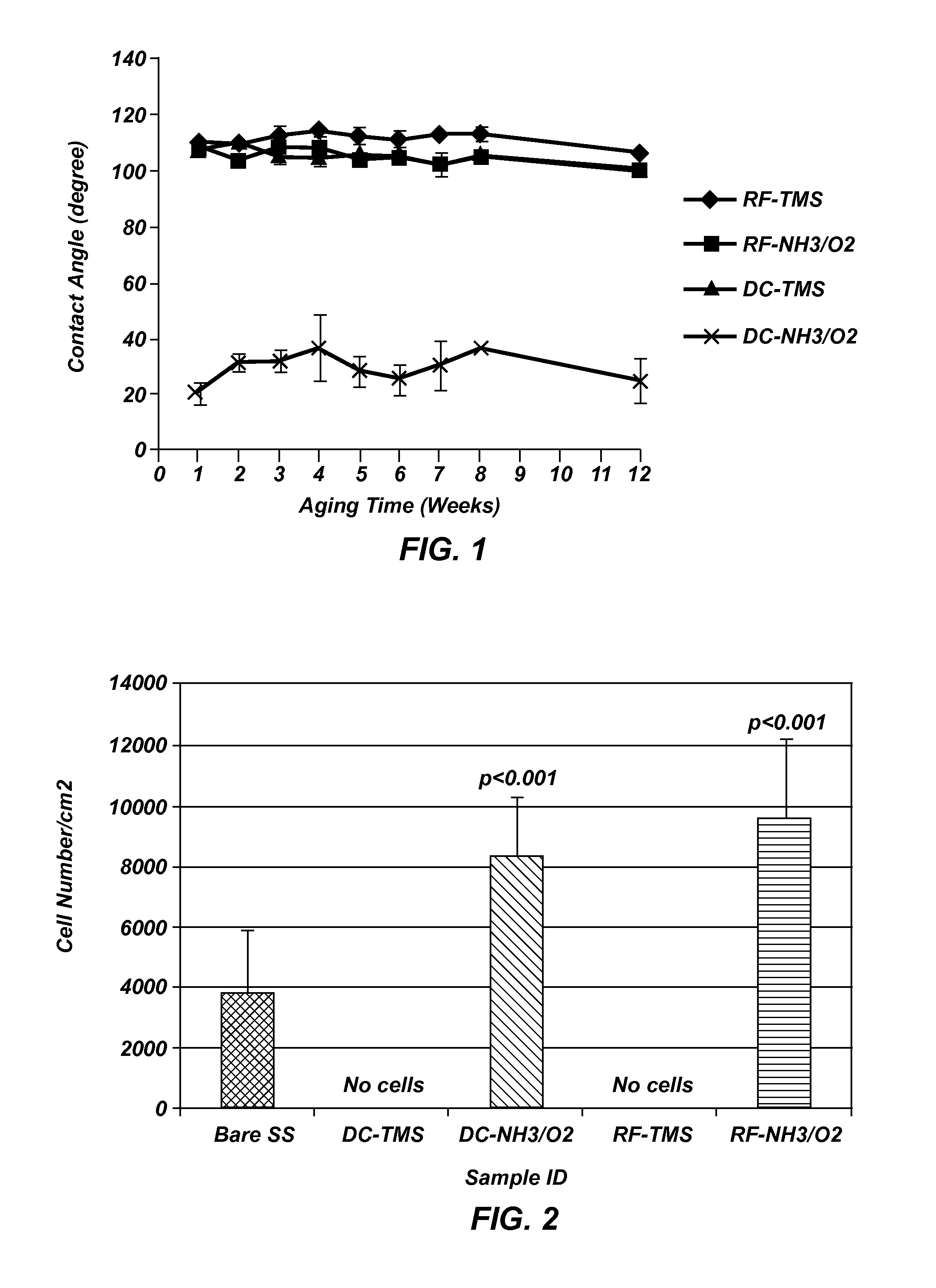
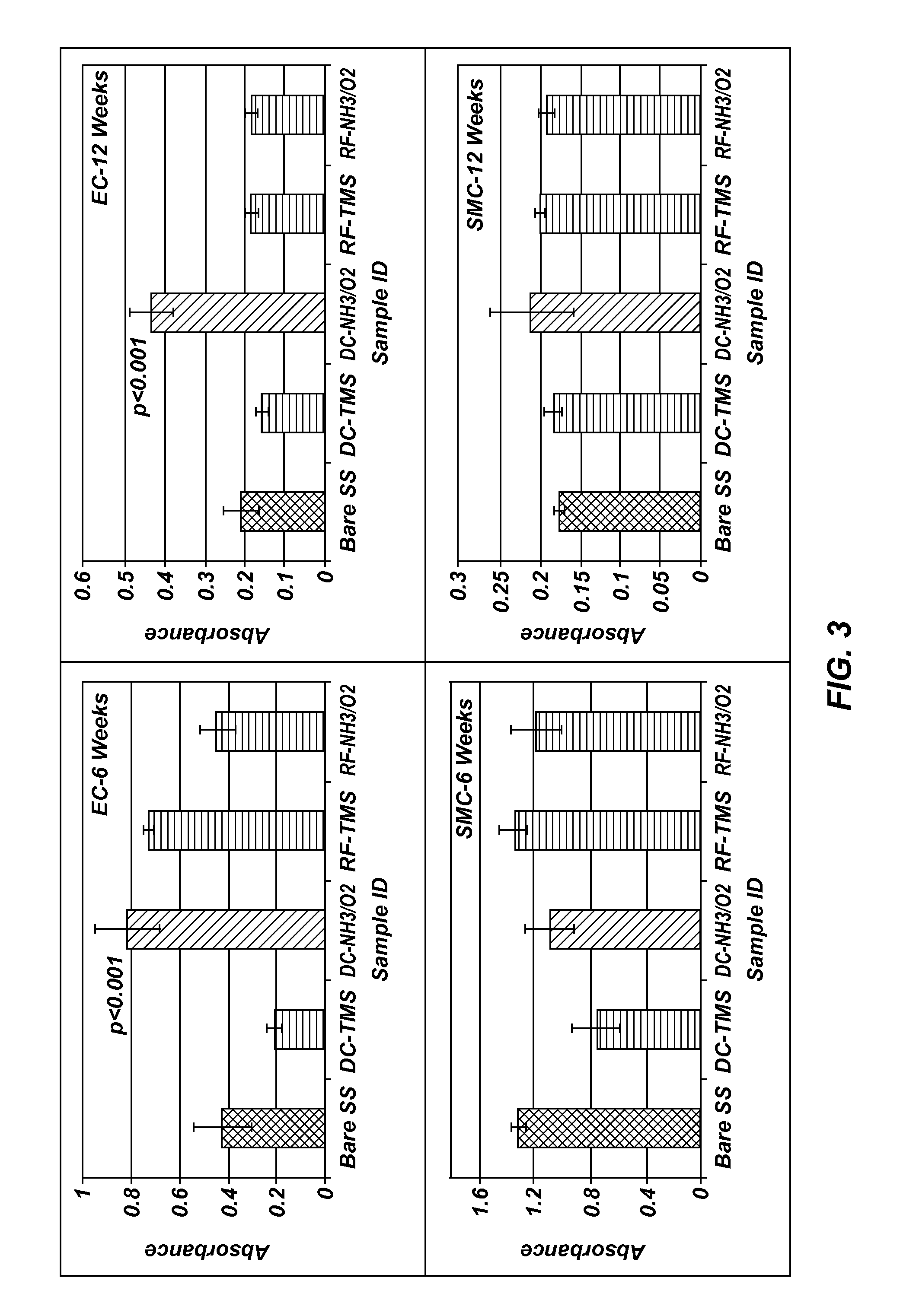
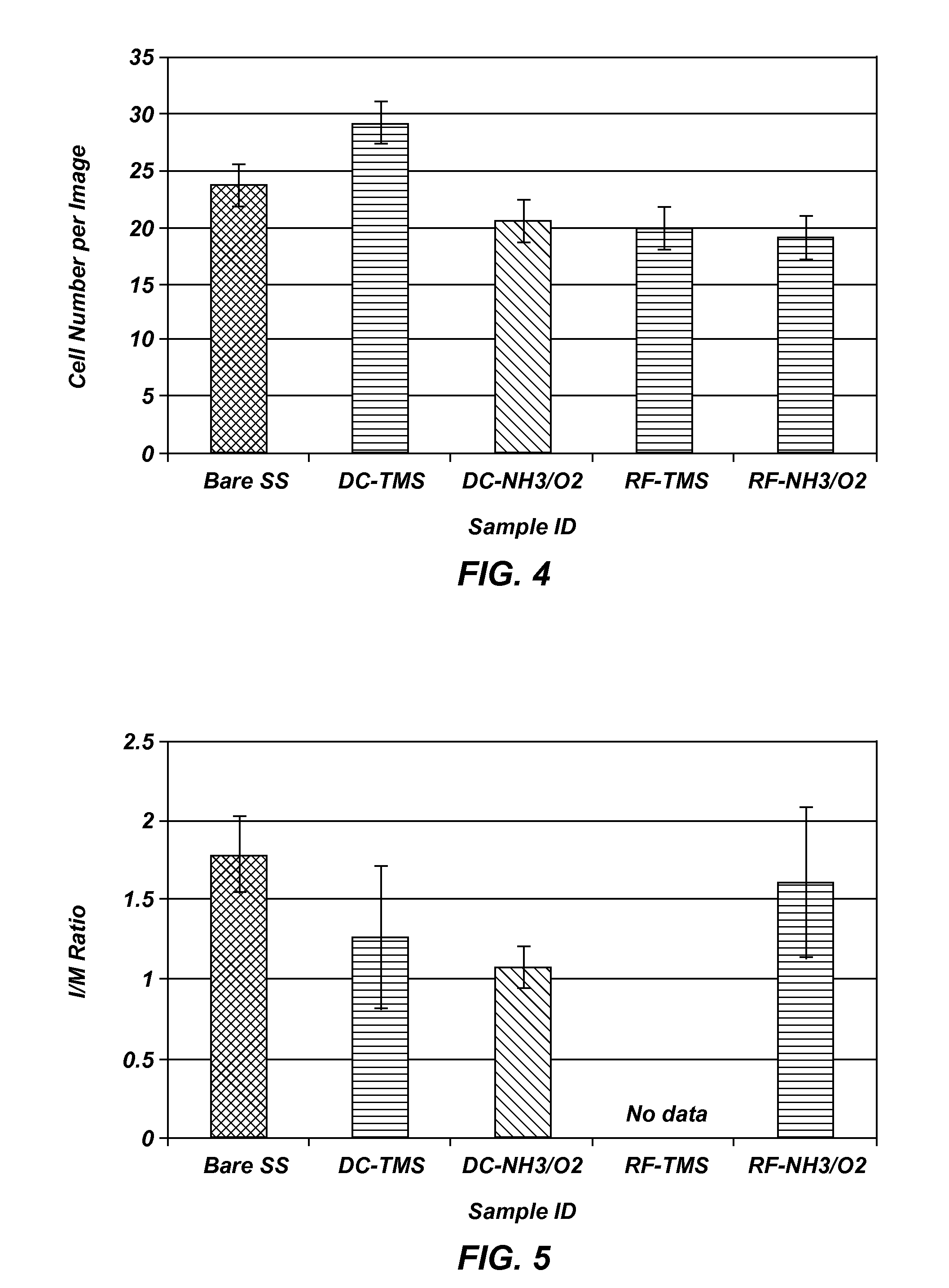
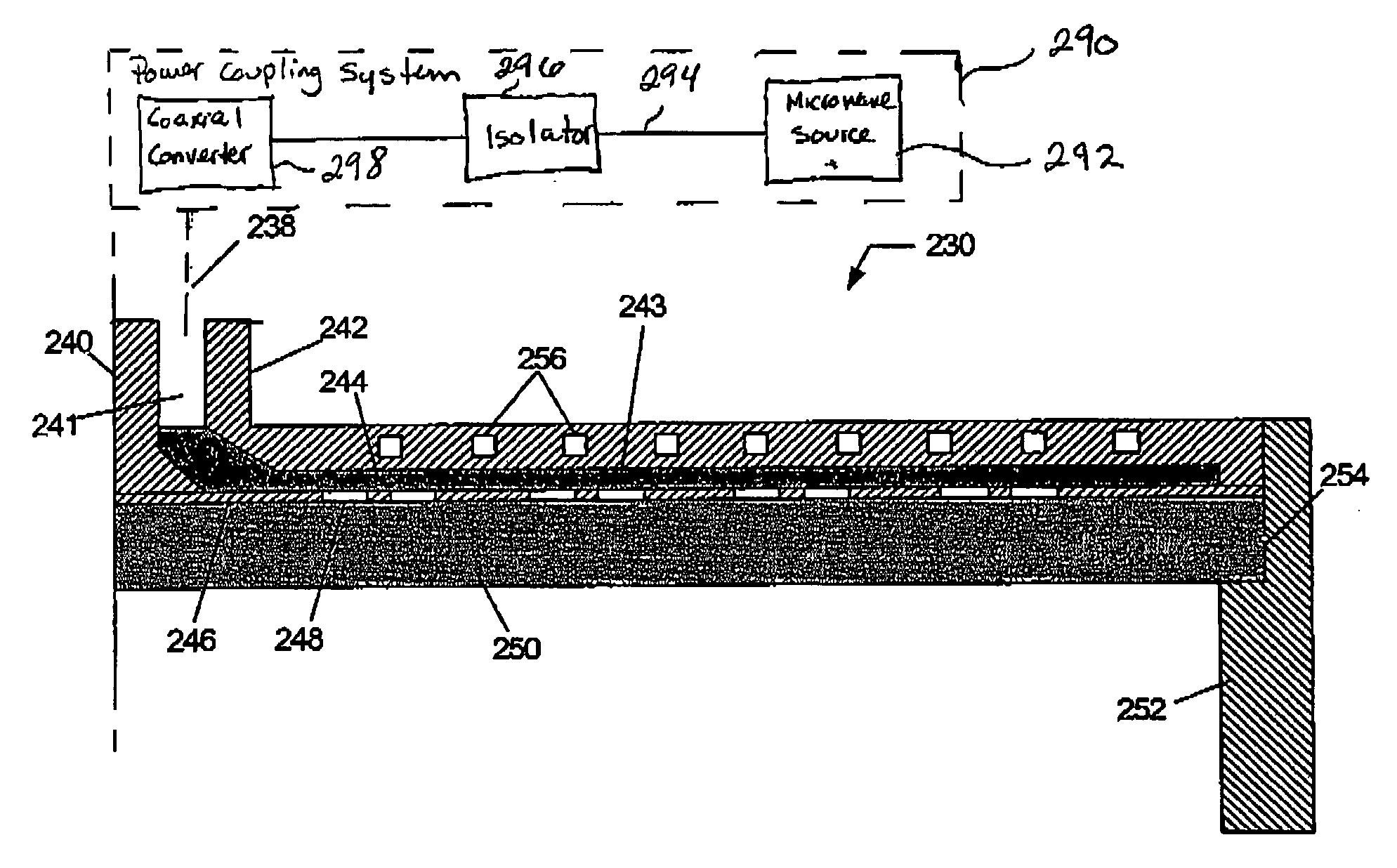
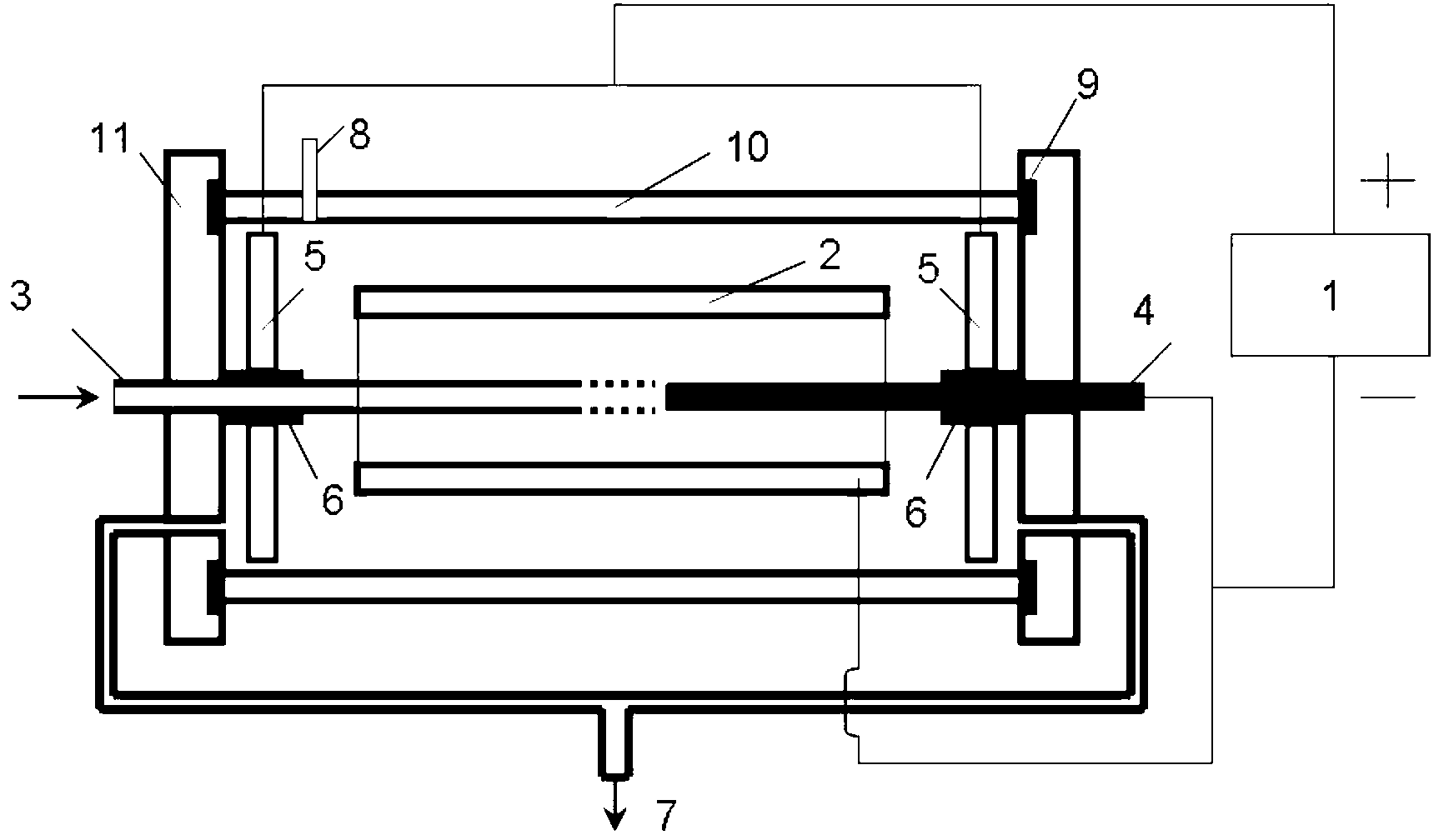
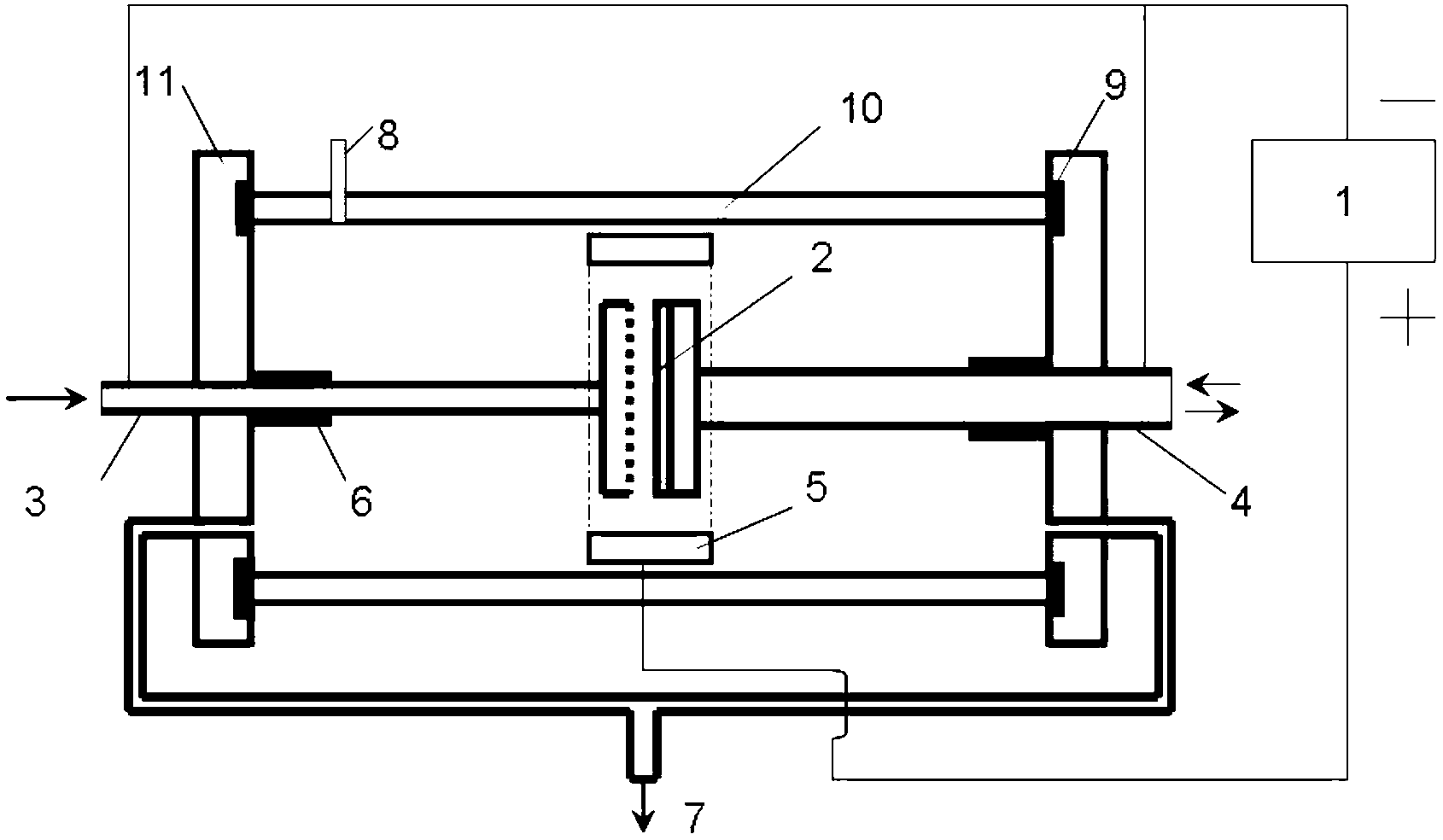
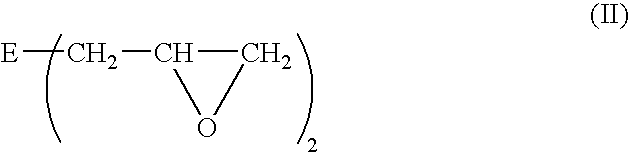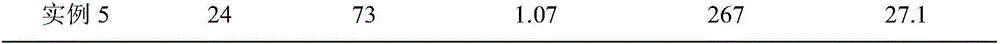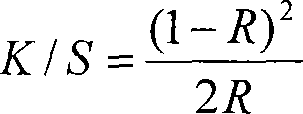Patents
Literature
727 results about "Plasma surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
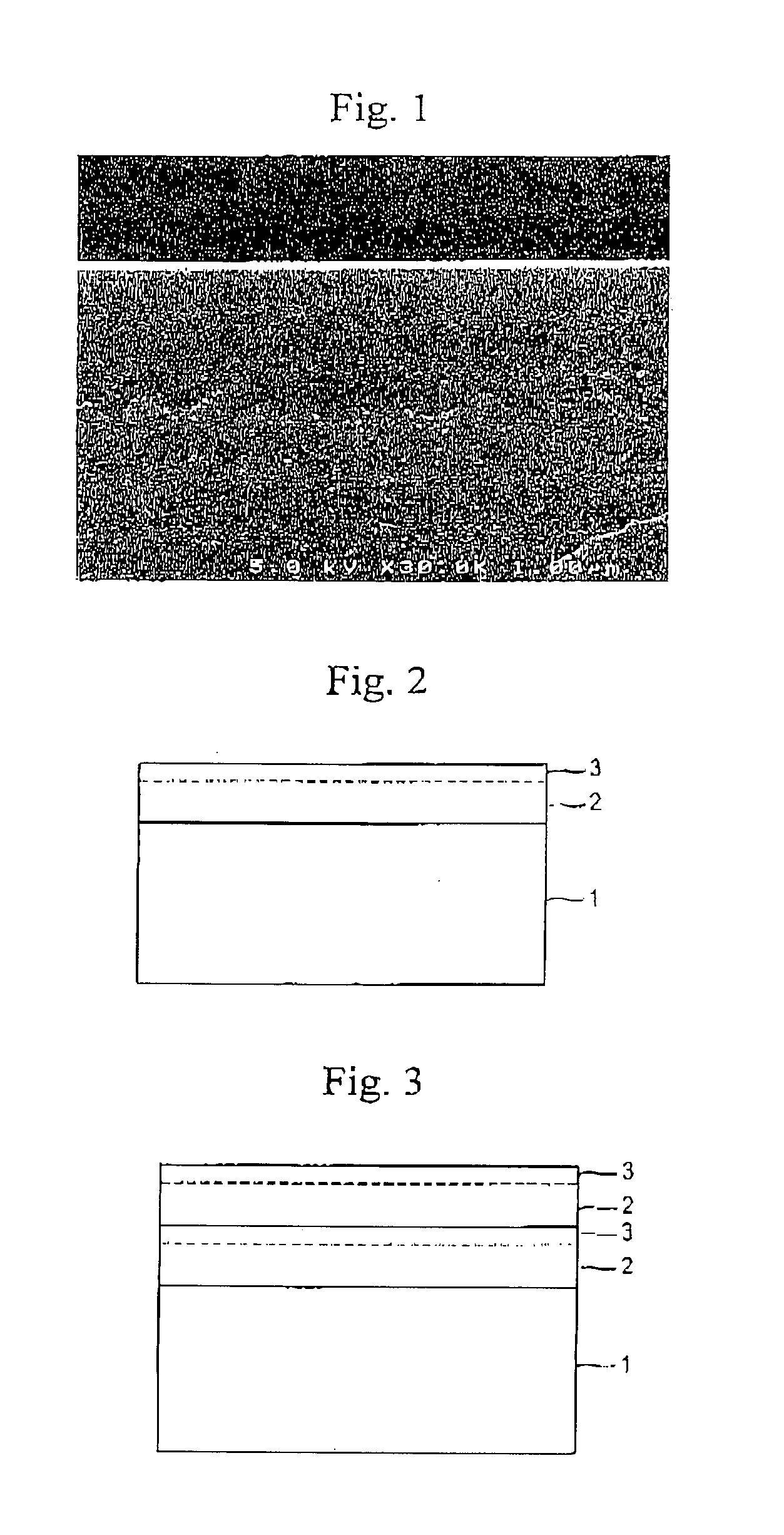
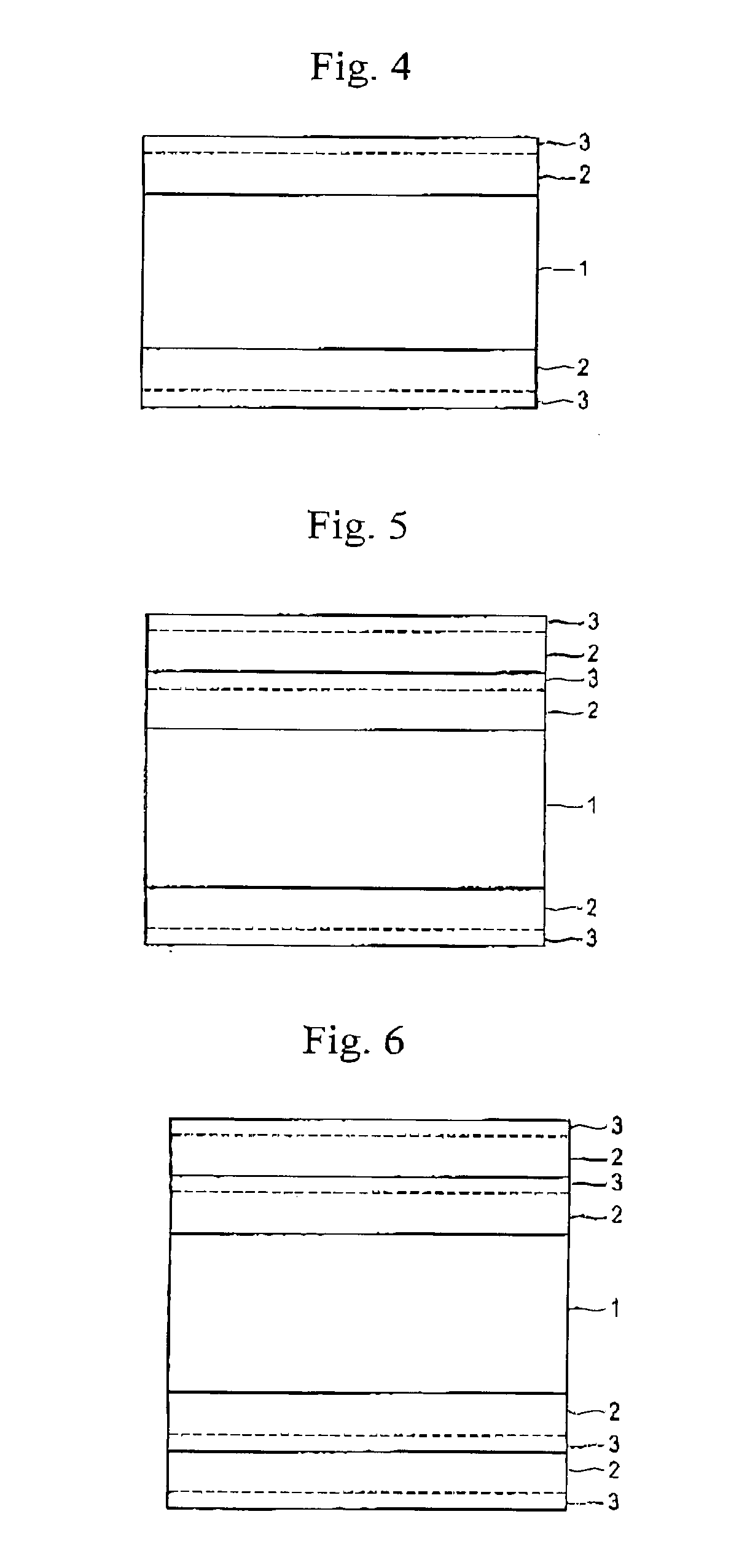
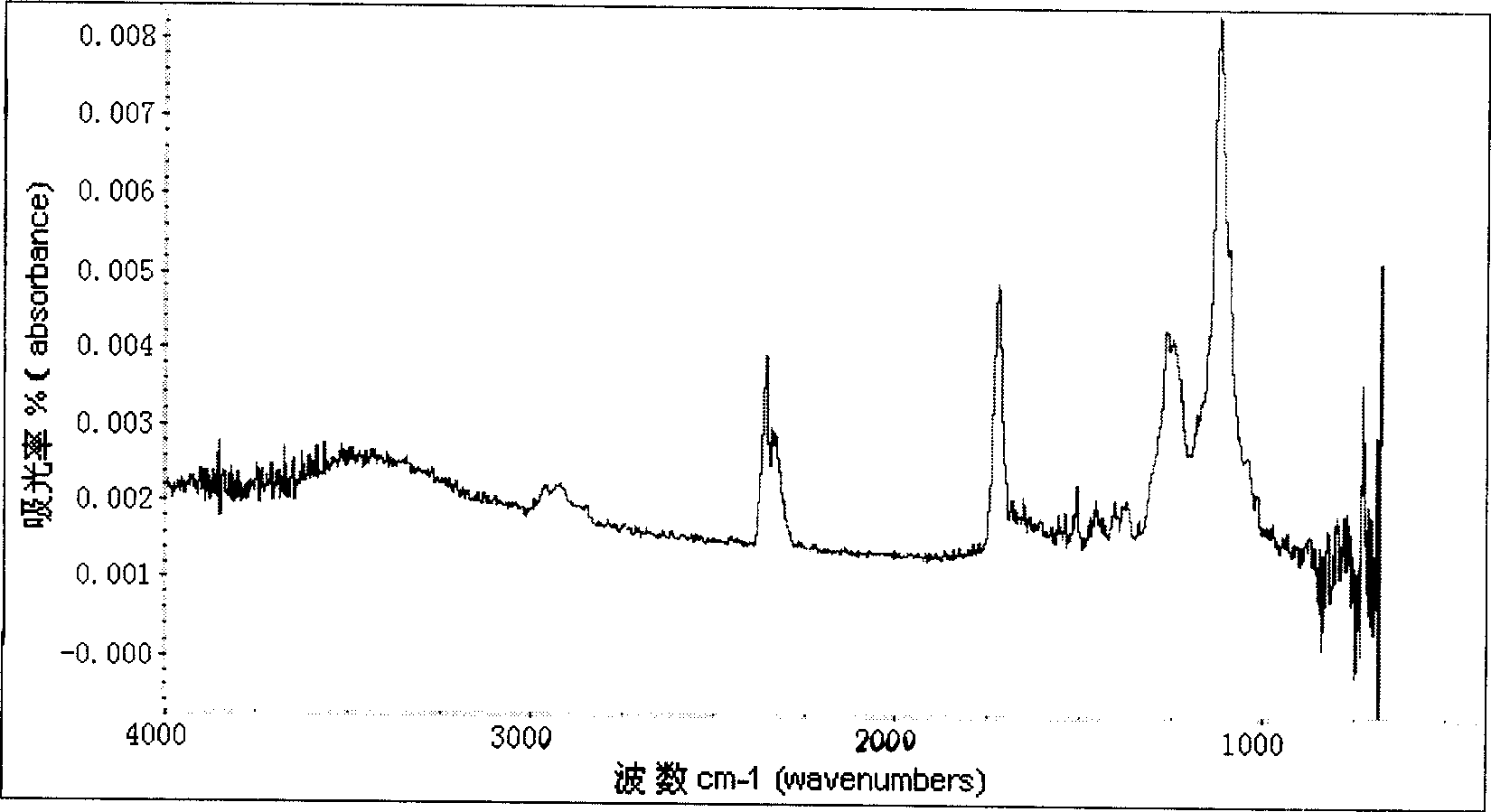
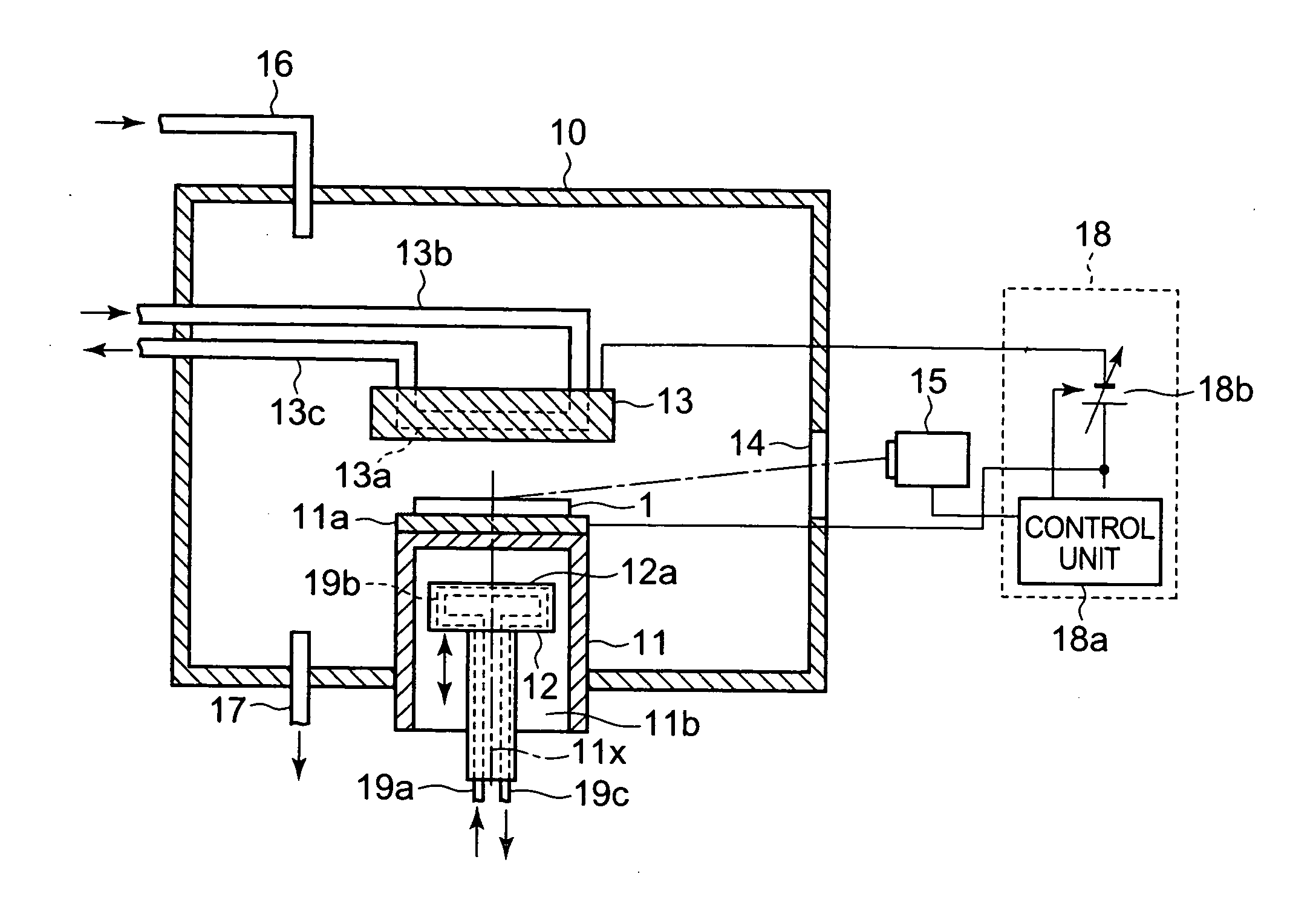
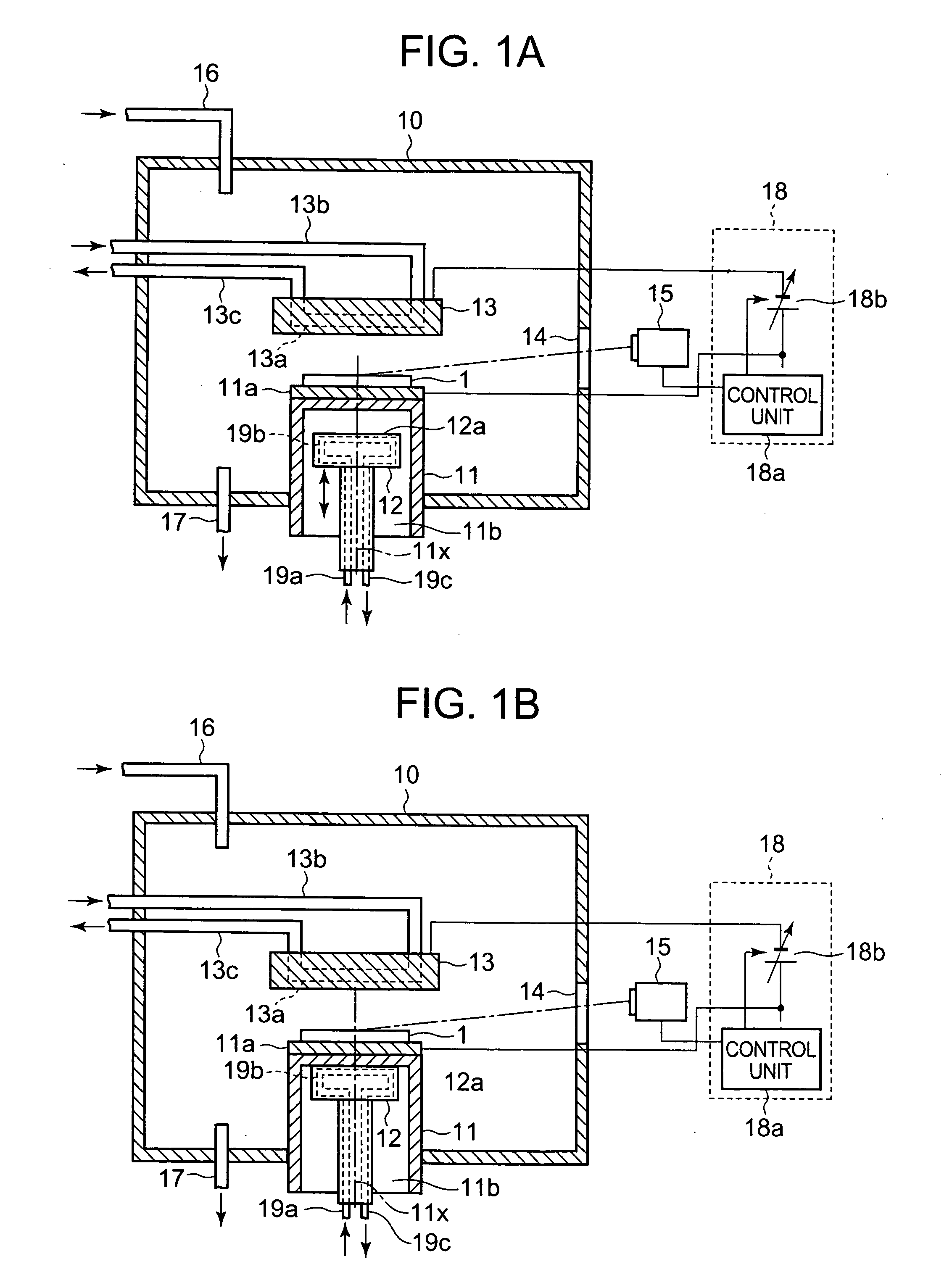
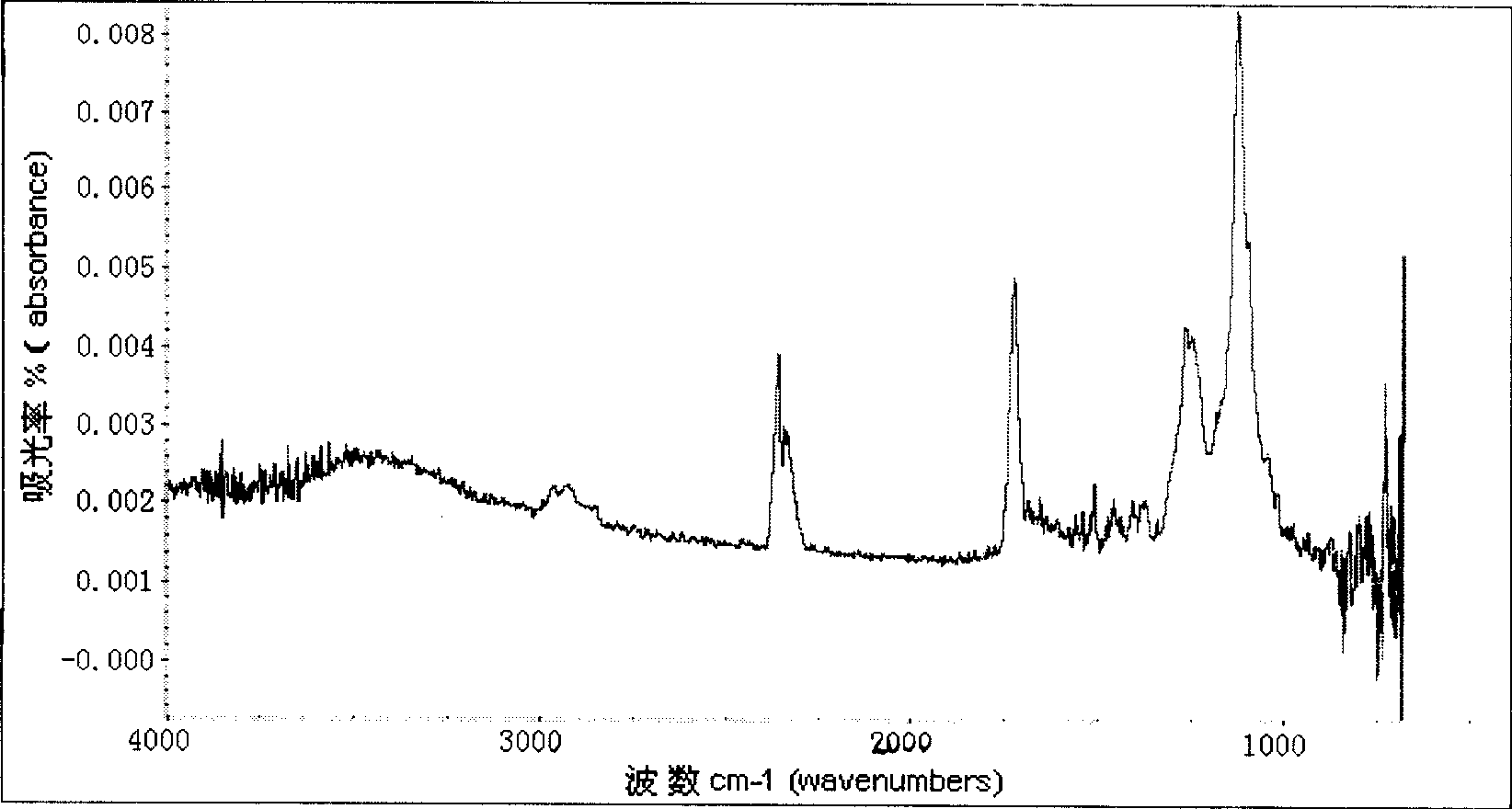
Method for fabrication of transparent gas barrier film using plasma surface treatment and transparent gas barrier film fabricated thereby
InactiveUS20100285319A1Excellent gas barrier performanceEconomical and simple methodSynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesOptoelectronicsInorganic layer
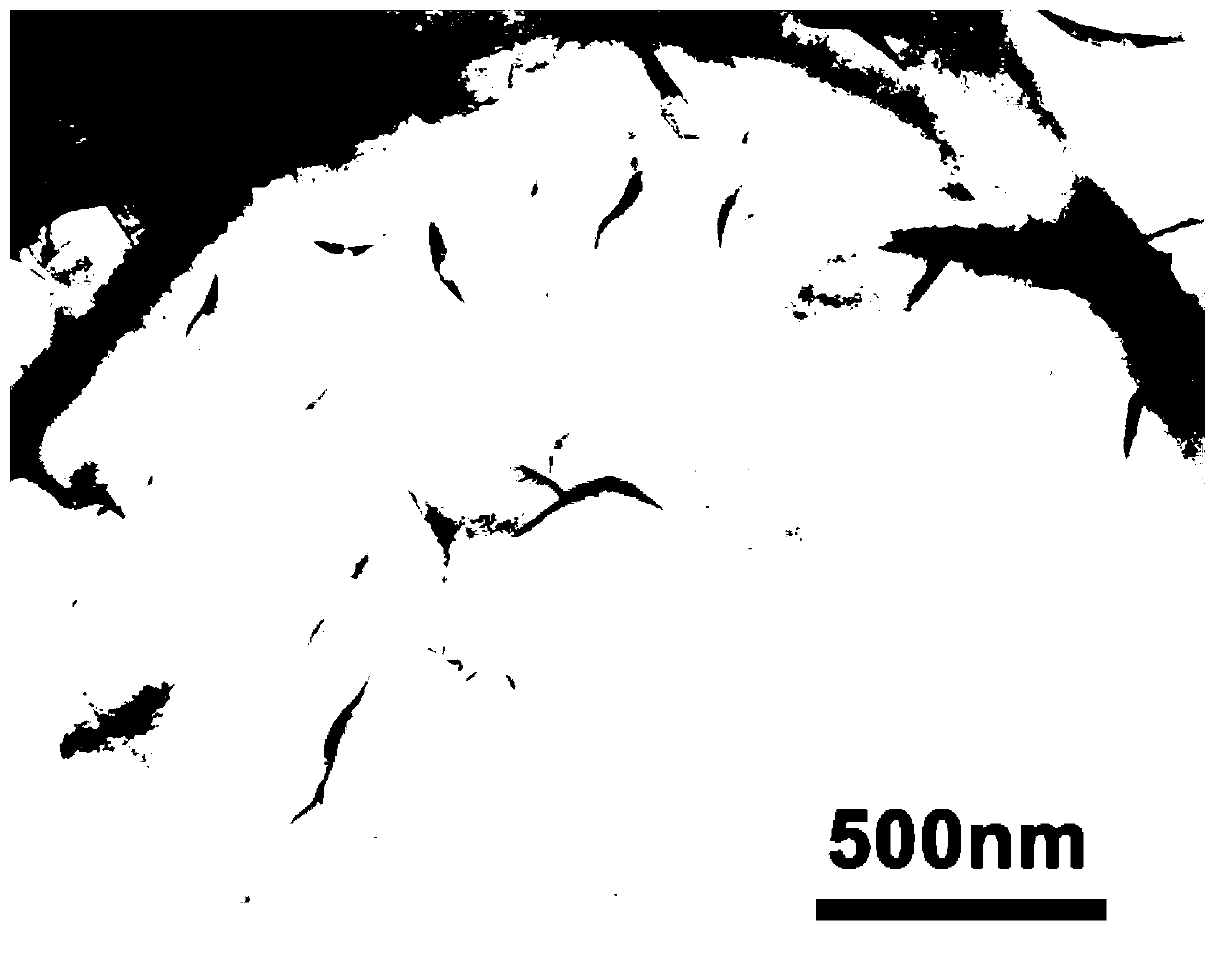
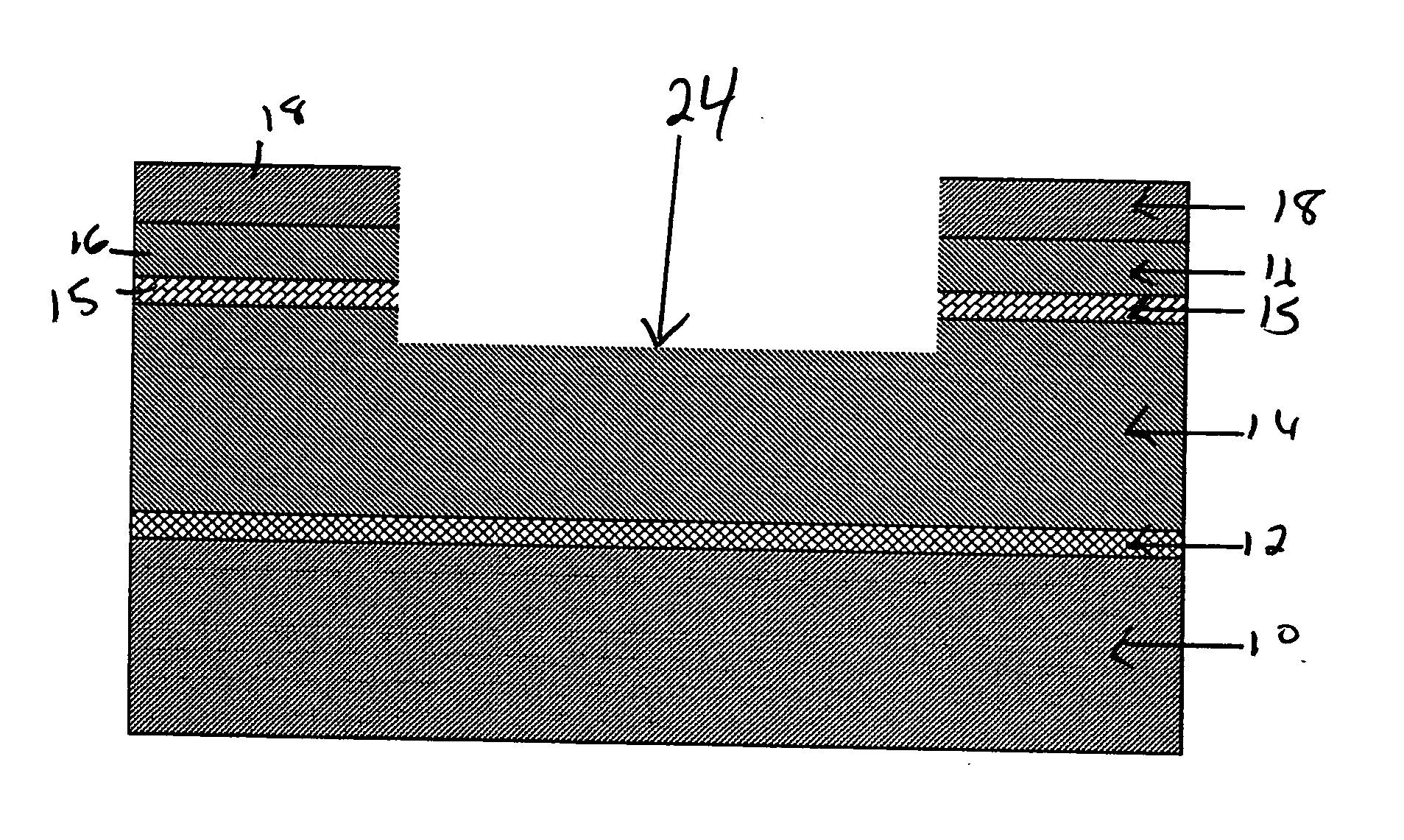
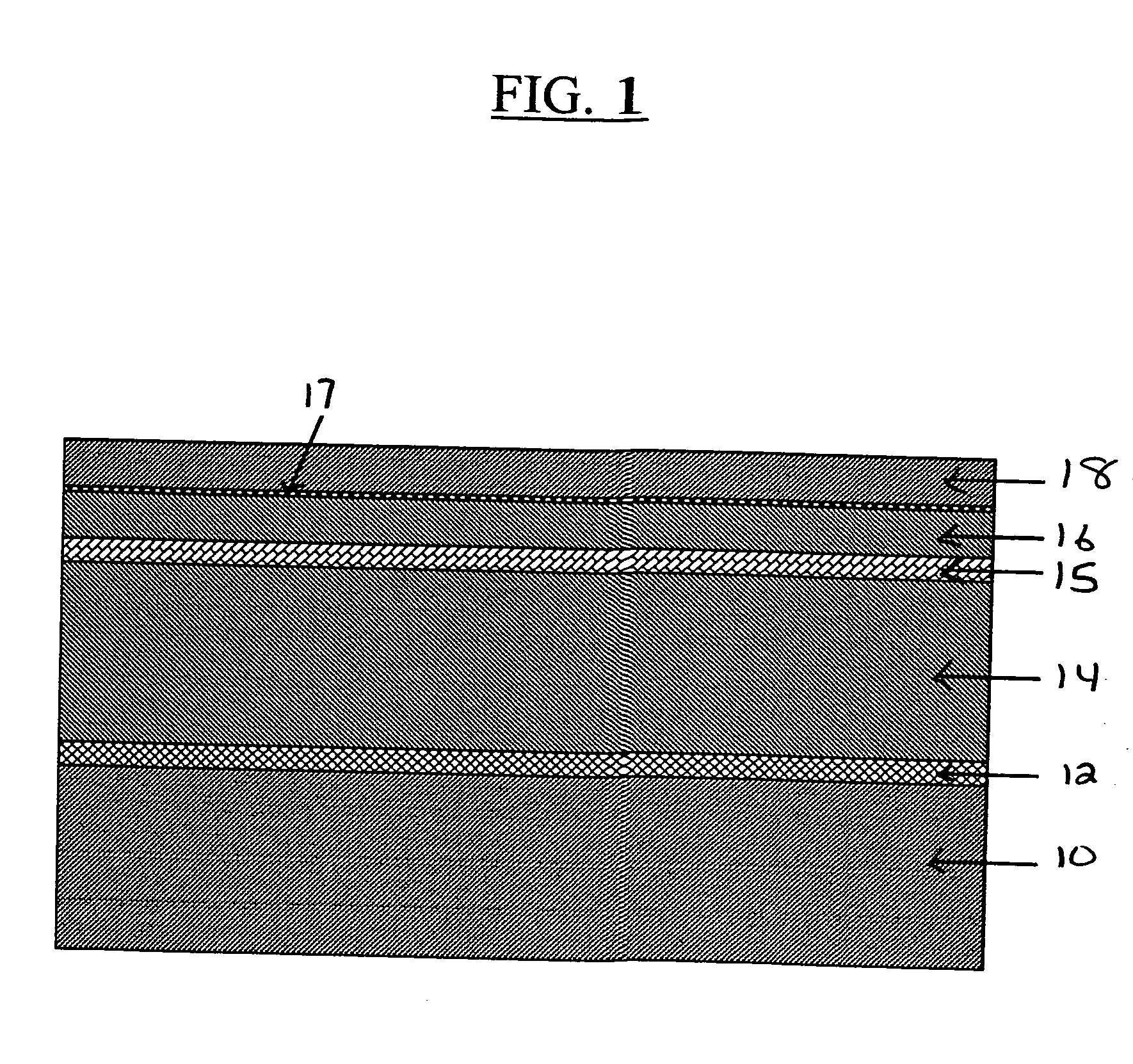
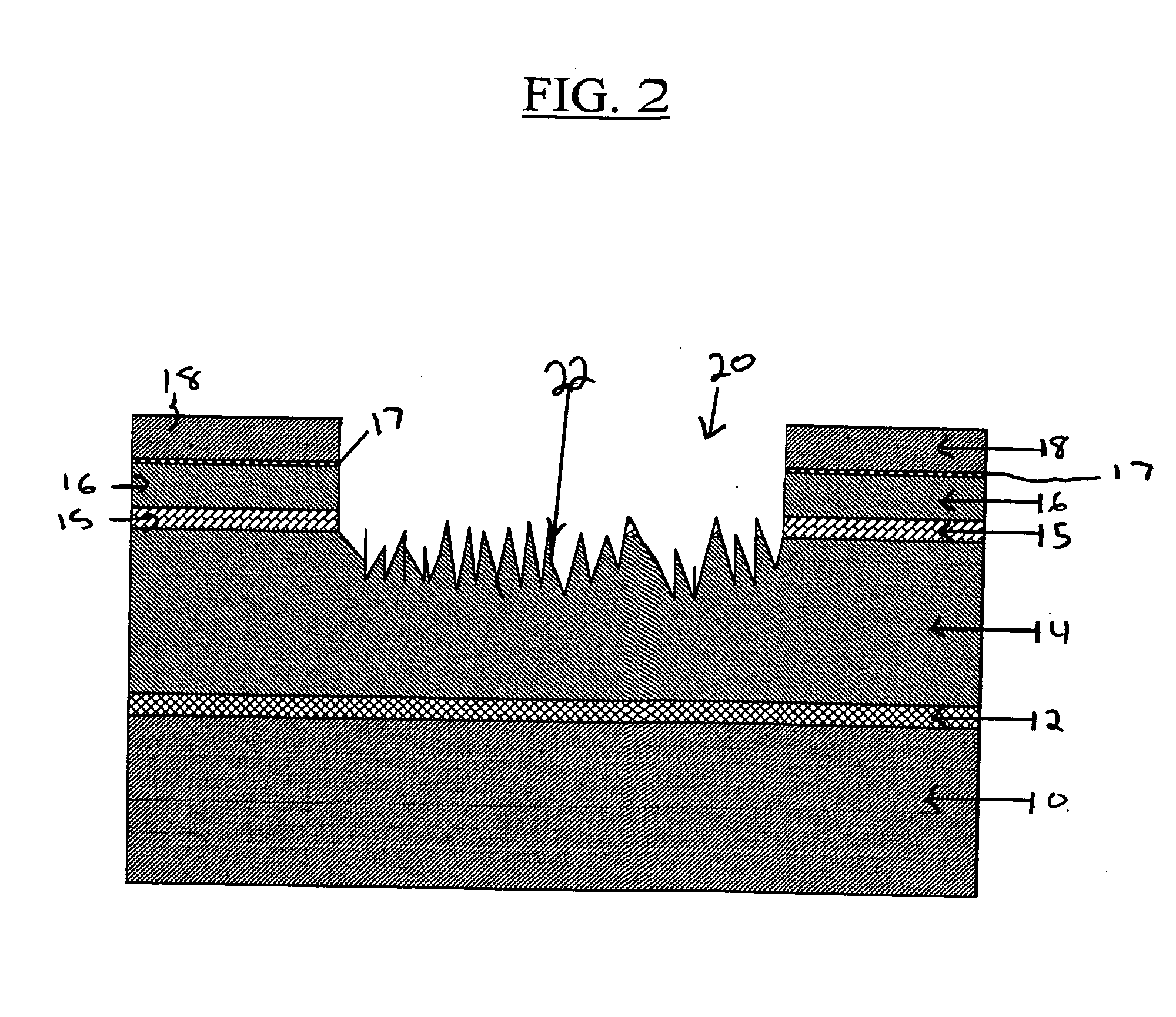
The present invention relates to a method of fabricating a transparent gas barrier film by using plasma surface treatment and a transparent gas barrier film fabricated according to such method which has an organic / inorganic gradient interface structure at the interface between an organic / inorganic hybrid layer and an inorganic layer. Since the method of the present invention is capable of fabricating a gas barrier film by plasma surface treatment instead of deposition under high vacuum, it can mass-produce a transparent gas barrier film with excellent gas barrier properties in an economical and simple manner. Further, since the transparent gas barrier film fabricated according to the method of the present invention shows excellent gas barrier properties and is free of crack formation and layer-peeling phenomenon, it can be effectively used in the manufacture of a variety of display panels.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
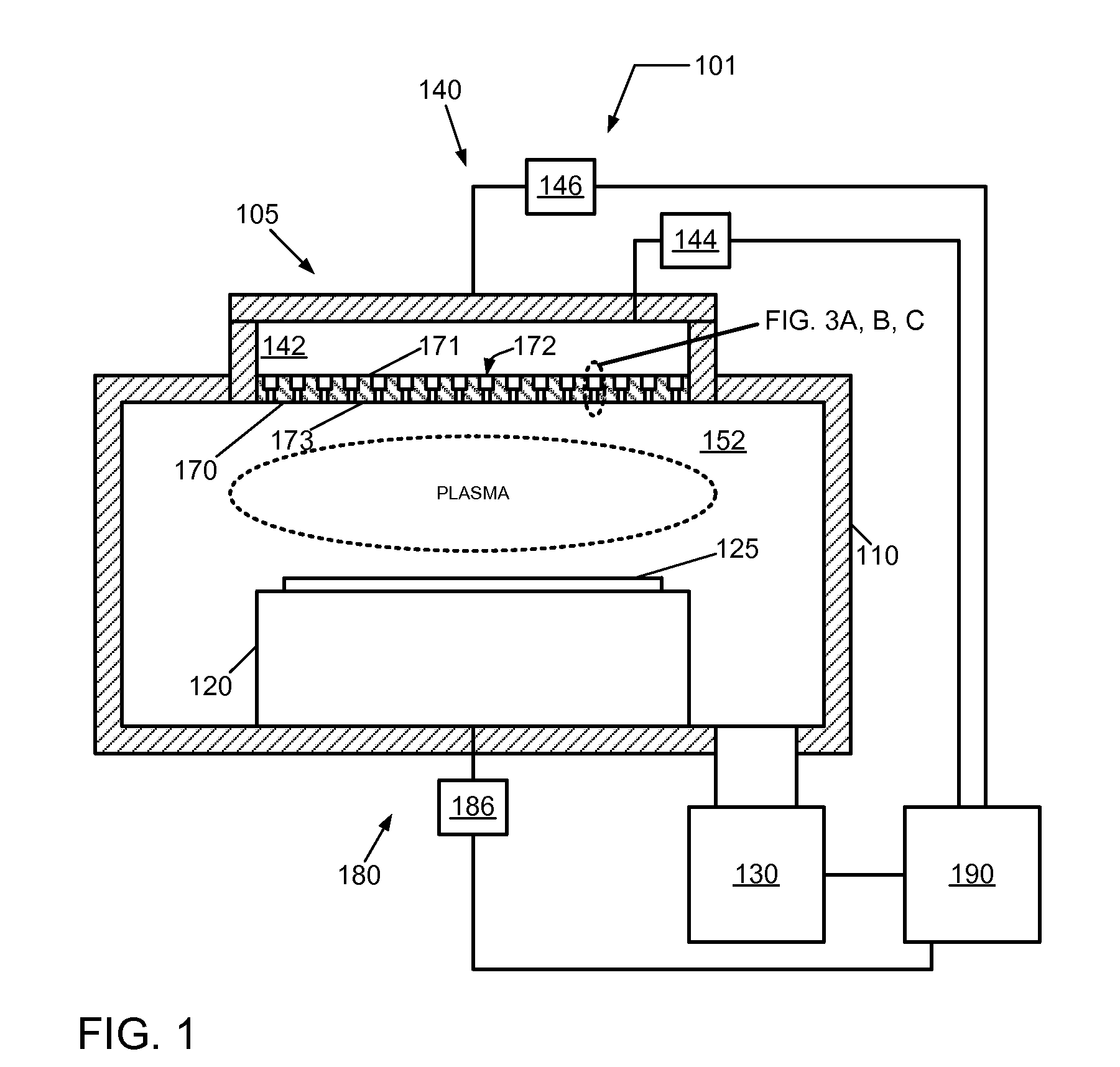
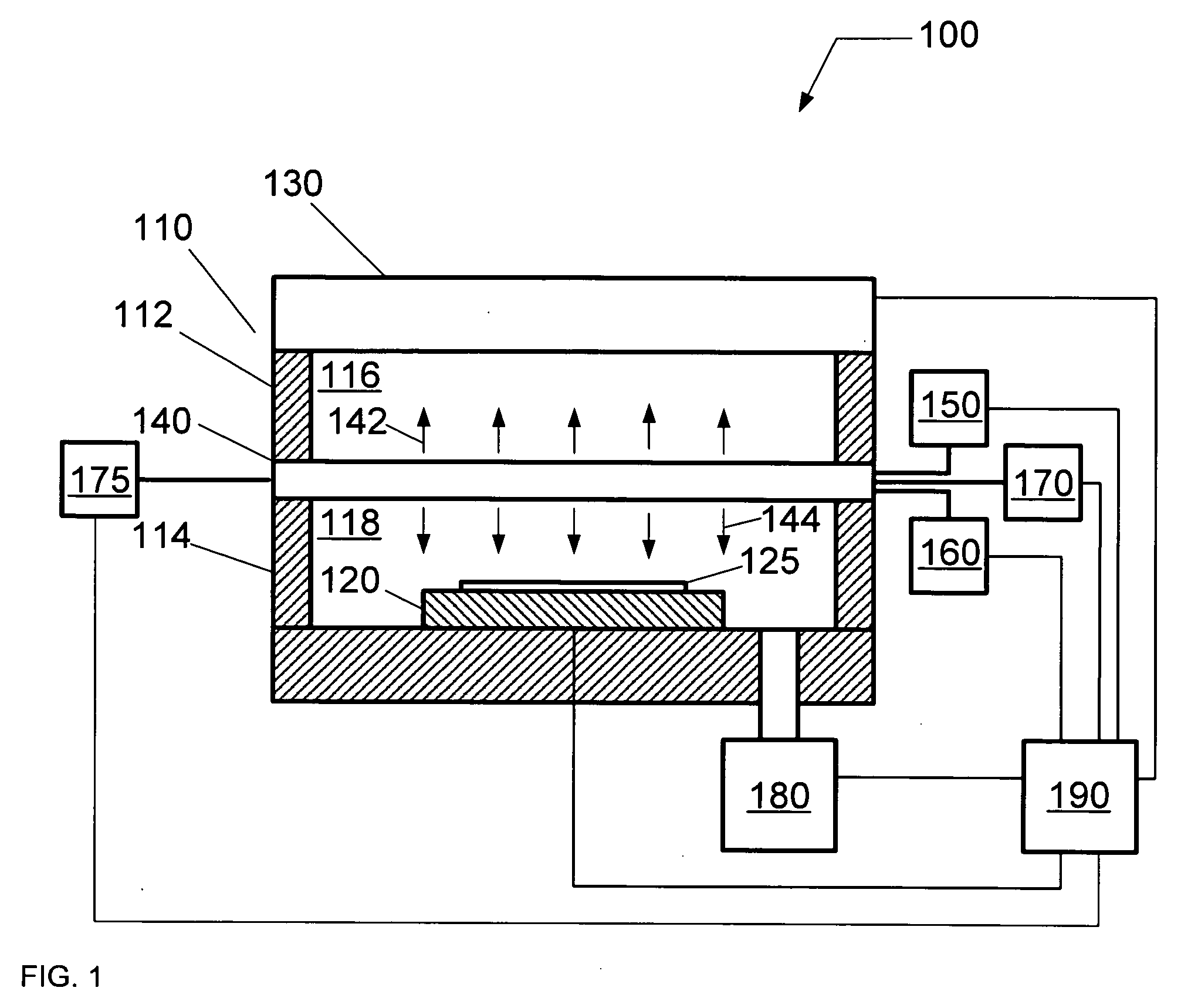
Surface wave plasma processing system and method of using
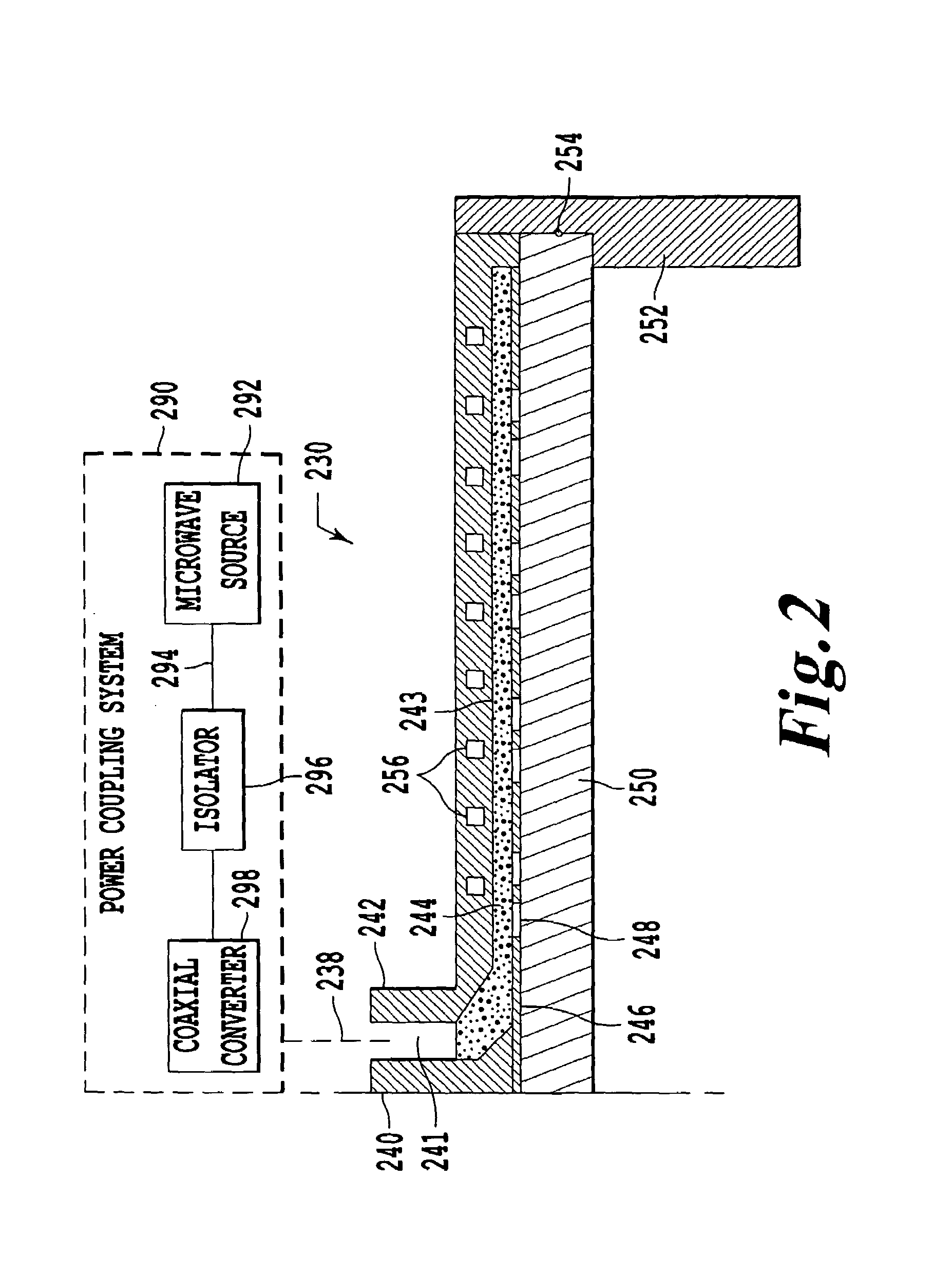
InactiveUS7138767B2Reduce harmReduce the possibility of damageElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsPower couplingPlasma processing
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
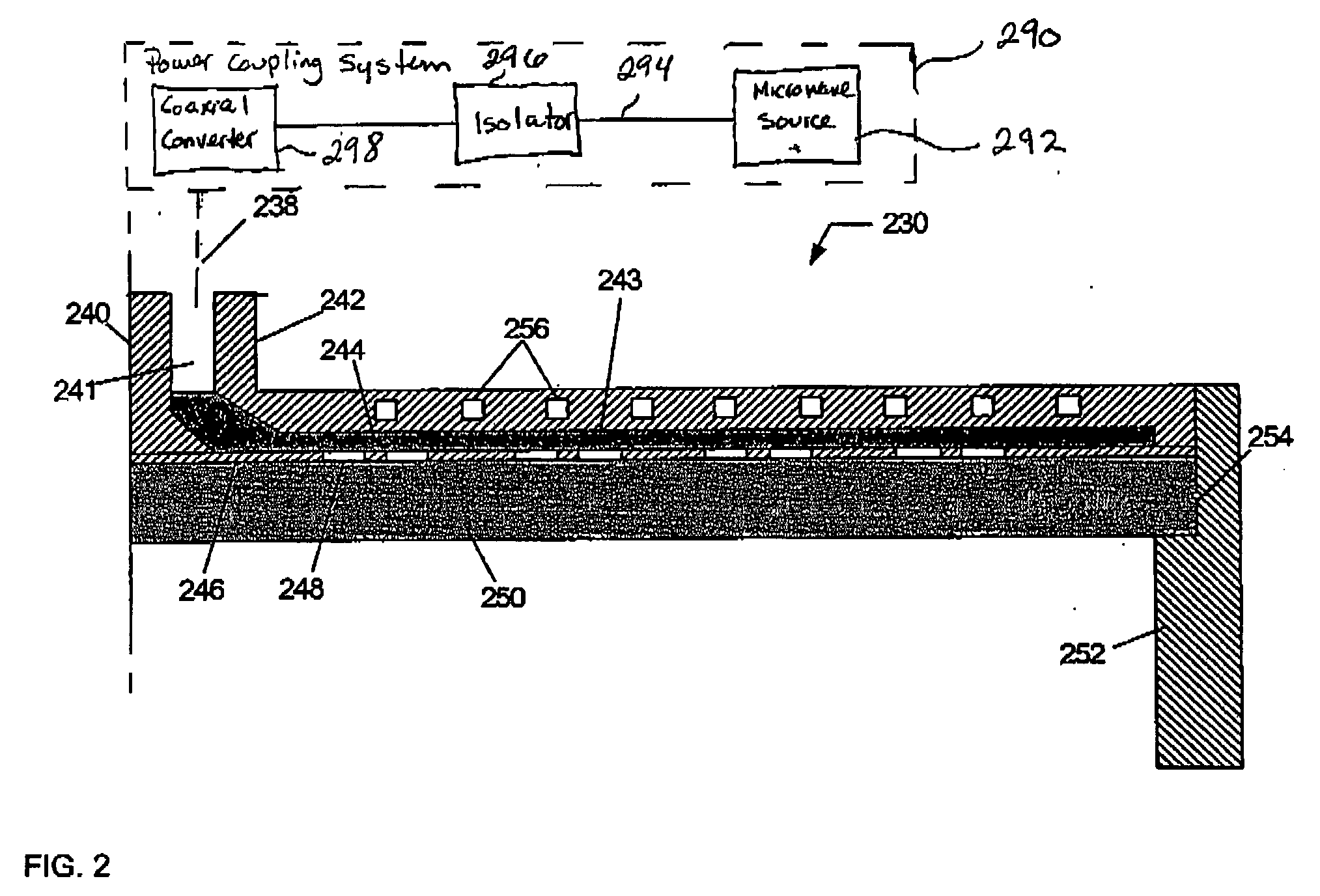
Adjustable slot antenna for control of uniformity in a surface wave plasma source
ActiveUS20140028190A1Avoid passingElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsPower couplingSurface wave
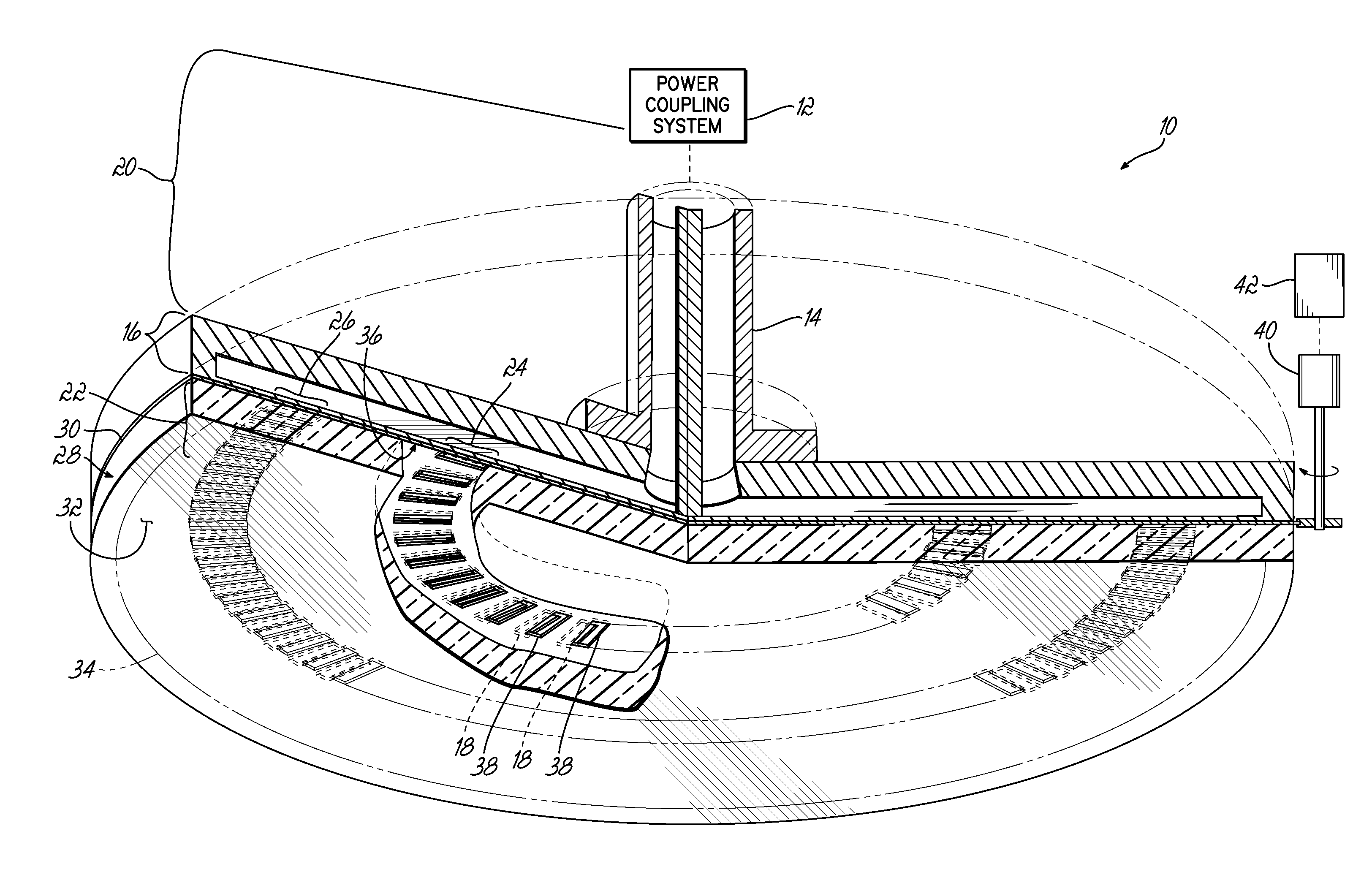
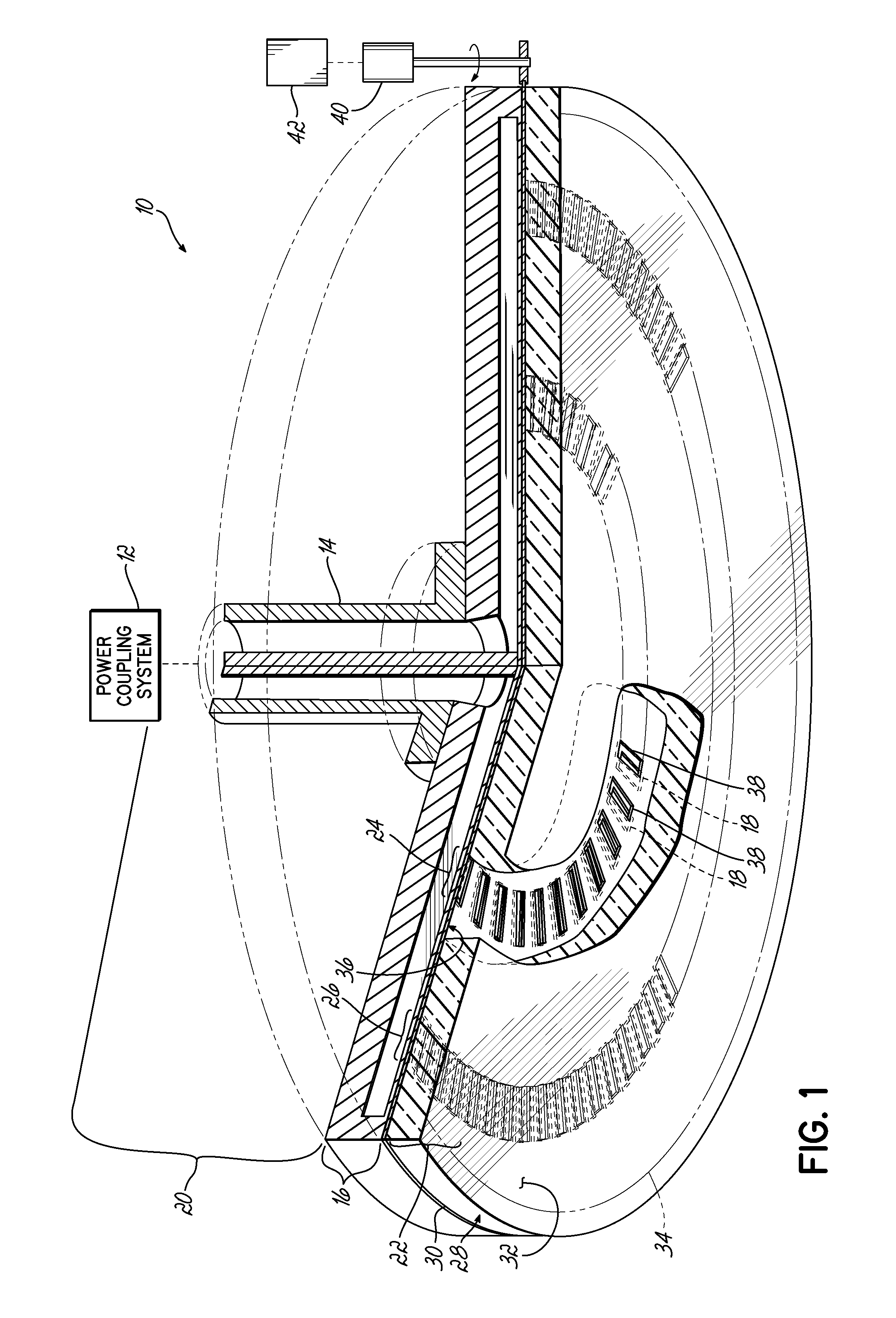
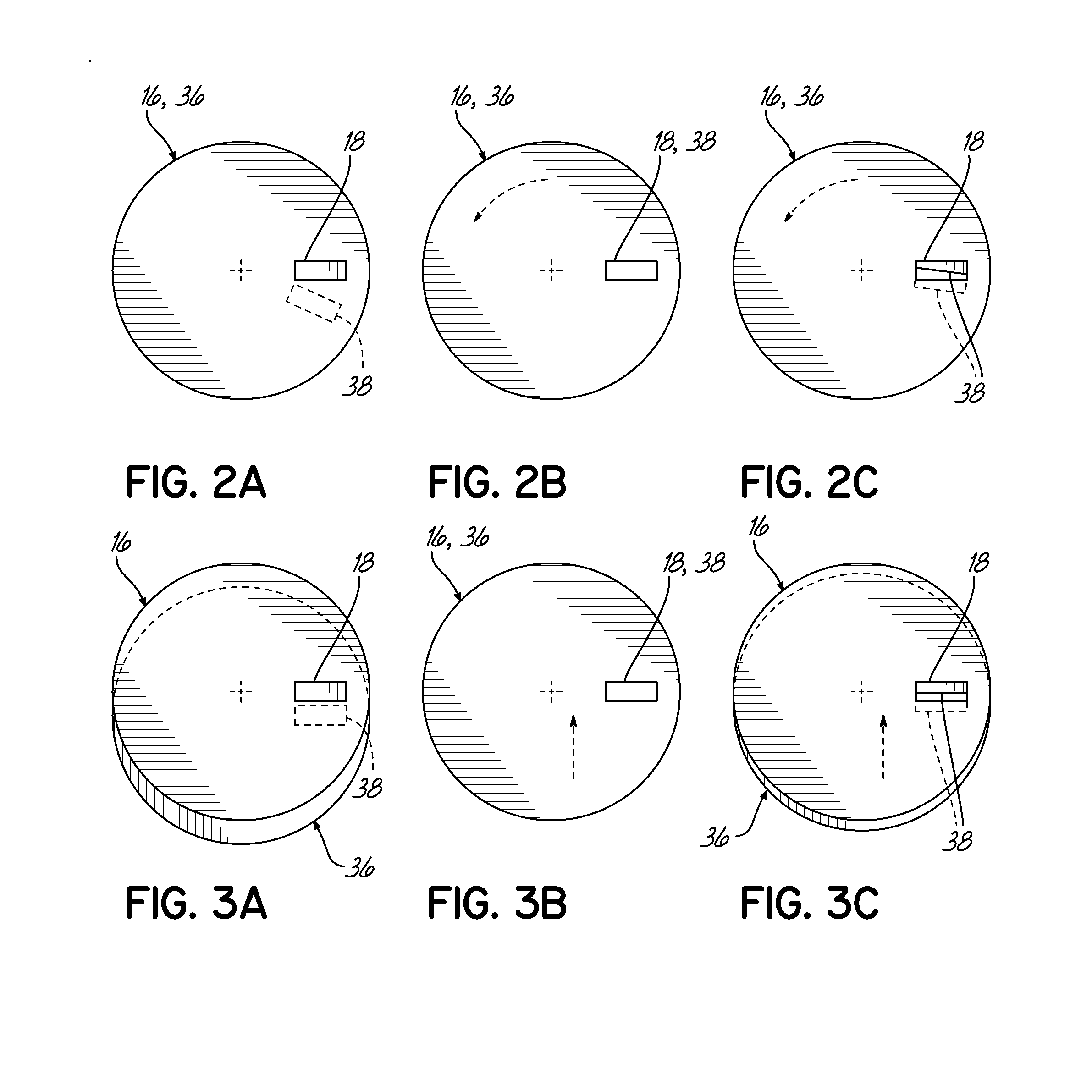
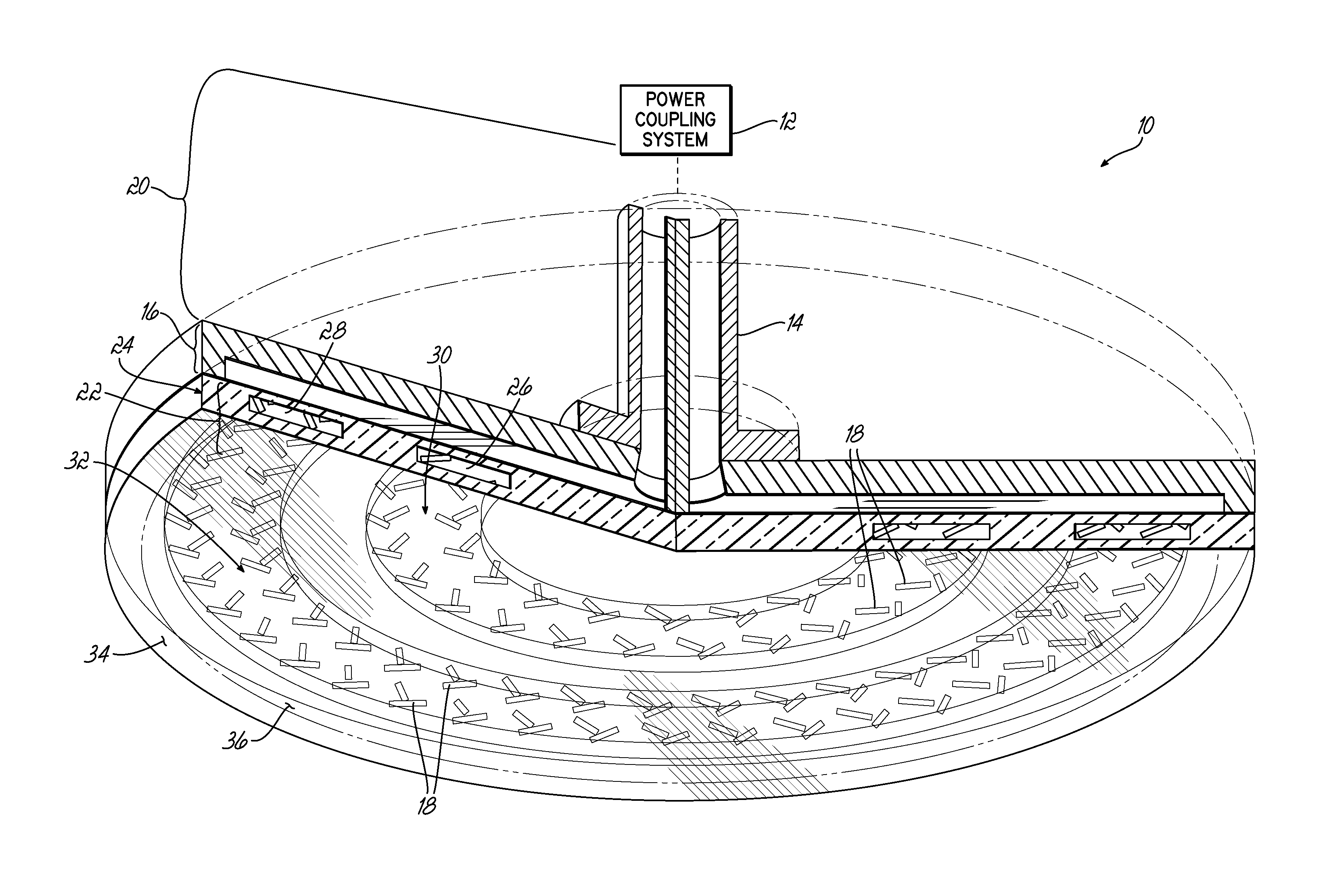
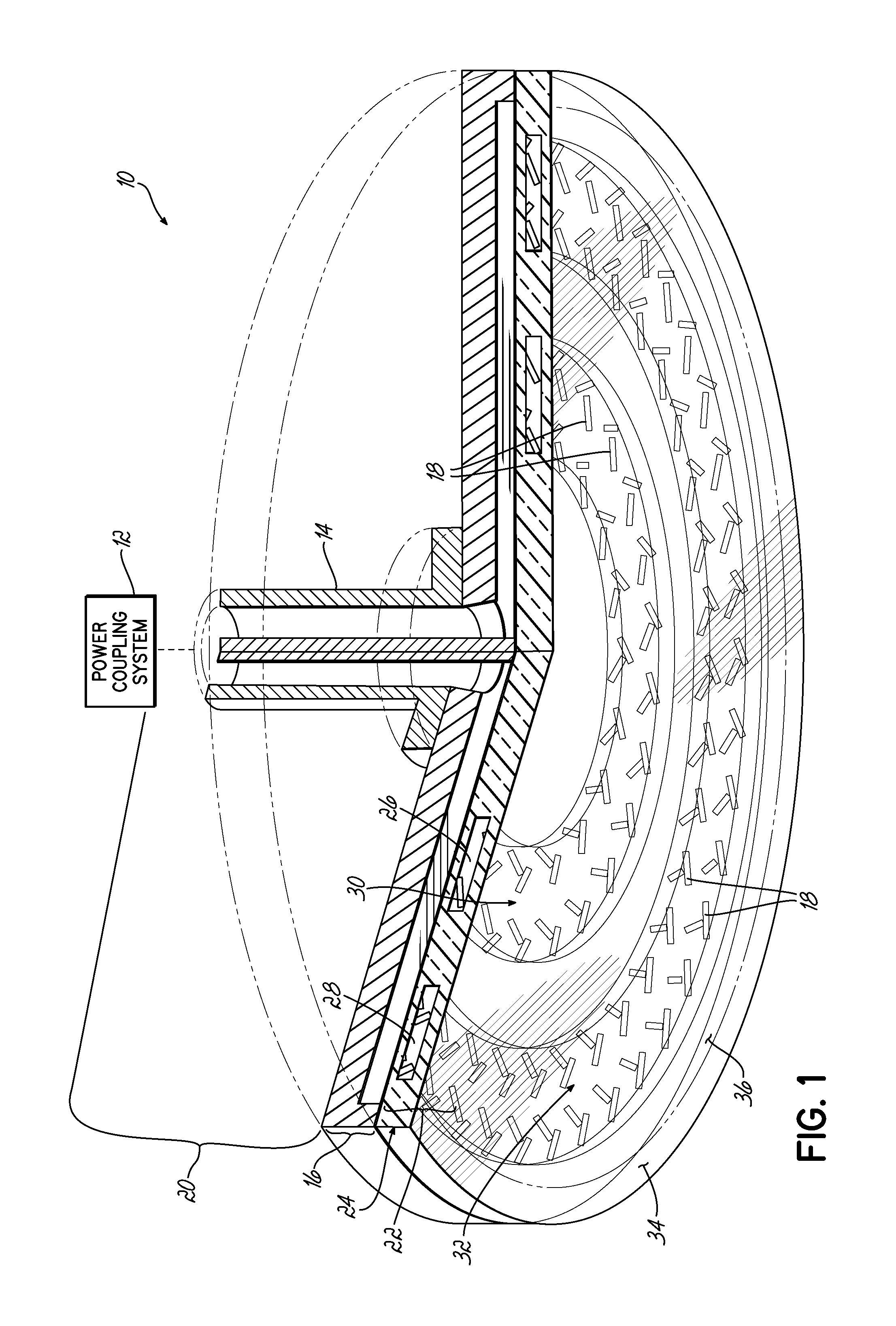
