Tellurium zincium vestalium thin-film solar cell
A solar cell, cadmium zinc telluride technology, which is applied to circuits, photovoltaic power generation, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of small shunt resistance of batteries, increase production costs, reduce solar cell performance, etc., to widen the spectral absorption range, improve Effectiveness of utilization efficiency, improvement of photoelectric conversion efficiency and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] The specific embodiment of the present invention is described in detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
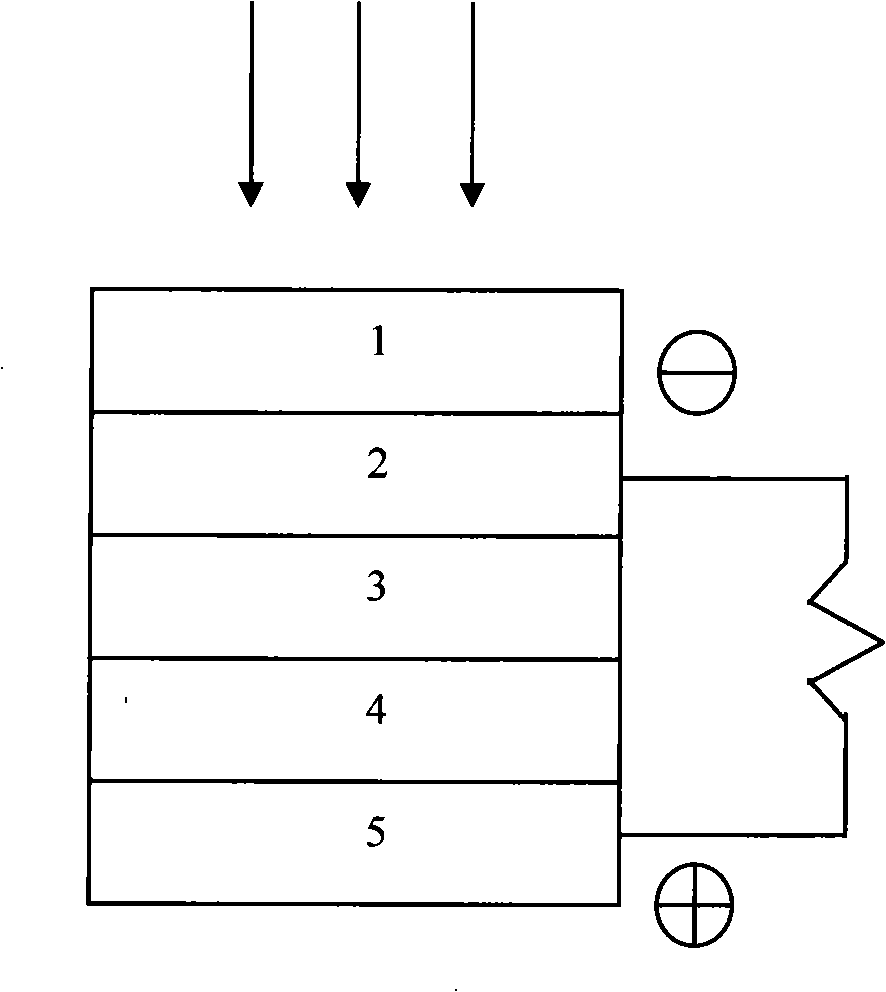
[0018] See figure 1 , the thin-film solar cell of the present invention comprises: a glass substrate 1, on which a transparent conductive oxide front electrode layer 2, an n-type CdS window layer 3, and a p-type CdS window layer 3 are sequentially deposited. 1-x Zn x Te absorption layer 4, back contact electrode layer 5.
[0019] The preparation technology of thin film solar cell of the present invention is as follows:
[0020] 1. The transparent conductive oxide front electrode layer 2 is thermally deposited on the surface of the glass substrate 1, and the transparent conductive oxide film can be ITO, SnO 2 : F, a kind of thermal deposition in ZnO: Al, the thickness of the front electrode layer 2 is 800-1500 nanometers.
[0021] 2. Depositing an n-type CdS window layer 3 on the front electrode layer 2 by magnetron sputtering, with a thickness of...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com