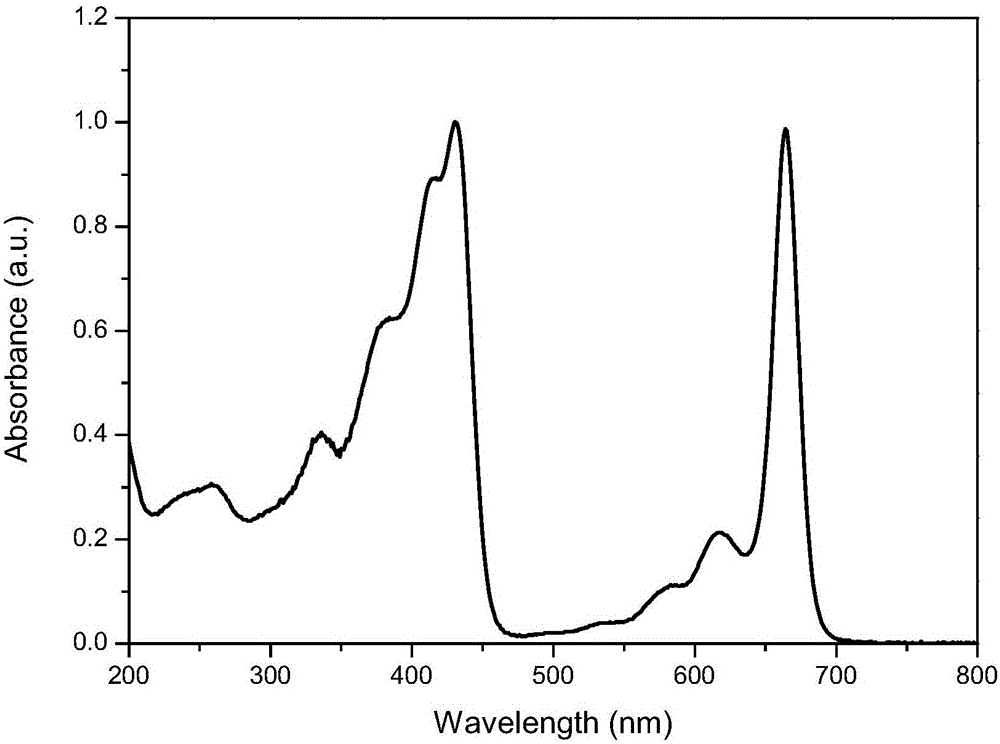
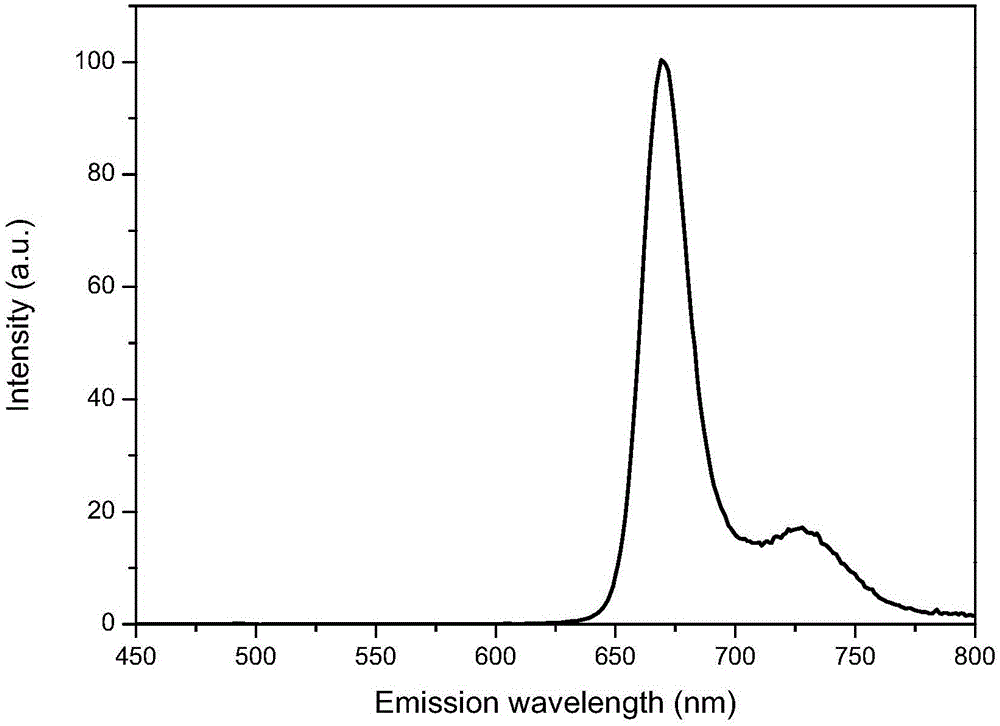
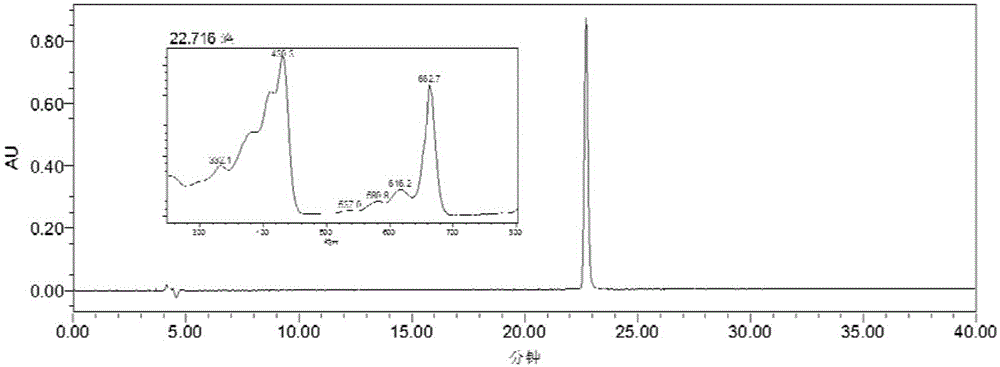
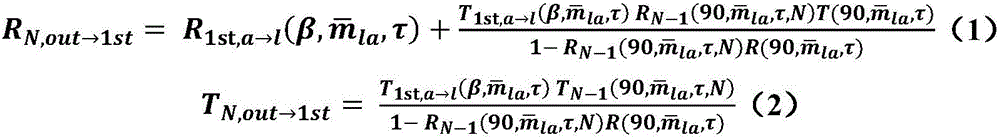Patents
Literature
67 results about "Chlorophyll b" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
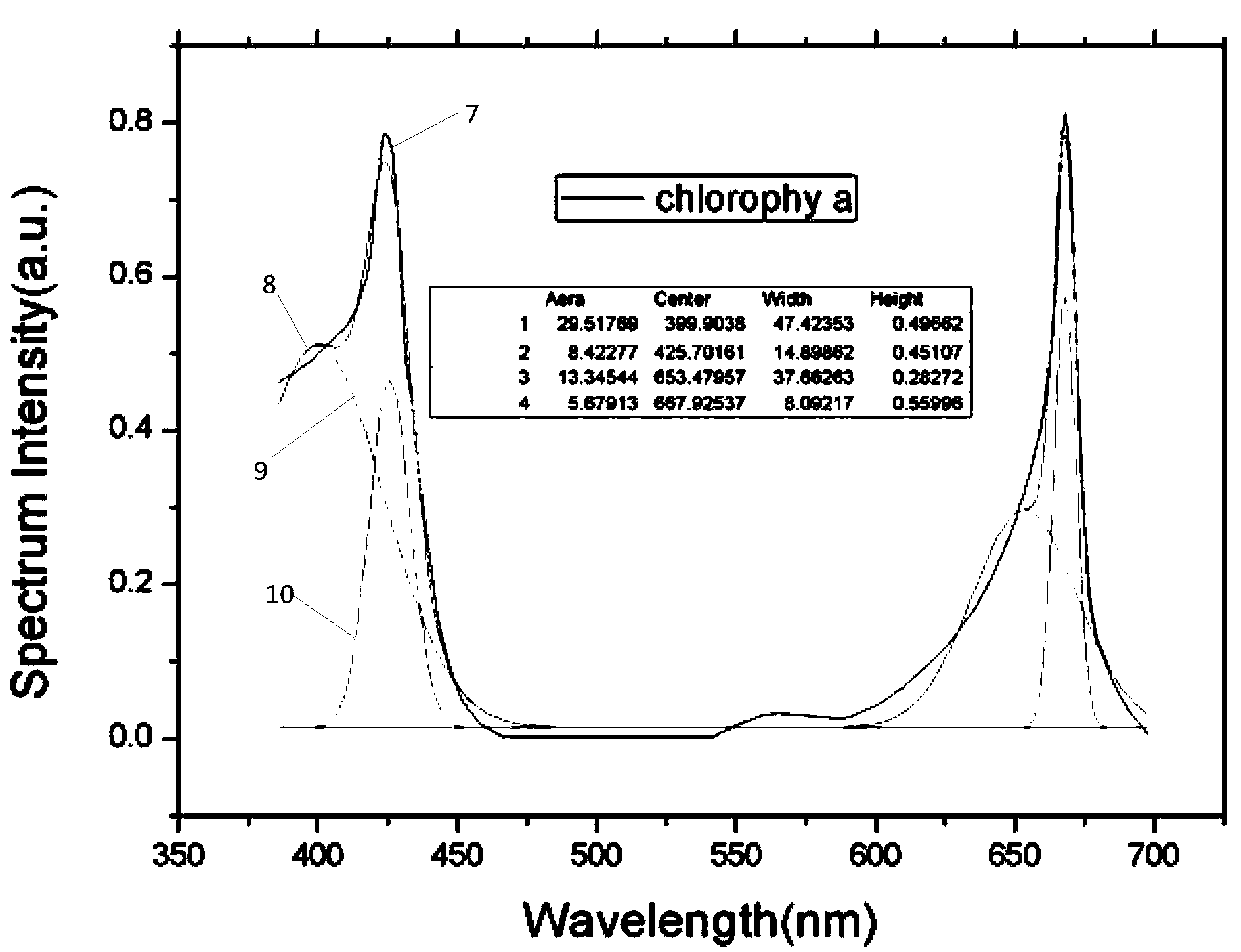
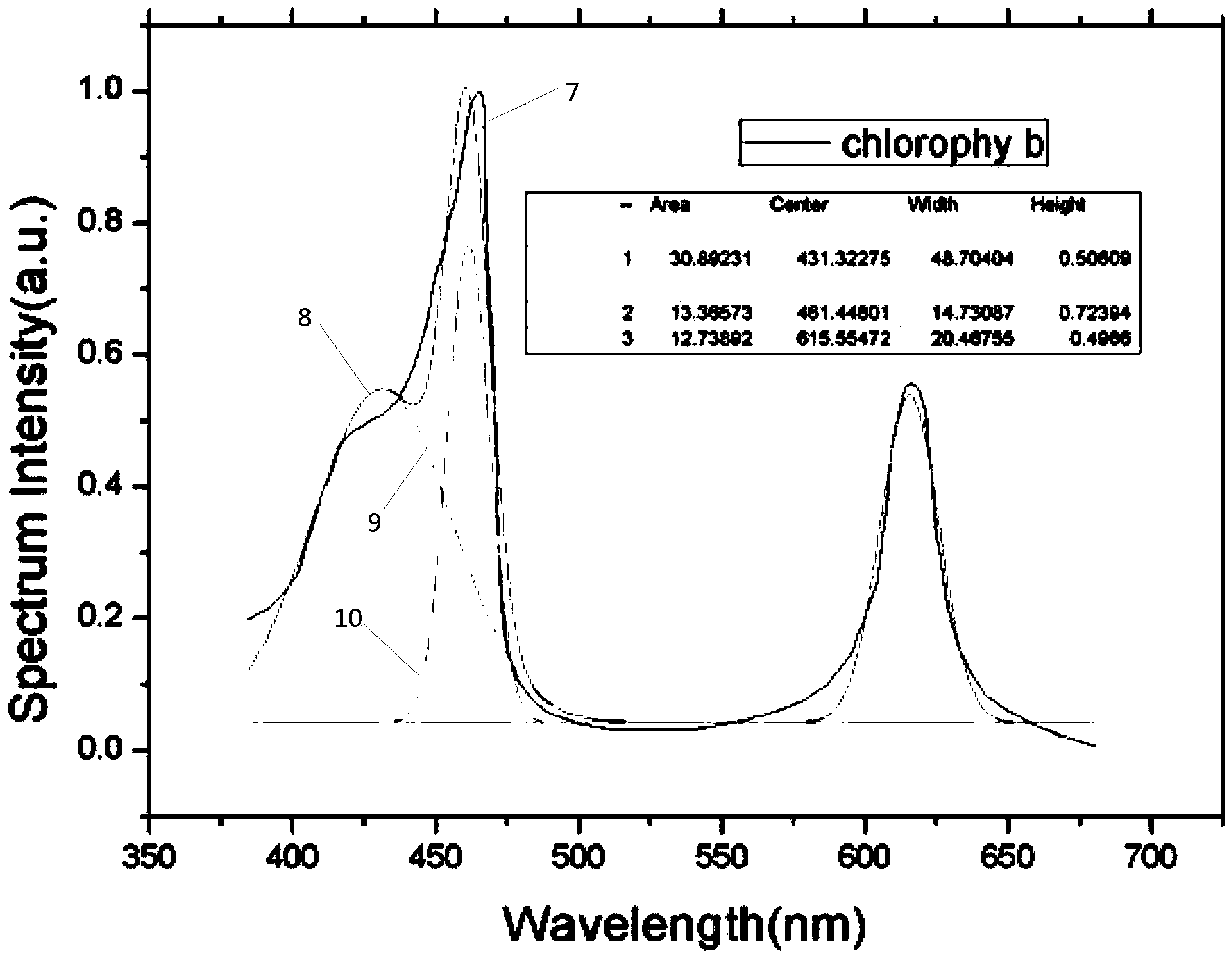
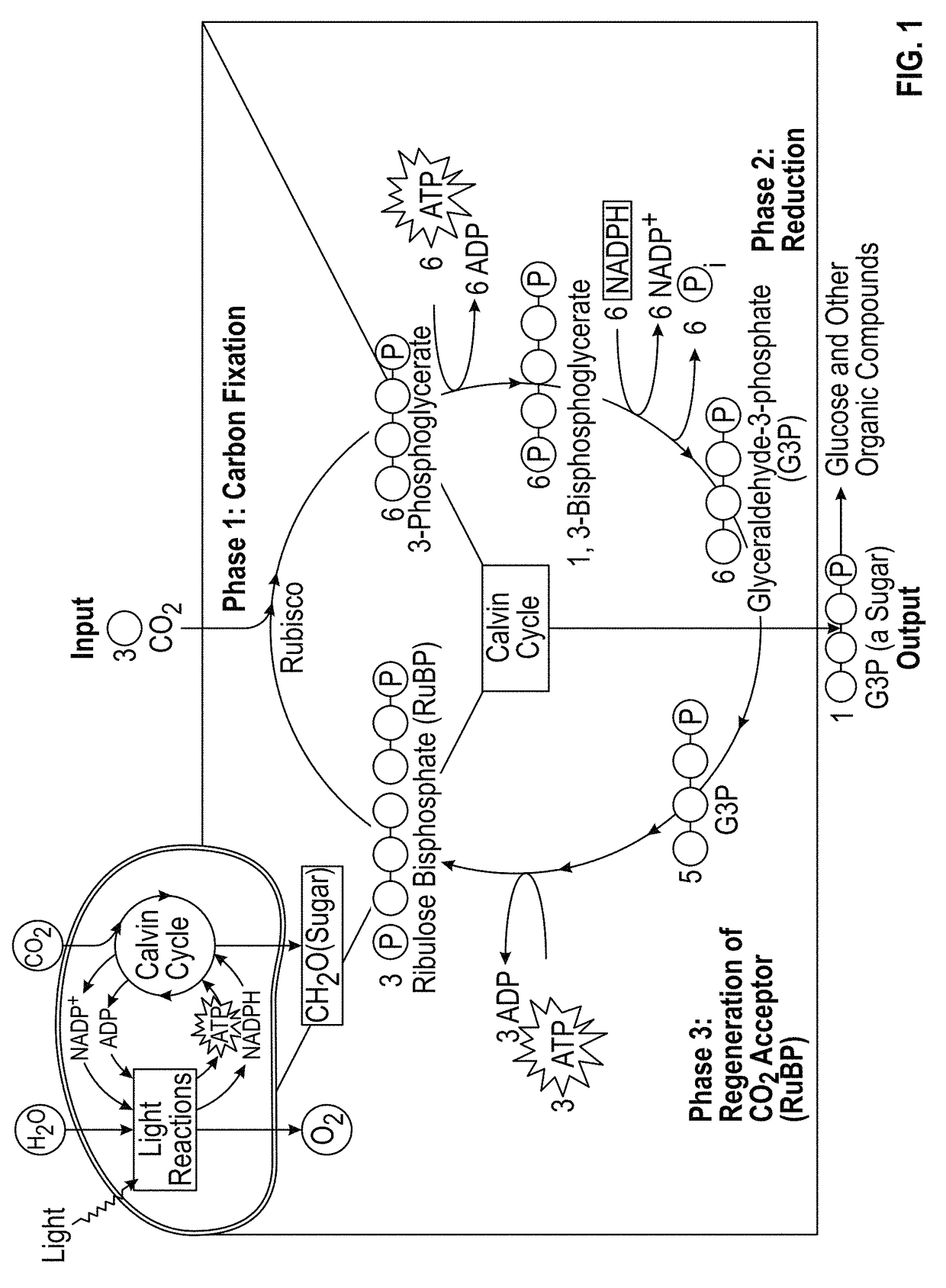
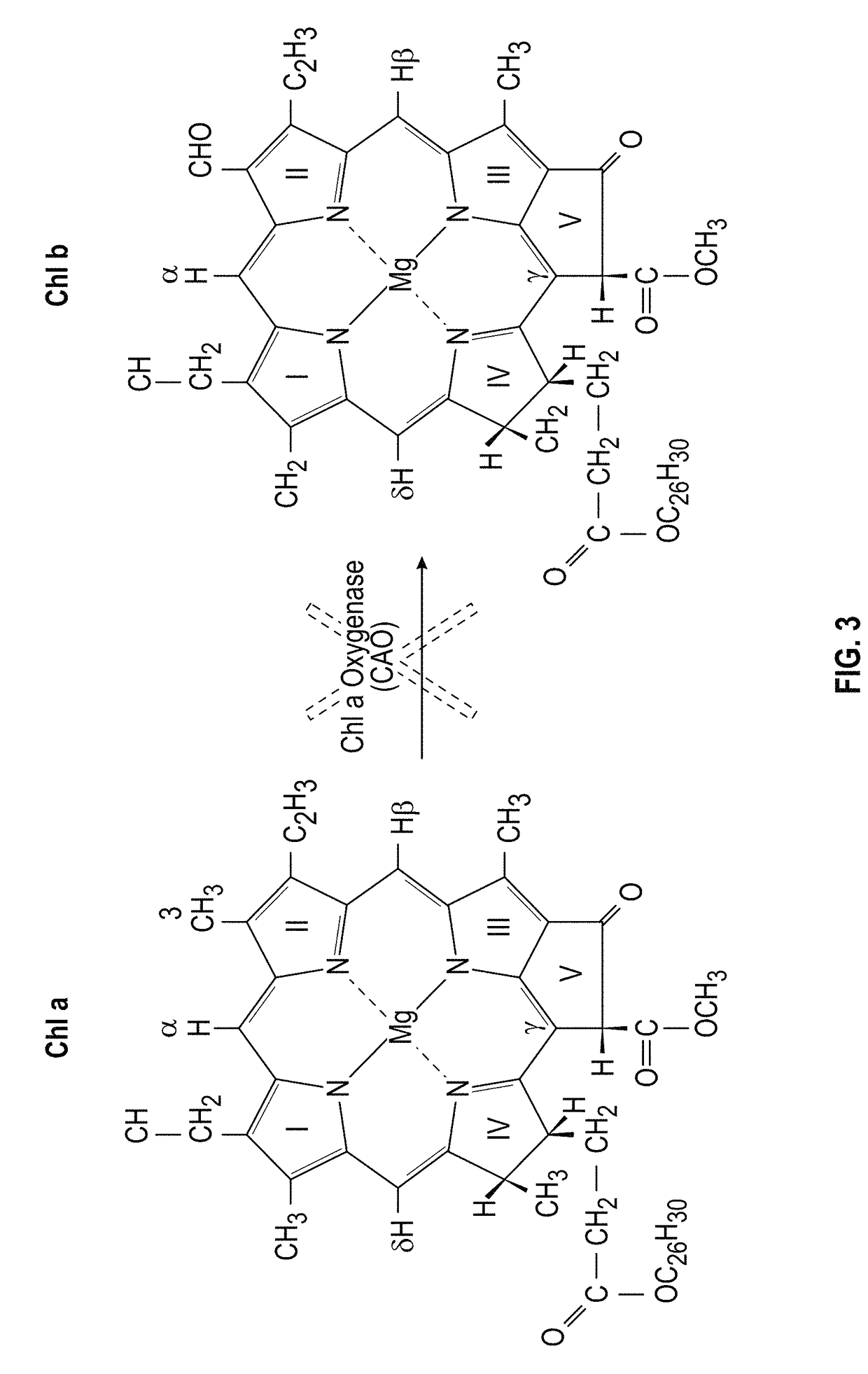
