New application of acyl coenzyme A/cholesterol acyltransferase-1 inhibitor
A cholesterol acyl and transferase technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as limited diagnosis and treatment methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
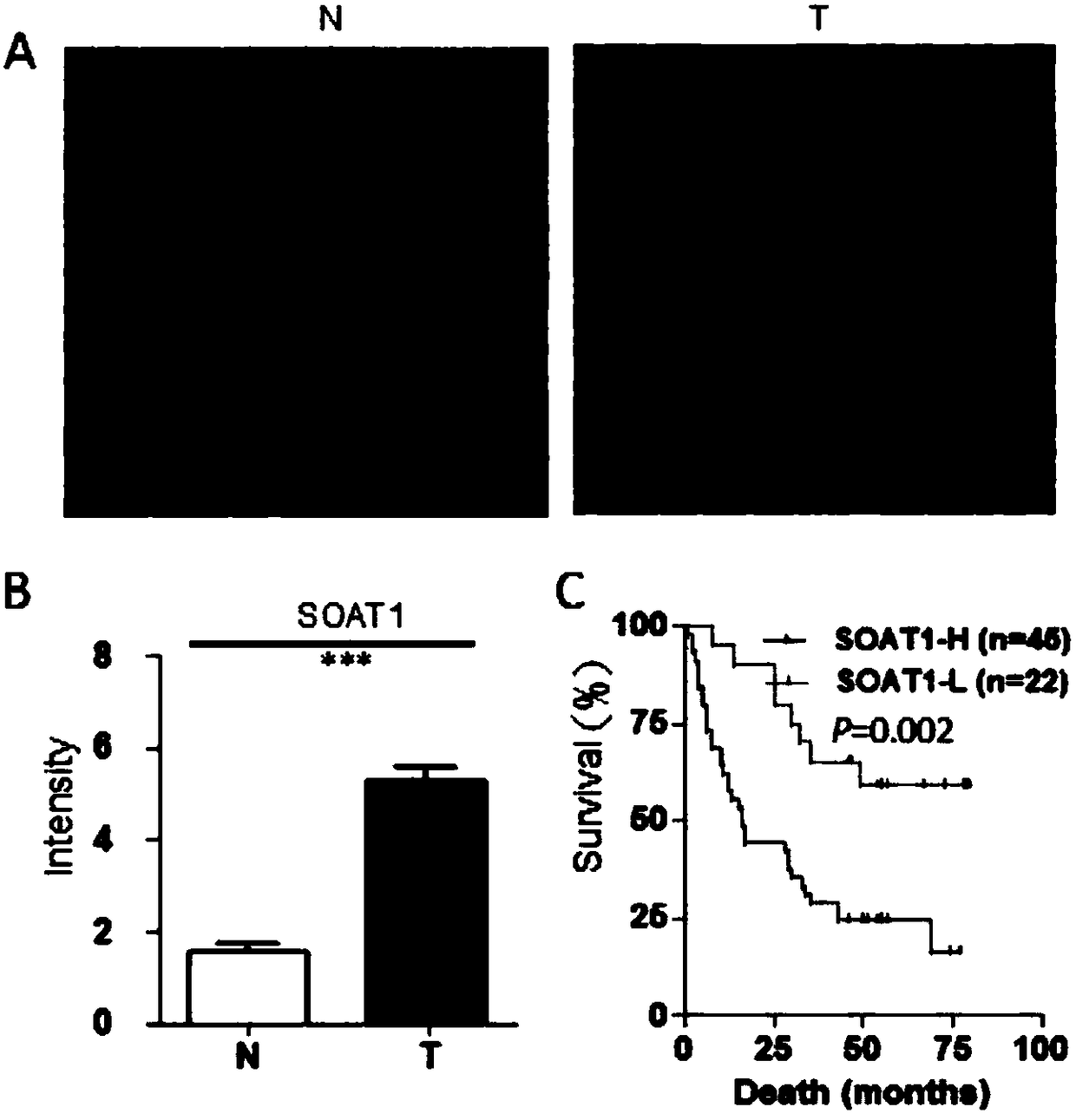
[0102] Example 1. The high expression of ACAT1 in liver cancer is closely related to the occurrence and prognosis of liver cancer
[0103] In order to confirm the high expression of ACAT1 in liver cancer, the inventors used the liver cancer tissue chip (95 liver cancer / 85 matching adjacent cancer) to detect the significantly high expression of ACAT1 in HCC ( figure 1 A, B), the overall survival of patients with high expression of ACAT1 was significantly lower than that of patients with low expression of ACAT1 ( figure 1 C). It is confirmed that ACAT1 is closely related to the occurrence and prognosis of liver cancer.
