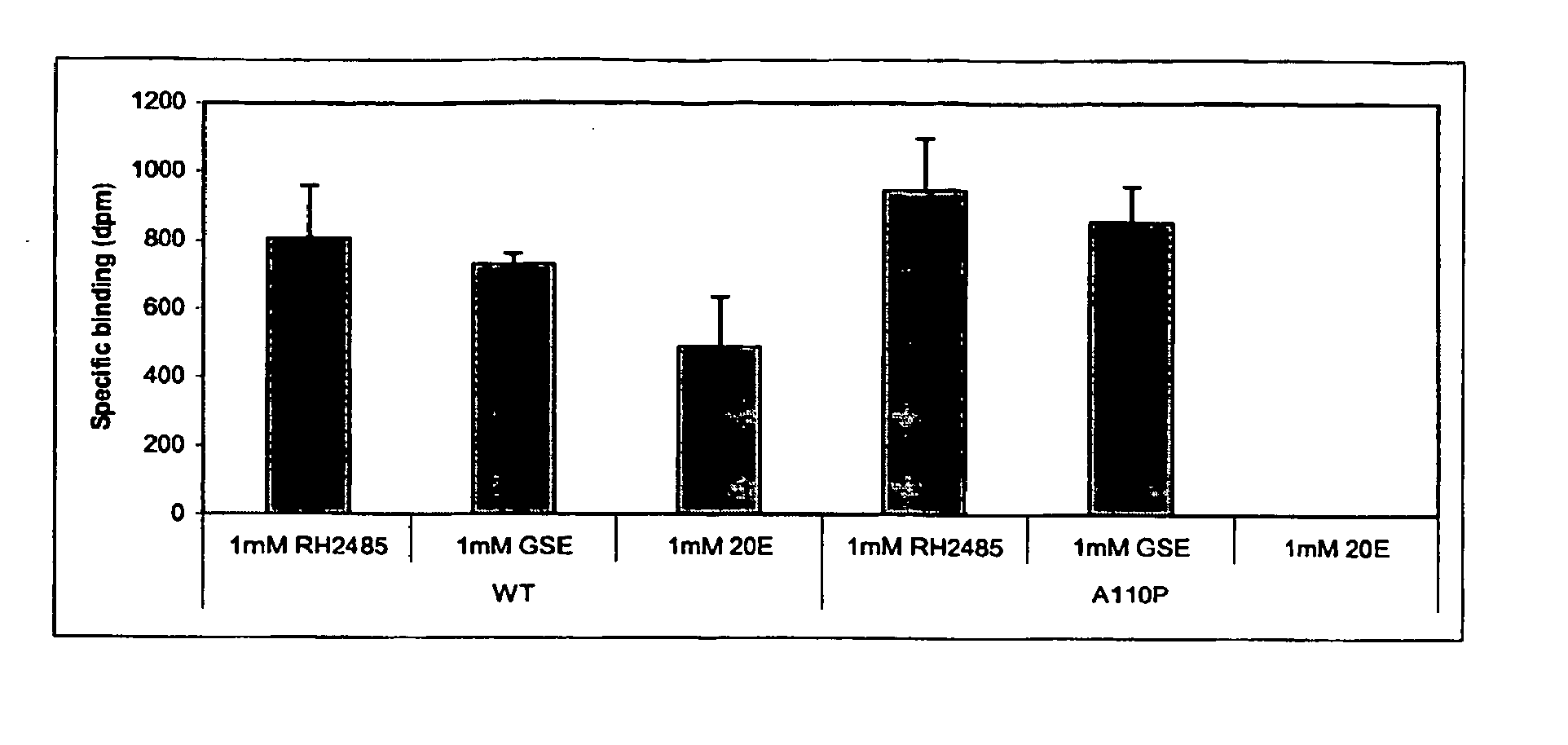
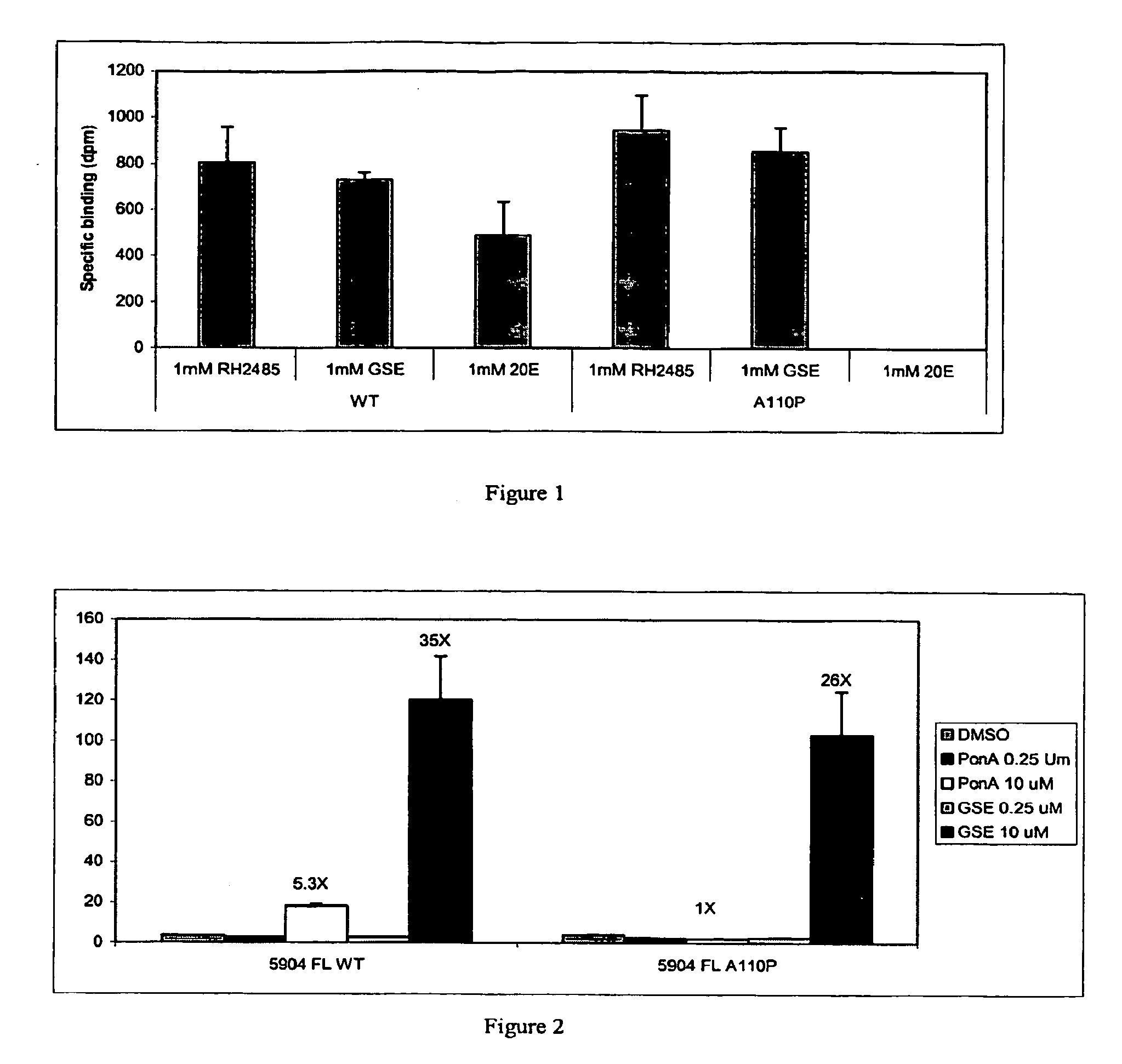
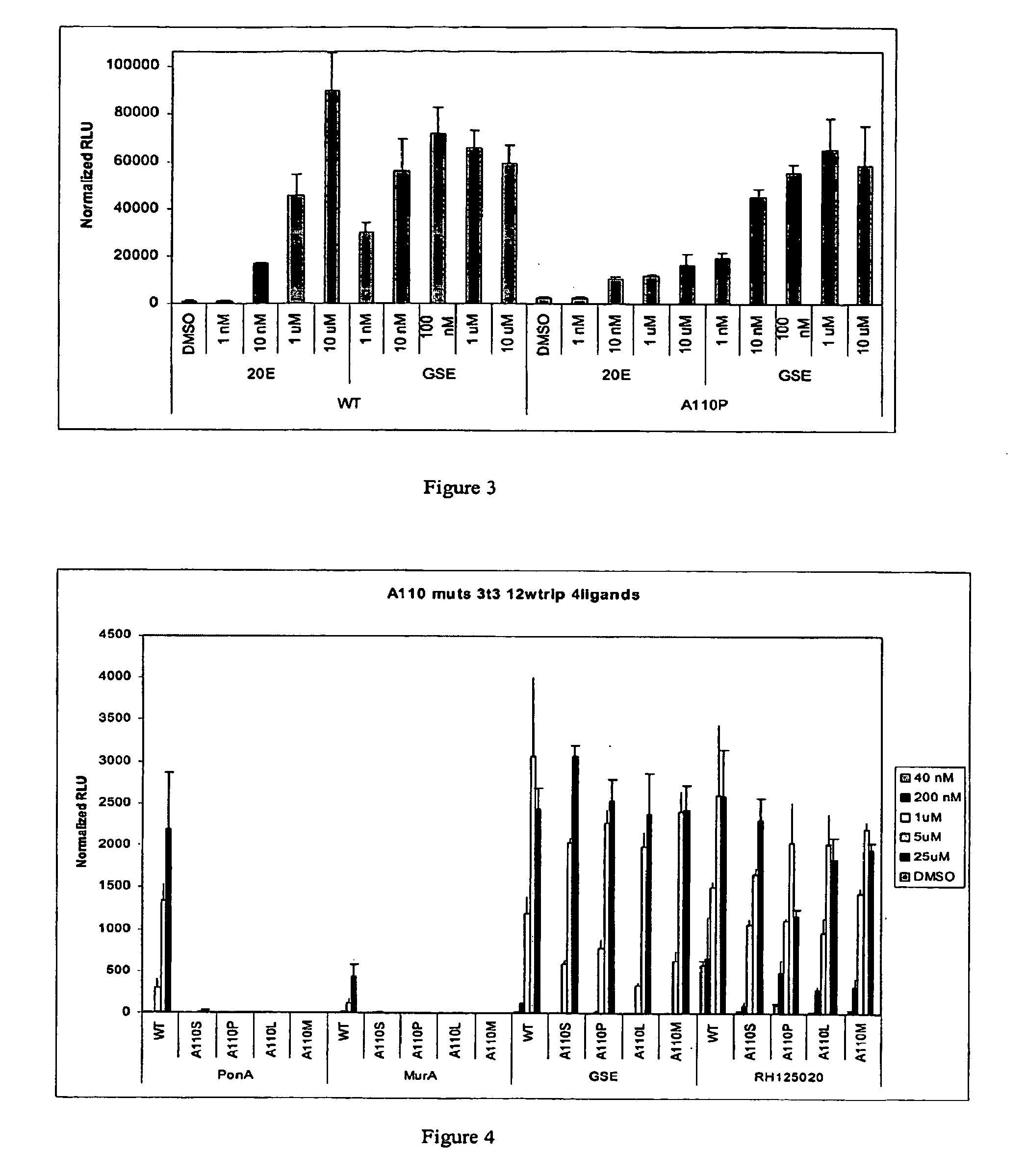
Novel substitution mutant receptors and their use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system
a gene expression system and nuclear receptor technology, applied in nuclear receptors, drug compositions, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of system limitations, leakage of systems, and limited use of pr1-a
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0267] This Example describes the construction of several gene expression cassettes comprising novel substitution mutated Group H nuclear receptor polynucleotides and polypeptides of the invention for use in a nuclear receptor-based inducible gene expression system. Applicants constructed several gene expression cassettes based on the spruce budworm Choristoneura fumiferana EcR (“CfEcR”), fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster EcR (“DmEcR”), ixodid tick Amblyomma americanum EcR (“AmaEcR”), locust Locusta migratoria ultraspiracle protein (“LmUSP”), an invertebrate RXR homolog of vertebrate RXR, and C. fumiferana USP (“CfUSP”). The prepared receptor constructs comprise a ligand binding domain