Patents
Literature
140 results about "Maintenance planning" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of forecasting maintenance of a machine
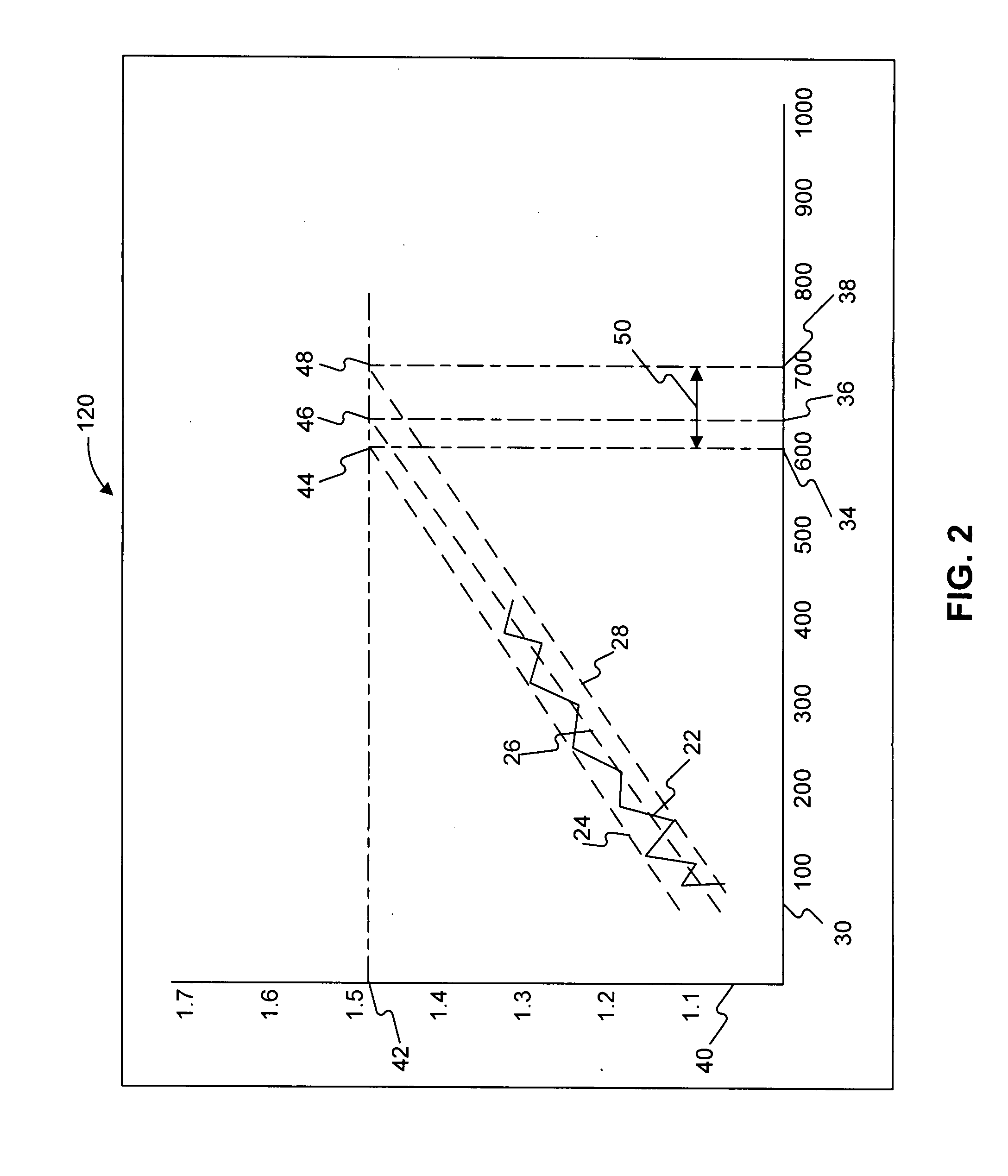
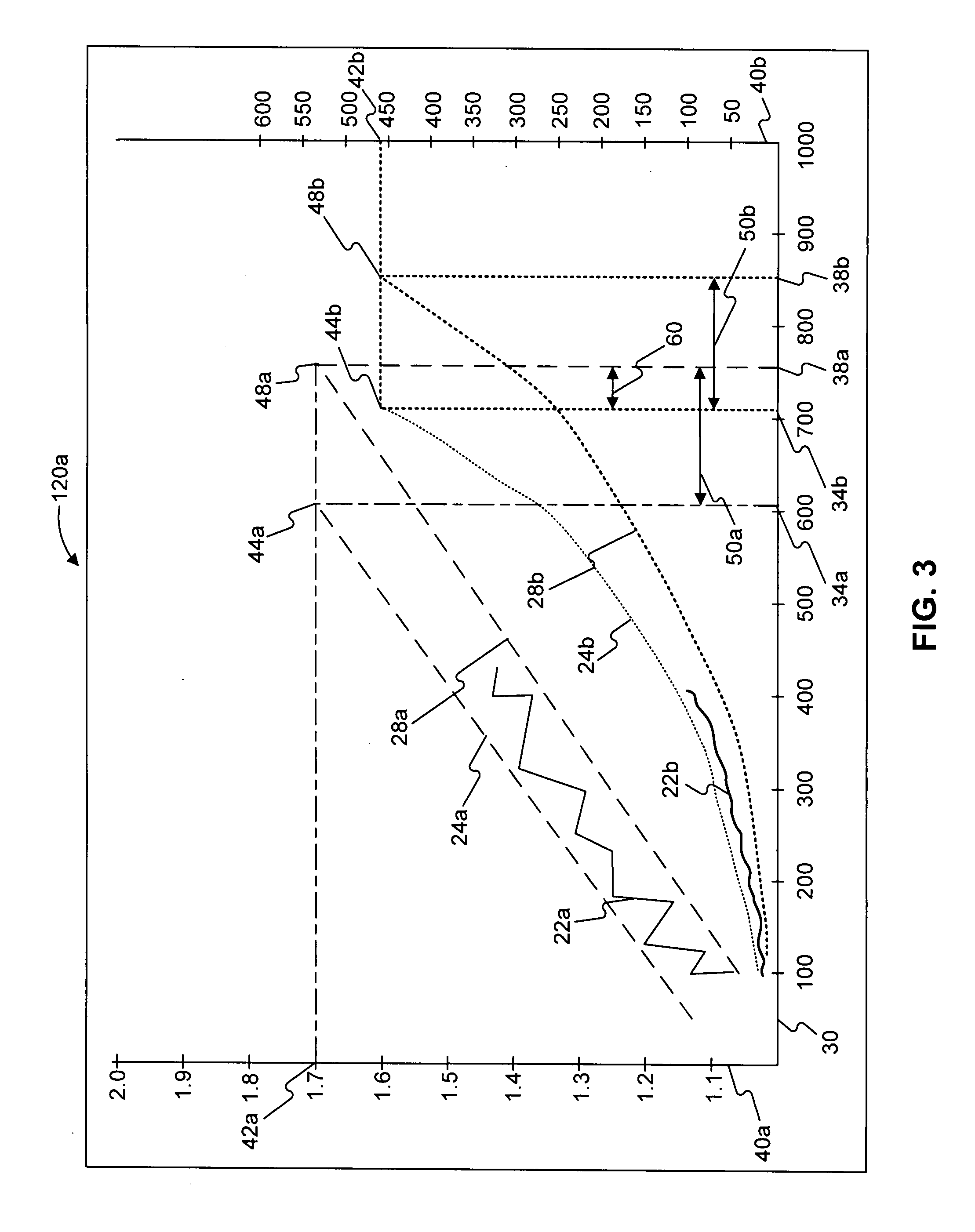
A method of forecasting maintenance of a machine is disclosed. The method includes measuring a parameter of the machine, the parameter being indicative of a condition of the machine, and transferring the measured parameter to a maintenance planning system. The method also includes predicting two or more parameter variation curves indicating the variation of the parameter over time, each parameter variation curve representing values of the parameter at a different confidence level. The method further includes identifying a first time period for maintenance of the machine based on the two or more parameter variation curves.
Owner:SOLAR TURBINES
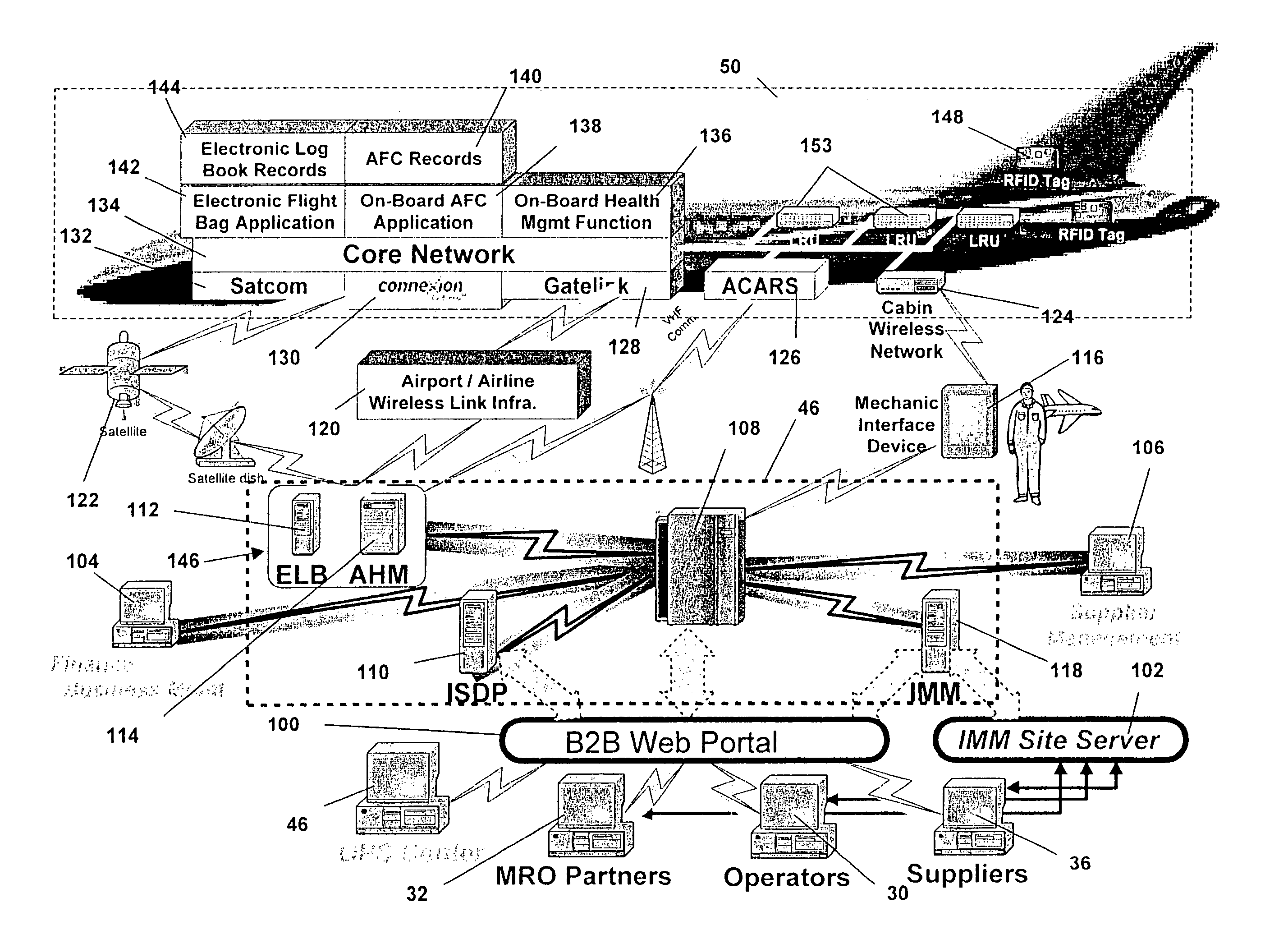
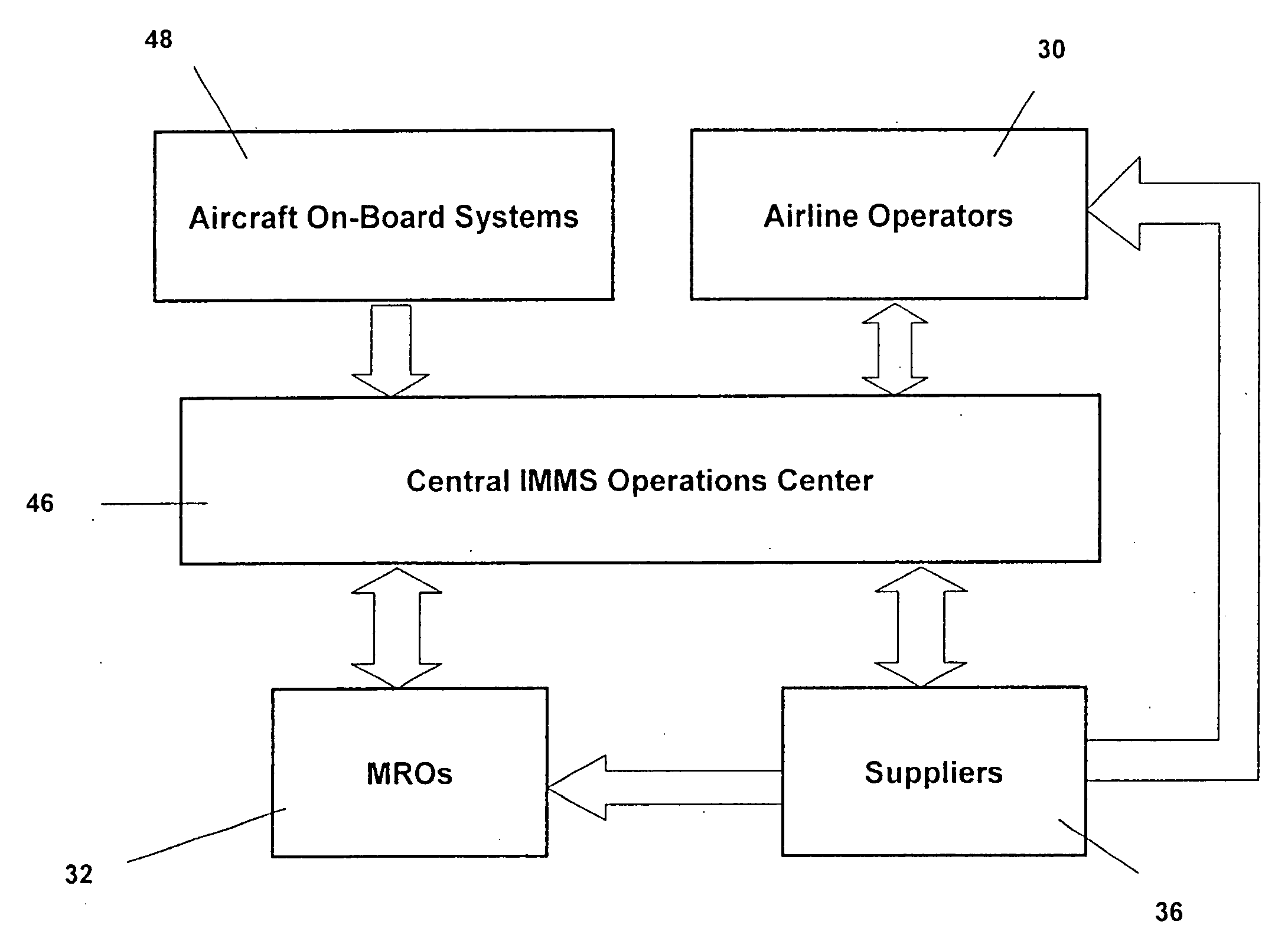