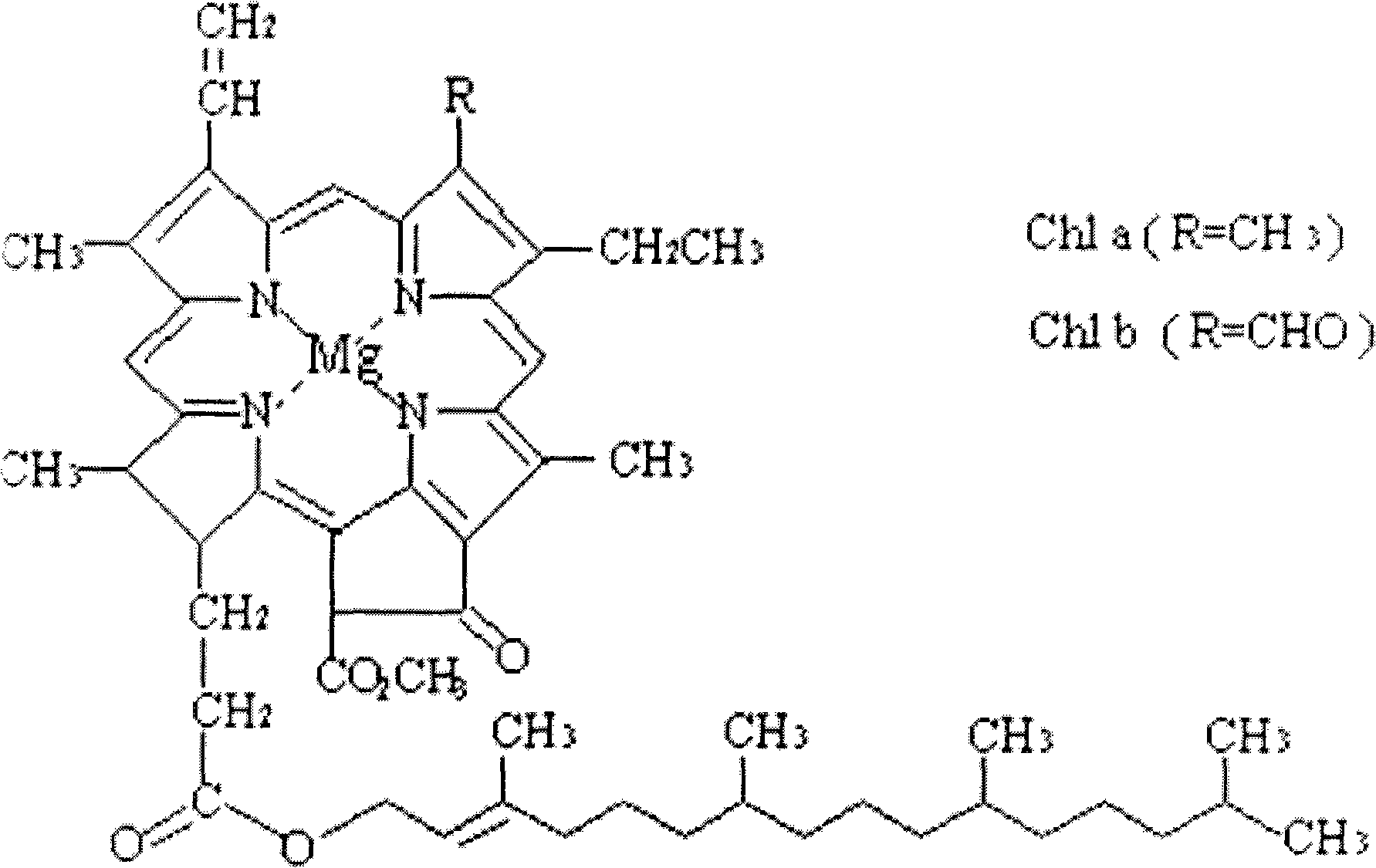
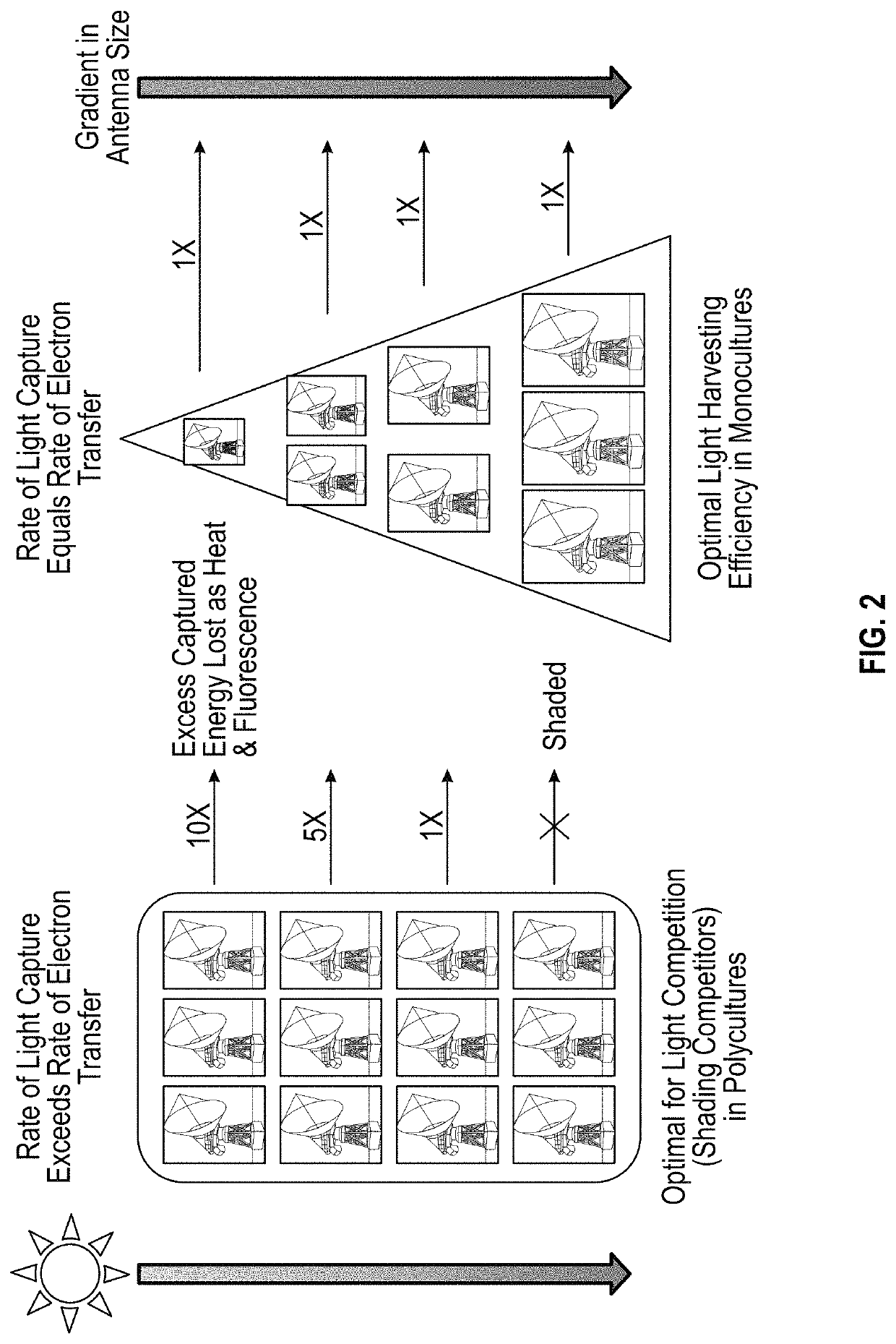
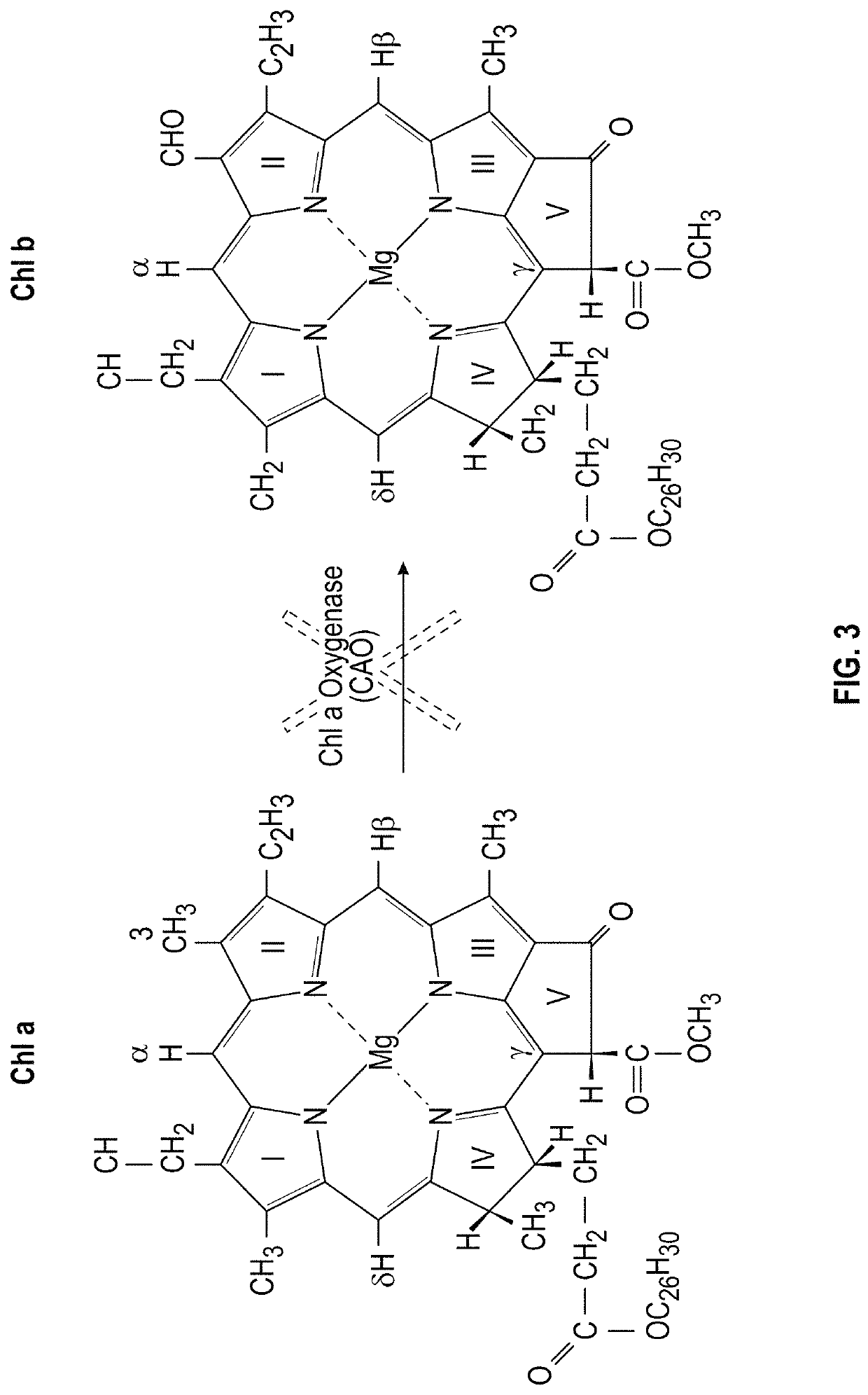
Chlorophyll b is a form of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll b helps in photosynthesis by absorbing light energy. It is more soluble than chlorophyll a in polar solvents because of its carbonyl group. Its color is green, and it primarily absorbs blue light.
