Light-emitting devices providing asymmetrical propagation of light
A technology of light-emitting devices and light-emitting elements, which is applied in the direction of lighting devices, components of lighting devices, semiconductor devices of light-emitting elements, etc., and can solve problems such as light energy loss and conversion properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
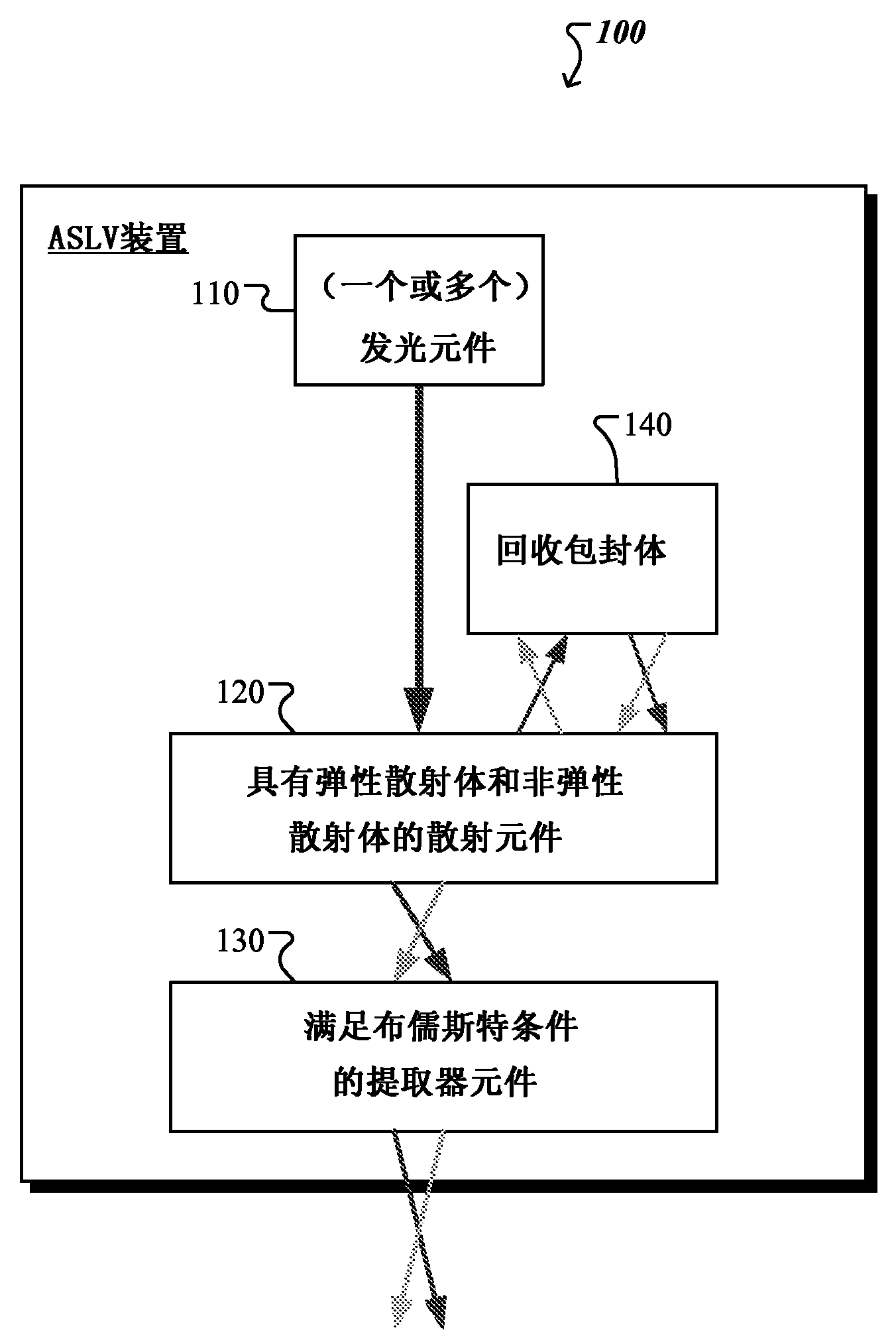
