Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Minimize measurement error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
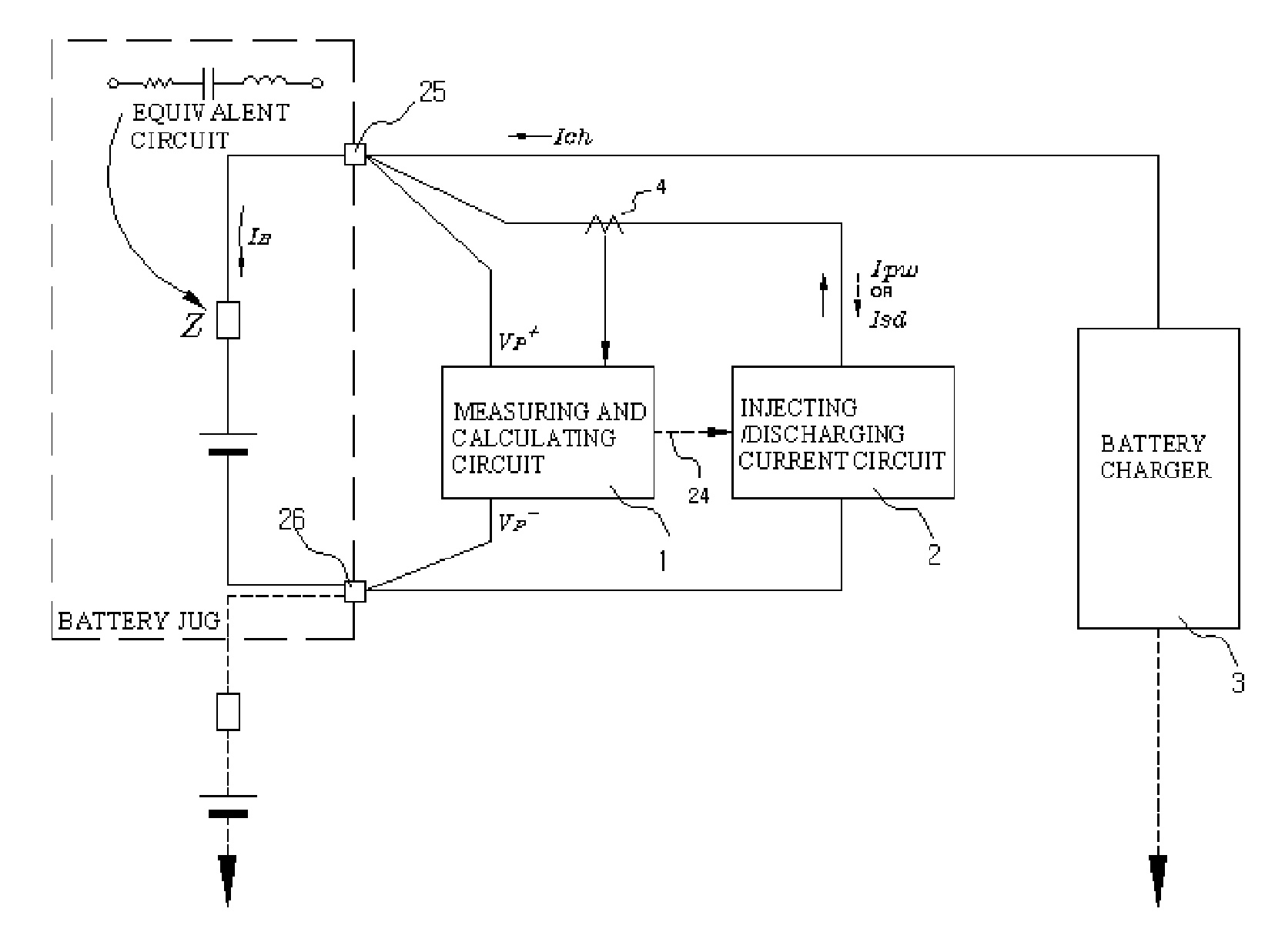
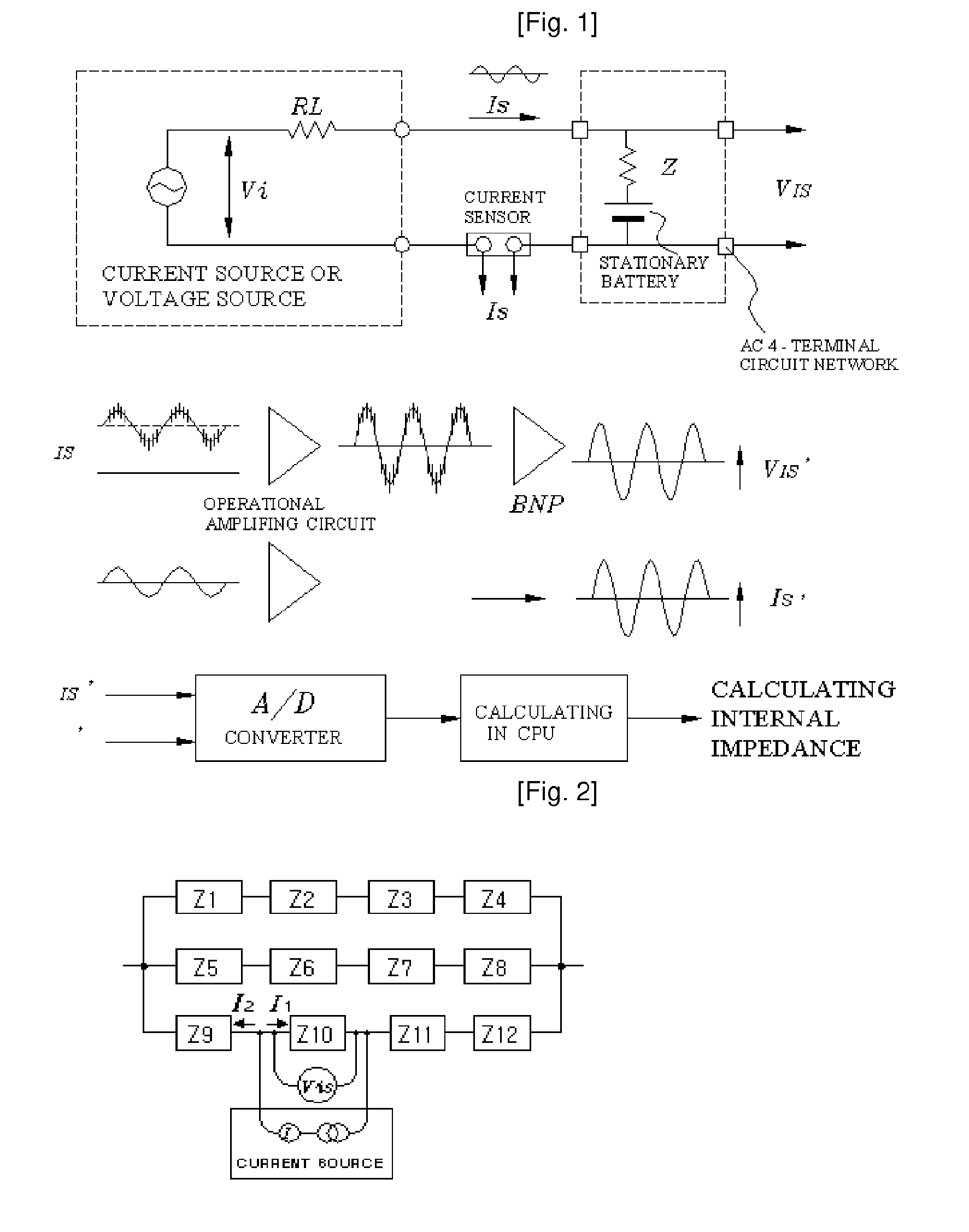
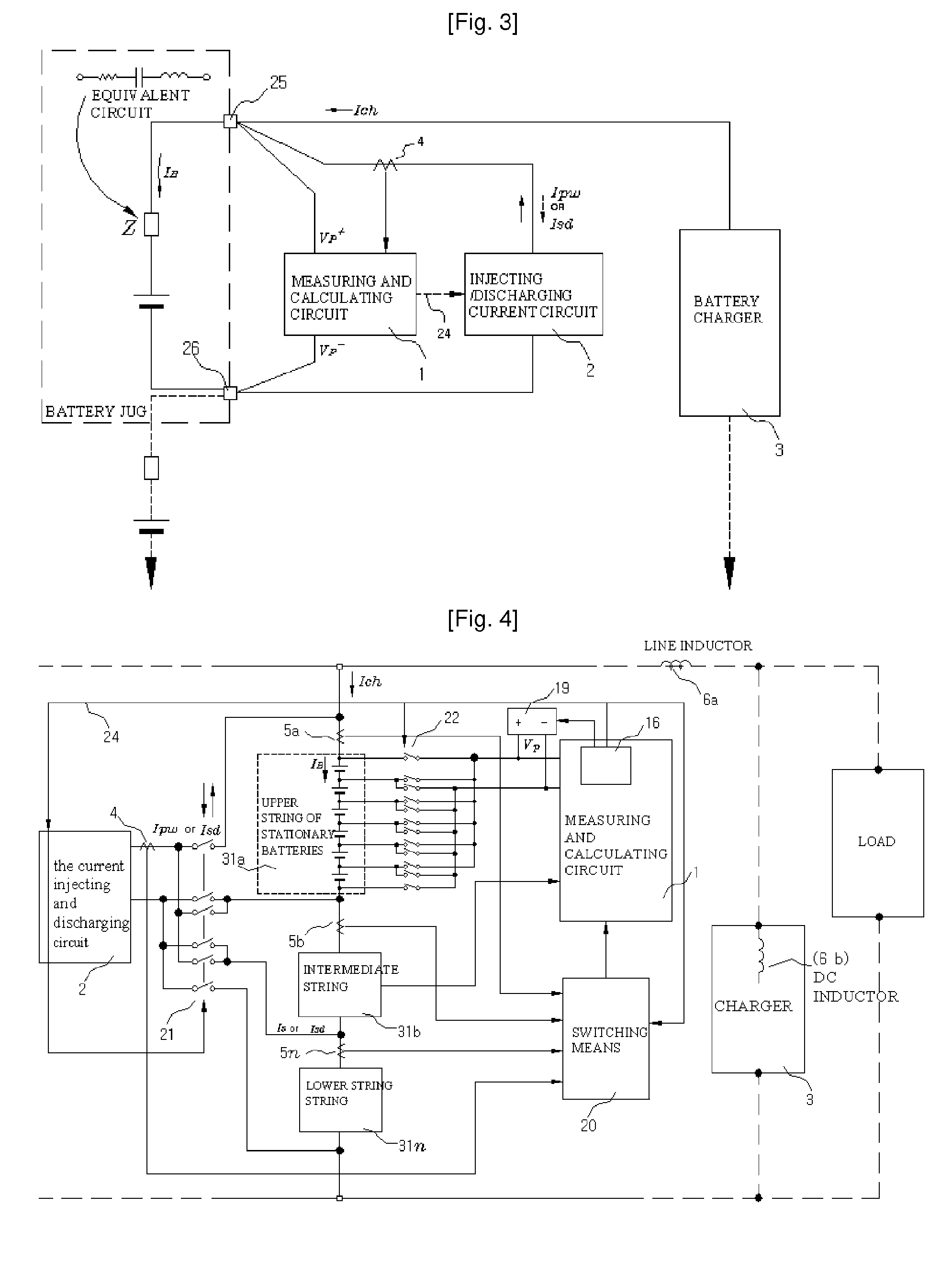
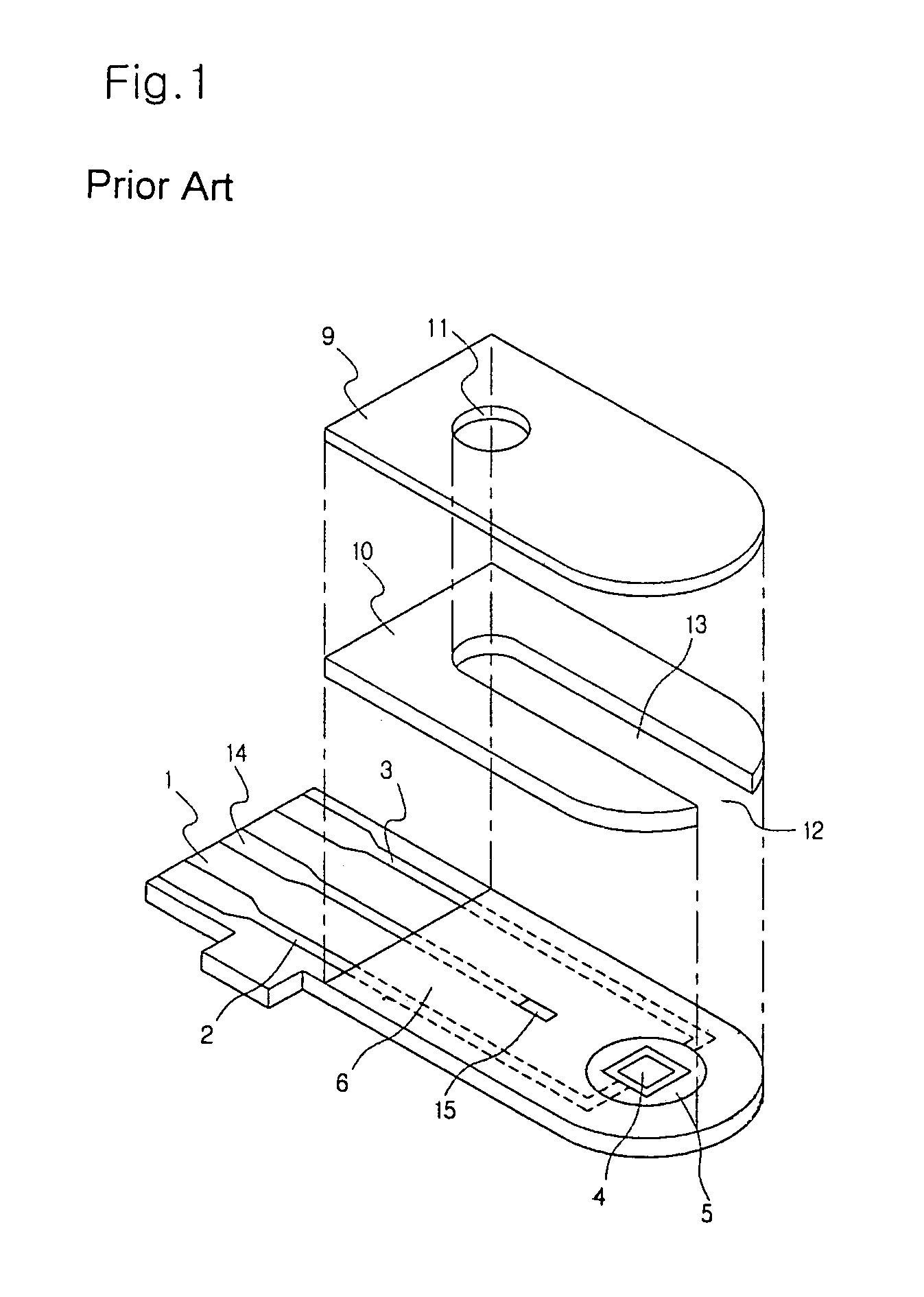
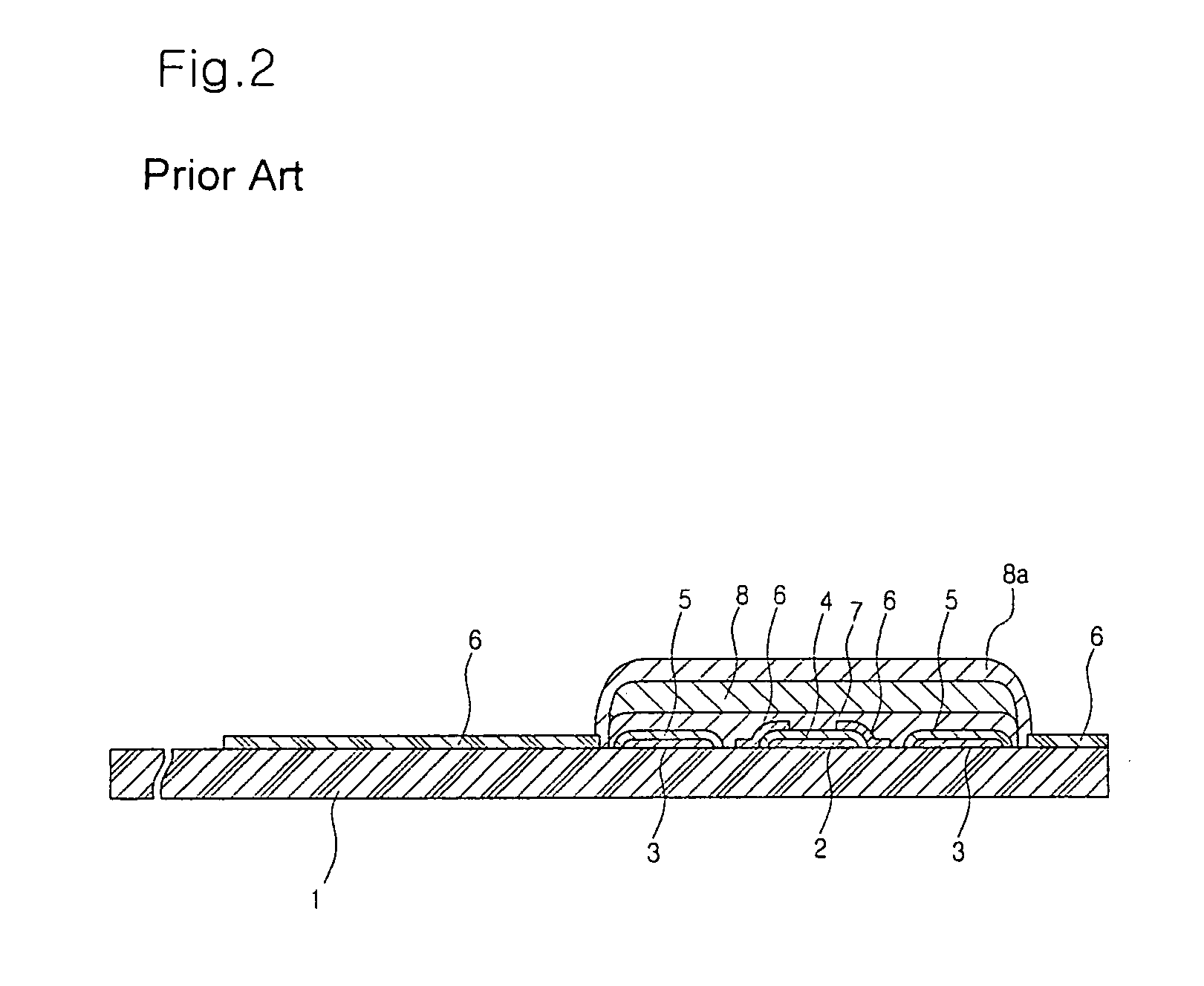
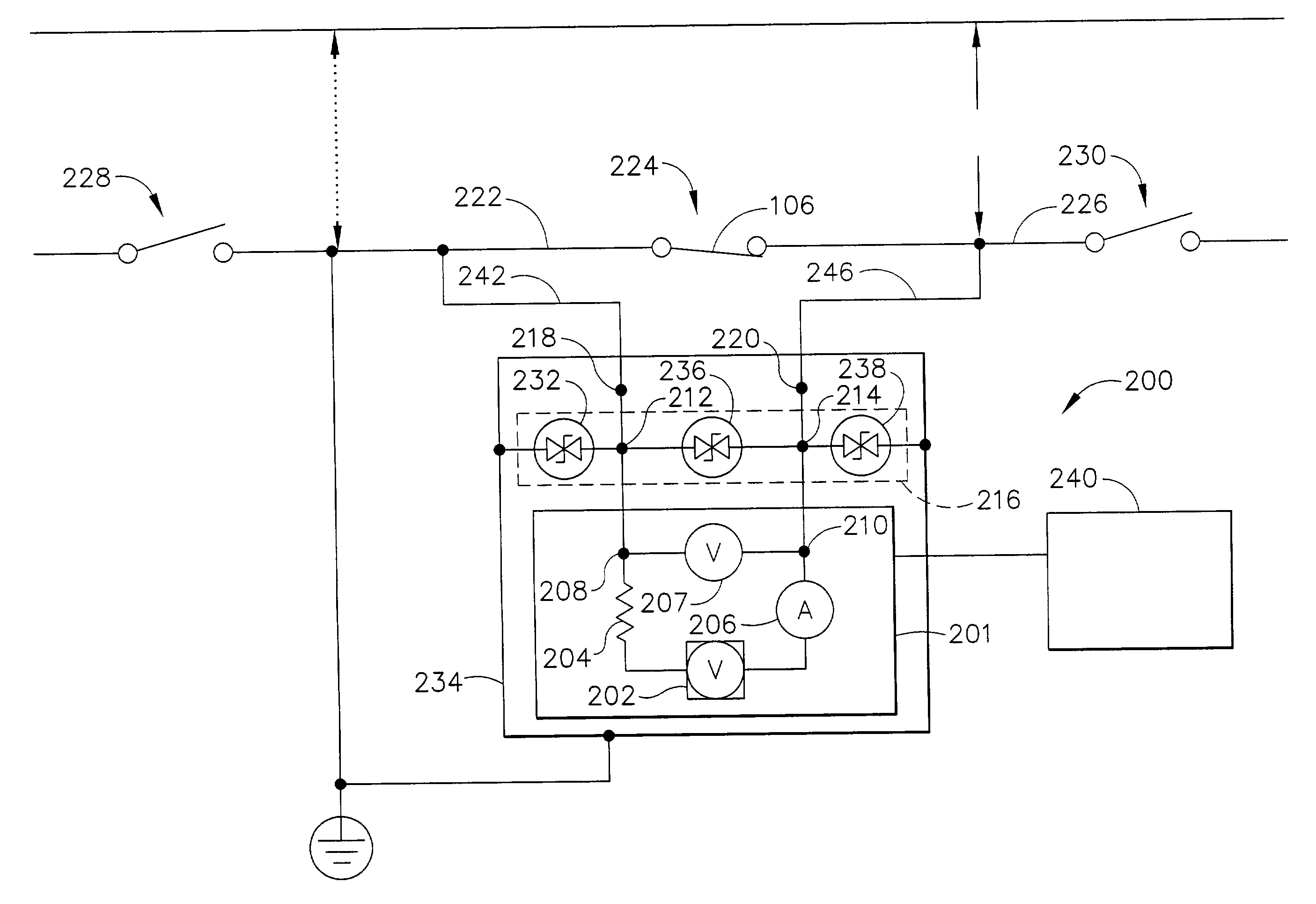
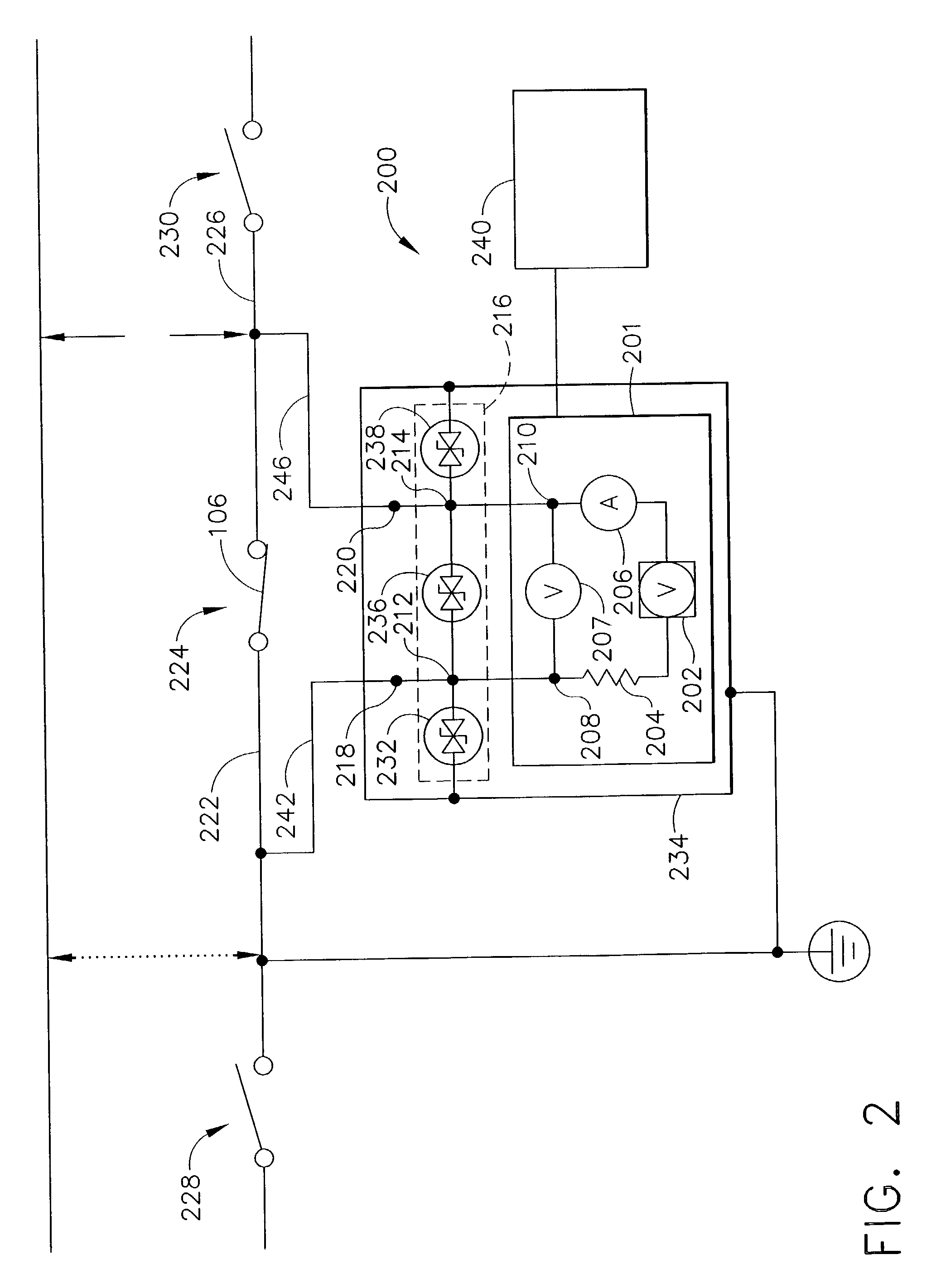
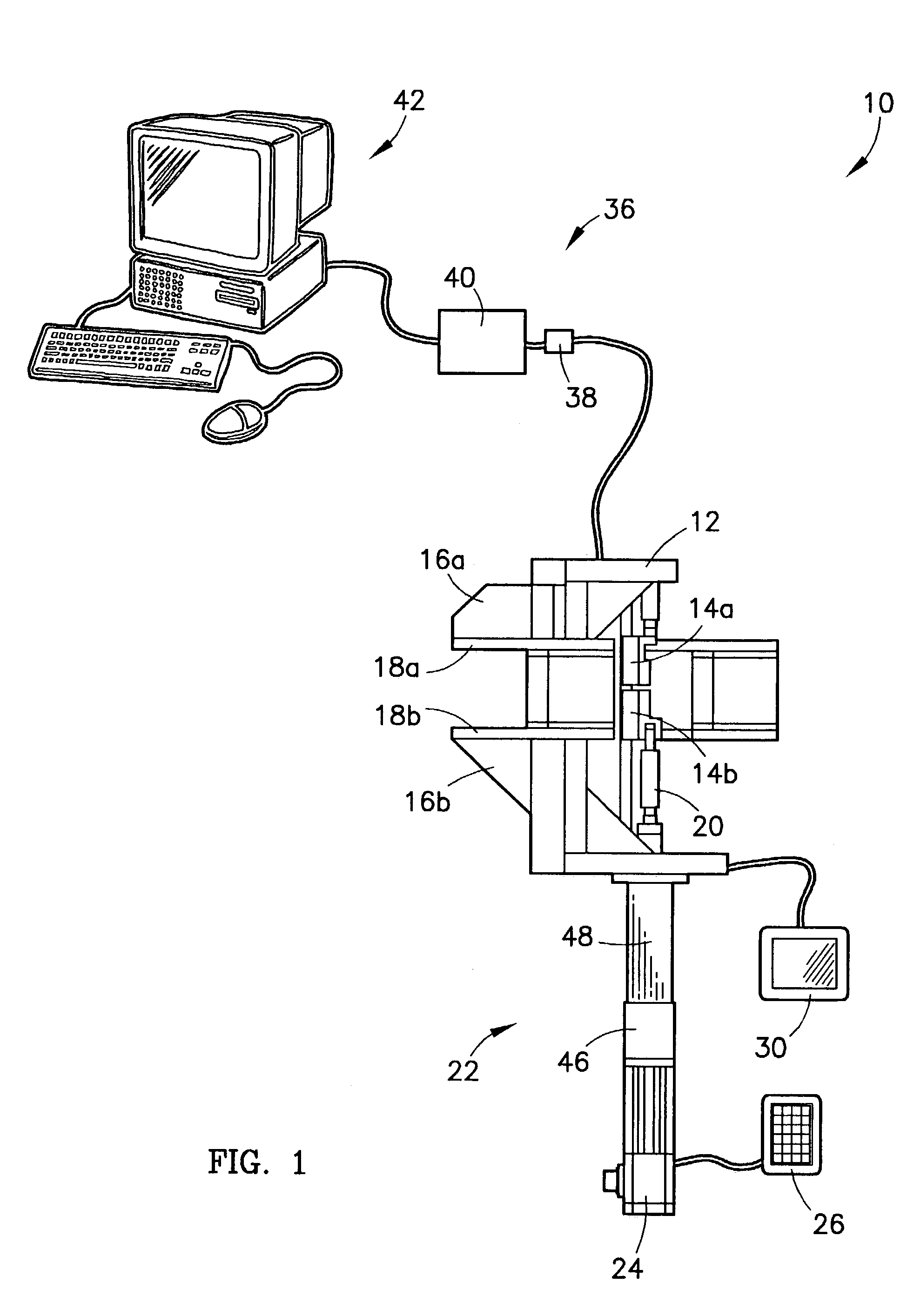
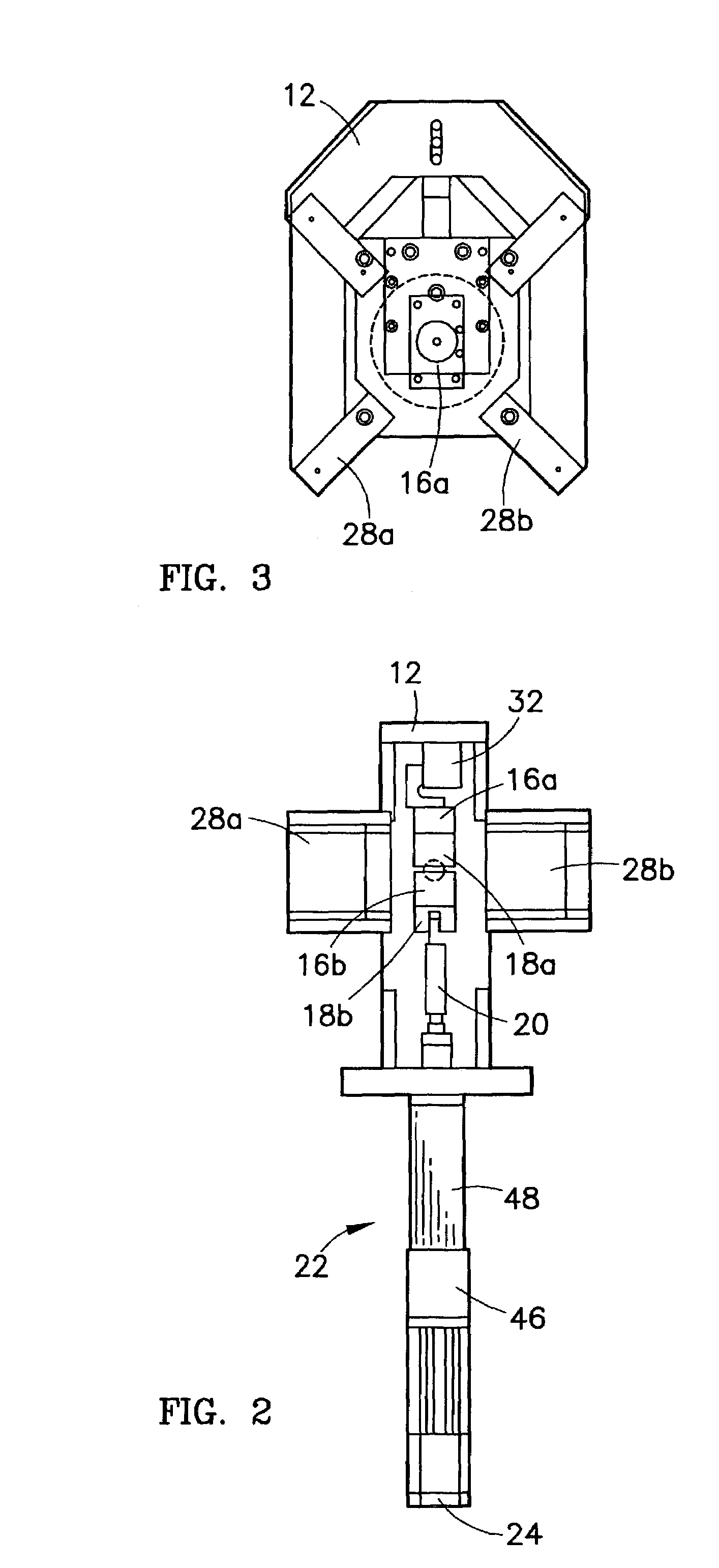
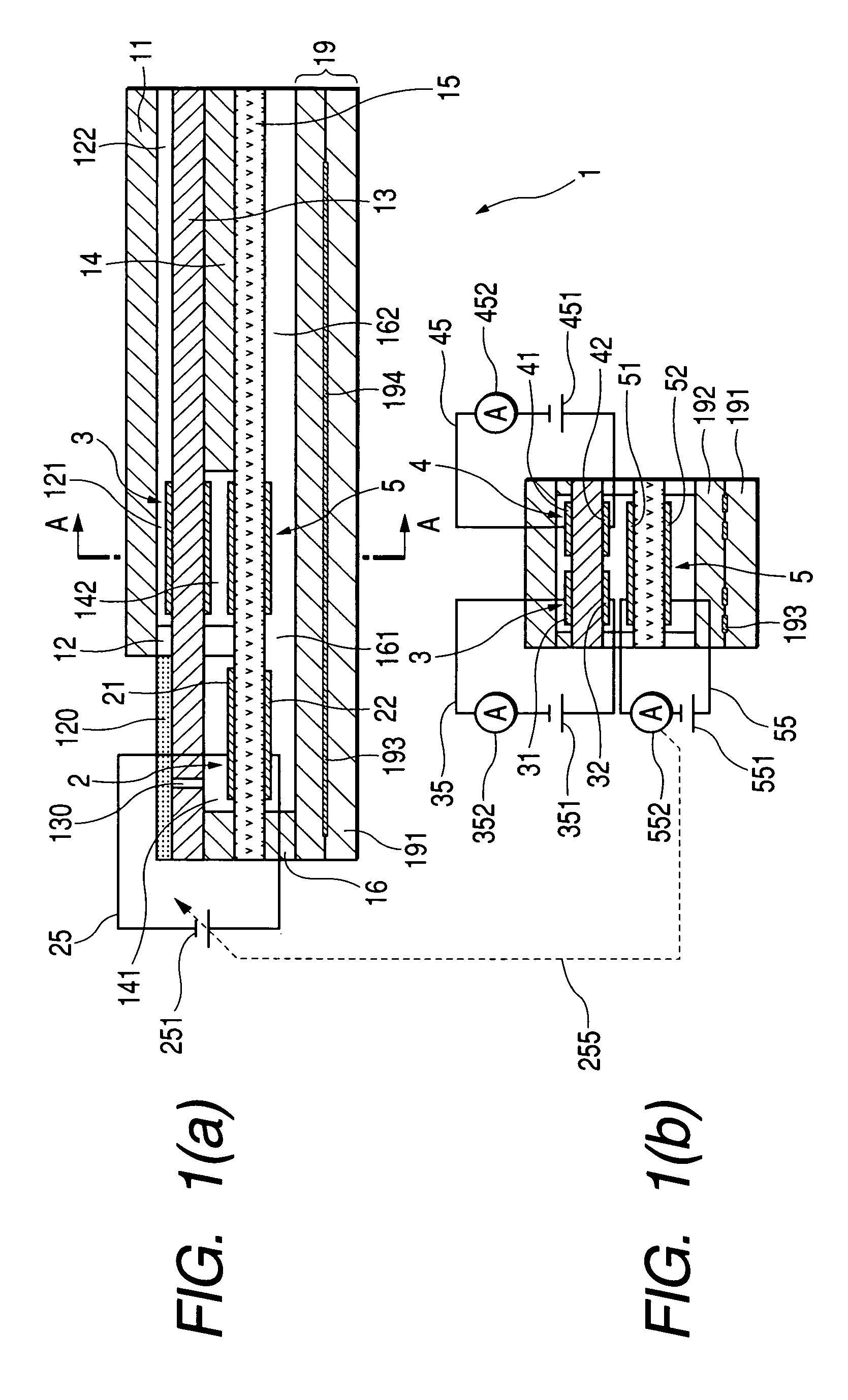
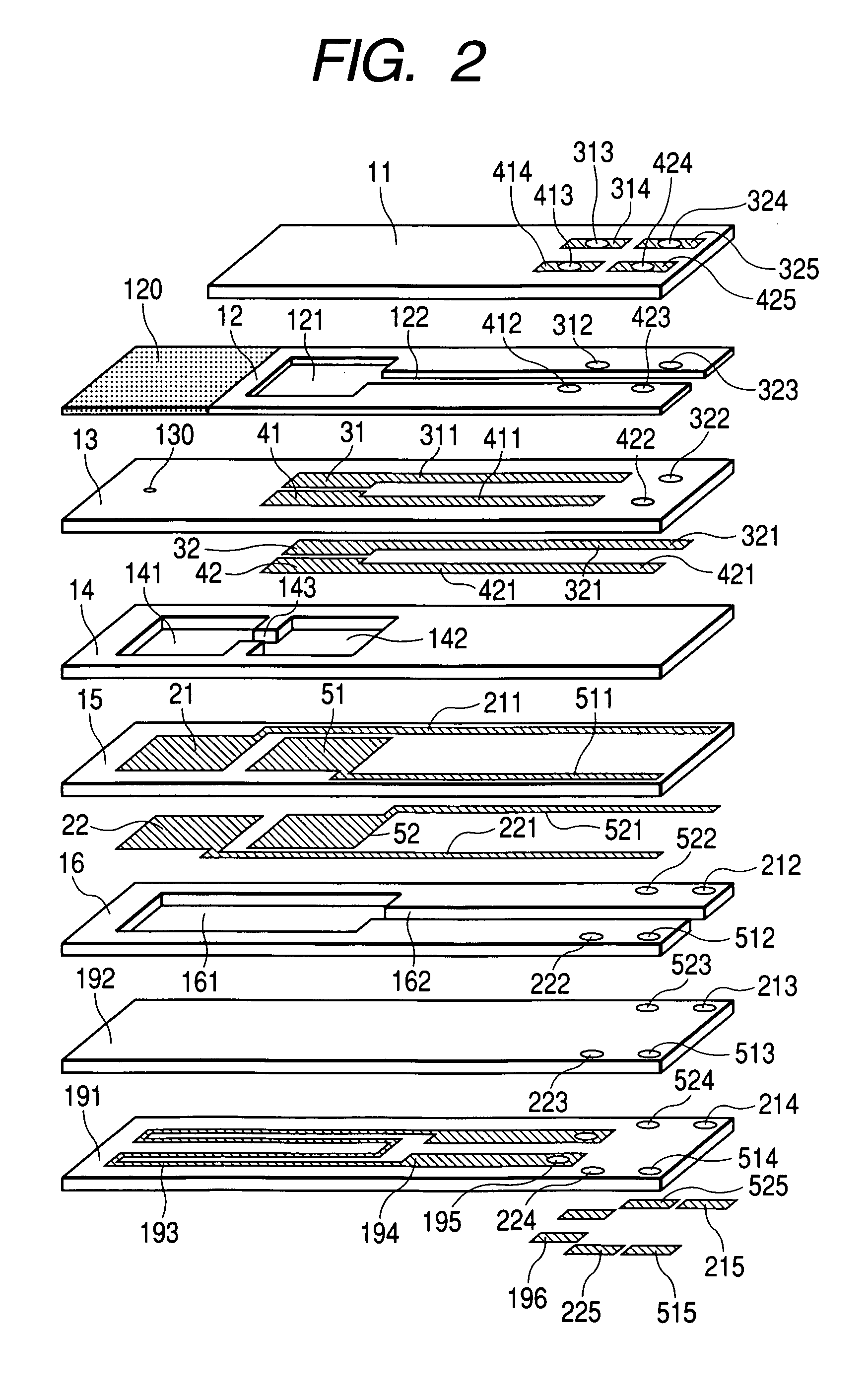
Method and Device for Measuring Internal Impedance of Stationary Battery
InactiveUS20080303528A1Precise calculationMinimize measurement errorElectrical testingMaterial electrochemical variablesFloating chargeCharge current
Battery system is widely used in emergent power plant or communication network power plant and its effective management is important. When any one of batteries connected to each other in series is failed during operation of the battery system, since reliability of the system cannot be secured, a problem is arisen to stable operation of the communication network. In a method of separating inferior battery, the battery is operated in floating charge state without separation to generate square current containing charge current and easily generated to flow through the battery cell, voltage signal generated from terminal voltage of the battery by the measuring signal is processed such that only internal impedance voltage signal is separated from harmonics ripple voltage and noise voltage by a synchronized detection calculating algorithm to calculate the internal impedance or effective value thereof (resistance component). When the algorithm is applied after filtering only fundamental frequency and similar component by general filter, measuring precision can be improved and measuring time can be reduced.
