Paddy rice leaf color regulation and control gene YL1 and use thereof
A technology for regulating genes and rice, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problems of rice leaf chlorosis and yellowing of rice leaves, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] 1. Rice material
[0036] Rice (Oryza sativa L.) yl1-1 mutant plants were obtained from the indica rice variety Shuhui 527 (purchased from the Crop Variety Resource Bank of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences) through EMS mutagenesis treatment.
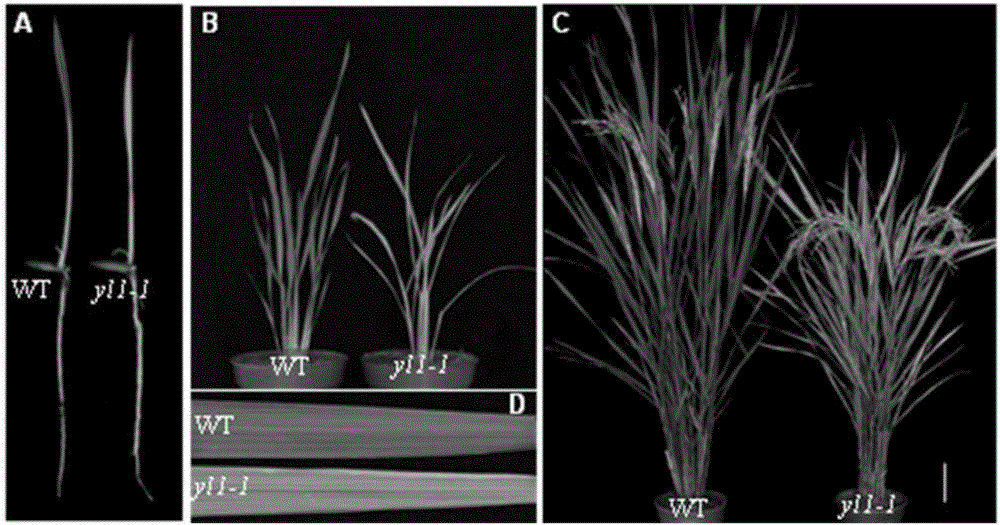
[0037] The yl1-1 mutant plants exhibited a distinct yellowish phenotype starting from the first fully expanded leaf (DAG6, true leaf expansion) of seedlings and continued throughout the growth period. Compared with the wild type (indica rice Shuhui 527), the yl1-1 mutant plants also showed delayed tillering period and reduced tillering number. In addition, there are also differences in plant height between the wild type and the mutant, and the difference is not obvious at the seedling stage (DAG6), and the plant height of the yl1-1 mutant is significantly lower than that of the wild-type plant at the mature stage, as shown in figure 1 shown.
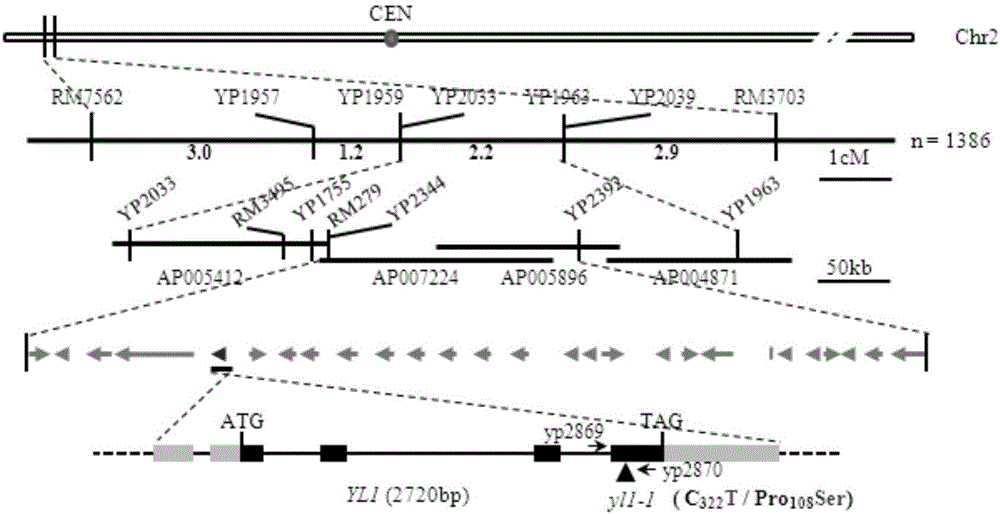
[0038] 2. Analyze and target groups
[0039] f 2 F 1 Generation, F 1 F...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Plant Transformation:
[0054] Primers pCYL1-F (5'-tctagaAGTCCCATGTAAATAGGGTC-3') and pCYL1-R (5'-gtcgacGCTTCTCGGATAACGACTCT-3') were designed according to the target gene (LOC_Os02g05890). The full length of the target gene and 1382bp downstream of the 3'-end. Genomic DNA of japonica rice variety Nipponbare was used as a template, and pCYL1-F and pCYL1-R were used as primers, and PCR amplification was performed using the Q5 high-fidelity enzyme system of NEB Company. The reaction system was (20 μL): DNA template 2 μL, 2×Master Mix 10 μL, Each 1 μL of upstream and downstream primers was made up to 20 μL with ultrapure water. The PCR reaction conditions were pre-denaturation at 98°C for 30s; denaturation at 98°C for 10s, annealing at 65°C for 30s, extension at 72°C for 2min for 30s, 30 cycles; extension at 72°C for 10min. After the PCR product was subjected to electrophoresis, the target fragment was recovered and inserted into the T5-zero vector (purchased from Beijin...
Embodiment 3
[0056] 1. Chloroplast ultrastructure observation
[0057] In order to study the effect of YL1 gene mutation on rice chloroplast development, we observed and analyzed the chloroplast ultrastructure of 40-day-old wild-type and mutant heart leaves and fourth leaves by transmission electron microscopy. result Figure 6 shown. The heart leaf and the fourth leaf of the wild-type plants showed relatively complete chloroplast structure, and the grana lamellar accumulation was regular. However, the chloroplast morphology in the yl1-1 mutant exhibited an irregular phenotype, loosely packed thylakoid membranes, and significantly less grana lamellar packing than the wild type. This indicated that loss of YL1 function impaired chloroplast development.
[0058] 2. Subcellular localization of YL1 protein
[0059]We constructed the full-length subcellular localization vector of YL1 to explore the subcellular localization of YL1 in rice. The plasmid construction method is the same as that...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com