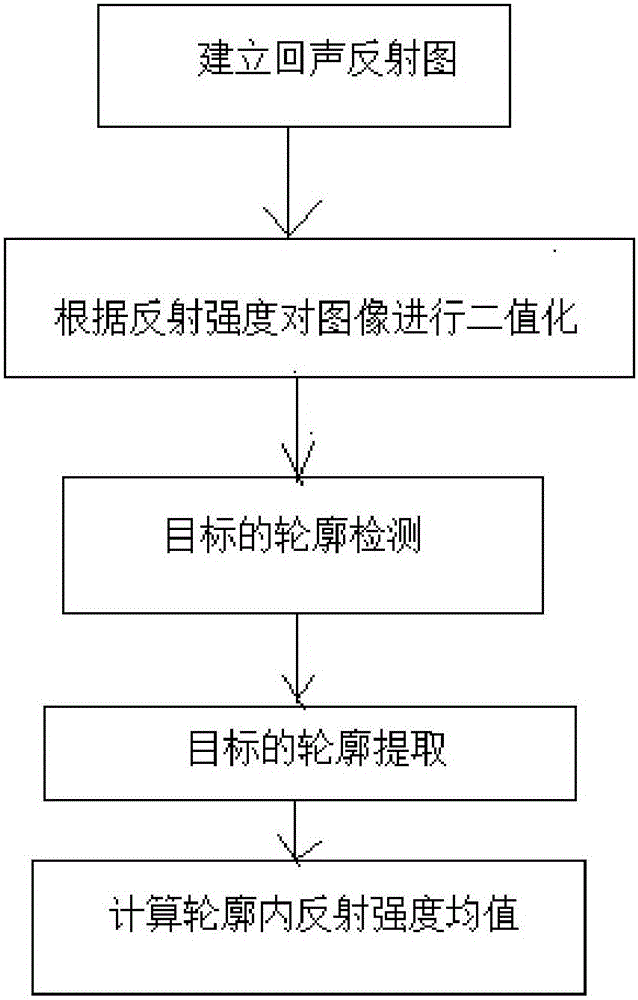
The invention provides a real-time fish stock monitoring and fish amount estimating system based on a wireless communication network, which mainly comprises an underwater acoustic transducer, a fish finder processor and a micro-processing unit, wherein the micro-processing unit detects echo reflection signals of a fish stock and extracts an average value of the rear echo reflection strength within a period of time in a specific water depth range; and fish stock mapping information in an echo reflection mapping graph formed by echo signals is extracted, and remote transmission and display of fish stock information are realized. The system can also be used for predicating the fishing yield besides displaying fish finder images in real time. The system provided by the invention can be applied to a plurality of fields such as real-time monitoring for fixed net fishery and the sea net cage breeding industry, observation of artificial reef fish-gathering effects, fish stock detection under an artificial fish-gathering device in tuna seine purse fishery and the like, and has very important significance for improving the production efficiency of marine fishery.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV +1
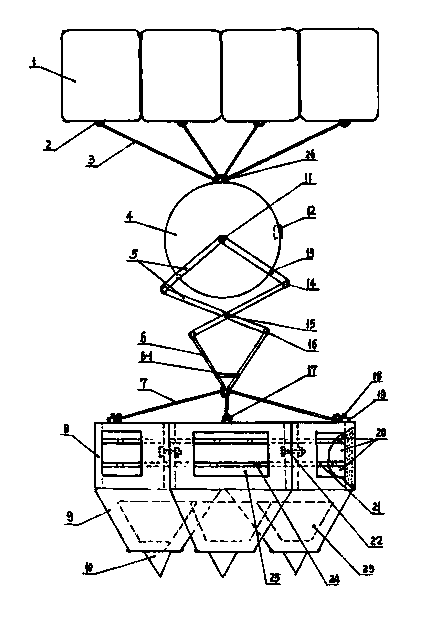
Artificial reef body
InactiveCN1695437AHigh densityImprove qualityPisciculture and aquariaCultivating equipmentsEngineeringBuoyancy
An artificial reef is composed of a top platform, a reef frame, a group of floating bodies in the upper part of said reef frame, at least three layered netted cases in the middle part of reef frame, a group of primary float controlling chambers, at the bottom of reef frame and a group of secondary float controlling chambers at the sides of reef frame.
Owner:张畅
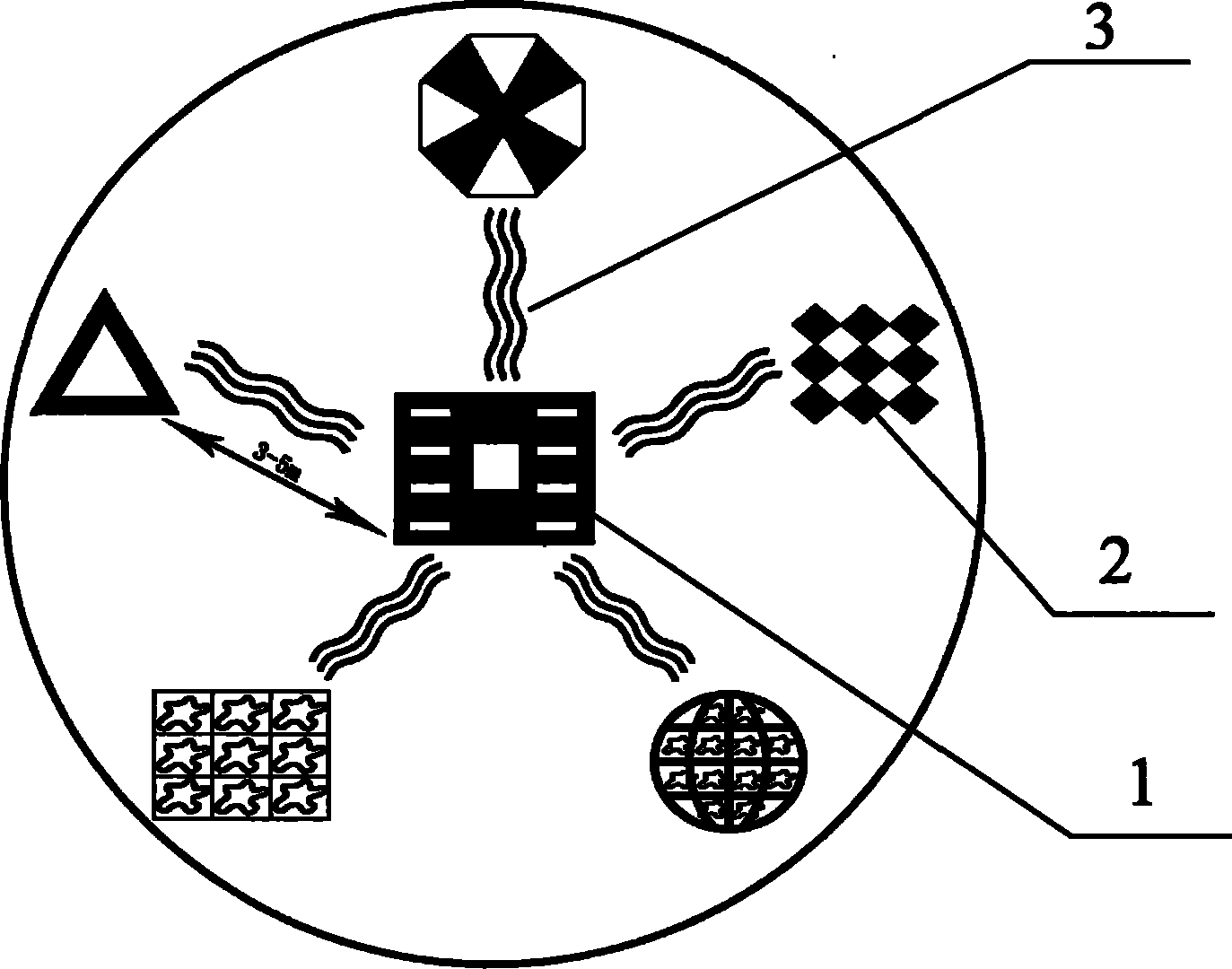
Star-like radial allocation method for artificial reefs
InactiveCN101766136AImprove balanceProliferation effect is goodClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSea urchinArtificial reef
The invention discloses a star-like radial allocation method for artificial reefs, which is characterized in that a cubic reef form with the side length of 1 to 2 meters is used as a main reef, 3 to 8 auxiliary reefs with the height of 80 to 120 centimeters are uniformly distributed on the circumference which uses the main reef as the central point, the main reef and each auxiliary reef are connected through a stone connection bridge with the length of 3 to 6 meters, and the categories of the adjacent auxiliary reefs are diverse. The artificial reefs are closer to the reality and are favorable for the balance of the ecological system, and the stone connection bridge serving as a radiation belt provides a bridge for the movement of rare seafood among the reefs and plays a role in sheltering. Through on-site sea area tests, the rare seafood such as sea cucumber, sea hedgehog, abalone and the like can rest in gaps among the main reef, the auxiliary reefs and the stone connection bridges or on the surfaces; the good growth condition of algae on the reefs provides baits for the rare seafood, so the proliferation effect of the rare seafood is obvious; and reef-associated fishes such as hexagrammos otakii, sebastes schlegeli and the like rest in the main reef and the auxiliary reefs, so the whole reef group structure is stable and forms a good small ecosystem.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Bowl-shaped floating artificial reef and throwing device
InactiveCN103651186APrevent from causingImprove air qualityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaElectrical controlEngineering
The invention belongs to a bowl-shaped floating artificial reef and throwing device. The device is characterized in that an artificial reef base (9) is manufactured into a bowl shape, the lower portion of the artificial reef base (9) is provided with conical positioning insertion heads (10), and fish inhabiting chambers (20) are arranged in an artificial reef body (8); artificial reef hanging rings (17) are connected with hooks (6) through artificial reef hanging ropes (7), the upper ends of the hooks (6) are movably connected with the end portions of lower connecting rods of four connecting rods (15) through a fourth connecting shaft (16), and two upper connecting rods are fixedly connected with a balloon (4) through connecting rod fixing ropes (13); the balloon (4) is provided with an electric control valve (12) and a balloon hanging ring (26); the balloon hanging ring (26) is connected with hanging rings (2) installed on the lower portions of four light air bags (1) through hanging ropes (3). The device has the advantages of enabling coastal or offshore fish farming to be greatly developed, improving air quality and improving living environment of people.
