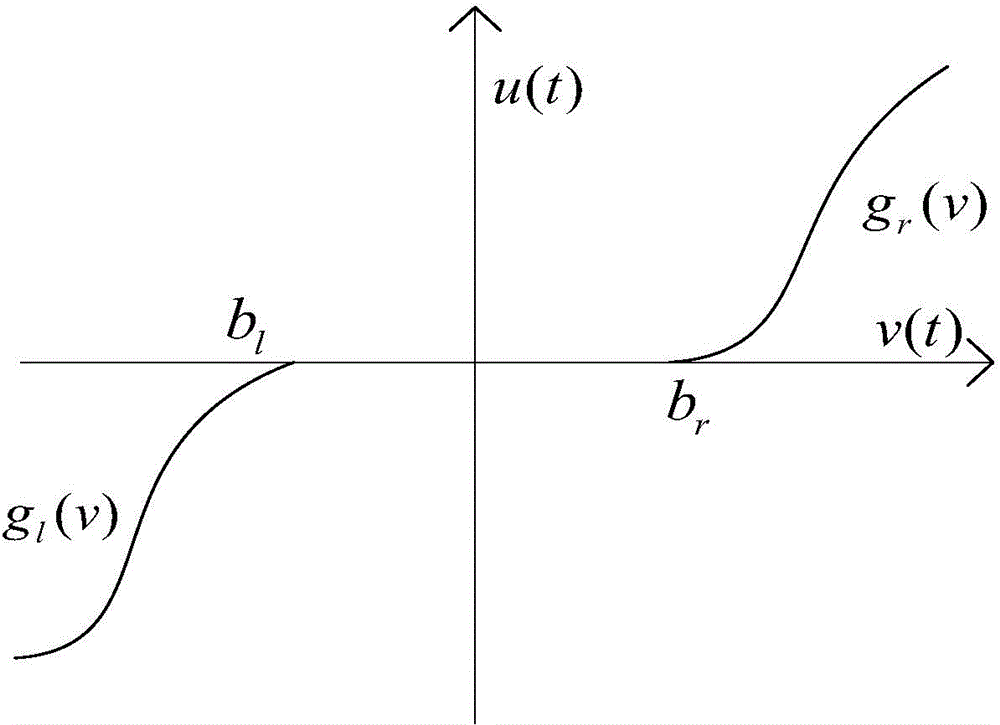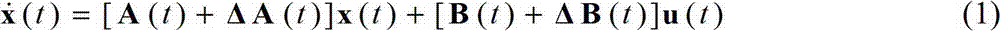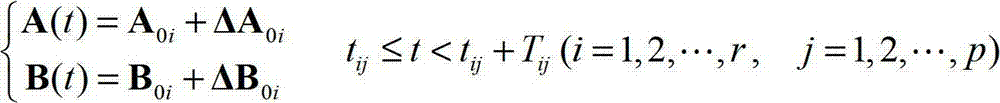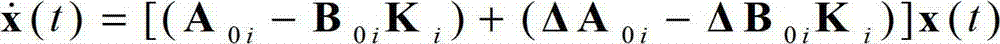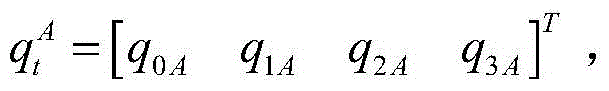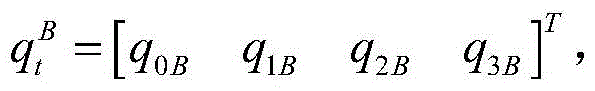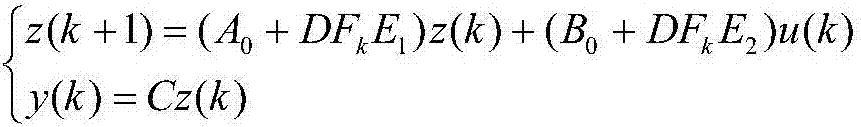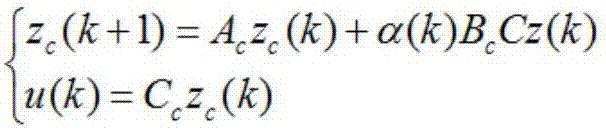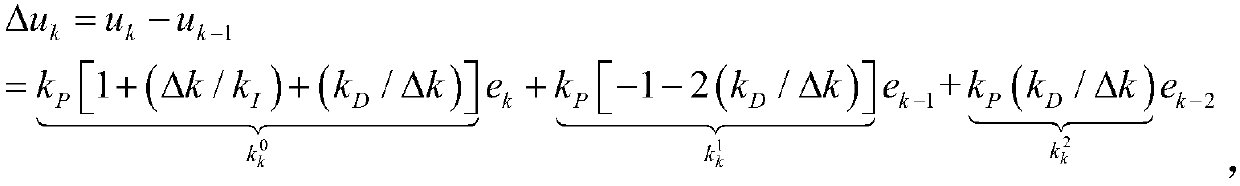Patents
Literature
98 results about "Time-variant system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A time-variant system is a system whose output response depends on moment of observation as well as moment of input signal application. In other words, a time delay or time advance of input not only shifts the output signal in time but also changes other paramters and behavior. Time variant systems respond differently to the same input at different times. The opposite is true for time invariant systems(TIV).
Method for real-time nonlinear system state estimation and control
InactiveUS6285971B1Computation using non-denominational number representationAdaptive controlOperating pointEngineering
A method for the estimation of the state variables of nonlinear systems with exogenous inputs is based on improved extended Kalman filtering (EKF) type techniques. The method uses a discrete-time model, based on a set of nonlinear differential equations describing the system, that is linearized about the current operating point. The time update for the state estimates is performed using integration methods. Integration, which is accomplished through the use of matrix exponential techniques, avoids the inaccuracies of approximate numerical integration techniques. The updated state estimates and corresponding covariance estimates use a common time-varying system model for ensuring stability of both estimates. Other improvements include the use of QR factorization for both time and measurement updating of square-root covariance and Kalman gain matrices and the use of simulated annealing for ensuring that globally optimal estimates are produced.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
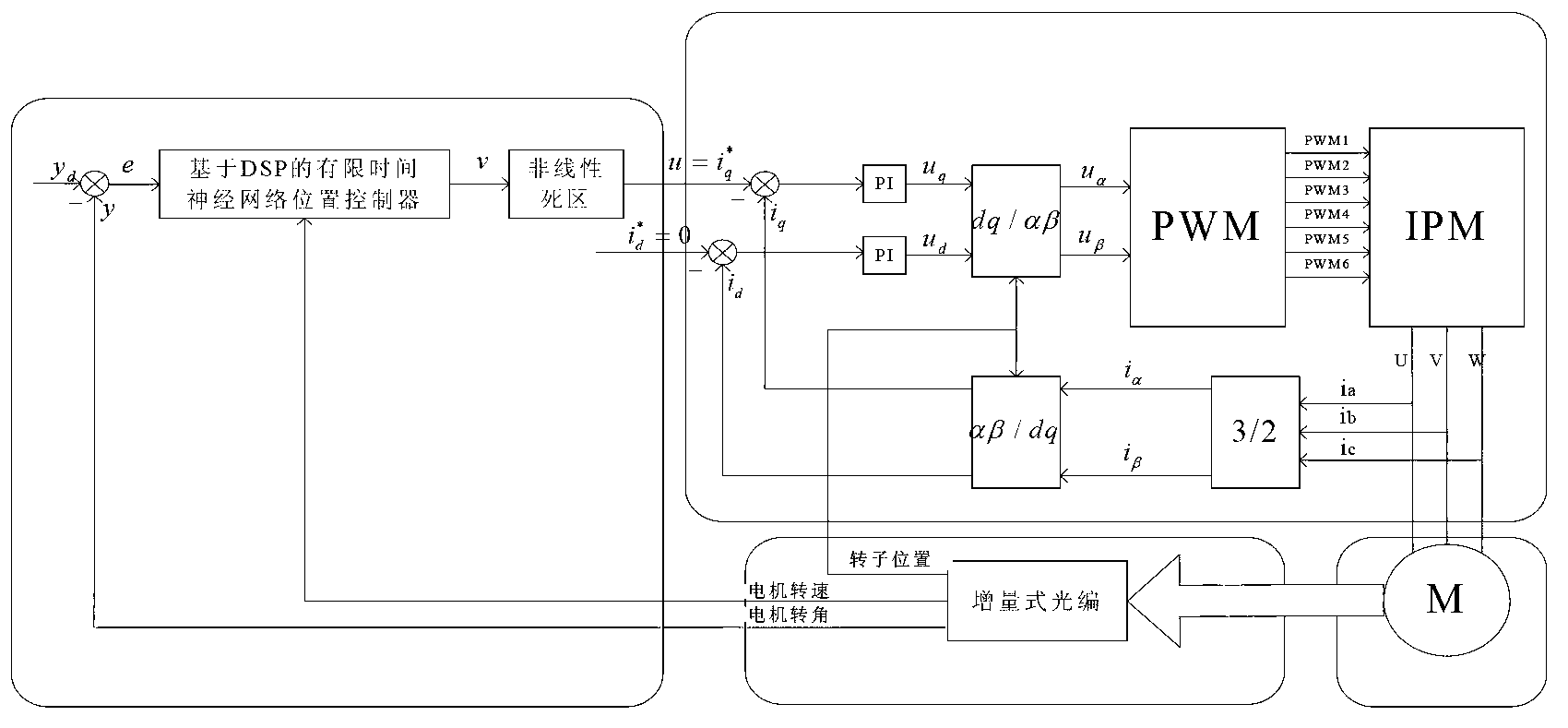
Limit time cooperative control method of mechanical arm servo system
InactiveCN104216284AAvoid Dead Zone Additional Inverse CompensationAvoid High Frequency ChatteringAdaptive controlDynamic modelsTime-variant system
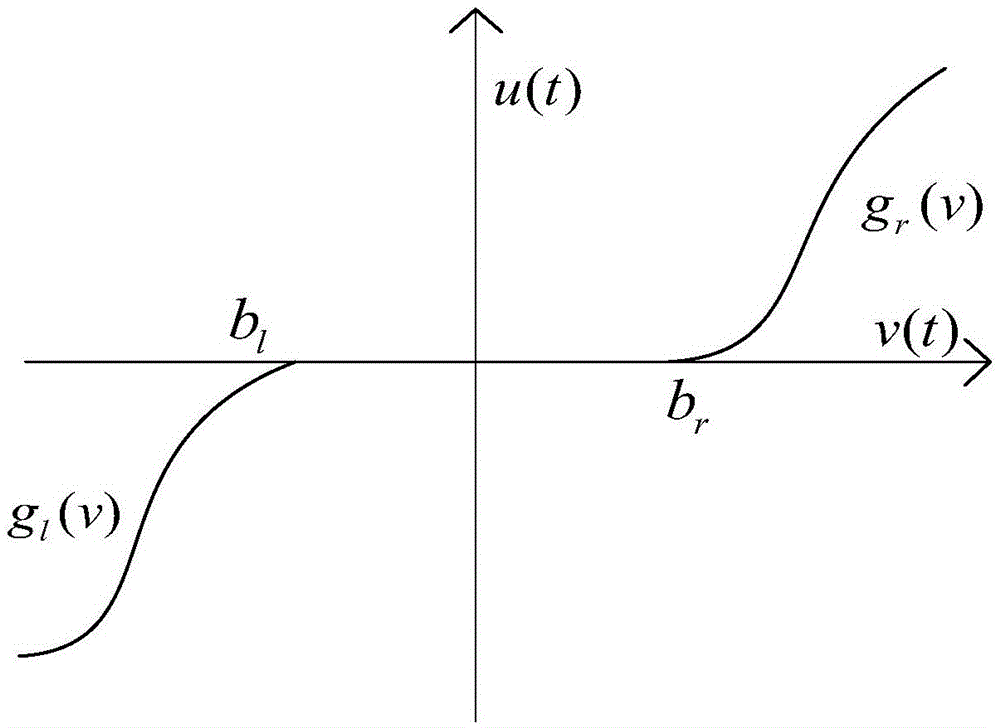
A limit time cooperative control method of a mechanical arm servo system includes: building the dynamic model of the mechanical arm servo system, and initiating the system state, sampling time and related control parameters; approximating the nonlinear input dead zone linearity in the system into a simple time-varying system according to the differential mean value theorem, and deriving a mechanical arm servo system model with an unknown dead zone; calculating the tracking error, the non-singular terminal sliding mode surface and the first derivative of a control system; selecting a neural network approximation unknown function on the basis of the mechanical arm servo system model with the unknown dead zone, designing a neural network limit time cooperative controller according to the system tracking error and the non-singular terminal sliding mode surface, and updating a neural network weight matrix. By the method, additional inverted compensation of a nonlinear dead zone can be avoided, sliding model high-frequency buffeting is reduced, and limit time fast tracking of the mechanical arm servo system is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Rotary-table servo system neural network control method
ActiveCN103197562AAvoid complex calculationsImprove algorithm efficiencyAdaptive controlDynamic modelsNetwork approach
A rotary-table servo system neural network control method comprises (1) building a mechanical dynamic model of a permanent magnet synchronous motor rotary-table servo system, and initializing the system state, sampling time and relative control parameters; (2) according to the differential mean value theorem, enabling a non-linear input dead zone in the system to linearly approximate to a simple time-varying system, avoiding complex calculation of dead-zone inverse compensation, and finally inferring a rotary-table servo system model provided with an unknown dead zone; (3) at each sampling moment, calculating and controlling a system tracking error, a fast terminal sliding mode surface and a first-order derivative of the system; (4) based on the rotary-table servo system model provided with the unknown dead zone, selecting a neural network approaching unknown trend, designing an adaptive robust finite-time neural network controller according to the system tracking error, the fast terminal sliding mode surface and the first-order derivative of the system, and updating a neural network weight matrix; and (5) entering the next sampling moment, and repetitively executing the steps from (3) to (5).
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
State of charge (SOC) estimation method of variable length sliding window by identifying battery parameters
ActiveCN104360282AEffective trackingNo dependencyElectrical testingSpecial data processing applicationsVariable-length codeEstimation methods
The invention relates to an SOC estimation method of a variable length sliding window by identifying battery parameters. The method comprises the steps that the battery parameters are identified in real time by a variable length sliding window least square method, then the battery parameters are used for conducting self-adaptive extended Kalman filter to estimate the battery SOC, and therefore the influence of the battery parameter change caused by battery ageing on estimation precision of the battery SOC is avoided. According to the method, the time-varying battery parameters can be tracked effectively, and no dependency exists to the selection of initial data; the self-adaptive extended Kalman filter is more suitable for the state estimation of a nonlinear time-varying system; a matrix inversion operation is converted into scalar division operation, and better real-time performance is achieved.