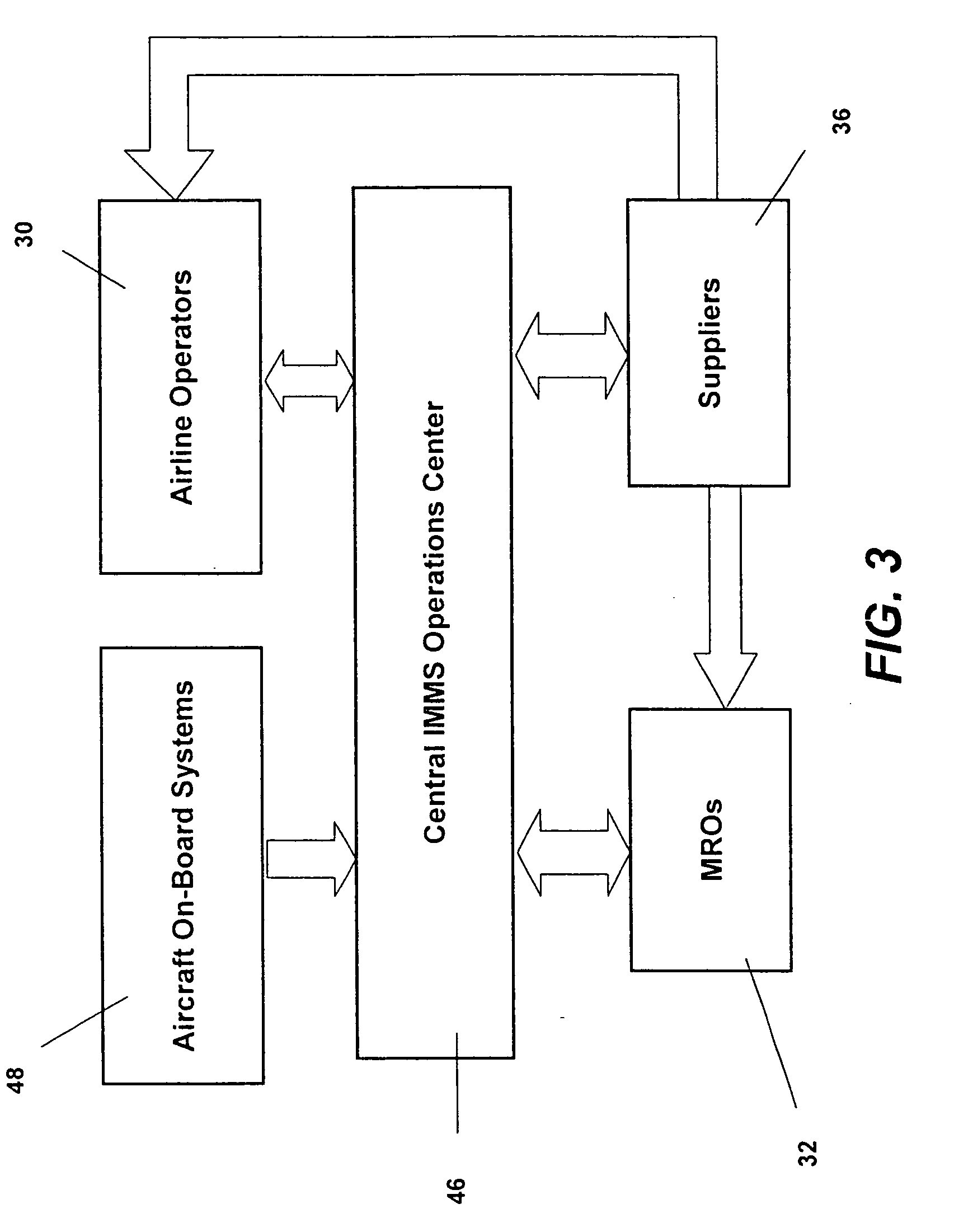
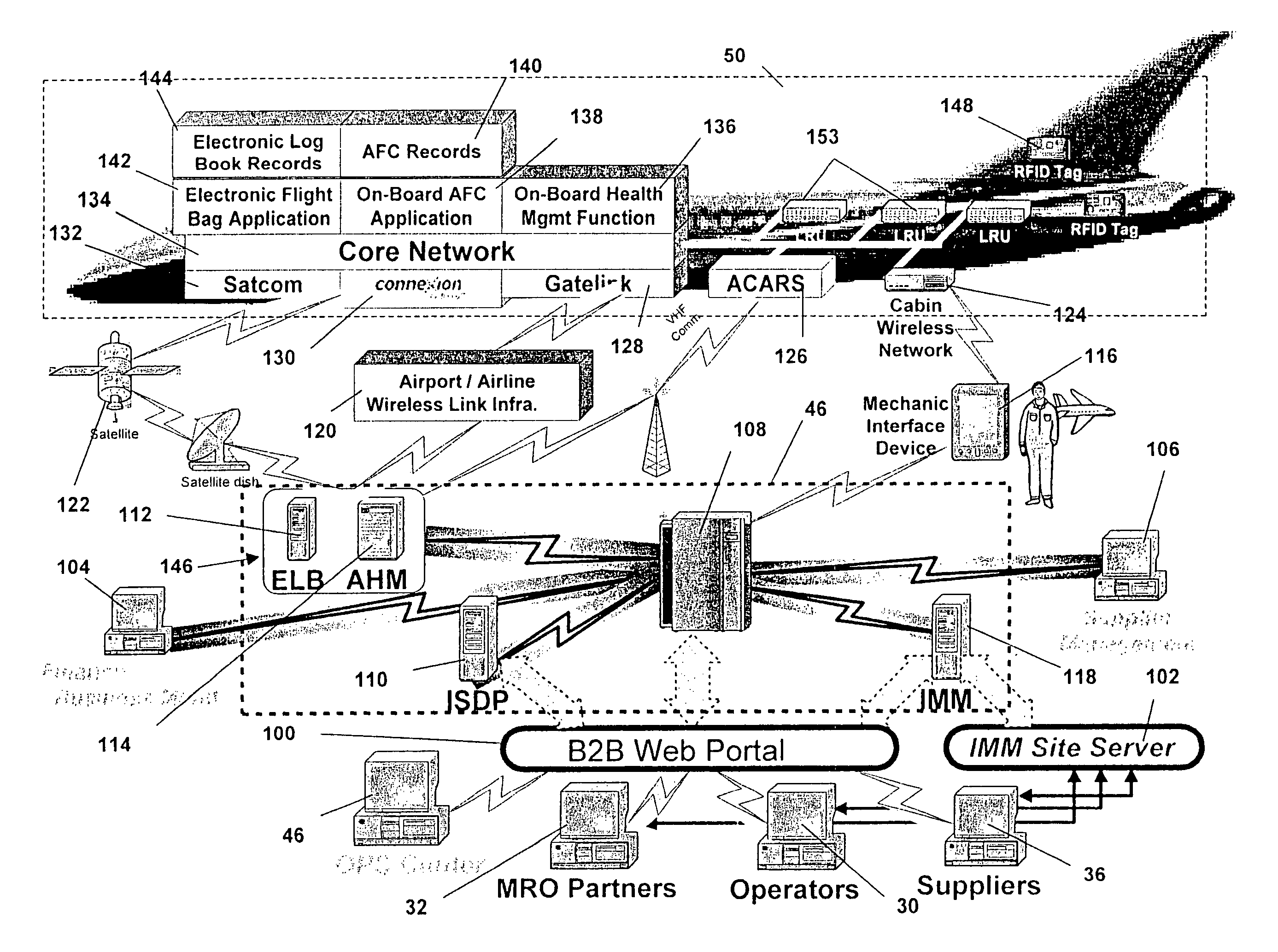
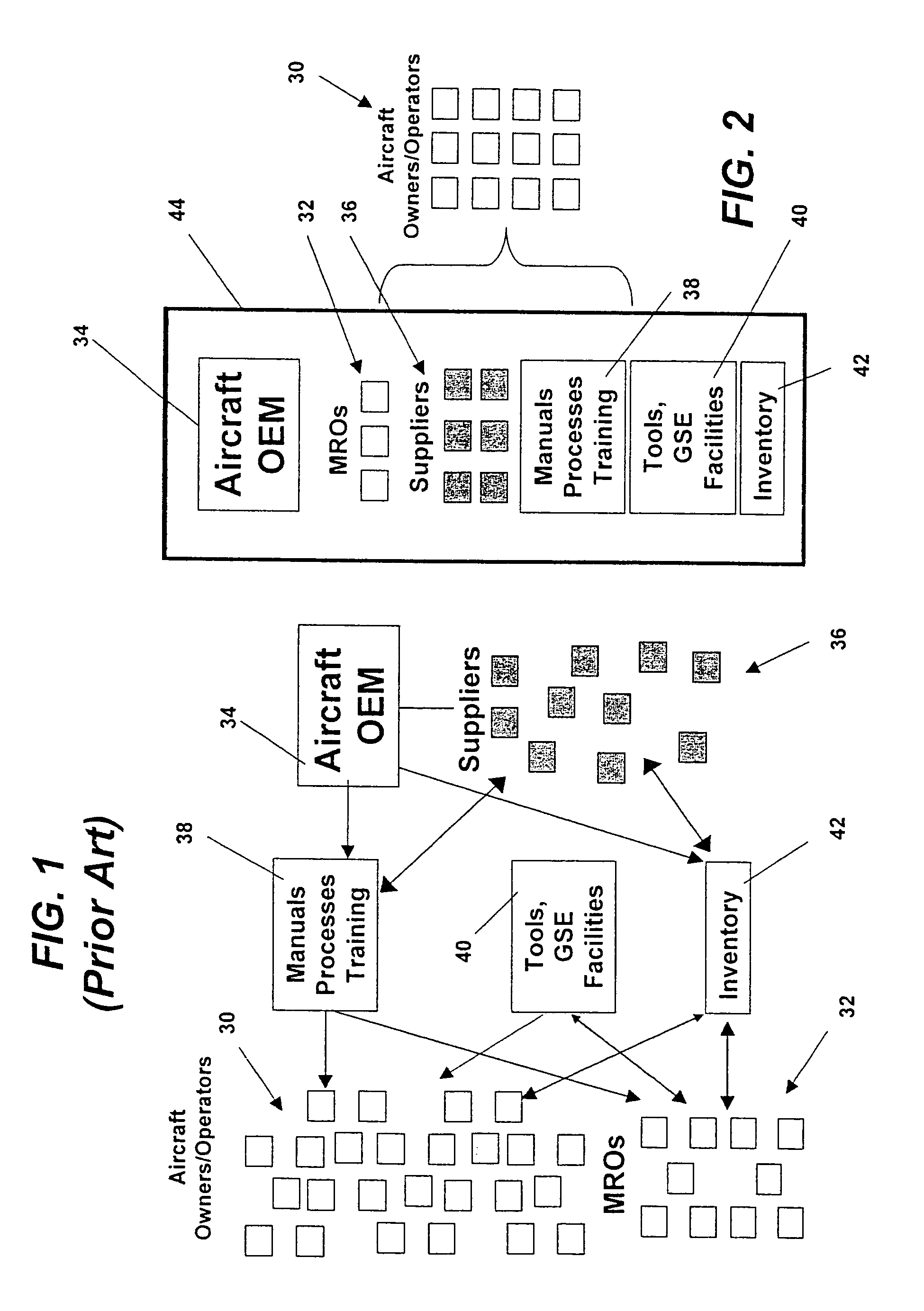
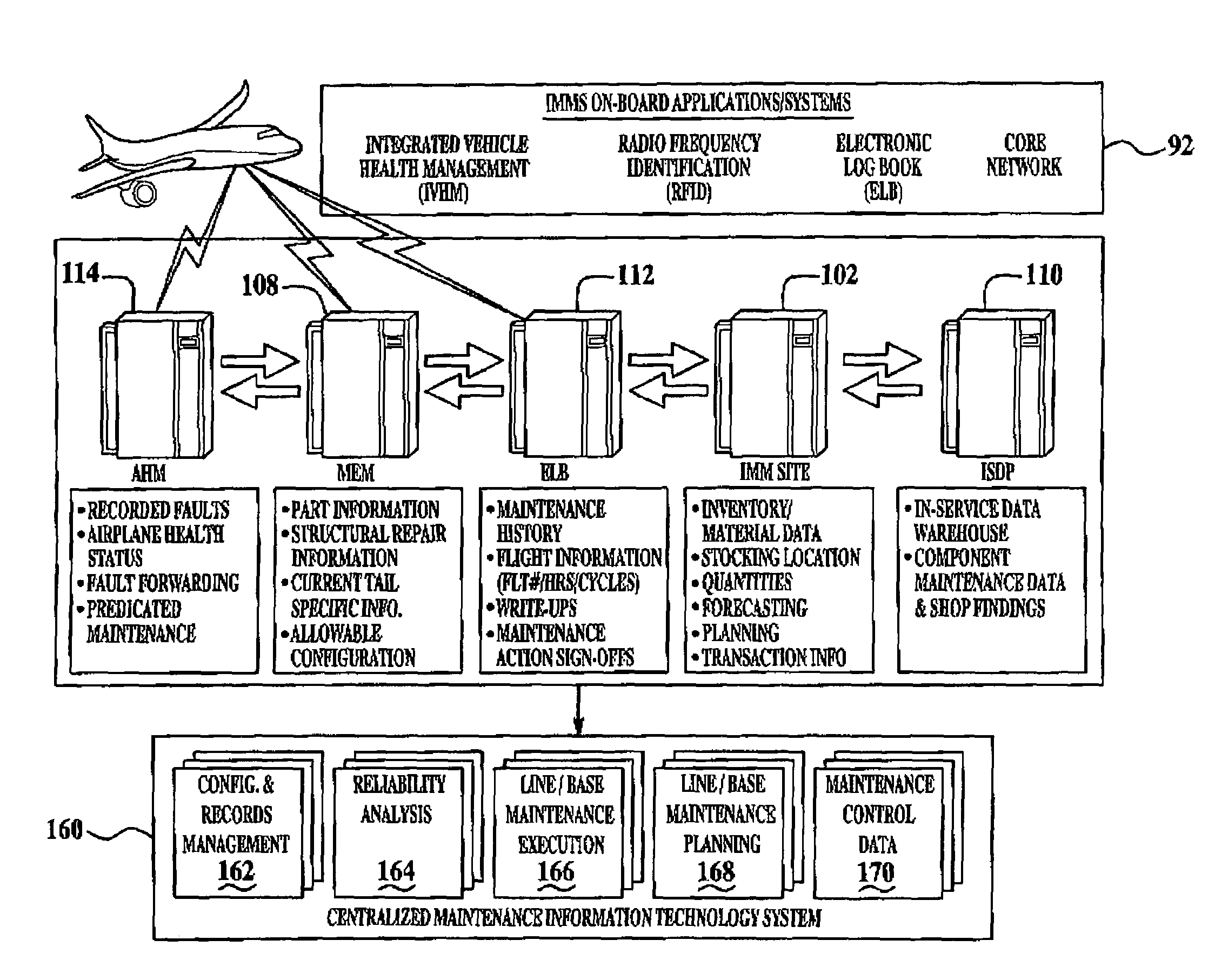
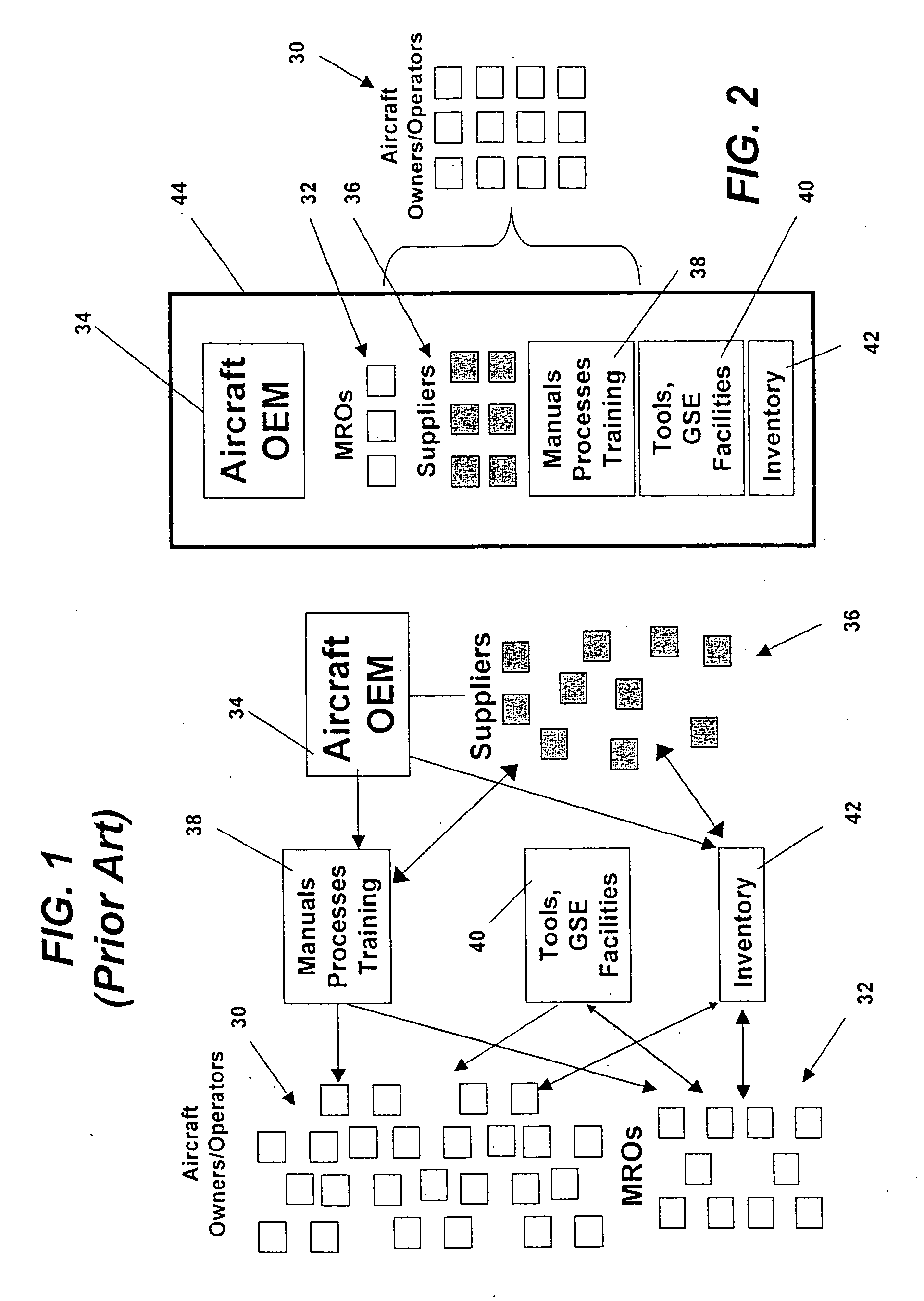
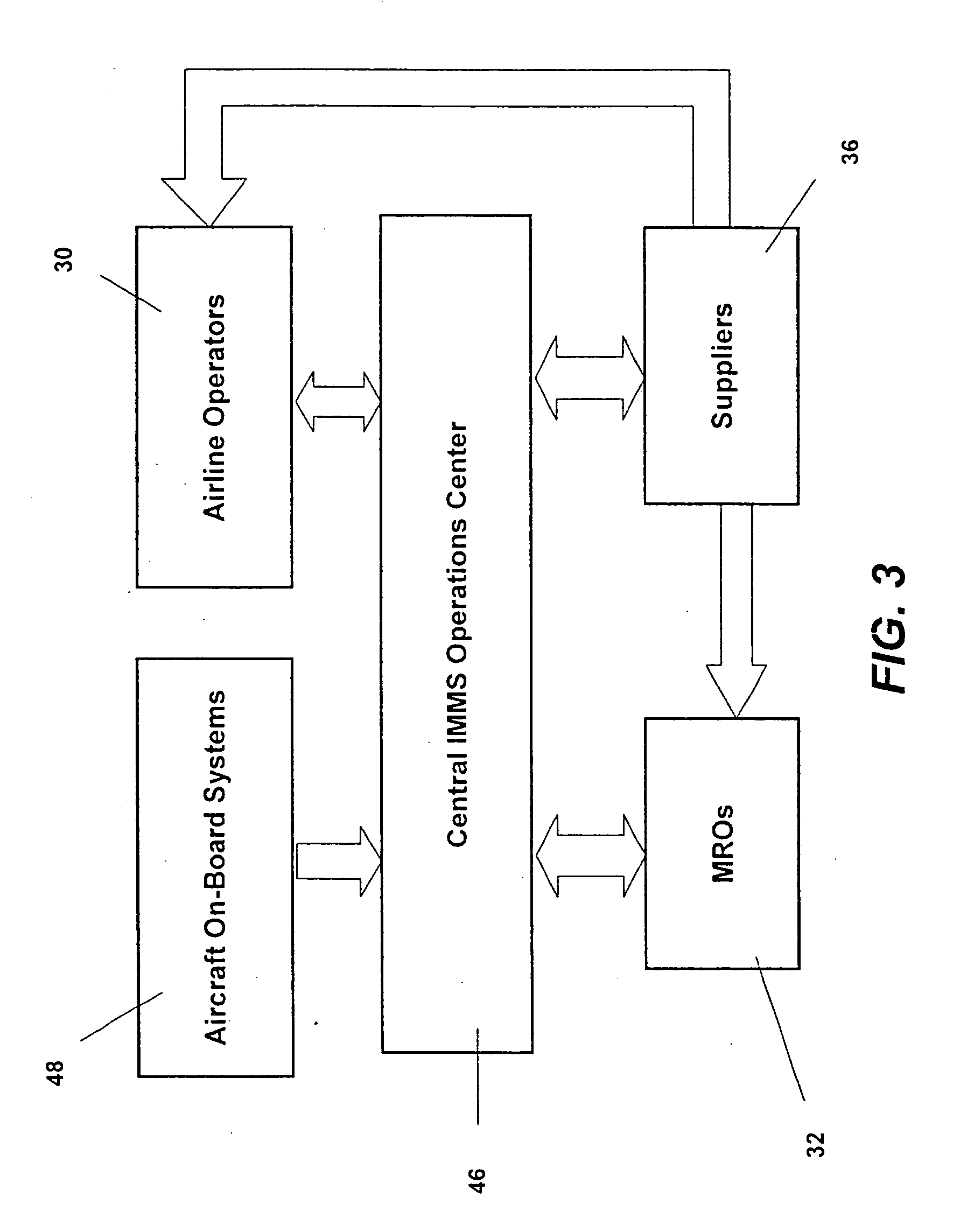
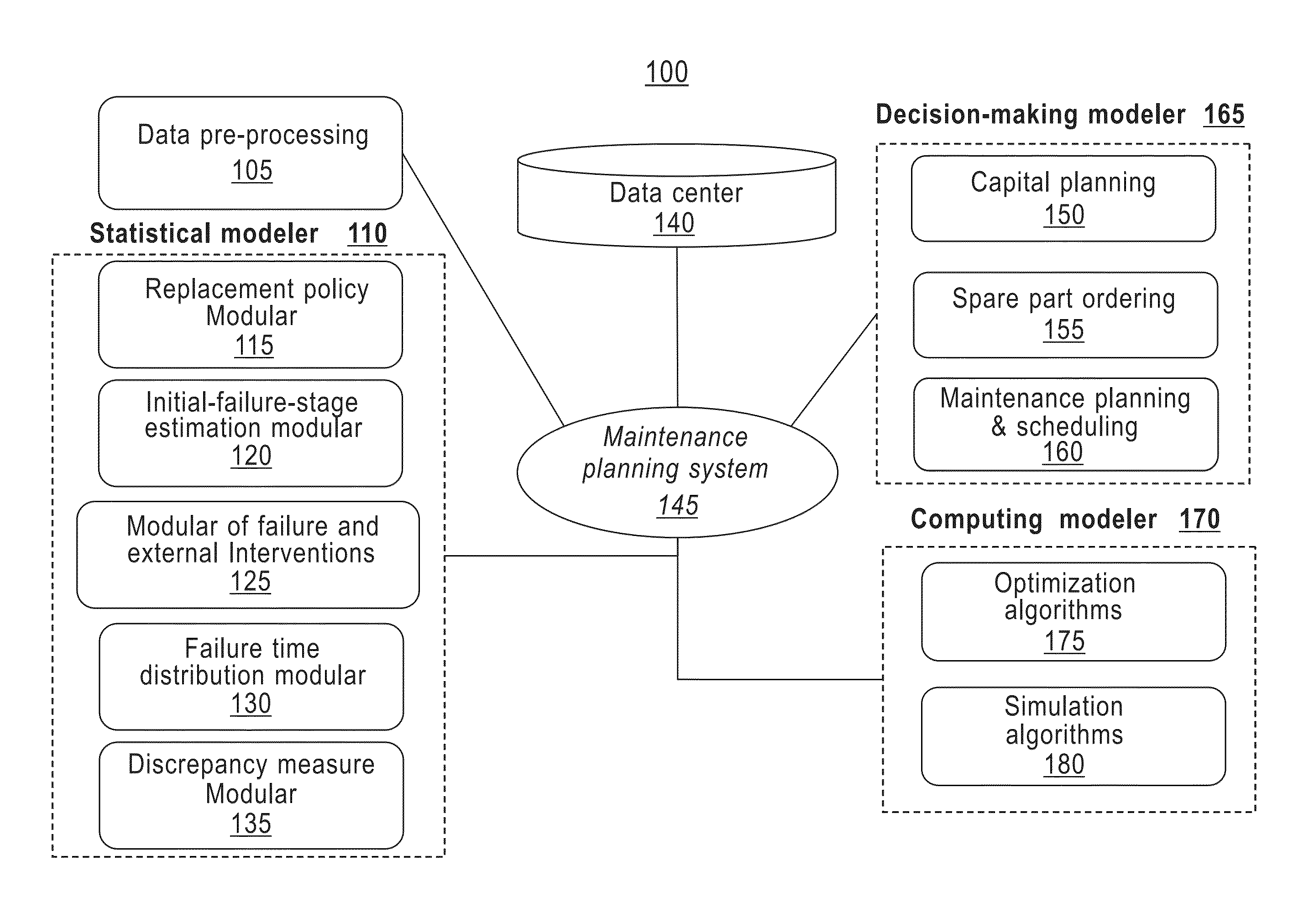
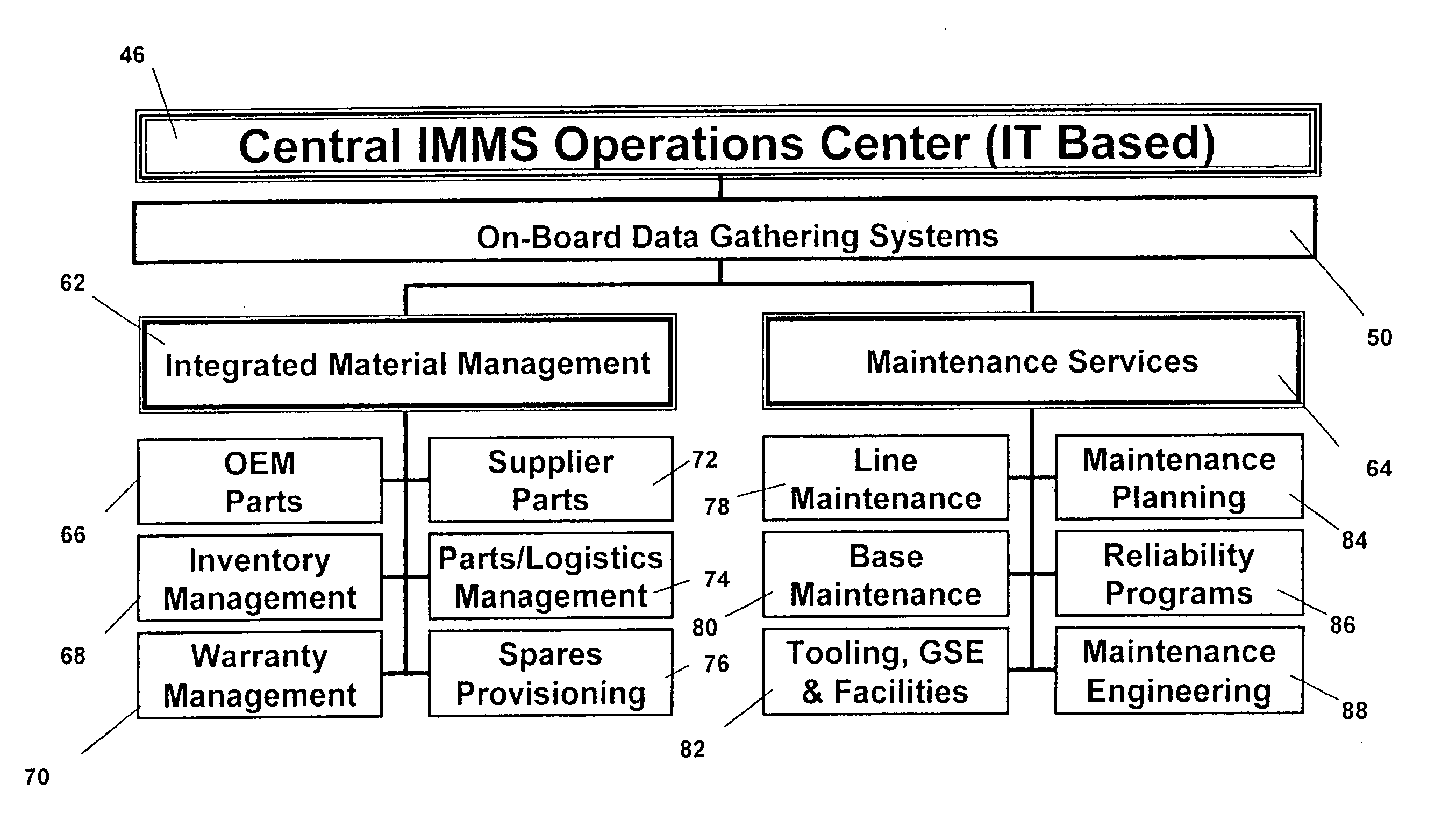
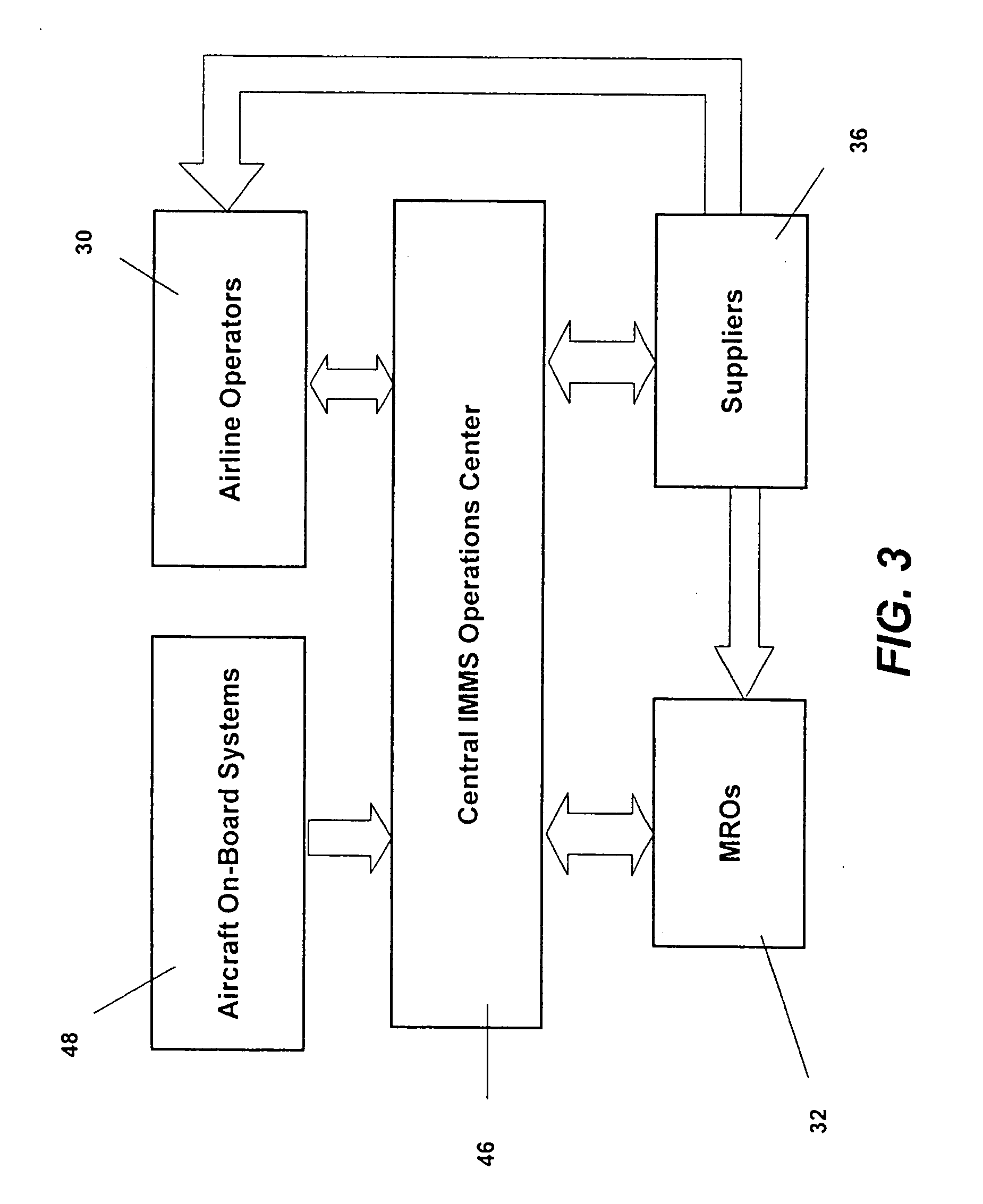
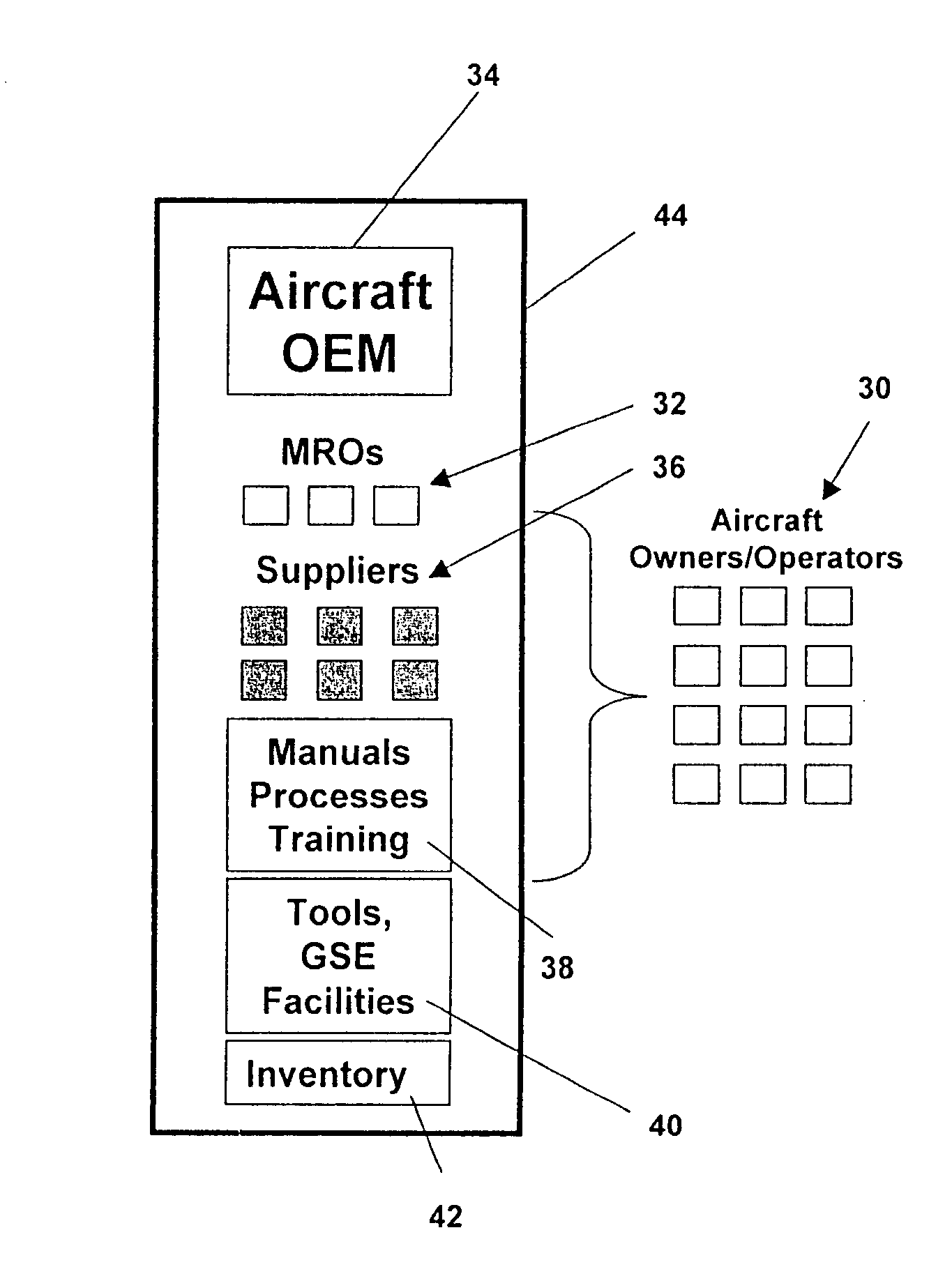
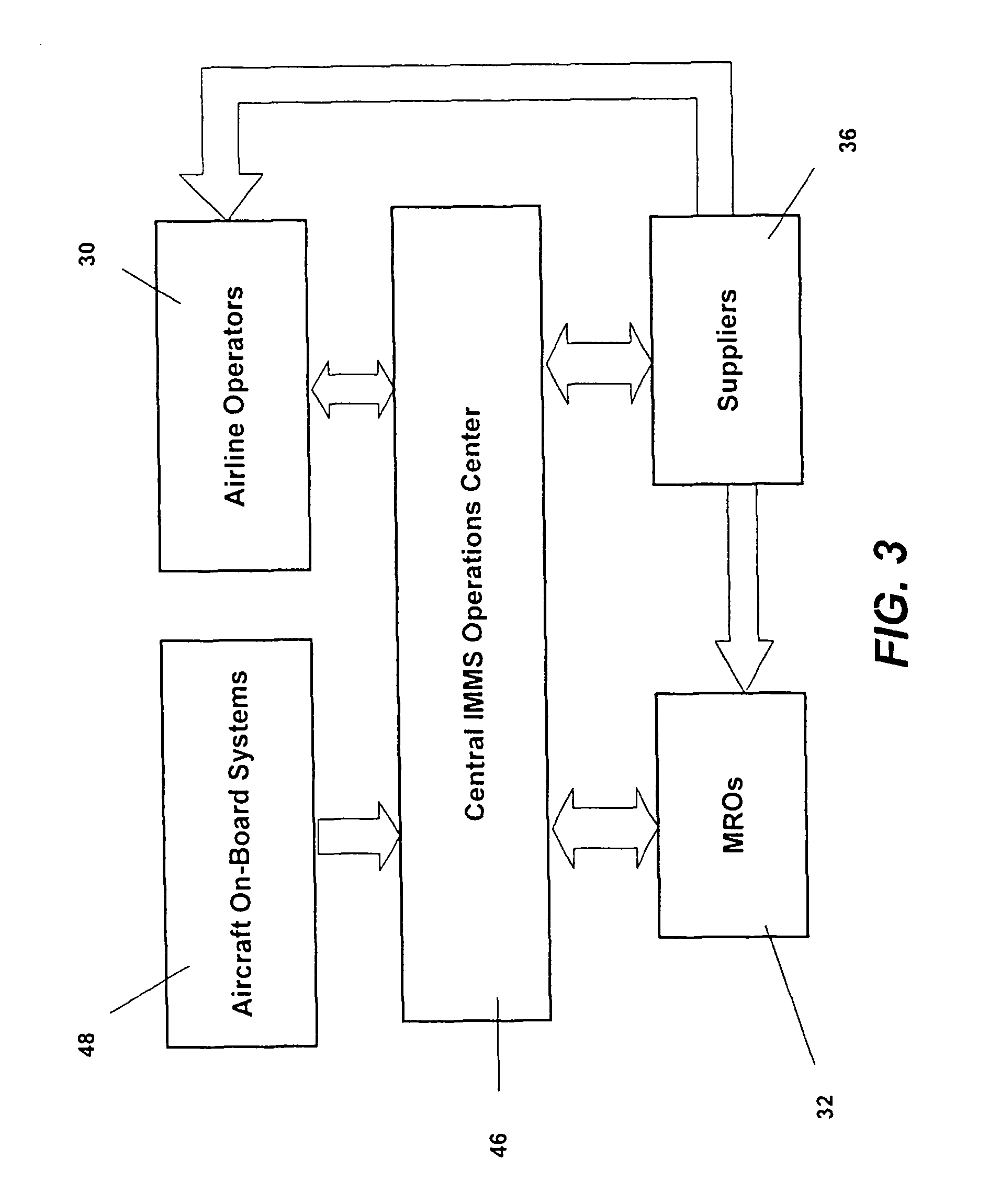
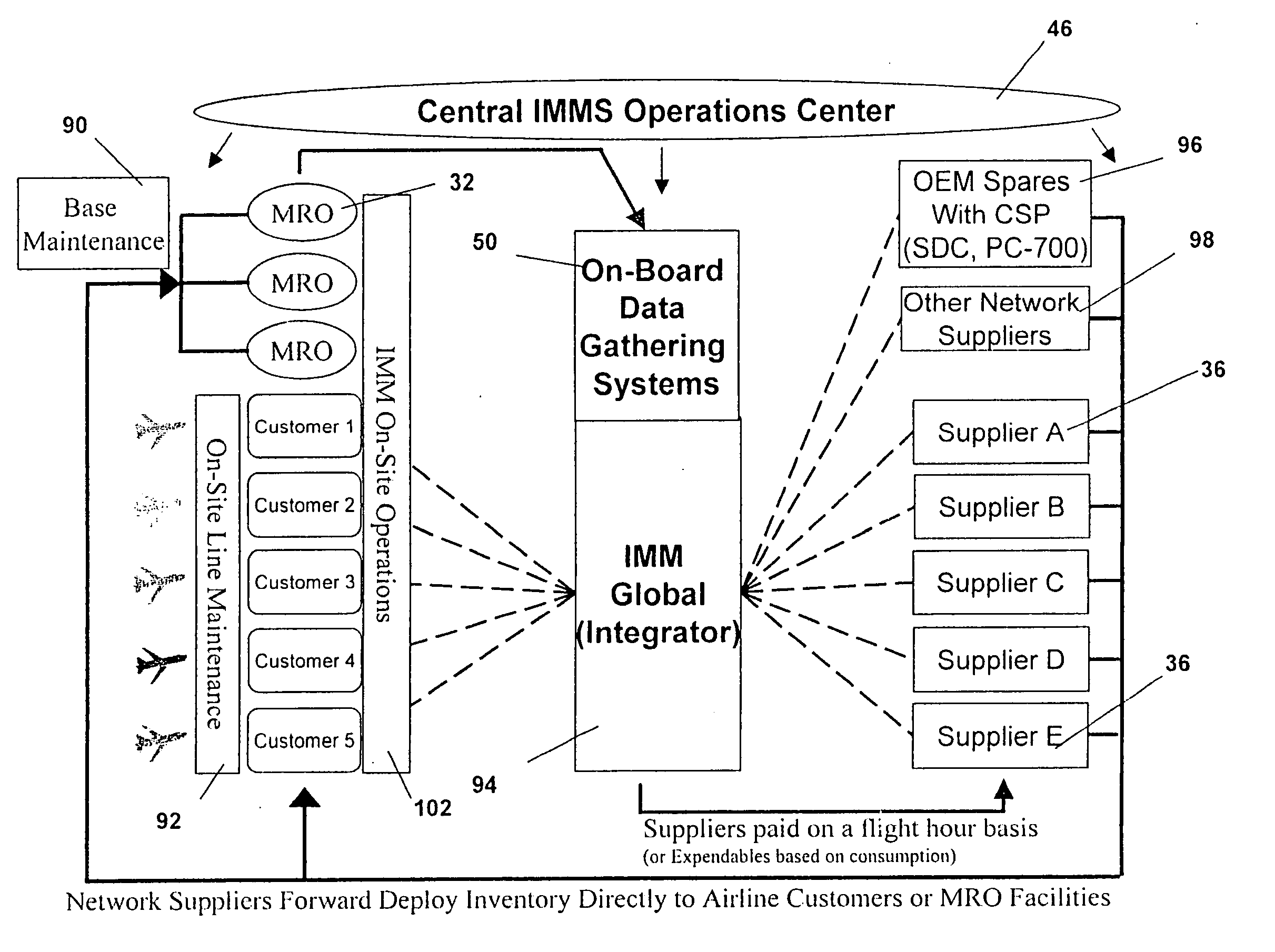
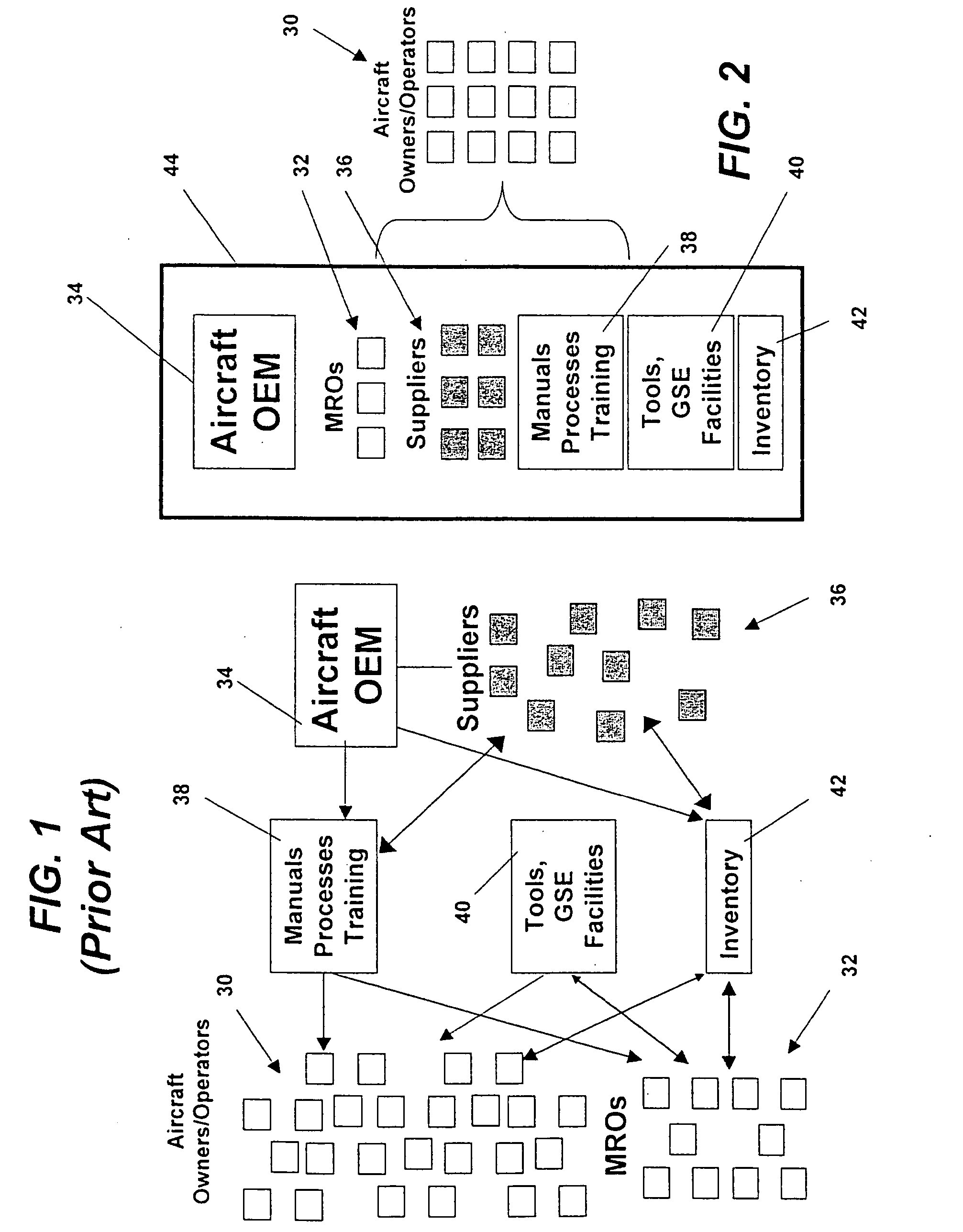
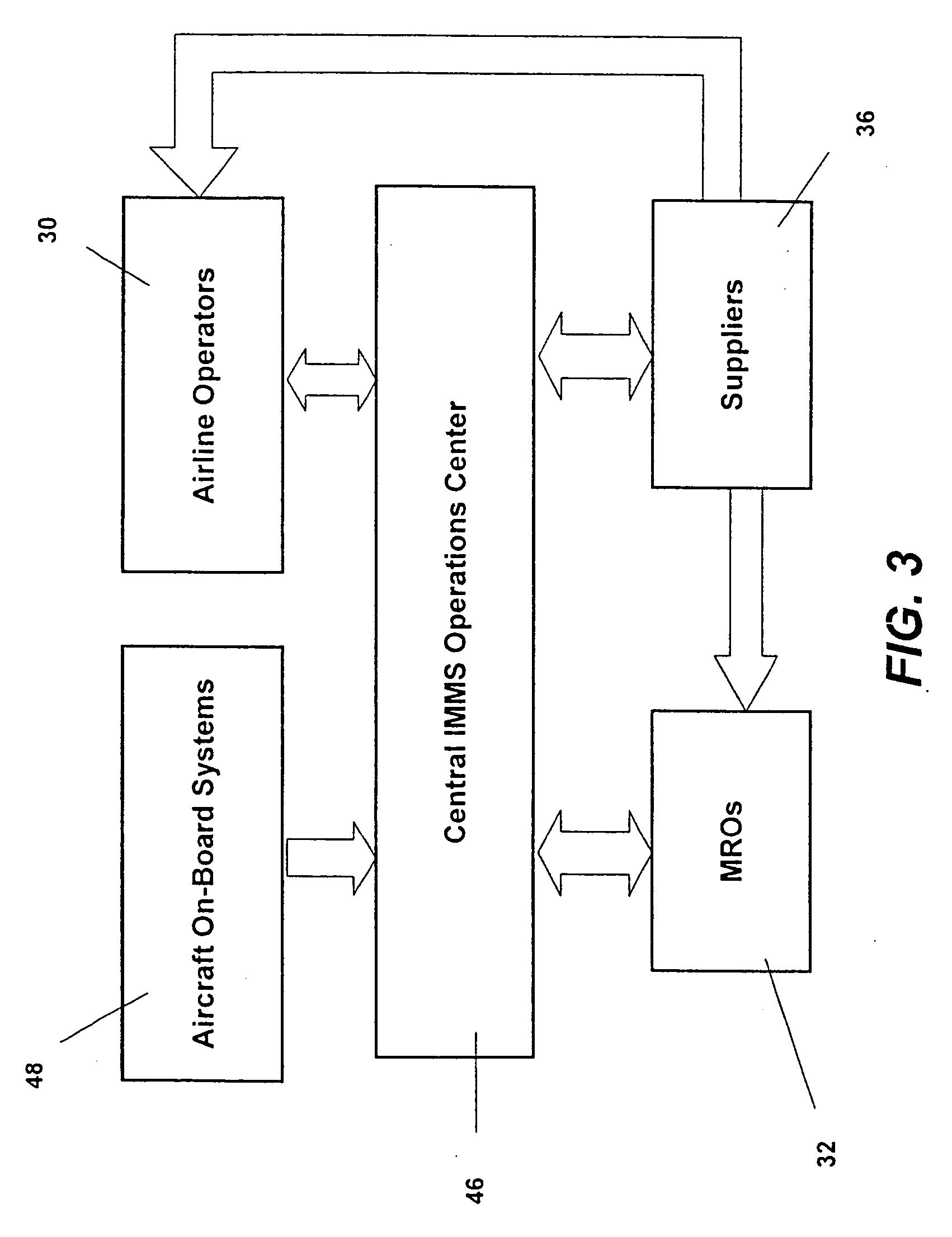
Integrated maintenance and materials services for fleet aircraft using aircraft data to improve quality of materials
ActiveUS7689329B2Improve efficiencyLow costVehicle testingAnalogue computers for trafficMaintenance planningOn board
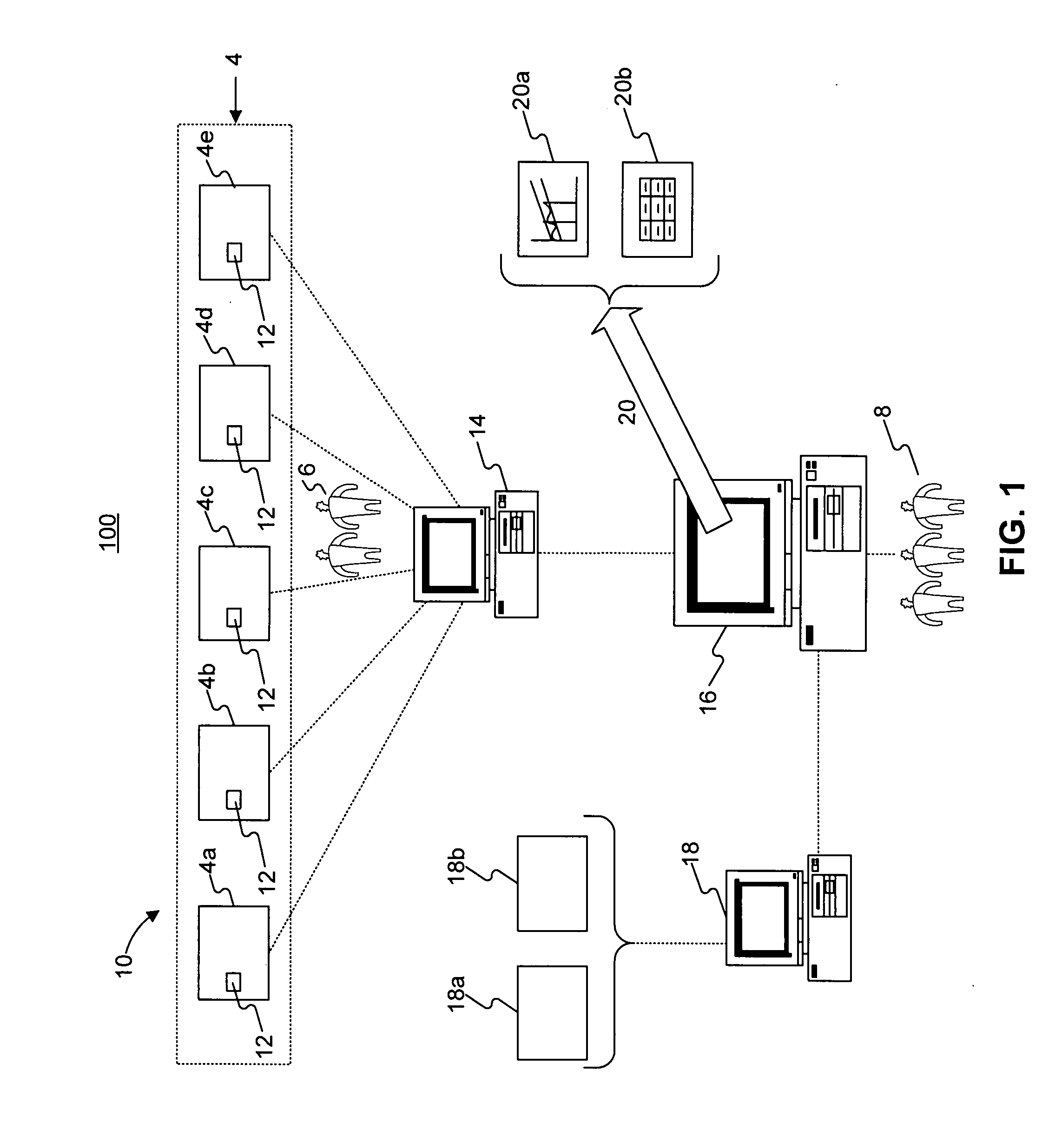
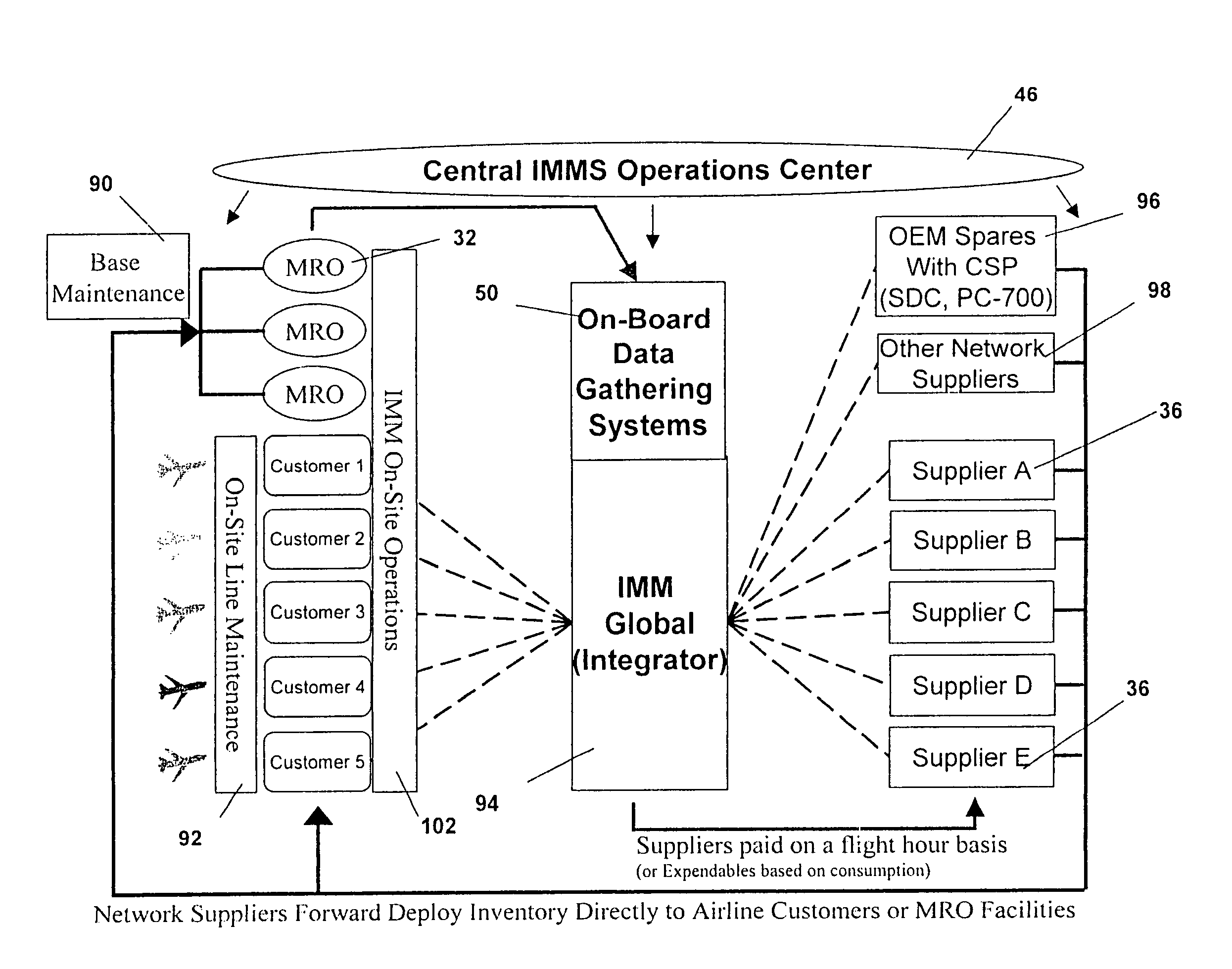
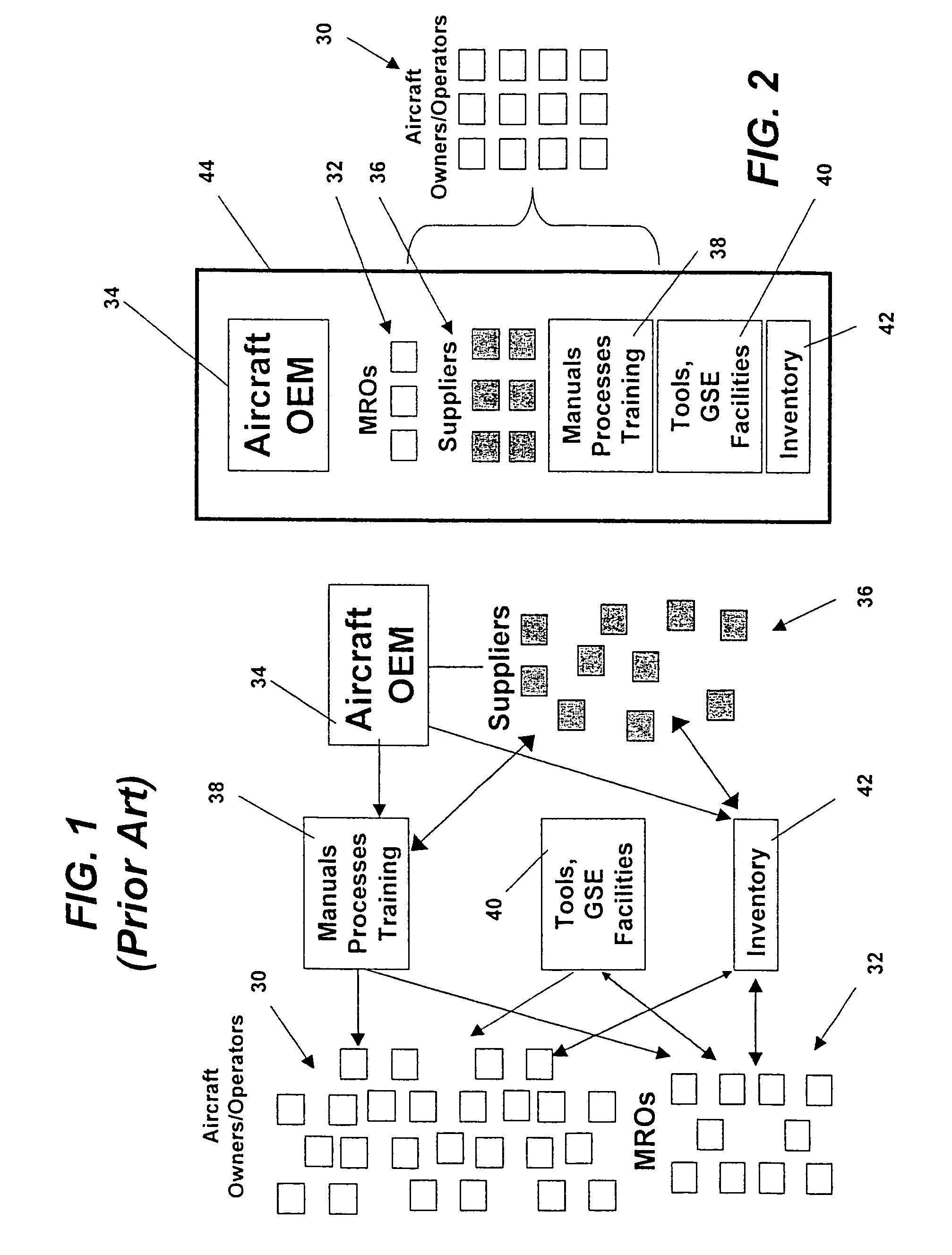