The present invention provides a surface wave plasma source including an electromagnetic (EM) wave launcher comprising a slot antenna having a plurality of antenna slots configured to couple the EM energy from a first region above the slot antenna to a second region below the slot antenna, and a power coupling system is coupled to the EM wave launcher. A dielectric window is positioned in the second region and has a lower surface including the plasma surface. A slotted gate plate is arranged parallel with the slot antenna and is configured to be movable relative to the slot antenna between variable opacity positions including a first opaque position to prevent the EM energy from passing through the first arrangements of antenna slots, and a first transparent position to allow a full intensity of the EM energy to pass through the first arrangement of antenna slots.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Control of uniformity in a surface wave plasma source
A surface wave plasma source (SWPS) is disclosed, having an electromagnetic (EM) wave launcher including a slot antenna configured to couple EM energy in a desired EM wave mode to a plasma by generating a surface wave on a plasma surface of the SWPS adjacent the plasma. The SWPS also includes a dielectric window positioned below the slot antenna, having a lower surface and the plasma surface. The SWPS further includes an attenuation assembly disposed between the slot antenna and the plasma surface. The attenuation assembly includes a first fluid channel substantially aligned with a first arrangement of slots in the slot antenna, and is configured to receive a first flow of a first fluid at a first fluid temperature. The SWPS finally includes a power coupling system coupled to the EM wave launcher and configured to provide EM energy to the EM wave launcher for forming the plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Surface coating for chamber components used in plasma systems
ActiveUS20170032942A1Low plasma surface recombination rateHigh trafficElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingBlood plasmaPlasma chamber
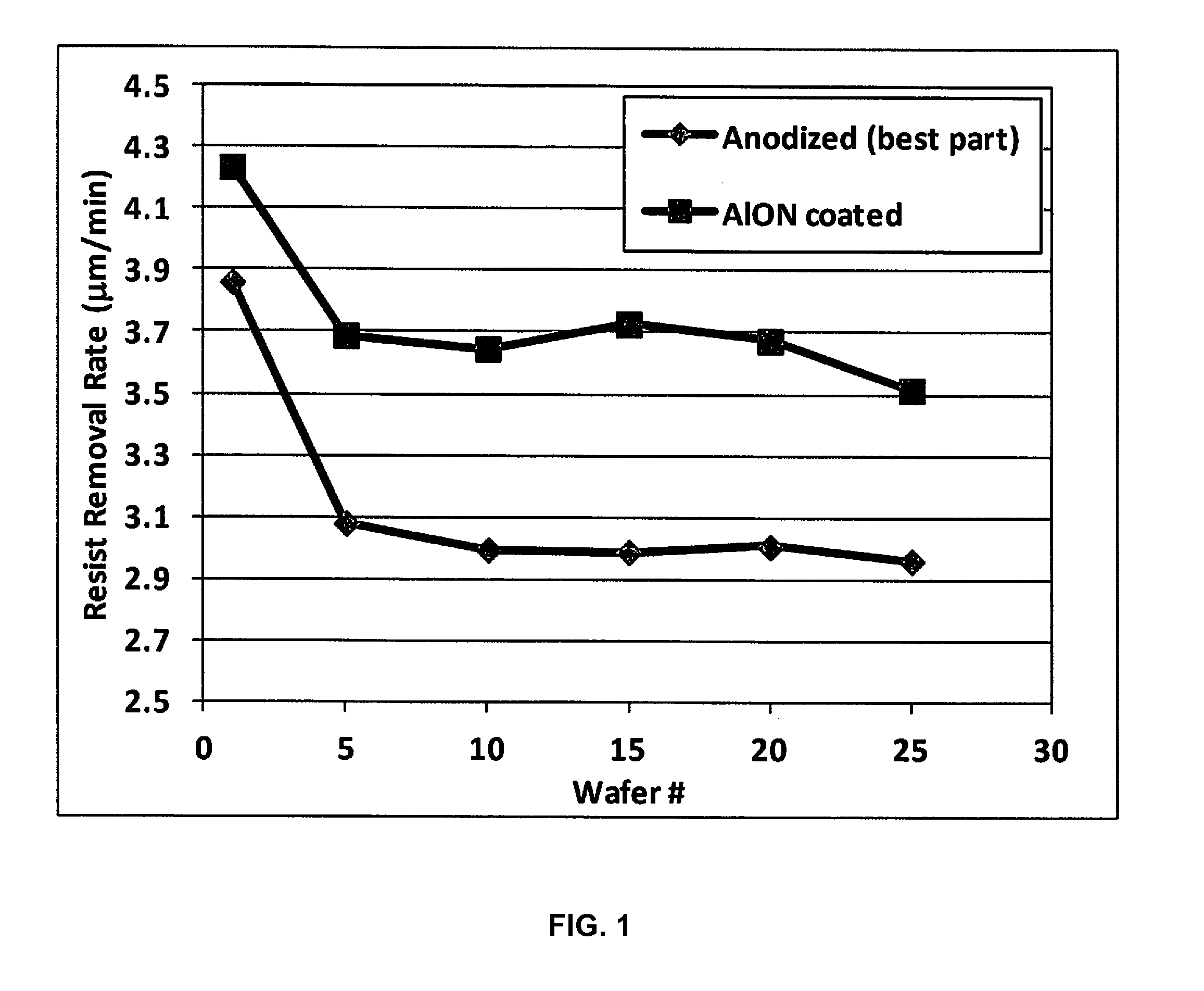
Disclosed herein are surface coatings for plasma components that have the benefit of being robust against chemical and plasma physical attack in aggressive (e.g., fluorine-based) plasma environments. The coatings also provide low plasma surface recombination rates for active oxygen, nitrogen, fluorine, and hydrogen species when compared with other known surface treatments. The coatings can be applied to any plasma system component not requiring etching or plasma cleaning including but not limited to materials like quartz, aluminum, or anodized aluminum. Additionally, the efficiency of the system is increased by applying a non-reactive coating to system components thereby increasing the flow of excited plasma species to the plasma chamber of the system.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Multilayer materials