Owner:DALIAN ZHONGNAN EXTENSION RESOURCES & ENVIRONMENTAL TECH RES
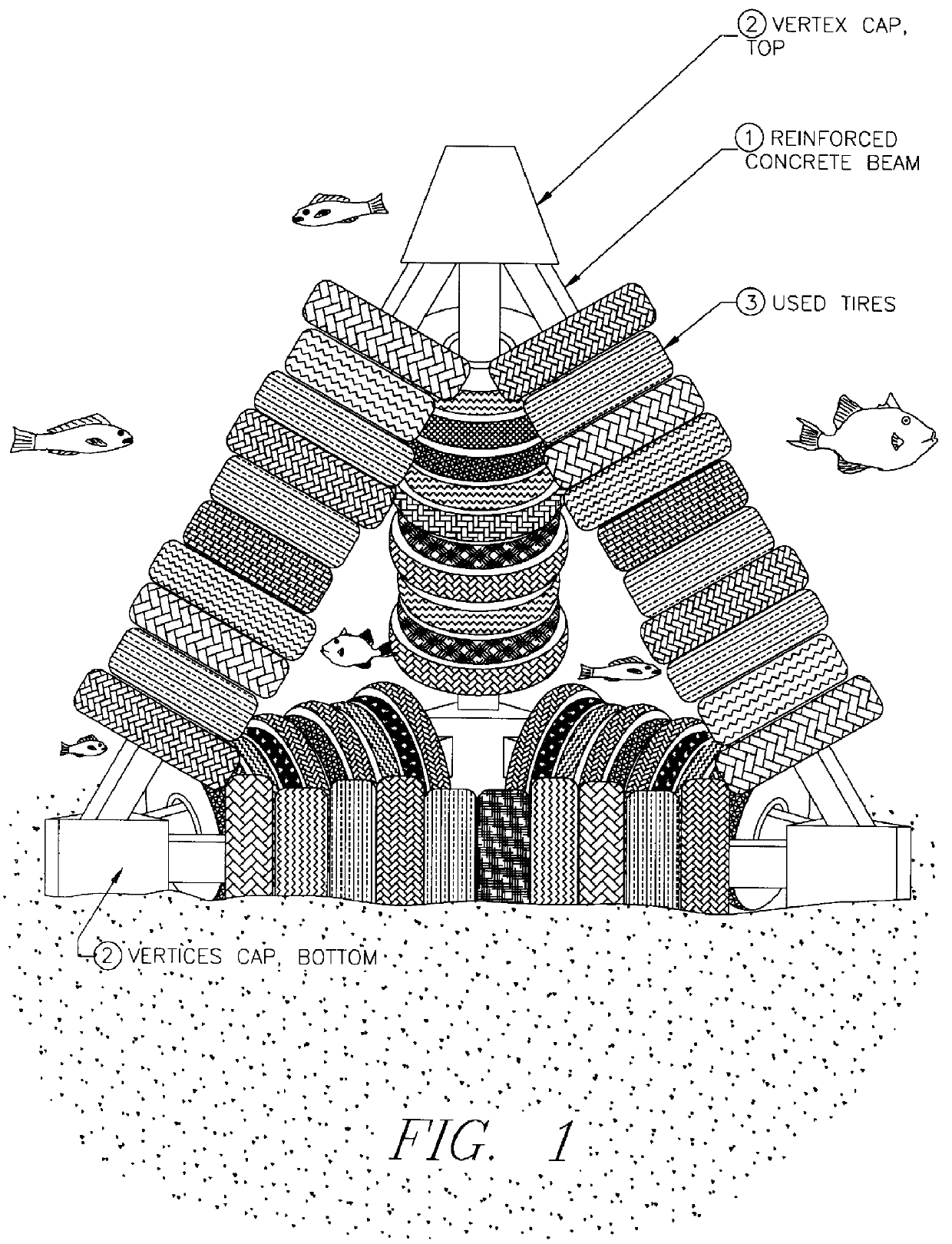
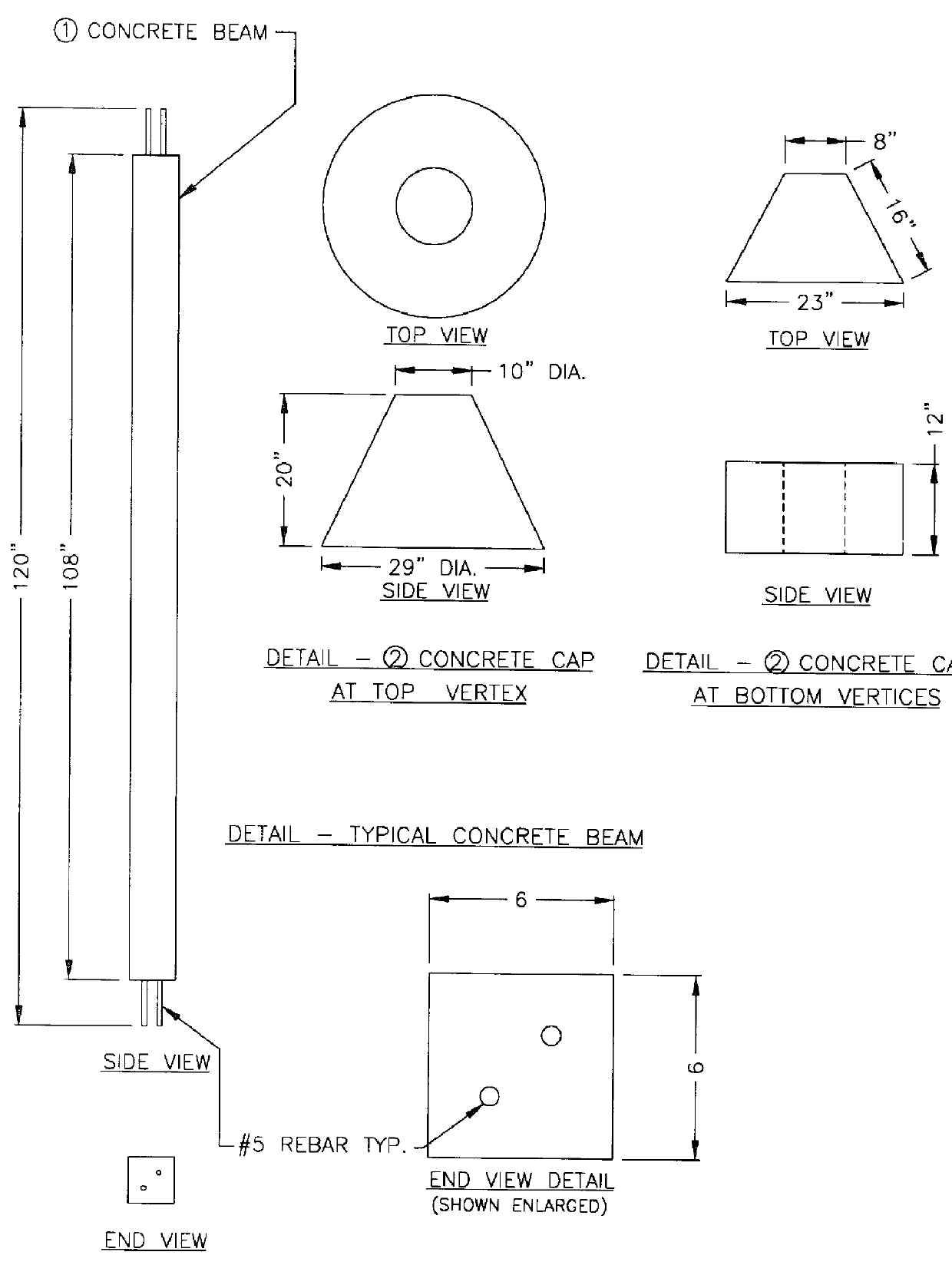
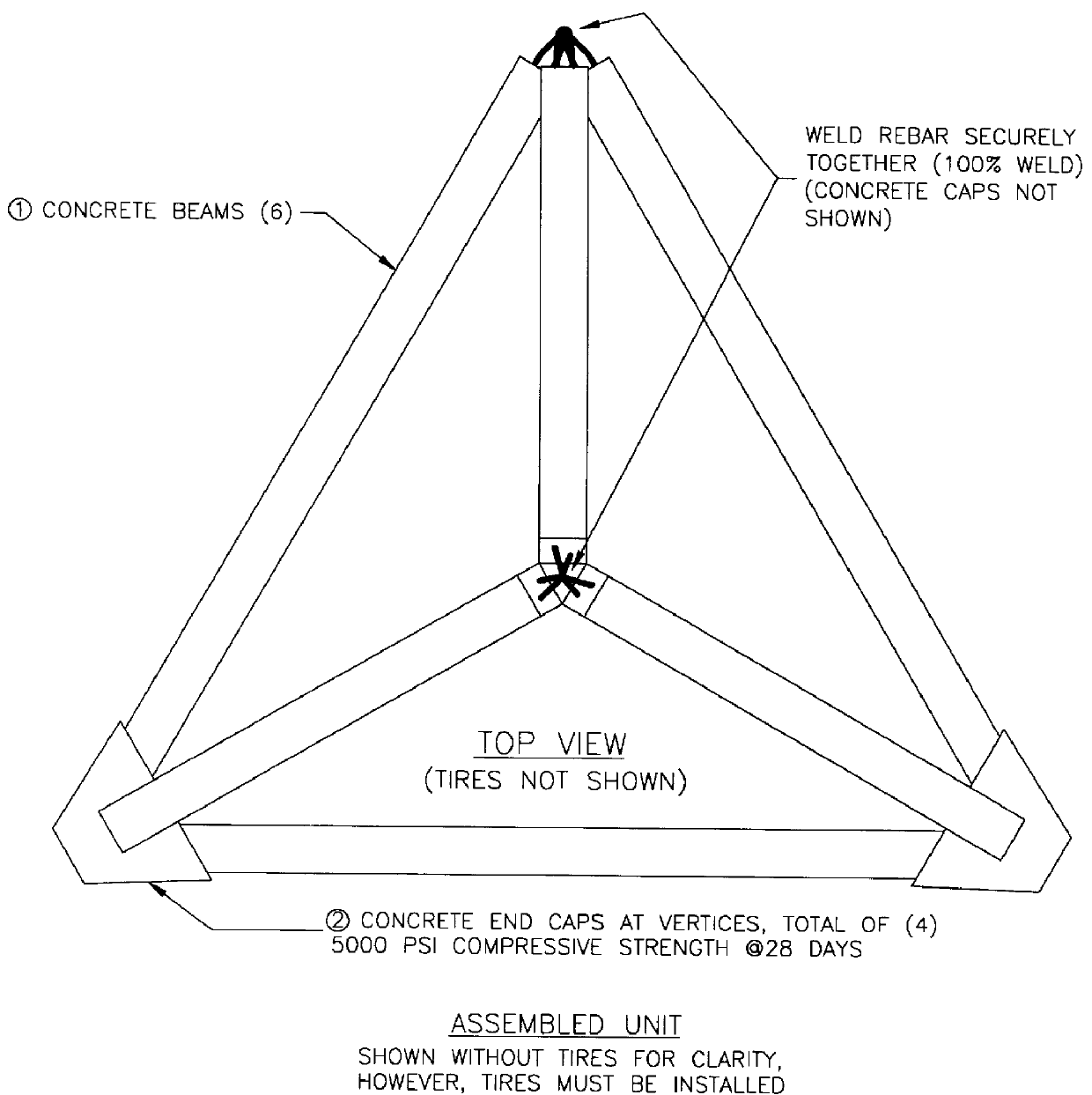
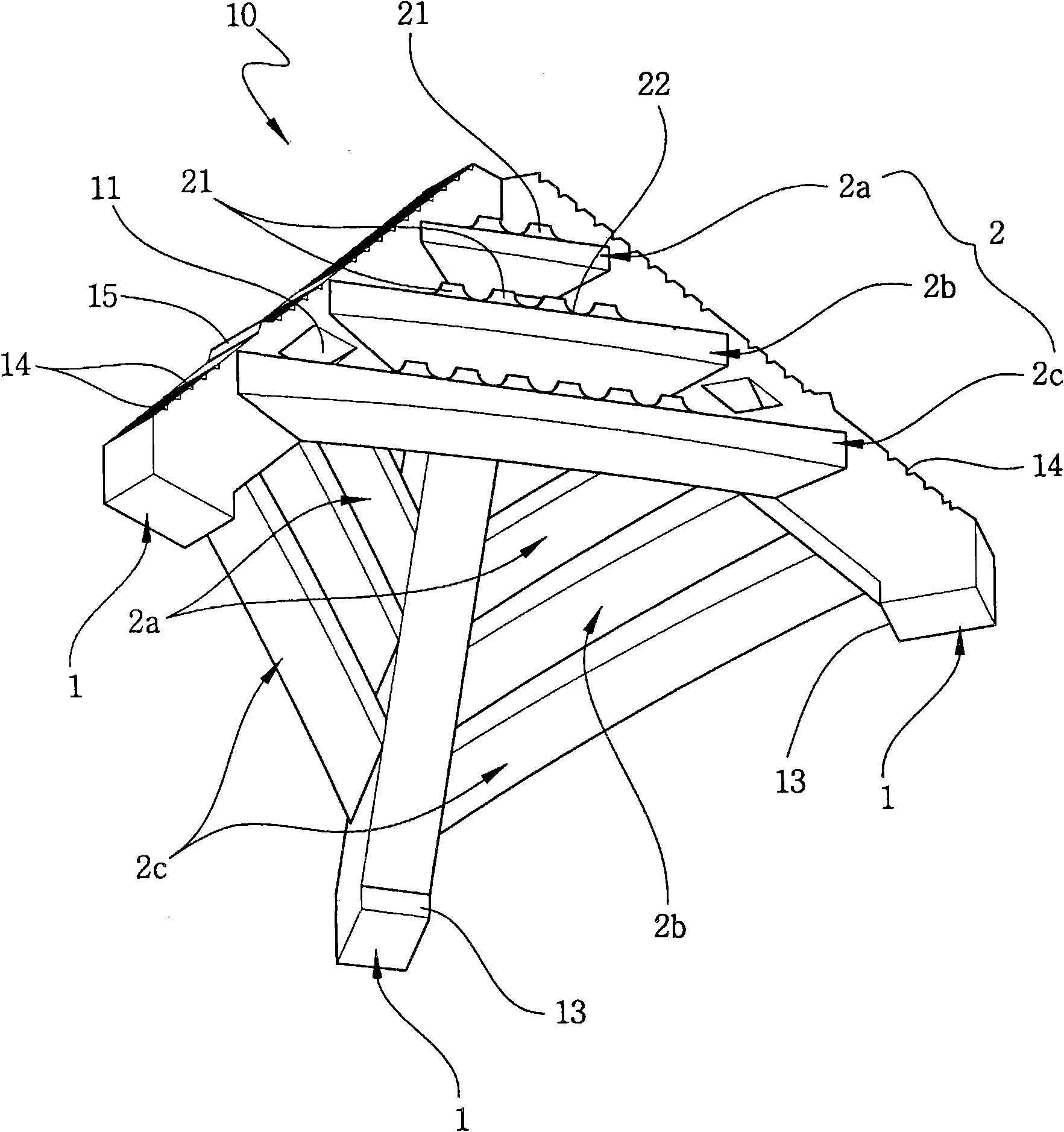
Concrete and tire artificial reef
An equilateral tetrahedral frame, comprising six concrete beams inserted through the center of a number of automotive tires. The ends of the concrete beams are fastened together at four points. These four points are covered by a cap of concrete to seal the fastening points. The reef device may be of any size. The design permits ease of transport due to its ability to stack one upon another uniqueness of this reef is in the design. Once the reef is transported to its desired location, it can lowered or dropped to the sea floor.