Embodiment 2
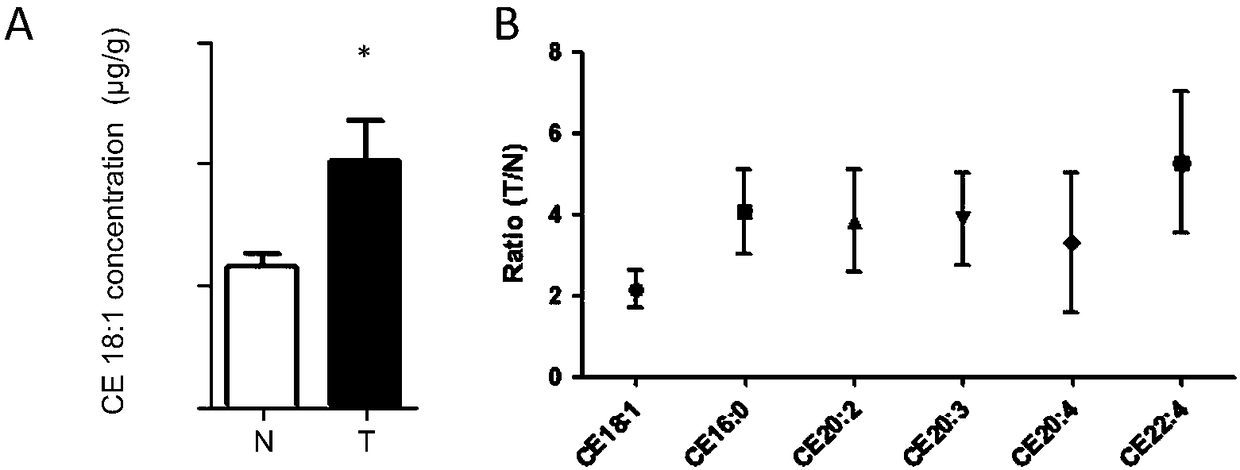
[0104] Example 2, the catalyzed product cholesteryl ester of ACAT1 is significantly highly expressed in human liver cancer tissue
[0105] In order to confirm the high expression of ACAT1 in liver cancer, the inventors used mass spectrometry to measure the content of ACAT1 catalytic product cholesteryl ester in 25 pairs of liver cancer and corresponding paracancerous tissues. The results showed that the main catalytic substrate of ACAT1 in cells, the concentration of cholesteryl ester standard (CE 18:1), was significantly higher in HCC than in the paired paracancerous tissues (Fig. 2A); the catalytic product of ACAT1, cholesteryl ester (6 species ) expression difference in human liver cancer (T) compared with paracancerous tissue (NT) ( figure 2 B). It further proved that the expression of its catalytic enzyme ACAT1 in liver cancer was significantly higher than that in matched paracancerous tissues.
Embodiment 3
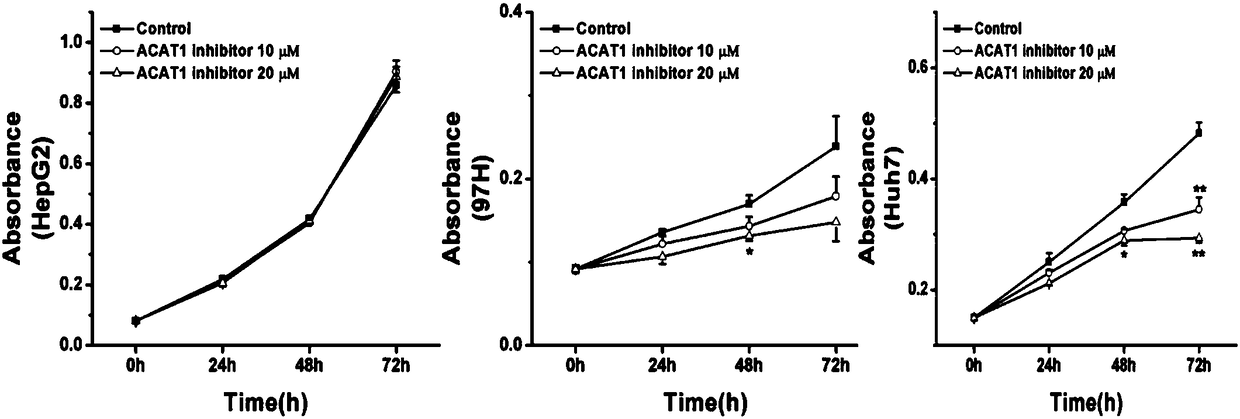
[0106] Example 3, ACAT1 inhibitors can inhibit the growth of liver cancer cells
[0107] In this example, the inventors studied the role of ACAT1 inhibitors in inhibiting the growth of liver cancer cells.
[0108] The results showed that the ACAT1 specific inhibitor K604 and the non-specific inhibitor Avasimibe could significantly inhibit the proliferation of liver cancer cells (HepG2, MHCC97H and Huh7) ( image 3 ,4). It shows that inhibiting ACAT1 can significantly inhibit the proliferation of liver cancer cell lines, suggesting that ACAT1 may be used as a target for liver cancer treatment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com