Biological treatment method of waste water from printing and dying
A technology for printing and dyeing wastewater and biological treatment, applied in biological sludge treatment, water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve good water quality, strong shock load resistance, improved treatment effect and operational stability Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
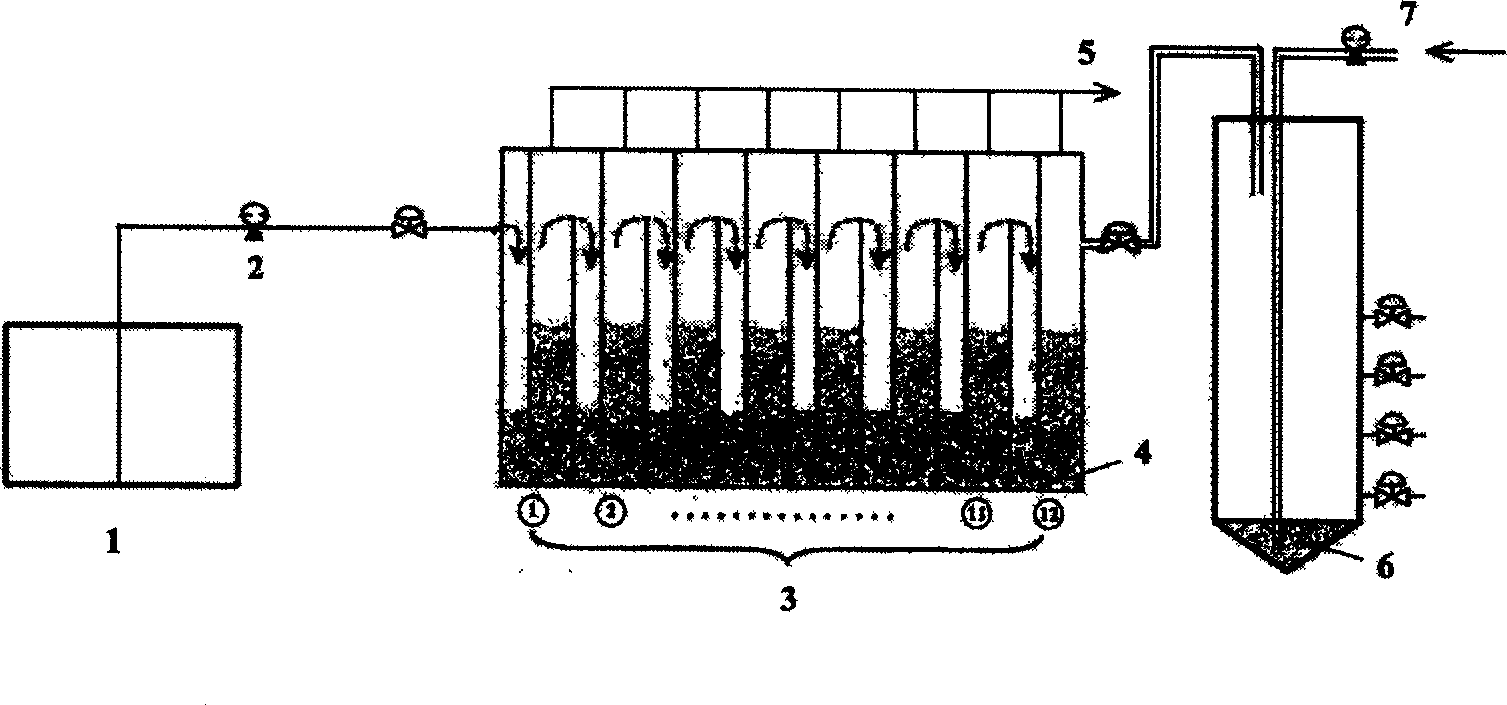
[0010] Embodiment 1: according to attached figure 1 The device and process shown are used to treat printing and dyeing wastewater. By inoculating facultative anaerobic aniline degrading bacteria and facultative anaerobic decolorizing bacteria on anaerobic sludge in ABR, and inoculating facultative anaerobic aniline degrading bacteria and facultative anaerobic decolorizing bacteria on SBR activated sludge, ABR and SBR The inoculated microorganisms were Pseudomonas putida, Shewanella oneidensis, Aeromonas punctata, and Salmonella bongori. Measures such as controlling the ABR hydraulic retention time to gradually shorten from 80 hours to 24 hours enable the ABR reactor to start relatively quickly and form granular sludge. The ABR hydraulic retention time is 36 hours, the pH value of the influent is 6.0-8.0, the temperature is 20°C-42°C, the dissolved oxygen of the SBR is controlled at 2mg / L-5mg / L, and the pH value of the activated sludge suspension is adjusted to 6.0 ~8.0, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0011] Embodiment 2: according to attached figure 1 The device and process shown are used to treat printing and dyeing wastewater. By inoculating facultative anaerobic aniline degrading bacteria and facultative anaerobic decolorizing bacteria on anaerobic sludge in ABR, and inoculating facultative anaerobic aniline degrading bacteria and facultative anaerobic decolorizing bacteria on SBR activated sludge, ABR and SBR The microorganisms inoculated were Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella terrigena, and Citrobacter freumdii. Measures such as controlling the ABR hydraulic retention time to gradually shorten from 80 hours to 24 hours enable the ABR reactor to start relatively quickly and form granular sludge. The ABR hydraulic retention time is 36 hours, the pH value of the influent is 6.0-8.0, the temperature is 20°C-42°C, the dissolved oxygen of the SBR is controlled at 2mg / L-5mg / L, and the pH value of the activated sludge suspension is adjusted to 6.0 ~8.0, the temperature is ...
Embodiment 3
[0012] Embodiment 3: according to attached figure 1The device and process shown are used to treat printing and dyeing wastewater. The anaerobic sludge in the ABR is inoculated with facultative anaerobic aniline degrading bacteria and facultative anaerobic decolorizing bacteria, and the microorganisms inoculated are Pseudomonas putida and Escherichia coli. The SBR activated sludge was inoculated with aerobic and facultative anaerobic aniline degrading bacteria and facultative anaerobic decolorizing bacteria. .), Paracoccus versutus, Escherichia coli. Measures such as controlling the ABR hydraulic retention time to gradually shorten from 80 hours to 24 hours enable the ABR reactor to start relatively quickly and form granular sludge. The ABR hydraulic retention time is 36 hours, the pH value of the influent is 6.0-8.0, the temperature is 20°C-42°C, the dissolved oxygen of the SBR is controlled at 2mg / L-5mg / L, and the pH value of the activated sludge suspension is adjusted to 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com