Owner:WALTER DAVID M
Method for constructing manually controlled submarine algae field
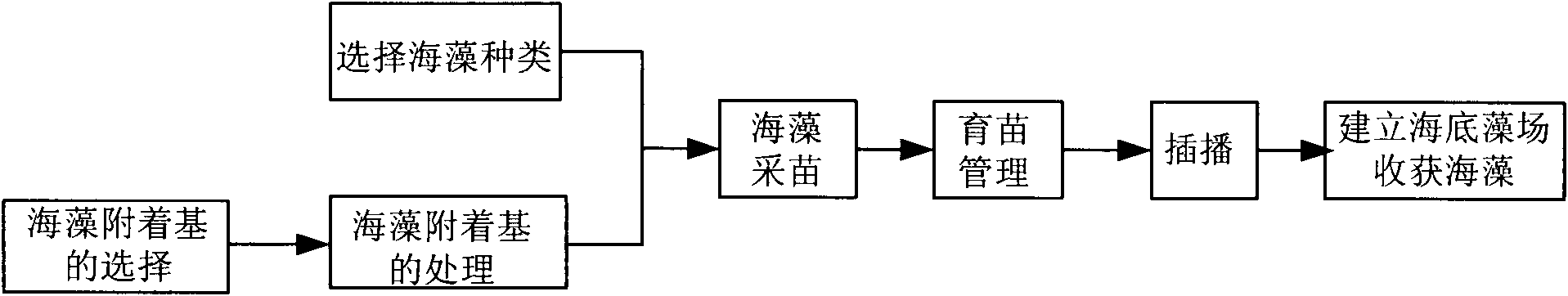
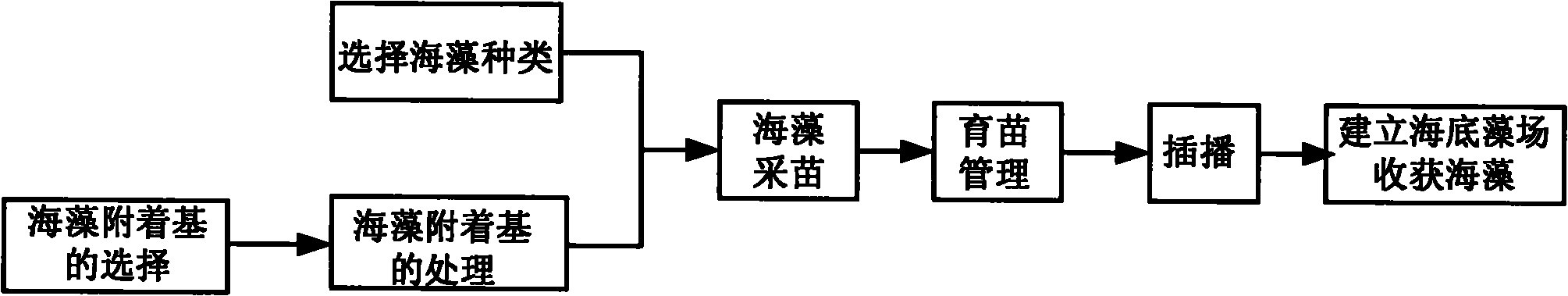
InactiveCN102138513AAchieve autonomous operationLow costClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsOcean bottomEmbryo
The invention provides a method for constructing a manually controlled submarine algae field. The method comprises the steps of selection and treatment of seaweed substrates, culture of seedlings of seaweeds, sowing and the like, wherein the seaweed substrates are breeding screens formed by weaving reddish brown ropes; the step of culture of seedlings of seaweeds comprises the substeps of collection of seedlings of seaweeds and management of culture of seedlings; after the water density of the collected spores during release in the substep of collection of seedlings of seaweeds reaches 10-15 zoospores in the field of 100-times microscope, the seaweed substrates are put in the seawater to adhere; and the adhesion density is 20-30 embryo spores in the field of 100-times microscope. The method has the following advantages and beneficial effects: the variety, density, place and sowing time of the submarine algae field achieve manual control; the fixed substances of the algae, such as C, N, P and the like, are taken from the sea to the land by harvesting the seaweed, so the effect on solving the ecological problems is longer; the cost is far lower than that of the artificial reefs; thenatural submarine geomorphology is not damaged; and the submarine algae field can be formed in a shorter time, thus rapidly increasing the resource quantity.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Tire recycling/disposal system and tire recycling/disposal annulet cylinder or construction block
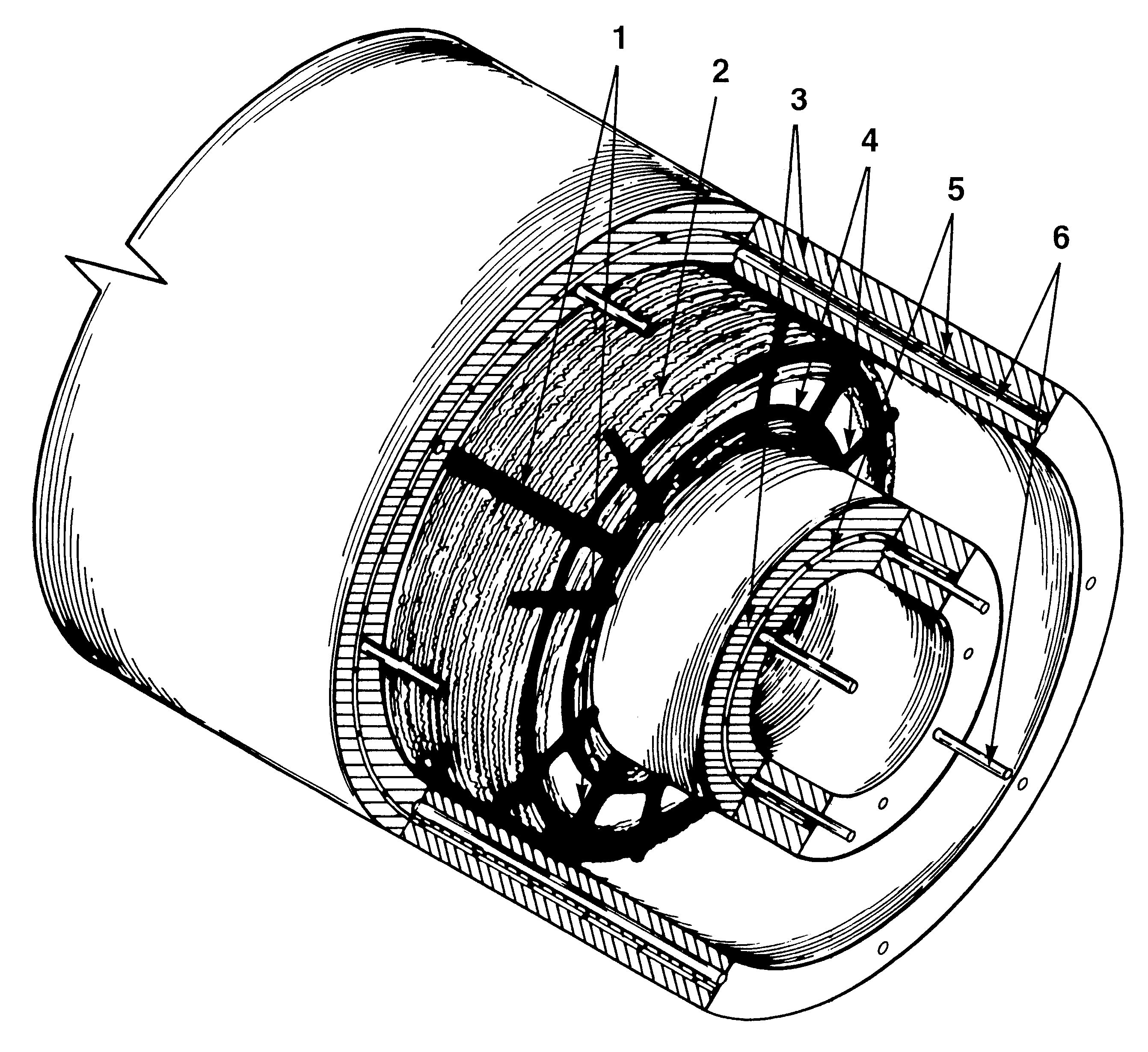
A method and means for making and using three composite concrete construction components that share a common matrix. The articles are comprised of: discarded whole tires 2, axially aligned, with rebar formed washers 4, transversely placed at intervals between the tires 2. The tire bundle 2, with the washers 4, are compressed, banded with metal or fiber strapping 1, reinforced with wire mesh 5, and rebar rods 6, and encased in a concrete shell 3, to form: cylinders; rectangular-blocks; or, half blocks. The concrete composite articles can be molded with hollow cores and used individually or in multiple configurations to construct environmentally safe structures such as: artificial reefs, beach erosion inhibitors, jetties and artificial islands; imbricated walls for: highway dividers, noise abatement, retaining and security walls around airports and buildings. These composite concrete articles will allow for millions of discarded tires to be recycled into non-polluting, environmentally friendly structures for use in virtually any construction project.
