Patents
Literature
283 results about "Device file" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
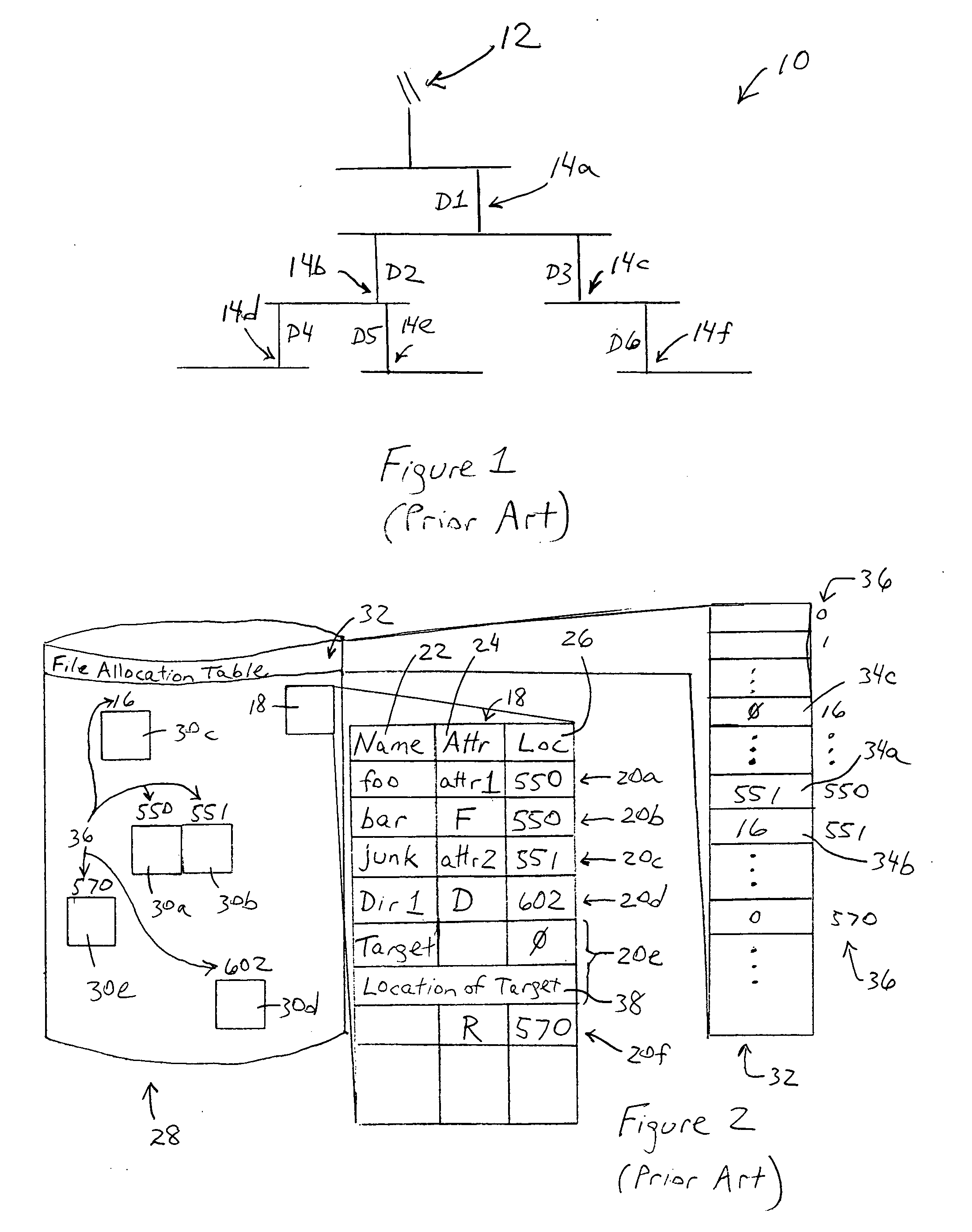
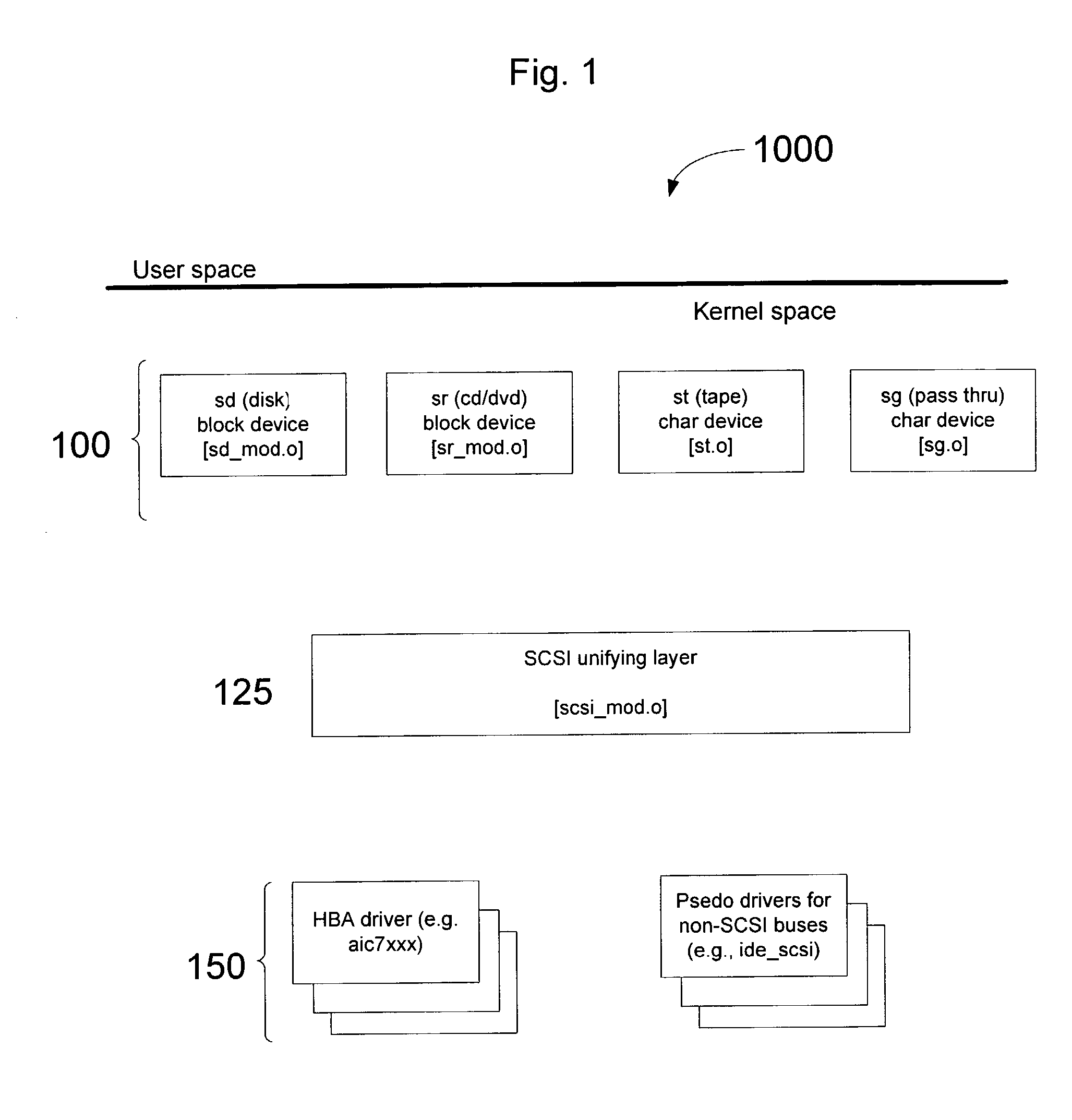
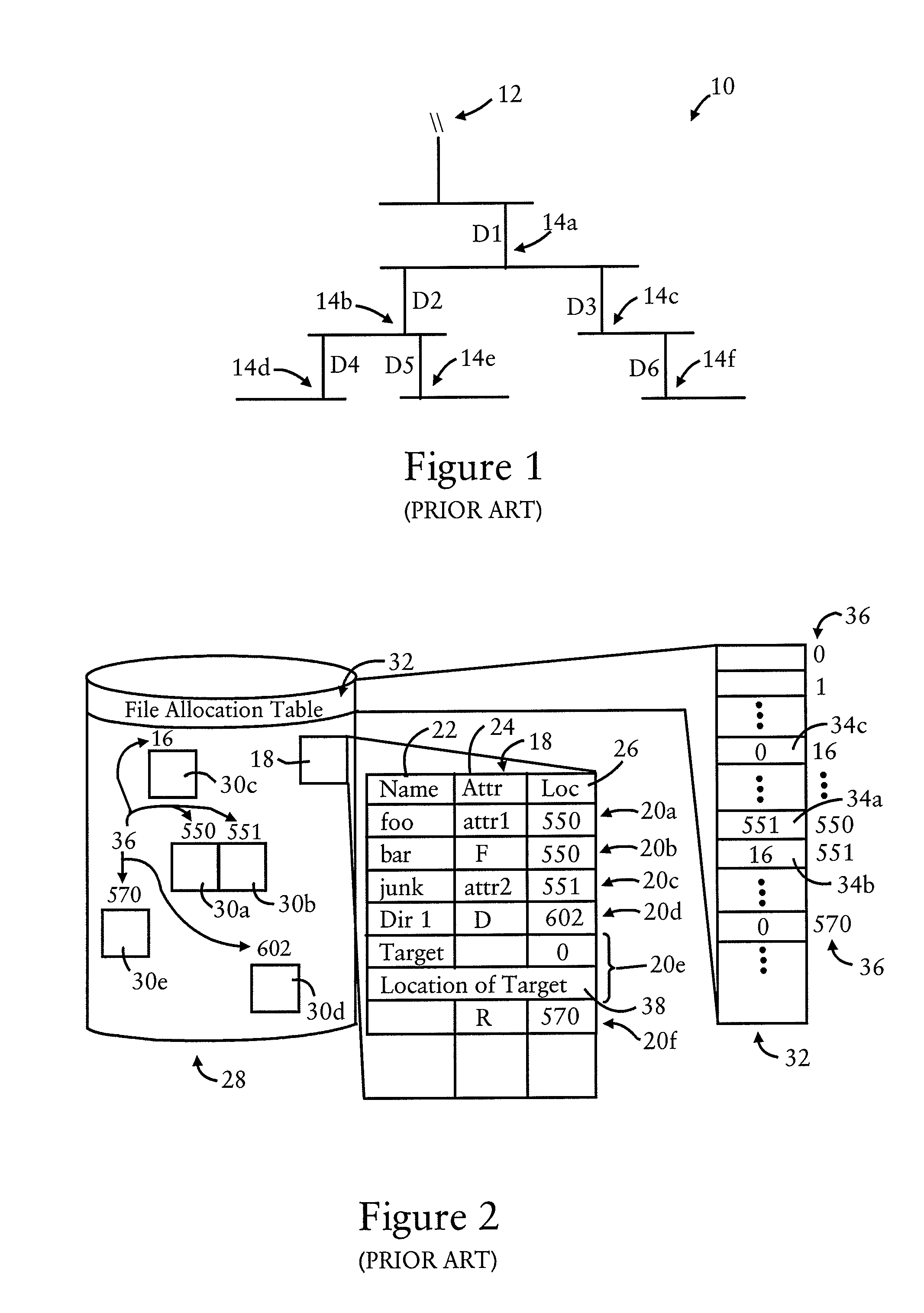
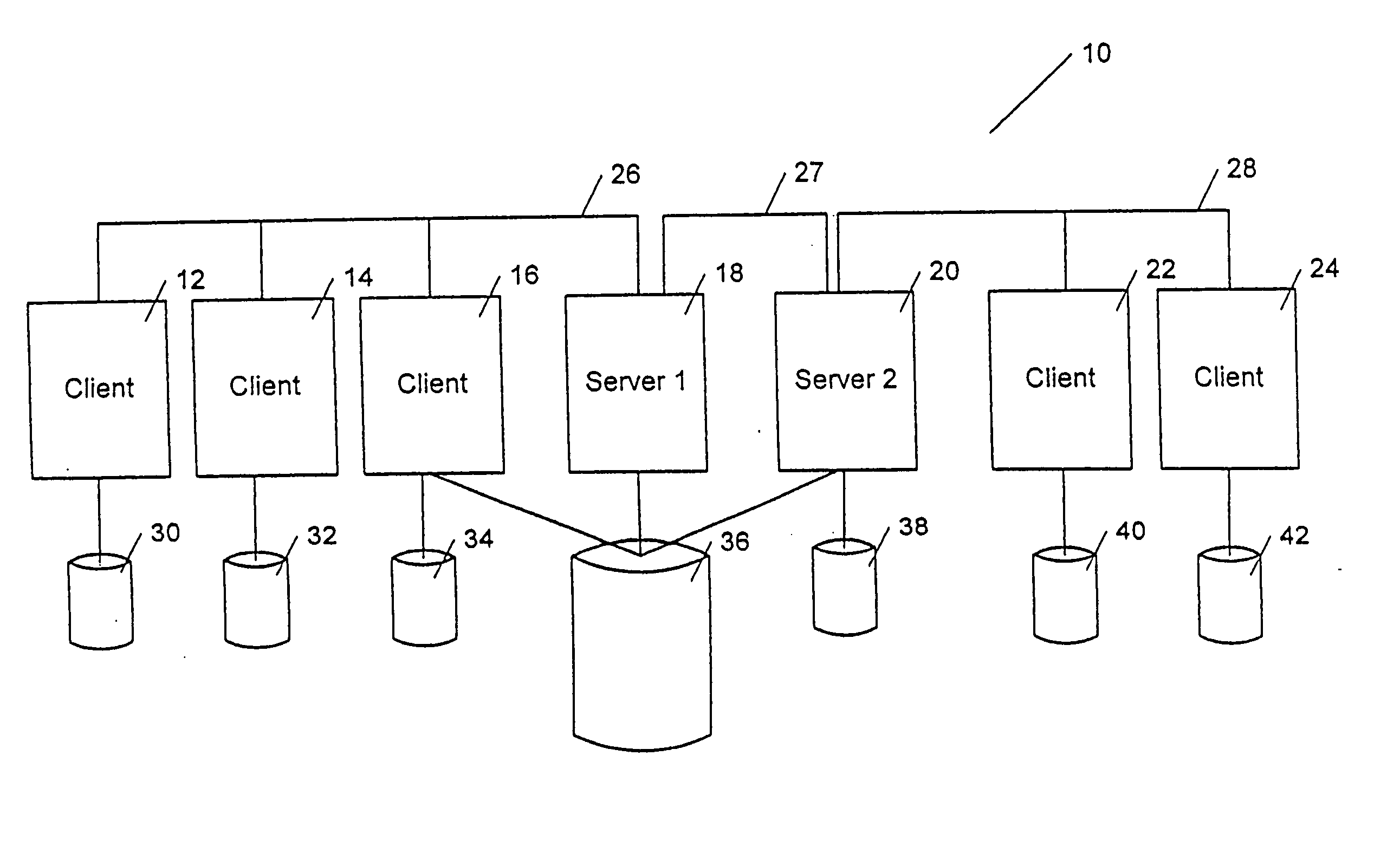
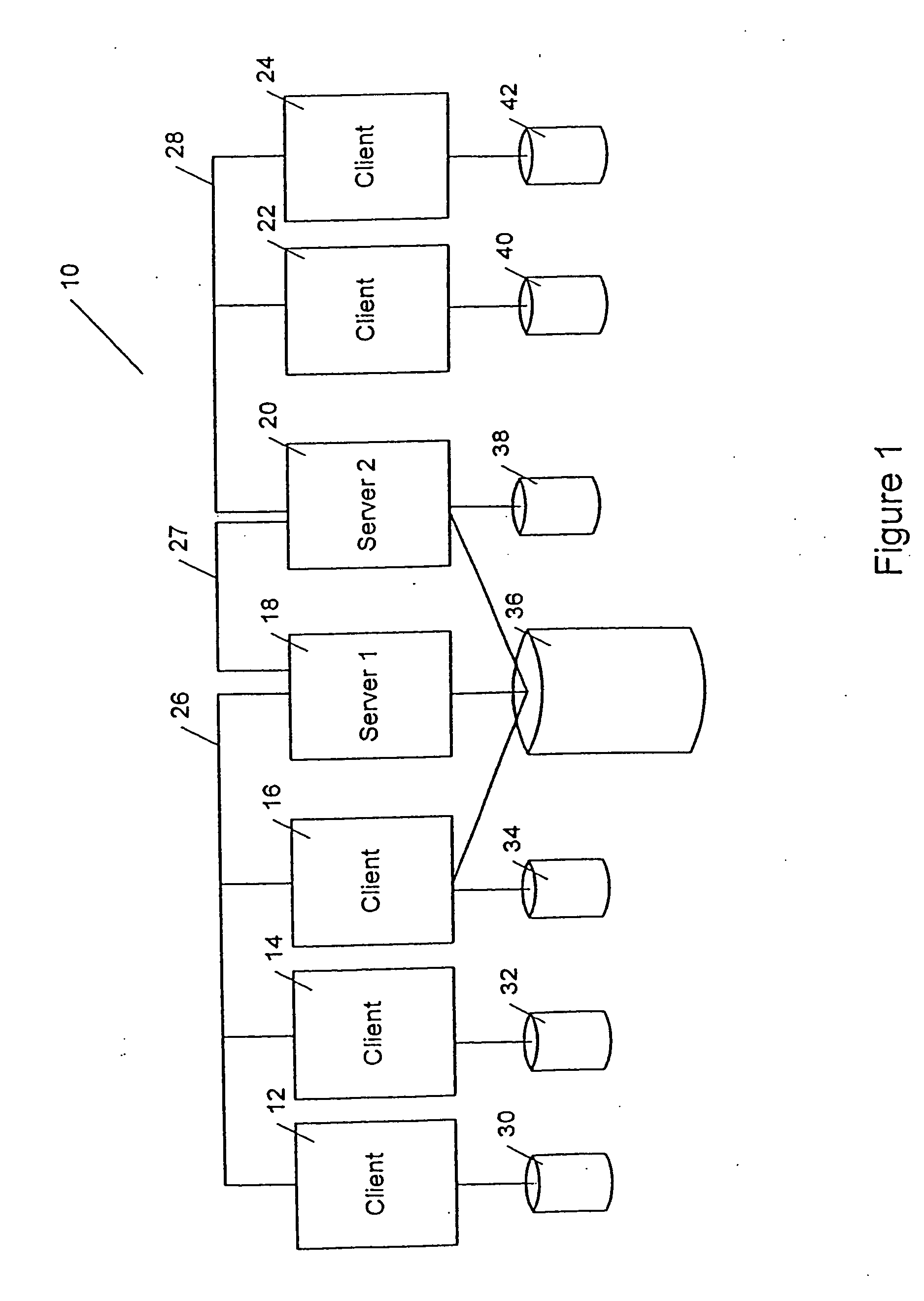
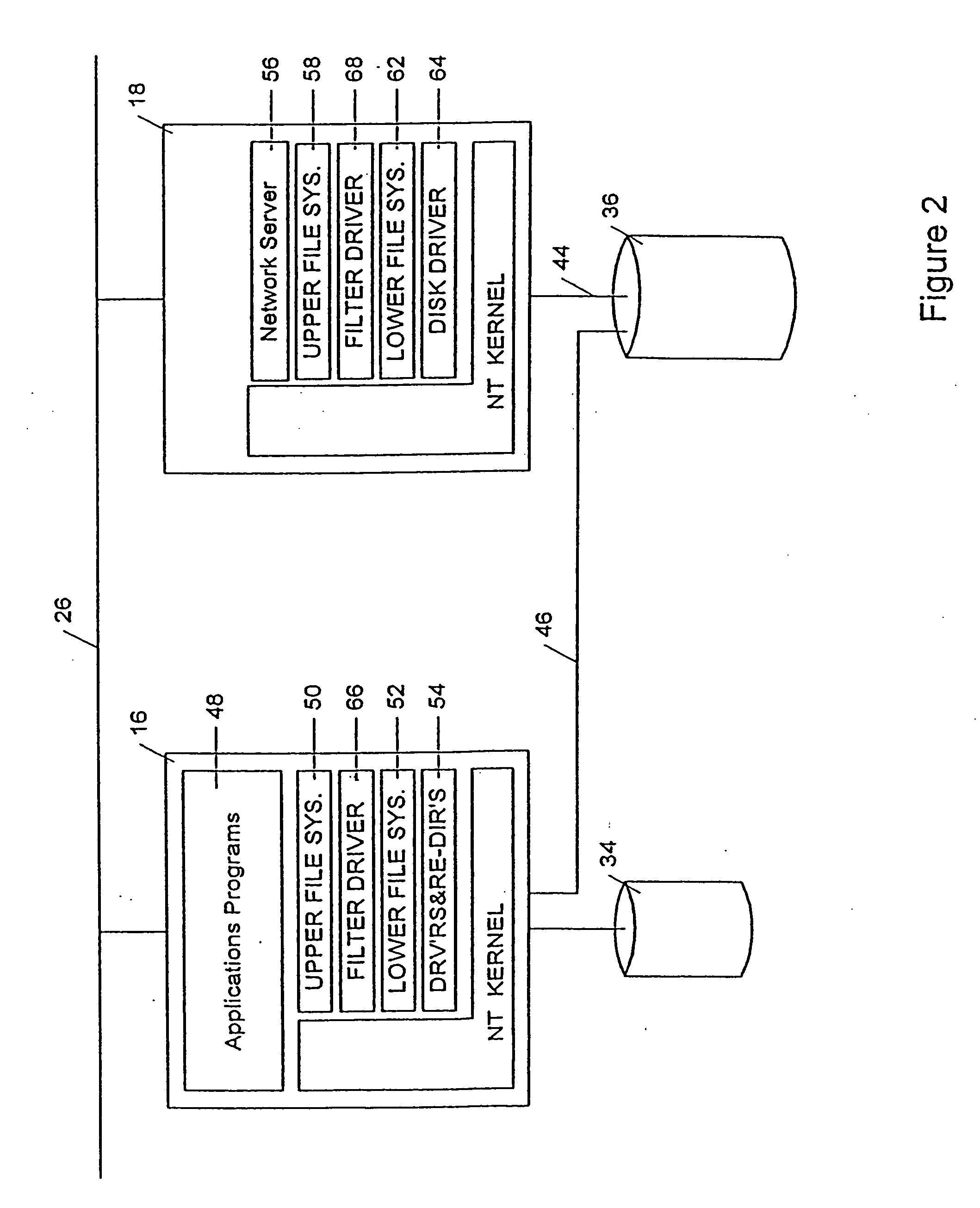
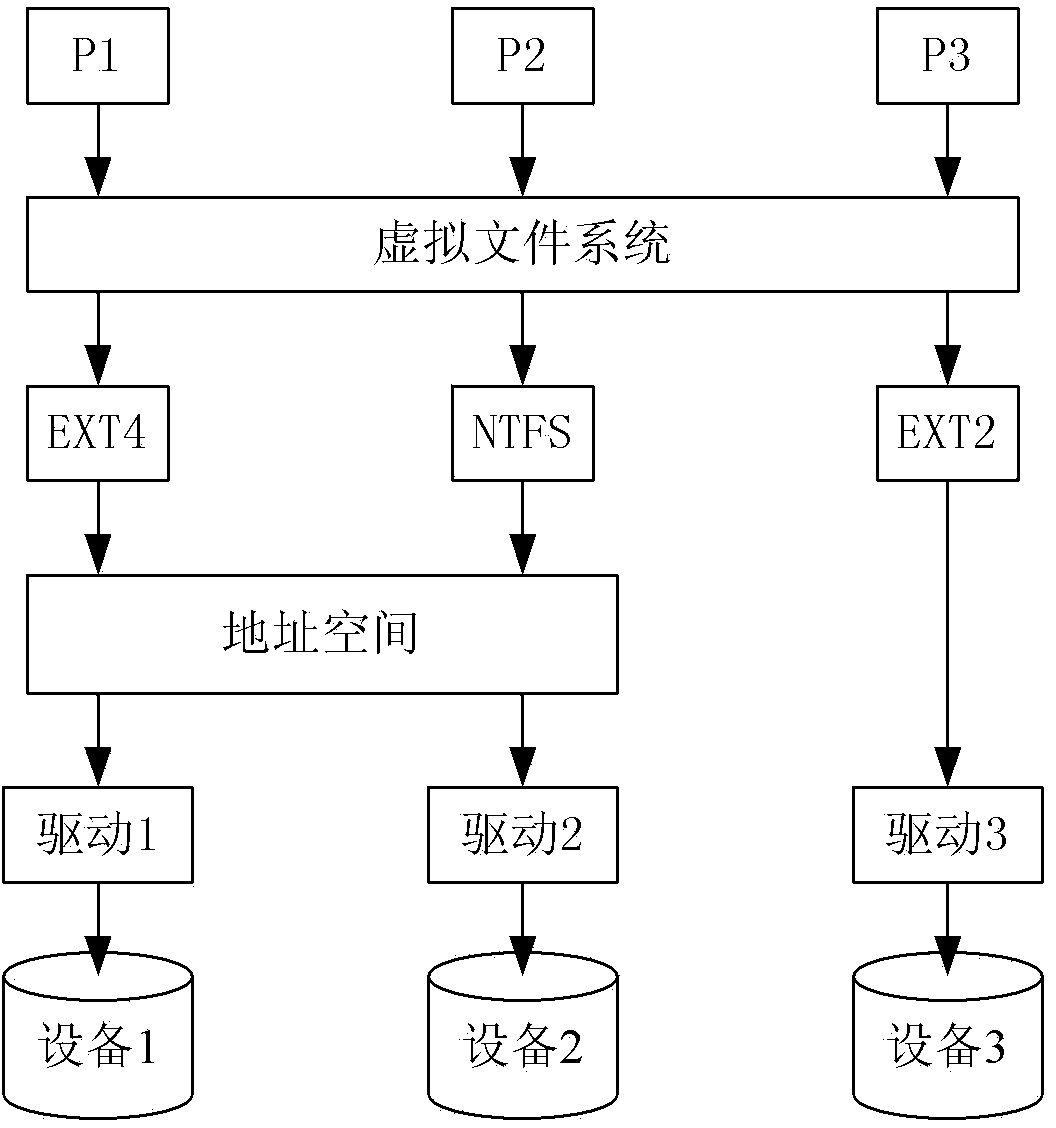
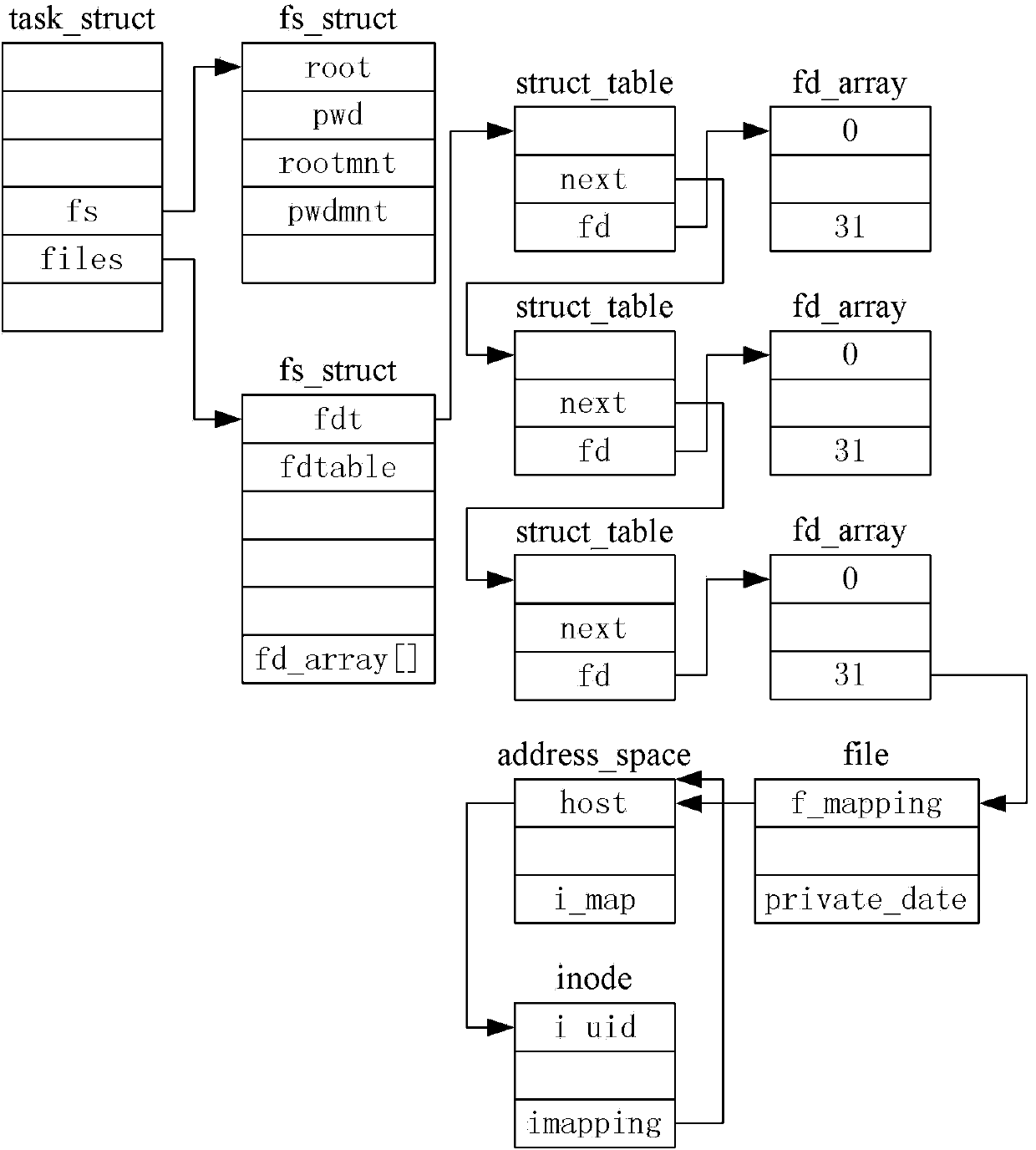
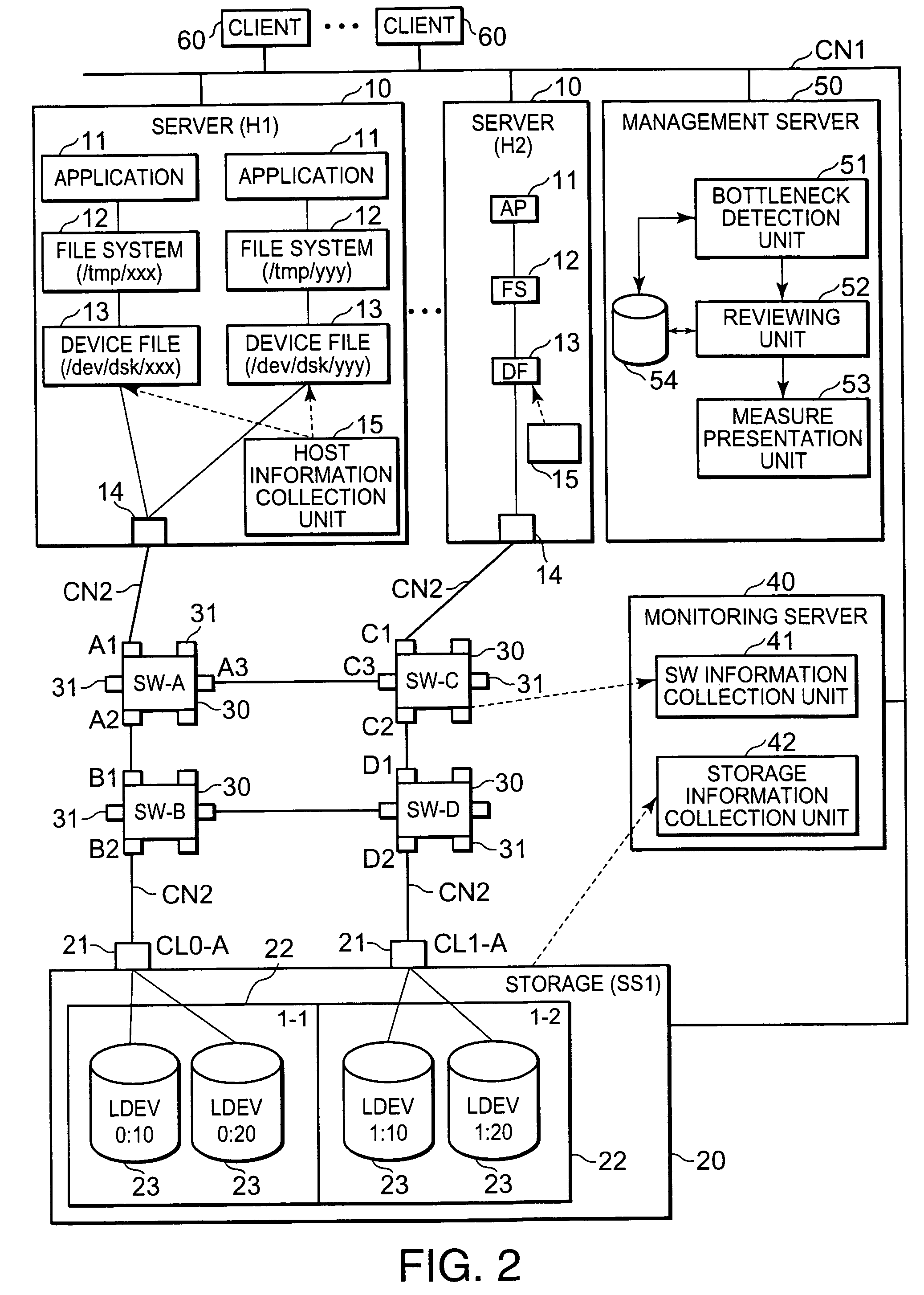
In Unix-like operating systems, a device file or special file is an interface to a device driver that appears in a file system as if it were an ordinary file. There are also special files in MS-DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows. These special files allow an application program to interact with a device by using its device driver via standard input/output system calls. Using standard system calls simplifies many programming tasks, and leads to consistent user-space I/O mechanisms regardless of device features and functions.