Owner:奇瑞新能源汽车股份有限公司
Specified performance back-stepping control method of mechanical arm servo system
ActiveCN104698846AAvoid dead zone with additional compensationAvoid buffetingAdaptive controlDynamic modelsTime-variant system
The invention provides a specified performance back-stepping control method of a mechanical arm servo system. The method comprises the steps of constructing a dynamic model of the mechanical arm servo system; initializing the system state, sampling time and control parameters; linearly approximating a nonlinear input dead area of the system as a simple time varying system according to the differential mean value theorem; deviating a mechanical arm servo system model with the unknown dead area; calculating the tracking error of the control system, FC (funnel control) error variation and differential. With the adoption of the method, the problem of control buffeting of a sliding die can be reduced, the system of the dead area input on the system can be effectively avoided, and the specified performance control of the mechanical arm control system can be achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Non-affine uncertain system self-adaptive control method with range restraint
The present invention relates to a non-affine uncertain system self-adaptive control method with a range restraint. In combination with the characteristic that system input and states are subject to the range restraint, based on a mean value theorem, a non-affine system is converted into a time varying system (a strict feedback system) with a linear structure, and a varying interval of time-varying uncertain parameters of the time varying system is obtained. On the basis, a parameter adaptive projection technique is utilized to carry out online estimation on bounded uncertain time-varying parameters and external disturbances, and a parameter estimation error is compensated by using the nonlinear dynamic damping technology. Based on the nonlinear mapping technology, a restraint amount is mapped to the whole real number space to solve a state restraint problem of the system, thus to ensure the state is always within a restraint range. A hyperbolic tangent function and the Nussbaum gain technology are simultaneously utilized to solve the problem that system input is subject to the range restraint or the problem of input saturation and the potential problem of singular values of a controller, and the controller is designed in combination with a method of inversion, thereby solving the problem of self-adaptive control of the non-affine uncertain system with the range restraint.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
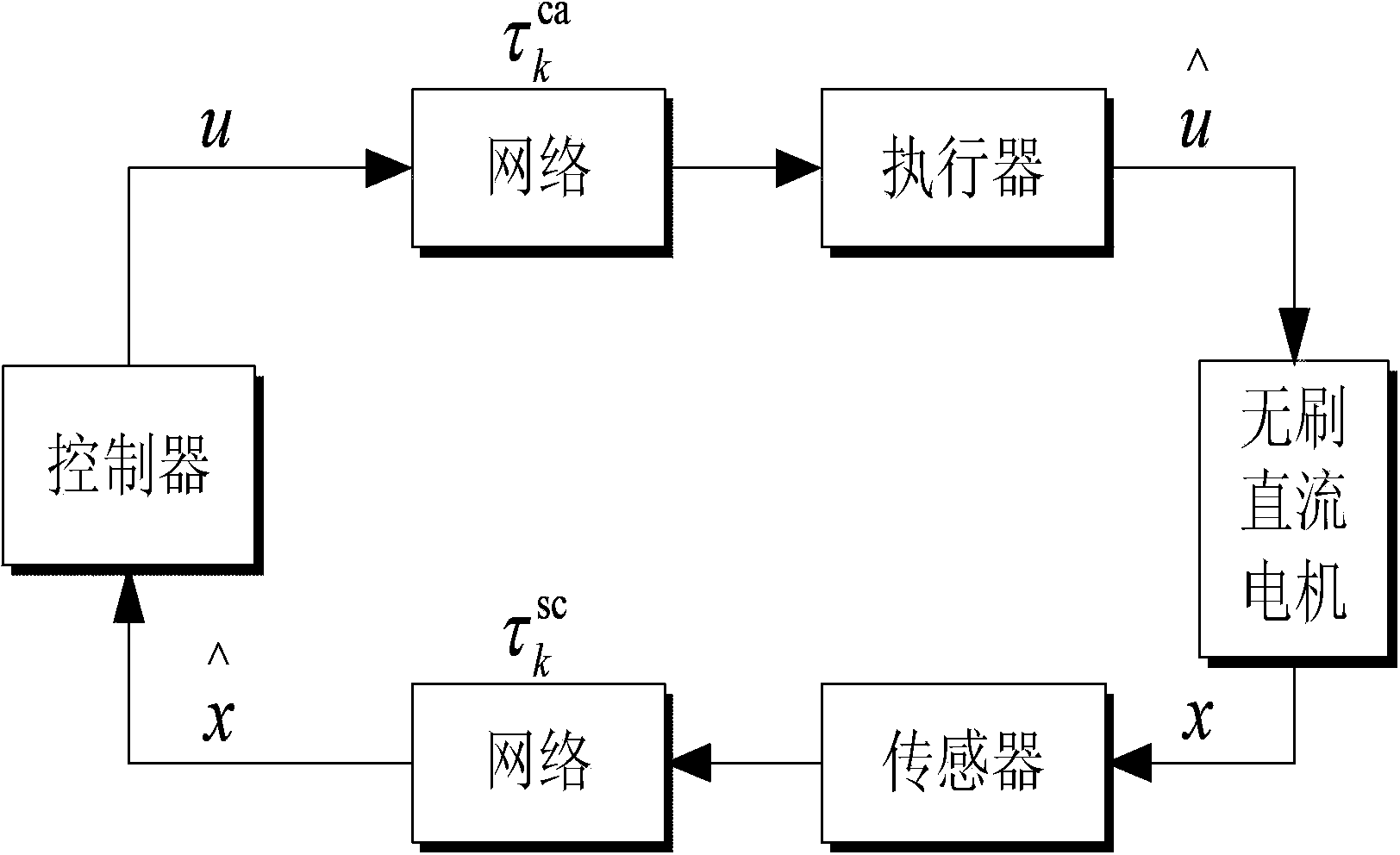
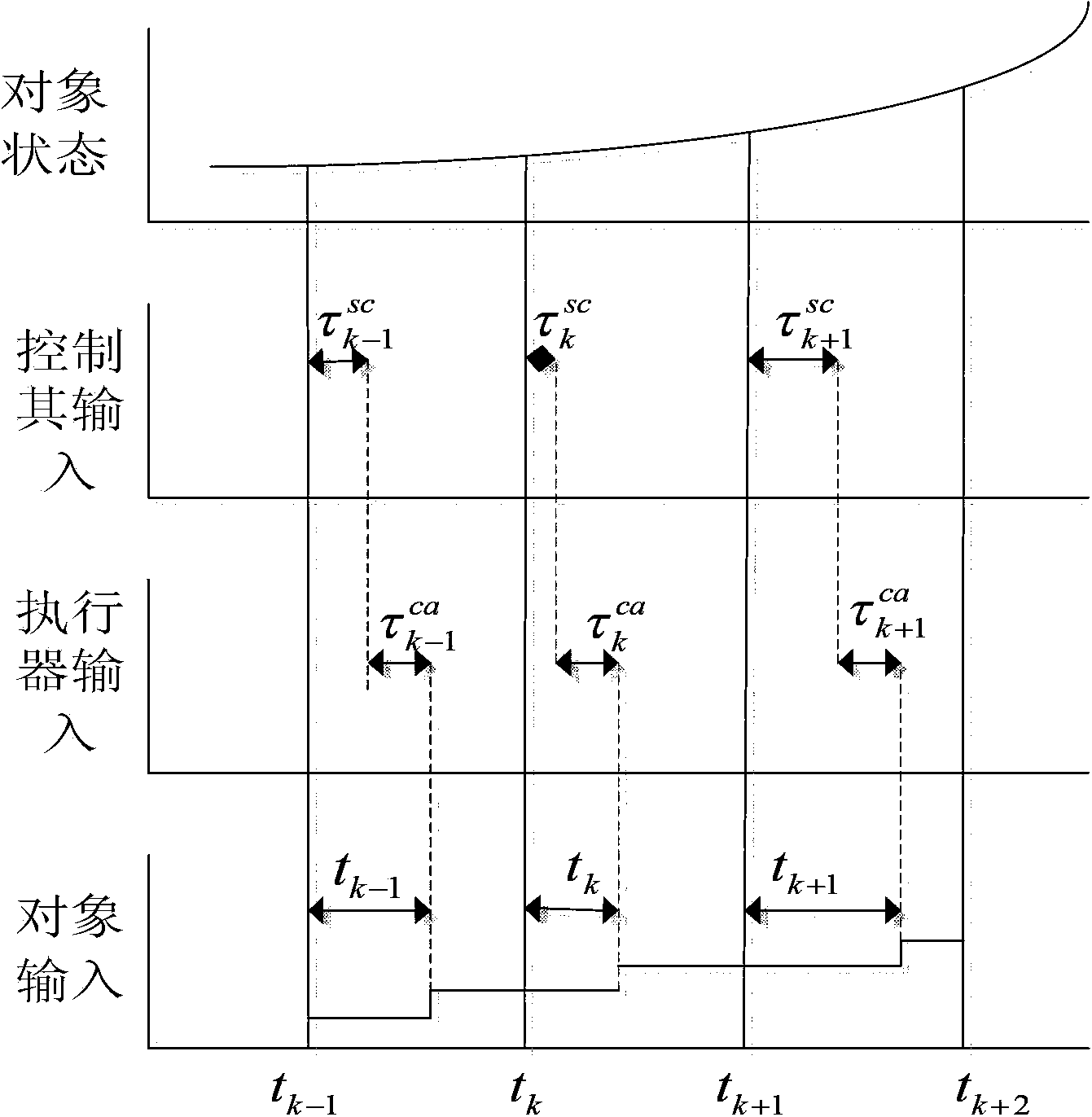
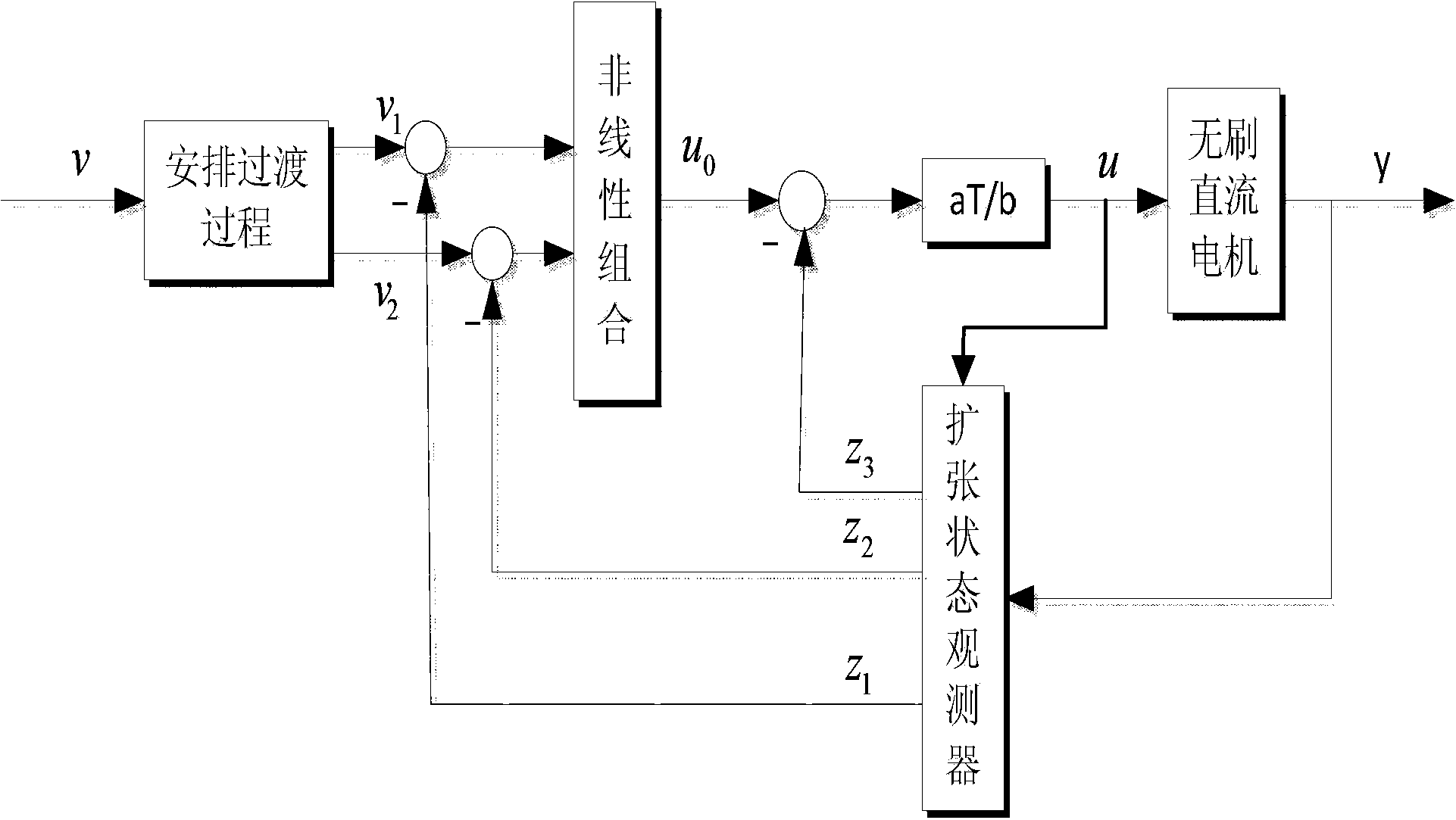
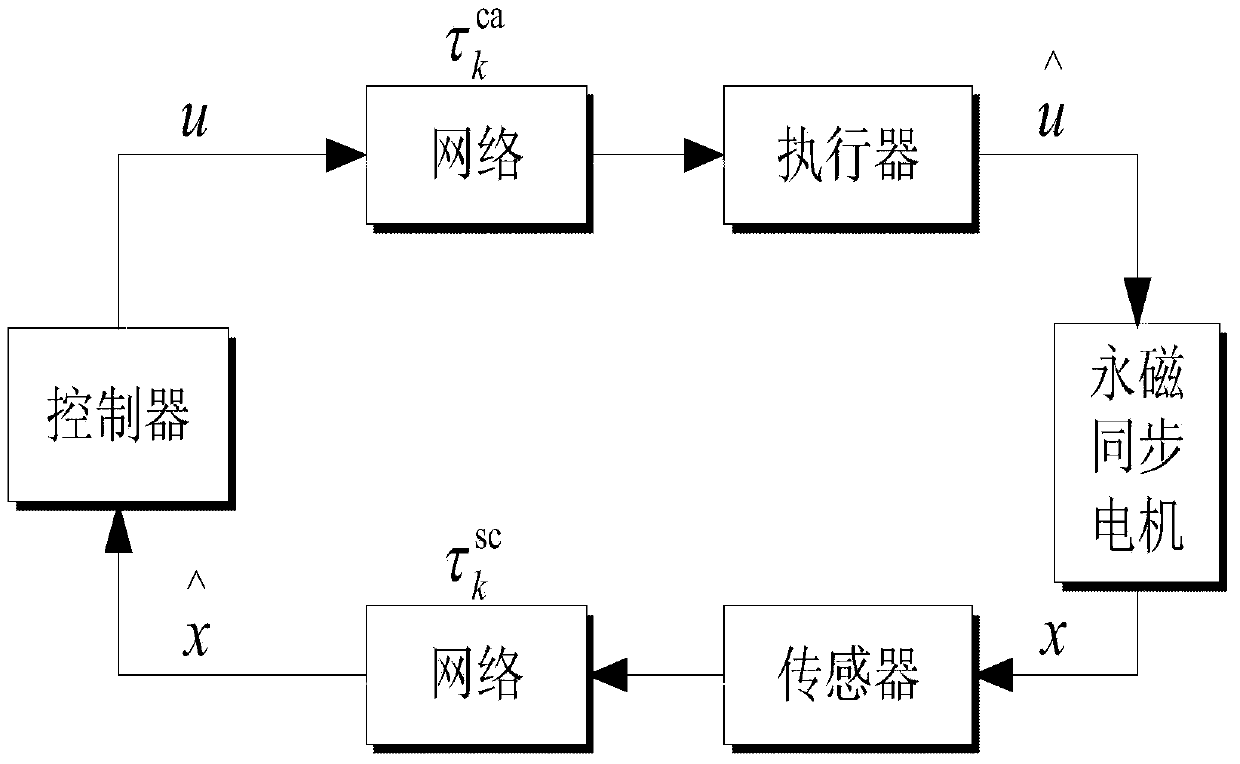
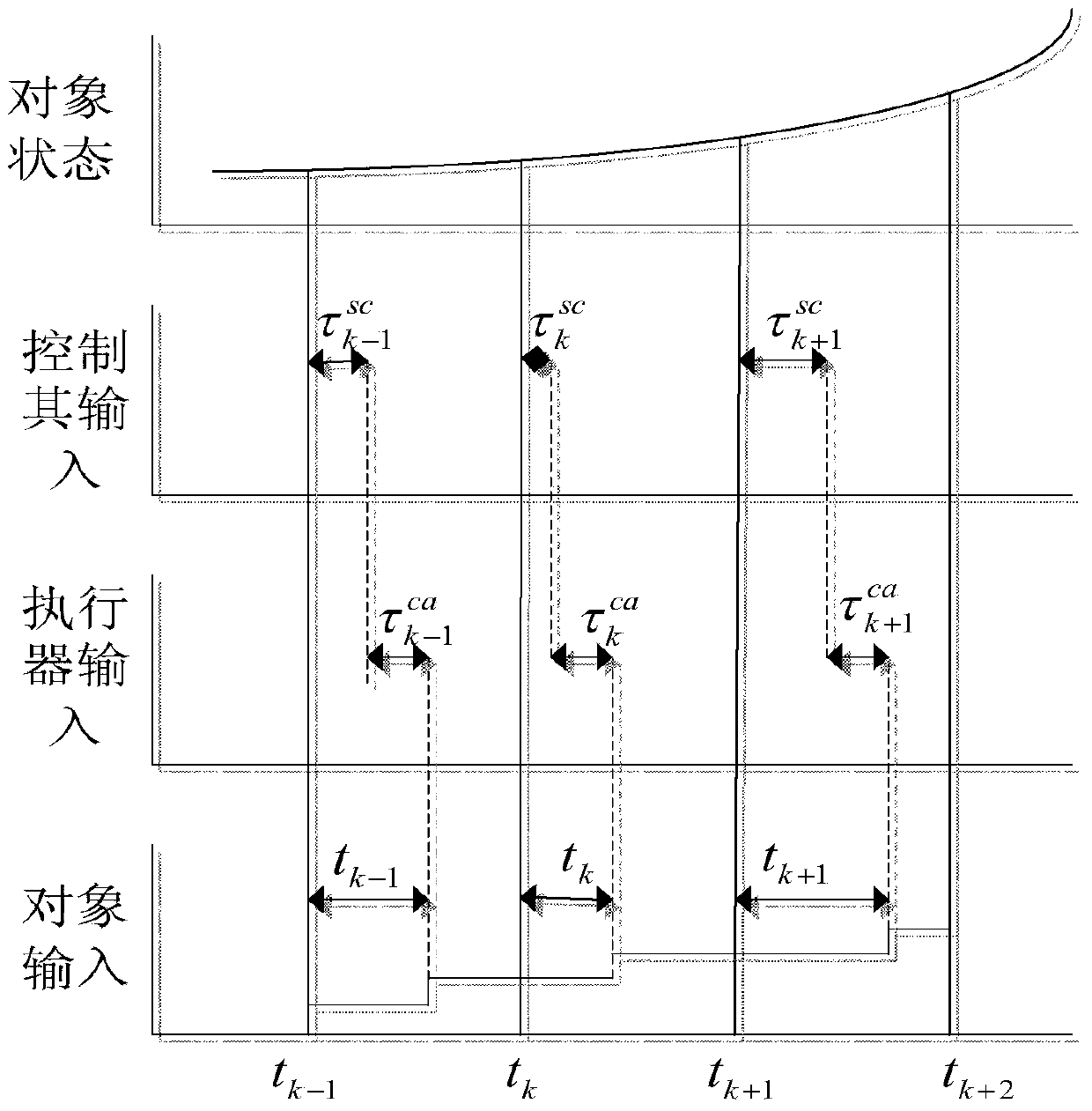
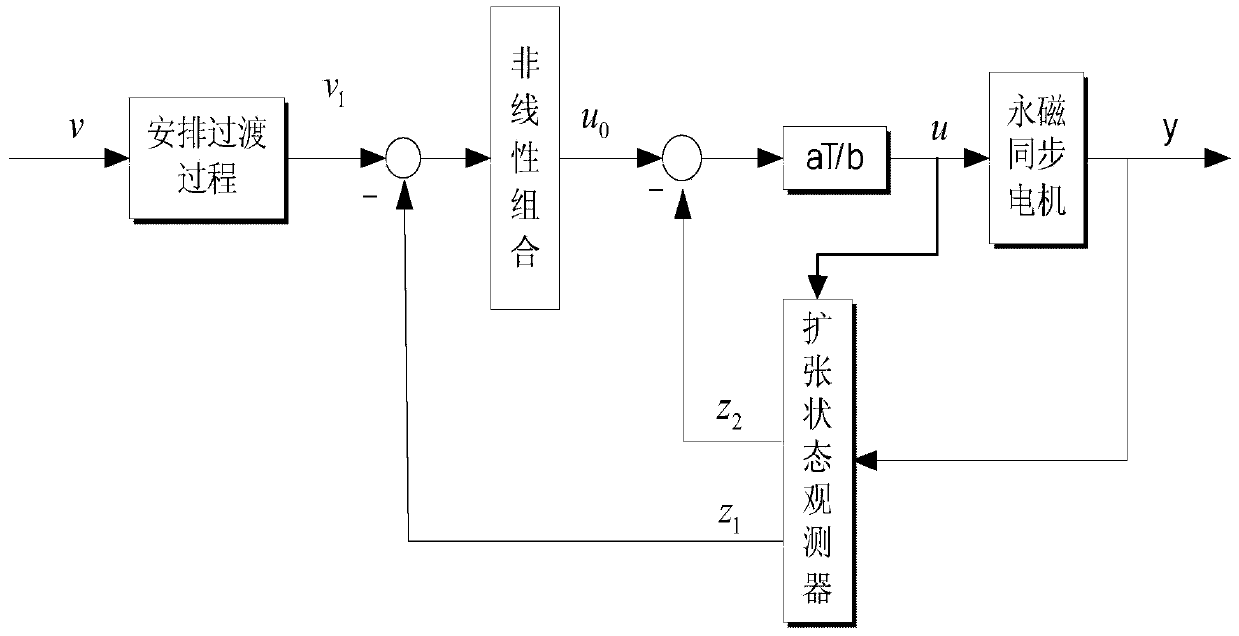
Networked brushless direct current motor time-delay compensation and control method using active-disturbance-rejection control technology
ActiveCN104142627AAccurate estimateSolving the difficult problem of accurate estimation of uncertain dynamicsAdaptive controlTime lagTime delays
The invention discloses a networked brushless direct current motor time-delay compensation and control method using the active-disturbance-rejection control technology. The method comprises the steps of (1) establishing a brushless direct current motor control system model containing time-varying network-induced delay, wherein the brushless direct current motor control system is described as a discrete time linear time-varying system containing single-step input time lag, and then the uncertain dynamic state, caused by time-varying delay, of the system is partially described as the additive noise of the system; (2) designing an extended state observer which is used for estimating the uncertain dynamic state caused by time-varying delay as a part of total disturbance; (3) conducting compensation on the time-varying delay item in the brushless direct current motor control system. The method can be used for effectively conducting real-time estimation and compensation on the uncertain dynamic state caused by time-varying network-induced delay by means of the extended state observer, and can well restrain the uncertainty caused by time delay, internal and external disturbance of the system and model uncertainty.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for designing controller of time-varying aircraft model with uncertainty