Owner:EL ADUMBRATE LLC A FLORIDA LIMITED LIABILITY ALL MEMBER OF EL ADUMBRATE LLC ARE US CITIZENS NUMBER L06000078373
Composite transplantation method of coral
InactiveCN101548661ASolve associativitySolve the massive proliferation of coralsAnimal husbandryBudHigh survival rate
The invention discloses a composite transplantation method of coral, comprising the following steps: cutting the corals to be transplanted into micro bud-seedlings and sterilizing the bud-seedlings; forming a network transplantation net using ropes and setting a micro artificial reef, respectively embedding the sterilized bud-seedlings into the micro artificial reef, then culturing the bud-seedlings in the sea of grade III standard; transplanting the transplantation net into the sea and wrapping round the sea bed matrix when the micro bud-seedlings of the coral on the transplantation net survive in the sea, after the coral grows up, the new coral firmly being combined with sea bed matrix to form a connected active coral reef, thereby repairing and rebuilding the coral reef ecosystem. The composite transplantation method uses the net transplantation way to combine the coral single with the natural coral reef, thereby effectively solves the technique problems of the combination of the coral to be transplanted with the sea bed matrix, coral mass multiplication, and disease control, with features of low cost, high survival rate and high benefit.
Owner:陈宏
Mooring habitat structure
InactiveUS20090304453A1Promote colonizationEasy accessAnchorsBulkheads/pilesMarine engineeringWater flow
A container for underwater placement on a sea, lake or river bottom. The container has openings in the sides, top and bottom and is filled with ballast of large boulders, cobble, crushed coral, cast concrete modules or other materials. The openings allow water and water currents, as well as marine organisms, to pass freely therethrough. Over time, a wide assortment of marine organisms infiltrate and colonize the nooks, crevices and cavities of the ballast, thus utilizing the habitat as they would an artificial reef. One or more hitch points are provided on the container for attaching mooring lines for ships, boats, floating wind turbines or other floating structures, thereby allowing the artificial reef to anchor such structures.
Owner:THE WIND REEF GRP
Method for distribution of offshore oil platform abandoned structures and laying of artificial reefs
InactiveCN102599092AReduce disposal costsImprove stabilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaReinforced concreteEnvironment of Albania
The invention provides a method for distribution of offshore oil platform abandoned structures and laying of artificial reefs. The method is characterized in that each offshore oil platform abandoned structure comprises an abandoned platform and auxiliary equipment and facilities thereof, the abandoned platform is used as a central frame for the artificial reefs, reef units which are disposed around the central frame and composed of single reefs, abandoned concrete structures and discarded ships form a reef group, and at least two reef groups built with the abandoned platforms form a reef belt along trestles between the respective independent platforms. The plurality of small-sized reef belts built with the abandoned platforms form a large-sized reef belt in a centralized oil production area. Each single reef is composed a tubular reinforced concrete reef and cubic-framed reinforced concrete reefs by stacking. By the method, economic cost, environmental cost and energy consumption in treatment of offshore oil platforms are lowered, the fishery enhancement function is given to play more effectively.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
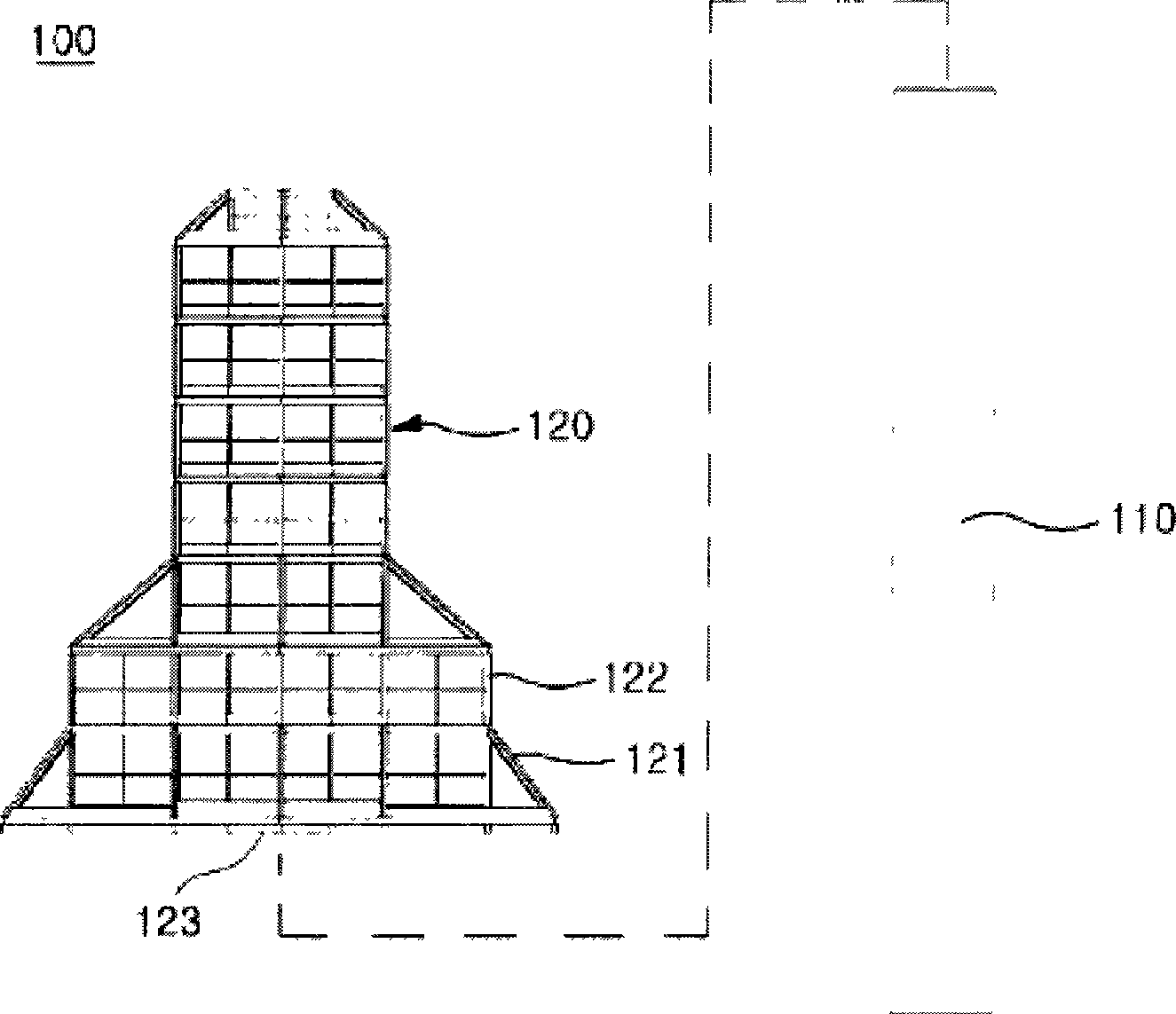
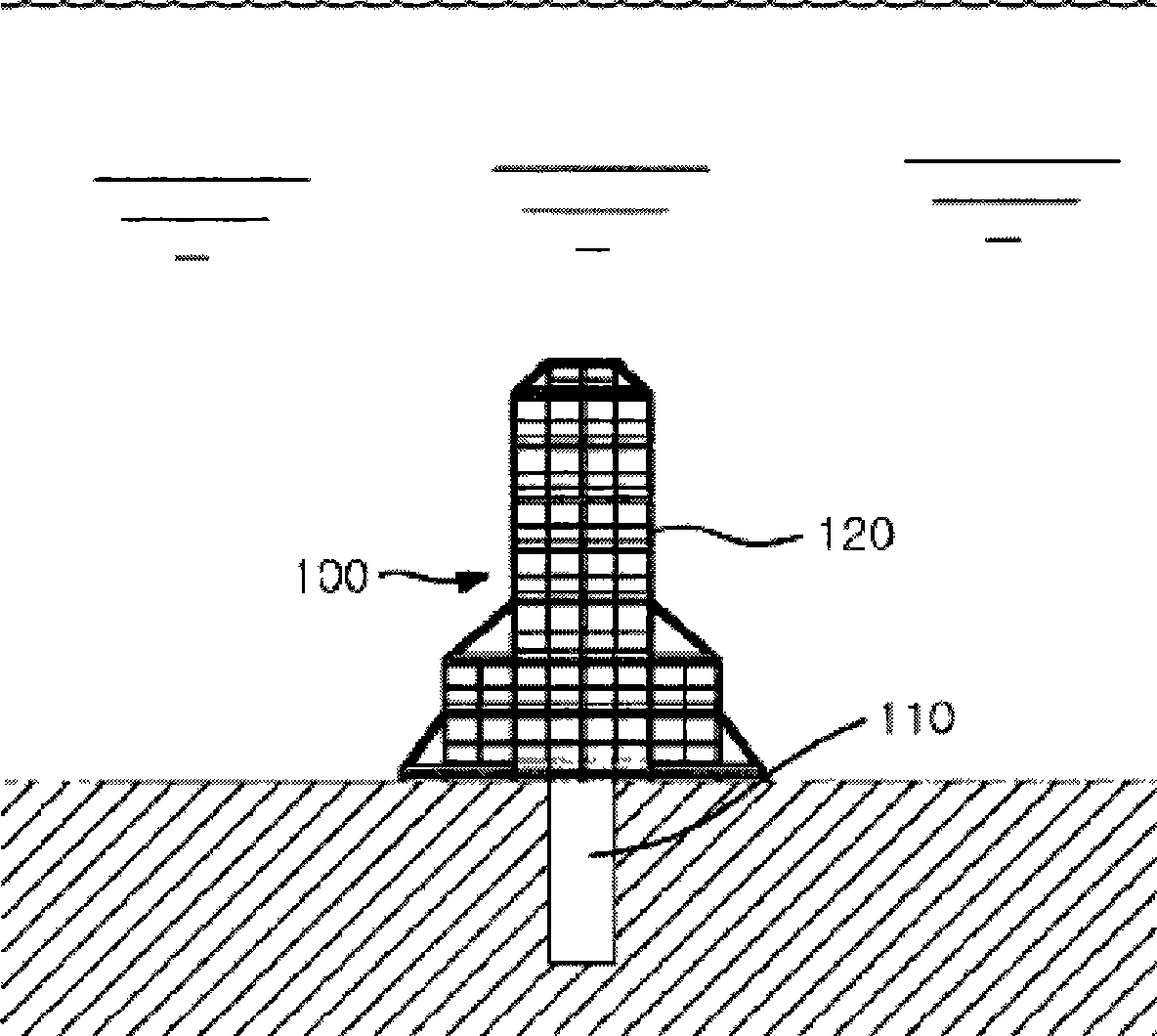
Seabed-fixed marine structure functioning as artificial reef and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101547600AEasy maintenanceEffective attractionArtificial islandsClimate change adaptationEngineeringSea level