InactiveUS6623747B1Improve comfortReducing rate and extentCoatingsOptical partsHydrophilic coatingContact lens
The invention is directed to a composite material, especially a biomedical device, e.g. an ophthalmic device, preferably a contact lens, with one or more wettable surfaces capable of holding a continous layer of aqueous fluid thereon which composite material comprises a bulk material and a hydrophilic coating characterized in that the hydrophilic coating consists of a carbohydrate attached covalently to reactive groups at the surface of the bulk material, either directly or via functional groups of an oligofunctional compound, said oligofunctional compound in turn having functional groups being capable of reacting with said reactive groups at the surface of the bulk material and with the carbohydrate, wherein said reactive groups are either inherently (a priori) present in the bulk material or wherein said reactive groups have been attached to the surface of the bulk material by a plasma surface preparation, as well as to a process of manufacture of such a composite material.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
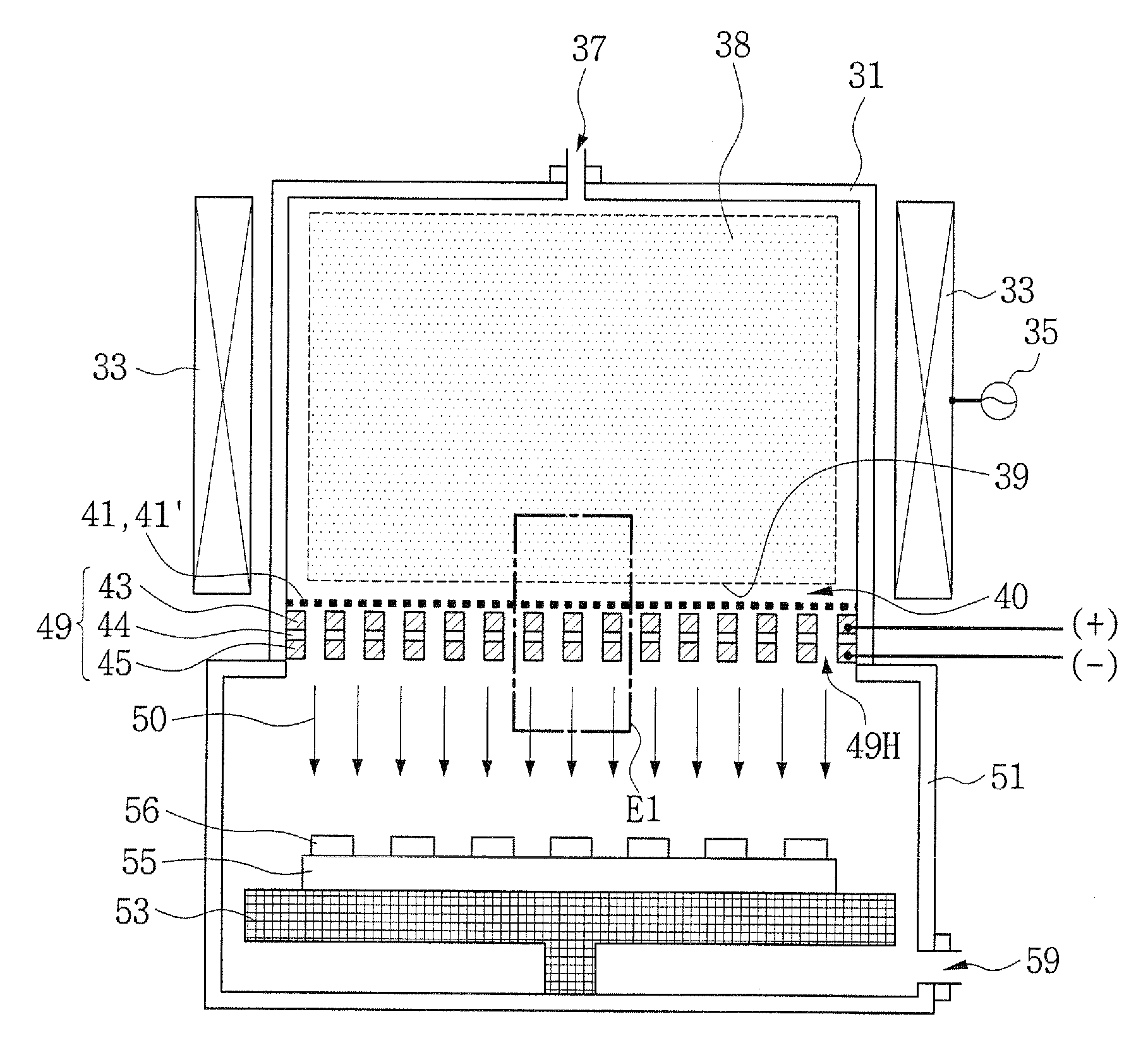
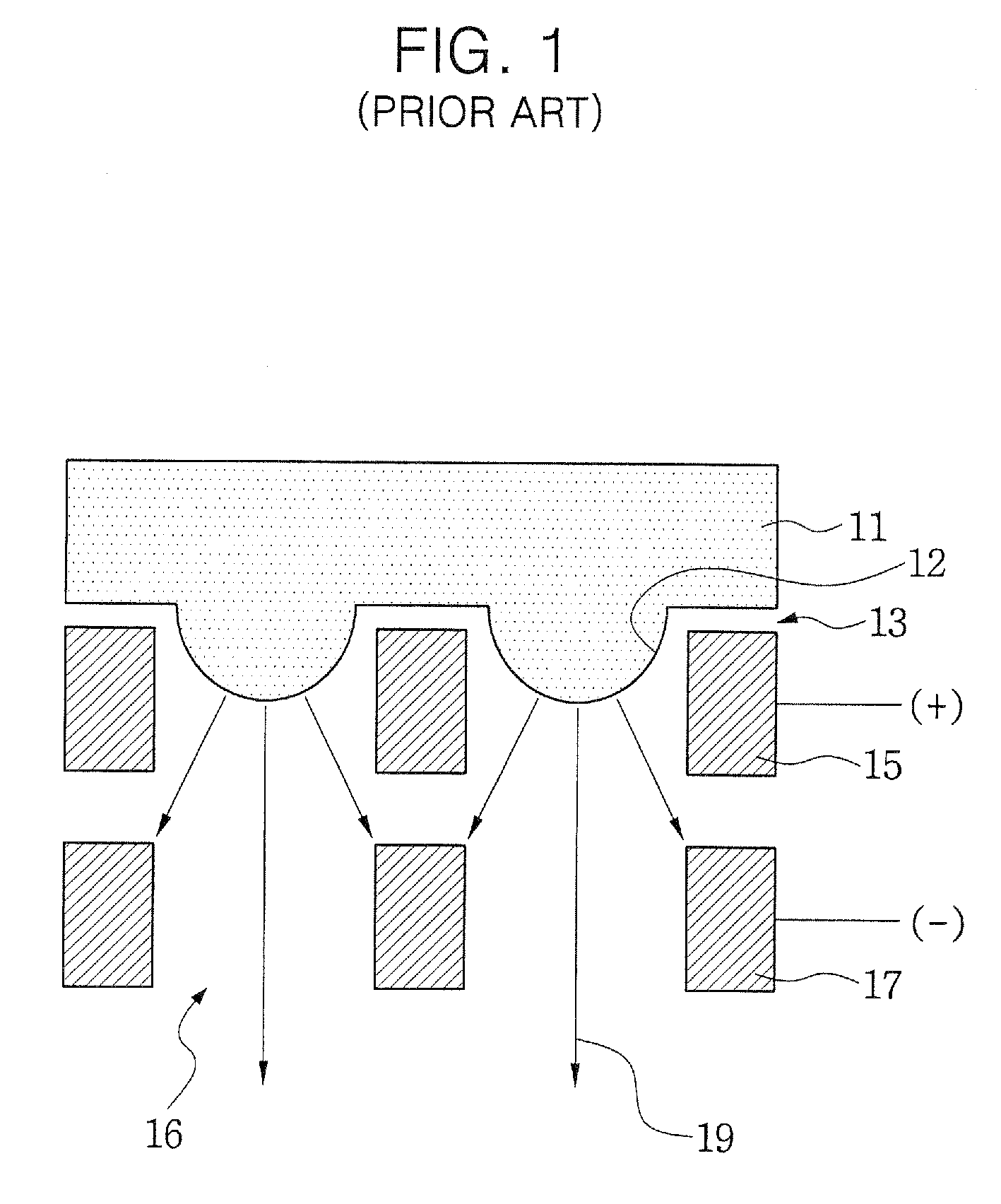
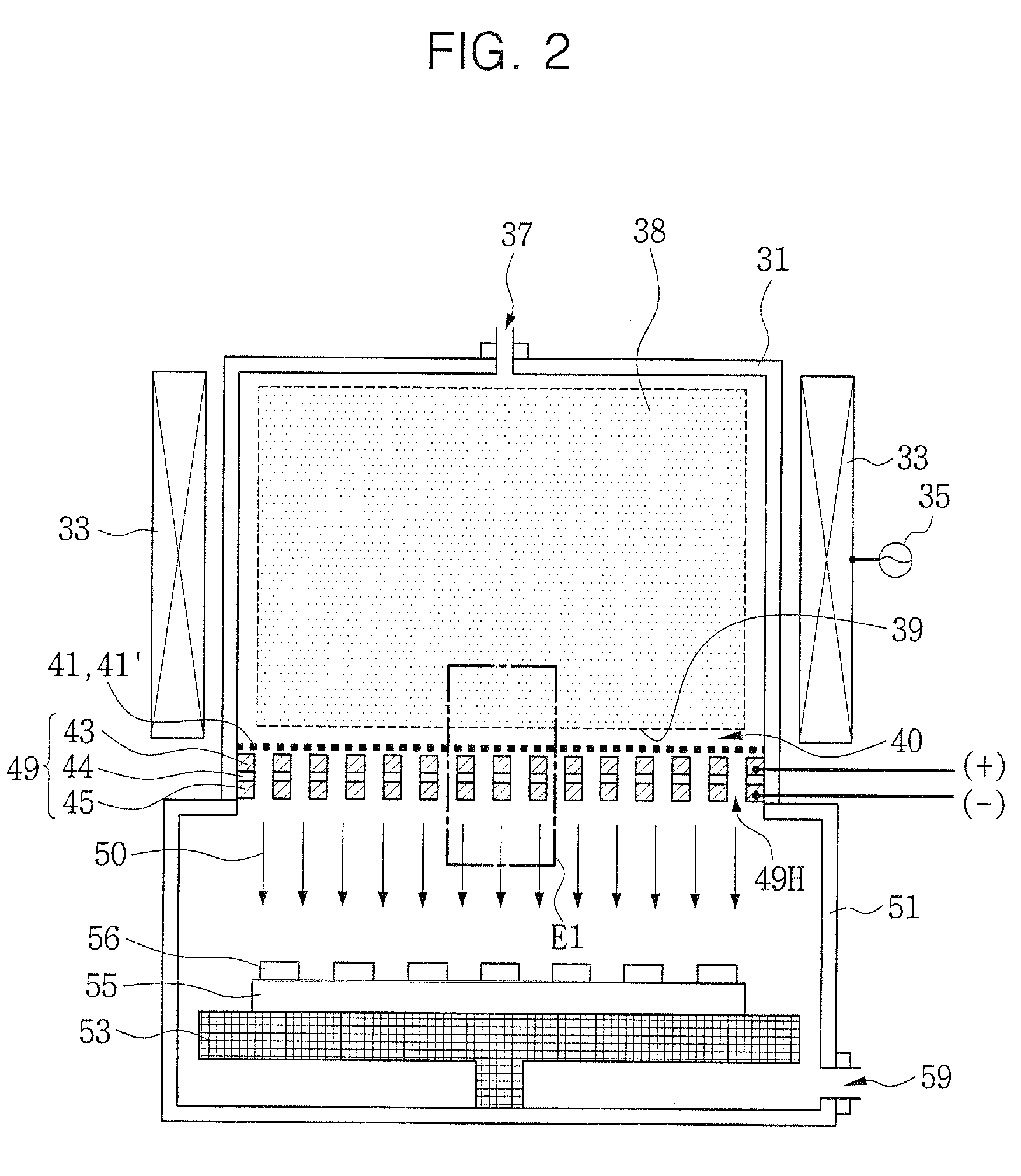
Plasma processing device for surfaces
InactiveUS6265690B1Rapid and efficient pretreatmentLow equipment costPretreated surfacesArc welding apparatusPlasma jetEngineering
Owner:PLASMATREAT GMBH
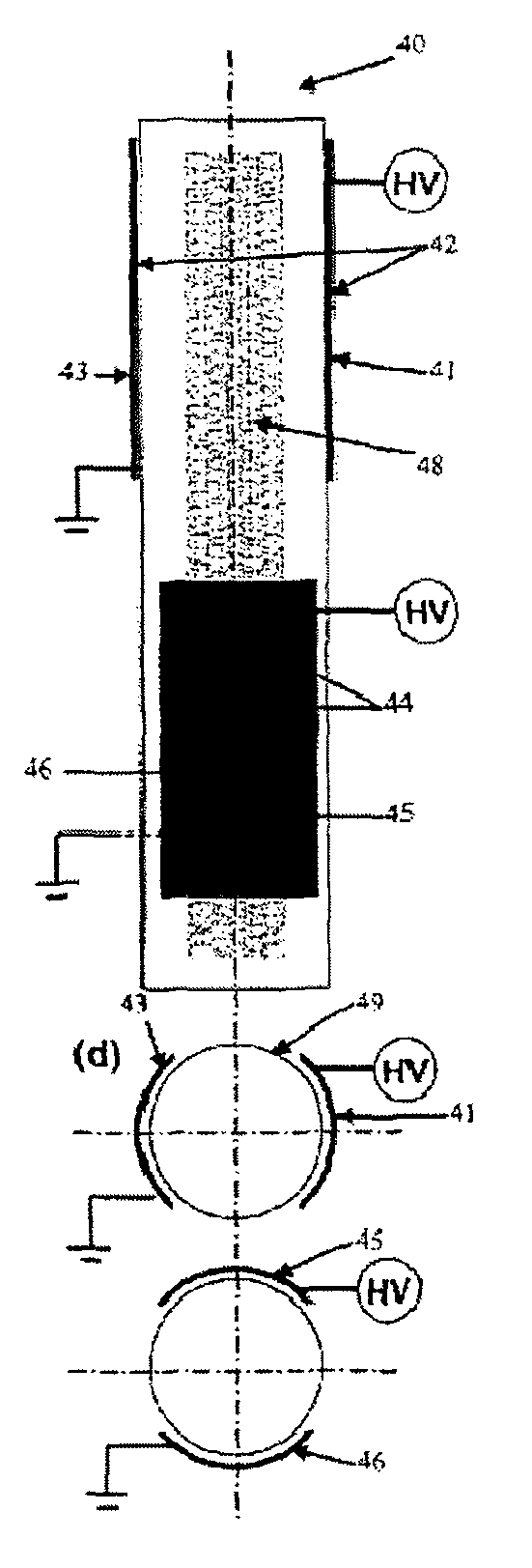
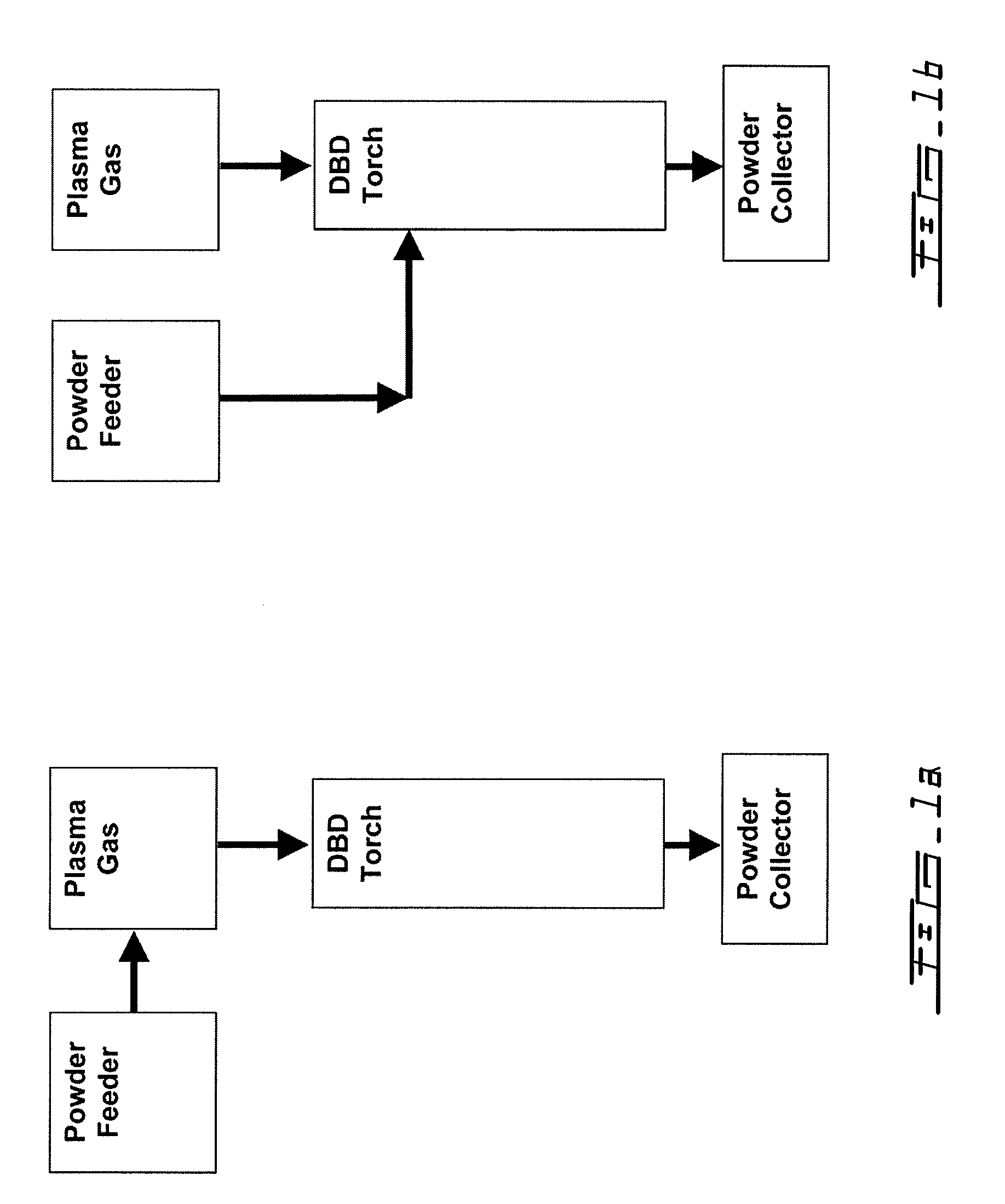
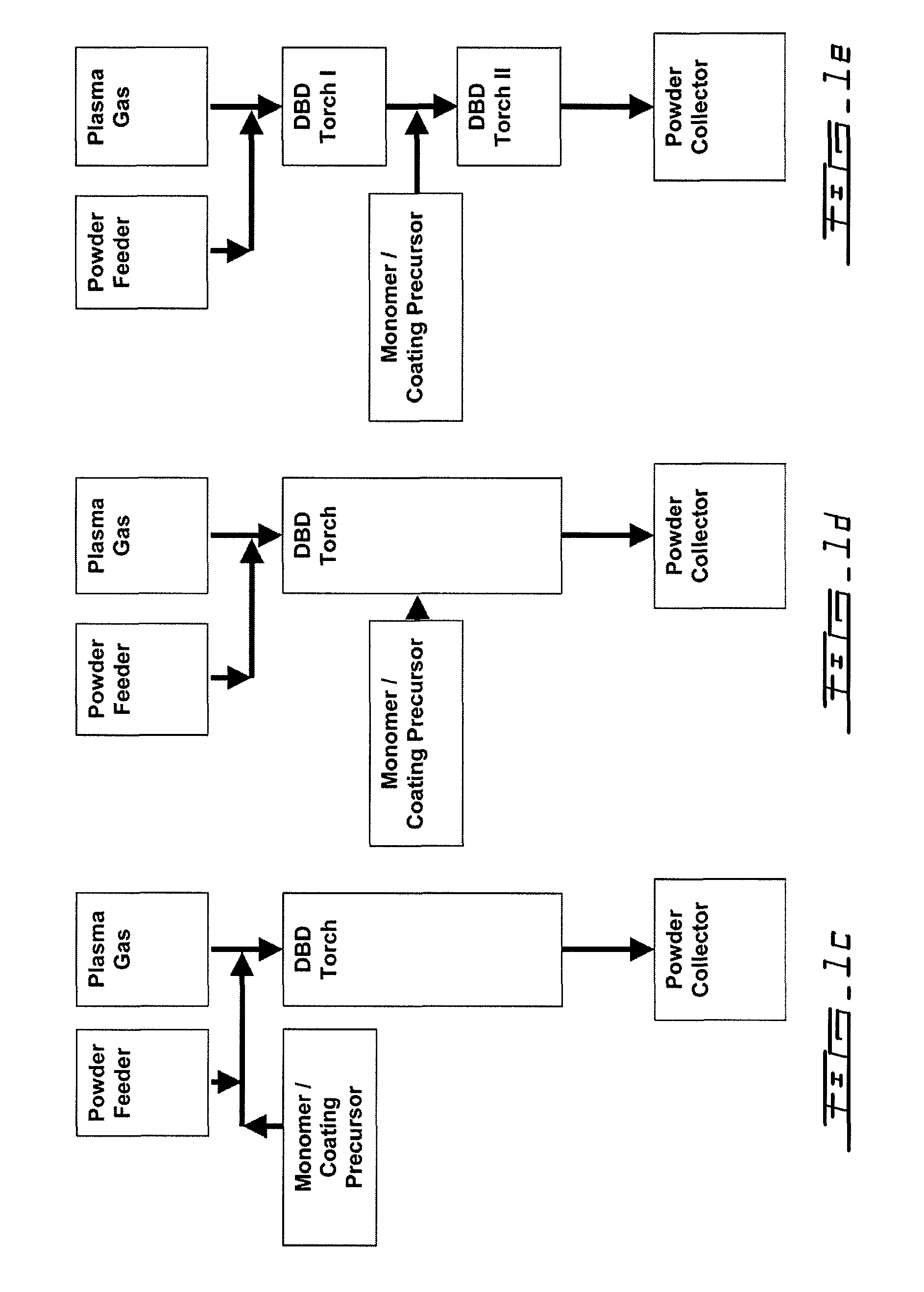
Plasma surface treatment using dielectric barrier discharges
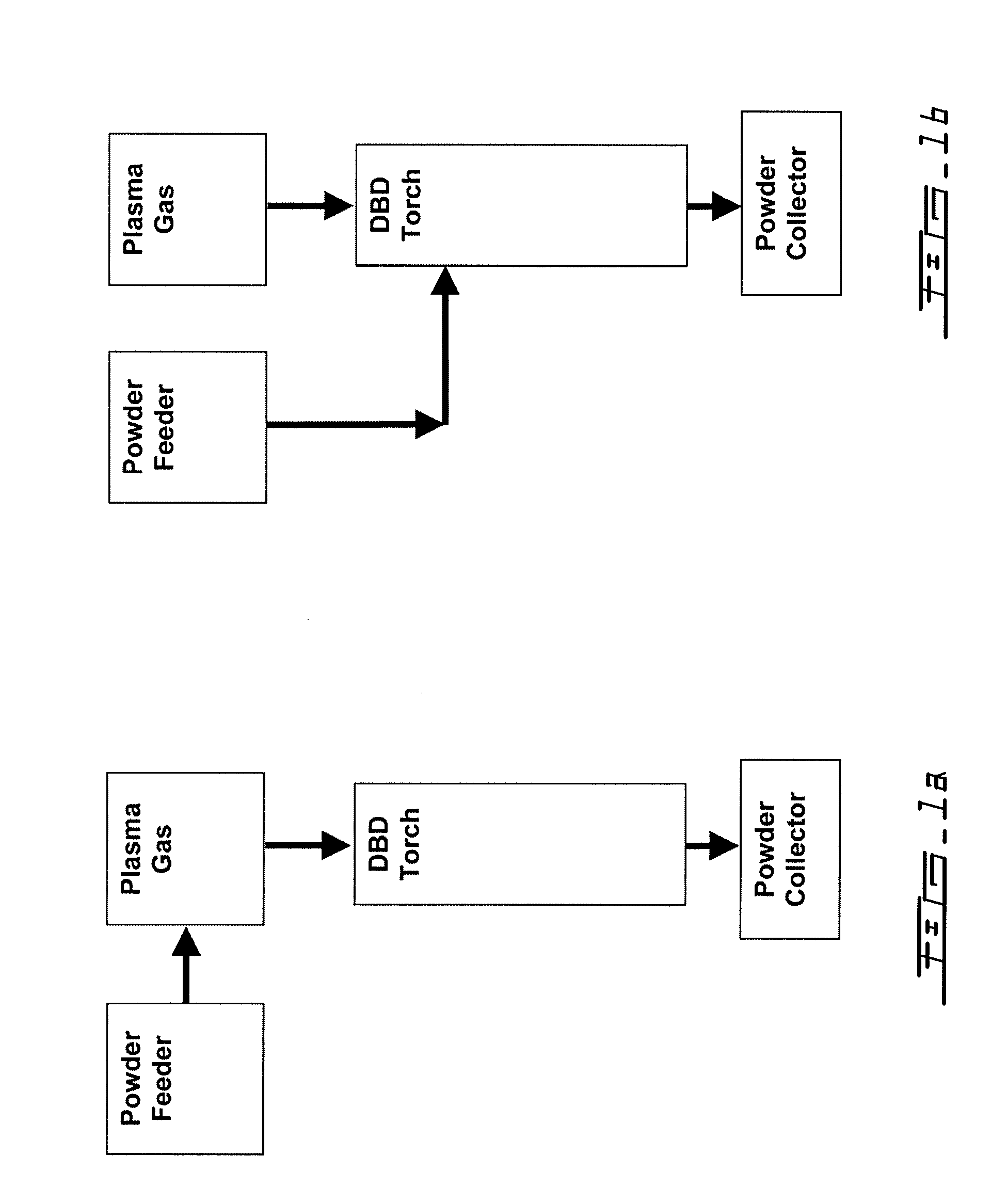
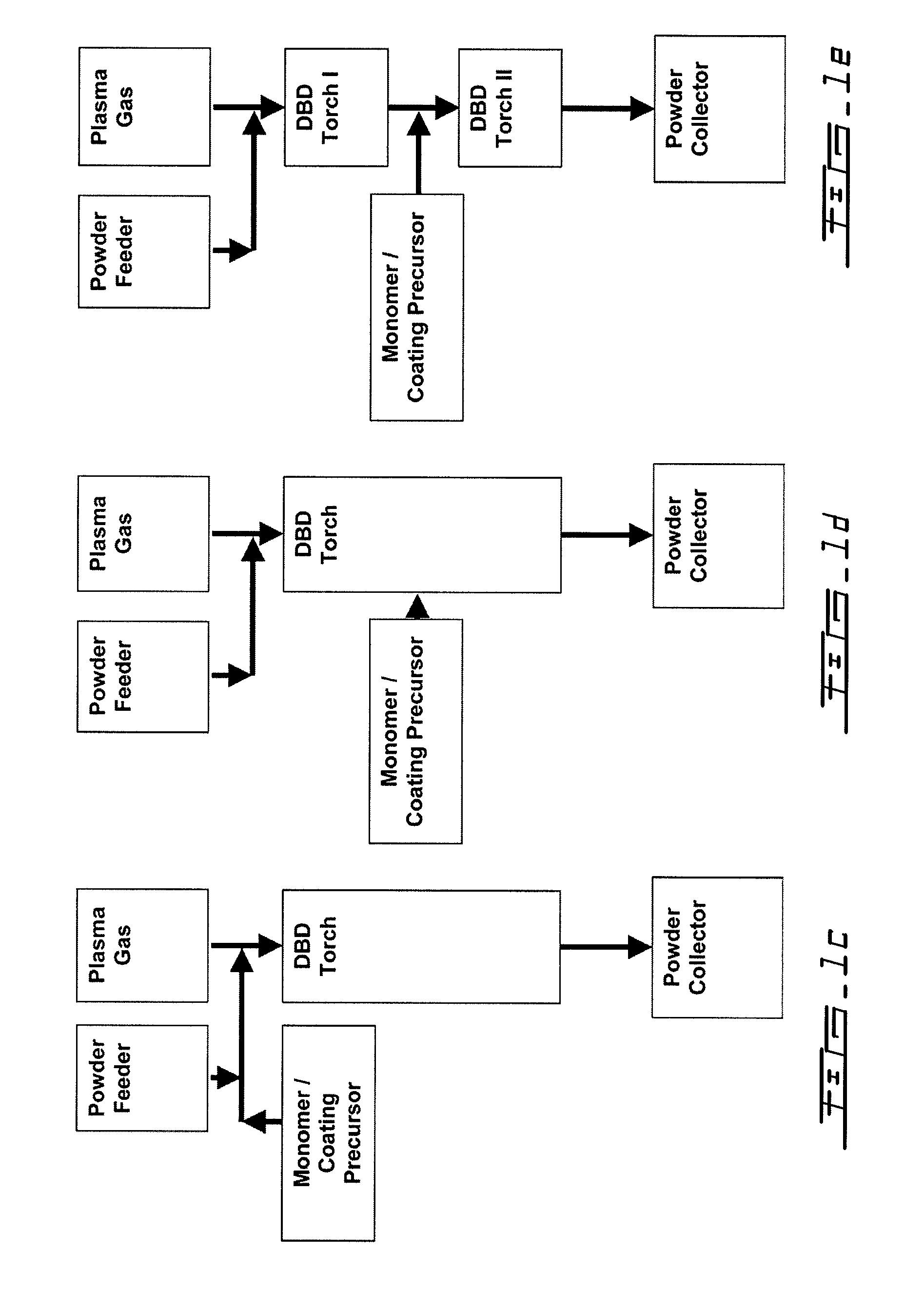
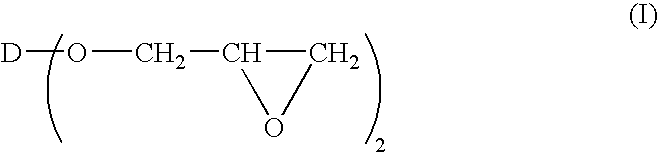
A process for the in-flight surface treatment of powders using a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Torch operating at atmospheric pressures or soft vacuum conditions is described herein. The process comprising feeding a powder material into the Dielectric Barrier Discharge Torch yielding powder particles exhibiting a reduced powder agglomeration feature; in-flight modifying the surface properties of the particles; and collecting coated powder particles. An apparatus for surface treating micro- and nanoparticles comprising a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Torch operating at atmospheric pressure or soft vacuum conditions is also described herein.
Owner:TEKNA PLASMA SYST INC
Multilayer materials
InactiveUS20030175325A1Reduce rateReducing extentPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsHydrophilic coatingContact lens
