A Method of Correcting the Influence of Atmospheric Refraction on the Accuracy of Star Sensor
A star sensor, atmospheric refraction technology, applied in the field of space science, to achieve the effect of improving efficiency and reducing fuel consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
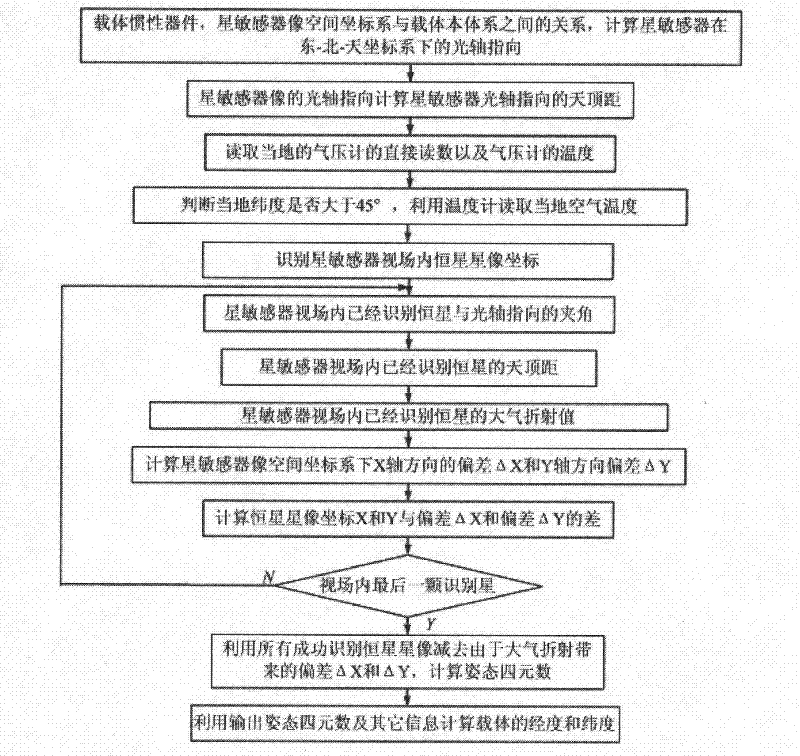
[0038] Example 1: Combining figure 2 , a method for correcting the influence of atmospheric refraction on the accuracy of star sensors in the present invention, the steps are as follows:
[0039] Step 1: Using the carrier inertial device, the relationship between the star sensor image space coordinate system and the carrier body system, calculate the optical axis pointing of the star sensor in the east-north-sky coordinate system;
[0040] Step 2: According to the optical axis pointing of the star sensor image, calculate the zenith distance of the star sensor optical axis pointing, that is, the angle between the star sensor optical axis pointing and the zenith;
[0041] Step 3: Use the barometer to take a direct reading of the local barometer and the temperature of the barometer;
[0042] Step 4: Determine whether the local latitude is greater than 45°, and use a thermometer to read the local air temperature;
[0043] Step 5: Use the star map recognition algorithm to identi...
Embodiment 2
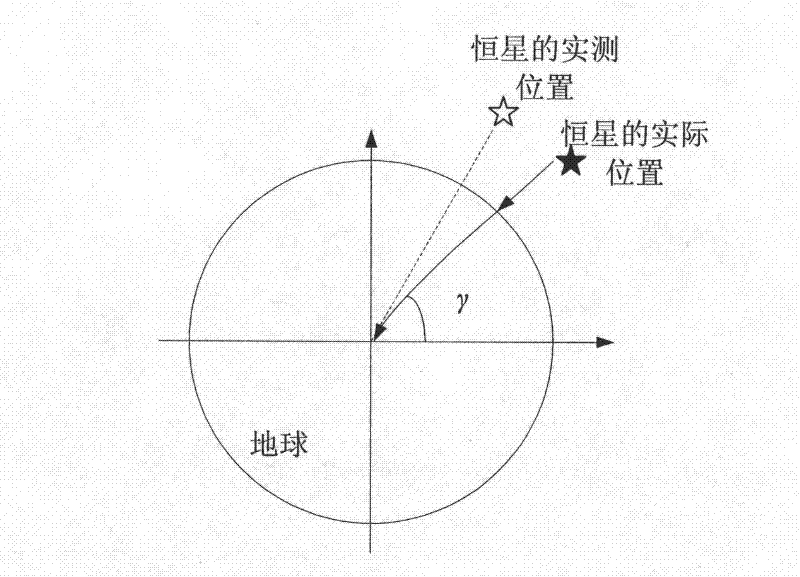
[0057] Example 2: Combining figure 1 , Figure 3-Figure 11 , in order to quantitatively analyze the atmospheric refraction in theory, and considering the complexity of the atmosphere itself, predecessors have established a simplified atmospheric model based on the quiet atmosphere, and established the corresponding atmospheric model on the basis of the model. Refraction tables, further research on atmospheric refraction. In view of the current level of understanding of the atmosphere and scientific and technological capabilities, it is more realistic to establish a more effective atmospheric refraction model that conforms to the geographical environment and meteorological characteristics of the observation point, fully considering complex conditions such as atmospheric tilt, so that it can achieve better accuracy And it can still have high accuracy in the case of large zenith distance (> 70°). Other correction methods for the measurement of atmospheric anomalous refraction sh...
Embodiment 3
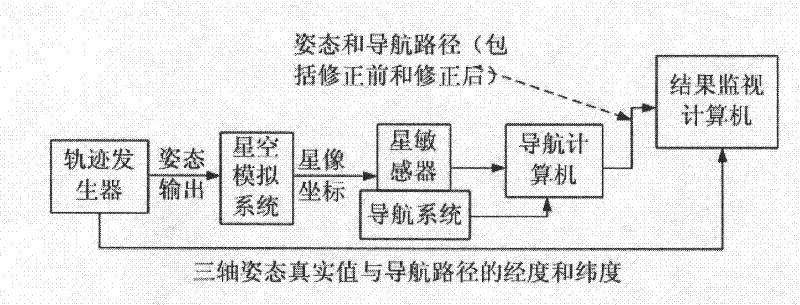
[0093] Example 3: Binding Figure 12 , the local longitude and latitude output by GPS are output to the star sensor in real time. The star sensor recognizes the coordinates of all star images in the field of view through the star map identification. At this time, due to the refraction of the atmosphere, there are deviations in the coordinates of all star images , so these star image coordinates cannot be directly used to calculate the attitude information, and because the angles between the star pointing and the zenith are different, the deviations are also different, so firstly, the local air pressure, air pressure temperature, local latitude and local temperature must be used to calculate these The deviation of the stellar image coordinates due to the atmosphere. The method of calculating the deviation of star image coordinates is as follows: calculate the rough attitude of the current carrier in the east-north-sky coordinate system according to the output of the carrier gyr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com