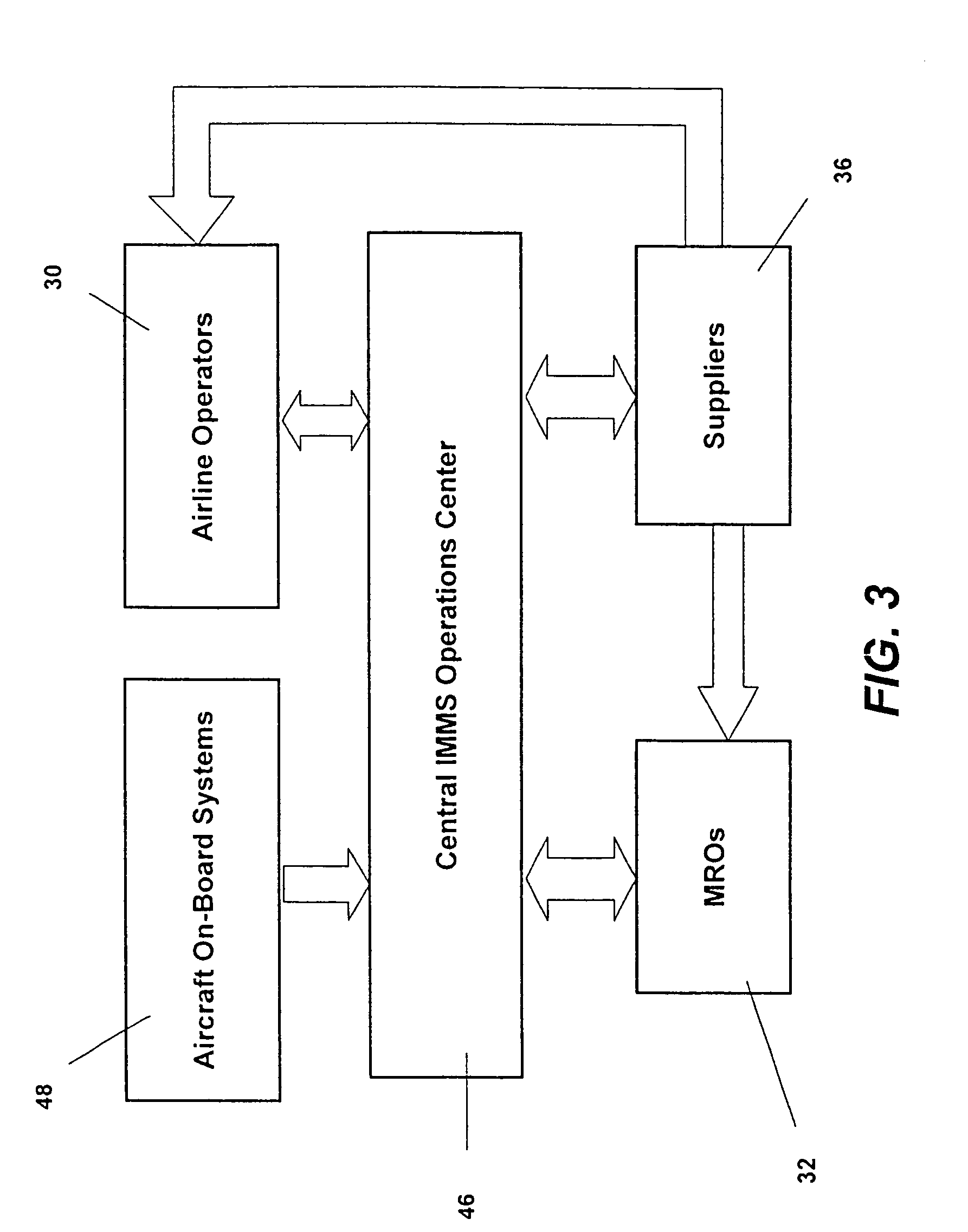
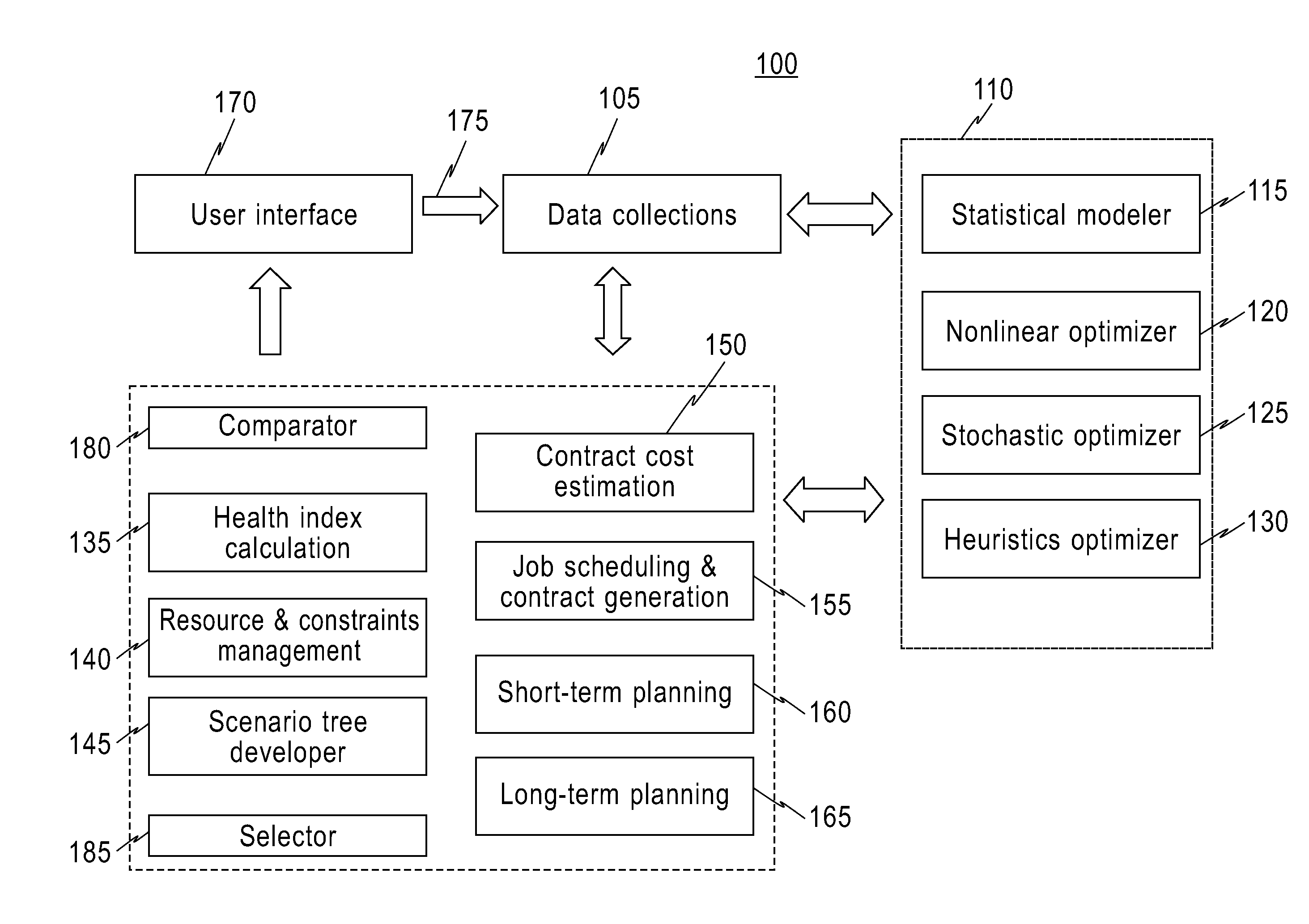
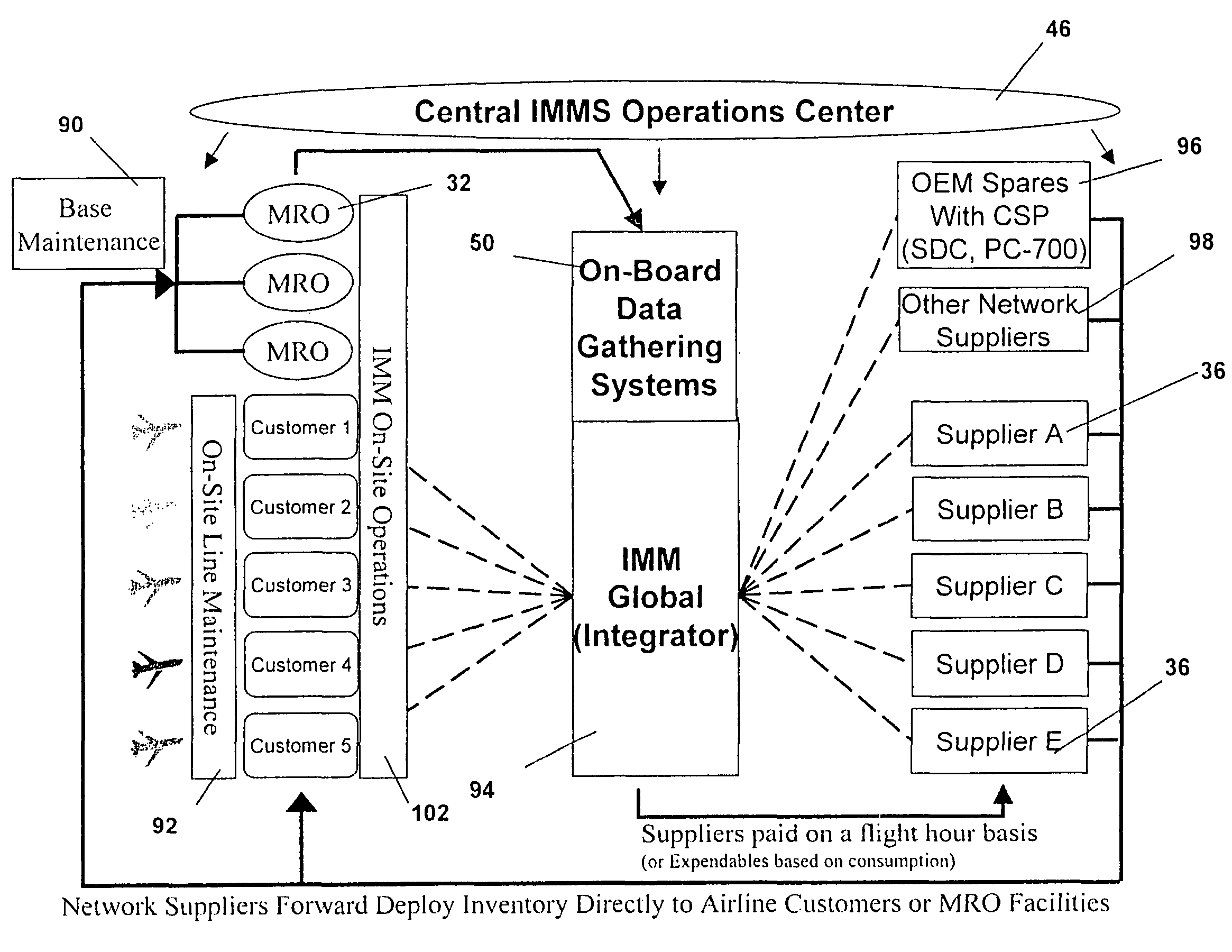
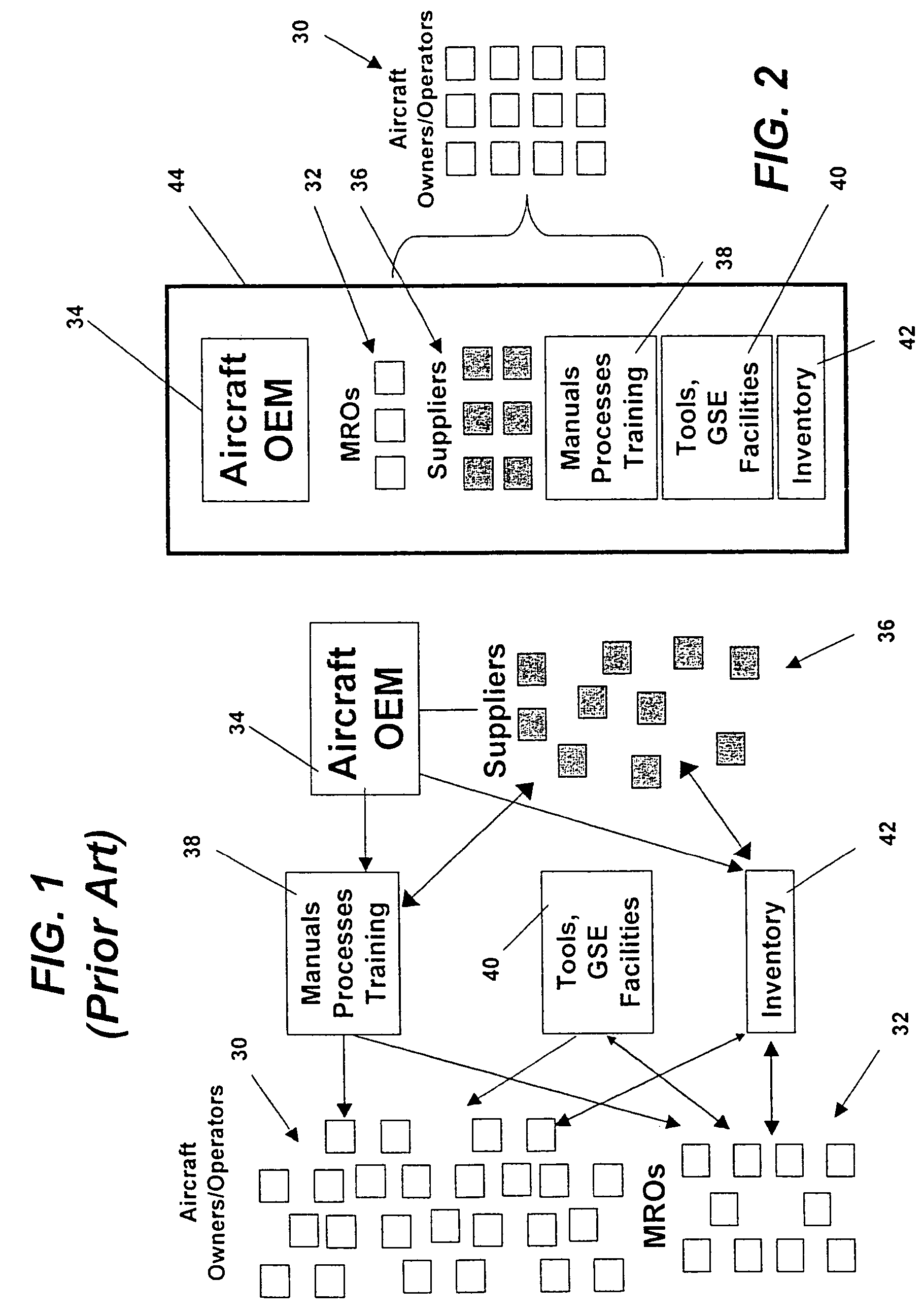
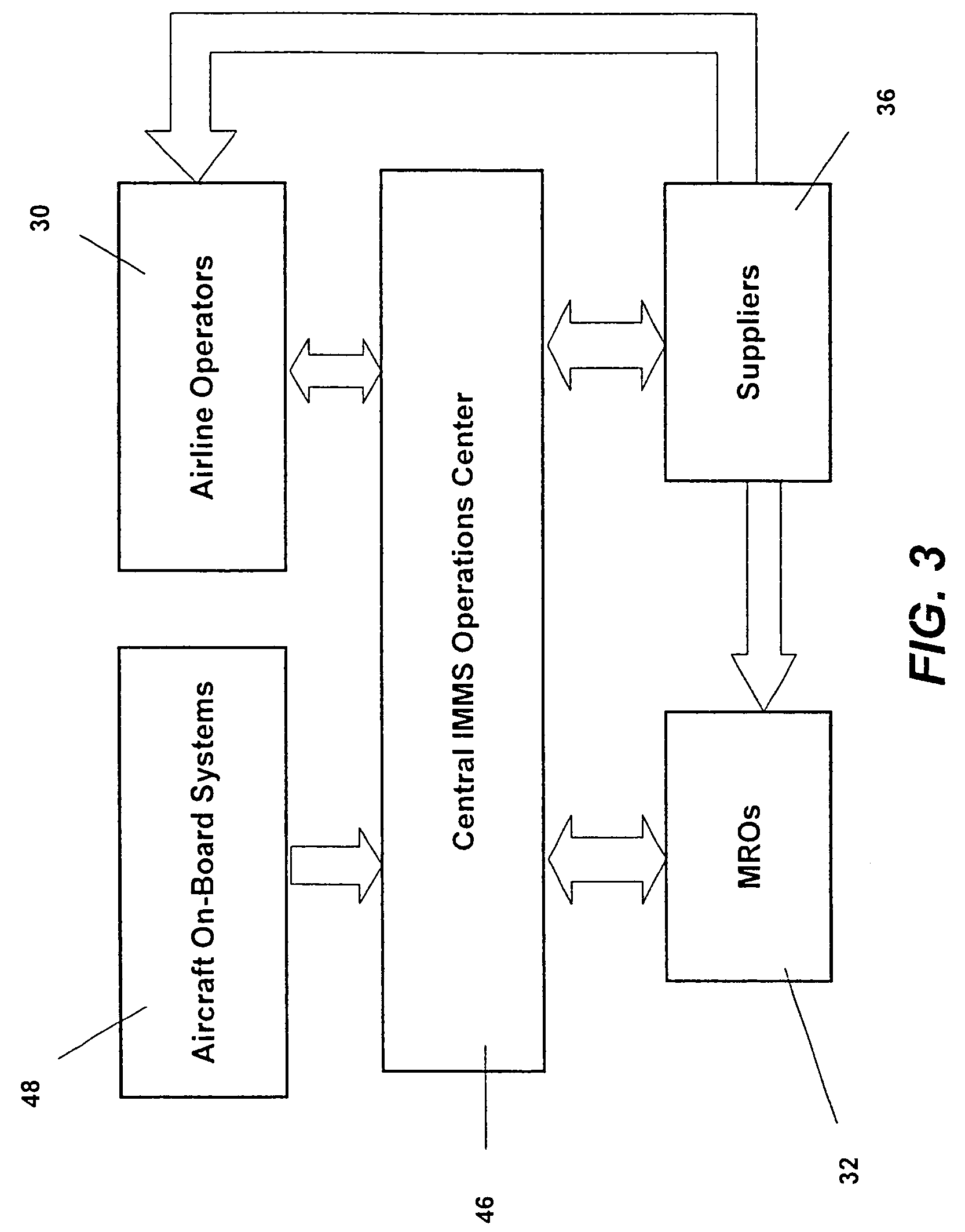
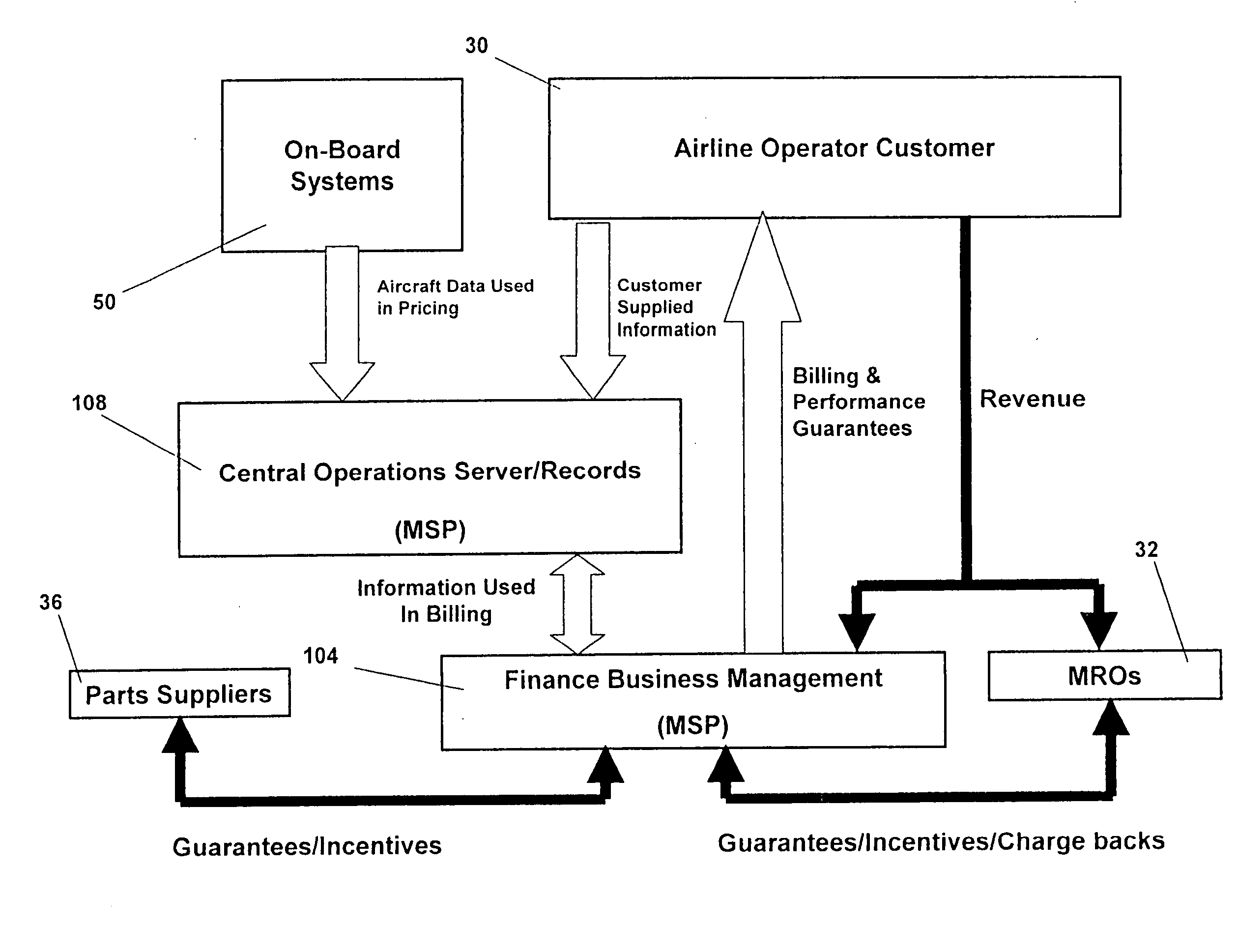
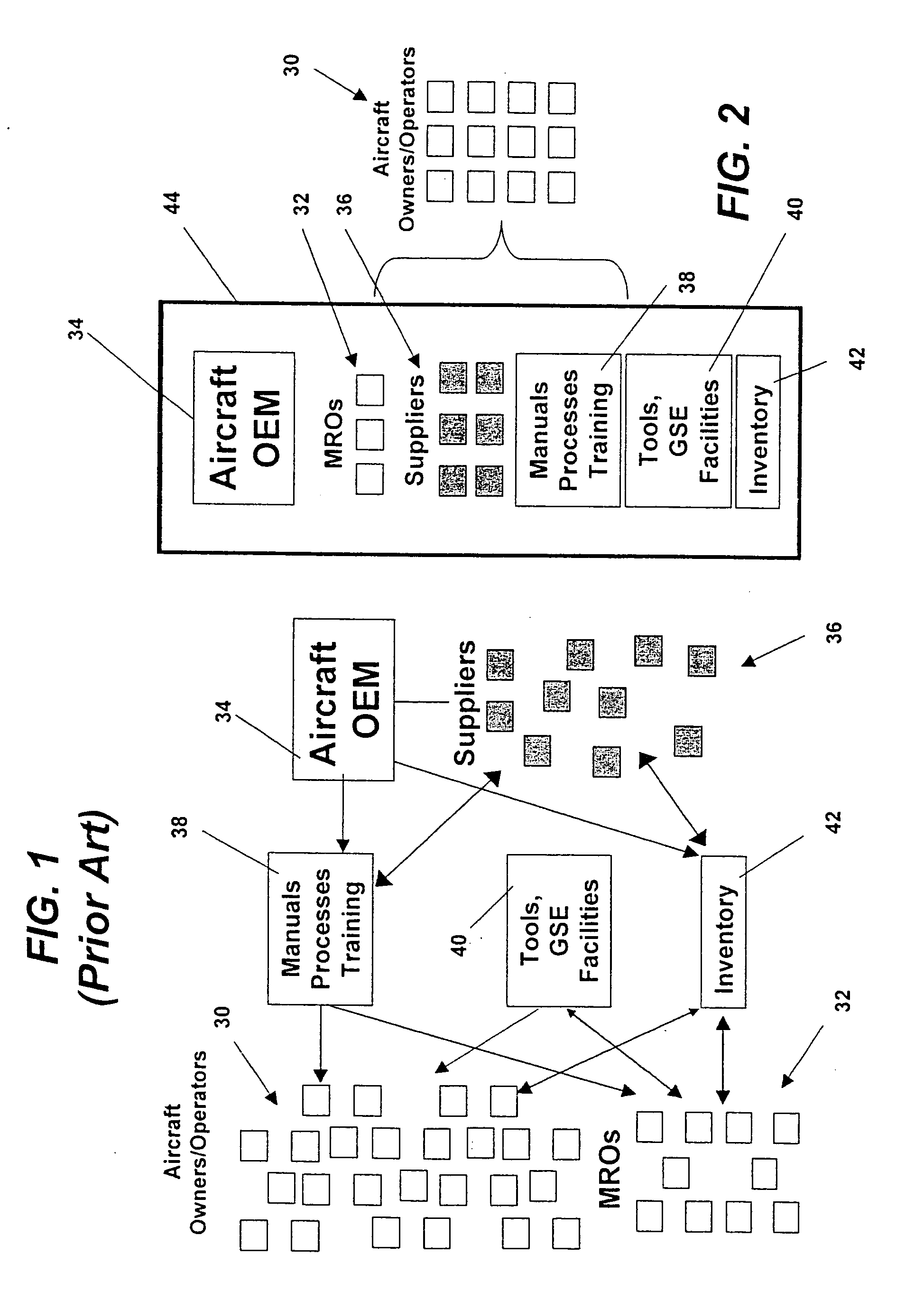
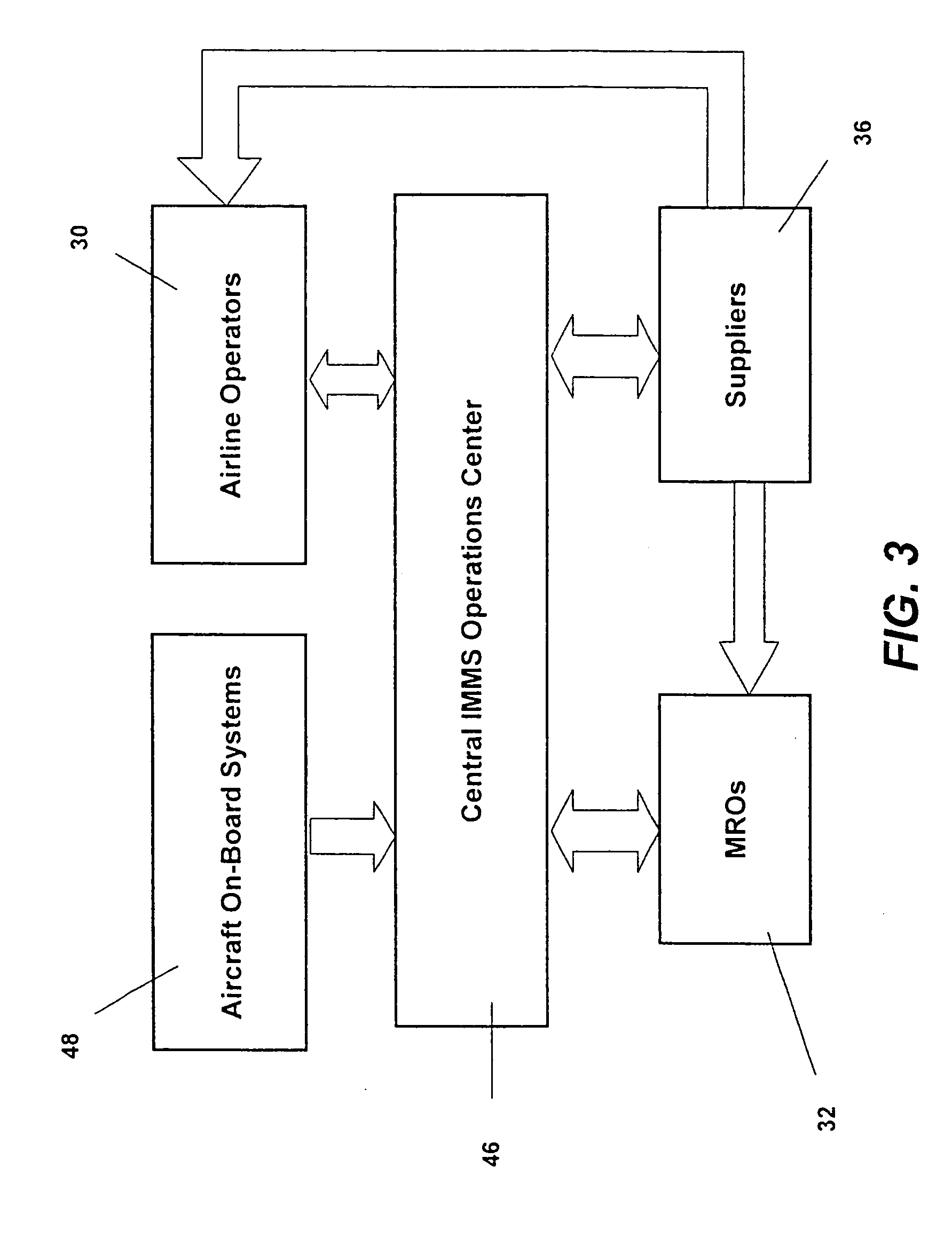
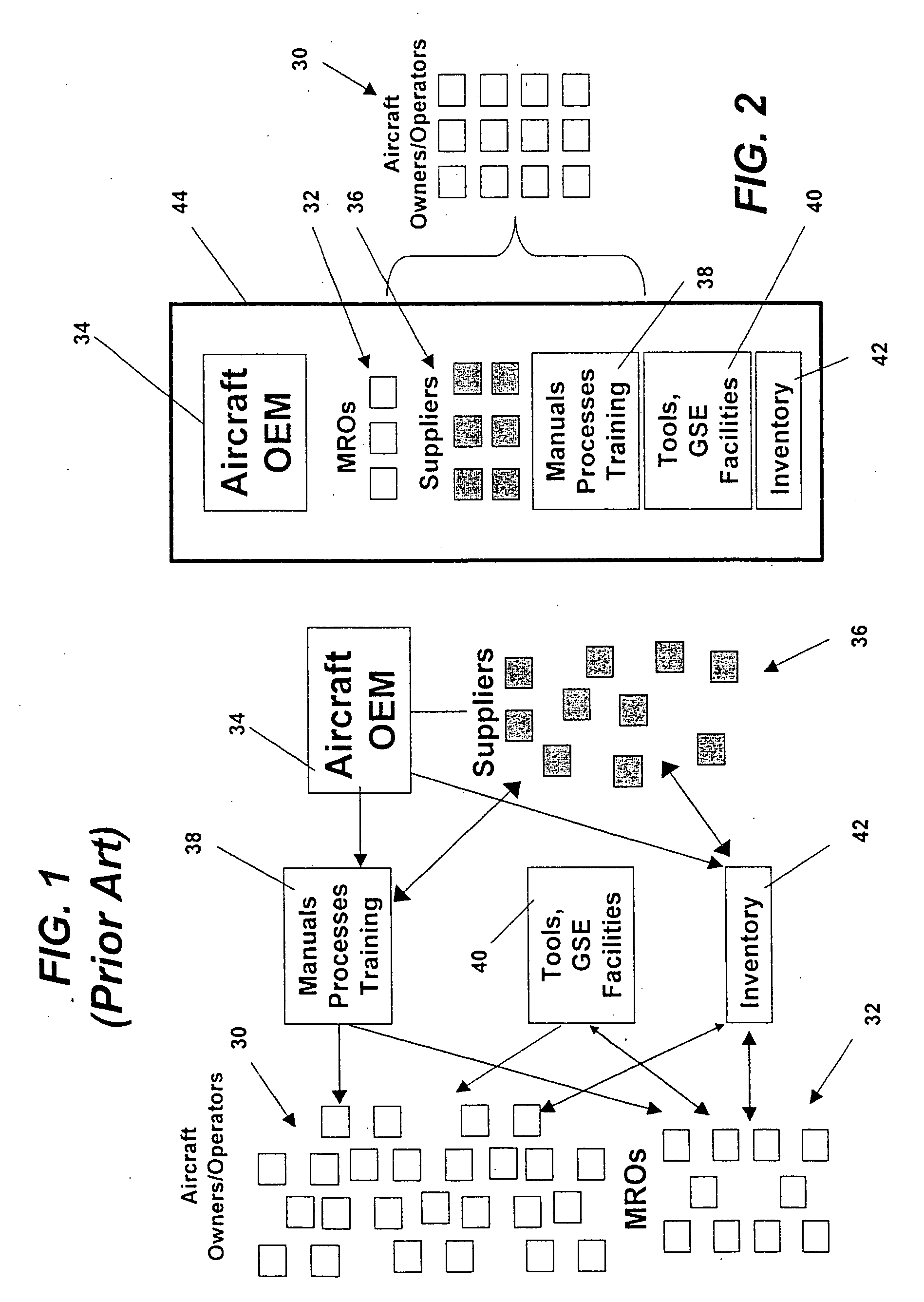
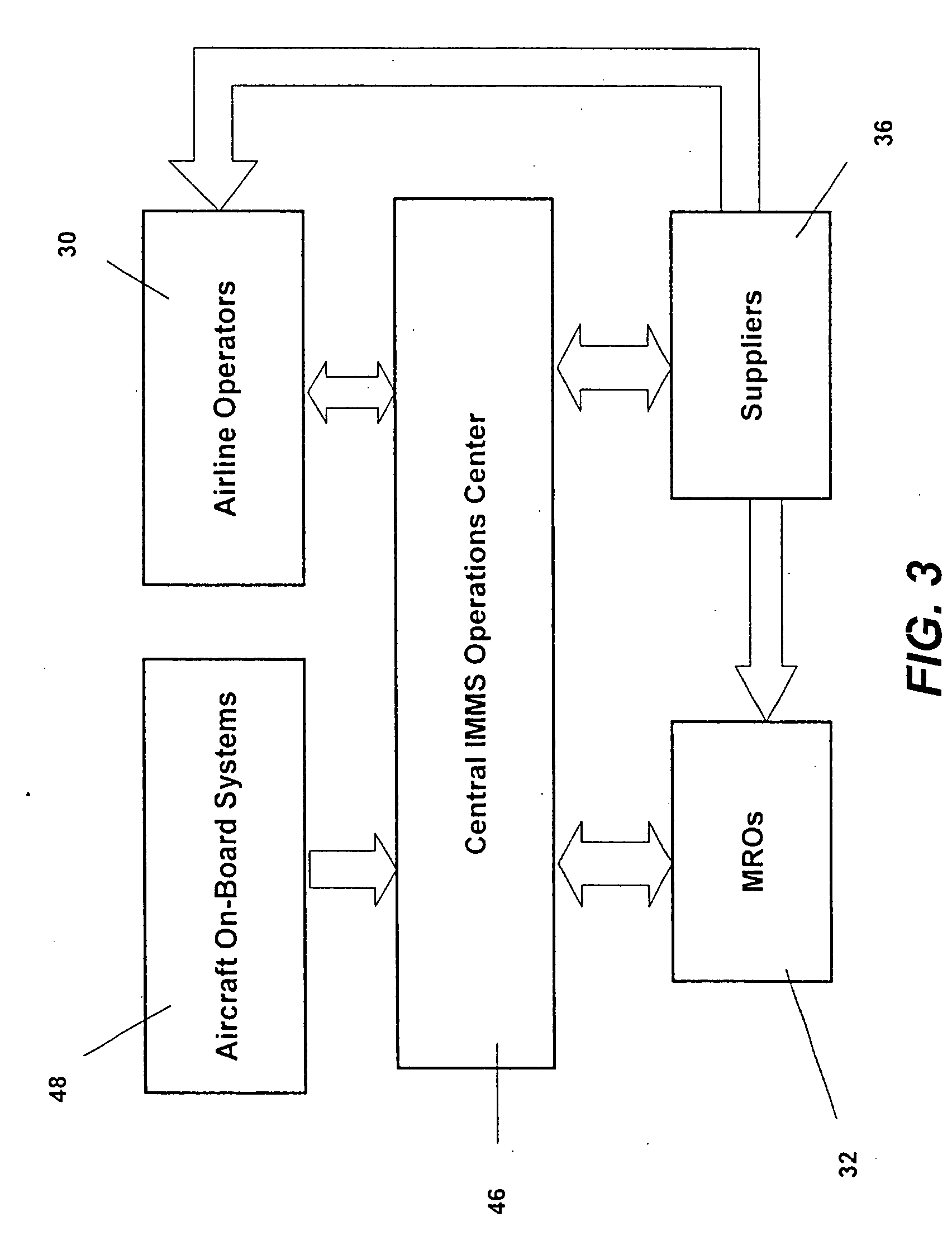
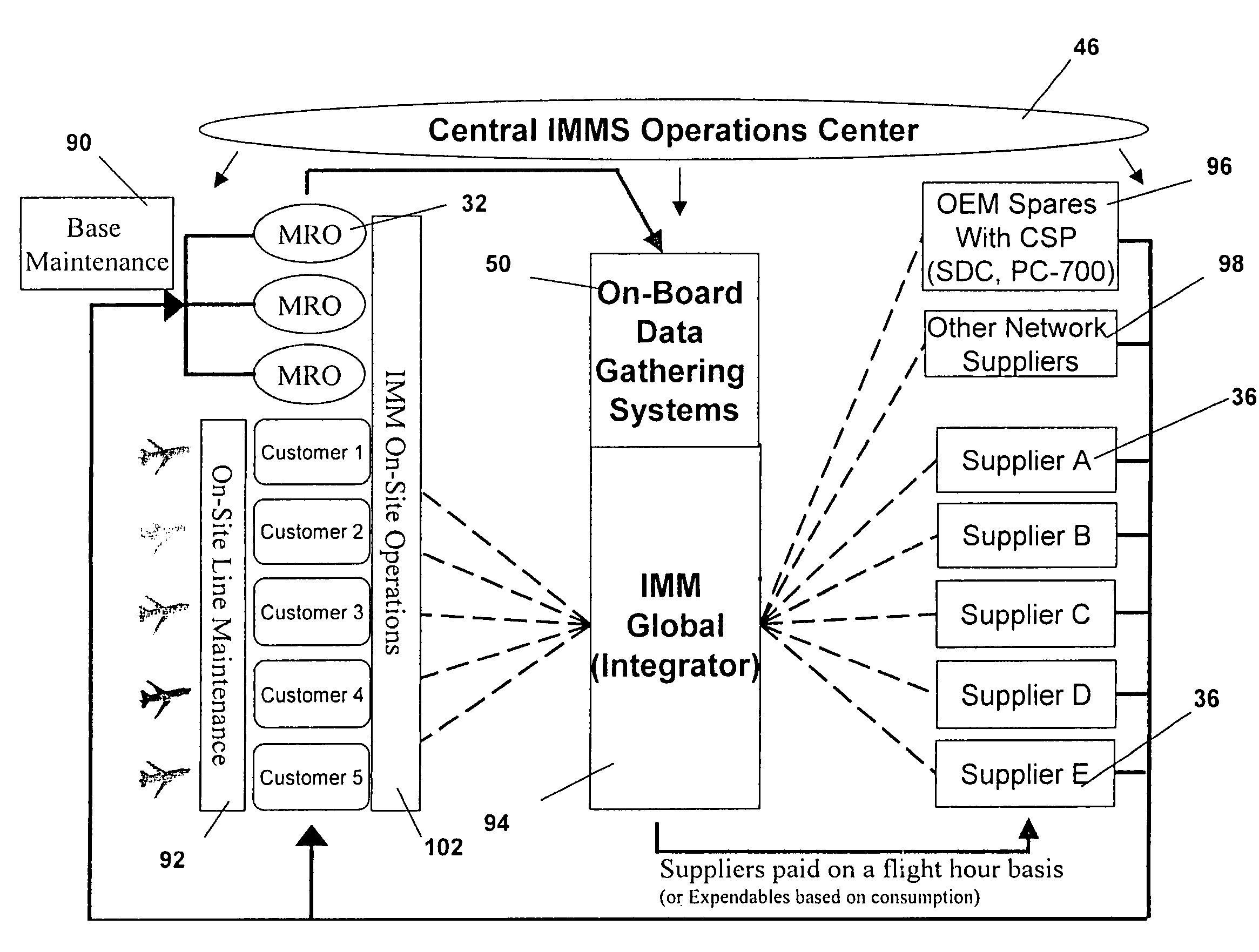
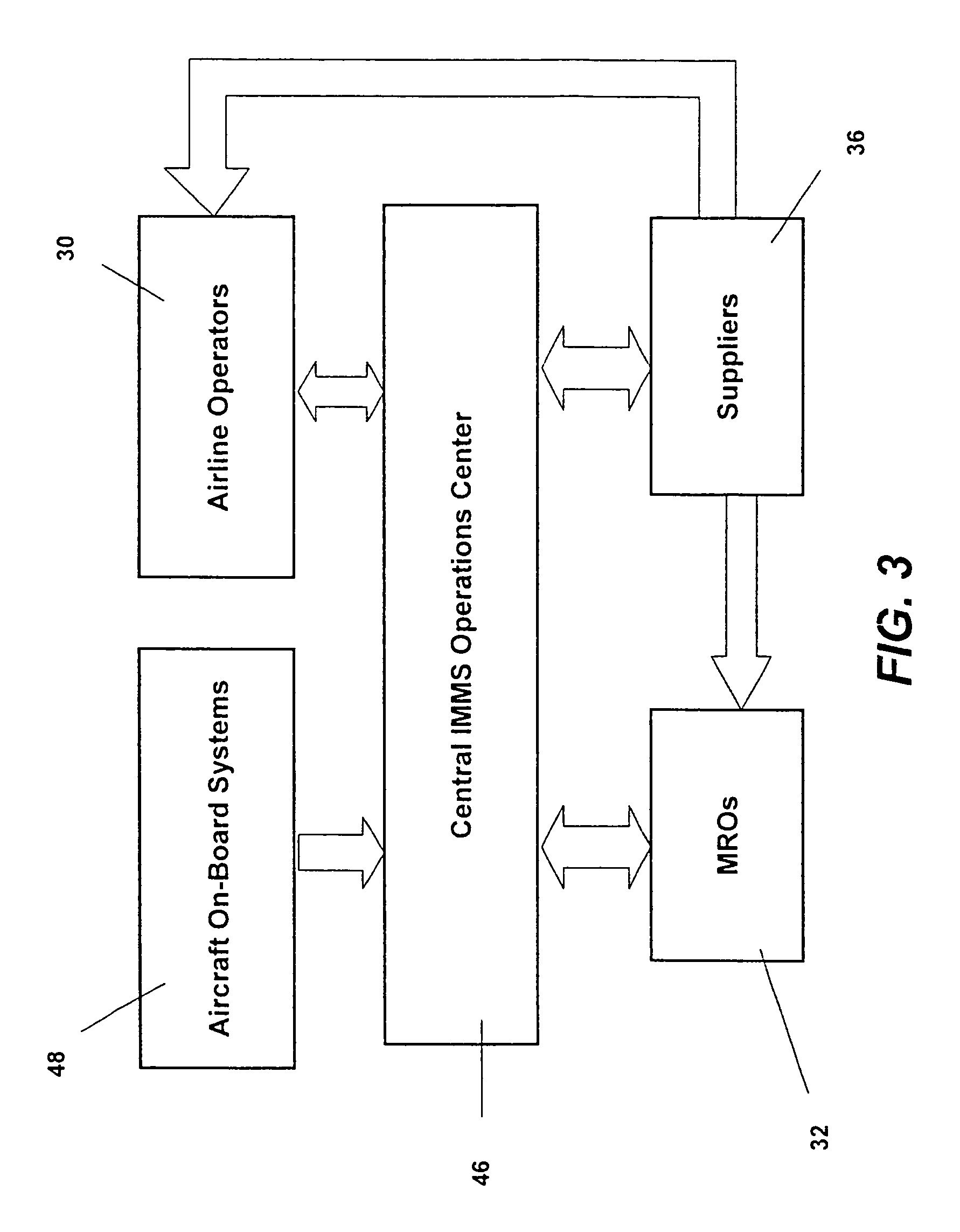
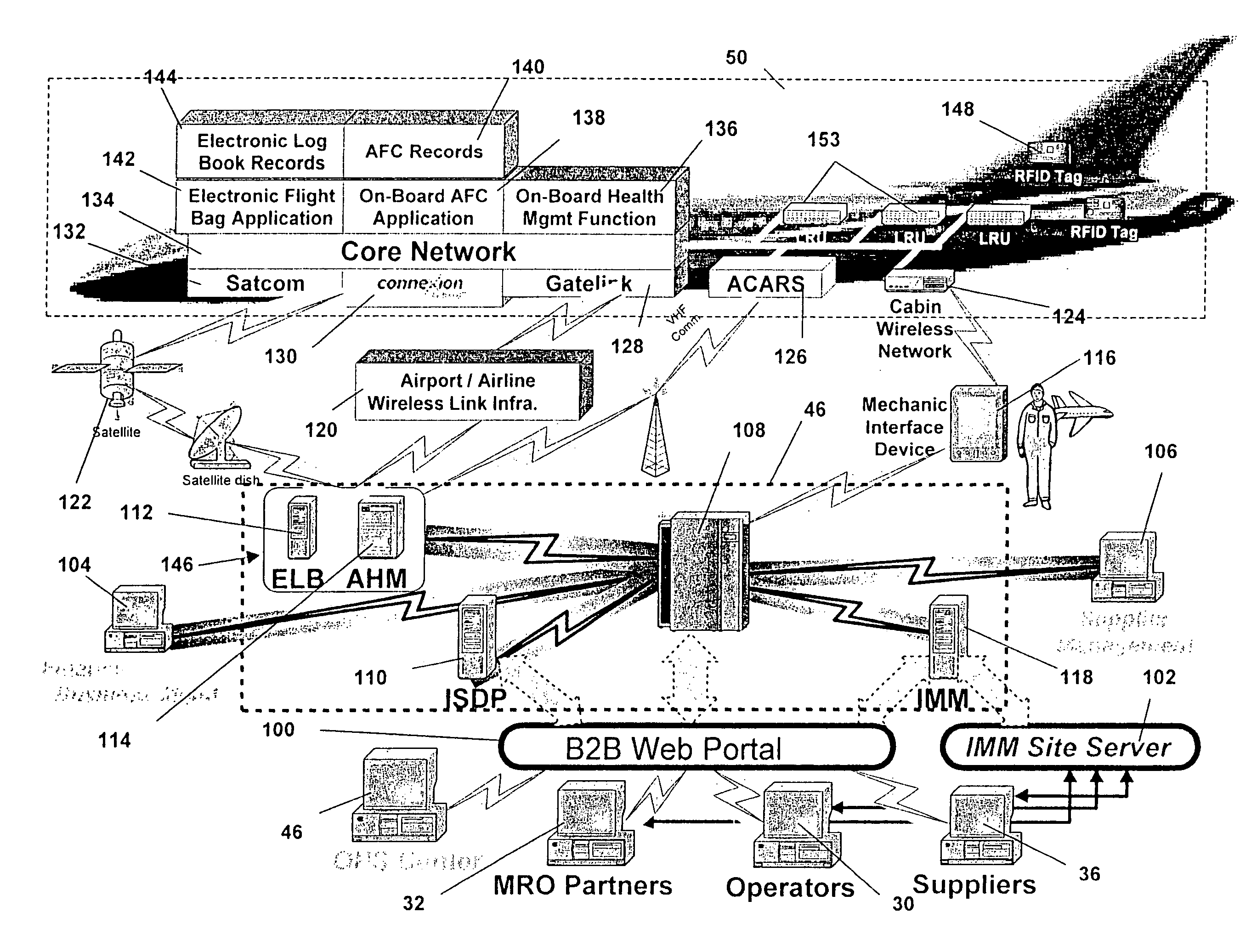
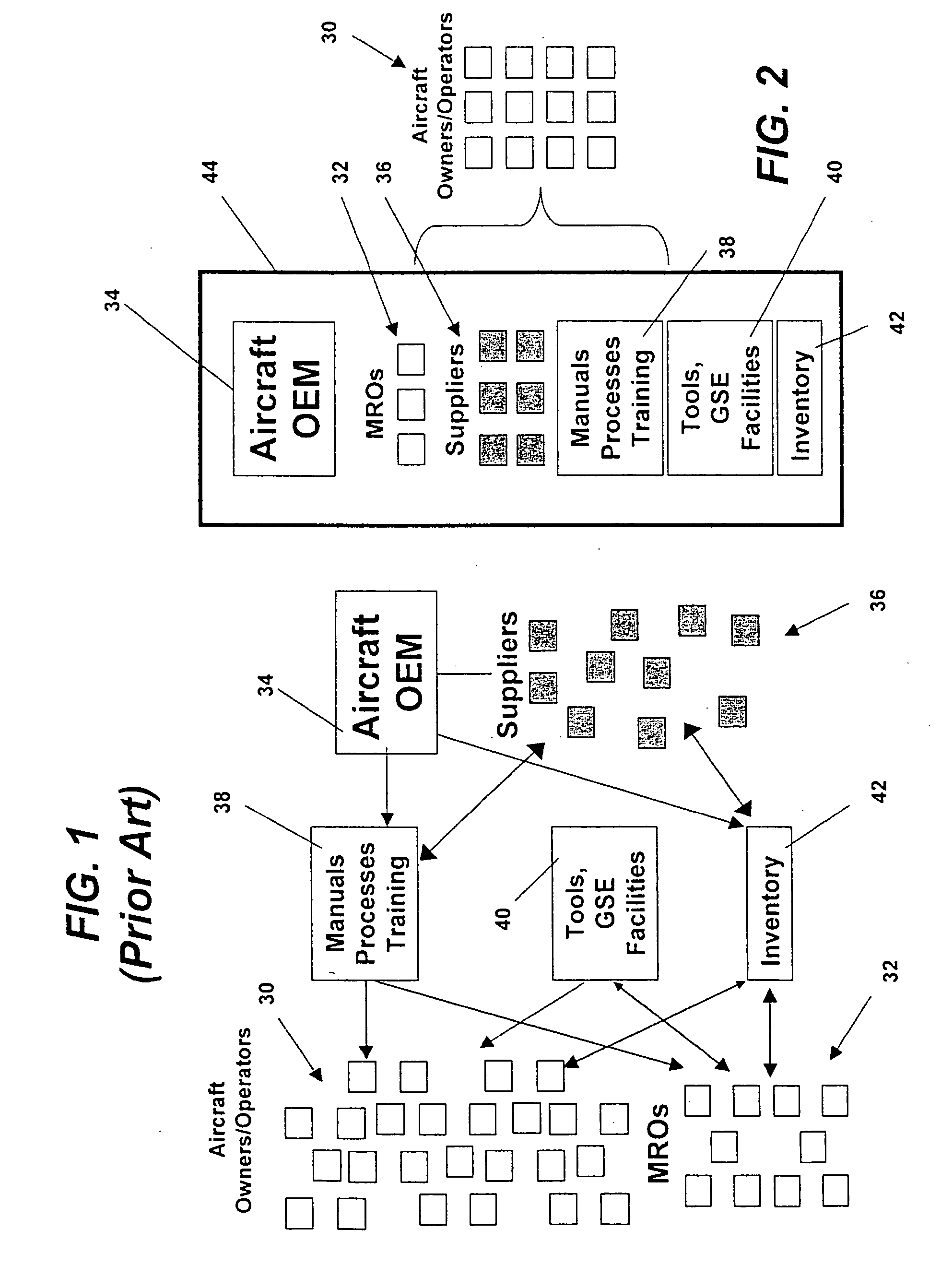
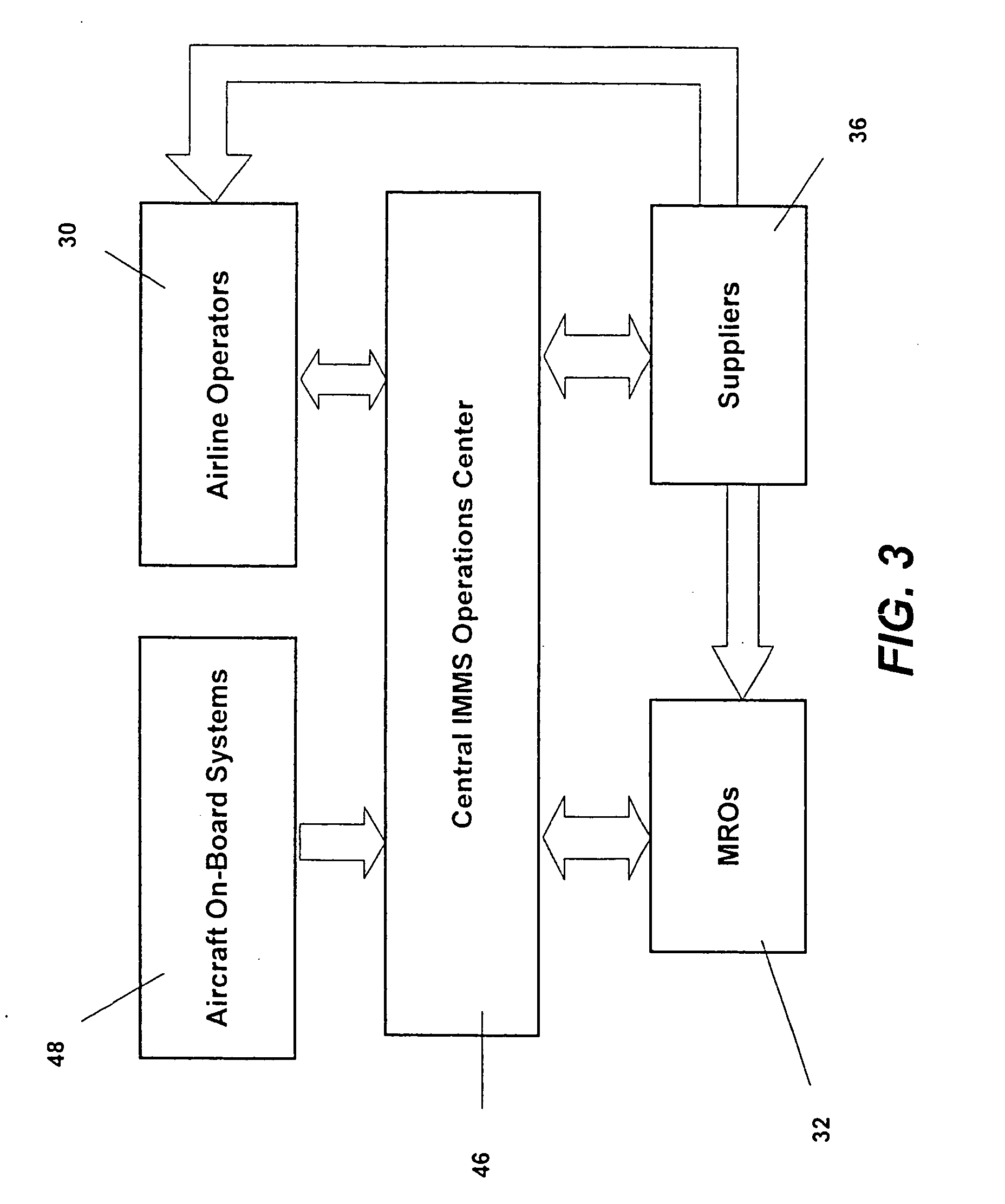
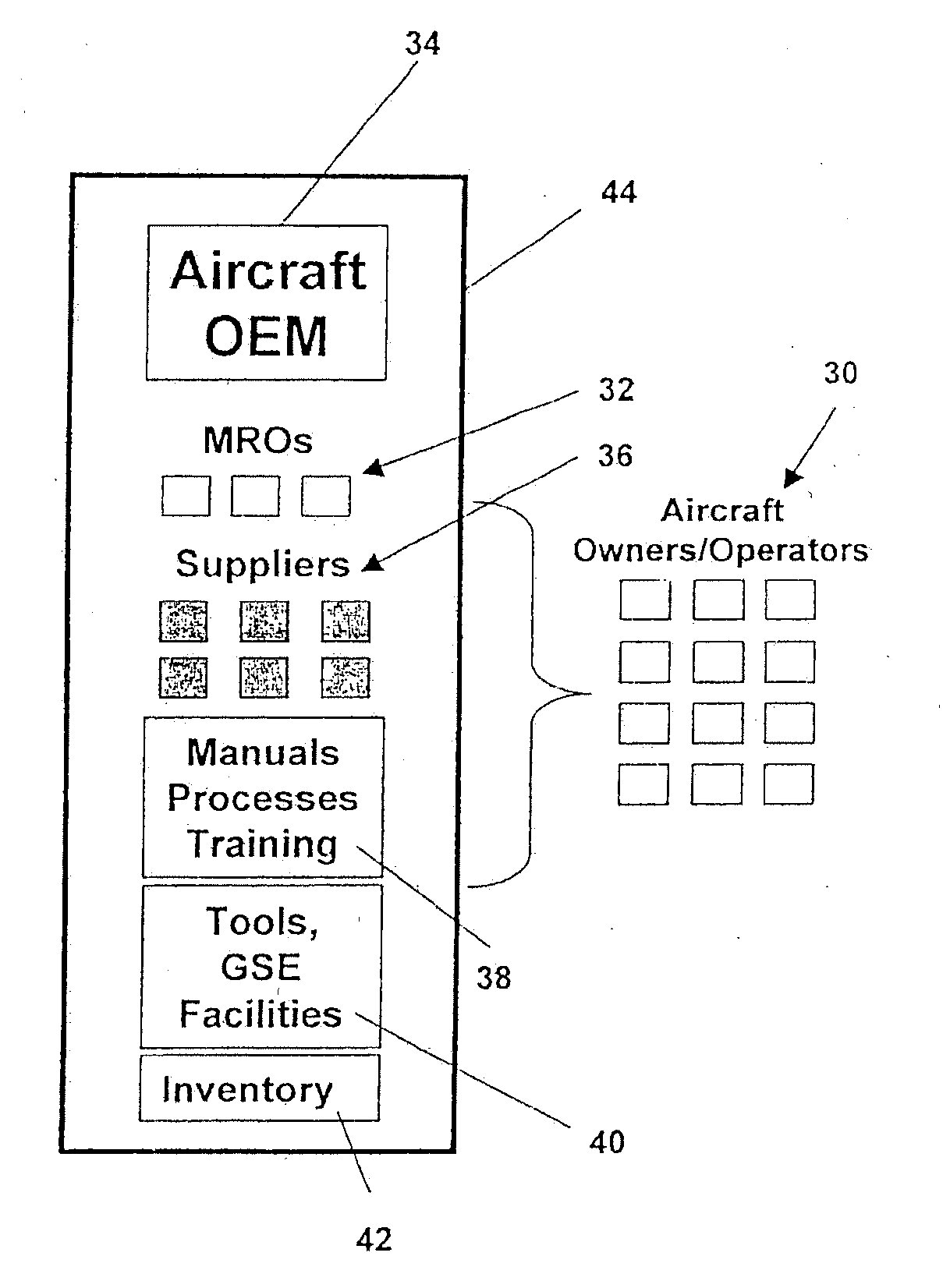
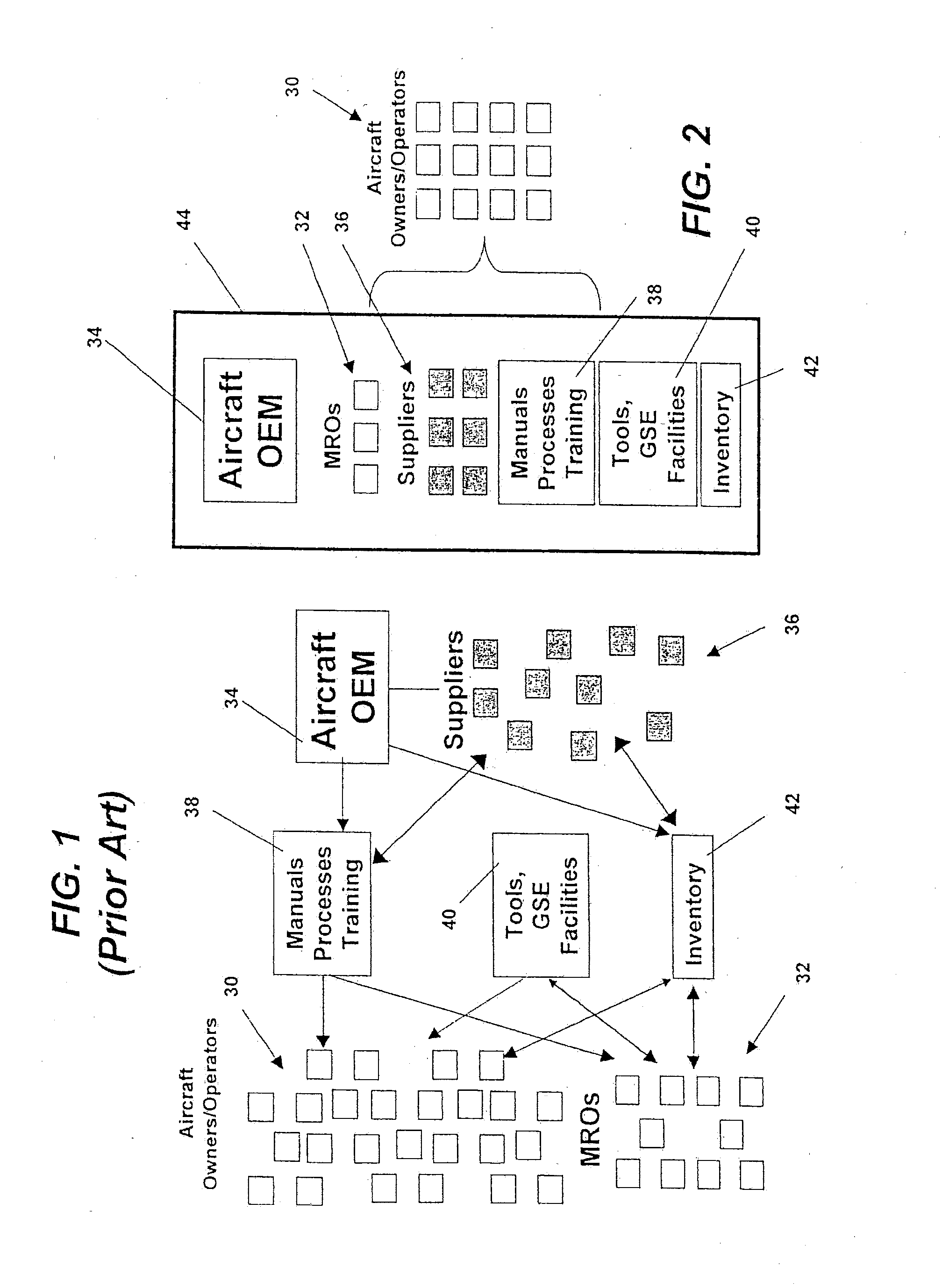
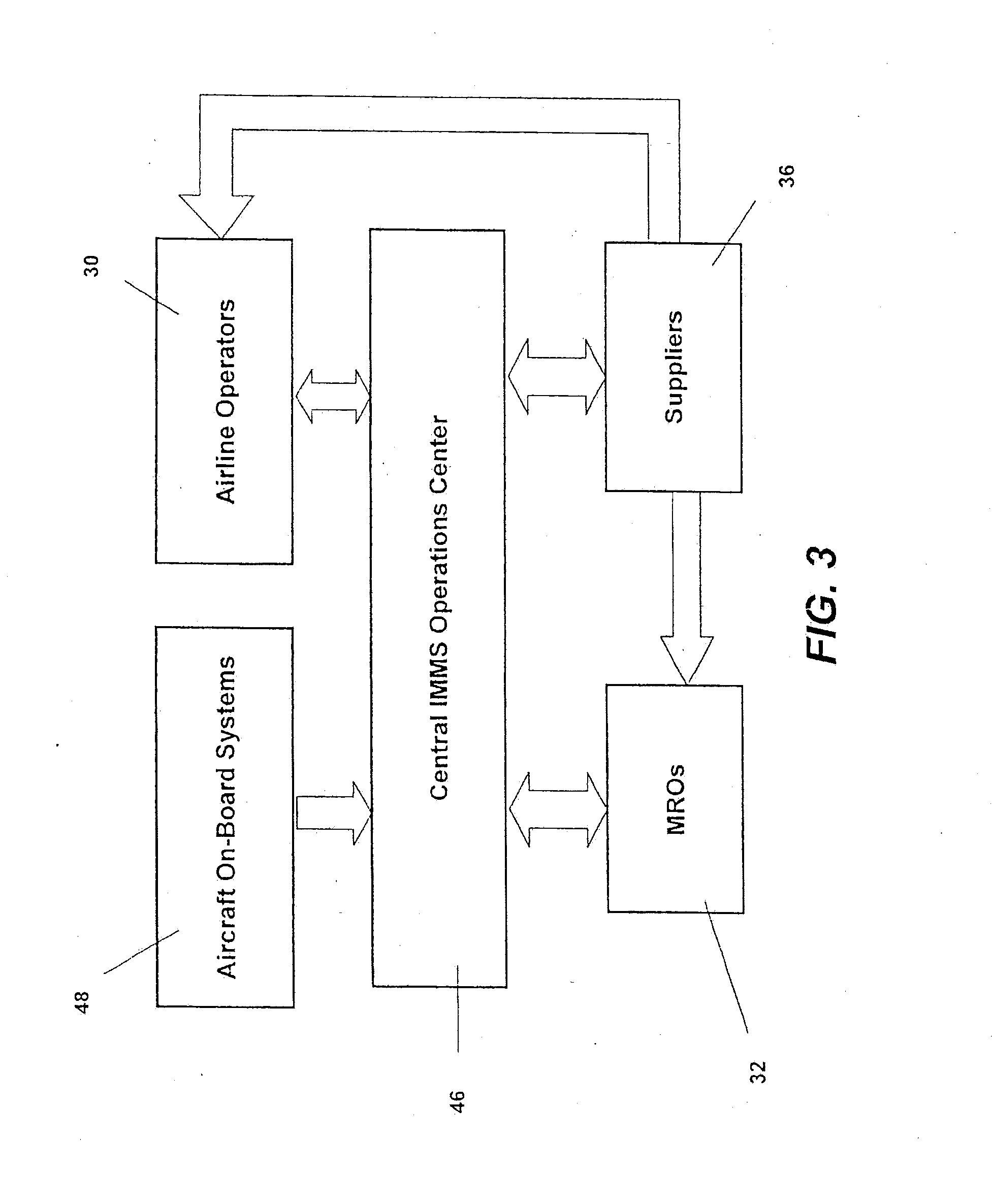
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
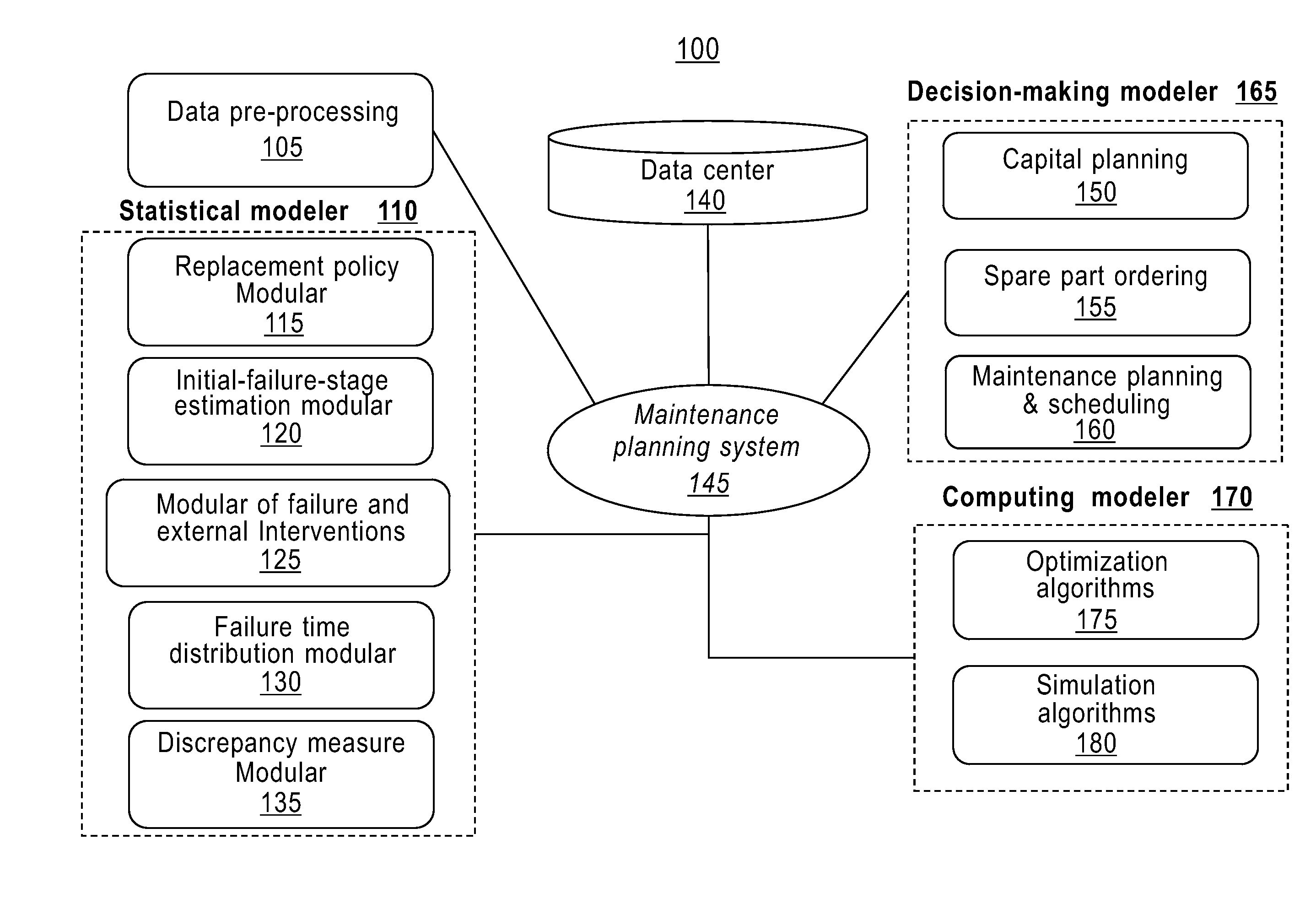
Distribution network maintenance planning
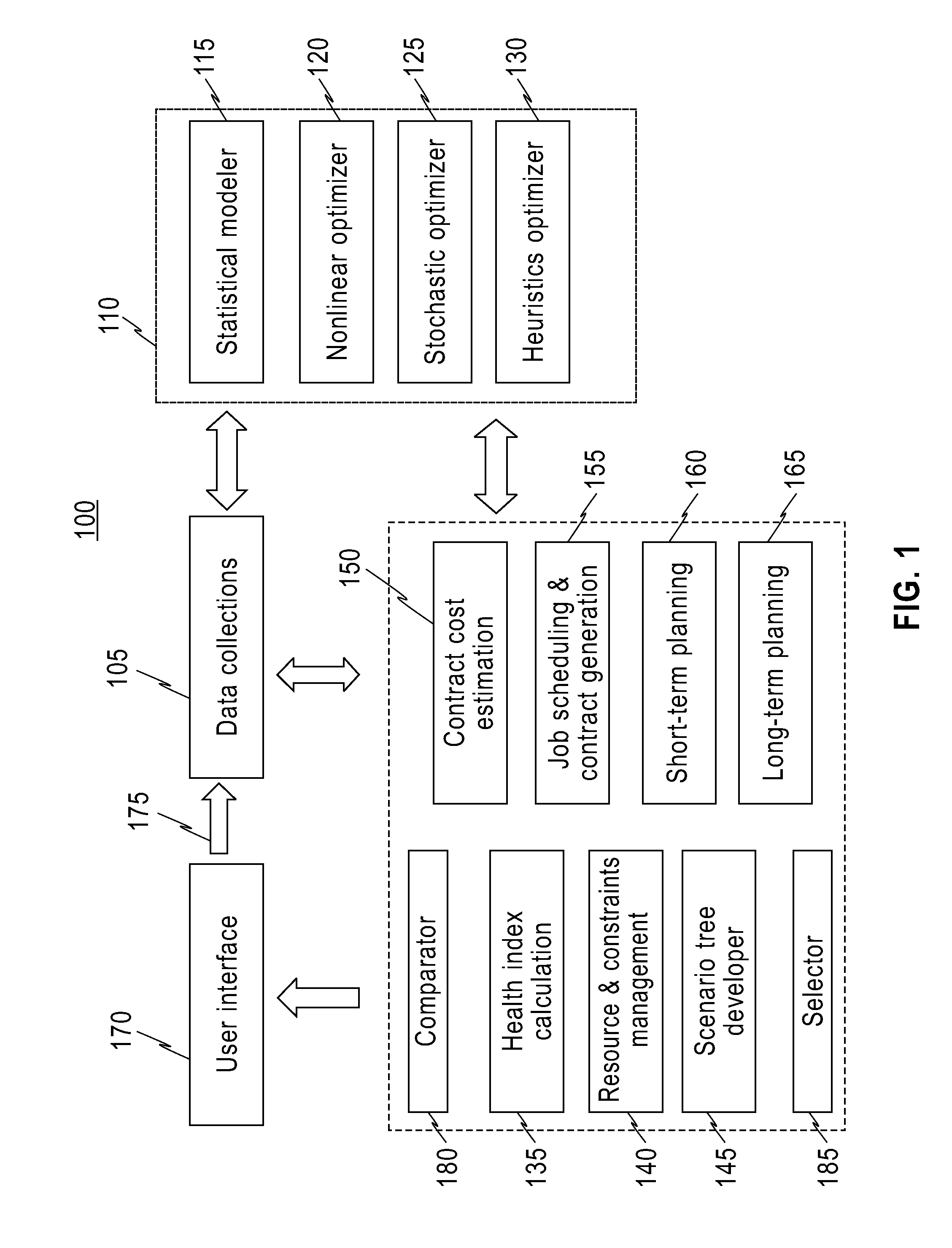
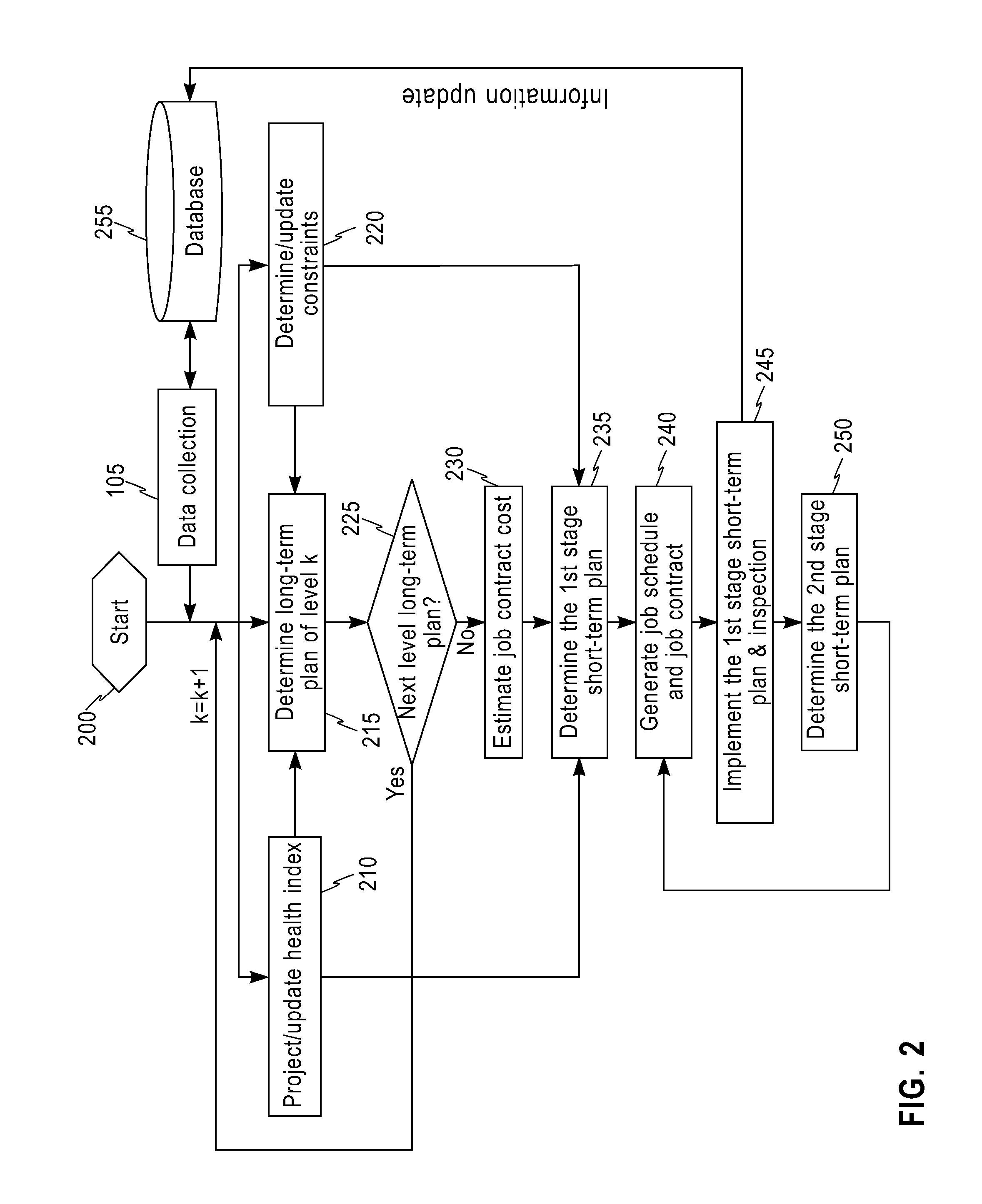
A system, method and computer program product for maintaining an infrastructure of components. The system receives structured data, unstructured data, and infrastructure data from a database. The system runs at least one statistical and optimization modeler with one or more of: the received structured data, the received unstructured data and the received infrastructure data, in order to calculate a health index of at least one component of the infrastructure. The health index represents a health attribute of the at least one component. The system establishes at least one maintenance plan of the infrastructure, based on the calculated health index. Each established maintenance plan is associated with at least one health index. The system compares health indices of the at least one established maintenance plan. The system selects a plan, among the at least one established maintenance plan, whose health index is a maximum among the compared health indices.
