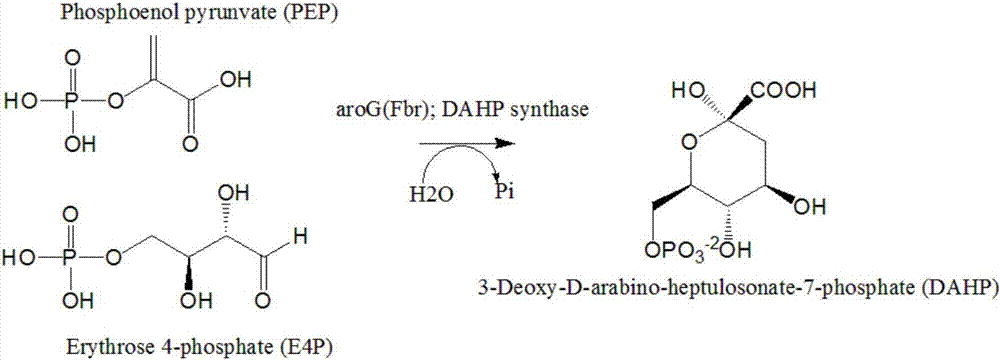
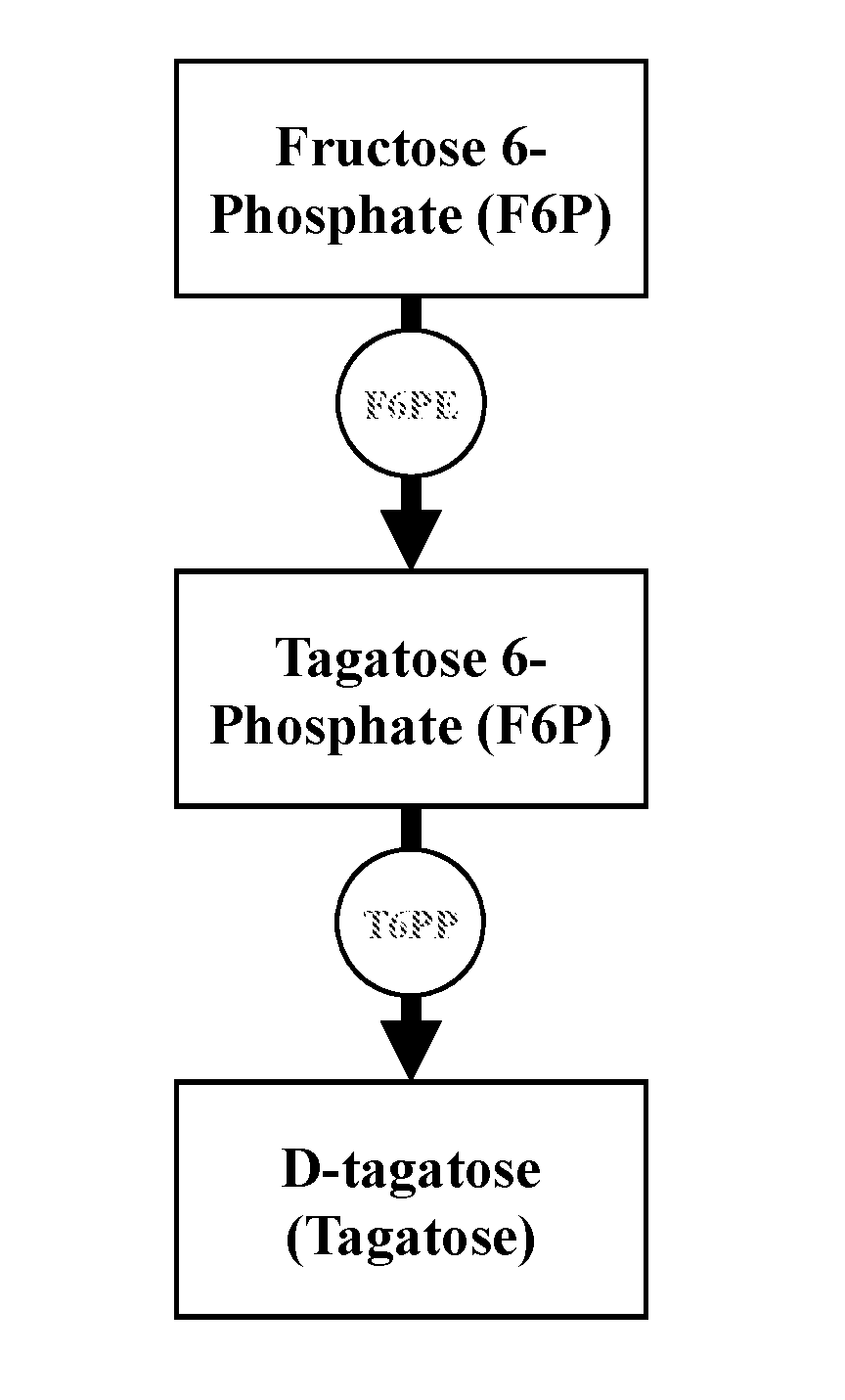
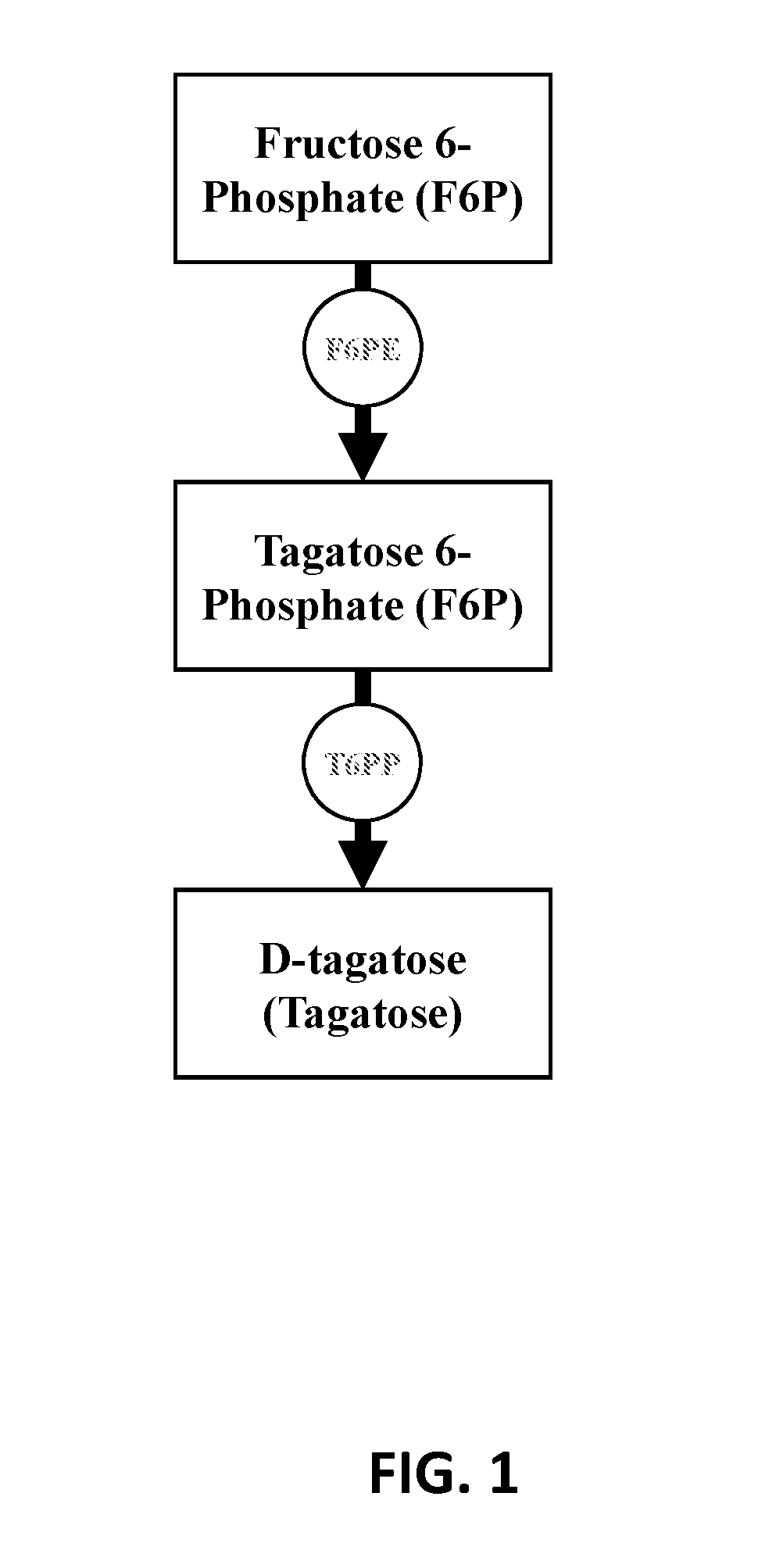
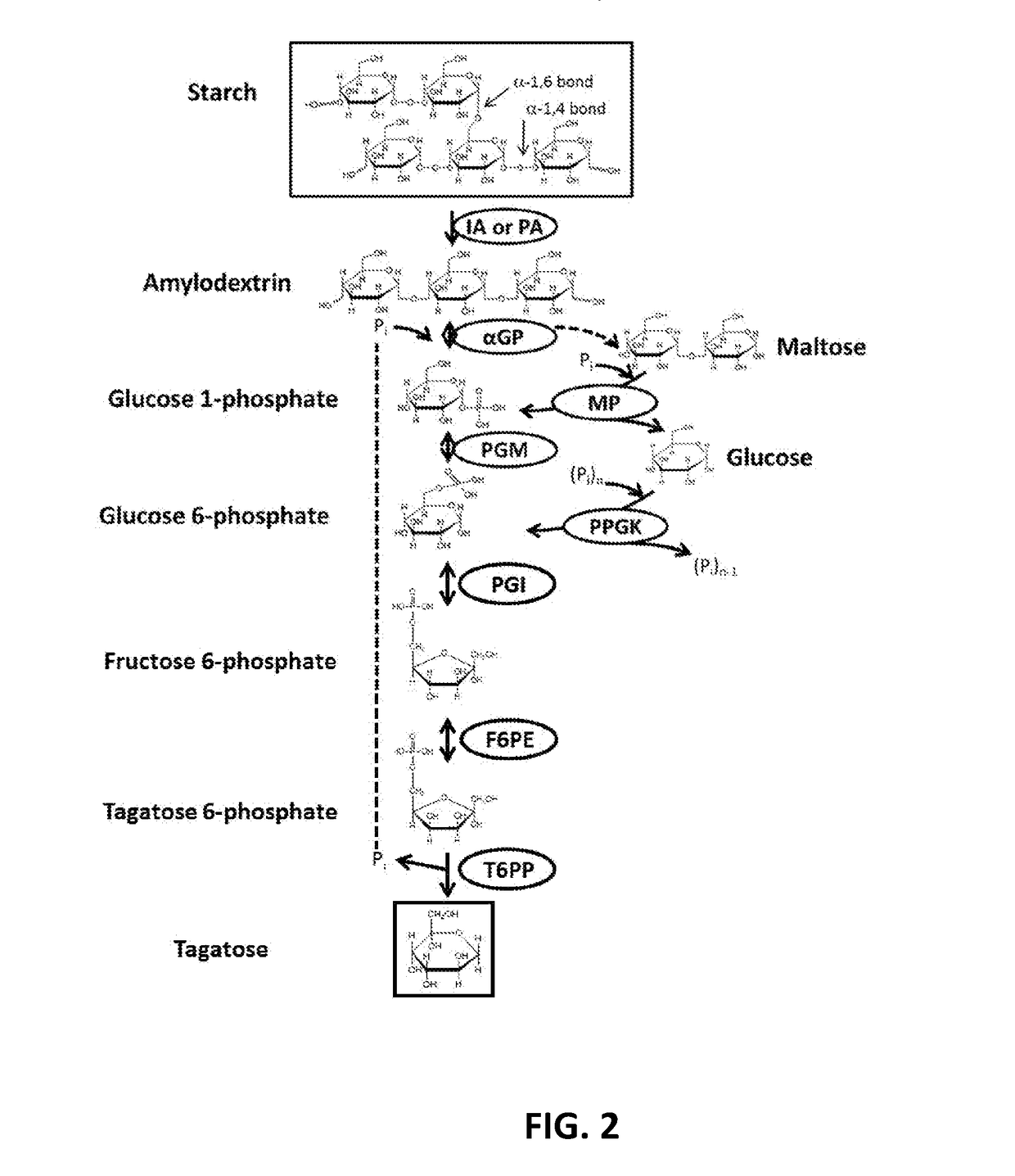
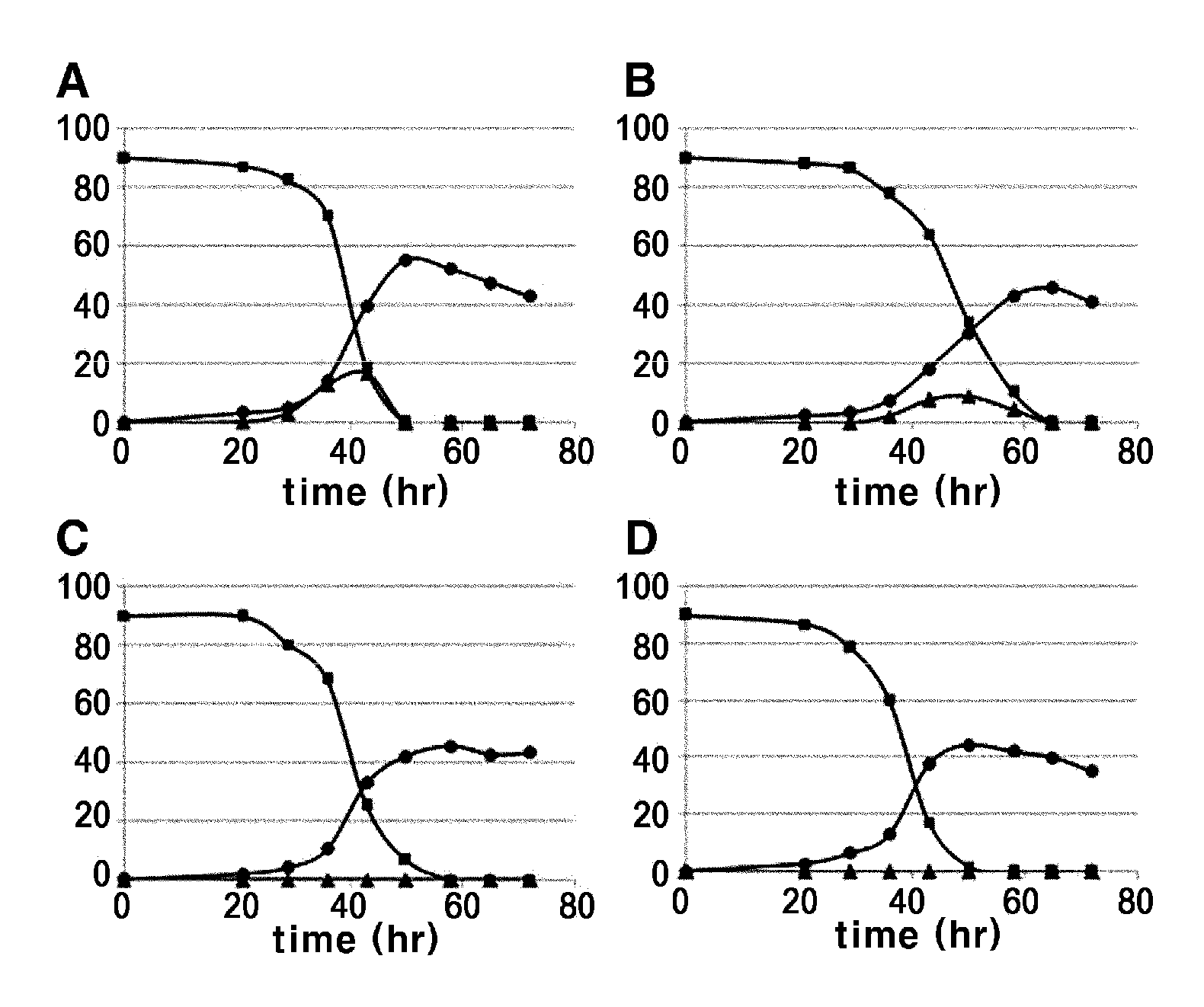
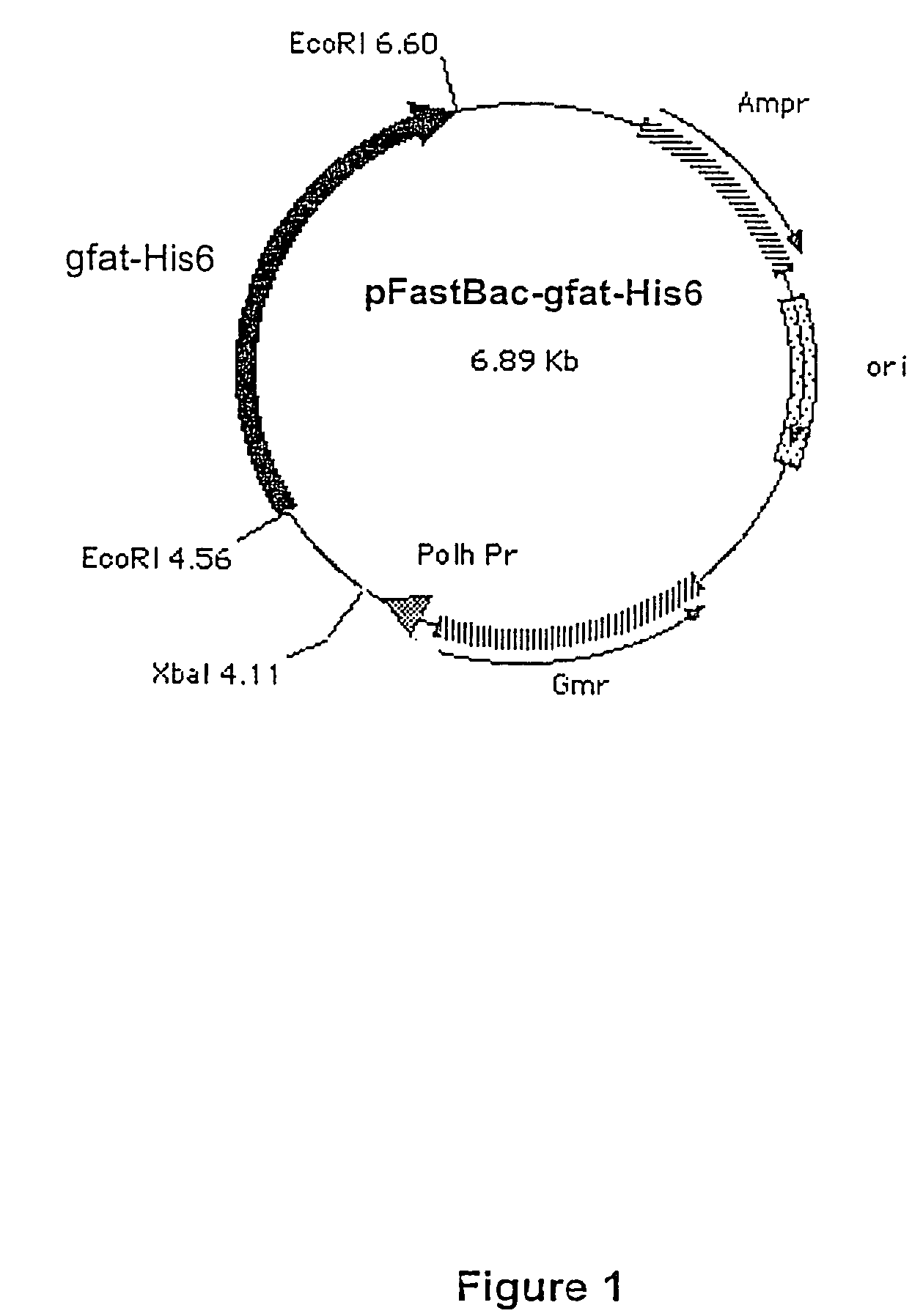
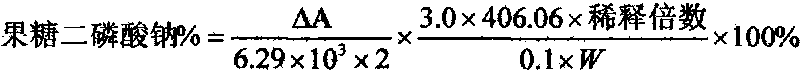Patents
Literature
31 results about "Fructose 6-phosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fructose 6-phosphate (sometimes called the Neuberg ester) is a derivative of fructose, which has been phosphorylated at the 6-hydroxy group. It is one of several possible fructosephosphates. The β-D-form of this compound is very common in cells. The great majority of glucose and fructose is converted to fructose 6-phosphate upon entering a cell.
Topically applied Glucosamine Sulfate and all its related, precursor, and derivative compounds significantly increases the skin's natural produciton of hyaluronic acid for the rejuvenation of healthier younger-looking skin; while PhosphatidylCholine is required to replace its deficiency caused by topical Dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE)
InactiveUS20070092469A1Reducing eczemaReducing psoriasisBiocideCosmetic preparationsWrinkle skinPhysiology
A topical skin rejuvenation preparation to relieve wrinkles, increase the skin's natural production of hyaluronic acid, reverse the lack of suppleness, hydrate from within, erase spider veins, reduce varicose veins, lighten aging dark blotches (“liver spots” / Lentigos, Senile Lentigines), decrease acne, and reduce under eye puffiness includes Glucosamine (2-amino-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucose), a hexosamine (6 carbon amino sugar), including its derivative and precursor compounds: Glucosamine Sulfate, Glucosamine Hydrochloride, Glucose-6-Phosphate, Acetyl Glucosamine, Fructose-6-phosphate, Glucosamine-6-Phosphate, to increase