The invention is directed to a composite material, especially a biomedical device, e.g. an ophthalmic device, preferably a contact lens, with one or more wettable surfaces capable of holding a continous layer of aqueous fluid thereon which composite material comprises a bulk material and a hydrophilic coating characterized in that the hydrophilic coating consists of a carbohydrate attached covalently to reactive groups at the surface of the bulk material, either directly or via functional groups of an oligofunctional compound, said oligofunctional compound in turn having functional groups being capable of reacting with said reactive groups at the surface of the bulk material and with the carbohydrate, wherein said reactive groups are either inherently (a priori) present in the bulk material or wherein said reactive groups have been attached to the surface of the bulk material by a plasma surface preparation, as well as to a process of manufacture of such a composite material.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Plasma surface graft process for reducing thrombogenicity
InactiveUS20050102025A1Enhance its interfacial reaction with a biological environmentSimple designPharmaceutical containersPretreated surfacesThrombogenicityVascular prosthesis
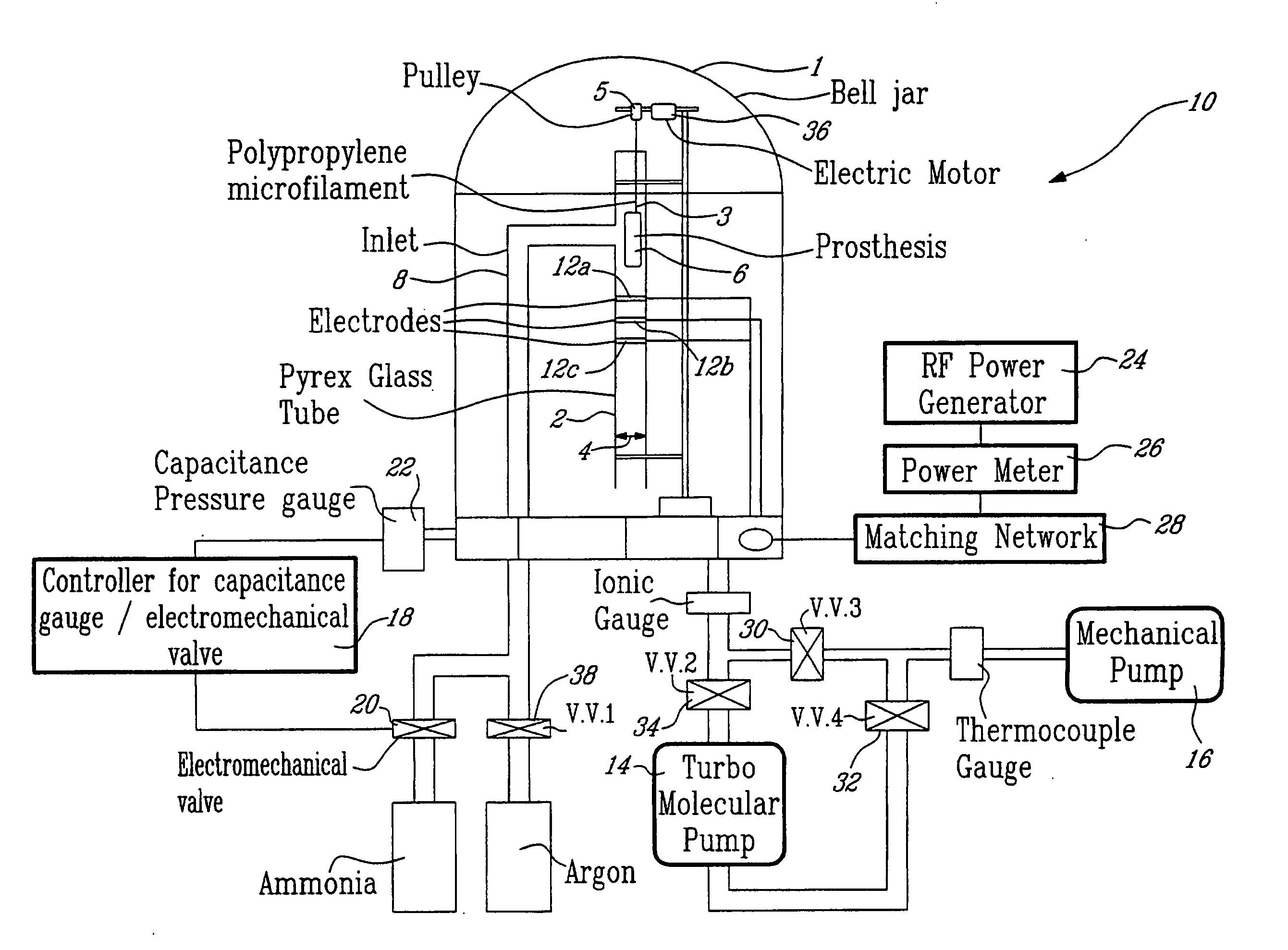
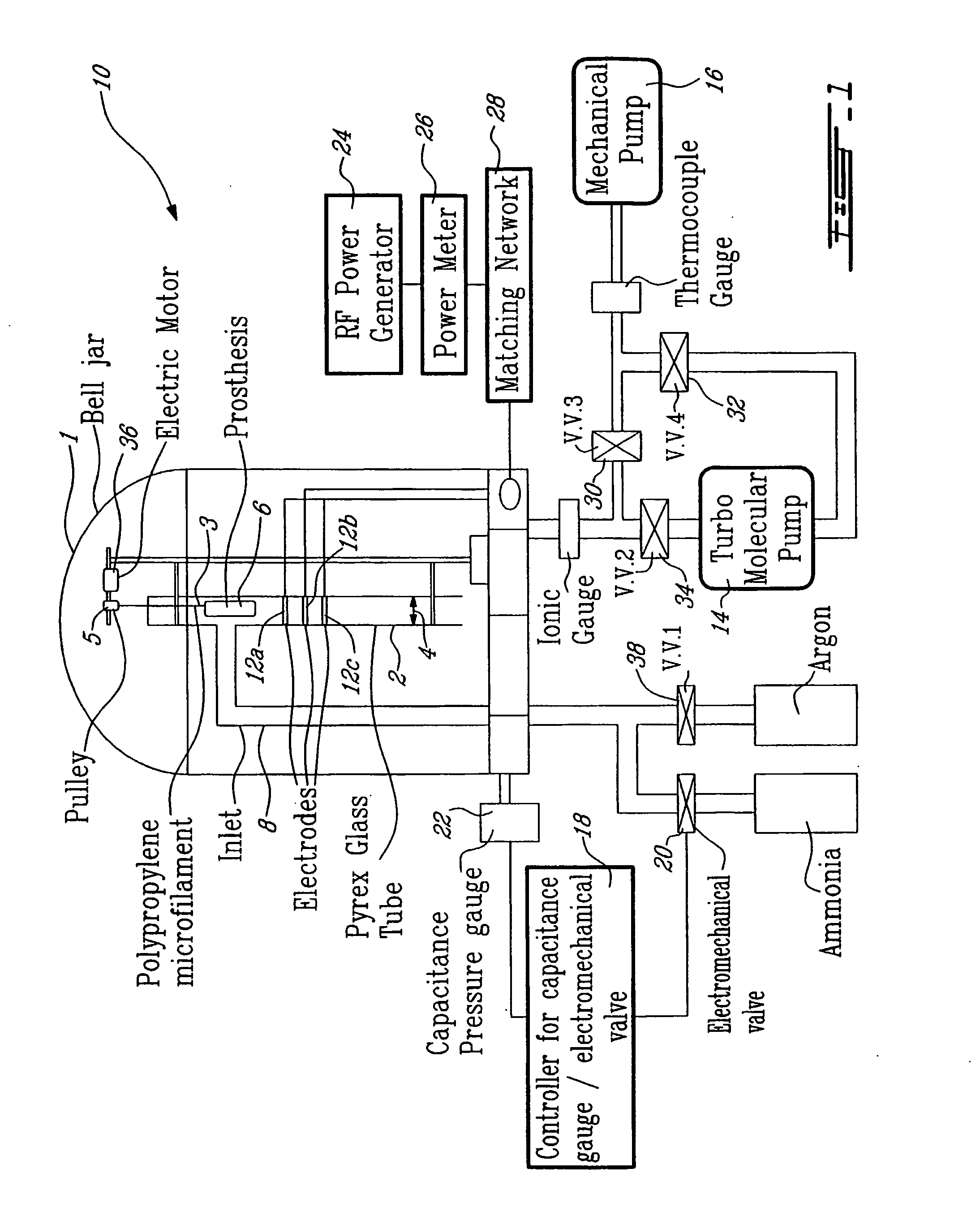
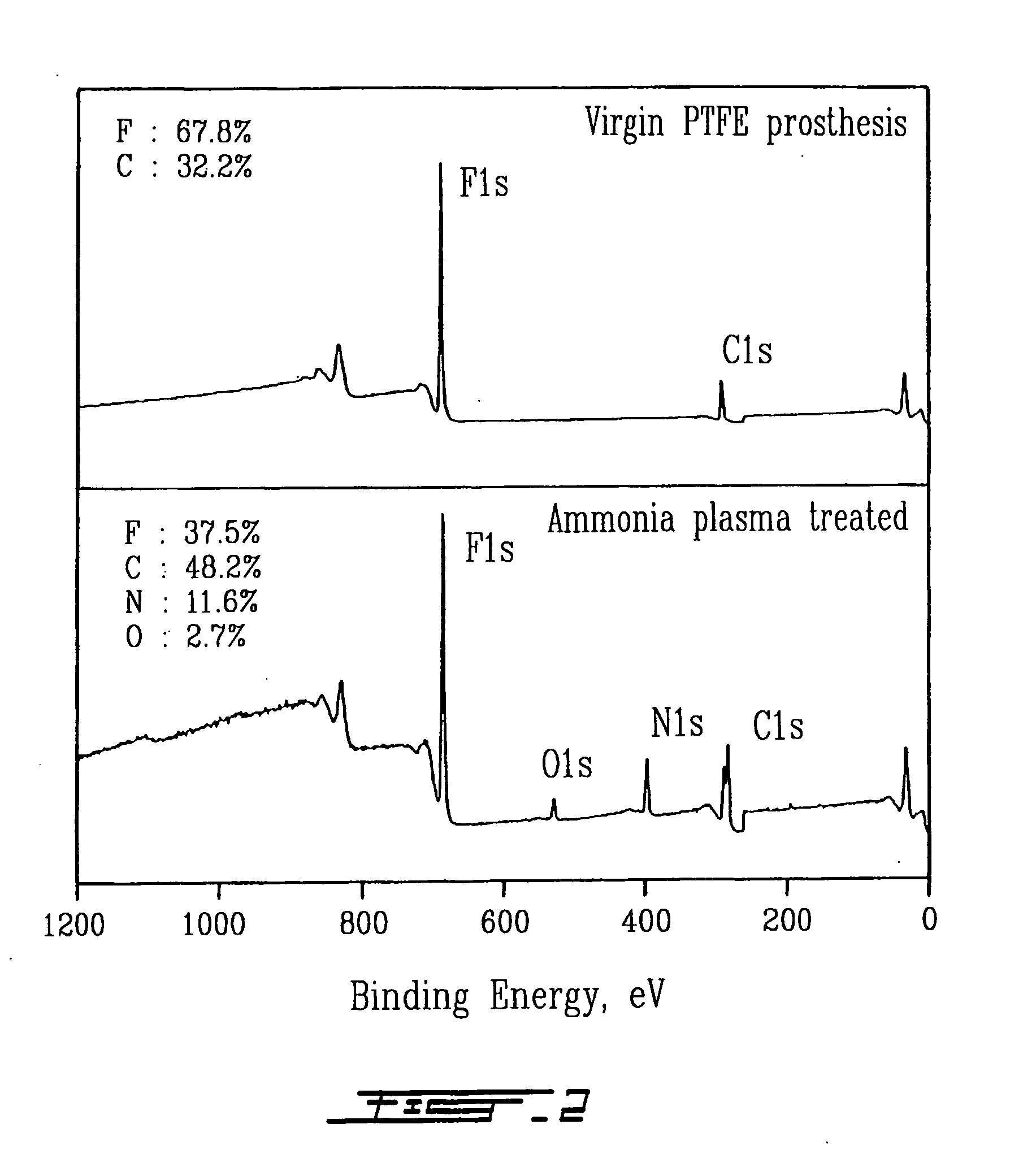
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a novel process for modifying the surface properties of a material that is suitable for contact with animal tissue so as to enhance its hemocompatibility and make it less thrombogenic when in use. This process comprises: Exposing the surface of the material to plasma treatment conditions in order to create reactive groups on said surface; activating a molecule with an activator to produce a reactive molecular species capable of forming convalent bonds with the reactive groups created on the surface of the material to form convalent bonds. The invention further encompasses the materials produced by this process as well as devices, such as vascular prosthesis, that are comprised of these process-modified materials.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
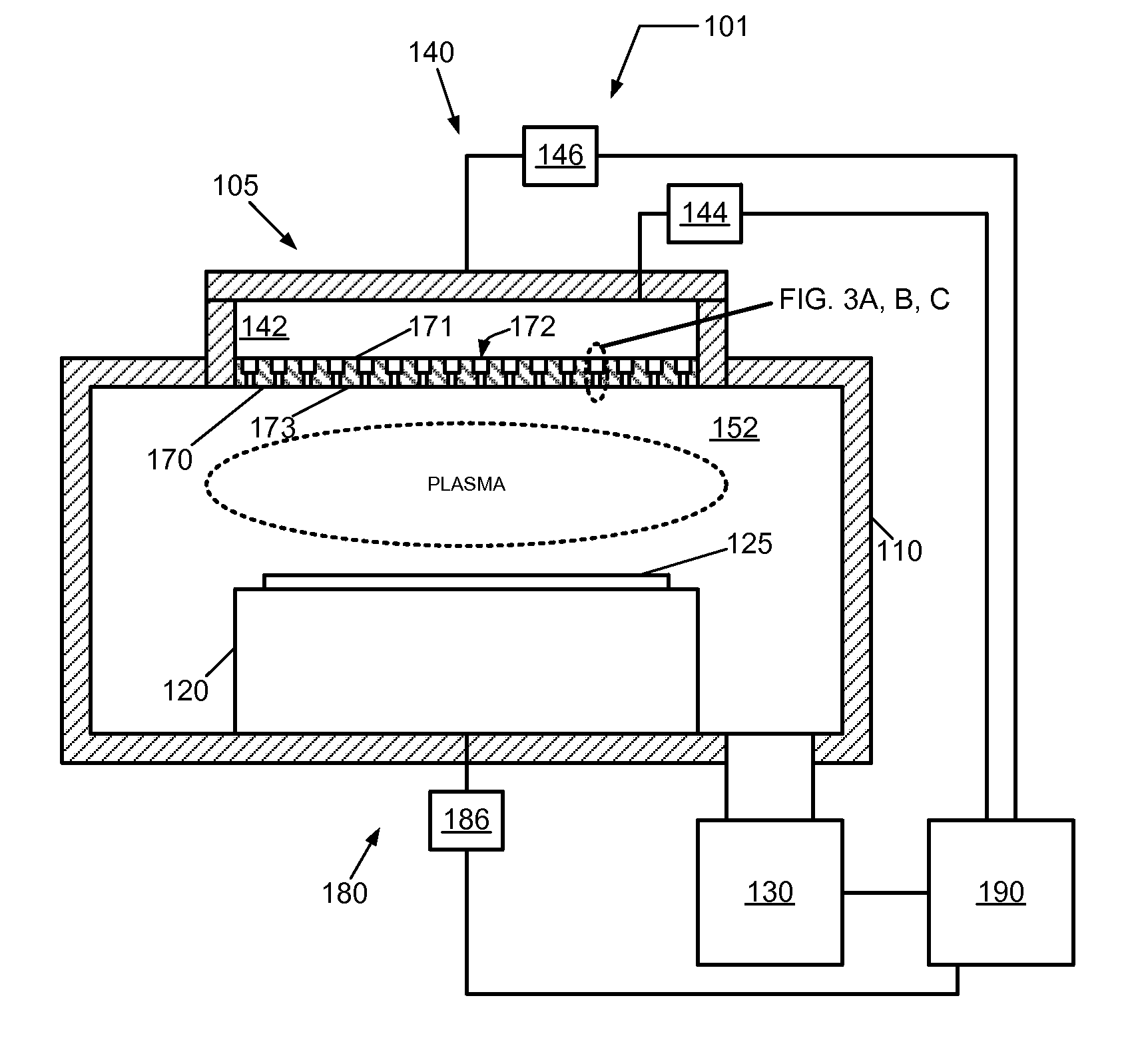
Ion beam apparatus having plasma sheath controller
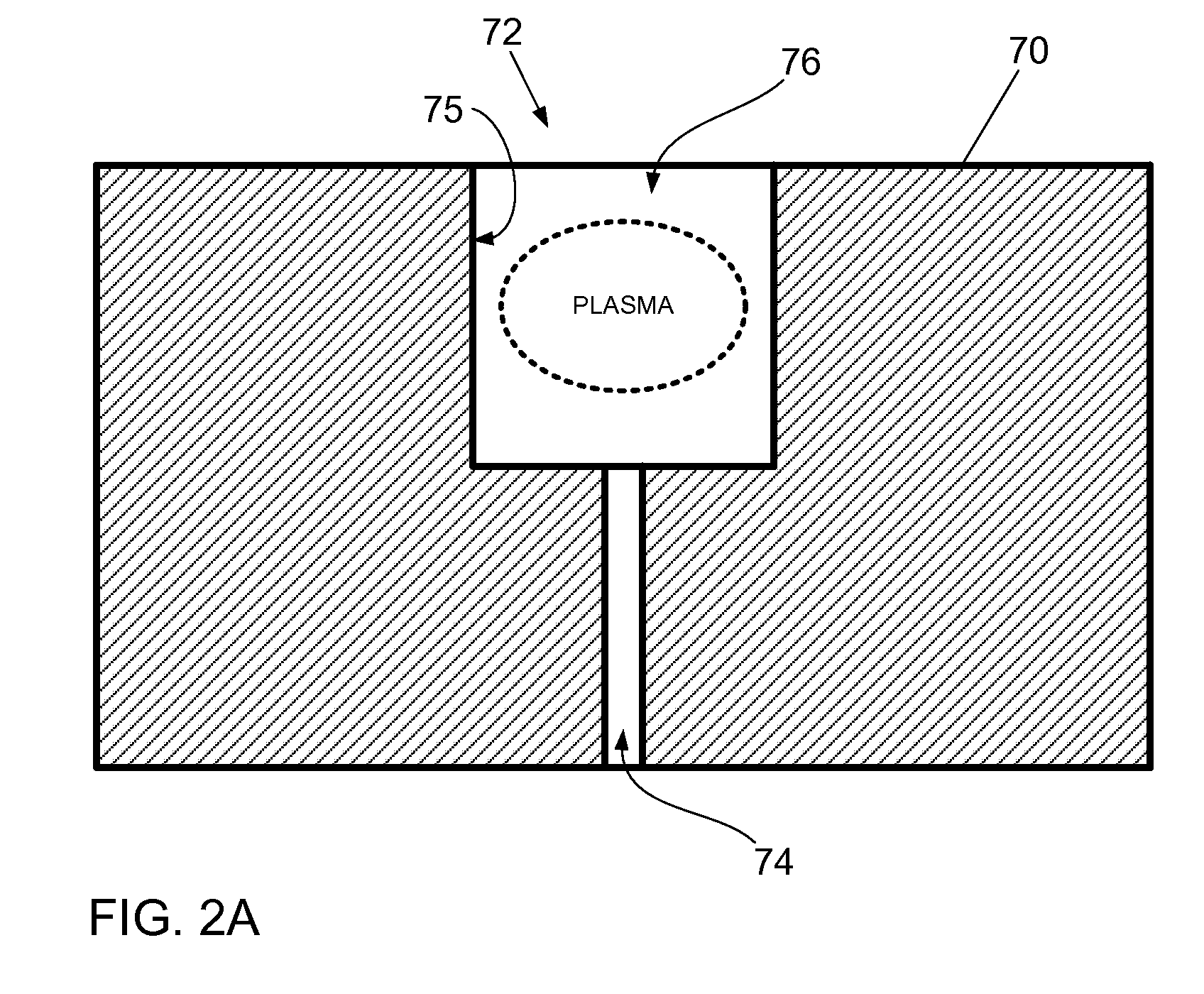
InactiveUS20080179546A1High ion fluxSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectric arc lampsManufactured apparatusIon beam
An ion beam apparatus includes a plasma chamber with a grid assembly installed at one end of the plasma chamber and a plasma sheath controller disposed between the plasma chamber and the grid assembly. The grid assembly includes first ion extraction apertures. The plasma sheath controller includes second ion extraction apertures smaller than the first ion extraction apertures. When the plasma sheath controller is used in this configuration, the surface of the plasma takes on a more planar configuration adjacent the controller so that ions, extracted from the plasma in a perpendicular direction to the plasma surface, pass cleanly through the apertures of the grid assembly rather than collide with the sidewalls of the grid assembly apertures. A semiconductor manufacturing apparatus and method for forming an ion beam are also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Hollow cathode device and method for using the device to control the uniformity of a plasma process