Owner:IBM CORP
Metallic constructions integrity assessment and maintenance planning method
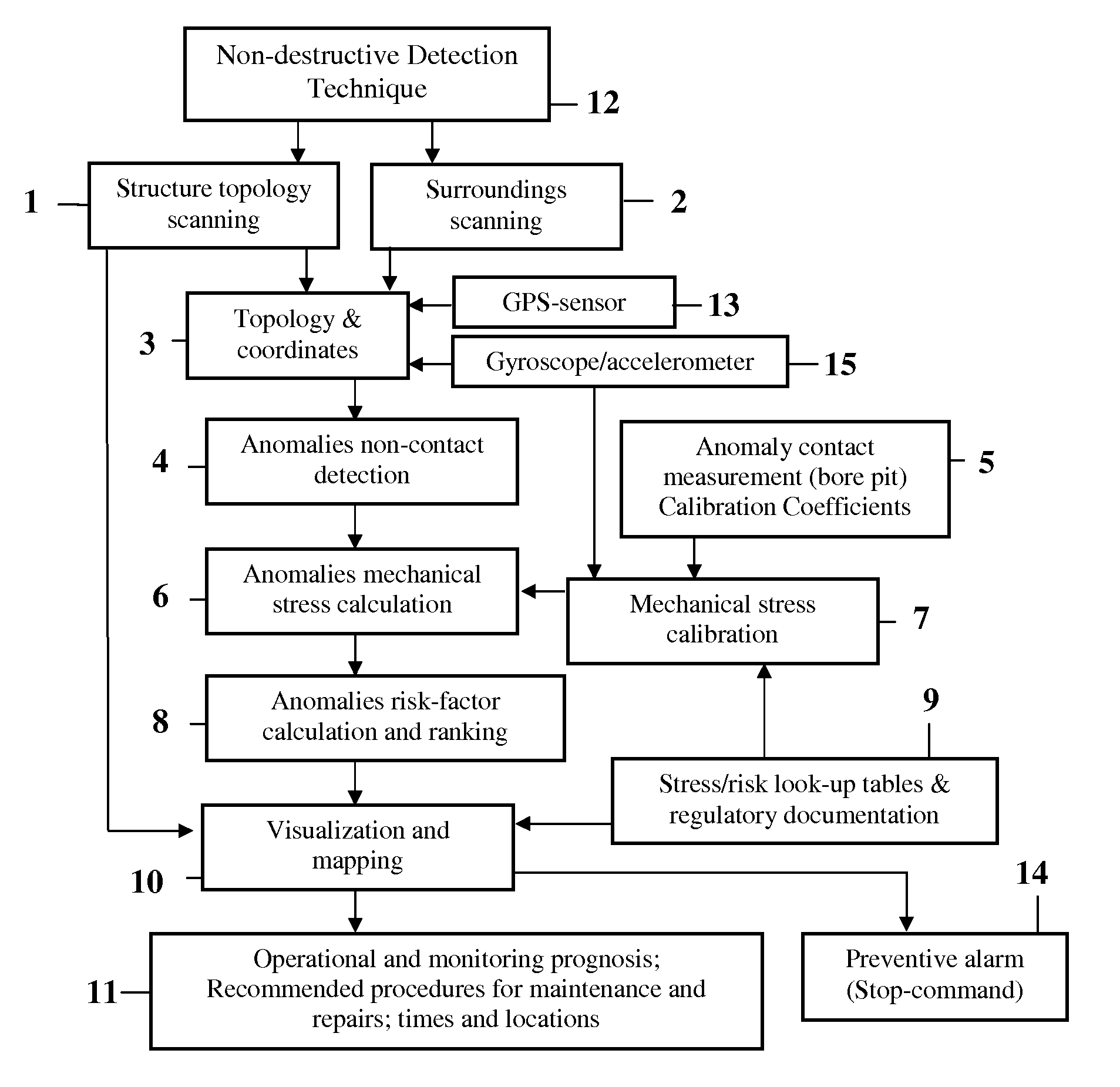
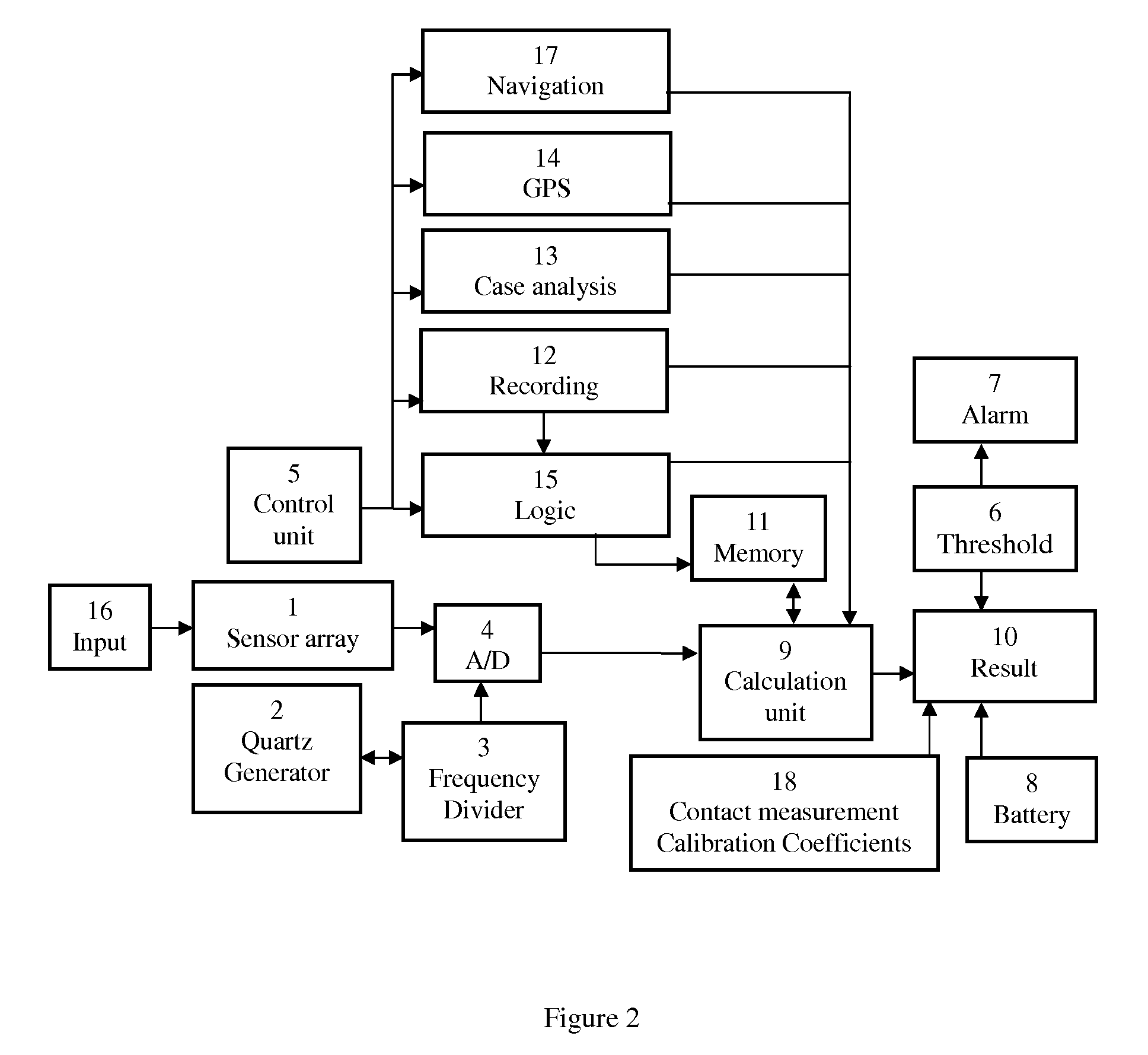
ActiveUS8447532B1Easy maintenancePromote repairPlug gaugesForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationMaintenance planningHeavy duty
A method for metallic structure maintenance is disclosed. The method includes a magneto-graphic / Magnetic Tomography technique to identify stress-related defects. The method is specifically optimized for extended, non-accessible underground and underwater metallic structures in providing quality control, emergency alarms as well as timeline planning for structural repairs and maintenance work. Examples of the method implementation include pipes for oil and gas industry, detection of flaws in rolled products in metallurgical industry, welding quality of heavy duty equipment such as ships reservoirs, etc. It is especially important for loaded constructions, such as pressured pipes, infrastructure maintenance, nuclear power plant monitoring, bridges, corrosion prevention and environment protection.
Owner:GOROSHEVSKIY VALERIAN +2
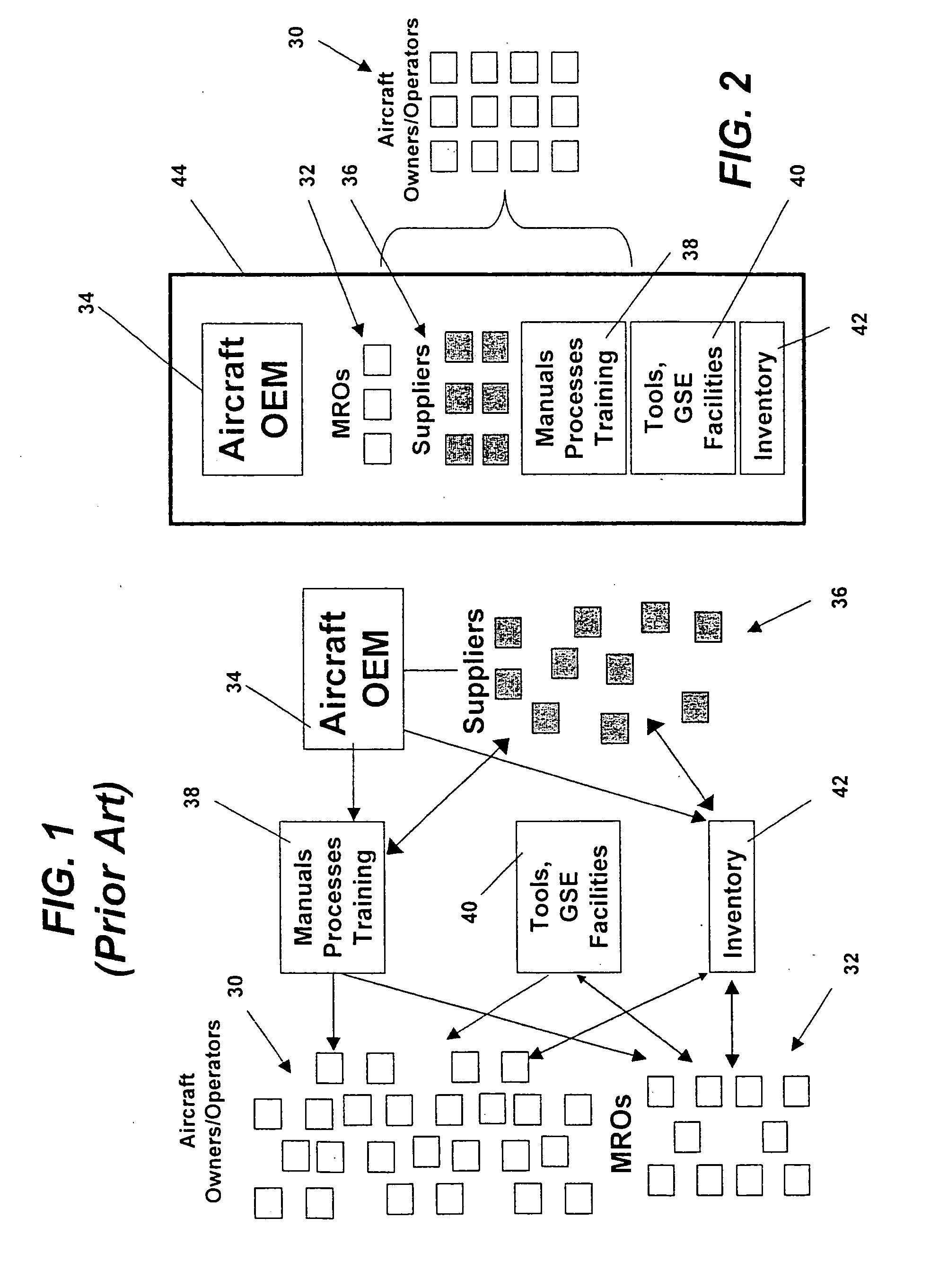
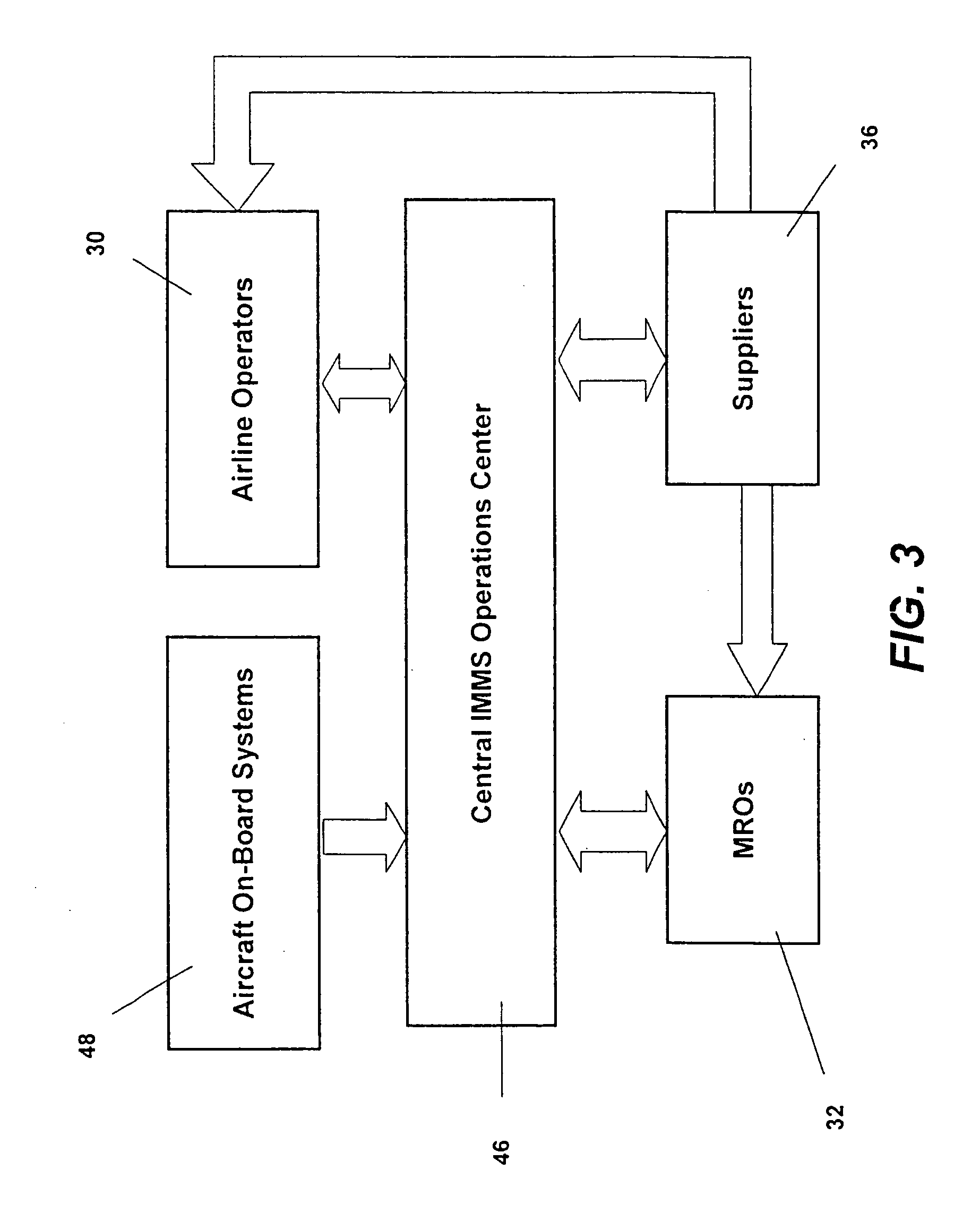
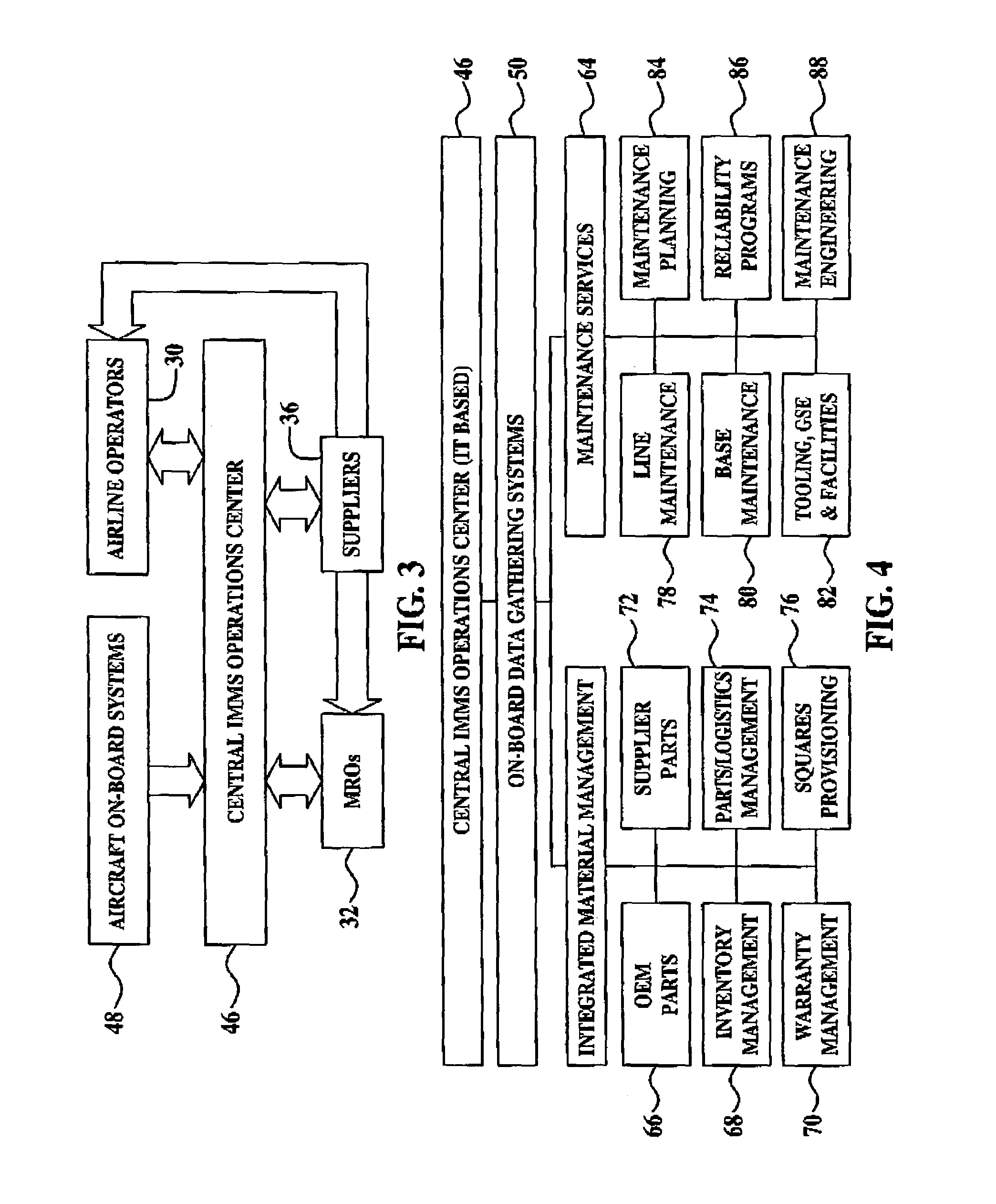
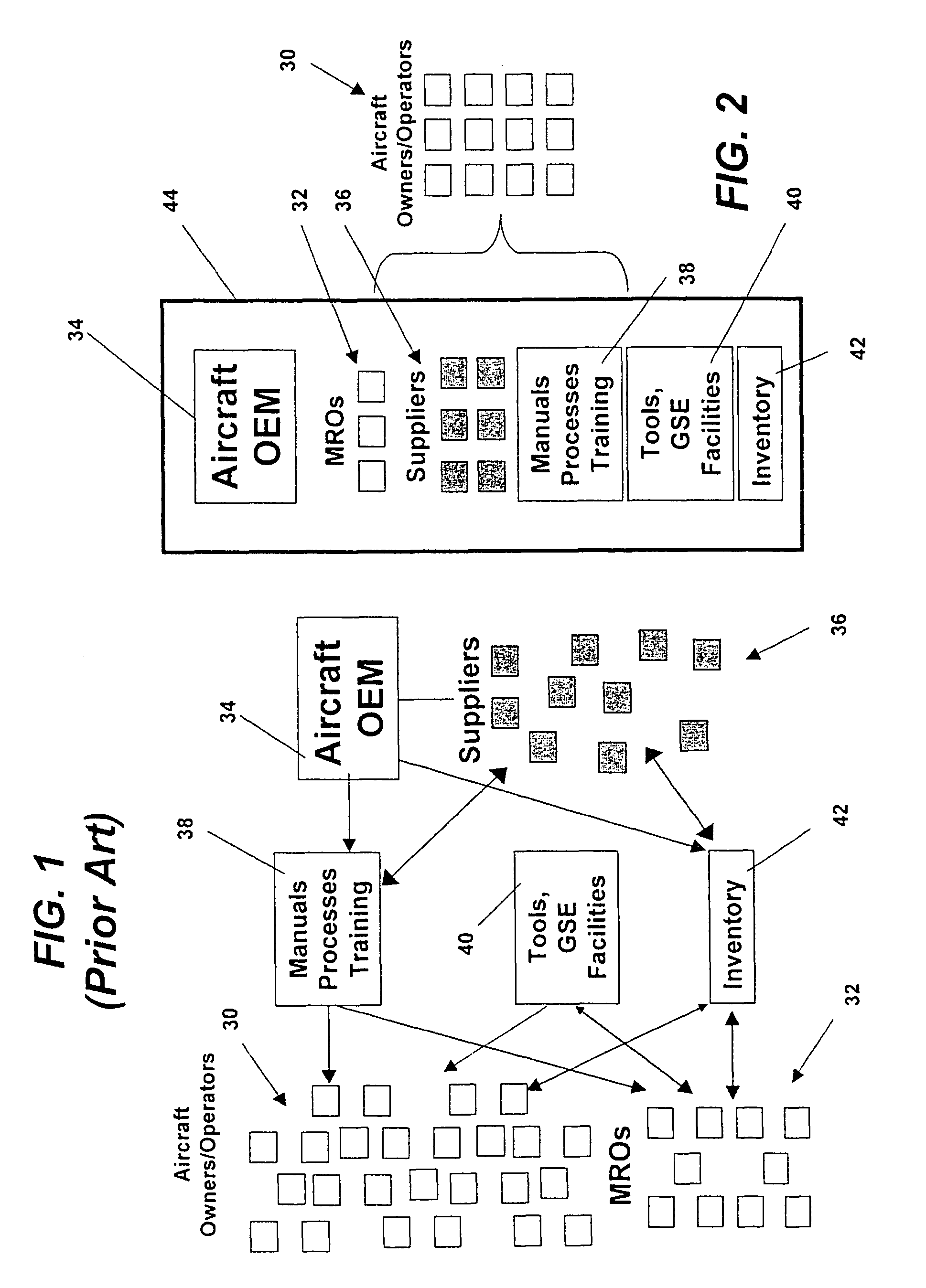
Centralized management of maintenance and materials for commercial aircraft fleets
ActiveUS20070112488A1Minimizes re-authoringEasy alignmentVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMaintenance planningOn board
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
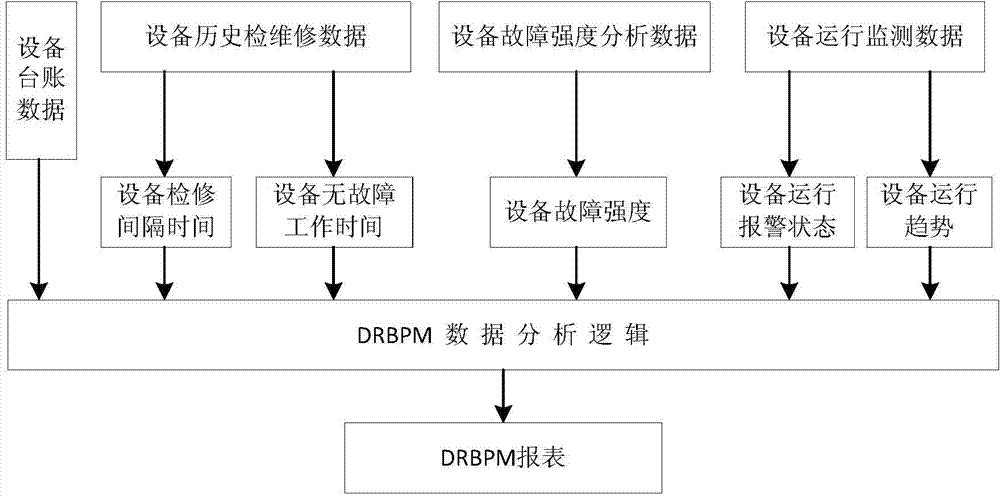
Preventative device maintenance method based on dynamic reliability
ActiveCN104268678ADecision scienceScientific and effective maintenance measuresResourcesAnalysis dataMaintenance planning
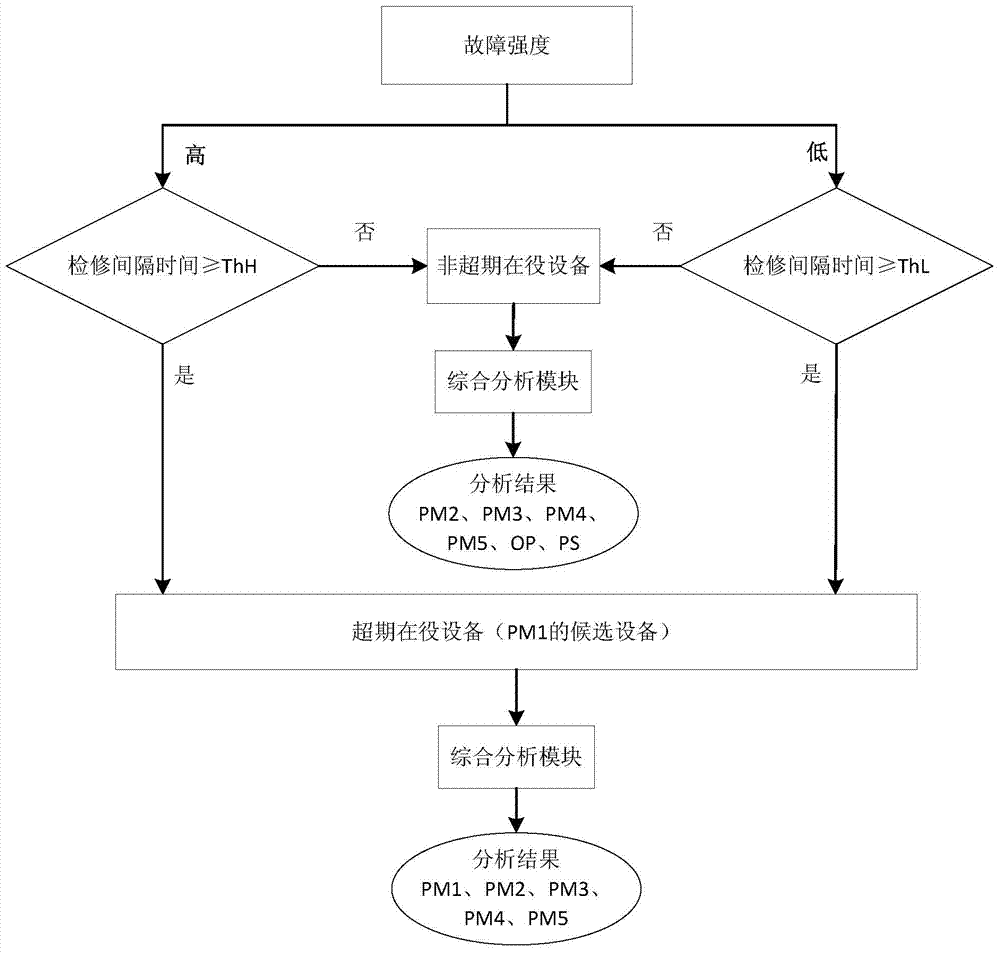
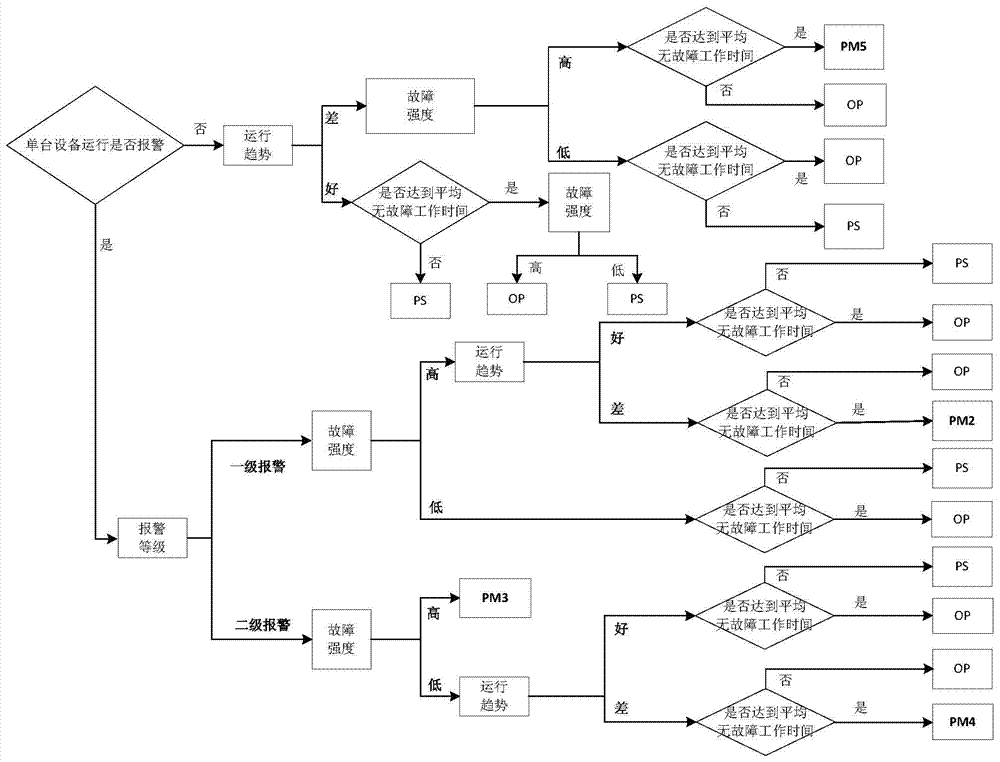
The invention discloses a preventative device maintenance method based on dynamic reliability and belongs to the technical field of petrochemical equipment management. The preventative device maintenance method based on the dynamic reliability comprises the following steps of 1 establishing a device basic database including equipment accounts, historical maintenance and repair data, a fault strength analysis data, operation monitoring data and the like; 2 utilizing basic data to conduct operation time analysis, fault strength analysis and alarm state and operation trend analysis on devices; 3 utilizing results to establish a device reliability level and fault strength incidence matrix, formulate DRBPM data analysis logic, automatically screen preventative maintenance devices and generate preventative maintenance planning reports of the devices; 4 examining, verifying and executing the preventative maintenance planning reports of the devices. The preventative device maintenance method based on the dynamic reliability can be used for dynamic analysis and management of states of petrochemical equipment, facilitate formulation of scientific and effective device maintenance measures and provide guarantee for timely device fault elimination and production continuity reliability and can be widely applied to the technical field of petrochemical equipment management.