The invention discloses a method for designing a controller of a time-varying aircraft model with uncertainty, which is used for solving the technical problem that the existing robust control theory lacks design steps, so the flight controller is hard to design directly. The technical scheme is as follows: the time-varying system segmentation robust stability and solvability conditions are given, selection of desired closed-loop poles of linear time-varying system state feedback is directly utilized and a constraint condition inequality direct design feedback matrix is given according to the characteristic that all the real parts of all the desired closed-loop poles are negative, so that the engineering technicians in the research field directly design the flight controller for the time-varying aircraft model with uncertainty obtained through wind tunnel or flight tests, thus solving the technical problem that the current researches only give the robust stability inequality but can not directly design the flight controller.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
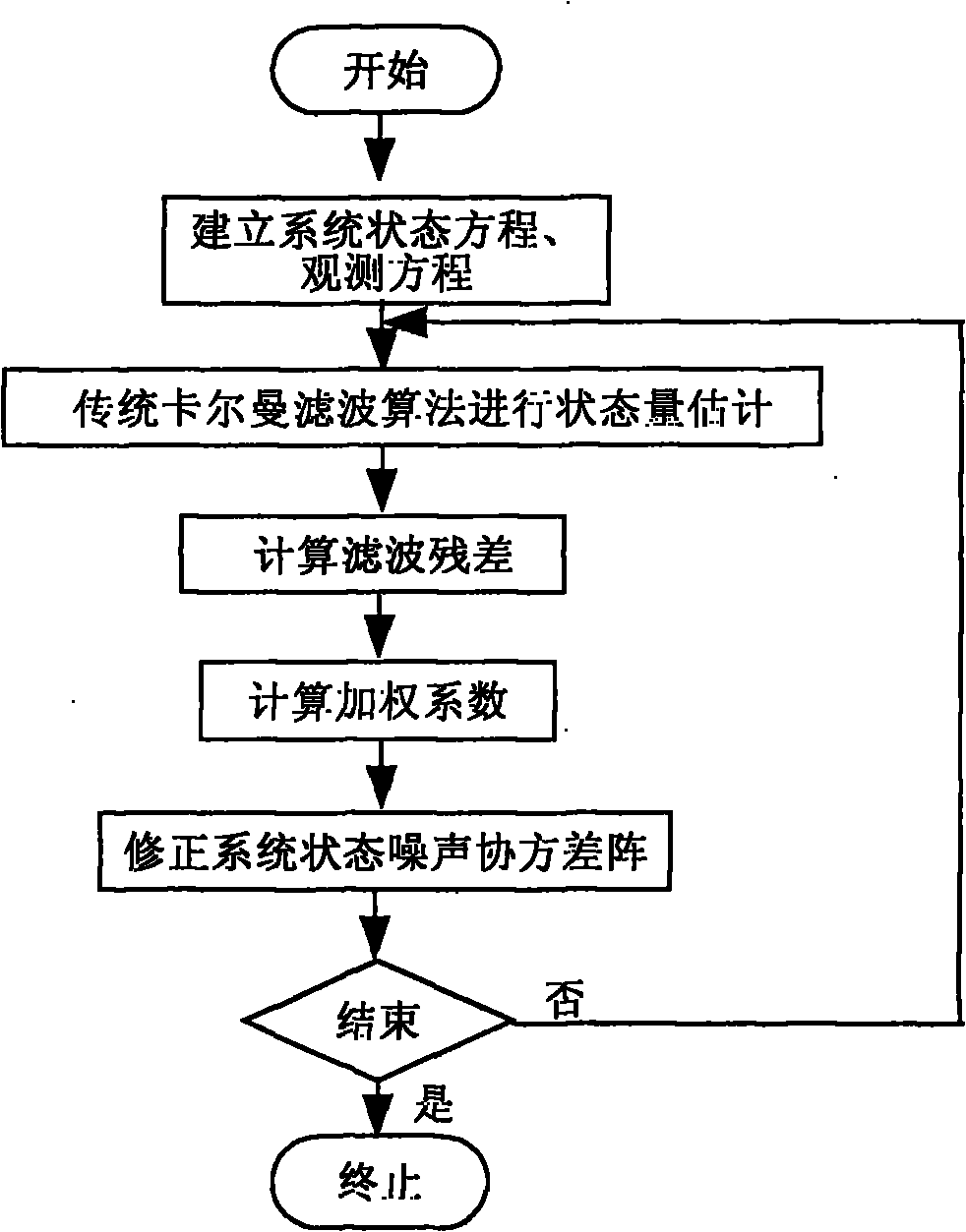
Unknown adaptive Kalman filter method for system model
InactiveCN101853243ASolve the problem that the filtering accuracy decreases or even divergesNavigation instrumentsComplex mathematical operationsDiffusionAlgorithm
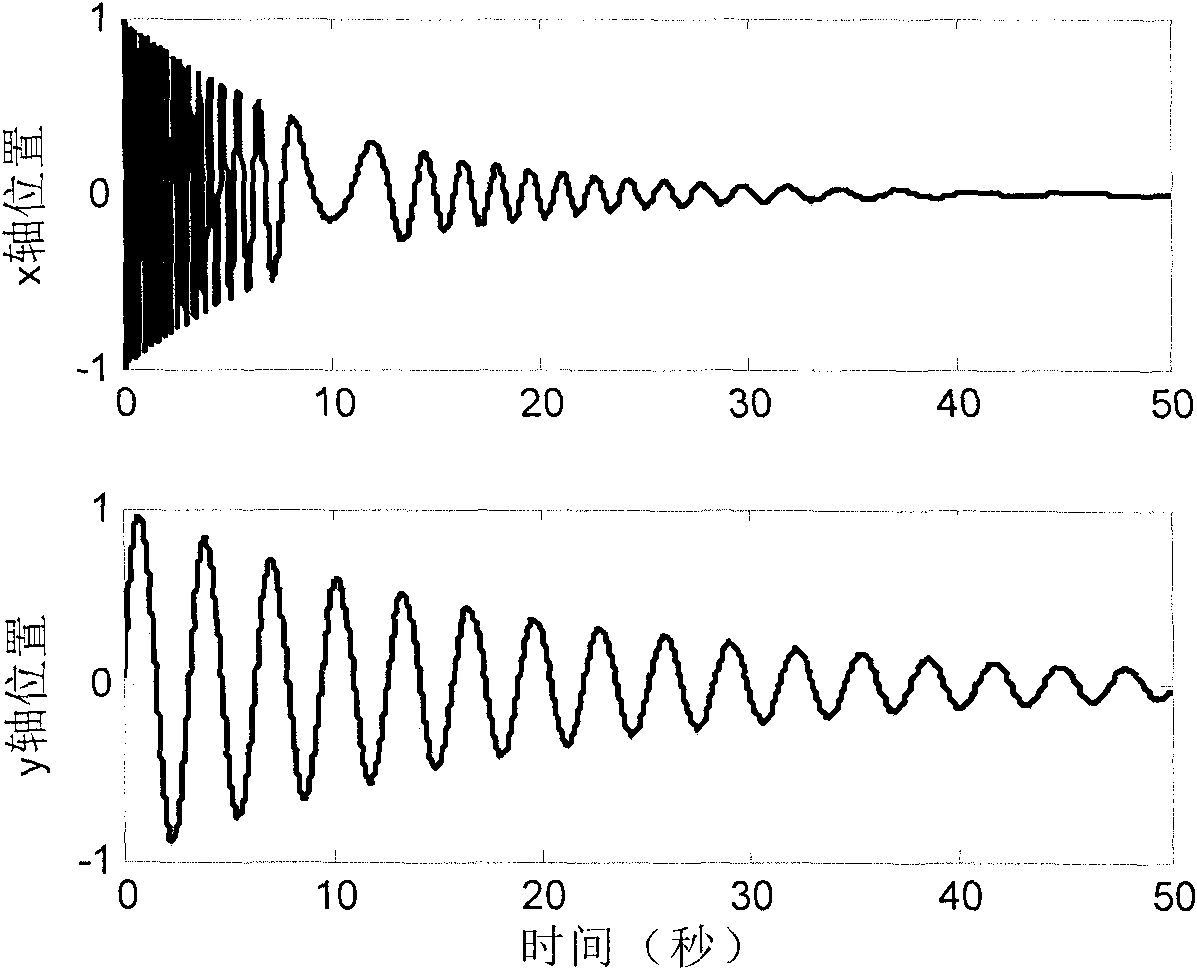
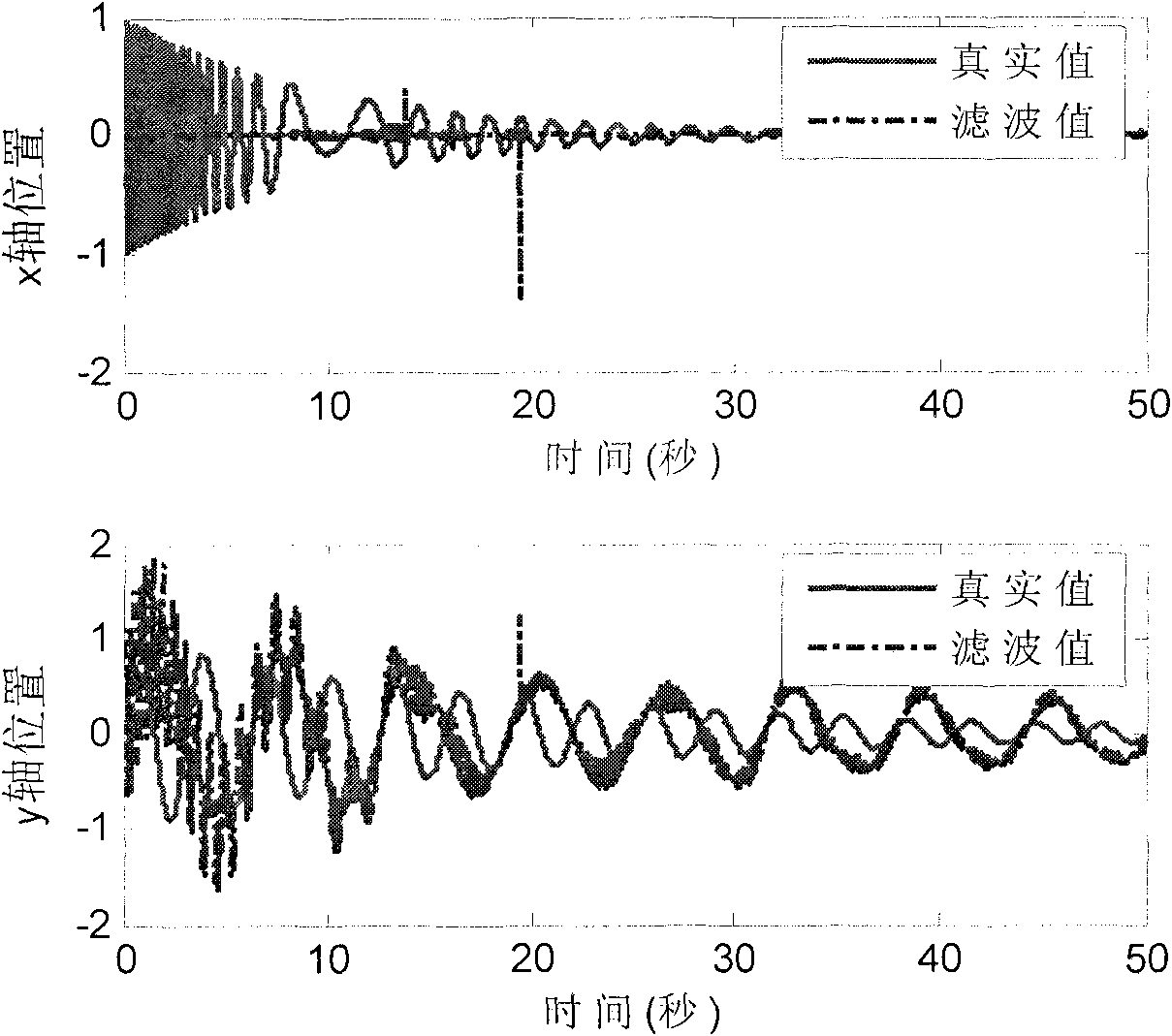
The invention discloses an unknown adaptive Kalman filter method for a system model, which aims at solving the problem that the filter of the Kalman filter method has reduced accuracy even is diffused under the condition that the system status model is unknown or time-variant. Aiming at the unknown or time-variant condition established by the system status model, information is adopted to calculate filter residues based on Kalman filter; a weighting efficient is calculated according to the filter residues and the ratio of measurement noise covariance; the noise covariance matrix of system status is revised in real time through the weighting efficient, so that the problem of accuracy reduction even diffusion of the Kalman filter caused by the unknown or time-variant system model can be solved effectively. Under equal conditions, the X axle filtering error mean is reduced to 0.0056 from 0.1231 in the prior art, and the Y axle filtering error mean is reduced to 0.0039 from 0.3895 in the prior art.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
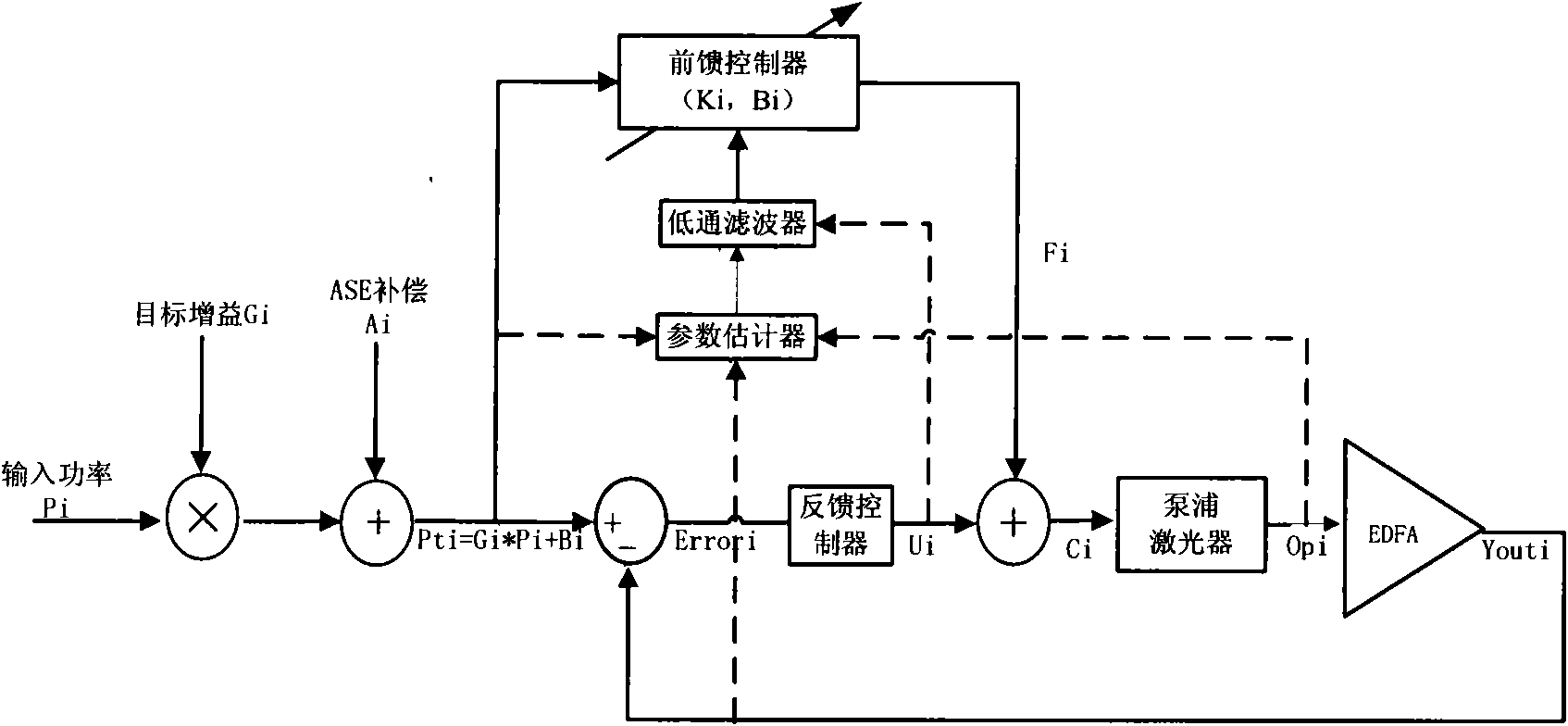
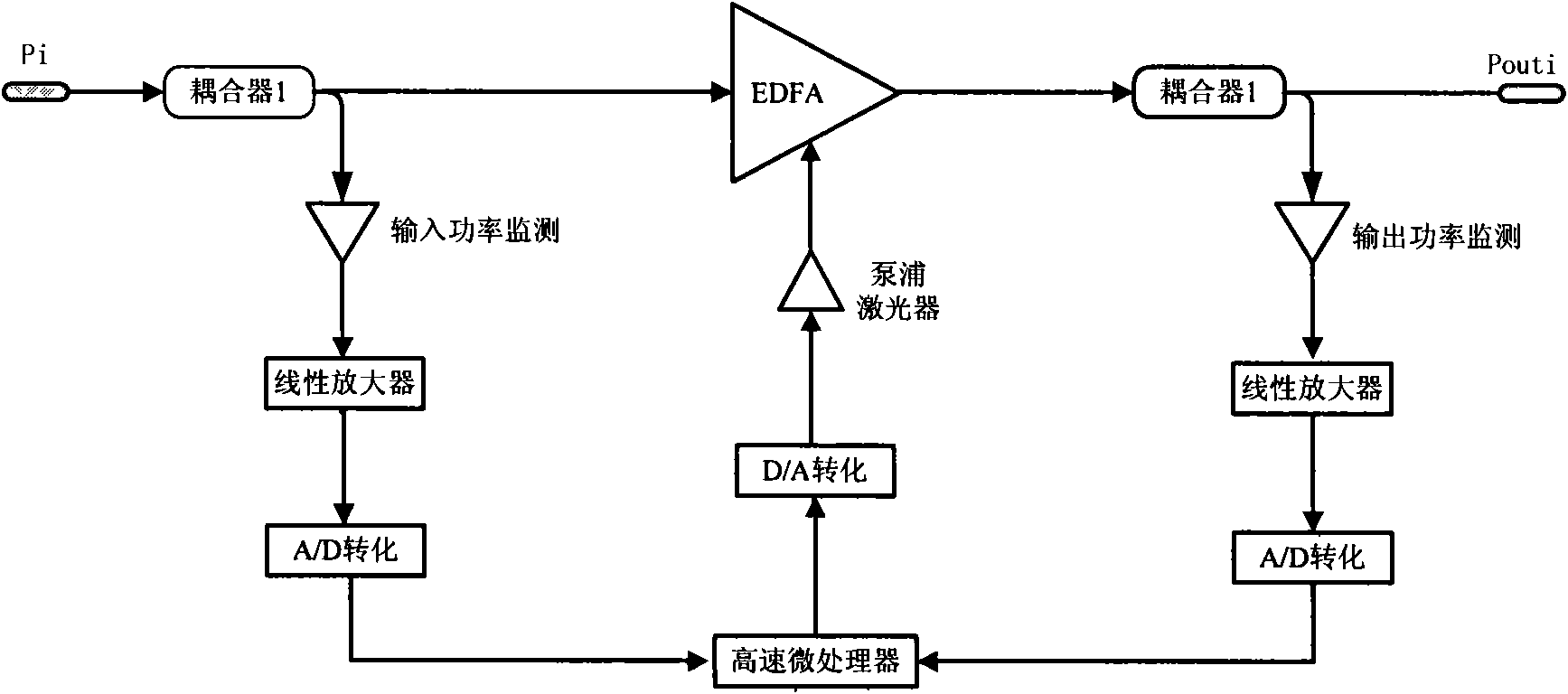
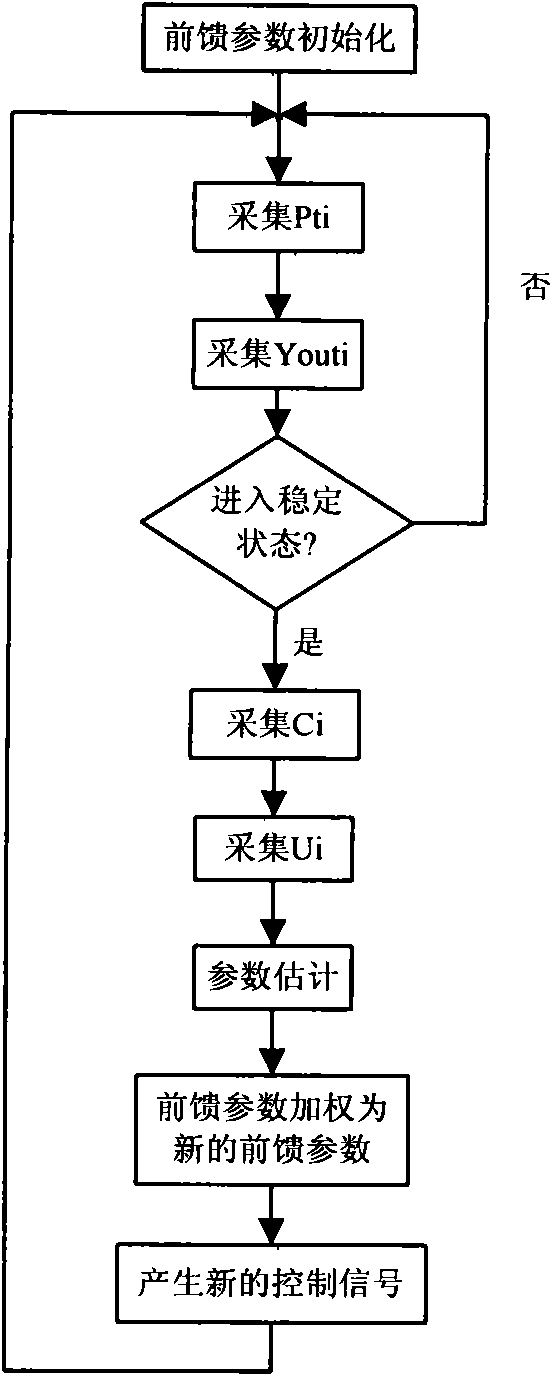
Adaptive feedforward control device and method of optical amplifier
ActiveCN101599803AReduce output powerTransient overshoot unchangedElectromagnetic transmissionTime domainEngineering
The invention relates to an adaptive feedforward control device and a method of an optical amplifier. The optical amplifier is a time-variation or slow time-variation system, the pumping luminous efficiency is reduced, devices are aged or no refrigeration pump works in a temperature variation environment, and therefore, feedforward parameters can be changed along with time. A time-domain transmission function of the optical amplifier is deduced in a steady state according to a dynamic transmission equation of the optical amplifier, then, a parametric estimator is designed according to the transmission function in the steady state so as to estimate and update a current feedforward value in real time, a new feedforward parameter can trace the change of system performance, and the instantaneous characteristic of the optical amplifier can not worsen for the time variation of a system parameter.