production of Hyaluronic acid and collagen from Glucosamine Sulfate, its precursors and derivatives and to increase skin muscle tone by Dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE) while over coming deficiency it creates in each cell's production of PhosphatidylCholine, whose deficiency damages cell membranes, as well as mitochondrial and lysosome membranes.
Owner:JACOBS ERIC
Use of phosphoketolase for producing useful metabolites
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
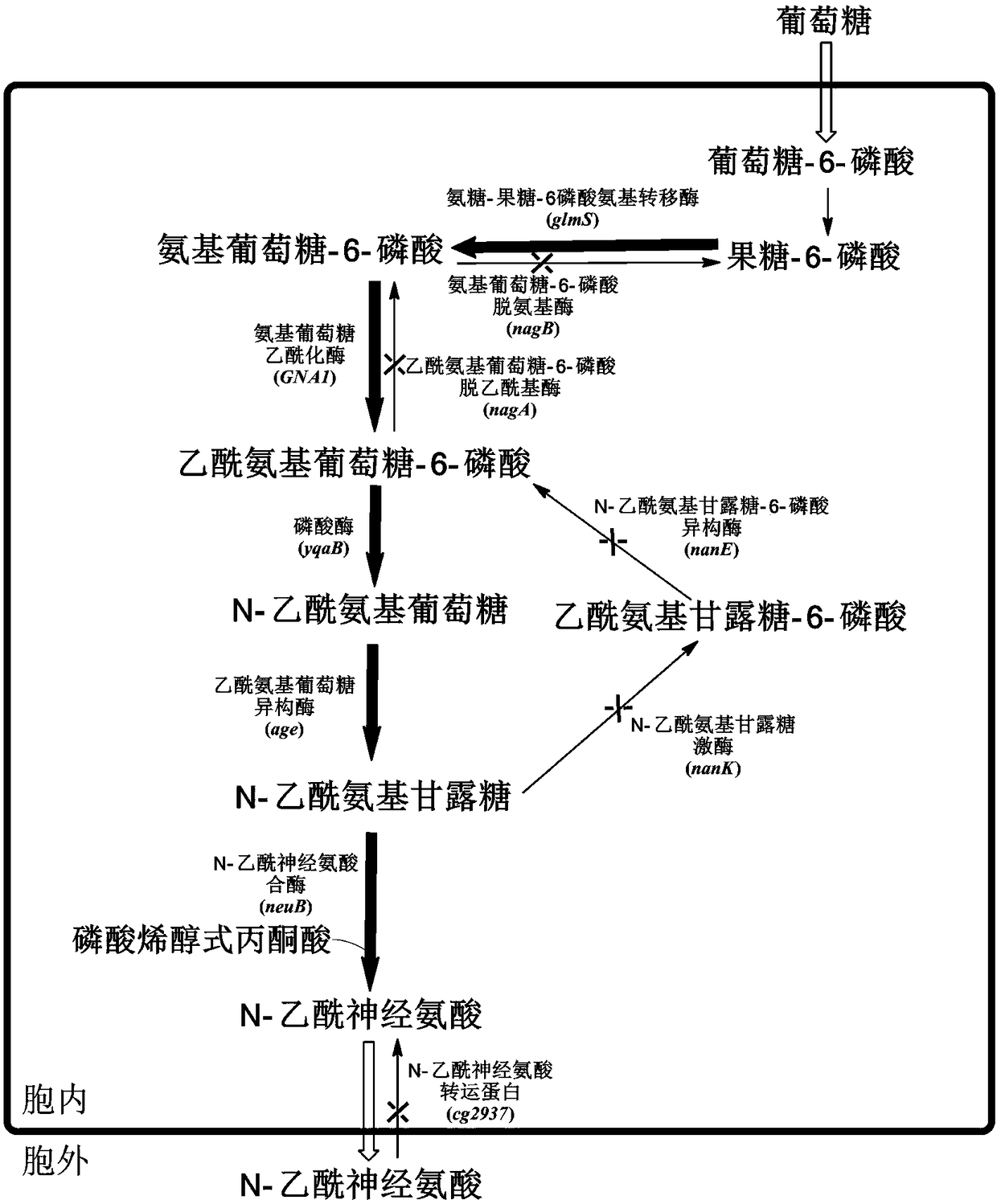
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid and application thereof
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid and application thereof and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum takes corynebacterium glutamicum as an expression host, and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis way is reinforced through over-expression of a glucosamine-fructose-6 phosphate aminotransferase gene, a glucosamine acetylase encoding gene, a phosphatase encoding gene, an acetylglucosamine isomerase encoding agene and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthase encoding gene; an N-acetylneuraminic acid transport protein encoding gene in the corynebacterium glutamicum and a related gene in an intracellular N-acetylneuraminic acid decomposition, utilization and metabolism are knocked off to obtain corynebacterium glutamicum genetically engineered bacteria for extracellularly accumulating the N-acetylneuraminic acid and the yield reaches 110mg / L; a foundation is laid for further modifying corynebacterium glutamicum through metabolic engineering to produce the N-acetylneuraminic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
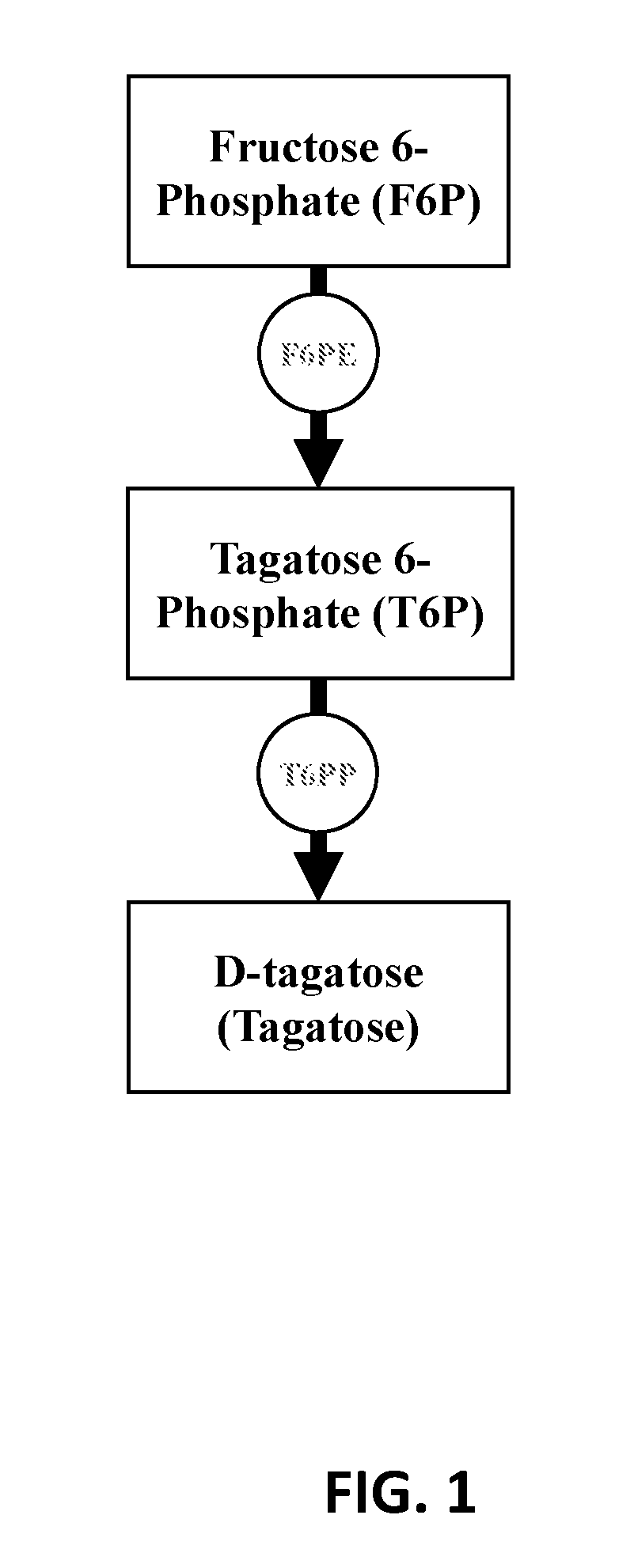
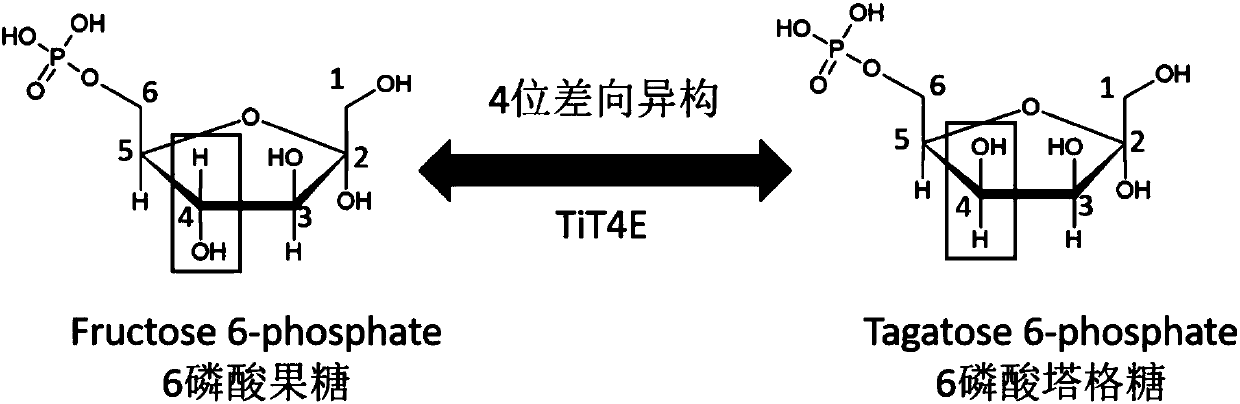
Enzymatic production of D-tagatose
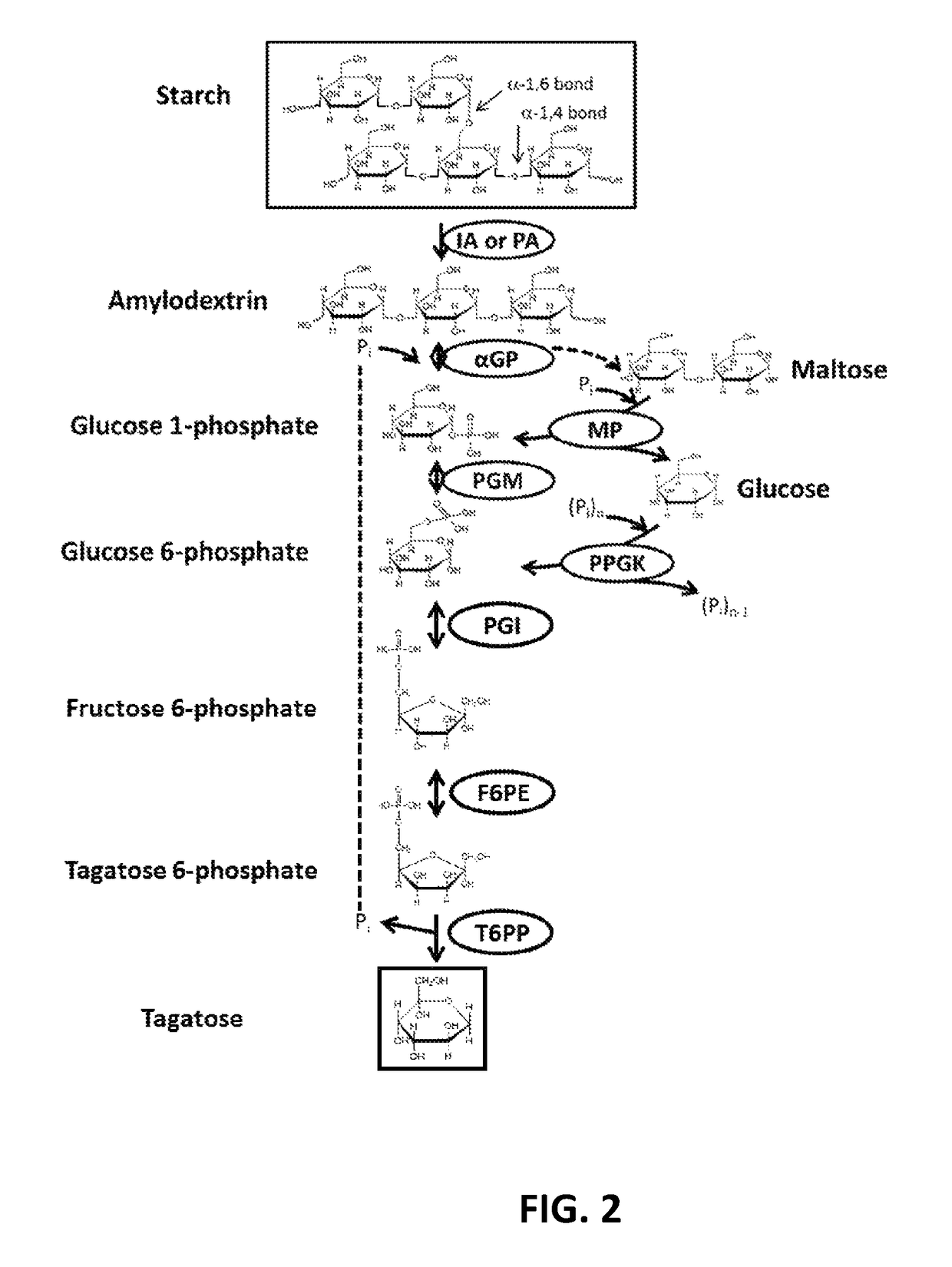