Owner:中国石油化工股份有限公司武汉分公司 +1
Integrated maintenance and materials services for fleet aircraft using aircraft data to improve maintenance quality
ActiveUS7761201B2Improve efficiencyLow costVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMaintenance planningOn board
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Centralized management of maintenance and materials for commercial aircraft fleets with access to real-time information
ActiveUS20100125468A1Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTime informationMaintenance planning
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
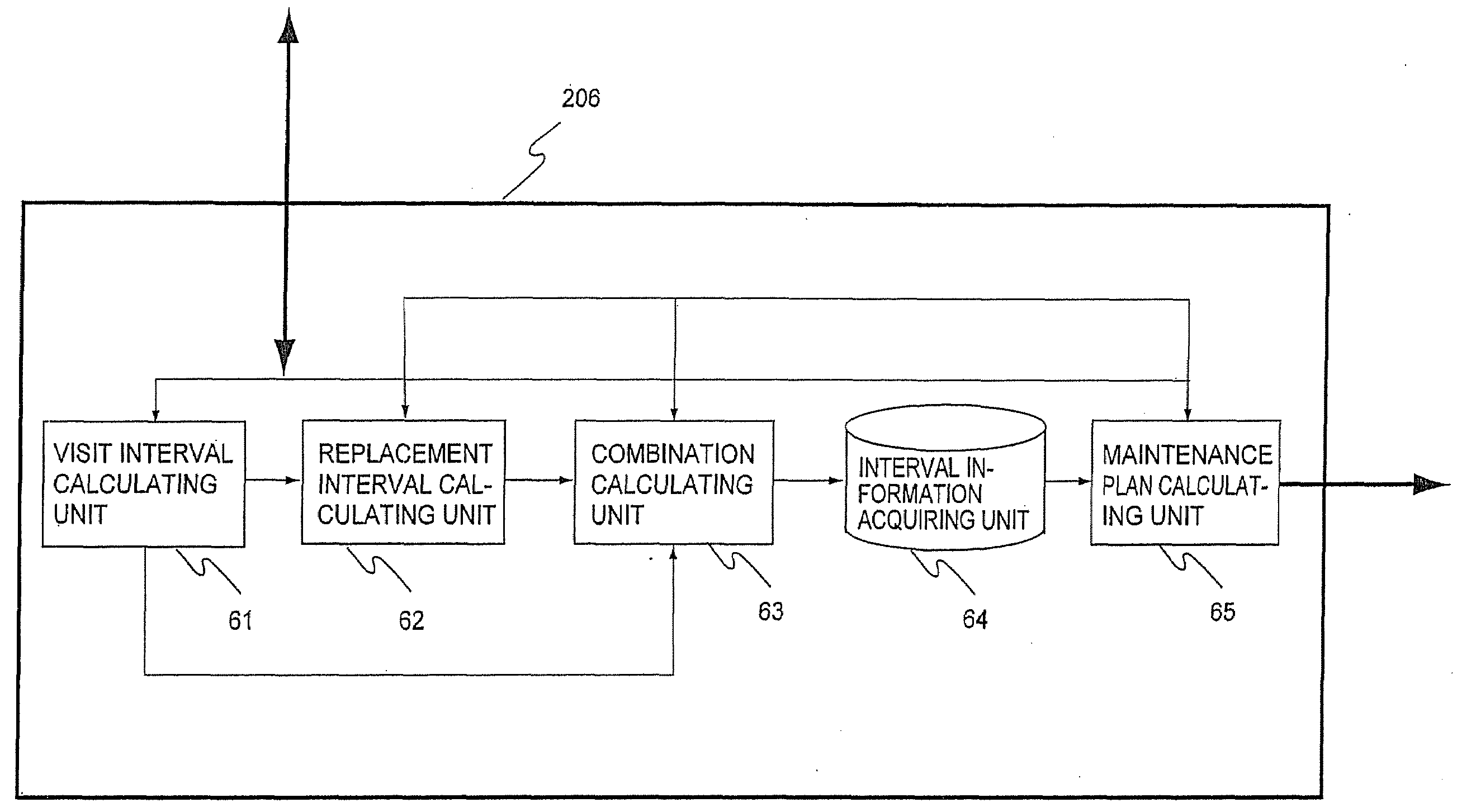
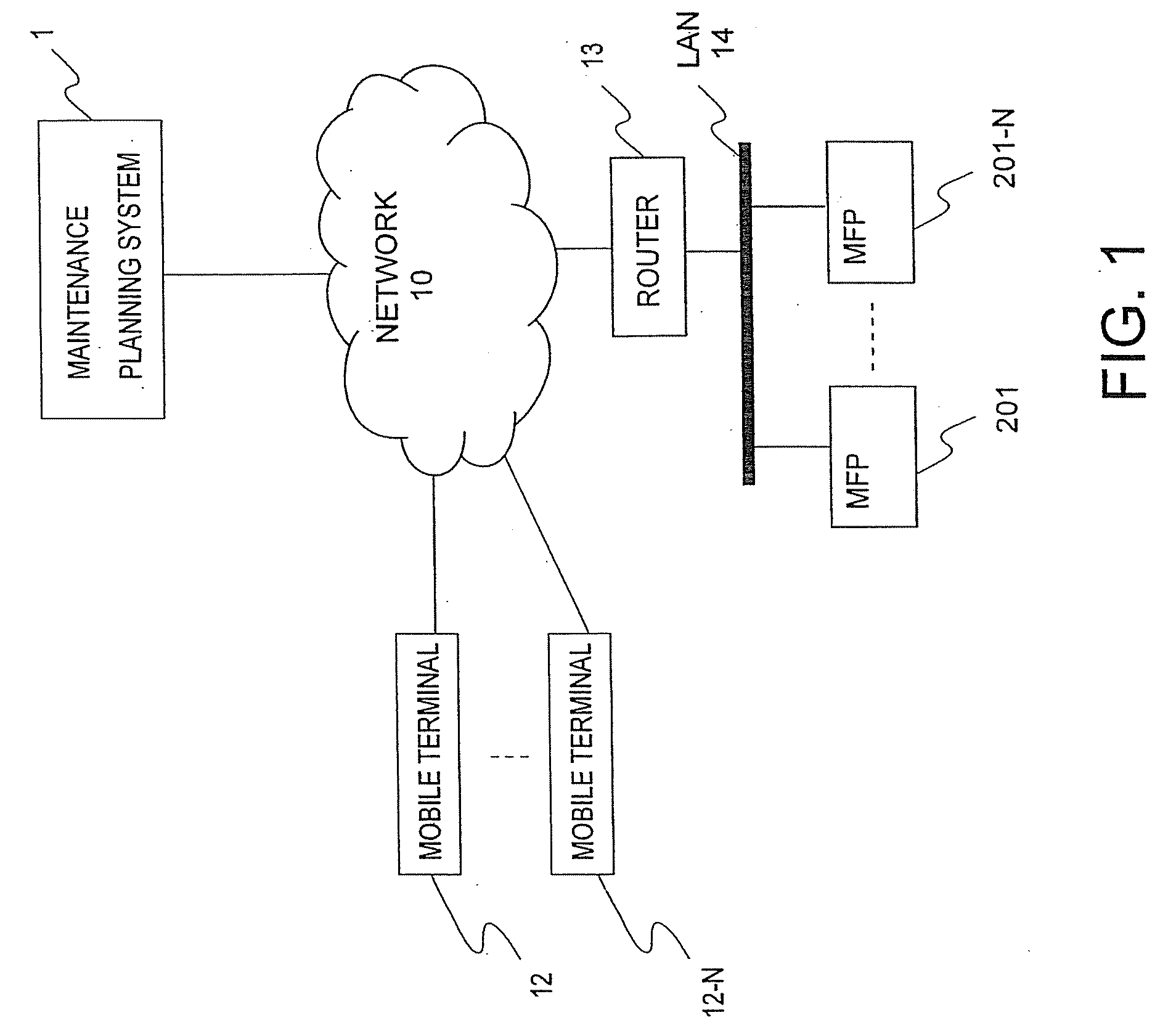
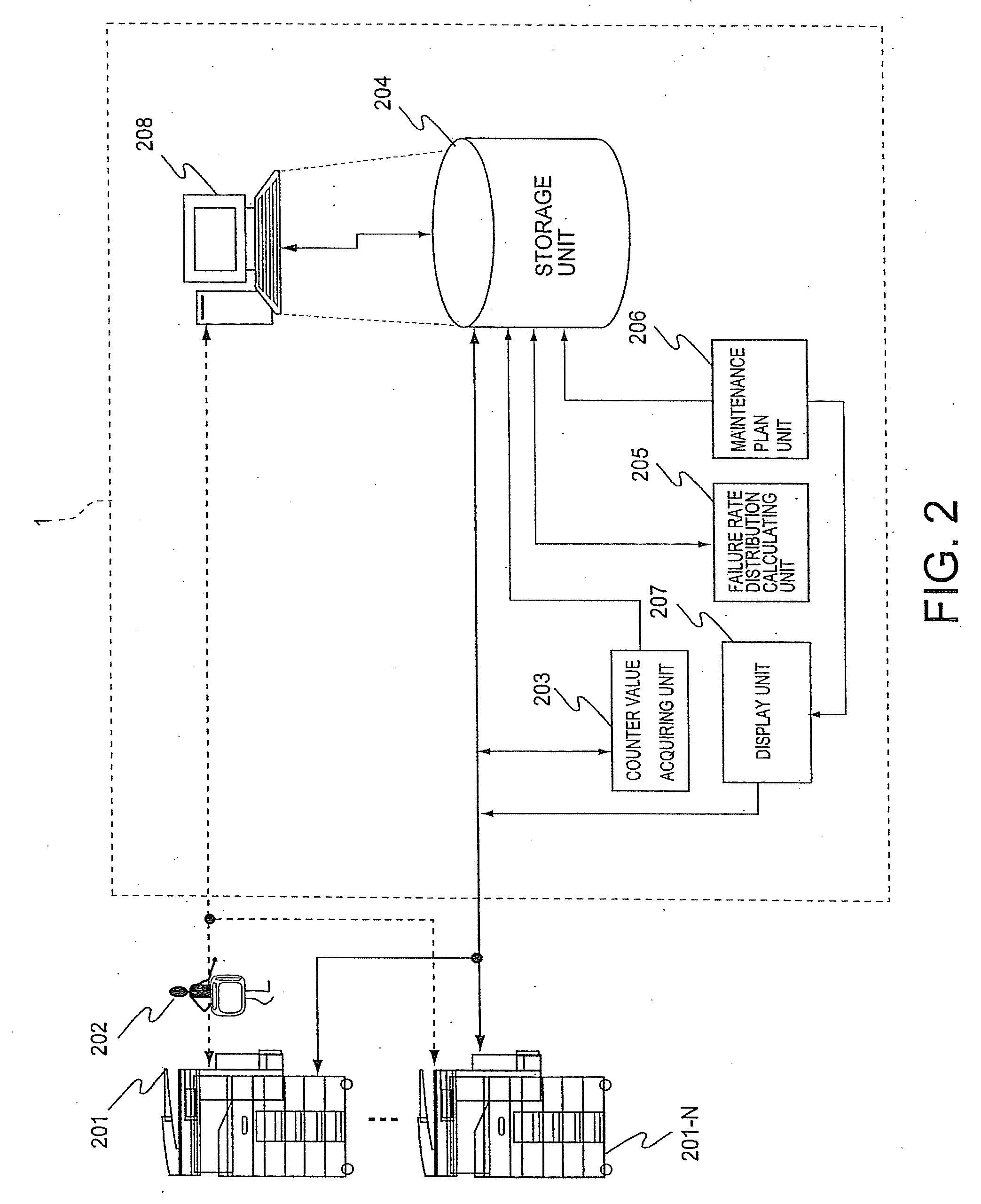
Maintenance planning system and maintenance planning method
A maintenance planning system comprises a counter value acquiring unit to acquire a counter value indicating use results of consumable parts of a plurality of apparatuses that are maintenance targets; an interval information acquiring unit, among information related to a combination of a visit interval to specify a time interval to visit installation places of the plurality of apparatuses that are maintenance targets to perform a maintenance check operation for the plurality of apparatuses that are maintenance targets with a replacement interval specified to replace each consumable part and associated with the visit interval, to acquire a combination of the visit interval and the replacement interval for minimizing a predetermined cost for each consumable part of the plurality of apparatuses that are maintenance targets; a maintenance plan creation unit, on the basis of the minimized visit interval and replacement interval acquired by the interval information acquiring unit and the counter value acquired by the counter value acquiring unit, to identify the apparatus that is a maintenance target to be visited next, timing of next visit, and a consumable part to be replaced at the timing; and a display unit to display information identified by the maintenance plan creation unit on a terminal.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
Centralized management of maintenance and materials for commercial aircraft fleets with fleet-wide benchmarking data
InactiveUS20070112576A1Improve efficiencyLow costRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesOffice automationMaintenance planningOn board
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Integrated materials management for commercial aircraft fleets
ActiveUS20070124223A1Part demand informationImproves part inventory controlDigital data processing detailsAnimal feeding devicesMaintenance planningOn board
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
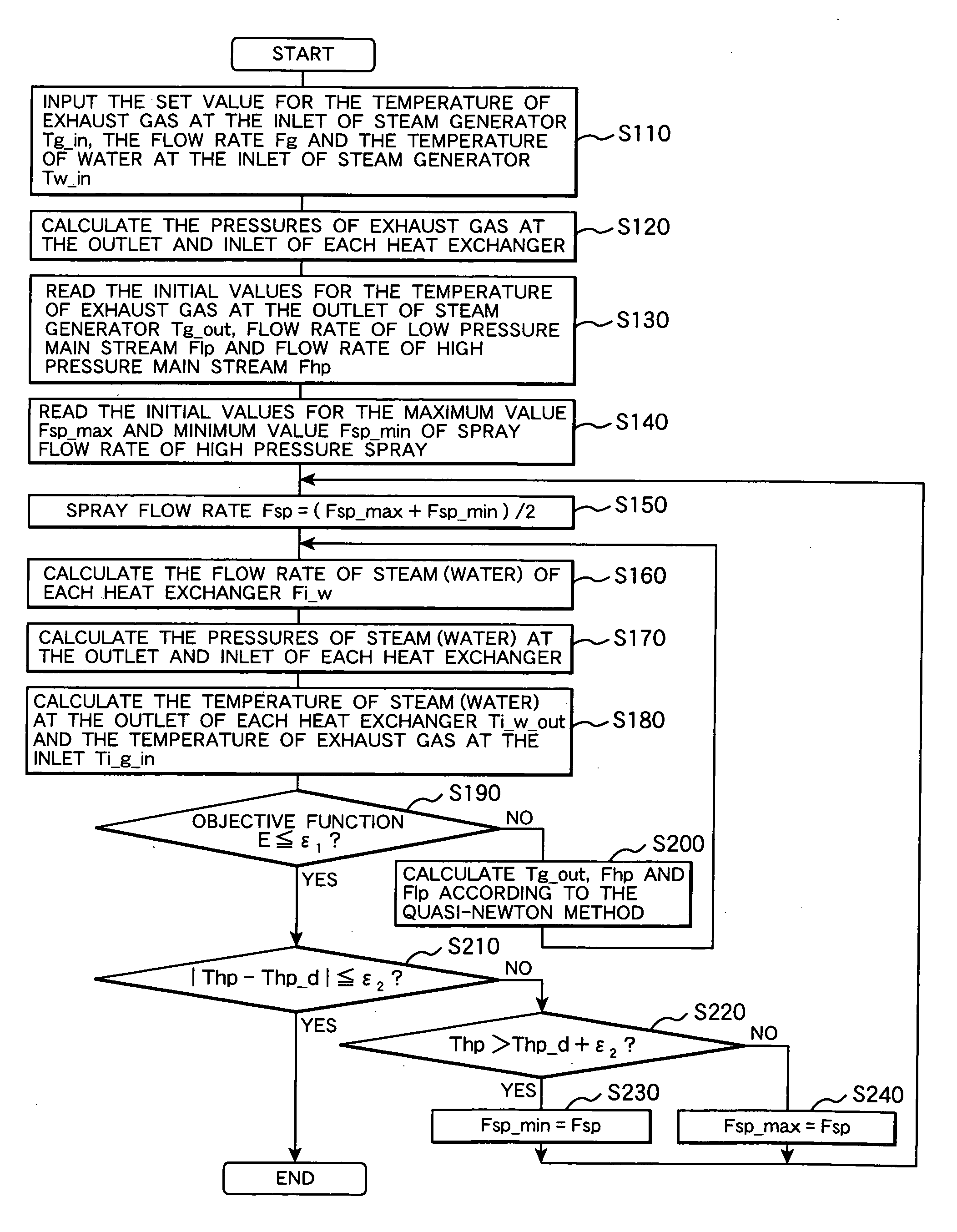
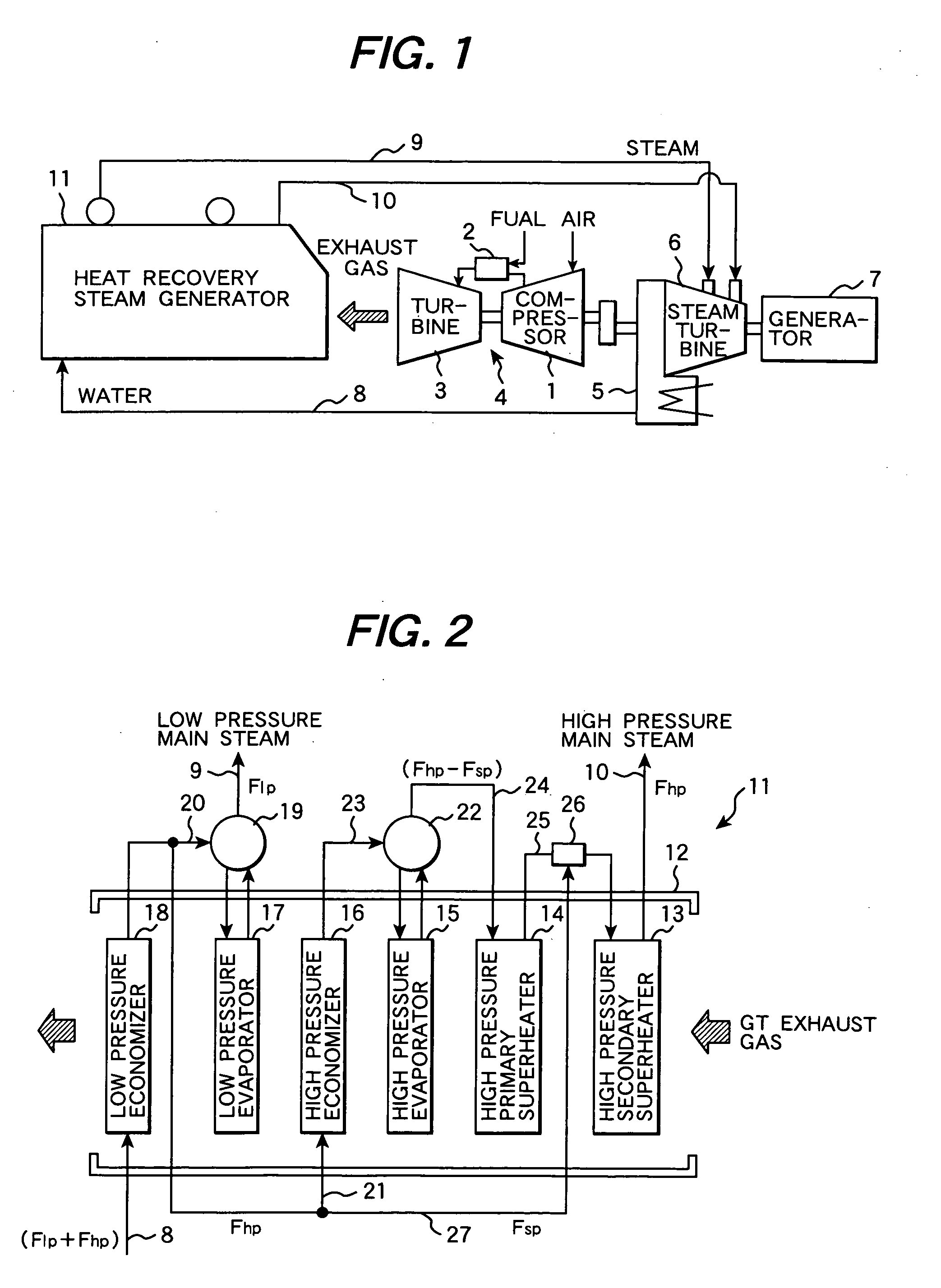
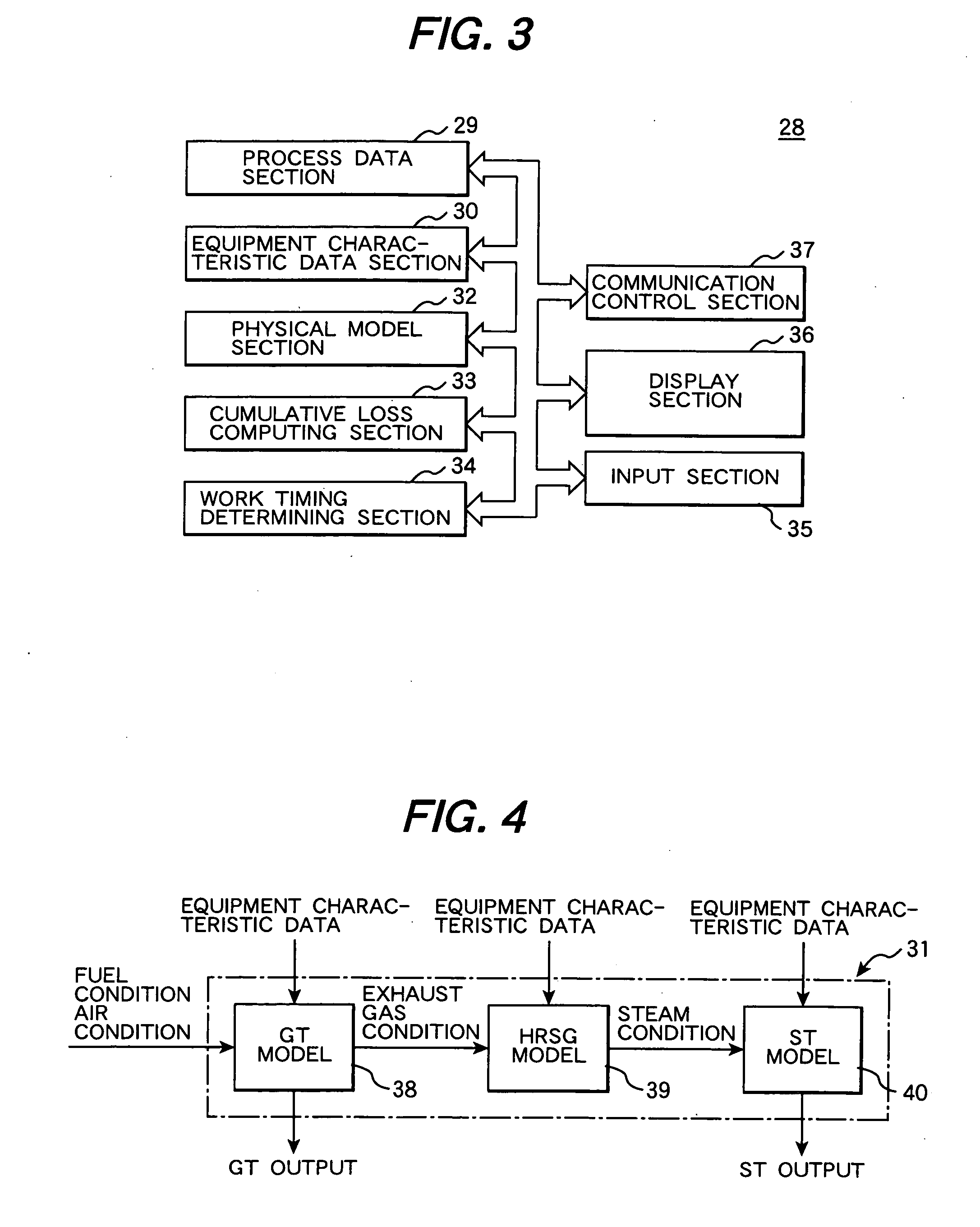
Generated steam estimation method and device for heat recovery steam generator, and maintenance planning support method and system for power generation facility
InactiveUS20060200325A1Level controlComputation using non-denominational number representationMaintenance planningEstimation methods
A method for configuring the physical model of a heat recovery steam generator that can estimate the state quantity of generated steam from the state quantity of the exhaust gas to be introduced, and capable of establishing the physical model of a combined cycle power generation facility thereby. The optimum values for the flow rates Flp and Fhp, pressures and temperatures Tlp and Thp of the low pressure main steam and high pressure main steam are computed in such a way as to ensure that an objective function E stored in advance will come close to zero.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Device management system
InactiveCN107203838AEasy to masterImprove management efficiencyOffice automationResourcesMaintenance planningSystems management
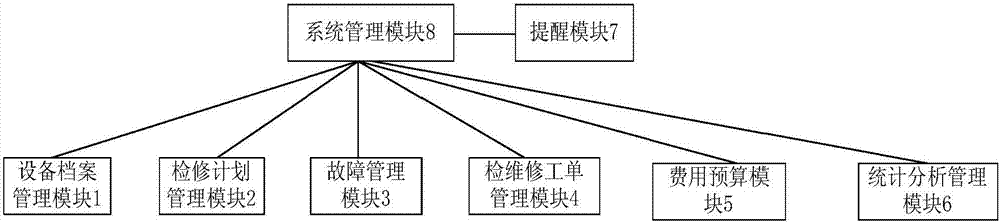
The present invention provides a device management system. The system comprises a device file management module, a maintenance planning management module, a fault management module, an inspection maintenance work order management module, an expense budget module, a statistic analysis management module, a prompting module and a system management module. The device file management module is configured to store and manage the basic static information, the whole life cycle document data, the device faults, the maintenance history and the device changing information of a device and provide functions of addition, deletion, modification, query and statistics analysis; and the maintenance planning management module is configured to perform establishment, examination and approval, issuing and execution, statistics and analysis query of a preset plan project; and the fault management module is configured to report fault records and start a fault confirmation process after device defects or faults are detected, eliminate faults according to the corresponding preset fault processing mode after confirmation of the faults and record the faults in the fault knowledge base. The efficiency and the precision of management are improved, and a lot of manpower is saved.