Owner:INCELLS
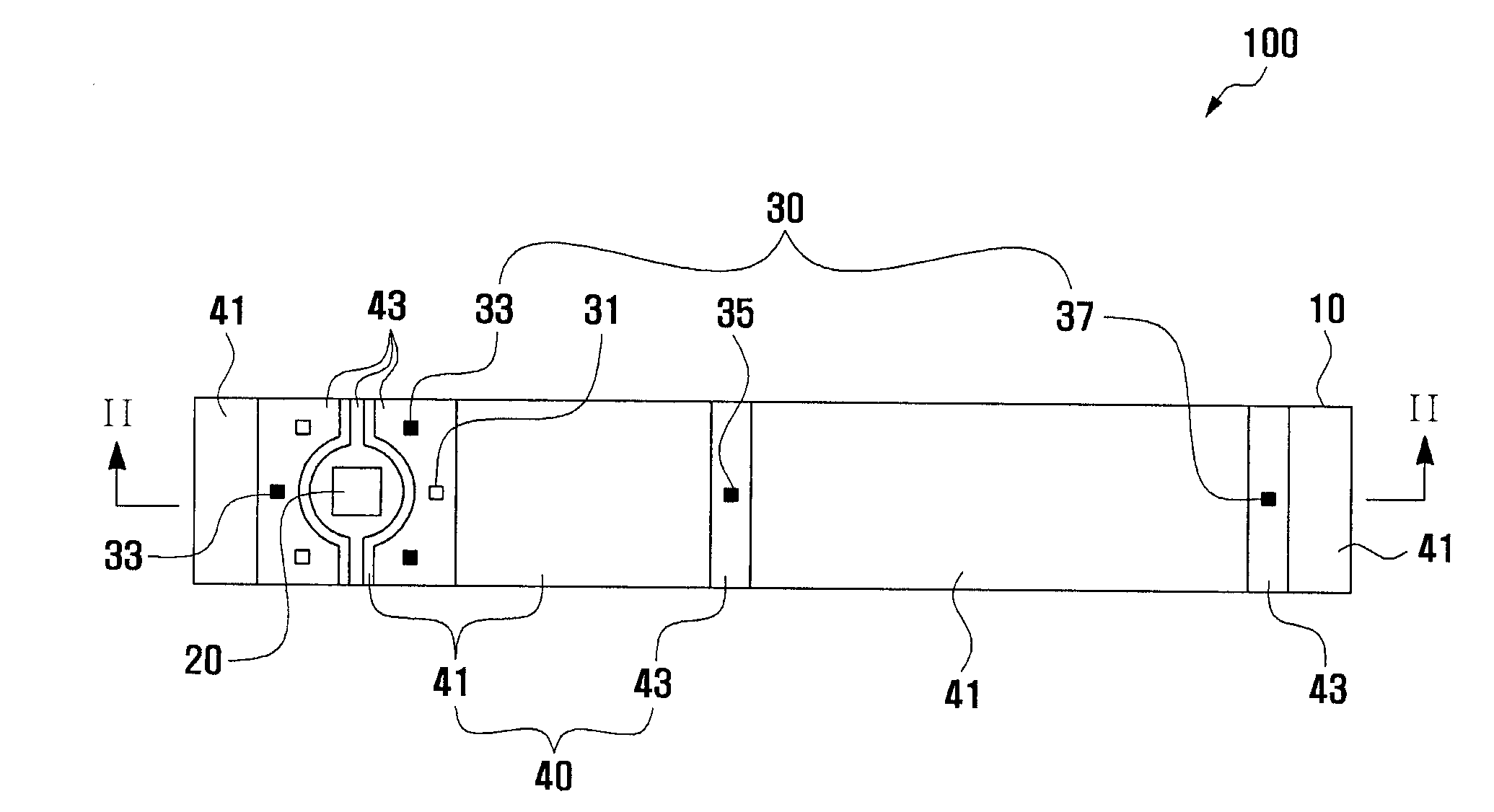
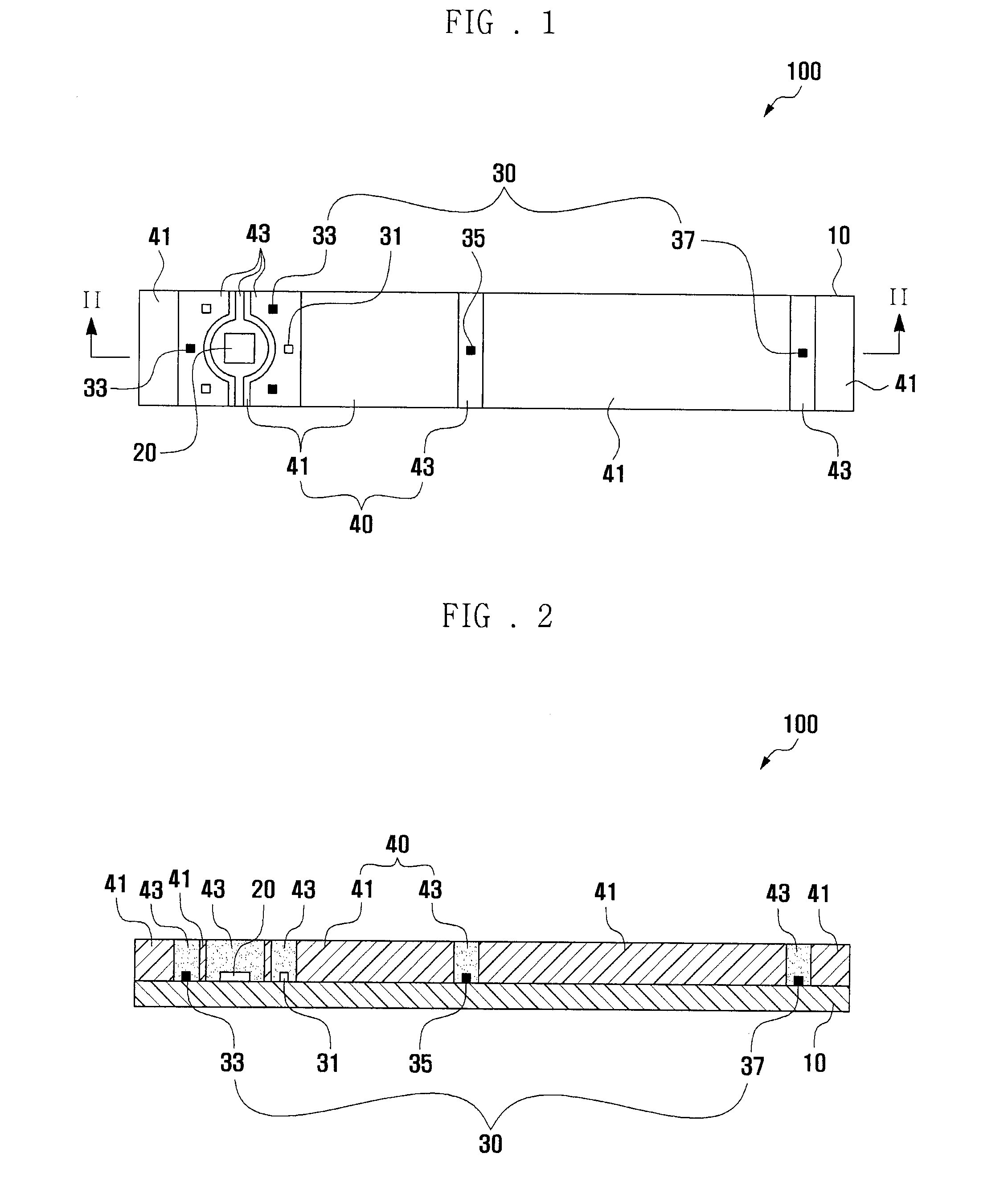
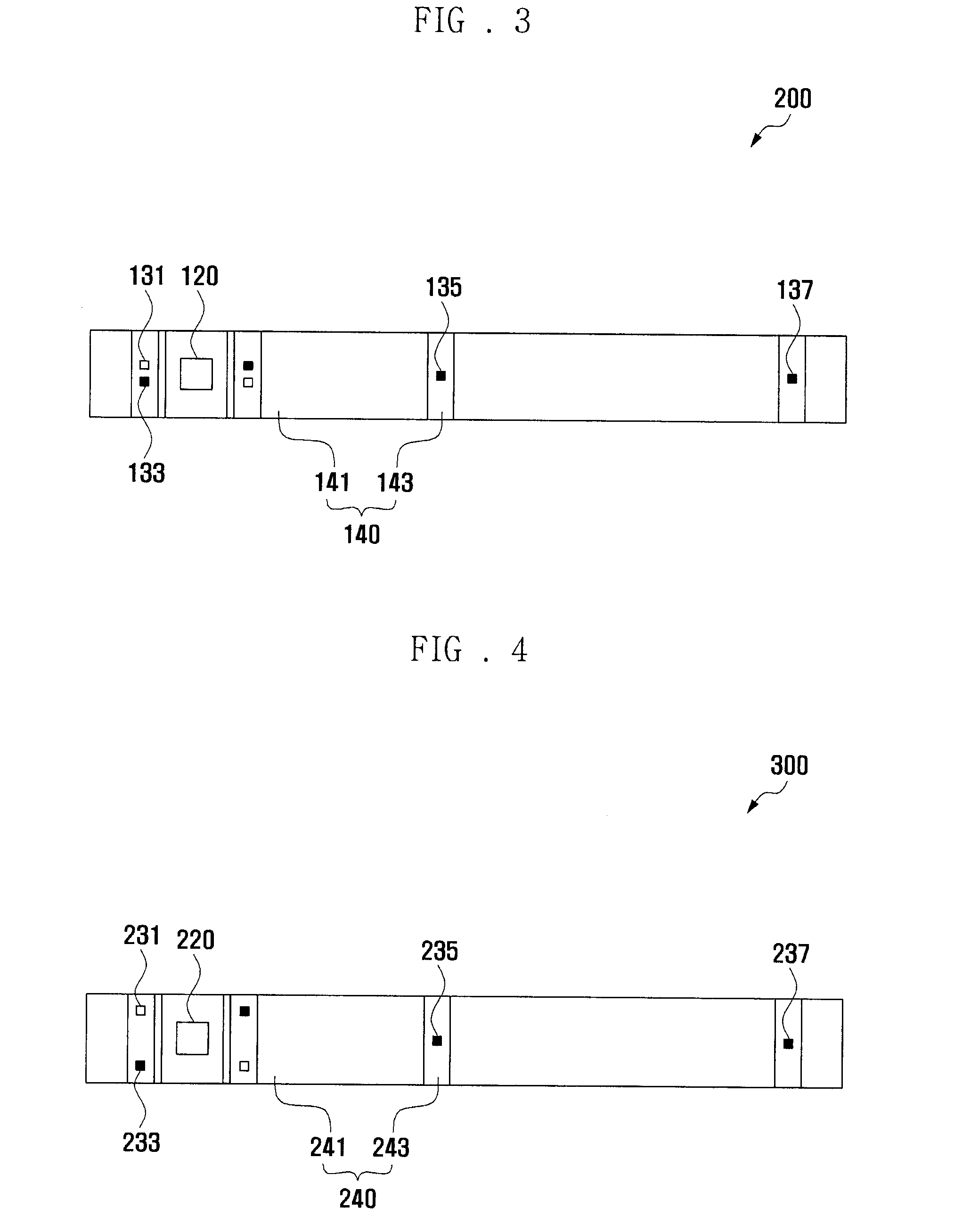
Biosensor
InactiveUS7070680B2Rapidly inducing absorptionMinimize measurement errorImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsReaction layerBiochemical engineering
A biosensor for quantifying a specific substance contained in a biological sample includes an electrically insulating base plate, a plurality of lead terminals formed on the base plate, a plurality of lead wires connected to the lead terminals, respectively, an electrode system including two working electrodes and one reference electrode connected to the lead wires, respectively, an insulating layer that insulates the electrodes, an enzyme reaction layer formed on the insulating layer and the electrodes, a spacer formed on the enzyme reaction layer so as to ensure a sufficient space that receives a sample, and a cover formed on the spacer. Further, the spacer has a sample introduction port opened at one side of the spacer, the cover has at least one slit for venting air existing in a sample receiving space defined by the spacer and the cover, and the slit extends to above the electrodes from one end of the cover.
Owner:INFOPIA CO LTD
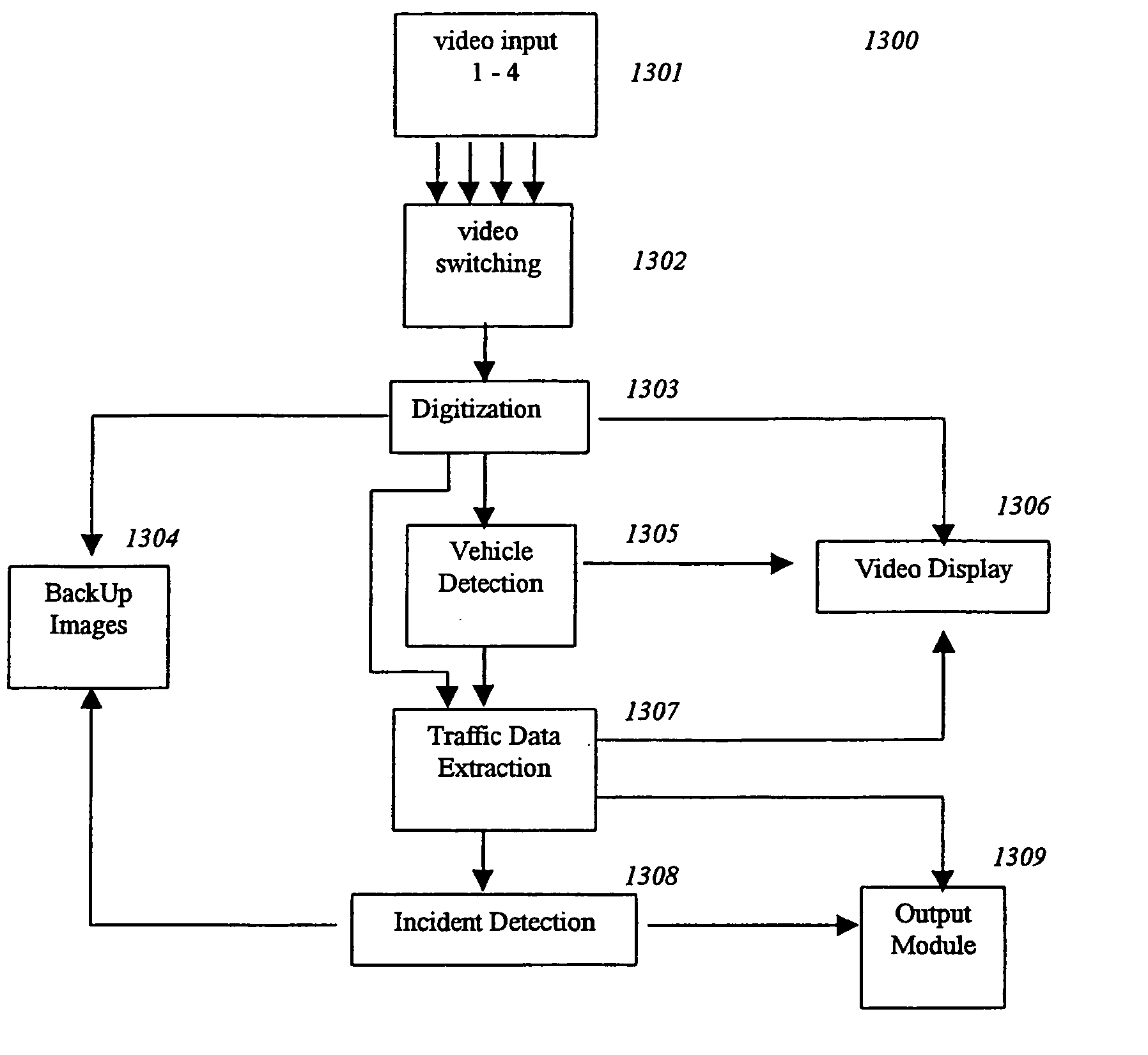
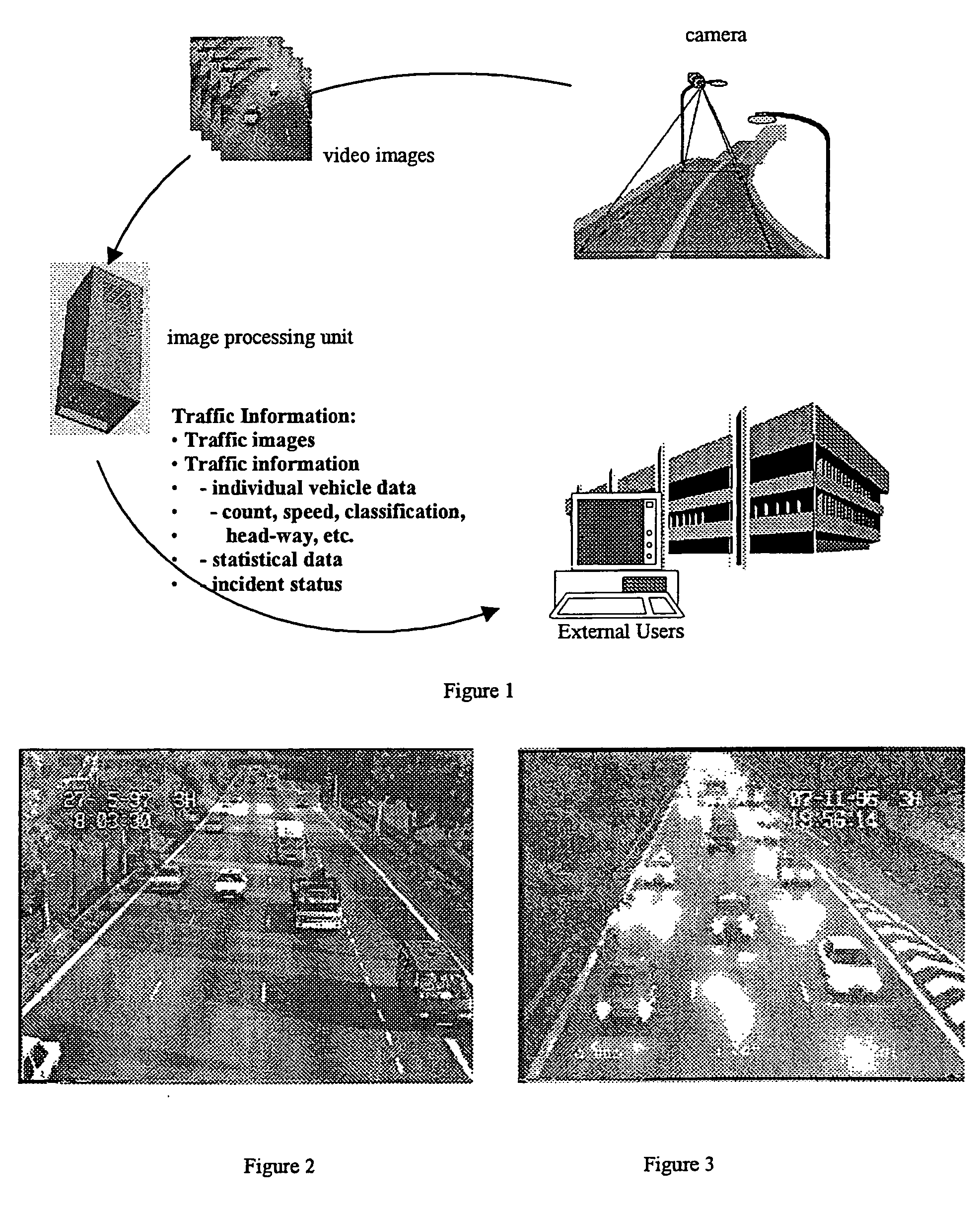
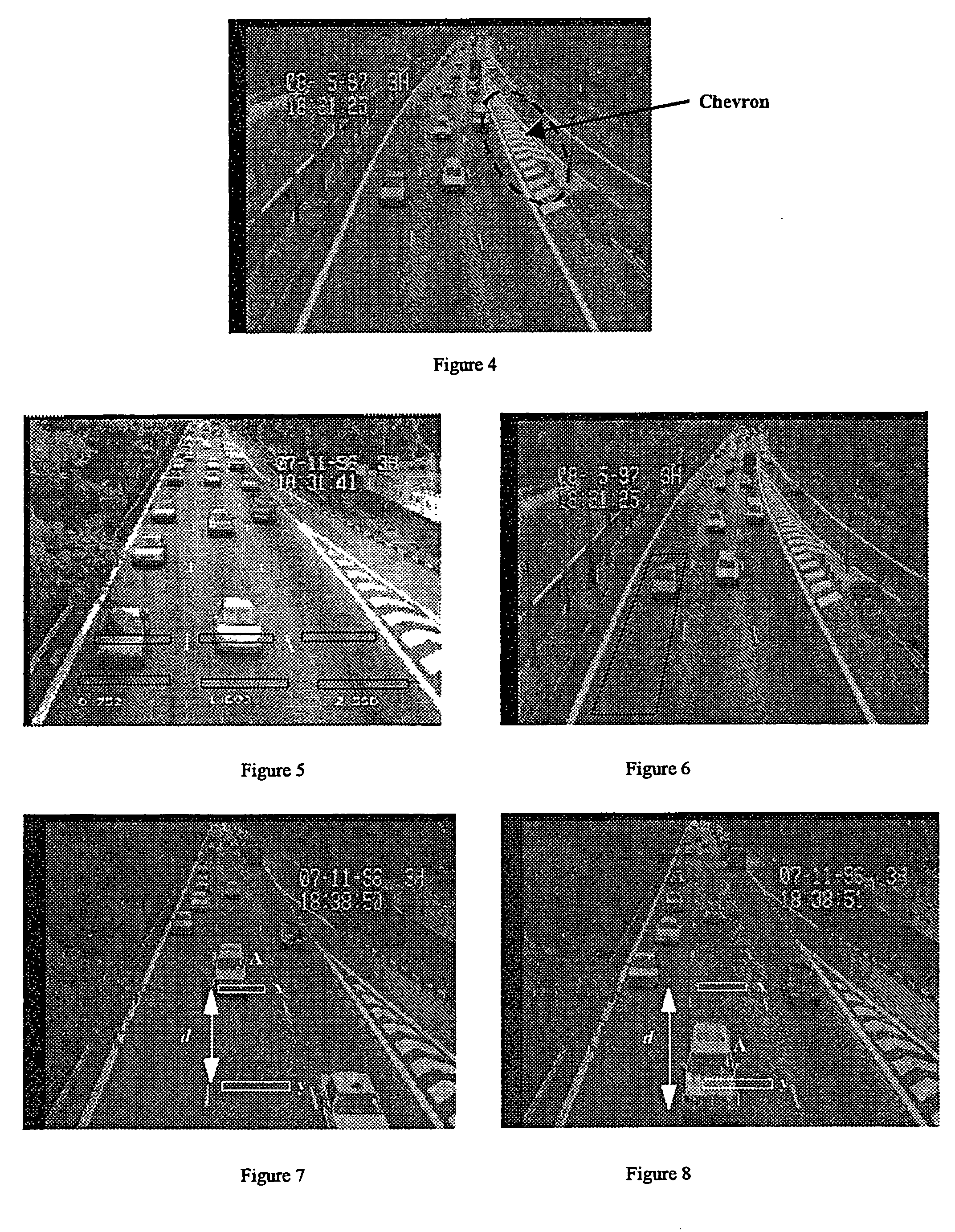
Image processing techniques for a video based traffic monitoring system and methods therefor
InactiveUS20060274917A1Less-intensive in computationCancel noiseDetection of traffic movementCharacter and pattern recognitionMobile vehicleImaging processing
The present disclosure relates to a number of inventions directed, generally, to the application of image processing techniques to traffic data acquisition using video images. The inventions reside in a traffic monitoring system, the basic function of which is for traffic data acquisition and incident detection. More specifically, the application of image processing techniques for the detection of vehicle, from sequence of video images, as well as the acquisition of traffic data and detection of traffic incident. In one aspect, the present invention provides a method of processing images received from a video based traffic monitoring system. In another aspect, the present invention is directed to a Region Of Interest (ROI) for detection of a moving vehicle and a further aspect is directed to a method of detecting day or night status in a traffic monitoring system. It's The application of various algorithms to a video based traffic monitoring system is also considered inventive. Other inventive aspects of the present traffic monitoring system are outlined in the claims.