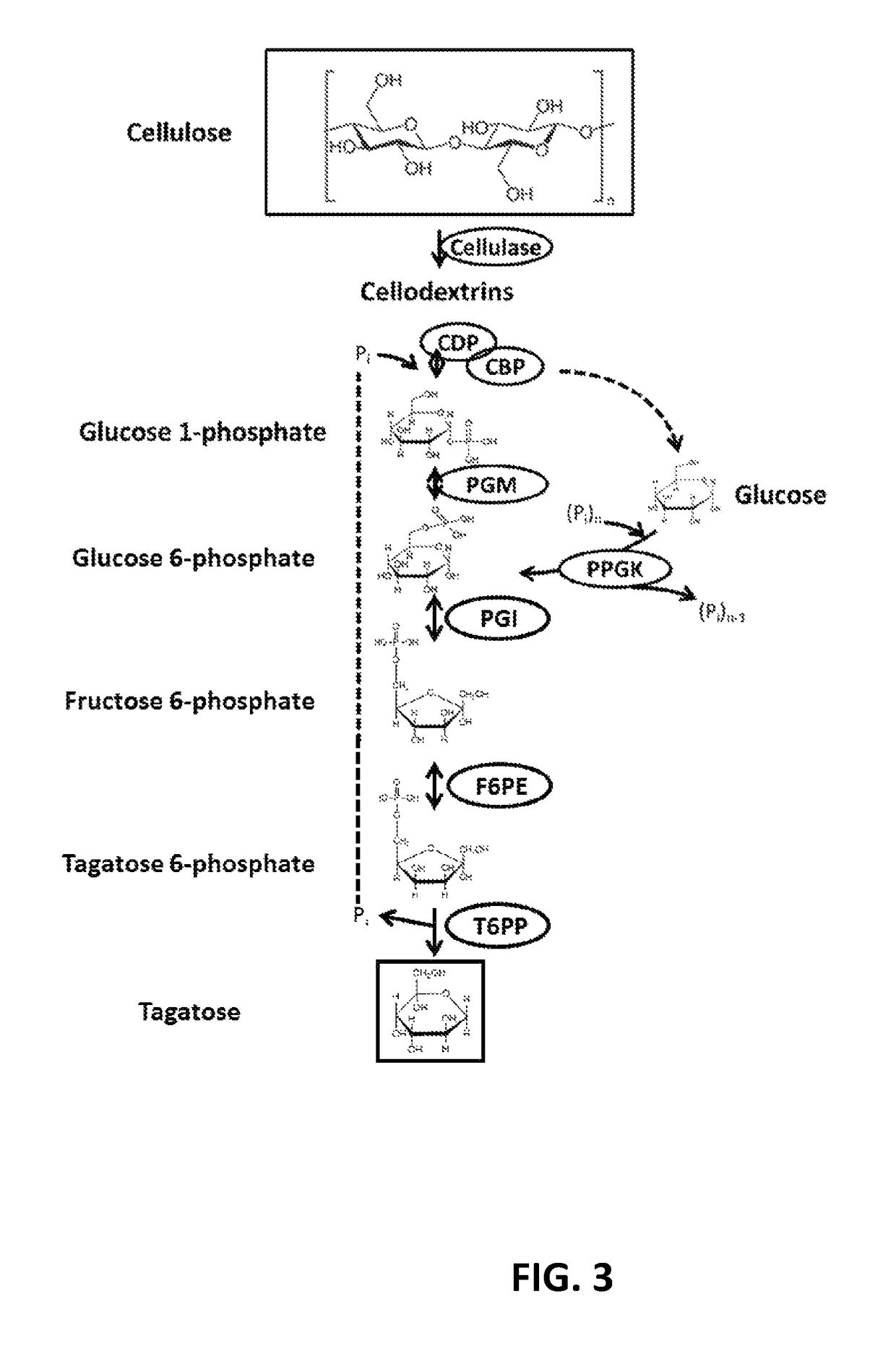
The current disclosure provides a process for enzymatically converting a saccharide into tagatose. The invention also relates to a process for preparing tagatose where the process involves converting fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) to tagatose 6-phosphate (T6P), catalyzed by an epimerase, and converting the T6P to tagatose, catalyzed by a phosphatase.
Owner:BONUMOSE INC
Engineered strain for producing tagatose and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109666620AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale productionBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologySynthesis methods
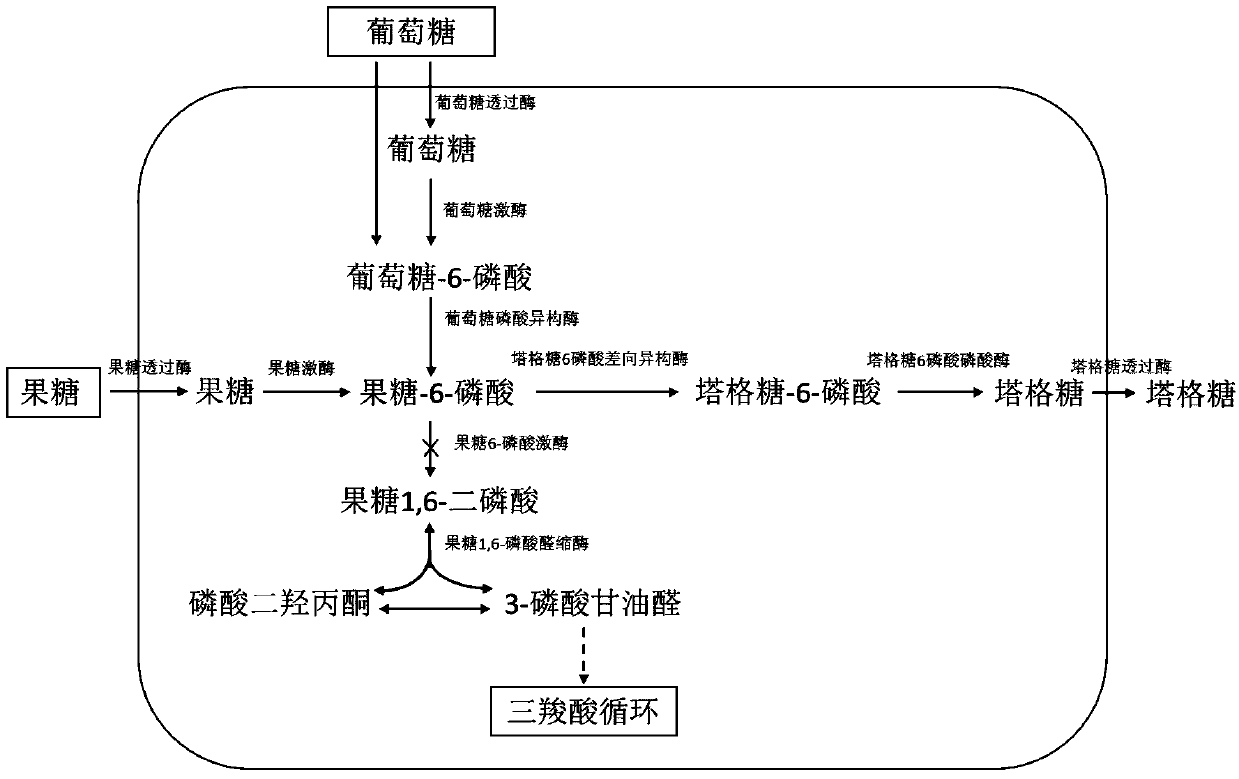
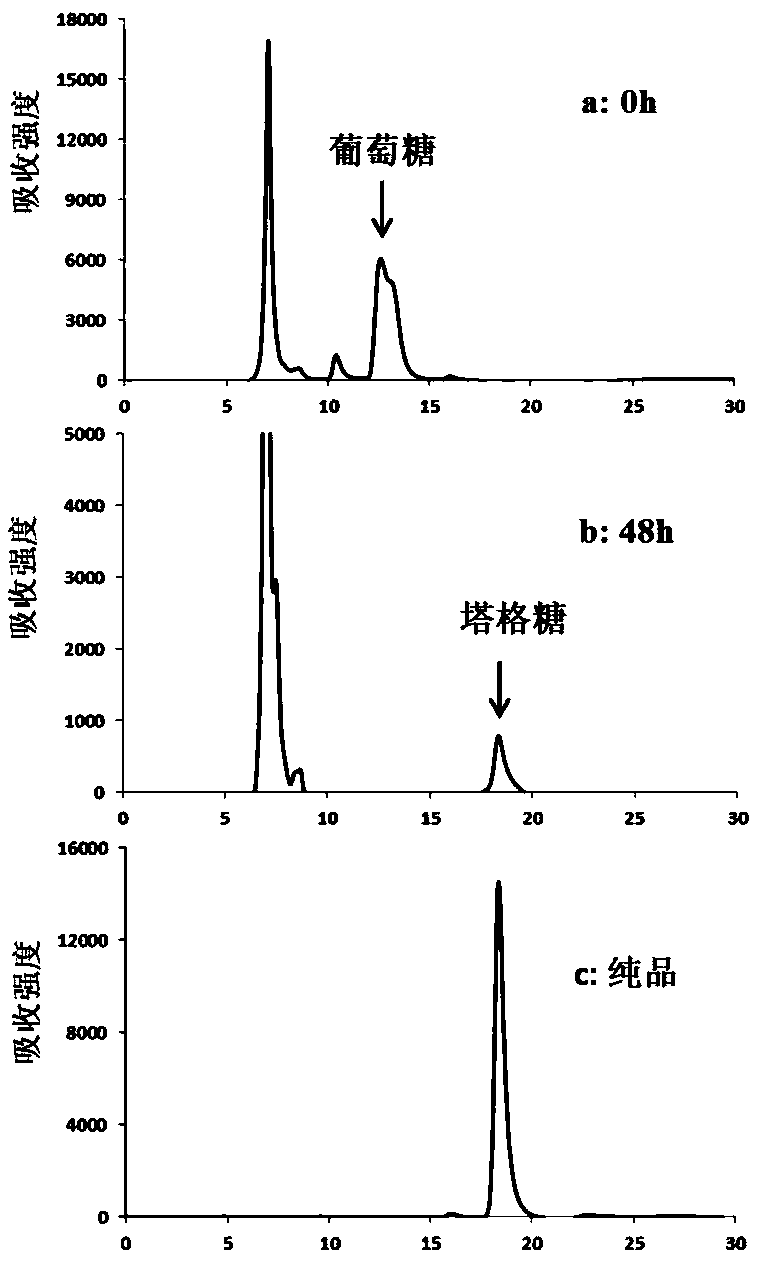
The invention discloses an engineered strain for producing tagatose and a construction method and application thereof. According to the construction method, by regulating intracellular glucose metabolism, the enzymatic activity of 6-phosphofructokinase in cells is reduced, the enzymatic activity of glucokinase and the enzymatic activity of glucose 6-phosphate isomerase are improved, therefore, thecontent of fructose-6-phosphate in the cells is increased, a tagatose synthesis path composed of tagatose-6-phosphate 3-epimeriase and tagatose-6-phosphate phosphorylase is constructed, and a fructose metabolism path composed of fructose permease and fructokinase is constructed. The glutamic acid corynebacterium recombination strain is obtained and can synthesize tagatose by metabolizing glucose,fructose or saccharose. Compared with currently reported fructose biotransformation tagatose synthesis methods, the construction method of the engineered strain has the advantages of being easy to operate and facilitating separation and is suitable for large-scale tagatose production.
