Biological improvement synthesis method of glutaric acid
A synthetic method, glutaric acid technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problem of loss of yield and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
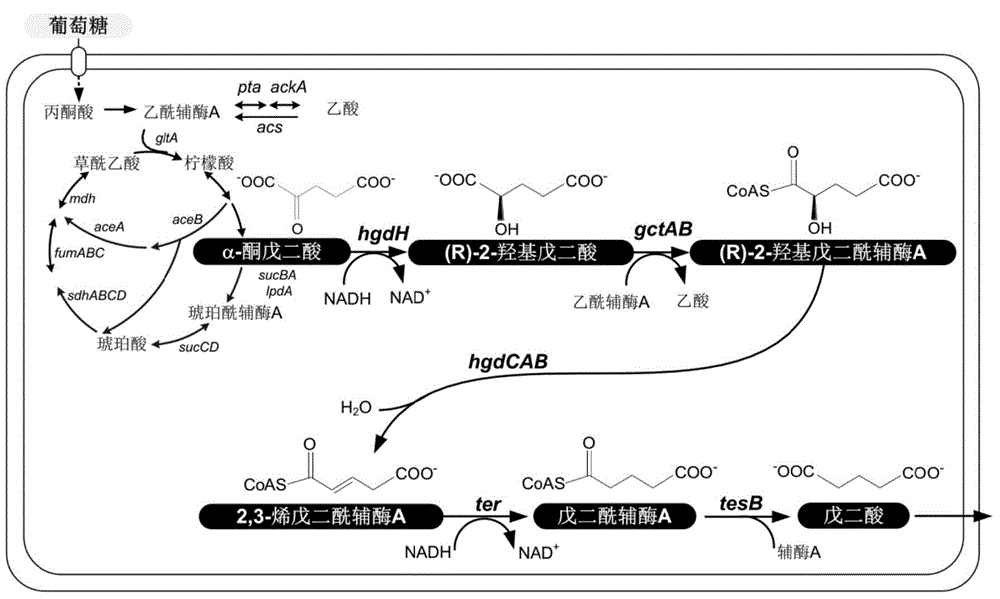
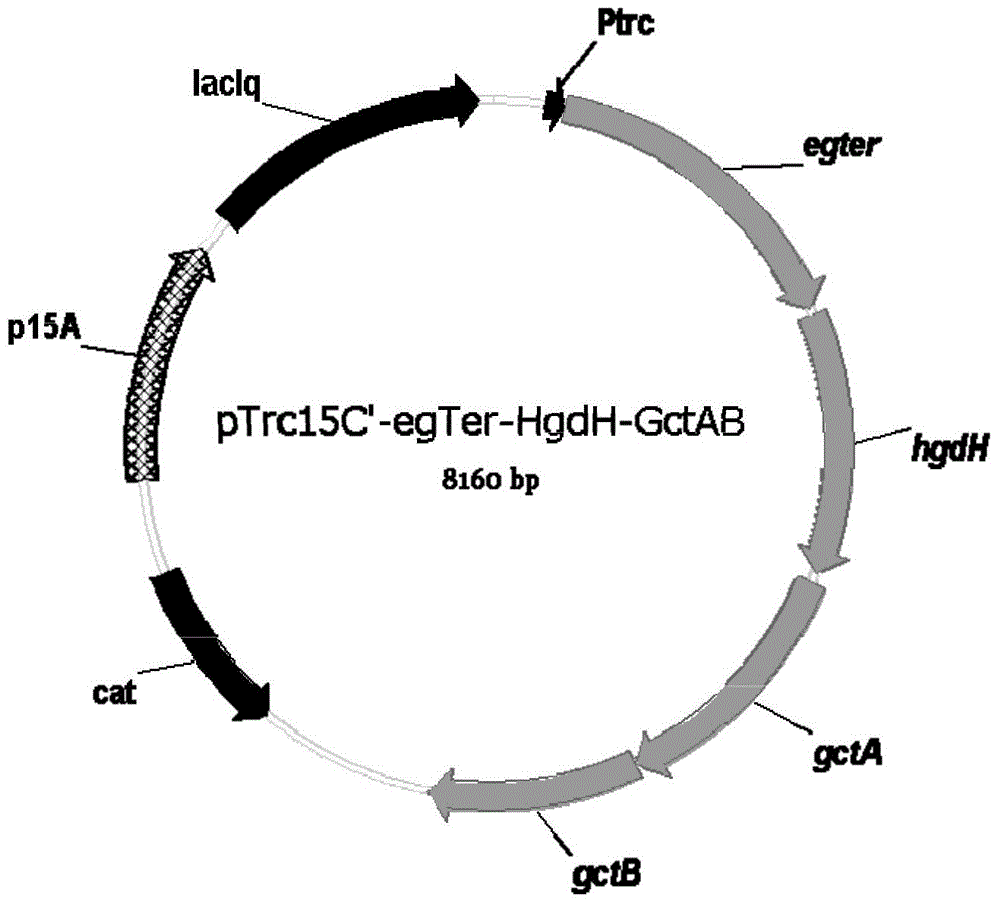
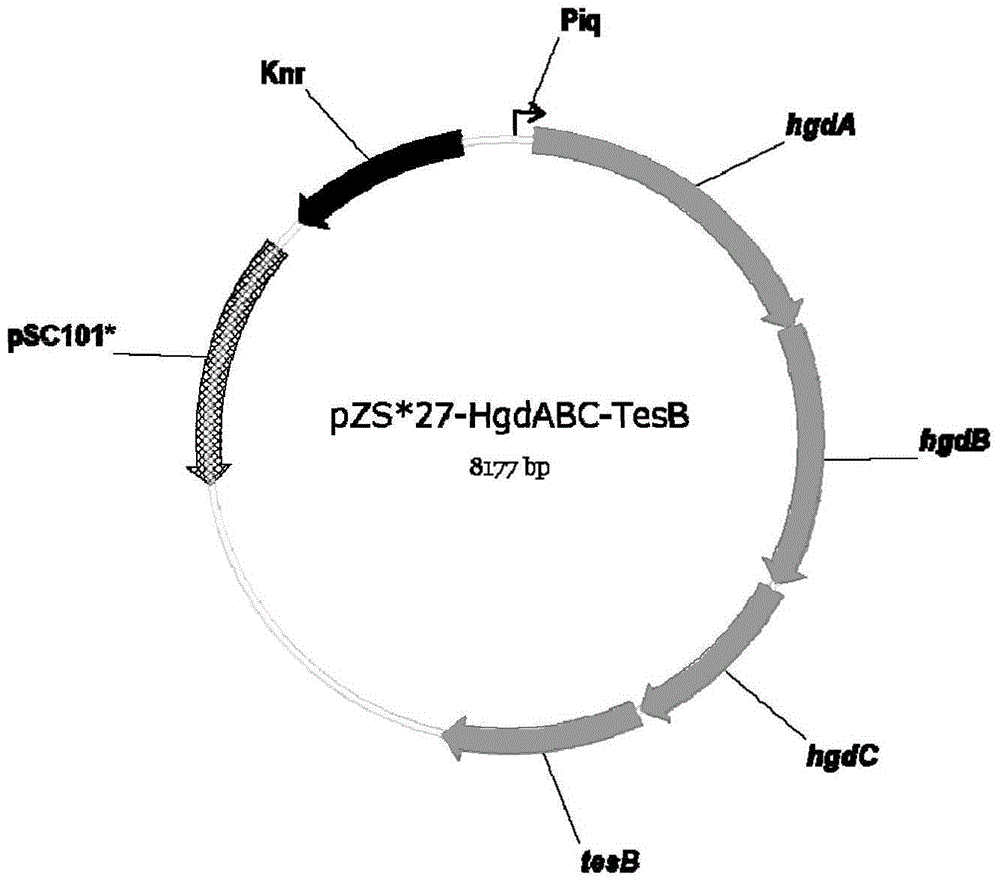
[0034]The construction of the biosynthetic pathway in this example is based on the heterologous expression of expression plasmids. The strains, plasmids, enzymes and culture media used include: the expression plasmids are pTrc15C'-egTer-HgdH-GctAB and pZS*27-HgdABC ‐TesB; expression host is E. coli MG1655; cloning host is E. coli DH5α; genetic manipulation tools include: restriction endonuclease, DNA polymerase, T4 DNA ligase; LB medium: each liter contains pancreatic Peptone 10g, yeast extract 5g, sodium chloride 10g, chloramphenicol concentration is 50mg / L, and kanamycin concentration is 50mg / L, and its specific steps include:
[0035] 1) PCR amplification and construction of recombinant plasmids: design primer sequences, amplify with the whole genome sequence of the corresponding strain or whole gene synthetic DNA as a template, cut with endonuclease and connect to the expressed On the plasmid vector, wherein: egter, hgdH, gctA and gctB are expressed in the pTrc15C' plasmid...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Fermentative Production of Glutaric Acid Using Recombinant Strains
[0055] Strains and culture conditions:
[0056] The medium used by the E.coli MG1655 recombinant Escherichia coli is a fermentation medium, specifically pH 7.4 supplemented Stand I medium, and its components and contents are: 15g / L beef peptone, 3g / L yeast extract, 50mM 3‐(N‐morpholine)propanesulfonic acid, 3mM L‐cysteine, 10mM sodium glutamate, 0.2mM riboflavin, 2mM ferric citrate.