of either an EcR, an invertebrate USP, or an invertebrate RXR; and a GAL4 DNA binding domain (DBD) or a VP16 transactivation domain (AD). The reporter constructs include a reporter gene, luciferase or LacZ (β-galactosidase), operably linked to a synthetic promoter construct that comprises a GAL4 respo...
example 2
[0292] This Example describes the identification of improved non-steroid responsive CfEcR ligand binding domain substitution mutants that exhibit increased activity in response to non-steroidal ligand and decreased activity in response to steroidal ligand. Briefly, Applicants mutated amino acid residues predicted to be critical for ecdysteroid binding into alanine and created GAL4 / mutantCfEcR-DEF cDNA gene expression cassettes as described in Example 1 above using the Quikchange PCR-mediated site-directed mutagenesis kit (Stratagene, La Jolla, Calif.). The mutated and the WT cDNAs were tested in GAL4-driven luciferase reporter assays.
[0293] Transfections: DNAs corresponding to the various switch constructs outlined in Example 1, specifically switches 1.1-1.2, were transfected into mouse NIH3T3 cells (ATCC) as follows. Cells were harvested when they reached 50% confluency and plated in 24 well plates at 12,500 cells / well in 0.5 ml of growth medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (...
example 3
[0295] This Example describes the identification of steroid responsive CfEcR ligand binding domain substitution mutants that exhibit increased activity in response to steroidal ligand and significantly decreased activity in response to non-steroidal ligand. In an effort to identify substitution mutations in the CfEcR that increase steroidal ligand activity, but decrease non-steroidal ligand activity, Applicants mutated amino acid residues predicted to be critical for ecdysteroid binding and created GAL4 / mutantCfEcR-DEF cDNA gene expression cassettes as described in Example 1 above using PCR-mediated site-directed mutagenesis kit. The mutated and the WT cDNAs corresponding to the various switch constructs outlined above in Examples 1.1 and 1.2 were made and tested in GAL4-driven luciferase reporter assays as described in Example 2 above. Fold activity was calculated by dividing RLUs in the presence of ligand with RLUs in the absence of the ligand.
[0296] Specific amino acid residues ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tm | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com