Owner:天津怡和生物科技有限责任公司
Glucosamine-6 phosphate synthase mutant
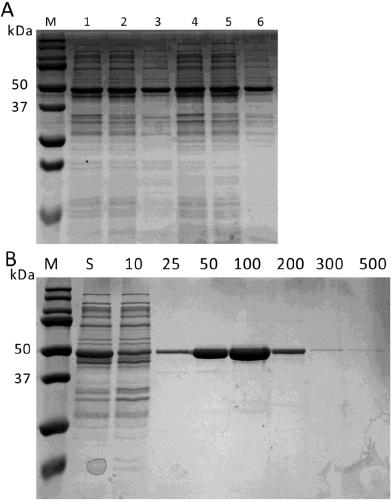
The invention discloses a glucosamine-6 phosphate synthase mutant, and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. A method for site-saturation mutagenesis of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase is adopted and provides the glucosamine-6 phosphate synthase mutant derived from E.coli. Compared with wild-type glucosamine-6-phosphate transferase, the catalytic activity of the mutant to fructose-6-phosphate is significantly improved, the yield of acetylglucosamine is higher, and the mutant is more suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for measuring 1,5-anhydroglucitol by oxidase
InactiveCN103725749AEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphoric acidGlucose polymers
The invention relates to a method for measuring 1,5-anhydroglucitol by oxidase, which can be widely applied in the field of medical and biochemical technologies. The method comprises the following steps of: converting glucose (Glu) in a sample into fructose-6-phosphate (Fru-6-P) by glucokinase (GK) and phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI), and establishing an ATP regeneration system by pyruvate kanise (PK) and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in the system so as to ensure that Glu is converted into Fru-6-P. In the sample, 1,5-AG reacts in the presence of pyranose oxidase (PROD) to produce 1,5-fructosan (1,5-AF) and H2O2, and then H2O2 is colored and quantified via a Trinder's system..
Owner:WENZHOU PEOPLES HOSPITAL
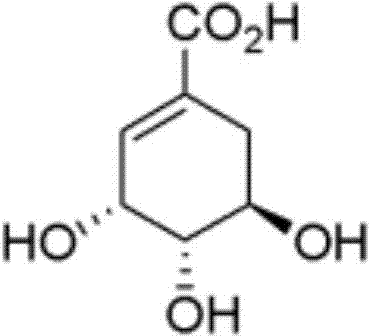
Shikimic acid synthesis method
The invention discloses a shikimic acid synthesis method. According to the method, fructose 6-phosphate and glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate ester serve as raw materials, and shikimic acid is generated under the catalytic function of various enzymes. The generation technology is simple in step, reagents are safe, byproducts are few in the reaction process, economic benefits are improved, the yield of the obtained shikimic acid is 50-86%, and the purity is 98.1-99.5%.
Owner:SUZHOU DUMEI BIOTECH CO LTD
Enzymatic synthesis of d-tagatose
The current disclosure provides a process for enzymatically converting a saccharide into tagatose. The invention also relates to a process for preparing tagatose where the process involves converting fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) to tagatose 6-phosphate (T6P), catalyzed by an epimerase, and converting the T6P to tagatose, catalyzed by a phosphatase.
Owner:BONUMOSE INC
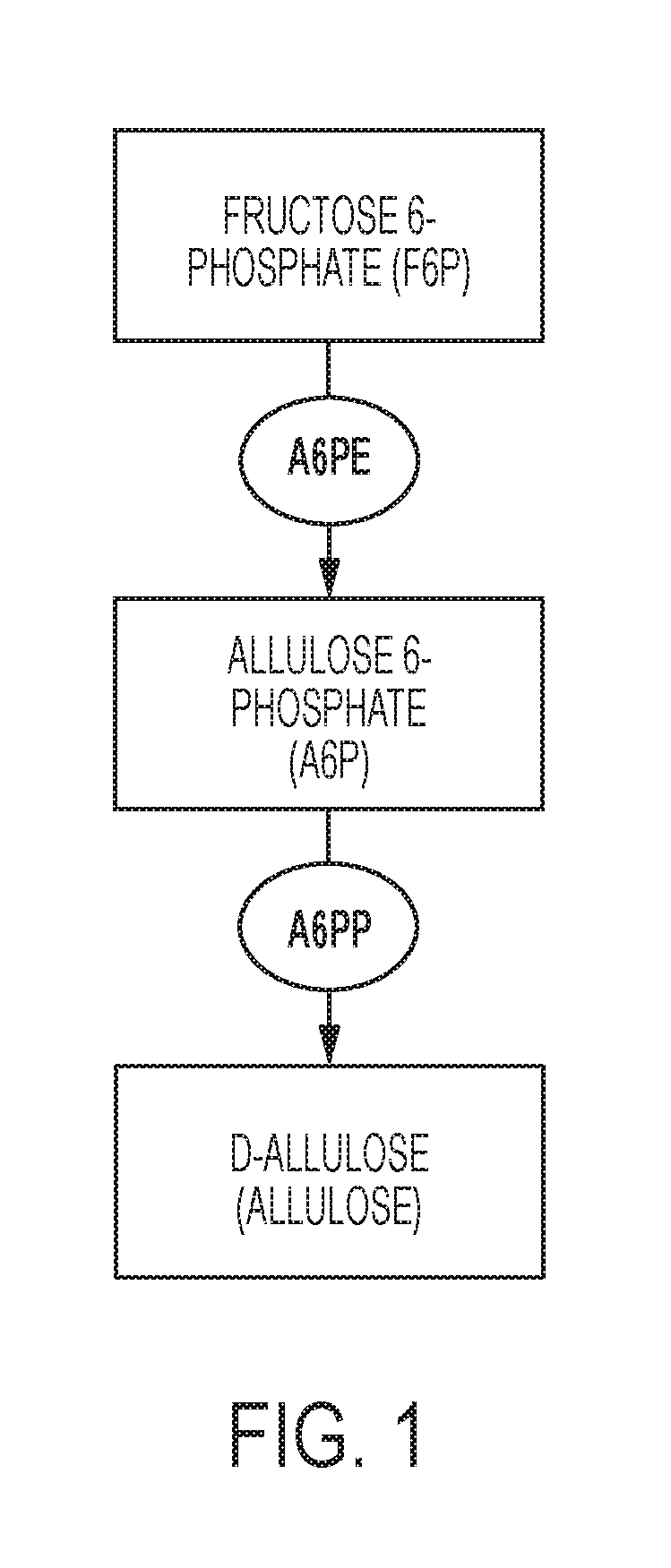
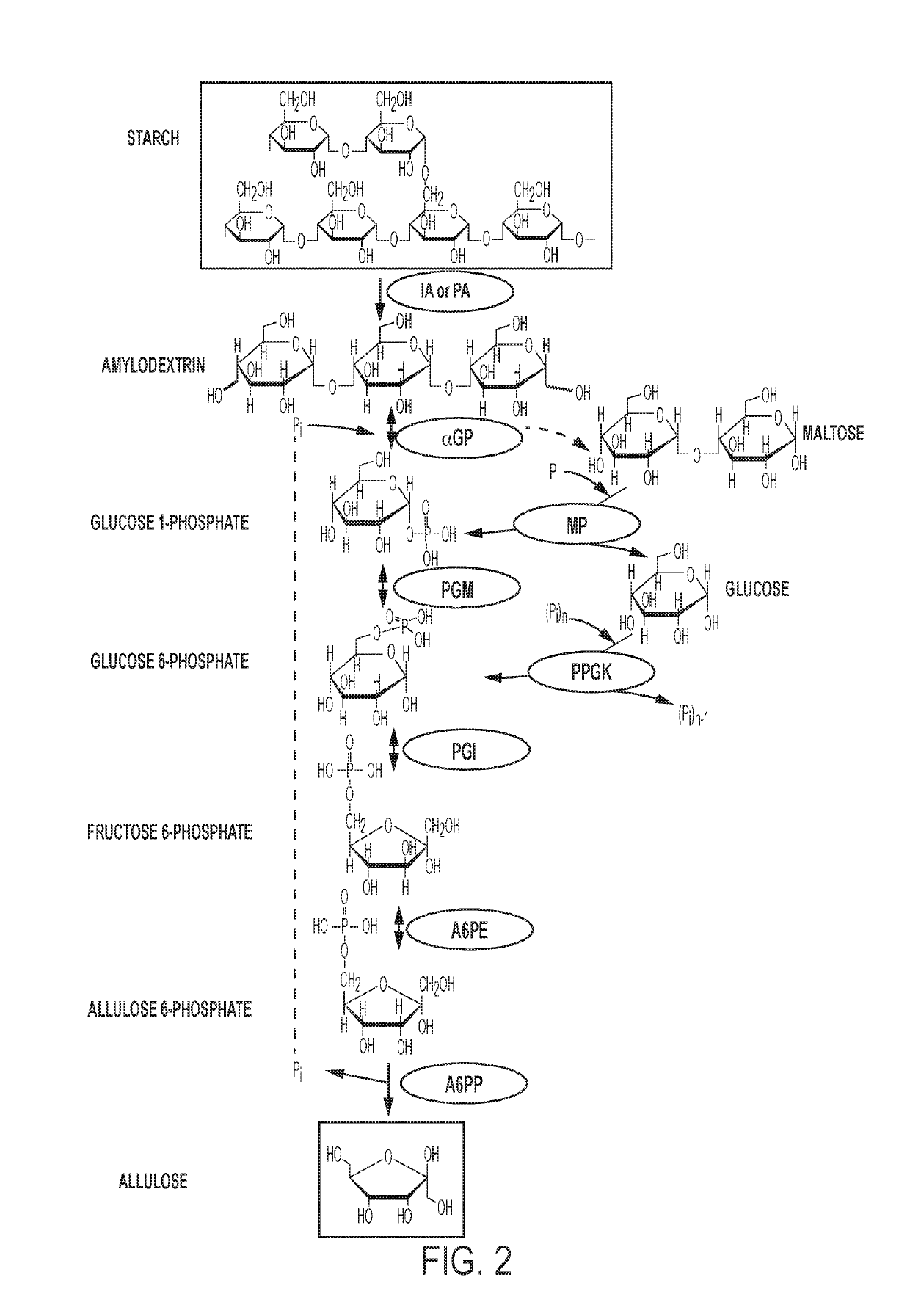
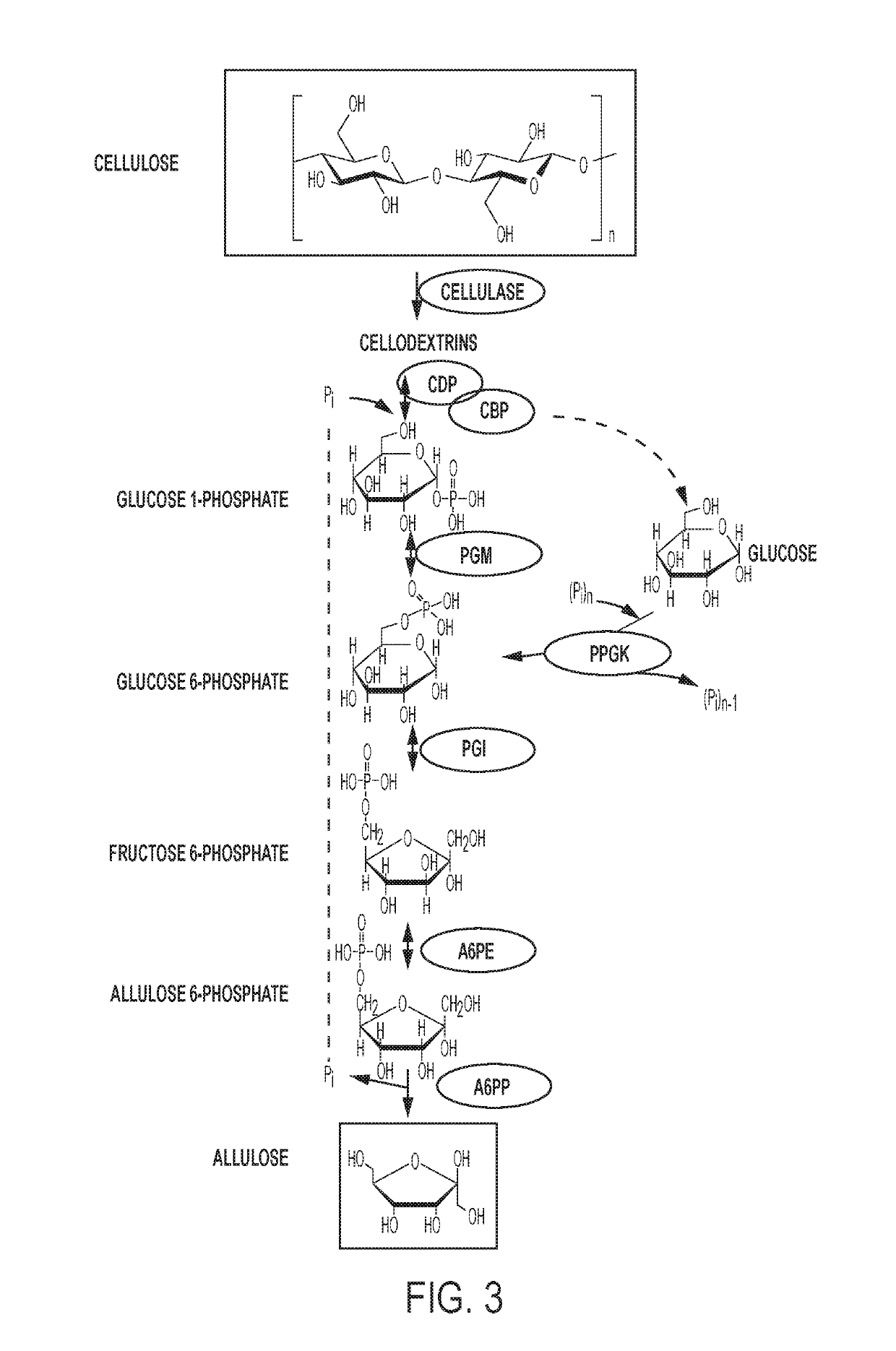
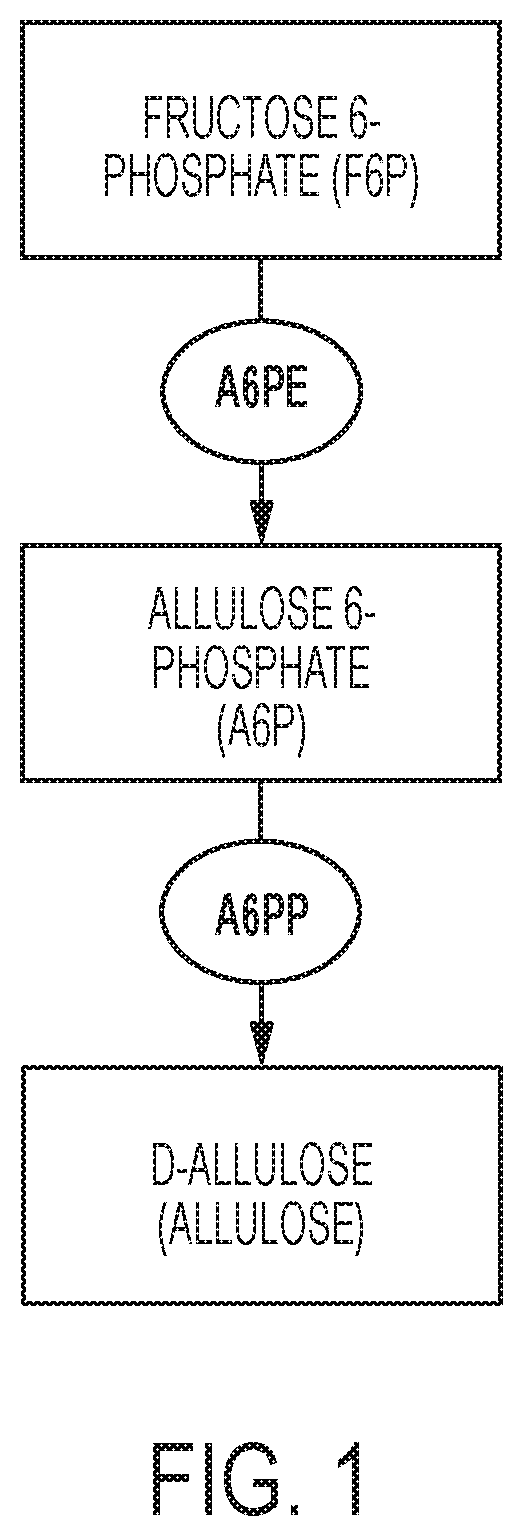
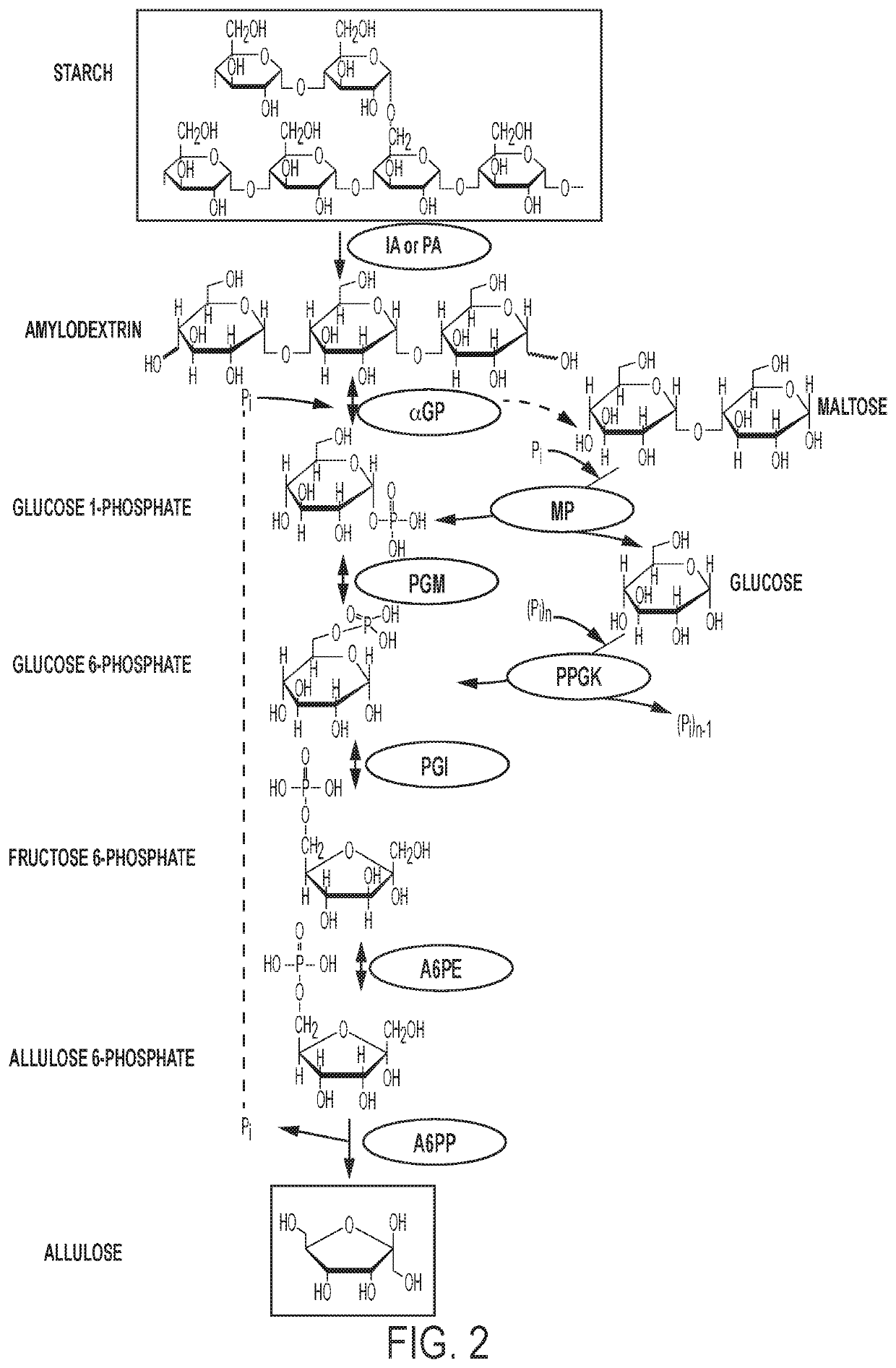
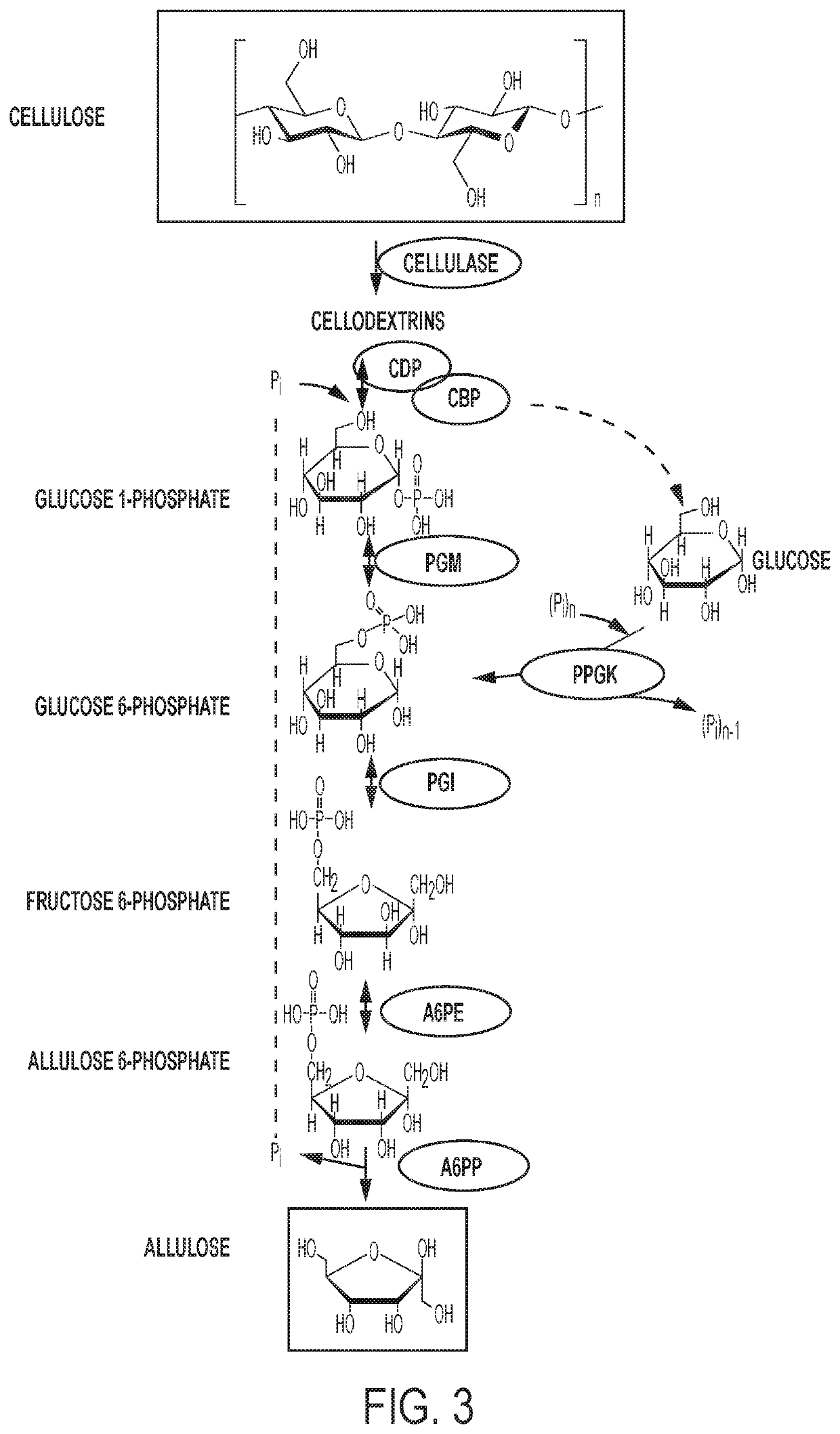
Enzymatic production of d-allulose
The current disclosure provides a process for enzymatically converting a saccharide into allulose. The invention also relates to a process for preparing allulose where the process involves converting fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) to allulose 6-phosphate (A6P), catalyzed by allulose 6-phosphate 3-epimerase (A6PE), and converting the A6P to allulose, catalyzed by allulose 6-phosphate phosphatase (A6PP).
