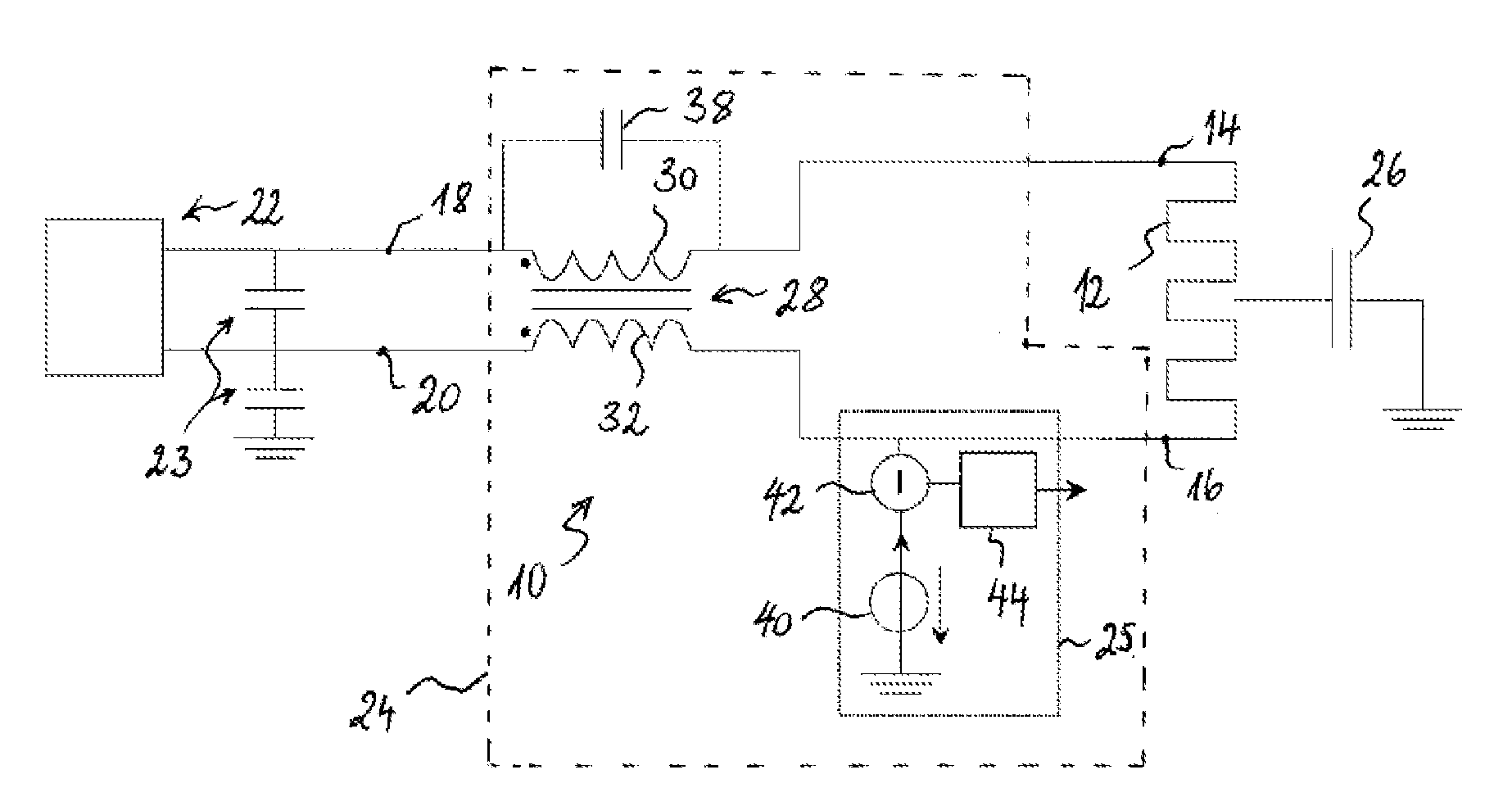
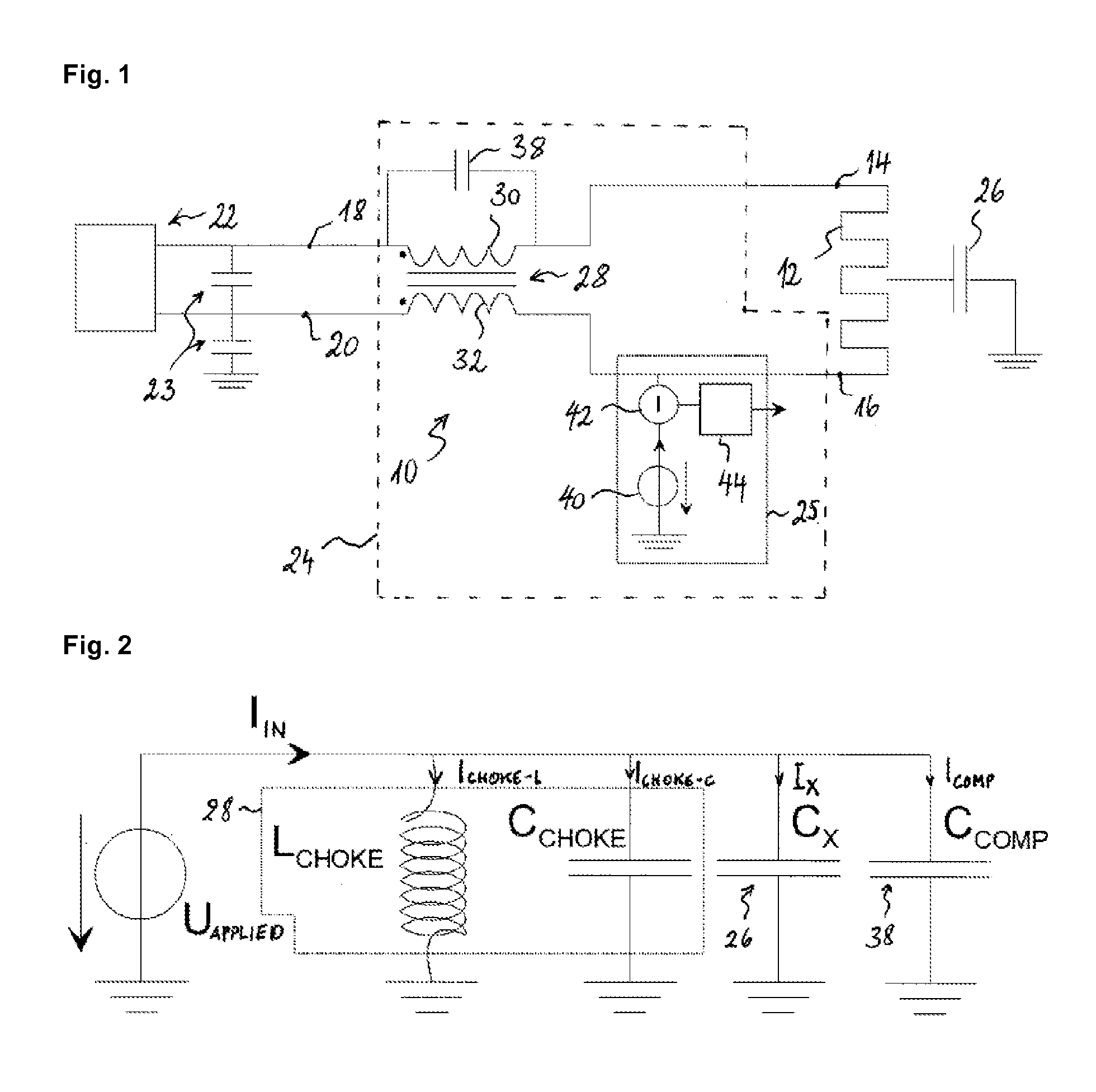
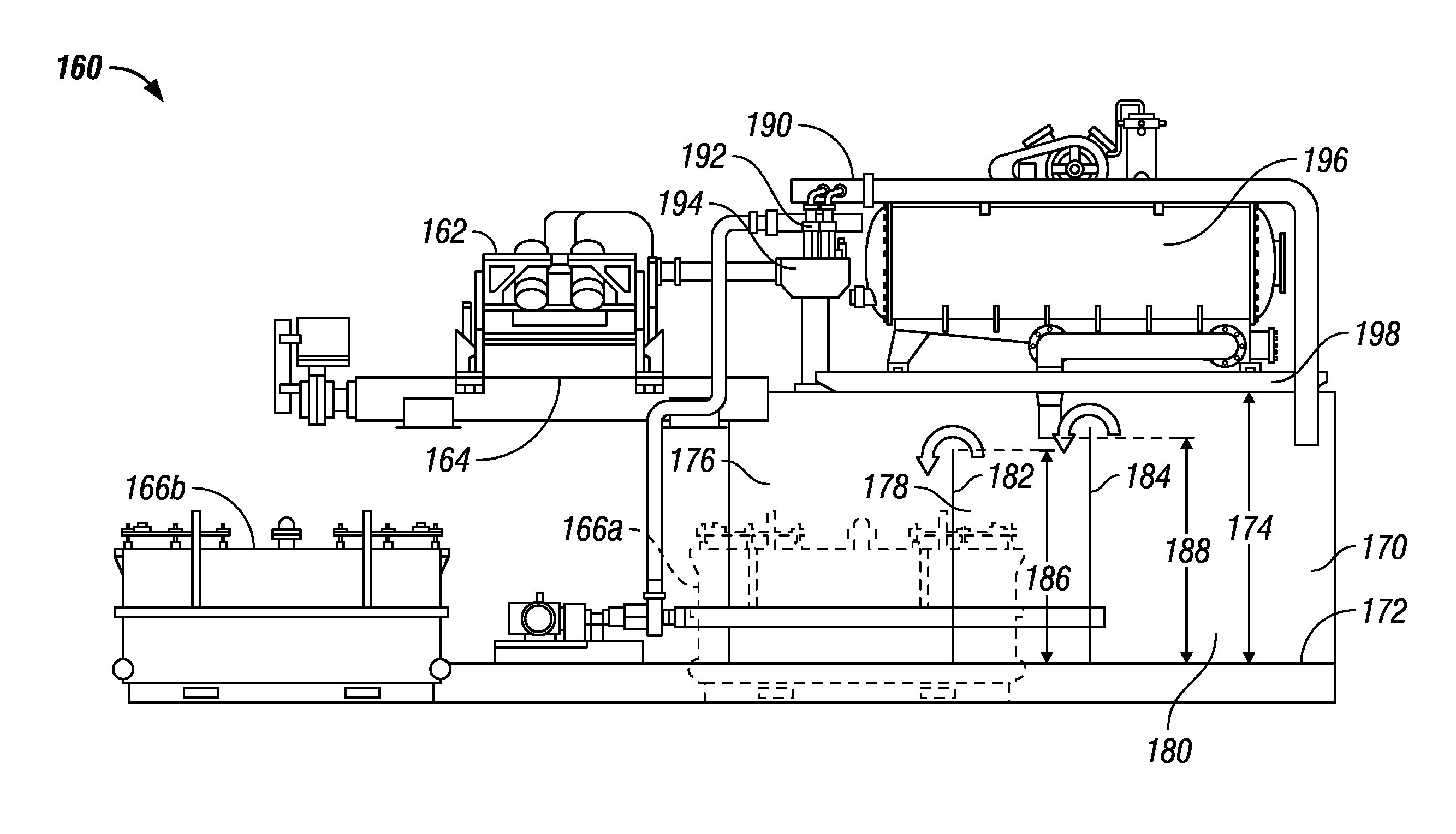
Patents
Literature
1274 results about "The chokes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The 'chokes' Sudden onset of respiratory distress in caisson's disease, which is associated with pulmonary edema, hemorrhage, atelectasis, and emphysema; the 'chokes' may be due to an ↑ in platelet adhesion to gas bubbles that release vasoconstrictors, platelet factor 3, causing coagulopathy.
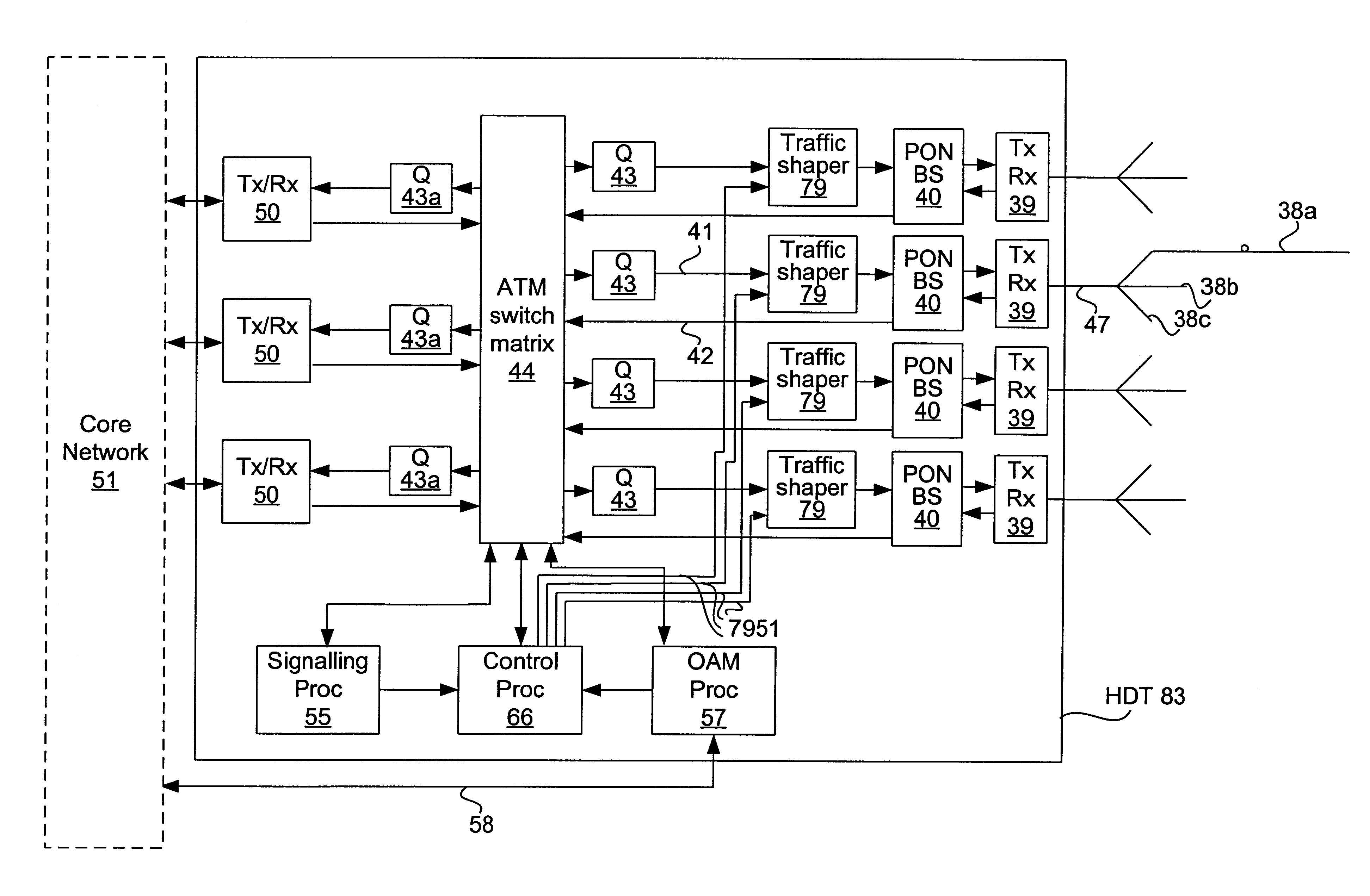
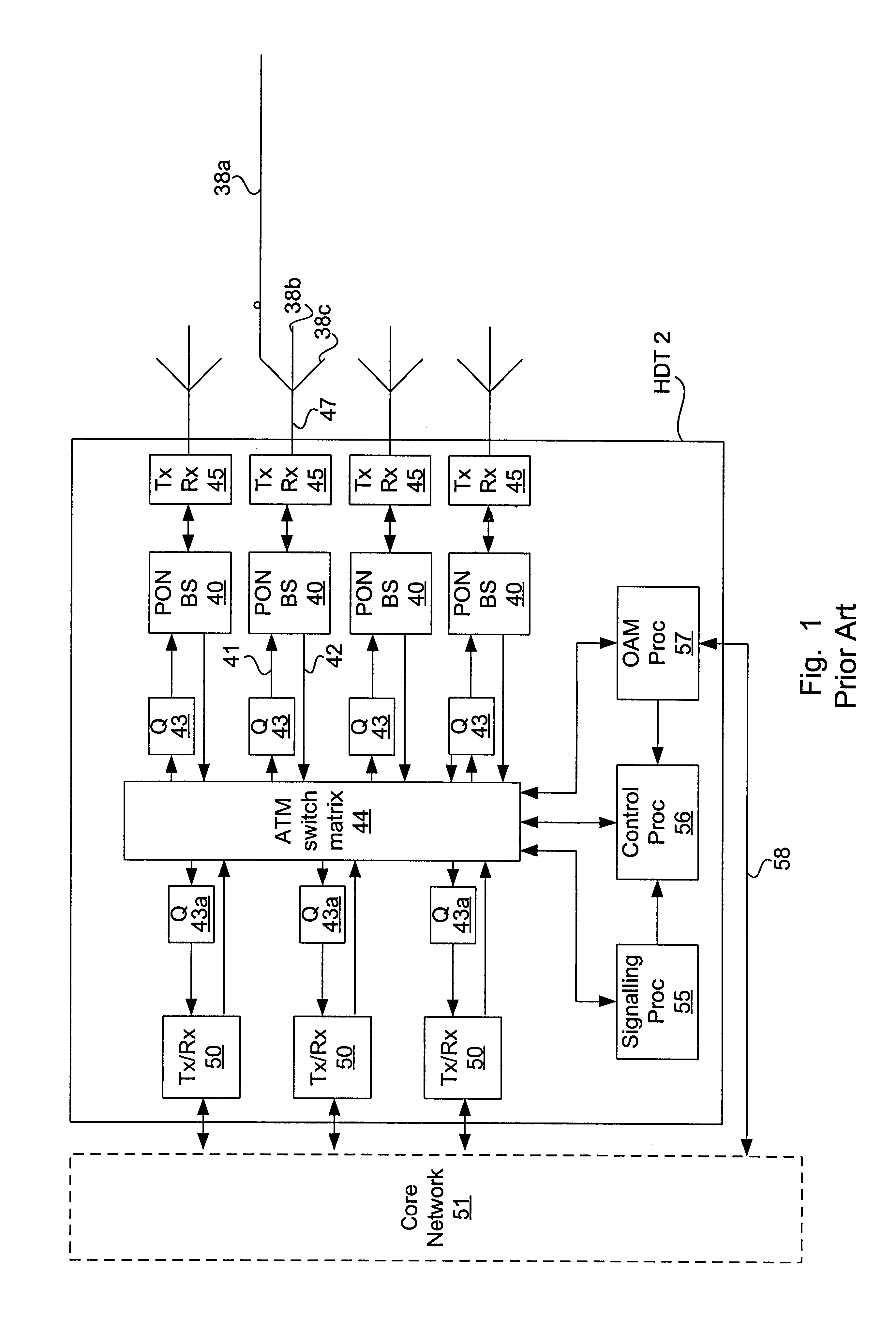
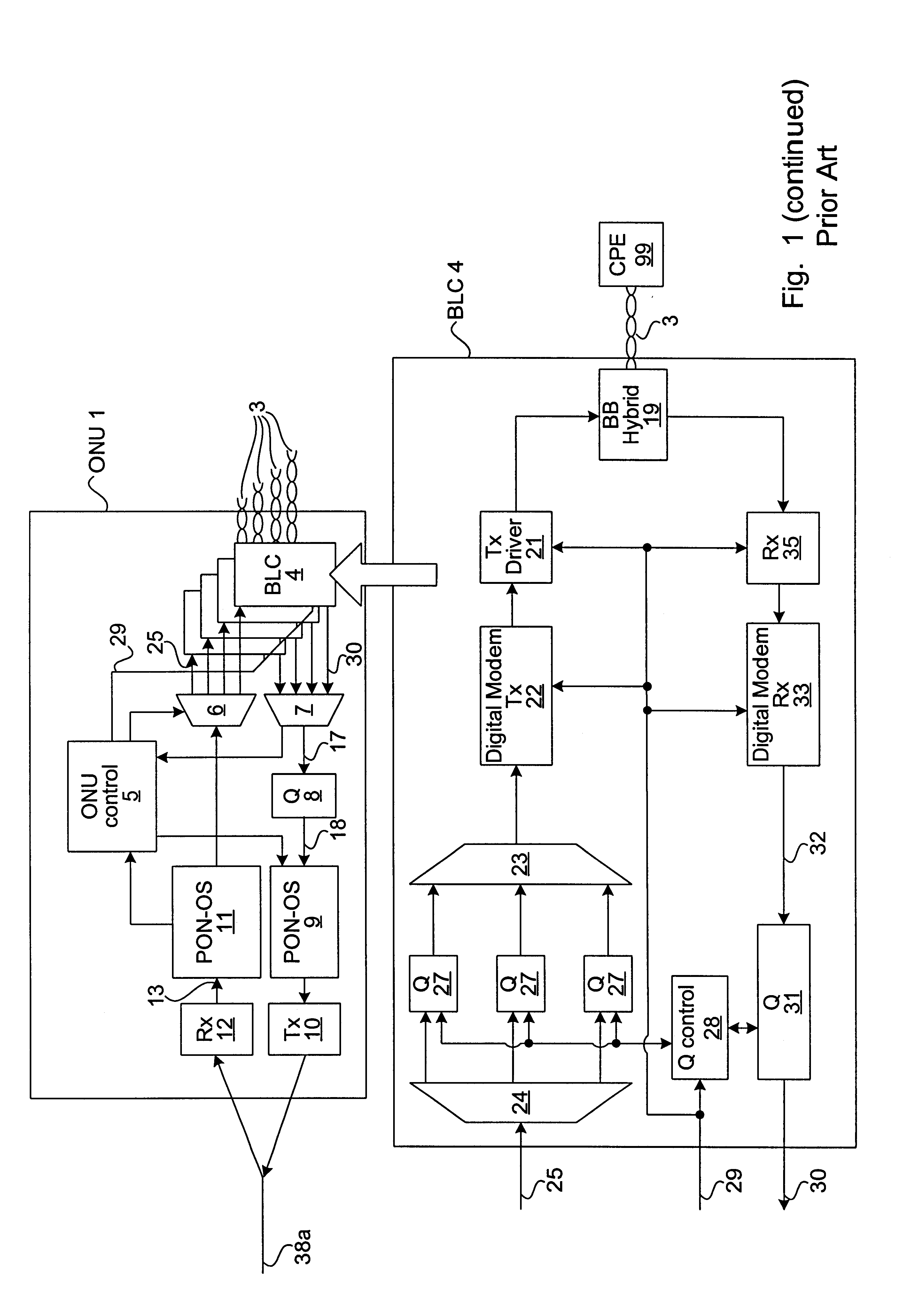
Method and apparatus for traffic shaping in a broadband fiber-based access system
InactiveUS6229788B1Increased complexityIncrease costError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFiberTraffic capacity
The invention is a novel method and apparatus for controlling the flow of traffic between a host digital terminal (HDT) and a plurality of optical network units (ONUs). Each ONU is connected to the HDT by optical fiber and to a plurality of subscribers by a respective plurality of subscriber drops (typically pre-existing copper twisted pairs). The bandwidth on the fiber, although large, is usually inferior to the total bandwidth that can be transmitted across the subscriber drops. Therefore, both upstream and downstream traffic may become congested at various "choke points" under certain circumstances of usage. Ordinarily, the data is buffered at the choke points, leading to the installation of large queues within each ONU. This solution is not only expensive, but is inadequate since the required queue size is dependent on the maximum transaction size, which has no hard upper bound. In contrast, the present invention provides a traffic shaper located in the HDT, which gives centralized control of the traffic flowing to and from the ONUs. Consideration of the priority and destination of each traffic cell is taken into account by the traffic shaper to ensure that the capacity of the fiber and of the individual drops is never exceeded, irrespective of the transaction sizes, thereby eliminating the need for costly buffers in the outside plant. Any maintenance or repairs of the traffic shaper can be easily effected without field visits, due to its centralized location.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
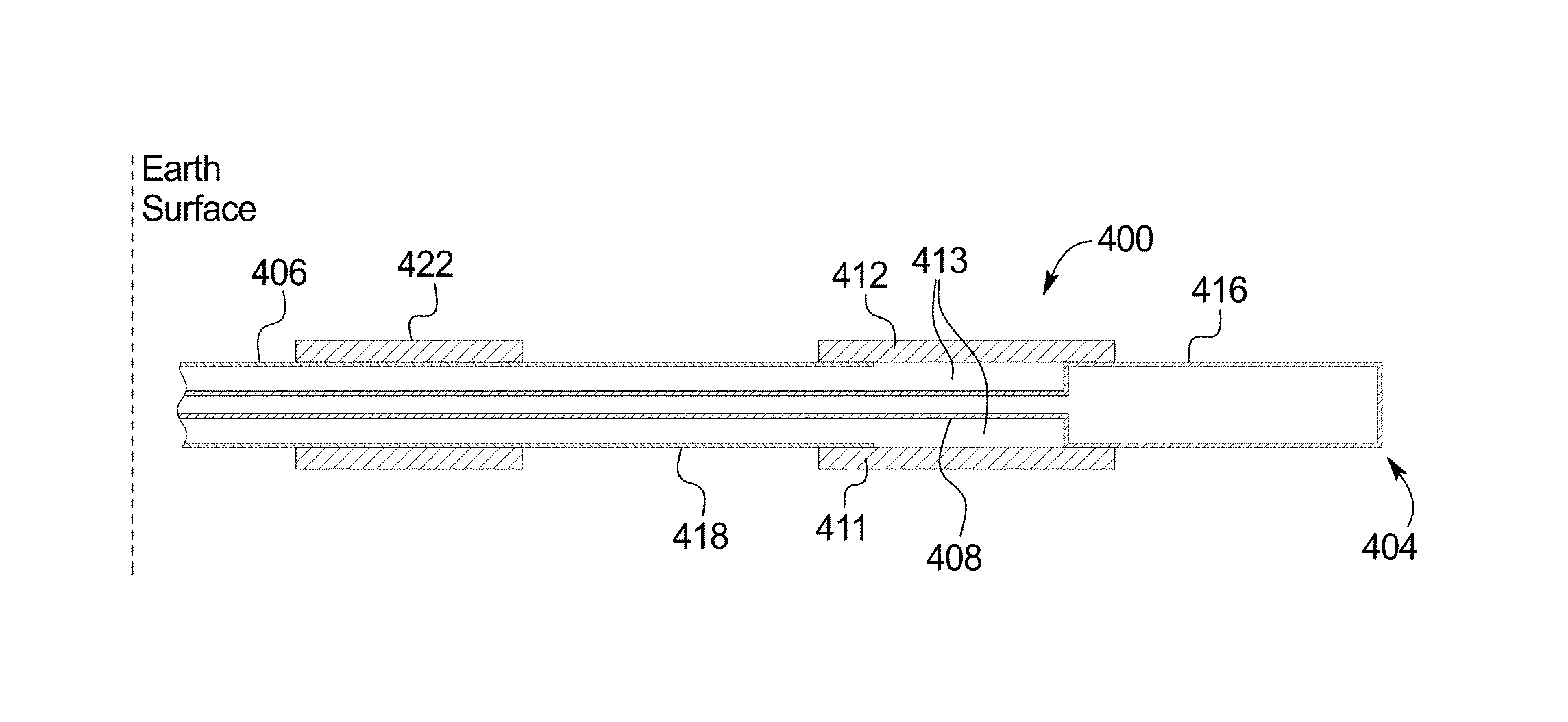
Stimulating production from oil wells using an RF dipole antenna
ActiveUS20140152312A1Reduced effectivenessLow thermal conductivityFluid removalDetection using electromagnetic wavesRf fieldElectrical conductor
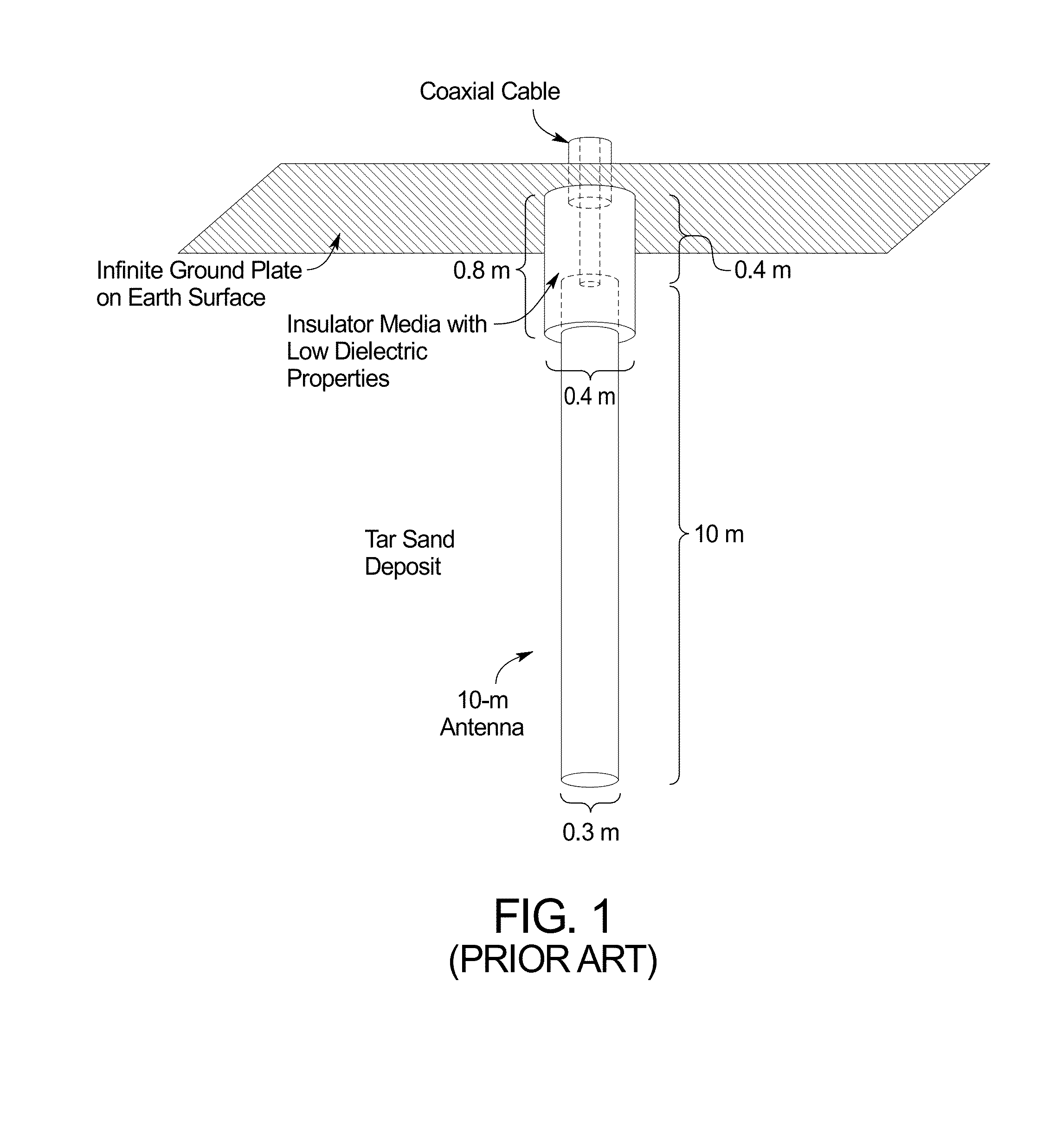
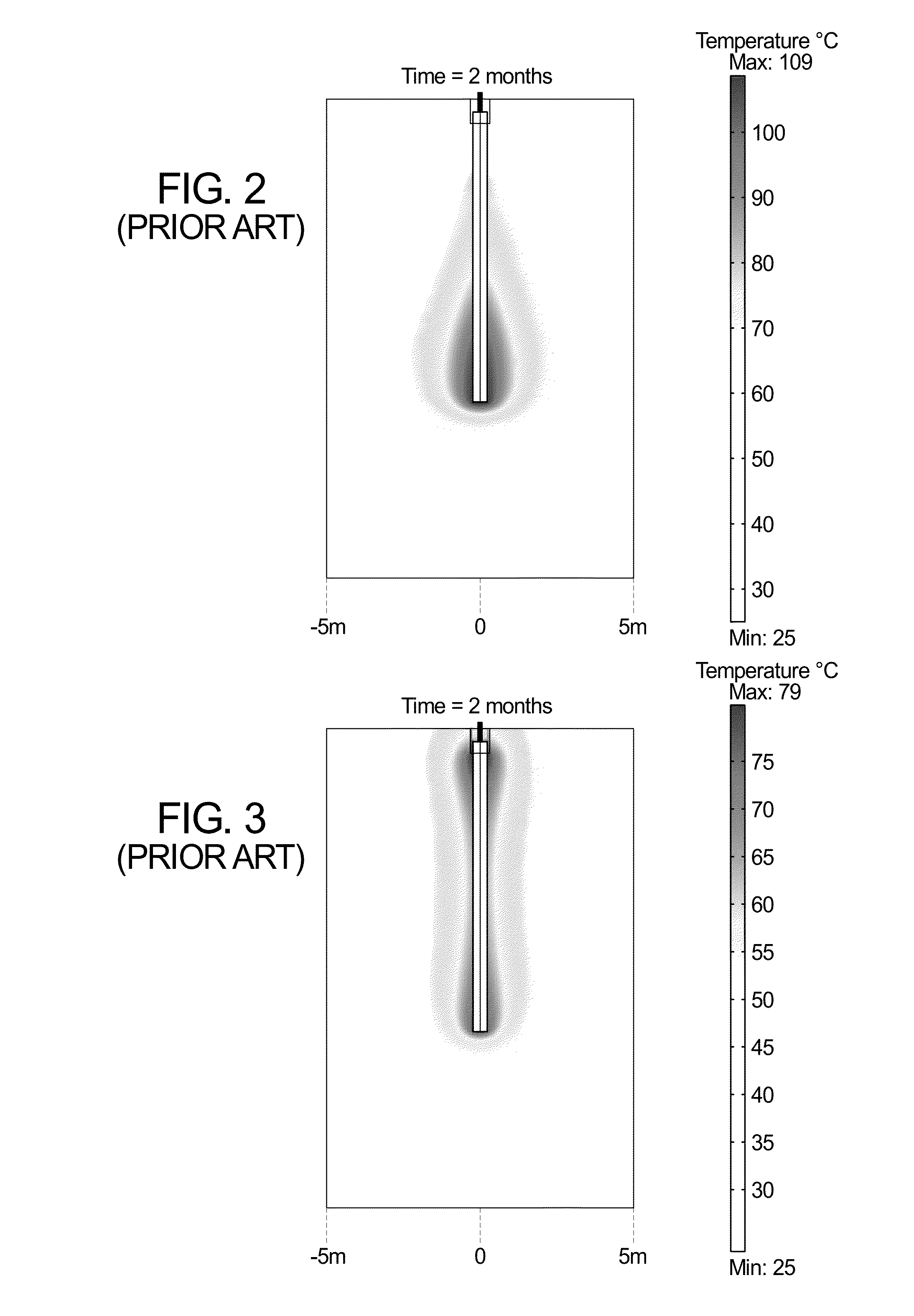