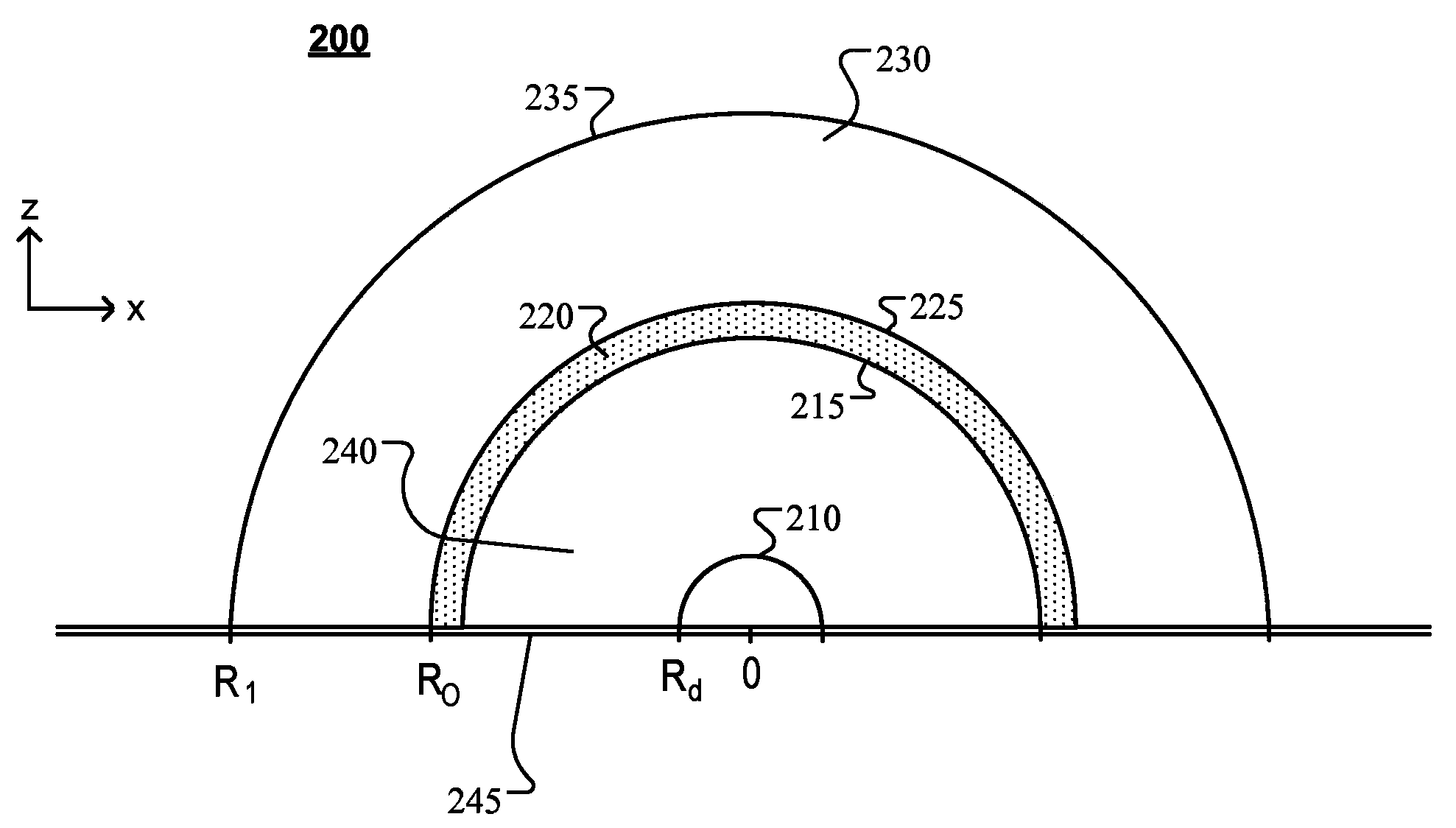
[0201] Figure 1A A schematic diagram showing an example of a light emitting device 100 comprising a light emitting element 110 (LEE), a scattering element 120 (also called first optical element), an extractor element 130 (also called second optical element) and recover the envelope 140 . The light emitting device 100 efficiently provides broadband homogeneous light to the surrounding environment across a wide range of angles.