Owner:O NET COMM (SHENZHEN) LTD
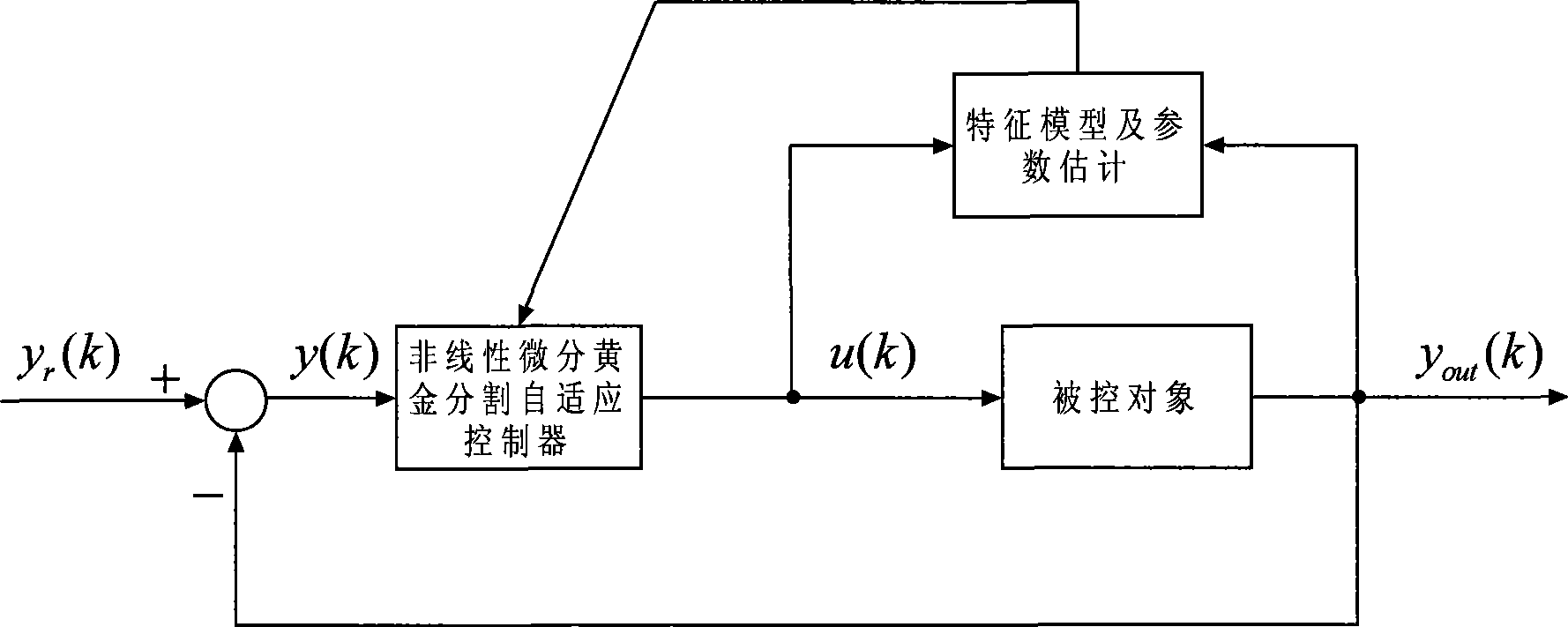
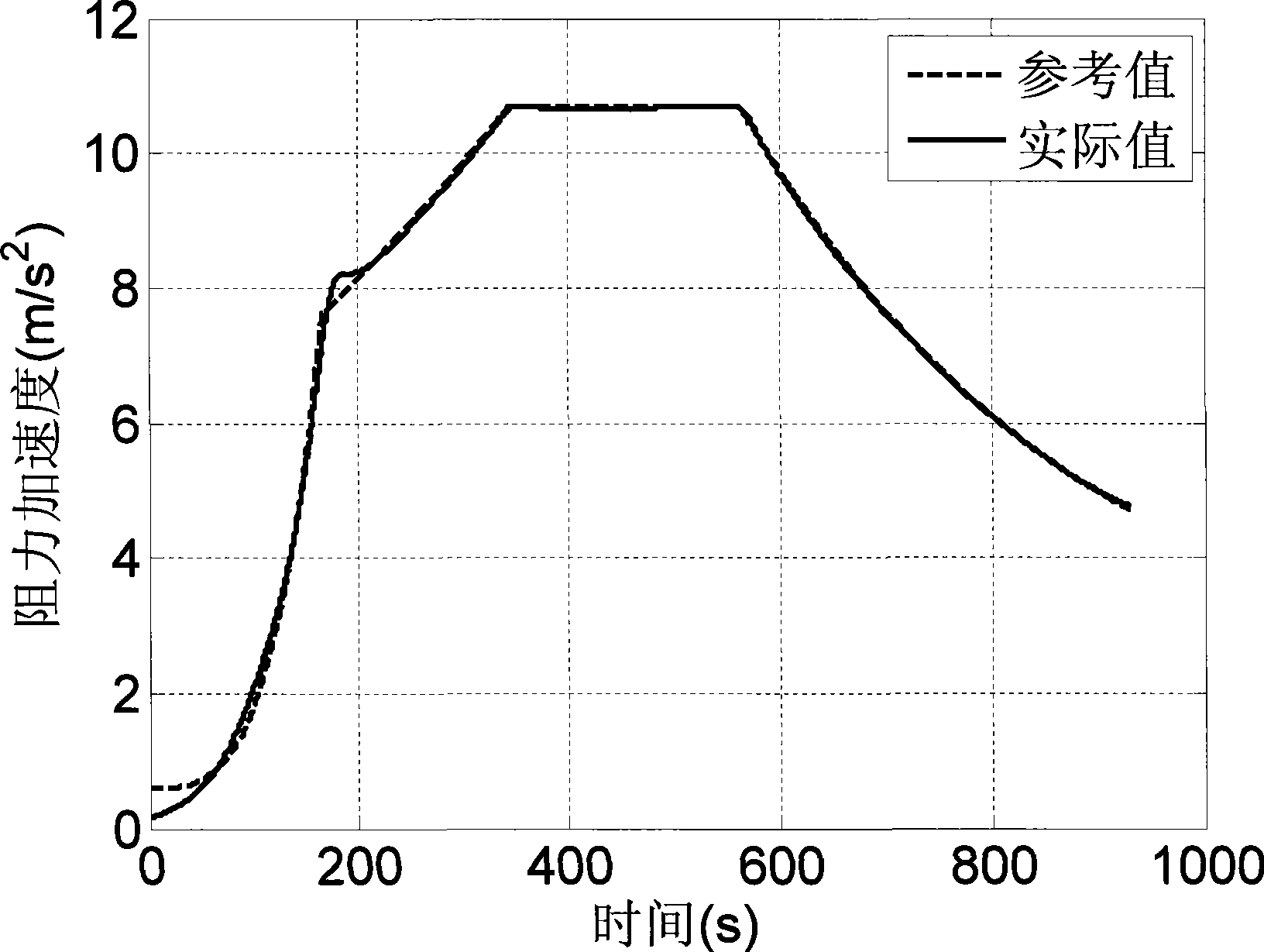
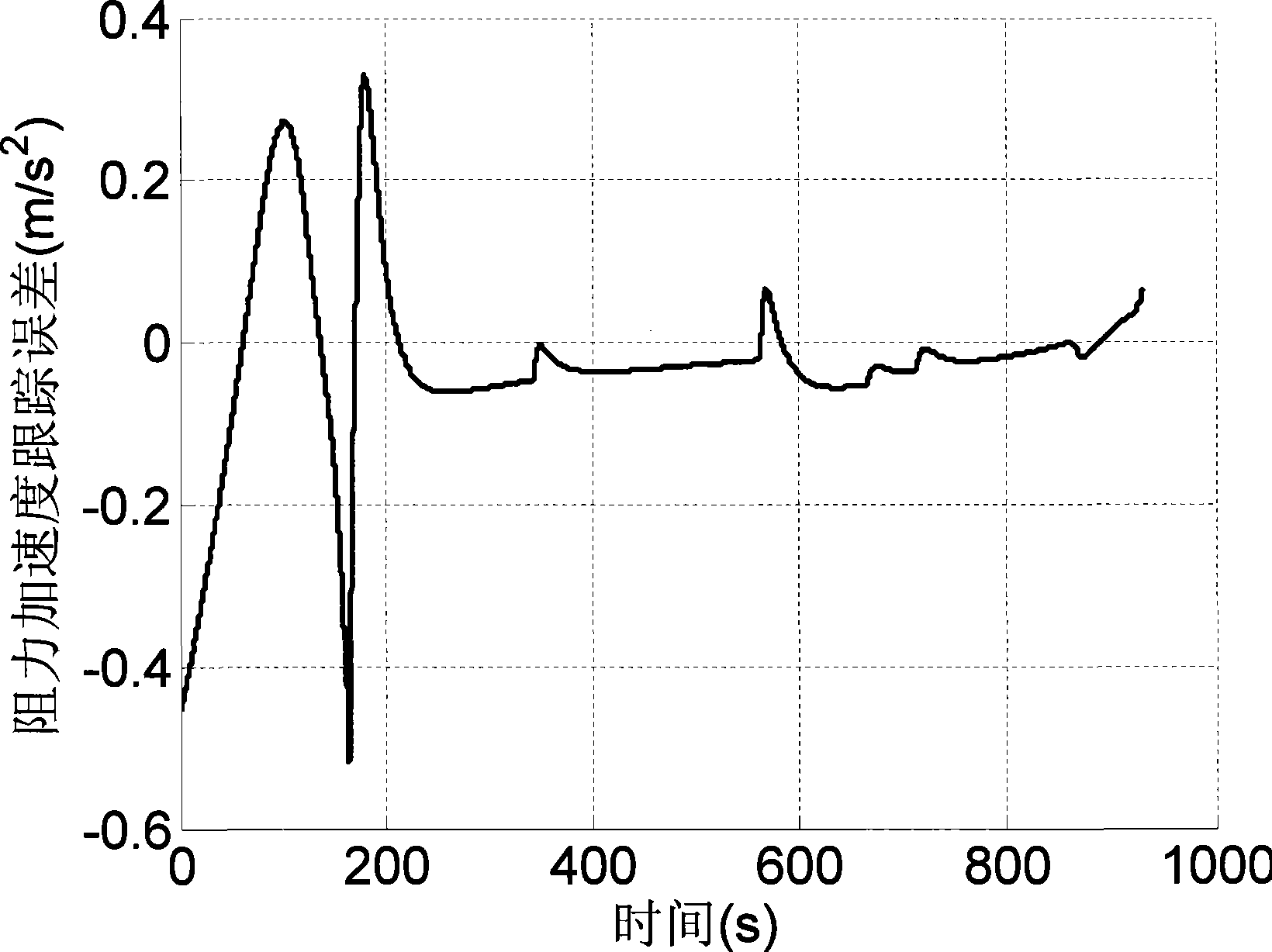
Non-linear differential calculus golden cut adaptive control method
The invention relates to a nonlinear differential golden section self-adapting control method which comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a characteristic model in relation to the a single-input / single-output linear time varying system; (2) determining a nonlinear differential golden section self-adapting control law according to the characteristic mode; and (3) performing the stability analysis of the closed-loop system formed by applying the control law to the characteristic mode and determining the stability conditions of the closed-loop system. The method overcomes the disadvantages of the prior art, provides the characteristic model in relation to the linear time varying system, and achieves the effect of section self-adapting control method using the nonlinear differential golden. The self-adapting control method can track the fast-varying signal and the signal with mutation slope.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
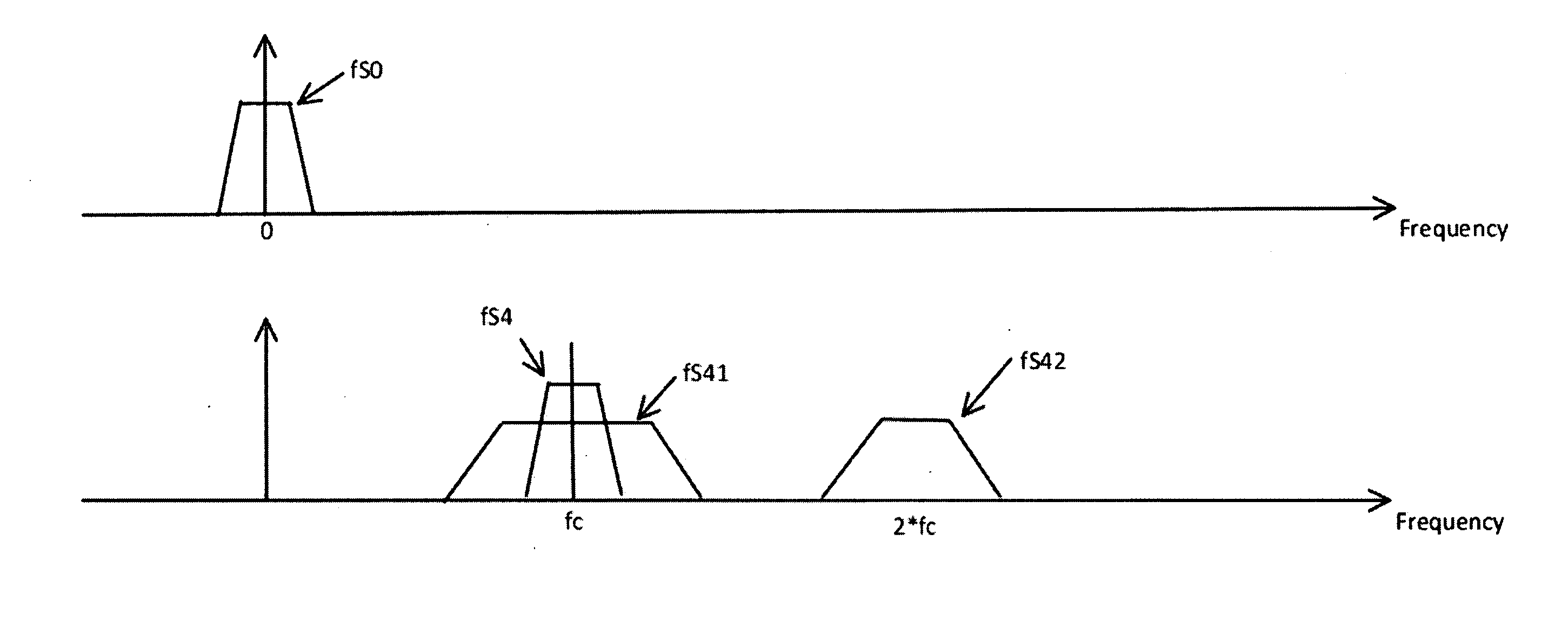
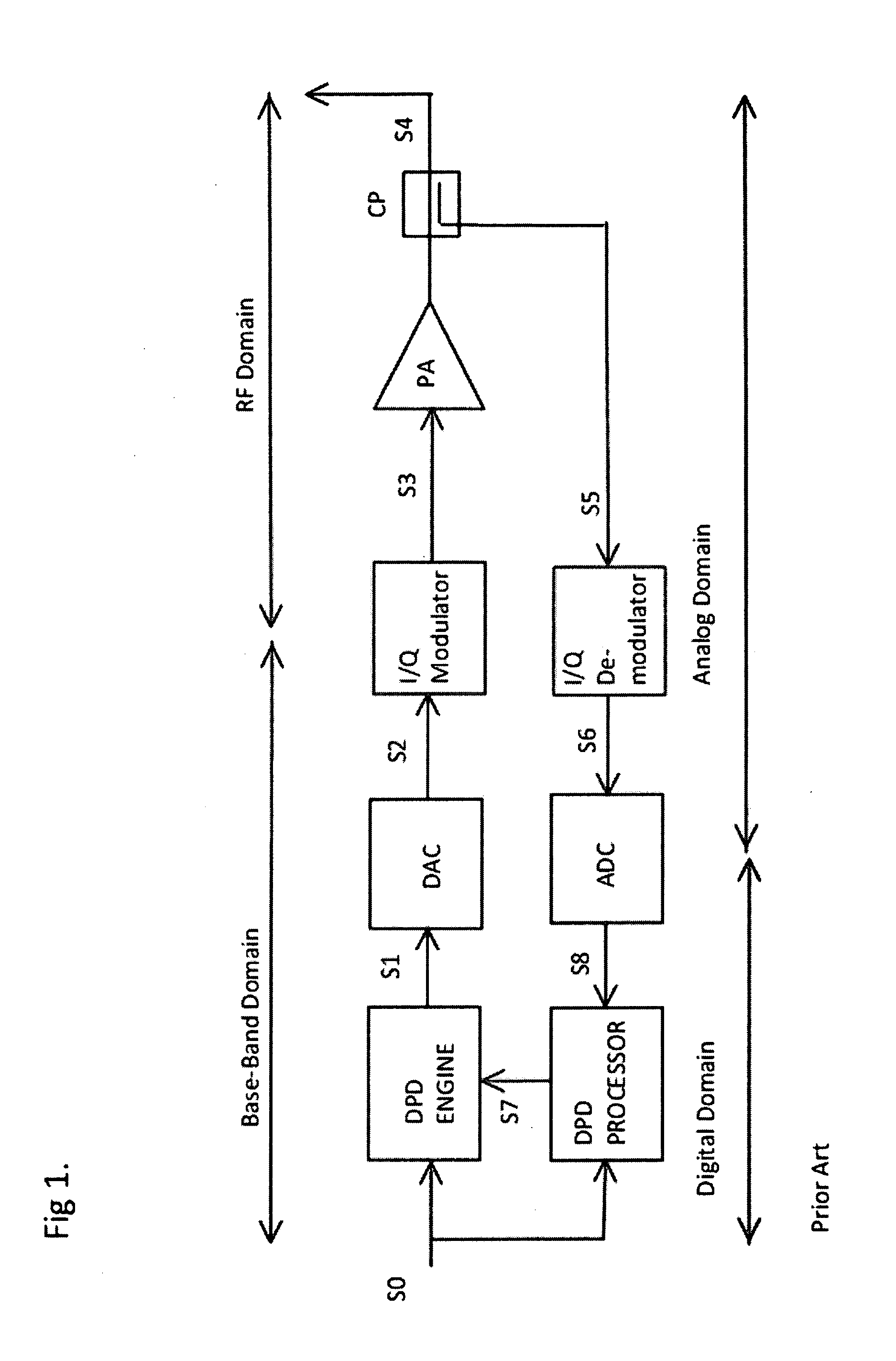
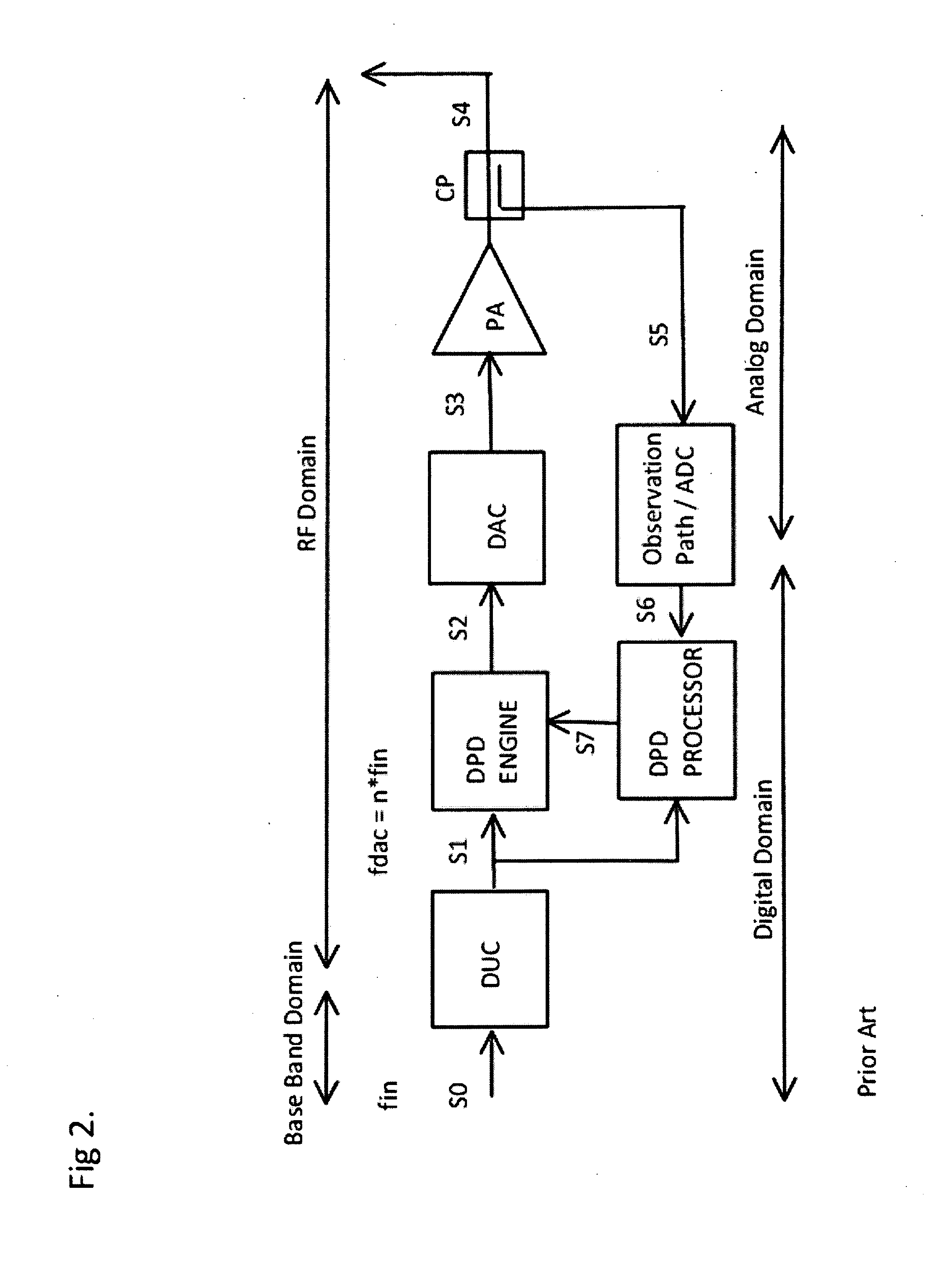
Methods, devices, and algorithms for the linearization of nonlinear time variant systems and the synchronization of a plurality of such systems
InactiveUS20140376676A1Electric signal transmission systemsModulated-carrier systemsCMOSDigital analog converter
Methods, devices and algorithms for the linearization of nonlinear time variant systems and the synchronization of a plurality of such systems. An example of such a system would be a transmit path, including the power amplifier, as used in wireless transmit systems. Advances made in CMOS technology, digital to analog converter (DAC) technology make it possible to implement a substantial part of such a system in the digital domain. Another aspect is the integration of a substantial part of such a transmit system in a single integrated circuit (IC). A digital implementation that allows for linearization of a broad range of nonlinear and time variant effects. Since this digital implementations operate a high clock frequency a energy efficient implementation is essential to keep the power consumption under control. Another aspects is the reuse of methods, devices and algorithms used for the linearization a transmit system to synchronize multiple transmit systems.