Owner:SENTRY TECH
Physiological signal measuring sensor and manufacturing method for the same
InactiveUS20090182208A1Minimize measurement errorMaintain measurement accuracyDiagnostics using lightWave amplification devicesObservational errorPrinted circuit board
A physiological signal measuring sensor that minimizes the measurement error due to a soldering tolerance during the manufacturing process, and a manufacturing method for the same is disclosed. The physiological signal measuring sensor includes a printed circuit board, a light receiving chip mounted to the upper surface of the printed circuit board, light emitting chips mounted to the upper surface of the printed circuit board adjacent to the light receiving chip and resin sealing portions sealing the light receiving chip and the light emitting chips mounted to the upper surface of the printed circuit board wherein a first resin is selected to have opaque optical characteristics and a second resin is selected to have transparent characteristics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
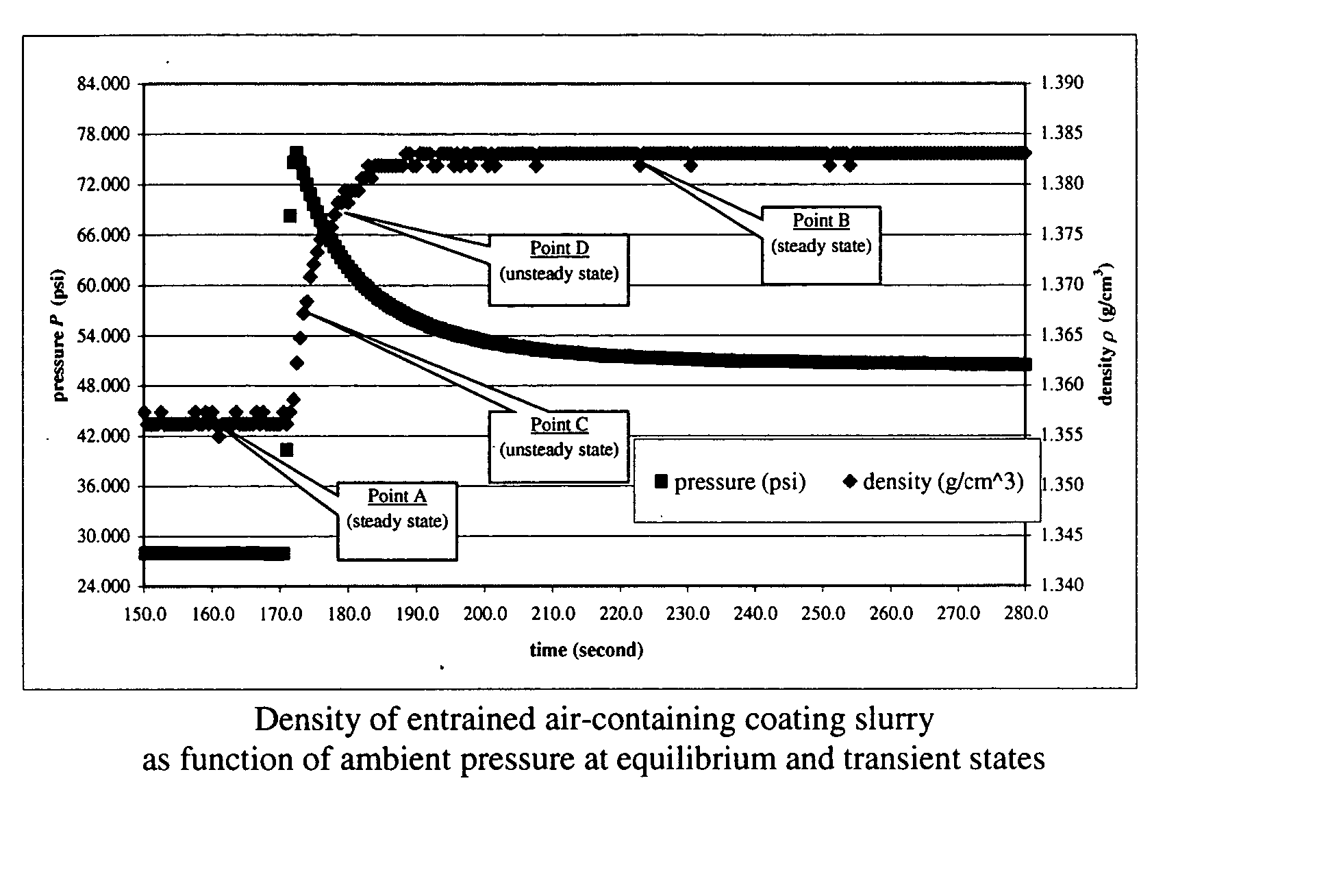
Real time determination of gas solubility and related parameters in manufacturing processes
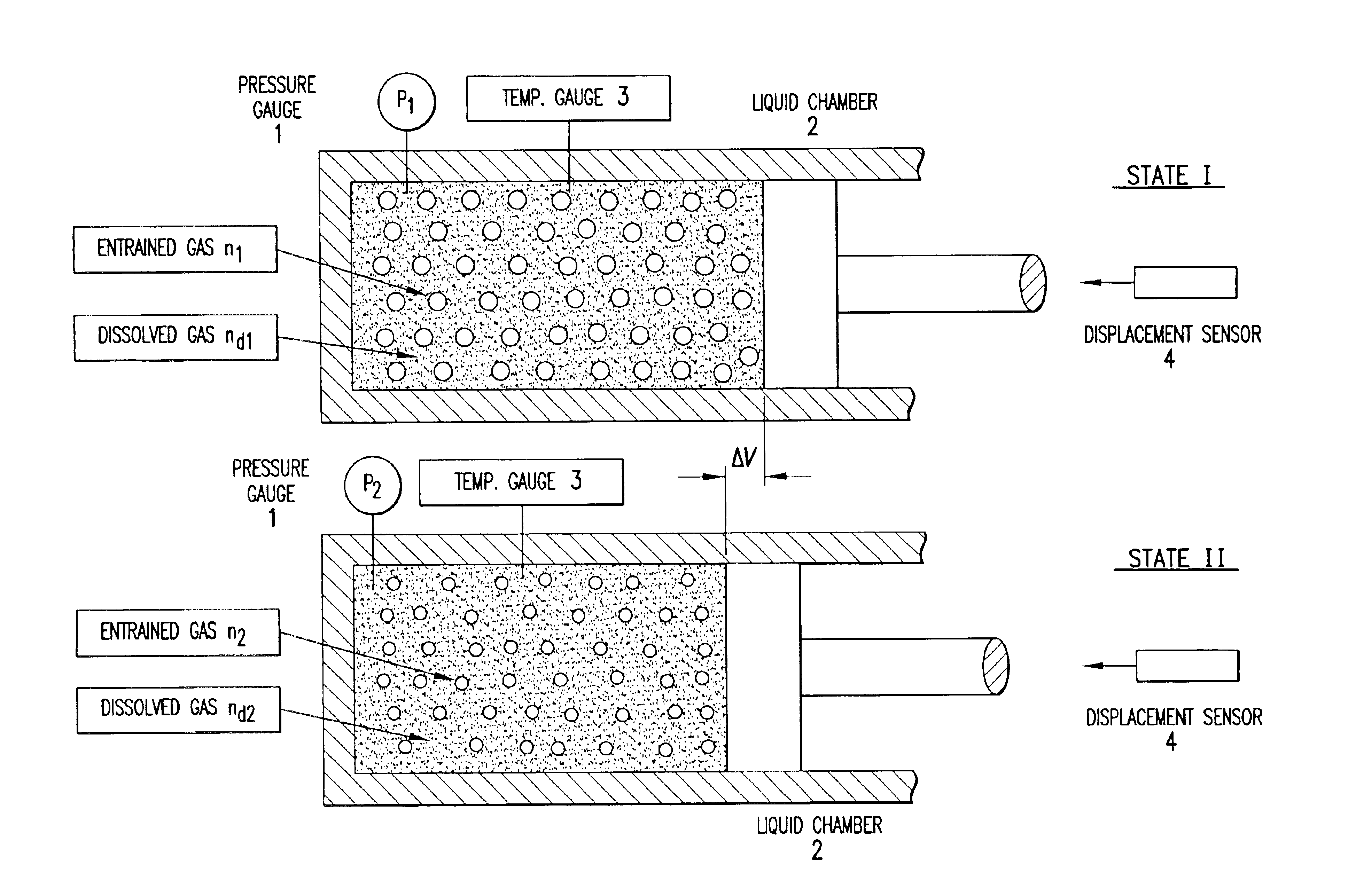
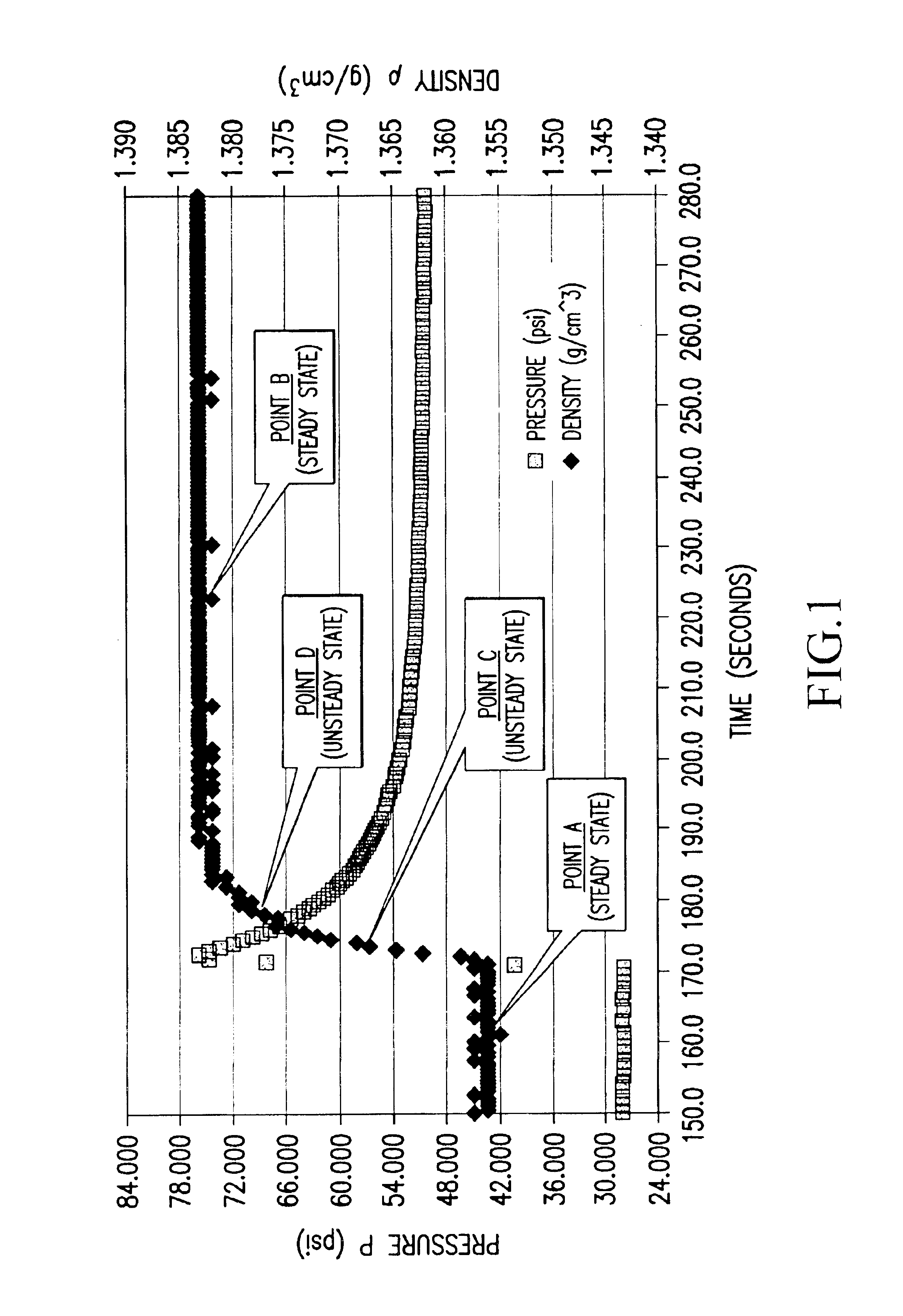
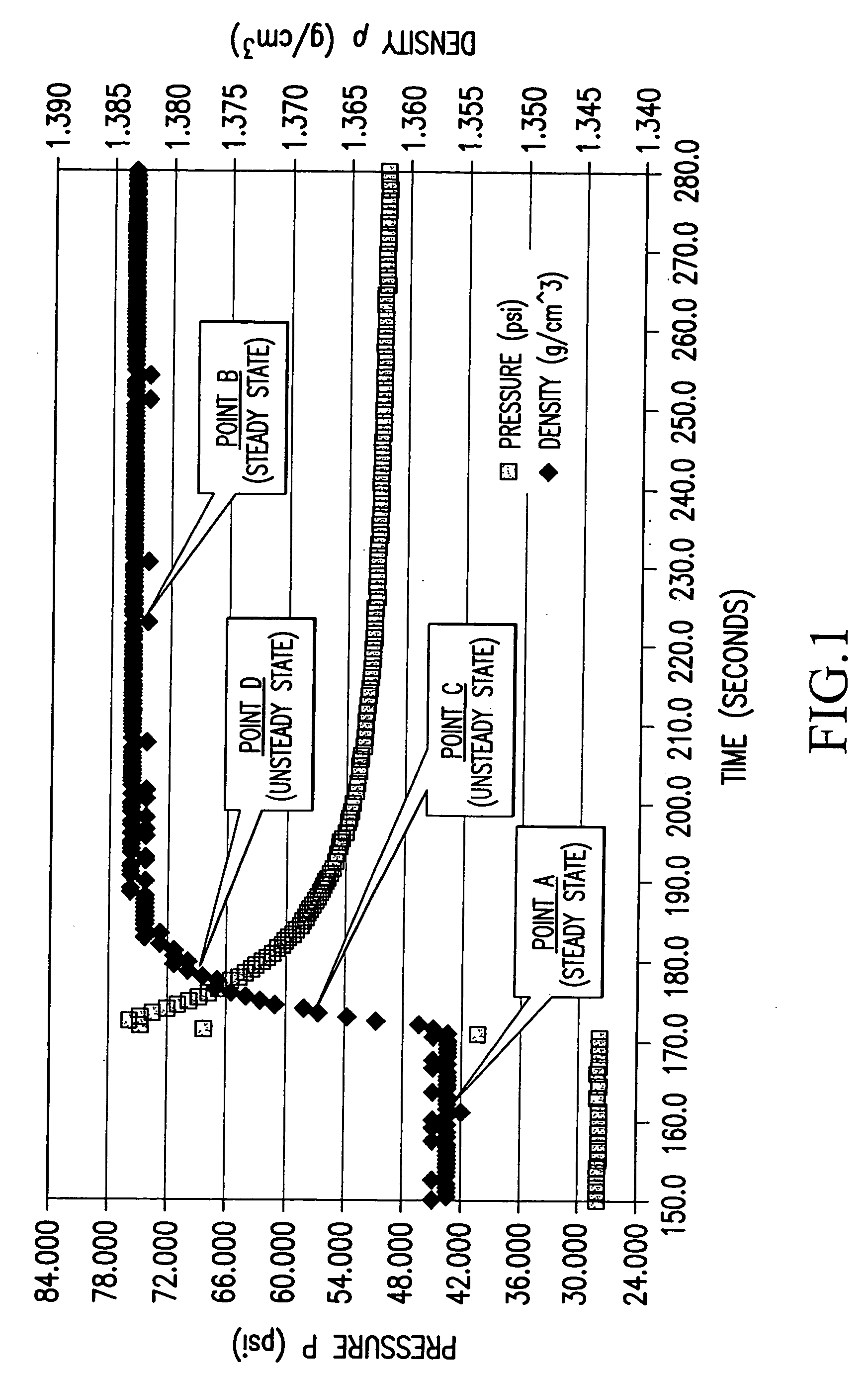
InactiveUS6847898B1Easy to controlEasy to handleTesting beveragesSpecific gravity by measuring pressure differencesSolubilityApparent density
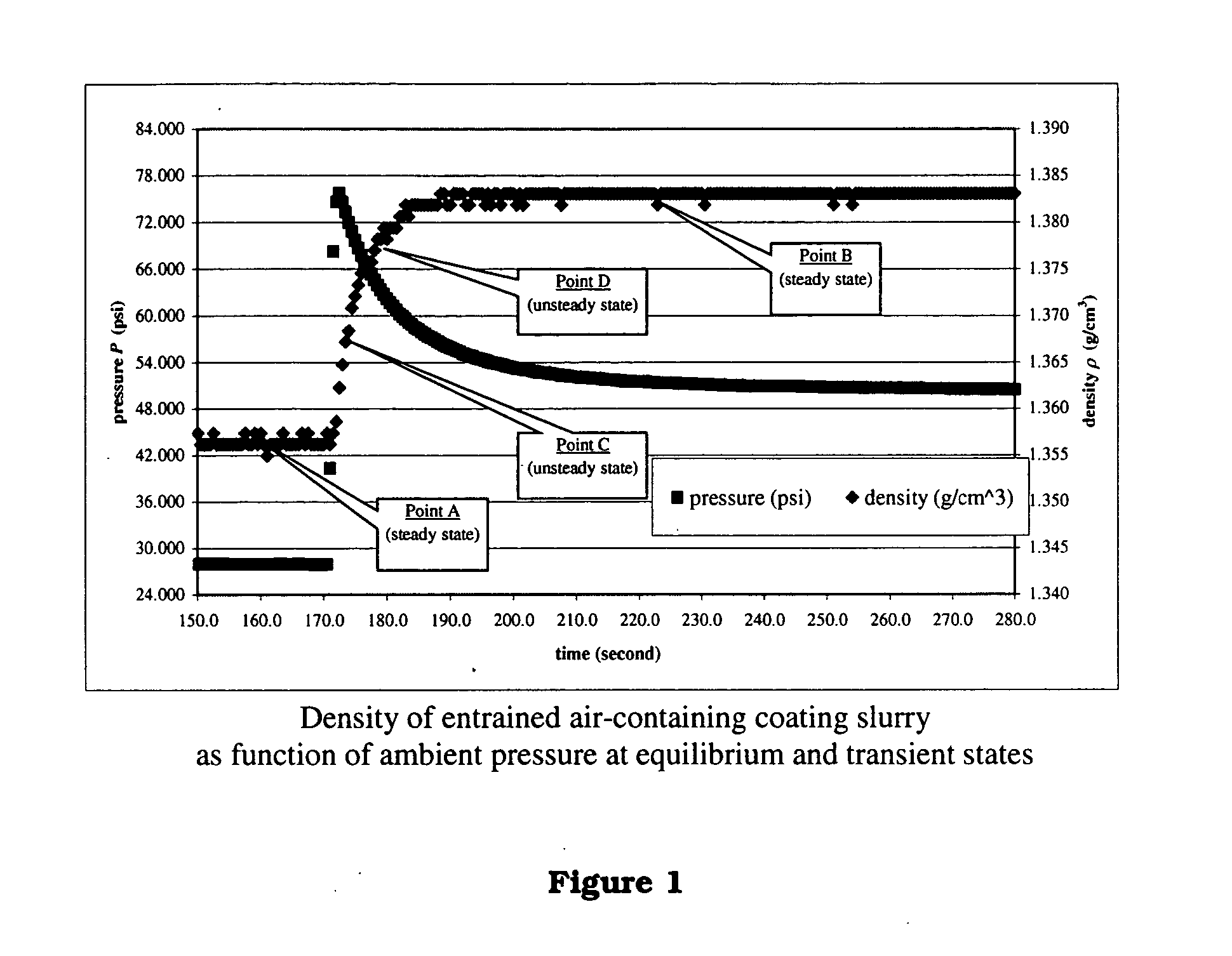
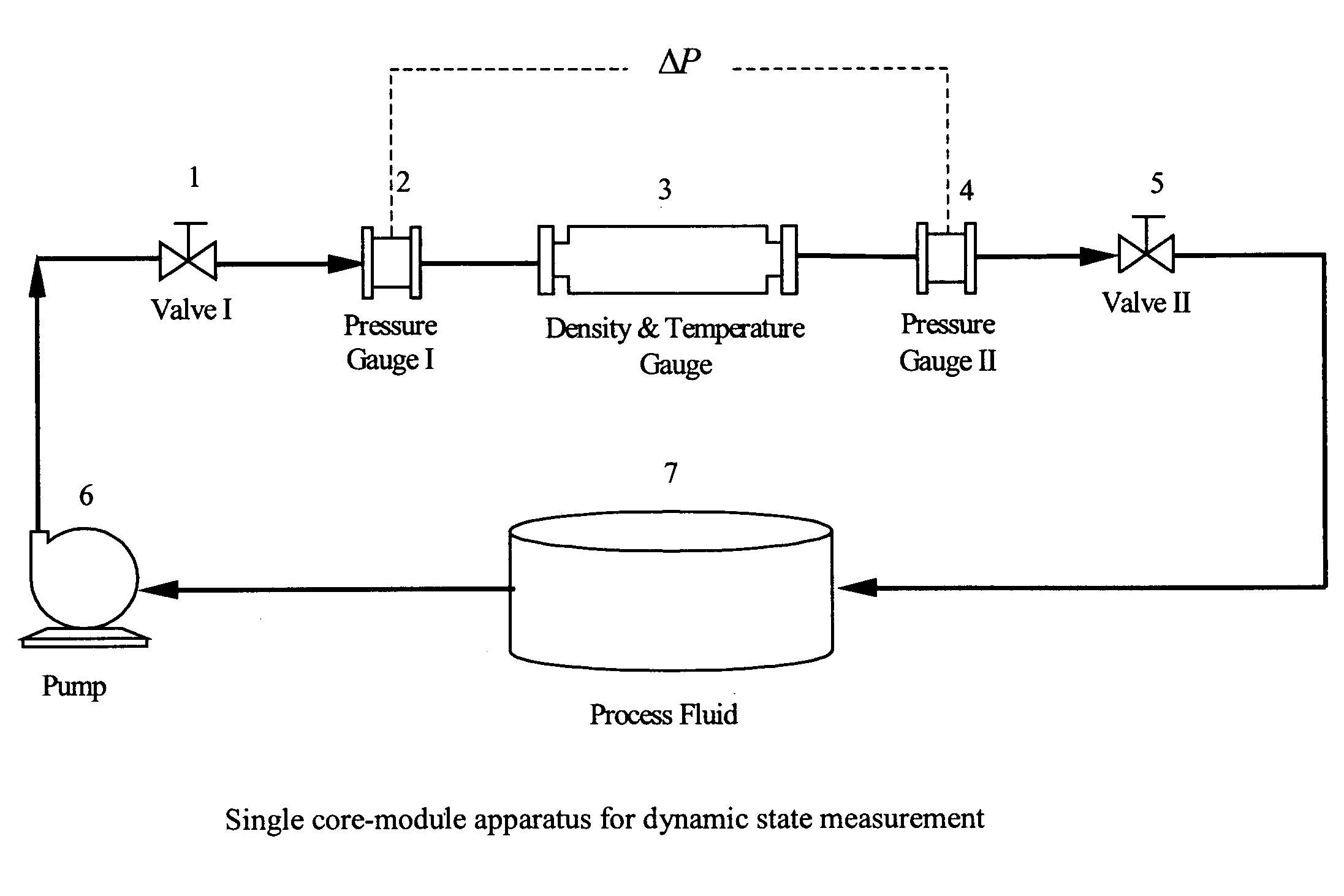
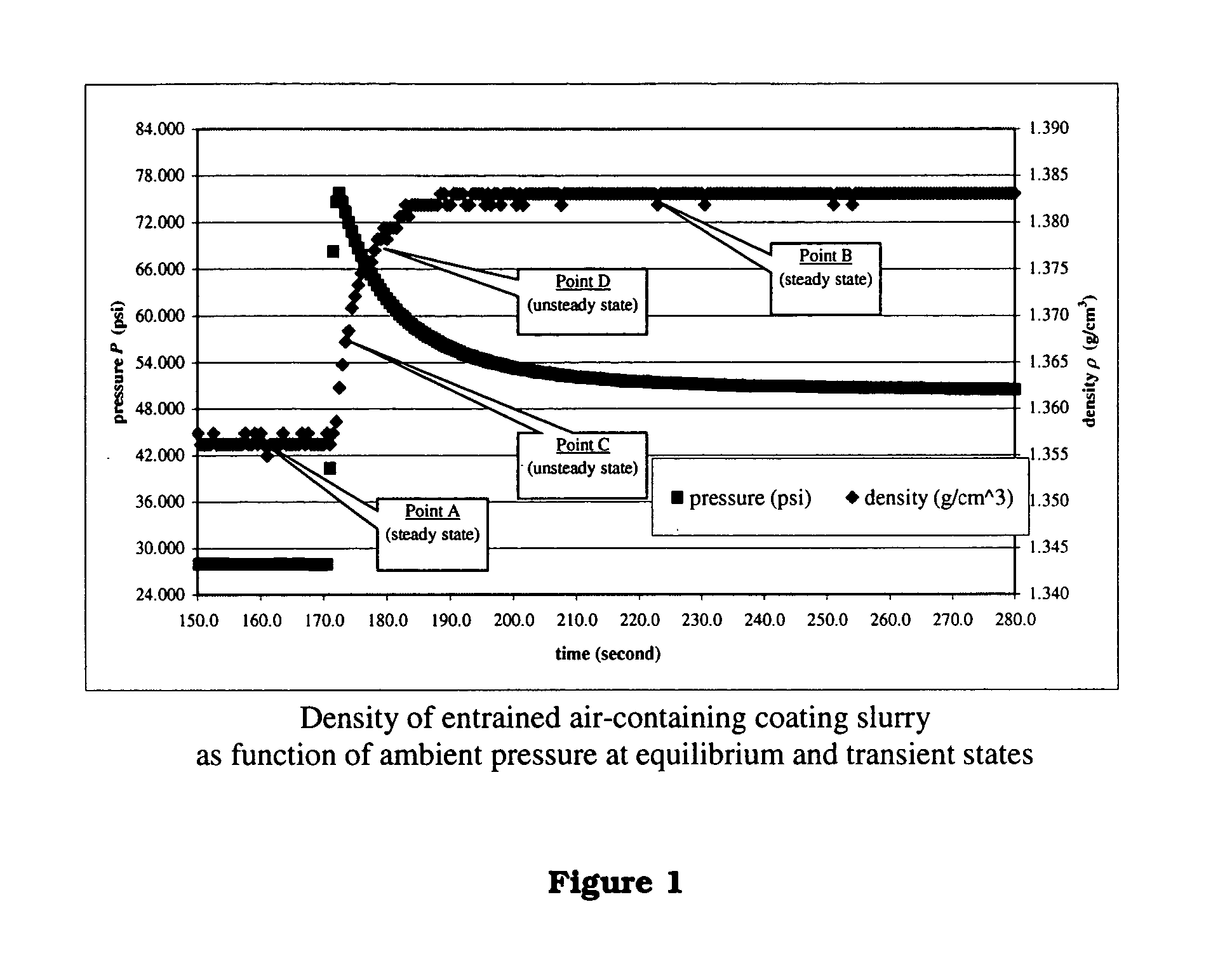
Methods and apparatuses for determining entrained and / or dissolved gas content of gas-liquid mixtures. Data generated is used to control the True (air-free) or Apparent (air-containing) Density or Entrained Air content of liquids within optimum ranges, e.g. in paper coating processes and in the manufacture of food products, personal care products, pharmaceutical products, paints, petroleum blends, etc. For example, an indirect method of continuously determining the amount of gas entrained in a liquid, by: continuously measuring the temperature, flow rate, and apparent density of the mixture at two different pressure states, and calculating the volume percentage of the gas in the liquid by using equation (28) x%=VsVs+V(28)wherein V is the volume of the gas-free liquid calculated by equation (23) V=1ρ1-[P2P2-P1(1ρ1-1ρ2)-RTP2-P1g(Δ PQa)](23)in which P1 and P2 are two different ambient pressures and ΔP=P2−P1, ρ1 and ρ2 are apparent densities of the liquid sample measured at P1 and P2, respectively, R is the constant of the Ideal Gas Law, T is the liquid temperature, Q is the flow rate, g(ΔP / Qa) is a function for determining the amount of gas being dissolved between P2 and P1, and Vs is determined by equation (27) Vs=TsTP1P2Ps(P2-P1)(1ρ1-1ρ2)-RTsPs(P1P2-P1g(Δ PQa)-g(P1-PsQa)).(27)
Owner:APPVION INC
Device and method for controlling a satellite tracking antenna
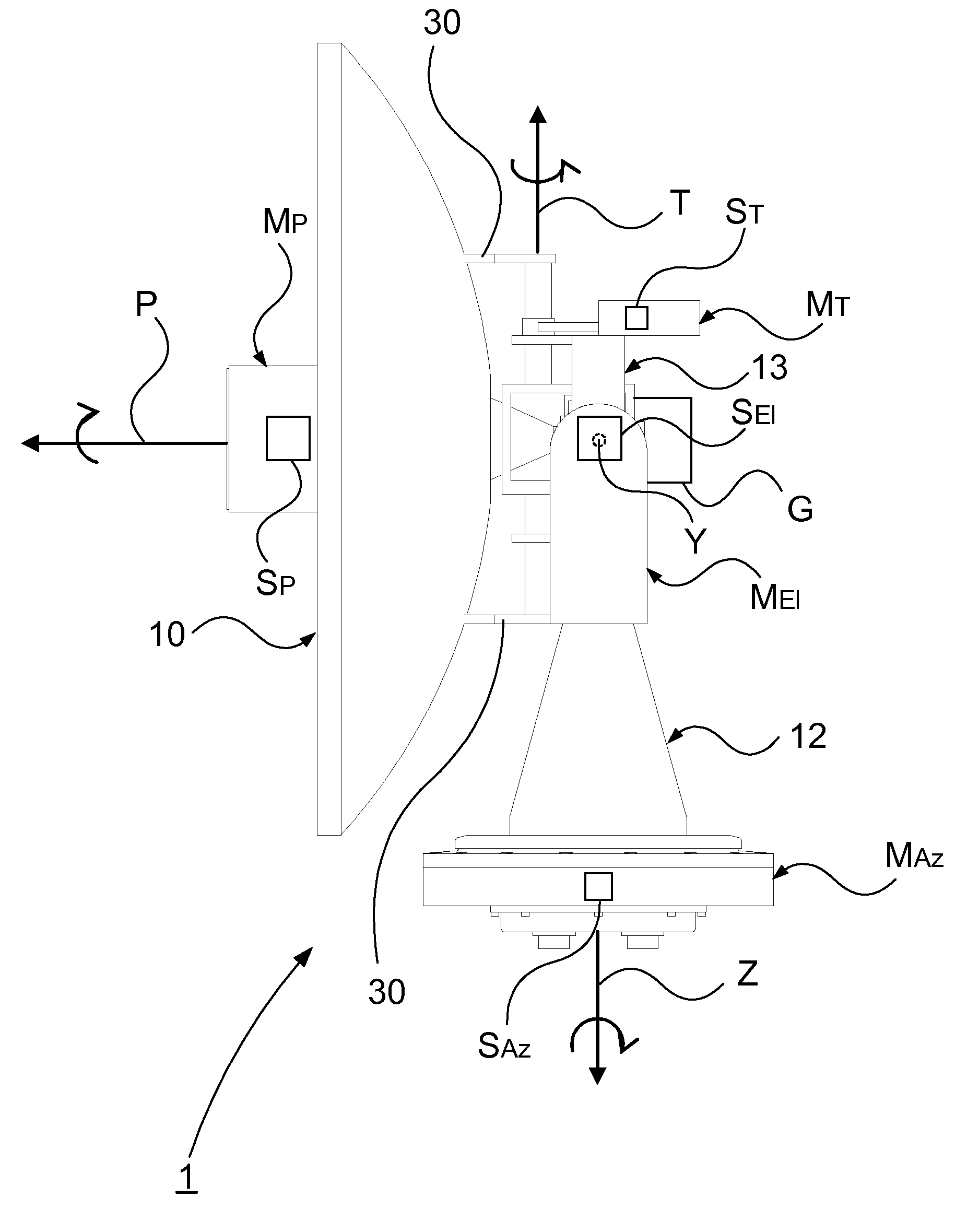
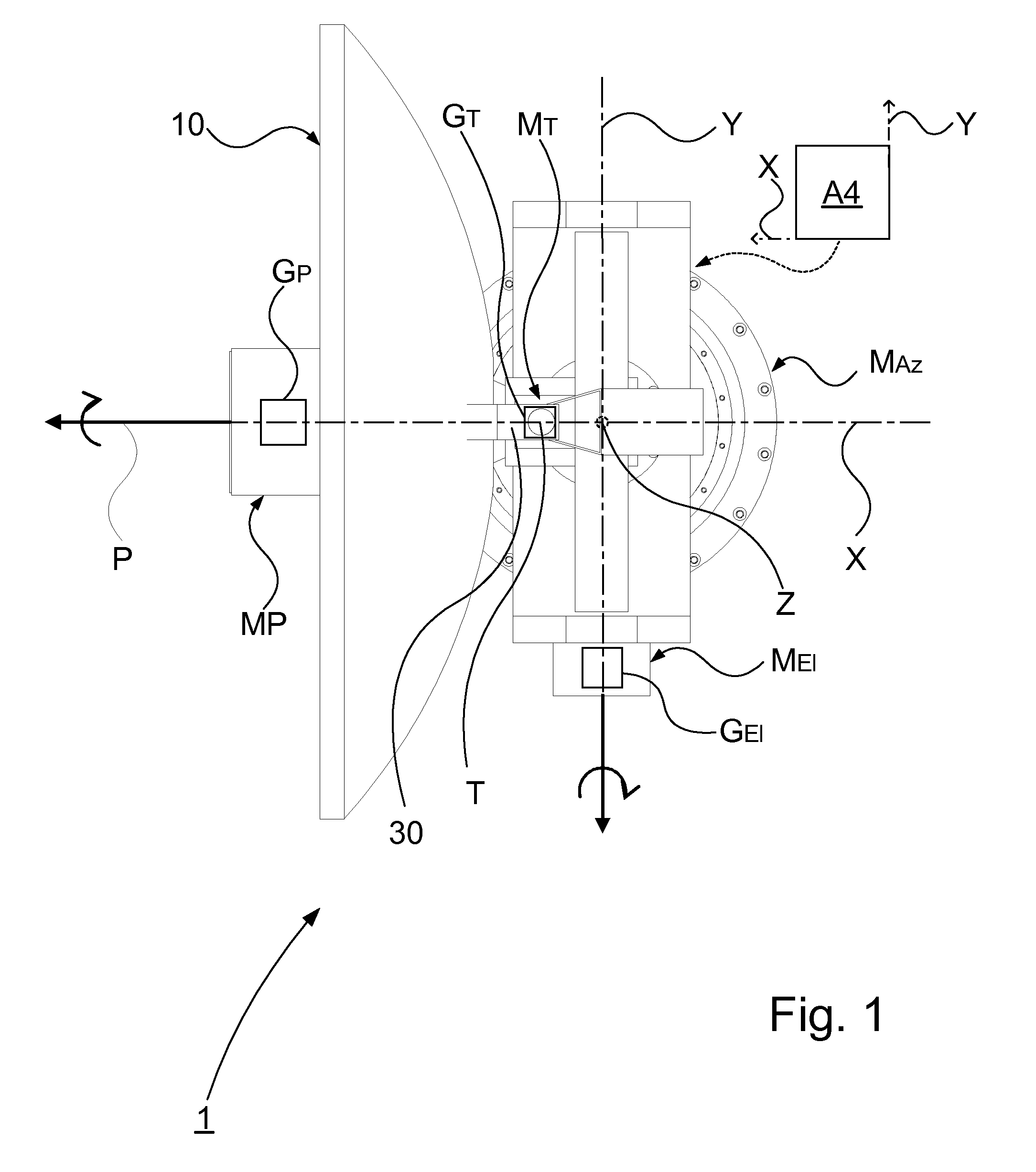
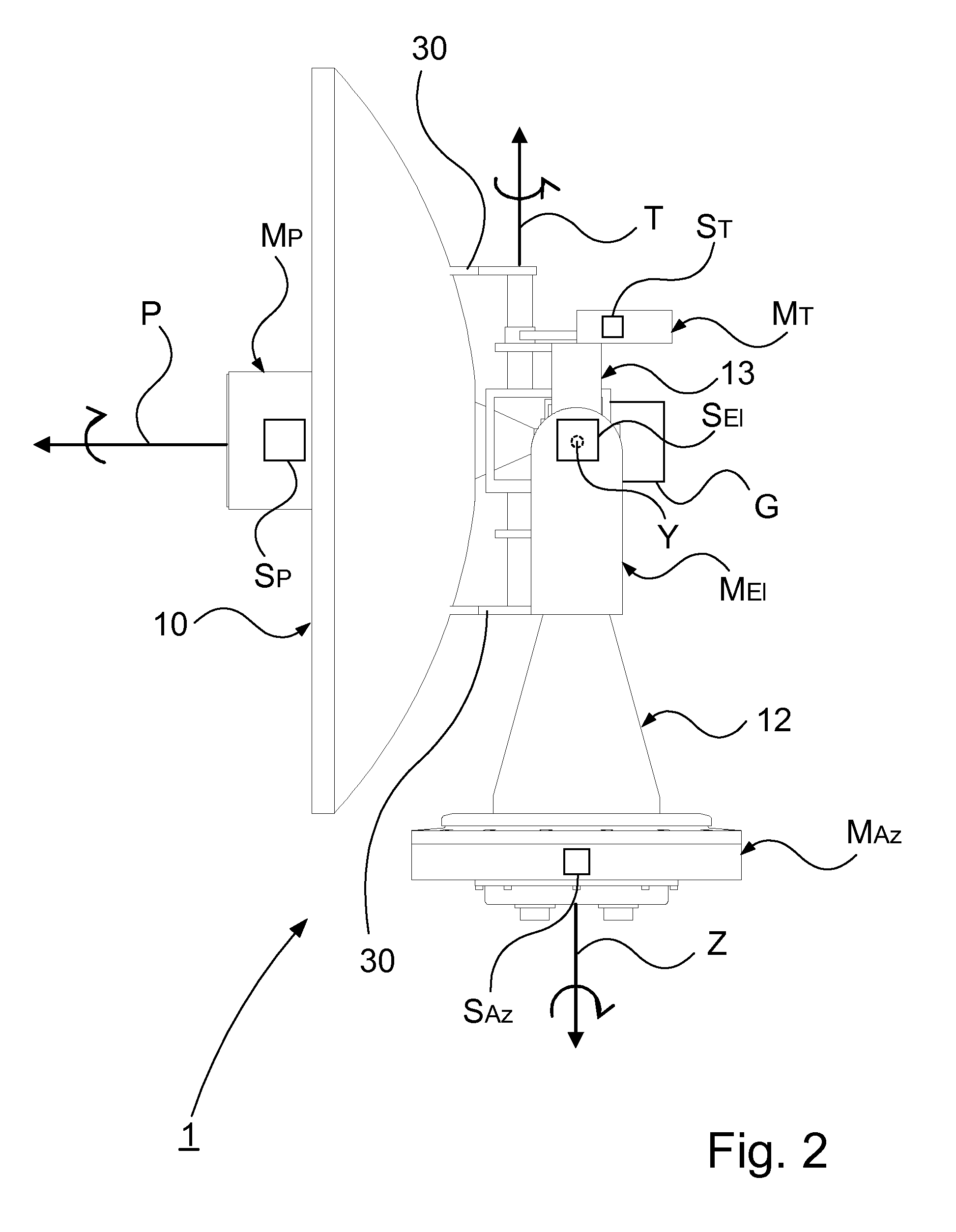
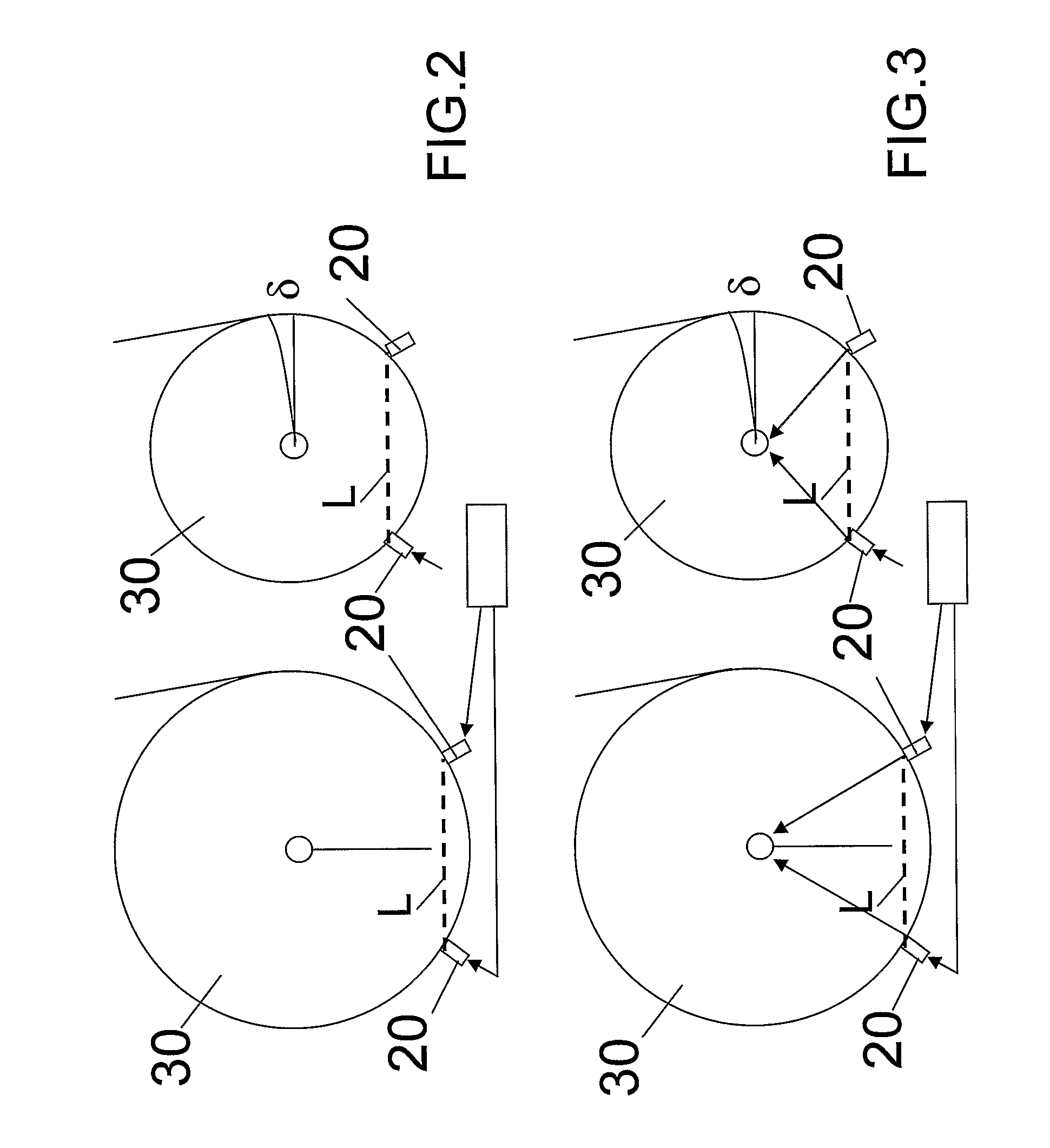
ActiveUS20100201589A1Improve abilitiesImprove device performanceAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesElevation angleRotational freedom
A device for controlling a satellite tracking antenna. An azimuth drive is configured to impart an azimuthal rotational motion to the antenna about an azimuth axis. An elevation axis drive is configured to impart a rotational motion to the antenna about an elevation axis orthogonal to the azimuth axis. A tilt axis drive is configured to impart a rotational motion to the antenna about a tilt axis. The tilt axis is connected to the elevation axis in such a way that the rotational freedom of motion of the antenna about the tilt axis is dependent on the elevation angle such that: at an elevation angle of 0° the rotational freedom of motion of the antenna about the tilt axis corresponds to the azimuthal rotational motion; at an increasing elevation angle the rotational freedom of motion about the antenna successively transcends into a roll rotation; and at an elevation angle of 90° the rotational freedom of motion of the antenna about the tilt axis corresponds to a roll rotation about a roll axis orthogonal to the azimuth axis and to the elevation axis. A control controls the operation of the azimuth axis drive, the elevation axis drive, and the tilt axis drive. The control includes a true north seeking gyro for tracking position, orientation, direction and speed of movement of the device. The control further includes an additional gyro comprising an elevation gyro axis arranged to sense the elevation movement and a tilt gyro axis arranged to sense the tilt movement, so as to minimize the angular velocity of the antenna pointing vector. A method for controlling a satellite tracking antenna, and a vessel including the device.