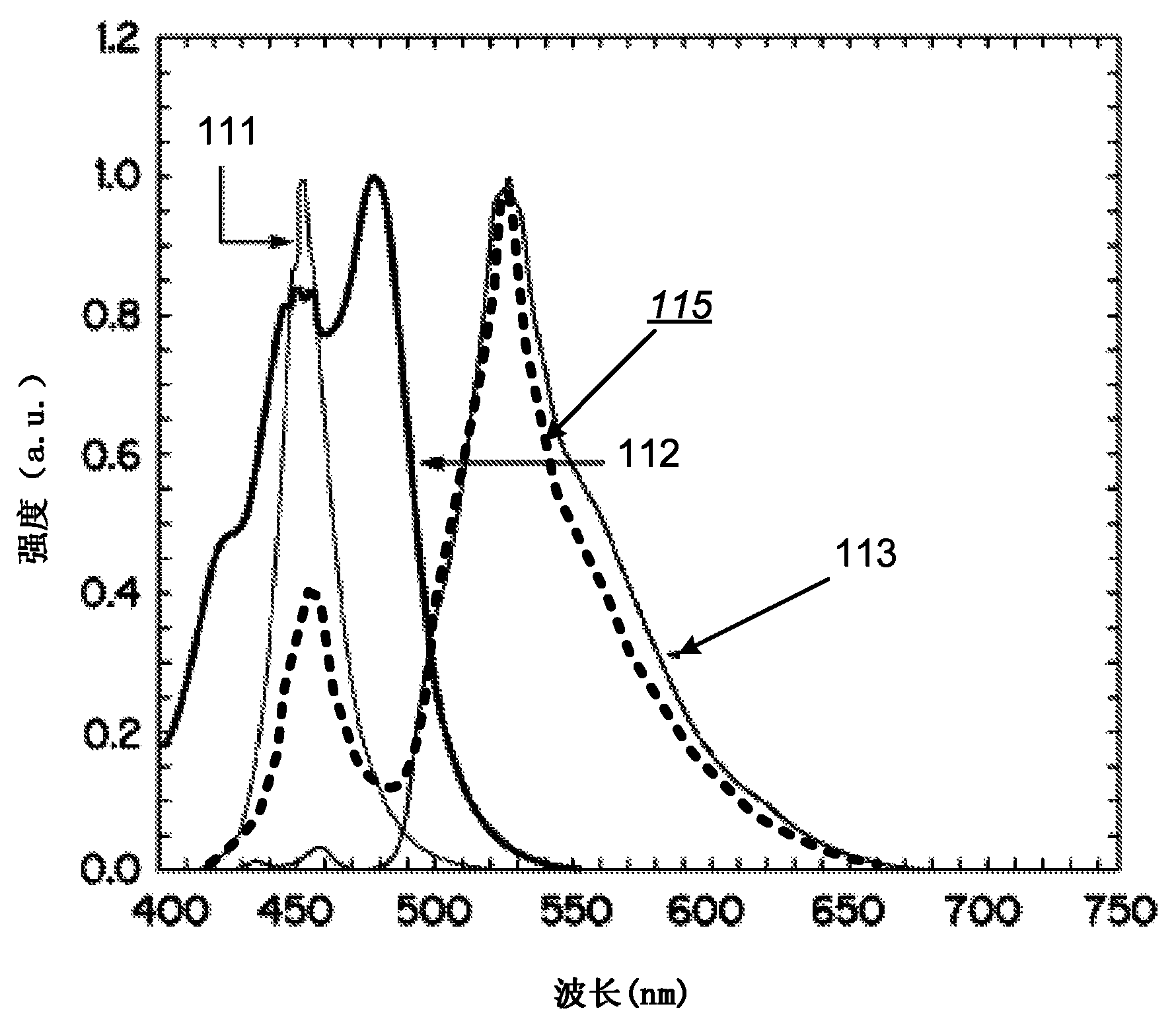
[0202] Light emitting element 110 is configured to generate and emit light during operation. For example, the spectral power distribution of the light (also referred to as pump light) emitted by the light emitting element 110 can be blue. The spectral power distribution of visible light is known as chromaticity. For example, in general, light-emitting element 110 is one that emits in a region or combination of regions of the electromagnetic spectrum for the visible, infrared, and / or ultraviolet regions when energized by applying a potential differenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com