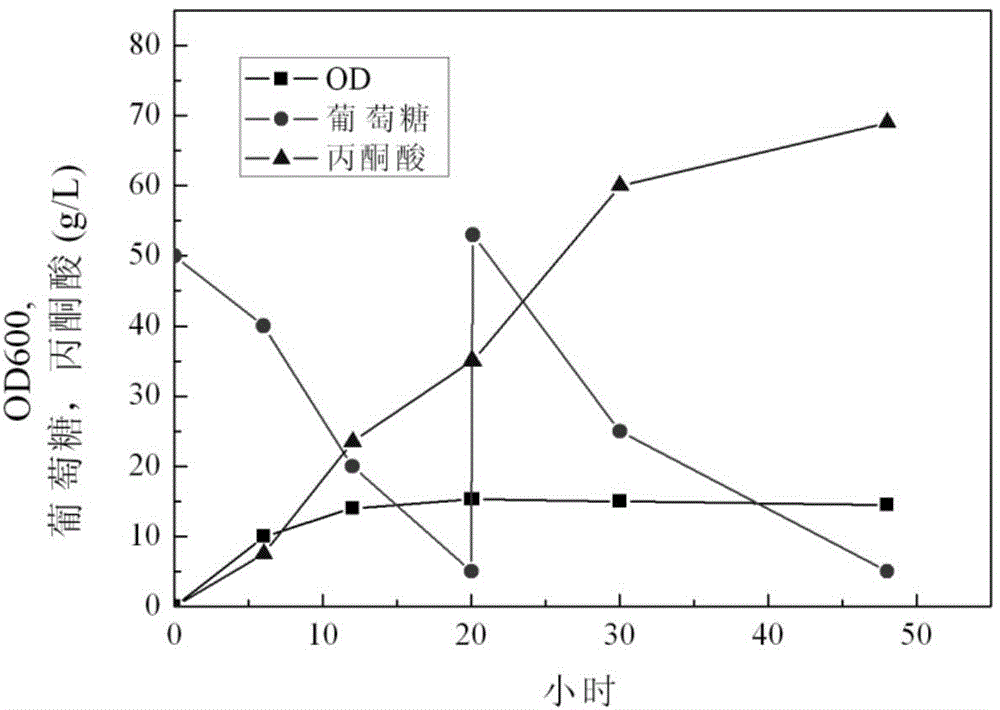
Escherichia coli gene engineering strain and construction method thereof, and application of strain in pyruvic acid production
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and Escherichia coli, applied to other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, bacteria, stably introducing foreign DNA into chromosomes, etc. Process control difficulty and fermentation cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
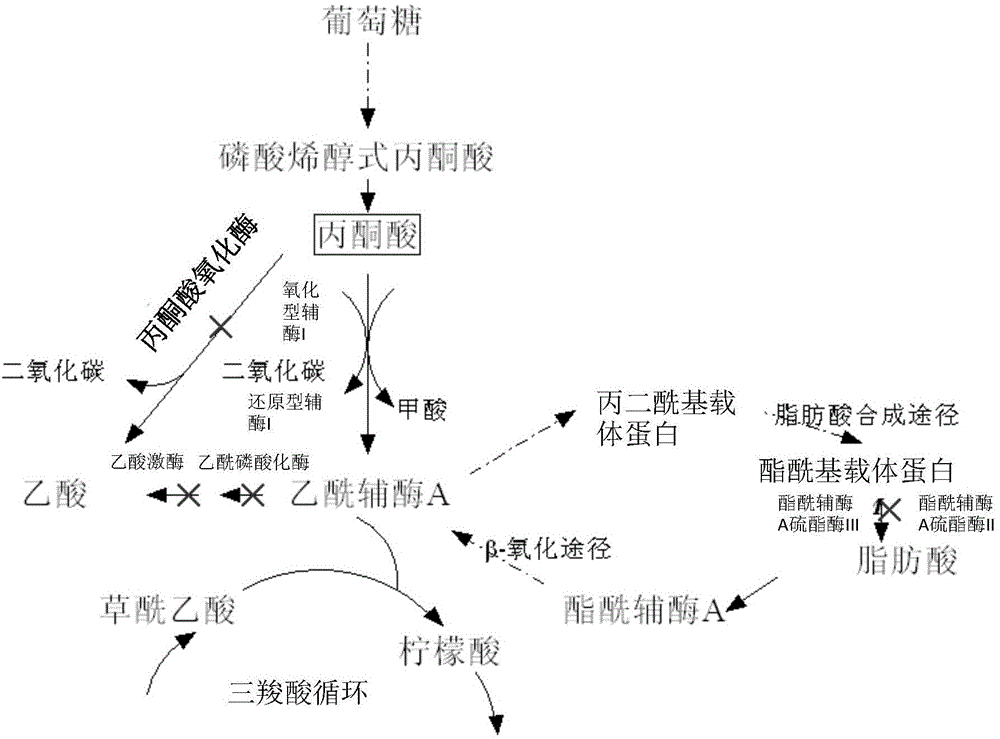
[0038] Embodiment 1, as figure 1 As shown, the construction of Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria Ⅰ
[0039] The construction of Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria I requires two steps.