Owner:BONUMOSE INC
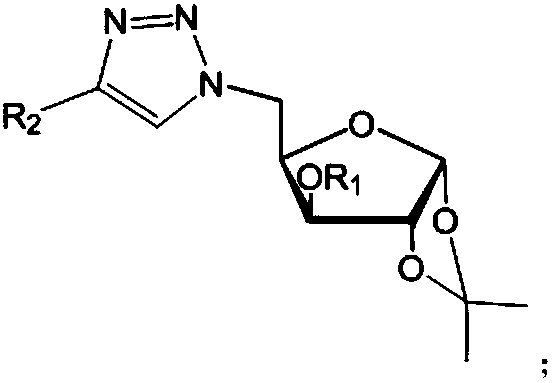
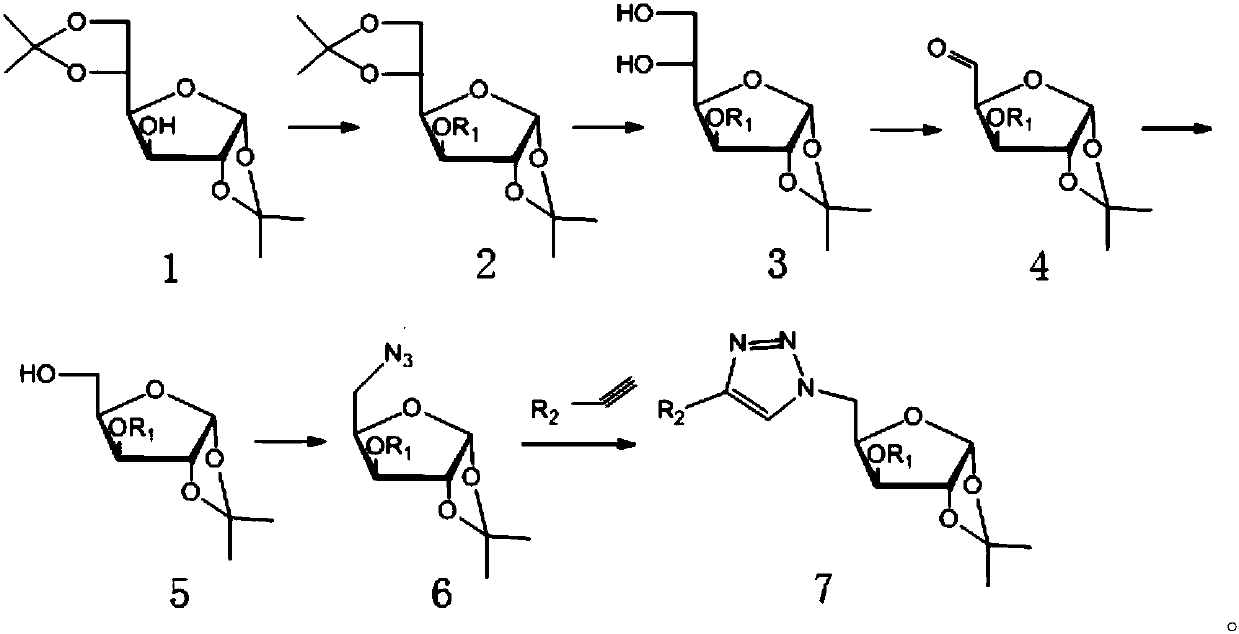
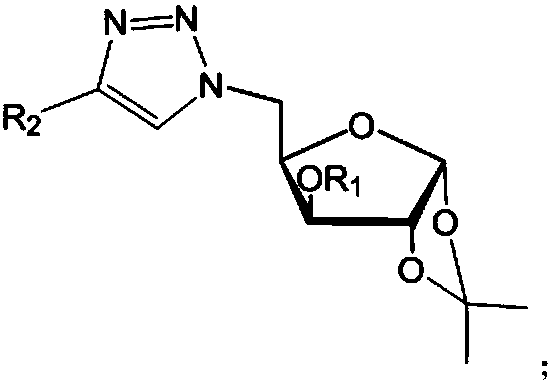
Furan glucosyl triazole type compound and preparation method and bactericide thereof
ActiveCN107857782AHigh antibacterial activityGood antibacterial effectBiocideSugar derivativesFuranPhenyl group
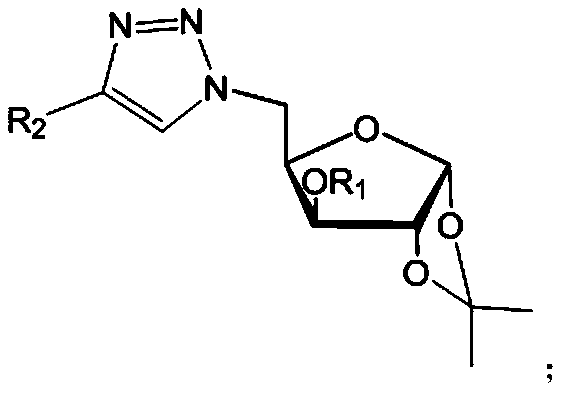
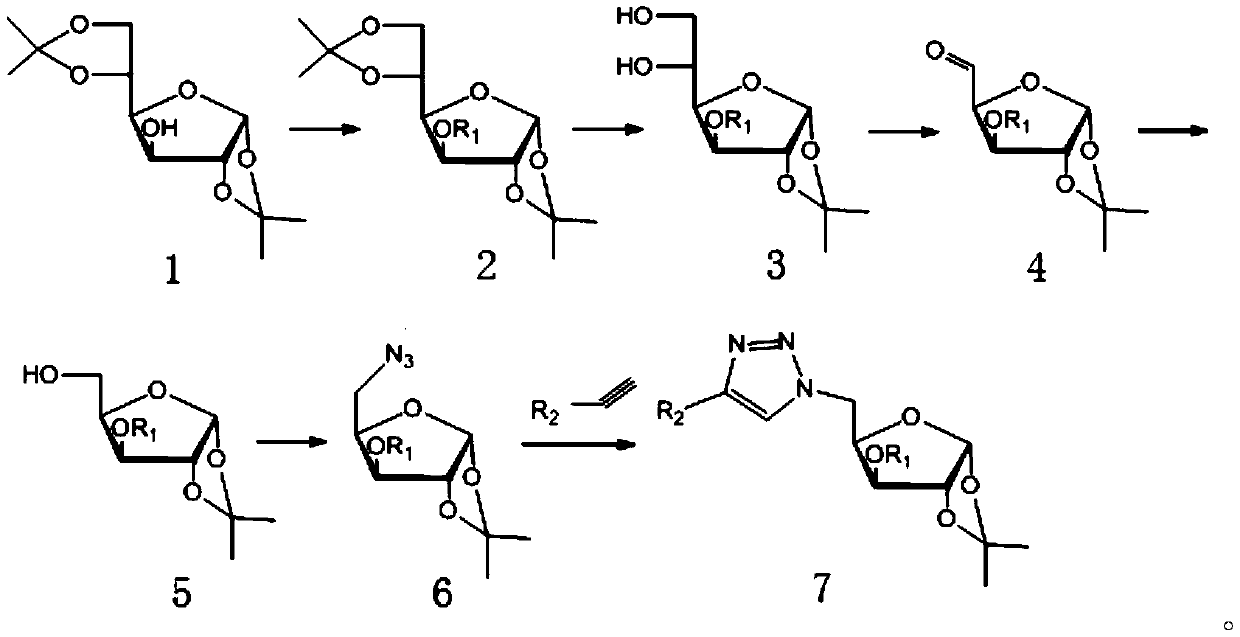
The invention relates to the field of bactericidal compounds, in particular to a furan glucosyl triazole type compound and a preparation and a bactericide thereof. The molecular formula of the furan glucosyl triazole type compound is shown in the following description, wherein R1 is methyl or benzyl, and R2 are phenyl and derivative of the phenyl or ethyl derivatives. Based on structural characteristics of the substrate fructose-6-phosphate and an ISOM catalytic hypothesis mechanism, the inventor adopts a five-membered furan glucose derivative with a similar structure as a basic skeleton, introduces an effective active group triazole structure of pesticides, designs a series of novel furan glucosyl triazole type compounds for the first time, studies the biological activities of the furan glucosyl triazole type compound, examines structure-activity relationships of the furan glucosyl triazole type compound, and lays the foundation for selecting better inhibitors.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Glucosamine-6 phosphate synthase mutant
The invention discloses a glucosamine-6 phosphate synthase mutant, and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. A method for site-saturation mutagenesis of glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase is adopted and provides the glucosamine-6 phosphate synthase mutant derived from E.coli. Compared with wild-type glucosamine-6-phosphate transferase, the catalytic activity of the mutant to fructose-6-phosphate is significantly improved, the yield of acetylglucosamine is higher, and the mutant is more suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Kit for detecting glucose-6-phosphate isomerase and use method of kit
InactiveCN109593825AShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementSolventFructose 6-phosphate
The invention provides a kit for detecting glucose-6-phosphate isomerase and a use method of the kit, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme detection. The kit comprises a first reagent and a second reagent, wherein the first reagent uses Tris buffer as a solvent and comprises adenosine triphosphate, beta-nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide trihydrate, a protective agent and a preservative; the second reagent uses the Tris buffer as the solvent and comprises magnesium chloride, fructose-6-phosphate, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, a stabilizer and the preservative; and the concentrationof the Tris buffer is 50-500 mmol / L. The kit provided by the invention can obtain a result of detecting glucose-6-phosphate isomerase at 6 min 20 s to 9 min 40 s, thereby shortening detection time.