Owner:SAAB AB
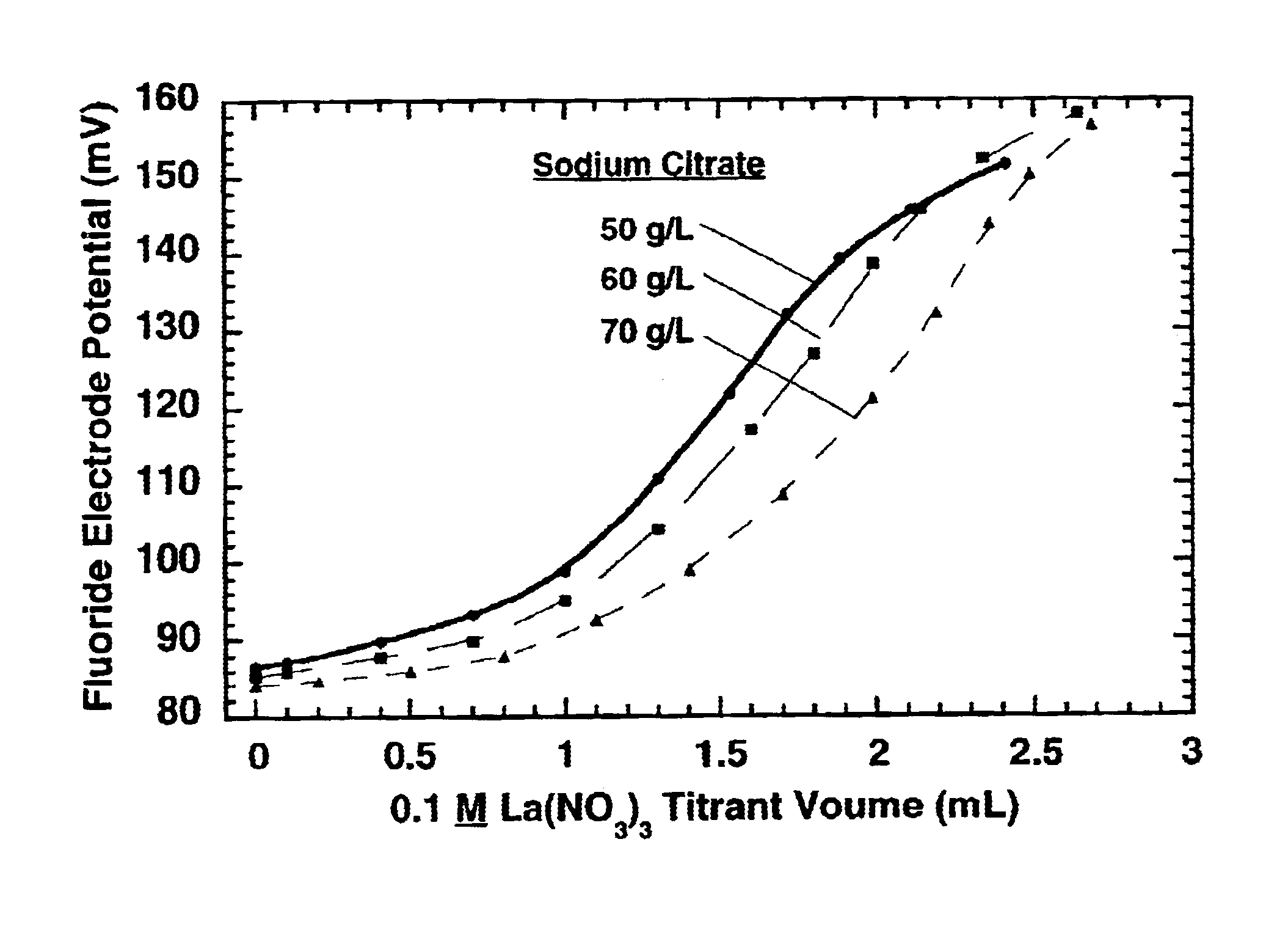
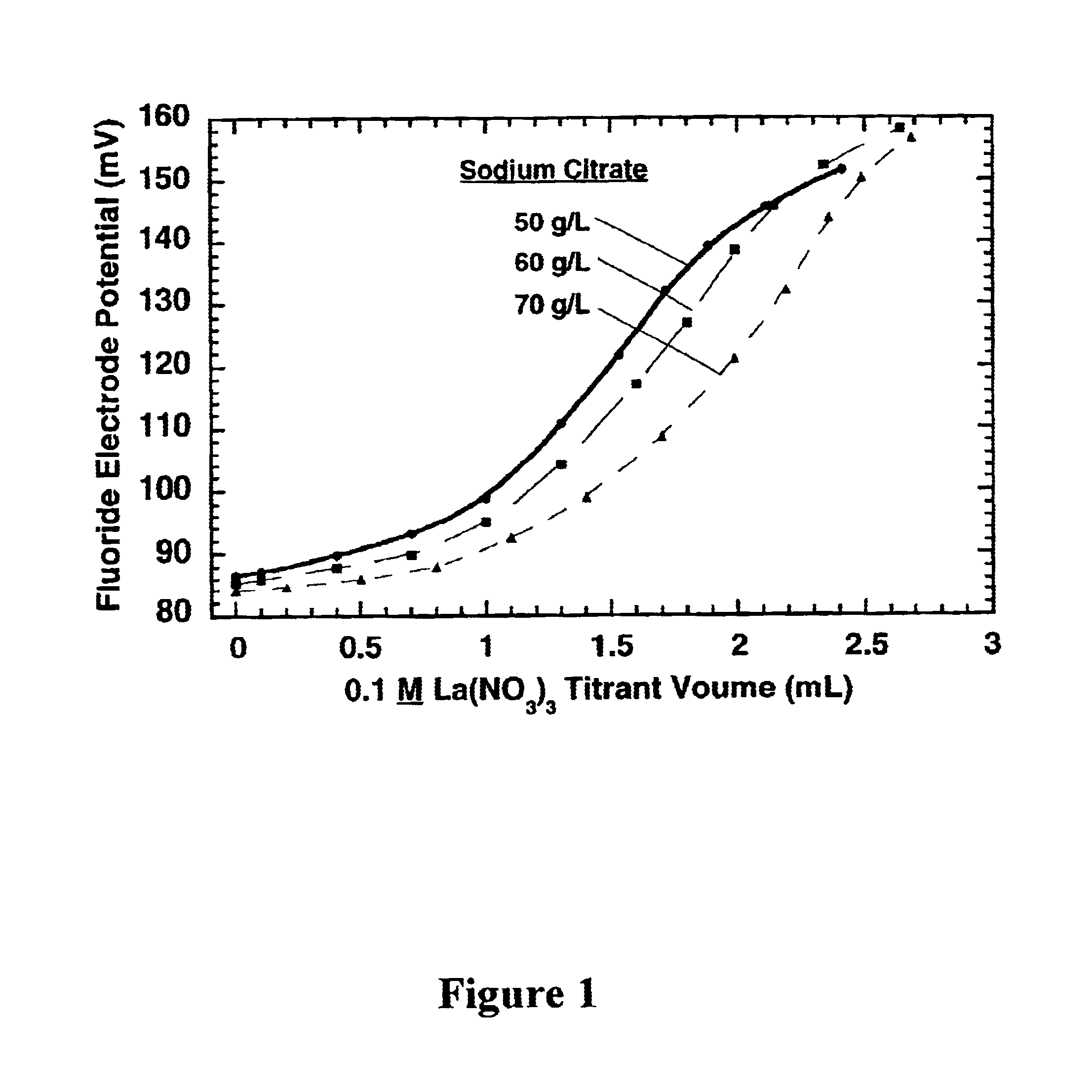
Measurement of complexing agent concentration in an electroless plating bath
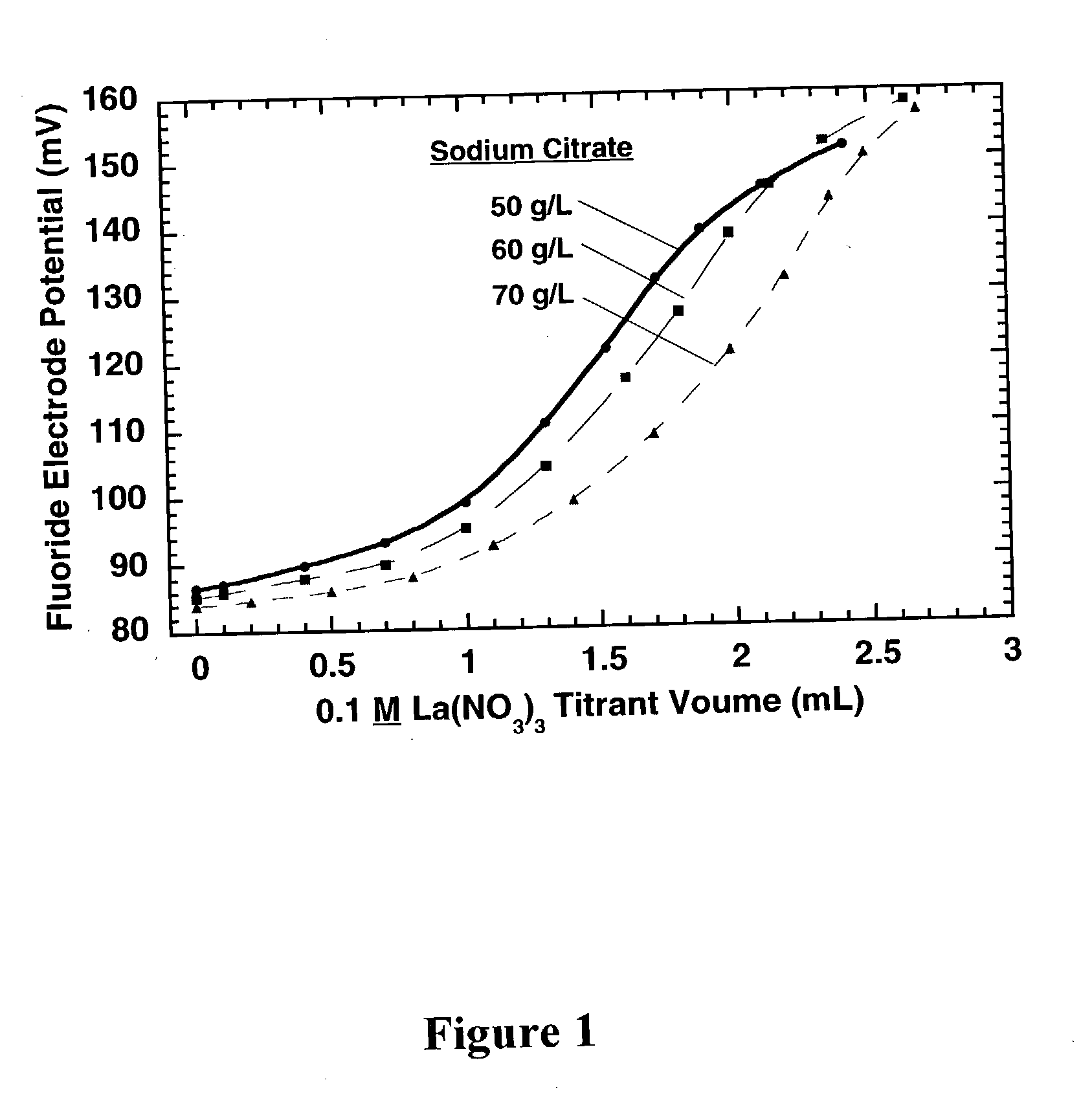
ActiveUS20040253740A1Minimize measurement errorEasy to rinseAnalysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using titrationCITRATE ESTERFluoride
The concentration of citrate complexing agent in an electroless cobalt or nickel plating bath is determined by titrating a sample of the electroless plating bath containing a small concentration of free fluoride ion with a standard lanthanum nitrate solution. During the titration, La<3+> ion first reacts preferentially with the citrate complexing agent and then with fluoride ion, which reduces the free fluoride ion concentration. The endpoint for the titration is indicated by a substantial decrease in the free fluoride ion concentration, which is detected via a fluoride ion specific electrode (ISE). The method can be used for analysis of other complexing agents.
Owner:ECI TECH
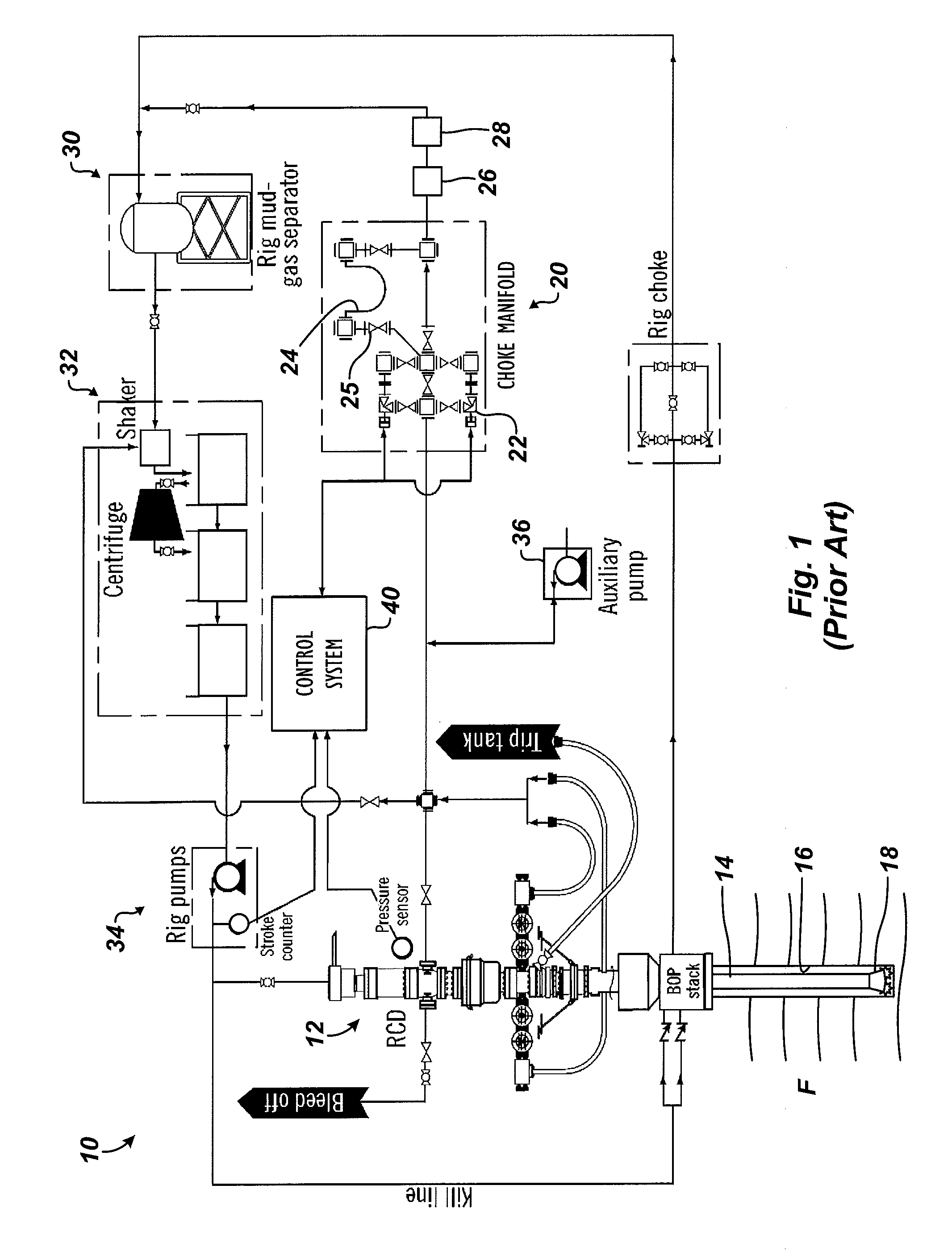
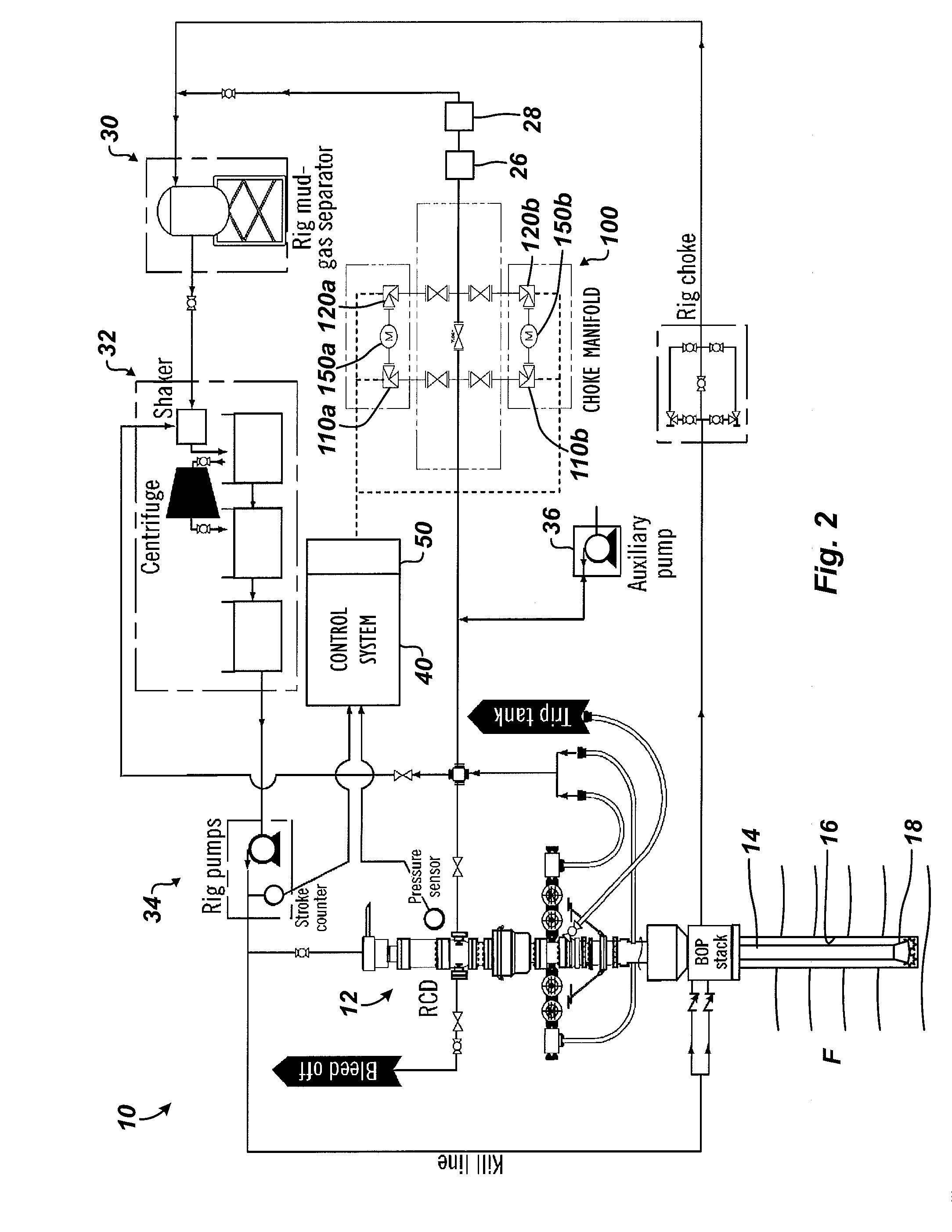
Controlled Pressure Drilling System with Flow Measurement and Well Control
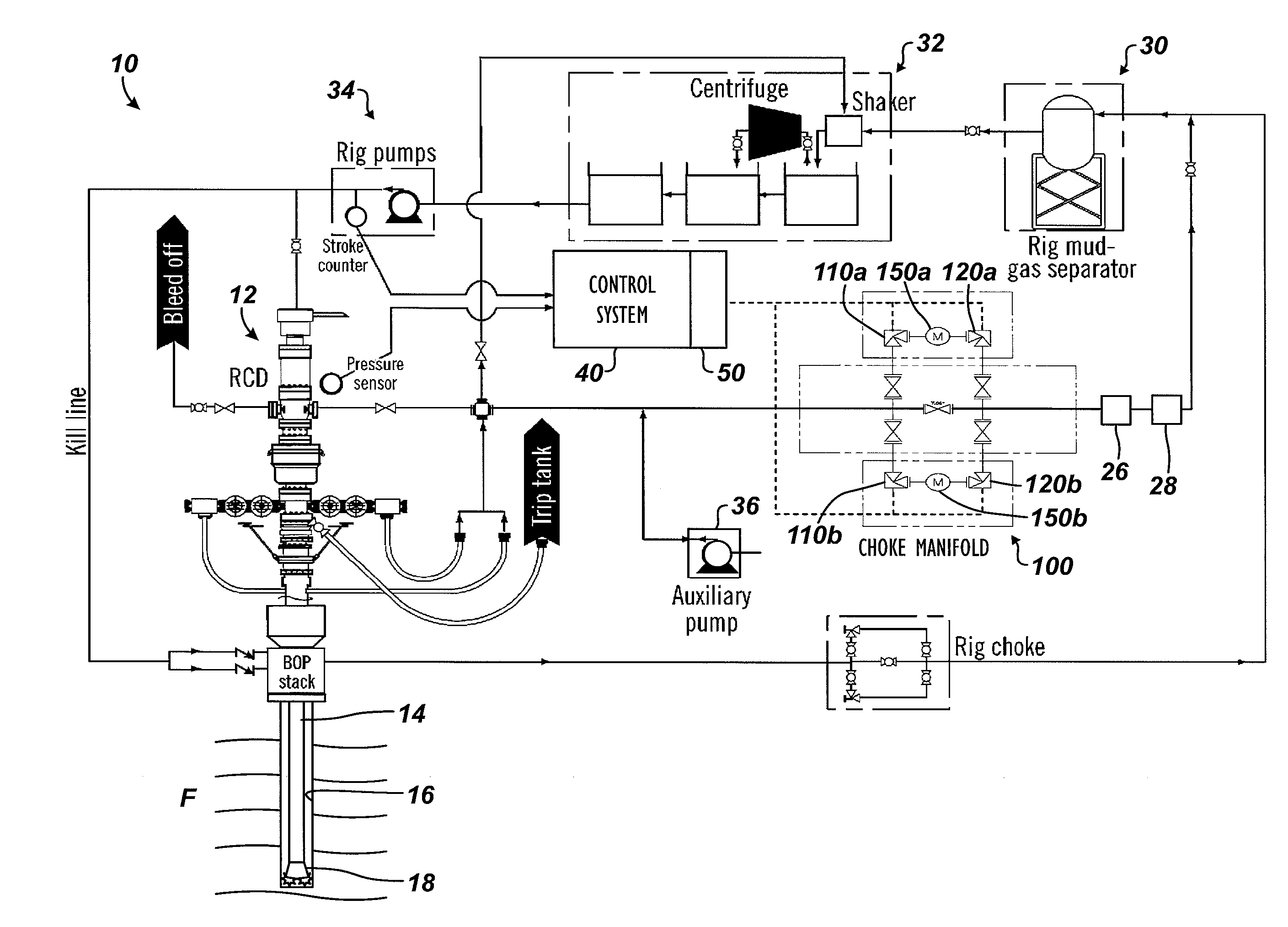
ActiveUS20160138351A1Minimize measurement errorMinimizes error measurementFlushingSealing/packingStream flowDrilling system
A drilling system for drilling a wellbore has one or more valves or chokes to control the upstream pressure of drilling fluid flow in a controlled pressure drilling operation. A measurement is obtained of the drilling fluid flow from the wellbore. Based on the obtained measurement, the drilling fluid flow is selectively distributed with a distributor through one or more of a plurality of flowmeters, such as Coriolis meters. A reading of the drilling fluid flow is obtained from the selected flowmeter(s). Upstream pressure in the drilling fluid flow is controlled with the one or more valve based at least in part on the reading from the one or more selected flowmeters. The reading can be a flow rate, a pressure, or the like compared to capacities of the flowmeters. Additional valves downstream of the flowmeters can be controlled based on cavitation that the valves are estimated to produce.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
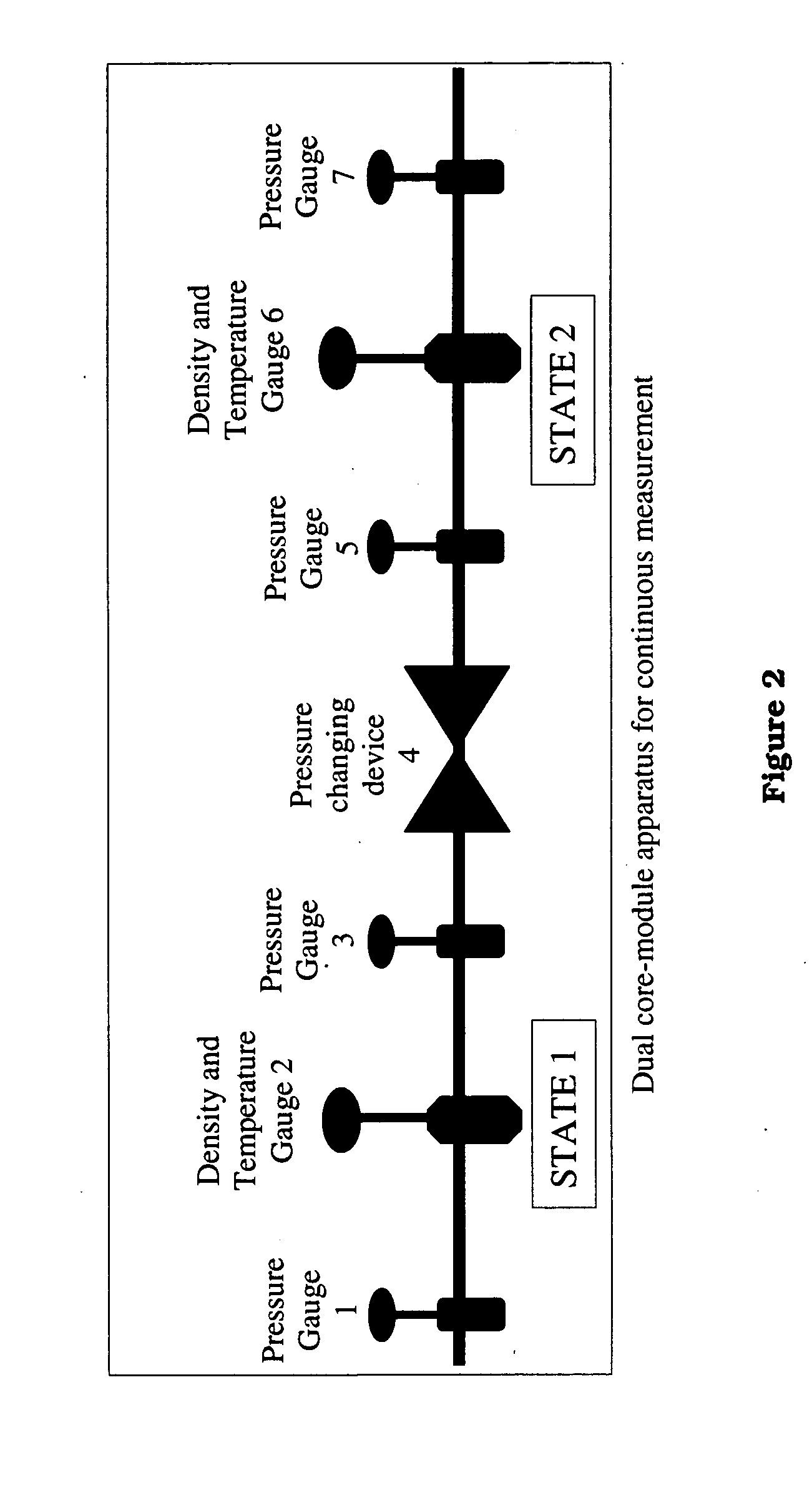
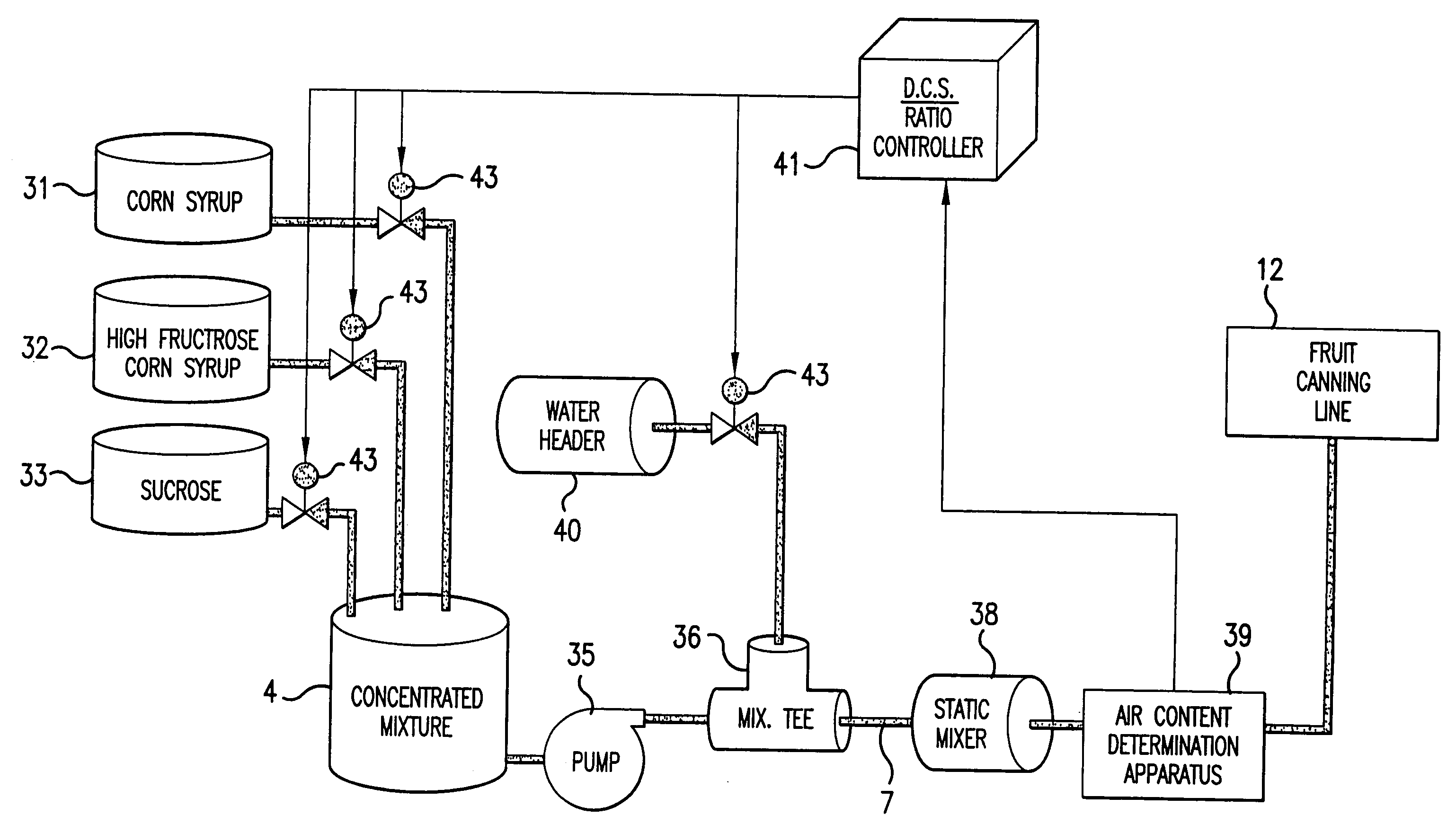
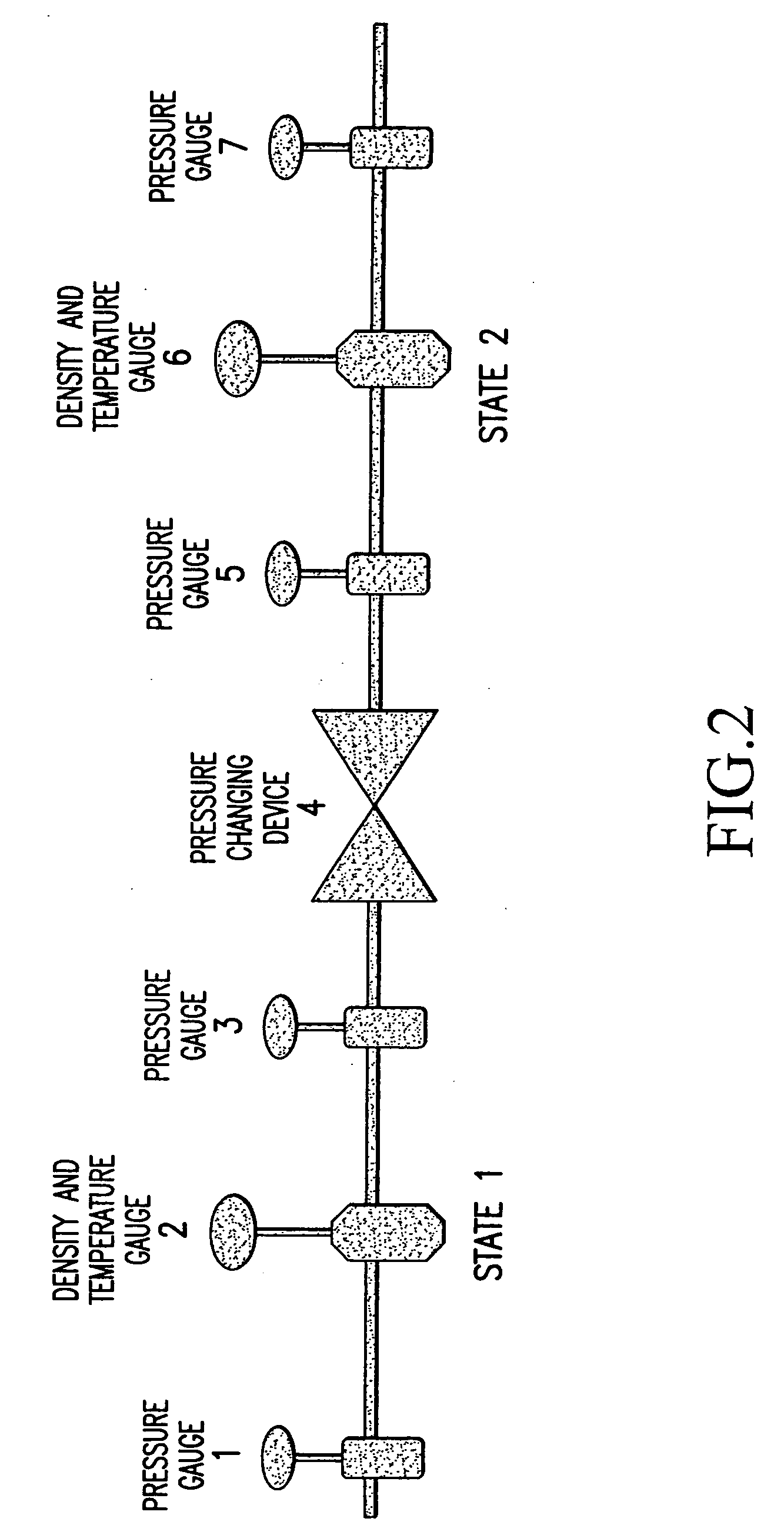
Apparatus and method for real time determination of density and related parameters in manufacturing processes
InactiveUS20050043900A1Easy to controlEffectively monitor processTransportation and packagingMixing methodsObservational errorKaolin clay
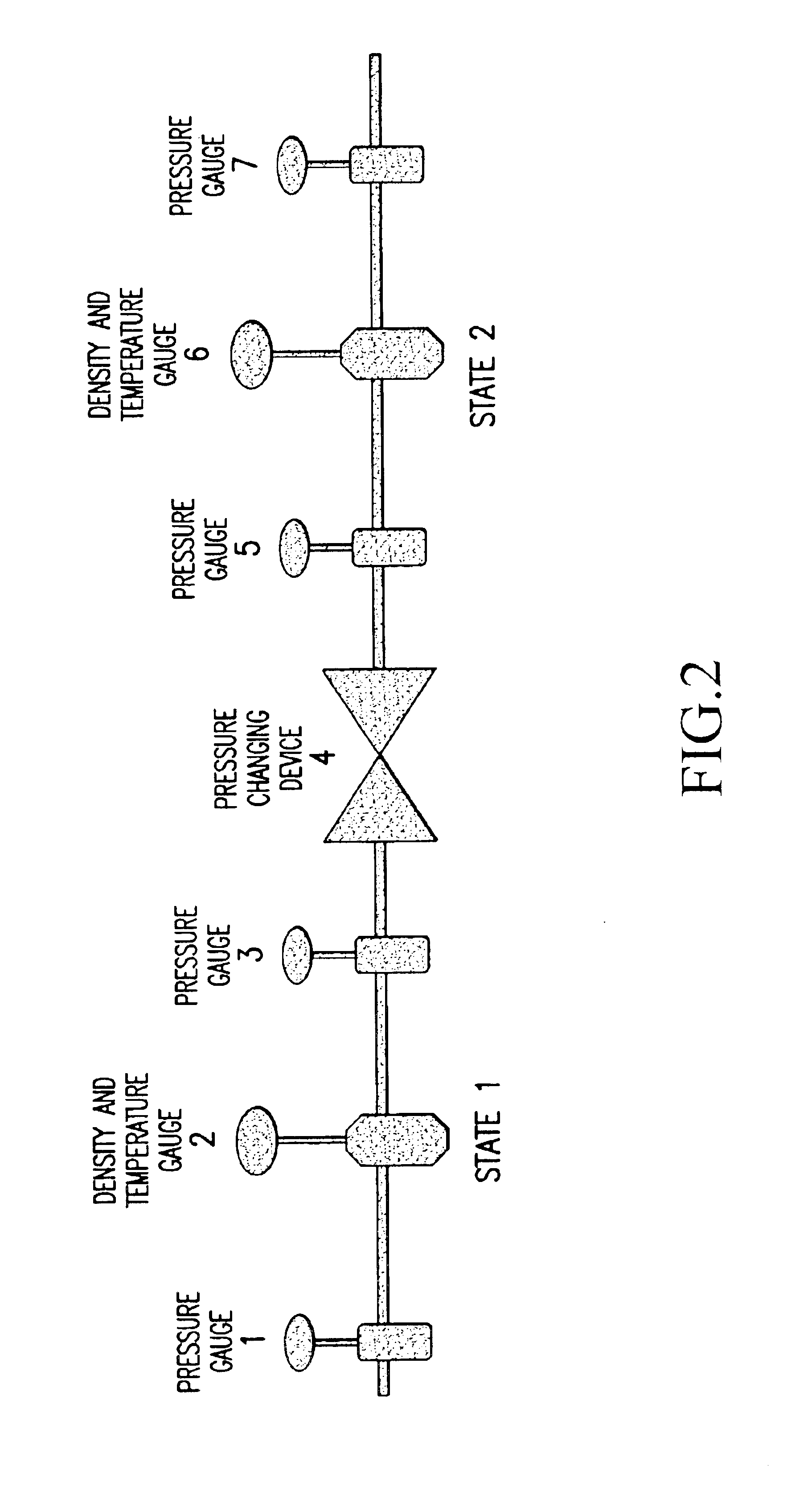
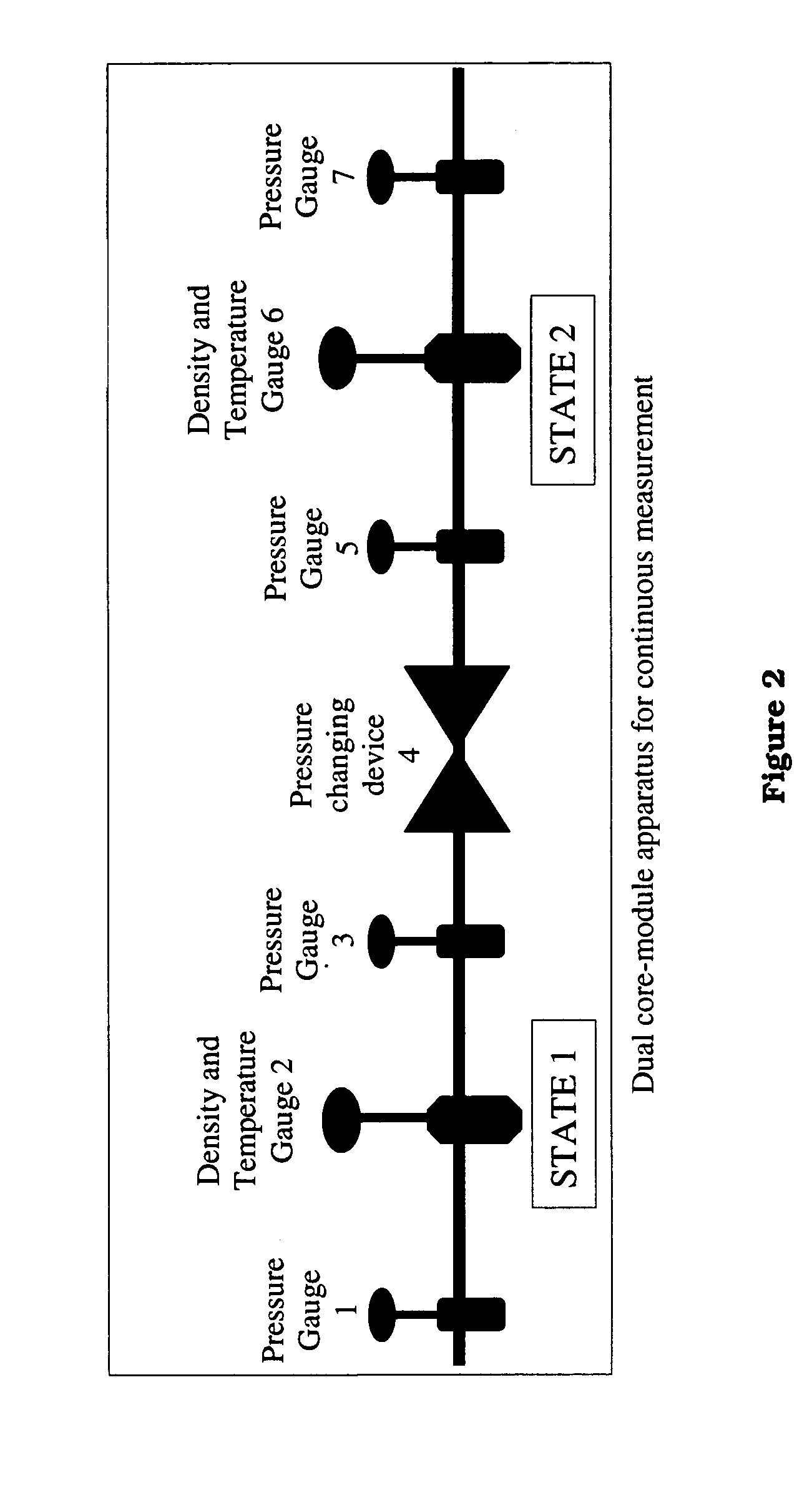
Methods and apparati for measuring entrained gas content. One of the disclosed apparatus embodiments includes a chamber and piping for process fluid, the piping including two different sectors each comprising a density and temperature gauge having a pressure gauge located upstream and a second pressure gauge located downstream, the two sectors being operatively joined together by a pressure-changing device. The pressure measurement feature may be incorporated into the combination density and temperature gauge, eliminating the need for separate pressure gauges. Data generated by this invention reduces measurement error caused by the