Owner:北京海顿中科技术有限公司
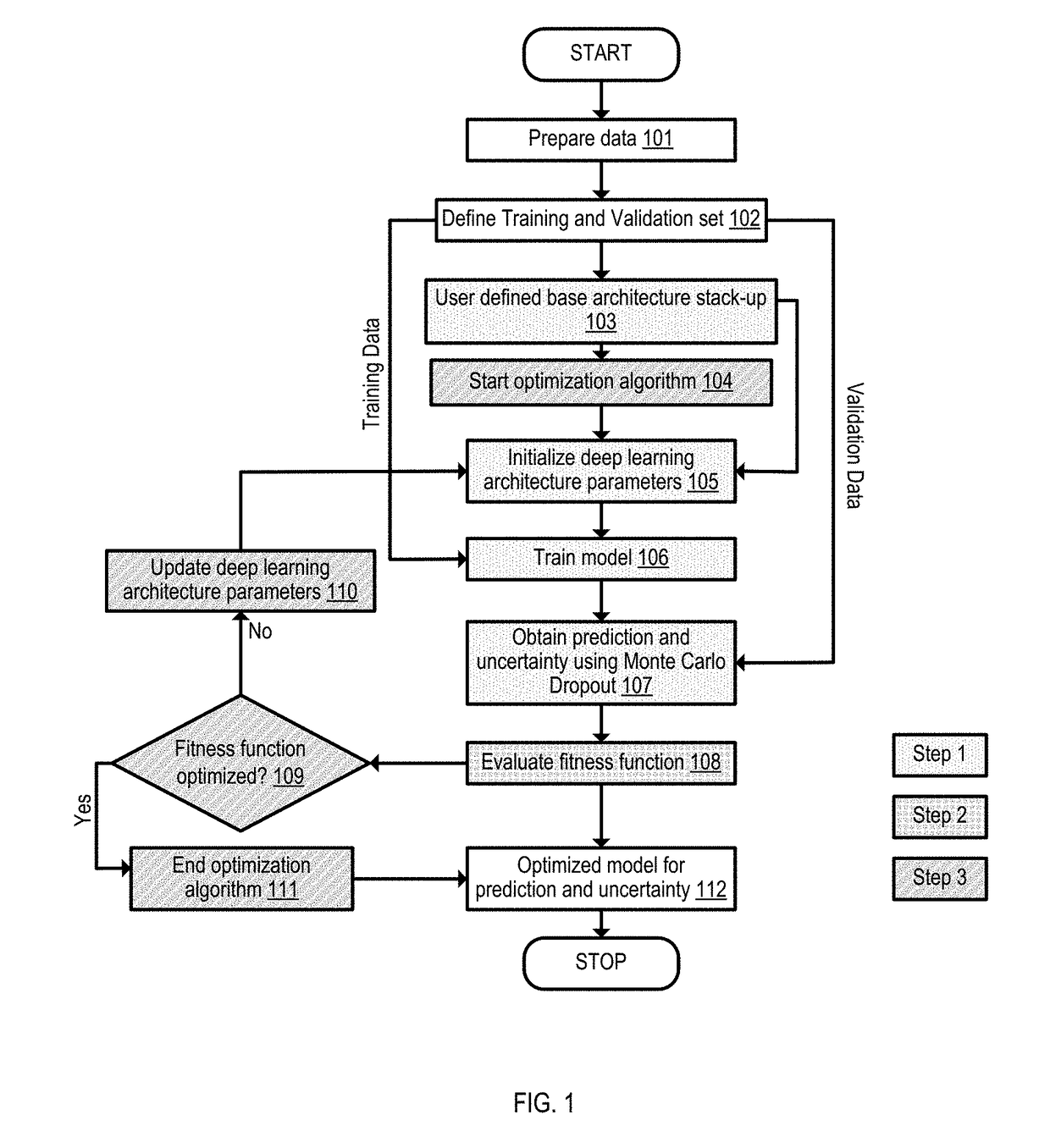
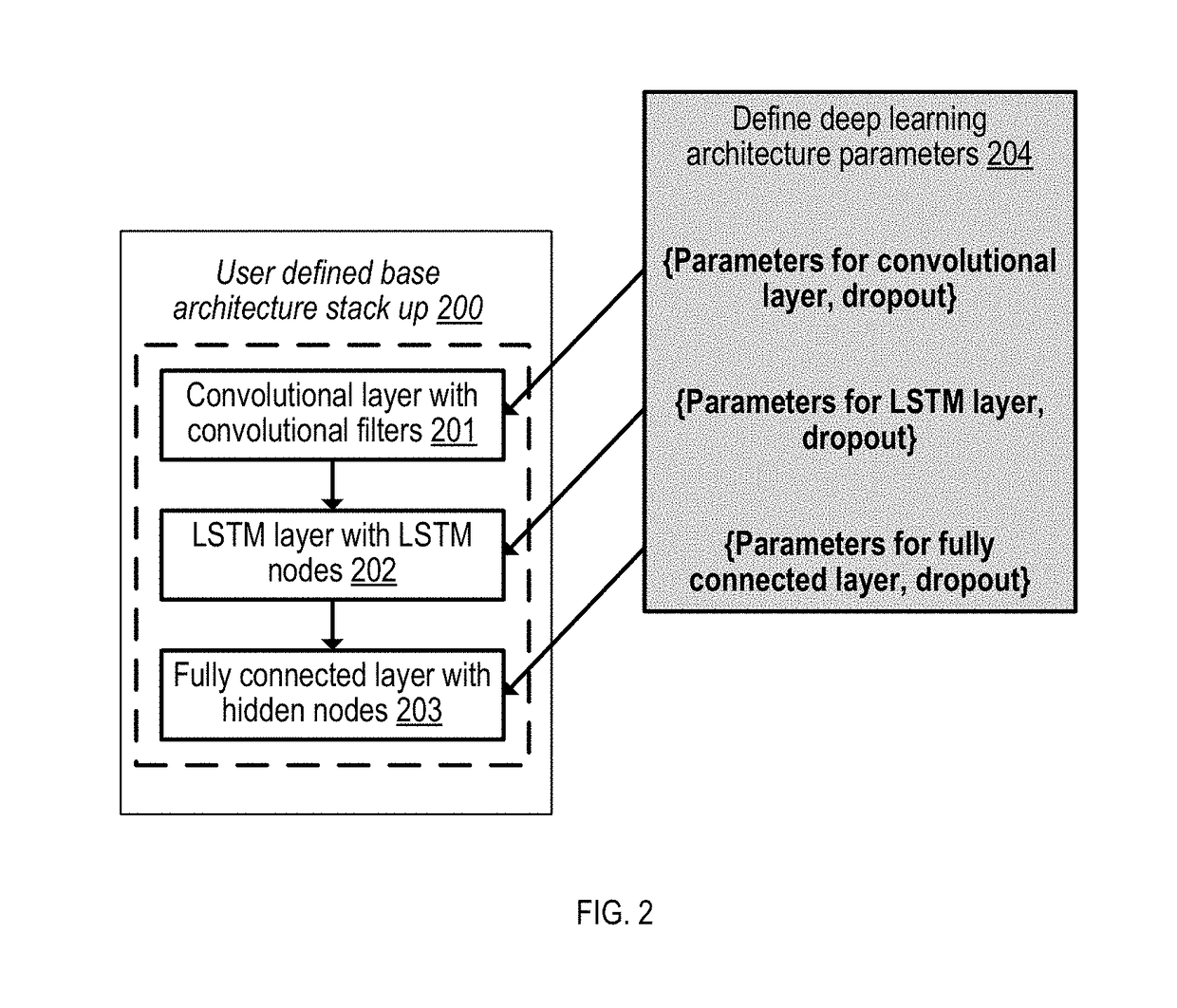
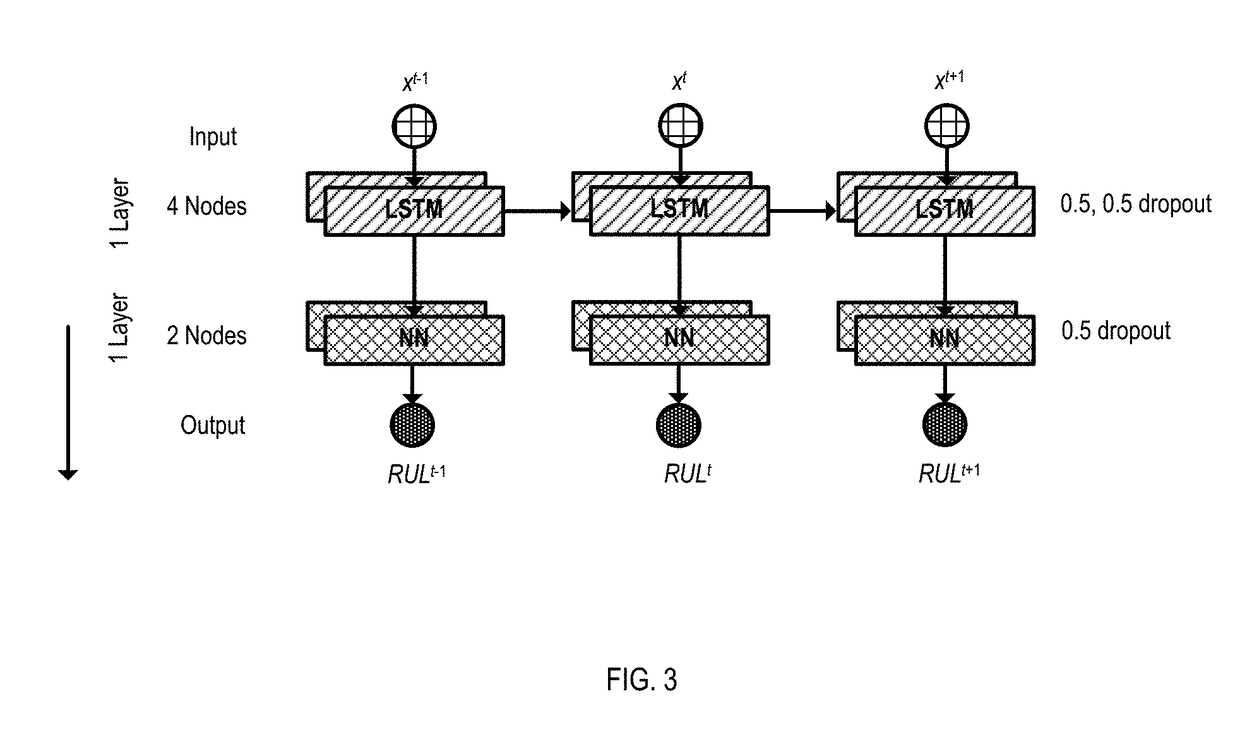
Deep learning network architecture optimization for uncertainty estimation in regression
InactiveUS20180341876A1Function increaseTesting/monitoring control systemsMachine learningMaintenance planningNetwork architecture
Equipment uptime is getting increasingly important across different industries which seek for new ways of increasing equipment availability. Detecting faults in the system by condition based maintenance (CBM) is not enough, because at the time of fault occurrence, the spare parts might not available or the needed resources (maintainers) are busy. Therefore, prediction failures and estimation of remaining useful life can be necessary. Moreover, not only predictions but also uncertainty in the predictions is critical for decision making. Example implementations described herein are directed to tuning parameters of deep learning network architecture by developing a mechanism to optimize for accuracy and uncertainty simultaneously, thereby achieving better asset availability, maintenance planning and decision making.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Centralized management of maintenance and materials for commercial aircraft fleets with access to real-time information
ActiveUS7761200B2Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesTime informationMaintenance planning
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Integrated maintenance services for fleet aircraft
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Centralized management of maintenance and materials for commercial aircraft fleets
ActiveUS7548802B2Minimizes re-authoringEasy alignmentVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMaintenance planningOn board
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Integrated maintenance and materials services for fleet aircraft using aircraft data to improve maintenance quality
ActiveUS20070112489A1Improve efficiencyLow costVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesMaintenance planningOn board
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
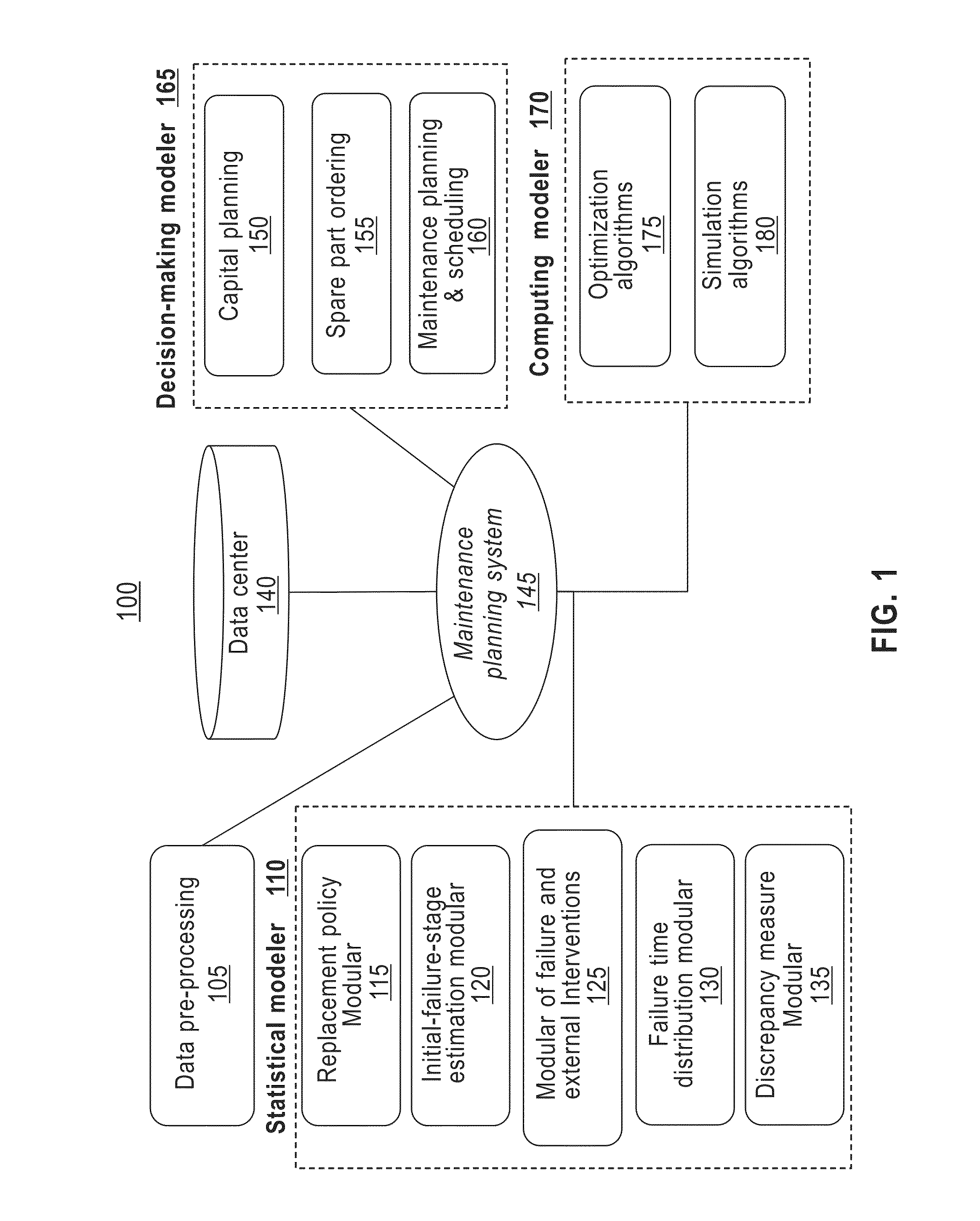
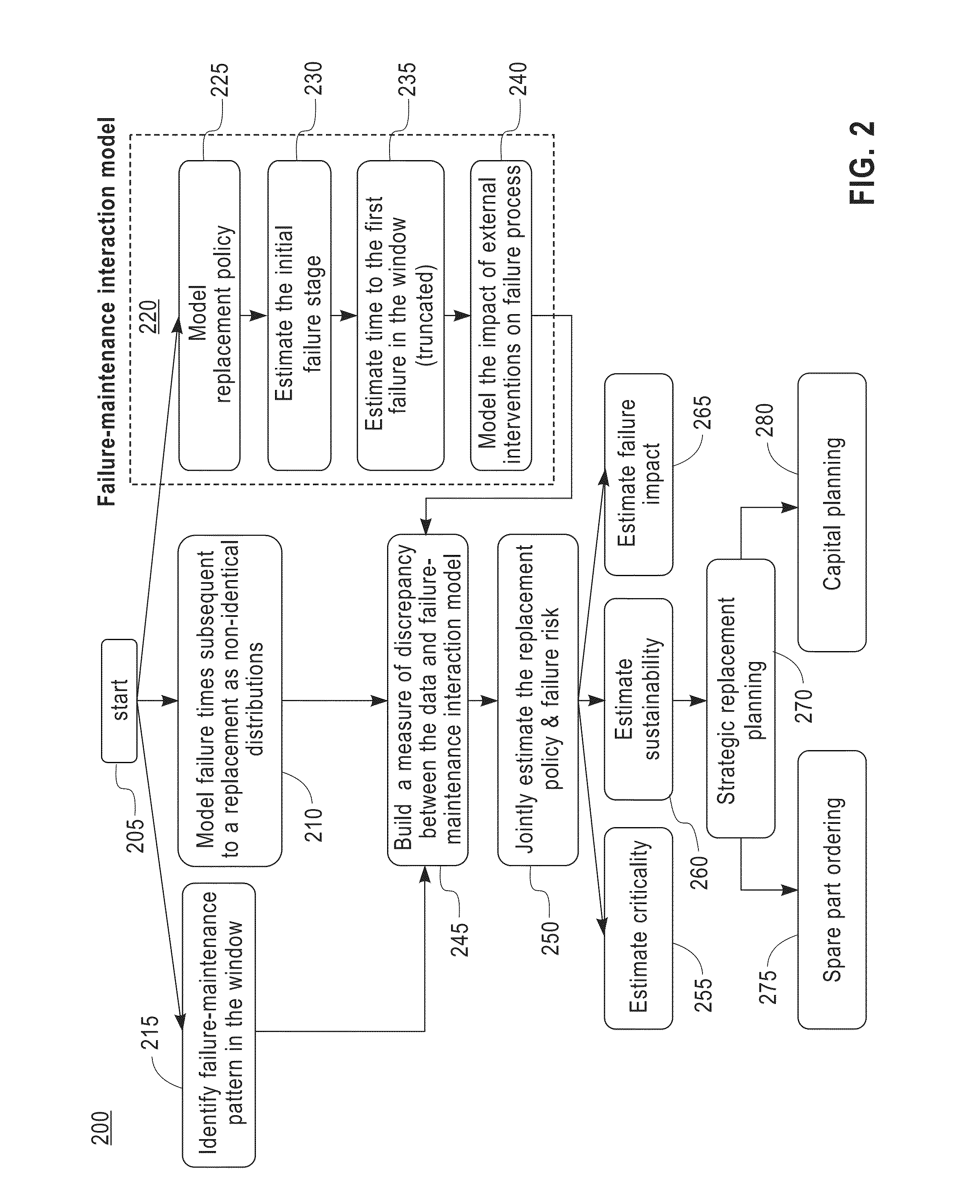
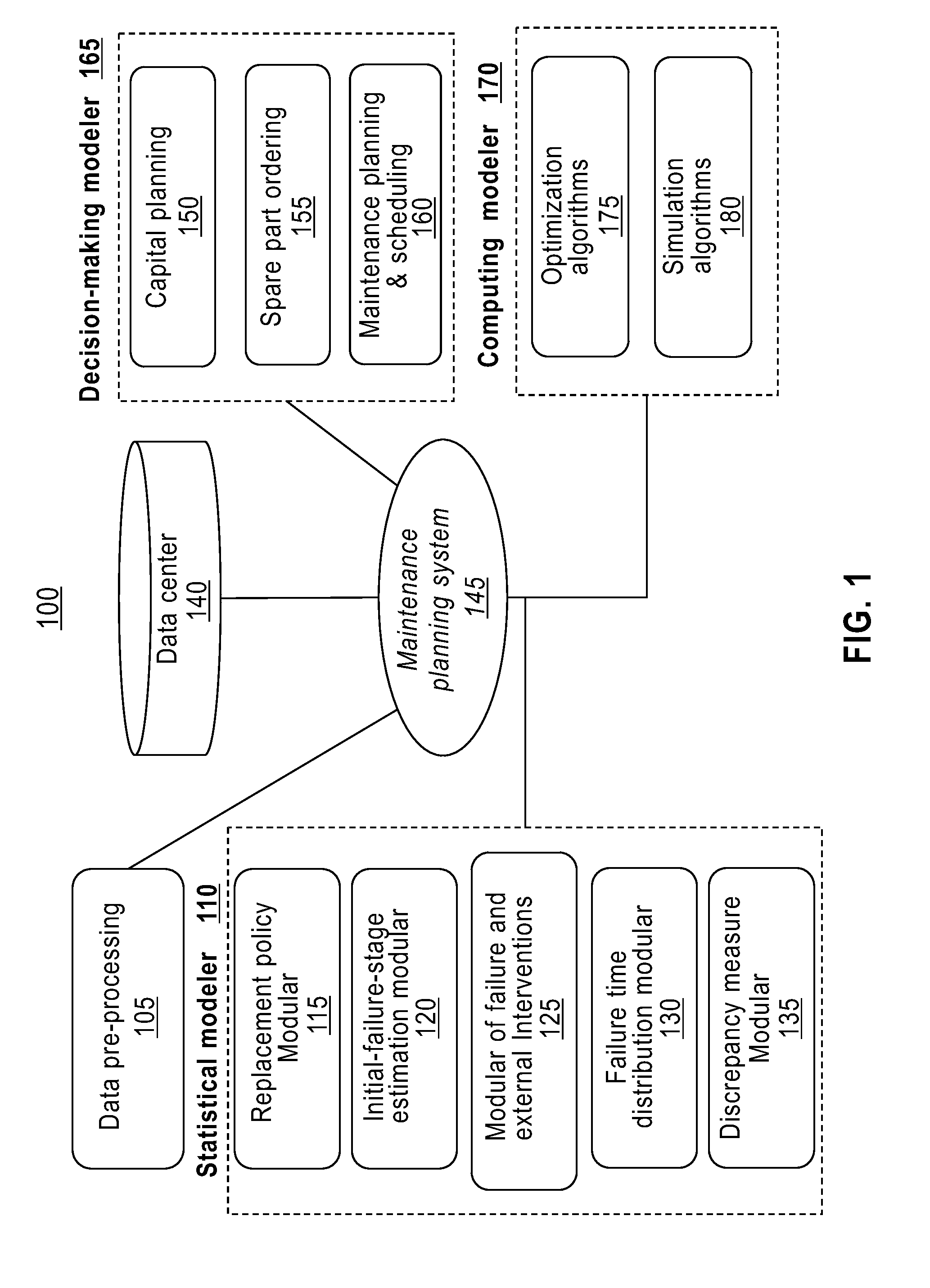
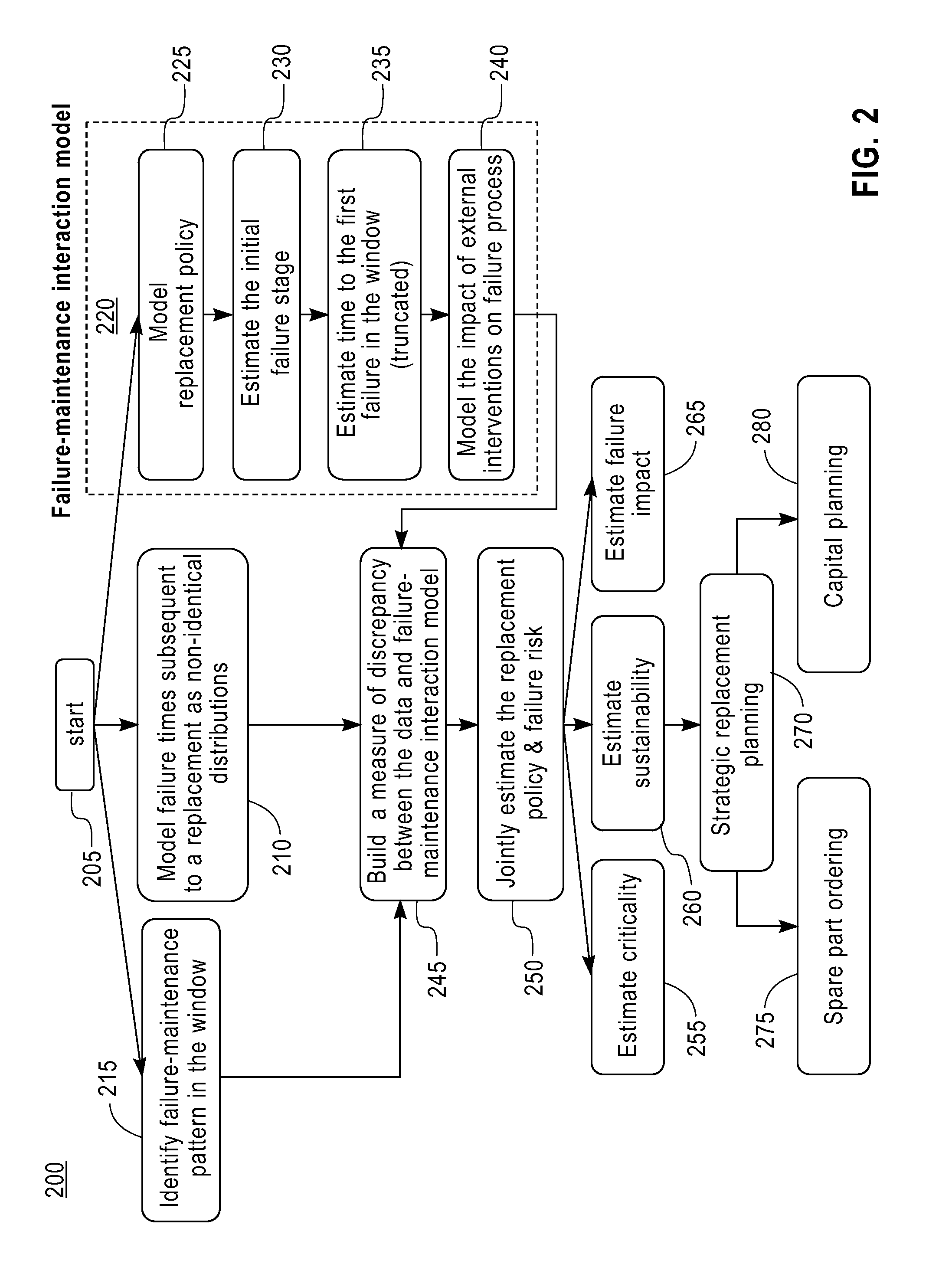
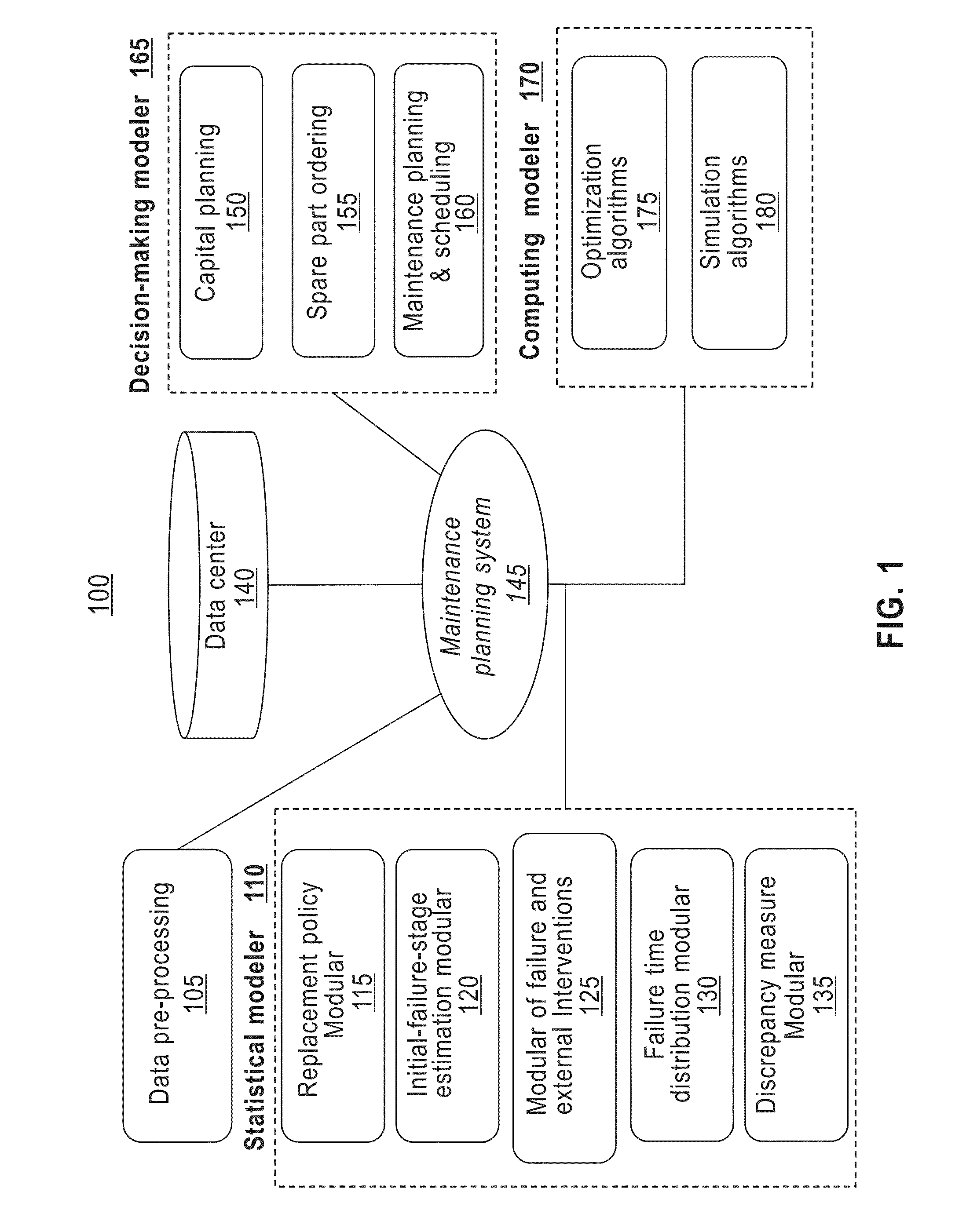
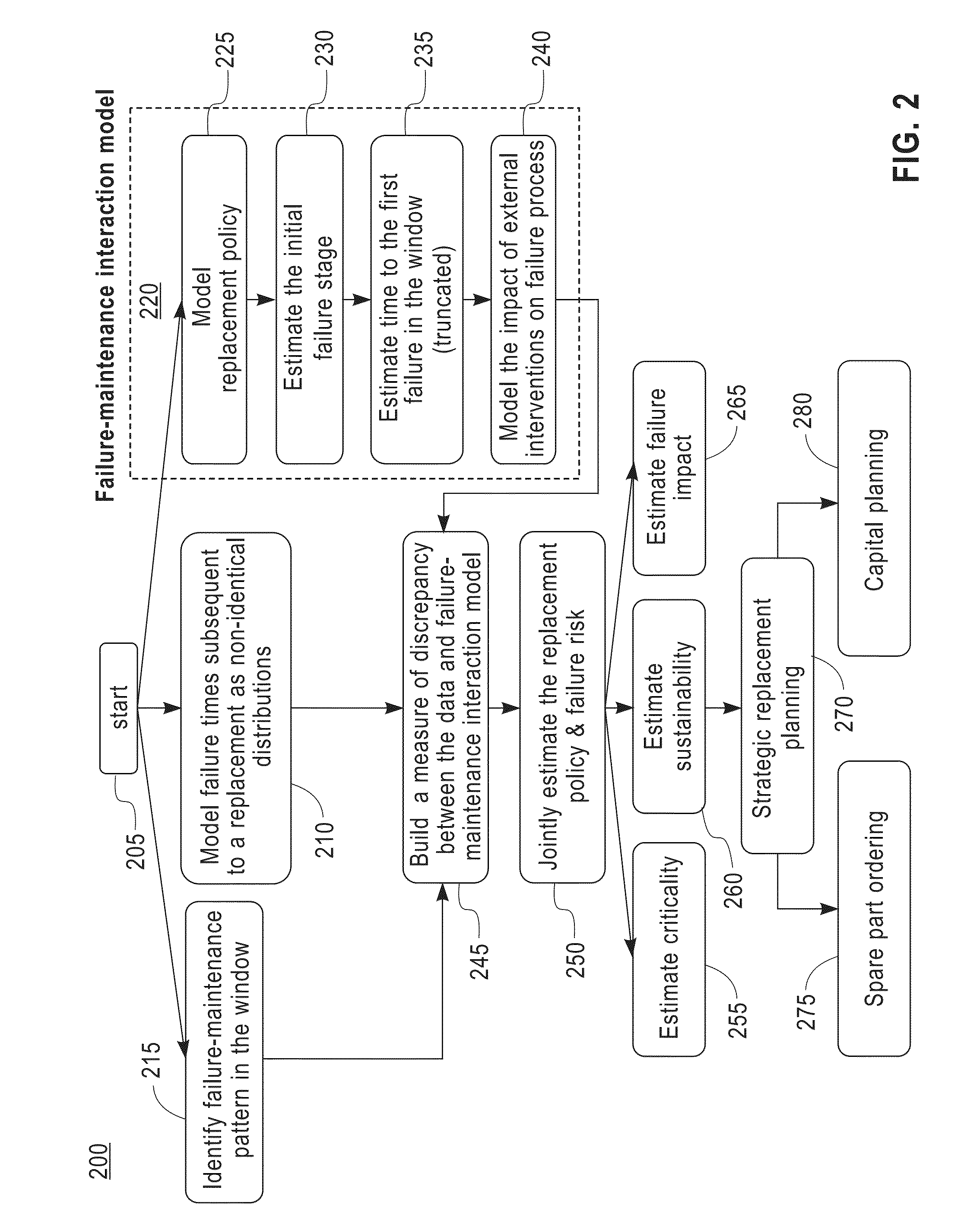
Maintenance planning and failure prediction from data observed within a time window
InactiveUS8880962B2Error detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsMaintenance planningProgram planning
A system, method and computer program product for predicting a failure of equipment from prior maintenance data of the equipment collected during a time duration estimate a number of preceding failures of the equipment prior to the time duration. The system, method and computer program product construct a model, based on the prior maintenance data, of an impact of an external intervention on a failure of the equipment. The system, method and computer program product construct a model, based on the constructed model of the impact of the external intervention and the estimated number of preceding failures, a replacement policy of the equipment and a probability of a subsequent failure of the equipment in a subsequent time period.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
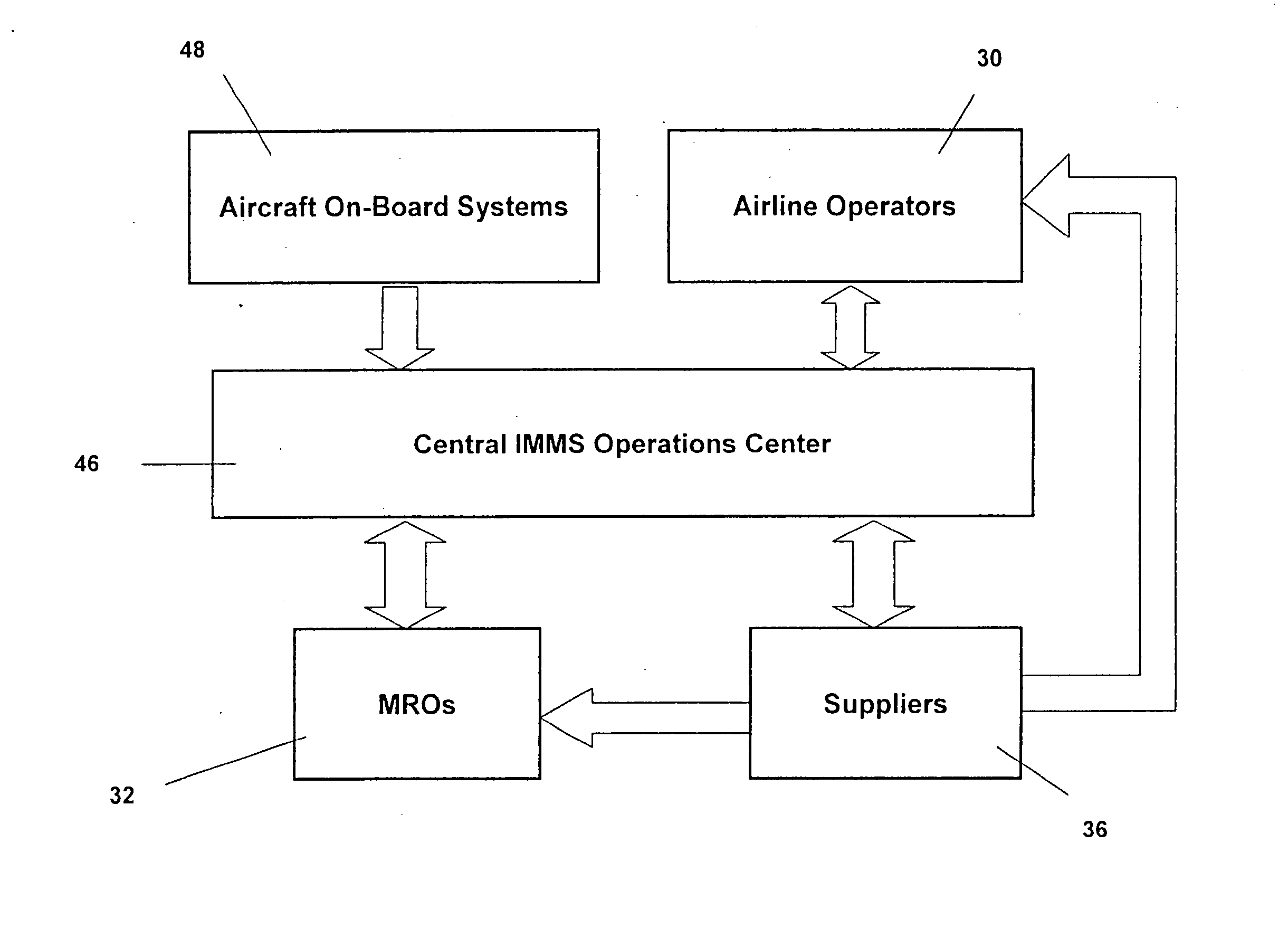
Centralized management of maintenance and materials for commercial aircraft fleets with information feedback to customer
ActiveUS20070112486A1Minimizes re-authoringLower life-cycle investmentVehicle testingAnalogue computers for vehiclesMaintenance planningOn board
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
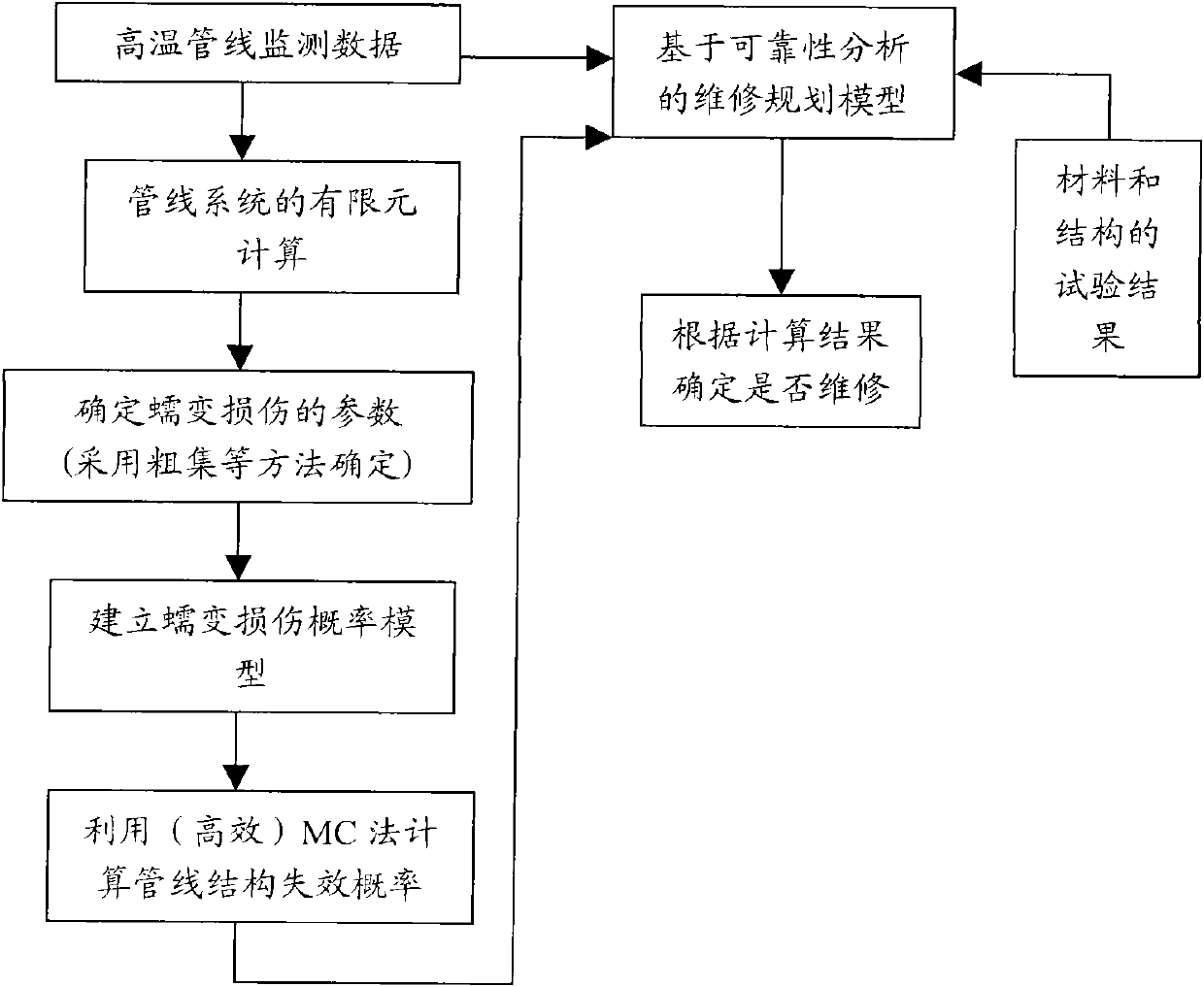
Method for realizing reliability maintenance planning of high temperature pipeline system
InactiveCN101994908AAccurately determineEfficient and accurate determinationStructural/machines measurementPipeline systemsStructural reliabilityMaintenance planning
The invention relates to a method for realizing reliability maintenance planning of a high temperature pipeline system, which comprises the following steps of: collecting and acquiring detection data of a high temperature pipeline system; calculating a finite element of the high temperature pipeline system; determining creep damage parameters according to the influence degree of all factors on the life of the high temperature pipeline; creating a creep damage probability model through determining the probability distribution of the creep damage parameters; calculating a structural failure probability according to the creep damage probability model; creating a maintenance planning model based on reliability analysis according to the detection data, test results of materials and structures of the high temperature pipeline system and the structural failure probability; and carrying out calculation processing according to the maintenance planning model to obtain the optimal maintenance time of the high temperature pipeline system. By adopting the method for realizing the reliability maintenance planning of the high temperature pipeline system, the structural reliability is determined efficiently and accurately, a maintenance scheme can be accurately determined, the similar problem of the maintenance planning of the high temperature pipelines in other fields can be solved, and the method has wider application range.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Maintenance planning and failure prediction from data observed within a time window
A system for predicting a failure of equipment from prior maintenance data of the equipment collected during a time duration estimate a number of preceding failures of the equipment prior to the time duration. The system constructs a model, based on the prior maintenance data, of an impact of an external intervention on a failure of the equipment. The system constructs a model, based on the constructed model of the impact of the external intervention and the estimated number of preceding failures, of a replacement policy of the equipment and a probability of a subsequent failure of the equipment in a subsequent time period.