A system emplaced in a subsurface formation configured to produce radio frequency (RF) fields for recovery of thermally responsive constituents includes coaxially disposed inner and outer conductors connected at an earth surface to an RF power source. The inner and outer conductors form a coaxial transmission line proximate said earth surface and a dipole antenna proximate said formation. The inner conductor protrudes from the outer conductor from a junction exposing a gap between the conductors to a deeper position within the formation. The RF power source is configured to deliver, via the conductors, RF fields to the formation. The system also includes at least one choke structure attached to said outer conductor at a distance at least ¼ wavelength above said junction. The choke structure is configured to confine a majority of said RF fields in a volume of said formation situated adjacent to said antenna.
Owner:PYROPHASE INC
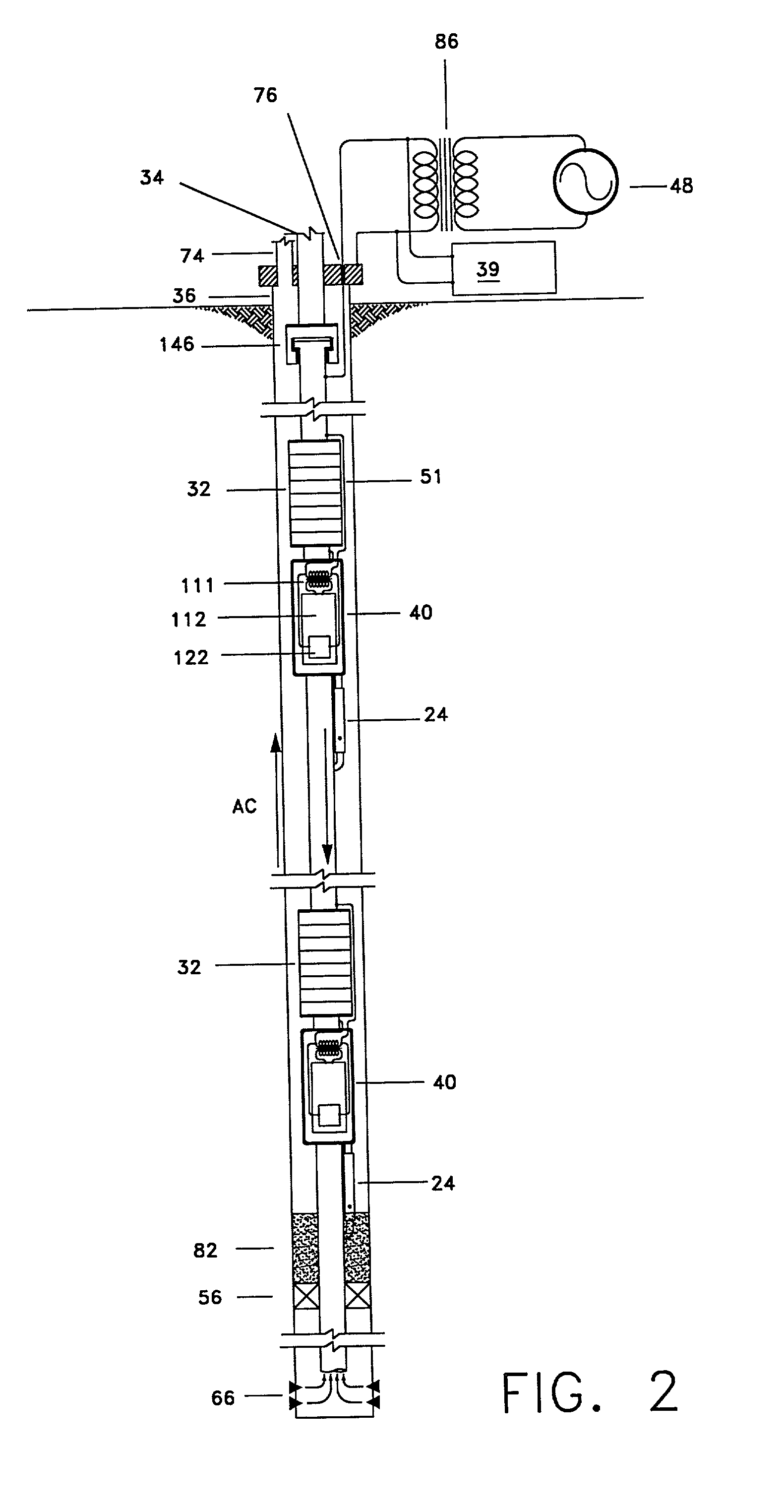
Toroidal choke inductor for wireless communication and control
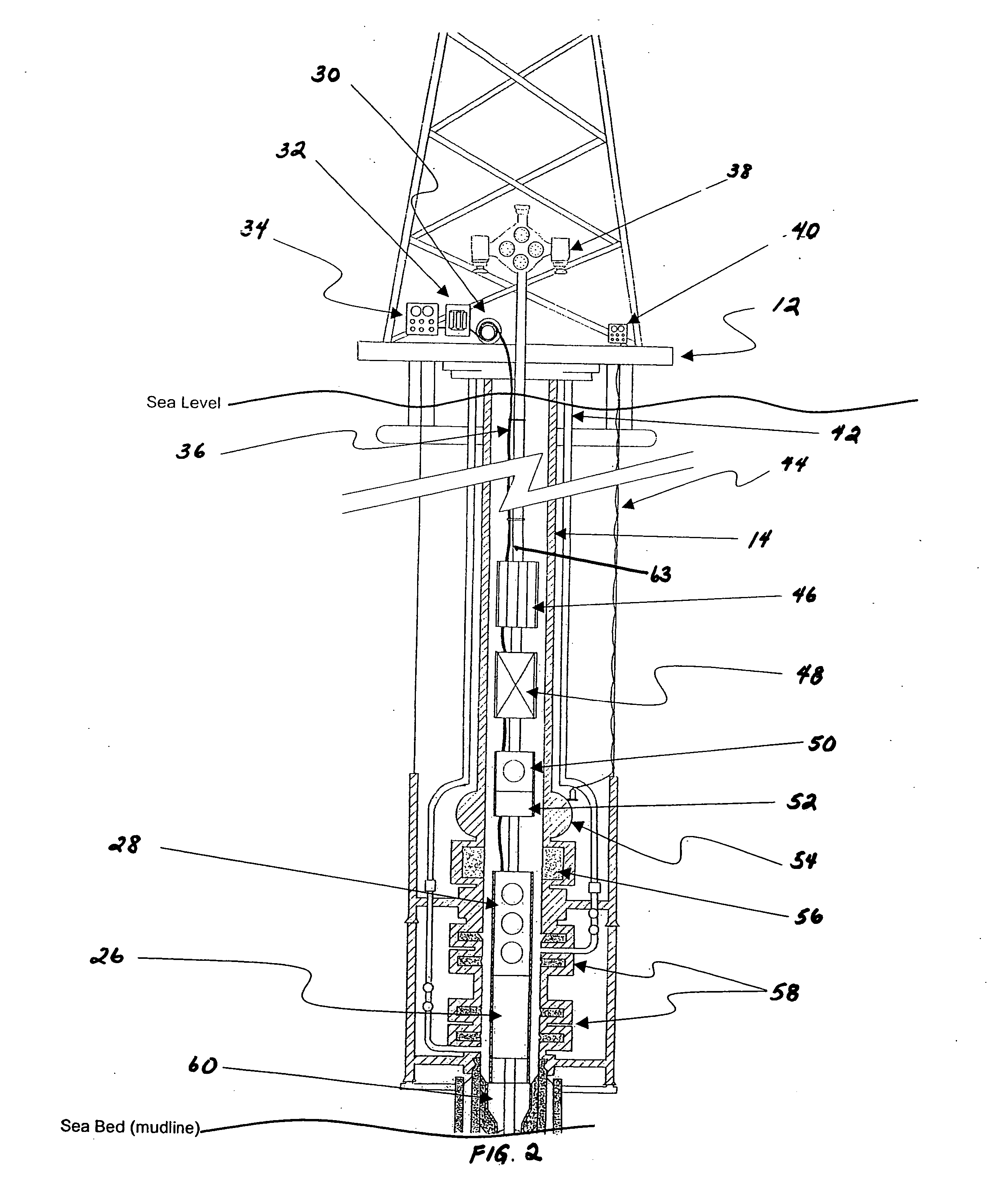
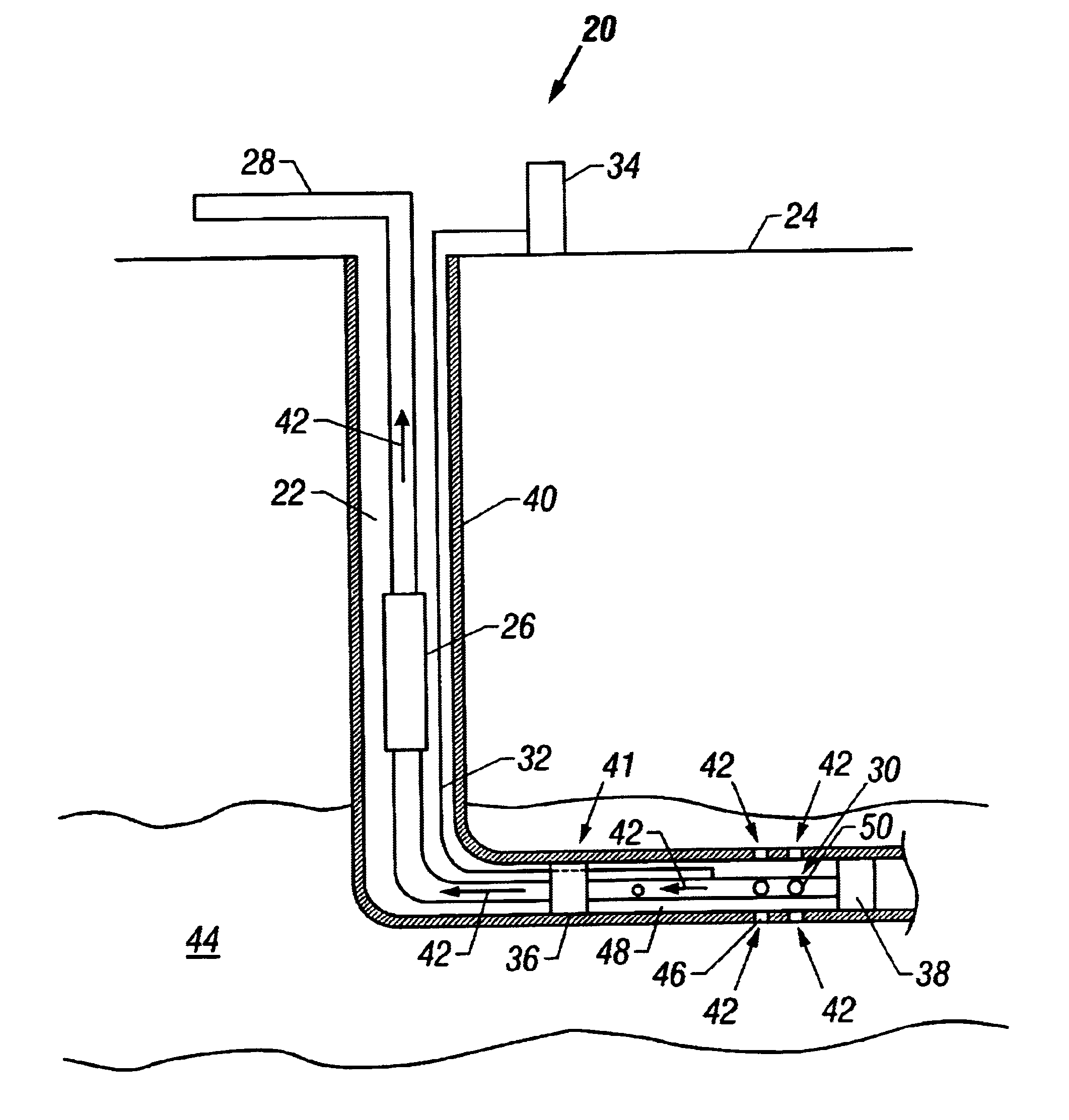
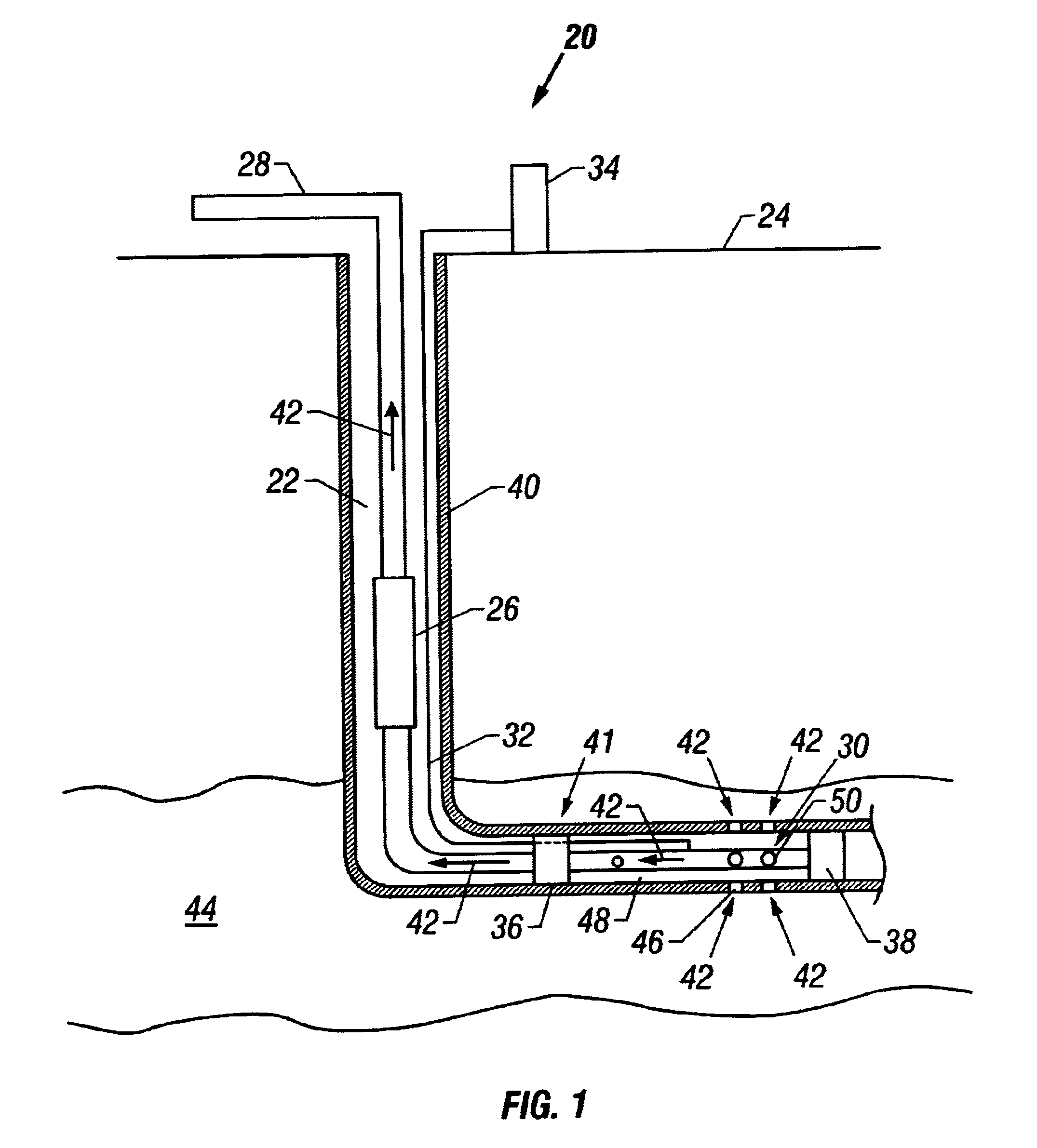
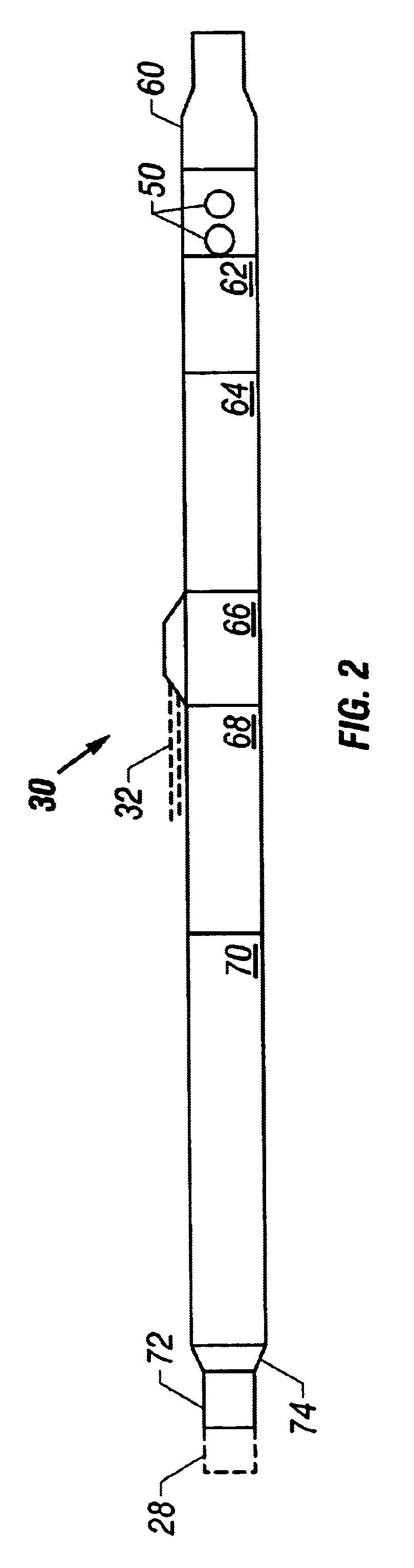
An induction choke in a petroleum well where a voltage potential is developed across the choke to power and communicate with devices and sensors in the well. Preferably, the induction choke is a ferromagnetic material and acts as an impedance to a time-varying current, e.g. AC. The petroleum well includes a cased wellbore having a tubing string positioned within and longitudinally extending within the casing. A controllable gas lift valve, sensor, or other device is coupled to the tubing. The valve sensor, or other device is powered and controlled from the surface. Communication signals and power are sent from the surface using the tubing, casing, or liner as the conductor with a casing or earth ground. For example, AC current is directed down a casing or tubing or a lateral where the current encounters a choke. The voltage potential developed across the choke is used to power electronic devices and sensors near the choke. Such induction chokes may be used in many other applications having an elongated conductor such as a pipe, where it is desirable to power or communicate with a valve, sensor, or other device without providing a dedicated power or communications cable.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
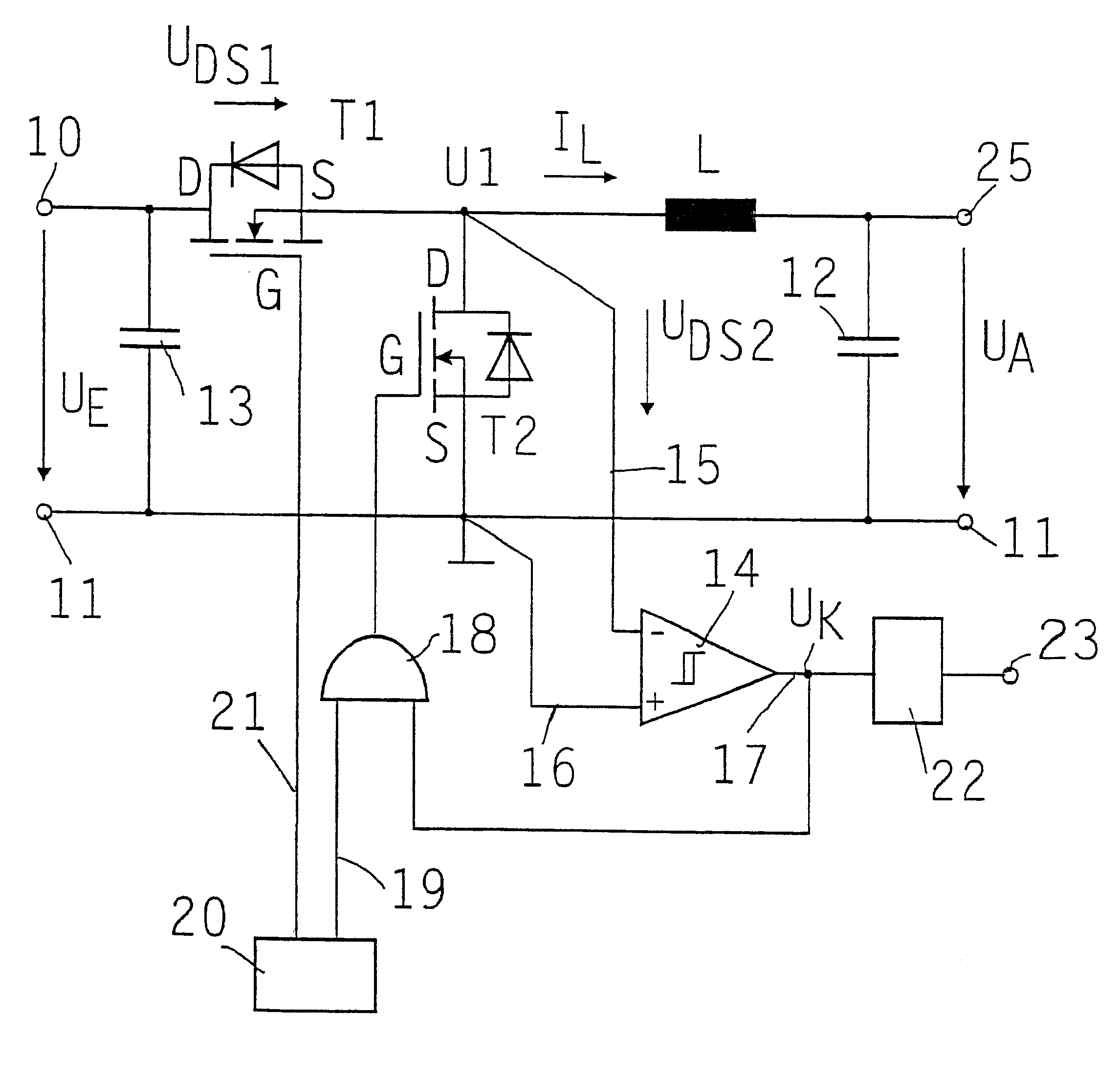
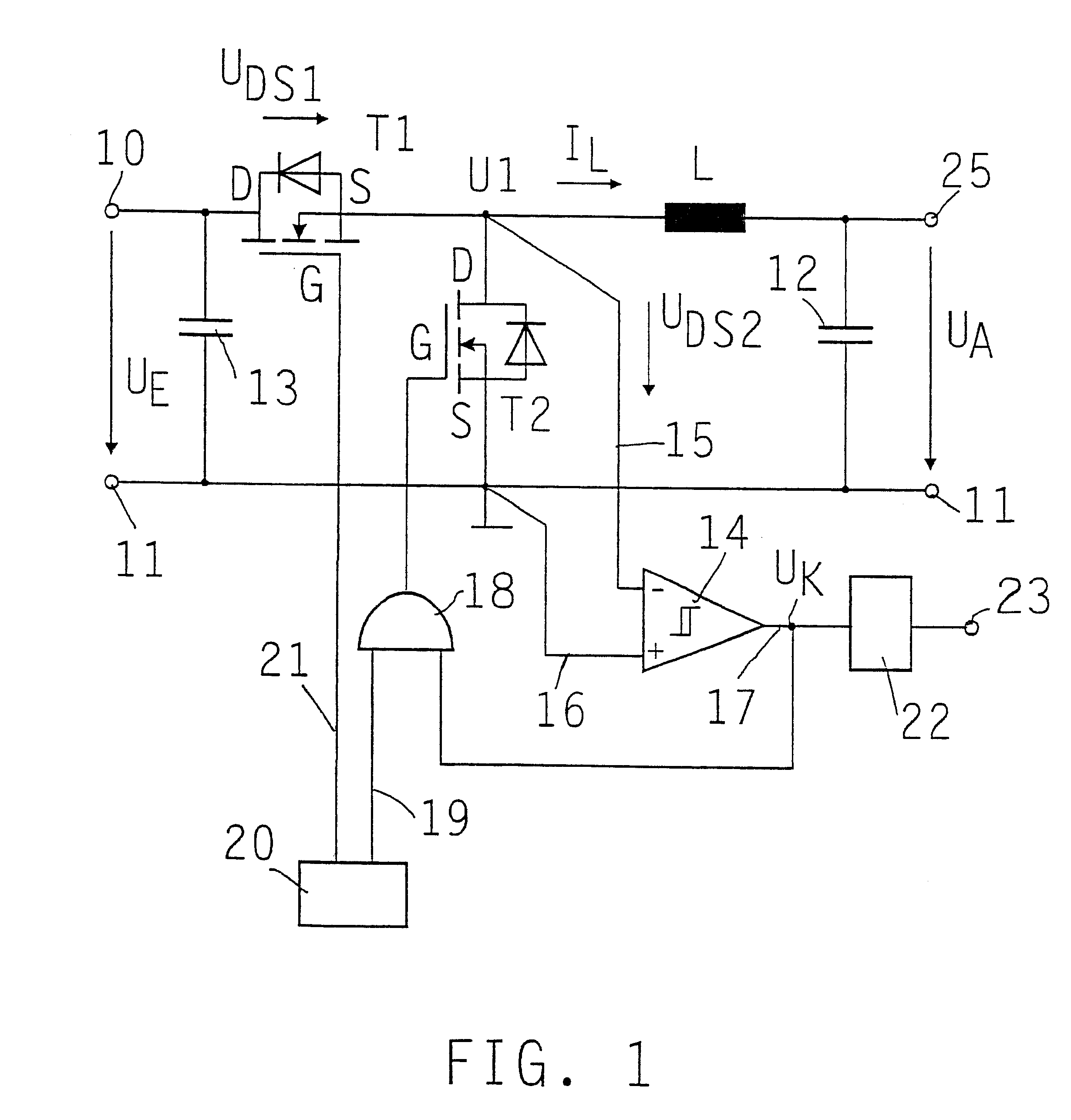
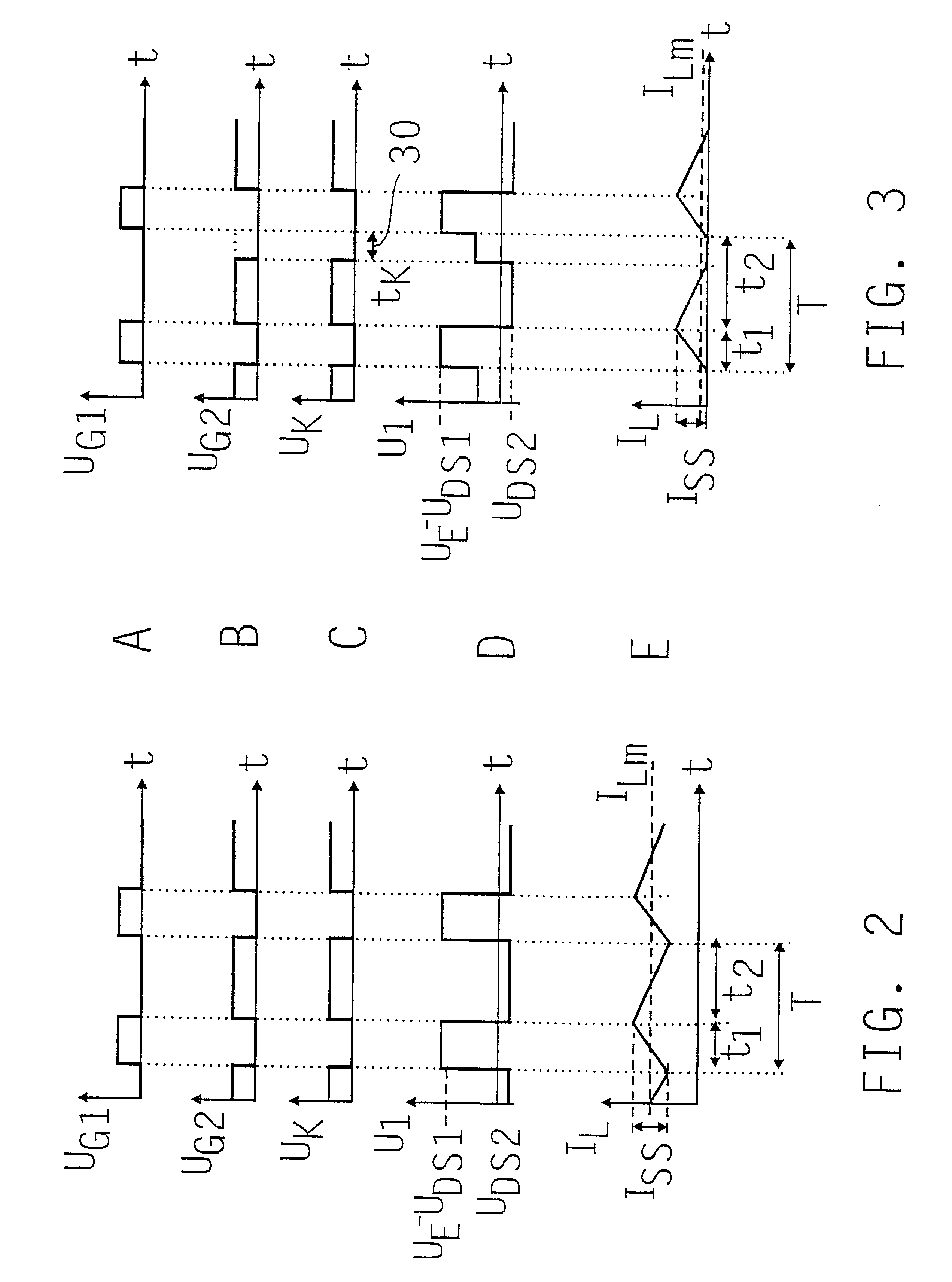
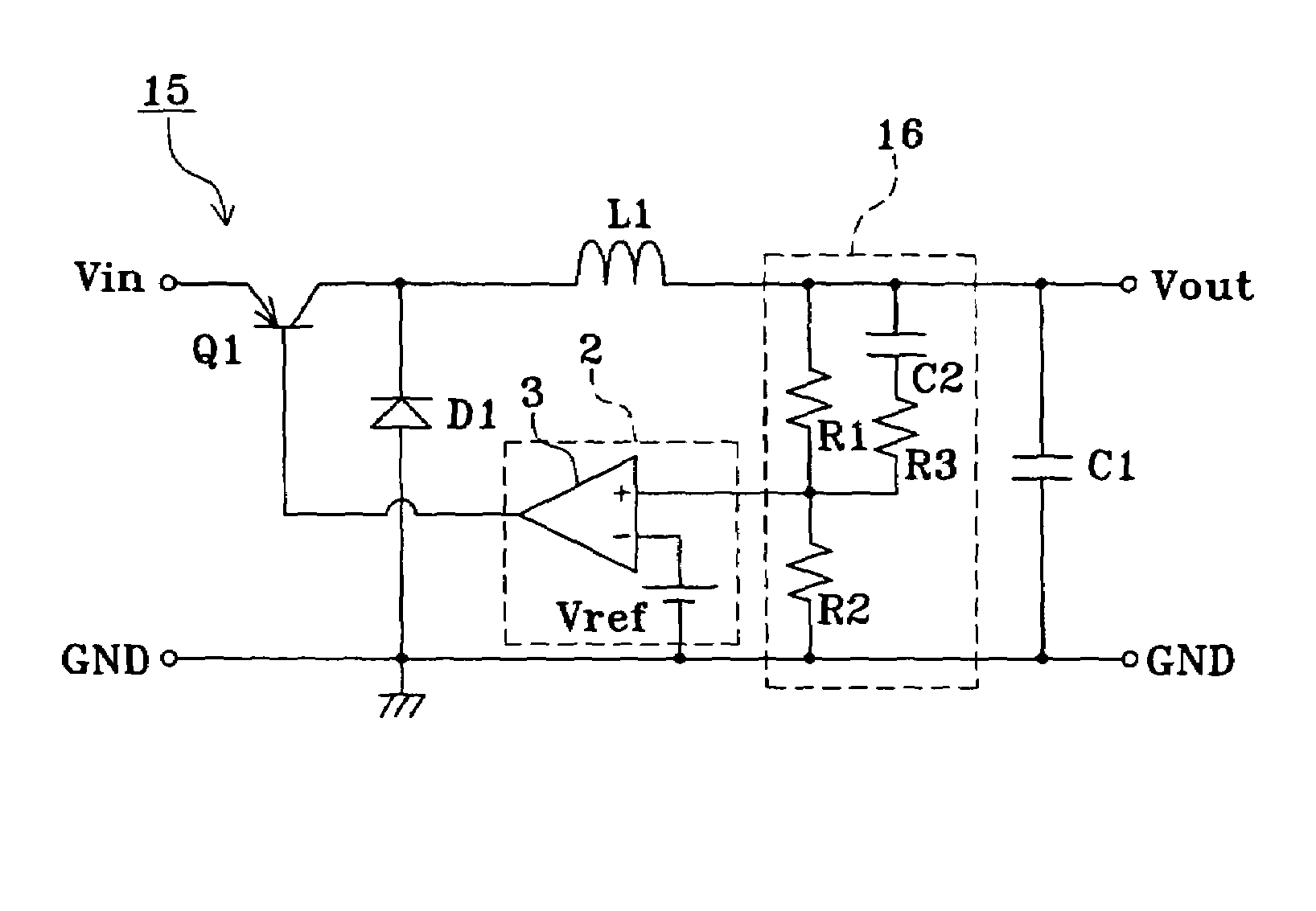
Step-down constant-current transformer
InactiveUS6541947B1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionMOSFETEngineering
A step-down constant-current transformer including a controllable switch downstream from the one input and connected in series to a choke, a capacitor connected in parallel at the output, and upstream from the choke, a second controllable switch in parallel. Both controlled switches are MOSFET transistors. A control unit, in particular a pulse-width control unit, is provided for the MOSFET transistors. The voltage across the parallel-connected MOSFET transistor is monitored to determine whether a reverse current, i.e., a current flowing through the choke from the output in the direction of the input of the constant-current transformer, or an electric potential at the center tap of the half-bridge formed by the two MOSFET transistors is detected. For this purpose, a comparator and an AND circuit are provided, which, in the event of such a reverse current, block the parallel-connected MOSFET transistor to prevent the reverse current.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
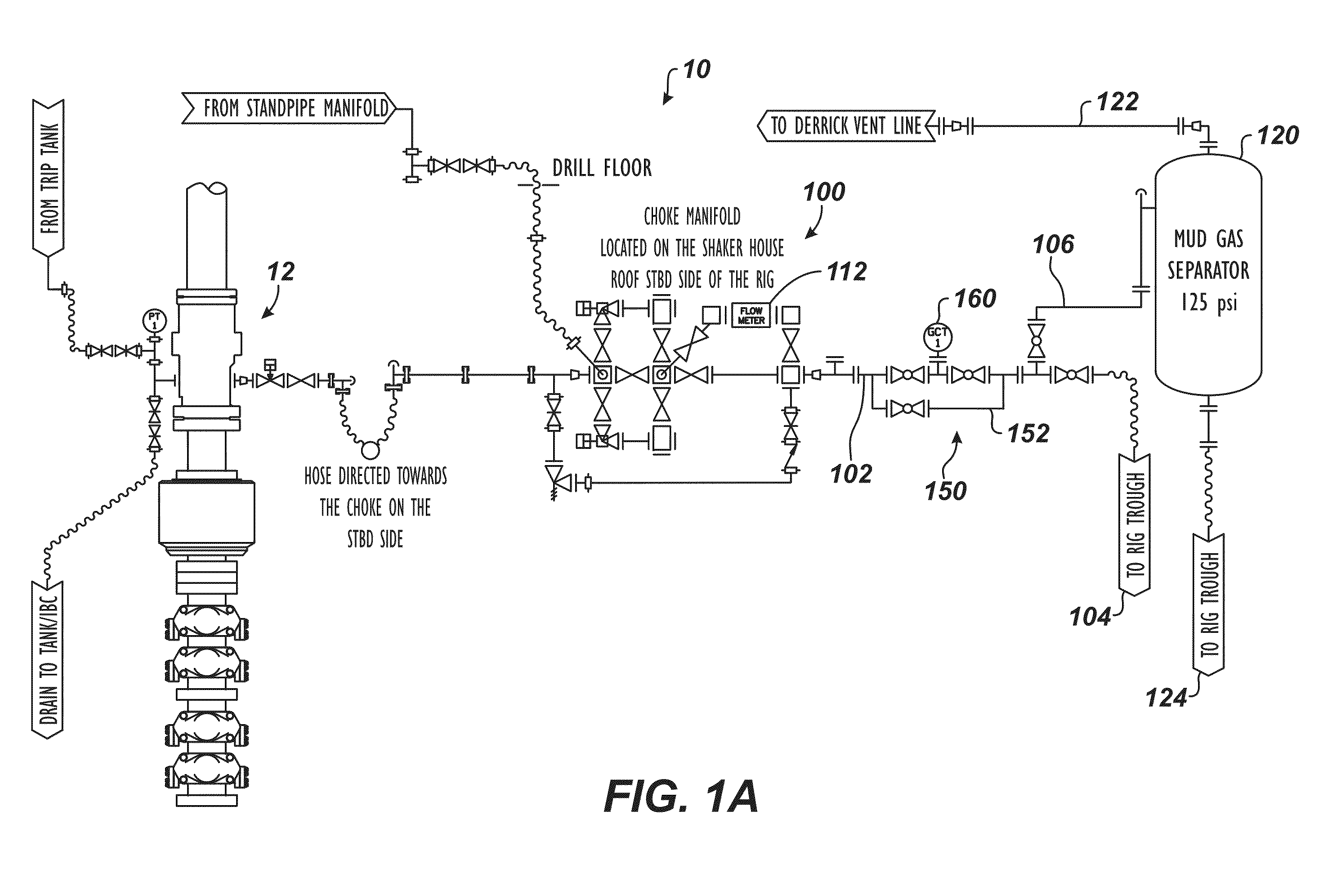
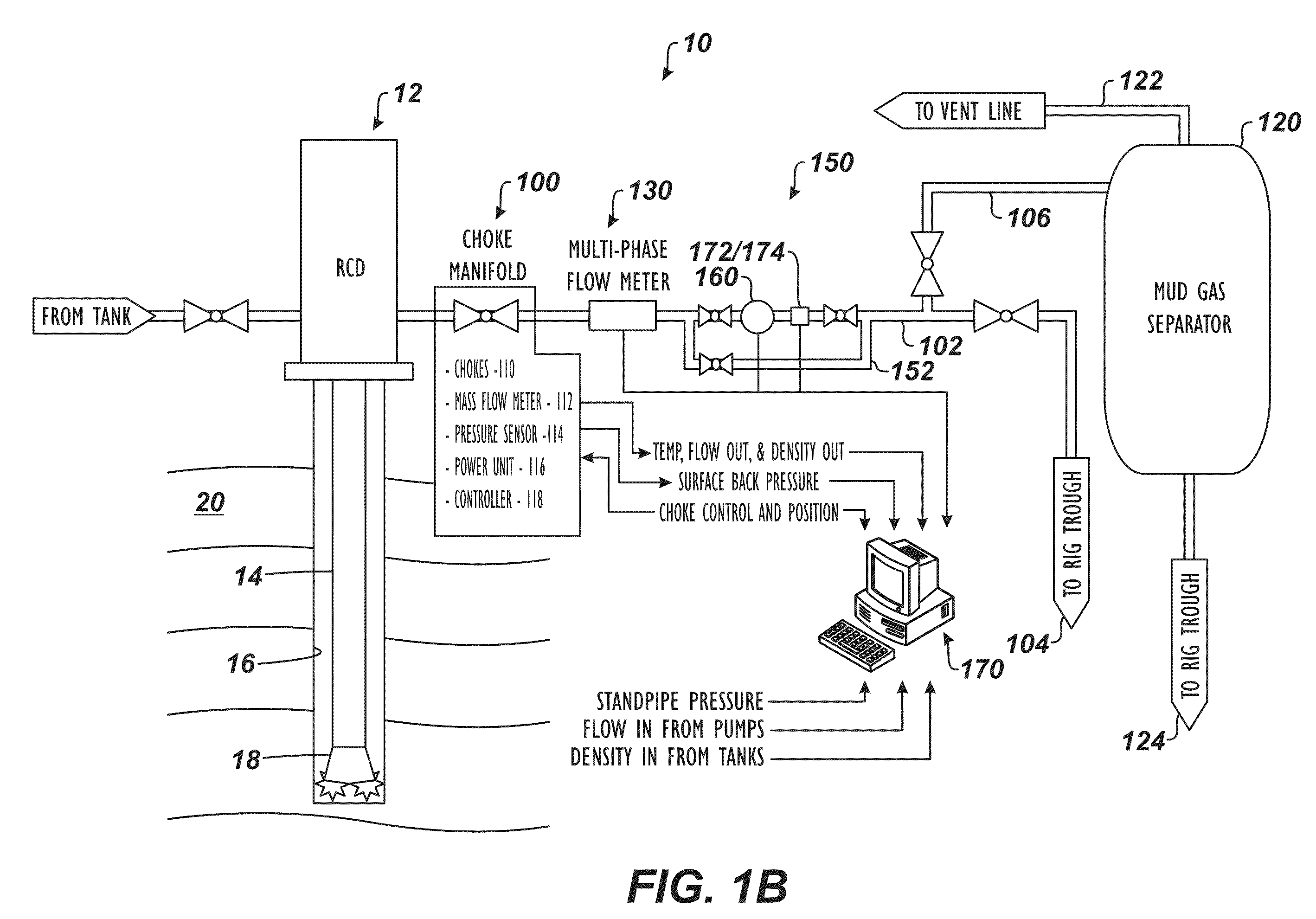
Surface Gas Evaluation During Controlled Pressure Drilling
A system and method have a choke in fluid communication with a rotating control device. The choke controls flow of drilling mud from the rotating control device to a gas separator during a controlled pressure drilling operation, such as managed pressure drilling (MPD) or underbalanced drilling (UBD). A probe is in fluid communication with the drilling mud between the choke and the gas separator. During operations, the probe evaluates gas in the drilling mud from the well passing from the choke to the gas separator.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Method for removing condensables from a natural gas stream, at a wellhead, downstream of the wellhead choke
InactiveUS6962199B1Easy to separateDissipates a substantial amount of kinetic energy of the streamSolidificationLiquefactionProduct gasEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for removing condensables from a natural gas stream, at a wellhead, downstream of the wellhead choke thereof. In accordance with the invention there is provided a method for removing condensables from a natural gas stream at a wellhead, the method comprising the steps of: (A) inducing the natural gas stream to flow at supersonic velocity through a conduit of a supersonic inertia separator and thereby causing the fluid to cool to a temperature that is below a temperature / pressure at which the condensables will begin to condense, forming separate droplets and / or particles; (B) separating the droplets and / or particles from the gas; and (C) collecting the gas from which the condensables have been removed, wherein the supersonic inertia separator is part of the wellhead assembly downstream of the wellhead choke. There is also provided a device for removing said condensables from said natural gas that is part of the wellhead assembly downstream of the choke, a wellhead assembly comprising said device.