dissolving or exsolving of gases with changes in pressure of a fluid, while providing instantaneous measurement, through apparatuses that measure system conditions at each of two pressure states within a very short period of time. For instance, in the context of continuously coating a substrate, the method of this invention comprises: a.) setting a quantitative target for weight-% of one or more solids, e.g. kaolin clay, calcium carbonate, titanium dioxide, or alumina trihydrate, to be coated onto a substrate such as a paper web; b.) continuously applying the solids to the substrate via a carrier fluid; c.) measuring the apparent density of the slurry; d.) determining the true density of the slurry; e.) calculating the weight-% of solids in the slurry as disclosed above; f.) comparing the calculated weight-% solids to the target weight-% solids; and, g.) if the calculated weight-% is greater or less than the target weight-%, lowering or raising the amount of solids applied in step b.). Many other method and apparatus embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:APPVION OPERATIONS INC
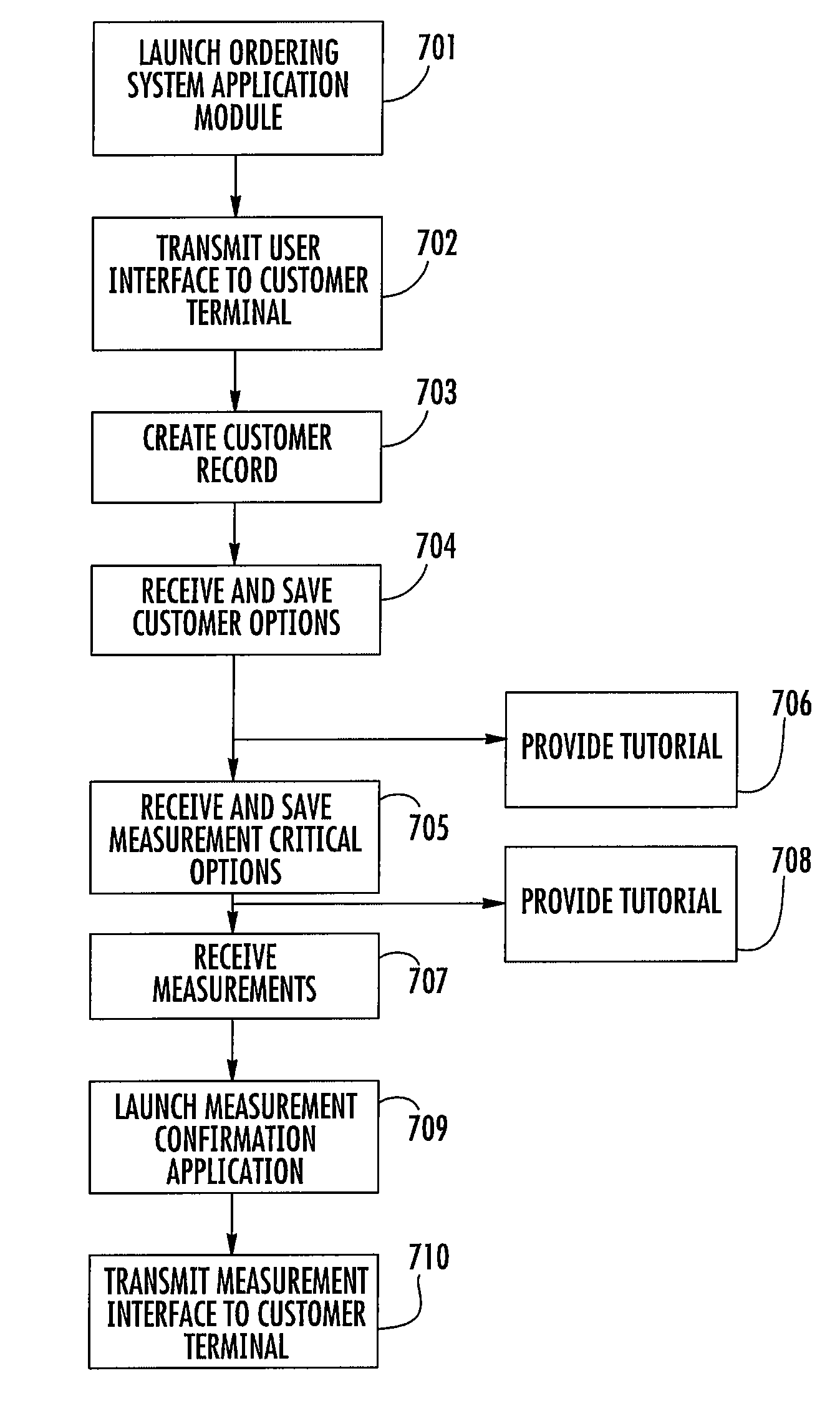
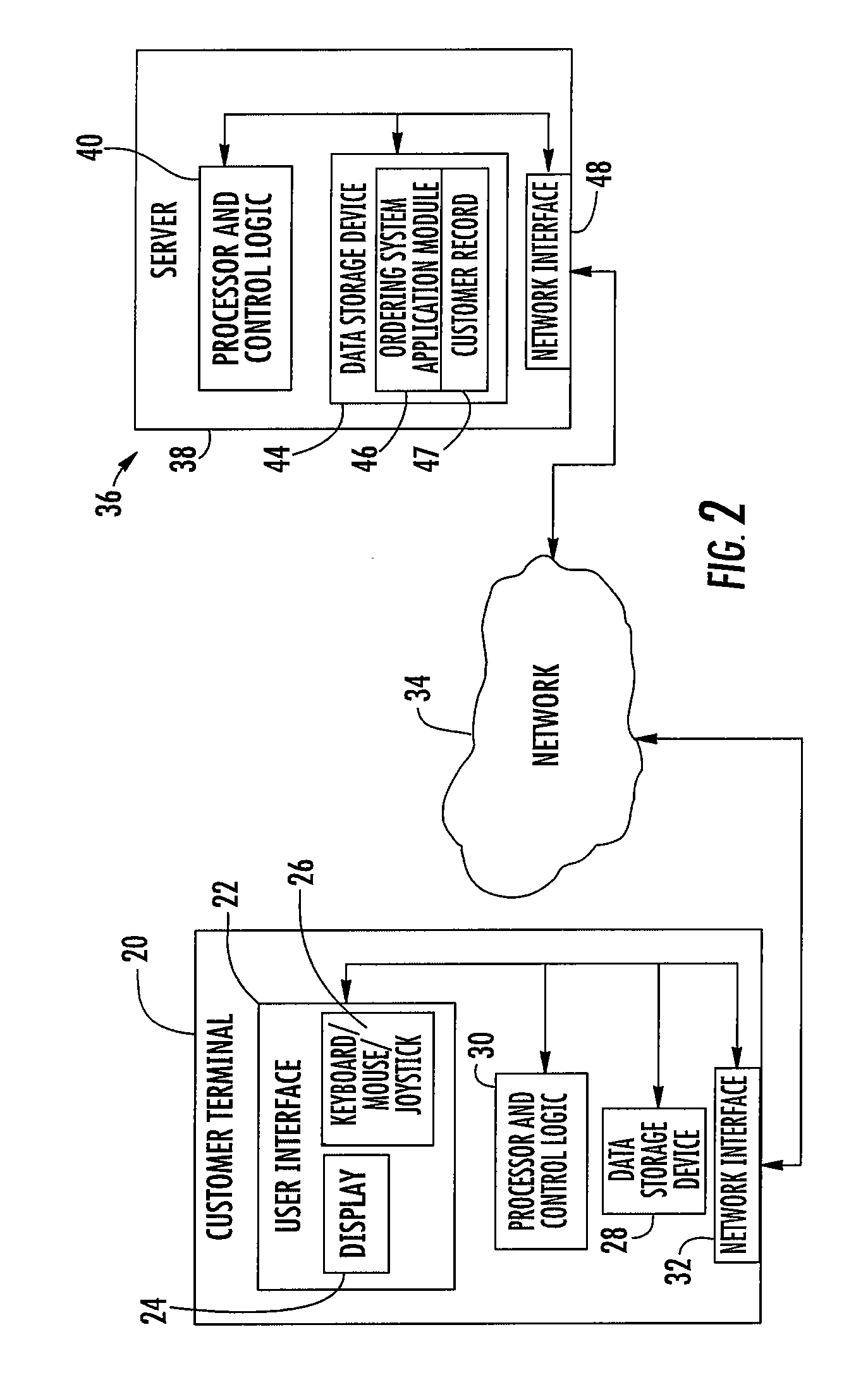
Method and apparatus for a product ordering system
InactiveUS20070239551A1Minimize measurement errorAccurate measurementBuying/selling/leasing transactionsProduct orderProduct characteristics
A customer is presented with a product ordering interface for a size dependent product such as a window covering. The customer is presented with ordering options. Once the customer has selected the desired product, the user is presented with a measurement confirmation interface. The customer is directed to enter at least one first measurement and one second measurement. The measurement(s) are entered into the customer ordering interface. From these measurements the system calculates a theoretical dimension for a product feature. The customer also measures the actual dimension of the product feature. The ordering system compares the calculated dimension to the customer measured dimension. If the calculated dimension matches the customer measured dimension, the measurement is confirmed.
Owner:HUNTER DOUGLAS INDS SWITZERLAND
Power transmission line dip measurement method
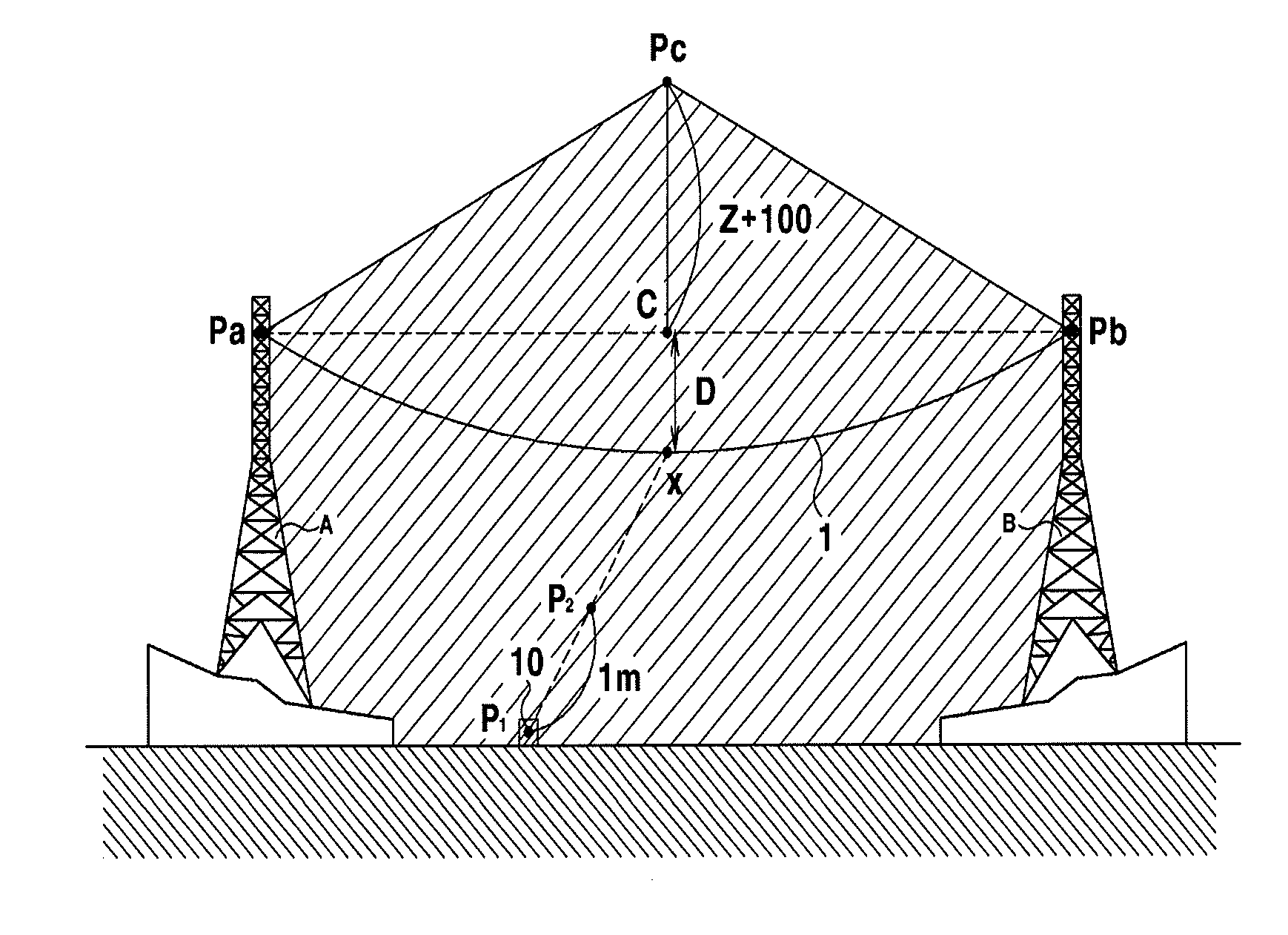
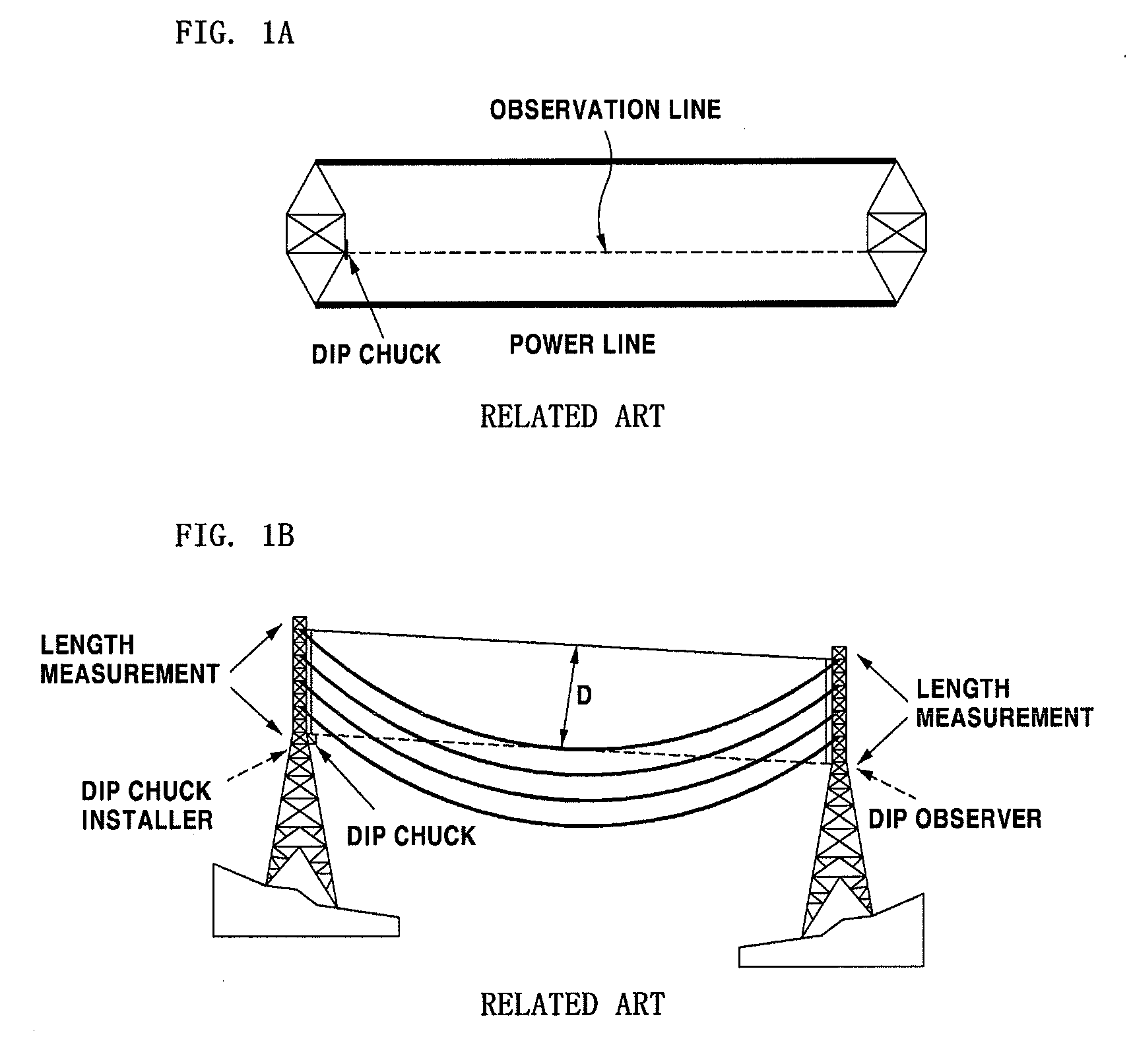
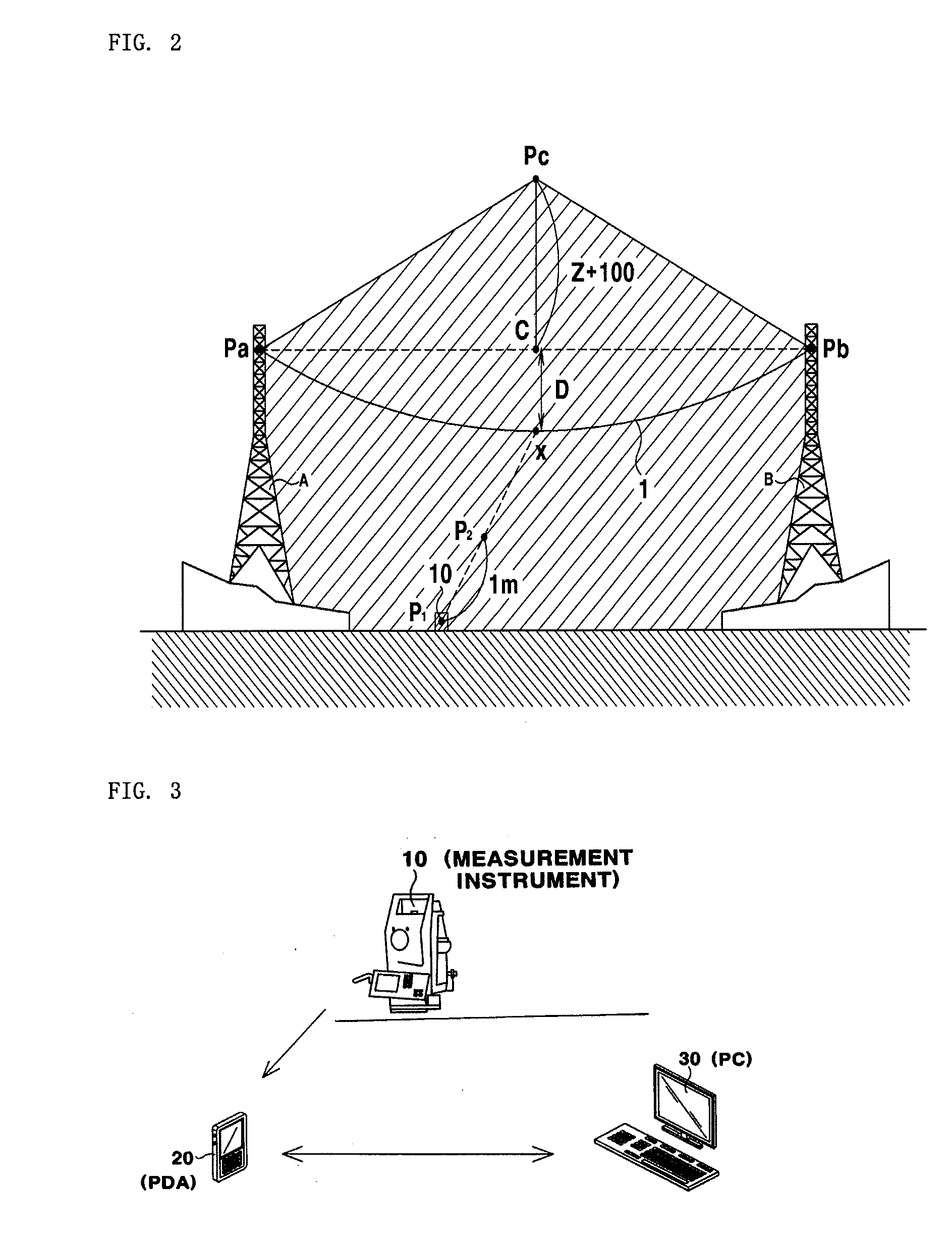
ActiveUS20100138186A1Minimize measurement errorImprove efficiencyMechanical depth measurementsDigital computer detailsMeasuring instrumentTower
A power transmission line dip measurement method is disclosed. The dip measurement method includes installing a measurement instrument at a place where power line support points of steel towers can be seen from the ground, collimating the measurement instrument at the power line support point of one of the steel towers, transmitting a collimated value to a PDA in a wired or wireless manner, collimating the measurement instrument at the power line support point of the other steel tower, transmitting a collimated value to the PDA, calculating the collimated values to display a horizontal angle position of a dip base line, and adjusting an angle of the measurement instrument based on the horizontal angle displayed on a screen of the PDA by a worker, collimating the measurement instrument at a power line dip point as a dip base point, and displaying a dip value on the screen of the PDA.