Using various flash memory cells to build USB data flash cards with multiple partitions and autorun function
Owner:SUPER TALENT ELECTRONICS
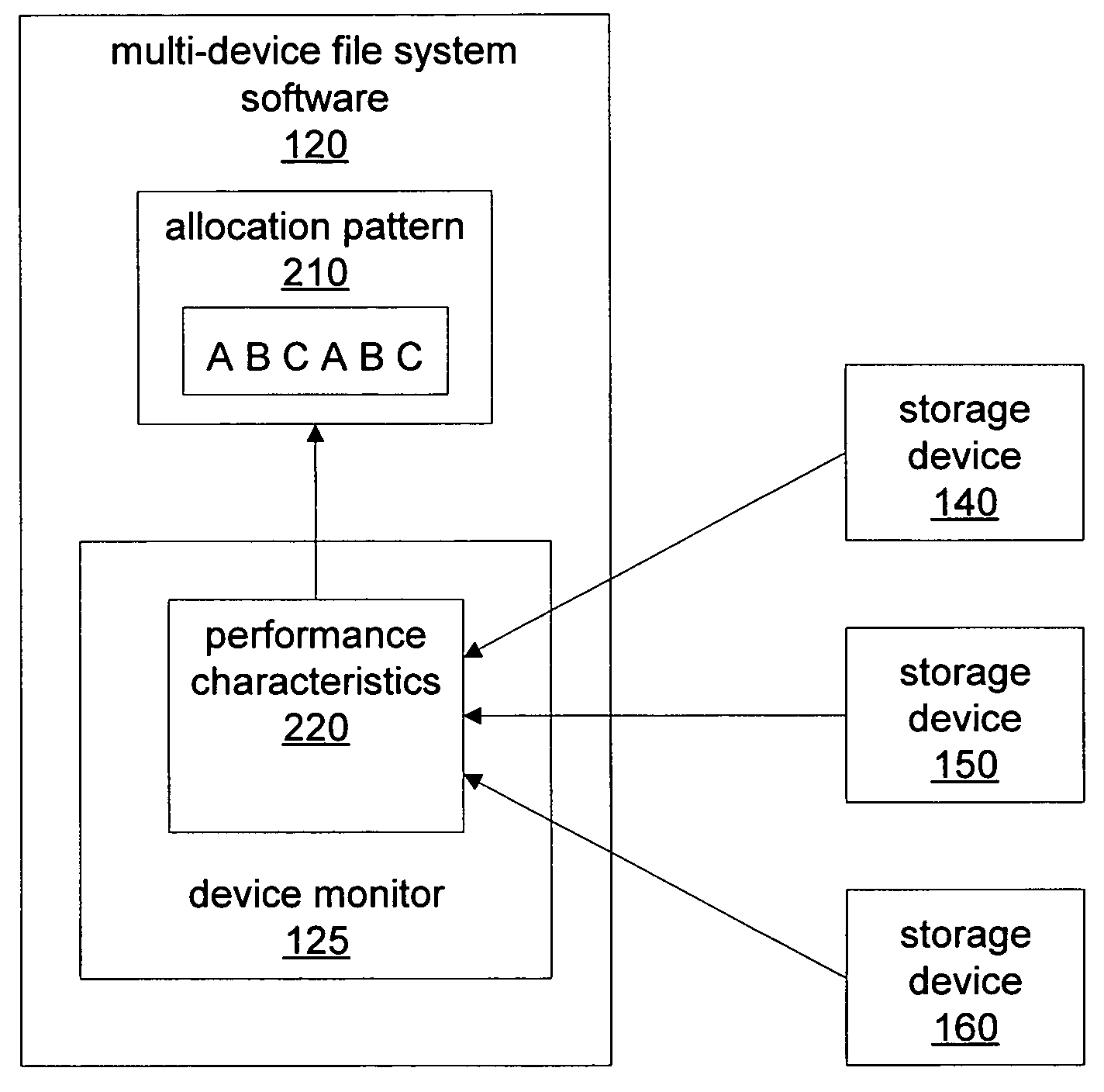
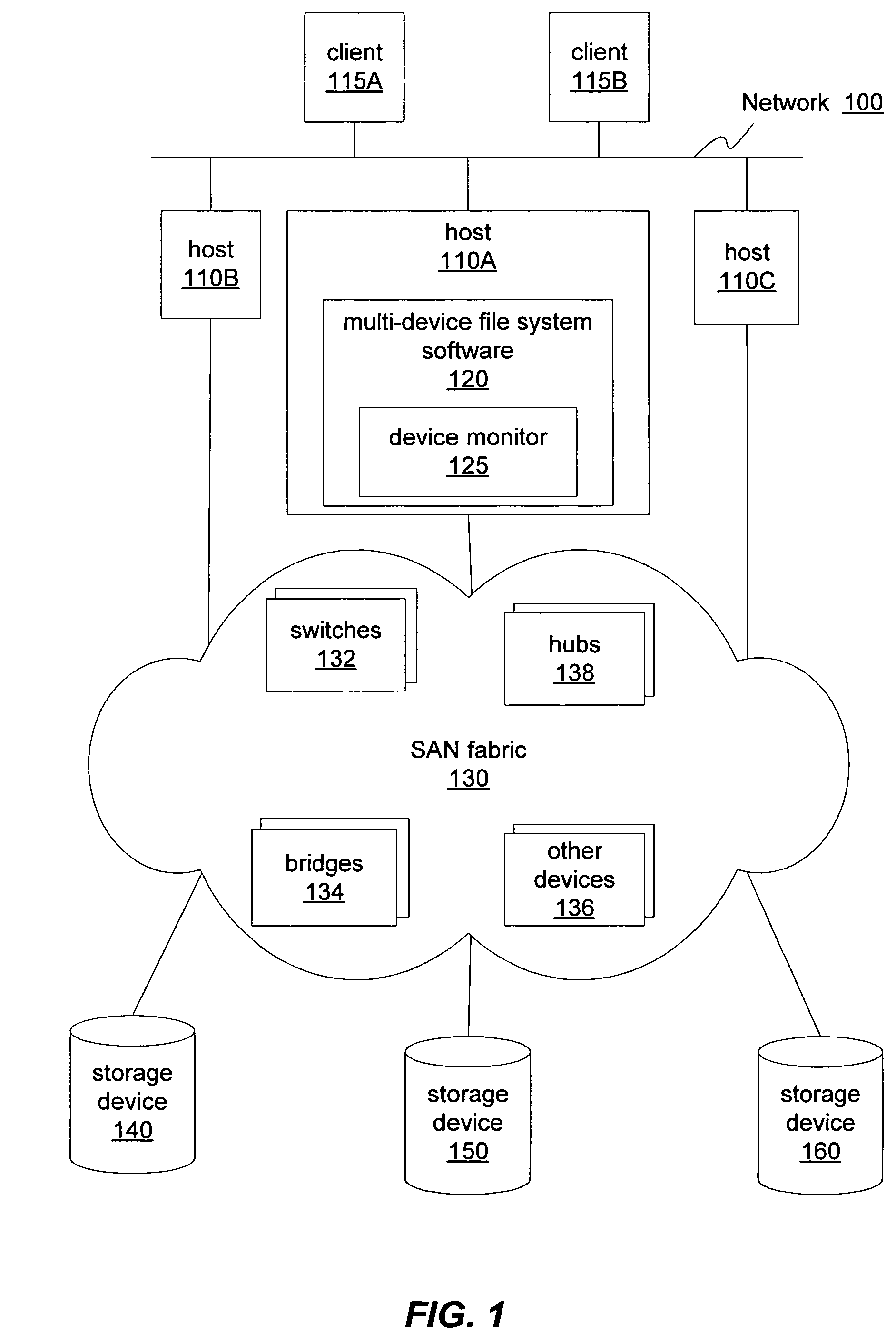
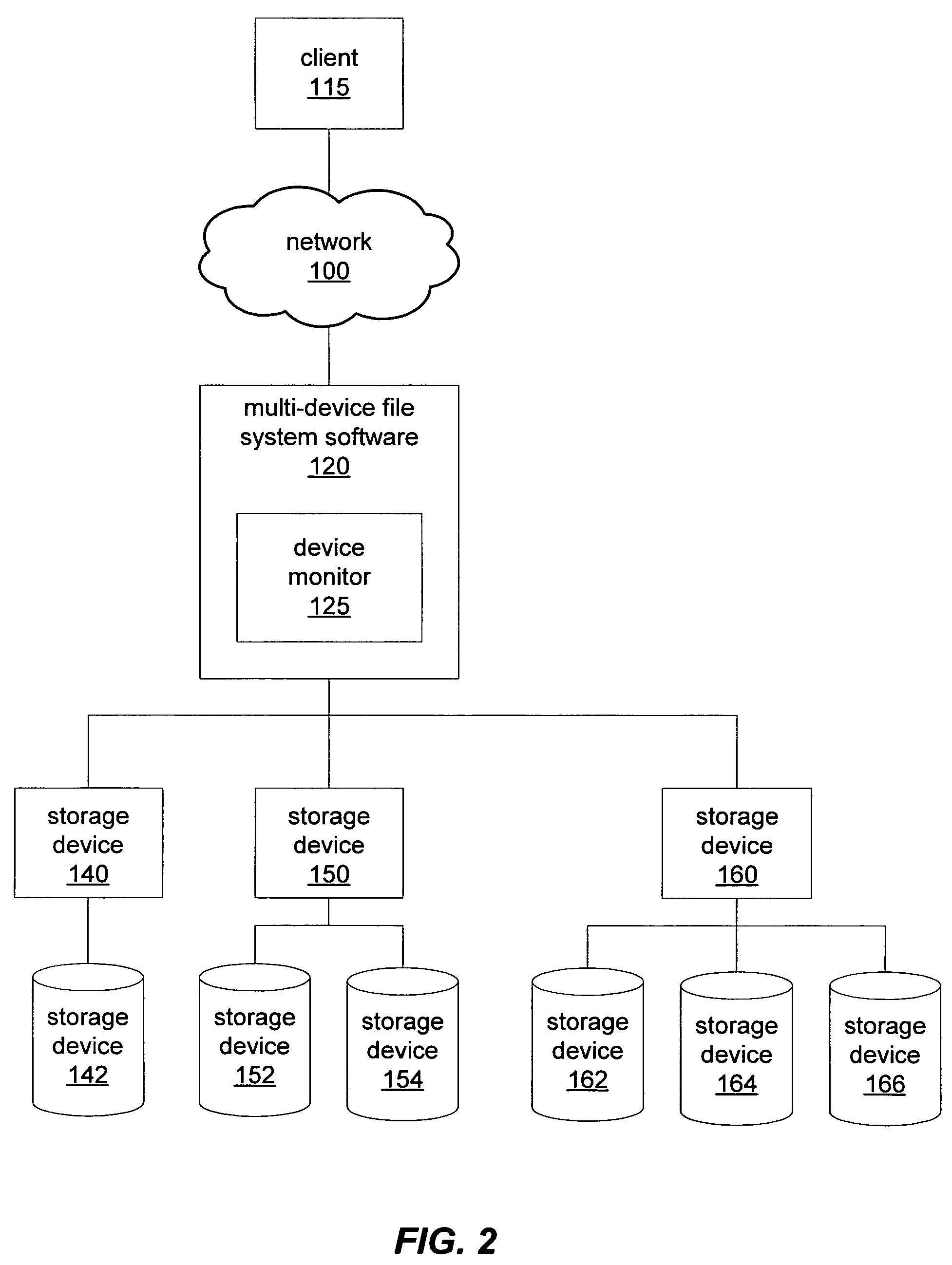
Performance-adjusted data allocation in a multi-device file system
InactiveUS7631023B1Faster access timeReduce throughputData processing applicationsError detection/correctionFile systemPerformance tuning
A file system may employ an enhanced or performance-adjusted allocation scheme when storing data to multiple storage devices. A file system may monitor one or more performance characteristics of storage devices. The file system may, in response to storage requests, select one or more of the storage devices for storing data associated storage requests based on differences among the respective monitored performance characteristics for the storage devices. Additionally, the file system may determine an allocation pattern for storing data to the storage devices and may modify the determined allocation pattern based on a detected change in the monitored performance characteristics of the storage devices. Further, the file system may store data based on both the allocation pattern and on data characteristics associated with a data storage request. The file system may also incorporate input specifying either new performance characteristics or a new allocation pattern.