Owner:浙江达美生物技术有限公司
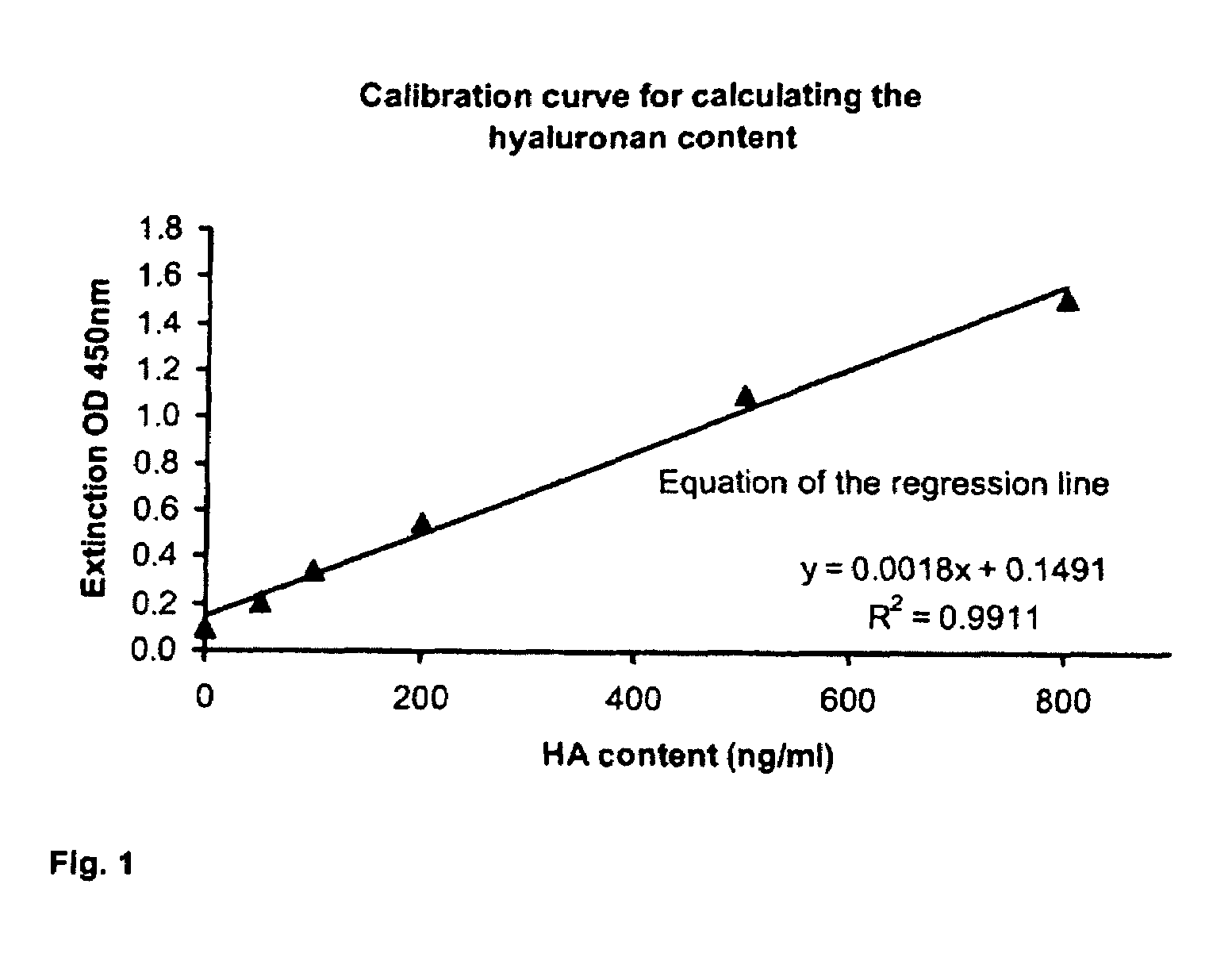
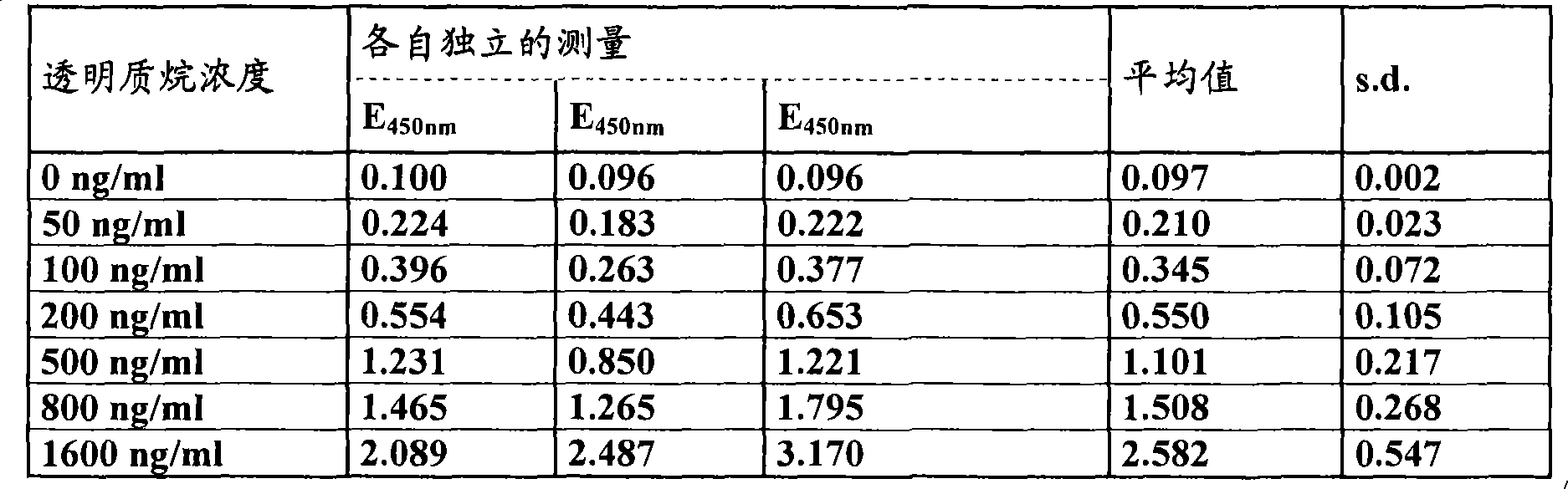
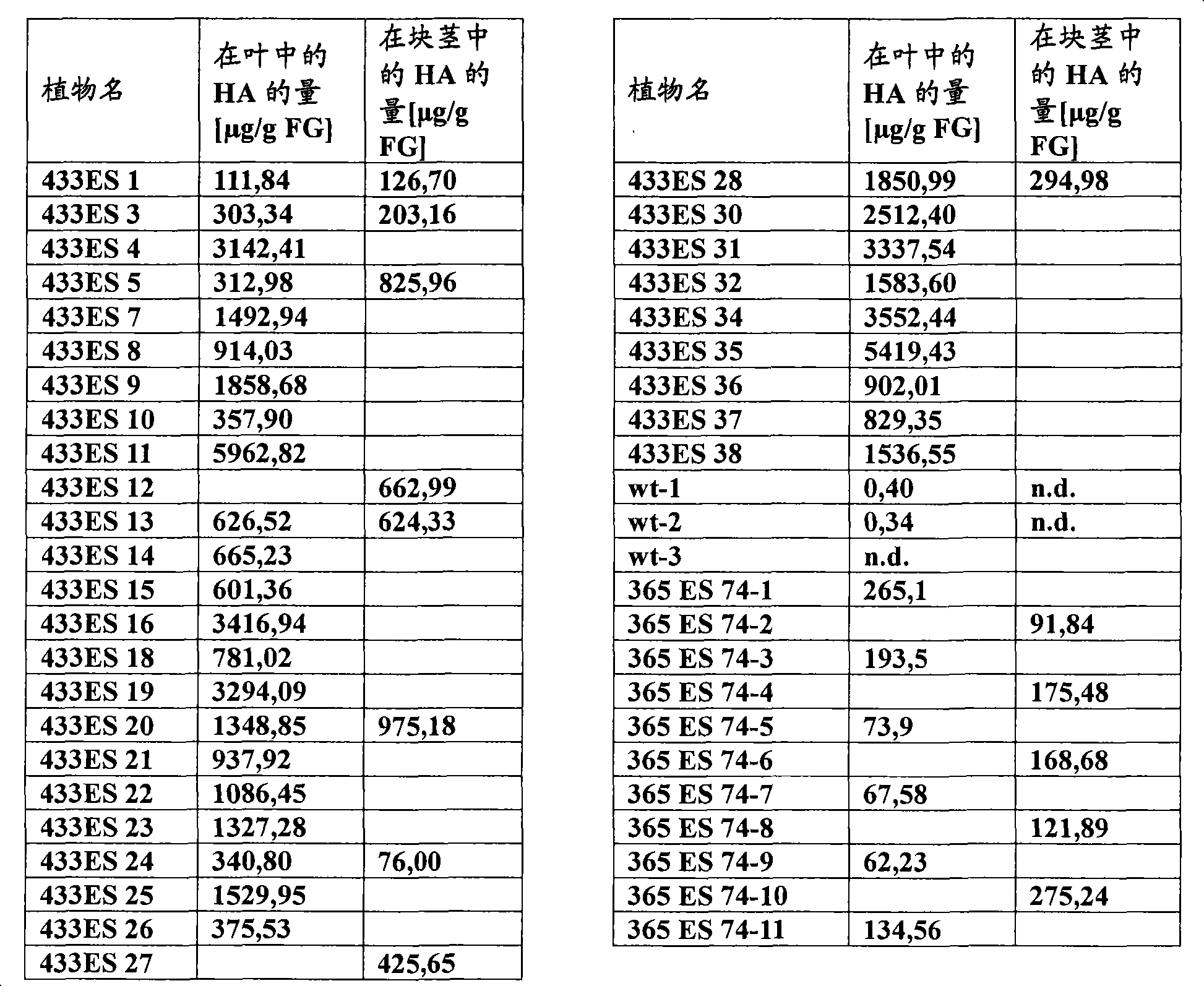
Methods and means for producing hyaluronan
ActiveUS8106256B2High hyaluronan contentSignificant positive effectBryophytesSugar derivativesPlant cellWild type
The present invention relates to plant cells and plants which synthesize an increased amount of hyaluronan, and to methods for preparing such plants, and also to methods for preparing hyaluronan with the aid of these plant cells or plants. Here, plant cells or genetically modified plants according to the invention have hyaluronan synthase activity and additionally an increased glutamine:fructose 6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT) activity and an increased UDP glucose dehydrogenase (UDP-Glc-DH) activity, compared to wild-type plant cells or wild-type plants. The present invention furthermore relates to the use of plants having increased hyaluronan synthesis for preparing hyaluronan and food or feedstuff containing hyaluronan.