Owner:TWISTER BV +1
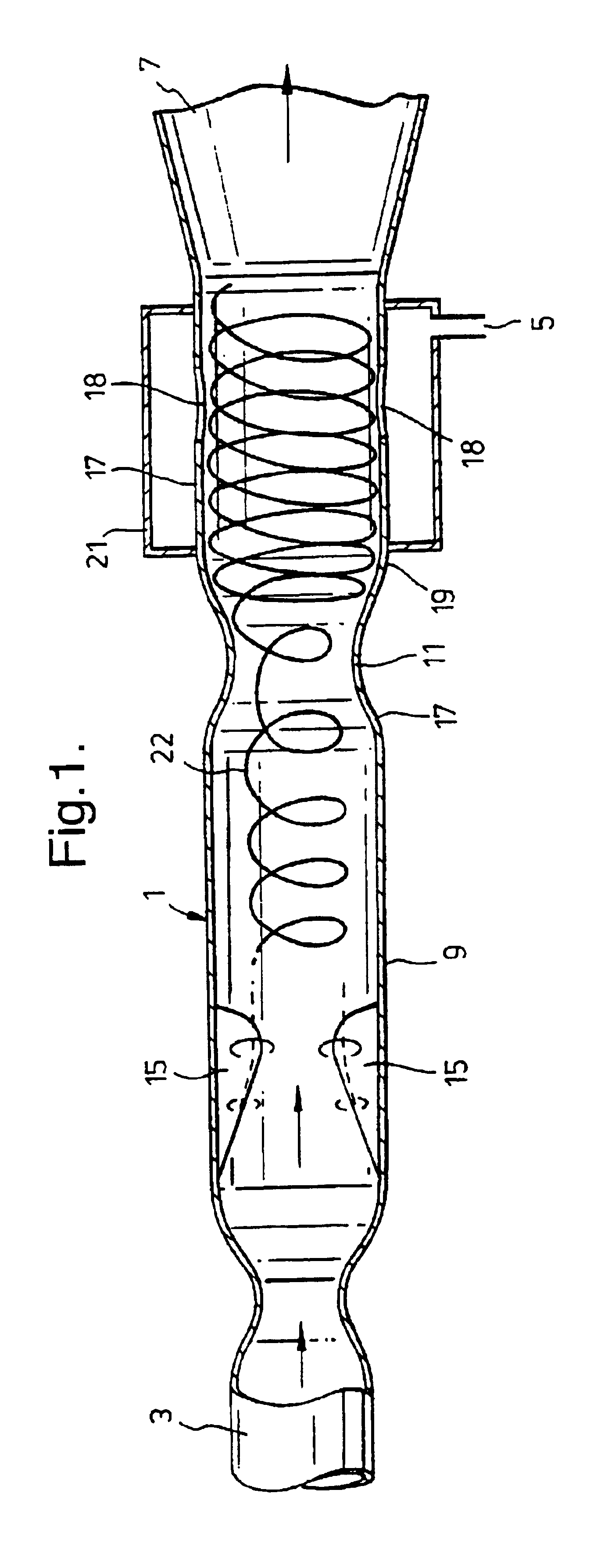
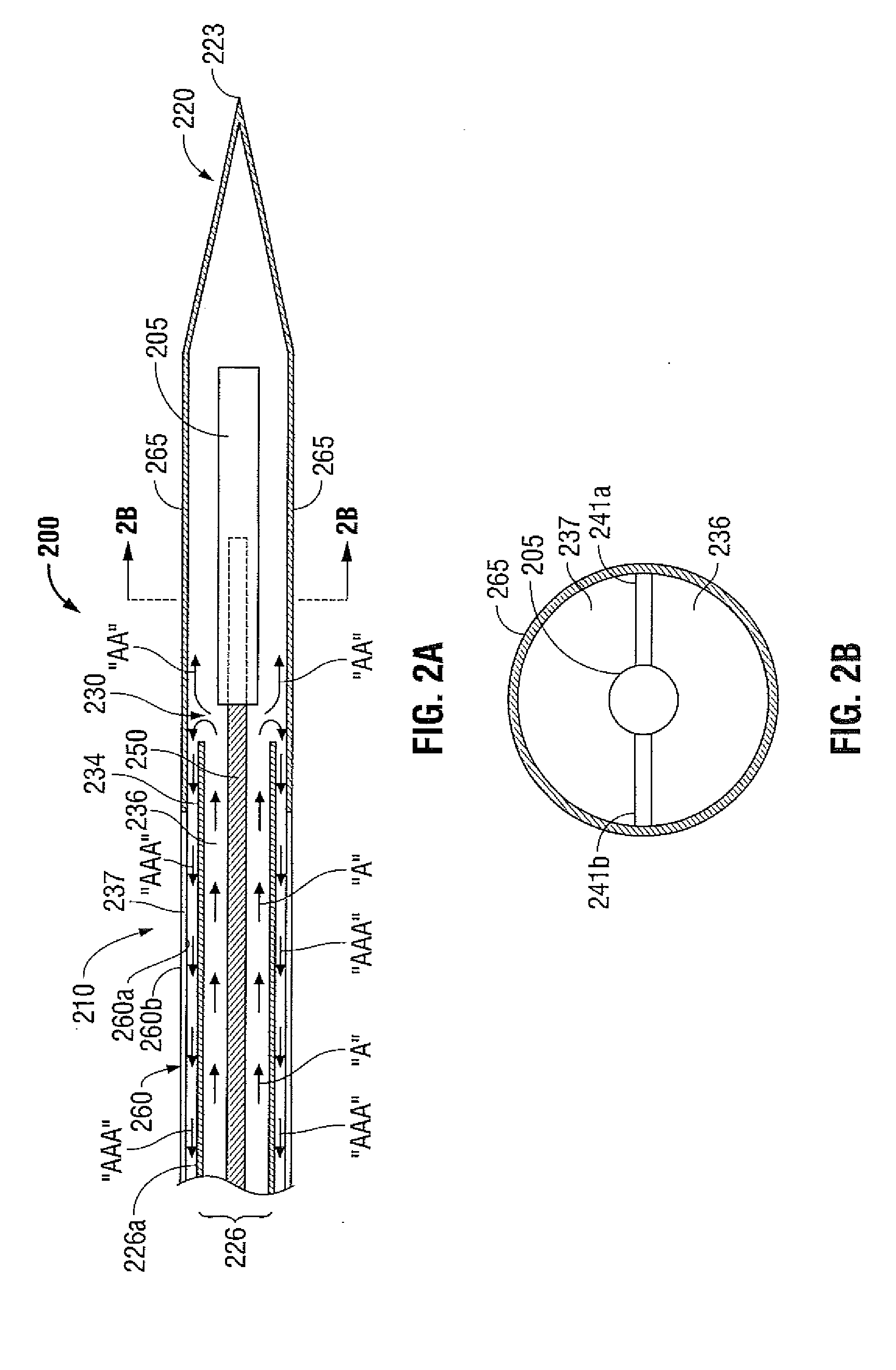
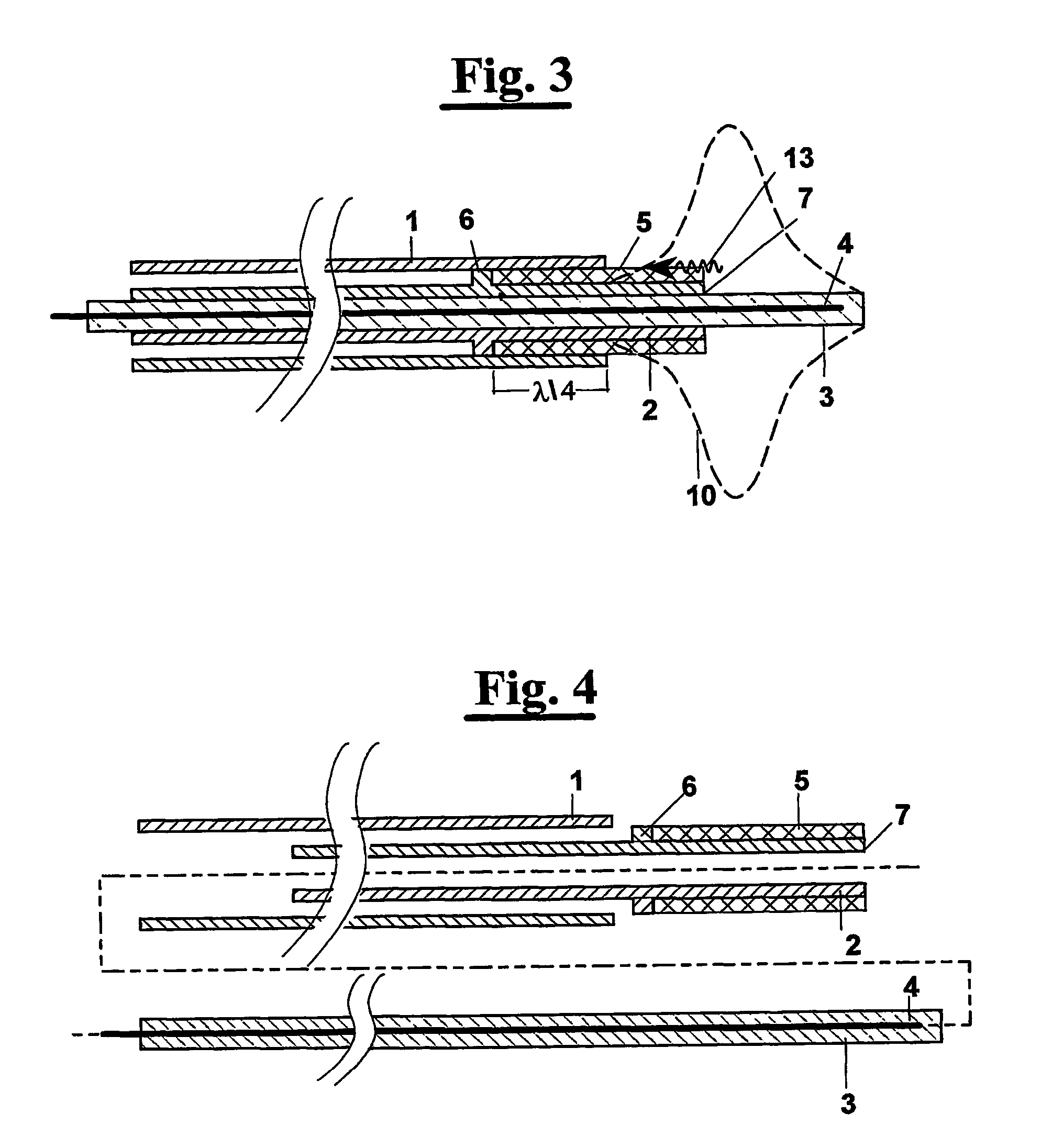
Interstitial microwave antenna with miniaturized choke hyperthermia in medicine and surgery
InactiveUS20040049254A1Minimally invasiveAllow useElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyElectrical conductorReflected waves
The present invention relates to minimally invasive surgery techniques. It provides a method for manufacturing an antenna for percutaneous acute hyperthermia microwave applications of the monopole or dipole co-axial type provided with trap, commonly called choke, for blocking the propagation of the backwards reflecting wave towards the generator. The miniaturisation of the device allows a use minimally invasive for interstitial hyperthermia in medicine and surgery, in particular for oncology. The method of manufacturing the antenna provides a metal needle (1) for the introduction of the antenna (2, 3, 4) in the target tissue. On the external conductor (4) of the antenna (2) a metal collar (6) is connected in a predetermined position; a plastics sheath (5) is applied in order to cover the external conductor (2) in the portion between the feed (7) and the collar (6); the inner wall of the metal needle (1) wherein the antenna is inserted is then used for containing and guiding the collar (6) and the sheath (5); in particular, the collar (6) being in electrical contact with the inner wall of the metal needle (1). An antenna is thus obtained with choke of variable length and with miniaturized diameter. A thermocouple can be introduced through the choke that protrudes the directly in the "feed" zone.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
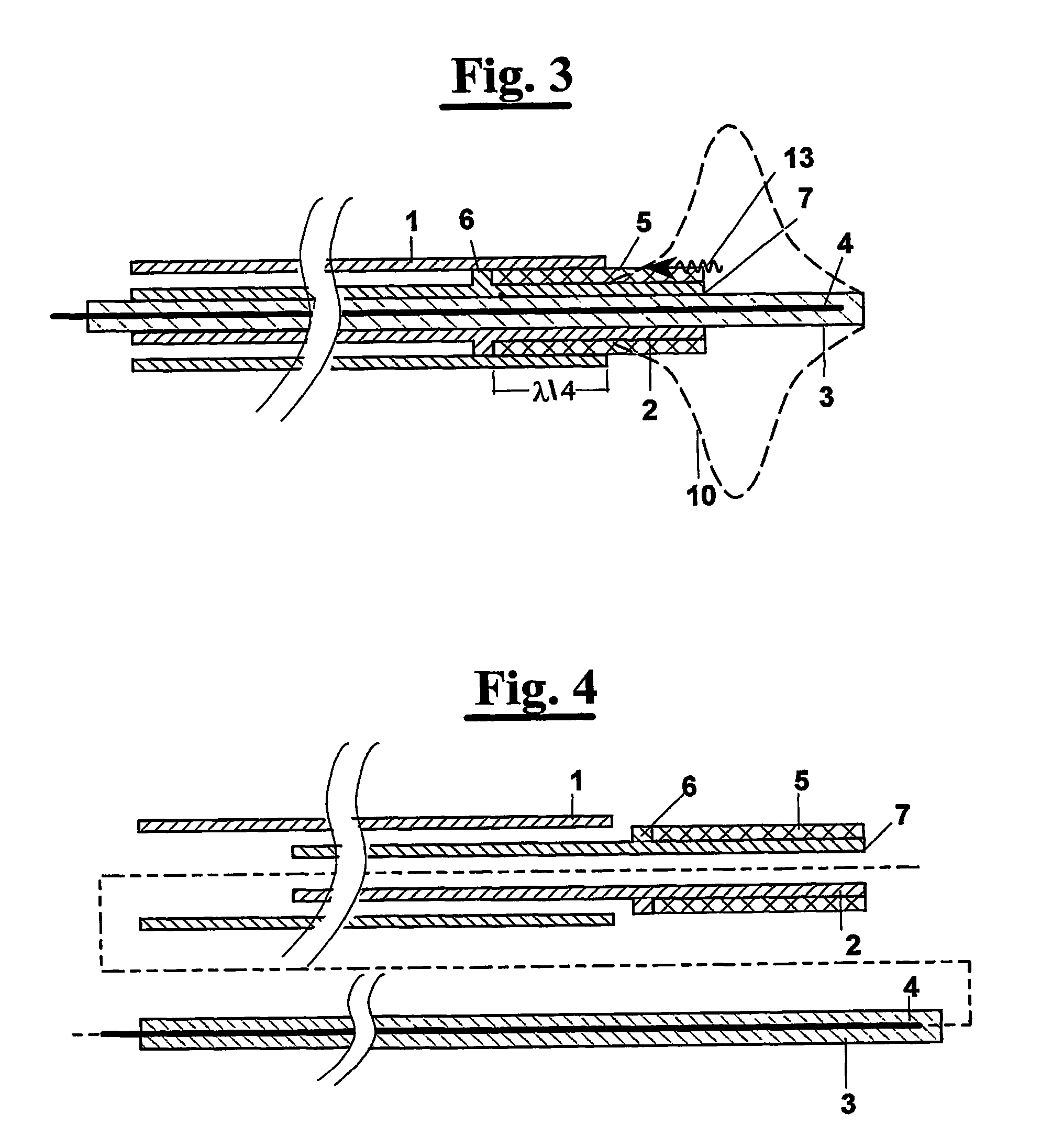
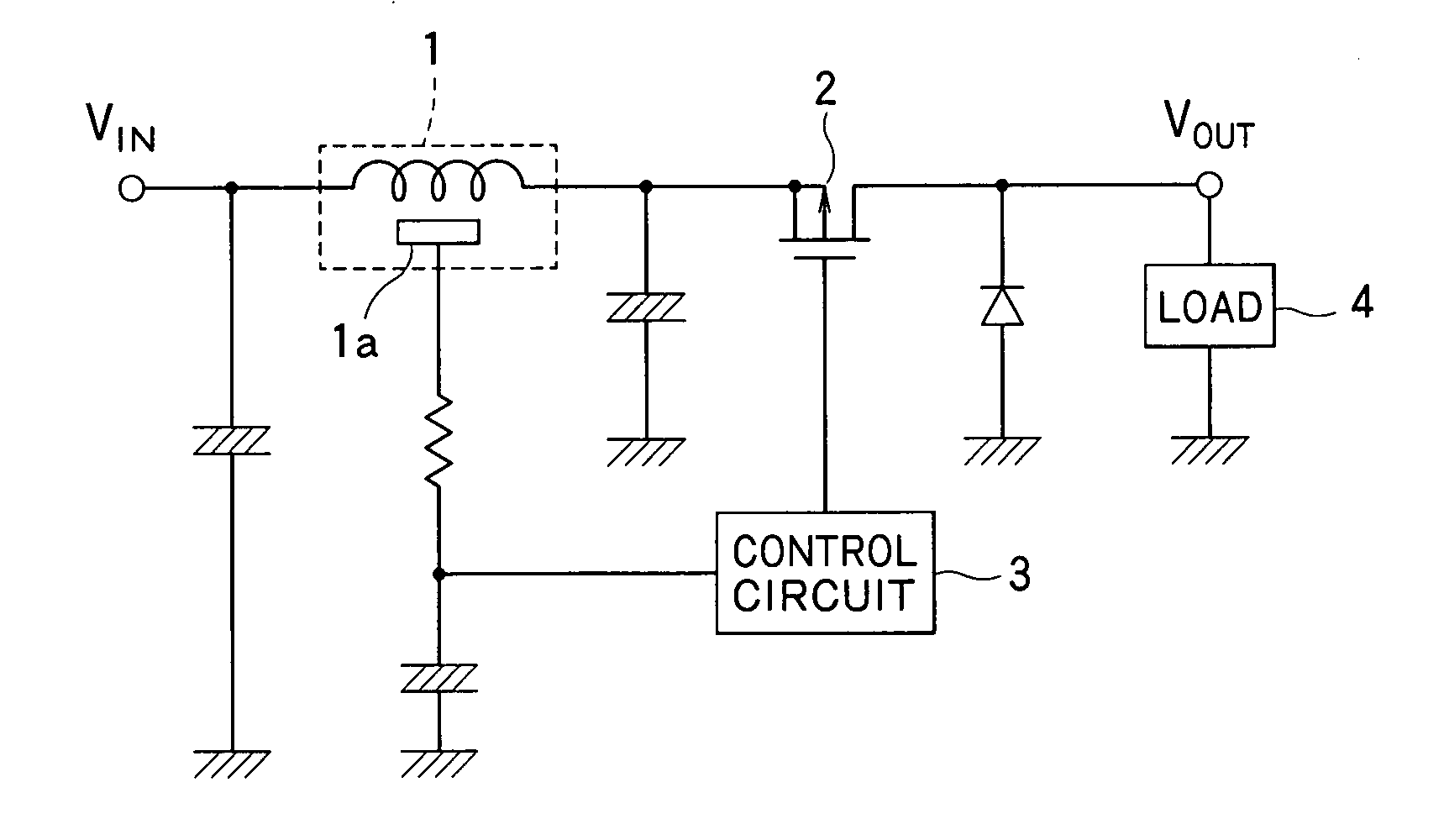
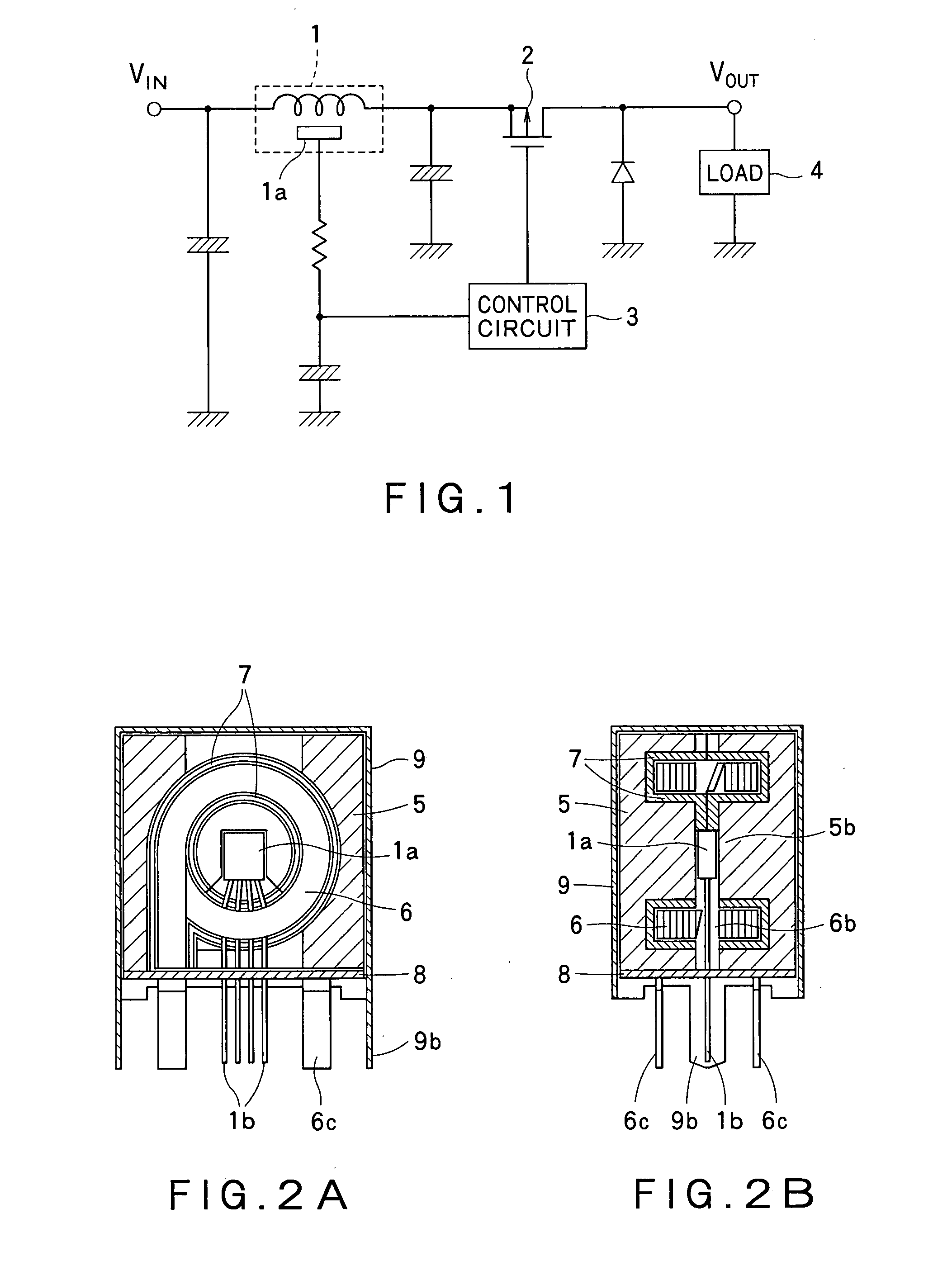
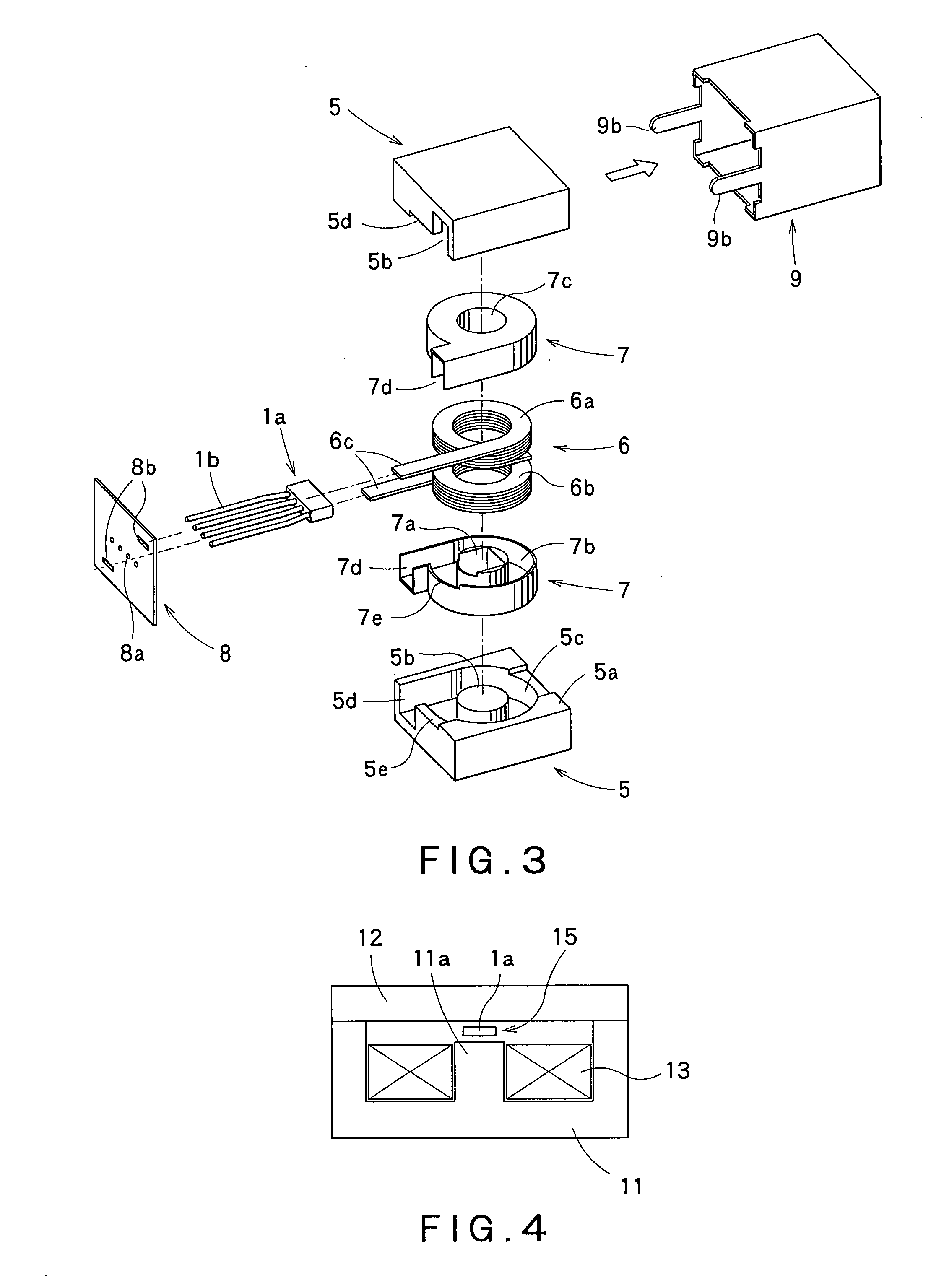
Current detection device
ActiveUS20070247135A1Easy to installLow costDc network circuit arrangementsTransformers/inductances casingsEngineeringAir core
The present invention provides a low-cost current detection device having a magnetic sensor easily placed on a choke coil, wherein assembly and manufacturing costs are reduced and a product is miniaturized. A current detection device including a choke coil for smoothing an input current or an output current and a magnetic sensor 1a built into the choke coil to detect the input current or output current, wherein the choke coil is composed of: a pair of cores 5 provided with an outer magnetic leg 5a constituting a closed magnetic circuit and a center magnetic leg 5b for providing a gap; and an air core coil 6 mounted on the center magnetic leg 5b, and space 6b is provided to a part of winding of the air core coil 6 with the magnetic sensor 1a placed in the gap between the space 6b and the center magnetic leg 5b.