Owner:SYMANTEC OPERATING CORP
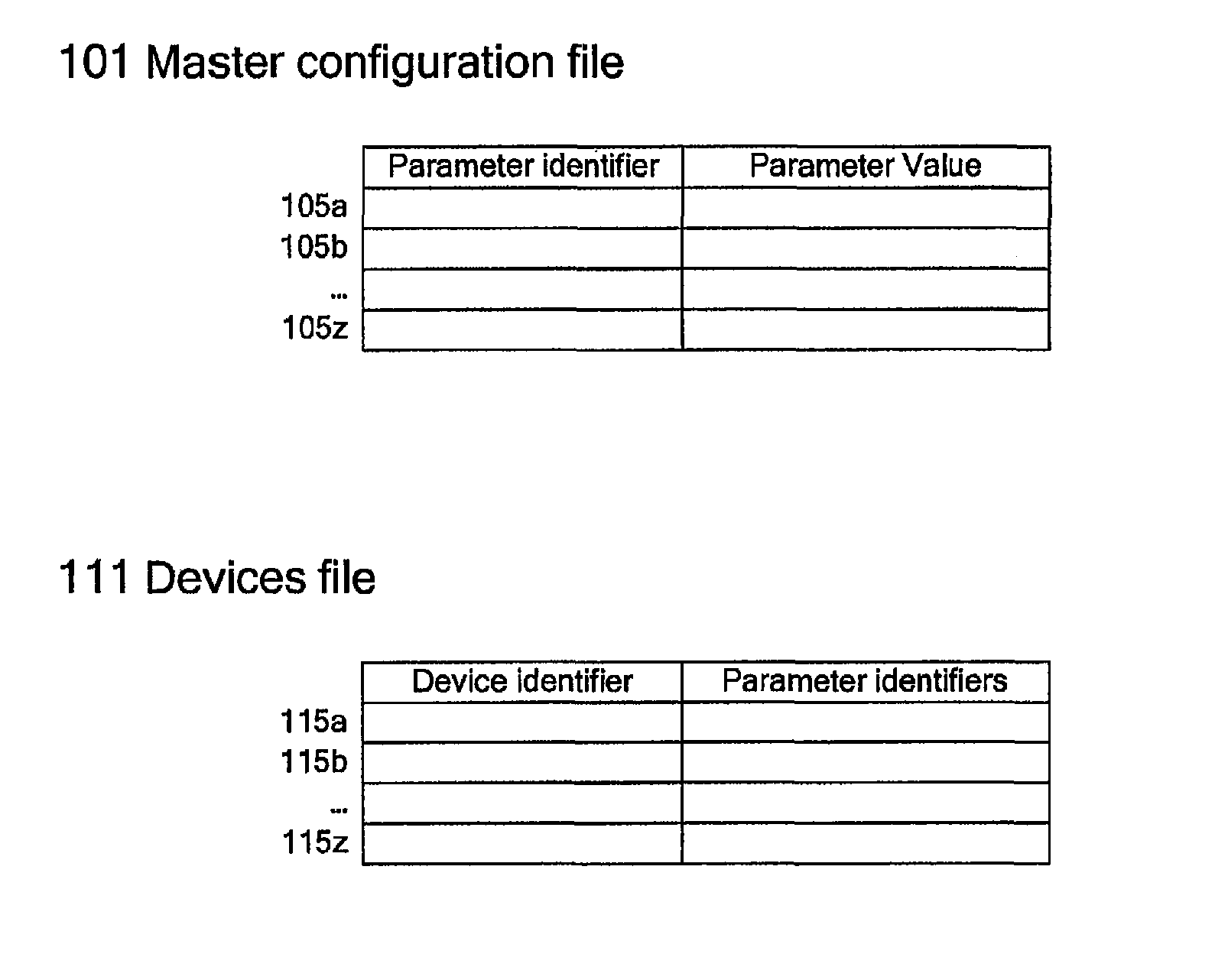
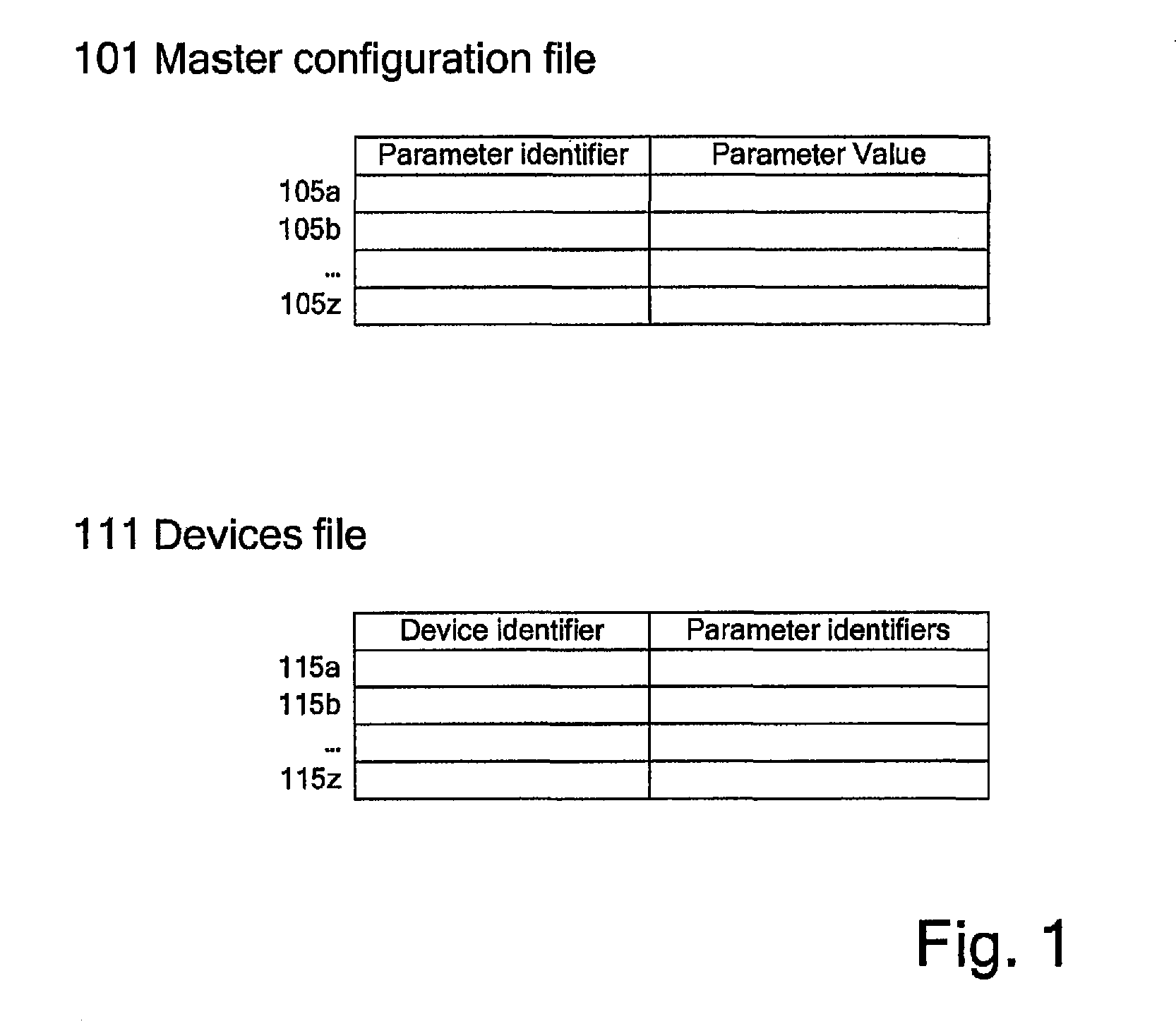
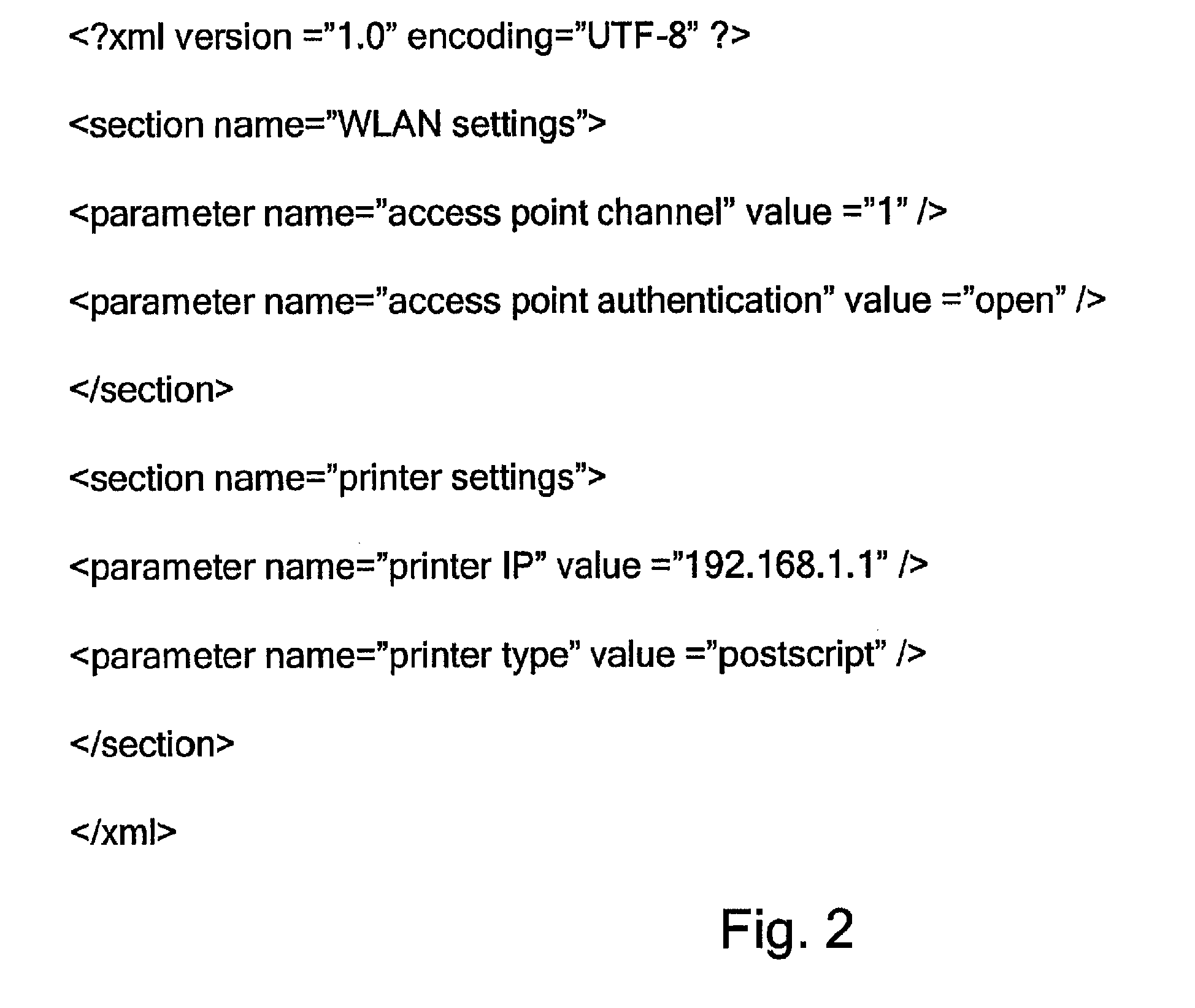
Method of configuring mobile computing device
ActiveUS9274812B2Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsDevice IdentifiersMobile computing
A method of storing configuration data for mobile computing devices can comprise the steps of providing a master configuration file including one or more parameter records and providing a device file including one or more device records. Each parameter record can map a parameter value to a parameter identifier. Each device record can map a parameter identifier to a mobile computing device identifier.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
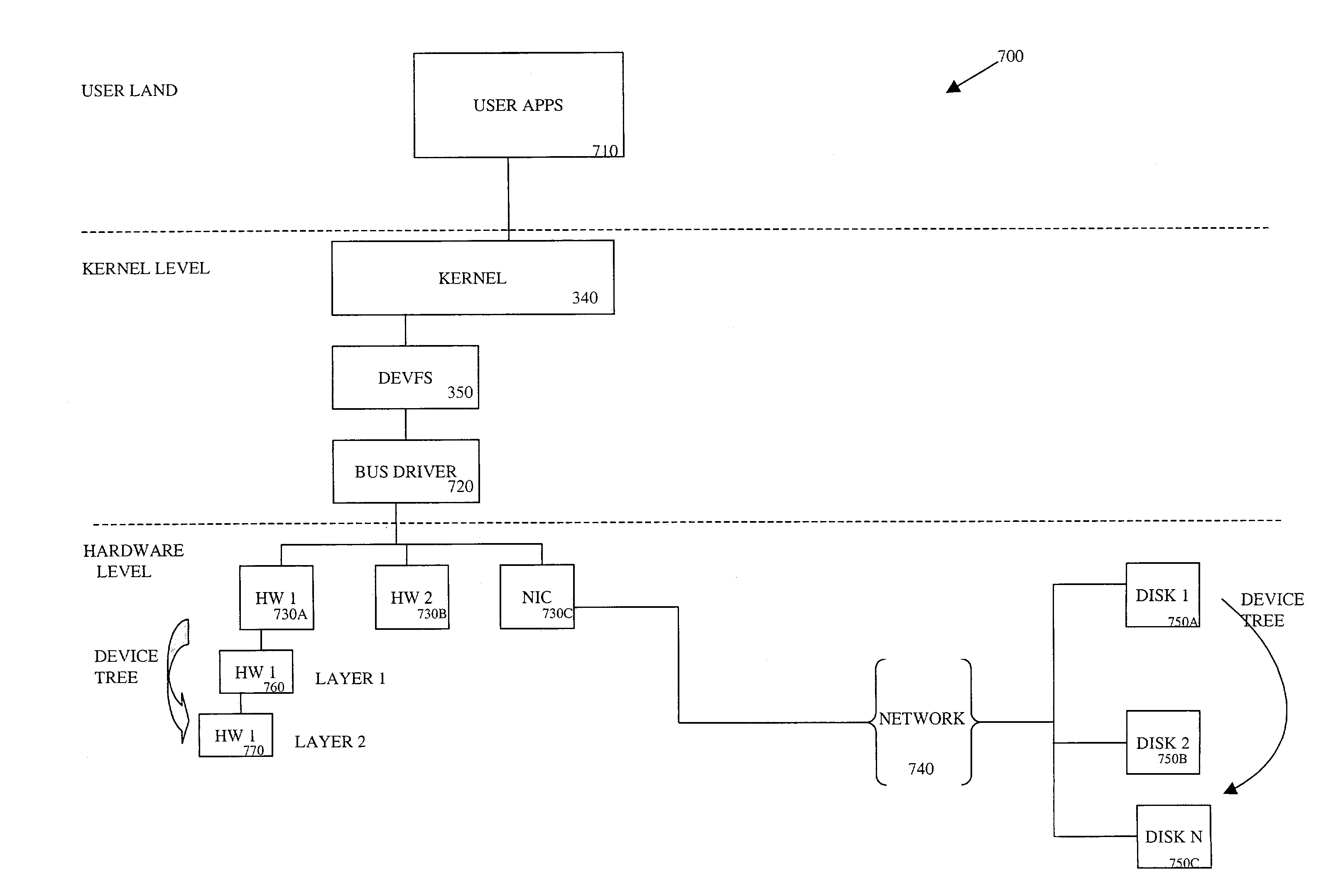
Bus specific device enumeration system and method
ActiveUS7203774B1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsEquipment findingFile system
A kernel device file system publication system for dynamically enumerating and configuring an instance of a device in the kernel device tree upon request by a user level application. The kernel device file system logically arranges system level devices in a hierarchical tree-like topology defining devices as nodes of a device tree to allow for a top-down access. The top-down access allows devices connecting to the computer system to be configured based on the physical path of the device. This process starts at a bus nexus and drives device configuration down the device tree. The bus configuration interfaces permit each nexus in the device tree hierarchy to participate in the device lookup and readdirs operations performed by the device file system. The device file system path operations are performed as an iterative sequence of bus configure operations, whereby each nexus controls the enumeration and configuration of that nexus' children.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
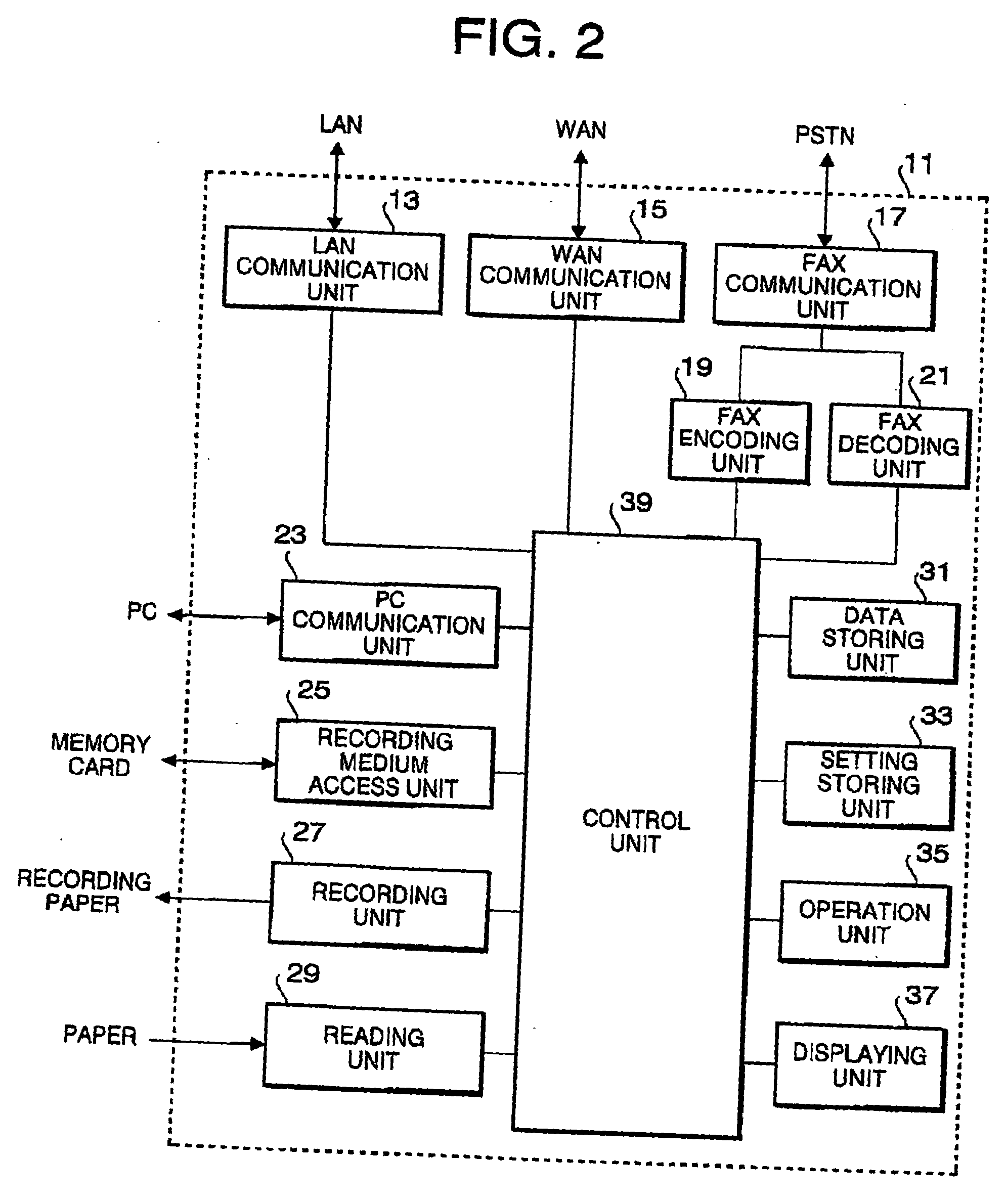
File transmitting device and multi function device
InactiveUS20060070120A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationCommunications systemControl system
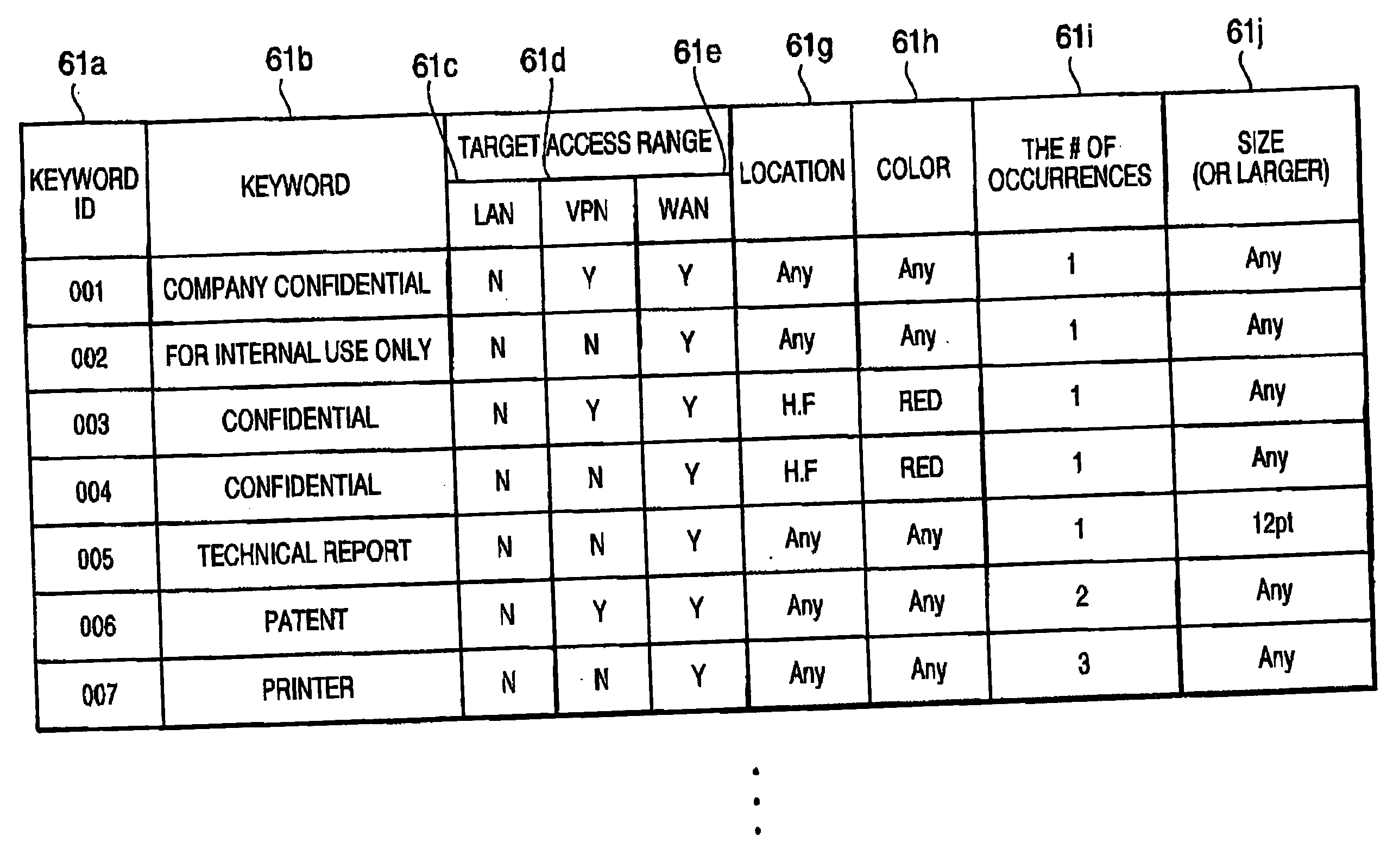
A file transmitting device is configured to transmit a designated file to an external device. The file transmitting device includes a file storage configured to store files to be laid open, and a communication system. The file transmitting device can communicate with the external device through a network. The file transmitting device further includes a file retrieving system that retrieves the designated file from the file storage, a judging system configured to judge whether the retrieved file is a confidential file based on word information included in the retrieved file, and a controlling system configured to apply an appropriate security process to the retrieved file in accordance with a result of judging of the judging system. The retrieved file is transmitted to the external device through the network.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
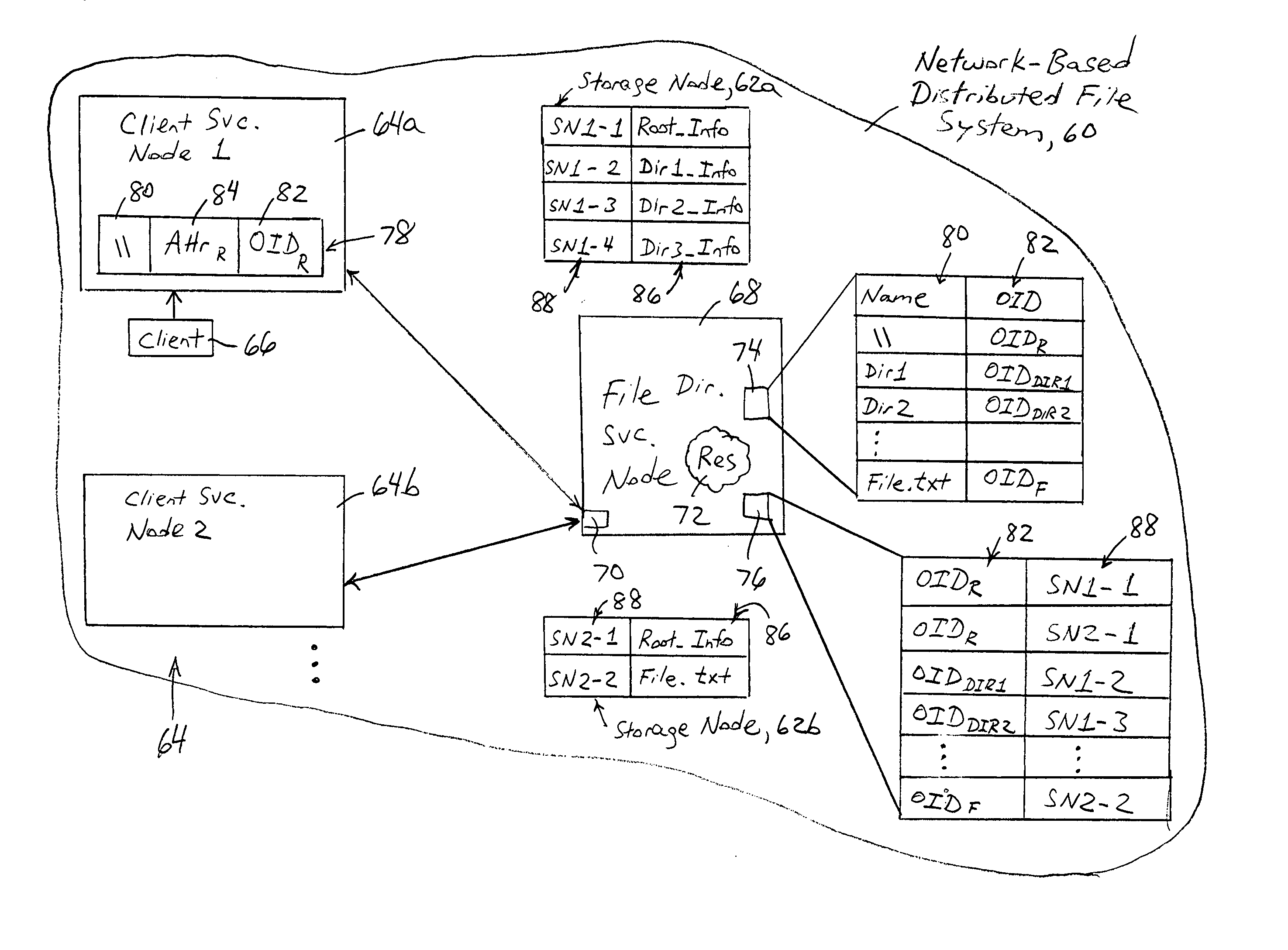
Arrangement for a distributed file system having data objects mapped independent of any data object attribute
ActiveUS20060179037A1Reduce necessityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDistributed File SystemImage resolution
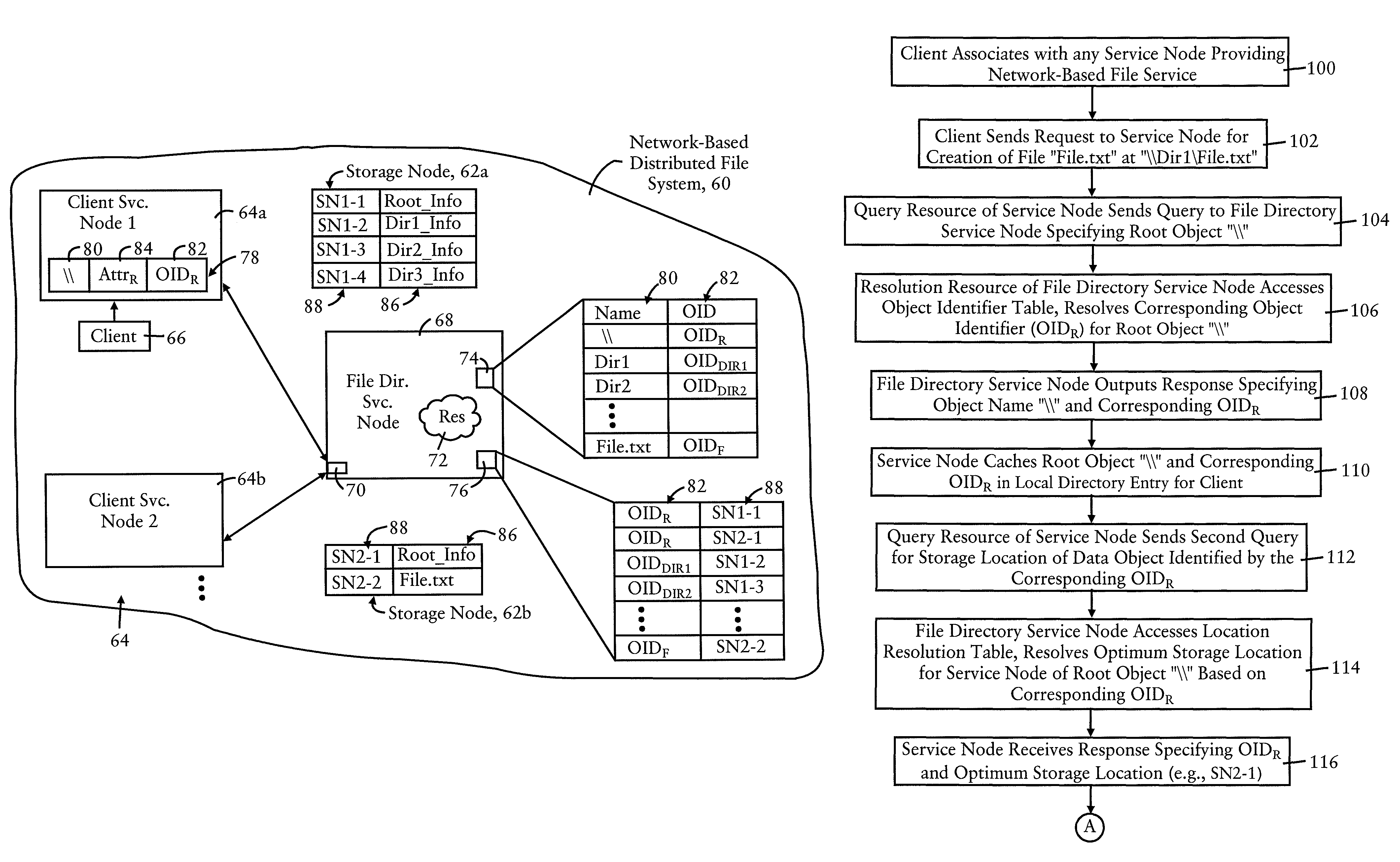
Each data file of a distributed file system is identified by a corresponding globally-unique object identifier that is independent of any attribute of the data file. A node in the distributed file system has a file system that includes a plurality of directory entries, where each directory entry has a file name field, an attributes field, and an object identifier field configured for specifying a globally-unique object identifier. The globally-unique object identifier is universally reachable by any node of the distributed file system and uniquely identifies the data file, enabling the data file to be universally identifiable by any node based on the corresponding object identifier. The data file can be stored independently of a device file system based on providing a resolution between the data file name and its object identifier, followed by a resolution between the object identifier and a selected location for the data file.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