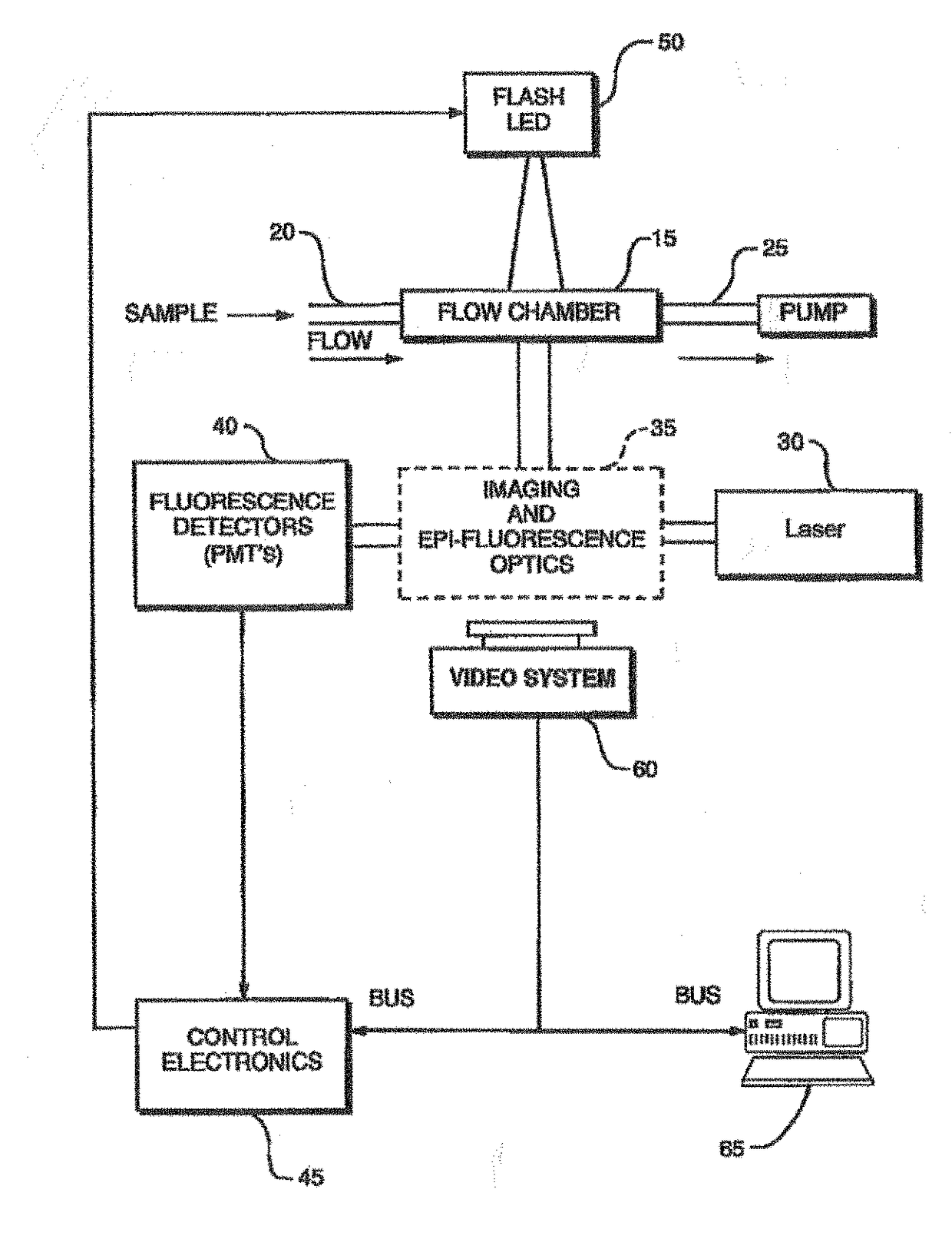
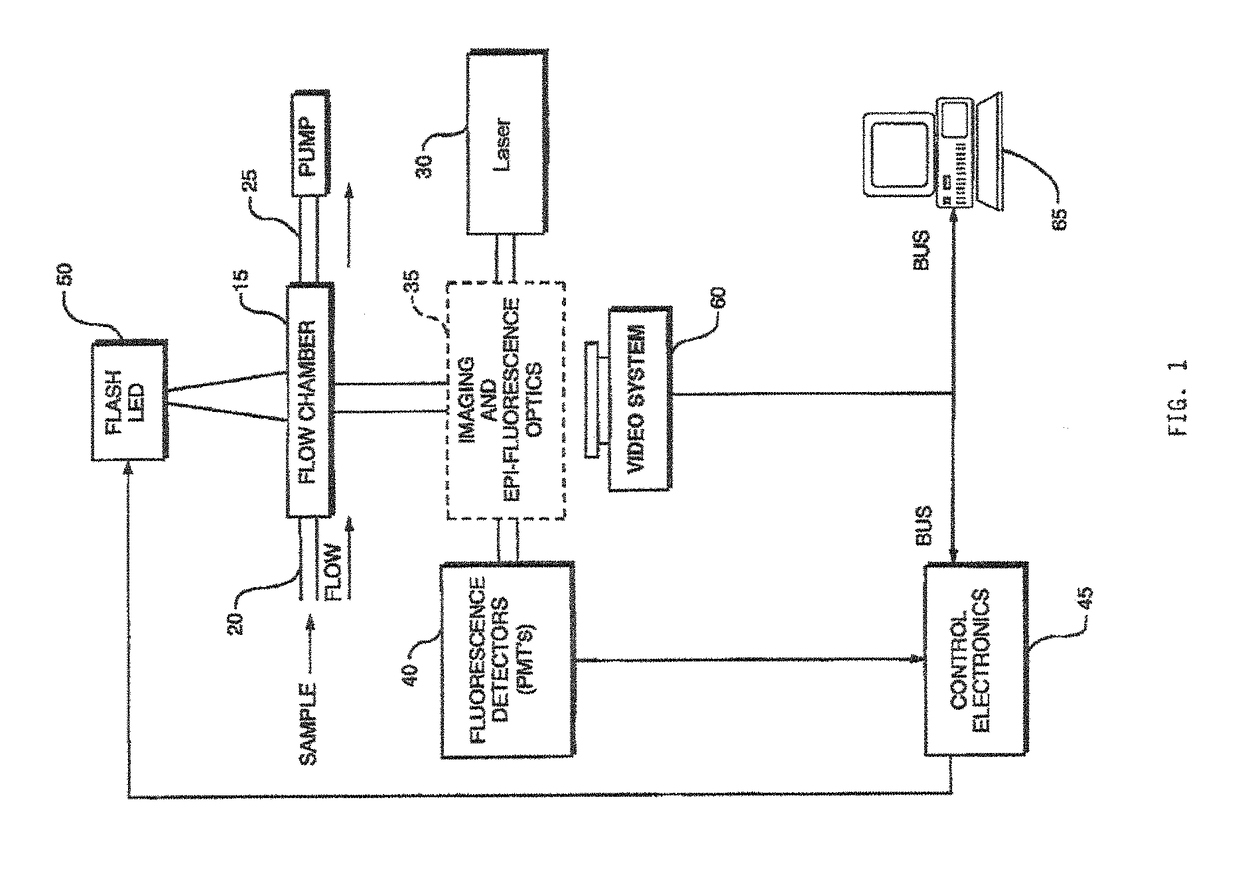
System and method for monitoring blue-green algae in a fluid
InactiveUS20090283697A1Accurate detectionHigh resolutionPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceChlorophyll b
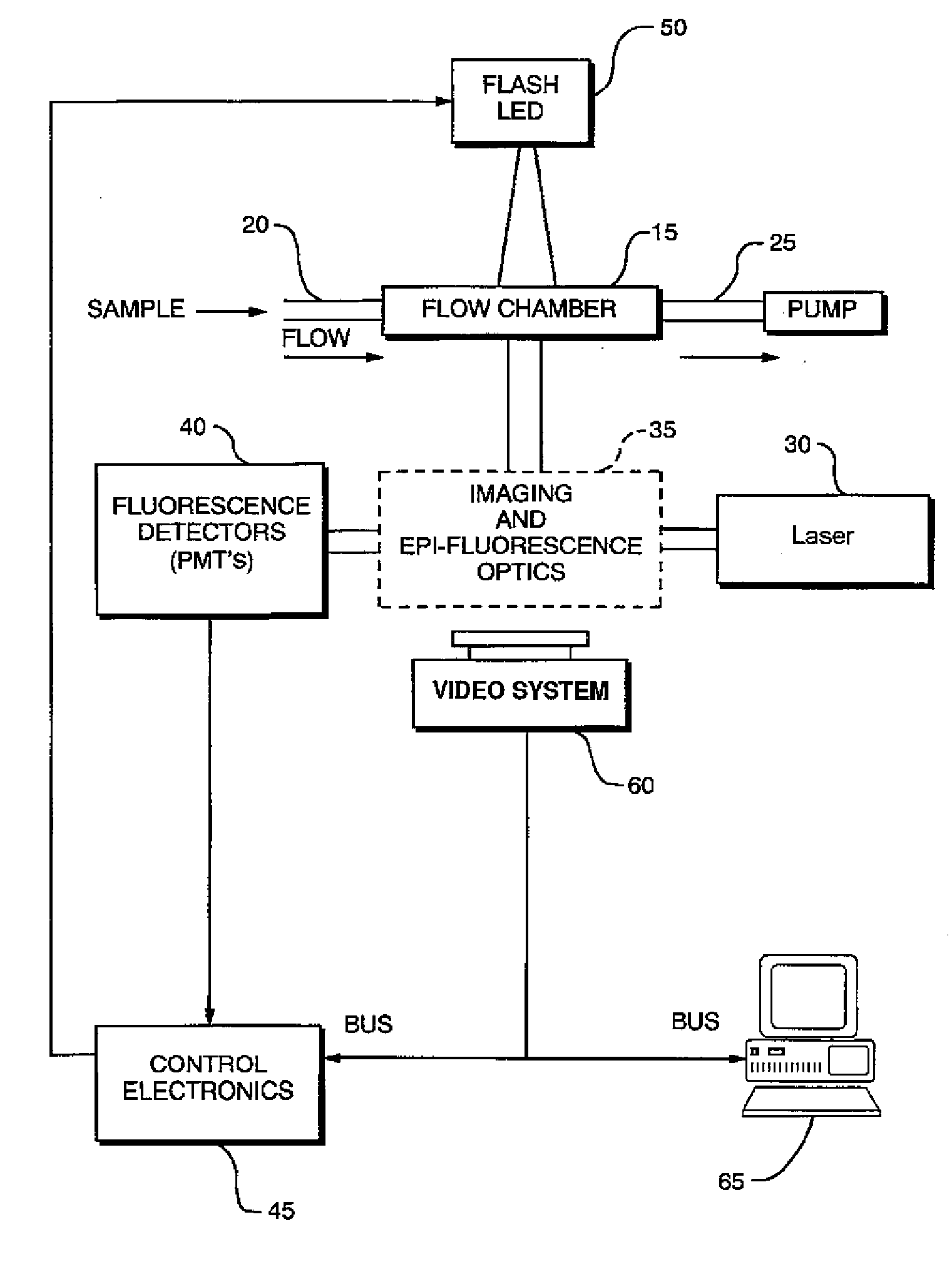
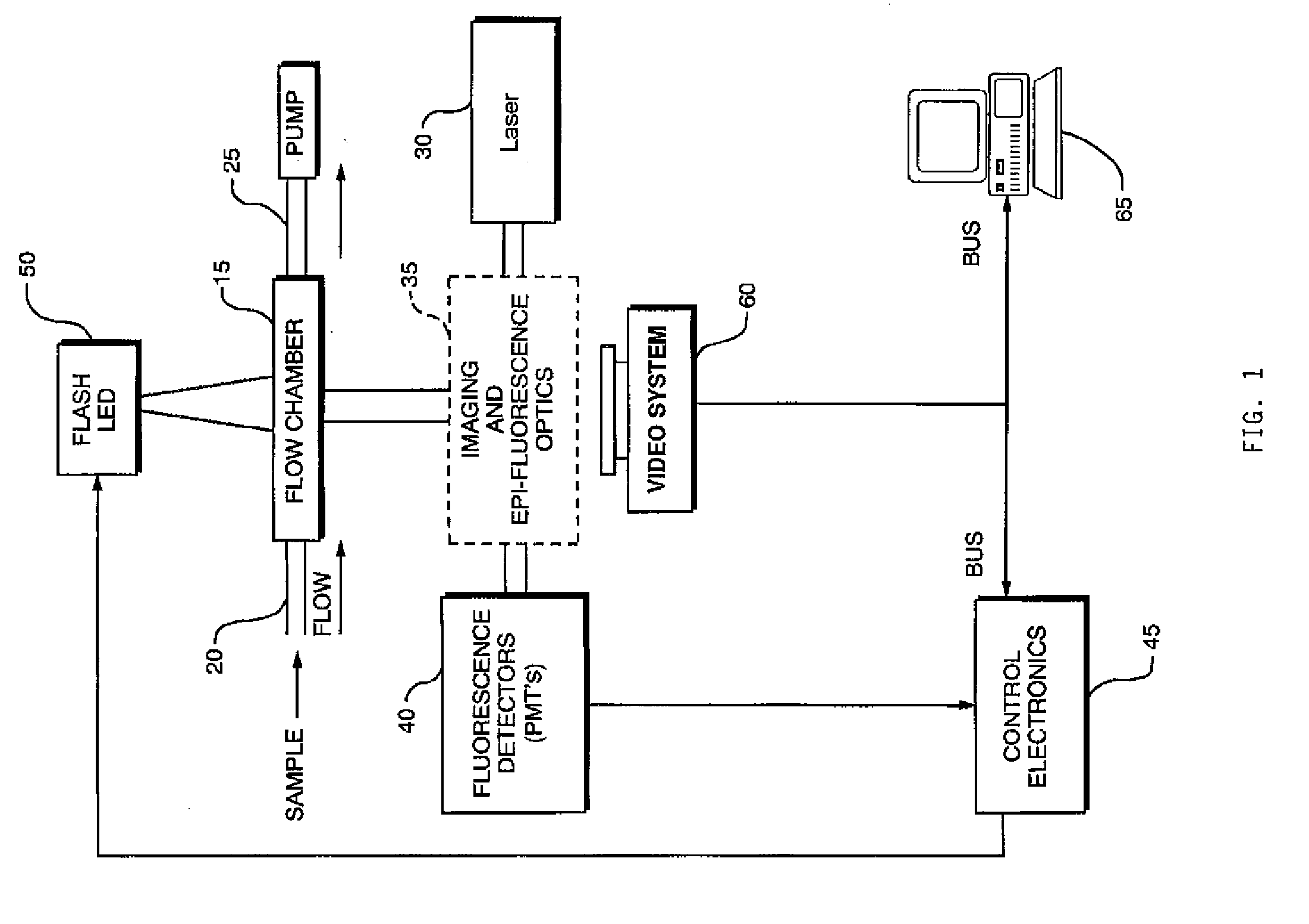
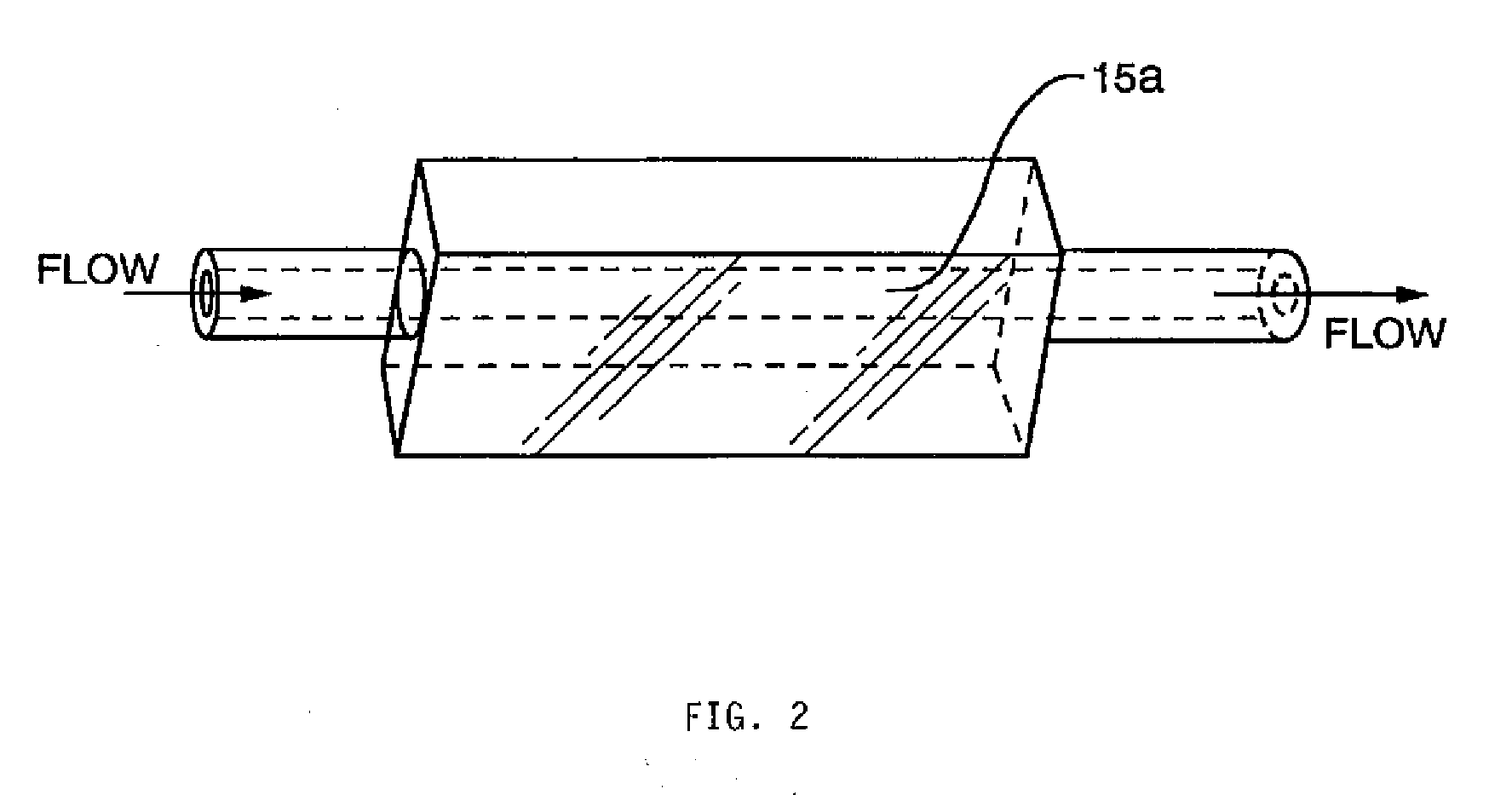
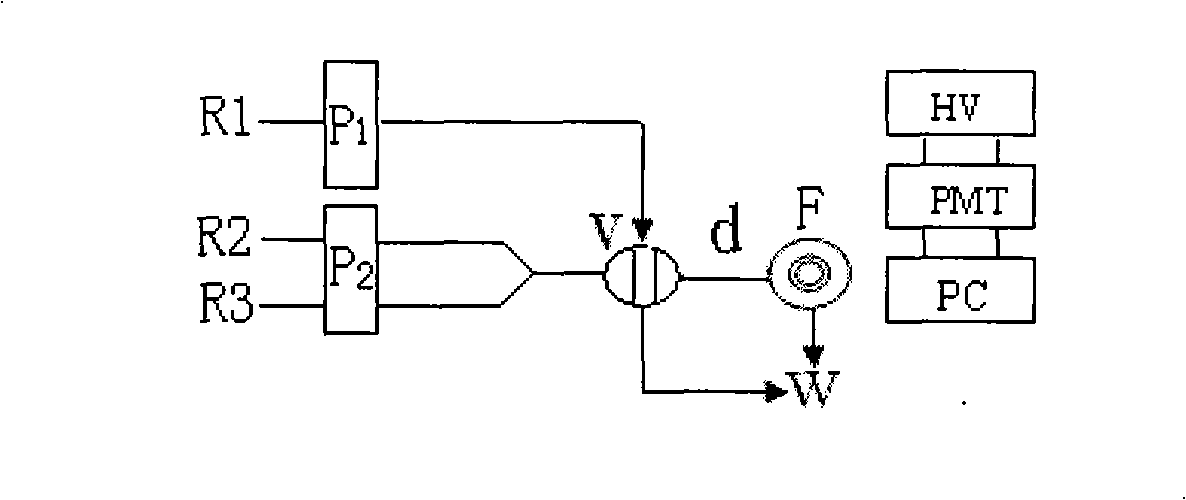
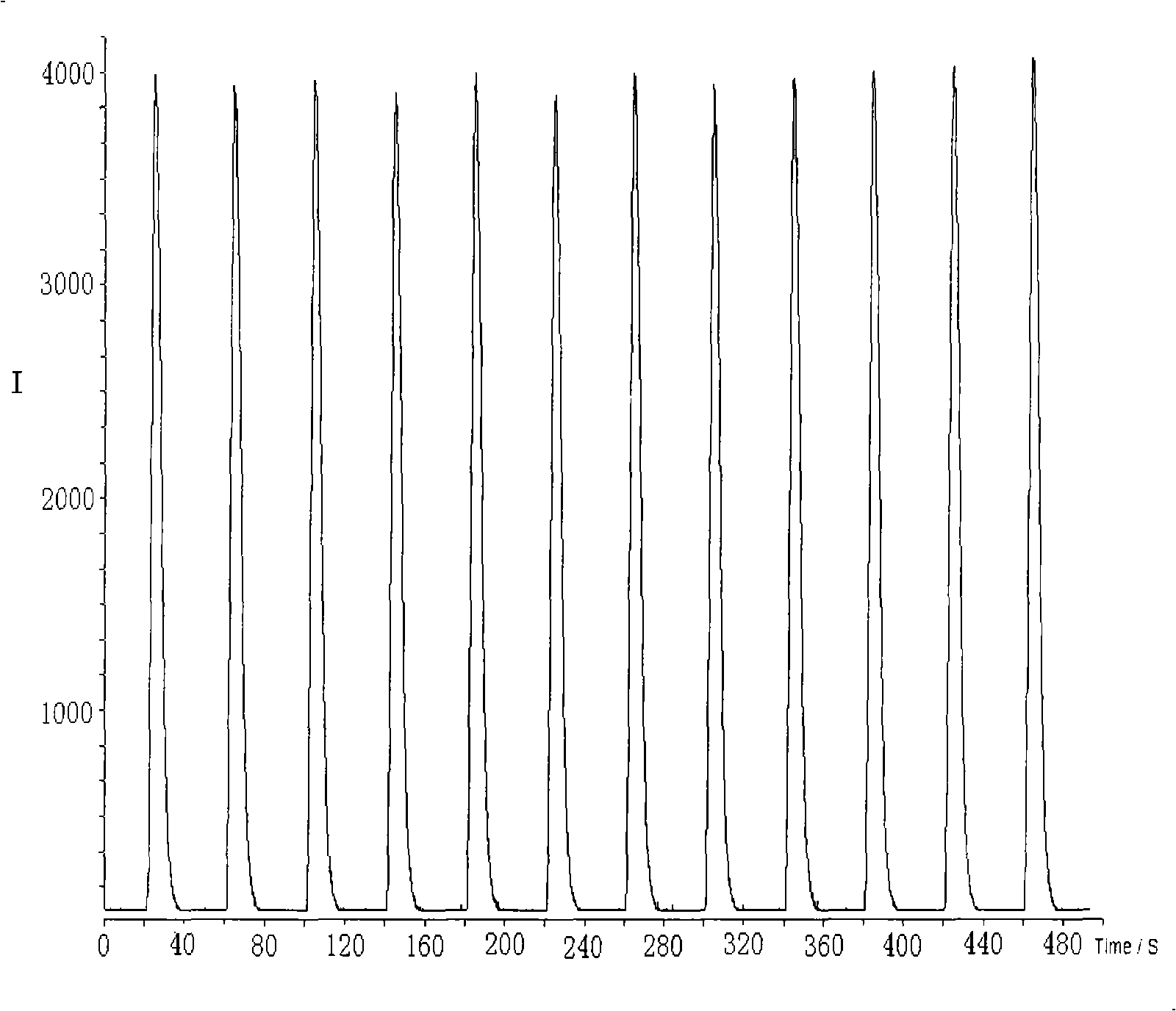
A particle detection system with a detection mechanism that includes detectors positioned to detect two different ranges of fluorescence produced by particles in the fluid in a flow chamber. Each of the detectors is arranged to generating a trigger signal whenever fluorescence is detected. The system and related method enhance the accuracy and sensitivity of blue-green algae monitoring by utilizing imaging flow cytometry combined with particle analysis and the measurement of the ratio of each particle's phycocyanin to chlorophyll b detected by using the two detectors configured for detection of two different fluorescence ranges, one associated with the phycocyanin and the other associated with the chlorophyll b. Optionally, captured images may be used in comparison to known images of a library of images.