Owner:VICTOR CO OF JAPAN LTD +1
Fluid Cooled Choke Dielectric and Coaxial Cable Dielectric
ActiveUS20110077635A1Antenna adaptation in movable bodiesSurgical instruments for heatingDielectricElectrical conductor
The microwave antenna assembly includes a feedline electrically connected to an elongated shaft by a choke electrical connector. The feedline includes an inner conductor, an outer conductor, an elongated shaft and a choke electrical connector. The inner conductor is disposed in coaxial arrangement with the inner conductor and forms a dielectric supply lumen therebetween. The elongated shaft at least partially surrounding the feedline and form a dielectric return lumen therebetween. The choke electrical connector surrounds at least a portion of the feedline and electrically connects the feedline outer conductor to the elongated shaft. A low-loss dielectric fluid is supplied between the inner conductor and the outer conductor of the feedline and forms a dielectric barrier therebetween. The low-loss dielectric fluid also forms a dielectric barrier between the outer conductor of the feedline and the elongated shaft and the choke electrical connector forms a plurality of apertures extending therethrough, the apertures forming at least a portion of the dielectric return lumen.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
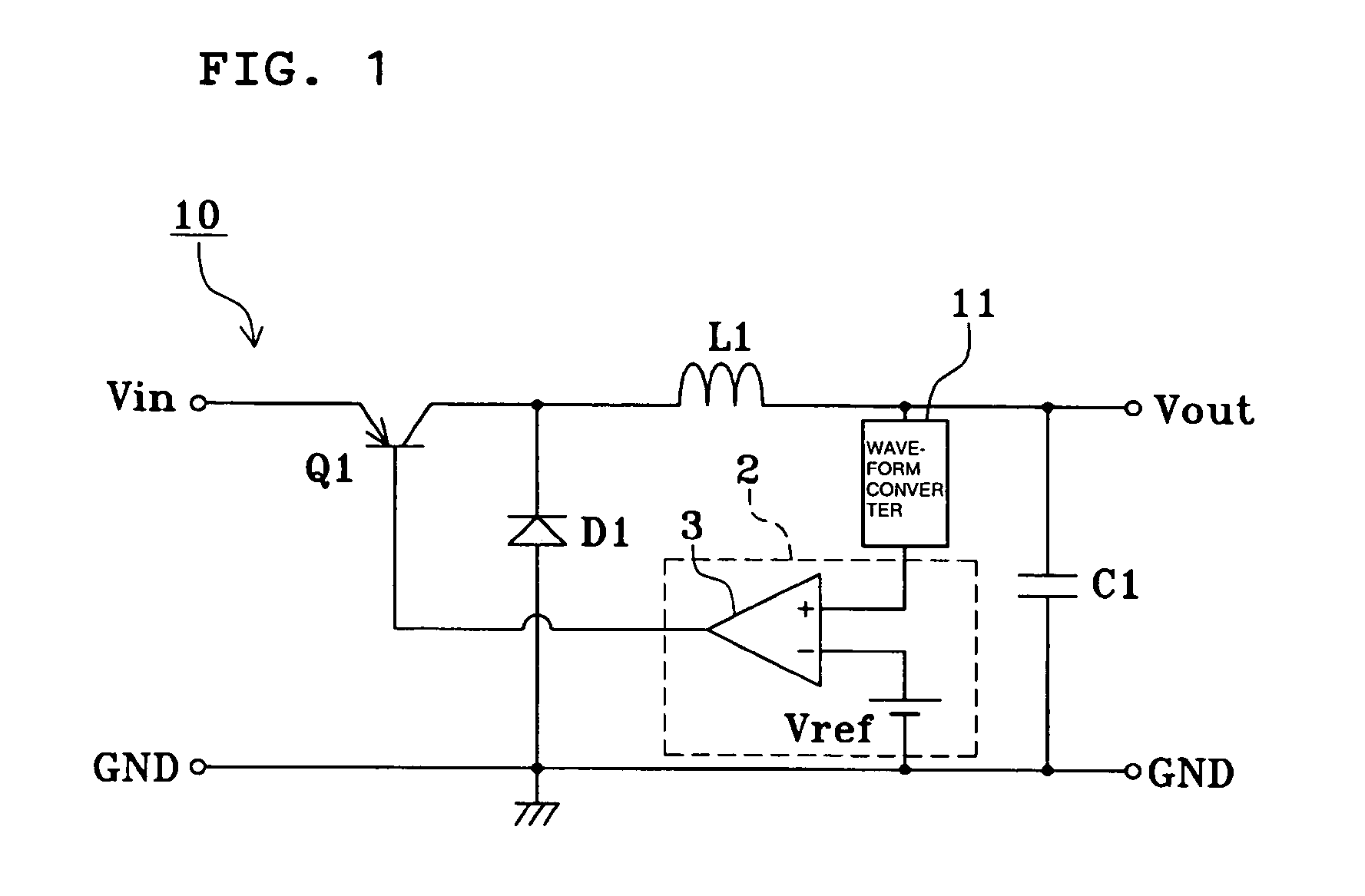
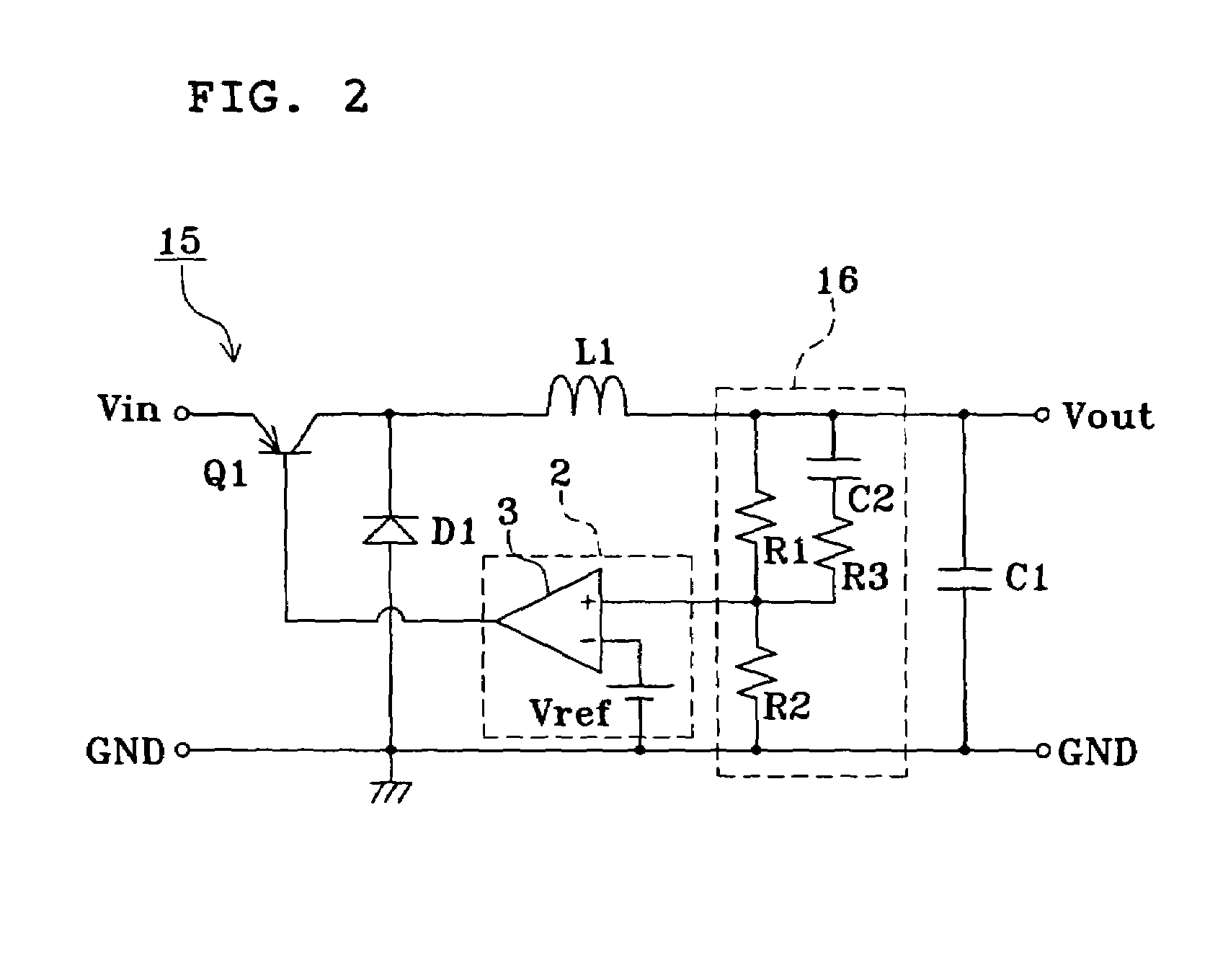
Ripple converter
ActiveUS7233135B2Oscillation stabilityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationFlyback diodeVoltage reference
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
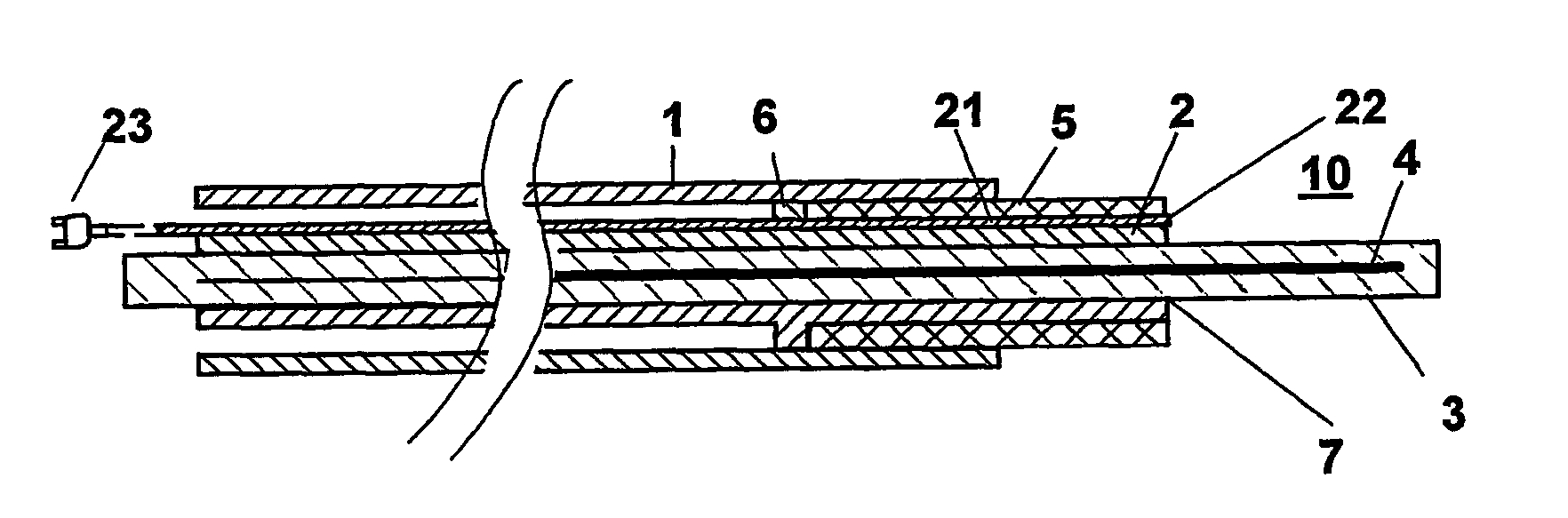
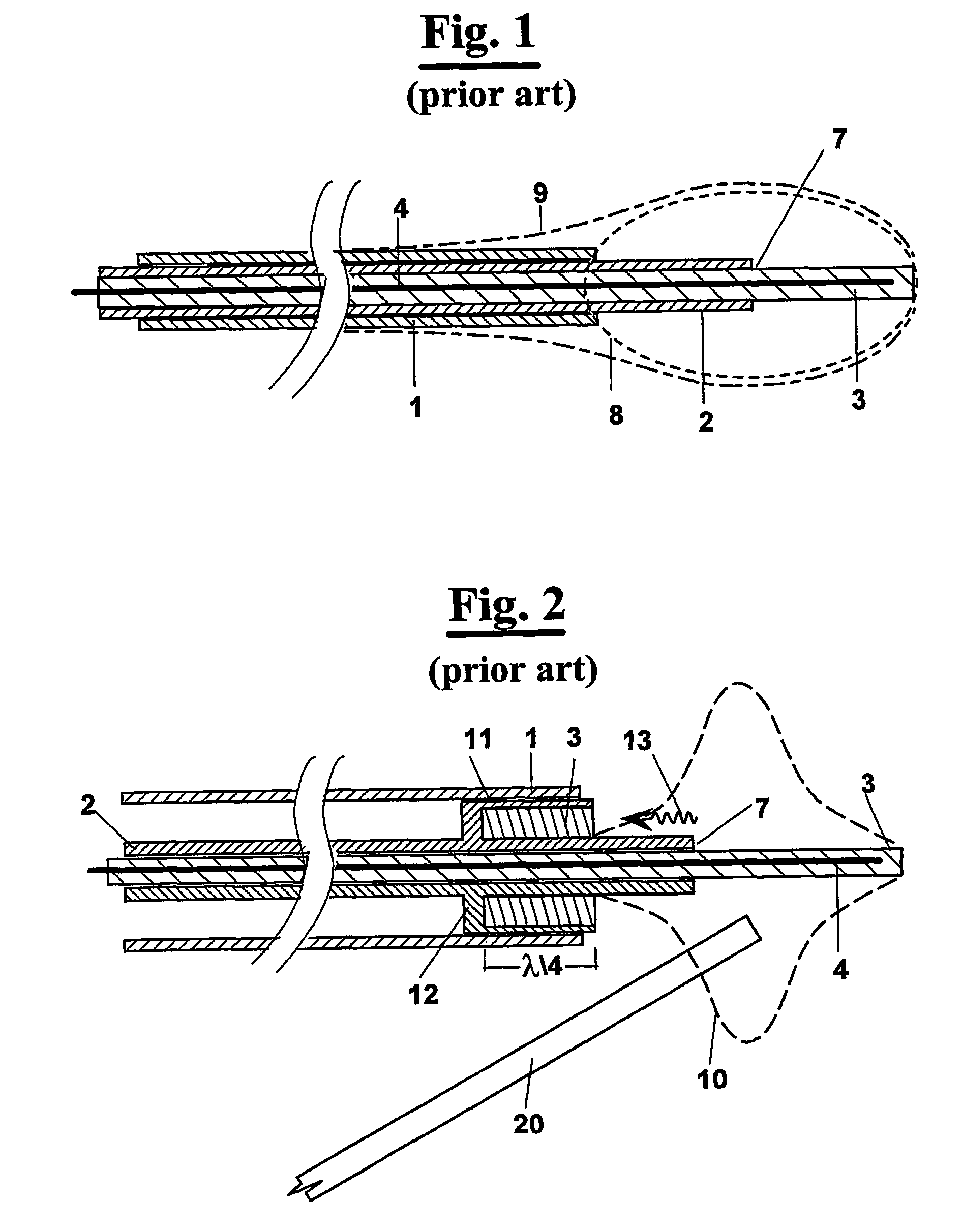
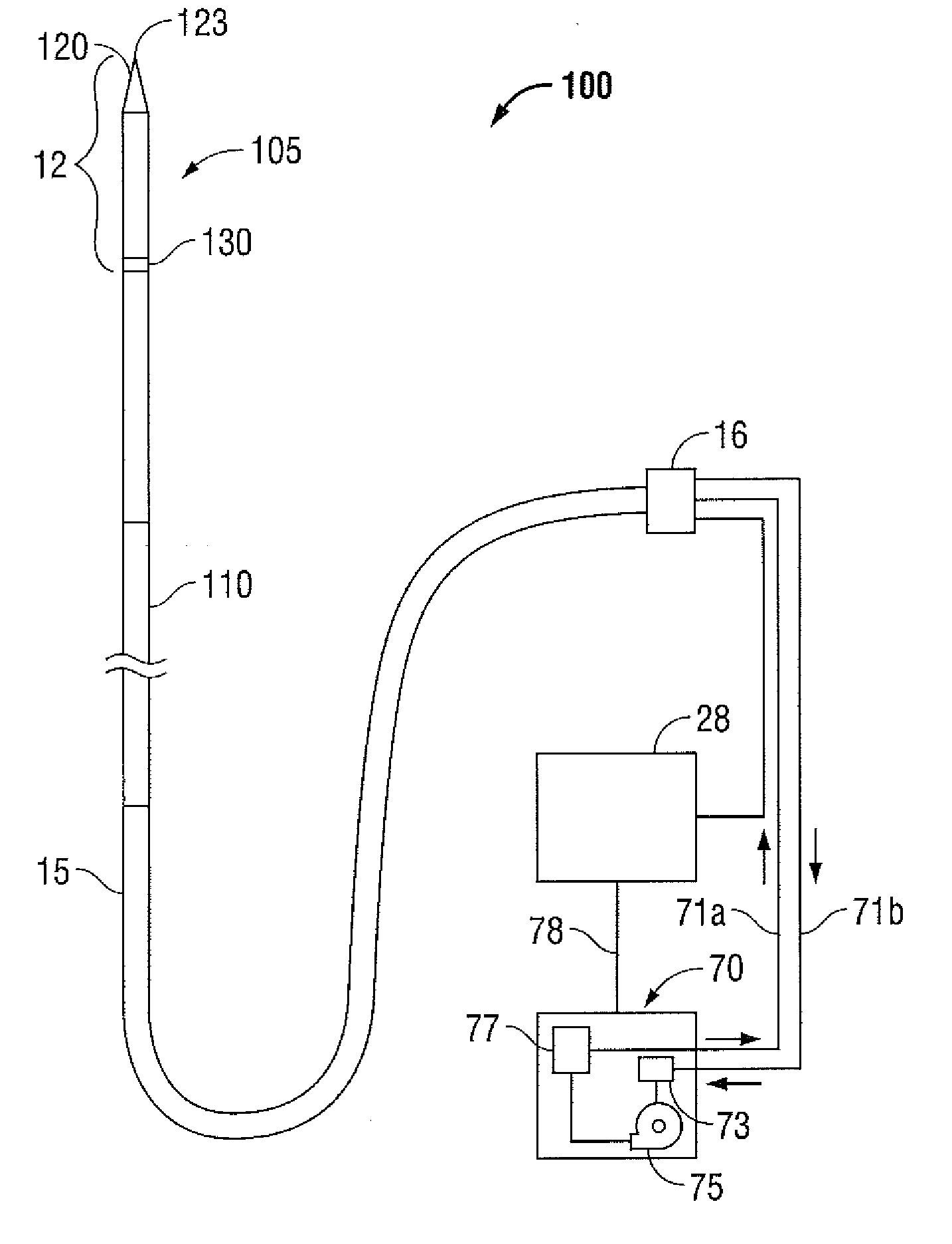
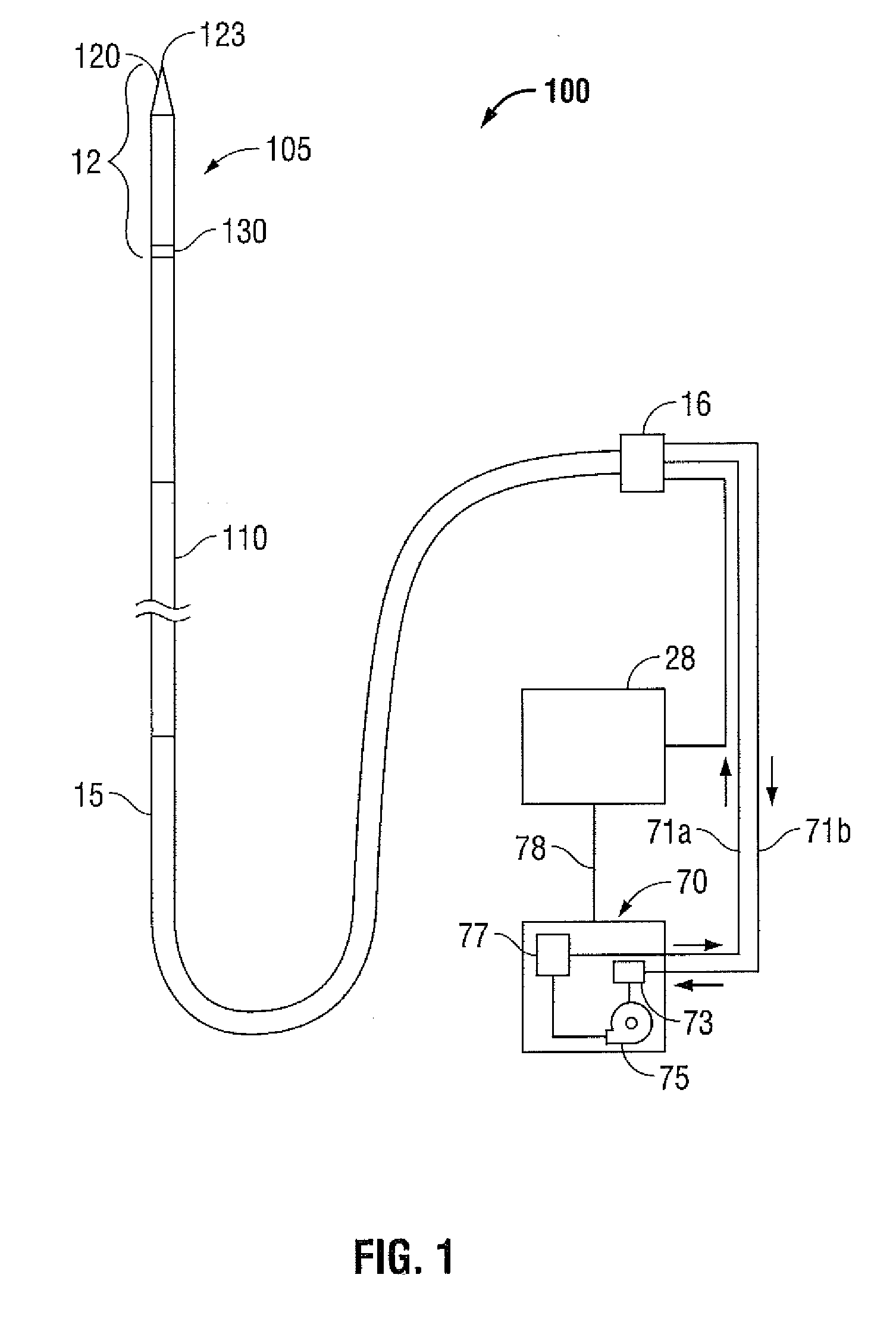
Impedance-matching apparatus and construction for intravascular device
InactiveUS7194297B2Improving Impedance MatchingEasy to manufactureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryCapacitanceElectrical conductor
Intravascular device for matching impedances of portions of an intravascular circuit and limiting RF signal-induced heating of intravascular conductors. An intravascular device includes alternating conductive and dielectric layers and an electrically conductive coil in a configuration that effects an impedance-matching circuit. Another embodiment of an intravascular device has cylindrical inner and outer walls formed of an expandable, electrically conductive material, the inner and outer walls being separated by a compressible dielectric material. Varying the pressure in the lumen defined by the inner wall changes the spacing between the inner and outer walls, thereby changing the capacitance between the inner and outer wall. Another embodiment of an intravascular device includes one or more coaxial chokes for limiting heating caused by currents induced by RF signals. A conductive shield of the choke is formed of a conductive polymer to further reduce heating effects. Other embodiments include different transmission lines and antenna structures.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Automated closed loop flowback and separation system
InactiveUS20100206560A1Realize automatic adjustmentSurveyDrilling rodsAutomatic controlHuman–machine interface
An automated closed loop flowback and separation system that allows automated control and remote operation of a flowback operation from a safe distance without any fluid or gas release to the atmosphere. Four-phase separation tanks allow the transport gas, well bore cuttings, produced oil, and produced water to be automatically separated and transported through process piping for reuse or sale, eliminating the need for auxiliary equipment. Flow measurement instruments, pressure transmitters, and level transmitters work in conjunction with an automated blast choke to send data to a programmable logic controller for use in calculating the erosion status of the choke restriction and adjusting the choke to compensate. The programmable logic controller works with a touch-screen or similar human-machine interface to allow remote monitoring and control or automated control of the system. The automated blast choke can vary the choke restriction opening based on the pressure differential and flow rate conditions.