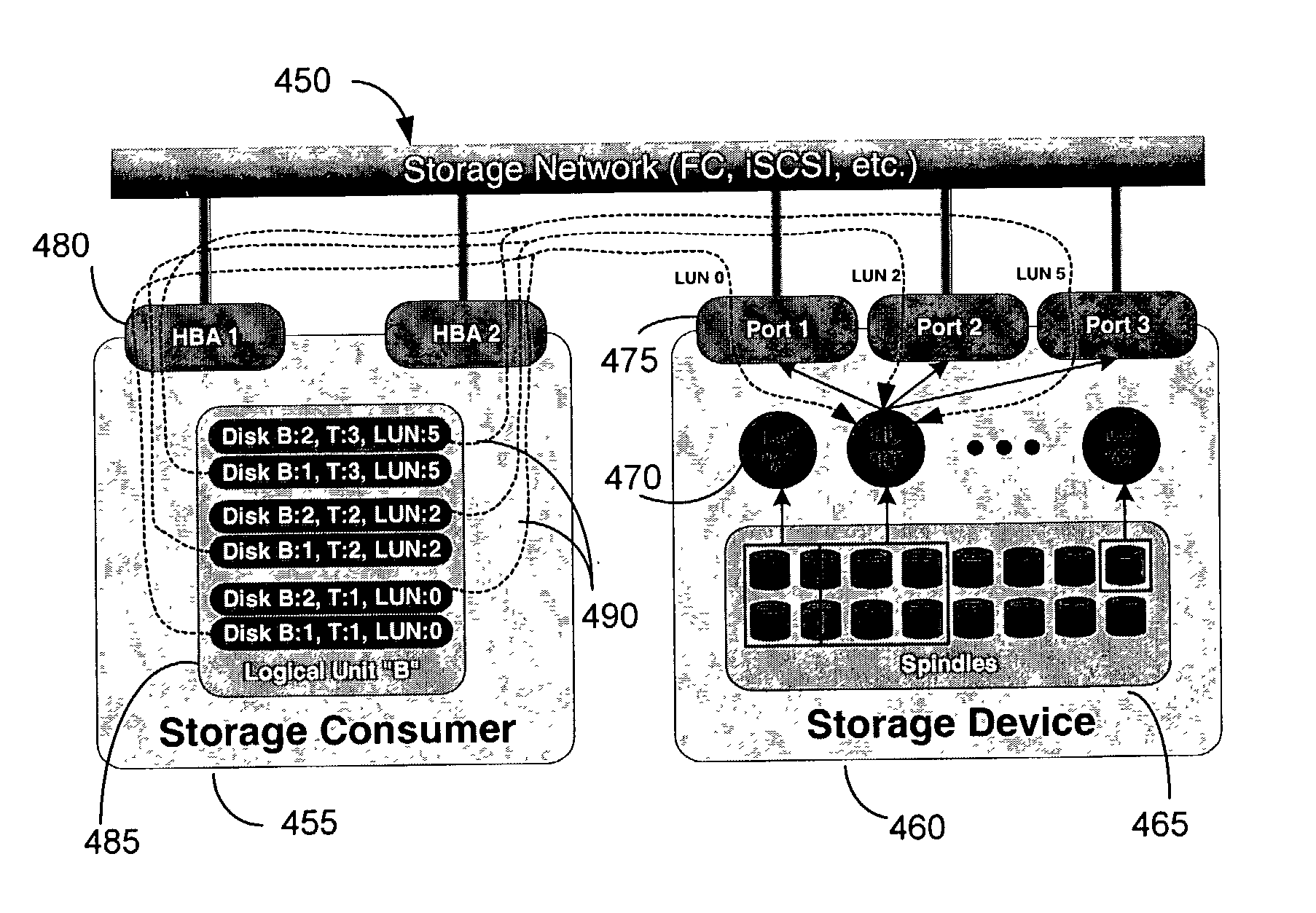
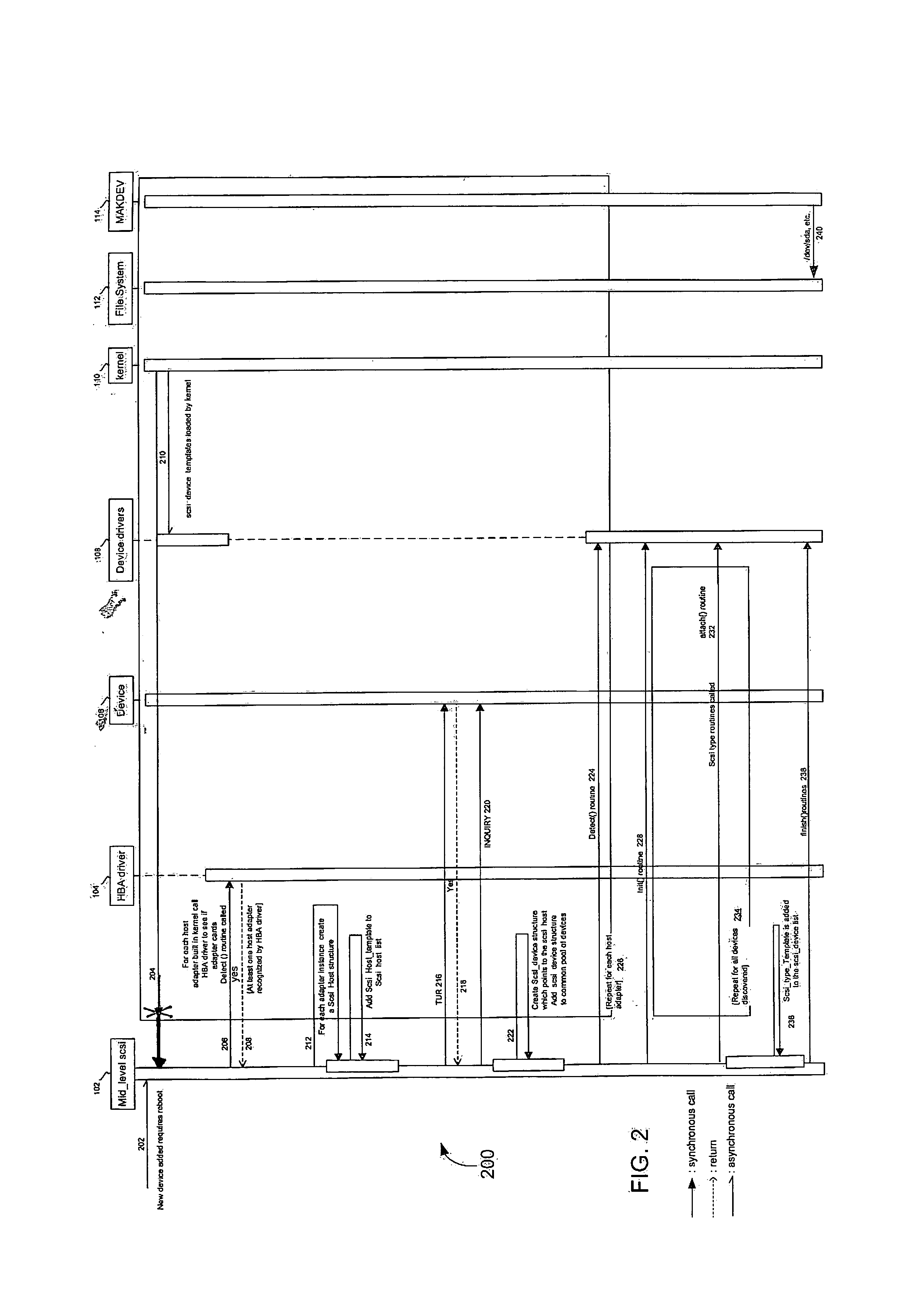
Method and apparatus for identifying multiple paths to a SCSI device using a calculated unique identifier
The method includes querying for one or more logical unit numbers (LUNs) pertaining to a small computer system interface device, each LUN representing a potential path from a host to the SCSI device. Response data indicative of multiple LUNs to the single SCSI device is treated as separate instances of independent SCSI devices, with each separate instance representing a different SCSI separate instances of independent SCSI devices, with each separate instance representing a different SCSI device structure. A unique identifier (UID) is calculated for each SCSI device structure, from which a device file is generated based on the UID and contains UID and path information that differentiates between multiple paths from the host to the SCSI device.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
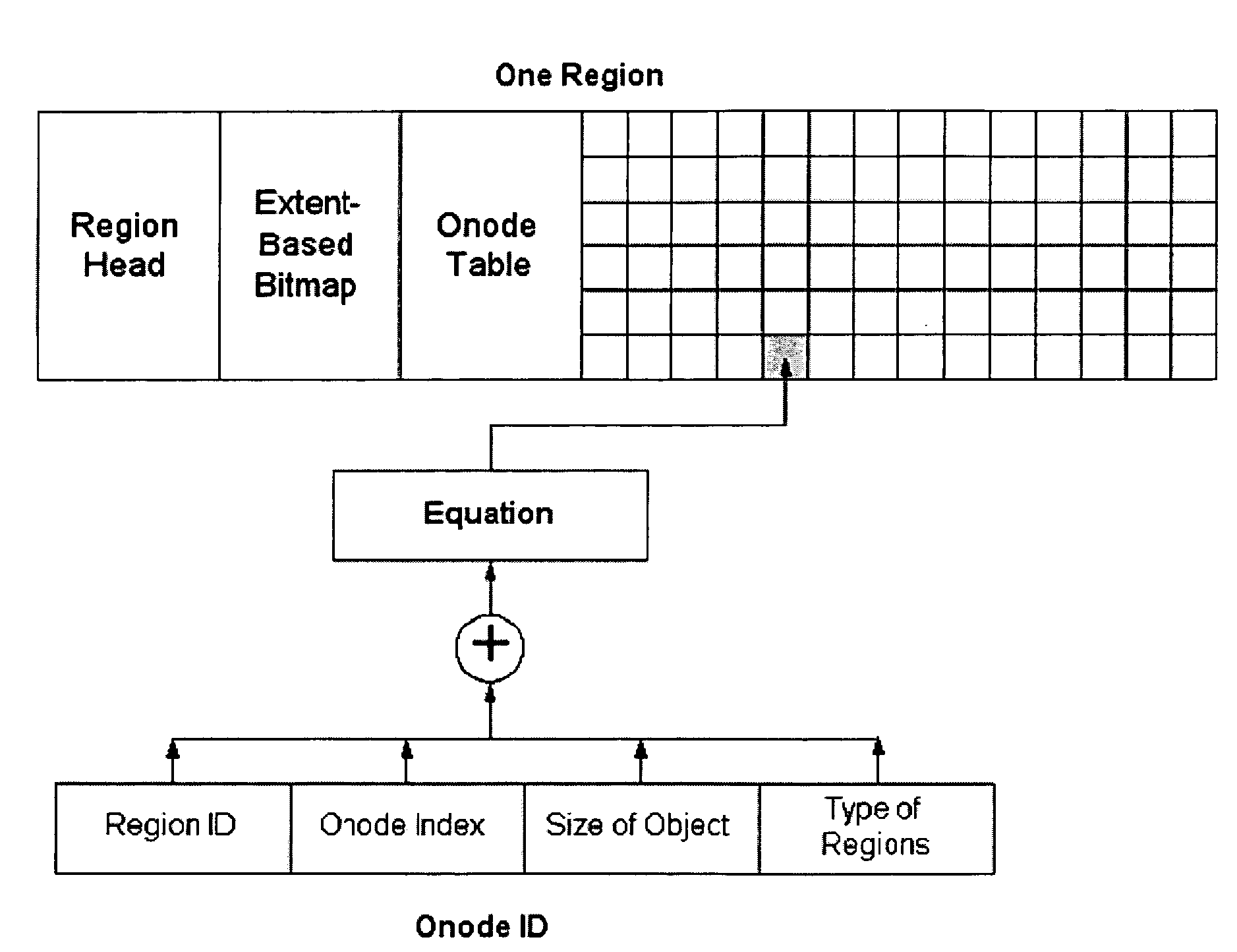
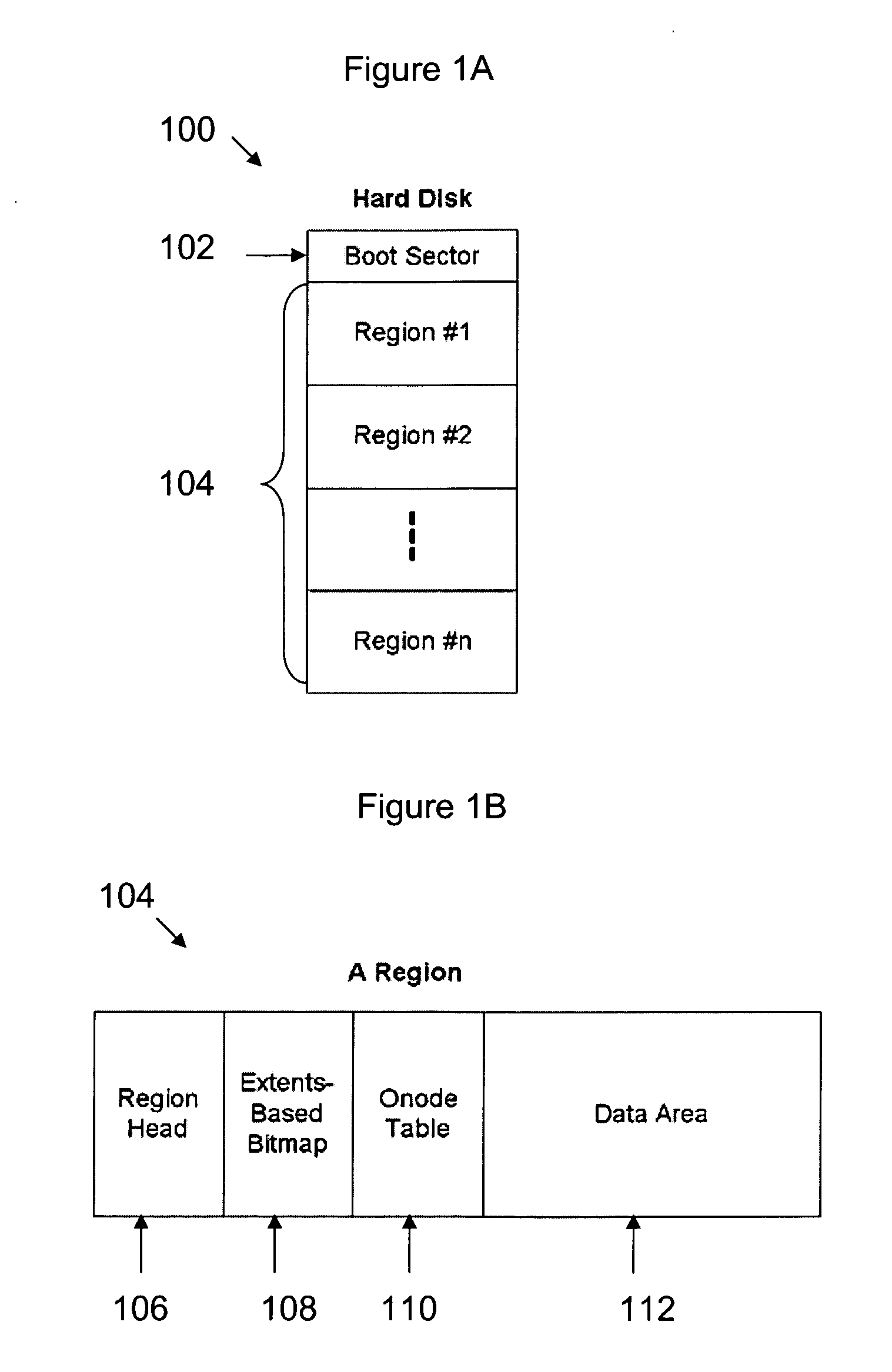
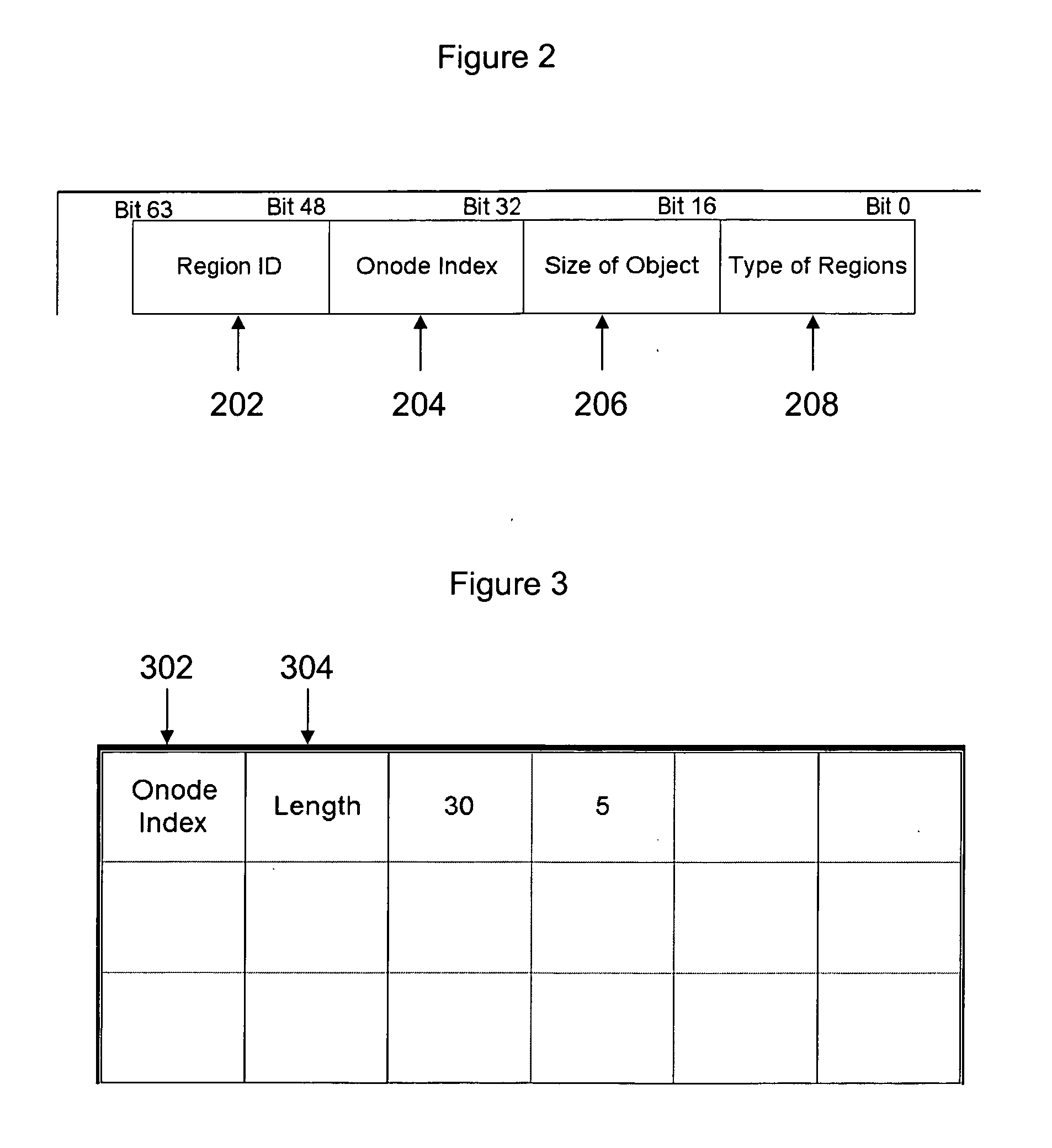
File system for a storage device, methods of allocating storage, searching data and optimising performance of a storage device file system
A file system for a storage device including a storage region, capable of storing one or more blocks of data; and a first data structure representing free space in the storage region, the first data structure comprising a location and a length of a block of free space in the storage region is disclosed. Methods of allocating storage, searching data and optimizing performance of the storage device file system are also disclosed
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Arrangement for a distributed file system having data objects mapped independent of any data object attribute
ActiveUS8229985B2Reduce necessityData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDistributed File SystemFile system
Each data file of a distributed file system is identified by a corresponding globally-unique object identifier that is independent of any attribute of the data file. A node in the distributed file system has a file system that includes a plurality of directory entries, where each directory entry has a file name field, an attributes field, and an object identifier field configured for specifying a globally-unique object identifier. The globally-unique object identifier is universally reachable by any node of the distributed file system and uniquely identifies the data file, enabling the data file to be universally identifiable by any node based on the corresponding object identifier. The data file can be stored independently of a device file system based on providing a resolution between the data file name and its object identifier, followed by a resolution between the object identifier and a selected location for the data file.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
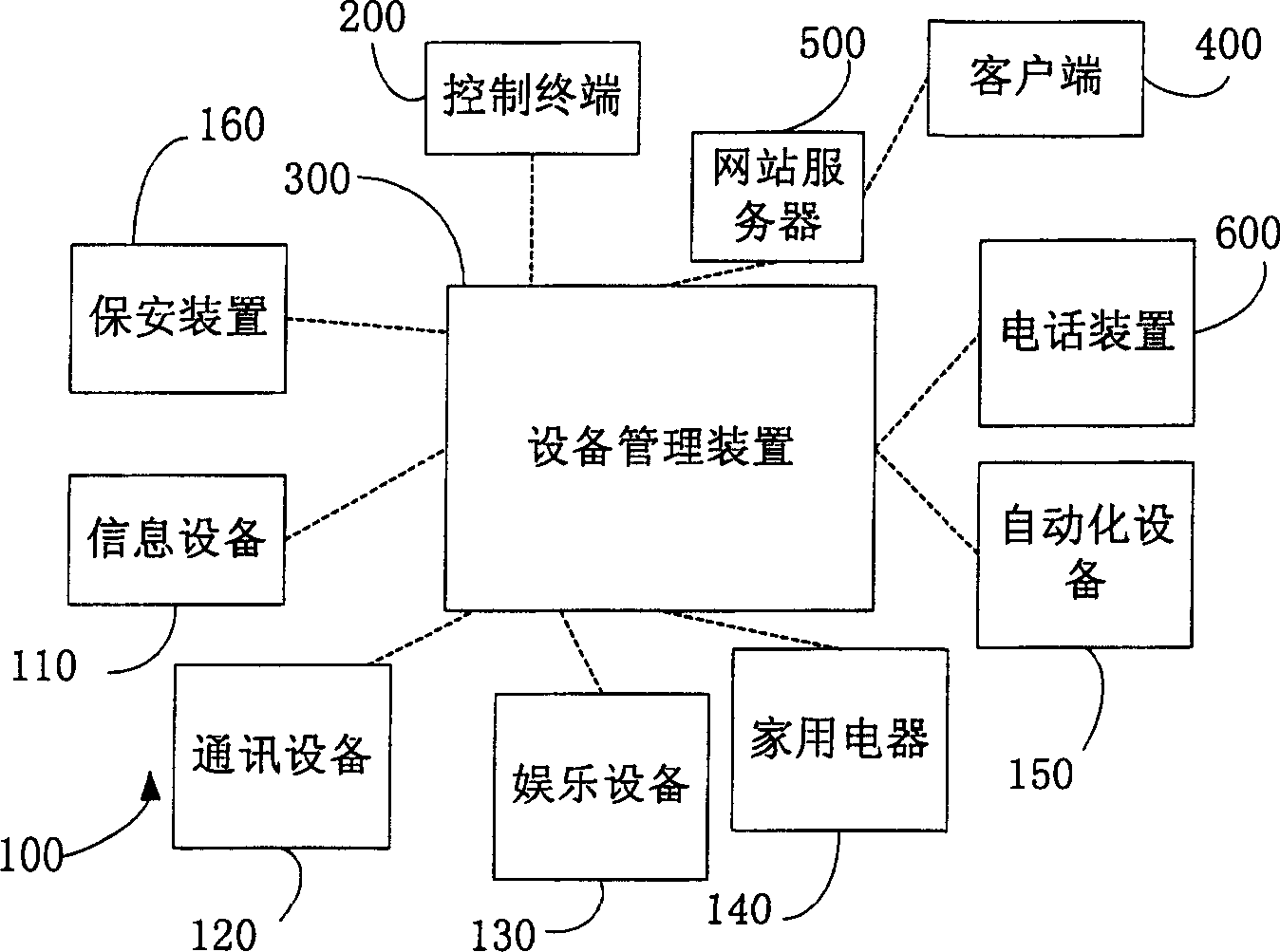
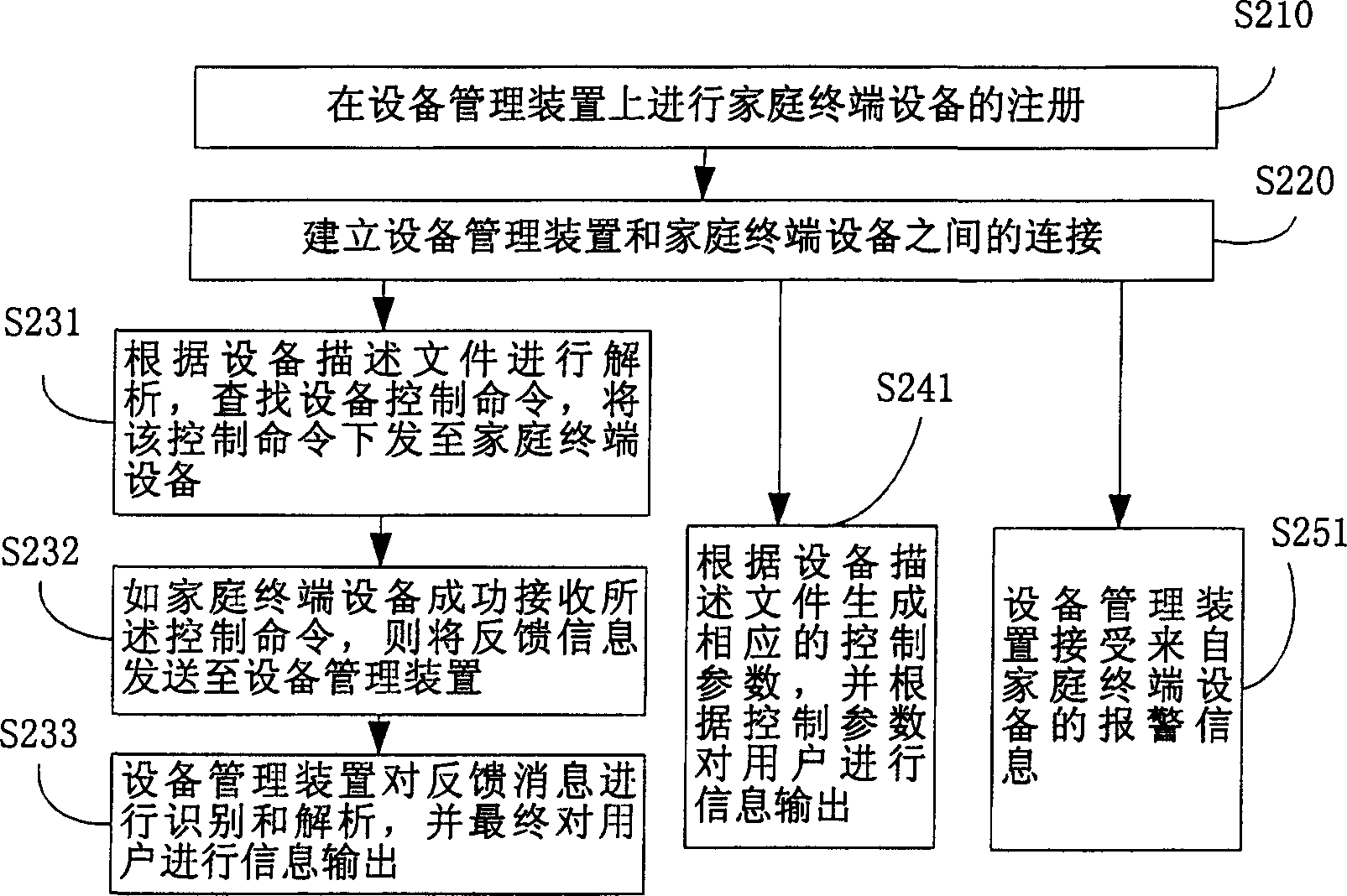
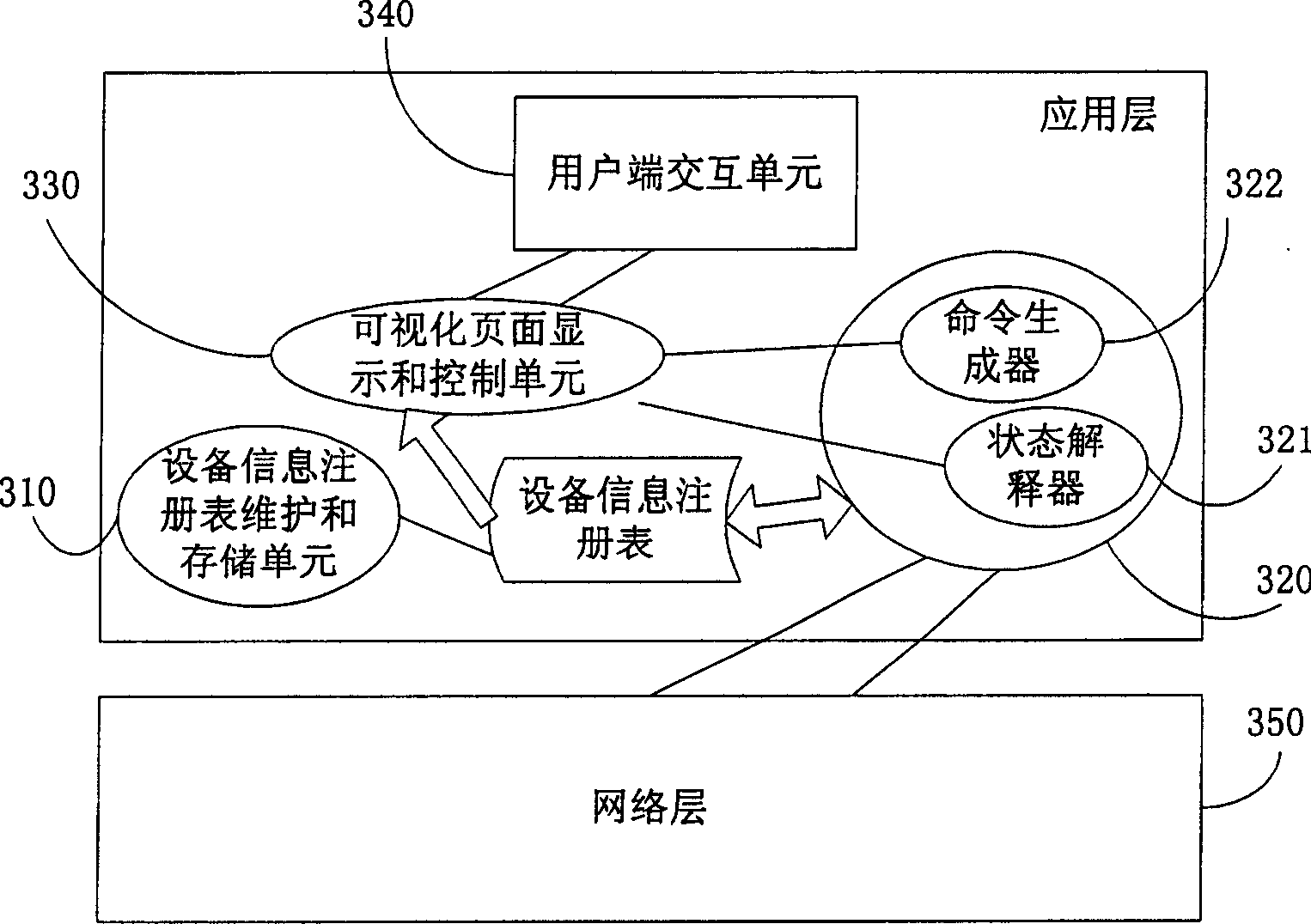
Household network device controlling method and equipment management apparatus
ActiveCN1845505AReduce resource overheadLow costData switching by path configurationUser inputTerminal equipment
The disclosed control method for household network device comprises: the manage device stores data and description file contained index of the terminal device data; it registers the terminal device on manage device and generates device list file according to terminal ID with corresponding relation to description file; the manage device receives directly user control or state query request, resolves the description file, and generates command to the terminal. Besides, it also discloses the corresponding device management device.