Owner:FLUID IMAGING TECH
Apple-specific rice husk charcoal base fertilizer and its preparation method
Owner:SHANDONG YANTAI AGRI SCI & TECH INST
Method for improving drought resistance of turf on garbage compost substrate
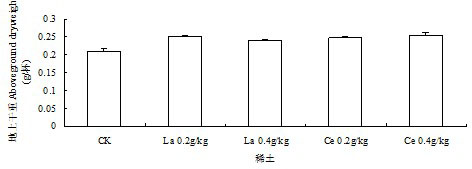
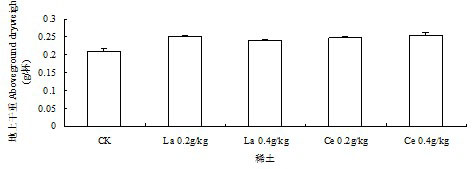
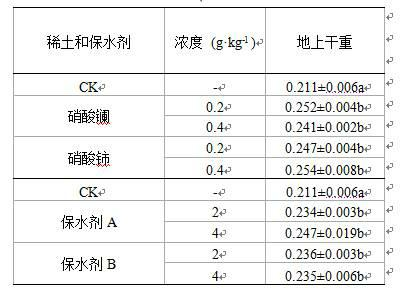
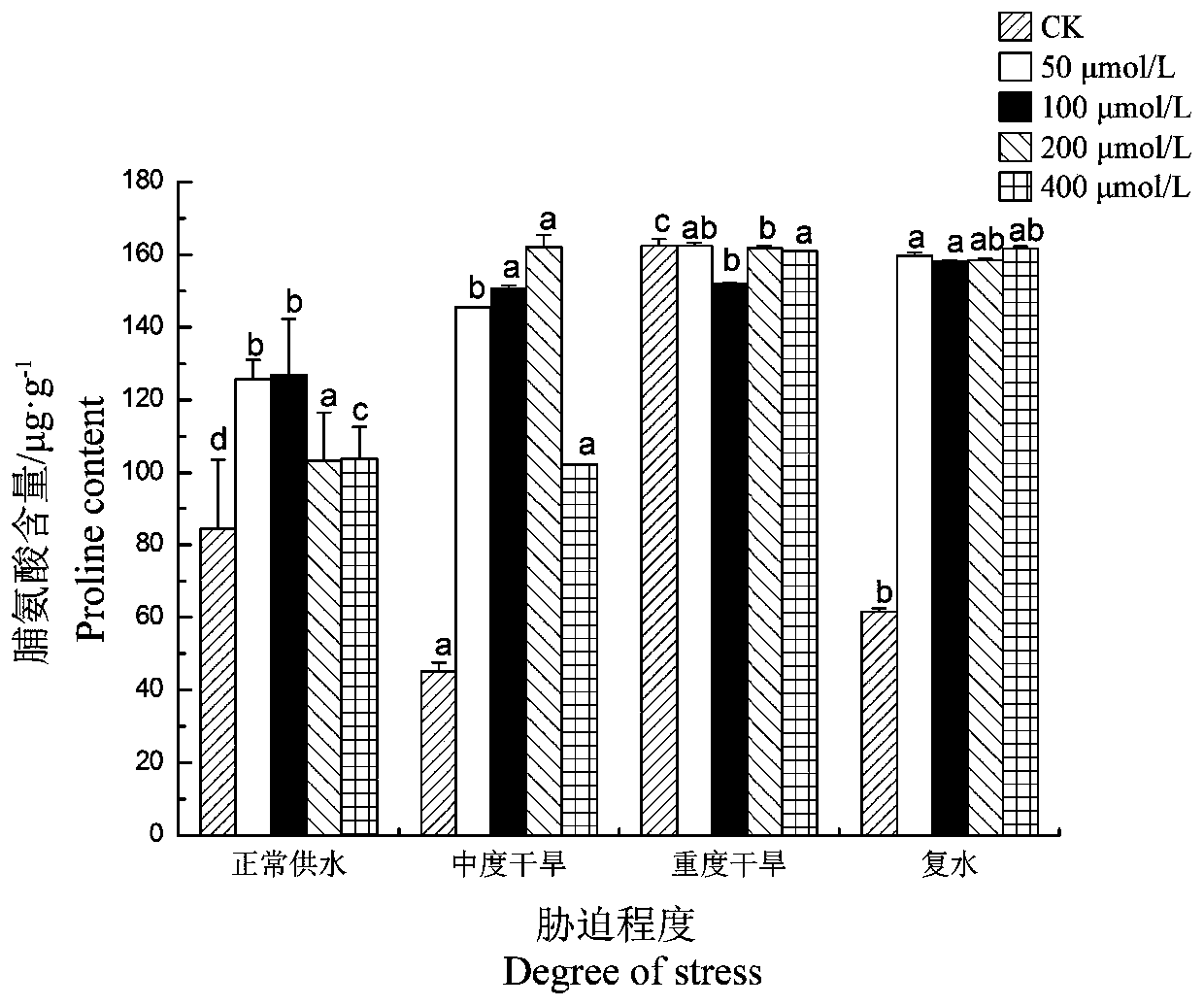
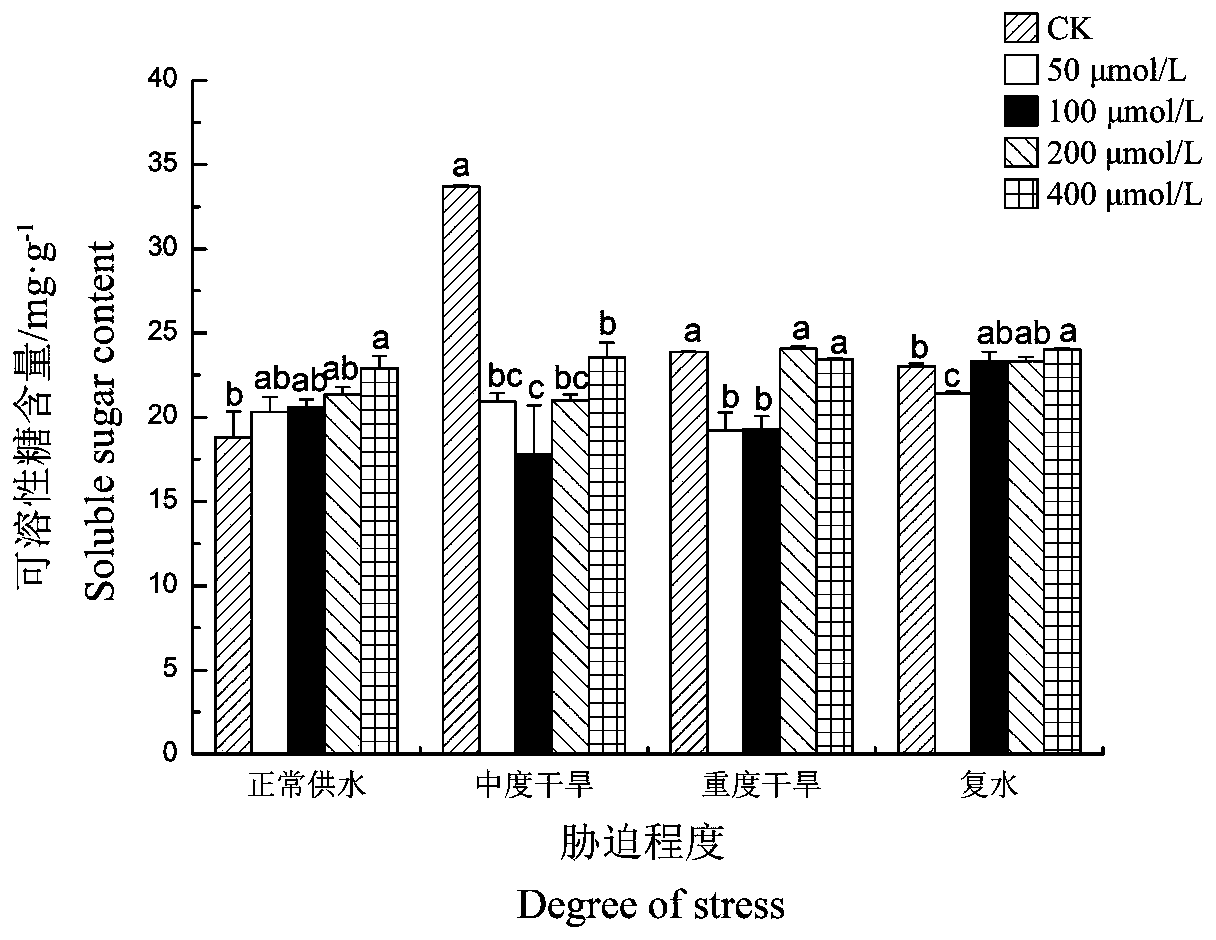
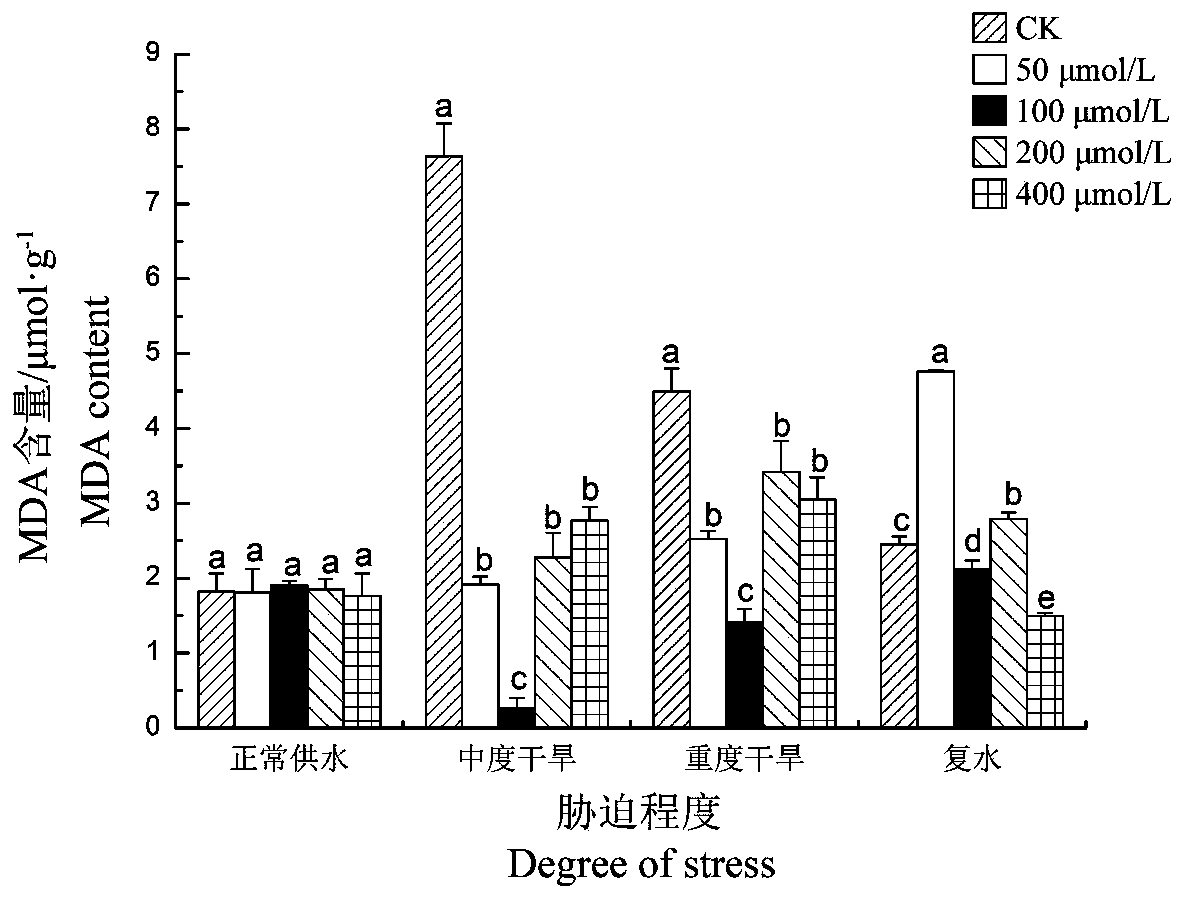
The invention discloses a method for improving drought resistance of turf on garbage compost substrate, which includes: selecting a lawn plant Festuca arundinacea and domestic garbage compost, applying 0.2-0.4Xkg-1 of rare-earth lanthanum nitrate or cerium nitrate per 60g of the compost, and mixing for use; respectively scattering 0.5g of Festuca arundinacea seeds into cups; controlling largest water-holding capacity of the compost in a field to be 66% and severe stress to be 35-50%, normally supplying water early in the experiment to guarantee smooth seed germination and seedling growth, quantitatively feeding water after 2 weeks according to the degree of severe stress, and controlling the degree of drought by weighing process; and finally measuring all indexes. Experimental results show that applying rear earth increases the ratio of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, content of total chlorophyll and chlorophyll a / b of Festuca arundinacea under drought stress, so that optical absorption of Festuca arundinacea is enhanced, accumulation of photosynthate is promoted, and stress resistance of the lawn plant Festuca arundinacea is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
LED plant lamp based on chlorophyll absorption spectrum feature design
InactiveCN104390158AGood compatibilityPromote growthPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsElectricityChlorophyll b
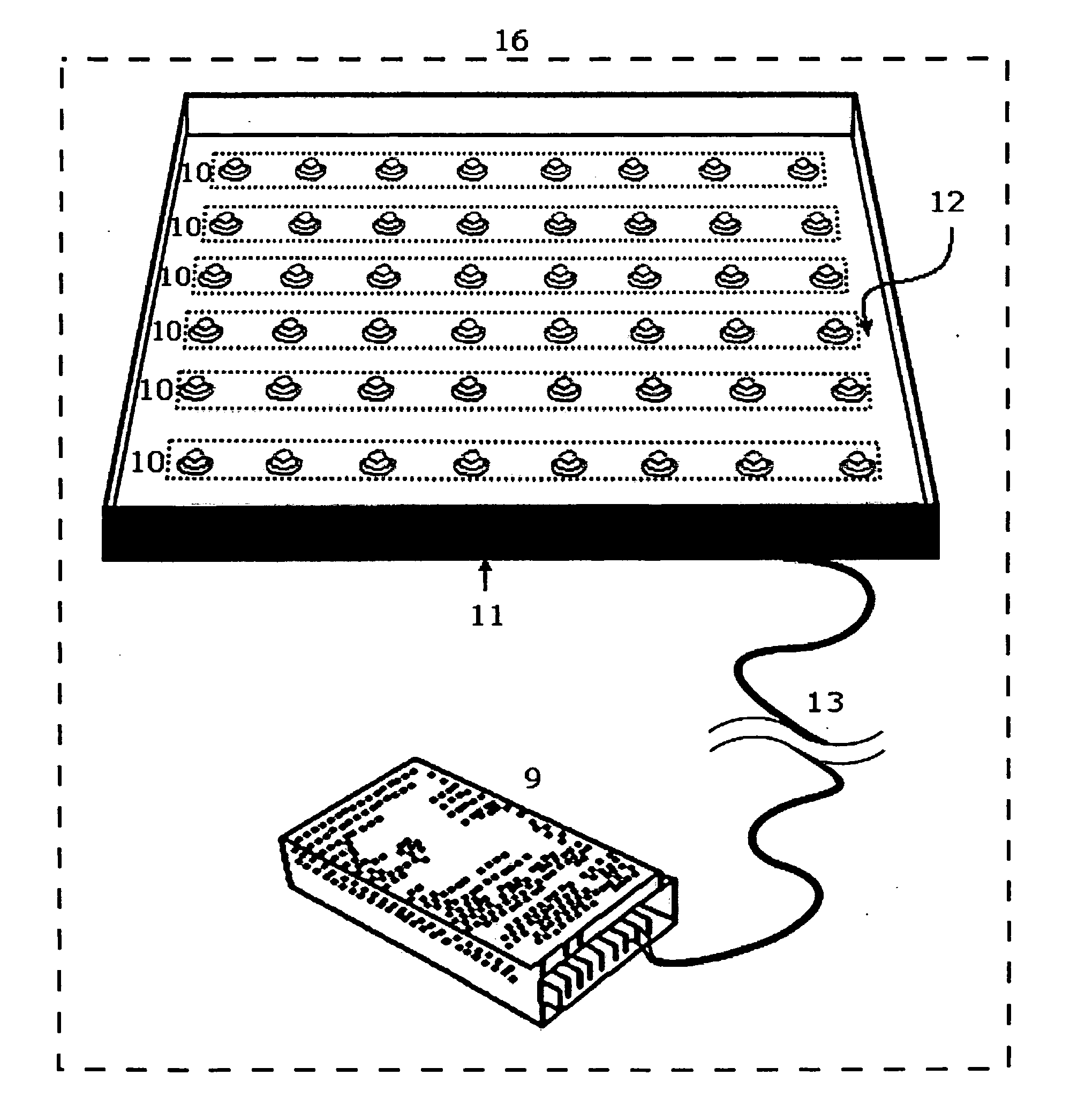
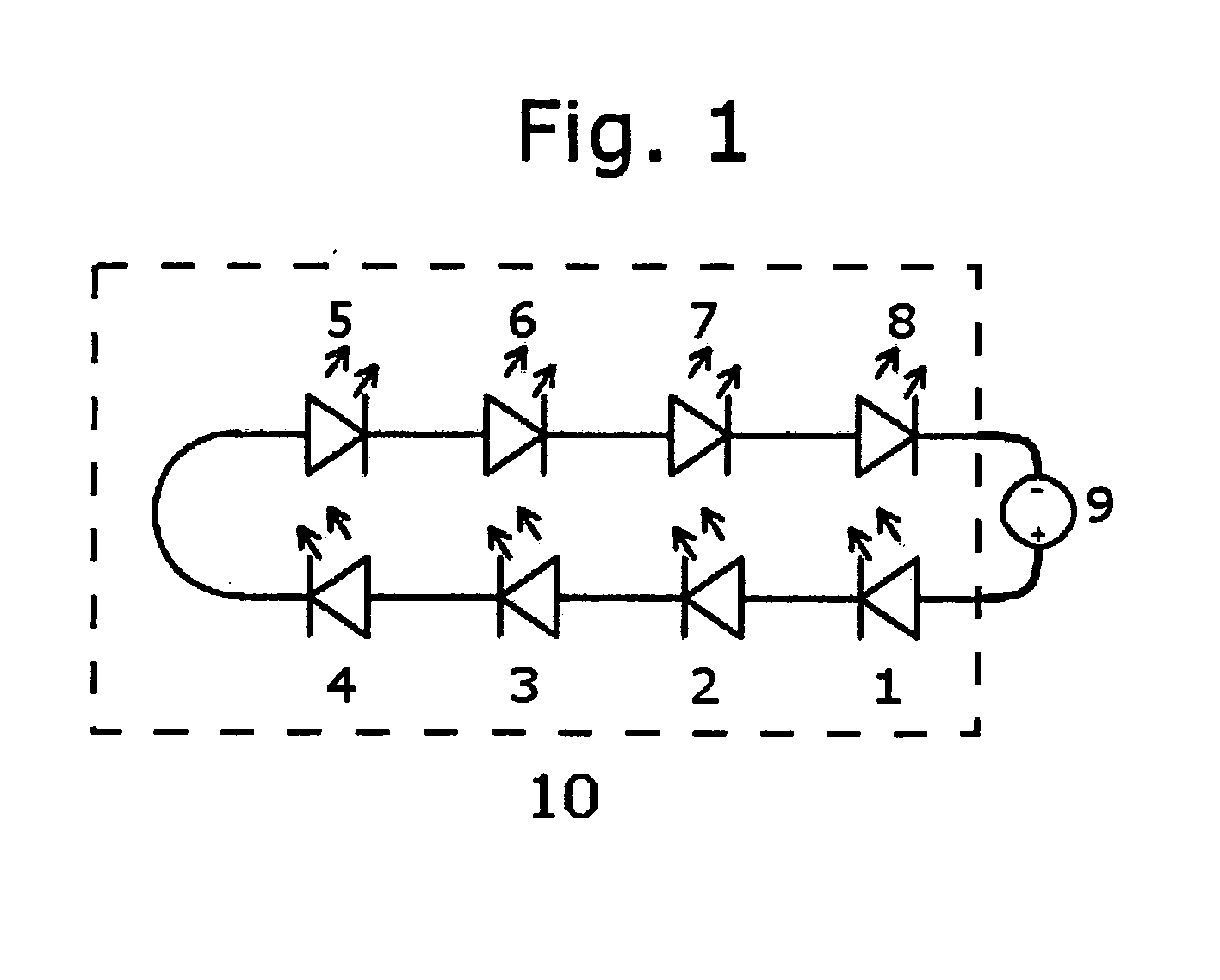
The invention relates to an LED (light emitting diode) illumination technique, in particular to an LED plant lamp based on chlorophyll absorption spectrum feature design. The LED plant lamp adopts the technical scheme that the LED plant lamp based on the chlorophyll absorption spectrum feature design comprises a light emitting body, a casing, a power source, a first controller, a second controller and wiring terminals, wherein the light emitting body is provided with a first LED light source module and a second LED light source module, the first LED light source module is used for outputting spectrum which is matched with absorption curve spectrum features of chlorophyll a, the second LED light source module is used for outputting spectrum which is matched with the absorption curve spectrum feature of chlorophyll b, the first controller is arranged in the casing, is electrically connected with the power source and is used for controlling the light emitting intensity of the first LED light source module, the second controller is arranged in the casing, is electrically connected with the power source and is used for controlling the light emitting intensity of the second LED light source module, and each wiring terminal is arranged on the casing, and is used for electrically connecting the corresponding controller and the corresponding LED light source module. The LED plant lamp has the advantages that the growth of plants is well promoted, the light intensity of different LED light source modules can be conveniently adjusted, and the requirements of different plants are met.
Owner:中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所湖州新能源产业创新中心
Rice chlorophyll synthase mutant gene and its application in gene engineering
InactiveCN101096676AHas chlorophyll synthase activityHigh homologyEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses a nucleotide sequence of rice chlorophyll synthase mutation gene Osygl1 and gene engineering application in the gene engineering domain, which is characterized by the following: the cDNA sequence of Osygl1 is SEQ ID NO.1 and its coded amino acid sequence is SEQ ID NO.2; the gene OsYGL1 is a chlorophyll synthase gene in the rice, which participates the synthesis of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b to display component expression; the mutation of the gene leads the leaf of rice to become yellow green, which can be genetic mark to identify the kind in the agricultural manufacturing and rice genetic breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Nondestructive measurement method of chlorophyll in leaf
InactiveCN103163094APositive and beneficial technical effectsDetermination successColor/spectral properties measurementsChlorophyll bLuminosity
The invention relates to a nondestructive measurement method of chlorophyll in a leaf. The method comprises the steps of irradiating the leaf and a reflector plate by rays with two (or three) specific wavelengths, and calculating a relative index (or actual content) of chlorophyll content according to the reflectivity, wherein the index (or actual content) and the total content of chlorophylls (or content of chlorophyll a, content of chlorophyll b, and total content) have obvious correlativity (or quantitative functional relation), so as to estimate and calculate or restore the content of chlorophylls (or calculating chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and total chlorophyll content) in the leaf according to the correlation. The method disclosed by the invention is not limited by the thickness of the leaf while the error is rapidly amplified by the existing transmission-type colorimetric assay method when the thickness of the leaf is large and the absorptivity A is greater than 1.0. According to the scattered reflection measurement method disclosed by the invention, diffuse reflection is carried out at any level inside the leaf, and the effect of the thickness of the leaf is small. The method disclosed by the invention is low in detection cost of the chlorophyll; no consumable items are used; and the technical preparation process of a conversion model is not needed.