ActiveUS20090218212A1Varies in sizeAdjustable intensityCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesDecorative surface effectsEngineeringCathode
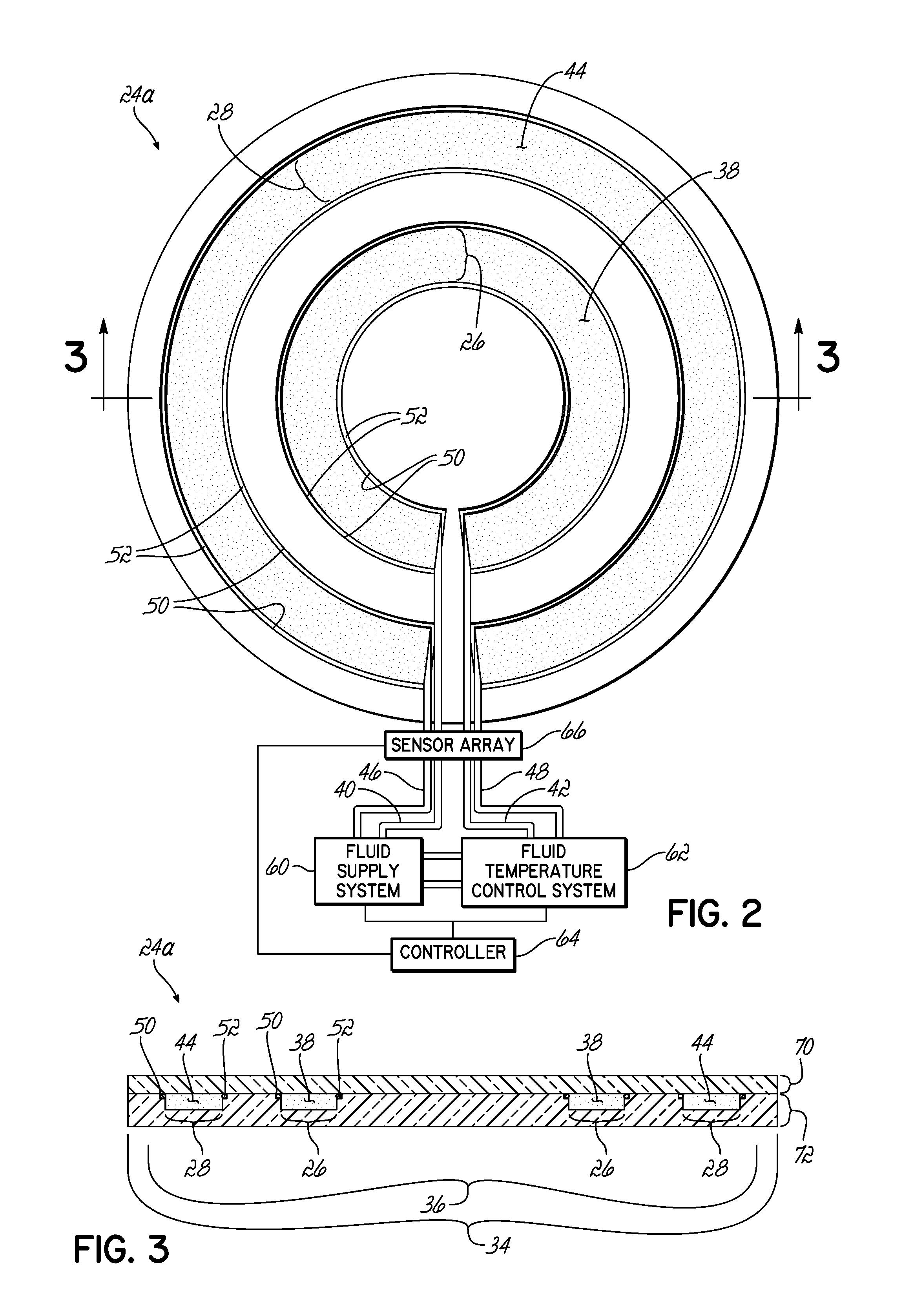
A chamber component configured to be coupled to a processing chamber is described. The chamber component comprises one or more adjustable gas passages through which a process gas is introduced to the process chamber. The adjustable gas passage may be configured to form a hollow cathode that creates a hollow cathode plasma in a hollow cathode region having one or more plasma surfaces in contact with the hollow cathode plasma. Therein, at least one of the one or more plasma surfaces is movable in order to vary the size of the hollow cathode region and adjust the properties of the hollow cathode plasma. Furthermore, one or more adjustable hollow cathodes may be utilized to adjust a plasma process for treating a substrate.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
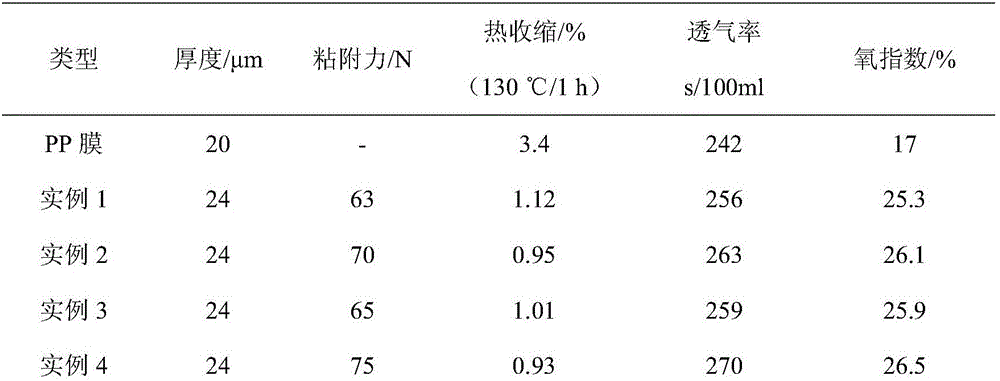
Anti-flaming ceramic modified size and lithium ion battery membrane coated with same
InactiveCN106519742AGood dispersionNot easy to reuniteFireproof paintsCell component detailsPolyolefinCeramic coating
The invention discloses anti-flaming ceramic modified size and a lithium ion battery membrane coated with same. A preparation method of the anti-flaming ceramic modified size comprises the following steps: carrying out surface pretreatment on inorganic particles and a flame retardant by utilizing a silane coupling agent, thus forming anti-flaming ceramic modified powder; then uniformly stirring in a solvent, and carrying out ball milling; sequentially adding a binding agent and a thickening agent, and stirring at high speed, thus forming the anti-flaming ceramic modified size. The lithium ion battery membrane is formed by coating a polyolefin microporous membrane, which is subjected to low-temperature plasma surface modification treatment, with the anti-flaming ceramic modified size. According to the anti-flaming ceramic modified size disclosed by the invention, the problems that a ceramic coating layer is easy to fall off from a membrane and the coating thickness or the surface density is non-uniform are effectively solved; meanwhile, the inorganic particles and the flame retardant in the ceramic coating layer take a synergistic effect, the inorganic particles are used for supporting the lithium ion battery membrane not to shrink when the lithium ion battery membrane is in over-charge heating, and the security of a battery is improved.
Owner:XUCHENG FUJIAN SCI & TECH
Plasma surface treatment using dielectric barrier discharges
