Measuring method for algae biomass in biological soil crust
A biological soil and measurement method technology, applied to the determination of algae crust biomass and the field of algae biomass measurement in biological soil crusts, can solve the problem of inability to compare the relationship between algae crusts and vascular plants, and the inability to accurately evaluate algae crusts. The skin biomass contribution rate and other issues can be easily realized in the cultivation environment, weight interference can be eliminated, and the results can be accurate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
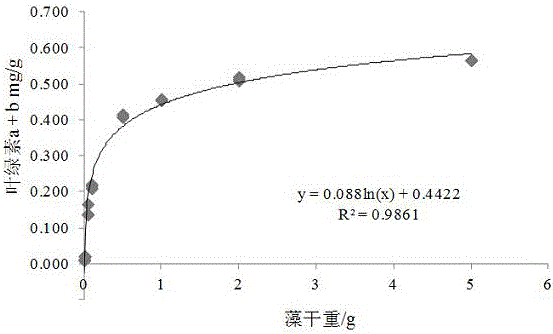
Image
Examples
example 1
[0023] Example 1: Determination of Algal Crust Biomass Developed in Interdune Lowlands
[0024] In August 2014, in the artificial vegetation sand fixation area established in 1990 at the Shapotou National Station of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Zhongwei City, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, 10 samples of well-developed algae crusts were collected from the lowland between dunes, each with an area of 9cm 2 . Sampling uses a self-made 3cm*3cm*0.5cm square stainless steel frame; specific methods, such as: algae crust sample sampling, sieving, cleaning, algae culture, determination of chlorophyll a and b, standard curve drawing and natural growth of algal organisms The determination of the quantity is described as follows:
[0025] a. When sampling, first press the sampling frame firmly into the soil until the sampling frame completely enters the soil, then gently take out about 50cm inside the stainless steel frame with a shovel sterilized with 75% alcohol 2 Algae crusts,...
example 2
[0032] Example 2: Determination of Algal Crust Biomass Developed on Sand Dune Tops
[0033] In August 2014, in the artificial vegetation sand-fixation area established in 1990 at the Shapotou National Station of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Zhongwei City, Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, 10 samples of well-developed algal crusts were collected from the lowlands on the top of the dunes, and the area of each sample was 9cm2. A self-made square stainless steel frame of 3cm*3cm*0.5cm was used for sampling; specific methods, such as sampling, sieving, cleaning, and culturing of algae crust samples were the same as in Example 1.
[0034] Determination of chlorophyll a and b: Chlorophyll is extracted by the mixed solution method (extract solution: absolute ethanol: acetone: water = 4.5:4.5:1). Put the collected algae crust sample into a test tube filled with 10mL extract solution, plug it with a rubber stopper, and repeat each treatment 3 times; put it in a thermostat at 45°C a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com