Owner:河南农大迅捷测试技术有限公司
Measuring method for algae biomass in biological soil crust
ActiveCN105092495AEasy to collectEasy to operateColor/spectral properties measurementsChlorophyll bNatural development
The invention discloses a measuring method for the algae biomass in a biological soil crust, and relates to the field of biology. The method includes the steps of sampling of an algae crust sample, sieving, cleaning, algae cultivating, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b measuring, standard curve drawing and algae biomass measuring (natural development). In the algae cultivating step, cultivating is carried out through BG11 cultivating media, and use algae are mixed algae. In the chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b measuring step, chlorophyll is extracted with a mixed solution method, wherein extracting solutions comprise absolute ethyl alcohol, acetone and water in the ratio of 4.5 to 4.5 to 1. The relationship between the gross of the chlorophyll a and the chlorophyll b of the algae and the algae biomass is regressed through a standard curve. Measuring of the natural developing algae biomass is converted through the standard curve between the gross of the chlorophyll a and the chlorophyll b and the cultivated algae biomass. Direct comparison between the algae crust and the vascular plant biomass is achieved, and a reliable approach is provided for more accurately calculating the productivity of the algae crust and the effect of the productivity in an ecological system.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES CAS
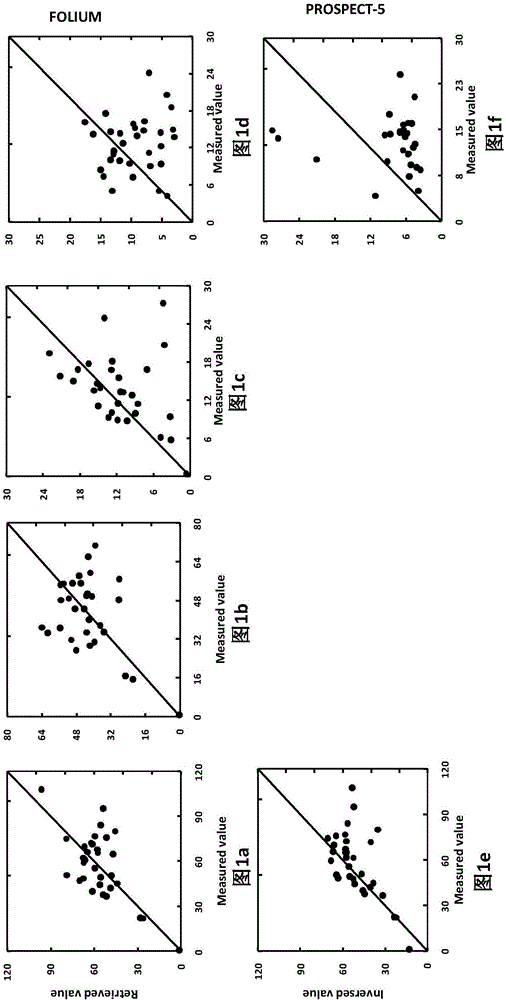
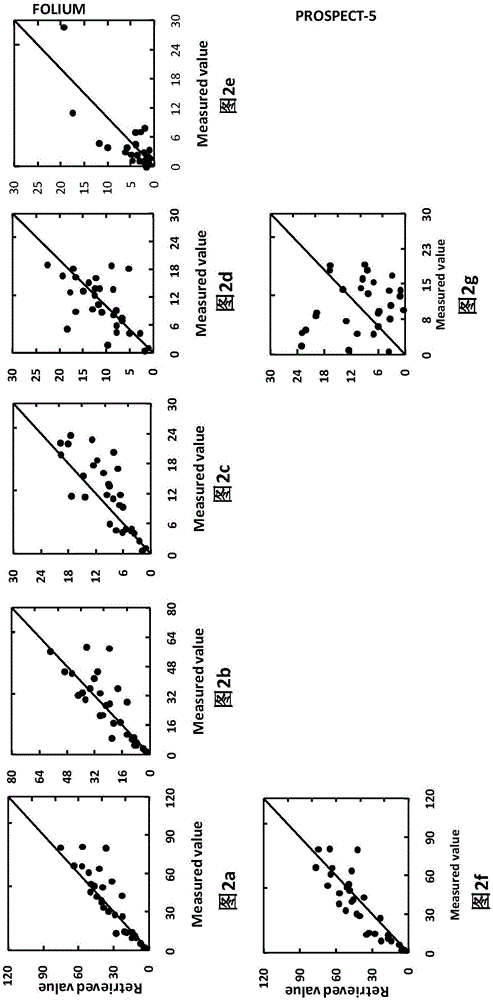
Leaf pigment remote sensing inversion method based on FOLIUM model
InactiveCN106202971AImprove inversion accuracyMonitoring Physiological and Ecological PropertiesInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsChlorophyll bPhotosynthetic pigment
The invention provides a leaf pigment remote sensing inversion method based on a FOLIUM model. The method comprises the steps that 1, on the basis of the FOLIUM model, green leaf LOPEX93 / colorful leaf LOPEX_ZJU data concentrated hemisphere reflection and transmission spectral data, various parameters of the FOLIUM model, a minimum distance spectral fitting method and a least square method optimization method are utilized, and a method for achieving inversion of contents of various pigments corresponding to green / colorful leaves is achieved; 2, the inversion function of the FOLIUM model on all the pigments is elaborated by constructing a scatter diagram by means of measured values and inversion values of all the pigments, and the function of the FOLIUM model is compared with that of a PROSPECT-5 model; 3, comparative evaluation utilizing a accuracy evaluation function root-mean-square error, a deviation, a corrected standard deviation and variation coefficient inversion accuracy is achieved. According to the leaf pigment remote sensing inversion method based on the FOLIUM model, a green / colorful leaf hemisphere reflection and transmission spectra can be utilized for inversion of contents of photosynthetic pigments including chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoid or non-photosynthetic pigments including anthocyanin, and compared with the PROSPECT-5 model, the inversion accuracy of total chlorophyll and carotenoid can be improved; physio-ecological characteristics of plant bodies can be monitored more accurately.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for detecting content of chlorophyll b in canopy of jujube tree
InactiveCN105954207ASimple and fast operationAccurate operationScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsWavelet denoisingChlorophyll b
The invention discloses a method for detecting content of chlorophyll b in canopy of jujube tree. The method comprises the following steps of collecting the high spectrum information of the canopy of jujube tree in sunny, cloudless or less-cloud weather with wind force less than 3; performing multiplicative scatter correction on the high spectrum data, and performing wavelet denoising and smoothing; extracting the spectrum reflectance values of the canopy of jujube tree with to-be-measured content of chlorophyll b in the wavelengths of 470nm, 610nm, 645nm, 652nm, 663nm, 985nm and 1160nm; substituting the spectrum reflectance values into a detection model, and calculating, so as to obtain the content of chlorophyll b in the canopy of jujube tree. The method has the characteristics that the pollution is avoided, the operation is simple, convenient, quick and accurate, and the method is suitable for being popularized and applied.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Transgenic plants with engineered redox sensitive modulation of photosynthetic antenna complex pigments and methods for making the same
ActiveUS20170356001A1Improve productivityIncrease probabilityClimate change adaptationOxidoreductasesDNA constructChlorophyll b
Embodiments of the present invention provide for a transgenic plan, methods of making and DNA constructs for use in the transgenic plant which transgenic plant is capable of modulating its photosynthetic antenna complex composition in response to increases or decreases in light intensity by modulation of the ratio of chlorophyll a to chlorophyll b such that there is an increase in the Chl a / b ratio at high light intensity and a decrease in the Chl a / b ratio at low light intensity versus wild-type plants grown in the same conditions.