A process for the in-flight surface treatment of powders using a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Torch operating at atmospheric pressures or soft vacuum conditions is described herein. The process comprising feeding a powder material into the Dielectric Barrier Discharge Torch yielding powder particles exhibiting a reduced powder agglomeration feature; in-flight modifying the surface properties of the particles; and collecting coated powder particles. An apparatus for surface treating micro- and nanoparticles comprising a Dielectric Barrier Discharge Torch operating at atmospheric pressure or soft vacuum conditions is also described herein.
Owner:TEKNA PLASMA SYST INC
Graphene auxiliary brazing method for ceramic matrix composite material and metal material
ActiveCN103341674AImprove surface conditionReduce residual stressSoldering apparatusGas phaseShielding gas
A graphene auxiliary brazing method for a ceramic matrix composite material and a metal material elates to a brazing method for the ceramic matrix composite material and the metal material and solves the problem that a brazed connector obtained by brazing the ceramic matrix composite material and the metal material is poor in mechanical property. The brazing method comprises the steps of placing the ceramic matrix composite material into plasma reinforcing chemical vapor deposition equipment to carry out plasma surface treatment, adding CH4 gas to regulate flow, opening a radio frequency power supply, regulating the radio frequency to deposit for 10-30min, using Ar and H2 as protection gas, cooling to the room temperature, obtaining the ceramic matrix composite material with graphene growing on the surface, placing Ti brazing filler metal between faces to be connected, placing the Ti brazing filler metal into a vacuum brazing furnace to be brazed, and finally cooling to the room temperature to finish brazing. The shear strength of a connector formed by the ceramic matrix composite material and the metal material in the brazing method can reach to 35Mpa at the room temperature.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Plasma surface modification and passivation of organo-silicate glass films for improved hardmask adhesion and optimal RIE processing
InactiveUS20050067702A1Strong adhesionImprove adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicate glassDevice material
Interconnect structure having enhanced adhesion between the various interfaces encompassing an organo-silicate glass (OSG) film, for use in semiconductor devices is provided herein. The novel interconnect structure includes a non-damaged plasma-treated low-k OSG surface to enhance the adhesion of the hardmask material to the OSG surface, and an unique deposition scheme for the hardmasks in order to make the entire structure pliant towards implementing mild processing condition during the reactive ion etch patterning of the dielectric structure in a damascene and dual-damascene scheme. The methods for making a semiconductor device having an enhanced adhesion and micromasks free profiles are also provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
Plasma modified medical devices and methods
InactiveUS20130046375A1Increased apoptosisGood biocompatibilitySurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismActive agentThrombus