[0057] The E.coli MG1655 recombinant Escherichia coli was first activated by LB medium, and then the initial inoculum was OD 600 =0.1 into the supplemented Stand I medium, and the cells were cultured to OD at 37°C 600 When it was about 1.0, 100 μM IPTG was added and cultured at 30° C. for several days.
[0058] In the above cultivation process, according to the difference in oxygen supply, it is divided into aerobic, microaerobic and anaerobic cultivation. Under aerobic conditions, the cells were cultured in a 100ml s...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Catalytic ability of different thioesterases for the hydrolysis of glutaryl-CoA.
[0065] In Example 2, the last reaction step, ie, the hydrolysis of glutaryl-CoA to glutaric acid, was catalyzed by the thioesterase TesB of Escherichia coli. TesB originally catalyzes the hydrolysis of short- and medium-chain fatty acyl-CoA in E. coli, but it is also active on some other substrates, including glutaryl-CoA. On the other hand, there are many different thioesterases in organisms, and their substrate selectivity and activity are different. Therefore, it is necessary to screen enzymes with higher activity for hydrolysis of glutaryl-CoA.
[0066] Strains and culture conditions:
[0067] The enzymes in this example were obtained through exogenous expression and purification. The exogenous protein expression host is E.coli BL21(DE3), the expression vector is pET-28a(+), and the gene to be expressed is inserted into the expression vector by restriction endonuclease for expressi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com