Owner:NMC INC
Method for judging quality of fresh tobacco leaf sample in tobacco metabonomics based on pigments
The invention provides a method for judging the quality of a fresh tobacco leaf sample in the tobacco metabonomics based on pigments. According to the method, the ratio of the content of carotene to the content of chlorophyll b in the fresh tobacco leaf sample is adopted as an index, the quality of the fresh tobacco leaf sample in the metabonomics is judged, and bases are provided for selection of qualified samples in the metabonomics. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of being easy and fast to operate and accurate and reliable in result and adopting fewer samples, and reference can be provided for tobacco metabolic characteristic analysis and relevant tobacco metabonomics study.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
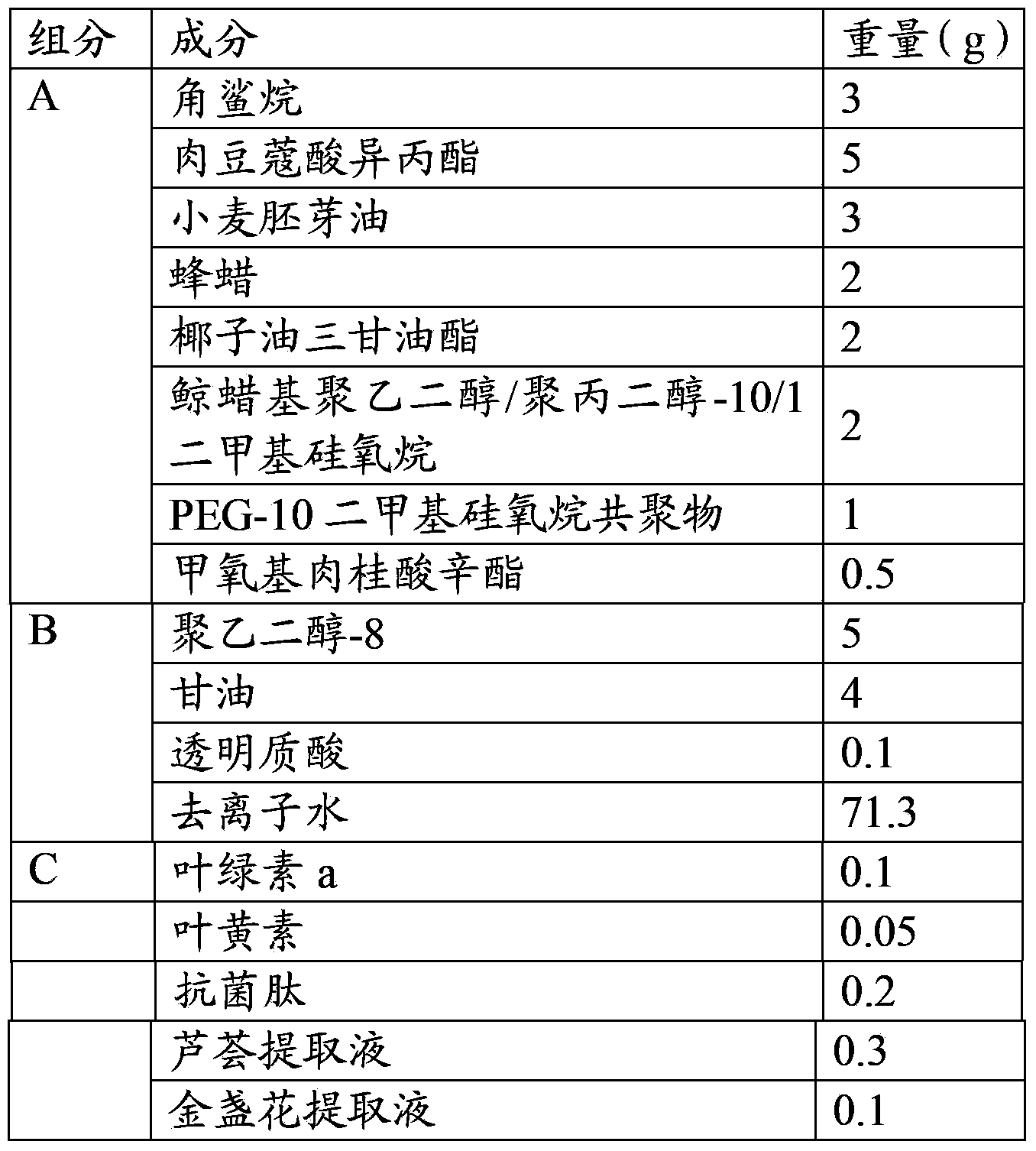
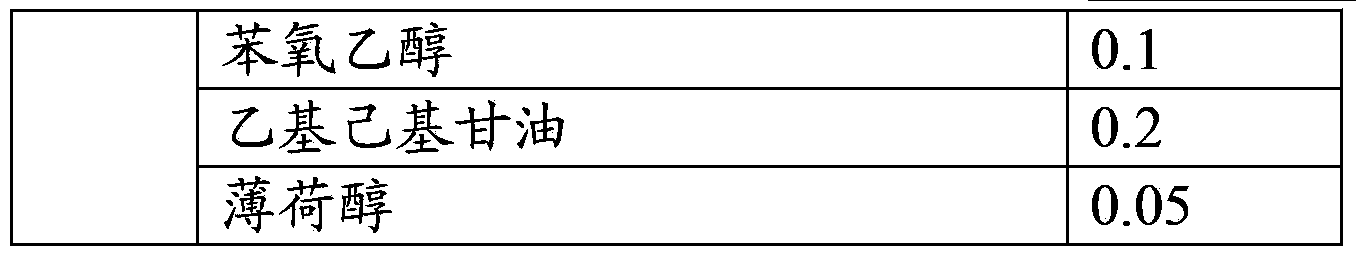
Sunscreen skin care product
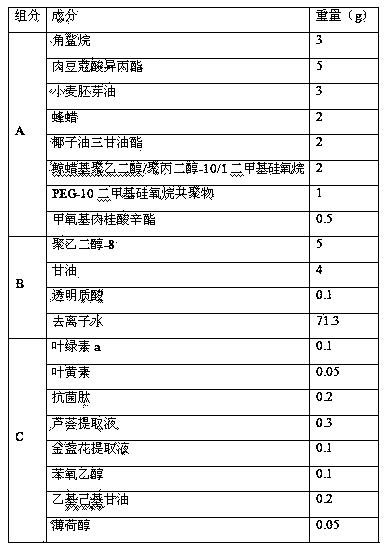
ActiveCN103211731BImprove sun protection effectReduce harmCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsSunscreen agentsChlorophyll b
The invention discloses a sunscreen skin care product comprising pigment, antimicrobial peptide, plant extracting solution, a sun-screening agent, grease, an emulsifying agent, a humectant and deionized water, wherein the pigment is selected from one or more from chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, chlorophyll c, chlorophyll d, carotene and xanthophyll. The chlorophylls are added in the sunscreen skin care product, thereby effectively blocking UVA (Ultraviolet A) and reducing injury of illumination on skin, UVB (Ultraviolet B) incapable of being absorbed by the chlorophylls is absorbed by the sun-screening agent, the chlorophylls are combined with the sun-screening agent to better block the ultraviolet radiated by the sun, thereby improving the sunscreen effect of the sunscreen skin care product. The added antimicrobial peptide and the plant extracting solution can effectively prevent and treat allergic inflammation phenomenon of skin, speed up the recovery of the injured skin and have the functions of maintaining moisture and moistening skin at the same time.
Owner:GUANGDONG COOWAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Chemiluminescence method for detecting chlorophyll alpha
InactiveCN101493419AQuick checkSensitive detectionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLuminolChlorophyll b
The invention discloses an analysis method for flow injection chemiluminescence chlorophyll a determination by a potassium ferricyanide-luminol system. The method comprises the processes of optimization of flow injection chemiluminescence analytic system test parameters establishment of a method for determining chlorophyll a by the potassium ferricyanide-luminol system and the like. The chlorophyll a can be determined by the method, but chlorophyll b can not be determined by the method. Mass concentration of the chlorophyll a within 0.5-10.0mg / L is subject to a good linear relation with a sensitization rate, a regression equation thereof is I=23.244C-4.2218(R=0.9991), and detection limit of the method is 0.13mg / L. Standard chlorophyll a solution with the concentration being 5.0mg / L is subject to 11 precision tests in parallel determination and repeated tests divided into 6 partial determinations, and RSD thereof is 1.17% and 3.74%. The method can rapidly and flexibly detect the chlorophyll a.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
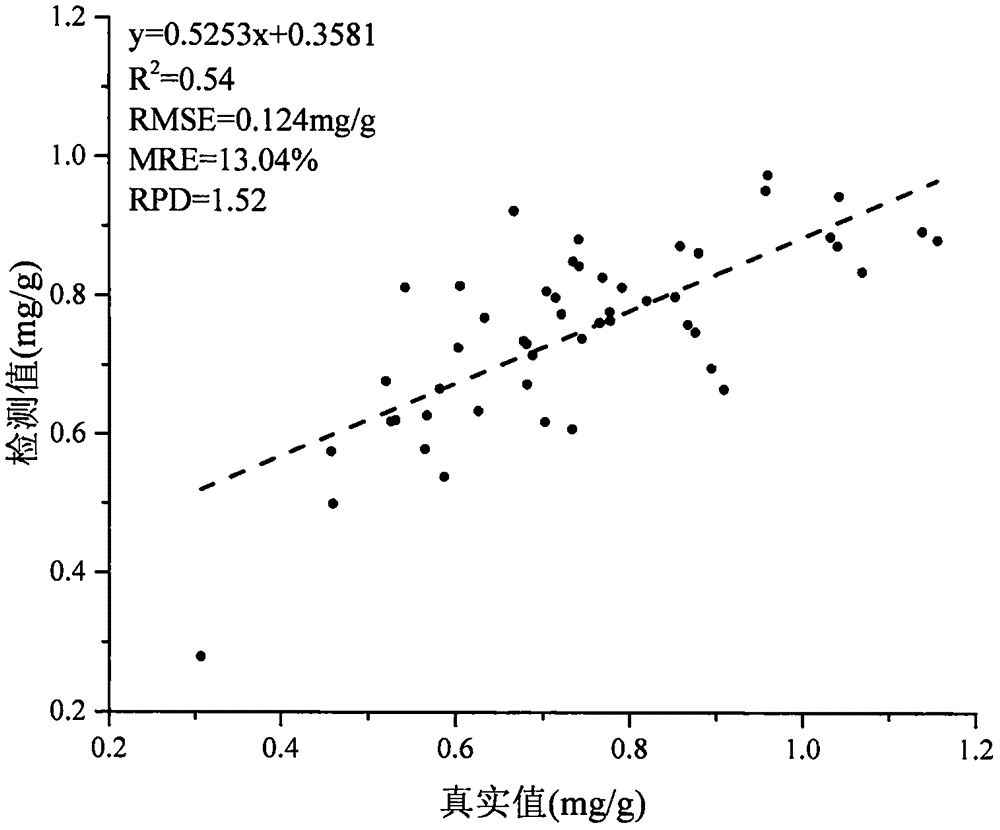
Satellite remote sensing monitoring method for jujube tree canopy chlorophyll b content
The invention provides a satellite remote sensing monitoring method for the jujube tree canopy chlorophyll b content. The method comprises the following steps that a to-be-monitored area is determined; a satellite remote sensing image of the to-be-monitored area is downloaded; geometric precision correction, radiation correction and atmospheric correction are sequentially conducted on the downloaded satellite remote sensing image; the satellite remote sensing image obtained after atmospheric correction is cropped to obtain a monitored area image; five vegetation indexes of each pixel selected from the monitored area are calculated through ENVI5.1 software; the five vegetation indexes are substituted into a model through waveband calculation, and the jujube tree canopy carotenoid content of each pixel is calculated, wherein Y is the jujube tree canopy chlorophyll b content, and the unit of the jujube tree canopy chlorophyll b content is mg / g. According to the method, the jujube tree canopy chlorophyll b content data is quickly and accurately acquired in an economical and environment-friendly mode on regional scale, pollution to the environment and harm to human bodies of chemical tail liquid discharge in the measurement process are avoided, the operation steps are greatly simplified, and the monitoring time is shortened.
Owner:TARIM UNIV
Array of LED lights optimized to produce light at the peack absorbance frequencies of the primary molecules involved in photosynthesis and plant growth
InactiveUS20150077984A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesGrowth plantBeta-Carotene
An Assembly is provided to produce light at the frequencies most readily absorbed by the primary molecules involved in the photosynthetic process, Chlorophyll A, Chlorophyll B, Beta-Carotene, P680 and P700.