Owner:SCHAFFERER BERND
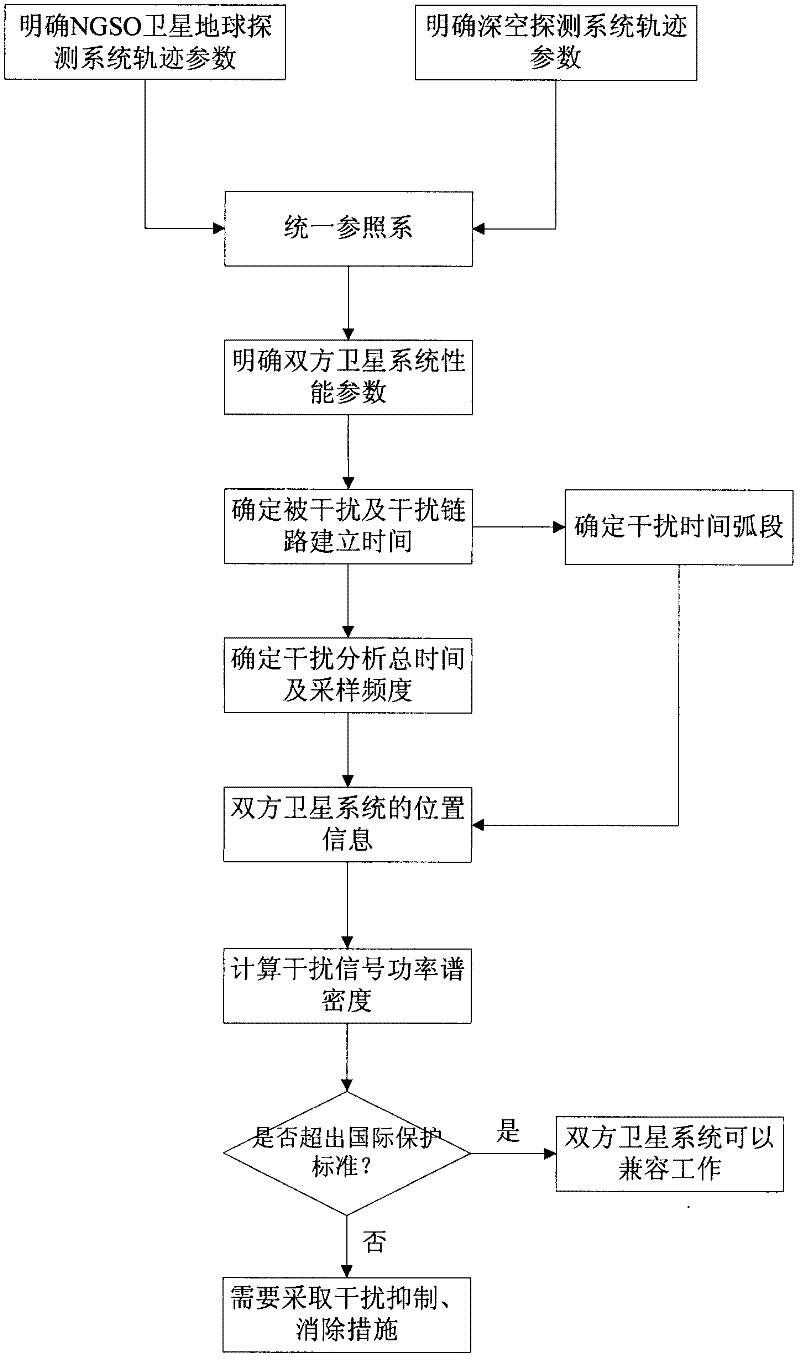
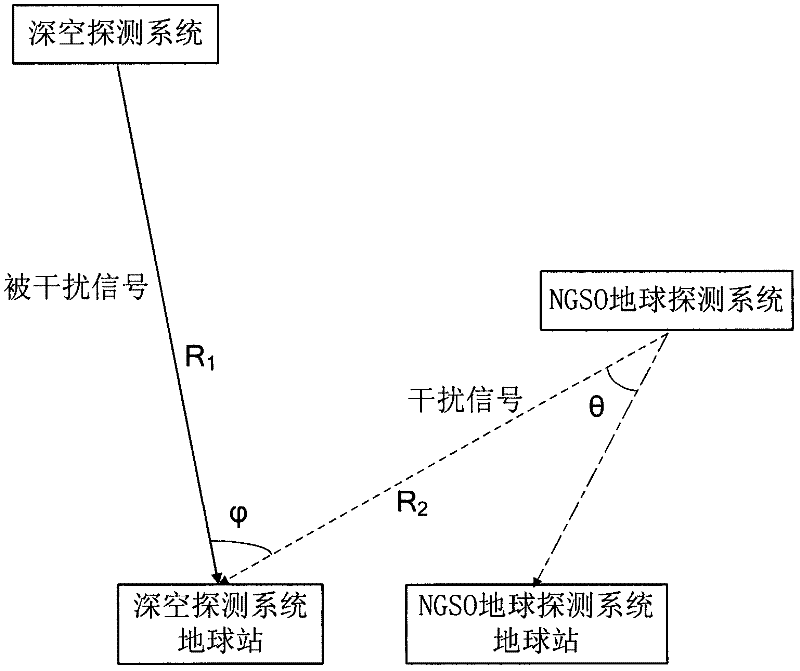
Method for determining interference from NGSO satellite earth detection system to deep space detection system
ActiveCN102520461AImprove anti-interference abilityEasy to implementGeological measurementsTime-variant systemSatellite
A method for determining interference from a NGSO satellite earth detection system to a deep space detection system is disclosed. The method comprises the following steps: pinpointing locus parameters of two time varying systems; unifying a reference system of the two time varying systems; pinpointing satellite system performance parameters of both sides; determining a time arc segment concerned by interference analysis; determining total time of the interference analysis and a sampling frequency; acquiring space position information of each sampling time corresponding to the two time varying systems in the interference time arc segment respectively and acquiring sending and receiving gain at a direction of a interference link and a interference link distance length; calculating a power spectrum density when each sampling time interference signal arrives at a disturbed link receiving system; determining same frequency interference by combining an international interference protection standard. By using the method of the invention, the interference generated by the NGSO satellite earth detection system on the deep space detection system in a corresponding frequency range can be accurately determined. An antijamming capability of the deep space detection system can be increased and a project is easy to be realized.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
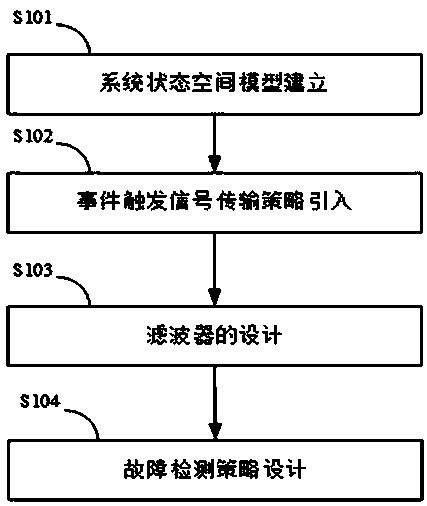
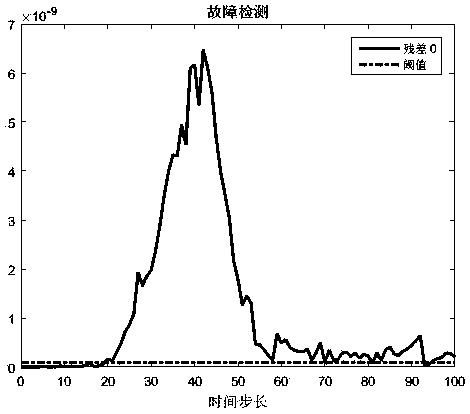
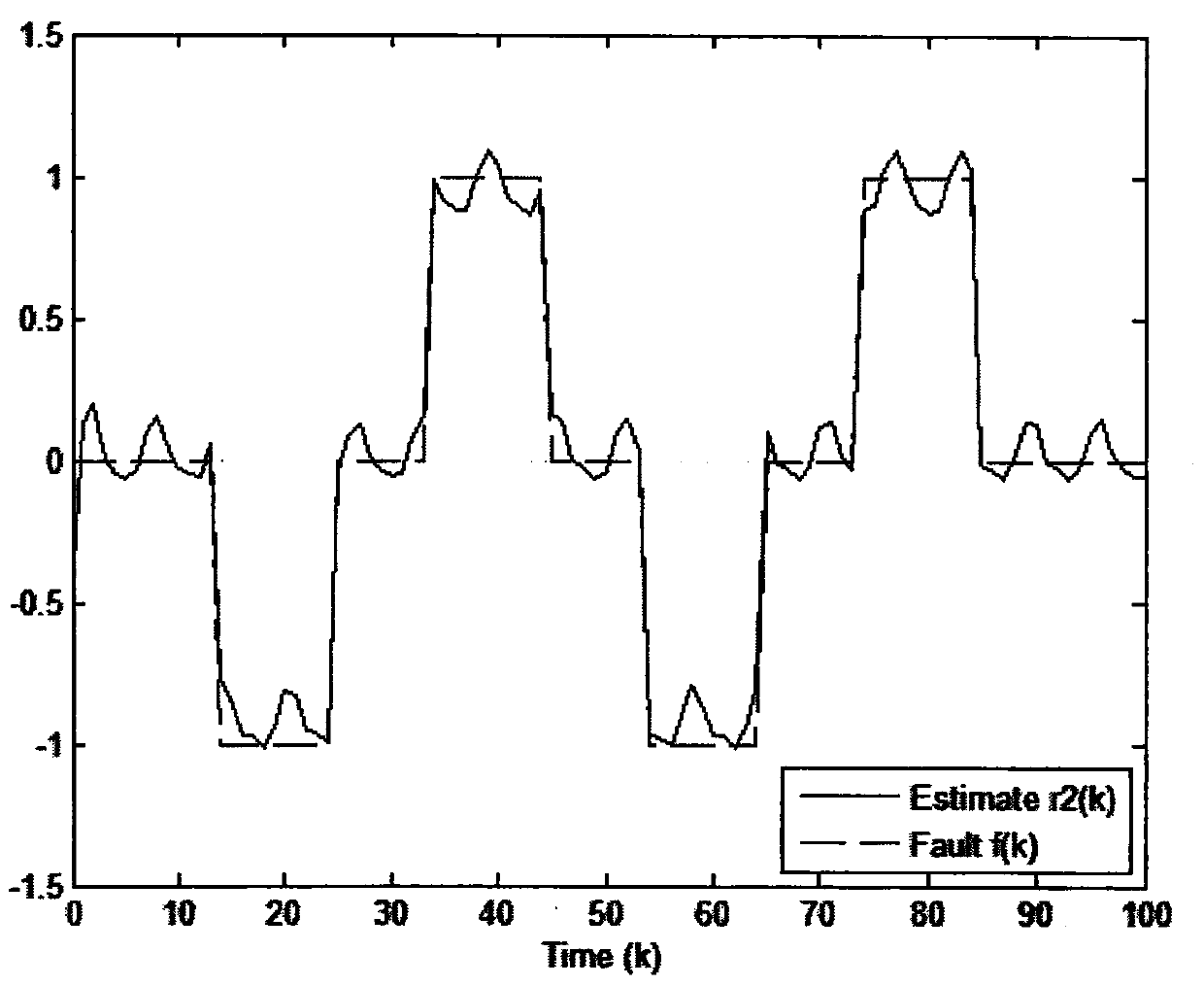
Fault estimation method for a class of event-triggered transmission time-varying systems based on unknown input observer technology
The invention discloses a fault estimation method for a class of event-triggered transmission time-varying systems based on an unknown input observer technology. The method comprises establishing a system state space model, and introducing an event trigger signal transmission strategy therein; respectively augmenting an original system state and each possible fault into new state signals, designing filter parameters, recursively solving the least upper bound of an error covariance and minimizing the least upper bound, and calculating the filter gain; utilizing a filter residue corresponding tothe normal situation and a reasonably set threshold to perform fault detection; utilizing a residual matching method to implement fault separation, and taking a fault corresponding component in the corresponding filtered estimation value as a fault estimation value.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Networking time-delay compensation and control method using active-disturbance-rejection control technology for permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN104201967AAccurate estimateSolving the problem of accurately estimatingSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor parameters estimation/adaptationElectric machineTime delays
The invention provides a networking time-delay compensation and control method using the active-disturbance-rejection control technology for a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: 1) building a permanent magnet synchronous motor control system model containing time-varying network-induced delay, and describing a permanent magnet synchronous motor control system as a discrete-time linear time-varying system with one-step input delay, so as to describe an undetermined dynamic part of the system caused by the time-varying delay as the additive noise of the system; 2) designing an expanding state observing device, and estimating the undetermined dynamic part caused by the time-varying delay as part of total disturbance through the expanding state observer; 3) compensating the undetermined dynamic state caused by the time-varying delay in the networking permanent magnet synchronous motor control system, wherein all undetermined dynamic parts caused by the time-varying delay and the internal and external disturbances in the system can be counteracted during compensating. The method shows high capability on inhibiting the nondeterminacy caused by time-varying delay, the internal and external disturbances of the system, and the nondeterminacy of a model.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
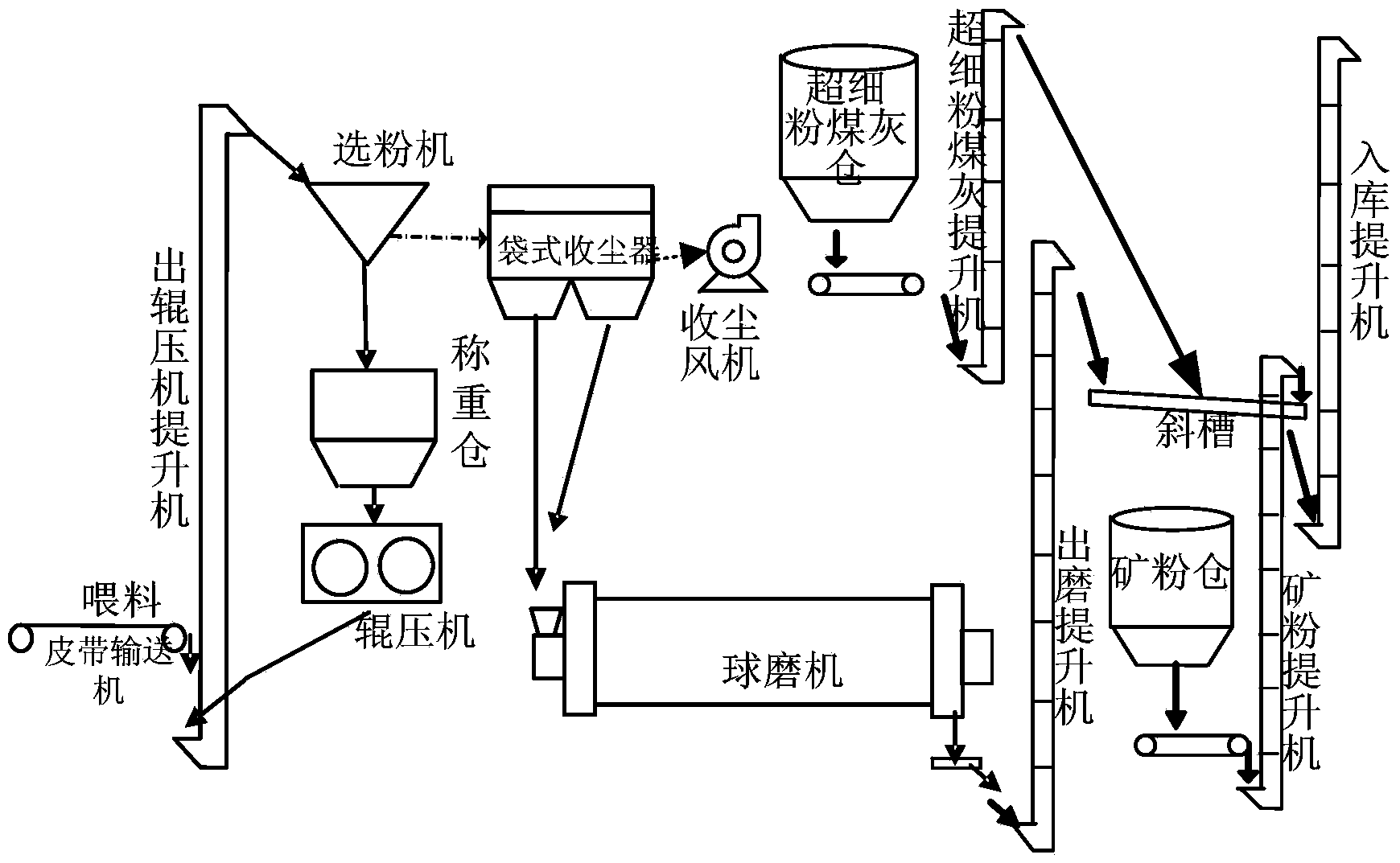
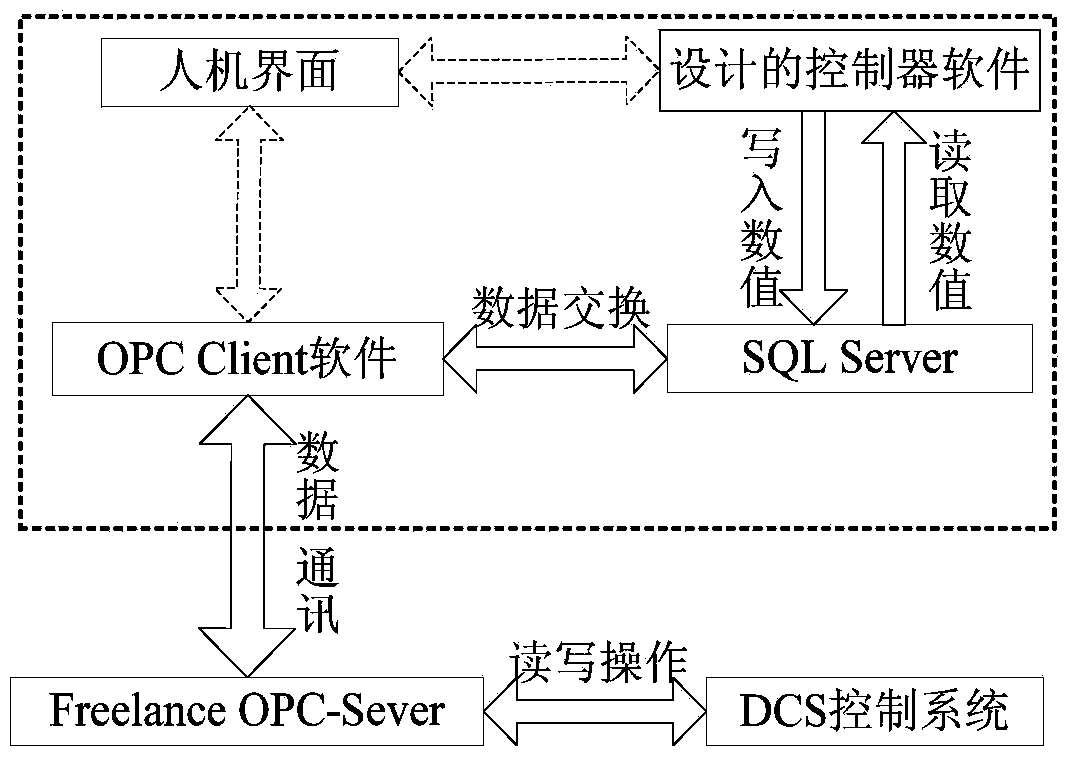
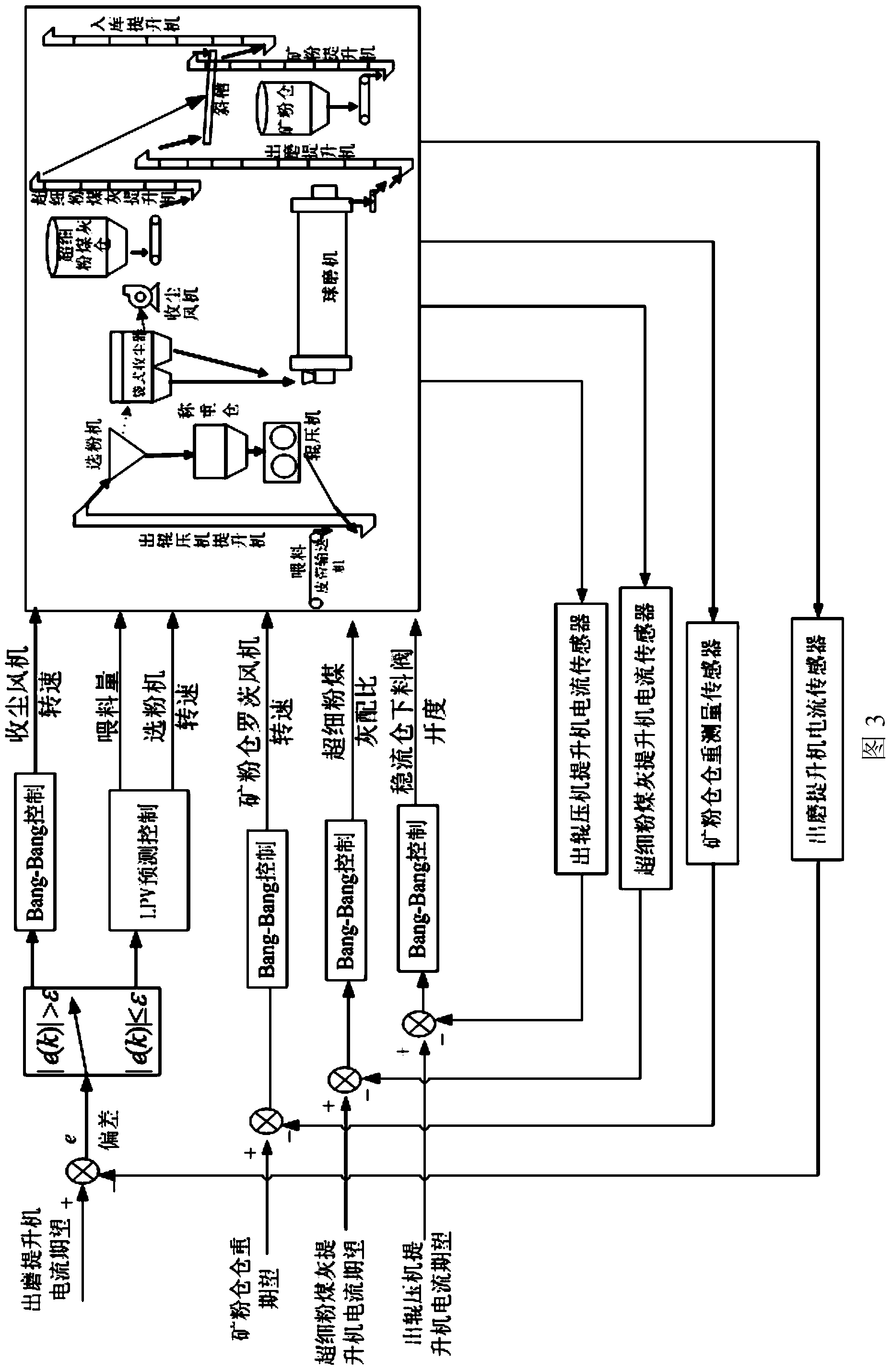
Cement combined-grinding prediction control method based on Bang-Bang control
ActiveCN104384009ASmall fluctuationAvoid the impact of subsequent controlGrain treatmentsControl theoryTime-variant system
The invention provides a cement combined-grinding prediction control method based on Bang-Bang control. The Bang-Bang control process is employed for mixing operation experiences such as observation, waiting, determination and adjusting of an operator into a control algorithm, the tracking error convergence rate is accelerated, and the system overshoot is reduced, and thus the combined-grinding system production process has good stability and the precise rapid control purpose is reached. Aiming at cement mill load control, LPV (Linear Parameter-Varying) prediction control is applied to solve control problems of variation and nondeterminacy of parameters of a linear time-varying system, and enable the system to have good robustness.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN +1
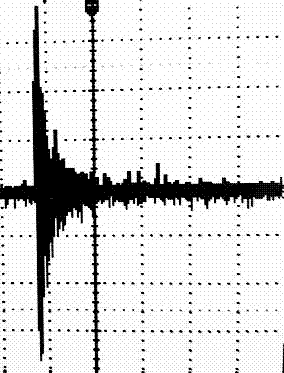
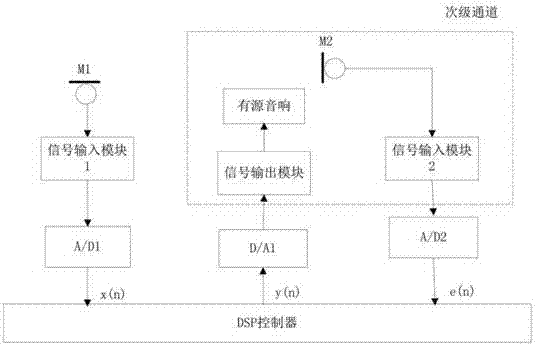
Active noise control system based on variable step LMS algorithm
InactiveCN106911320AFast convergenceFast noise reductionAnalogue adaptive filtersNoise controlActive noise control system
The invention discloses an active noise control system based on a variable step LMS algorithm. According to the system, a filter based on the variable step LMS algorithm is applied to identification of a secondary channel; a filter weight value is updated by adjusting a step value of the filter; in order to obtain a relatively fast convergence rate, the step value of self-adaptive filtering in an initial phase is relatively high; and when the self-adaptive filtering approaches a steady state, the step size is reduced, so a relatively low steady state error can be obtained. The variable step LMS algorithm is applied to the identification of the secondary channel of the active noise control system, and the contradiction among the convergence rate, the steady state error and a tracking capability of a time-varying system can be solved well.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
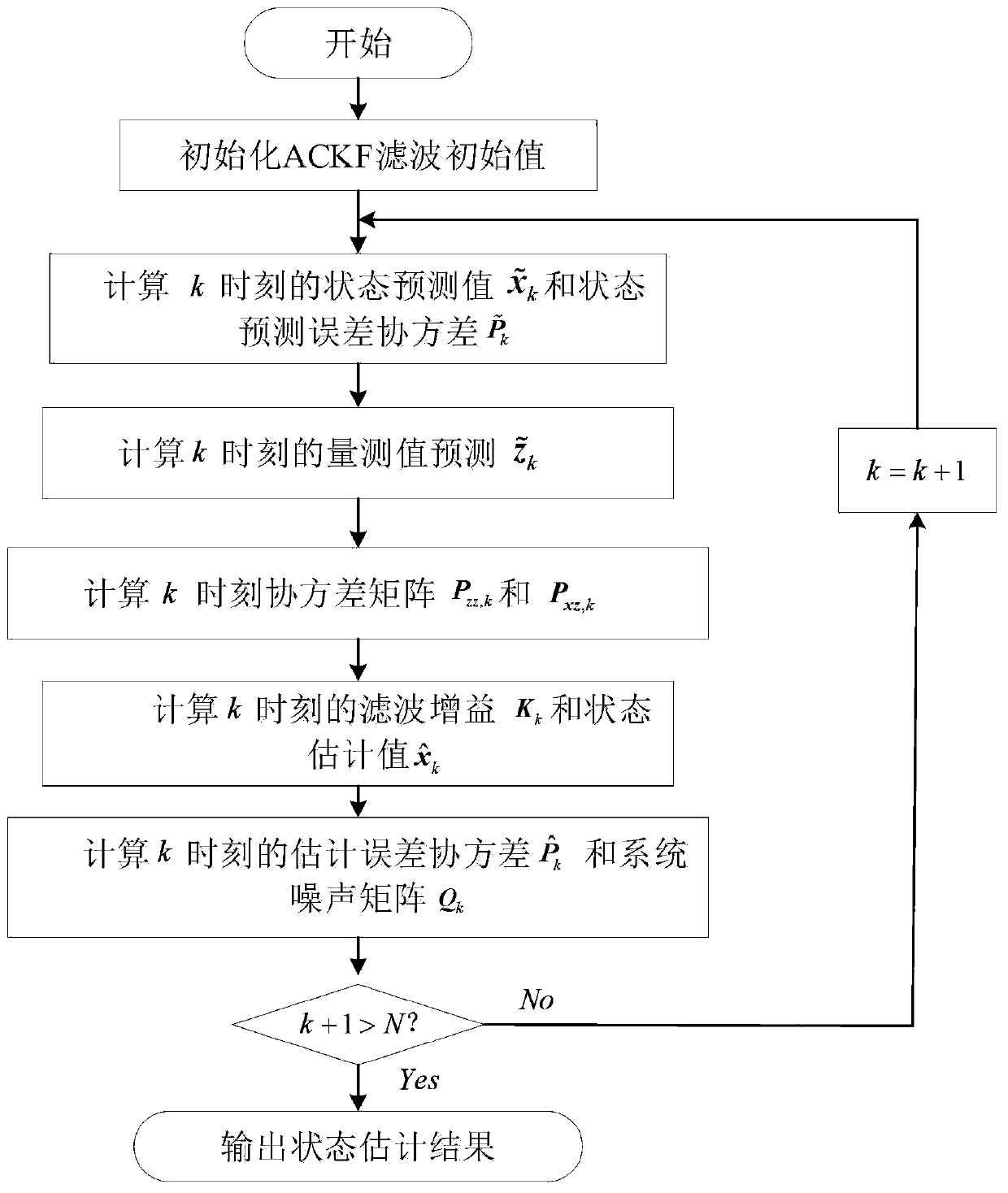
Dynamic state estimation method based on self-adaptive volume Kalman filtering