Owner:HAIER GRP CORP +1
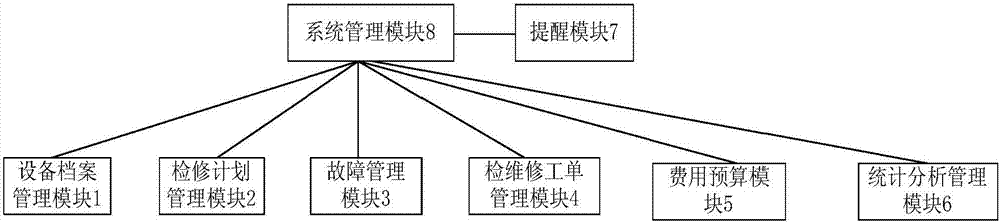
Device management system
InactiveCN107203838AEasy to masterImprove management efficiencyOffice automationResourcesMaintenance planningSystems management
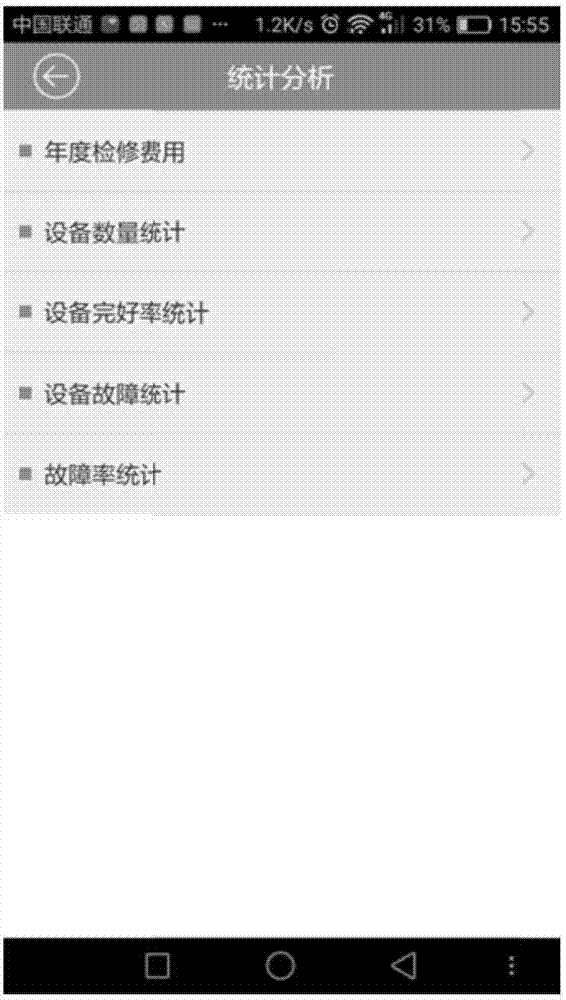
The present invention provides a device management system. The system comprises a device file management module, a maintenance planning management module, a fault management module, an inspection maintenance work order management module, an expense budget module, a statistic analysis management module, a prompting module and a system management module. The device file management module is configured to store and manage the basic static information, the whole life cycle document data, the device faults, the maintenance history and the device changing information of a device and provide functions of addition, deletion, modification, query and statistics analysis; and the maintenance planning management module is configured to perform establishment, examination and approval, issuing and execution, statistics and analysis query of a preset plan project; and the fault management module is configured to report fault records and start a fault confirmation process after device defects or faults are detected, eliminate faults according to the corresponding preset fault processing mode after confirmation of the faults and record the faults in the fault knowledge base. The efficiency and the precision of management are improved, and a lot of manpower is saved.
Owner:北京海顿中科技术有限公司
Method, system, and computer readable medium for remote assistance, support, and troubleshooting
InactiveUS20110213821A1Reduce eliminateMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionWeb serviceXML
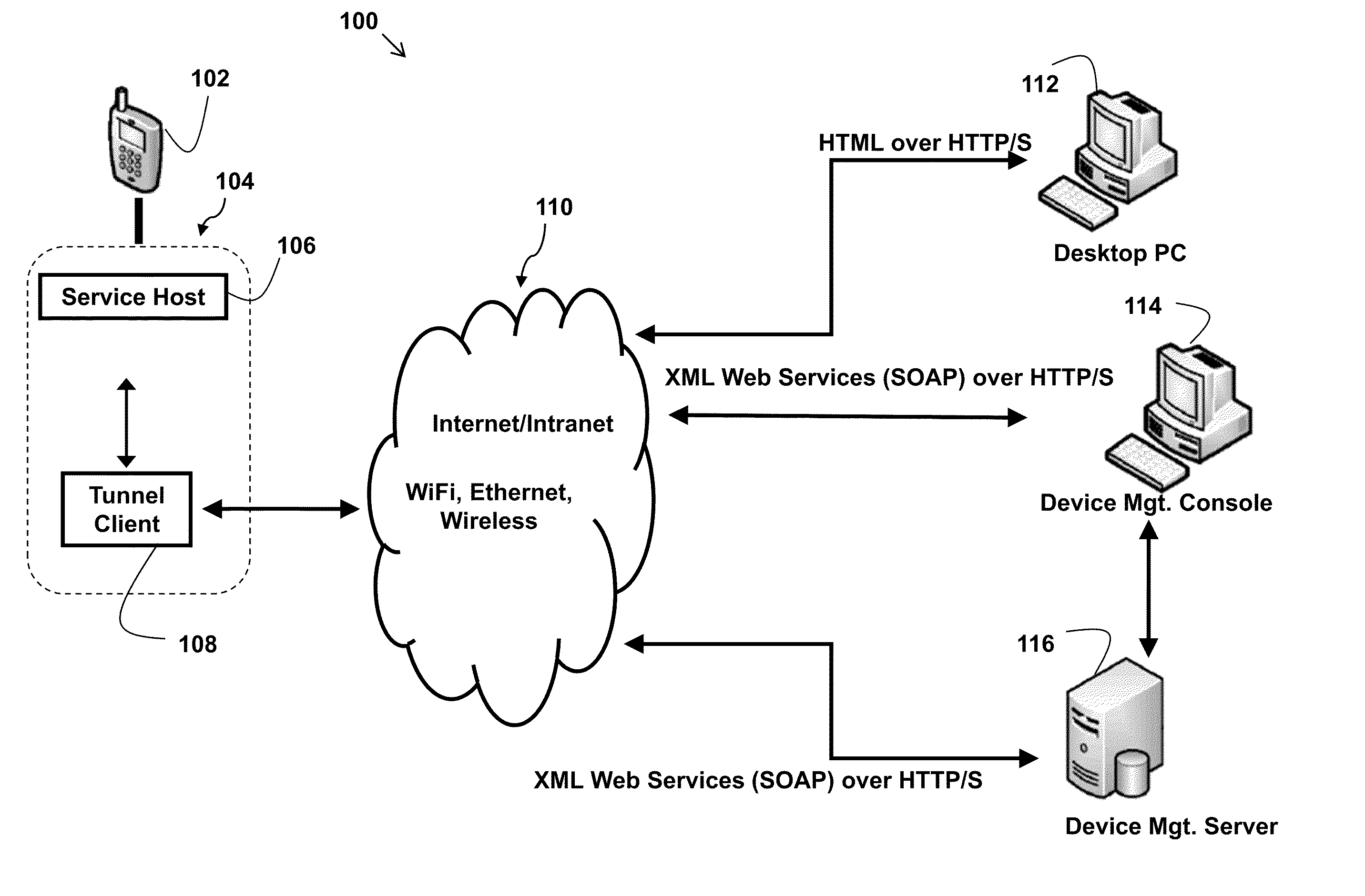
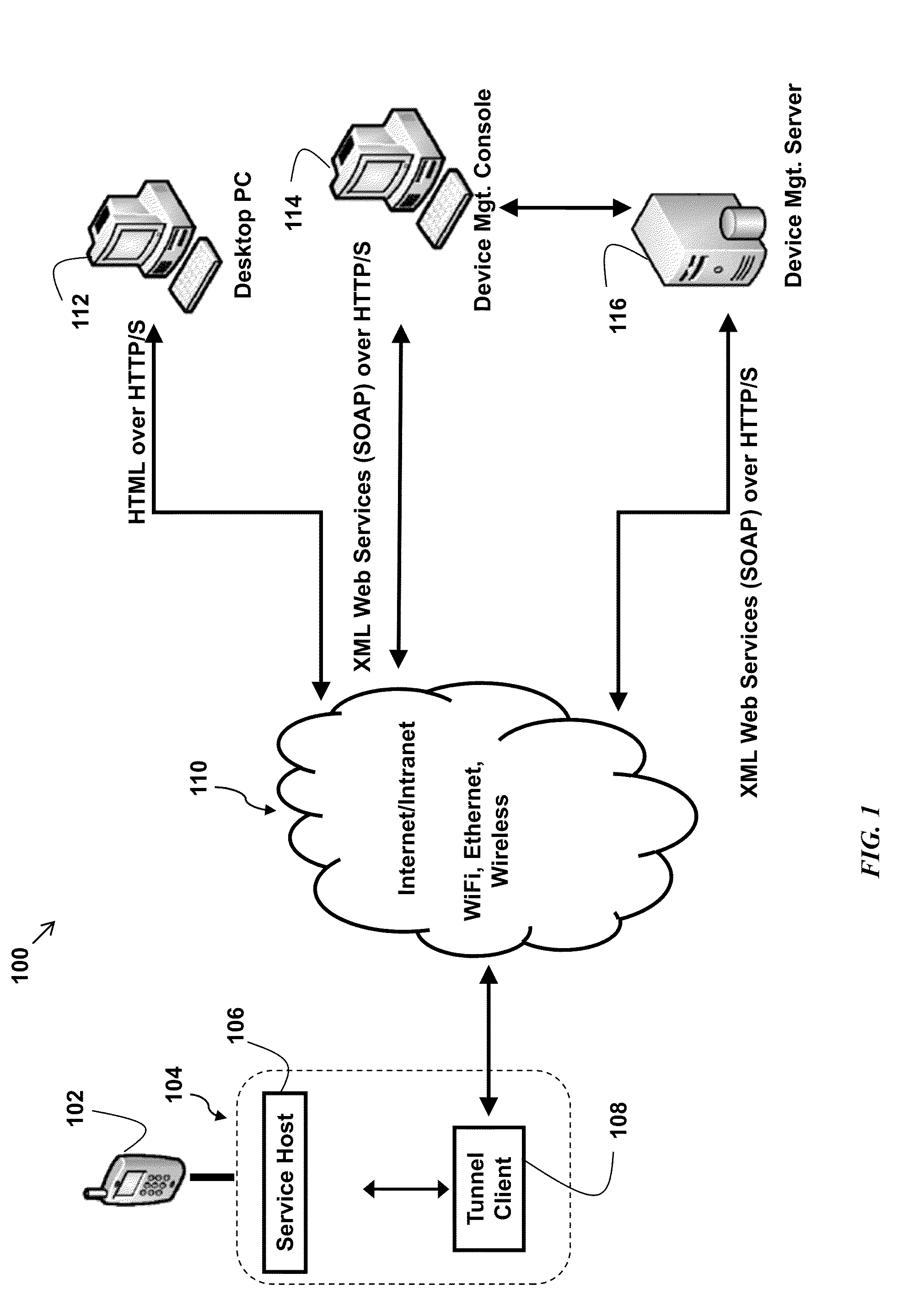
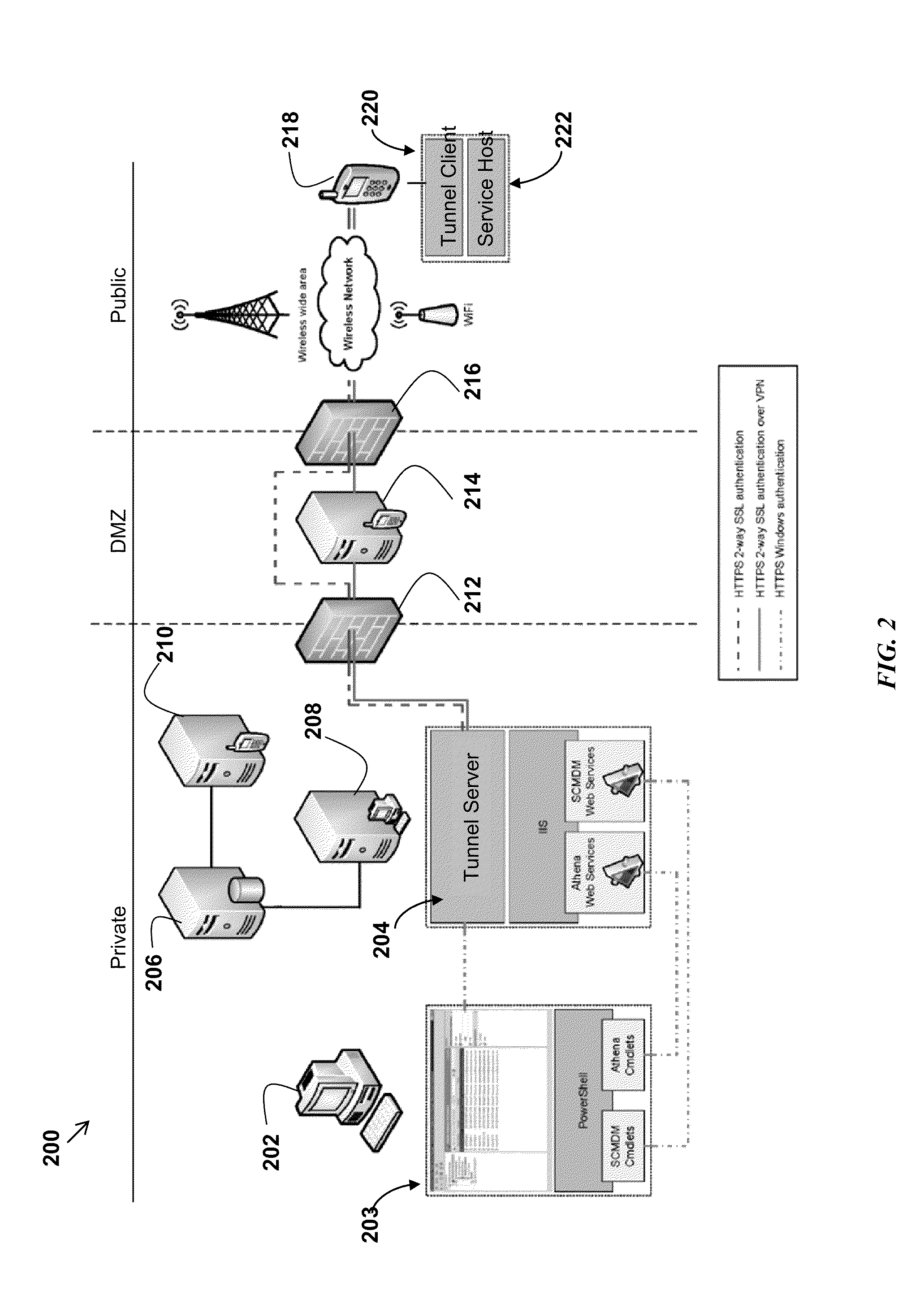
The present disclosure enables remote device management. A programmatic interface is associated with each application plug-in. A web server included with the on-device agent provides access to the programmatic interfaces according to open standards such as HTML or XML. The present disclosure enables access to remote devices through existing infrastructure without the need for proprietary systems. An IT administrator or other administrator may remotely access and update software and hardware, track device data plan usage statistics, provide live support, and track current and historical device locations. Through the support features of the present disclosure an IT administrator or other support operator may remotely operate a device as if they were actually holding the device. This feature provides direct access to device files and software while also showing the IT administrator screen views of the remote device. Thus, the IT administrator actually sees what the remote user also sees.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Methods and apparatus for high-speed access to and sharing of storage devices on a networked digital data processing system
InactiveUS20050251516A1Prevents the nodes from “hoggingData processing applicationsInput/output to record carriersDigital dataFile system
The invention provides a digital data processing system with improved access to information stored on a peripheral device. The system has a plurality of nodes, a peripheral device, a file system and a bypass mechanism. A first node (e.g., a client node) is connected to a second node (e.g., a server node) over a first communications pathway (e.g., a network). The second node is itself connected to a peripheral device (e.g., a disk drive) over a second communications pathway. The first node, too, is connected to the peripheral device over a third communications pathway. The file system, executing on the first and second nodes, is capable of responding to access requests generated by the first node for transferring data between that node and the peripheral device, via the second node and via the first and second communications pathways. The file system also maintains administrative information pertaining to storage on the peripheral device of data designated by such requests. That information includes, for example, physical storage location mappings for files and other data stored on the peripheral device. The bypass mechanism, which executes on at least the first node, intercedes in the response to at least selected input / output, or access, requests generated by that node. The bypass transfers data designated by such requests between the first node and the peripheral device over the third communications pathway, in lieu of transferring that data via the second node and the first and second communications pathways. Such transfers by the bypass, however, are made using the administrative information maintained by the file system relating to storage of such data on the peripheral device.