Coatings, devices and methods are provided, wherein the contacting surface of a medical device with at least one contacting surface for contacting a bodily fluid or tissue, wherein long-lasting and durable bioactive agents or functional groups are deposited on the contacting surface through a unique two-step plasma coating process with deposition of a thin layer of plasma coating using a silicon-containing monomer in the first step and plasma surface modification using a mixture of nitrogen-containing molecules and oxygen-containing molecules in the second step. The two-step plasma coating process enables the implantable medical device to prevent both restenosis and thrombosis under clinical conditions. The invention also relates to surface treatment of metallic and polymeric biomaterials used for making of medical devices with significantly improved clinical performance and durability.
Owner:CHEN MENG
Surface wave plasma processing system and method of using
InactiveUS20060071607A1Reduce harmReduce the possibility of damageElectric discharge tubesElectric arc lampsPower couplingEnergy coupling
A SWP source includes an electromagnetic (EM) wave launcher configured to couple EM energy in a desired EM wave mode to a plasma by generating a surface wave on a plasma surface of the EM wave launcher adjacent the plasma. A power coupling system is coupled to the EM wave launcher and configured to provide the EM energy to the EM wave launcher for forming the plasma. A cover plate coupled to the plasma surface of the EM wave launcher protects the EM wave launcher from the plasma.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
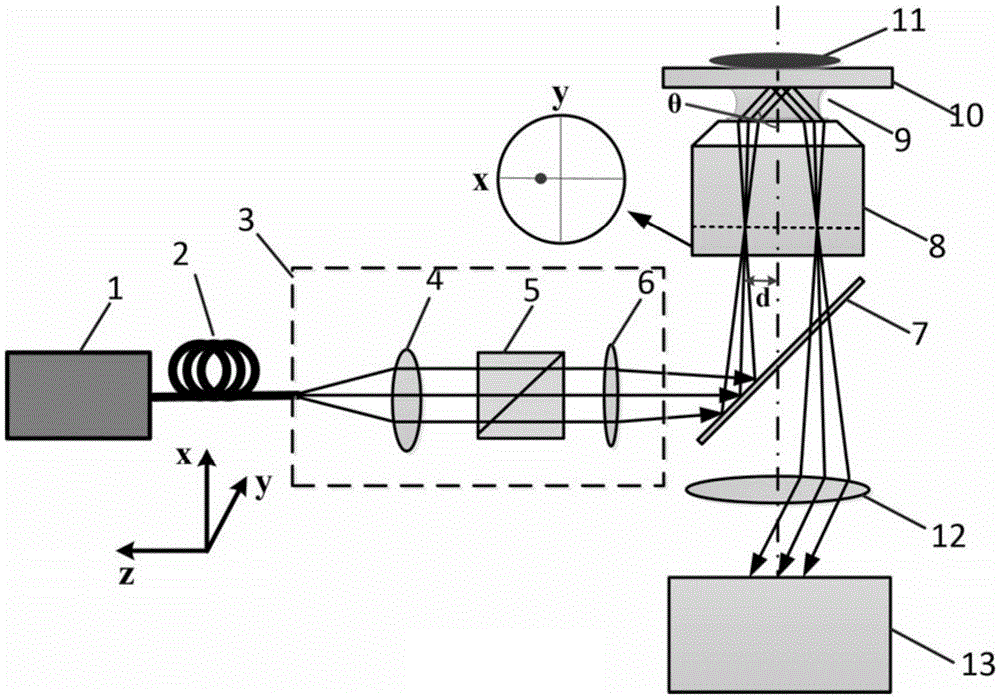
Optical microscope based on surface plasma resonance
ActiveCN105628655AHigh resolutionHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splitterFluorescence
The invention discloses an optical microscope based on surface plasma resonance. The optical microscope comprises a laser generator, an incident angle adjusting module, a beam splitter, an optical microscopic amplification objective lens and a plasma resonance sensing chip all of which are arranged along a light path in sequence, and further comprises an image sensor. The incident angle adjusting module comprises a polarizing film used for transforming incident light into polarized light p. The incident light of the laser generator is incident on the plasma resonance sensing chip through the incident light adjusting module, the beam splitter and the optical microscope amplification objective lens at the surface plasma resonance angle theta to stimulate plasma surface resonance on the plasma resonance sensing chip, and the reflected light on the plasma resonance sensing chip is incident on the imaging sensor in an imaging mode through the optical microscope amplification objective lens and the beam splitter. The optical microscope has the advantages of being high in resolution ratio and free of fluorescence labeling.