PendingCN110032812AImprove estimation accuracyMeet monitoring needsData processing applicationsDesign optimisation/simulationEstimation methodsState variable
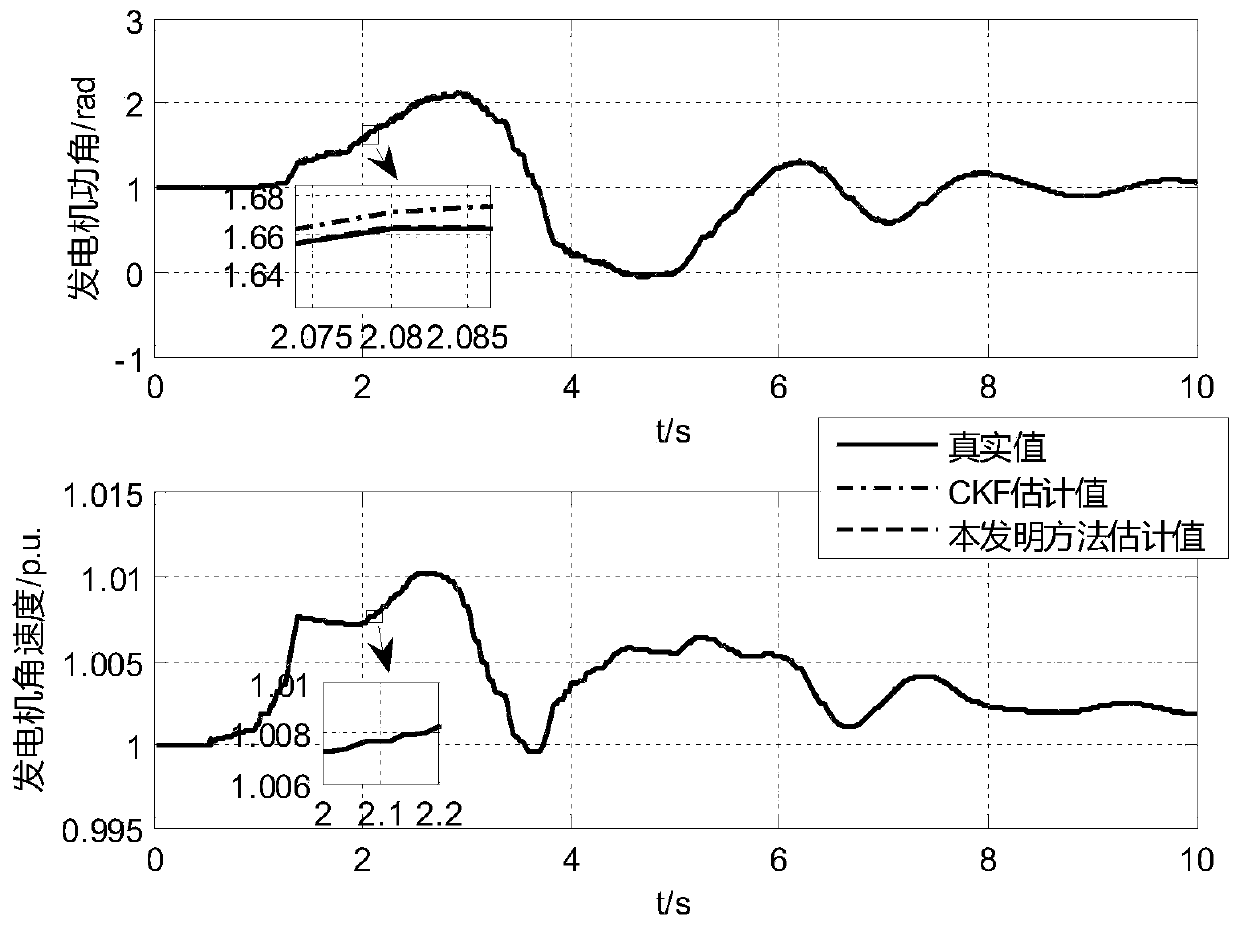
The invention discloses a dynamic state estimation method based on self-adaptive volume Kalman filtering, which is used for realizing accurate estimation of a dynamic state variable of an electric power system generator. According to the method, a fading memory index weighted Sage- Husa noise statistical estimator is introduced into volume Kalman filtering; and the mean value and the variance of the time-varying system noise are dynamically estimated and corrected, the influence of system noise matrix mismatching on the state estimation precision is inhibited, and the accurate estimation of the state variable of the generator is improved. The algorithm considers the actual engineering background, is simple and convenient, and has high engineering application value.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Error modeling compensation method and system of optical remote sensing satellite image time-varying system
ActiveCN105698764AAchieve low frequency errorReduce the impact of errorsPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryObservation dataInformation integration
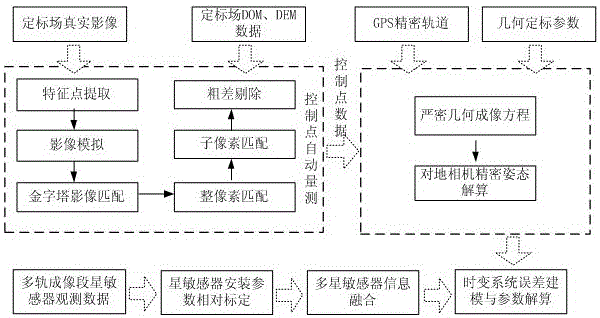
The invention provides an error modeling compensation method and system of an optical remote sensing satellite image time-varying system. The error modeling compensation method comprises the following steps: based on observation data of a plurality of satellite sensors at a plurality of imaging time periods of a ground camera, obtained by an optical remote sensing satellite, resolving a relative mounting parameter change sequence between the satellite sensors to obtain an optimal mounting parameter estimated value; according to the observation data of the plurality of imaging time periods of the plurality of satellite sensors and the mounting parameters obtained by calibration, realizing optimal information fusion of the plurality of satellite sensors, and outputting high-precision attitude data; realizing ground camera precise attitude inversion by adopting a strict geometrical imaging model; constructing a time-varying system error compensation model by adopting Fourier series; and fusing attitude and ground camera precise attitude results according to information of the plurality of satellite sensors, and realizing optimal estimation of parameters of the time-varying system error compensation model based on a least squares principle. With the adoption of the error modeling compensation method and system, on-track compensation of low-frequency errors and non-uniform attitude standard errors of the satellite sensors can be realized, and influences on errors of a high-resolution-ratio optical remote sensing image out-of-control positioning time-varying system are effectively weakened.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Distributed fusion filtering method for simultaneously estimating unknown input and state
ActiveCN107994885AImprove estimation accuracyDigital technique networkFilter algorithmEquation of state
The invention discloses a distributed fusion filtering method for simultaneously estimating an unknown input and a state, which is used for solving a problem that an existing distributed filter does not give out a state equation for estimating the unknown input. The distributed fusion filtering method comprises the following steps of: establishing a discrete linear time-varying system with a plurality of sensors; based on an observed quantity of each sensor, designing a three-step recursive filter; and deducing a cross-covariance matrix between any two local estimations, and then according tothe acquired local estimations and the cross-covariance matrix, giving out a distributed scalar weighting fusion filter of each component of the state by utilizing a linear minimum variance componenton the basis of a scalar weighting fusion estimation algorithm. The distributed fusion filtering method disclosed by the invention is superior to an existing distributed fusion filtering method in estimation accuracy on the state, and gives out unbiased estimation on the unknown input by utilizing the filtering algorithm for simultaneously estimating the unknown input and the state when the systemhas the unknown input with unknown statistic characteristics, and yet no estimation on the unknown input is given out in existing literatures.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
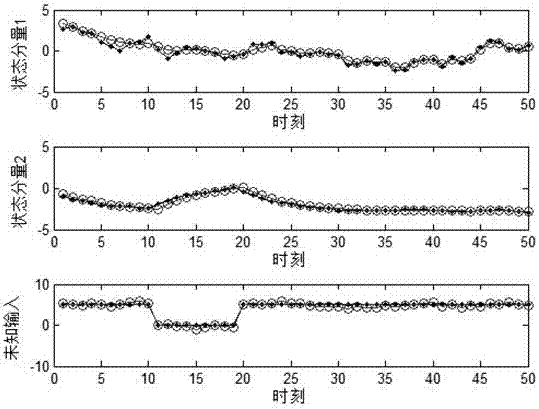
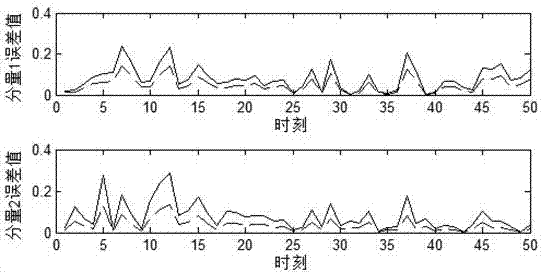
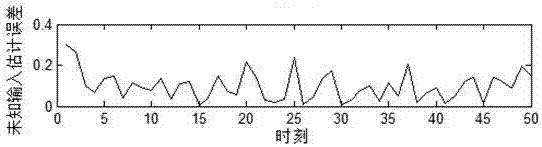
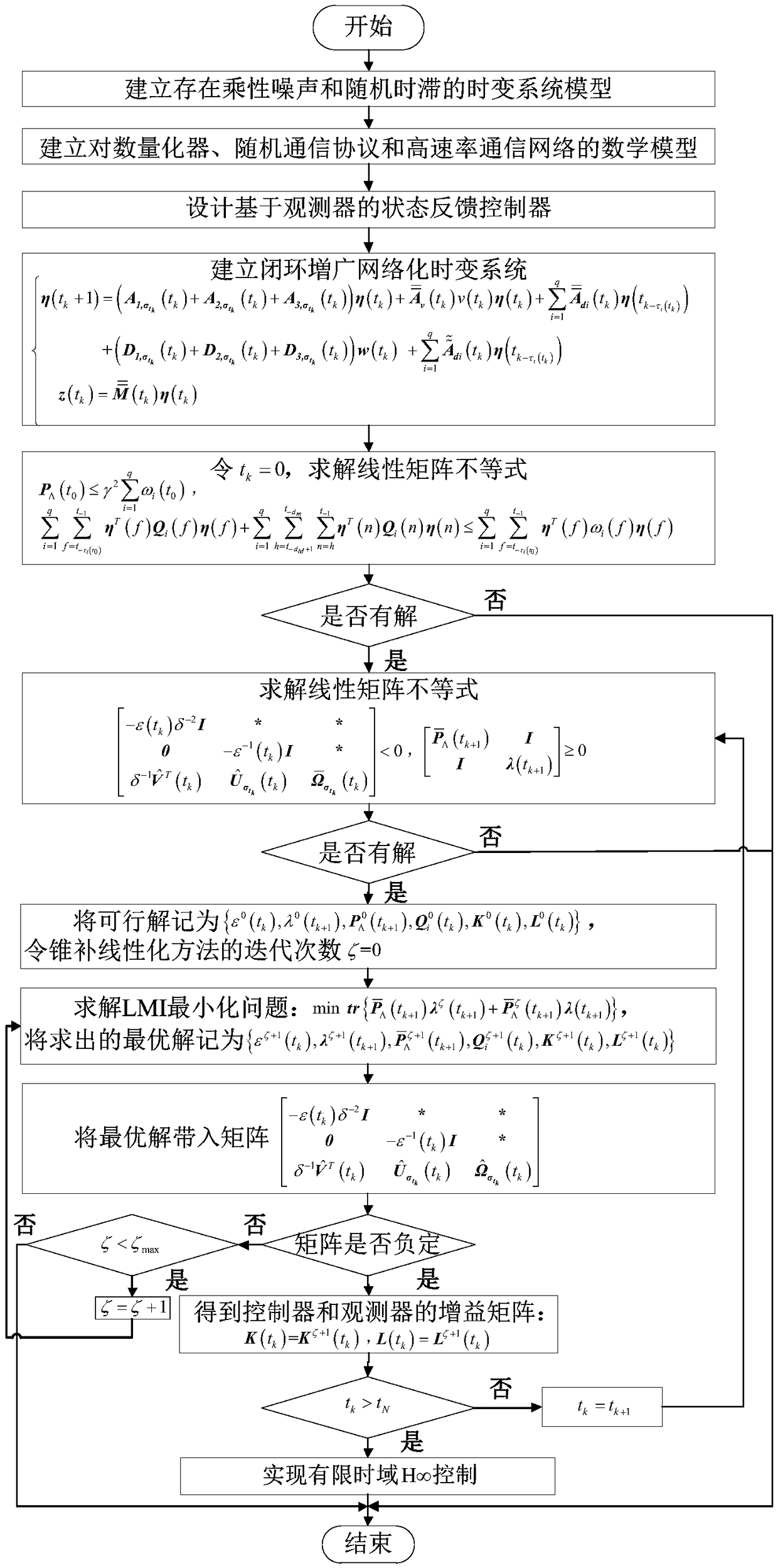
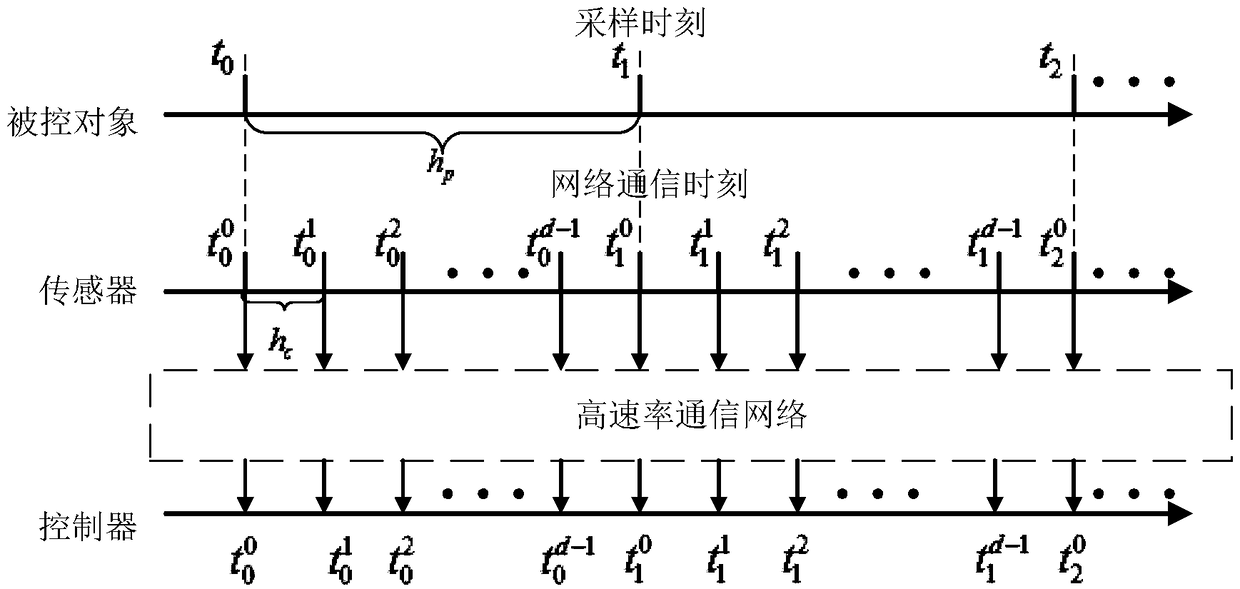
A finite-time-domain Hinfinite control method for time-varying systems under the influence of high-rate communication networks is proposed
The invention provides a finite time domain Hinfinite control method of a time-varying system under the influence of a high-speed communication network, belonging to the networked control system field. At first, under the influence of random communication protocol and high-speed communication network, a networked time-varying system model with multiplicative noise, stochastic time delay and quantization error is proposed. Then observer-based state feedback controller is designed. By using Lyapunov stability theory and linear matrix inequality analysis method, the sufficient conditions for theclosed-loop system to satisfy the Hinfinite performance requirement are obtained. Finally, a finite-time-domain Hinfinite controller design algorithm based on cone-complementary linearization is proposed, and the time-varying gain matrices of the observer and the controller are obtained by using Matlab LMI toolbox. The invention considers the influence of the stochastic communication protocol andthe high-speed communication network on the networked time-varying system under the actual situation, and the existence of multiplicative noise, the stochastic time delay and the quantization error ofthe system, and is suitable for the finite time domain Hinfinite control of the general networked time-varying system, and reduces the conservatism.
Owner:单旭
Mechanical-arm servo-system neural-network full-order sliding mode control method with dead-zone compensation
ActiveCN105182745AStable controlConvergent stabilityAdaptive controlStabilization controlSingular problems