The present invention provides a seabed-fixed marine structure functioning as an artificial reef and the manufacturing method thereof. The seabed-fixed marine structure includes a support column (110), which is fixed to a seabed by pegging a lower end thereof into the seabed to a predetermined depth such that the upper end of the support column is disposed below sea level, and an artificial reef body (120), which is provided so as to be separable from the support column and is manufactured of a plurality of members. A column insertion space (123) is defined in the artificial reef body for insertion of a support column. Thus, the artificial reef body is fitted around the support column through the column insertion space thereof such that the lower end of the artificial reef body is seated on the seabed.
Owner:REEF T MAX
Artificial material conducive to attract and grow oysters, mollusks or other productive and/or stablizing organisms
InactiveUS20070107663A1Easy to set upPromote growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOysterArtificial materials
Structures constructed from an artificial material facilitate the setting and growing of oysters, other mollusks, and other organisms for the purposes of food production, artificial reefs / breakwaters, and the like. The artificial material is a composite that acts as both an attractant and nutrient environment for mollusks and other aquatic organisms. The binder for the composite material includes both cement and an organic material. The organic material is selected to attract and feed the aquatic organisms.
Owner:ORA TECH
Artificial reef
An artificial reef comprises at least one bag which is generally configured to define at least a portion of a reef and which is at least partially fillable with air. An anchor is attached to the bag for maintaining the bag at a desired location substantially underwater. A plurality of such bags may be attached to one another and configured so as to define a reef which enhances the suitability of waves for surfing or which mitigates beach erosion.
Owner:JOHNSON GARRET T
Artificial reef module for coral reef remediation
InactiveUS20020119006A1Aid in disseminationPromote reproductionBreakwatersQuaysEngineeringArtificial reef
The artificial reef module for coral reef remediation of the present invention includes a central body having an upper settling plate, a middle settling plate, and a lower settling plate. Extending from the central body is a plurality of primary tines which further include a plurality of secondary tines extending from them. The primary tines include the supporting tines, the stabilizing tines, and the space filling tines. The branching of the tines closely replicates the appearance of natural branching coral. Over time the individual artificial reef modules for coral reef remediation would slowly degrade and allow the tines to break off. This degradation closely approximates the fragmentation that occurs with natural branching coral.
Owner:MOORE MICHAEL D
Method for culturing crabs in seawater by using breeding cage
InactiveCN101692795AFast growthPrevent escapeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMaricultureEcological environment
The invention provides a method for culturing crabs in the seawater by using a breeding cage, which can complete the cultivation of the crabs through the process of selecting a culture area, arranging the breeding cage, putting bait into the breeding cage, bait natural propagation and ingestion as well as harvesting. The breeding cage has the structure that a cage frame is made of a steel tube and is covered by a packet net at the periphery; and a cage body is internally provided with a polygonal artificial reef which is attached and fixed with a decrustation box. The method has the advantages that 1. the crabs can be cultured by the seawater breeding cage; 2. the crabs can be prevented from escaping and being invaded by external natural enemy; 3. the bait can be conveniently thrown into the cage; 4. micro-ecological environment can be created by the artificial reef, so as to be beneficial to generating living bait eaten by the crabs; 5. the decrustation box can be used for ensuring the safety of crab decrustation; and 6. as the crabs cultured inside the breeding cage has high growing speed, the bait can be saved, and the yield is high. Therefore, the method is suitable for being applied to seawater breeding metal of the crabs.