Owner:CANADIAN FRACMASTER
Oil rig choke control systems and methods
InactiveUS20050222772A1Reduce stepsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingValve members for absorbing fluid energyIsolation valveControl system
A choke diagnostic system with a positioner for moving a choke mechanism of a choke, a choke isolation valve for placing the choke in standby mode, and a processor controlling the choke and, in certain aspects, the processor for commanding the positioner to move the choke mechanism while the choke is in standby mode.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
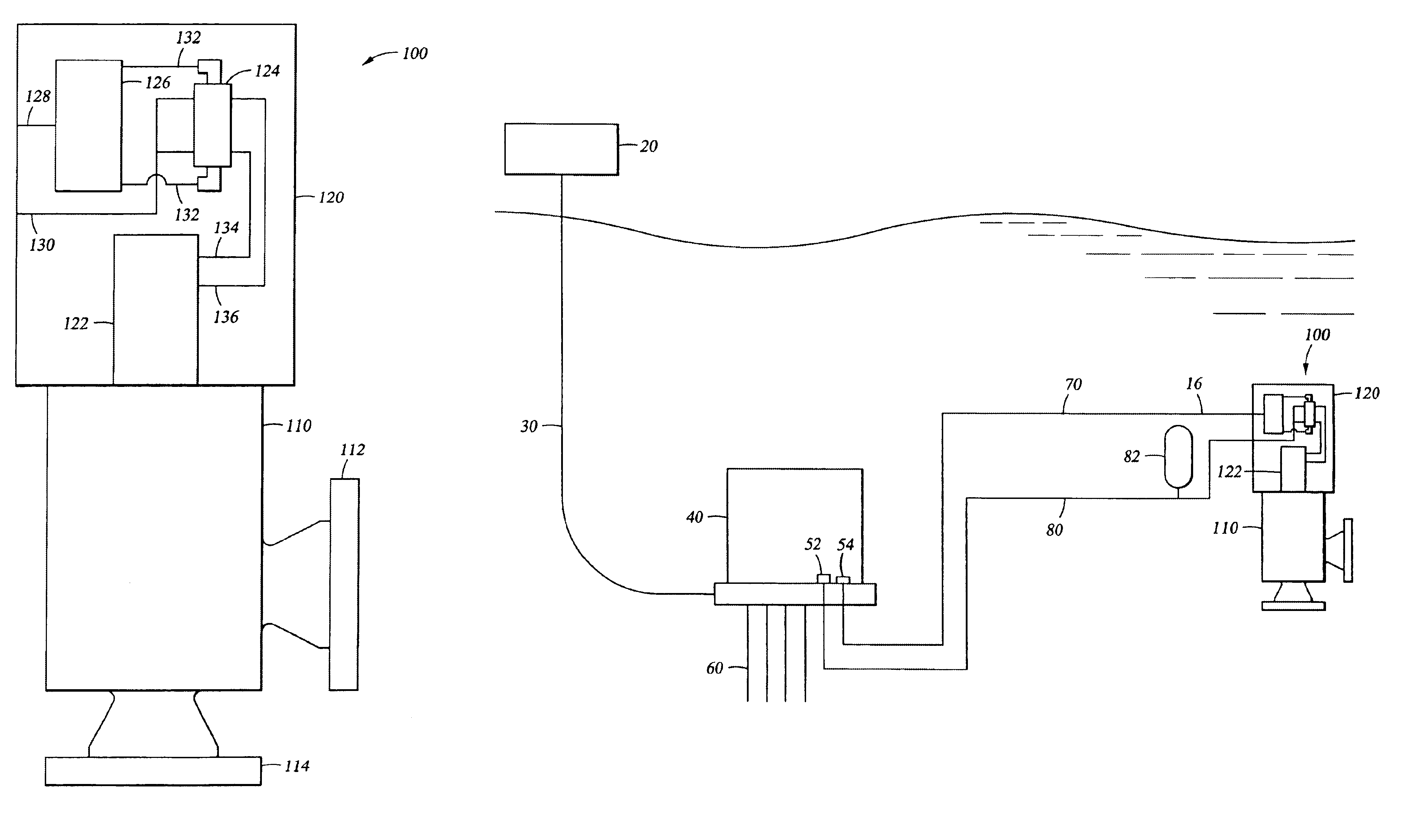
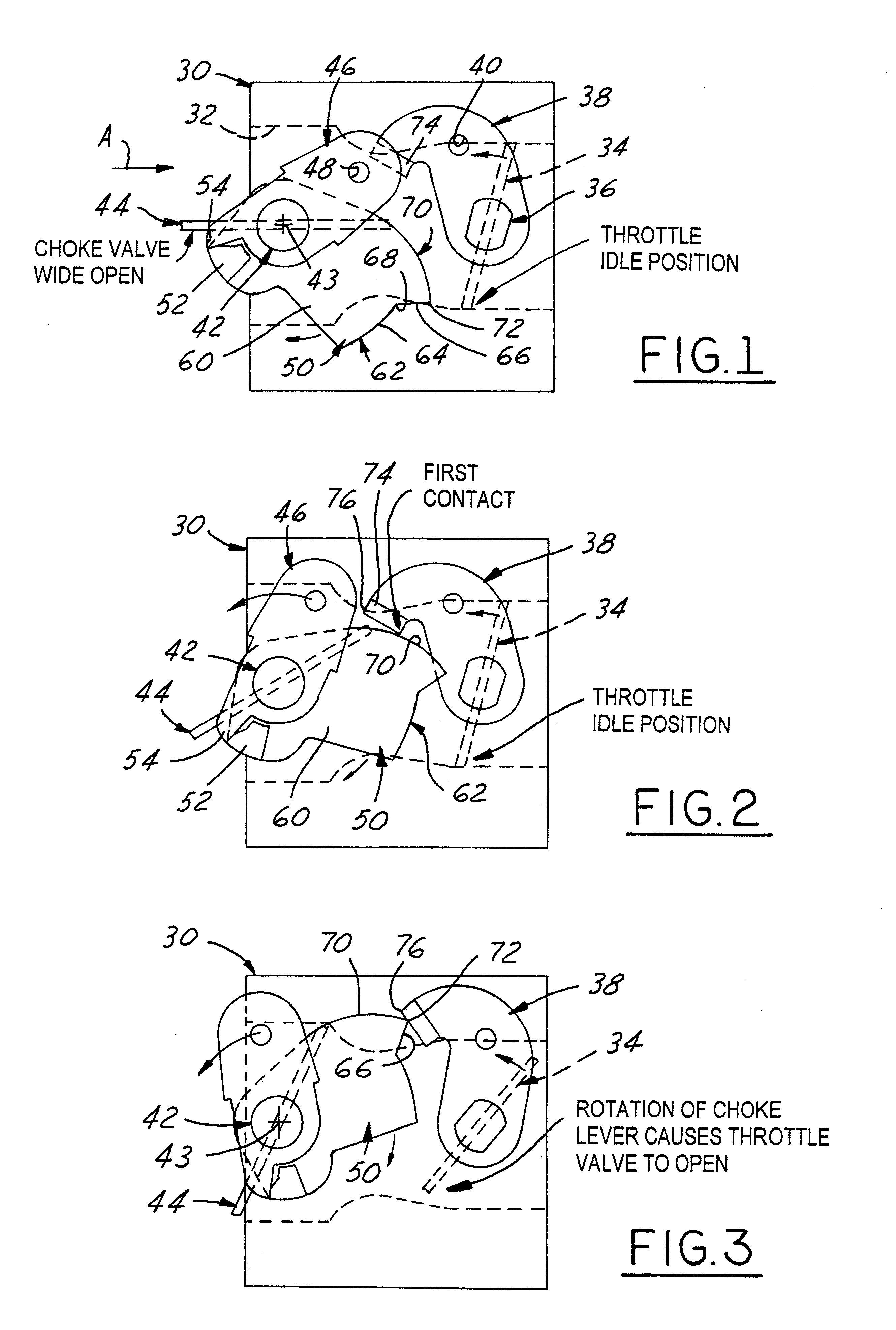
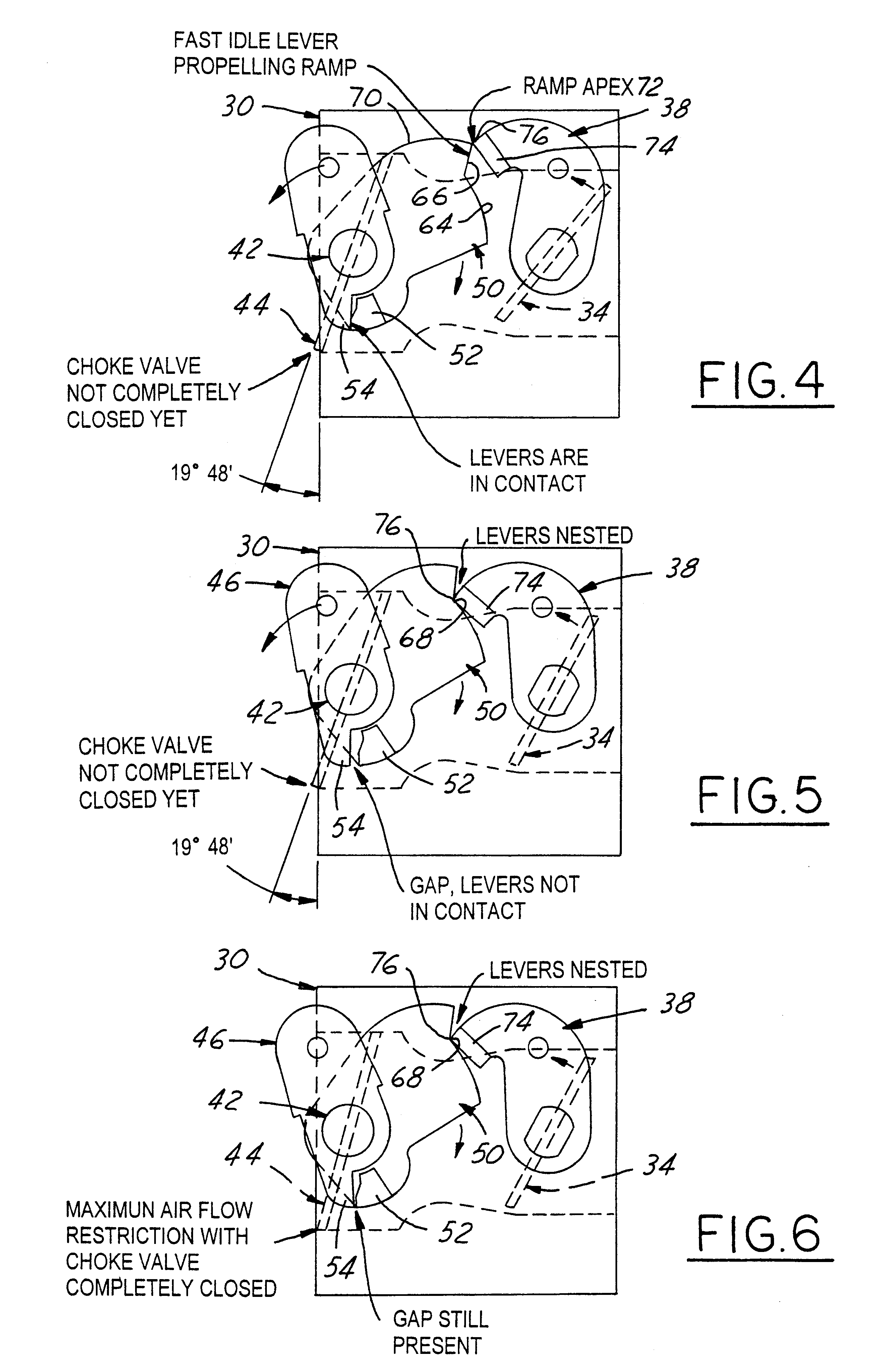
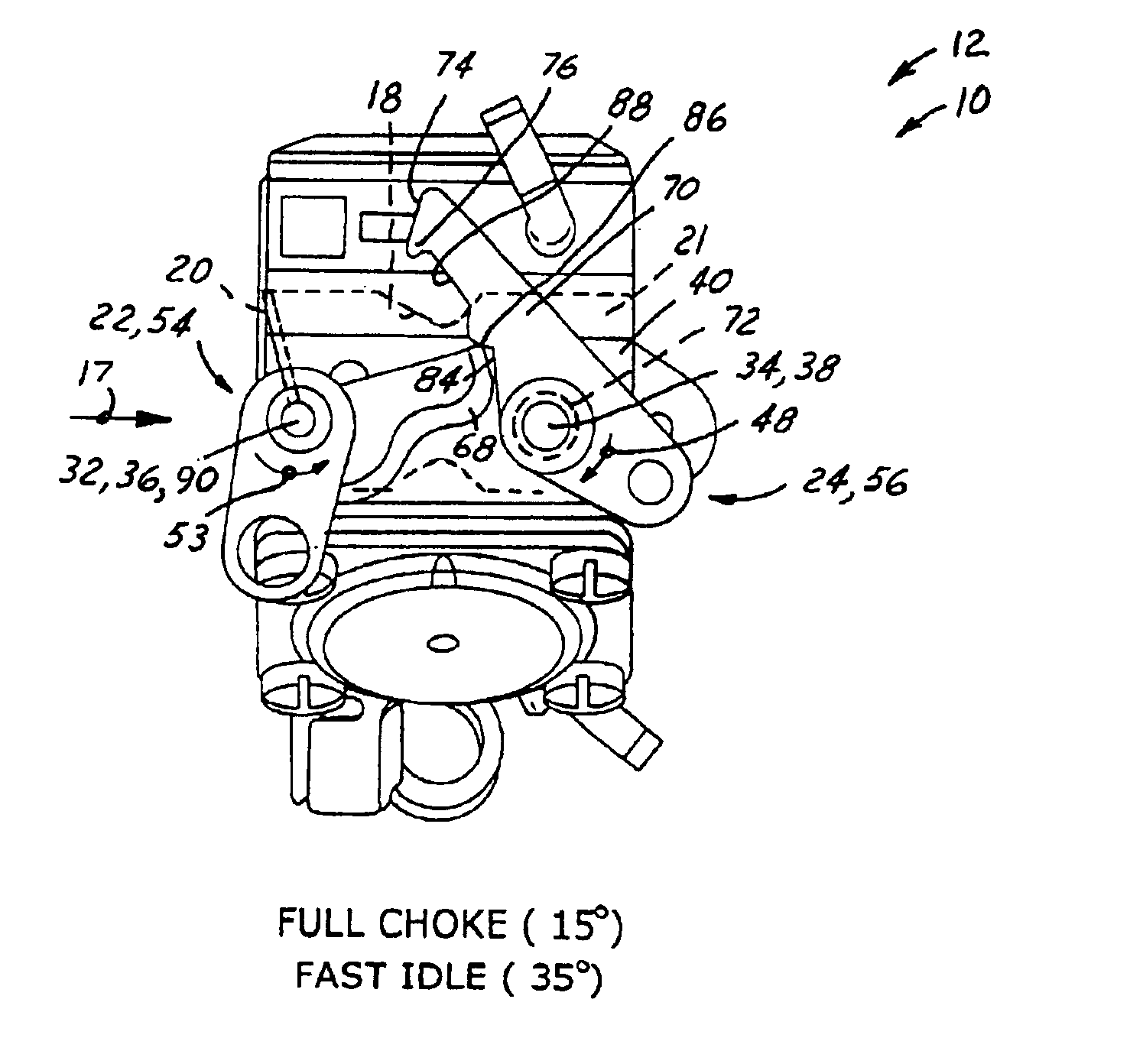
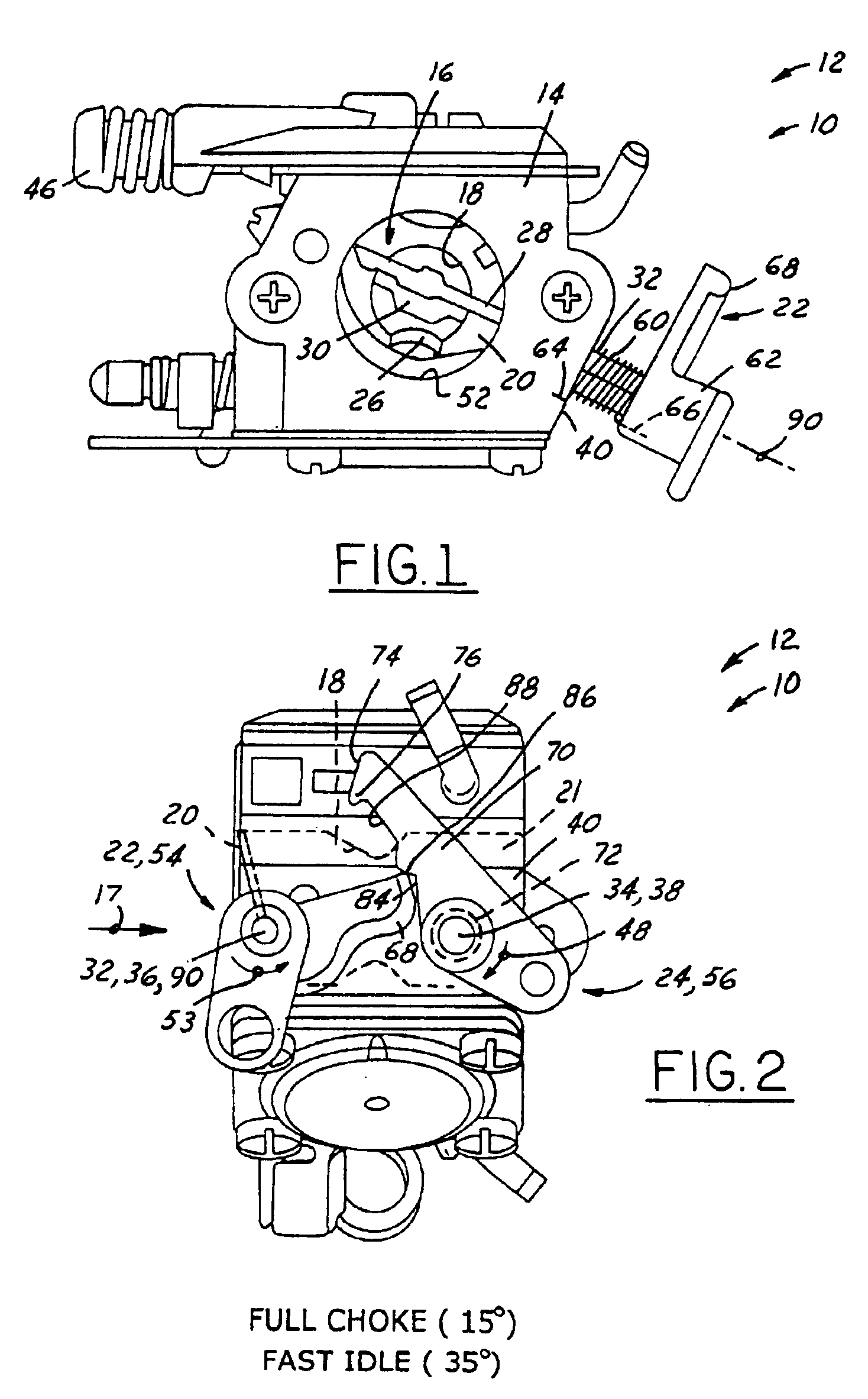
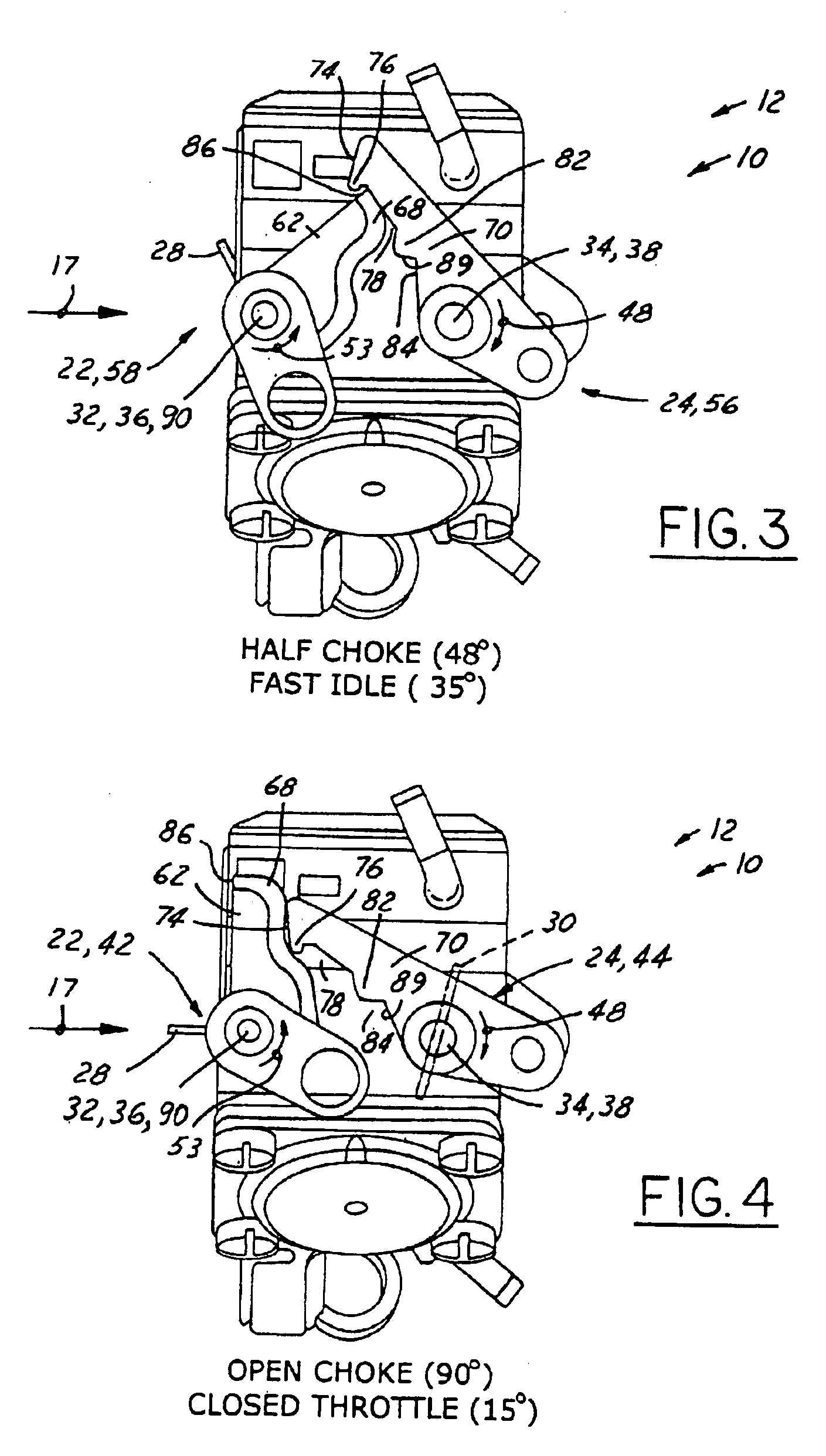
Carburetor throttle and choke control mechanism
InactiveUS6202989B1Low costEasy to modifyElectrical controlLighting and heating apparatusIdle speedCarburetor
A control mechanism for a carburetor having a throttle valve and a choke valve each having at least a cold-starting position and a full-speed position. The throttle valve is spring biased toward its third, low idle position, and the choke valve is mounted on a choke shaft and is spring biased toward its full-speed open position. When the choke valve is moved by a choke shaft lever from its open position toward its cold start closed position a fast idle lever associated with the choke valve shaft engages, via releasable latch parts, a throttle lever associated with the throttle valve. The interengaging latch parts of these fast idle and throttle levers hold both valves in their respective cold-starting positions in opposition to their respective biasing springs. These latch levers can be released by operator actuation of the throttle valve control, thereby causing the choke valve to be automatically returned to its open position by its biasing spring, or, alternatively, the choke valve can be moved independently to its full-speed position. One of these fast idle and throttle latch levers has a notch, and the other has a pawl selectively engaging the notch when it becomes aligned therewith when the latch levers are operator-actuated to their respective cold start positions. The choke shaft is torsionally resilient so that when the choke shaft lever is forced to override initial-choke-closed position, it thereby twists the choke shaft after the choke valve has been bore-stopped at closed position. Upon release of operator actuating force, this feature prevents most, if not all of the previous retrograde movement of the choke and throttle valves out of their design cold start positions, despite operating slack in the latch system due to manufacturing tolerance stack-up in the various parts of the latch system parts and / or control mechanism in their assembly and operation.
Owner:WALBRO ENGINE MANAGEMENT
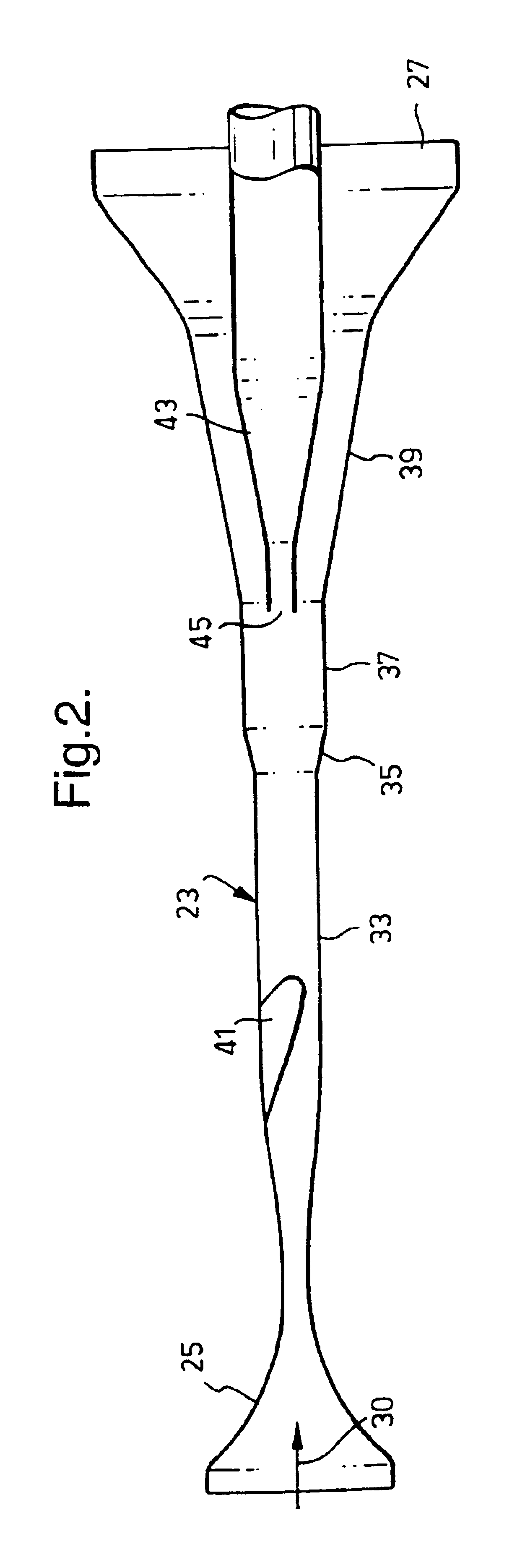
Interstitial microwave antenna with miniaturized choke hyperthermia in medicine and surgery
InactiveUS7113832B2Minimally invasiveAllow useElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyElectrical conductorReflected waves
The present invention relates to minimally invasive surgery techniques. It provides a method for manufacturing an antenna for percutaneous acute hyperthermia microwave applications of the monopole or dipole co-axial type provided with trap, commonly called choke, for blocking the propagation of the backwards reflecting wave towards the generator. The miniaturization of the device allows a use minimally invasive for interstitial hyperthermia in medicine and surgery, in particular for oncology. The method of manufacturing the antenna provides a metal needle (1) for the introduction of the antenna (2,3,4) in the target tissue. On the external conductor (4) of the antenna (2) a metal collar 6 is connected in a predetermined position; a plastics sheath (5) is applied in order to cover the external conductor (2) in the portion between the feed (7) and the collar 6; the inner wall of the metal needle 1 wherein the antenna is inserted is then used for containing and guiding the collar 6 and the sheath 5; in particular, the collar 6 being in electrical contact with the inner wall of the metal needle 1. An antenna is thus obtained with choke of variable length and with miniaturized diameter. A thermocouple can be introduced through the choke that protrudes the directly in the “feed” zone.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Automated closed loop flowback and separation system
InactiveUS8424599B2Realize automatic adjustmentSurveyDrilling rodsHuman–machine interfaceAutomatic control
An automated closed loop flowback and separation system that allows automated control and remote operation of a flowback operation from a safe distance without any fluid or gas release to the atmosphere. Four-phase separation tanks allow the transport gas, well bore cuttings, produced oil, and produced water to be automatically separated and transported through process piping for reuse or sale, eliminating the need for auxiliary equipment. Flow measurement instruments, pressure transmitters, and level transmitters work in conjunction with an automated blast choke to send data to a programmable logic controller for use in calculating the erosion status of the choke restriction and adjusting the choke to compensate. The programmable logic controller works with a touch-screen or similar human-machine interface to allow remote monitoring and control or automated control of the system. The automated blast choke can vary the choke restriction opening based on the pressure differential and flow rate conditions.
Owner:CANADIAN FRACMASTER
Capacitive sensing system configured for using heating element as antenna electrode
A capacitive sensing system for a heating element comprises a capacitive detector connectable to the heating element and a common mode choke for connecting the heating element with a heating current supply. The detector drives an alternating current into the heating element and produces an output depending on the capacitive load, which the alternating current is subject to. Depending on the object sensed, the load varies in a range between a minimum and a maximum value. The choke represents an inductive load in parallel of the capacitive load. The capacitive load and the inductive load contribute to a complex impedance dominated by the inductive load. A compensation capacitor arranged parallel to the choke represents an additional capacitive load also contributing to the complex impedance. The compensation capacitor is dimensioned such that the sum of additional capacitive load and maximum value amounts to at least 50% of the inductive load.
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
Modular pressure control and drilling waste management apparatus for subterranean borehole operations
ActiveUS7207399B2Waste water treatment from quariesWater/sewage treatment with mechanical oscillationsDegasserDisposal waste
Owner:MI
Tubing hanger running tool and subsea test tree control system
InactiveUS20050217845A1Reduced rig timeImprove securityFluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsControl systemTubing hanger
A system for providing power to elements down-hole in a subsea well includes a control pod having at least one shuttle valve, a down-hole hydraulically-actuated device having at least one internal porting mechanism in fluid communication with the at least one shuttle valve, a blowout preventer stack connected to the down-hole device, the blowout preventer stack including a first ram and a second ram, and a choke line in fluid communication with an area between the first ram and the second ram. The at least one shuttle valve controls distribution of hydraulic pressure applied through the choke line to the internal porting mechanism for selective distribution of power to the hydraulically-actuated device.