A mechanical-arm servo-system neural-network full-order sliding mode control method with dead-zone compensation is disclosed. Aiming at a mechanical arm servo system which contains a dynamic execution mechanism and is with unknown dead-zone input, a full-order sliding mode control method is used and a neural network is combined so as to design the mechanical-arm servo-system neural-network full-order sliding mode control method with the dead-zone compensation. A dead zone is converted into a linear time-varying system, and then the neural network is used to approach an unknown function so as to compensate an additional influence of a traditional unknown dead zone and an unknown parameter of the system. In addition, a full-order sliding mode surface is designed so as to guarantee rapid and stable convergence of the system; generation of a differential term is avoided in an actual control system so that buffeting is improved and a singular problem is solved. The invention provides the control method which can improve a buffeting problem of the sliding mode surface, solve the singular problem and can effectively compensate a system unknown dynamic parameter and unknown dead zone input so that rapid and stable control of the system is realized.
Owner:扬州祥帆重工科技有限公司
Finite-time decoupling control method of cart inverted pendulum system
ActiveCN104267596AReduce complexityAvoid Saturation EffectsAdaptive controlDynamic modelsEngineering
A finite-time decoupling control method of a cart inverted pendulum system includes the steps that a fourth-order dynamic model of the cart inverted pendulum system is set up, and the system state and sampling time first-order related control parameters are initialized; a saturation function in the system is approximated to be a simple time-varying system, and a system model with the saturation function is deduced; the cart inverted pendulum system is divided into two second-order subsystems, and the tracking error, the nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface and the first-order derivative of a control system are calculated; aiming at the cart inverted pendulum system, a neural network is selected to approximate an unknown function, a finite-time decoupling controller of the neural network is designed according to the tracking error and the nonsingular terminal sliding mode surface of the system, and a weight matrix of the neural network is updated. The influence of the saturation function can be avoided, the complex degree of the controller is reduced, and the cart inverted pendulum system can be fast stabilized within finite time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Dead zone compensating control method for mechanical arm servo system with guaranteed transient performance
ActiveCN105549395ASimple structureAvoid dead-zone inverse computation operationsAdaptive controlDynamic modelsVirtual control
A dead zone compensating control method for a mechanical arm servo system with guaranteed transient performance comprises following steps: a dynamic model of a mechanism arm servo system is established, and the system state, sampling time and control parameters are initialized; according to the differential mean value theorem, a non-linear input dead zone in the system is linearly approximated as a simple time-varying system, and a mechanism arm servo system model with unknown dead zones is deduced; a bounded function limiting the tracking error transient performance is introduced; a conversion error variable is defined by use of a error conversion method; a virtual control quantity of the system is designed by use of the Lyapunov method; an unknown virtue control quantity is estimated by use of a neural network; a first-stage wave filter is added to avoid problems such as inversion complexity blast. The invention provides a method for effectively compensating the influence of unknown dead zone input on the system and avoiding the problem of complexity blast brought by the inversion method, and for increasing the system transient tracking performance and guarantying stable tracking control of position signals.
Owner:NANJING CHENGUANG GRP
A design method for an output feedback controller with a time varying sampling period
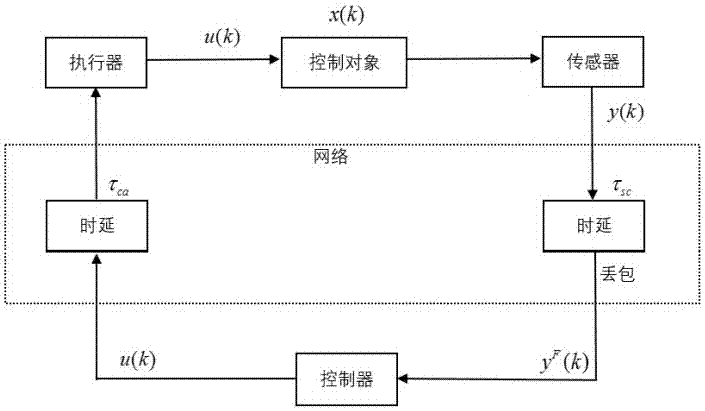
ActiveCN107463095ASimple designConsider comprehensivelyData switching networksAdaptive controlLyapunov stabilityPacket loss
The invention provides a design method for an output feedback controller with a time varying sampling period. The method comprises the steps of setting time delay of a network control system to be a constant value and to be less than a sampling period, wherein a time varying sampling period is bounded, packet loss meets a Bernoulli random sequence and the probability is known; discretizing an original linear time invariant network control system and obtaining a discrete time varying system with uncertain items through conversion; obtaining the maximum singular value of a matrix and a conjugate transpose matrix through solving to obtain parameters in the discrete time varying system; according to state variables received by a controller and the obtained parameters in the discrete time varying system, building a dynamic output feedback controller; combining the built linear matrix inequality and the Lyapunov stability principle, solving the matrix in the feedback controller to determine and obtain a dynamic output feedback controller. The method takes into consideration the instability of sampling periods of network control systems, has the advantages of clear design thought, high stability and simple operation and can be applied to engineering practices.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Control strategy for achieving multivariable PID in PLS frame on basis of Gaussian process model
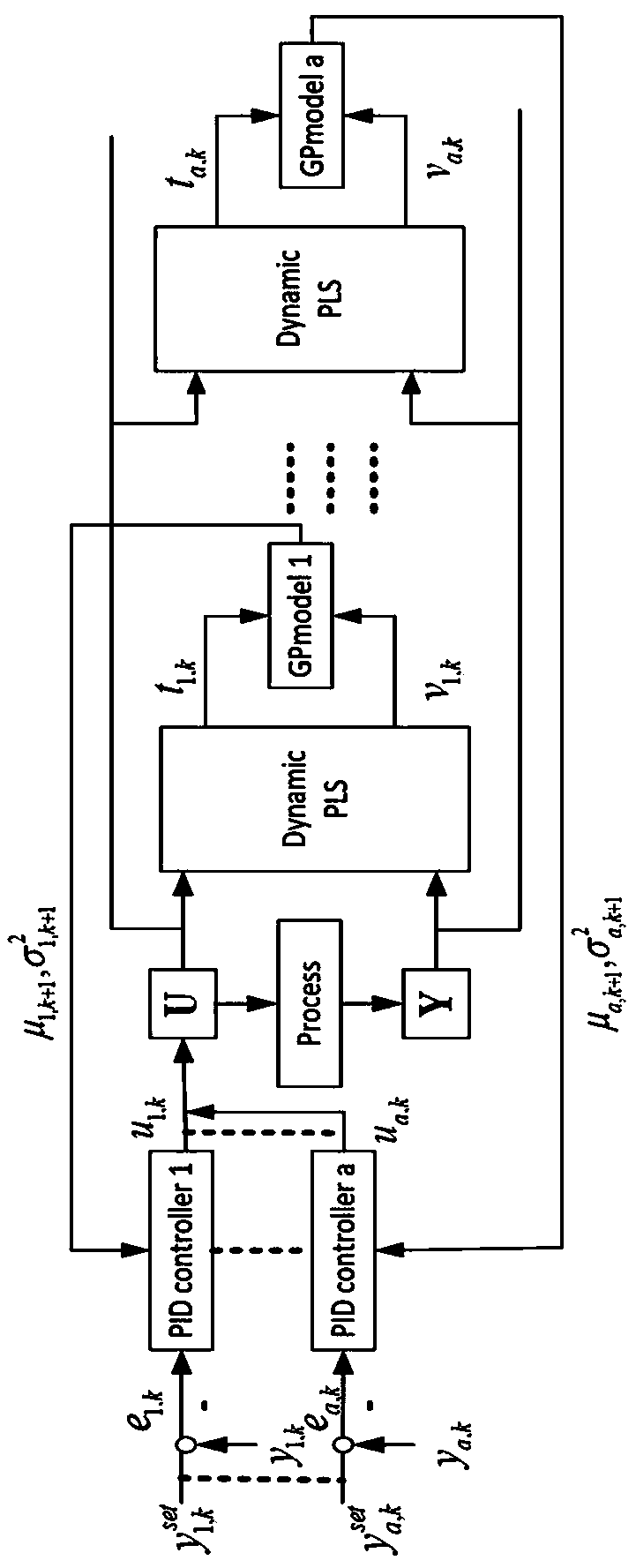
InactiveCN108897212AControllers with particular characteristicsCovariance functionSystem optimization
The invention relates to the field of nonlinear time-varying system optimization control, in particular to a control strategy for achieving multivariable PID in a PLS frame on the basis of a Gaussianprocess model. The problems that by means of existing control strategies, interaction among multiple loops cannot be eliminated, a built model is not complete, and the control performance is poor aresolved. The control strategy for achieving multivariable PID in the PLS frame on the basis of the Gaussian process model comprises the steps that 1, parameters of a PID controller are given; 2, the GP(Gaussian process) model is used for achieving the control strategy of multivariable PID, wherein firstly, an MIMO system is subjected to decoupling, secondly, the model uncertainty is improved, thirdly, a covariance function is chosen, and the parameters are optimized; 3, the PID controller is set, wherein a gradient-based optimization algorithm is used for using the GP model for adjusting the PID controller. The control strategy for achieving multivariable PID in the PLS frame on the basis of the Gaussian process model has the advantages that the GP model is used for providing a predictionvariance, and the prediction reliability of a local random area is shown; cross coupling effects brought by a multivariable control process are taken into account, through the PLS frame, the MIMO system is decoupled into single loops, and then based on the GP model, the PID controller parameters are adjusted separately.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Time-varying neural dynamics system identification method based on chebyshev polynomial expansion