Owner:SMITH DANIEL
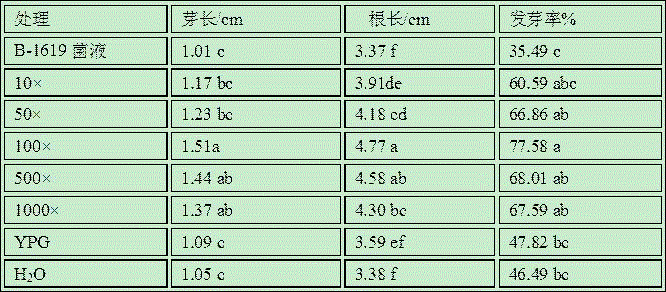
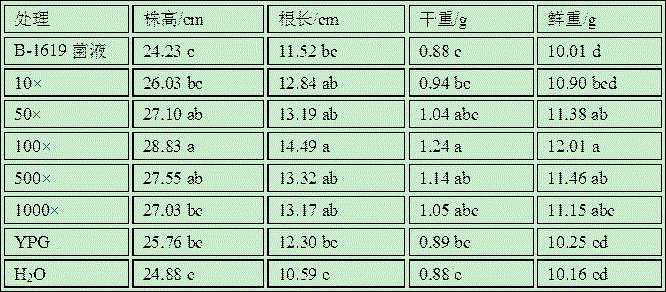
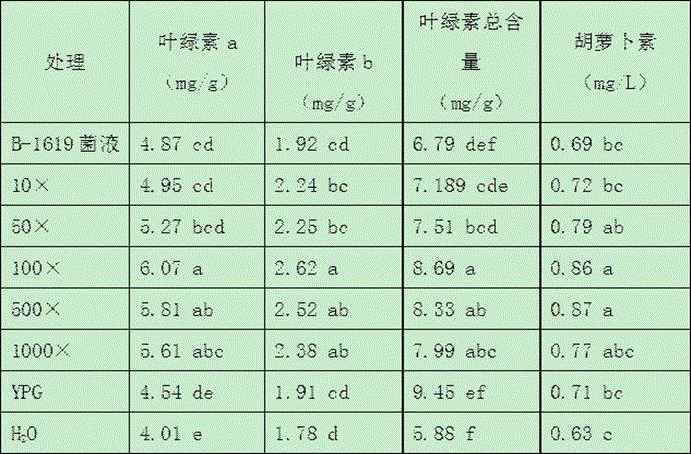
Application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens B-1619 in aspect of promoting growth of greenhouse vegetables
ActiveCN105746033AIncrease productionNon-pathogenicSeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsDry weightGrowth promotion
The invention discloses application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens B-1619 in aspect of promoting growth of greenhouse vegetables. 10-1000 times of diluent of B-1619 bacterium liquid with microbial content of 10<9-10>cfu / ml is watered to vegetables before sowing, in the seedling stage and after field planting, has a growth promotion effect on root length, fresh weight and dry weight of seedlings of greenhouse vegetables such as tomatoes or cucumbers, and has an effect of improving the total content of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and chloroplast pigments in plants and the content of carotene. Moreover, the crop yield can be obviously improved, and the bacterium liquid is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
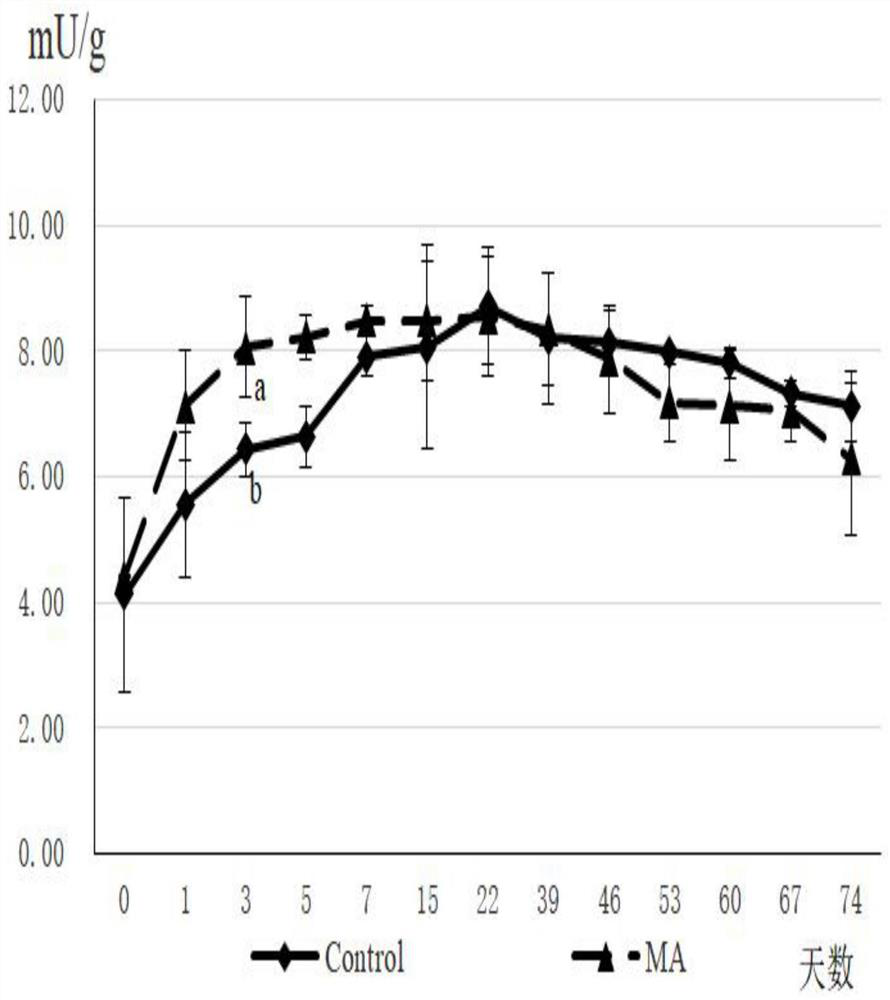
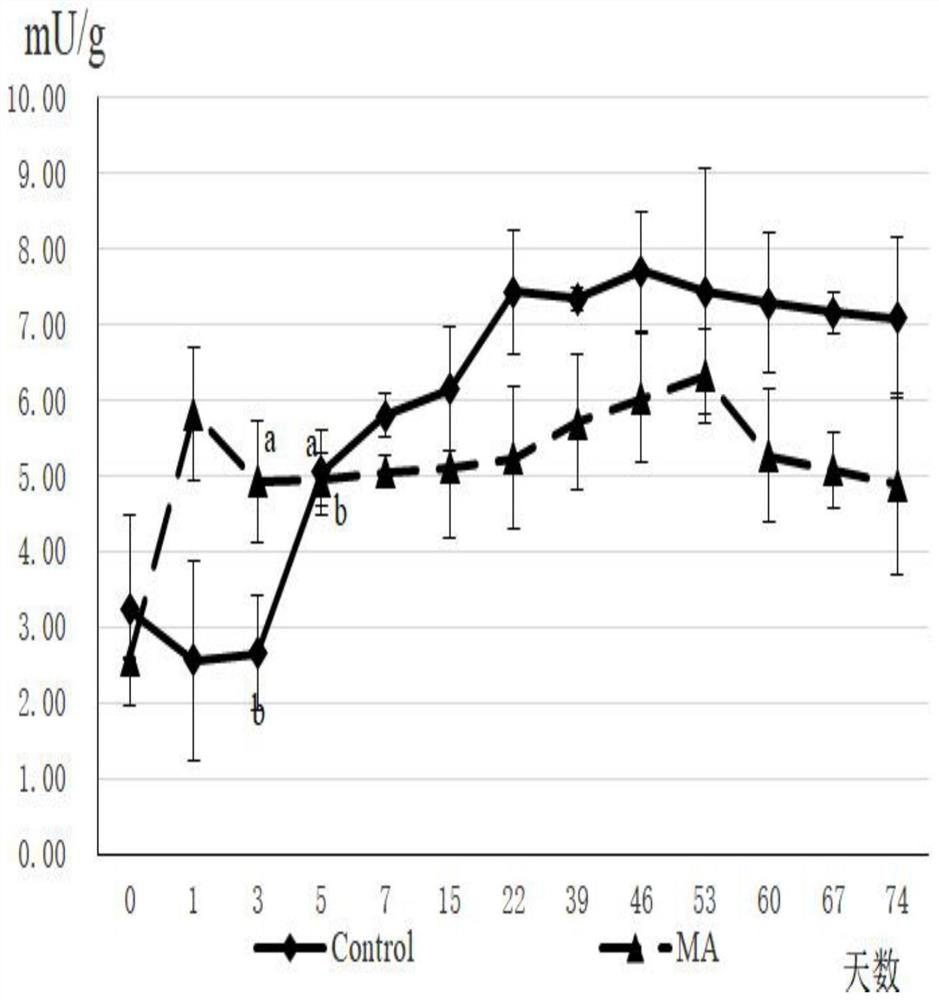
Method of reducing decomposition of chlorophyll in alfalfa silage
InactiveCN111616269AImprove fermentation qualityImprove degradation rateAnimal fodder preservationChlorophyll bChlorophyllin
The invention provides a method of reducing decomposition of chlorophyll in alfalfa silage. The method comprises the following steps of airing an alfalfa raw material at a dark and ventilation place until being semi-dry with the water content of the alfalfa raw material being about 50 percent, cutting up the alfalfa raw material into 2-3 cm, mixing the alfalfa raw material with 1mol / L sulfuric acid and 2mol / L hydrochloric acid according to a volume ratio of 1 to 4 to prepare mixed acid, adding the mixed acid with an addition amount being 2-10 percent (by mass percentage), treating a sample, weighing 200g of the treated samples, charging the weighed samples in 16*25cm black polyethylene bags respectively, performing sealing packaging with a vacuum machine, performing small-scale fermentation in a room-temperature dark environment, and performing unsealing at day 0, day 1, day 3, day 5, day 7, day 15, day 22, day 39, day 46, day 53, day 60, day 67 and day 74 respectively with unsealing 3bags at each time. By means of the method, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b are gradually decreased along with extension of a fermentation time in the silage process, and chlorophyll loss in the latestage of alfalfa silage can be reduced by adding MA.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Culture method of phobotaxis insect resisting rice
The invention relates to a culture method for phobotaxis insect resisting rice, which comprises the following steps: collecting rice materials, soaking seeds and sprouting, seedling the seeds to a rice seed-bed, and measuring the contents of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b in leaves at 5 to 7 leaf age before transplanting; selecting and remaining the rice materials the total contents of the chlorophylls of which are lower than 3.5 mg / g and the ratio of the chlorophyll a and the chlorophyll b is greater than 3.3; transplanting single plants to the field without spraying medicine, respectively observing rice leaf roller at the stooling stage, the jointing stage and the heading stage, observing striped rice borer and yellow rice borer at the heading stage, and observing the damage of rice planthopper at flowering period and the mature period; selecting and remaining the rice material insusceptible to the damage of insect pests; evaluating and verifying the total content and the ratio of the chlorophyll a and the chlorophyll b, and the stability for resistance of the rice leaf roller, the striped rice borer, the yellow rice borer and the rice planthopper; and propagating the stable materials to obtain a novel rice material with phobotaxis insect resistance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Transgenic plants with engineered redox sensitive modulation of photosynthetic antenna complex pigments and methods for making the same
ActiveUS10745708B2Optimize production systemIncrease flexibilityClimate change adaptationOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyDNA construct
Embodiments of the present invention provide for a transgenic plan, methods of making and DNA constructs for use in the transgenic plant which transgenic plant is capable of modulating its photosynthetic antenna complex composition in response to increases or decreases in light intensity by modulation of the ratio of chlorophyll a to chlorophyll b such that there is an increase in the Chl a / b ratio at high light intensity and a decrease in the Chl a / b ratio at low light intensity versus wild-type plants grown in the same conditions.
Owner:NMC INC
Chloroplast pigment paper chromatography separation method
InactiveCN104077949AReduce pollutionSimple processing methodEducational modelsBeta-CaroteneChlorophyll b
The invention relates to a pigment paper chromatography separation method, in particular to a chloroplast pigment paper chromatography separation method. The method includes the steps that first, pigment extract is prepared and stored in a place kept out of sun for use; then, cylindrical filter paper is made; finally, sample application is performed, after sample application pigment is dried through an electric hair drier, a small hole is made in the center of the sample application pigment, one end of the cylindrical filter paper is inserted in the small hole, the other end, namely a base end, of the cylindrical filter paper is placed in a culture dish with layer unfolding agent, the round filter paper subjected to the sample application is placed on the culture dish, and chromatography starts. After four colored ribbons (beta-carotene, lutein, chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b) are all separated, the chromatography is completed. According to the method, while the chromatography separation effect, for instance, the color of the colored ribbons is pure and the edges of the colored ribbons are clear, is improved, investment of a chromatography container is reduced and saved by 60 percent, tedious processing of the chromatography filter paper is reduced, and toxic pollution generated when acetone serves as the extraction agent, and the carbon tetrachloride serves as the layer unfolding agent is reduced. The separation method is good in separation effect, time and labor are saved, and environmental pollution and toxicity are reduced.
Owner:SHENYANG UNIV
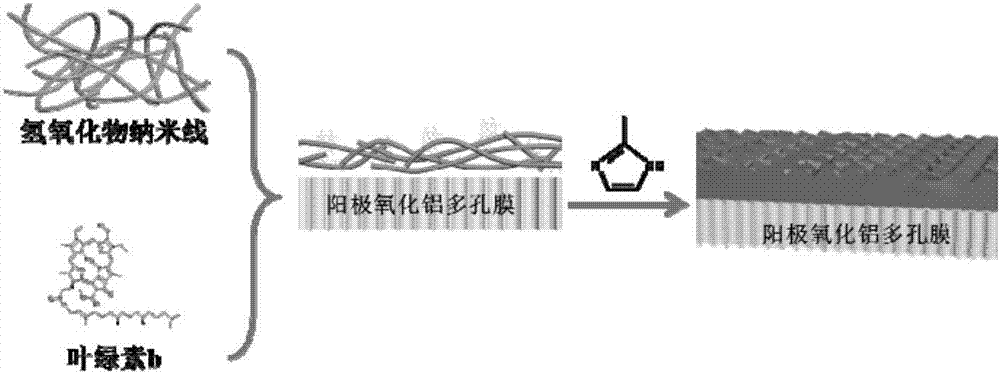
Preparation method of metal organic framework film modified by chlorophyll b and application thereof to photocatalytic reduction carbon dioxide
InactiveCN106975374AImprove light energy utilizationImprove photocatalytic efficiencySemi-permeable membranesDispersed particle separationComposite filmNanowire
The invention discloses a preparation method of a metal organic framework film modified by chlorophyll b and application thereof to photocatalytic reduction carbon dioxide. The method comprises the following steps of (1) preparing a hydroxide nanowire solution; then, mixing the prepared hydroxide nanowire solution with the chlorophyll b solution; uniformly stirring the mixture; performing vacuum suction filtering to obtain a composite film of the hydroxide nanowire and the chlorophyll b; (2) dissolving organic ligands into a mixed solution of ethyl alcohol and water to obtain an organic ligand solution; putting the composite film of the hydroxide nanowire and the chlorophyll b into the organic ligand solution; performing room temperature reaction for 2 to 24 hours; then, obtaining the metal organic framework film modified by the chlorophyll b. The goals of mixing the chlorophyll b with the nanowire through physical stirring and static absorption and introducing the chlorophyll b to the inside of the metal organic framework film in situ are realized so as to realize the functionalization; the advantages of low energy consumption, no pollution, high speed and high efficiency are achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing high-purity chlorophyll a from spirulina platensis
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity chlorophyll a from spirulina platensis. The method includes the steps that 1, the spirulina platensis cultivated to the later stage of the logarithm growth period serves as raw materials, and platensis bodies are centrifugally collected; 2, the platensis bodies are extracted three times through ethyl alcohol, and extract liquor is combined; 3, an appropriate amount of normal hexane or petroleum ether is added into the extractor liquor, water is added to phase splitting, back extraction is performed, and a solution with pigment is rinsed with water two times; 4, neutral alumina of 100-200 meshes is adopted for column chromatography isolation and purification to obtain chlorophyll a, first, a normal hexane or petroleum ether solution containing ethyl alcohol of 0.3% is used for moistening and rinsing an alumina column, and after sample loading, ethyl alcohol-normal hexane or ethyl alcohol-petroleum ether mixed solvent is used for gradient elution; 5, the solution containing the chlorophyll a is subjected to vacuum-rotary evaporation to recover solvent and obtain the high-purity chlorophyll a. The prepared chlorophyll a does not contain chlorophyll b, wherein the HPLC purity is larger than 99.5%.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Method for culturing microalgae by using benzoic acid
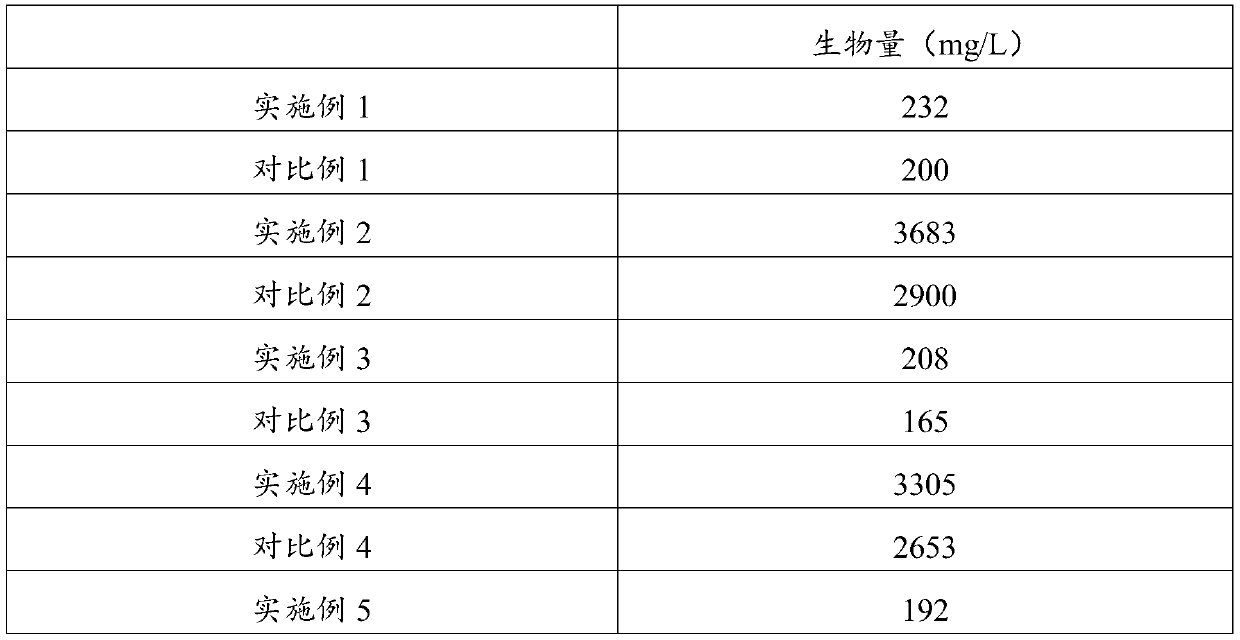
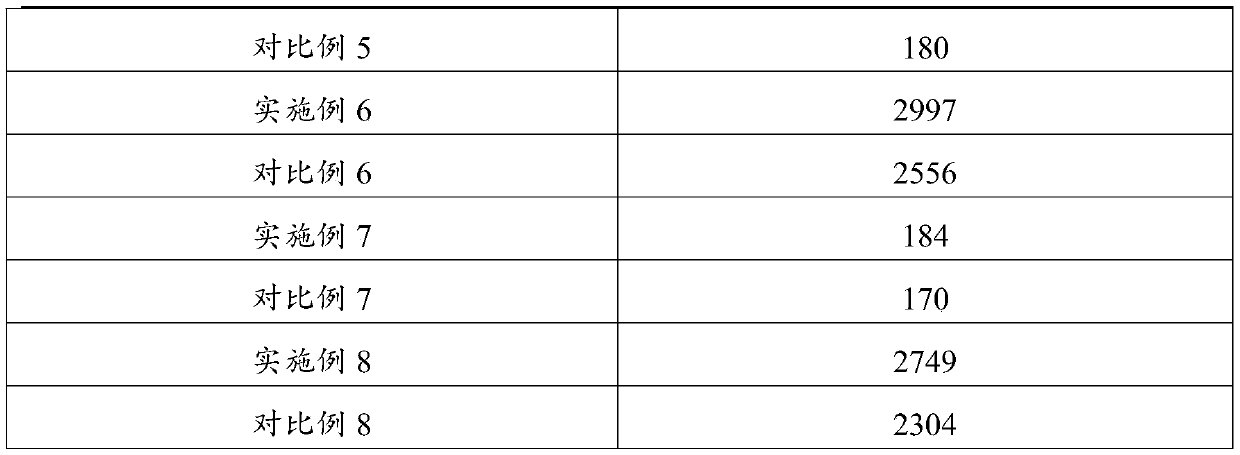
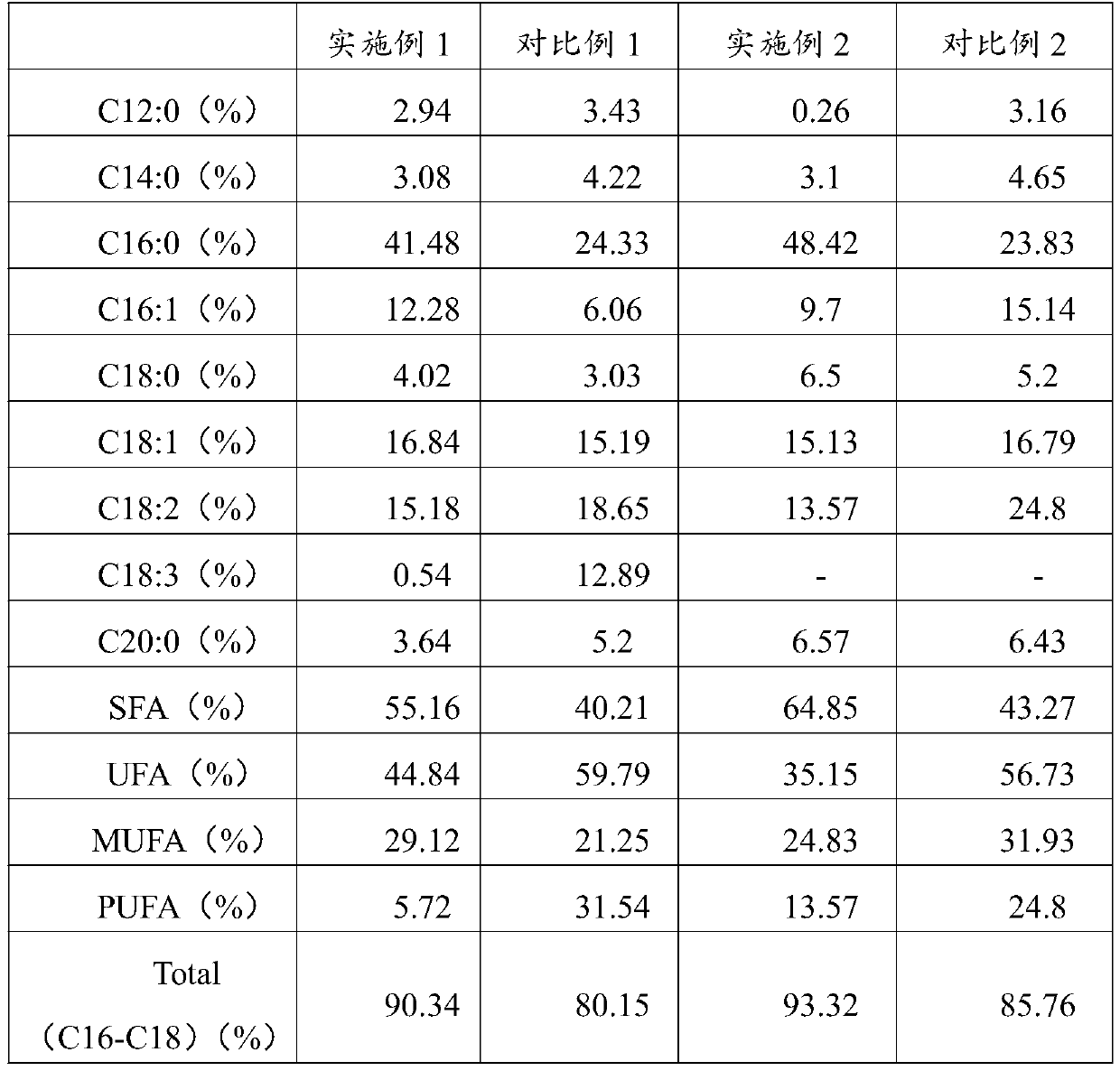
ActiveCN111548942AIncrease biomassIncrease contentBacteriaUnicellular algaeBiotechnologyBenzoic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of microalgae culture, and particularly relates to a method for culturing microalgae by using benzoic acid. The method comprises the following steps of: adding benzoic acid at the initial stage of the growth regulation period of microalgae, and continuing culture, wherein the addition amount of benzoic acid is 50-2,000 microgram / L. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the biomass of the microalgae is increased by 6.67%-27%, the grease content is improved by 13.65%-45.6%, the content of chlorophyll a is increased by 4.55%-60%, the content of chlorophyll b is increased by 7.14%-71%, especially the content of carotenoid is increased by 31.9%-153%, the protein yield is increased by 26.2%-28.6%, and the saccharide yield is increased by 11.8%-18.2%.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of mixed and compounded turf matrix in promoting growth of festuca arundinacea of lawn plants