Owner:IBM CORP
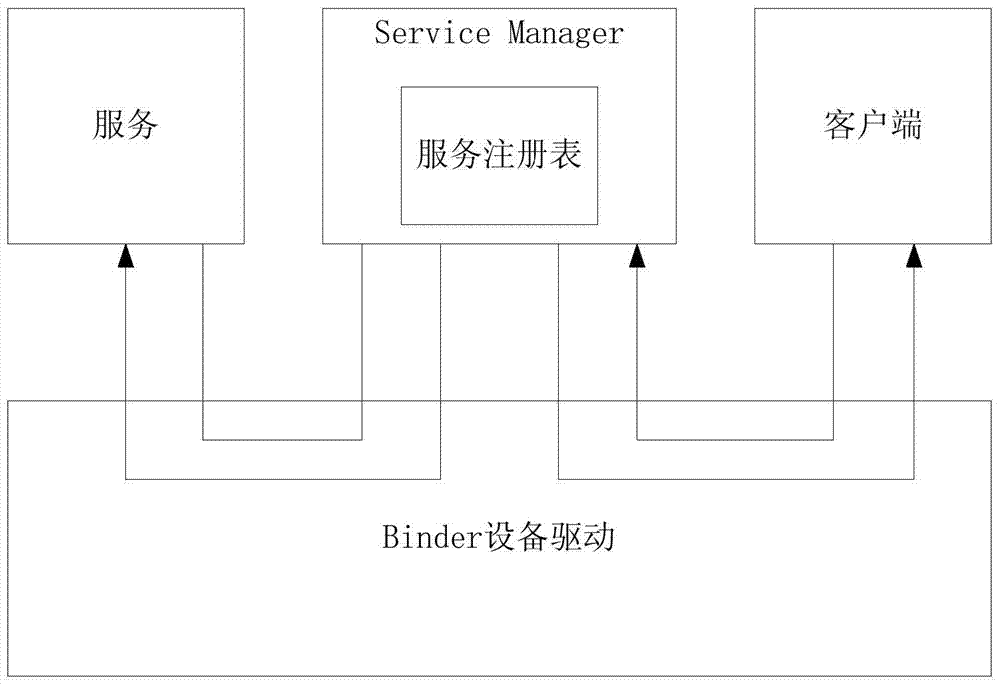
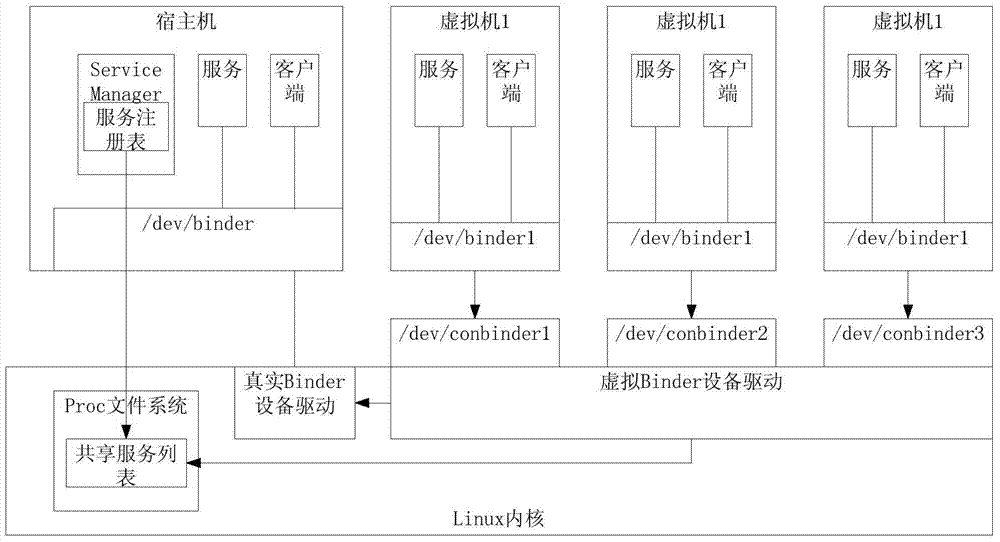
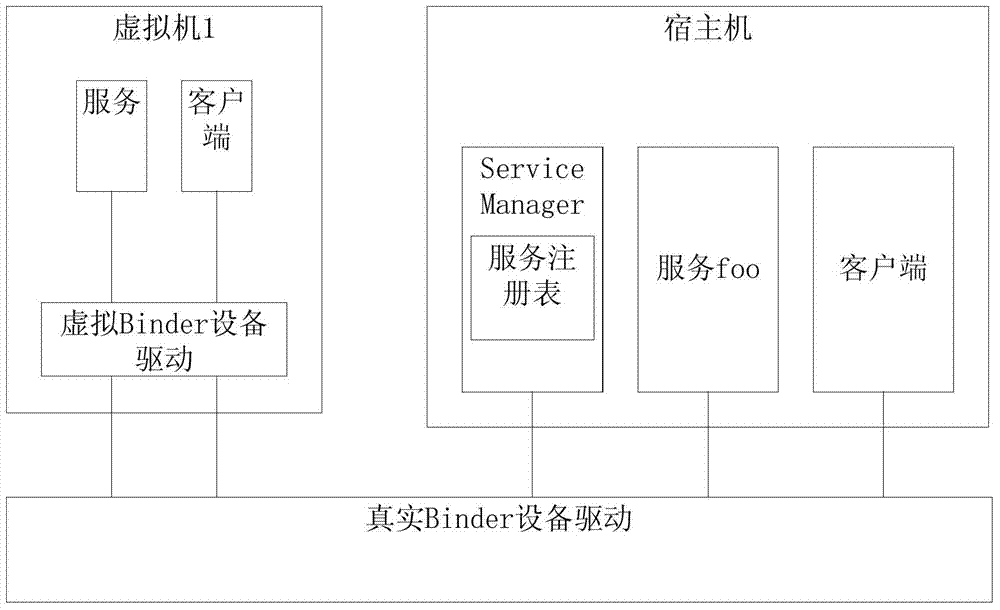
Method for multiplexing Binder IPC mechanism by multiple Android systems in mobile virtualization scene
ActiveCN103593225ASolve the problem of service name conflictIncrease flexibilitySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationVirtualizationFile allocation
The invention discloses a method for multiplexing a Binder IPC mechanism by multiple Android systems in a mobile virtualization scene. The method comprises the steps that a virtual Binder device drive is set up in the Android systems of a host machine, the virtual Binder device drive is used for logging in multiple virtual Binder devices to a Linux inner core, and device files corresponding to the virtual Binder devices are distributed into virtual machines; when the virtual machines send out access requests of the Binder devices, firstly the virtual Binder device drive is called, and then use requests are forwarded to a real Binder device drive through the virtual Binder device drive; in the process of forwarding the operation to the real Binder device drive, the virtual Binder device drive conducts corresponding interception, filter and modification on conflicting service names. On the premise that operation of the multiple Android systems is achieved, the high efficiency of the system performance is ensured.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
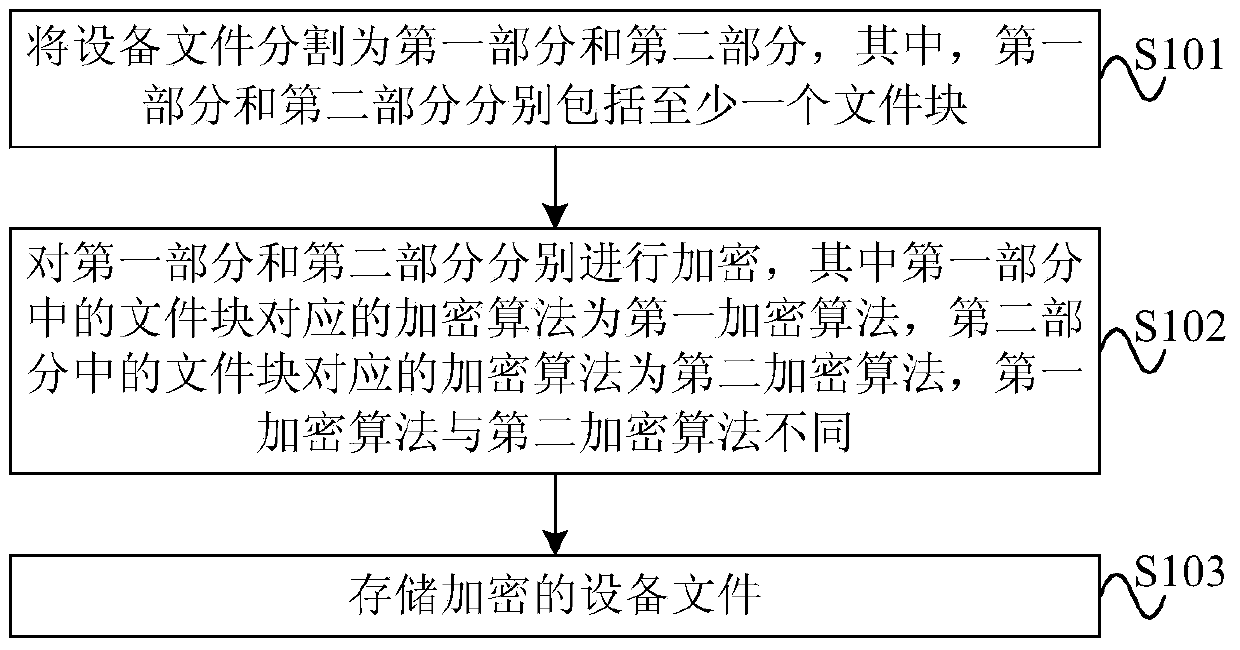
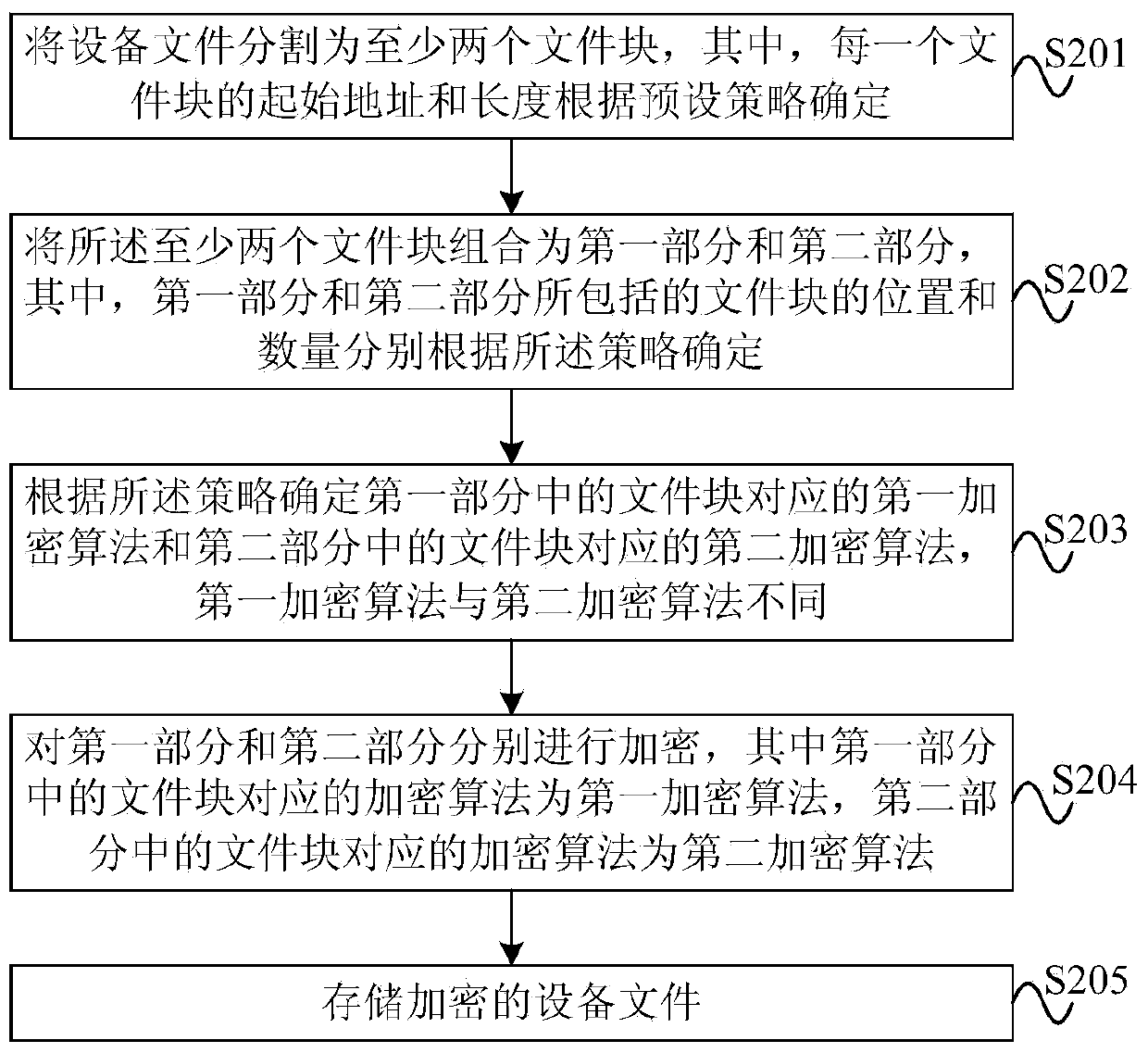
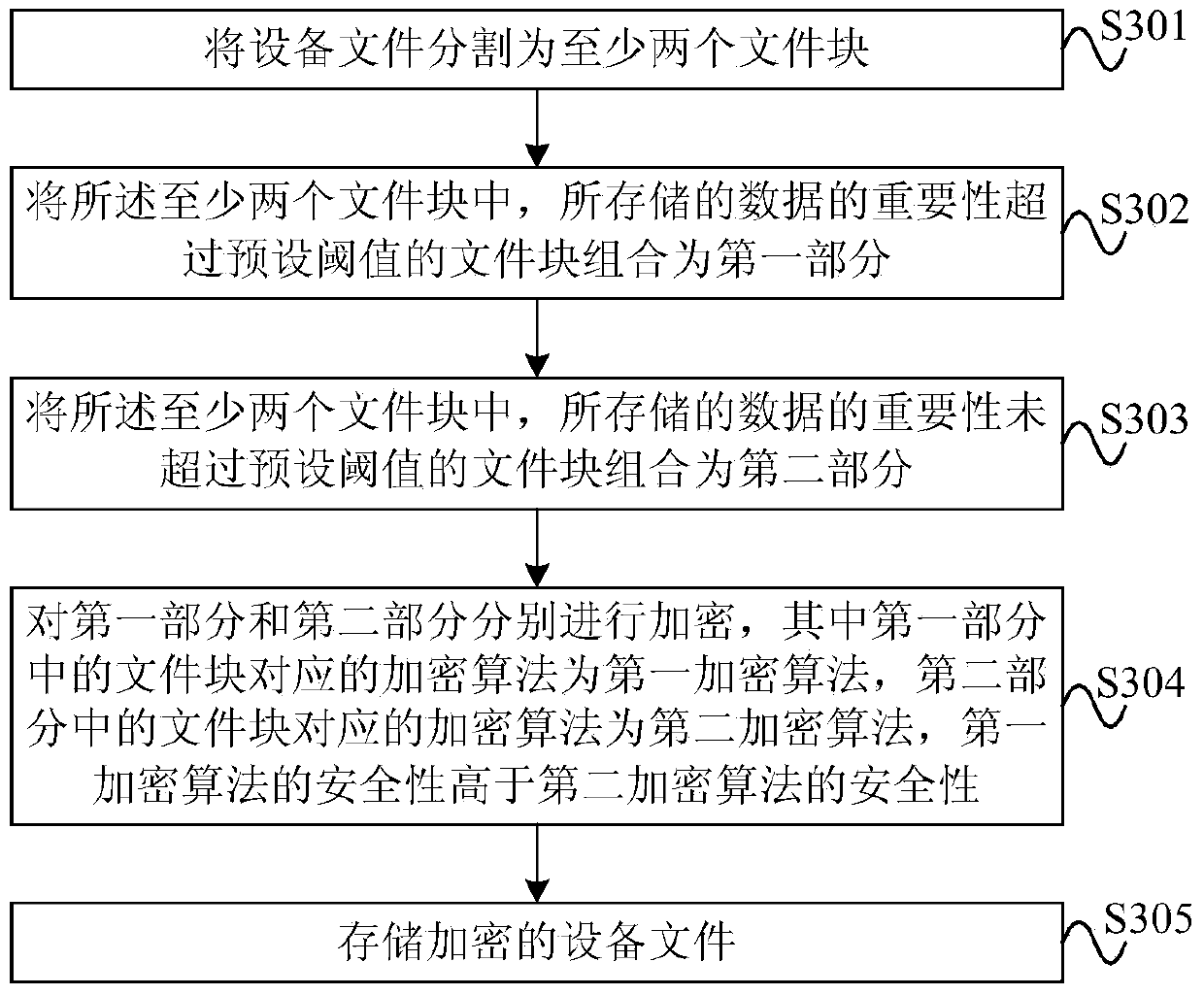
Device file encryption and decryption method and device
ActiveCN104205117AMultiple keys/algorithms usageEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareEncryption
The embodiment of the present invention provides a device file encryption and decryption method and device. The device file encryption and decryption method comprises dividing a device file into a first portion and a second portion, the first portion and the second portion individually comprising at least one file block; encrypting the first portion and the second portion individually, the encryption algorithm corresponding to the file block in the first portion being a first encryption algorithm while the encryption algorithm corresponding to the file block in the second portion being a second encryption algorithm, and the first encryption algorithm being different from the second encryption algorithm; and storing the encrypted device file. With adoption of the device file encryption and decryption method and device provided by the utility model, the device file can be encrypted, and security and processing speed are also considered.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
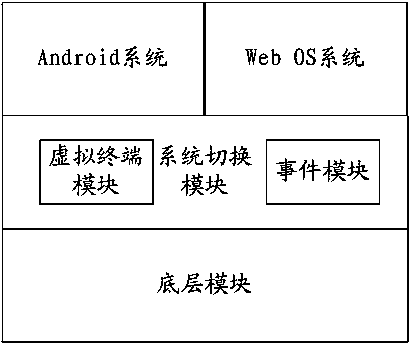
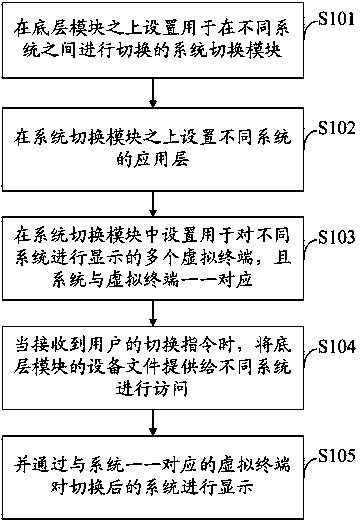
Device and method for obtaining multiple systems through linux kernel
The invention discloses a device and method for obtaining multiple systems through a linux kernel. The device comprises a bottom layer module shared by the different systems, a system switching module arranged on the bottom layer module and used for switching the different systems and the different systems arranged on the system switching module. The system switching module comprises a virtual terminal module and an event module. The virtual terminal module comprises multiple virtual terminals used for displaying the different systems and the systems correspond to the virtual terminals one to one. The event module is used for enabling the different systems to have access to a device file of the bottom layer module according to a switching order of a user.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
Storage system and a method for dissolving fault of a storage system
InactiveUS20050262386A1Hinder performance improvementQuick selectionInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionComputer scienceDevice file
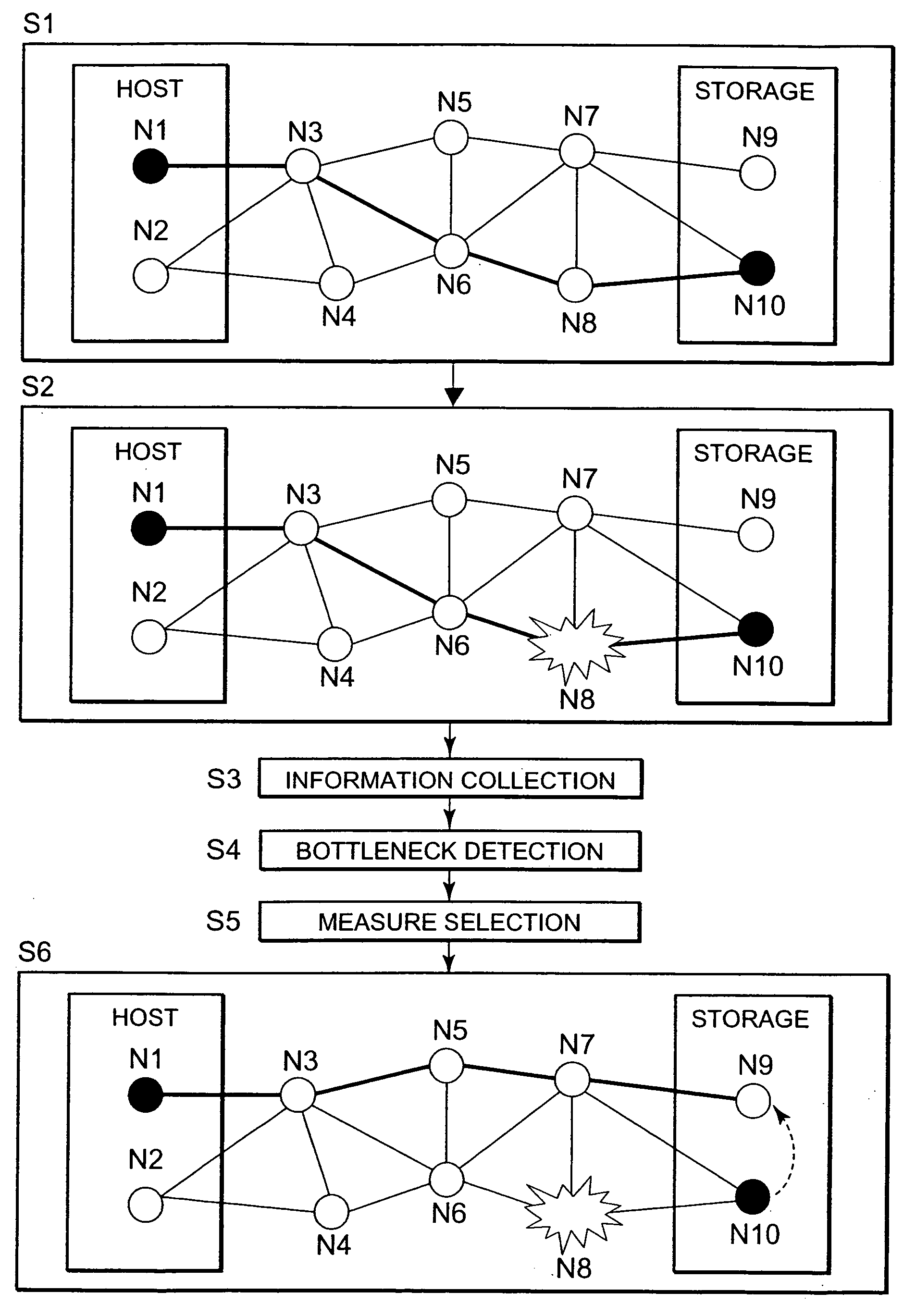
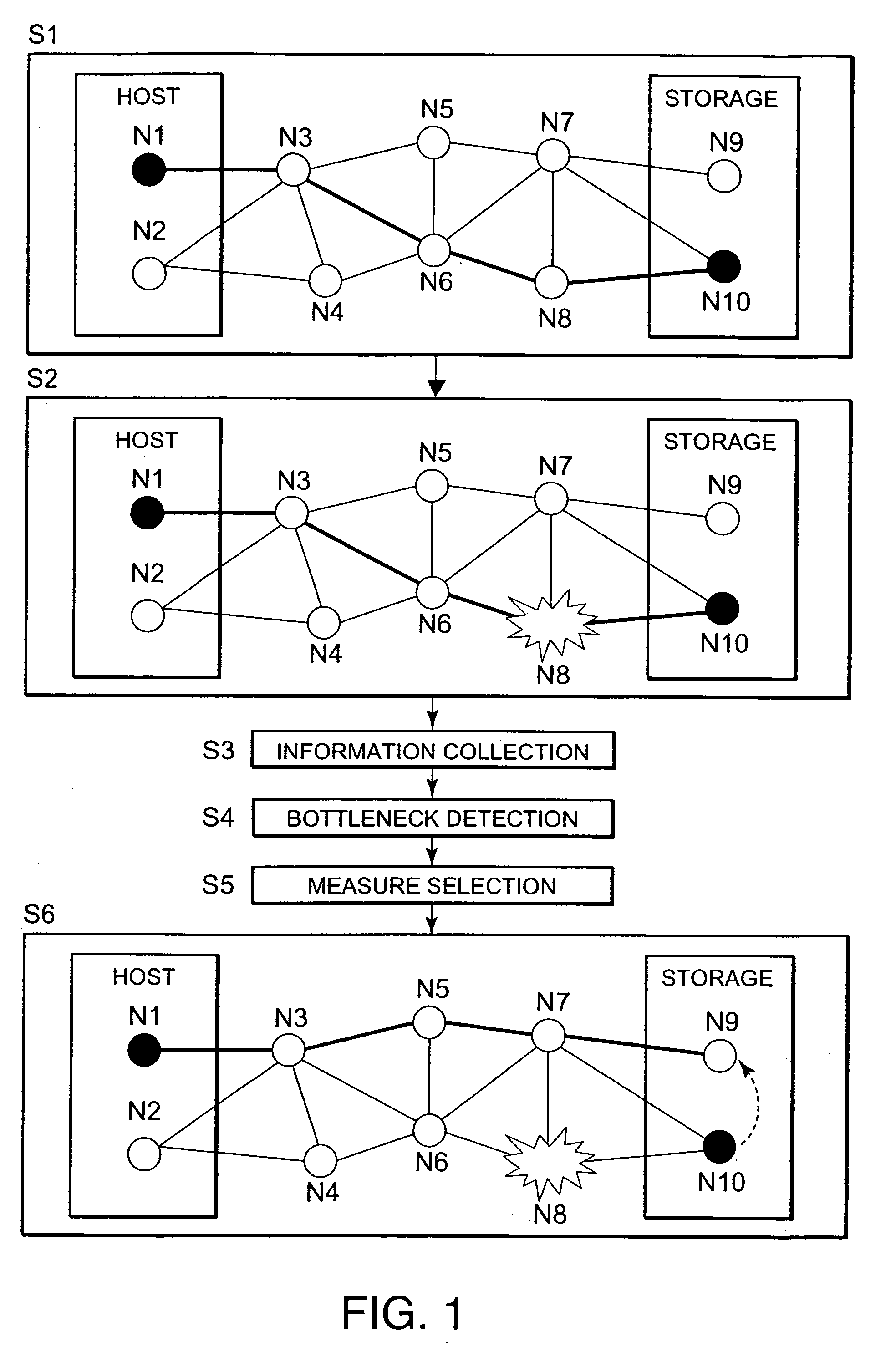
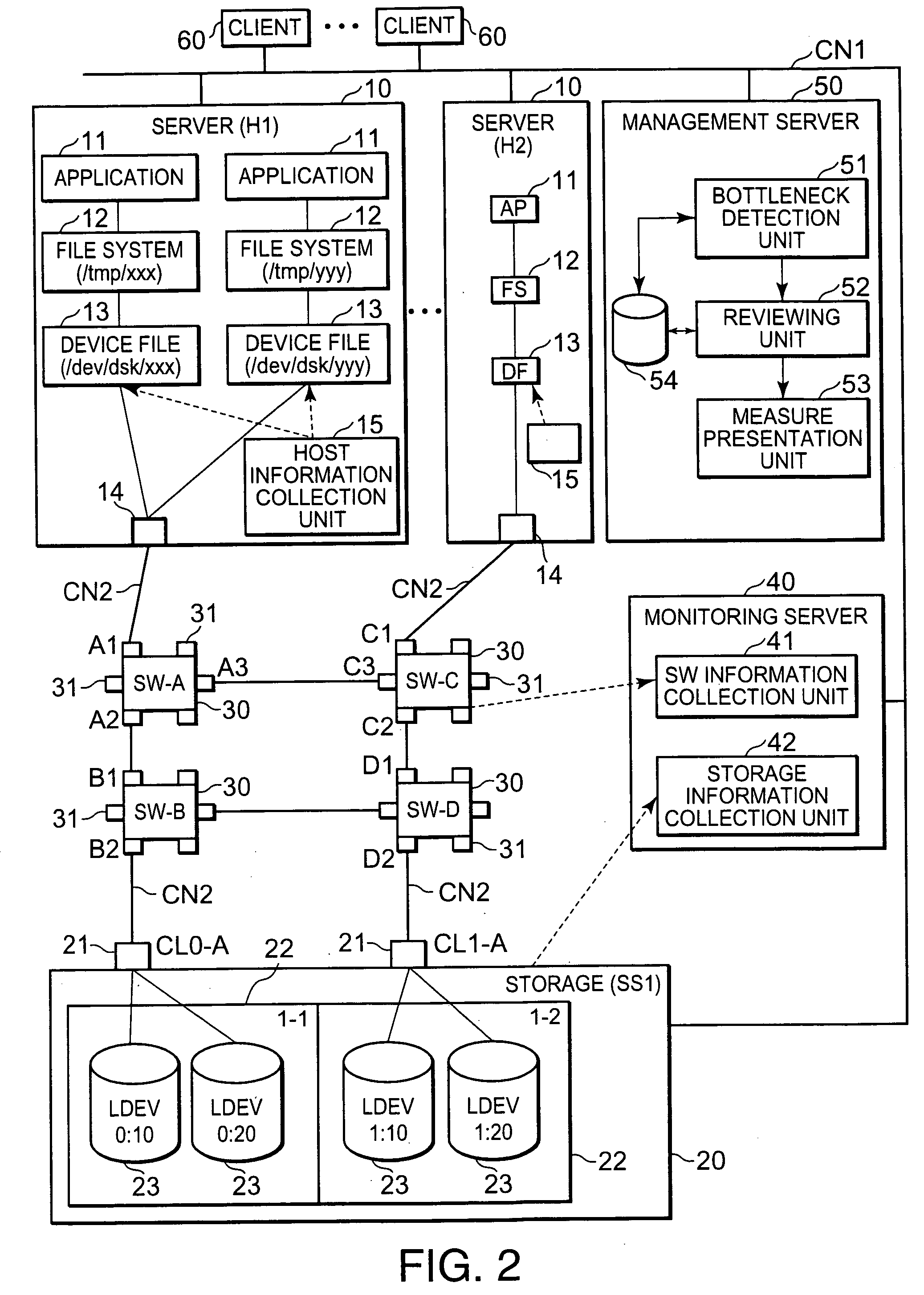
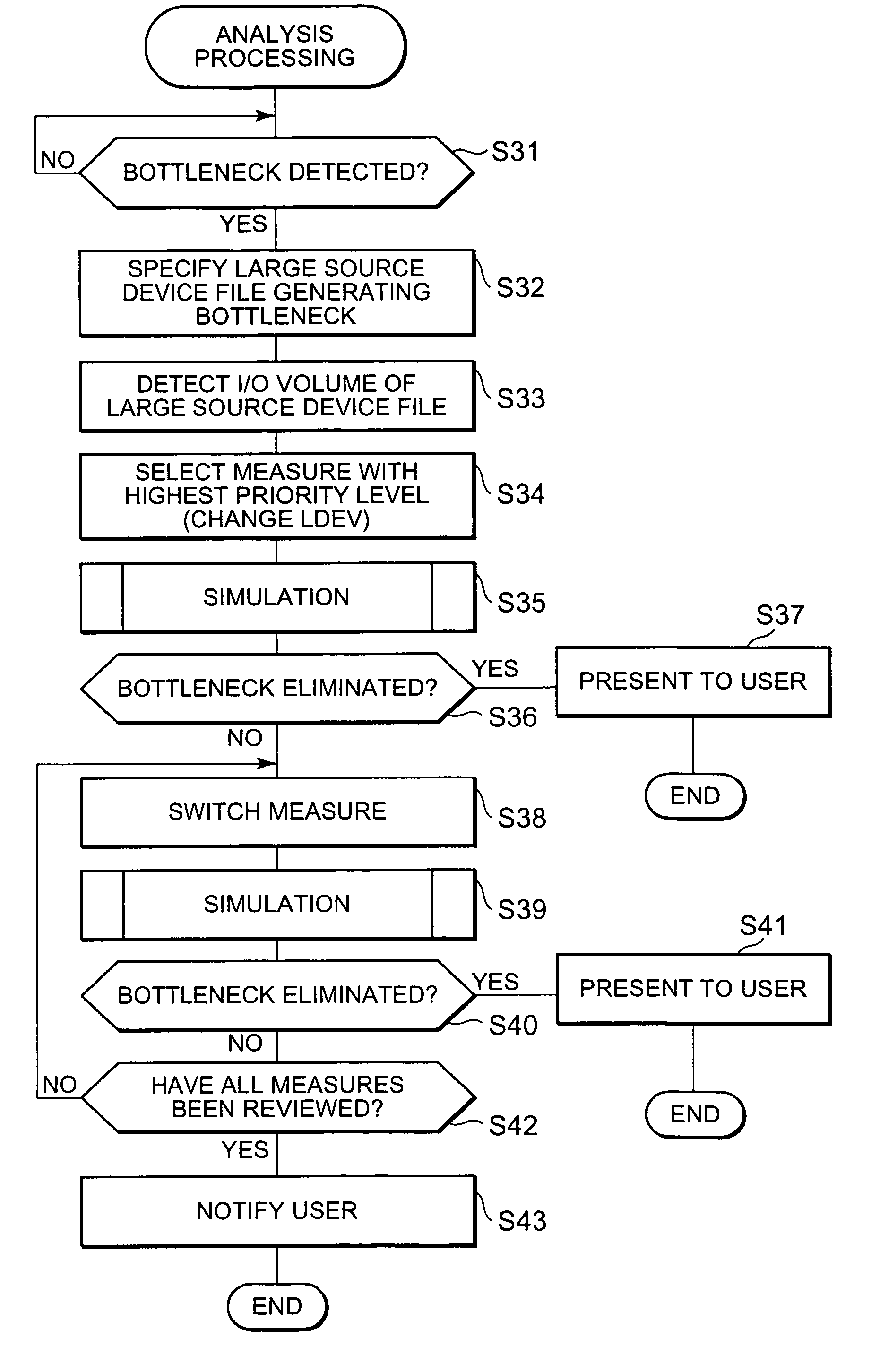