Owner:IBM CORP
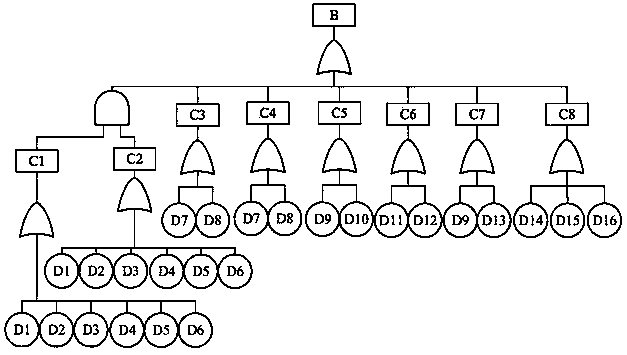
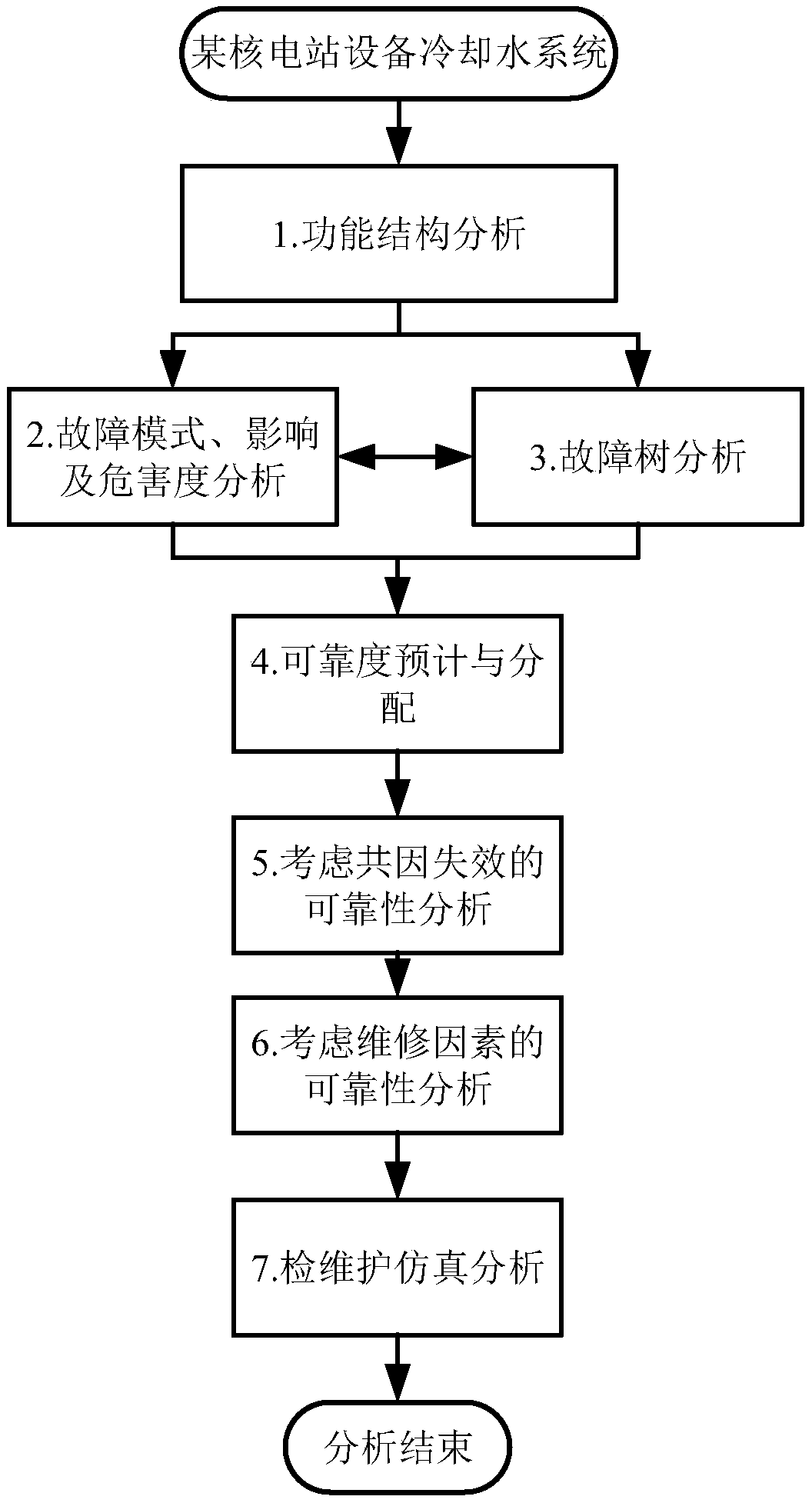
A system reliability evaluation method for nuclear power equipment
InactiveCN109559048APerfect reliability assessmentAvoid accidentsDesign optimisation/simulationResourcesMaintenance planningDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of system reliability analysis and design, and particularly discloses a nuclear power equipment system reliability assessment method, which comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out fault mode and influence analysis on equipment according to functional structure decomposition and related fault information of nuclear power equipment; establishing a fault tree model of the equipment based on a fault tree analysis method; then, establishing a reliability prediction and distribution model of the equipment; establishing a reliability analysismodel considering common cause failure; On the basis of previous analysis, after maintenance factors in the service period are considered, a maintenance strategy analysis model based on reliability isestablished to formulate a periodic maintenance strategy; and finally, based on a human factor engineering simulation platform, establishing an equipment inspection and maintenance simulation model to analyze a specific inspection and maintenance process. The model established by the invention can provide important reference and guidance for actual nuclear power equipment design, operation, maintenance planning and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Centralized management of maintenance and materials for commercial aircraft fleets with information feedback to customer
ActiveUS8296197B2Minimizes re-authoringEasy alignmentAnalogue computers for vehiclesHand manipulated computer devicesMaintenance planningOn board
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
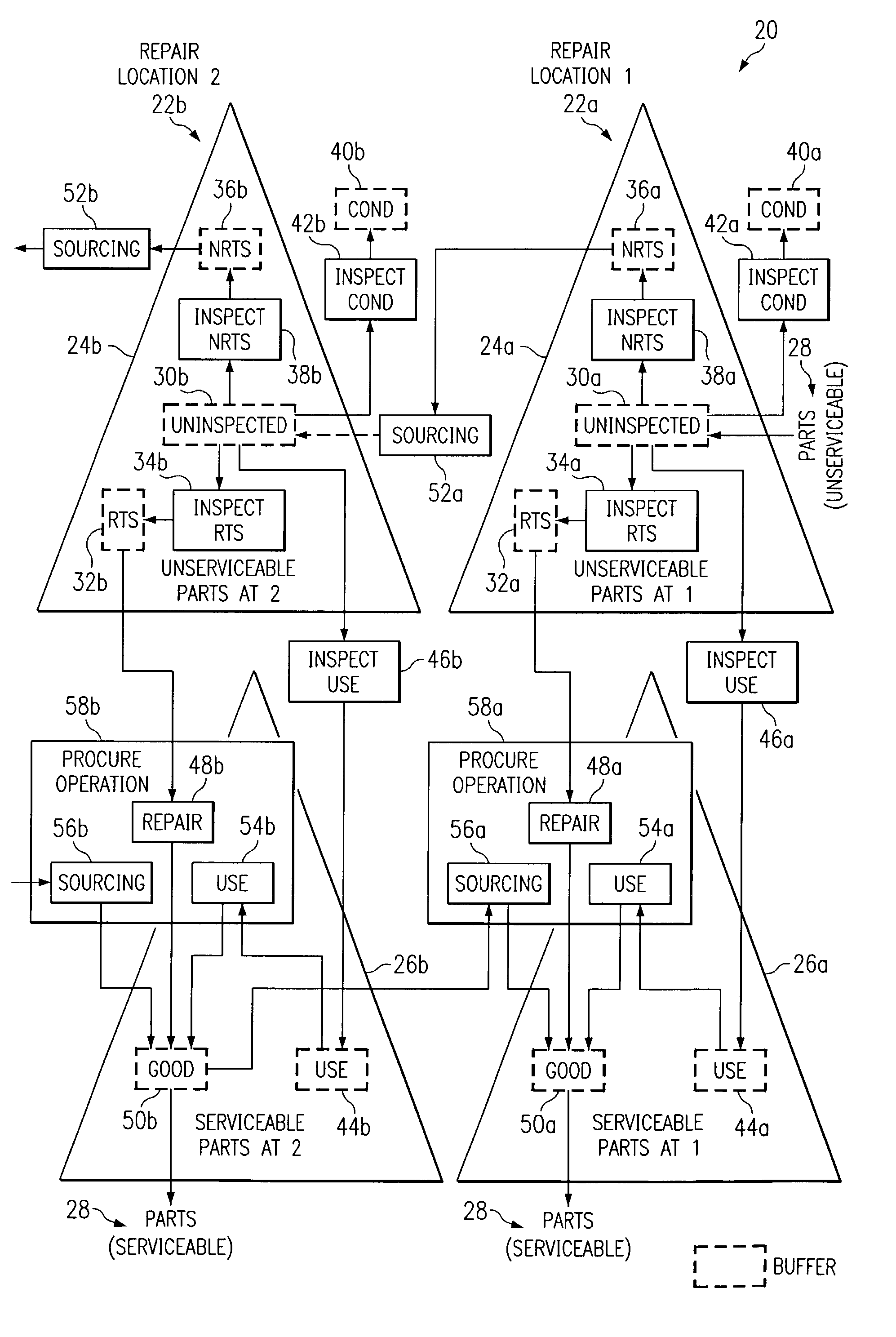
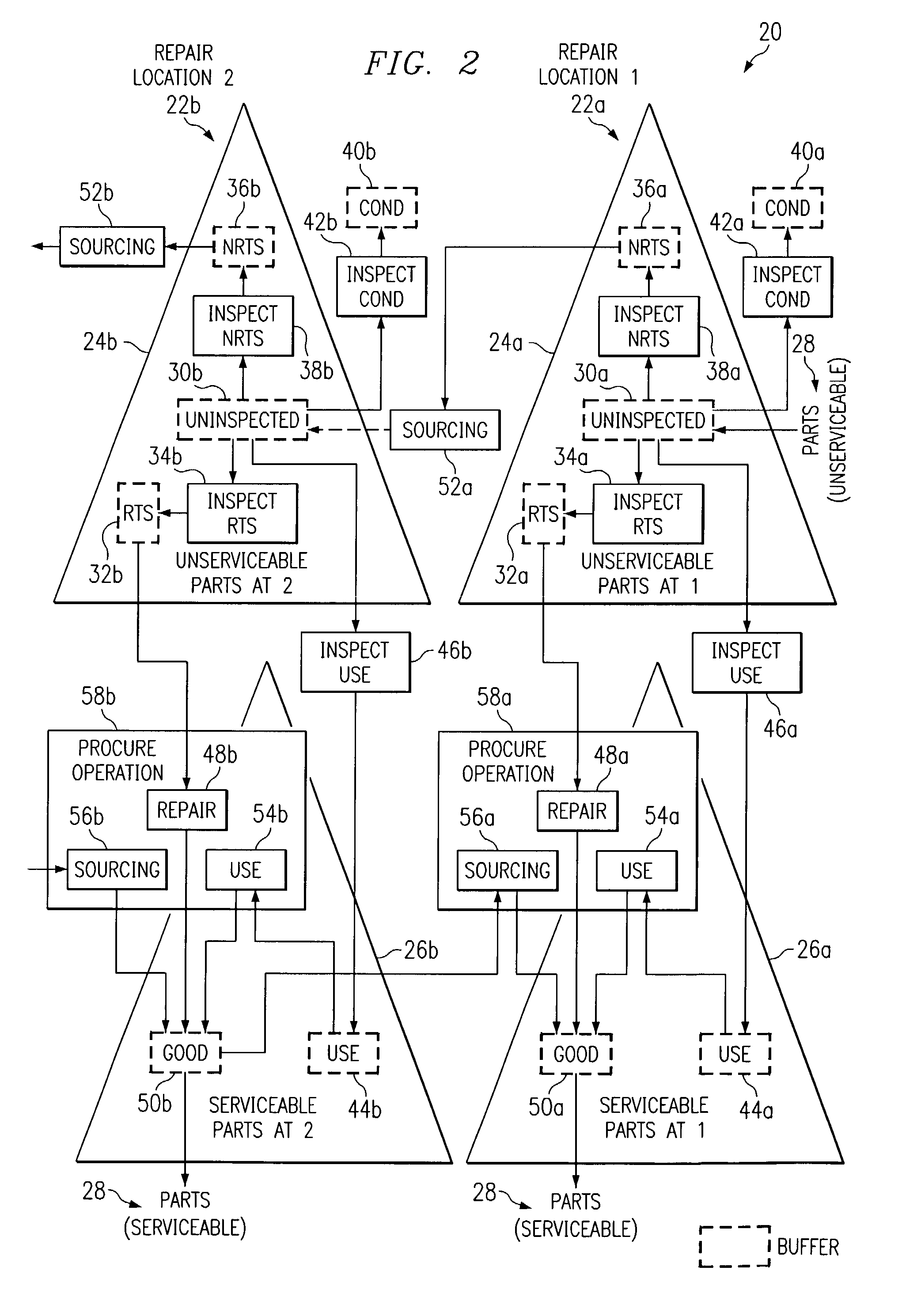
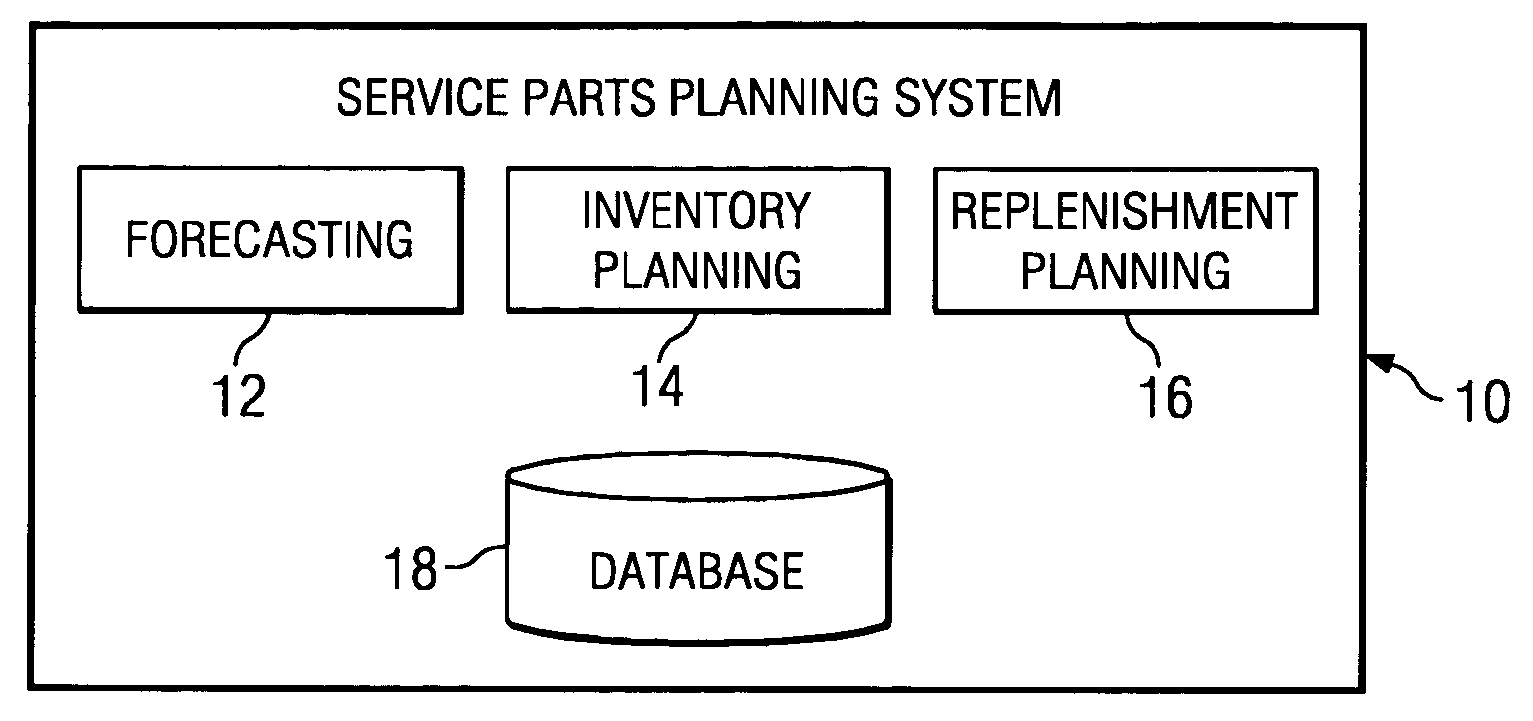
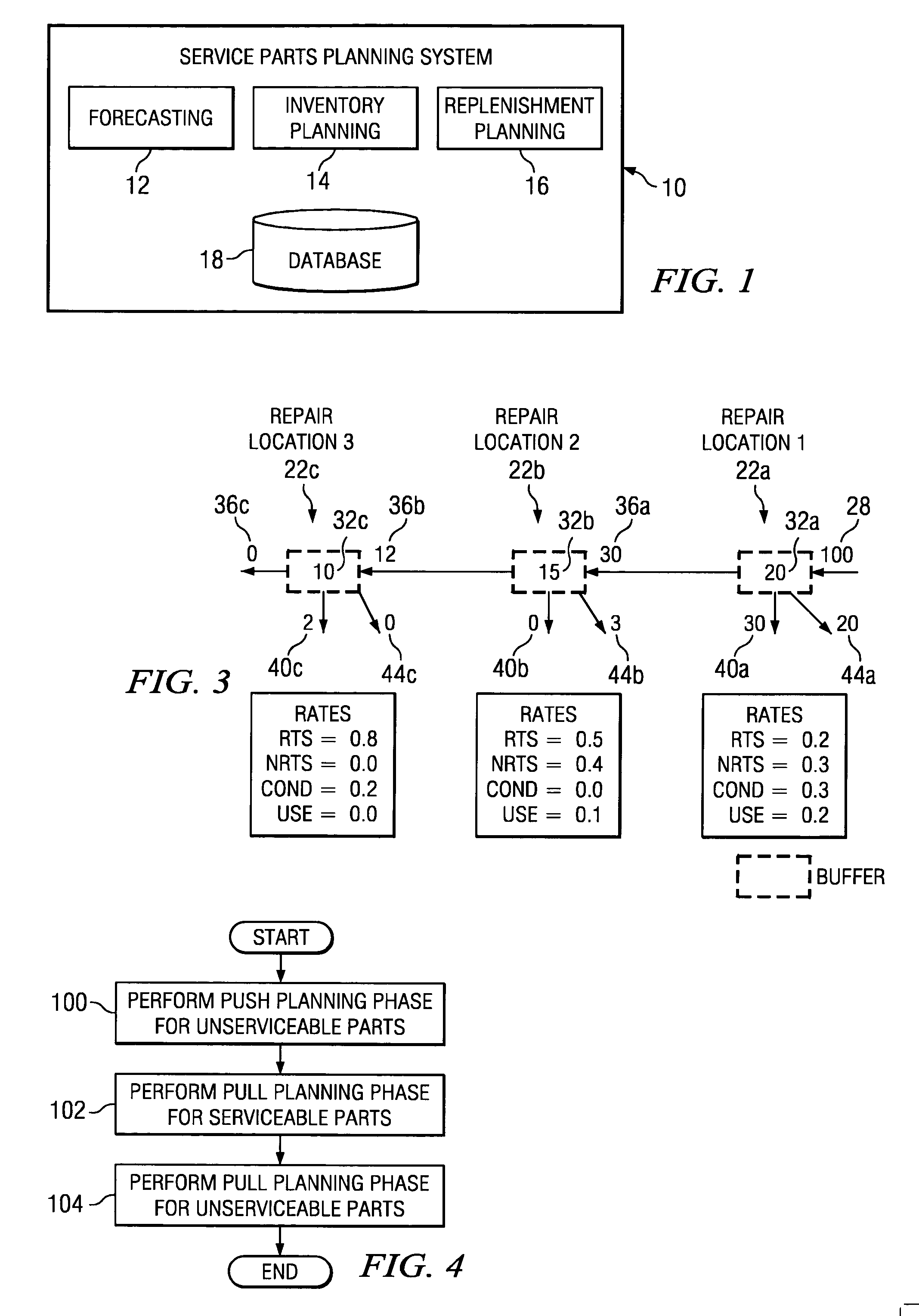
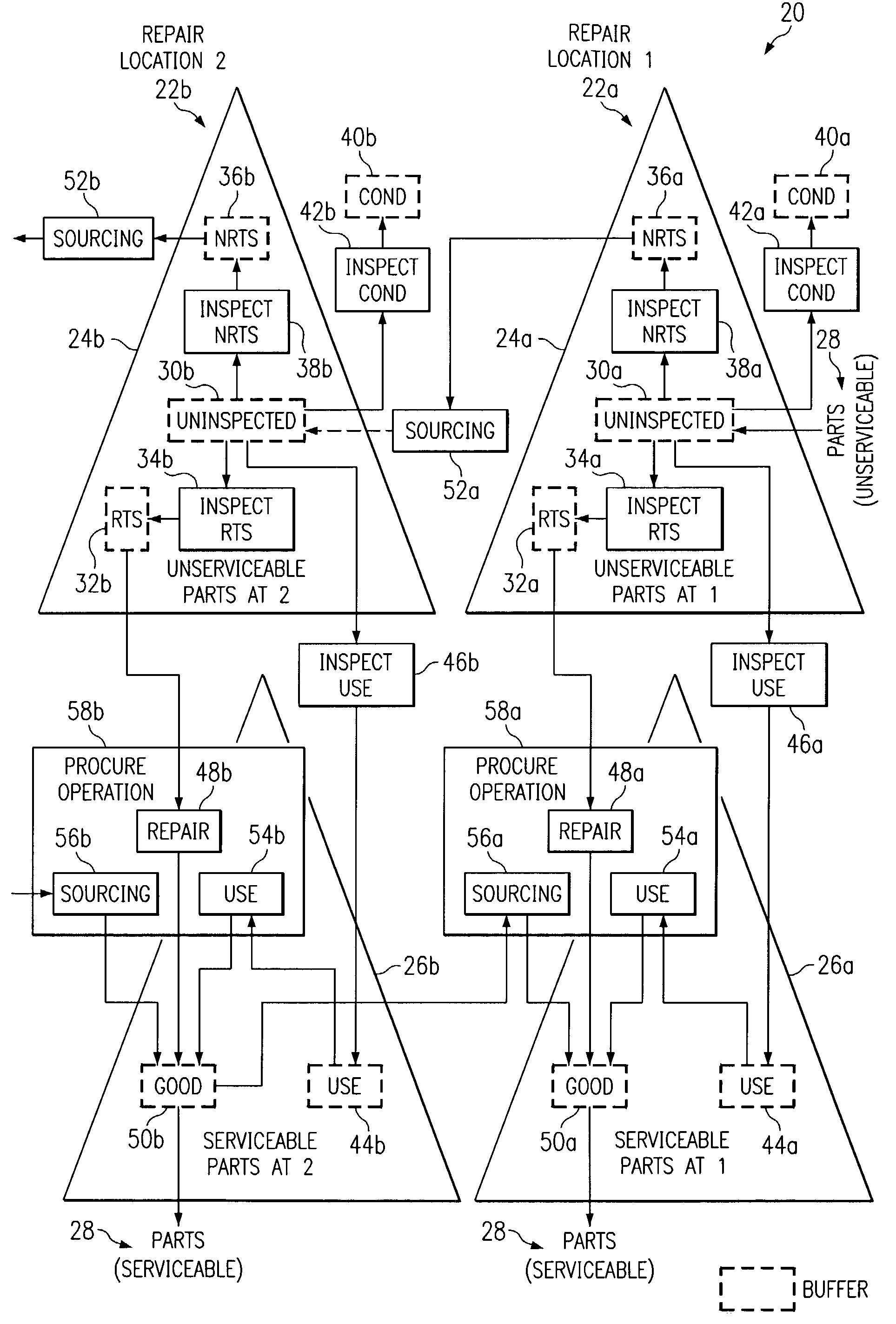
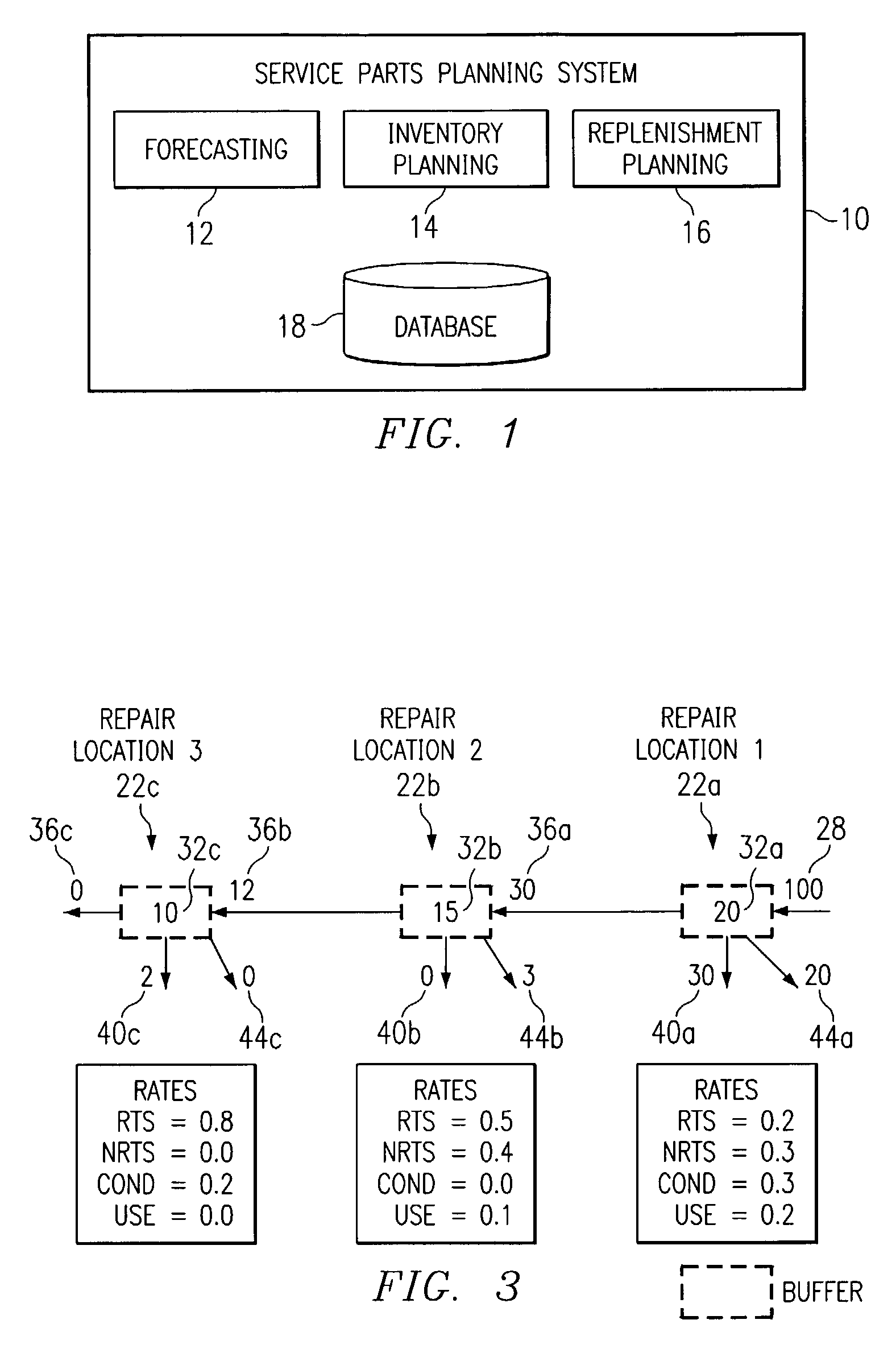
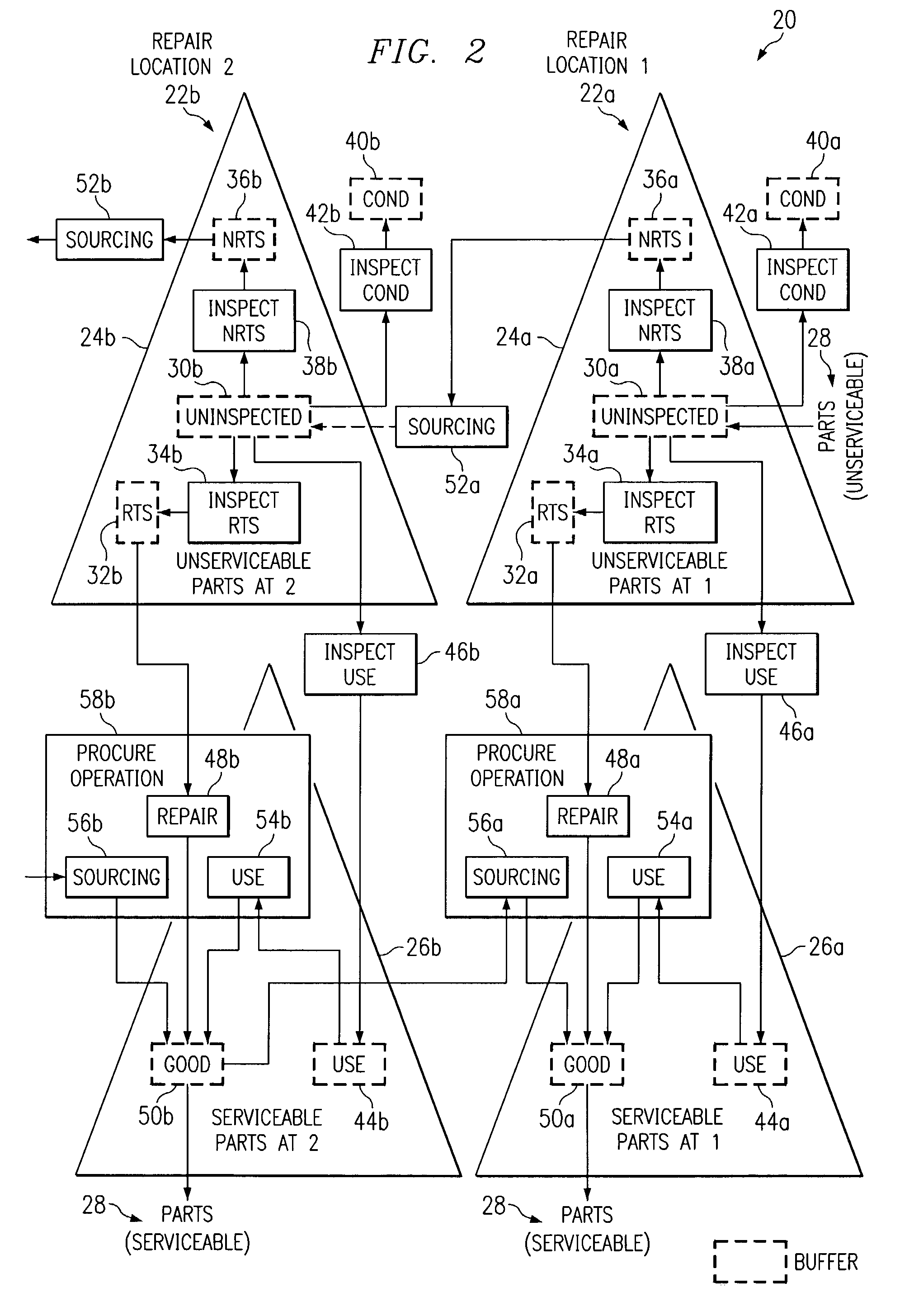
Push planning for unserviceable parts to facilitate repair planning in a repair network
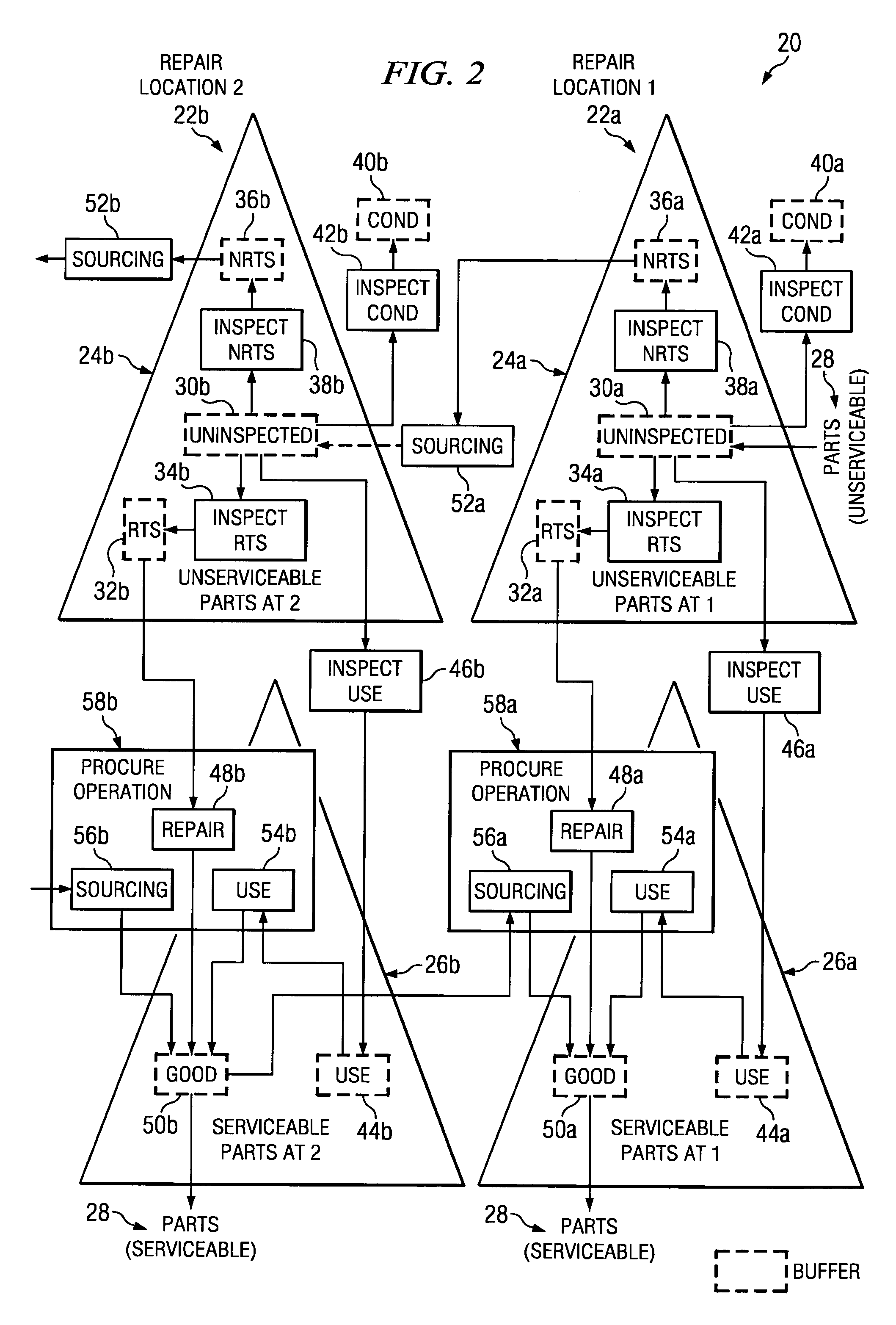
ActiveUS7277862B1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedIncrease supplyMultiprogramming arrangementsComputation using non-denominational number representationMaintenance planningRepair time
In one embodiment, a method for repair planning for a location in a repair network includes modeling: (1) an uninspected buffer for parts received but not yet inspected at the location; (2) a first buffer for parts inspected at the location and repairable at the location; (3) a second buffer for parts inspected at the location and not repairable at the location; (4) a third buffer for parts inspected at the location and not repairable at any location in the repair network; and (5) a fourth buffer for parts inspected at the location and serviceable without repair. The parts in the uninspected buffer are assigned to the first, second, third, and fourth buffers at corresponding rates according to an inspection operation. One or more operation plans are generated to push parts out of the uninspected buffer to the first, second, third, and fourth buffers according to the corresponding rates, a part pushed out being available within the first, second, third, or fourth buffer only after a predetermined disposition time has elapsed. An operation plan is generated to push parts out of the second buffer to one or more upstream locations, a part pushed out being available at an upstream location only after a predetermined move lead time has elapsed. For each part pushed out of the uninspected buffer to the first or second buffer, the earliest time at which repair can begin for the part is estimated, this earliest repair time determining the earliest time at which, after the part has been repaired to make it serviceable, the part can be available to satisfy a demand at the location.
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
Maintenance planning and failure prediction from data observed within a time window
InactiveUS20130282355A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusSpecific program execution arrangementsMaintenance planningProgram planning
A system, method and computer program product for predicting a failure of equipment from prior maintenance data of the equipment collected during a time duration estimate a number of preceding failures of the equipment prior to the time duration. The system, method and computer program product construct a model, based on the prior maintenance data, of an impact of an external intervention on a failure of the equipment. The system, method and computer program product construct a model, based on the constructed model of the impact of the external intervention and the estimated number of preceding failures, a replacement policy of the equipment and a probability of a subsequent failure of the equipment in a subsequent time period.
Owner:IBM CORP
Pull planning for unserviceable parts in connection with on-demand repair planning
InactiveUS20050091070A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedMinimize undesirable costResourcesSpecial data processing applicationsMaintenance planningStart time
In one embodiment, planning repairs in response to demand in a multi-level repair network includes accessing a forecasted demand for serviceable parts at a repair location and, for each inspected unserviceable part at the location that is not repairable at the location: (1) planning a move of the part to an upstream repair location such that the part can be available for repair at the upstream location at an estimated earliest time; (2) estimating a latest time at which a repair of the part can begin at the upstream location to help satisfy the forecasted demand, according to the forecasted demand and the estimated earliest time, and planning a repair at the upstream location at the estimated latest time; and (3) re-planning the move, according to the start time of the repair, by modifying a move delivery time according to a repair start time and modifying a move start time according to the modified delivery time. The re-planned move start time is an estimated latest time at which the part can be moved to the upstream location for repair to help satisfy the forecasted demand.
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
Central server for managing maintenance and materials for commercial aircraft fleets with fleet-wide benchmarking data
ActiveUS20160042325A1Improve efficiencyLow costRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesOffice automationBaseline dataMaintenance planning
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
On-demand repair planning
InactiveUS7620561B1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedIncrease supplyError detection/correctionResourcesMaintenance planningProgram planning
Owner:BLUE YONDER GRP INC
Integrated materials management for commercial aircraft fleets including access to real-time on-board systems information
ActiveUS20070124222A1Part demand informationImproves part inventory controlAnimal feeding devicesSpecial data processing applicationsMaintenance planningOn board
Turnkey maintenance of a customer's aircraft fleet is managed by a single management service provider (MSP) controlling integrated maintenance and materials services from a central operations site. The MSP converts data received directly from on-board aircraft systems into information it uses to manage maintenance service providers and parts suppliers. The MSP contracts with and manages maintenance, repair and overhaul organizations (MROs) who perform the maintenance on the customers' aircraft at line and base stations. The MSP either remotely manages part inventories at the customer's site, or manages suppliers who deliver the parts to the MROs. Maintenance planning, scheduling and execution information is exchanged between the MSP, MROs, part suppliers and the customers through a shared data communication network controlled by the MSP. The MSP charges the customer for the maintenance services based on a flat rate per unit of aircraft flying time.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com