InactiveCN101880185AReduce contentPromote growthFertiliser formsFertilizer mixturesPopulus grandidentataChlorophyll b
The invention relates to application of a mixed and compounded turf matrix in promoting growth of festuca arundinacea of lawn plants. The germination percentage, the growth height, the single plant net photosynthesis amount, the dry and fresh ratio, and indexes of chlorophyll A, chlorophyll B, carotenoid and the like in the cytochrome are measured and compared, results show that crushed Chinese white poplar bits and fined life refuse are compounded to be beneficial to the growth of the festuca arundinacea, all indexes are remarkable and higher than those of a contrast group, wherein the ratios of 28+2, 27+3, 26+4 and 25+5 are relatively better. It proves that the compounded raw materials can improve the property of the matrix, have a certain nutrition function, and ensure that the turf matrix and the root system of the lawn plants have better bonding effect.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving drought resistance of Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. for oil by using methyl jasmonate
InactiveCN110972797ASolve the problem of poor growthIncrease net photosynthetic rateCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsPaeonia suffruticosaChlorophyll b
The invention discloses a method for improving drought resistance of Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. for oil by using methyl jasmonate. The drought resistance of Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. for oil is induced by using methyl jasmonate. The method comprises the following steps: 1) cultivating annual seedlings of Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. for oil in October, wherein the seedlings are accordant in growthvigor and free of disease or insect; 2) cultivating the seedlings in a greenhouse till May of a next year, and performing normal water management in the process; and 3) spraying the methyl jasmonate to the Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. for oil once per 3 days for two times in all, so as to obtain the Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. for oil with drought resistance. After induction treatment with the methyljasmonate, the net photosynthetic rate, the transpiration rate, the intercellular CO2 concentration, the stomatal conductance, the content of free proline and the content of soluble sugar in leaves are all to increase, the contents of malondialdehyde, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoid are all to decrease, the net photosynthetic rate of the leaves of the Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. for oil is remarkably increased, damage of drought stress to Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. is reduced, and the capability of the Paeonia suffruticosa Andr. in resisting to drought stress is improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
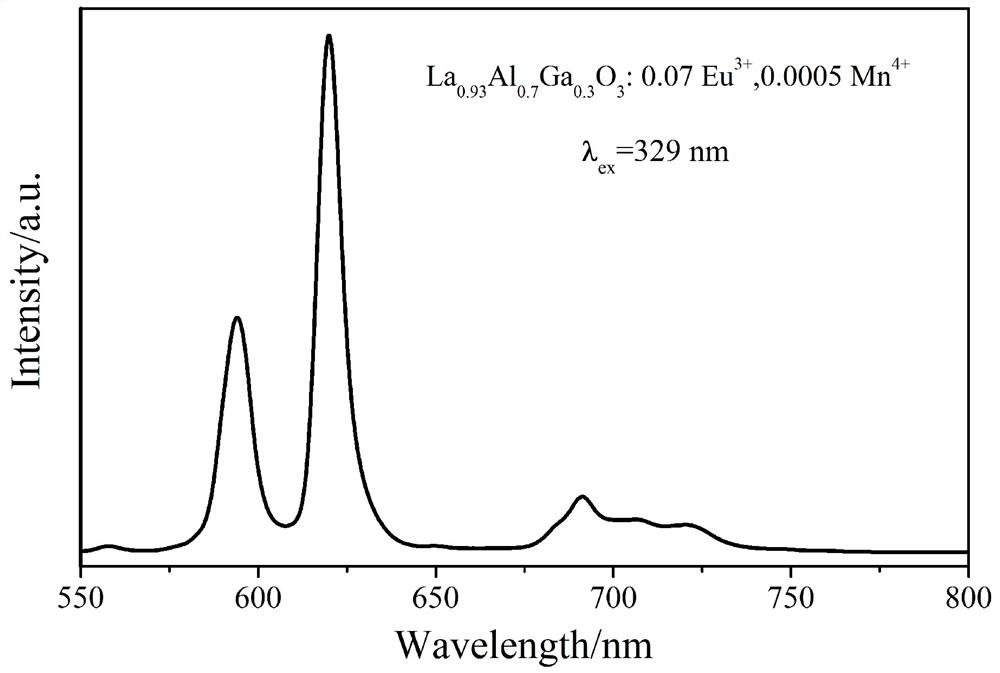
Red fluorescent powder excited by dual-band ultraviolet light as well as preparation method and application of red fluorescent powder
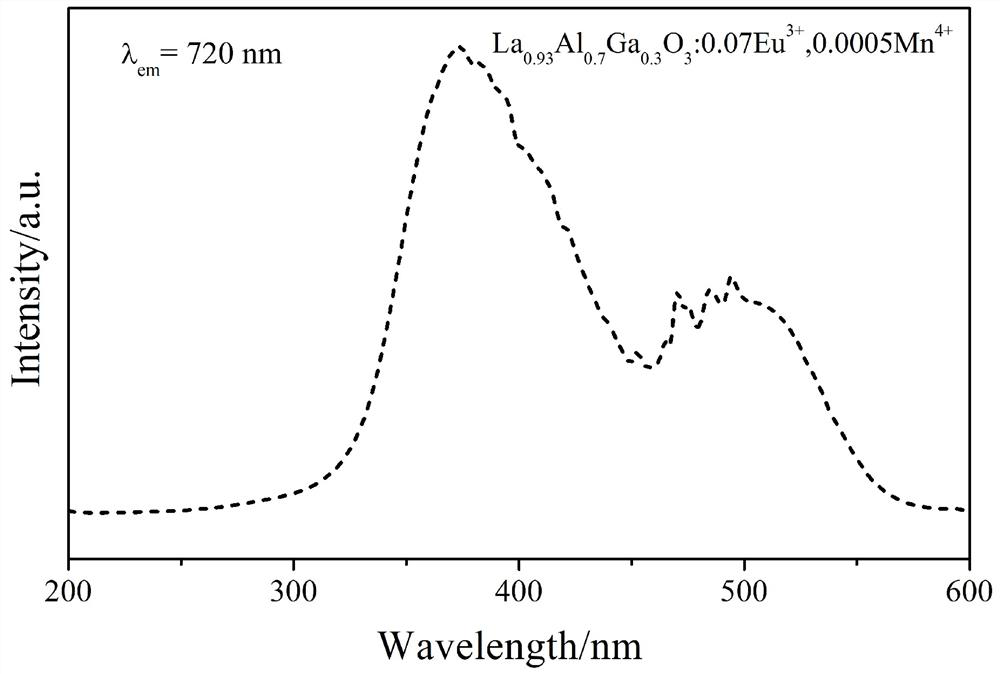
PendingCN113999677APromote growthHigh degree of absorption spectrum matchingHorticulture methodsLuminescent compositionsAir atmosphereUltraviolet lights
The invention provides red fluorescent powder as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The red fluorescent powder is a compound represented by a formula I: REmMaO3: bEu<3+>, cMn<4+>, wherein RE comprises one or two selected from the group consisting of La, Y, Gd, Lu and Sc; the sum of the atomic numbers of RE elements is m, and m is more than 0 and less than 1; M comprises one or two selected from Al and Ga; and the sum of the atomic numbers of M elements is a, and a is more than 0 and less than 1. The preparation method comprises the following steps: with lanthanum oxide, aluminum hydroxide, gallium oxide, europium oxide and manganese carbonate as raw materials, carrying out high-temperature solid-phase reaction in an air atmosphere, and carrying out maintaining for 4-6 hours at 1400-1600 DEG C in a box-type furnace. The fluorescent powder has the properties of converting B-band ultraviolet light into red light with a main peak of 619 nm and converting A-band ultraviolet light into far-red light with a main peak of 720 nm, the emission spectrum of the fluorescent powder is overlapped with the absorption spectrum of plant chlorophyll b and the absorption spectrum of PFR pigment, and when the red fluorescent powder is applied to the field of gardening or agriculture, growth of plants can be promoted.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
System and method for monitoring particles in a fluid using ratiometric cytometry
ActiveUS9983115B2High resolutionAccurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisFluorescenceChlorophyll b
A particle detection system with a detection mechanism that includes detectors positioned to detect two different ranges of fluorescence produced by particles in the fluid in a flow chamber. Each of the detectors is arranged to generating a trigger signal whenever fluorescence is detected. The system and related method enhance the accuracy and sensitivity of blue-green algae monitoring by utilizing imaging flow cytometry combined with particle analysis and the measurement of the ratio of each particle's phycocyanin to chlorophyll b detected by using the two detectors configured for detection of two different fluorescence ranges, one associated with the phycocyanin and the other associated with the chlorophyll b. Captured images are be used in comparison to known images of a library of images using a support vector machine classifier.
Owner:YOKOGAWA FLUID IMAGING TECH INC
A method for estimating chlorophyll a/b ratio of vegetable soybean leaves
PendingCN109241659AWon't hurtReduce precisionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsQuantum yieldChlorophyll b
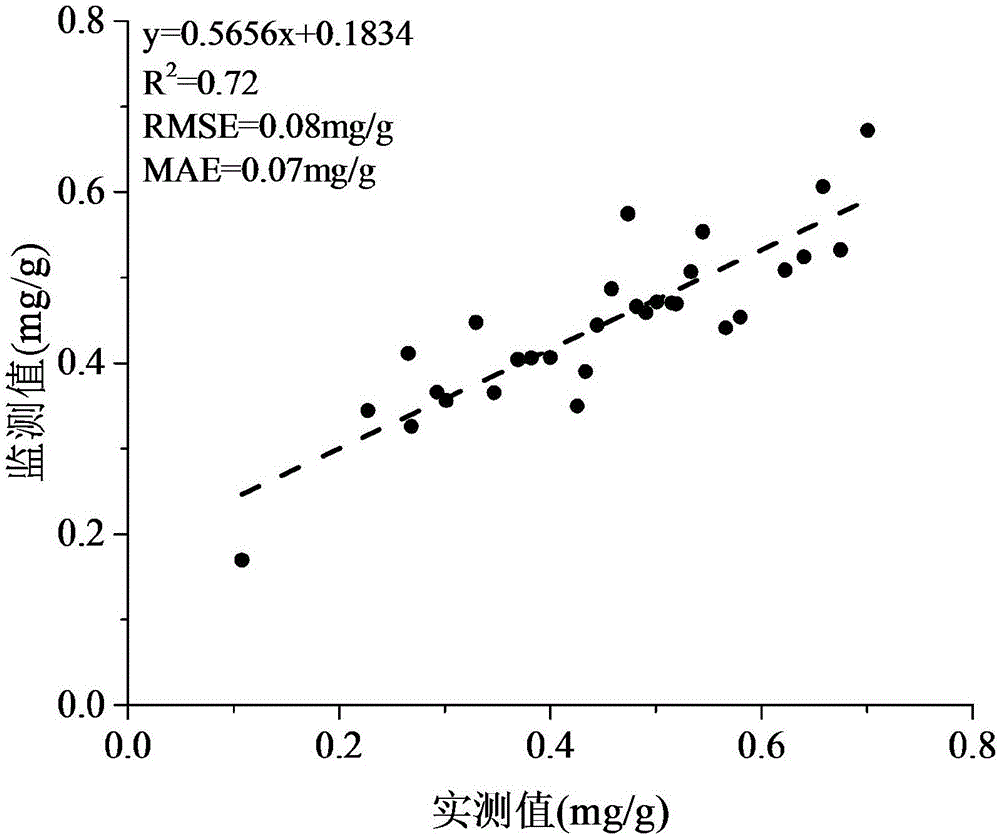
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology. A method for estimating chlorophyll a / b ratio of vegetable soybean leaves is disclosed, including obtaining 14 parameter values of the blade to bedetected: the actual photosynthetic efficiency Y (II) value X1, non-photochemical quenching coefficient NPQ value X2, the quantum yield Y (NO) value X3 of non-regulatory energy dissipation, quantum yield Y (NPQ) value X4 of the regulatory energy dissipation, maximum fluorescence Fm value X5 of dark-adapted samples, maximum photosynthetic efficiency Fv / Fm value X6 of PS II, Anthocyanin reflex indexARI1 value X7, Anthocyanin reflex index ARI2 value X8, Carotenoid reflectance index CRI1 value X9, carotenoid reflectance index CRI2 value X10, structure-insensitive pigment index SIPI value X11, vegetation senescence reflectance index PSRI value X12, photochemical vegetation index PRI value X13 and moisture index WBI value X14; substituting 14 parameter values into an estimation model of chlorophyll a / b to obtain a ratio D of chlorophyll a to chlorophyll b content. The method provided by the invention can efficiently and accurately realize the estimation of the chlorophyll a / b ratio.
Owner:JIANGHAN UNIVERSITY
Method of improving blue algae in-situ detection precision by using anti-fluorescent interference decoupling algorithm
ActiveCN106970054AAvoid purification processAvoid fluorescence interferenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceChlorophyll bWavelength
The invention discloses a method of improving blue algae in-situ detection precision by using an anti-fluorescent interference decoupling algorithm. The method depends on a fluorescent analysis method, and measurement can be achieved by taking phycocyanin as a major pigment index for detecting blue algae biomass, and using a fluorescent spectrophotometer that is relatively simple to operate in a laboratory. The method can effectively avoid mutual influence of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and the phycocyanin; the blue algae biomass in fresh water is monitored accurately; relatively precise alga biomass data is provided for early warning of blue algae water bloom; a theoretical basis is provided for subsequent design of a blue algae biomass detection sensor; the method can be also used for avoiding interference among multiple pigments to the greatest extent when the fluorescent pigments are detected by a fluorescent method; a theoretical basis is provided for scientific and reasonable screening excitation light wavelength and emitting light wavelength in fluorescent analysis; a multivariant correcting feedback piecewise linear detection model is established when an algal pigment concentration in a water body is detected by the fluorescent method; and precise detection of the pigment concentration is achieved.
Owner:威海慧视生物科技有限公司
Plant low-temperature damage evaluation and early warning system based on cumulative air temperature deficiency
ActiveCN113575240AGuaranteed real-time evaluationAccurate evaluationThermometer applicationsFluorescence/phosphorescenceEarly warning systemChlorophyll b
The invention discloses a plant low-temperature damage evaluation and early warning system based on cumulative air temperature deficiency. The evaluation and early warning system is composed of a sensor, a displayer, a gateway and a control unit, and the evaluation basis of the evaluation and early warning system is the cumulative air temperature deficiency, The principle of taking the cumulative air temperature deficiency as the basis for judging the low-temperature damage degree of plants is that a low-temperature damage degree SI model is constructed by utilizing nine low-temperature damage indexes, namely Fv / Fm, chlorophyll a content, chlorophyll b content, total chlorophyll, FO / 50us, Fk / 300us, FJ / 2ms, FI / 30ms and Fm / maximum fluorescence, each physiological parameter is substituted into the model SI to calculate a score, the cumulative temperature deficiency corresponds to the low-temperature damage degree through the SI value, and the low-temperature damage degree is directly monitored and evaluated. According to the system, the low-temperature damage degree is evaluated according to the cumulative air temperature deficiency, whether plants are subjected to low-temperature damage or not is judged according to the temperature deficiency, the damage degree is monitored, the judgment accuracy is improved, the monitoring cost is reduced, and the technical effects of energy conservation and high efficiency are achieved.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com