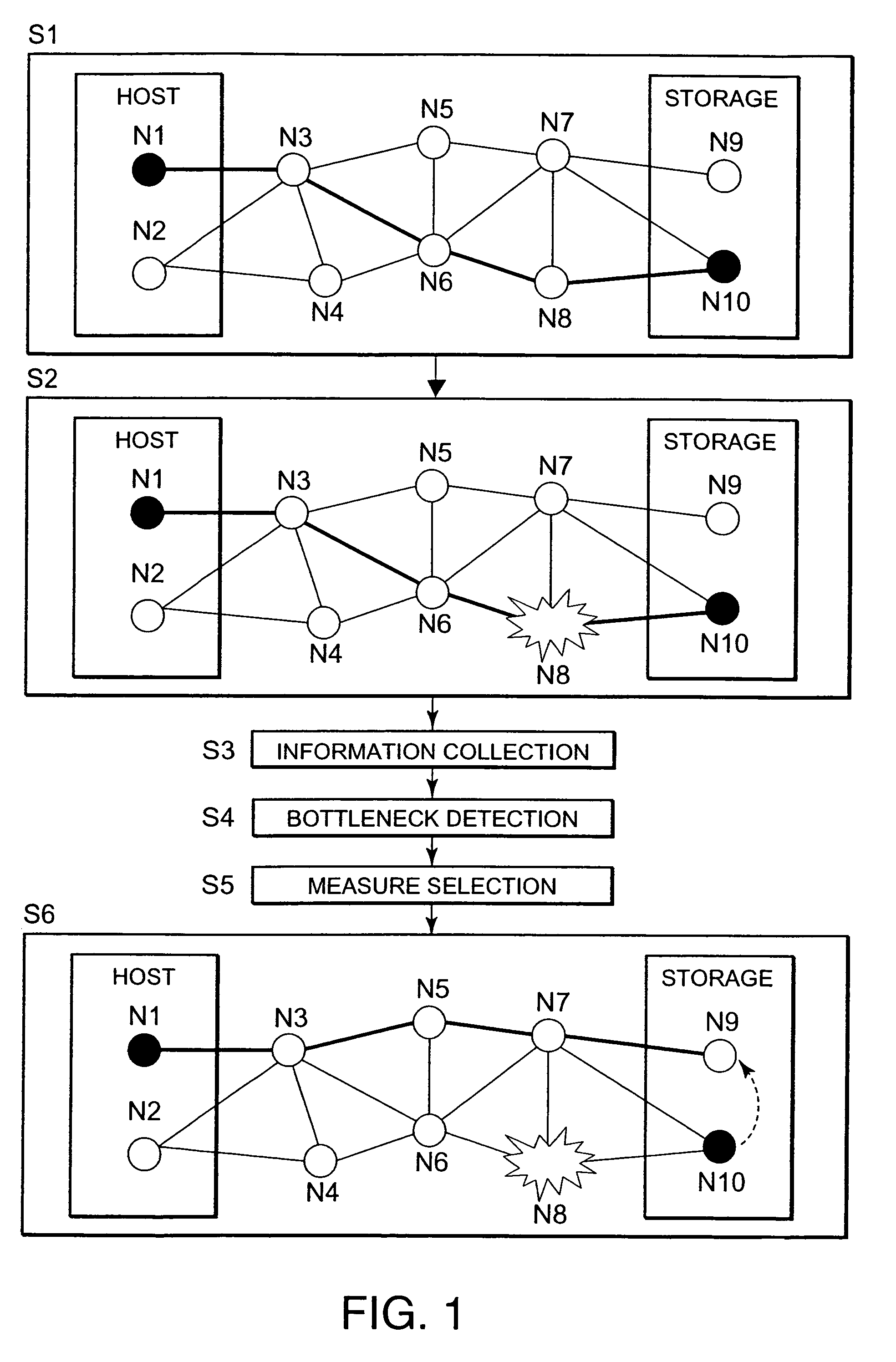
The present invention detects the occurrence of a bottleneck on the basis of the states of respective elements of the storage system and presents a measure for eliminating the bottleneck before actually changing the constitution of the storage system. The host element N1 is connected to the element N10 in the storage device via the elements N3, N6 and N8 (S1). Element N1 is a device file or the like, for example. Element N10 is a logical volume or the like, for example. When a bottleneck occurs in the intermediate element N8 (S2), the bottleneck is detected (S4) on the basis of collected information on the respective elements of the storage system (S3). A measure that is effective in eliminating the bottleneck is then reviewed and selected (S5, S6). This measure manipulates any of the elements N1 and N2 or N9 and N10 located at the two ends of the path.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Drive letter drifting preventing and treating method and device
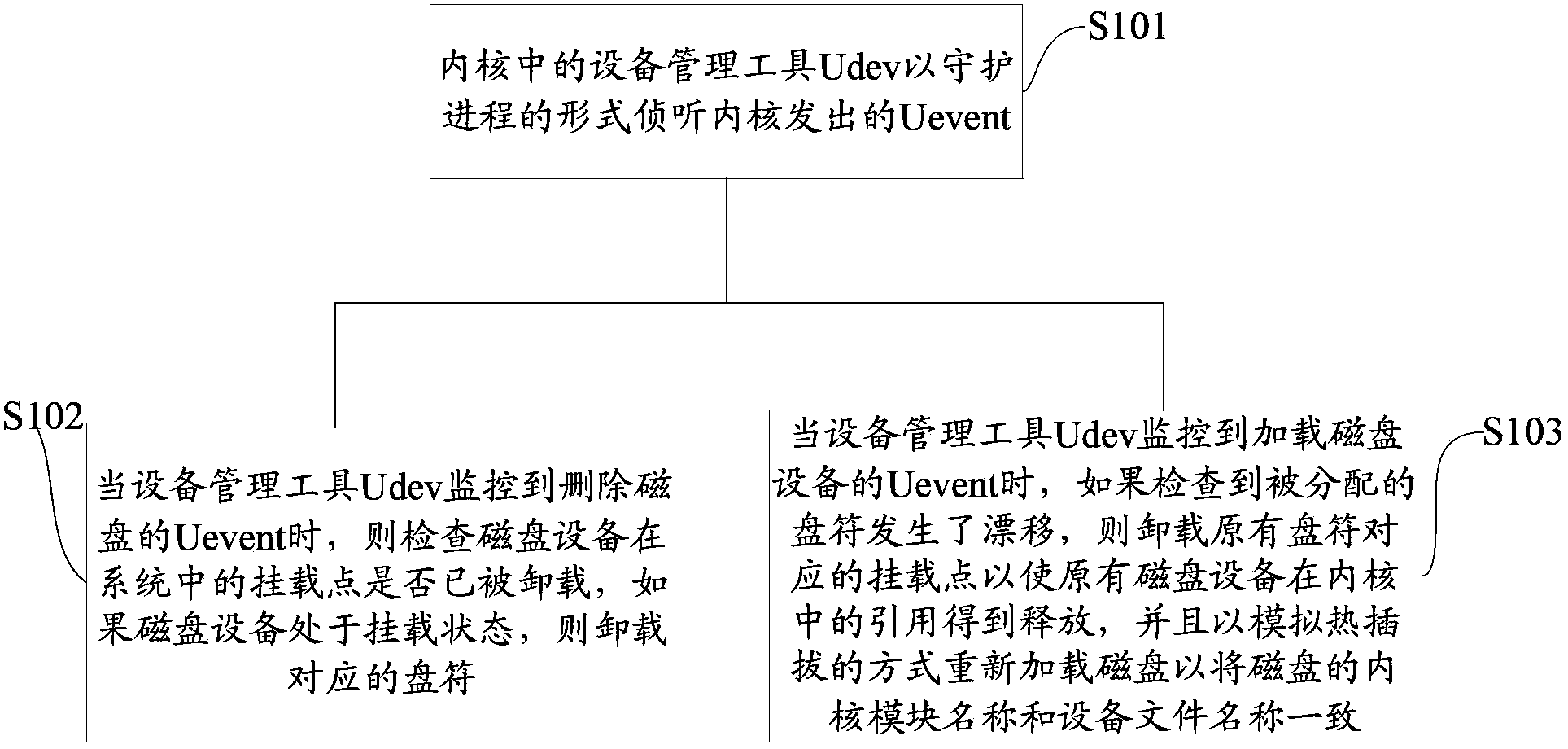
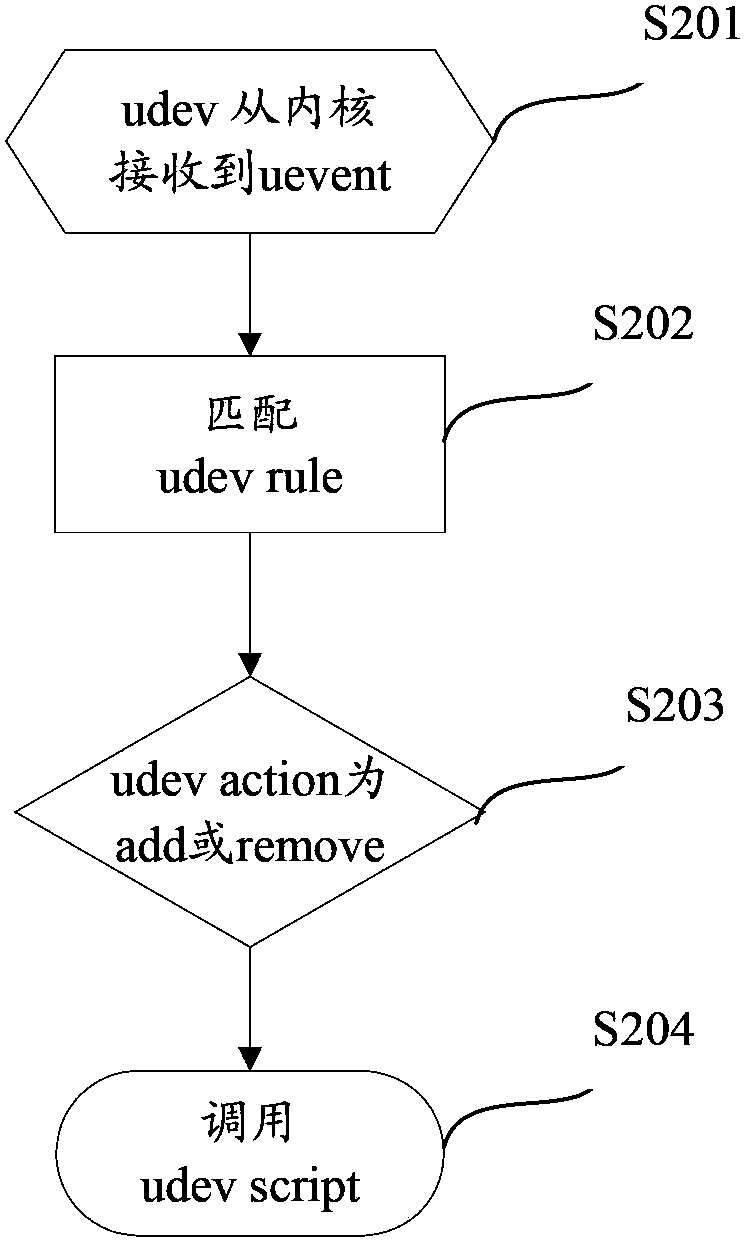
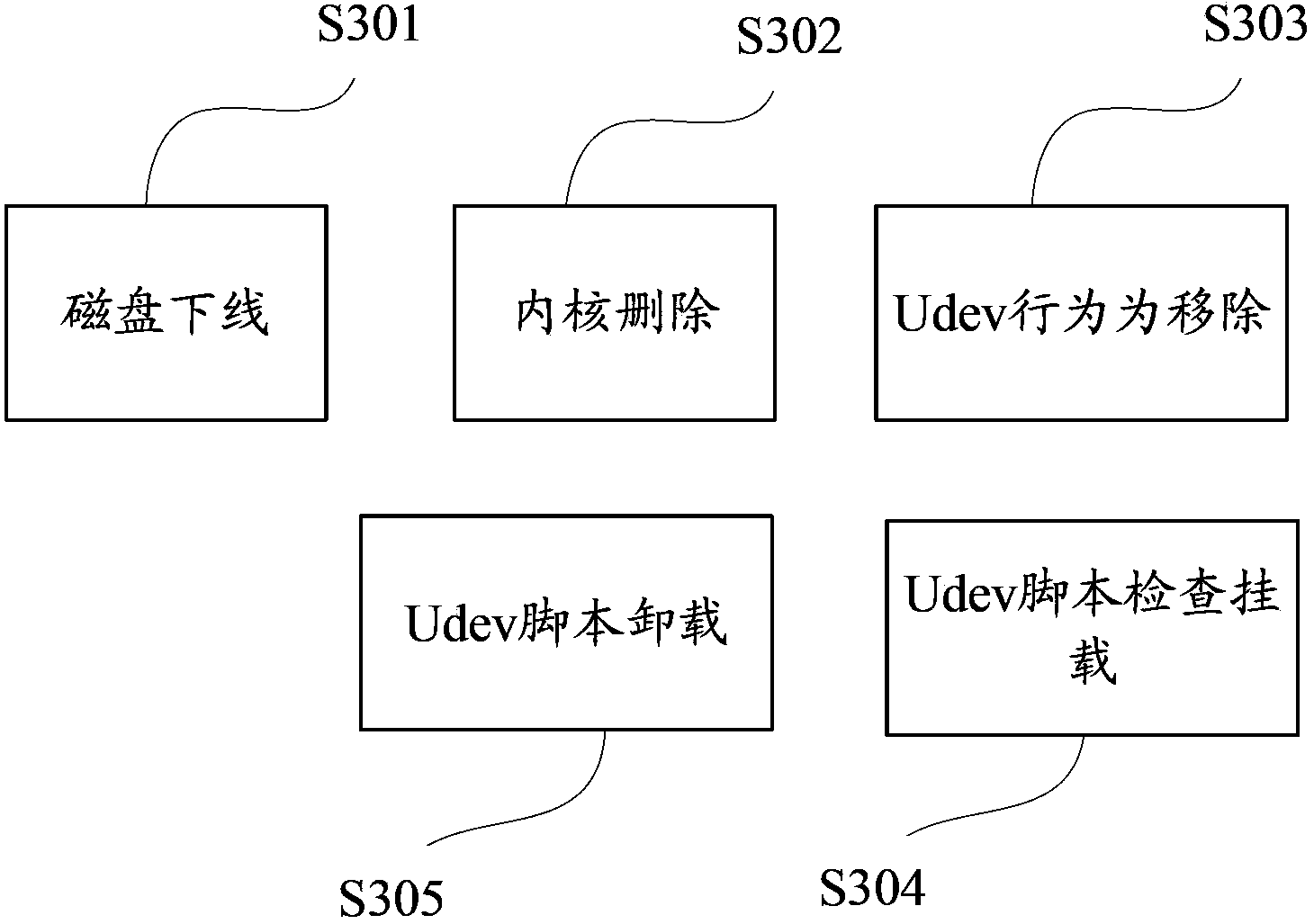
ActiveCN103677650AAvoid driftingEasy to useInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionDevice fileComputer engineering
The invention discloses a drive letter drifting preventing and treating method. The method comprises the following steps that a device management tool Udev in a kernel monitors a Uevent in a daemon process mode, wherein the Uevent is sent by the kernel; when the device management tool Udev monitors that the Uevent of a disk is deleted, whether a mount point of a disk device in a system is unloaded or not is detected, and a corresponding drive letter is unloaded if the disk device is in the mount state; when the device management tool Udev monitors that the Uevent of the disk device is loaded, the corresponding mount point of the original drive letter is unloaded to enable the reference of the original disk device in the kernel is released if the situation that drifting happens to the distributed drive letter is detected, and the disk is reloaded in a simulation hot plug mode to enable the name of a kernel module of the disk to be the same as that of a device file. The invention further discloses a drive letter drifting preventing and treating device. According to the drive letter drifting preventing and treating method and device, drifting is prevented from happening to the drive letter sequence when the disk is reloaded.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Method and device for eliminating sensitive data of Linux system memory
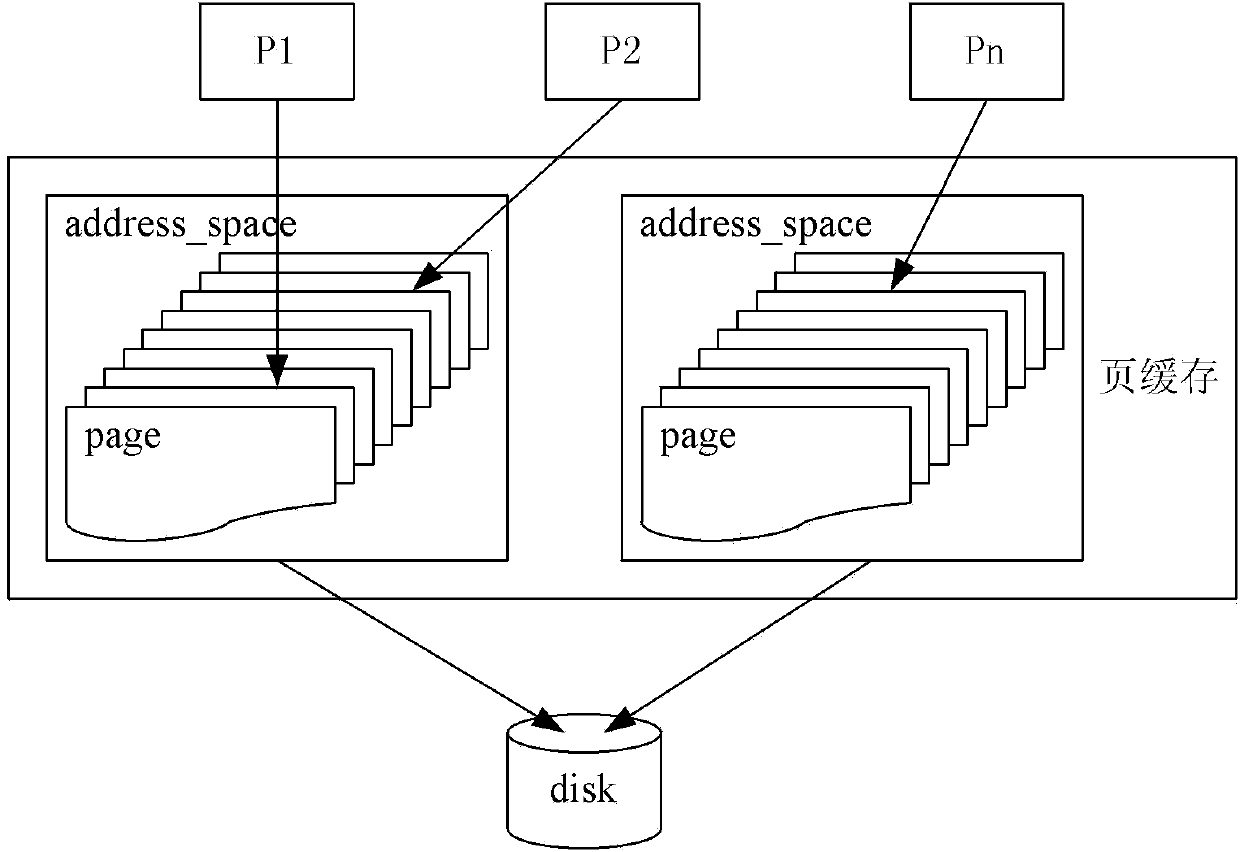
The invention provides a method and device for eliminating sensitive data of a Linux system memory. The method includes the steps that when a course calls a close system to call a closed file or exit_files are called for closing an unclosed file due to course exit, the unclosed file is located to corresponding struct address_space through a struct file, and if it is judged that a dirty page exists in an inode structure corresponding to the file to be closed, a vfs_fsync function is called so that the dirty page in the file can be written back to a disk; cardinal number trees in the located address space structure is traversed and all pages in the cardinal number trees are deleted and reset and then released to a free zone; a read-write chain table is established in each course, the start address and the data length in a device cache are recorded when data of a device file are read or written; when calling of a read or write system exits, the read-write chain tables are traversed, so that data in the address space from the address to the address plus the length of each node is reset.
Owner:INST OF INFORMATION ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and systems for imaging device metadata management
InactiveUS20060092097A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInternal/peripheral component protectionMetadata managementData management
Embodiments of the present invention comprise systems, methods and devices for imaging device file metadata management.