Owner:BASF AG
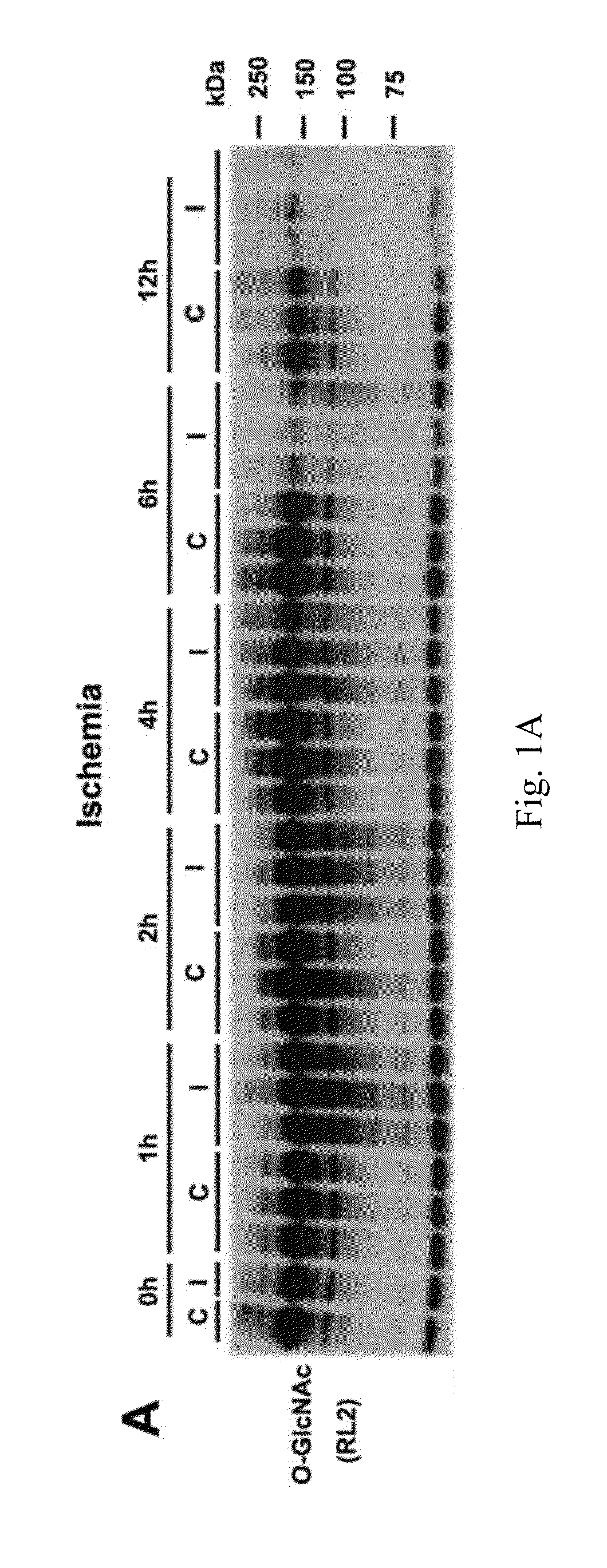
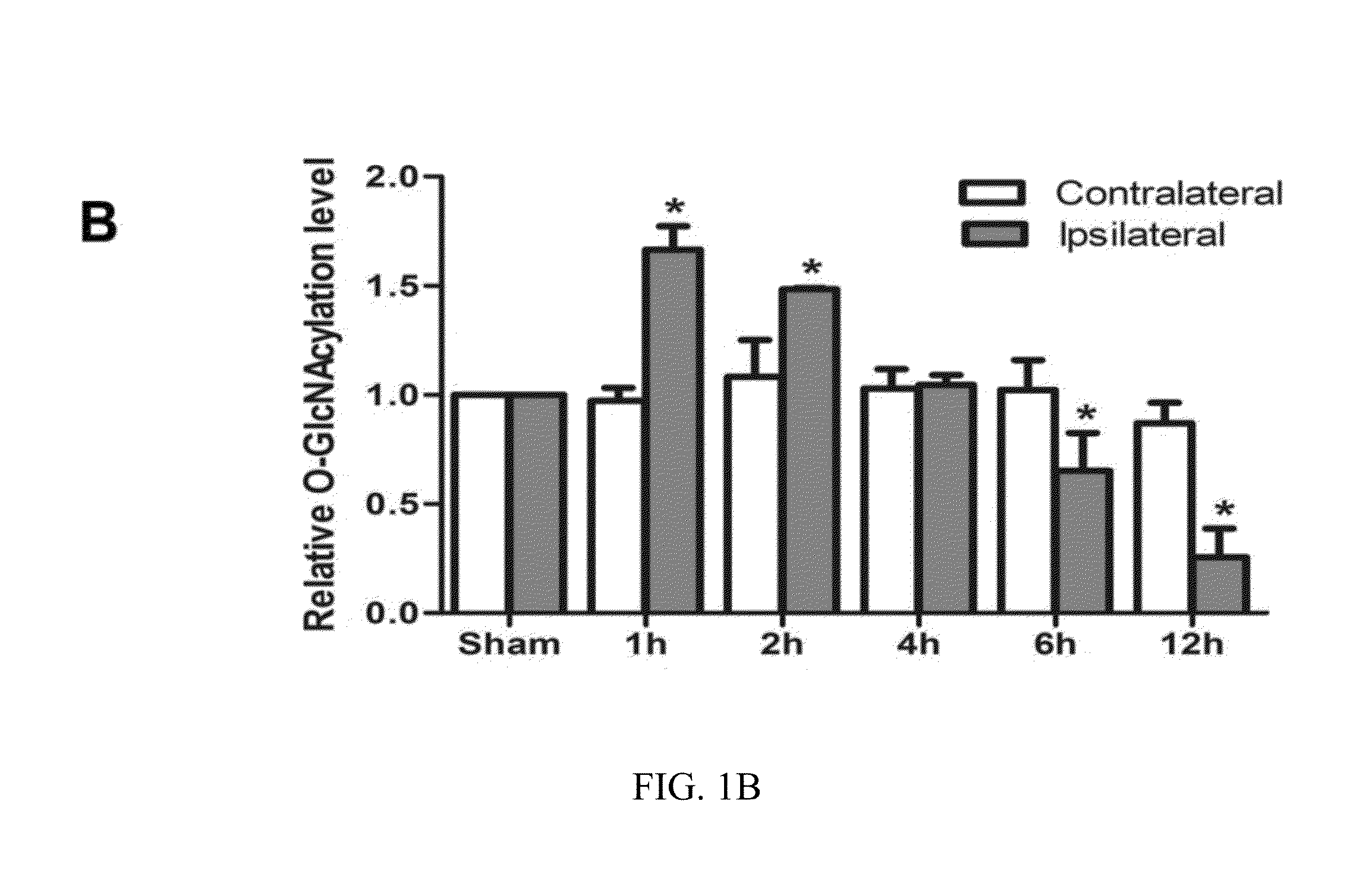
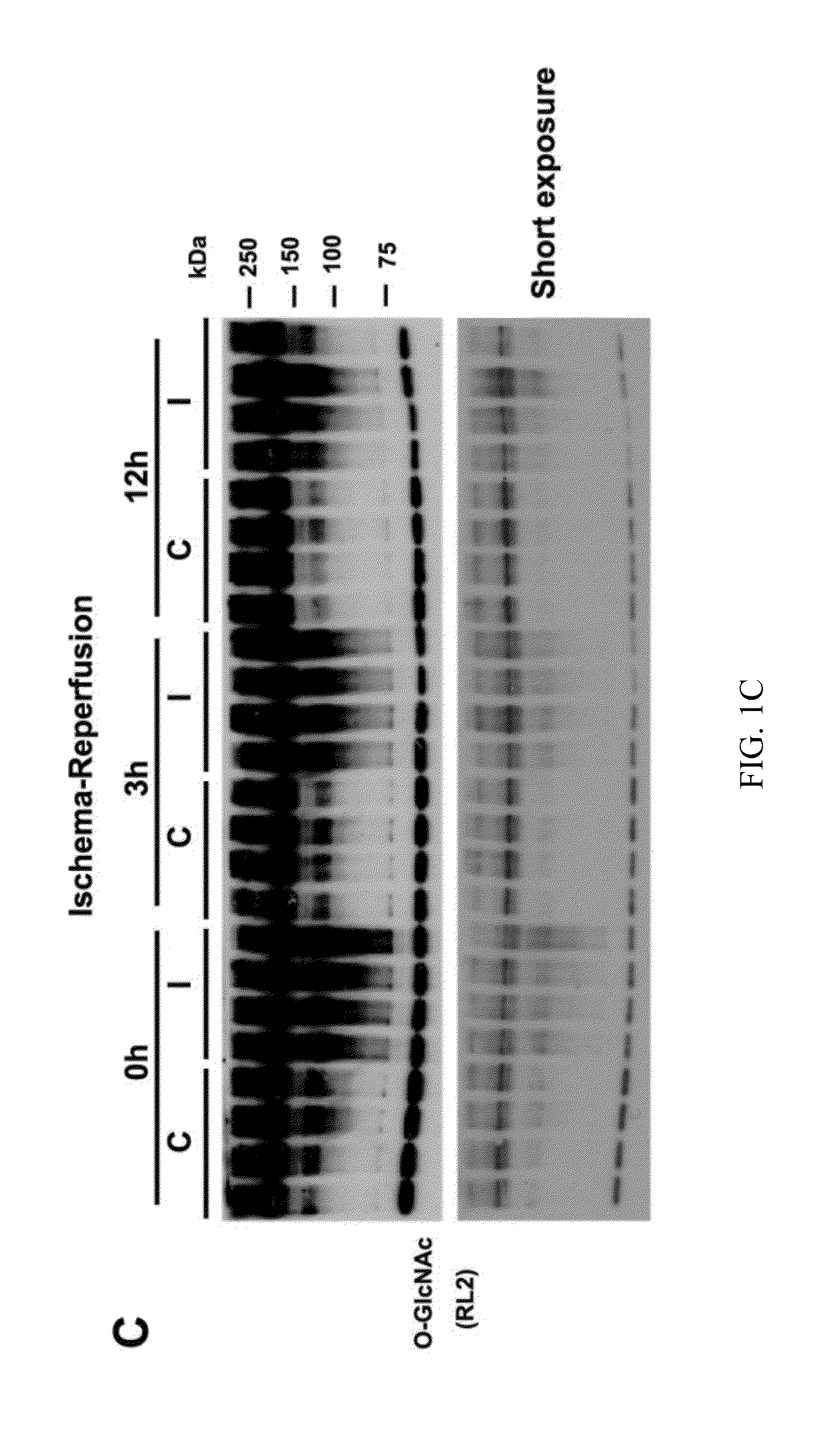
O-glcnacylation treatment for ischemic brain injury
InactiveUS20160022714A1Ameliorate ischemia-reperfusion-induced brain injuryIncrease heightBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismInjury brainReperfusion injury
Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury may be treated by compounds that increase brain O-GlcNAcylation, such as a therapeutic amount of a compound that increases the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway flux that bypasses glutamine / fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase 2 or a therapeutic amount of a compound that inhibits OGA. The initial and transient elevation of brain O-GlcNAcylation is neuroprotective and helps ameliorate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury when administered within three hours of the ischemia-reperfusion-induced brain injury and continues for at least two days.
Owner:RES FOUDATION FOR MENTAL HYGIENE INC
Inositol Biotransformation
InactiveUS20160168607A1Easy to disassembleStabilise and maintain enzyme activityFermentationD-myo-inositol-3-phosphate synthasePhosphoric acid
Disclosed is a method of preparing pure or substantially pure D-myo-inositol-3-phosphate from glucose-6-phosphate and / or fructose-6-phosphate. The method may also be applied to protected and / or derivative forms of glucose-6-phosphate and / or fructose-6-phosphate so as to form protected / derivative forms of D-myo-inositol-3-phosphate, for use in further chemical reactions. The enzyme D-myo-inositol-3-phosphate synthase (INO1) is contacted with the glucose-6-phosphate and / or fructose-6-phosphate to generate labeled or unlabeled, protected or unprotected D-myo-inositol-3-phosphate, which may be further reacted and / or purified.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase, its production and use
This invention relates to glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase, or its partial peptide or a salt thereof; a DNA coding for the protein; a recombinant vector; a transformant; a method for producing the protein; a pharmaceutical composition comprising the protein, its partial peptide or a salt thereof; and an antibody against the protein or its partial peptide. The protein, its partial peptide or a salt thereof, and the DNA are useful for a prophylactic or therapeutic agent for hypoglycemia. The antibody can be used in the assay of the protein, its partial peptide or a salt thereof. The protein, its partial peptide or a salt thereof is useful as a reagent for the screening for candidate medical compounds.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Plants with increased hyaluronan production
InactiveCN101273135ASeparation is cost-effectiveSave plant areaTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionPlant cellWild type
The present invention relates to plant cells and plants which synthesize an increased amount of hyaluronan, and to methods for preparing such plants, and also to methods for preparing hyaluronan with the aid of these plant cells or plants. Here, plant cells or genetically modified plants according to the invention have hyaluronan synthase activity and additionally an increased glutamine:fructose 6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT) activity compared to wild-type plant cells or wild-type plants. The present invention furthermore relates to the use of plants having increased hyaluronan synthesis for preparing hyaluronan and food or feedstuff containing hyaluronan.
Owner:BASF AG
Special solid complex enzyme (ALD, TIM and GDH) reagent for determining content of fructose diphosphate sodium (FDP)
ActiveCN101691566AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesPhosphoric acidFructose 6-phosphate
Owner:张莉莉
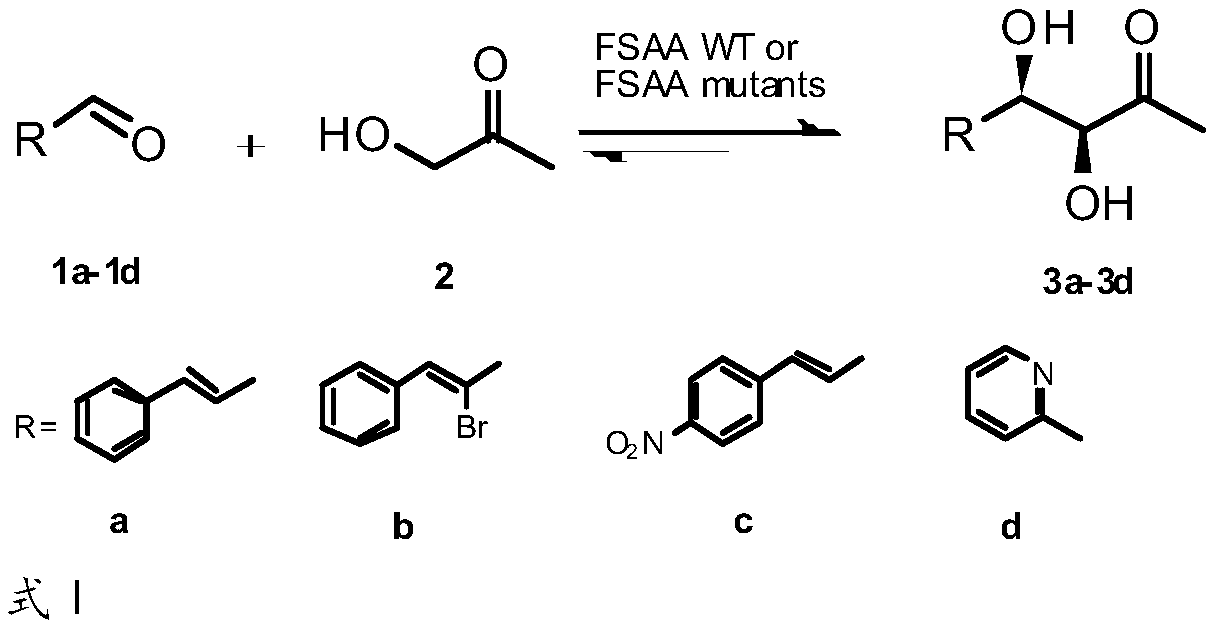
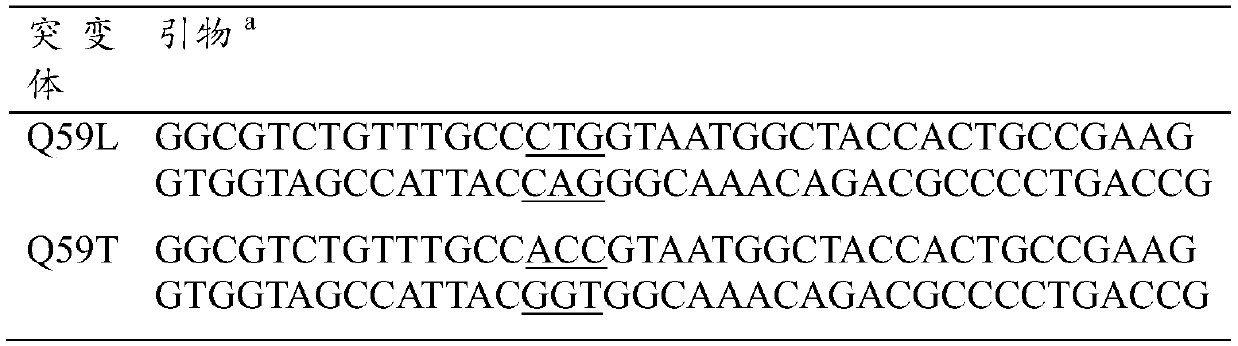
D-fructose-6-phosphate aldolase a mutant, recombinant expression vector, genetically engineered bacteria and its application and reaction products
ActiveCN106701723BHigh catalytic activityEasy to manufactureFermentationLyasesMutated proteinPhosphate
The invention provides an FSAA mutant with remarkably increased catalytic activity, a nucleotide sequence thereof, a recombinant expression vector containing a corresponding mutant gene and a genetically engineered bacterium. A chiral product with high optical purity can be prepared by aldol condensation reaction in which cinnamyl aldehyde / alpha-bromocinnamaldehyde / 4-nitrocinnamaldehyde / pyridine-2-formaldehyde and hydroxyacetone (HA) are asymmetrically catalyzed by the FSAA mutants or the genetically engineered bacteria containing a corresponding mutant protein, the chiral product can serve as a valuable chiral building block, and important potential application value in the field of medicines is realized.