Owner:MCGUIRE LINDELL V
Valve for use in wells
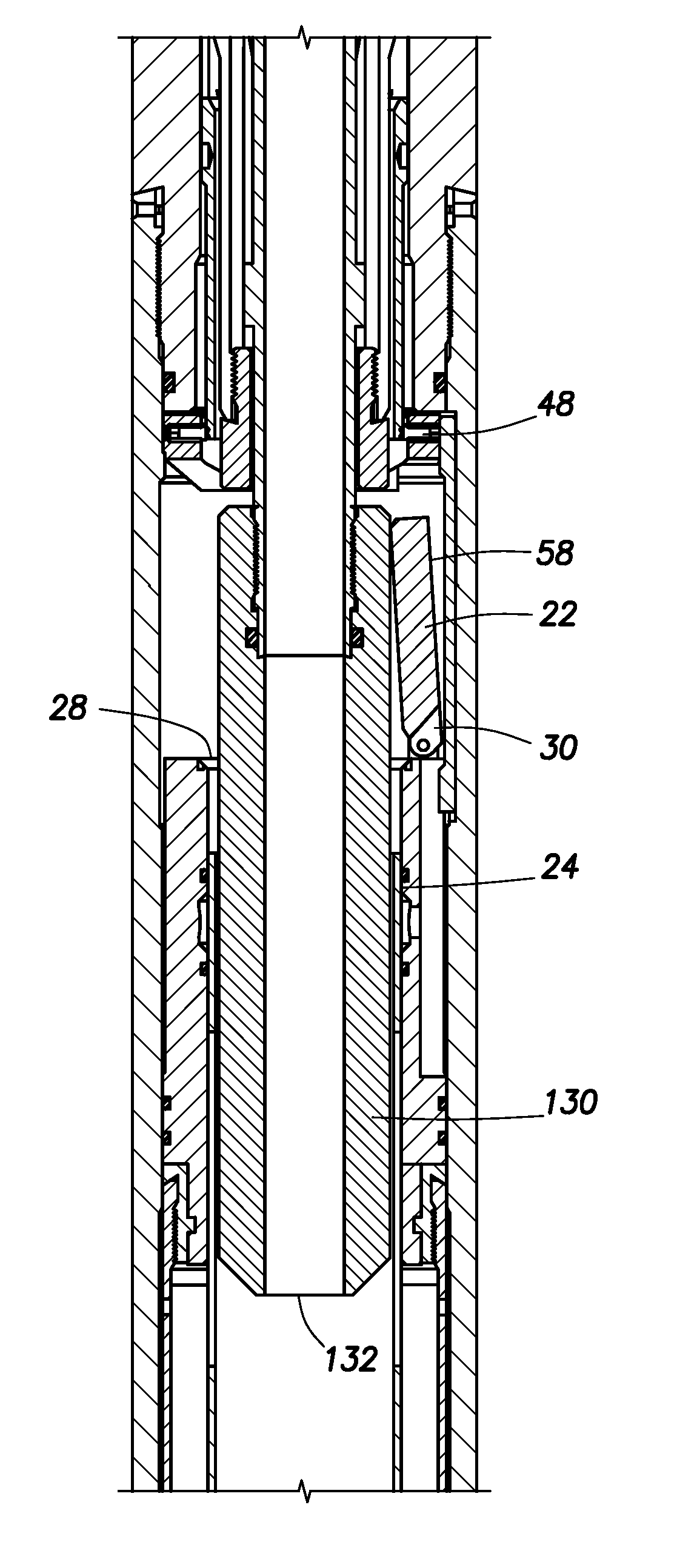
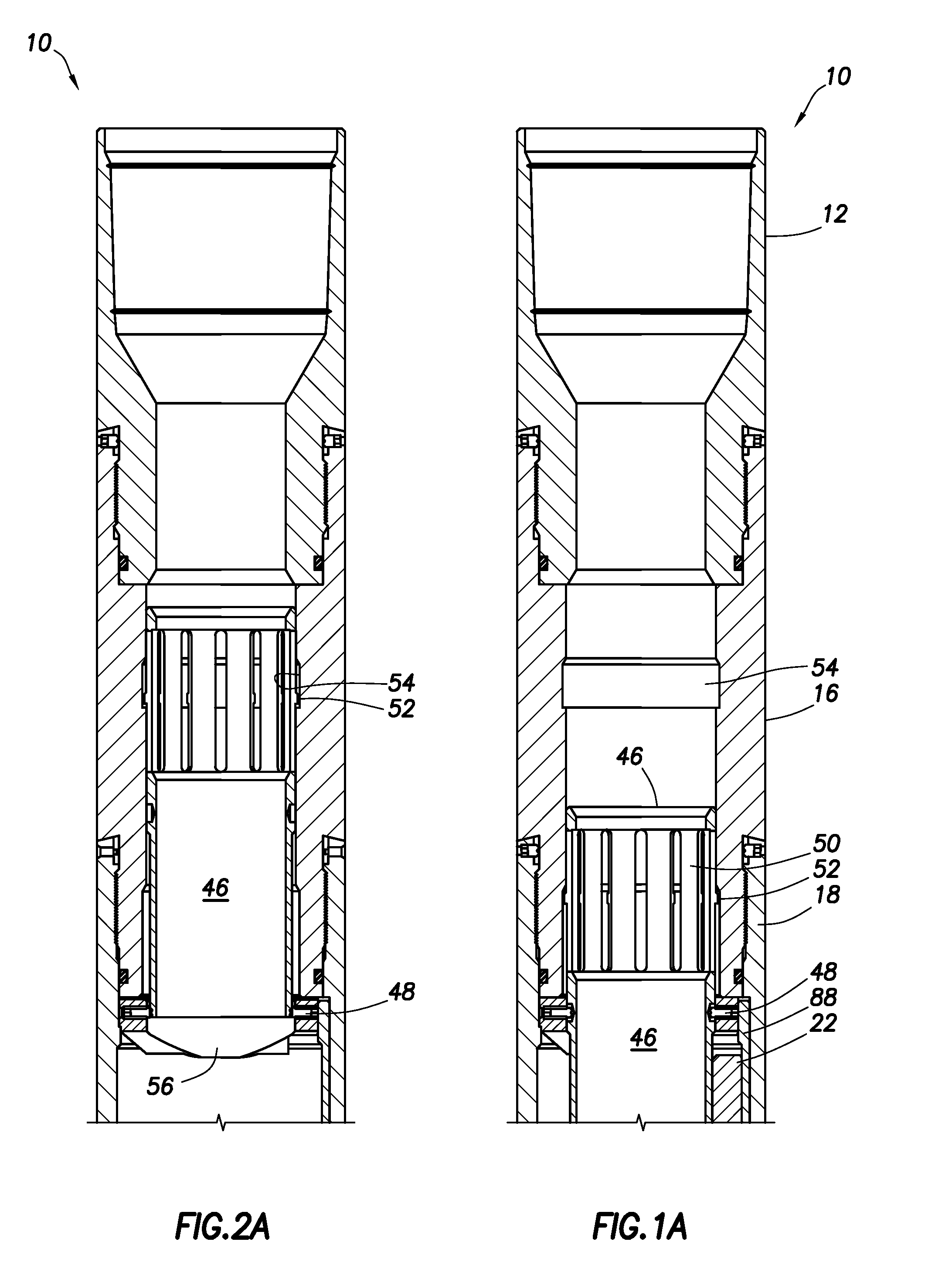
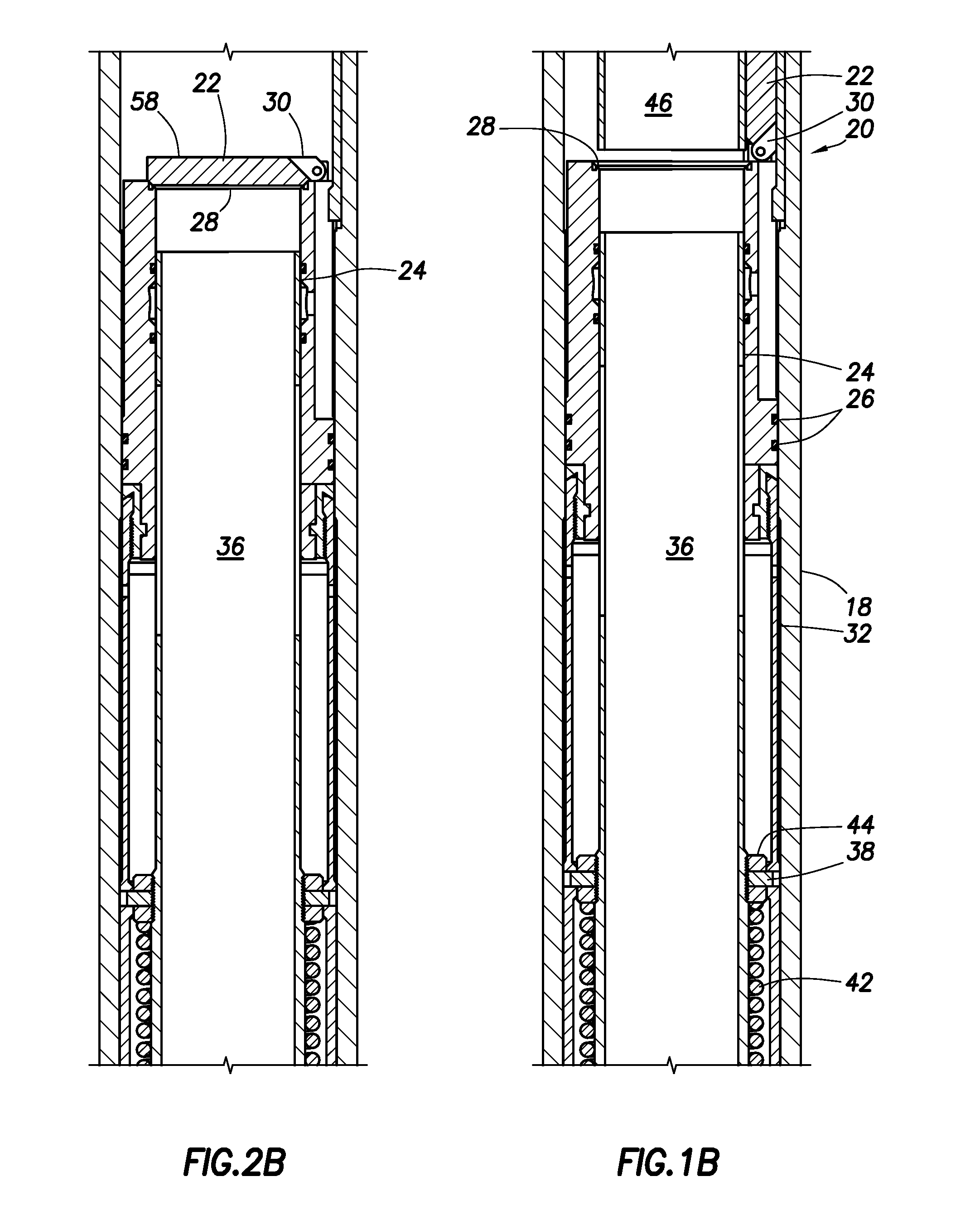
A valve assembly to control the intake of fluid. The valve assembly has a valve body and a valve choke disposed therein. The valve choke has a choke bore through the interior of the valve choke. The valve choke has a plurality of orifices to the choke bore spaced at intervals along the valve choke. A seal is disposed between the valve body and valve choke. The valve system is operable to position the valve choke so that the seal is positioned between the valve body and the valve choke at the intervals between the plurality of orifices.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
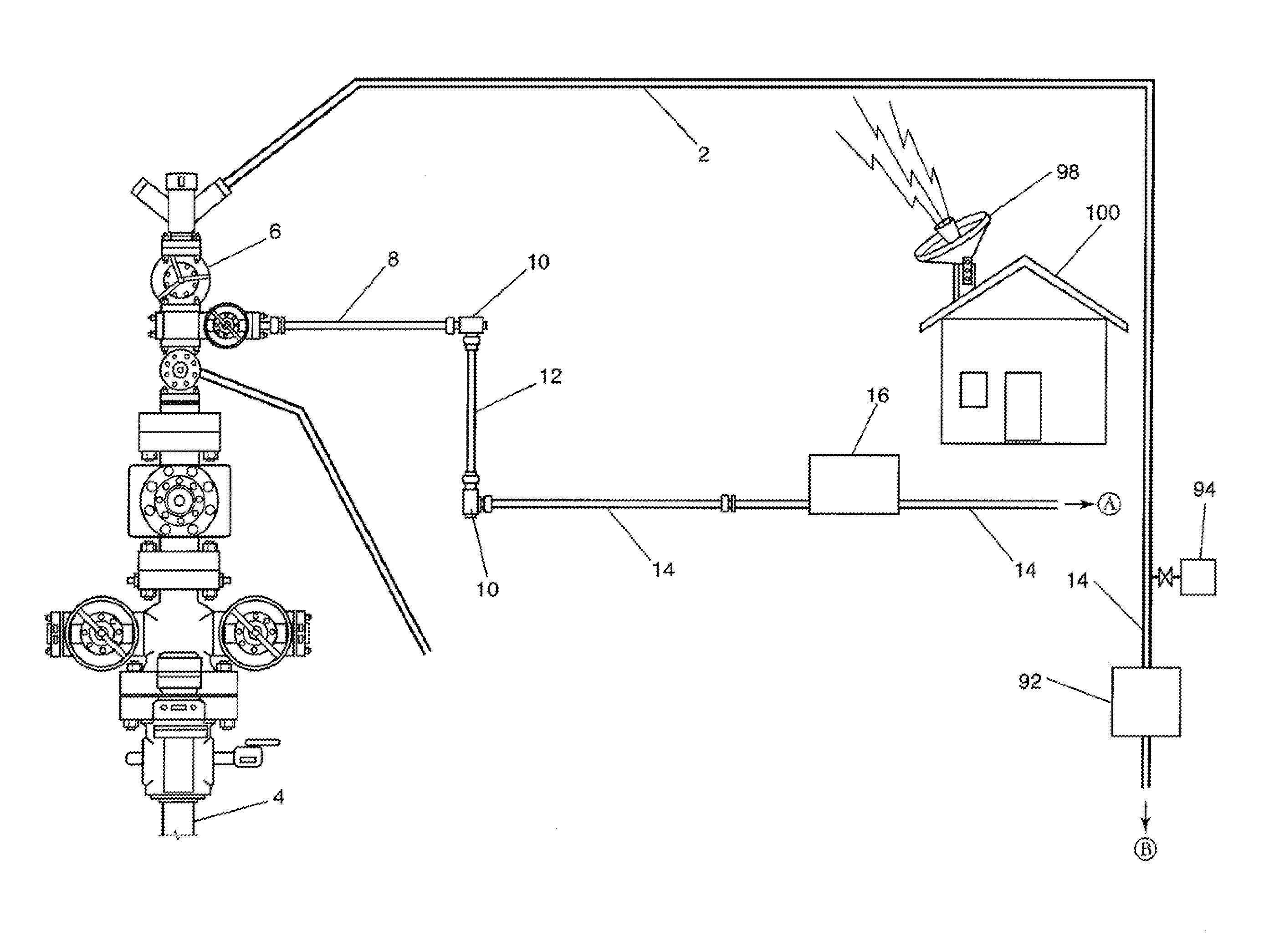
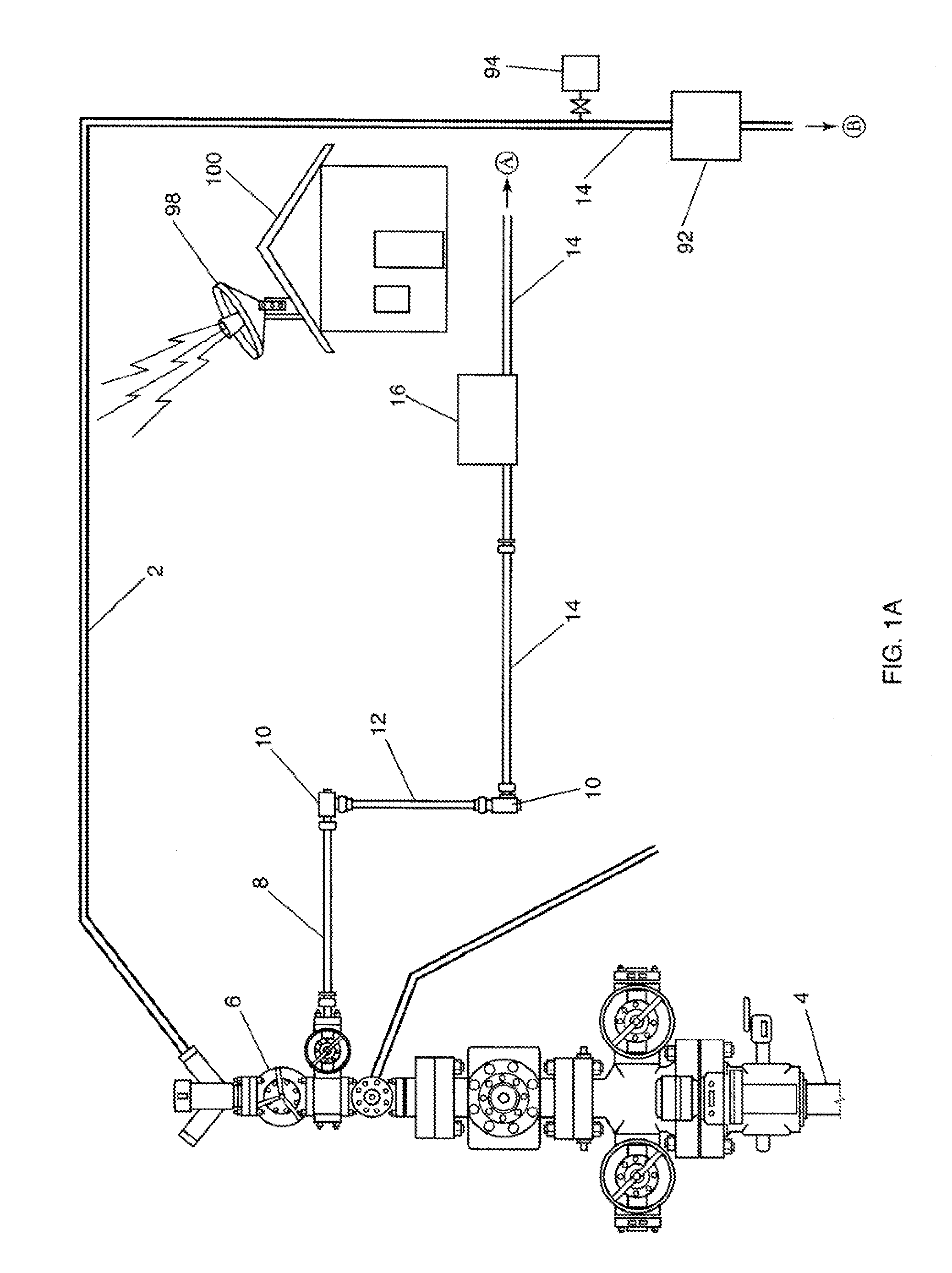
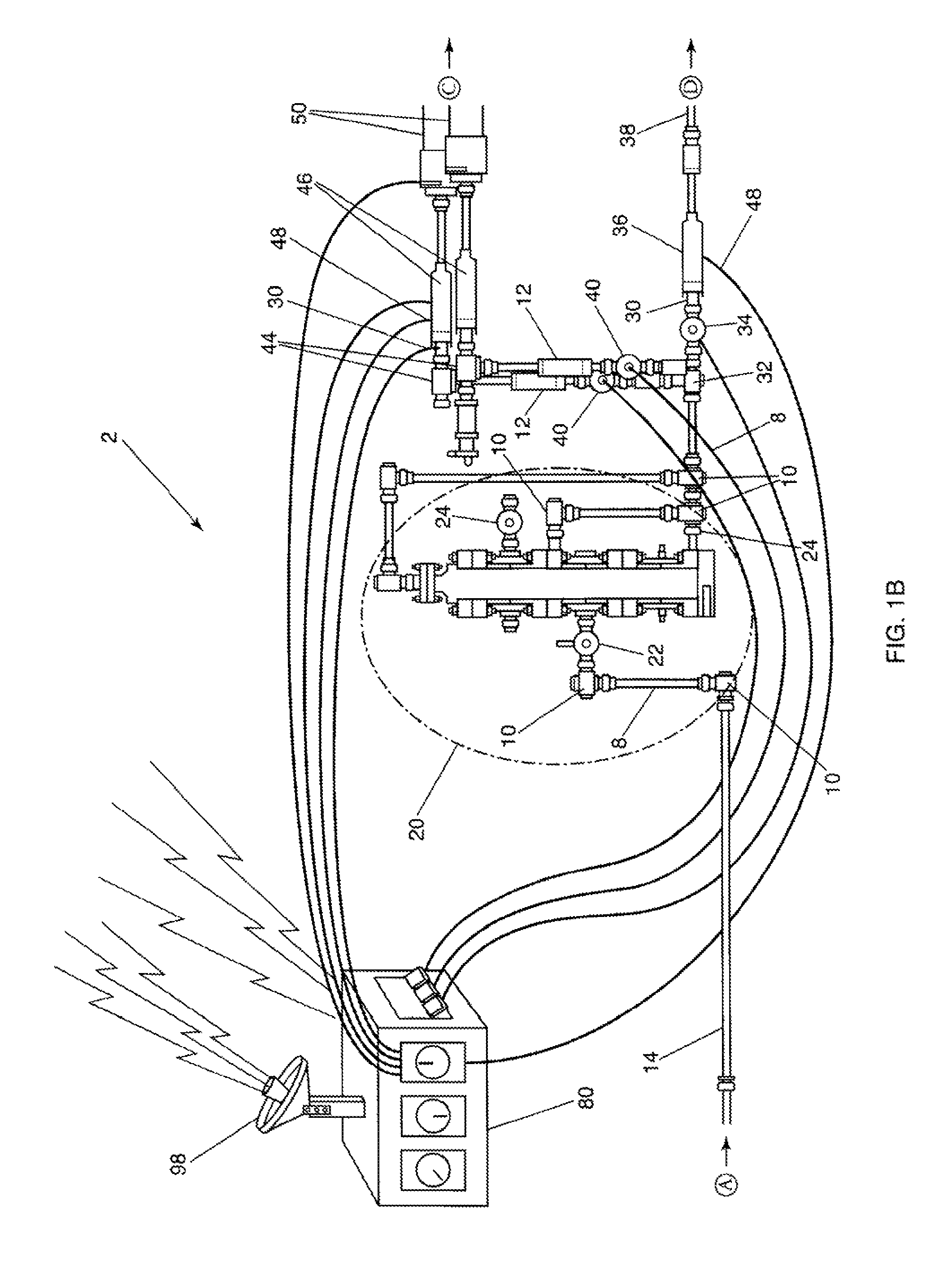
Subsea choke control system
A choke actuator having an integrated choke control system enabling fast closure and opening of the choke. The choke control system includes integral electronics to receive signals from a surface or subsea control module and control directional control valves to regulate the flow of hydraulic fluid from a local hydraulic supply to the choke actuator. Response times for choke actuation are greatly reduced by locating the electronic control system and directional control valves in an integrated package with the choke actuator and providing a local hydraulic supply. Additional embodiments may also include other electronic sensing and instrumentation enabling the choke control system to monitor and adjust the choke to maintain selected flow characteristics or in accordance with a predetermined production scheme. Any or all of the components of the choke, the choke control system, or the choke actuator may also be retrievable separately from the other components so as to allow maintenance and replacement.
Owner:COOPER CAMERON CORP
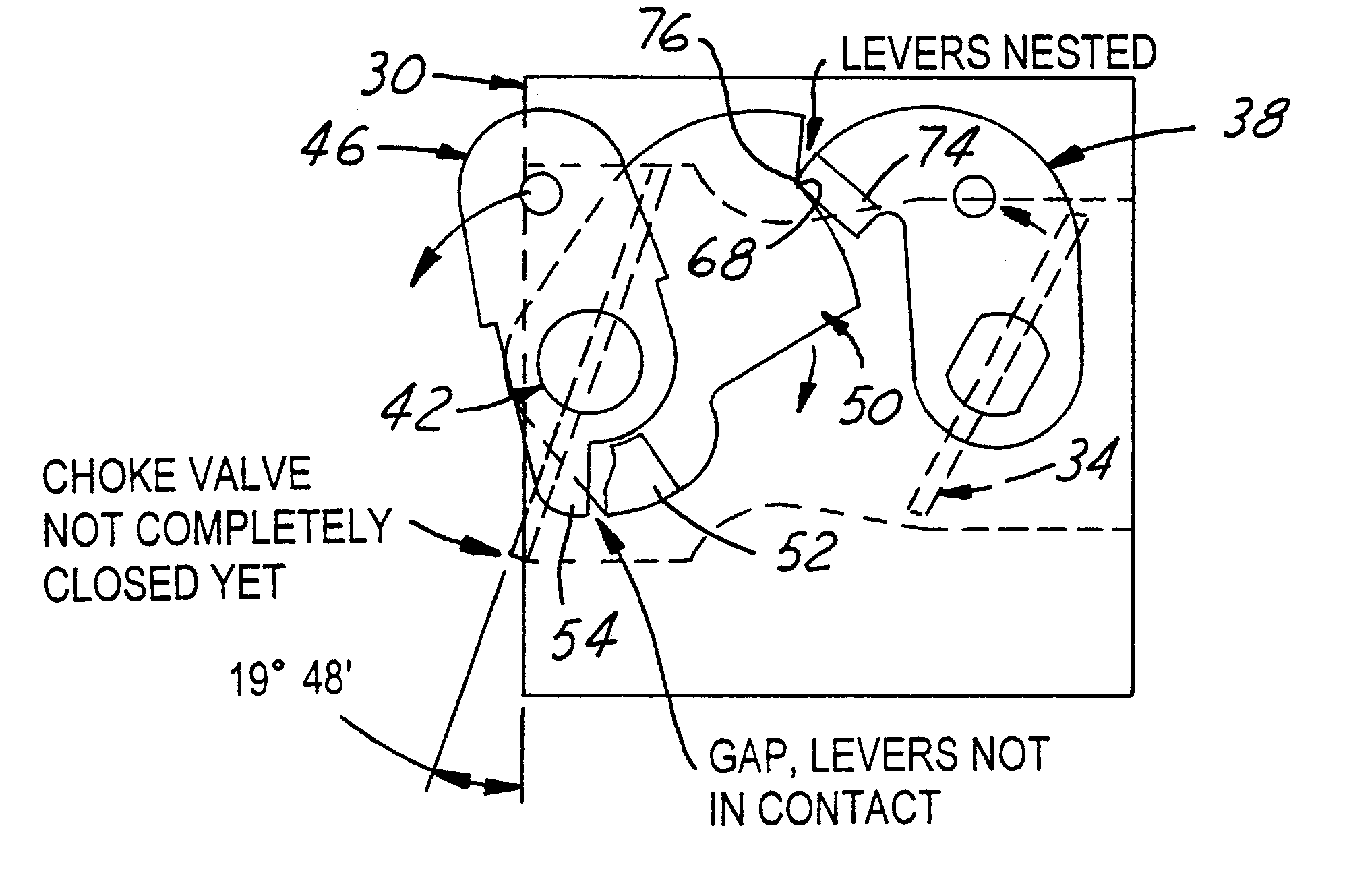
Carburetor throttle and choke control mechanism
InactiveUS6439547B1Low costEasy to modifyElectrical controlLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringAbutment
A carburetor throttle and choke control mechanism incorporating a choke-throttle cold-start fast idle setting latch mechanism having, in a first embodiment, a blade of a fast idle lever specially contoured for creating upon interengagement with a tang on a throttle lever initial torque resistance to co-rotation of the fast idle lever toward latched condition and then effecting force reversal for creating aiding torque to accelerate the fast idle lever relative to choke lever and thereby open a gap in the push coupling that remains in the latched position of the choke and throttle valves. The choke lever has a relatively rigid pusher leg portion adapted for abutment in push relation with a fast idle lever tang. In a second embodiment an extension of the leg portion in the form of a generally U-shaped resilient spring hook portion is adapted to overlap the tang and releasably hook engage the same when the leg portion is brought into full push abutment with said tang. The U-shaped hook portion is resiliently flexible to act as a spring to develop a torque on the choke by pulling the choke valve fully closed when said fast idle lever is moved to fully latched condition while flexing so that the gap remains between the pusher leg portion and the tang.
Owner:WALBRO LLC
Annulus check valve with tubing plug back-up
A subsea well has a tubing hanger which has an annulus bore and a production bore. A check valve is located in the annulus bore. A running tool runs the tubing hanger on a monobore riser such as a drill string while holding the check valve in the open position. After setting and testing, the running tool is lifted and a blowout preventer is closed around the landing string. The operator monitors the choke and kill line of the drilling riser, which will be in communication with the check valve. If the check valve is leaking, an annulus plug may be installed in the annulus bore. The installation of the annulus plug may be handled by using a retrieval tool configured to align the annulus bore with the landing string passage. A wireline tool may be lowered through the landing string and retrieval tool to retrieve the check valve and install the plug. Alternately, the check valve may remain in the tubing hanger and the plug is set in the annulus bore above it. The check valve is retained in the open position, if so.
Owner:ABB VETCOGRAY
Standpipe distributor for short time contact of hydrocarbon compounds with particles
InactiveUS6143253ACompact and convenientSmall and convenientCatalytic crackingFluidised-bed furnacesParticle flowJet flow
An arrangement for the controlled production of an essentially linear array of hydrocarbon feed injection jets reduces required clearances and elevation while facilitating modification of the contacting locating a feed distributor containing a linear array of jets at a standpipe junction point to provide choke point for particle flow control. The flow properties of the extended particle layer are controlled by adjusting the density of the particles above the choke point created by the upper part of the standpipe inside diameter and the top of the distributor. Steam or another fluidization medium may be added to the particles directly above the distributor for this purpose. This invention can also modify the particle or feed injection characteristics by changing the projection of the distributor into the standpipe to adjust the flow area over the choke point and by the use of bottom slides or baffles to change the flow area size and configuration. Location of the distributor at a standpipe junction will also typically allow the placement of the distributor at a lower location in the process which eliminates the need to add vessel height for supplying pressure drop for the particle discharge point. The distributor arrangement also fits compactly into most common standpipe junctions. Thus, the arrangement of this invention solves the problem of inserting an extended array of feed injection points into a fluidized particle contacting process without providing a large amount of clearance or additional vessel height.