Owner:KPS CO LTD
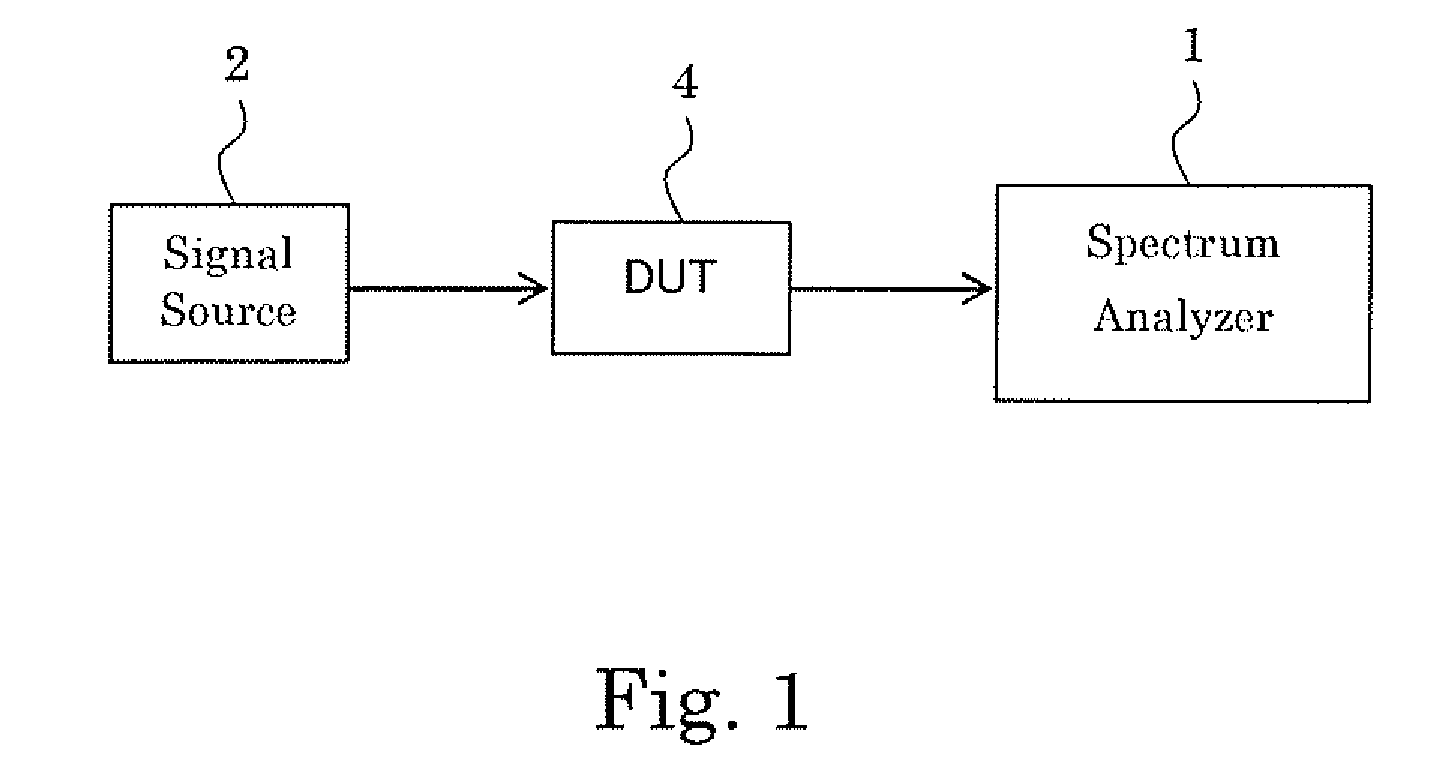
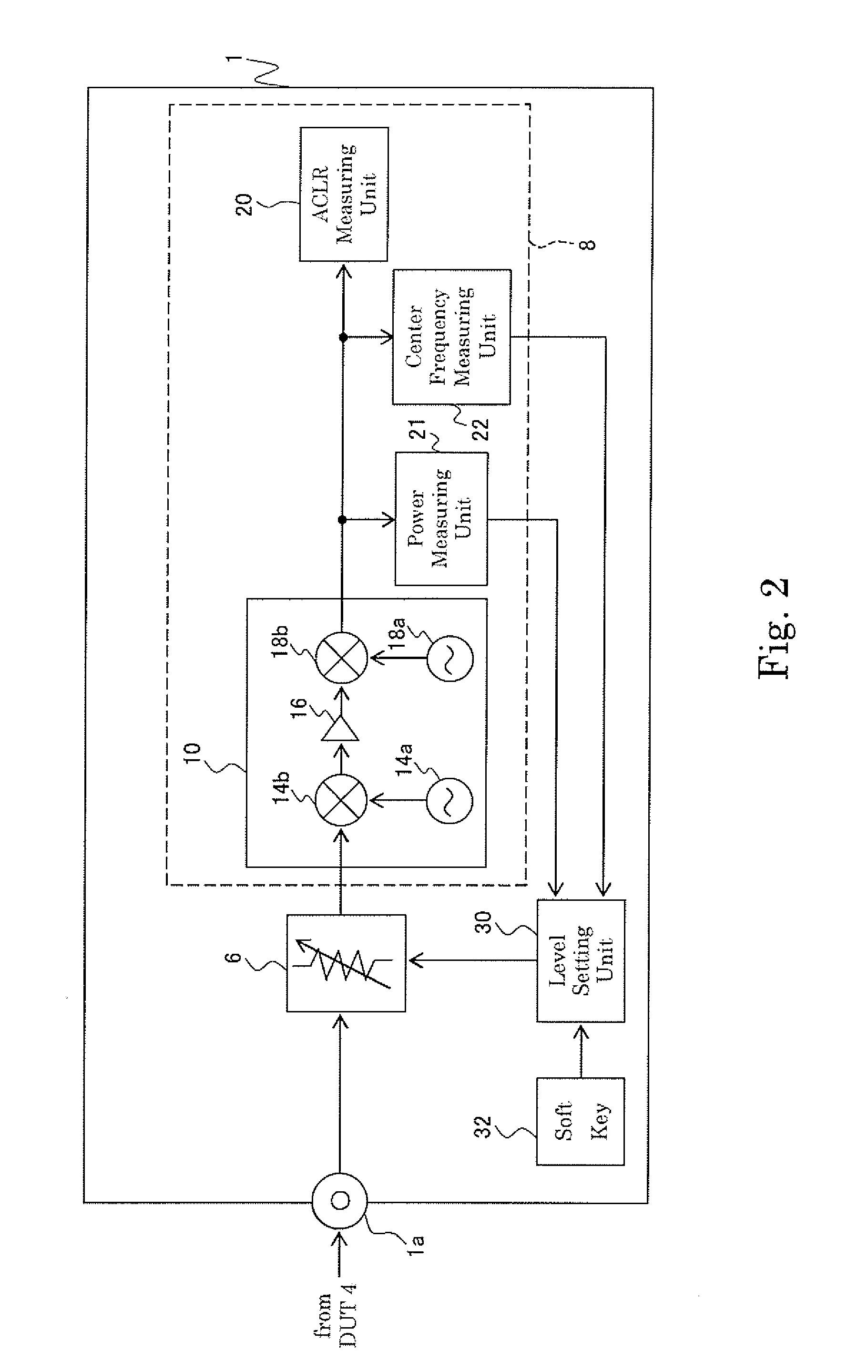
Measurement device, method, program, and recording medium
InactiveUS20080054880A1Minimize measurement errorDigital circuit testingCurrent/voltage measurementObservational errorMeasurement device
The level of an output signal output from a device under test is easily adjusted in order to restrain an adverse effect on a result of measuring characteristics of the device under test. A measuring device includes a characteristic measuring unit for measuring characteristics of a device under test based on the output signal output from the device under test, an attenuator for receiving the output signal and adjusting the level of the output signal before supplying it to the characteristic measuring unit, and a level setting unit for setting the degree of the level adjustment of the output signal by the attenuator so as to minimize a measurement error which is caused by the characteristic measurement unit, and changes according to the level of the output signal supplied to the characteristic measuring unit.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
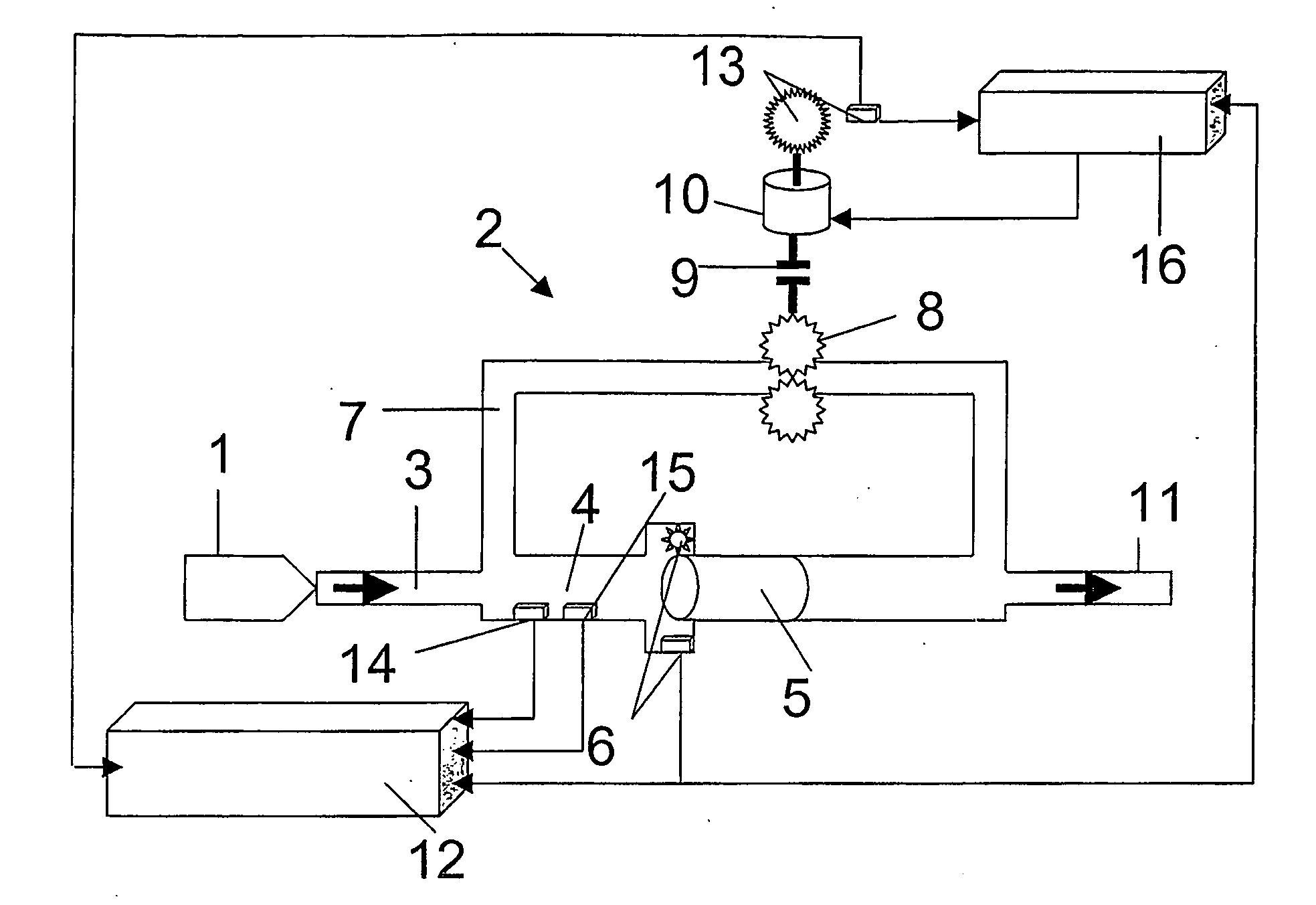
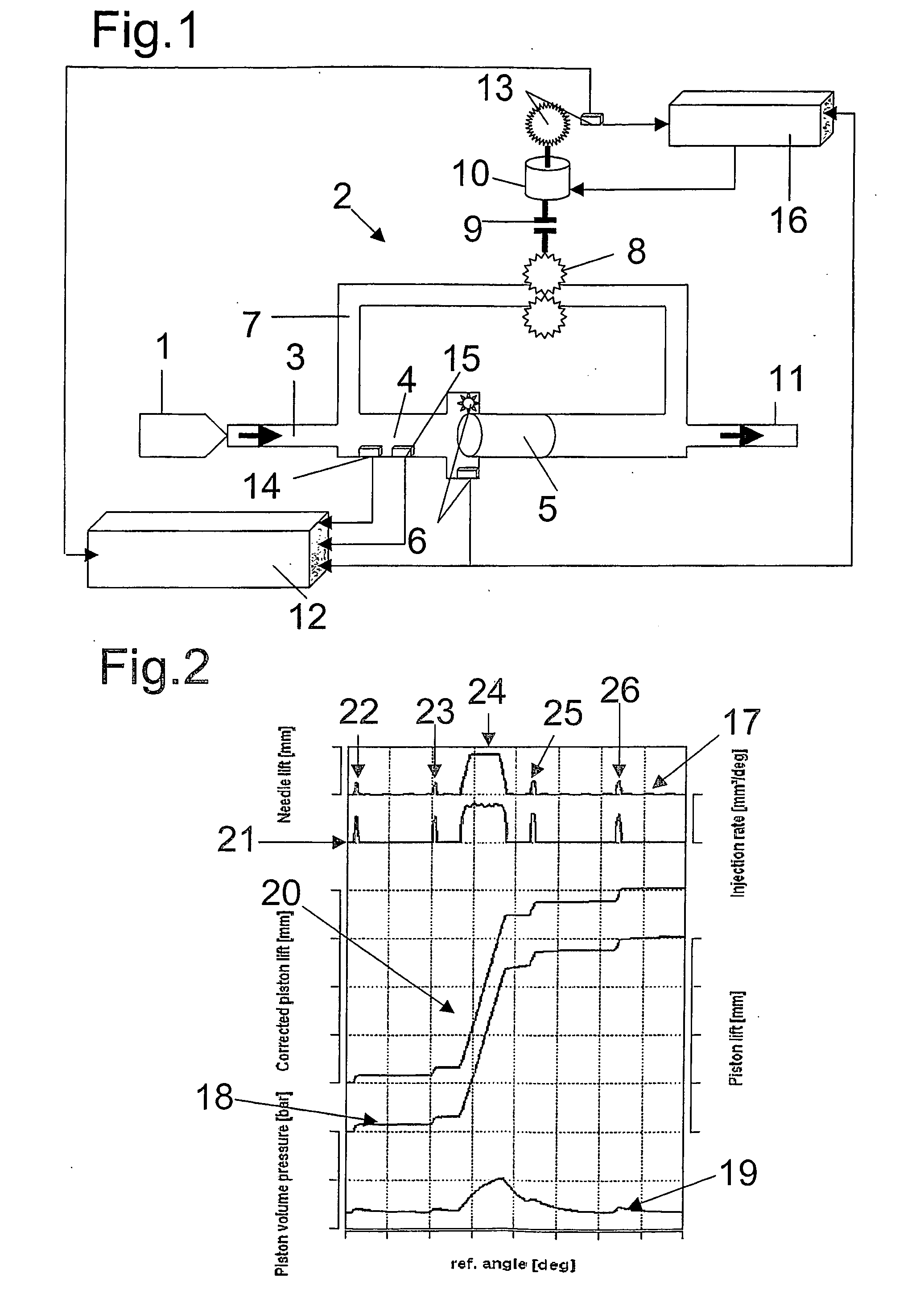
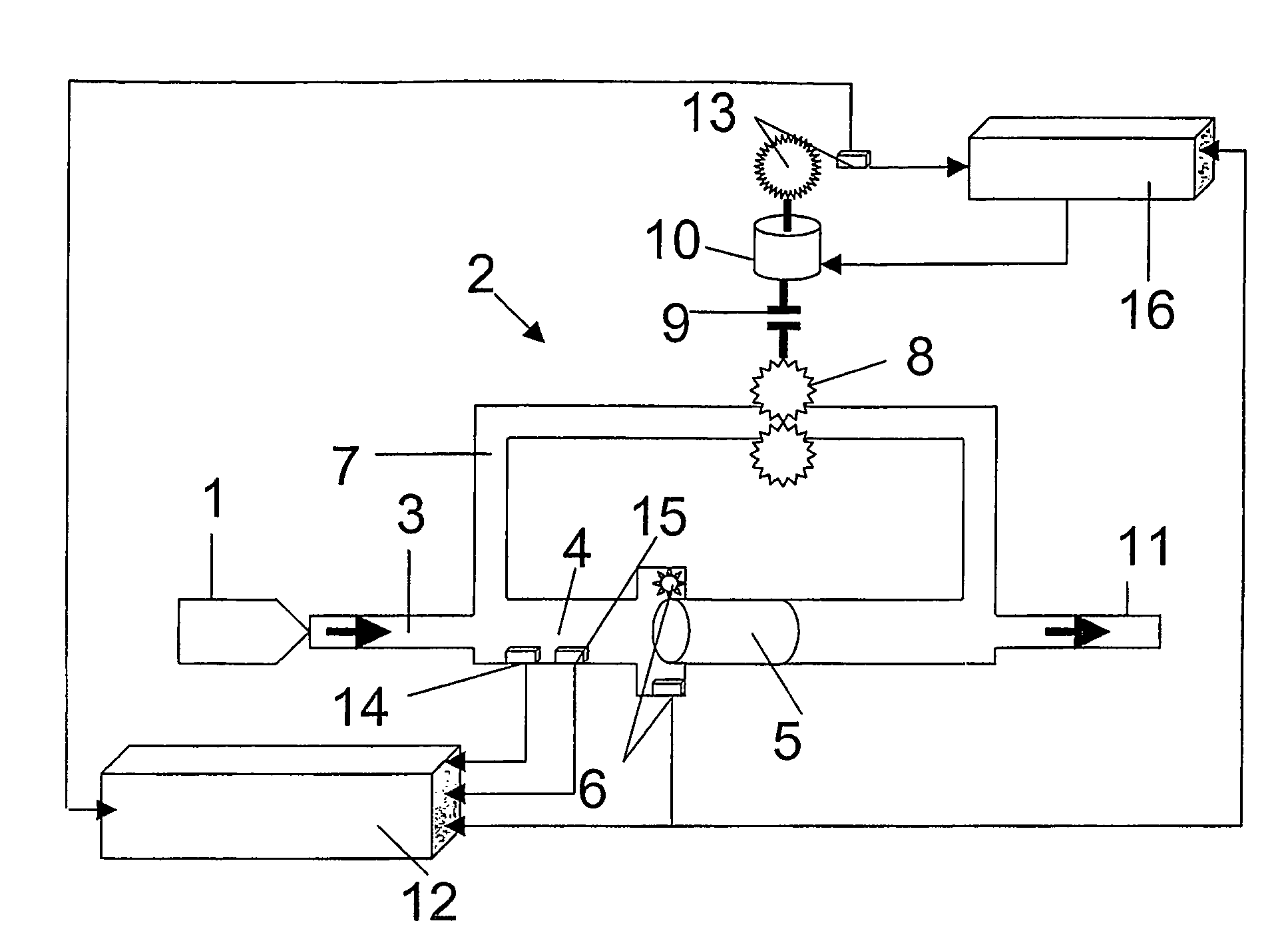
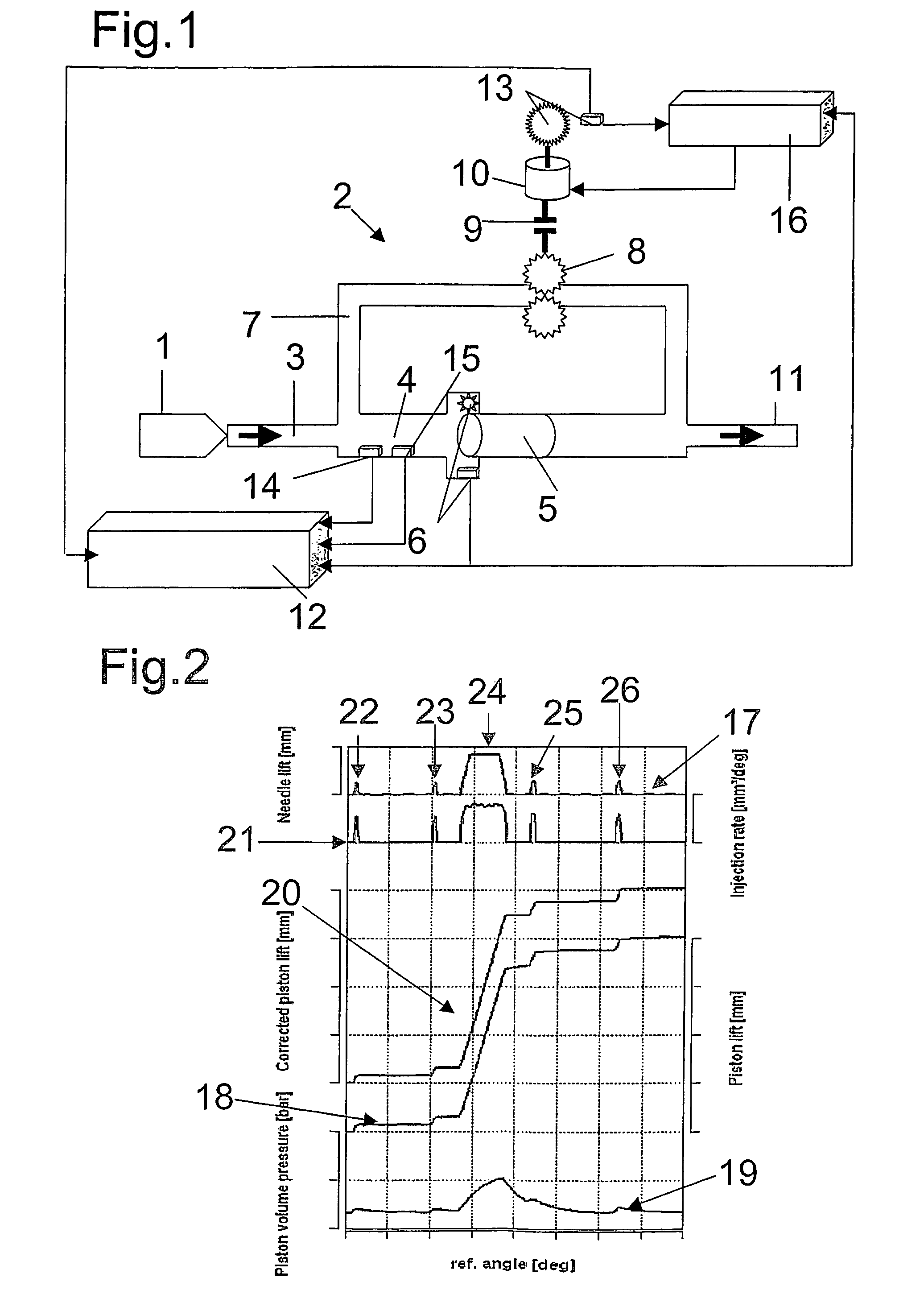
Device for measuring time-resolved volumetric throughflow processes
InactiveUS20060201244A1High measurement accuracySimple designEngine testingVolume/mass flow measurementCombustionInternal combustion engine
The invention relates to a device for measuring time-resolved volumetric throughflow processes, especially injection process in internal combustion engines, having a translational volume difference sensor having a piston disposed in a measuring compartment and a detection device detecting the excursion of the piston, the detection device being linked with an evaluation unit. According to the invention, a pressure sensor is mounted in the measuring compartment in addition to the detection device which detects the excursion of the piston. The signal of the detection device corresponding to the excursion of the piston can be better evaluated as the compressivity of the fluid in the measuring compartment can be taken into consideration for the calculation of the amount to be injected. The inventive device allows for a highly time-resolved representation of throughflow processes so that both overall amount and exact course of the throughflow can be represented and evaluated.
Owner:AVL LIST GMBH
Methods and apparatus for analyzing high voltage circuit breakers
InactiveUS6965238B2Facilitate minimizing induced current measurement errorMinimize measurement errorProduction of permanent recordsFault locationProgram segmentOvervoltage
Methods, computer program segment and apparatus for analyzing high voltage circuit breakers are provided. The method includes determining a circuit breaker contact closing time, determining a circuit breaker contact opening time, and determining a circuit breaker pre-insertion resistor resistance value using at least three voltage samples and three current samples to facilitate reducing an induced current measurement error. The computer program segment is embodied on a computer readable media and is programmed to determine a circuit breaker contact closing time, determine a circuit breaker contact opening time, and determine a circuit breaker pre-insertion resistor resistance value using at least three voltage samples and three current samples that facilitate minimizing an induced current measurement error. The apparatus includes a testing circuit, an overvoltage protection circuit, and a processor programmed to determine a circuit breaker contact timing measurement and a circuit breaker contact resistance measurement.
Owner:MEGGER SWEDEN
Biosensor
InactiveUS20080128278A1Fast absorptionMinimize measurement errorImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteEnzyme
A biosensor measuring an analyte contained in a sample is disclosed, including: a lower insulating substrate having formed thereon a working electrode and a reference electrode connected to lead terminals through leads, and an enzyme reactant layer formed on the electrodes to react with the analyte contained in the sample; a spacer which is interposed between the lower substrate and an upper substrate, is attached to the lower and upper substrates, and has a sample guide area to guide the sample to reach to the electrodes through the enzyme reactant layer; and an upper insulating substrate which faces the lower substrate through the spacer, where a dummy electrode is formed on the lower substrate, the dummy electrode being separated from the working electrode and the reference electrode, fixing the enzyme reactant layer, and being not connected to the leads.