Owner:李宝明
Bottle hole reef in frame structure
ActiveCN103168716ASolve resource problemsResolve no valid cavesClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEngineeringPrism
The invention relates to an artificial reef. A bottle hole reef in a frame structure comprises a hole attachment body and a plurality of first plastic bottles, wherein bottle openings of the first plastic bottles are provided with threads, and bottle bottoms of the first plastic bottles are removed. The hole attachment body is a prism-frustum-shaped frame formed by rods, the first plastic bottles are in threaded connection with the hole attachment body through the threads on the bottle openings, the bottom ends of the first plastic bottles incline upwards, inner cavities of the first plastic bottle form a hole, and the open bottom ends of the first plastic bottles form a hole opening. The bottle hole reef in the frame structure can be conveniently manufactured through utilization of wastes and is convenient to recover and good in protective performance, and the problems that an existing fish reef wastes effective resources, no effective holes exist, or holes in dense quantity are hard to manufacture, recovery is not convenient, and stability is poor are solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Artificial reef construction method for recovering oyster reef biological resources of Oyster Aphid Mountain
InactiveCN104663545AIncrease the areaReduce corrosionClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaOrganismArtificial reef
The invention relates to an artificial reef construction method for recovering oyster reef biological resources of the Oyster Aphid Mountain. The artificial reef construction method comprises the following steps: setting the geographic position, the substrate type and the construction area of each construction place; manufacturing reef bags; distributing the manufactured reef bags on a beach, and constructing a reef on the preset construction place, wherein the constructed reef comprises a side-by-side reef used for recovery, a spacing type reef used for reducing sediment deposition and a double-layer reef used for preventing quick sediment deposition. The artificial reef is formed by placing a certain number of reef bags, so that an oyster body is assisted to resist coverage of ocean current sediment, the corrosion and wave erosion processes are reduced, and the aim of repairing oyster reefs of the Oyster Aphid Mountain and an environment ecological system is achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for improving attaching effect of algas on surface of artificial reef
ActiveCN102177841AEasy to operateImprove growth efficiencyClimate change adaptationFertilising methodsEcological environmentNitrogen
The invention discloses a method for improving the attaching effect of algas on the surface of an artificial reef. In the method, a certain amount of slow release fertilizer is added in the building material of the existing artificial reef, or a coating layer which is rich in slow release fertilizer is added onto the surface of the shaped reef, thus increasing the capability of the reef for continuously releasing nutritive salt into water body. Concretely, the method includes the steps of mixing the materials for preparing the artificial reef with the slow release fertilizer and then pouring for shaping, thus obtaining the product; or pouring for shaping the artificial reef, then coating the surface of the artificial reef with the coating layer which is rich in slow release fertilizer, thus obtaining the product. The result of an experiment in a pond shows that the amount of the algas attached on the artificial reef which is produced by the method is 1.5-3 times that of the algas attached on the common artificial reef, the phosphorus-releasing rate of the artificial reef to surrounding sea water is 1.2-1.3 times that of the contrast, and the nitrogen-releasing rate of the artificial reef is 7-8 times that of the contrast. The method is simple in process, the prepared reef can effectively induce the algas to grow on the surface of the reef, and the method has great significancein restoring the marine ecological environment as well as improving the output of the bred rare seafood.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High Fixation Strength Anchoring System
ActiveCN104186383BReduce horizontal elevationPrevent lateral movementClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaElevation angleTraction frame
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
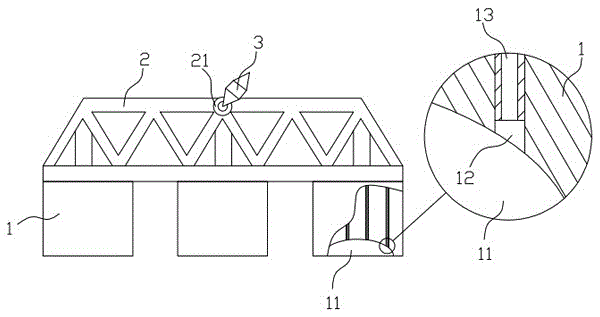
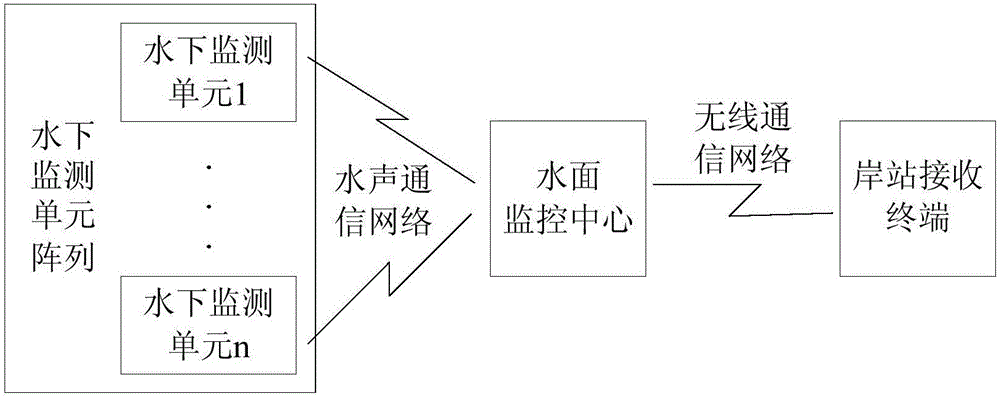
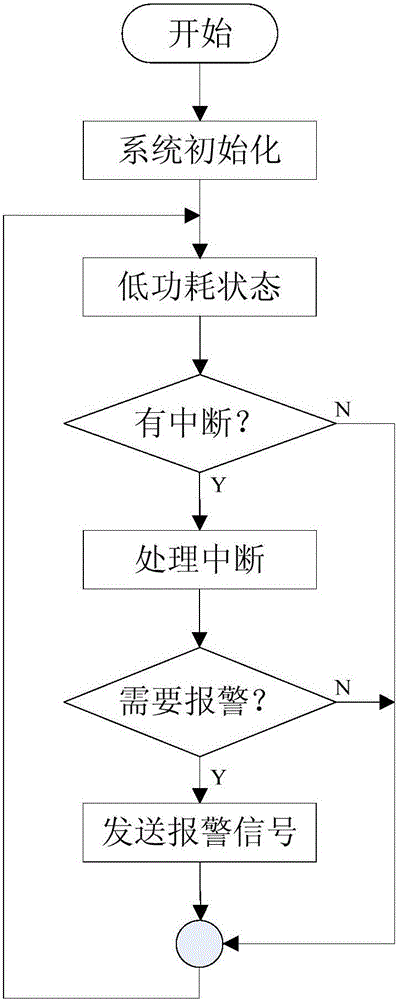
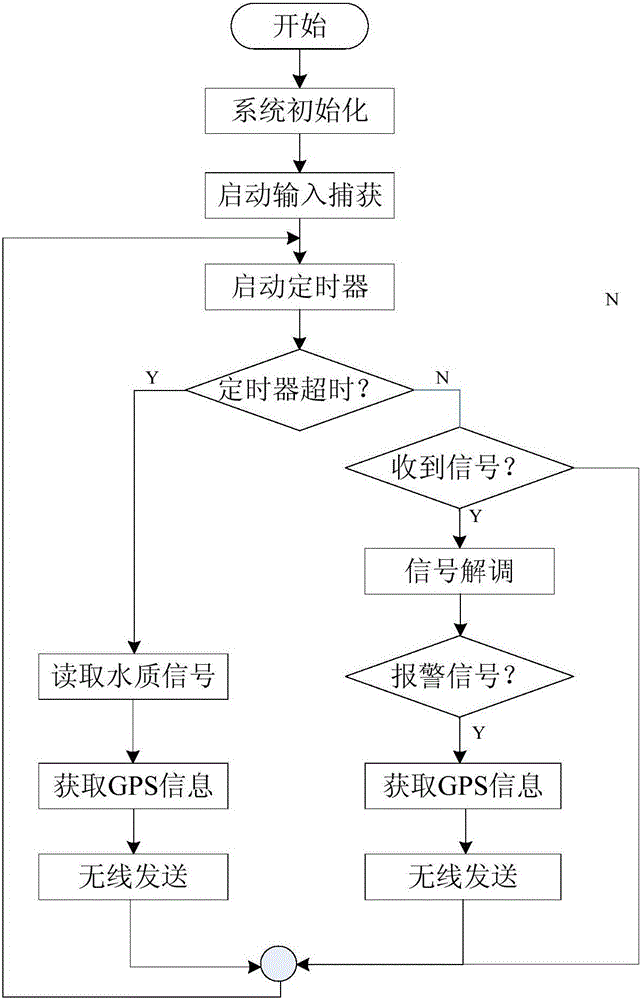
Alarming and monitoring system and method for sea cucumber culture farm with artificial reefs
InactiveCN105118202AEnsure safetyReduce lossesPisciculture and aquariaBurglar alarmBuoyShore station
The invention discloses an alarming and monitoring system and method for a sea cucumber culture farm with artificial reefs. The monitoring system an underwater monitoring unit array, a water surface monitoring center installed on a buoy in the culture farm or a boat body, and a shore station receiving terminal. With the system and method, safety of the culture farm can be guaranteed and the user losses can be reduced. When abnormal situations like stealing of e sea cucumbers cultured with artificial reefs occur, the alarming and monitoring system can carry out alarming rapidly and the user can check the abnormal situation, thereby effectively reducing the losses of the farmer; and the information transparency of the culture farm is improved. With real-time transmission of correlated sea water parameters containing the water temperature and dissolved oxygen, the user can know the situation of the culture frame better.