Owner:WENZHOU INST OF BIOMATERIALS & ENG
Hydrophilization modification method of polyolefin hollow fiber ultrafiltration membrane
ActiveCN104248913AModification is stable and reliableAvoid structural impactSemi-permeable membranesFiberPolyolefin
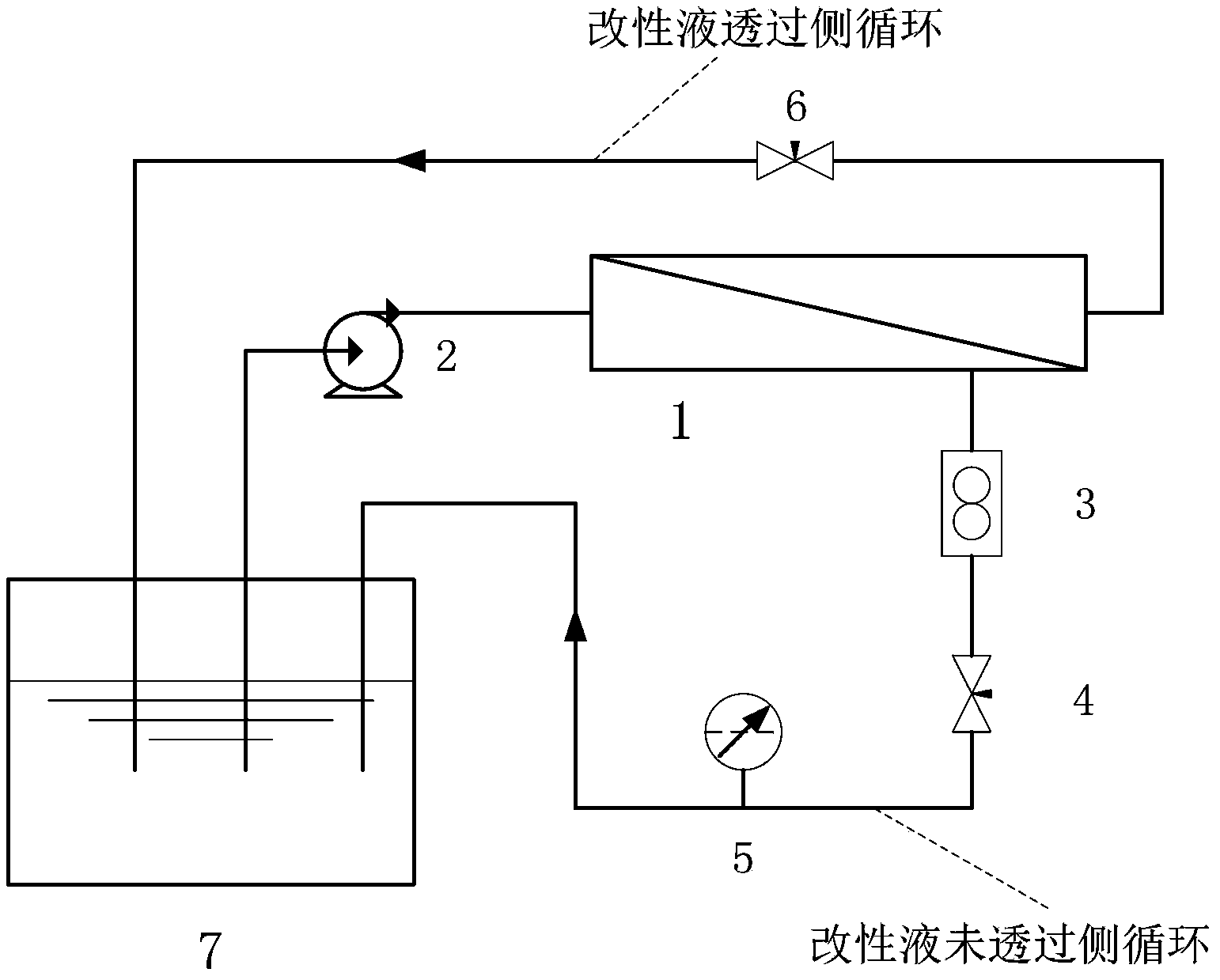
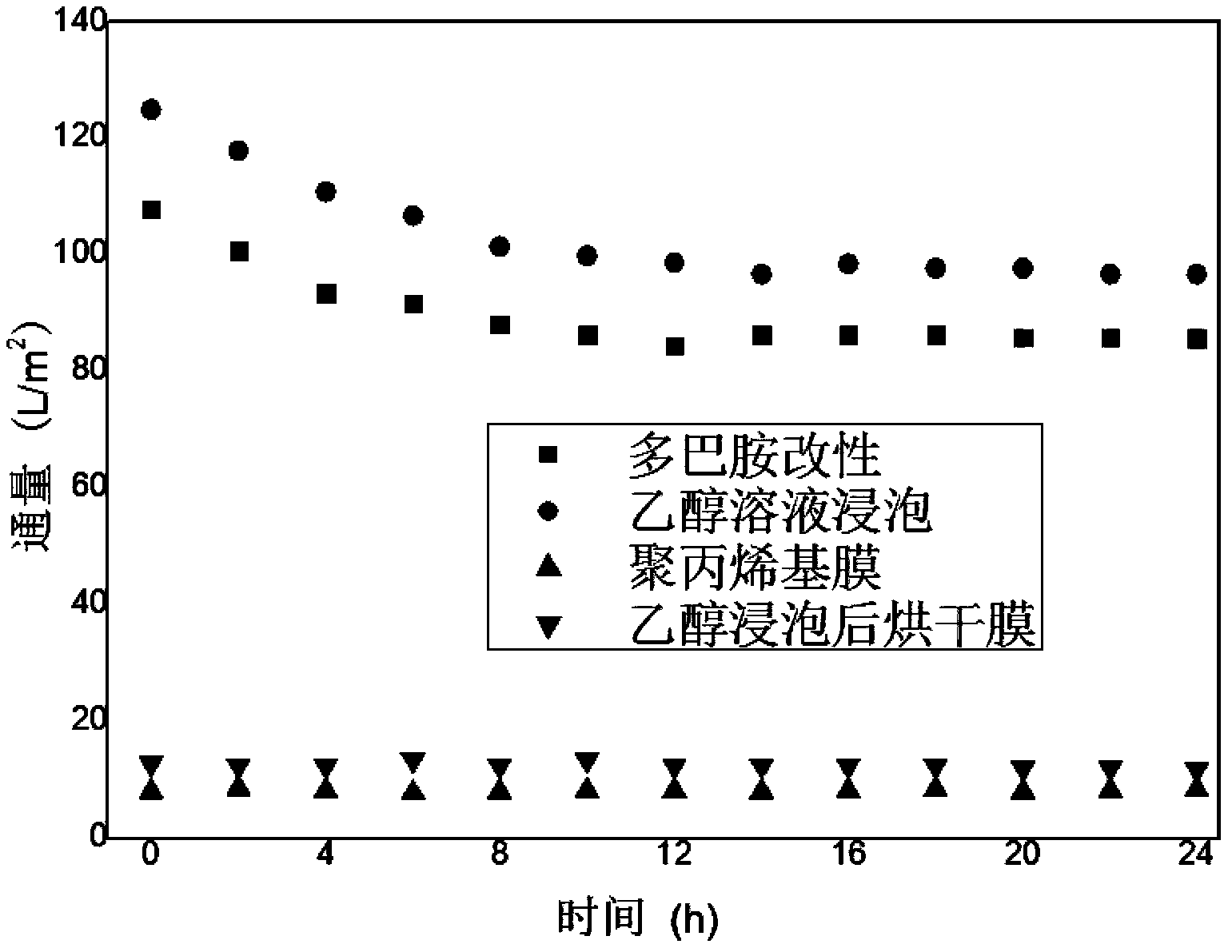
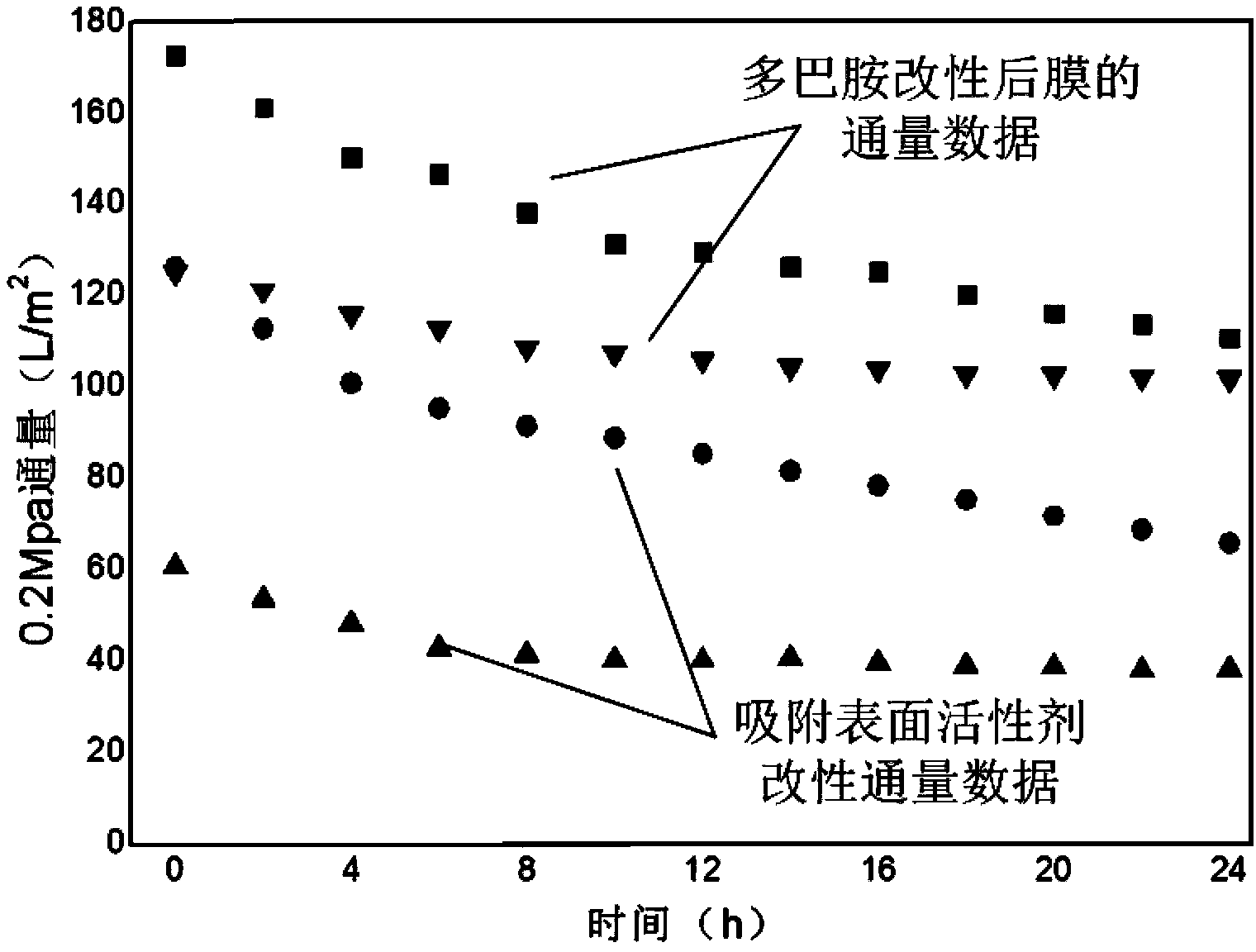
The invention relates to a hydrophilization modification method of a polyolefin hollow fiber ultrafiltration membrane, especially relates to a method using dopamine or dopamine derivatives for forming a hydrophilic modification layer on the polyolefin hollow fiber ultrafiltration membrane surface and in membrane holes. The method avoids the influence of polyolefin material structure, can effectively maintain the structural and mechanical properties of the polyolefin membrane, and overcomes the shortcomings that modification in the membrane holes cannot be achieved by irradiation grafting and plasma surface grafting technology. According to the method, an ultrathin poly dopamine or dopamine derivative hydrophilic modification layer prepared by the method can be combined firmly with a polyolefin hollow fiber ultrafiltration membrane material may not be lost in the use process, the modified membrane is stable and reliable in properties, and has good application prospects in water treatment, petrochemical, pharmaceutical, biological, energy and other areas.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Normal-pressure low-temperature plasma preprocessing technique of textile for digital inking printing
InactiveCN101100808AImprove clarityImprove color vibrancyUltrasonic/sonic fibre treatmentDyeing processEngineeringPre treatment
The invention relates to fabric plasma surface modification processing technology used in dye ink digital inking printing. The fabric is processed inking printing by dye ink in the digital inking printing machine after processing by impulse normal pressure air low temperature plasma, then baking to form the finished product. Compared with the traditional preprocessing technology, the invention has the advantages of fast, convenient, saving water and energy, low cost, no social effects of pollution, suiting for industrialization continuous production etc.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Titanium alloy surface high temperature oxidation resistance and wear resistance oxide gradient coat, and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102732832ADense tissueSolve the problem of poor high temperature oxidation resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAntioxidant capacityCoated surface
The invention relates to a titanium alloy surface high temperature oxidation resistance and wear resistance oxide gradient coat. According to the coat, the surface of the coat is an oxide film layer comprising Al2O3, Cr2O3 and NiO2, wherein the thickness is 4-6 mum; the middle of the coat is an Al-Cr-Ni alloy layer, wherein the thickness is 2-4 mum; and an Al-Cr-Ni-Ti interdiffusion layer is arranged between the coat and a substrate to achieve metallurgical collection, wherein the thickness of the Al-Cr-Ni-Ti interdiffusion layer is 4-6 mum. According to the present invention, the oxide film layer on the surface of the coat has characteristics of compactness, flatness and strong antioxidant capacity; the Al-Cr-Ni alloy layer in the middle of the coat has characteristics of compact structure and high hardness so as to greatly improve wear resistance of the titanium alloy; the metallurgical collection of the coat and the substrate is achieved through the Al-Cr-Ni-Ti interdiffusion layer, and the combination strength is high; and a double glow plasma surface metallurgy technology is adopted to prepare the Al-Cr-Ni alloy layer on the surface of the titanium alloy, and then a plasma oxygen permeation treatment is performed on the Al-Cr-Ni alloy layer to prepare the high temperature oxidation resistance and wear resistance coat, such that the efficiency is high, and the process is simple.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for enhancing capsule wall toughness of self-repairing microcapsules, and self-repairing microcapsules prepared by the same
ActiveCN102728288AImprove efficiencyNo pollution in the processMicroballoon preparationMicrocapsule preparationPolymer scienceEmulsion
The present invention provides a method for enhancing mechanical toughness of a capsule wall of a self-repairing microcapsule. The method comprises: 1, adopting a plasma surface modification method to carry out modification on a carbon material to obtain a functional filler; 2, preparing a wall material prepolymer solution for forming the capsule wall of the self-repairing microcapsule, and adding the functional filler obtained from the step 1 to the prepolymer solution; 3, preparing an O / W type emulsion for forming a capsule core material of the self-repairing microcapsule; 4, mixing the prepolymer solution from the step 2 and the O / W type emulsion from the step 3, and carrying out condensation polymerization to obtain a microcapsule suspension; 5, carrying out centrifugating, washing, and vacuum drying to obtain the microcapsule. According to the self-repairing microcapsules prepared by the method of the prevent invention, the mechanical toughness of the capsule wall is improved, such that the problem of microcapsule breaking easily caused by the stirring process during the intelligent anticorrosive coating preparation process can be overcome.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Method for modifying ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber by plasma treatment
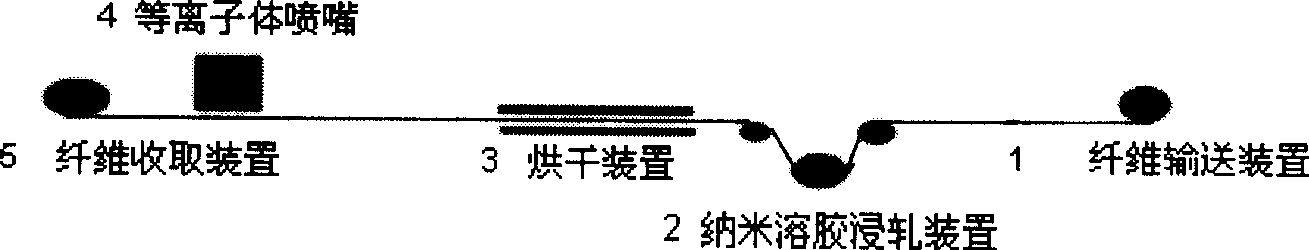
InactiveCN101532244AIncrease infiltration speedImprove wettabilityPhysical treatmentFibre typesFiberPlasma generator
The invention relates to a method for modifying ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber by plasma treatment. The method comprises that: (1) a nanometer particle of silicon dioxide is prepared into an organic solvent or water solution of sol of which the mass percent is 0.01 to 15 percent, by an ultrasonic shock technique; or (2) a precursor solution of the organic-inorganic nanometer particle is subjected to hybridization reaction with the nanometer particle of silicon dioxide to prepare the nanometer silicon dioxide sol solution; (3) the sol solution is coated on the surface of the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber by spraying or padding; and (4) the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber is dried at a temperature of 10 to 150 DEG C, and the solvent is collected; and the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber is introduced in a plasma atmosphere region by a plasma generator for plasma surface modification. The compound property between the treated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber and the organic matrix materials is greatly improved; moreover, the method also has the advantages of simple process, good treatment effect, low cost, environmental protection and low energy consumption.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Method for surface treatment of metal alloy
ActiveCN102181861AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove the decorative effectVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingMetal alloyCopper
The invention relates to a method for surface treatment of a metal alloy. The method comprises the following steps of: performing oil removal and normal pressure plasma surface activation on the surface of the metal alloy, wherein the metal alloy is magnesium alloy or aluminum alloy; spraying a layer of powder coating on the surface of the metal alloy after pretreatment; after performing electrostatic powder coating on the surface of the metal alloy, putting the metal alloy into a physical vapor deposition (PVD) physical deposition furnace to perform plasma glow activation, and then physically depositing a layer of metallic copper film by adopting PVD; and after physically depositing the layer of the metallic copper film by adopting the PVD, performing electro-coppering, electro-nickelling and electro-chromeplating in turn on the metal alloy to form three metal coatings. According to the method, the metal alloy has excellent corrosion resistance and good decorative effect, and simultaneously meets the requirements on high performance and highly-attractive appearance of magnesium alloy or aluminum alloy products in the industries of bathroom, household electrical appliances, automobiles, electron and the like. After the surface treatment, the CASS corrosion resisting time of the magnesium alloy and the aluminum alloy is 24 hours.
Owner:XIAMEN RUNNER IND CORP
Method for manufacturing stamper, stamper and optical recording medium
InactiveUS20050045481A1Reduce defectsEasy to separateRecord carriersRecord information storageOptical recordingNickel
When producing a second stamper by forming a nickel electroformed film on a father stamper having patterns of pits and lands, defects appear on the second stamper during the stage of separating the second stamper from the father stamper. The object of the present invention is to decrease these defects. A method for manufacturing a stamper comprises performing a plasma surface treatment on a surface of a father stamper 106 having patterns of pits and lands, forming a nickel electroformed film (II) 107 on the surface of the father stamper 106, and separating the nickel electroformed film (II) 107 from the father stamper 106 so as to form a mother stamper 108.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Plasma CVD apparatus and plasma surface treatment method
InactiveUS20070074664A1Low process temperatureQuick changeElectric discharge tubesChemical vapor deposition coatingCarbon nanowallsOptoelectronics
A substrate is mounted on a mount surface of an anode in a chamber. A flow path is formed in a cathode facing the anode, and cooling water is circulated therethrough. A voltage is applied across the anode and the cathode to form a layer of carbon nanowall on the substrate by plasma, and thereafter the anode is cooled by a cooling member to rapidly cool the substrate to a predetermined temperature.
Owner:KOICHI IND PROMOTION CENT +1
Method for modifying nanometer sol ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber by plasma treatment
InactiveCN101532239AImprove permeabilityHigh chemical activityPhysical treatmentFibre typesFiberTherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a method for modifying a nanometer sol ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber by plasma treatment. The method comprises that: (1) inorganic nanometer particle is prepared into a sol solution by an ultrasonic shock technique; or (2) a precursor solution of the organic-inorganic nanometer particle is subjected to hybridization reaction with the inorganic nanometer particle to prepare the sol solution; (3) the sol solution is coated on the surface of the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber; and (4) the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber is dried at a temperature of 10 and 150 DEG C, and the solvent is collected; the ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber is introduced in a plasma atmosphere region by a plasma generator for plasma surface modification; and the treated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber is on-line rolled by an automatic rolling machine. The compound property between the treated ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fiber and the organic matrix materials is greatly improved; moreover, the method also has the advantages of simple process, good treatment effect, low cost, environmental protection and low energy consumption.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Surface treatment method for improving corrosion stability of magnesium alloy
The invention provides a method of handling electron surface to increase its corrosion resistance, which is characterized in that electron surface is processed with catelectrode cataphoretic coating treatment or plasma surface treatment before cataphoretic coating treatment. In the invention, catelectrode cataphoretic coating treatment provides an antiabrasion layer for electron surface to increase its corrosion resistance, while plasma surface treatment before cataphoretic coating treatment can increase adhesive force of cataphoretic coating on surface. The invention has the advantages of simple process, convenient application, and low cost and notable effect.
Owner:重庆工学院
Metal inner surface modification device and method
InactiveCN103320772AAchieve chemical permeationImprove surface modification efficiencySolid state diffusion coatingChemical vapor deposition coatingDiamond-like carbonNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a metal inner surface modification device and method and belongs to the technical field of plasma surface modification. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: generating plasmas on a metal inner surface by utilizing the principle of hollow-cathode discharge, and nitriding or depositing diamond like carbon, so as to improve the hardness, the wear resistance and the corrosion resistance of the metal inner surface; by taking a treated piece as a cathode, arranging the cathode inside, adjusting the distance and the vacuum degree between a workpiece and the cathode to reach the discharge condition, arranging an anode at the periphery of a cathode cavity, and adding a direct current pulse power supply between the anode and the cathode, wherein reaction gas is nitrogen or ammonia gas and carrier gas is argon gas during the nitriding, and the reaction gas is methane or acetylene and the carrier gas is argon gas in the process of depositing a hard carbon film. The method has the effects and advantages of simple process, low cost and high efficiency and is particularly suitable for treating the metal inner surface and pipe fittings of large draw ratios.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com