Owner:INFOPIA CO LTD
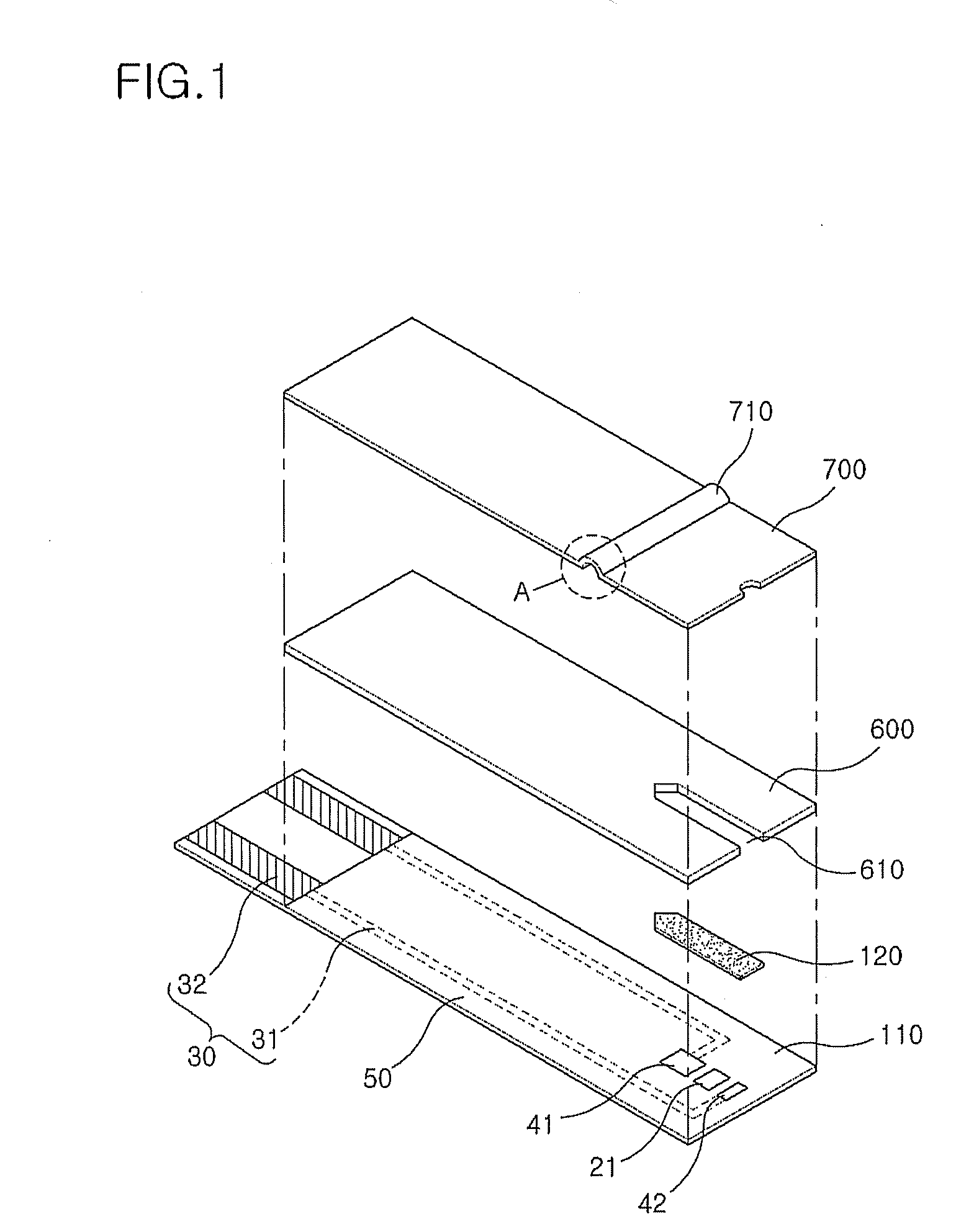
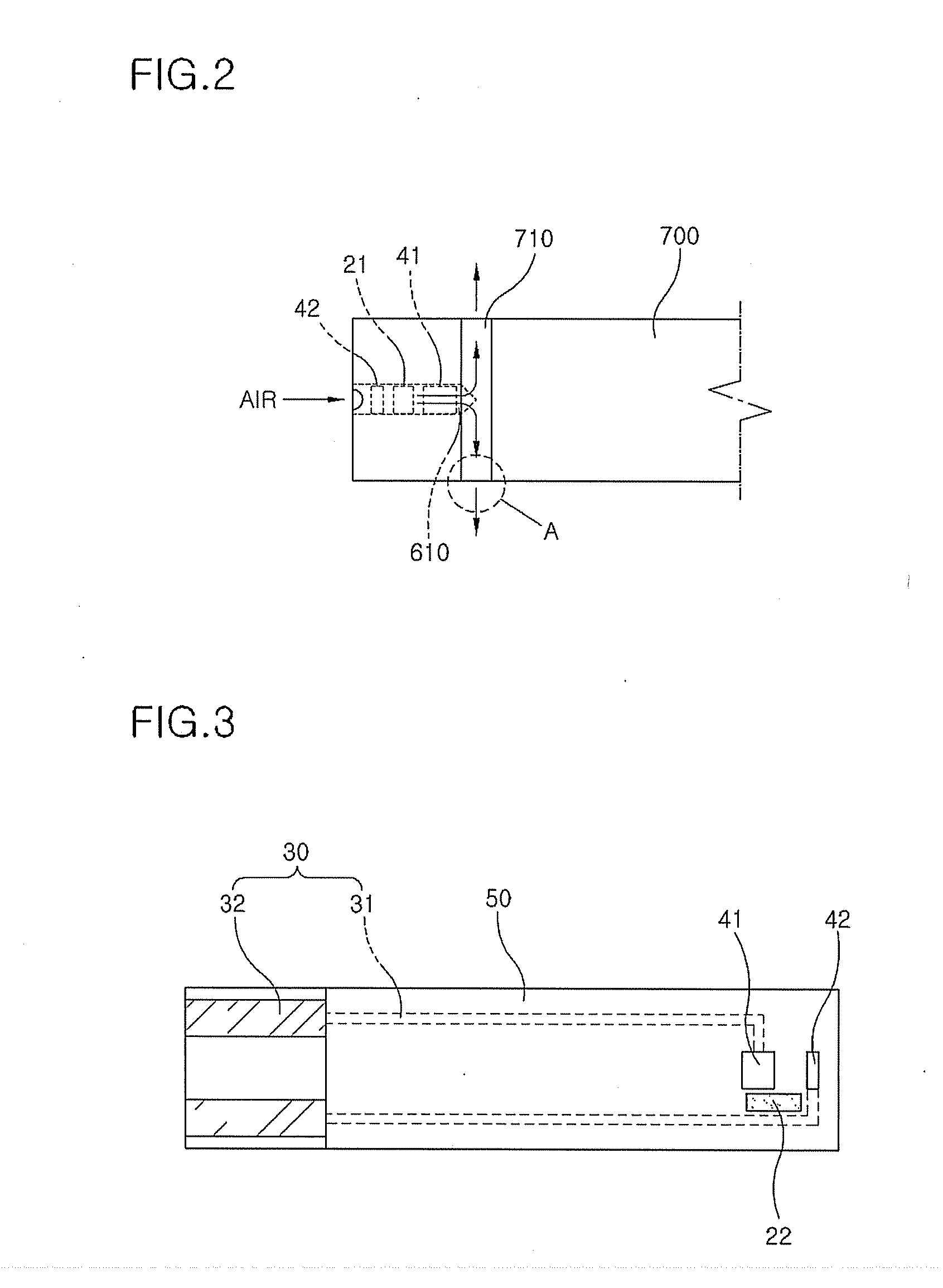
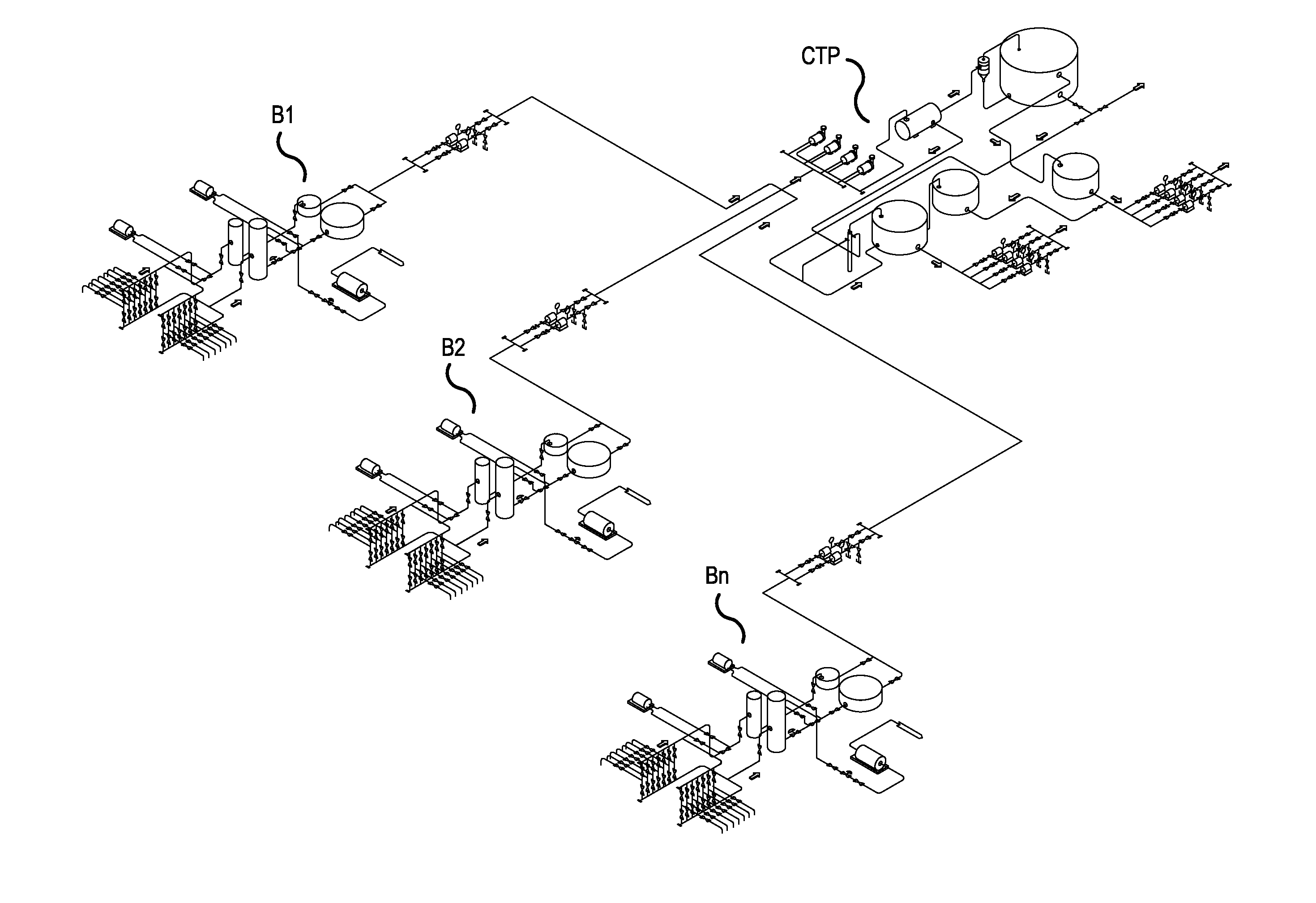
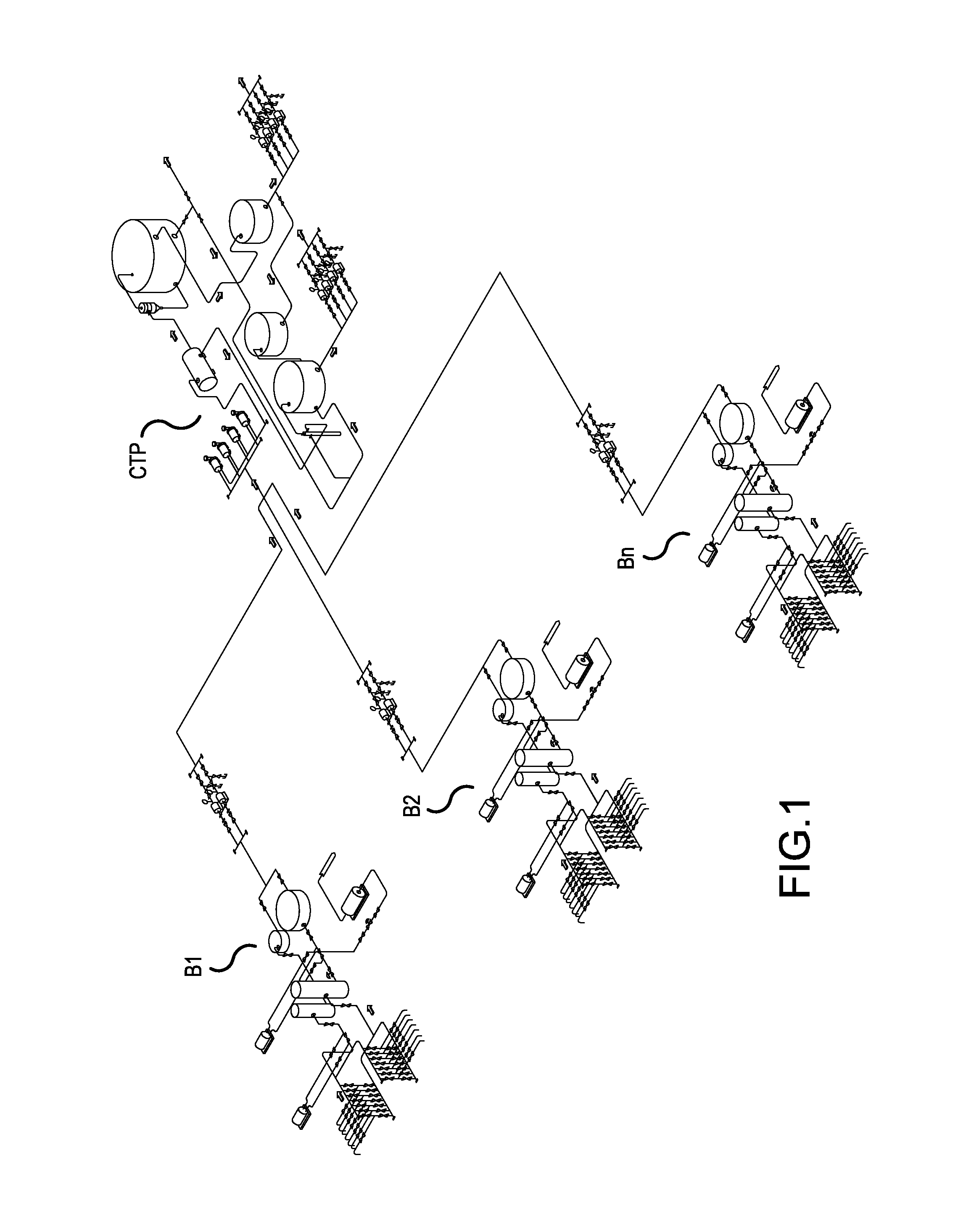
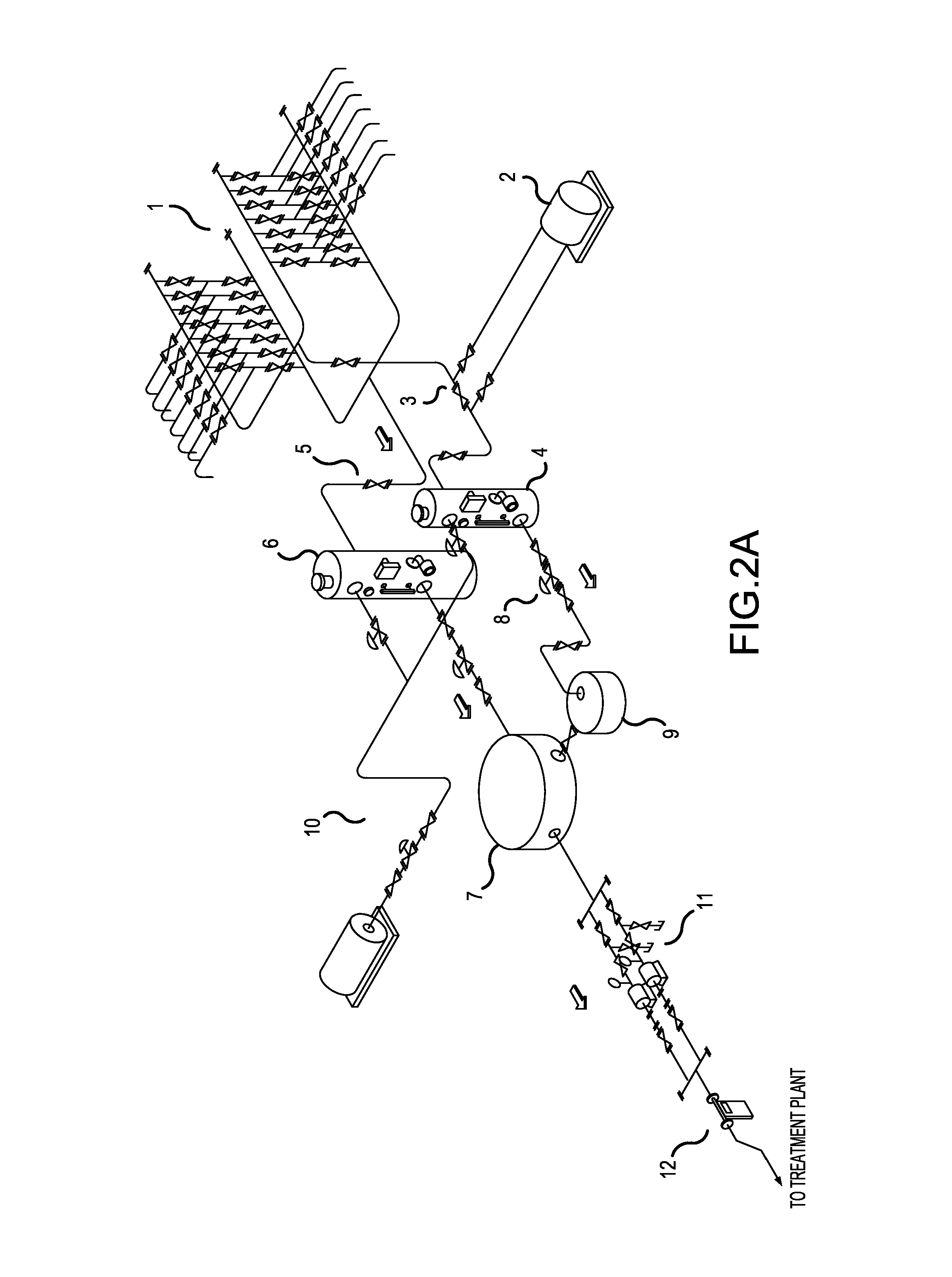
Reeling Method and System as Well as an Measuring Apparatus
ActiveUS20080017341A1Minimize measurement errorCost-effectiveAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPaper testingPaper sheetMeasurement device
A method and a system to control a reeling profile of a material web reel (30), when, in the forming of a material web reel (30), a web is reeled around a reeling core and when in an adjustment of CD-directional profiles of the web reel, profiling devices (8) have been applied. For adjusting quality profiles and reeling profiles of the web, profiling devices are managed with the help of profile measurings of the roller nip and / or of the profile measurings of the reel (30), which are obtained from the reel-up (2). A measuring device (40) for a measuring of a CD-directional hardness profile of the fiber web reel includes a measuring head (43), which is connected with a loading means (41, 42), which loads the measuring head against the fiber web reel. The motion course of the measuring head is linear.
Owner:VALMET TECHNOLOGIES INC
Real time determination of gas solubility and related parameters in manufacturing processes
InactiveUS20050109078A1Easy to controlEasy to handleAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTesting beveragesApparent densitySolubility
Owner:APPVION OPERATIONS INC
Method and automated system for control of oil well production and modular skid for use in said method
InactiveUS20140096836A1Easy to measureReduce errorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFluid removalProcess engineeringControl valves
Automated measurement and oil well production control may be achieved by using a vertical separator, the discharge flow of which is continuously adjusted by setting the opening of a control valve, determined by the liquid level inside the separator. The automation of the control method allows real-time measurements of several process variables as well as reduced measurement times and also works as a safety layer for a production process. The control method is independent of well production and is therefore suited to controlling marginal wells.
Owner:YPF TECHA
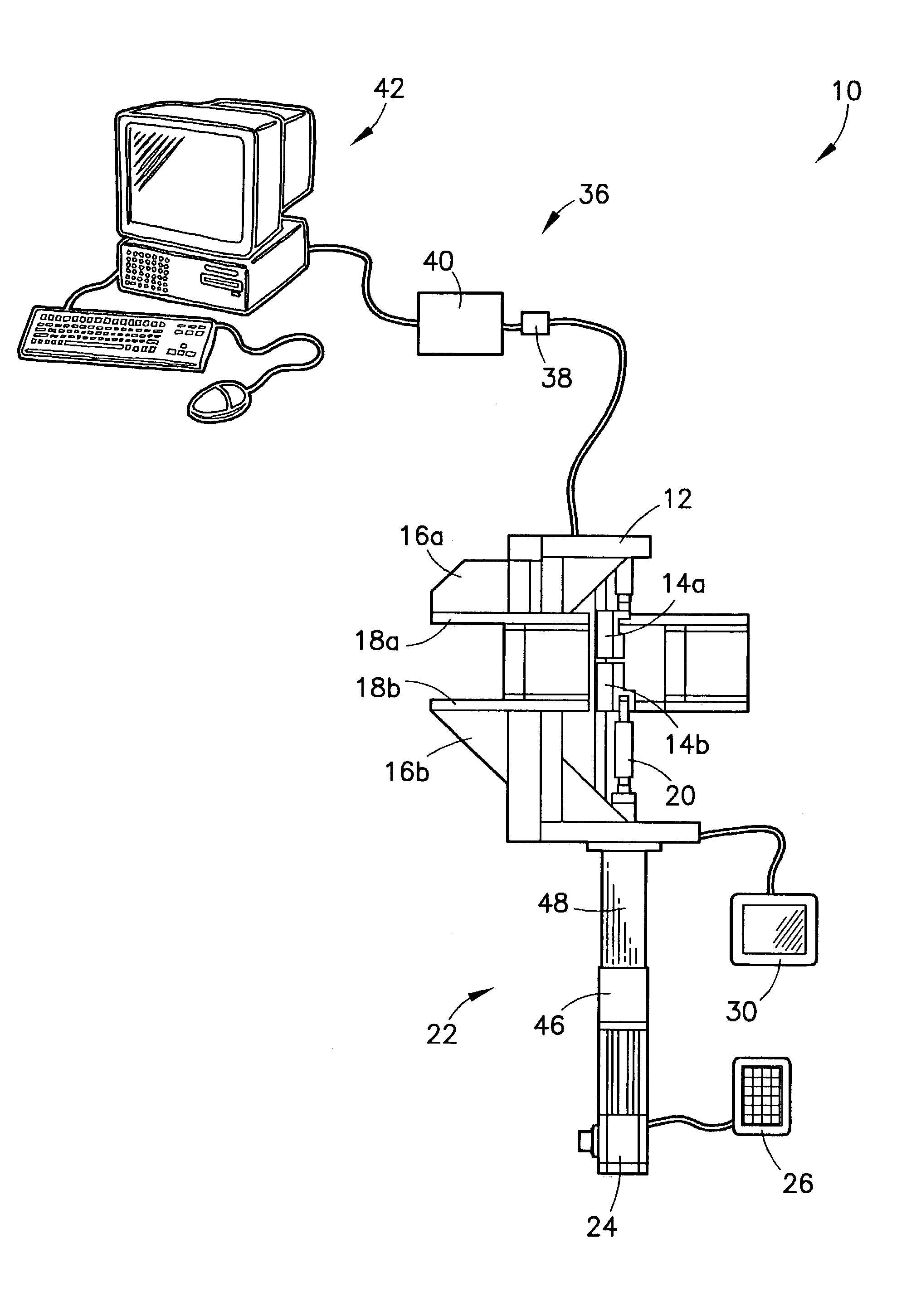
Micro-tensile testing system
InactiveUS6983658B2Advantageously minimizing deflectionAdvantageously minimizing bendingForce measurement by measuring optical property variationStrength propertiesObservational errorCyclic test
Owner:HONEYWELL FED MFG & TECHNOLOGI
Measurement of complexing agent concentration in an electroless plating bath
InactiveUS6890758B2Minimize measurement errorEasy to rinseAnalysis using chemical indicatorsChemical analysis using titrationCITRATE ESTERFluoride
The concentration of citrate complexing agent in an electroless cobalt or nickel plating bath is determined by titrating a sample of the electroless plating bath containing a small concentration of free fluoride ion with a standard lanthanum nitrate solution. During the titration, La3+ ion first reacts preferentially with the citrate complexing agent and then with fluoride ion, which reduces the free fluoride ion concentration. The endpoint for the titration is indicated by a substantial decrease in the free fluoride ion concentration, which is detected via a fluoride ion specific electrode (ISE). The method can be used for analysis of other complexing agents.
Owner:KLA CORP
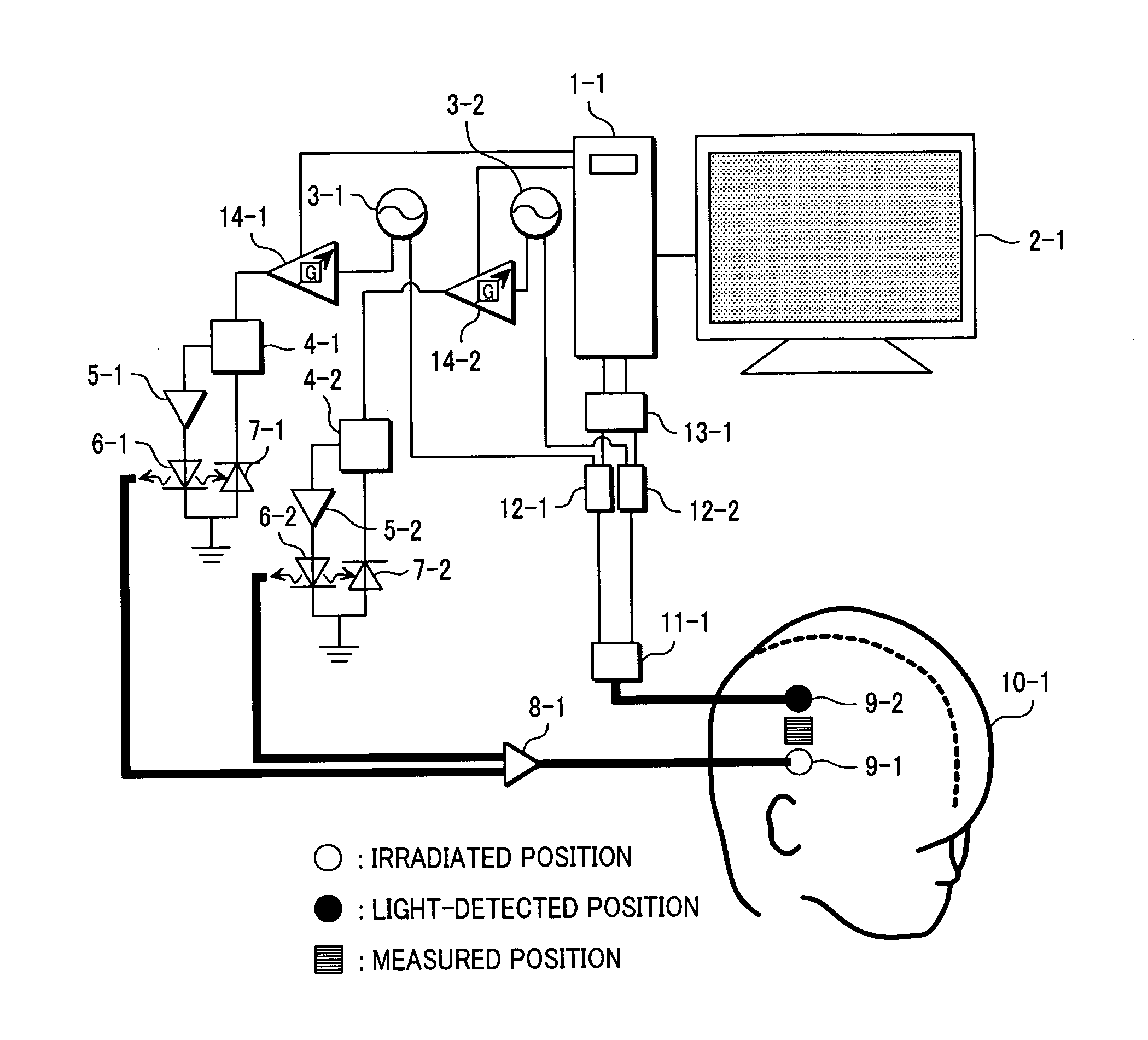
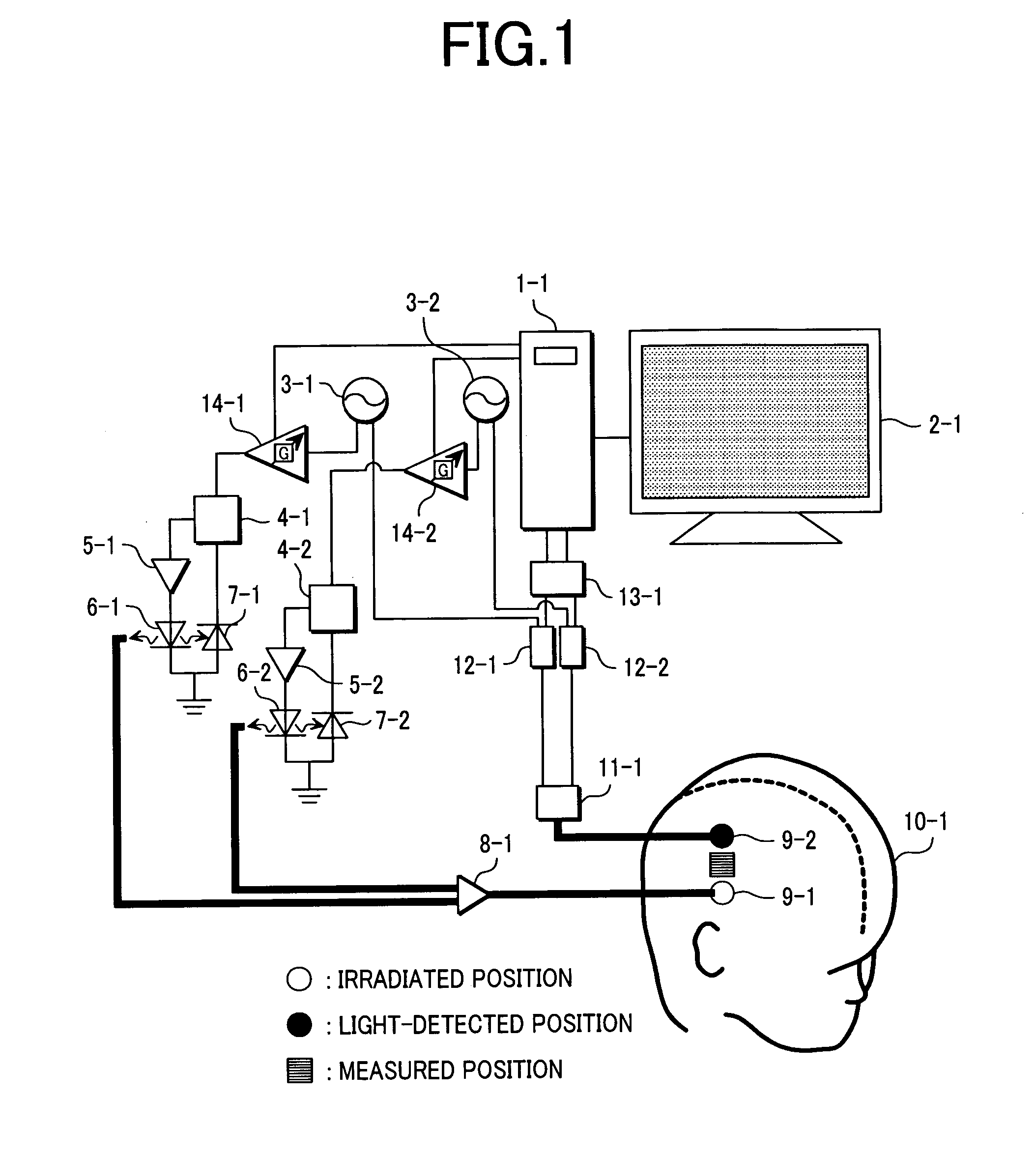
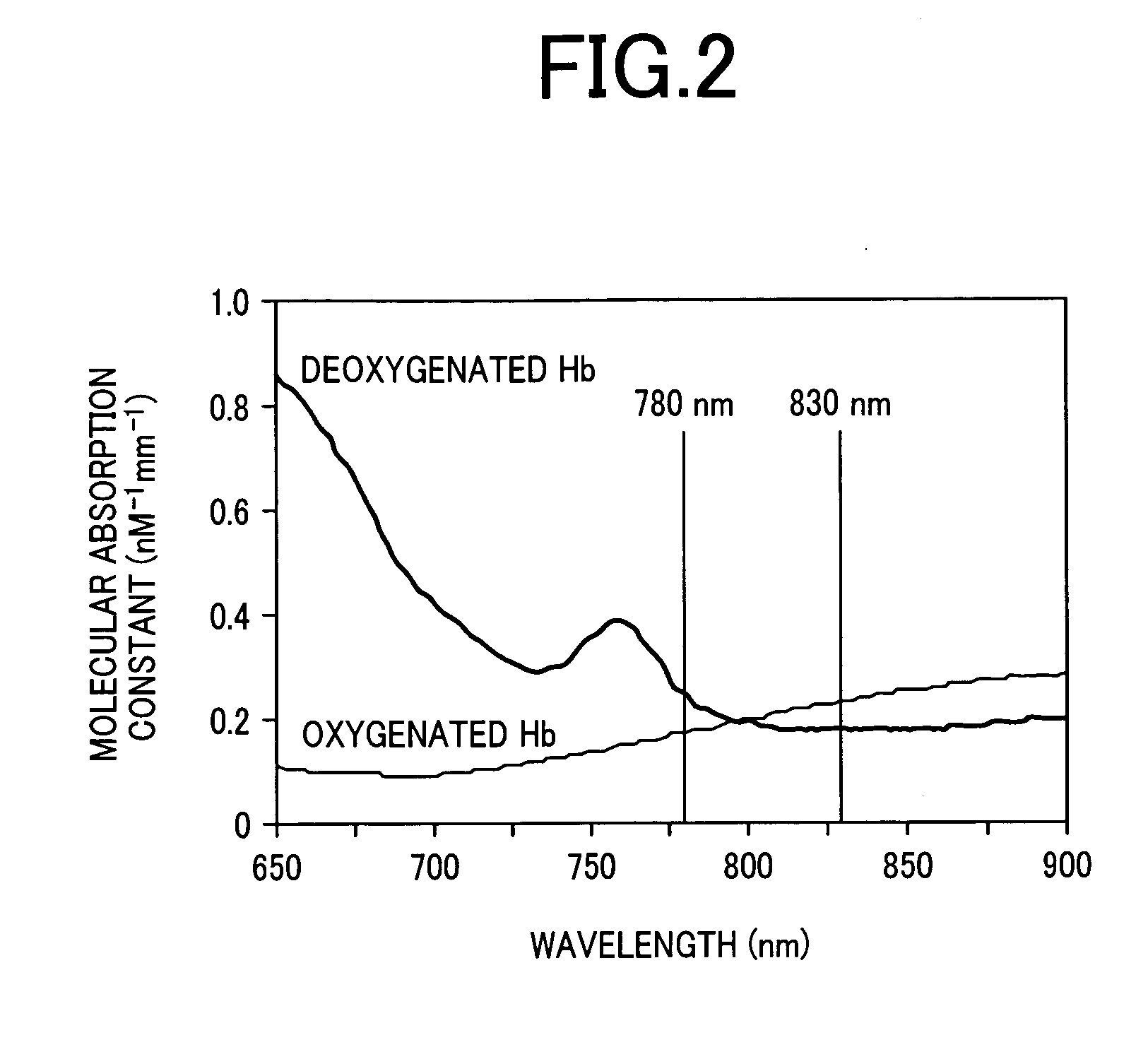
Biological photometric equipment
InactiveUS20070135694A1Reduce measurement errorAccurate measurementSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsLuminosityPeak value
To control information obtained from inside of a living body with higher precision as compared to that in the conventional technology by controlling a ratio of intensities of light, directed to a trial body, in a plurality of wavelength ranges different in peak wavelength from each other, a measurement error included in information obtained from the living body can be controlled by changing a ratio of intensity of the light in the first wavelength range against that of the light in the second wavelength range. When intensity of irradiated light is limited from the viewpoint of safety to the trial subject, by keeping a ratio of the light irradiated to the trial body in the first wavelength range against that of the light in the second wavelength range under a prespecified value and also by changing the ratio of irradiated light intensities under the prespecified value, a measurement error included in information obtained from the living body can be controlled.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
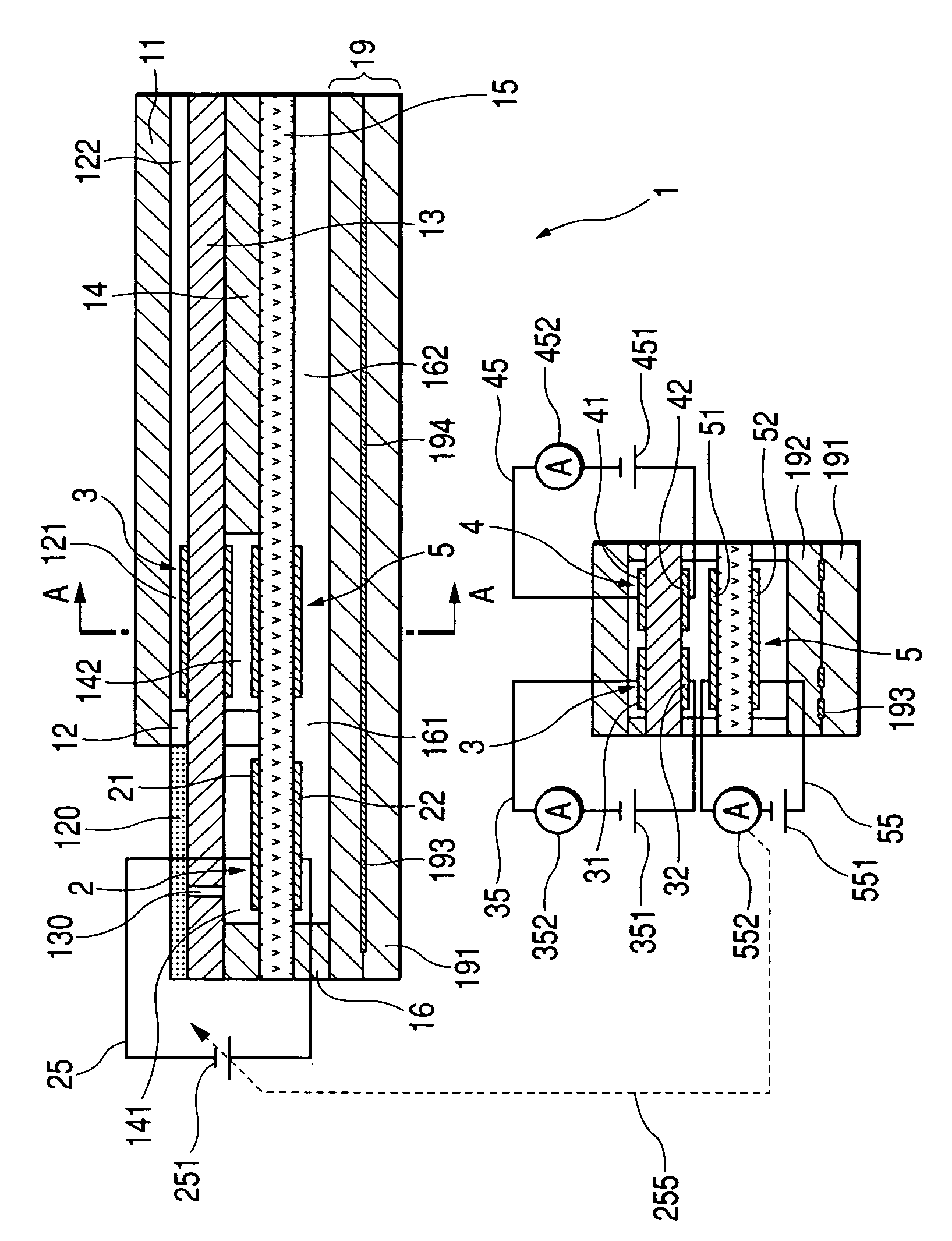
Hydrogen-containing gas measurement sensor element and measuring method using same
InactiveUS7182846B2Minimize adverse effectsEasy to useWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementHydrogenSolid mass
A gas sensor element is provided which is designed to measure the concentration of hydrogen-containing gas accurately. The sensor element includes an oxygen pump cell working to keep the concentration of oxygen contained in measurement gasses entering a measurement gas chamber at a low concentration level and a hydrogen-containing gas measurement cell. The hydrogen-containing gas measurement cell is made up of a proton-conductive solid electrolyte body and a first and a second gas measurement electrode affixed to the proton-conductive solid electrolyte body. The first gas measurement electrode is exposed to the measurement gas chamber and serves to produce a signal between the first and second gas measurement electrodes as a function of the concentration of the hydrogen-containing gas.