Owner:青岛森科特智能仪器有限公司
Experimental device for studying fish behavior
InactiveCN101766139AReduce in quantityStudy data scienceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaArtificial reefsArtificial reef
The invention discloses an experimental device for studying fish behavior, which belongs to technical field of fishery industry. The invention relates to a reef composition and the application in internal structure of a simulated artificial reef thereof, and mainly solves the problem in the prior art that: low reliability of research result is caused by that the reef model adopted in the study on fish-gather effect of the artificial reef can not reflect the actual structural characteristics of the artificial reef under flow situation; a single reef is designed to replace the beam structure in the actual artificial reef, the reef composition composed of different compositions of the single reef is used for stimulating the internal structure of the actual artificial reef, thereby truly reflecting the changes of flow field around artificial reef under the flow situation, and providing real and effective data for the study on fish-gather effect of the artificial reef.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
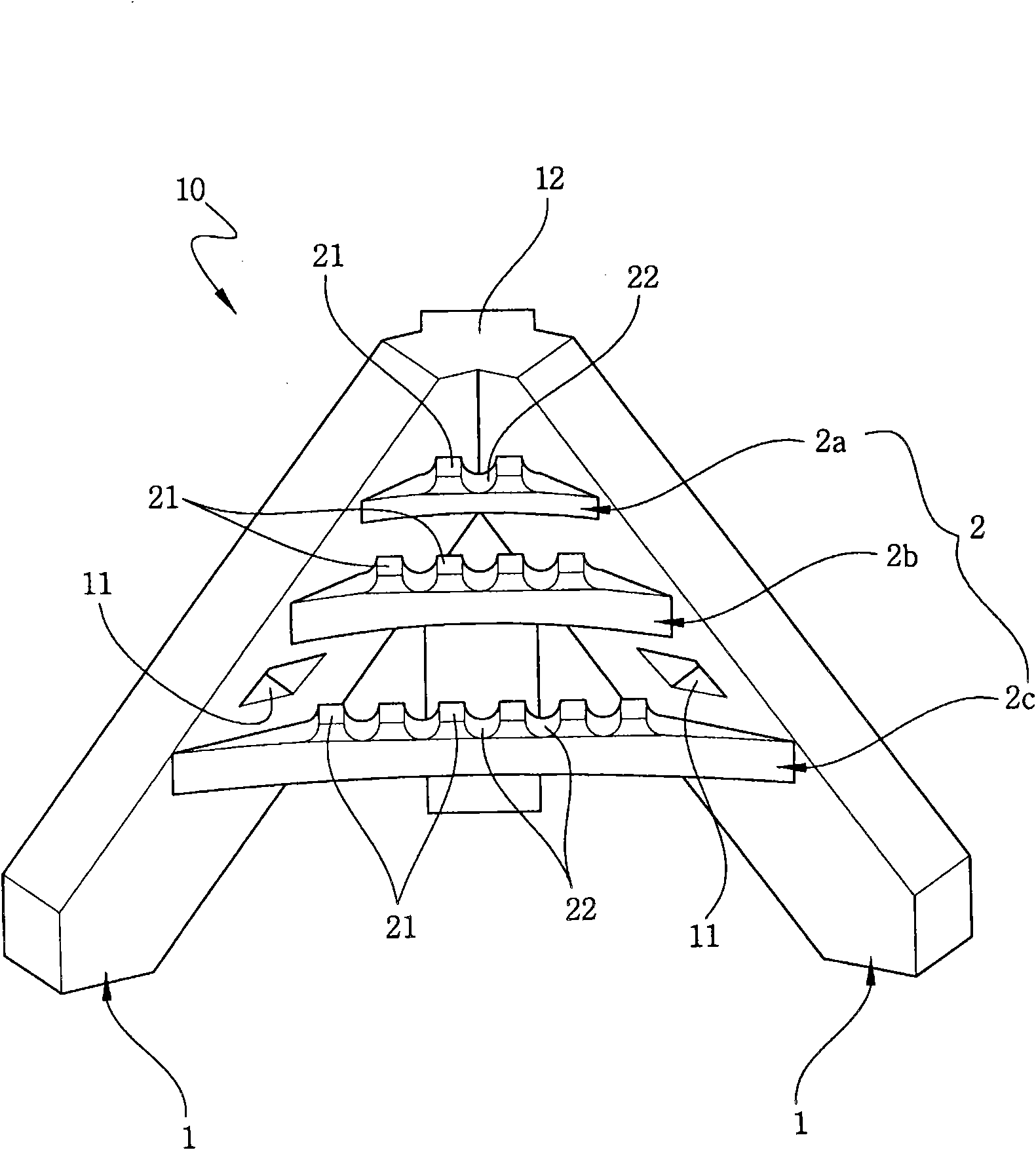
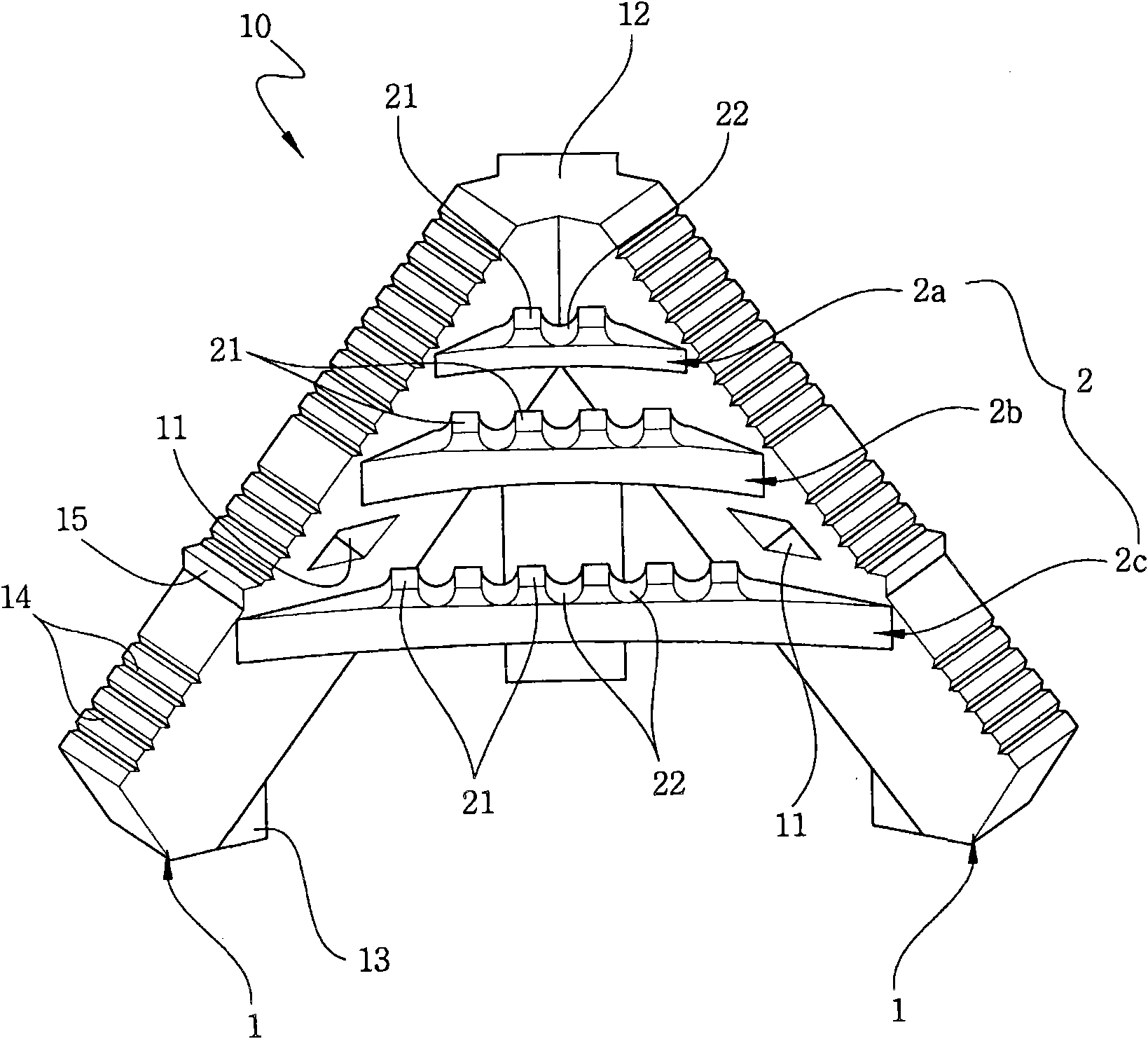
Tripod-type artificial reef for a seaweed forest
InactiveCN101861826AReduce in quantityLower distribution costsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMarine habitatsEngineering
The invention discloses a tripod-type artificial reef for a seaweed forest, which has a surface structure suitable for various seaweeds to be naturally and effectively planted and rooted thereon. The artificial reef with a simple structure can reduce volume of stacked artificial reefs and greatly decrease transportation and installation time and cost. Waves and tides in change will not turnover the artificial reef on the seabed or make it separate from the initial installation position, thus significantly improving the reliability of the seaweed forest and making it easy to use. The tripod type artificial reef for seaweed forest comprises: support legs which are arranged in the form of tripod at the regular interval; a connection plate which is installed in the space formed by support legs and is ranged in an order of vertical arrangement and horizontally extended between support legs; and seaweed attachment ridges which are projected upwards from the upper surface of the connection plate so as to link a food supply area benefitial to growth of shellfish or fish fry, passages and spaces for egg laying and inhabit by means of seaweeds; and a concealment space for seaweeds is formed between the seaweed attachment ridges.
Owner:HAEJOO ENC
Apparatus for artificial reef
The present invention disclosed an artificial reef system having a plurality of tire casings tethered onto a cable-like line which reef system is supported in an upright position by a flotation device and which artificial reef system is anchored to the bottom of the ocean by another tire casing filled with concrete having an anchoring device disposed on its underside. The cable-like line may be monofilament. The reef system of tire casings is disposed upwardly due to the buoyancy of the flotation means and is free to move with the current in a natural manner to the extent that the cable-like line allows.
Owner:HALL JOHN W
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com