Non-transgenic genome directed molecule improvement method and application of main crops
A non-transgenic, genome-specific technology, applied in the field of targeted modification of crop genome designated sites, can solve problems such as silencing and gene loss, and achieve the effects of improving quality, rapid targeting, and eliminating safety risks.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
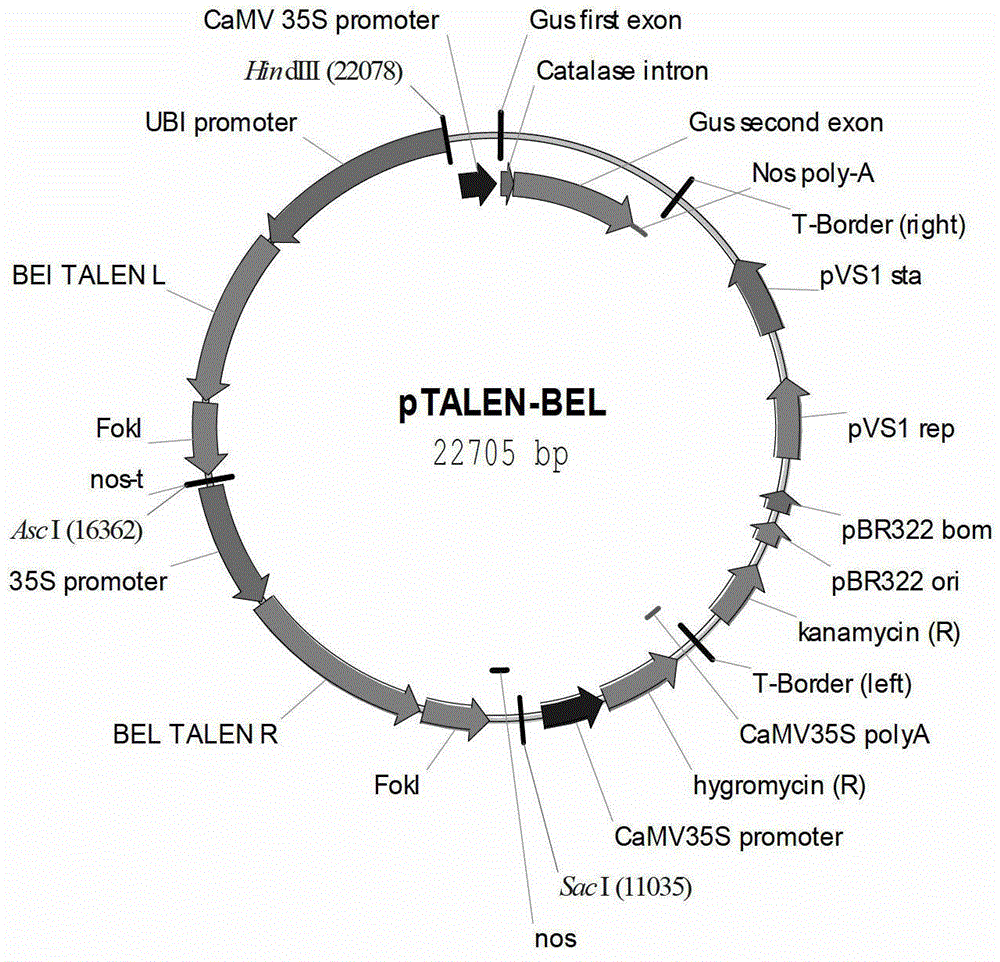
[0029] Example 1 against bel Construction of gene TALEN action plasmid
[0030] Step 1. Selection of target sites and TALEN recognition sites
[0031] According to the rice variety Nipponbare ( Oryza sativa L cv. Nipponbare) whole genome sequence, obtained bel For the genome sequence, according to the general design principle of TALEN function, the target fragment is selected as the 18 base sequence from the 22nd to the 39th position of the first exon:
[0032] 5'-gccattctctctgtagct-3',
[0033] The corresponding TALEN left and right arms are identified as the immediately adjacent 15bp (left arm) and 16bp sequences (right arm):
[0034] bel TALEN left arm recognition: 5'-aacgcctacattatt-3'
[0035] bel TALEN right arm recognition: 5'-ggagcaagaagaggat-3'
[0036] Step 2. Targeting vector pTALEN- bel the acquisition
[0037] Using the TALEN vector construction kit (purchased from Shanghai Steinsel Company), based on the principle of GG vector method, the lef...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2 Transformation of Agrobacterium and T 0 Acquisition of transgenic rice
[0040] Step 1: Obtaining Agrobacterium
[0041] The pTALEN obtained from Example 1- bel Binary vector, using the freeze-thaw method to transfer the expression vector into Agrobacterium tumefaciens ( Agrobacterium tumefaciens ) EHA105 (preserved by the Rice Group of the Supervision, Inspection and Testing Center for Components of Genetically Modified Biological Products, Ministry of Agriculture, Anhui Academy of Agricultural Sciences).
[0042] Step 2: Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of rice
[0043] After the chaff is removed from the mature seeds, soak the seeds with 70% alcohol for 1 min, and pour off the alcohol. Soak the seeds in a solution of 50% sodium hypochlorite (the concentration of available chlorine in the stock solution is greater than 4%) containing 1 drop of Tween 20 for 40 min (150 r / min). Pour off the sodium hypochlorite, wash with sterile water...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 T 0 transgenic rice bel Detection of gene targeting effect
[0048] Use the plant genomic DNA mini-extraction kit to extract each T 0 Leaf DNA of transgenic lines. Using this DNA as a template, bel Gene-specific primers:
[0049] Bel seq FP: GCACCAGAGTCACAGAAACACA
[0050] Bel seq RP: CGAAGGTCACGTCGTGCTCGGT
[0051] amplify bel The 341bp bases near the targeting sequence of the first exon of the gene were identified by sequencing. Sequencing results showed that the targeting sites in 38 transgenic rice plants had different degrees of small fragment DNA deletions, insertions or substitutions ( figure 2 ), resulting in a nonsense mutation, causing bel Gene translation terminates. Among them, 7 transgenic plants had nonsense mutations at the same allele on the two chromosomes, and were selected as materials for further screening.
[0052]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com