Owner:UOP LLC
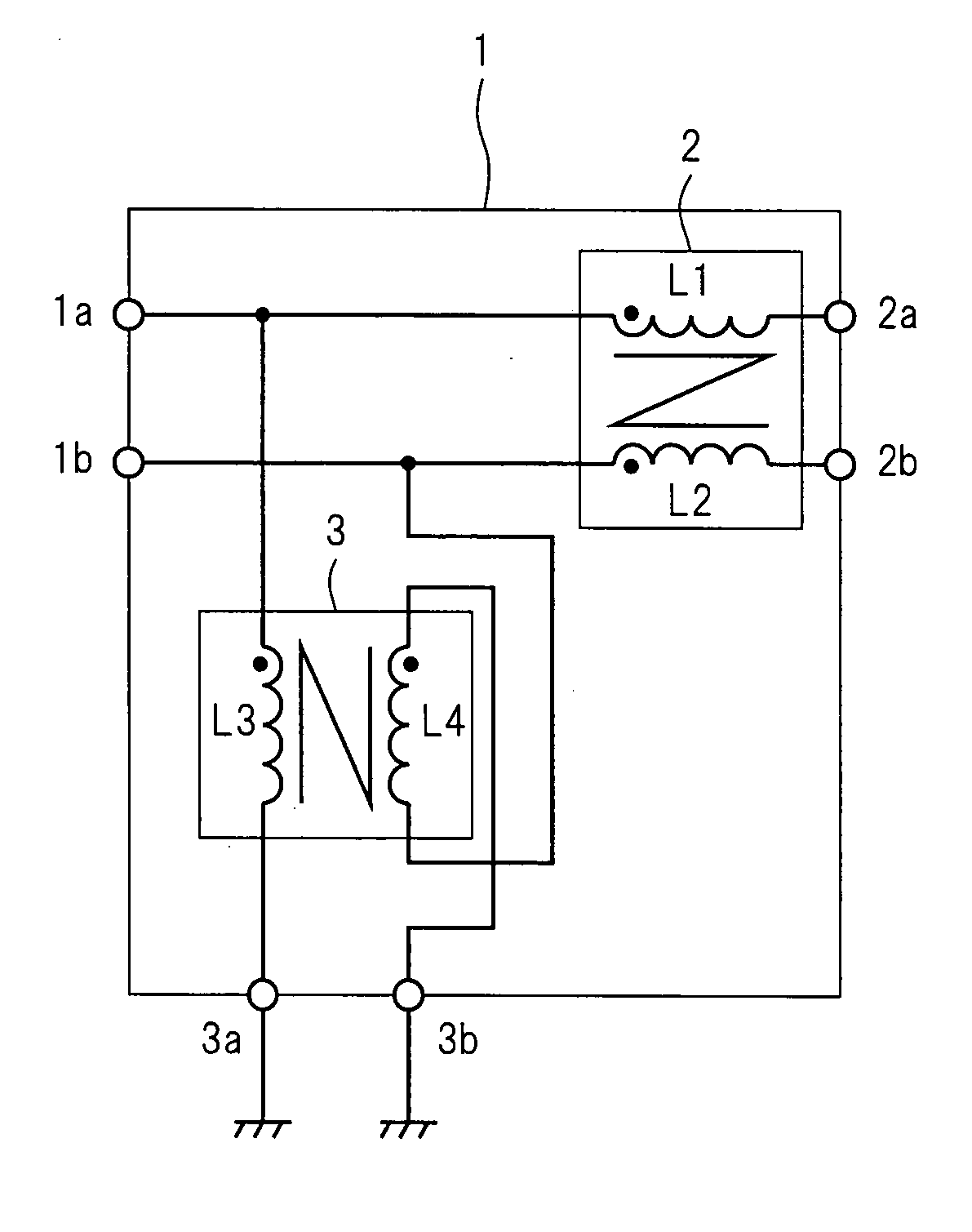
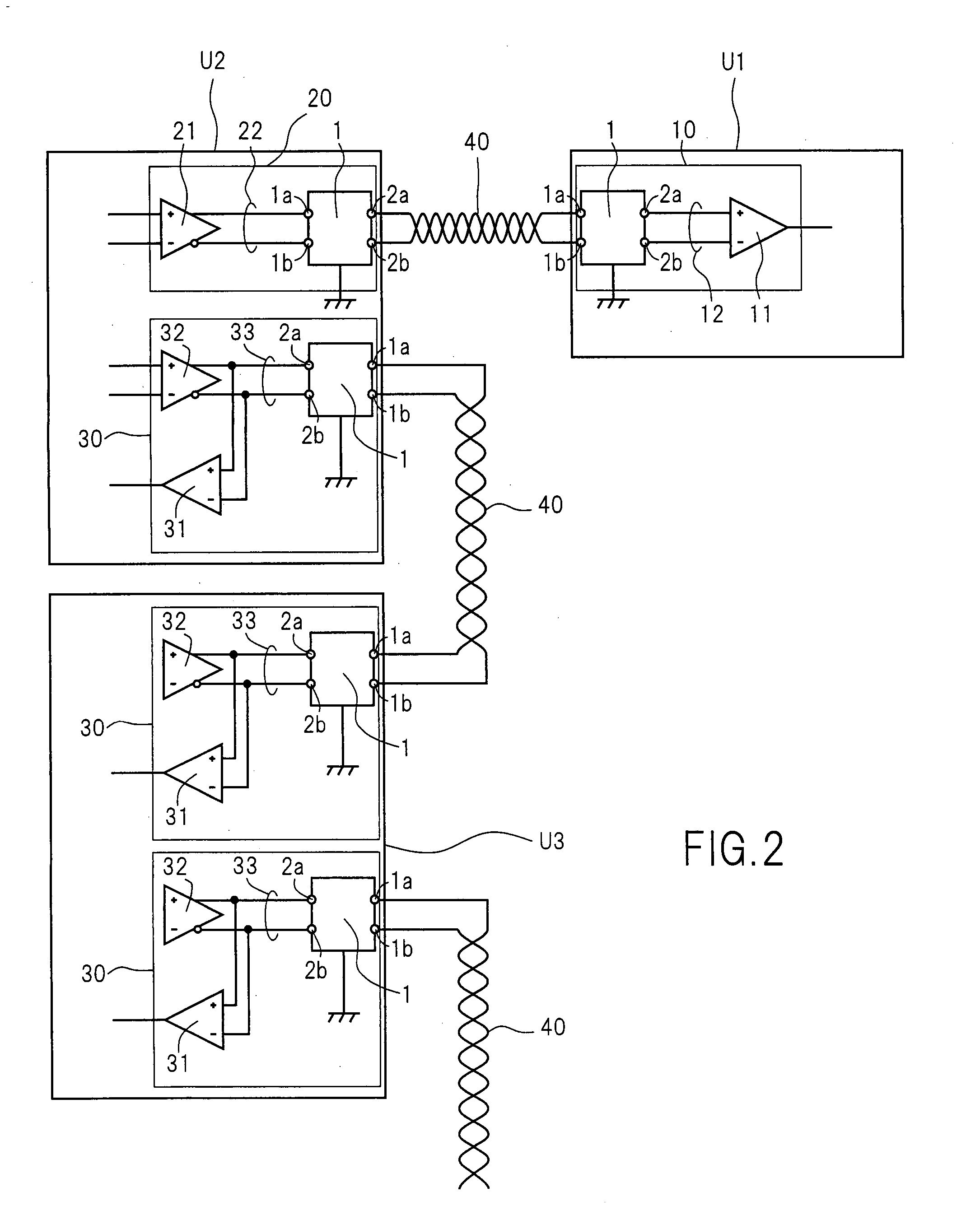
Filter Circuit, Differential Transmission System Having Same, and Power Supply
InactiveUS20070252659A1Quality improvementEnhanced inhibitory effectMultiple-port networksUnbalanced current interference reductionTransfer systemNormal mode
In a filter circuit (1), a common mode choke (2) and a normal mode choke (3) have extremely high and low impedances, respectively, for common mode signals received through two input terminals (1a and 1b). The chokes have the opposite impedance characteristics for differential signals. In particular, the difference in impedance is large. Furthermore, the normal mode choke (3) is installed as a previous stage of the common mode choke (2). Accordingly, common mode noises which enter the two input terminals (1a and 1b) penetrate the normal mode choke (3), but neither penetrate the common mode choke (2) nor are reflected from the common mode choke (2). In particular, common mode currents flow through the normal mode choke (3) but do not flow through the common mode choke (2).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
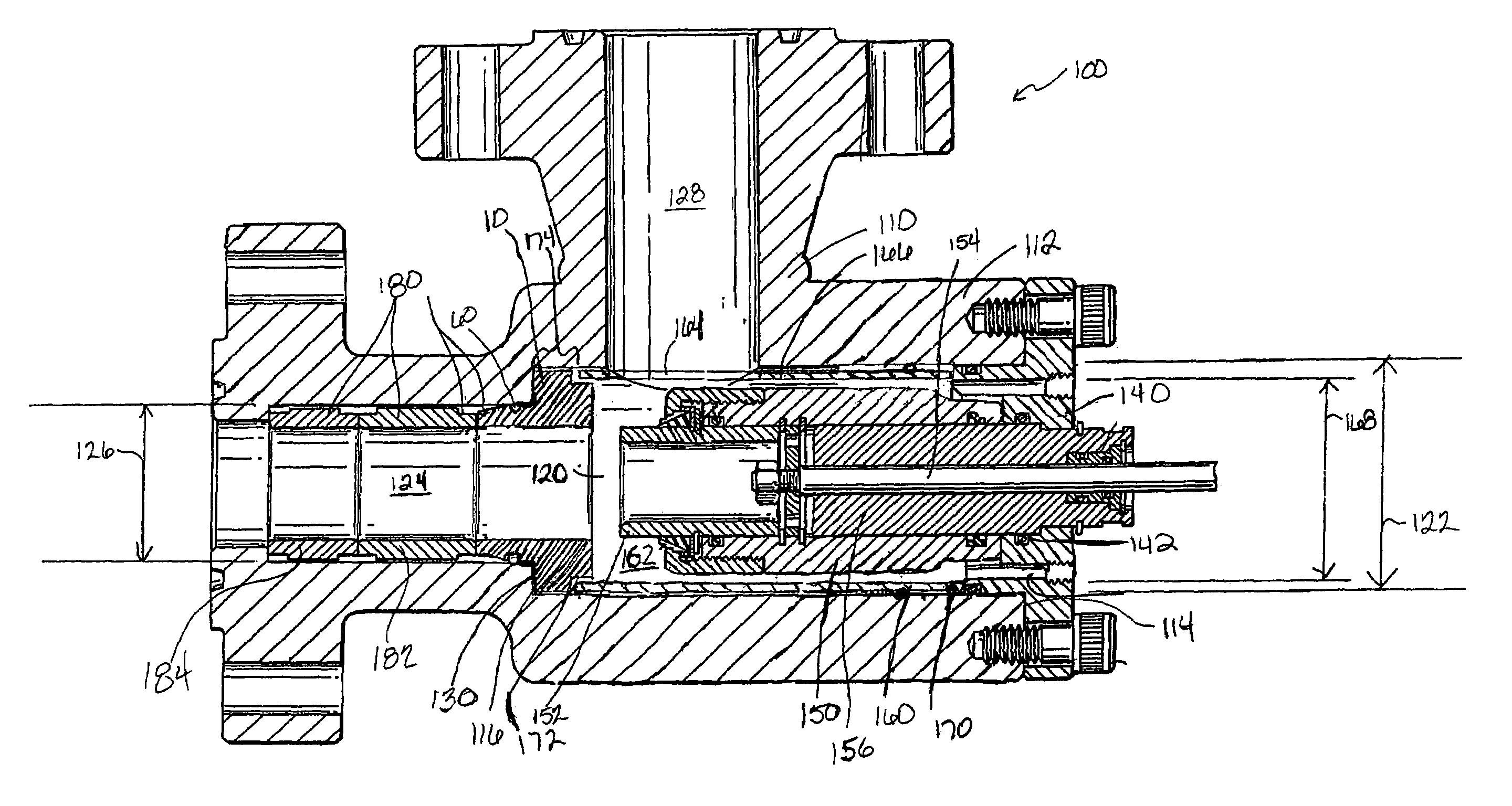
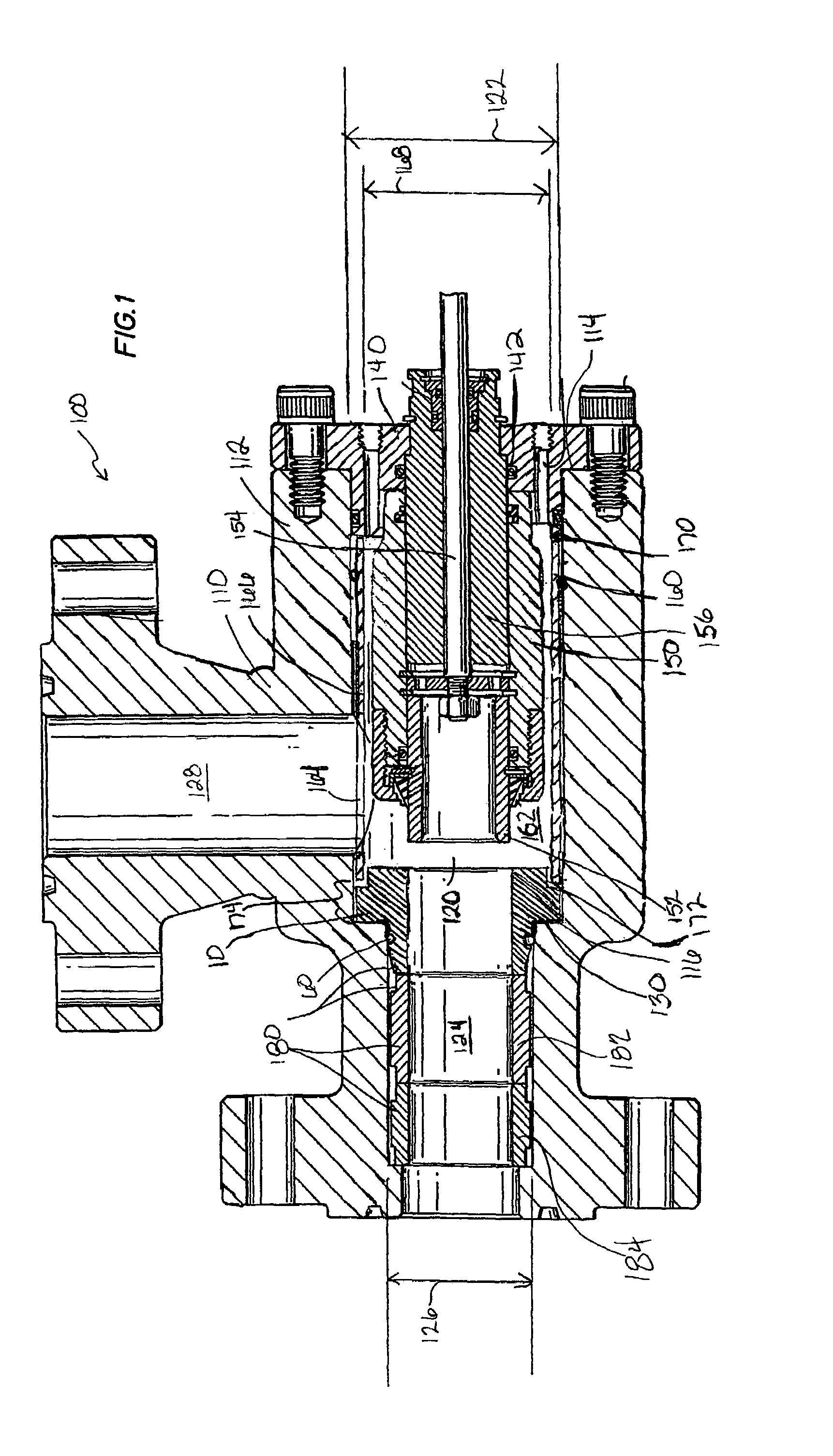
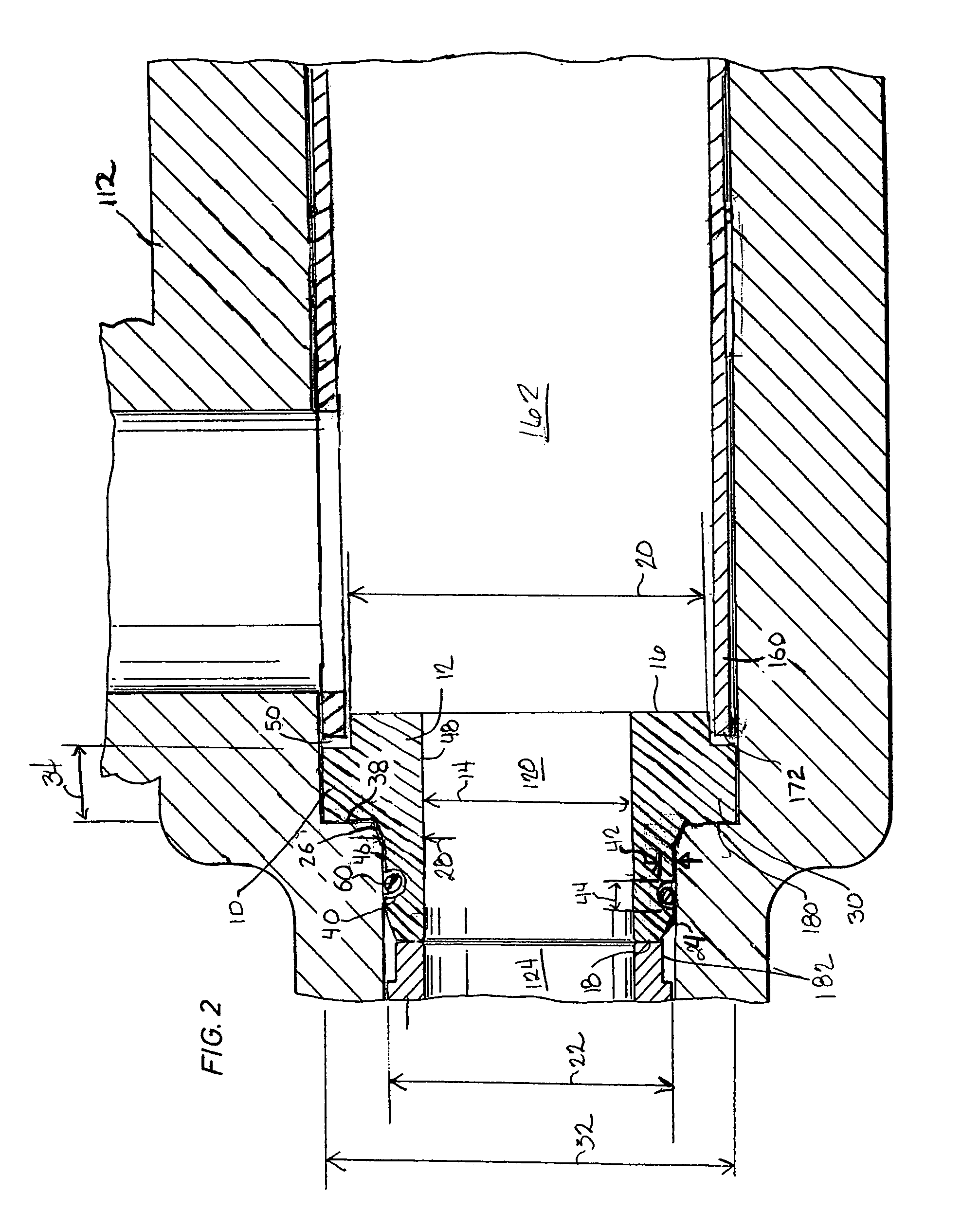
Trim insert for choke assembly
A trim insert for a choke assembly is disclosed, wherein the trim insert is a tubular member with a substantially constant inner diameter. A first end of the device is positioned within an adjacent upstream sleeve and a second end is sealingly retained within the discharge channel of the choke assembly. A flange coaxially retains the tubular member between the sleeve and a shoulder of the choke body. The trim insert is made of an erosion resistant material, such as tungsten carbide, hardened steel, or a ceramic. Additionally, the inner surface of the tubular member may be coated with a hardening compound to provide additional erosion resistance.
Owner:MI
Distributed well drilling simulation system and operation method
InactiveCN101789191AEnhanced sense of presenceShorten the training cycleCosmonautic condition simulationsSimulatorsTraining periodTop drive
The invention discloses a distributed well drilling simulation system and an operation method. The distributed well drilling simulation system comprises a choke-line manifold (101), a high pressure manifold (102), a blowout preventer console (103), a flow blocking machine console (104), a long-distance console (105), a driller console (106), a teacher console (107) and a figure projecting unit (108), wherein the driller console (106), the long-distance console (105), the blowout preventer console (103), the flow blocking machine console (104), the choke-line manifold (101) and the high pressure manifold (102) are interconnected through a PPI (processor / peripheral interface) protocol, and the teacher console (107) is connected with the PPI protocol through a PPI interface. The operation method comprises the steps of drilling down, pilling out of a hole, drilling, accident and complex condition processing, well shutting, well killing and the like. The invention has the advantages of realizing the simulation of a top driving well drilling simulation with highly simulation, enhancing the liveness of teaching and training, shortening training period and reducing the training cost.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Self-relieving choke starting system for a combustion engine carburetor
InactiveUS6848405B1Improves engine start-upAvoids engine stallingElectrical controlLighting and heating apparatusCombustion chamberEngineering
A self-relieving choke starting system for a carburetor of a combustion engine has an elongated cammed latch which projects radially outward from a rotating shaft of a choke valve located in an upstream region of a fuel-and-air mixing passage carried by a body of the carburetor. During a first attempt at starting a cold engine, the user manually rotates the choke valve from a spring biased open to a full choke position whereupon a cam end of the latch contacts a follower arm, which projects radially outward from a rotating shaft of a throttle valve located downstream of a venturi of the mixing passage. As the choke valve manually rotates closed, the throttle valve automatically rotates in an open direction against the biasing force of a throttle spring from a slow idle state, for normal engine operation, to a fast idle state for engine starting. Once the choke valve is in the full choke position and the throttle valve is in the fast idle position, a rich mixture of fuel-and-air will flow into the combustion chamber of the engine during the first attempt at starting the cold engine. If the first attempt should fail, the user can manually rotate the choke valve in an open direction to a half-choke position while the throttle valve is automatically maintained in the fast idle position to provide a slightly leaner mixture of the fuel-and-air to the engine for following attempts at cold starting.
Owner:WALBRO ENGINE MANAGEMENT
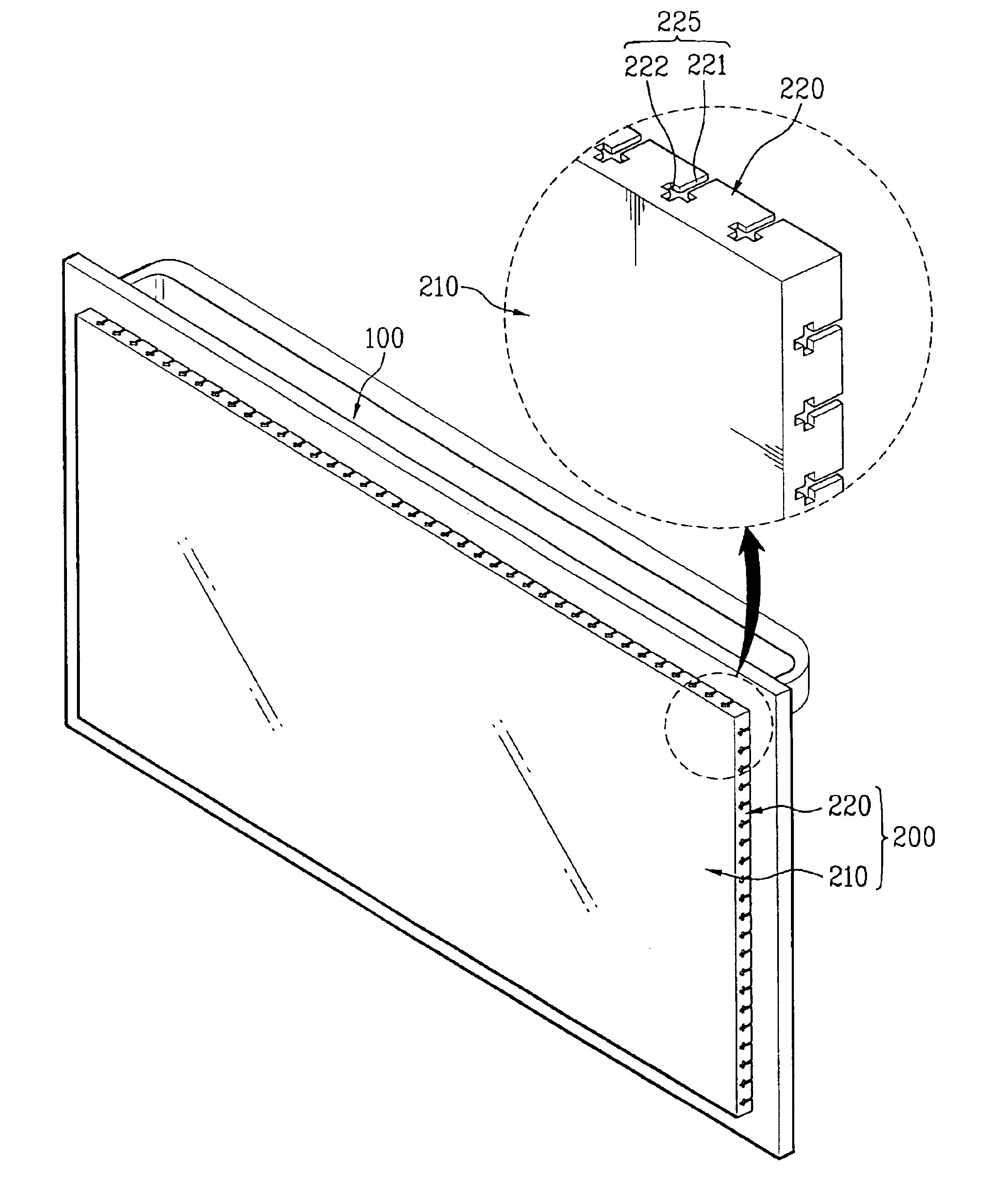
Door assembly of microwave oven
ActiveUS6927374B2Simple structureElectrically conductive connectionsDomestic stoves or rangesMicrowave ovenEngineering
A door assembly for a microwave or electric oven in which an optimum microwave-shielding frequency is not changed even though an incident angle of microwaves is changed, to enhance a user's convenience in cleaning a door. The door assembly for a microwave oven includes a door frame to open and close a cooking cavity, a door filter having a filter plate adhered to one side of the door frame, a choke portion bent to an opposite side of the cooking cavity in an edge of the filter plate, a first slot formed in a width direction of the choke portion, and a second slot formed in a length direction of the choke portion.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Positioning tool with valved fluid diversion path and method
A positioning tool for moving an element in a flow path of a down hole system without actuating a pressure actuated device in the system. The positioning device includes a choke for restricting flow of fluid between the positioning device and the down hole system, a flow diversion path from the upper end of the positioning device to a lower end of the positioning device, and a valve allowing fluid to flow through the diversion path when the choke is proximate the pressure actuated device and blocking flow of through the diversion path when the choke is displaced from the pressure actuated device. The down hole system may be a flapper type fluid loss device with a pressure actuated opening prop.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com