[0040] (1) Knockout of the acyl-CoA thioesterase III gene (fadM) of Escherichia coli K-12MG1655
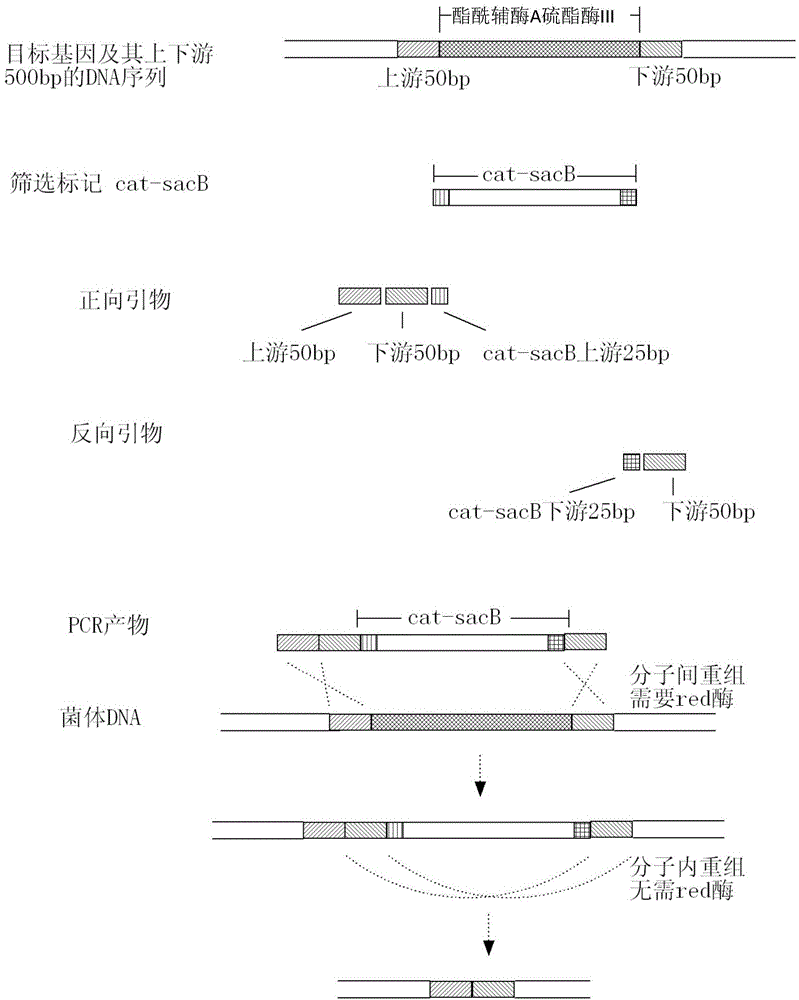
[0041] Such as figure 2 As shown, the gene knockout adopts the method of two-step homologous recombination.
[0042] In the first step, the pKD46 plasmid was transferred into the starting strain Escherichia coli K-12MG1655 by heat shock transformation method to obtain recombinant Escherichia coli A. The specific operation is as follows: absorb 1 μL of pKD46 plasmid and add it to the competent cells to mix evenly. After resting for 5 minutes, place in a water bath at 42°C for heat shock for 90 seconds, and then bathe in ice water for 3 minutes. Then add 800 μL of LB medium without antibiotics, incubate at 30°C, 140rpm for 1h, spread on the Amp resistant plate, and ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Embodiment 2, as figure 1 As shown, the construction of Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria II
[0064] The acetyl phosphorylase gene (pta) and the acetate kinase gene (ackA) of Escherichia coli genetically engineered strain I were knocked out to construct Escherichia coli genetically engineered strain II.
[0065] Such as figure 2 As shown, the gene knockout adopts the method of two-step homologous recombination.
[0066] In the first step, the NDA sequences of ackA and pta genes were found in the NCBI database, and primers ackA-pta-F / ackA-pta-R were designed based on this, where ackA-pta-F included 50bp upstream of ackA and cat-sacB ackA-pta-R includes 50 bp upstream of ackA, 50 bp downstream of pta, and 25 bp downstream of cat-sacB. The plasmid p EASY-cat-sacB was used as a template for PCR amplification. The primer sequences are:
[0067] ackA-pta-F (SEQ ID NO: 9):
[0068] CTATGGCTCCCTGACGTTTTTTTAGCCACGTATCAATTATAGGTACTTCCGTGACGGAAGATCACTTCGCAGA ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3, as figure 1 As shown, the construction of Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria III
[0075] The pyruvate oxidase (poxB) of Escherichia coli genetically engineered strain II was knocked out to construct Escherichia coli genetically engineered strain III.
[0076] Such as figure 2 As shown, the gene knockout adopts the method of two-step homologous recombination.
[0077] In the first step, the NDA sequence of the poxB gene was found in the NCBI database, and based on this, the primers poxB-F / poxB-R were designed, wherein poxB-F included 50 bp upstream of poxB, 50 bp downstream of poxB and 25 bp upstream of cat-sacB, poxB-R includes 50 bp downstream of poxB and 25 bp downstream of cat-sacB. PCR amplification was performed using the plasmid p EASY-cat-sacB as a template. The primer sequences are:
[0078] poxB-F (SEQ ID NO: 11):
[0079] TATGCCCGATGATATTCCTTTCATCGGGCTATTTAACCGTTAGTGCCTCCAAAGGGTGGCATTTCCCGTCATAATAAGGACATGCCATGATTGATTTACGGTGAC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com