Owner:DENSO CORP +1
Particulate matter detection device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100071441A1Reduce manufacturing costAccurate and stable detectionWave amplification devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansParticulatesElectricity
A particulate matter detection device including a main body which has one end provided with a through hole; a pair of electrodes embedded in a wall through which the through hole is formed, and covered with a dielectric material; wires extending from the electrodes to the other end of the main body; and a ground electrode provided at a position sandwiched between the wires. The device can electrically adsorb, on the wall surface of the through hole, a charged particle in a fluid flowing into the through hole, or a particle charged by electric discharge caused in the through hole by applying a voltage across the pair of electrodes. The device can measure the changes of the electric properties of the wall through which the through hole is formed, thereby detecting particles adsorbed on the wall surface of the through hole.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Direct determination of rigid body motion using data collected from independent accelerometers
ActiveUS7657394B1Minimize measurement errorRepeatable determinationSpeed measurement using accelerationDigital computer detailsLeast squaresAngular velocity
System and method for enabling direct determination of rigid body motion using data collected from a plurality of independent accelerometers are disclosed. A mechanical object that can be theoretically emulated as a rigid body is instrumented with a plurality of accelerometers at different locations. Direct determination of rigid body motion at a location of interest includes following operations at each solution time step: transform local acceleration to global, integrate accelerations to obtain velocities, calculate direction cosine matrix using the angular velocity matrix, form a first set of redundant equations, obtain the angular velocity by solving the first set of equations using either least squares fitting or a selective Gaussian elimination scheme, form a second set of redundant equations and obtain the translational velocity by solving the second set of equations using either the averaged value or a pre-defined rule such as minimizing the contribution from the rotational term.
Owner:ANSYS
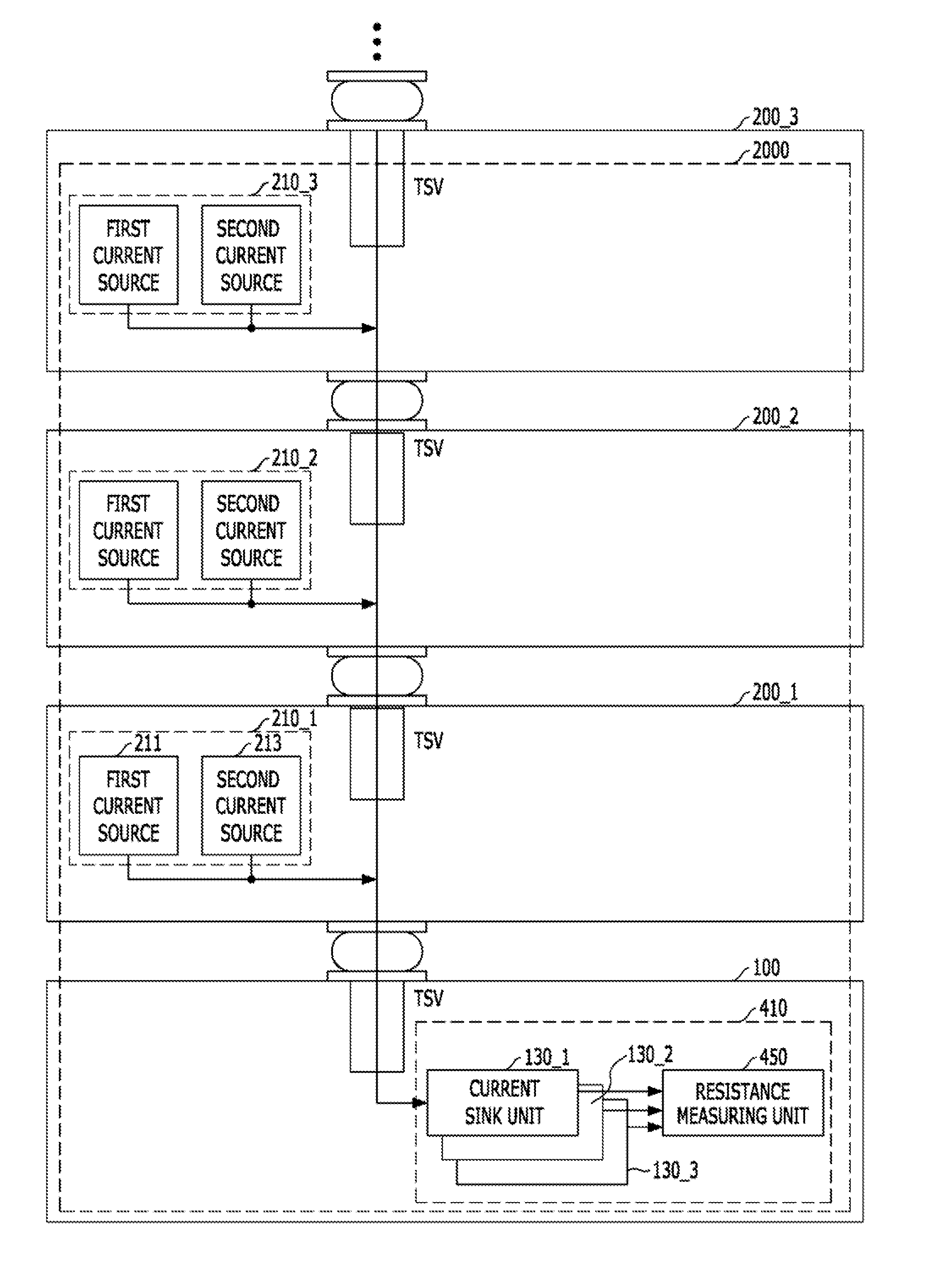
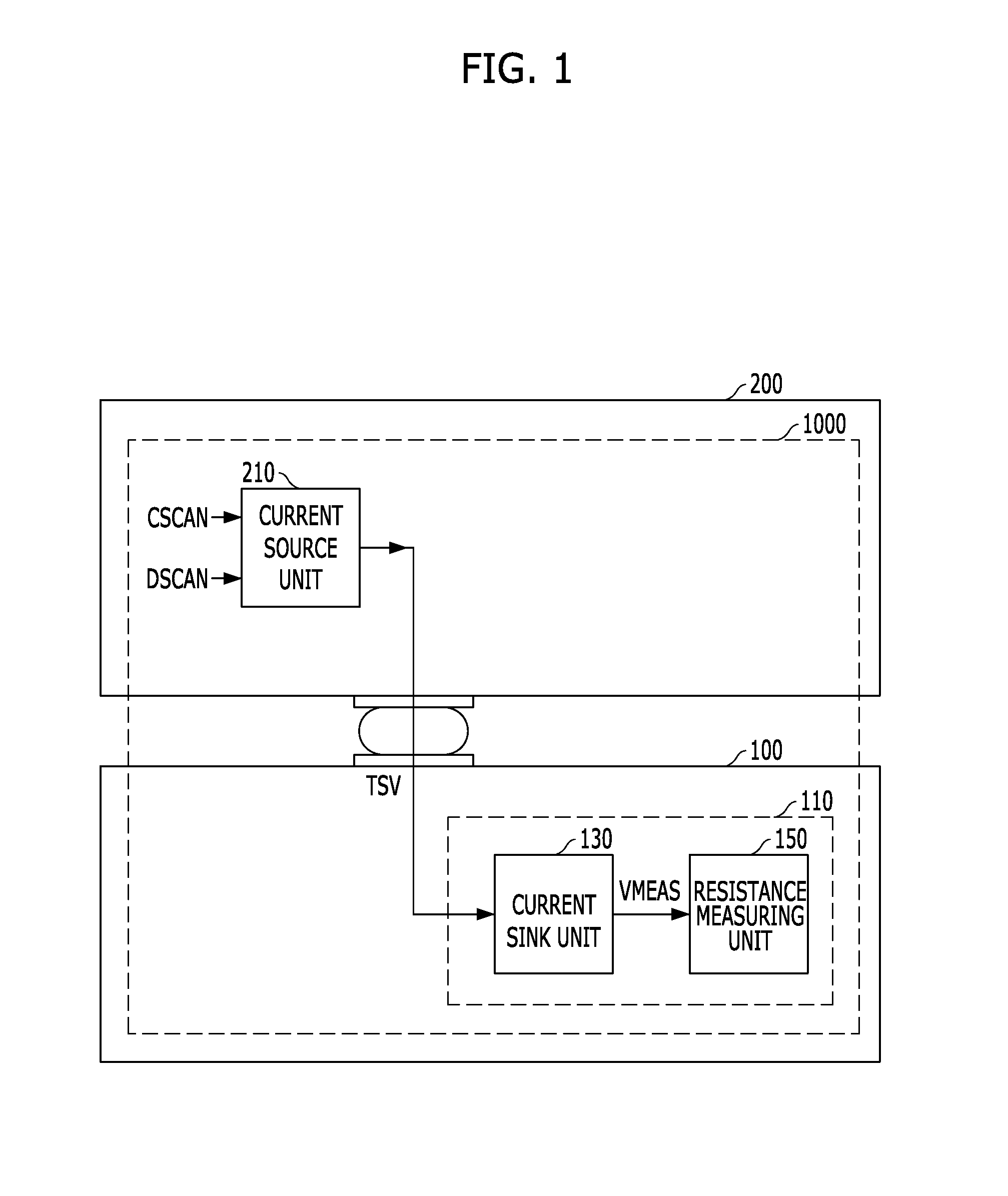
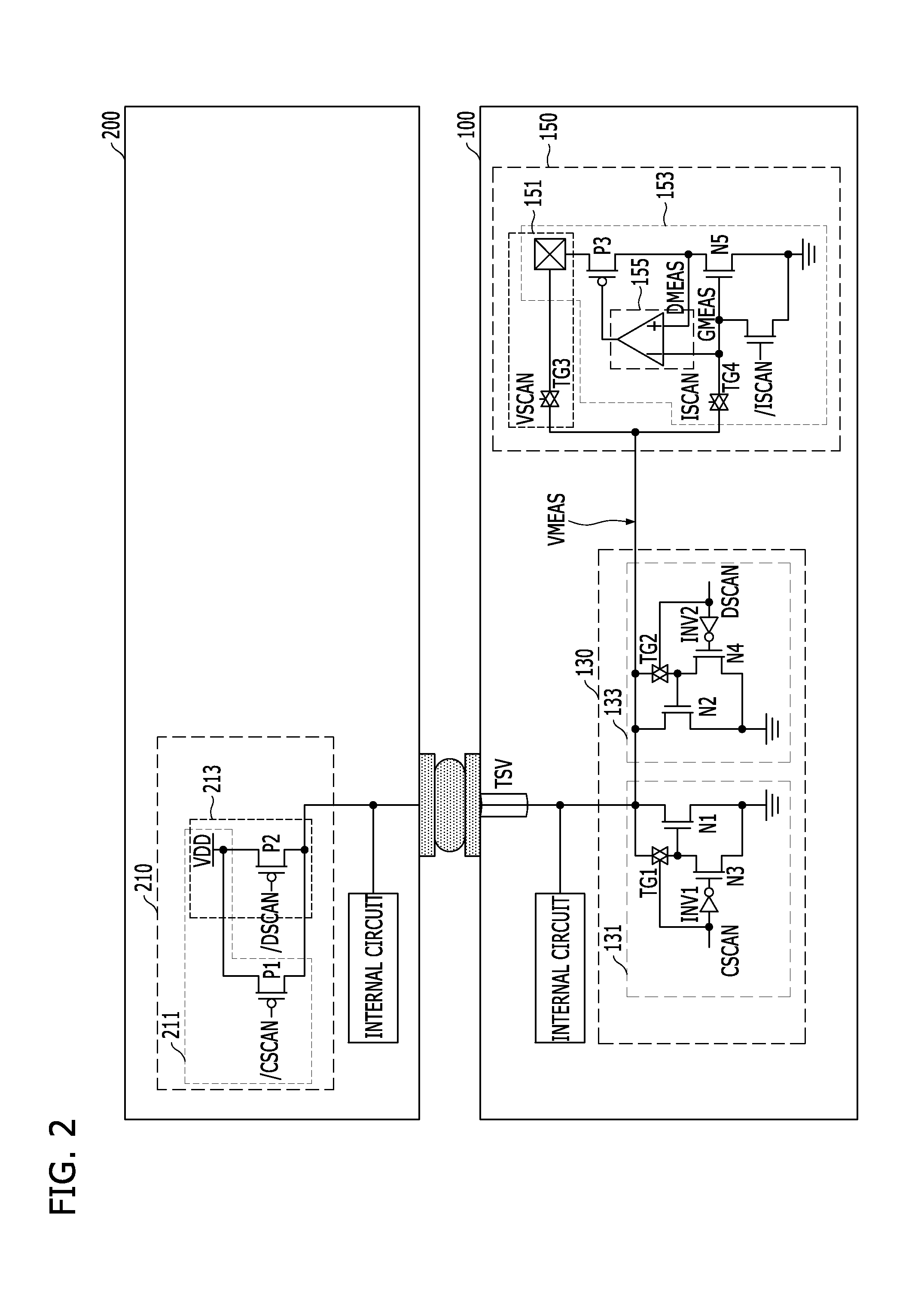
Test circuit and method for semiconductor device
ActiveUS20140368224A1Minimize measurement errorSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementResistance/reactance/impedencePower semiconductor deviceEngineering
A semiconductor device includes a first die, a second die coupled to the first die through a Through-Silicon-Via (TSV), and a test circuit suitable for measuring a resistance of the TSV by controlling an amount of current flowing through the TSV.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
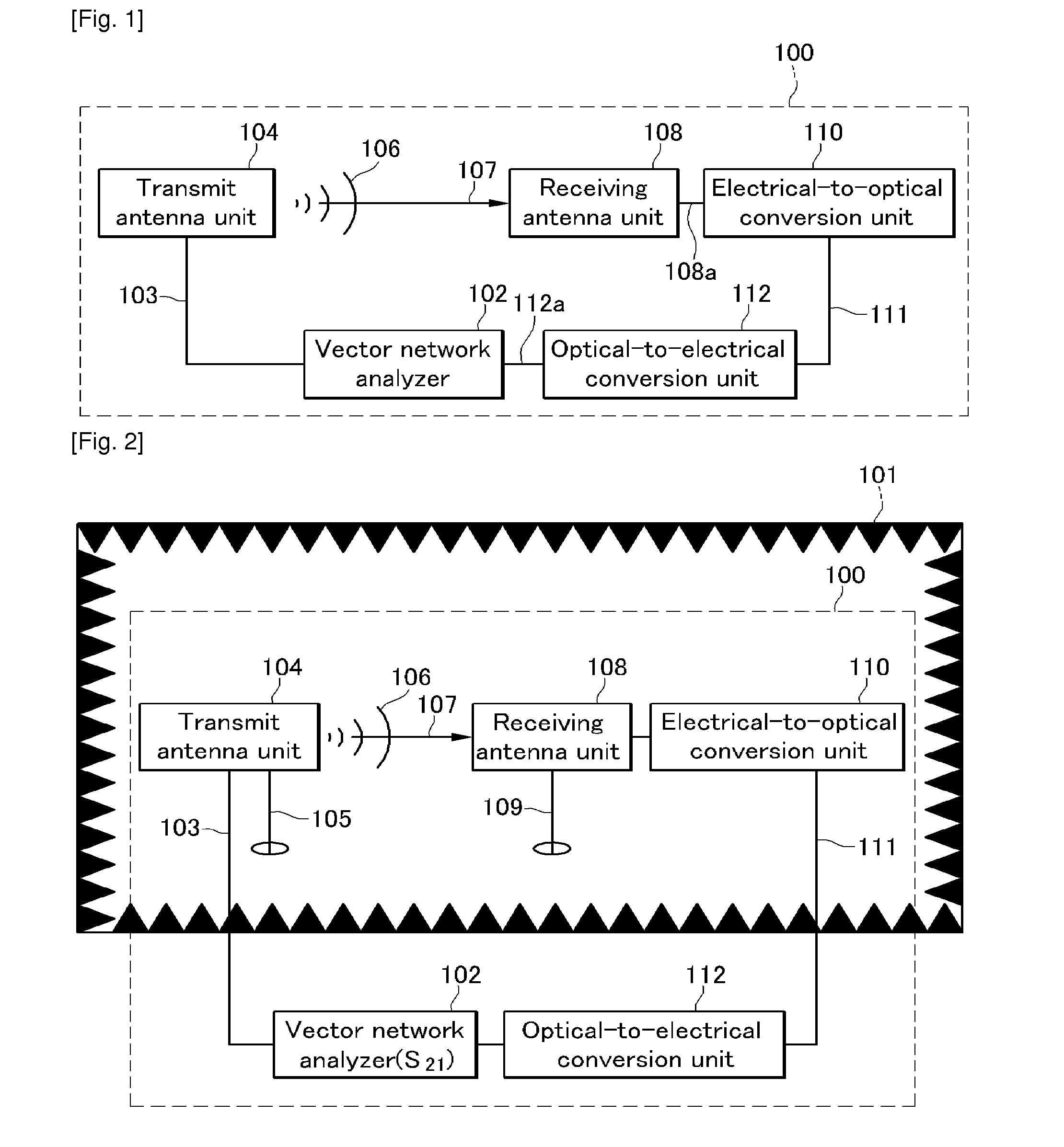
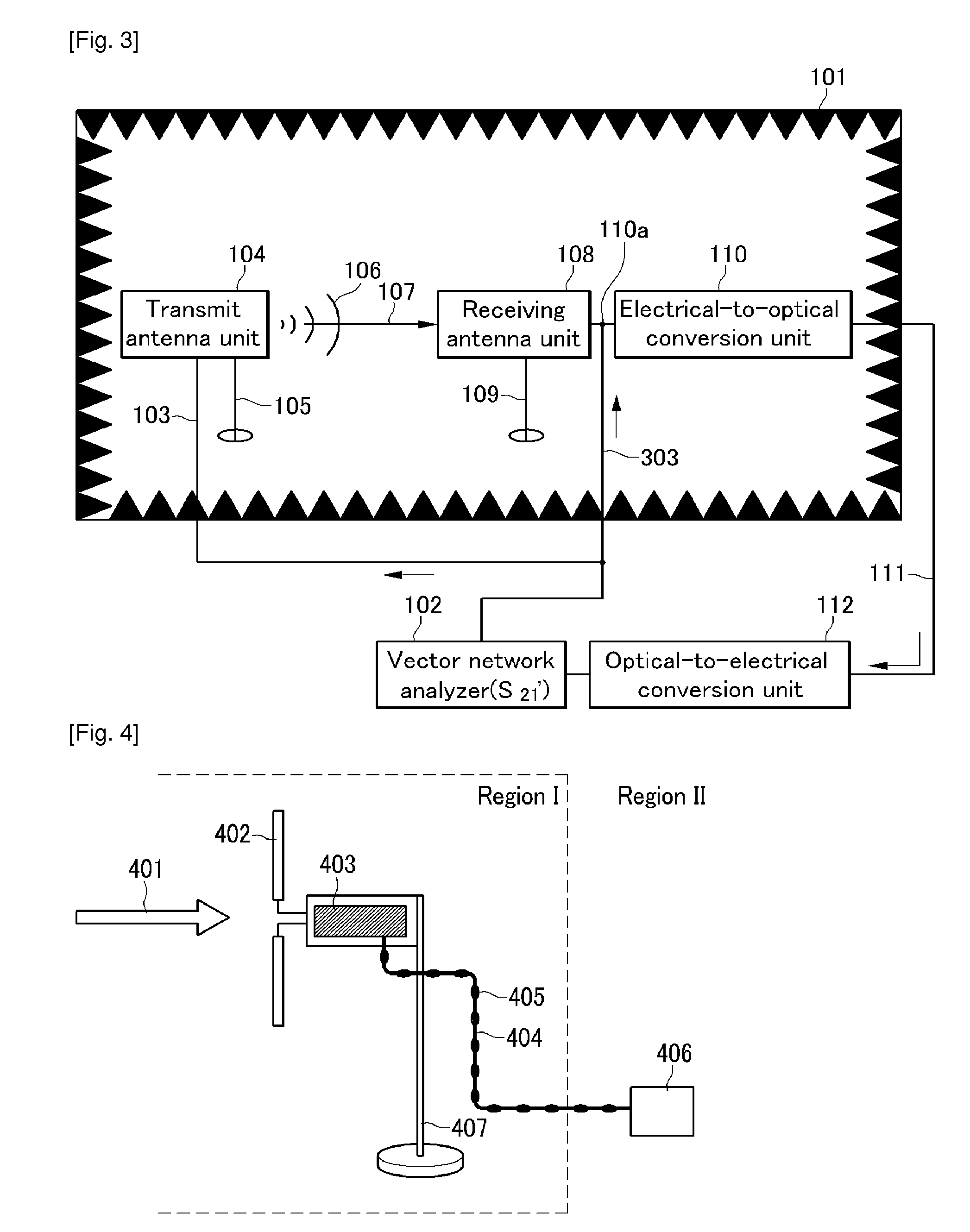
System and Method for Receiving Antenna Measuring Signal and System for Measuring Antenna
InactiveUS20100238077A1Minimize measurement errorEliminate coupling effectsAntenna supports/mountingsElectromagentic field characteristicsPhysicsCoupling effect
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for receiving an antenna measuring signal, and a system of measuring an antenna. In particular, the present invention relates to an apparatus and method for receiving an antenna measuring signal that can remove a measurement error caused by motion of an antenna cable, and a system for measuring an antenna. According to the apparatus and method for receiving an antenna measuring signal and the system and method for measuring an antenna according to the present invention, it is possible to remove a coupling effect of an RF cable of a receiving antenna side while measuring antenna characteristics, thereby minimizing a measurement error of the antenna.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Device for measuring time-resolved volumetric flow processes
InactiveUS7254993B2Minimize measurement errorClear qualitative and quantitative improvementEngine testingVolume/mass flow measurementCombustionInternal combustion engine
The invention relates to a device for measuring time-resolved volumetric throughflow processes, especially injection process in internal combustion engines, having a translational volume difference sensor having a piston disposed in a measuring compartment and a detection device detecting the excursion of the piston, the detection device being linked with an evaluation unit. According to the invention, a pressure sensor is mounted in the measuring compartment in addition to the detection device which detects the excursion of the piston. The signal of the detection device corresponding to the excursion of the piston can be better evaluated as the compressivity of the fluid in the measuring compartment can be taken into consideration for the calculation of the amount to be injected. The inventive device allows for a highly time-resolved representation of throughflow processes so that both overall amount and exact course of the throughflow can be represented and evaluated.
Owner:AVL LIST GMBH
Apparatus and method for real time determination of density and related parameters in manufacturing processes
InactiveUS7257985B2Easy to controlEasy to handleMixing methodsTransportation and packagingObservational errorKaolin clay
Owner:APPVION OPERATIONS INC
Assembly for an Angular Position Measuring Device
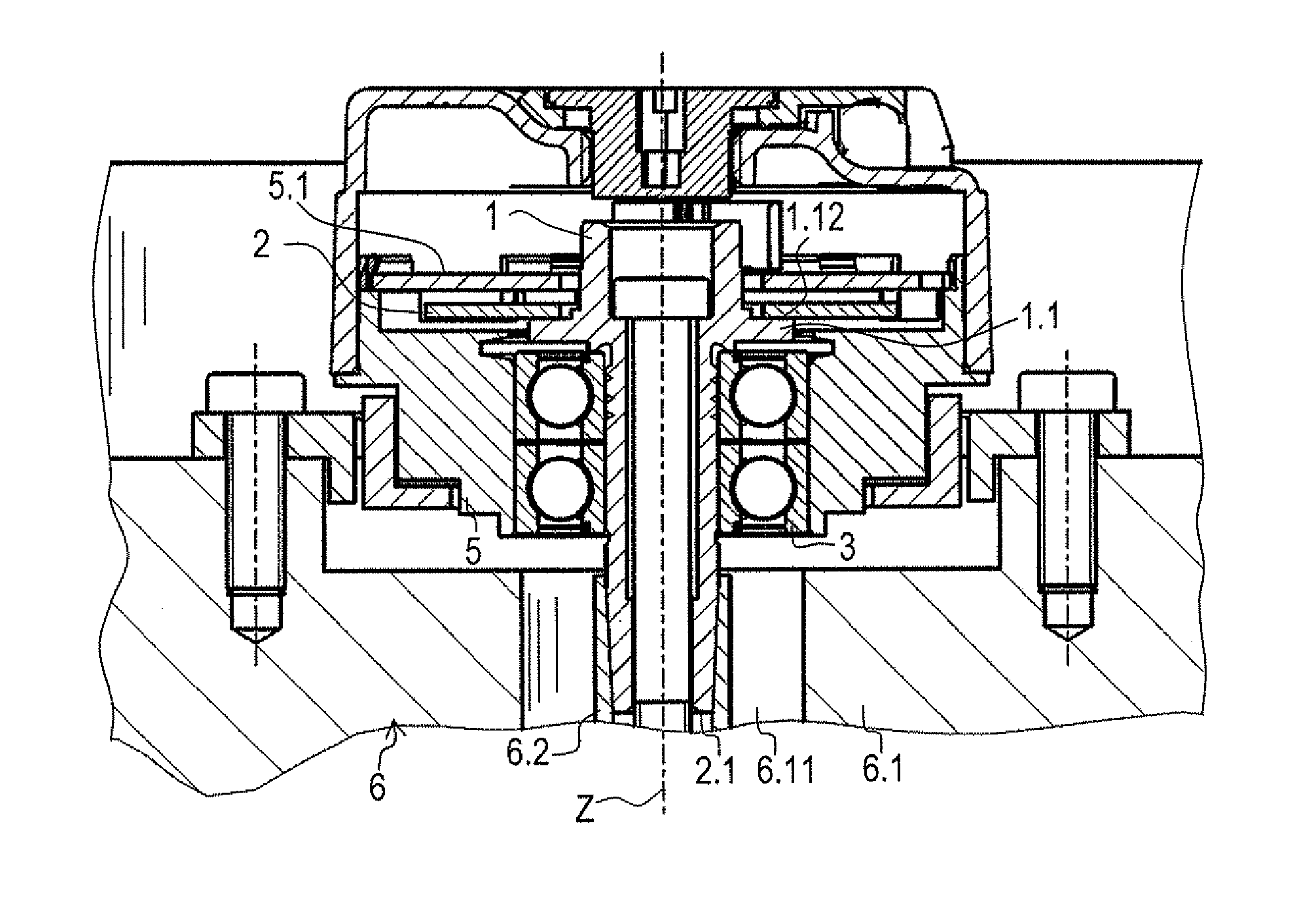
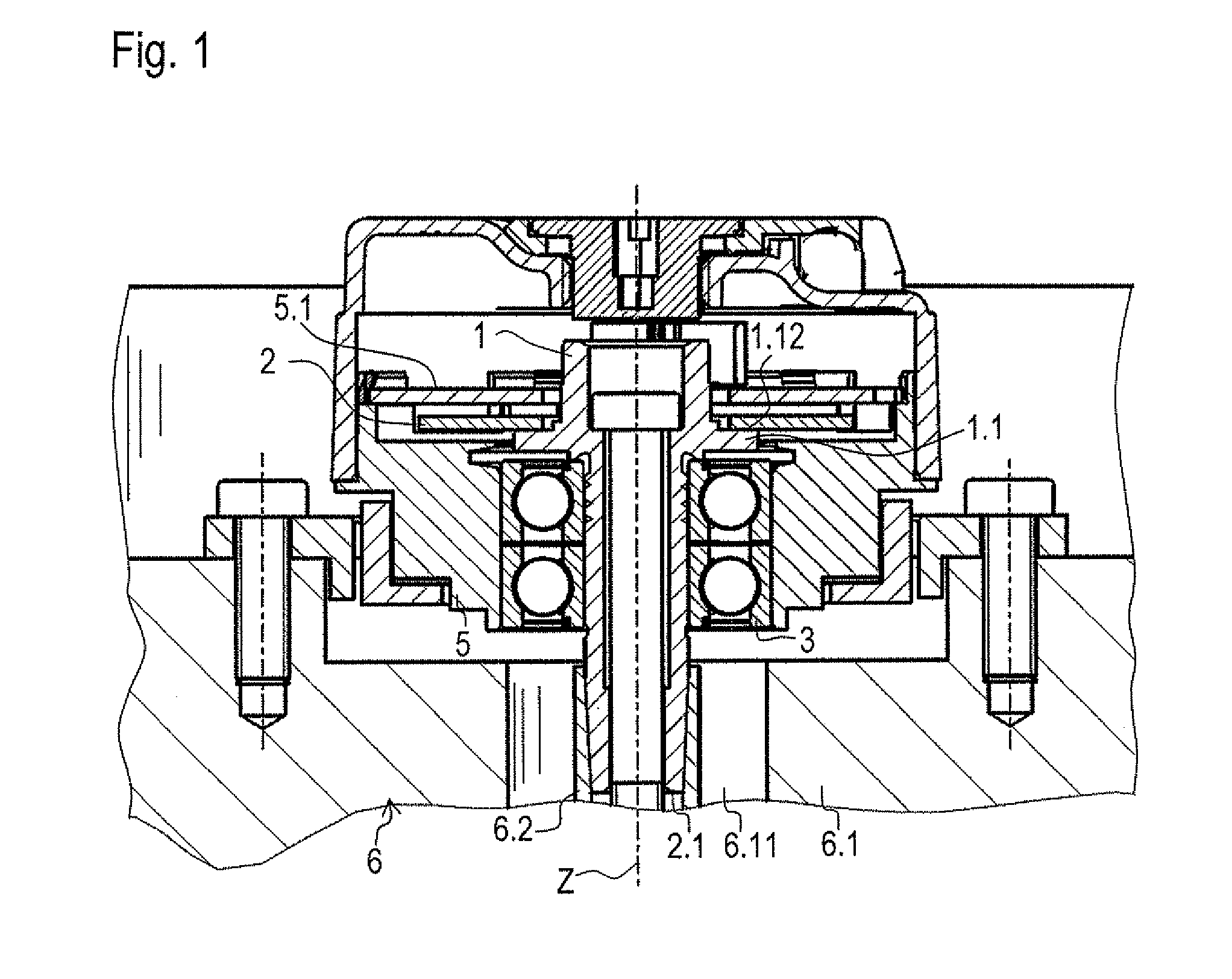
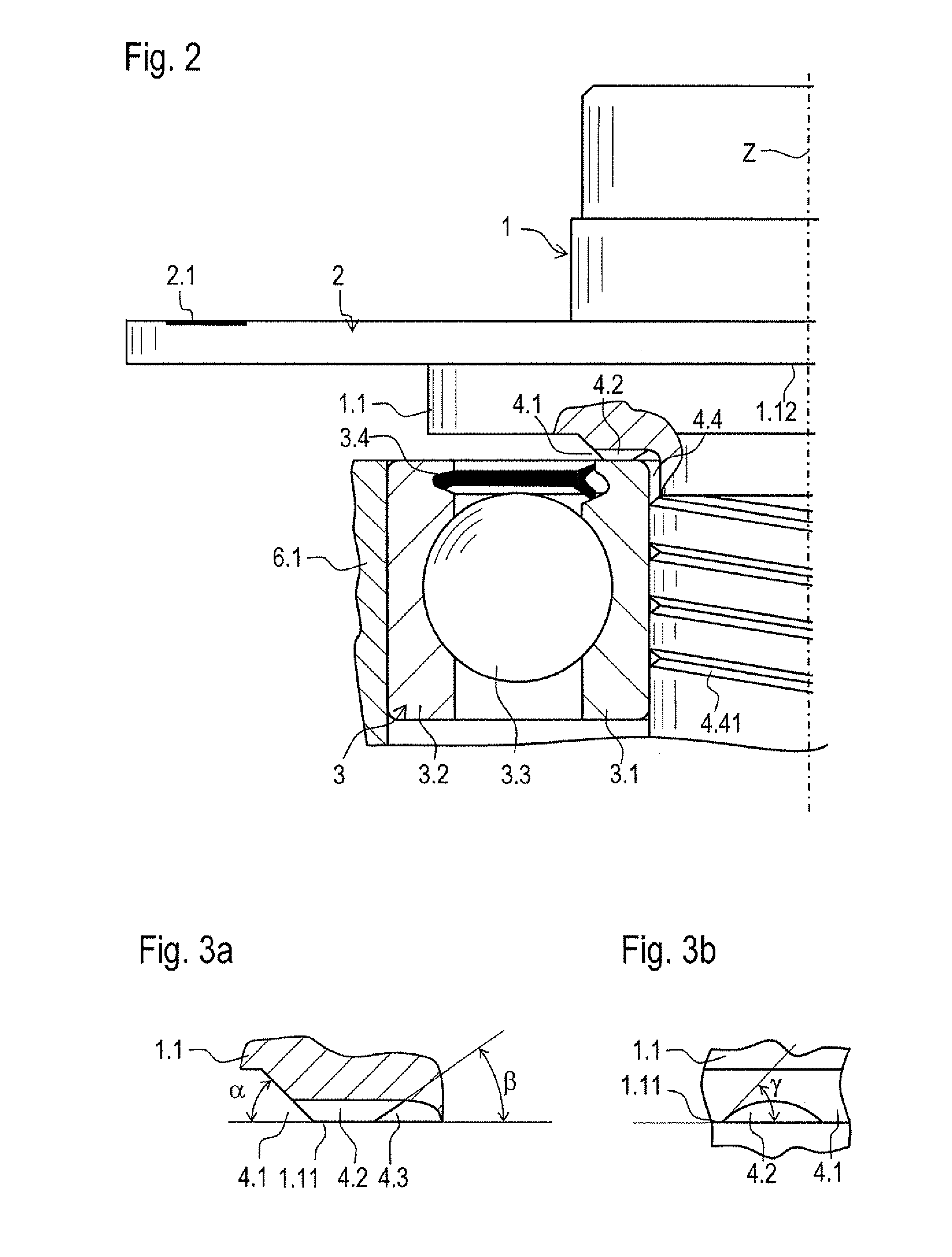
ActiveUS20110254542A1High measurement accuracyForming accuratelyShaftsBearing componentsEngineeringRoller bearing
An assembly for an angular position measuring device includes a shaft having a measuring standard for measuring a rotational movement about an axis. The shaft has a shoulder as an integral component, on which a roller bearing is mounted in axial abutment. Arranged between the shoulder of the shaft and the roller bearing is a groove which is oriented with a radial directional component and is connected to a hollow space for receiving lubricant, the hollow space being bounded in the radial direction by a ring of the roller bearing and by the shaft.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Method for determining a highly accurate position of routes and/or objects
InactiveUS20080208520A1Minimize measurement errorImprove accuracyAnalogue computers for vehiclesInstruments for road network navigationComputer visionSurveyor
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com