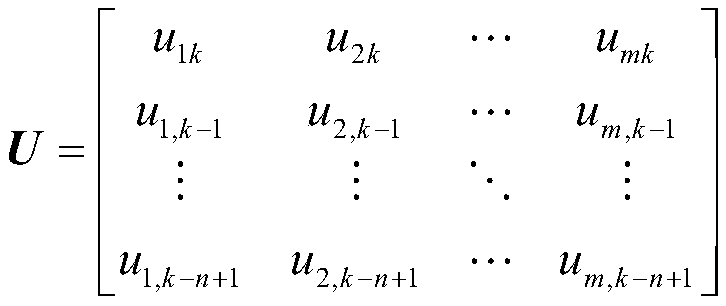
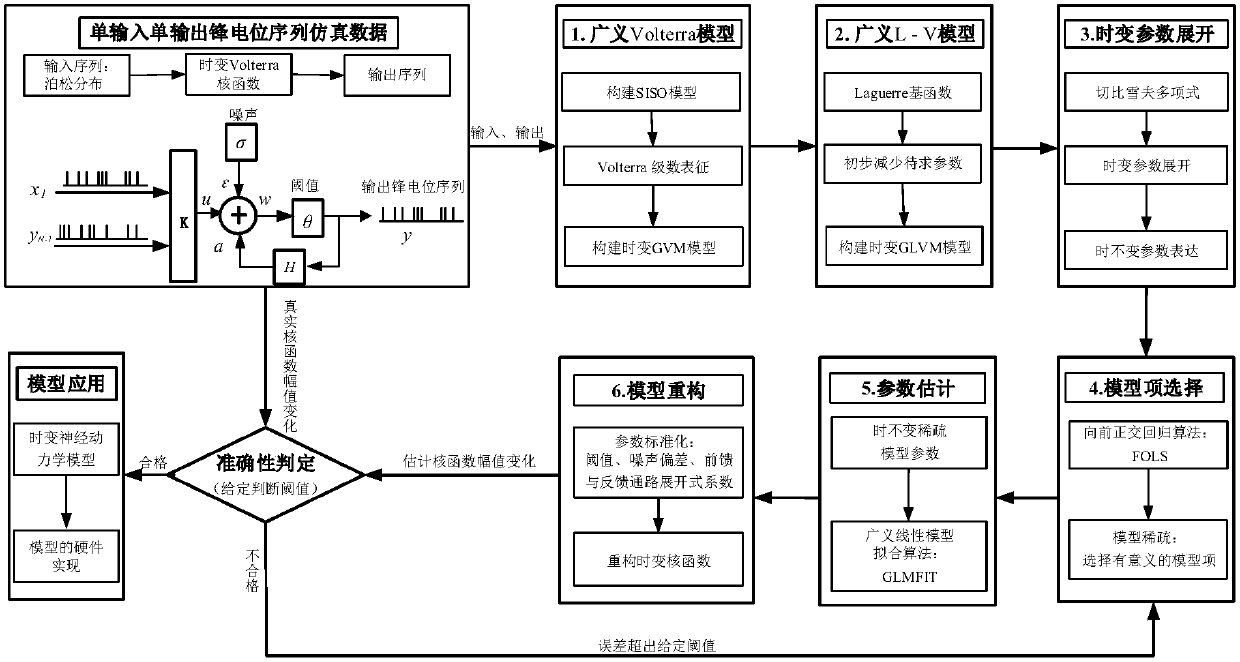
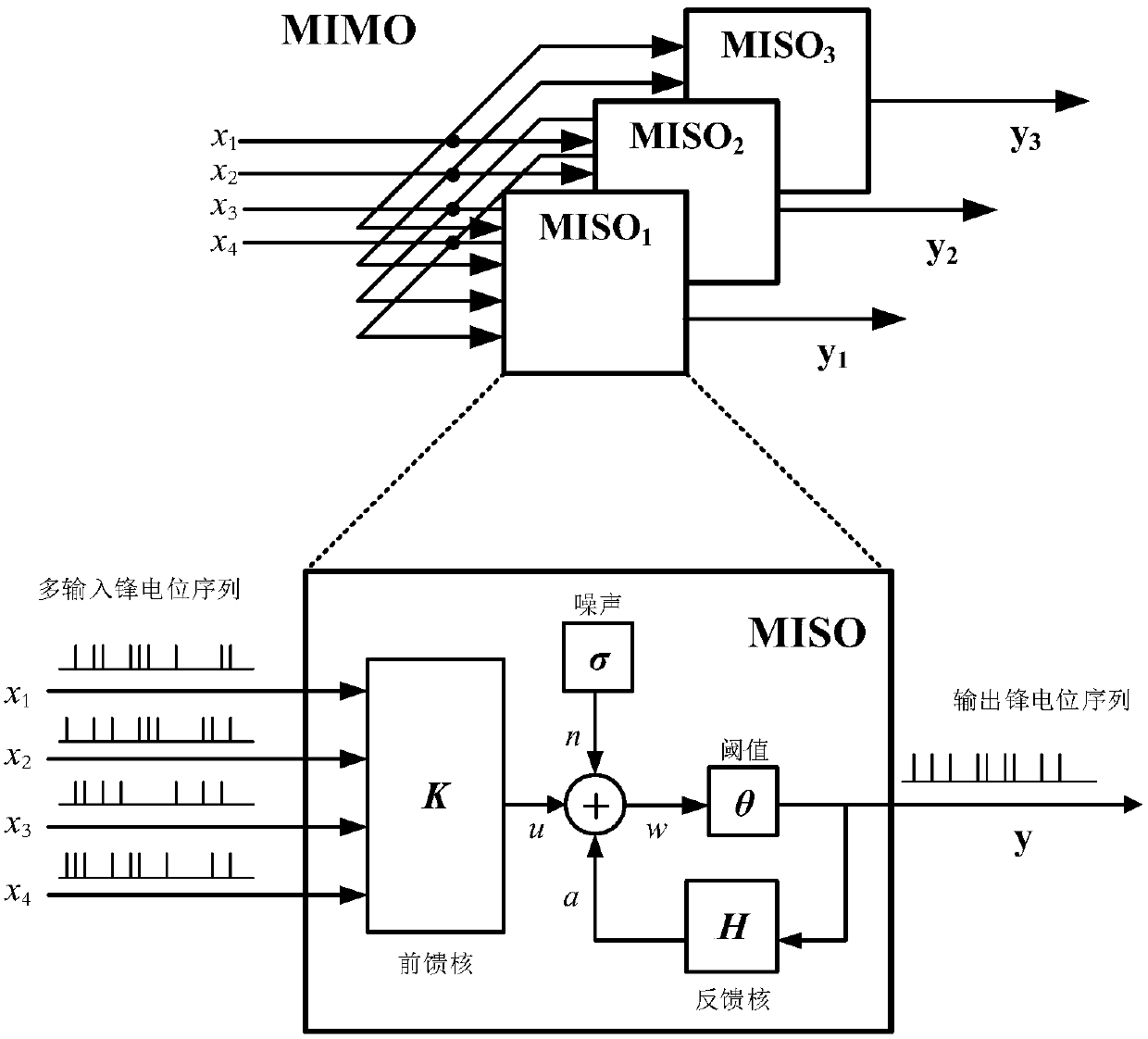
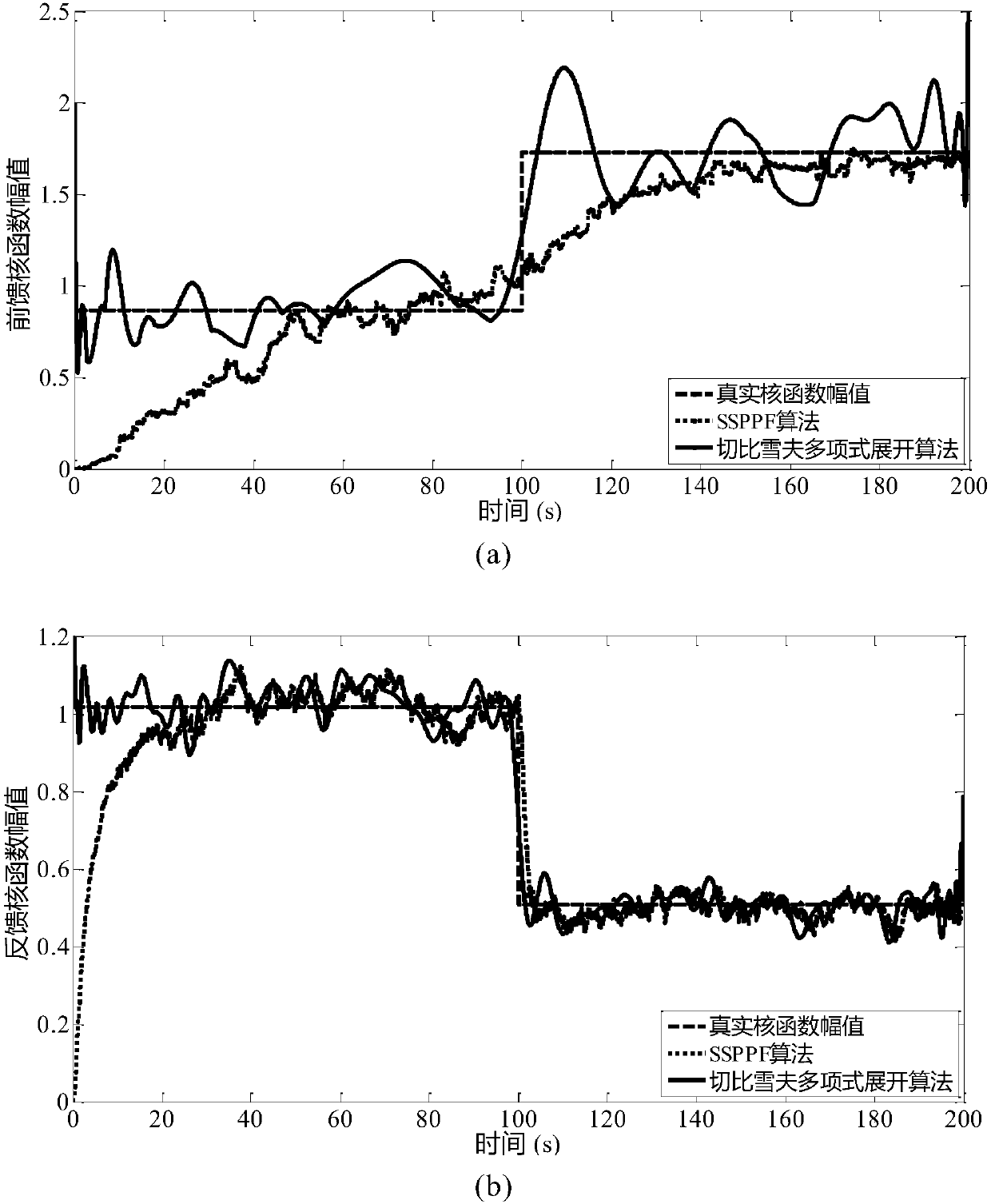
The present invention puts forward a time-varying neural dynamics system identification method based on chebyshev polynomial expansion. The time-varying neural dynamics system identification method comprises the steps of: representing a time-varying neural system consisting of simulation input / output spike potential sequences with a Volterra series, and representing feedforward and feedback kernel functions with different Volterra kernels; expanding the time-varying Volterra kernel with a Laguerre primary function to obtain a time-varying generalized Laguerre-Volterra model; expanding time-varying parameters of the time-varying generalized Laguerre-Volterra model with a chebyshev polynomial, so as to convert the time-varying model into a time-invariant model; and selecting significant model items by using a forward orthogonal regression algorithm, estimating time-invariant parameters by using a generalized linear fitting algorithm, and then obtaining the time-varying parameters and the original time-varying kernel functions through reverse solution. Compared with an adaptive filtering technology in the prior art, the time-varying neural dynamics system identification method of the present invention has a better tracking capability for a strong non-stationary neural system signal, can achieve accurate tracking for the time-varying system kernel functions, can achieve modeling for the neural system, especially provides a new research method for system modeling of massive high-dimensional data, and has an important meaning for revealing a complex neural dynamics mechanism for completing information processing by a cerebrum.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
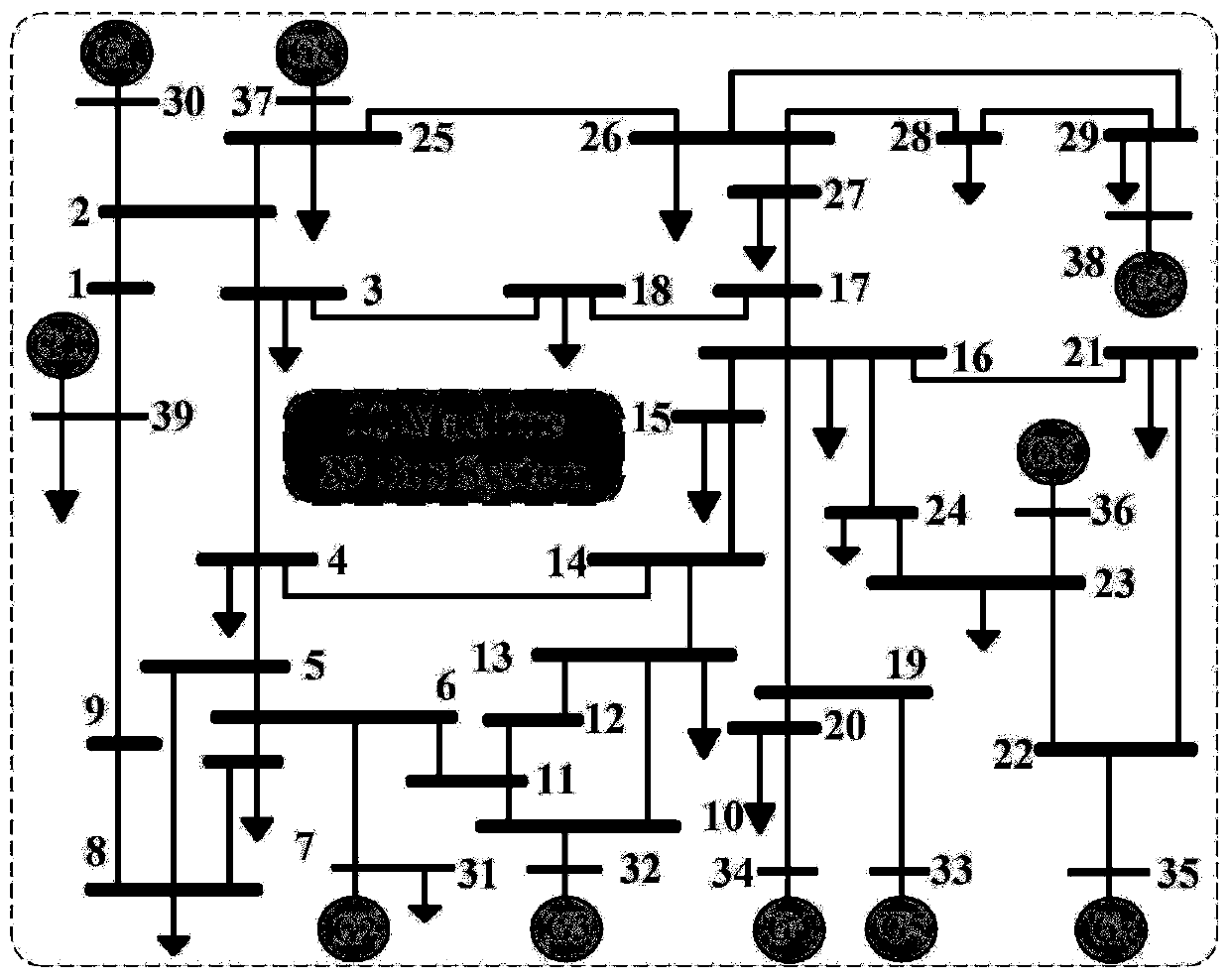
Stability analysis system and method of time-varying power system
ActiveCN104680017ASolve the difficult problem of variable stabilitySolve the problem that the stability is not easy to judgeClimate change adaptationSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsElectric power systemSlope stability analysis
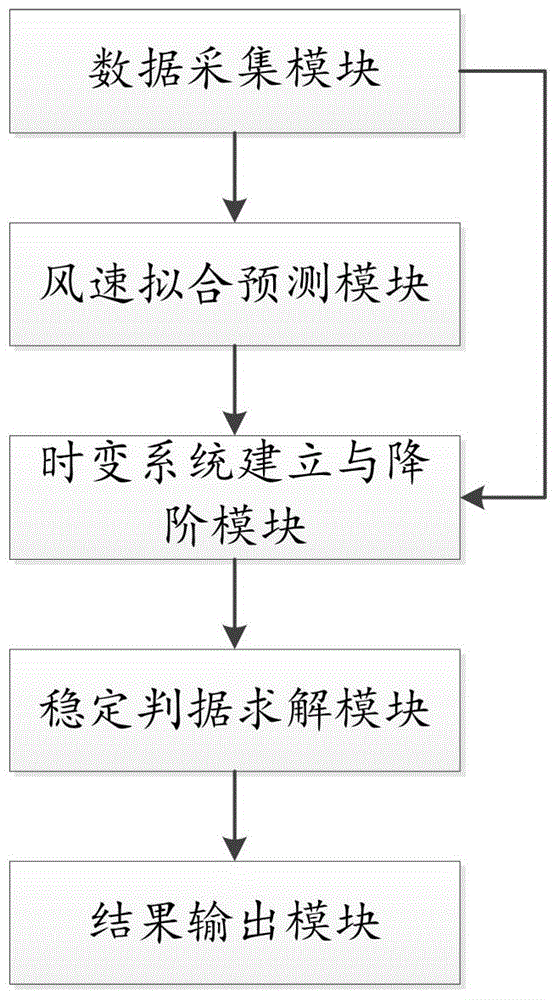
The invention discloses a stability analysis system and method of a time-varying power system. The system comprises a data acqusition module, a wind velocity fitting prediction module, a time-varying system establishment and order reduction module, a stability criterion solving module and a result output module, wherein the data acqusition module is used for acquiring data; the wind velocity fitting prediction module is used for performing fitting prediction on conditional wind velocity trend in short time, sectioning the wind velocity and calculating a conditional characteristic wind velocity probability density matrix of each section according to a fitting model; the time-varying system establishment and order reduction module is used for establishing a continuous markov time-varying power system model considering a wind velocity random characteristic and reducing order of the system; the stability criterion solving module is used for solving whether the system is stable by using a feasibility problem solving method in a linear matrix inequality. Through the stability analysis system and method of the time-varying power system, the problem that the stability of the time-varying power system is difficult to distinguish caused by the wind velocity random characteristic in case of fan connection can be effectively solved.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Fault estimation method under sensor network environment and based on Green space theory
InactiveCN104714520AHandle Coupling Problems EfficientlyReduce conservatismTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlDynamic modelsEstimation methods
The invention provides a fault estimation method under a sensor network environment and based on the Green space theory. The method includes the following steps that a dynamic model of a time-varying system with actuator and sensor faults is established; various sensors and measurement output adjacent to the sensors are synthesized; distributed fault estimation is conducted on the dynamic model; the existence judgment conditions of fault estimators on nodes are acquired through the linear estimation theory of Green space; if the existence conditions are satisfied, estimator parameter matrixes on the nodes are acquired through the update analysis and projection theorem in the Green space; the estimator parameter matrixes are substituted into a distributed fault estimation formula, and distributed fault estimation of the time-varying system with the actuator and sensor faults is conducted under the sensor network environment. The method can effectively solve the coupling problem between the sensor nodes under the sensor network environment and achieve the purposes of a small conservative property and high estimation accuracy.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
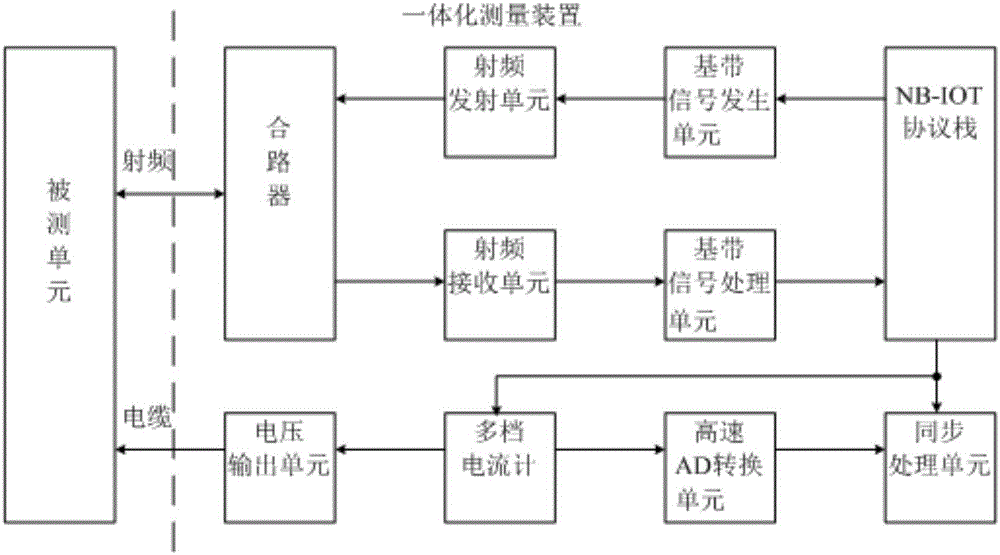
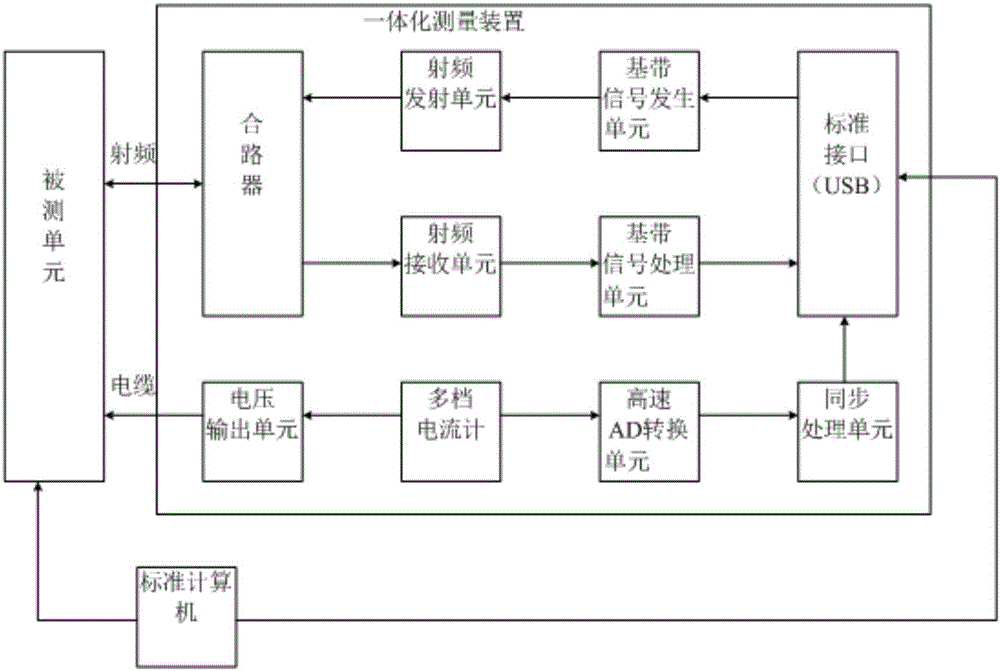
Precision current detection apparatus of NB-IOT terminal under multiple operation modes
PendingCN106597081ASolving Current Measurement ProblemsRealize measurementMeasurement using digital techniquesHigh level techniquesOperation modeEngineering
The invention discloses a precision current detection apparatus of an NB-IOT terminal under multiple operation modes. The apparatus comprises an overall scheduling unit, a radio frequency unit, a base-band signal generating unit, a base-band signal processing unit, a combiner, a synchronous processing unit, a high speed AD conversion unit, a multi-range galvanometer and a voltage output unit. The radio frequency unit comprises a radio frequency emission unit and a radio frequency receiving unit. The apparatus is integrally designed with a power supply current through a protocol stack and accurate current measurement to an NB-IOT module at any moments is realized so that a current measurement problem of a time-varying system is solved and dynamic current measurement at a microsecond grade can be realized, a measured speed is fast and good synchronization is possessed. Besides, the apparatus possesses a good cost performance, the size is small and weight is light. Compared to a traditional measurement system, usage convenience of the apparatus is greatly increased. Under signaling mode measurement, without any external design, whole measurement can be completed so that measurement efficiency is greatly increased.
Owner:TRANSCOM INSTR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com