Owner:杭州馨海酶源生物科技有限公司
Enzymatic production of d-allulose
The current disclosure provides a process for enzymatically converting a saccharide into allulose. The invention also relates to a process for preparing allulose where the process involves converting fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) to allulose 6-phosphate (A6P), catalyzed by allulose 6-phosphate 3-epimerase (A6PE), and converting the A6P to allulose, catalyzed by allulose 6-phosphate phosphatase (A6PP).
Owner:BONUMOSE INC
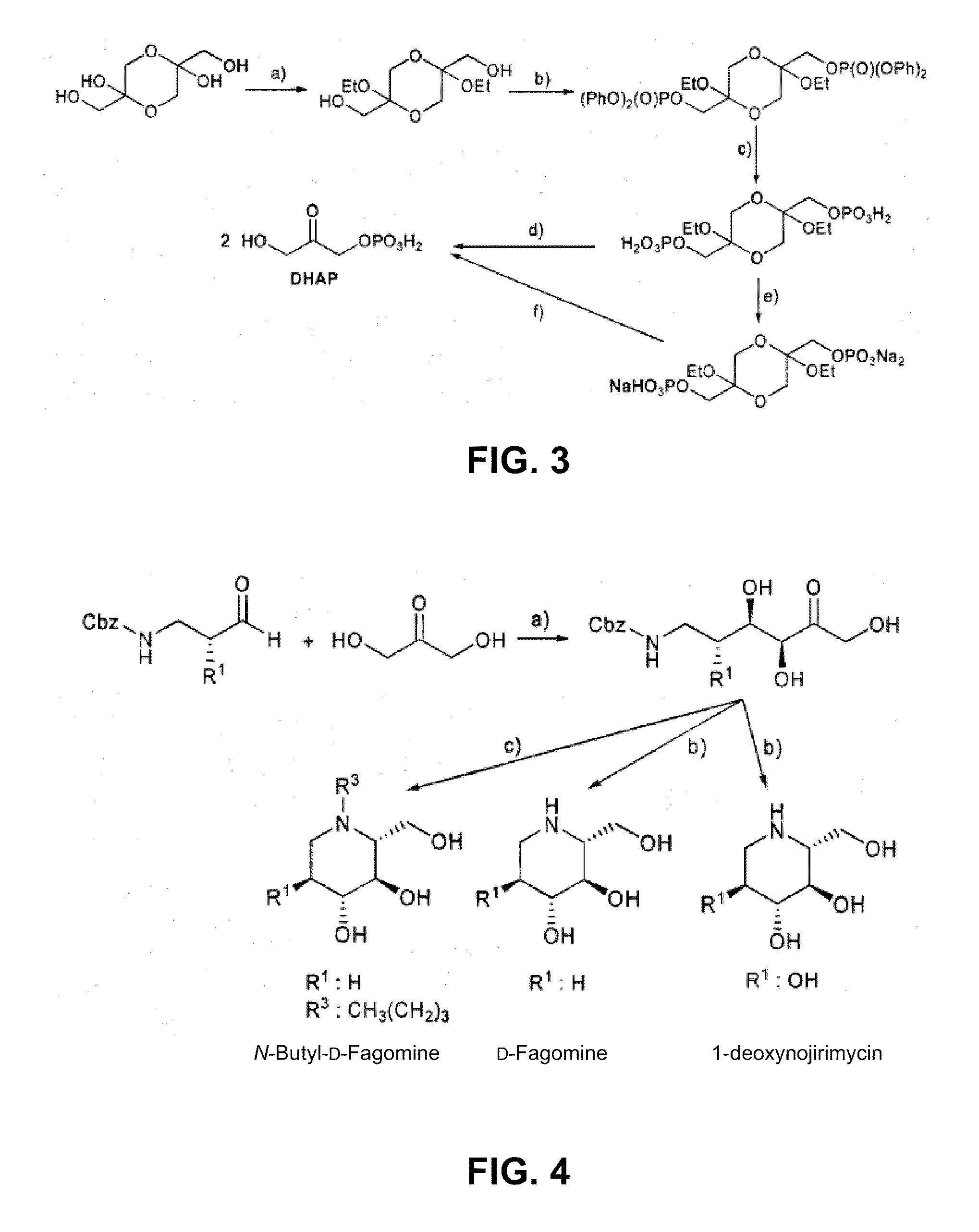
Chemoenzymatic process for the preparation of iminocyclitols
InactiveUS20100009417A1Different propertyAldol addition is carried out efficientlyFermentationLyasesAldehydeFructose 6-phosphate
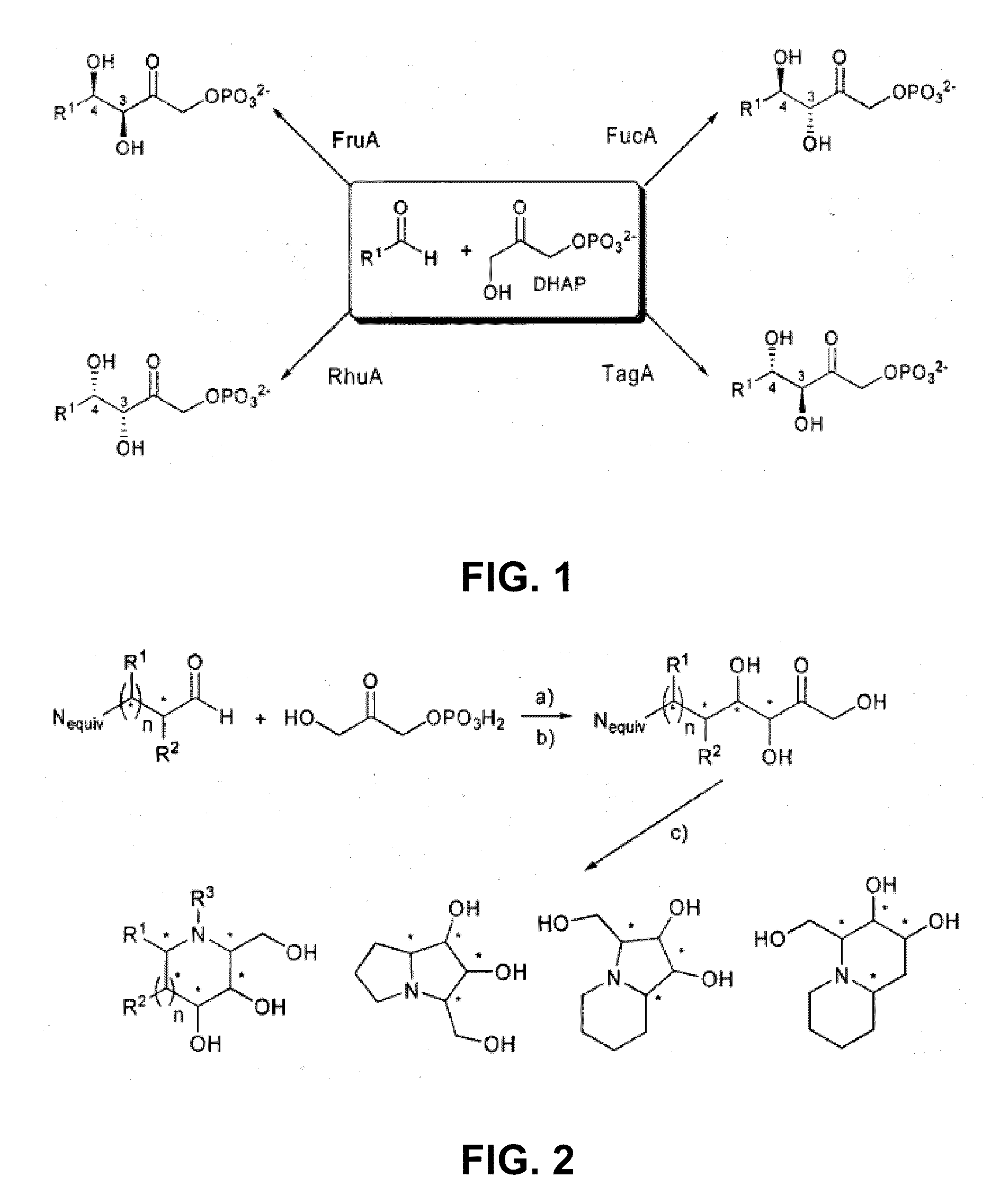
The present invention discloses a chemoenzymatic process for the preparation of an iminocyclitol corresponding to formula (I), (II), (III) or (IV), wherein: R1 and R2 are the same or different, and independently selected from the group consisting of: H, OH, hydroxymethyl, methyl, ethyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, octyl, isopropyl, isobutyl, 2-methylbutyl, and benzyl; R3 is selected from the group consisting of: H, hydroxymethyl, hydroxyethyl, ethyl, butyl, pentyl, hexyl, octyl, dodecyl, isobutyl, isopropyl, isopentyl, 2-methylbutyl, benzyl, and phenylethyl; n: 0 or 1; the process comprising: (i) an aldol addition catalyzed by a D-fructose-6-phosphate aldolase enzyme (FSA) and an acceptor aminoaldehyde; and (ii) an intramolecular reductive amination of the addition adduct obtained in step (i) with H2, in the presence of a metallic catalyst, optionally being carried out said step (ii) in the presence of an aldehyde of formula R3—CHO, wherein R3 is as defined above.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Cotton fibers with increased glucosamine content
An isolated nucleic acid molecule is provided comprising a nucleotide sequence which encodes a glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase from E. coli which is particularly suitable for expression in cotton plant cells. The invention also relates to plant cells or plants, in particular to cotton plant cells or cotton plants which produce an increased amount of positively charged polysaccharides in their cell walls. Furthermore methods and means are provided to increase the content of positively charged polysaccharides in the cell walls of cotton cells, in particular in cotton fibers. Fibers obtained from such cotton plants have an altered chemical reactivity which can be used to attach reactive dyes or other textile finish reagents to these fibers.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Novel tagatose 6-phosphate 4-locus epimerase and application thereof
Owner:TIANJIN YEAHE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
A kind of glucofuranosyl triazole compound and its preparation method and fungicide
ActiveCN107857782BHigh antibacterial activityGood antibacterial effectBiocideSugar derivativesFuranFungicide
The invention relates to the field of bactericidal compounds, in particular to a furan glucosyl triazole type compound and a preparation and a bactericide thereof. The molecular formula of the furan glucosyl triazole type compound is shown in the following description, wherein R1 is methyl or benzyl, and R2 are phenyl and derivative of the phenyl or ethyl derivatives. Based on structural characteristics of the substrate fructose-6-phosphate and an ISOM catalytic hypothesis mechanism, the inventor adopts a five-membered furan glucose derivative with a similar structure as a basic skeleton, introduces an effective active group triazole structure of pesticides, designs a series of novel furan glucosyl triazole type compounds for the first time, studies the biological activities of the furan glucosyl triazole type compound, examines structure-activity relationships of the furan glucosyl triazole type compound, and lays the foundation for selecting better inhibitors.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Inositol biotransformation
InactiveUS10131928B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingD-myo-inositol-3-phosphate synthaseChemical reaction
Disclosed is a method of preparing pure or substantially pure D-myo-inositol-3-phosphate from glucose-6-phosphate and / or fructose-6-phosphate. The method may also be applied to protected and / or derivative forms of glucose-6-phosphate and / or fructose-6-phosphate so as to form protected / derivative forms of D-myo-inositol-3-phosphate, for use in further chemical reactions. The enzyme D-myo-inositol-3-phosphate synthase (INO1) is contacted with the glucose-6-phosphate and / or fructose-6-phosphate to generate labeled or unlabeled, protected or unprotected D-myo-inositol-3-phosphate, which may be further reacted and / or purified.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Plants with increased hyaluronan production
The present invention relates to plant cells and plants which synthesize an increased amount of hyaluronan, and to methods for preparing such plants, and also to methods for preparing hyaluronan with the aid of these plant cells or plants. Here, plant cells or genetically modified plants according to the invention have hyaluronan synthase activity and additionally an increased glutamine:fructose 6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT) activity compared to wild-type plant cells or wild-type plants. The present invention furthermore relates to the use of plants having increased hyaluronan synthesis for preparing hyaluronan and food or feedstuff containing hyaluronan.
Owner:BASF SE
Corynebacterium sp. transformed with a fructokinase gene derived from escherichia sp. and process for preparing l-amino acid using the same
ActiveUS20140099680A1Prevent unnecessary energy consumptionCost effective productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliCorynebacterium efficiens
The present invention relates to Corynebacterium sp. that is transformed with an Escherichia sp.-derived fructokinase gene to express fructokinase showing a sufficient activity of converting fructose into fructose-6-phosphate, thereby preventing unnecessary energy consumption, and a method for producing L-amino acids using the strain. The transformed Corynebacterium sp. of the present invention is able to express fructokinase from the Escherichia-derived fructokinase gene to prevent unnecessary energy consumption during fructose metabolism, leading to more cost-effective production of L-amino acids. Therefore, it can be widely used for the effective production of L-amino acids.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Corynebacterium sp. transformed with a fructokinase gene derived from Escherichia sp. and process for preparing L-amino acid using the same
ActiveUS9267161B2Prevent unnecessary energy consumptionCost effective productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliFructose metabolism
The present invention relates to Corynebacterium sp. that is transformed with an Escherichia sp.-derived fructokinase gene to express fructokinase showing a sufficient activity of converting fructose into fructose-6-phosphate, thereby preventing unnecessary energy consumption, and a method for producing L-amino acids using the strain. The transformed Corynebacterium sp. of the present invention is able to express fructokinase from the Escherichia-derived fructokinase gene to prevent unnecessary energy consumption during fructose metabolism, leading to more cost-effective production of L-amino acids. Therefore, it can be widely used for the effective production of L-amino acids.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Glutamine:fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase (GFAT) comprising an internal purification marker and use thereof for the screening of compounds
InactiveUS7625734B2High level of of activityHigh level of purityBacteriaSugar derivativesBiologyFructose 6-phosphate
The invention relates to a protein with enzymatic activity, comprising a GFAT sequence and at least one sequence of a purification marker, the sequence for the purification marker being inserted between two consecutive amino acids of the GFAT sequence.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com