Owner:SHARP KK
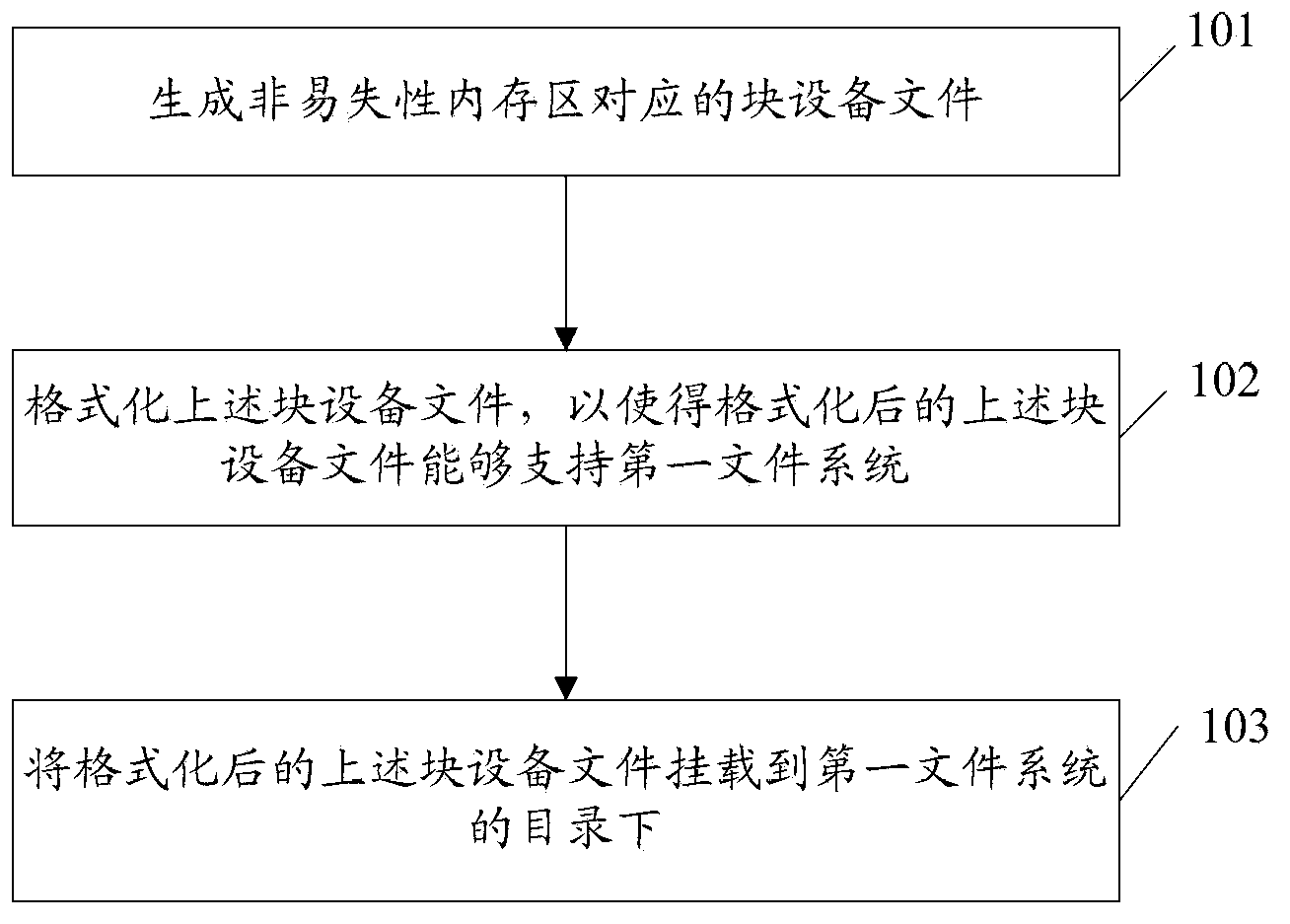
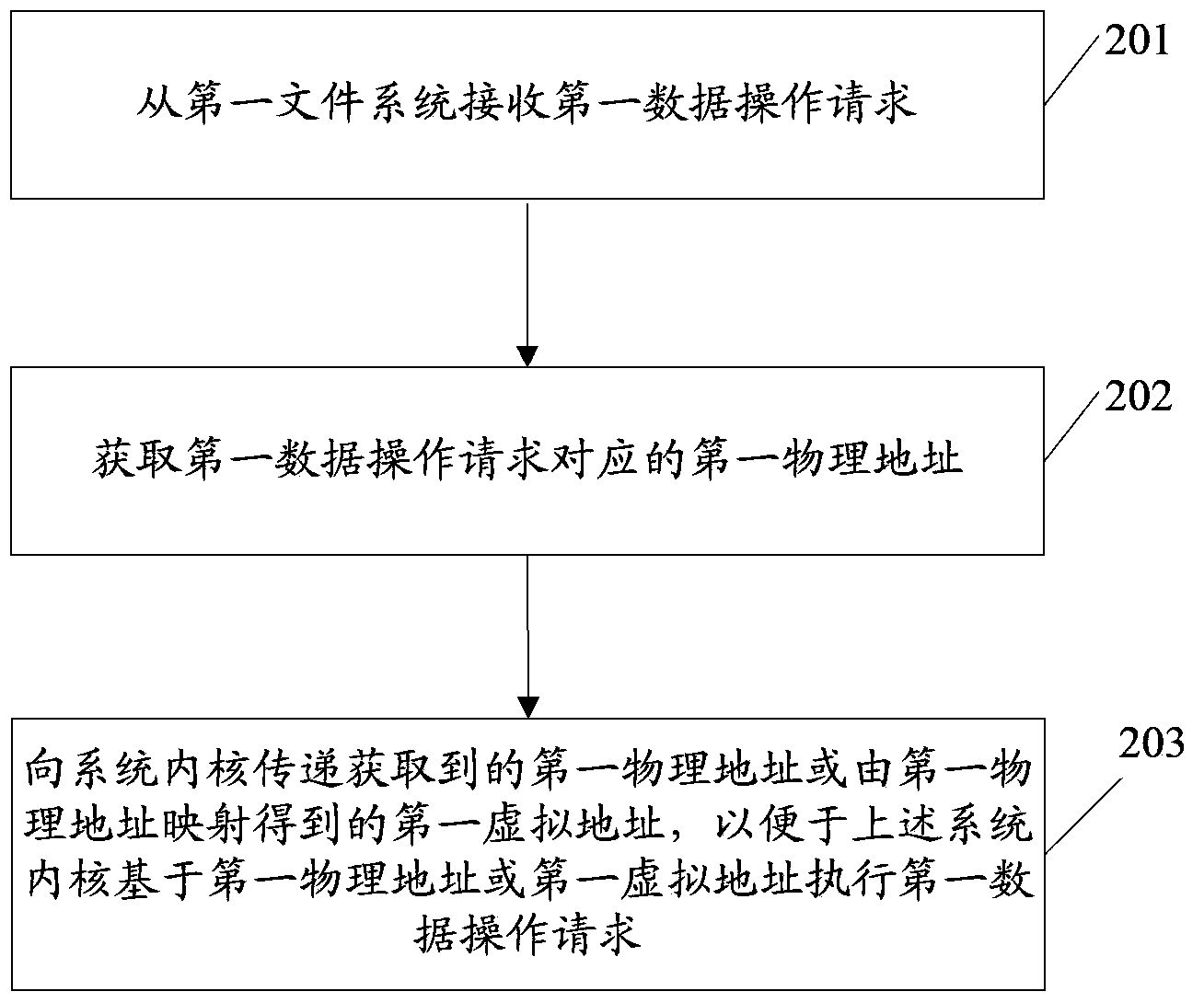
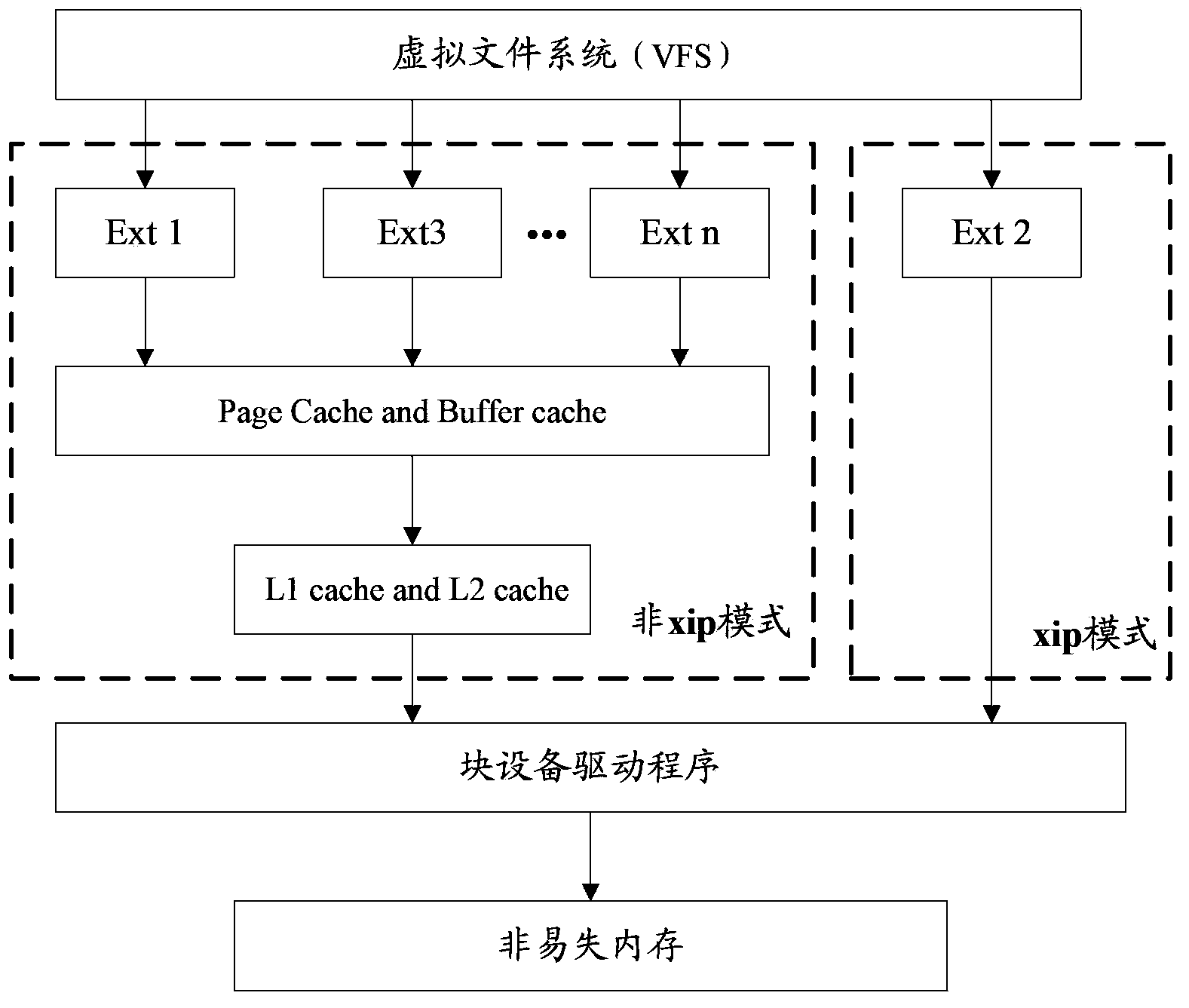
Operation method of non-volatile RAM, data operation method and relevant device
ActiveCN103412822AAchieve direct accessAchieve no lossMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFile systemData operations
The embodiment of the invention discloses an operation method of a non-volatile RAM, a data operation method and a relevant device. The operation method of the non-volatile RAM comprises the following steps: a block device file corresponding to a non-volatile RAM area is generated; the block device file is formatted so as to enable the formatted block device file to support a first file system; the formatted block device file is mounted under the catalog of the first file system. The technical scheme provided by the embodiment of the invention facilitates the realization of no loss of data after the system is subjected to warm start or abnormal reset on the premise of being safe and reliable as far as possible.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Electronic device management method, and electronic device management system and host electronic device using the method
InactiveUS20100180209A1Digital data processing detailsInput/output processes for data processingClient-sideDevice file
An electronic device managing method and system, and a host electronic device using the method are disclosed. The host electronic device may be connected to a plurality of client electronic devices. The host electronic device may perform file storage state management, remaining battery capacity management, and file reproduction management to integrally and efficiently managing the plurality of client electronic devices. The file storage state management includes managing file storage states corresponding to the memories of the plurality of client electronic devices. The remaining battery capacity management includes managing the remaining capacity of the batteries of the plurality of client electronic devices. The file reproduction management includes managing reproduction of at least one of the files stored in the plurality of client electronic devices.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
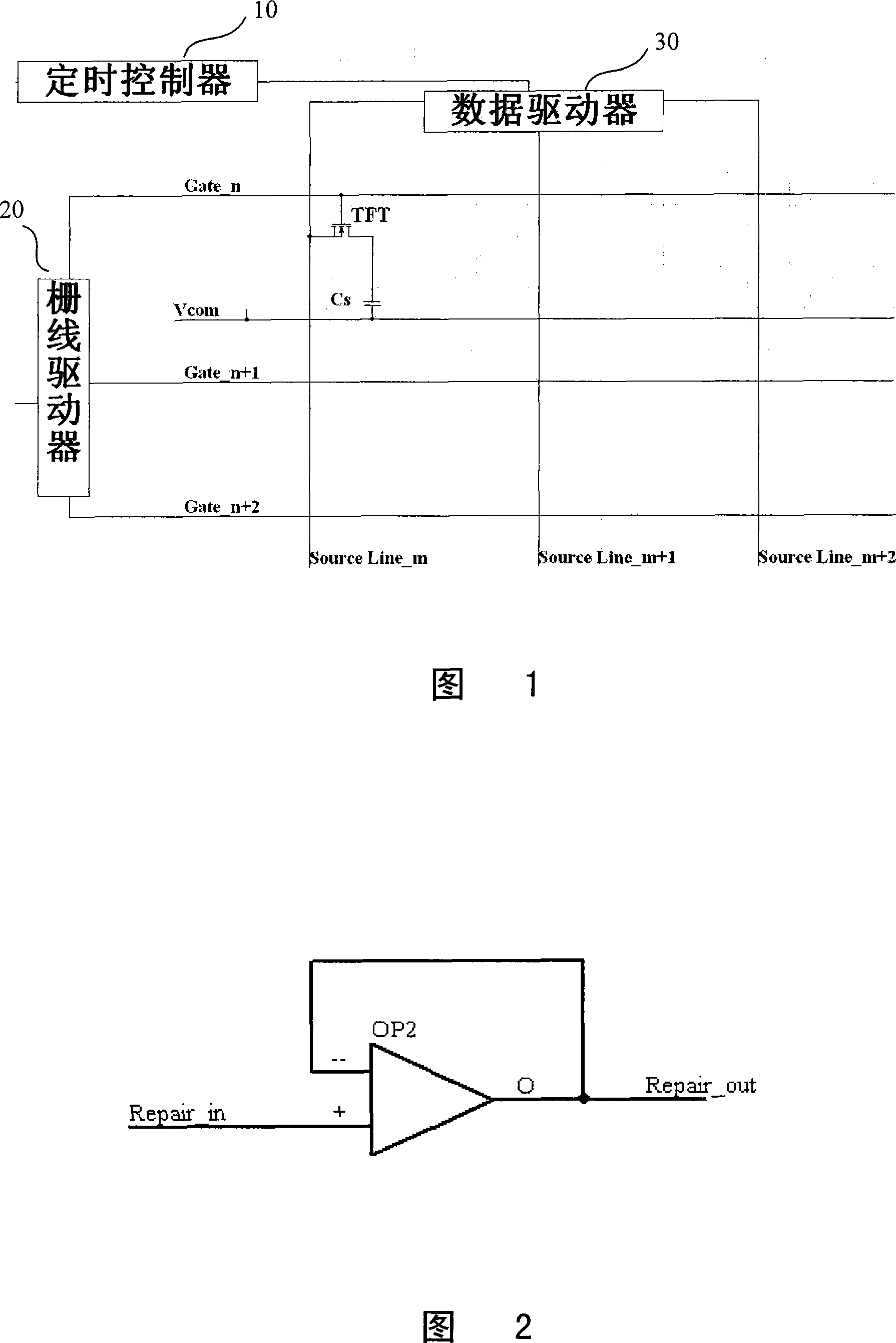
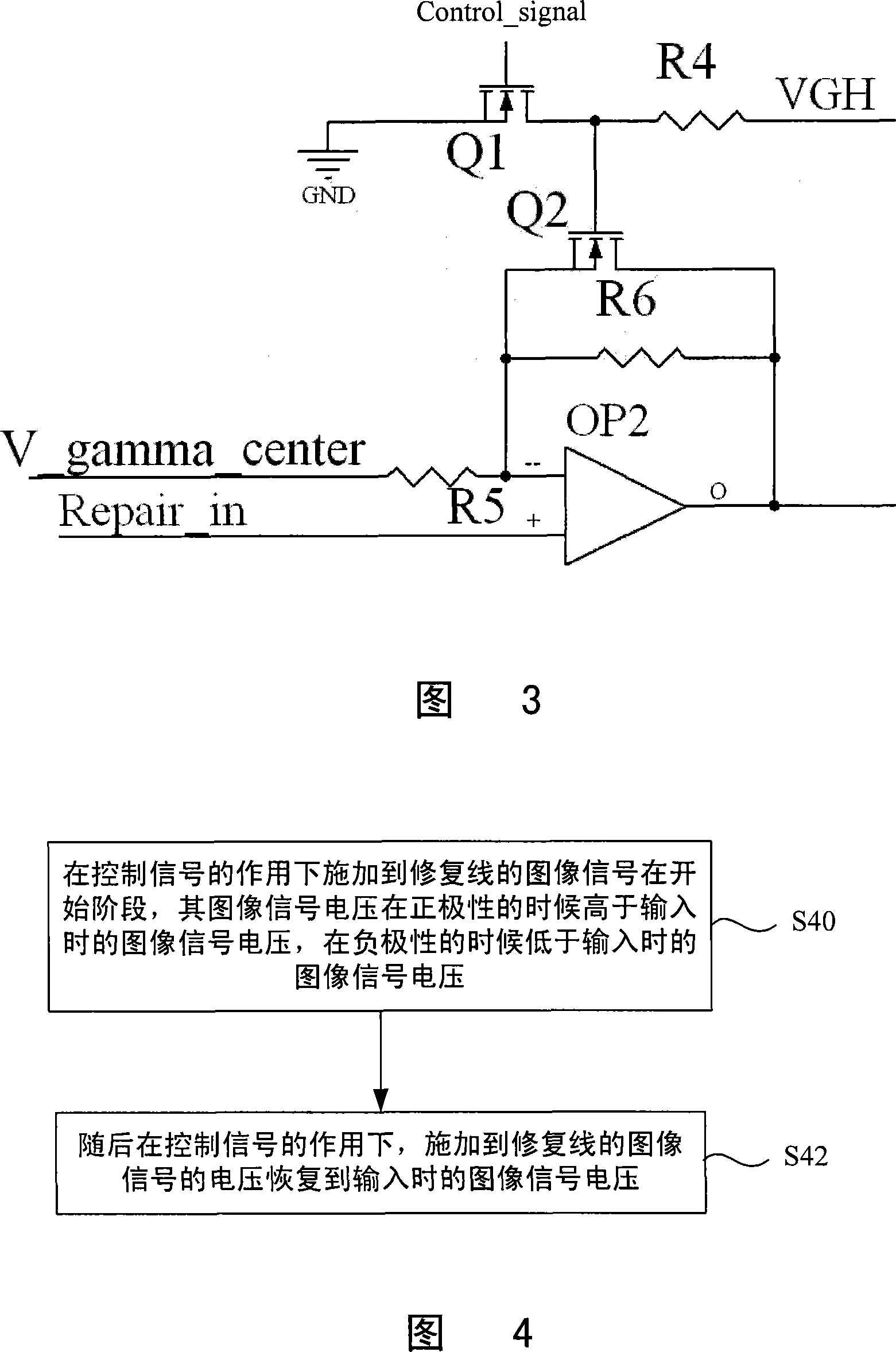
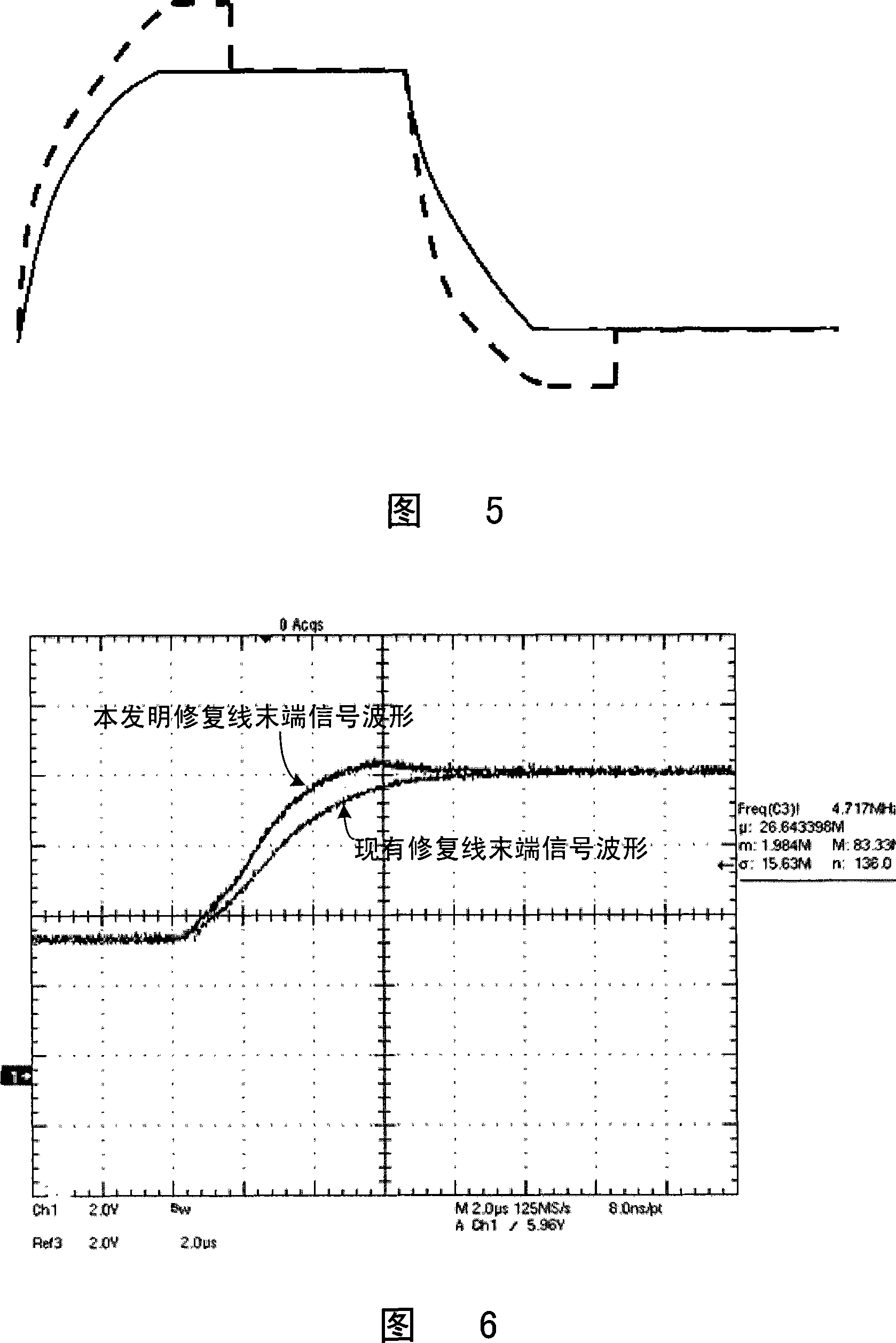
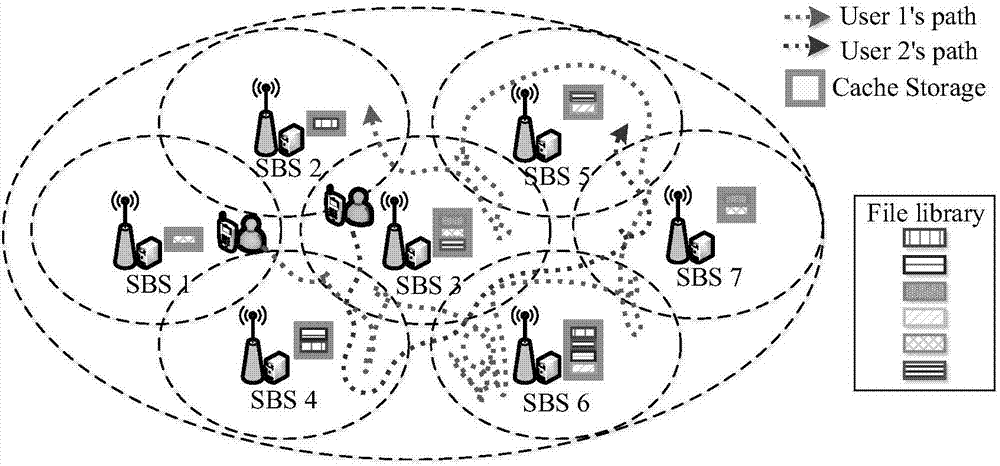
LCD device repairing line operation amplification circuit and its drive method
InactiveCN101236738AShorten the timeStatic indicating devicesDifferential amplifiersLiquid-crystal displayAudio power amplifier
The present invention discloses a repairing line operational amplifying circuit of a liquid crystal display devices and a driving method thereof; the amplifying circuit shortens the time of an end of the repairing line reaching a normal image signal voltage. The technical proposal is that: the circuit of the invention comprises a first MOS tube in which a grid is connected with a control signal, a drain is grounded and a source cathode is connected with a high-level voltage via a first resistor; an operational amplifier in which a first input end is connected with the central voltage of a gray scale voltage via a second resistor, a second input end is connected with a voltage of the repairing line image signal, and an output end is connected with the repairing line; a second MOS tube in which the grid is connected with the source cathode of the first MOS tube, a third resistor is connected between the source and the drain, and the source and the drain are connected between the first input end and the out end of the operational amplifier. The present invention is applied in the liquid crystal display device filed.
Owner:NANJING CEC PANDA LCD TECH
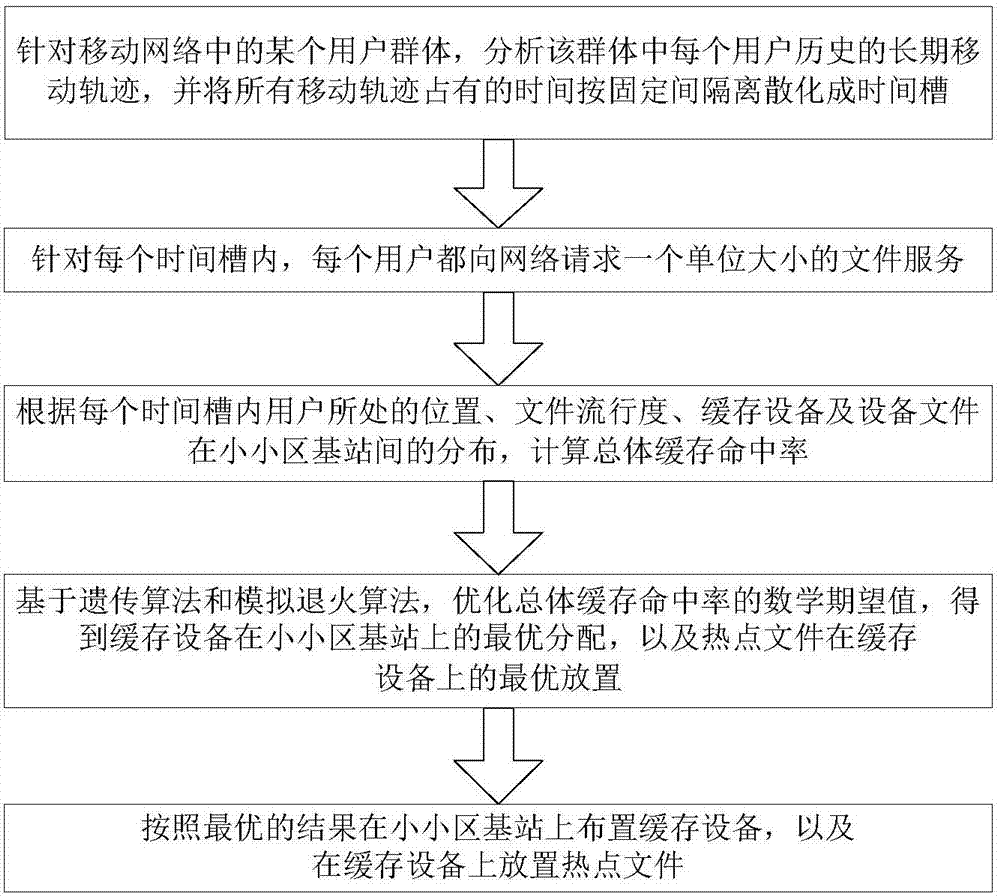
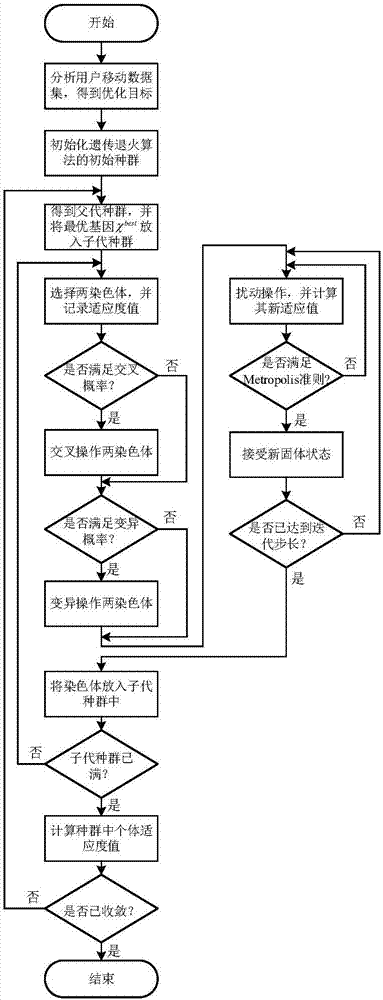
Tiny cell cache device allocation algorithm based on user mobility
ActiveCN107466016AImprove cache hit ratioImprove cache hit rate performanceLocation information based serviceData setParallel computing
The invention discloses a tiny cell cache device allocation algorithm based on user mobility and belongs to the field of wireless communication. The method comprises the following steps: performing data set analysis on a long-term user group mobility track at an initialization phase, and dividing system time of a user mobility track data set into discrete time slots according to certain time intervals; enabling the user to request a file once in each time slot, and calculating the total cache hit rate; converting a cache allocation problem into an integer programming problem; searching an optimal solution of the initial allocation problem of cache device capacity in a solution space by using a genetic-annealing algorithm, wherein the optional solution comprises specially optimized design operations such as an a fitness function, a selection operation and an interlace operation; and outputting the allocation of device files among tiny cell base stations if the solution is converged, and allocating the cache device among the tiny cell base stations according to the allocation, thereby obtaining the optimal cache device allocation scheme. Therefore, the cache hit rate performance of users is improved, and the device installation cost is effectively saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Handheld smart device data security protection method
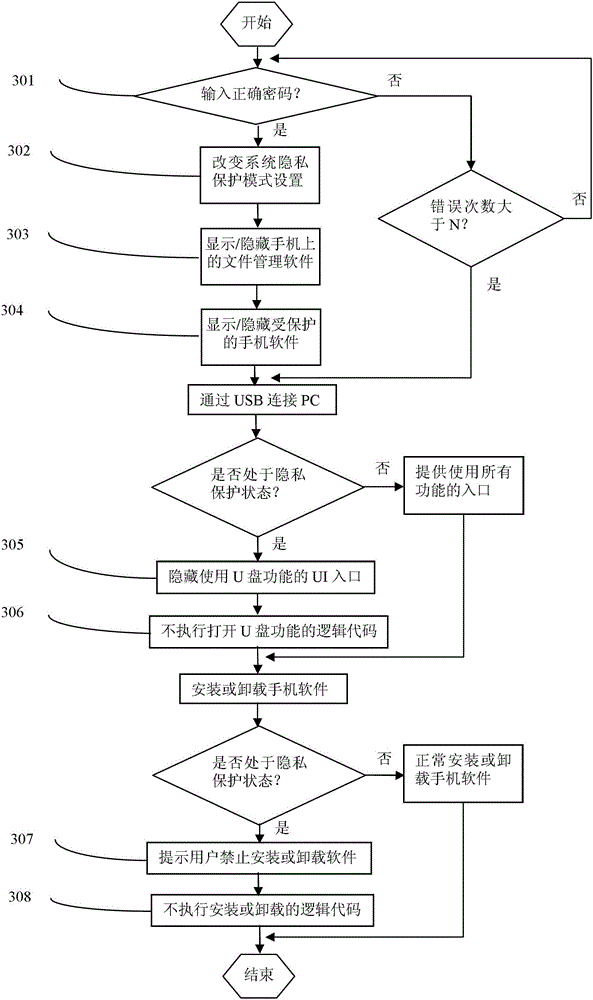
ActiveCN102722663ACannot uninstallReduce security breachesComputer security arrangementsPasswordPrivacy protection
The invention relates to a handheld smart device data security protection method, comprising steps that: whether a password input by a user through human-computer interaction is correct is judged and if so, a setting of a privacy protection status is changed, and if not, the setting of the privacy protection status remains unchanged; and according to a true record of the privacy protection status, device file management software and protected software are hidden, and otherwise, the device file management software and the protected software are shown and used normally. The method of the invention further comprises steps that: 1101) connection between the handheld smart device and a computer via a USB port is detected and judged; 1102) whether the device is in the privacy protection status is judged and if so, a user interface entrance which has a U disc using function is hidden and a logic code of opening the U disc is not performed; and otherwise, normal operation is carried out; 1201) installation or unloading of application software is detected and judged; and 1202) whether the device is in the privacy protection status is judged, and if so, a user operation instruction or a logic code for the installation or unloading is not performed; and otherwise, normal installation or unloading is performed.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Method and a system for building a virtual mechanism based on a processor
ActiveCN109522087ARealize the virtualization functionSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationFile systemDisplay device
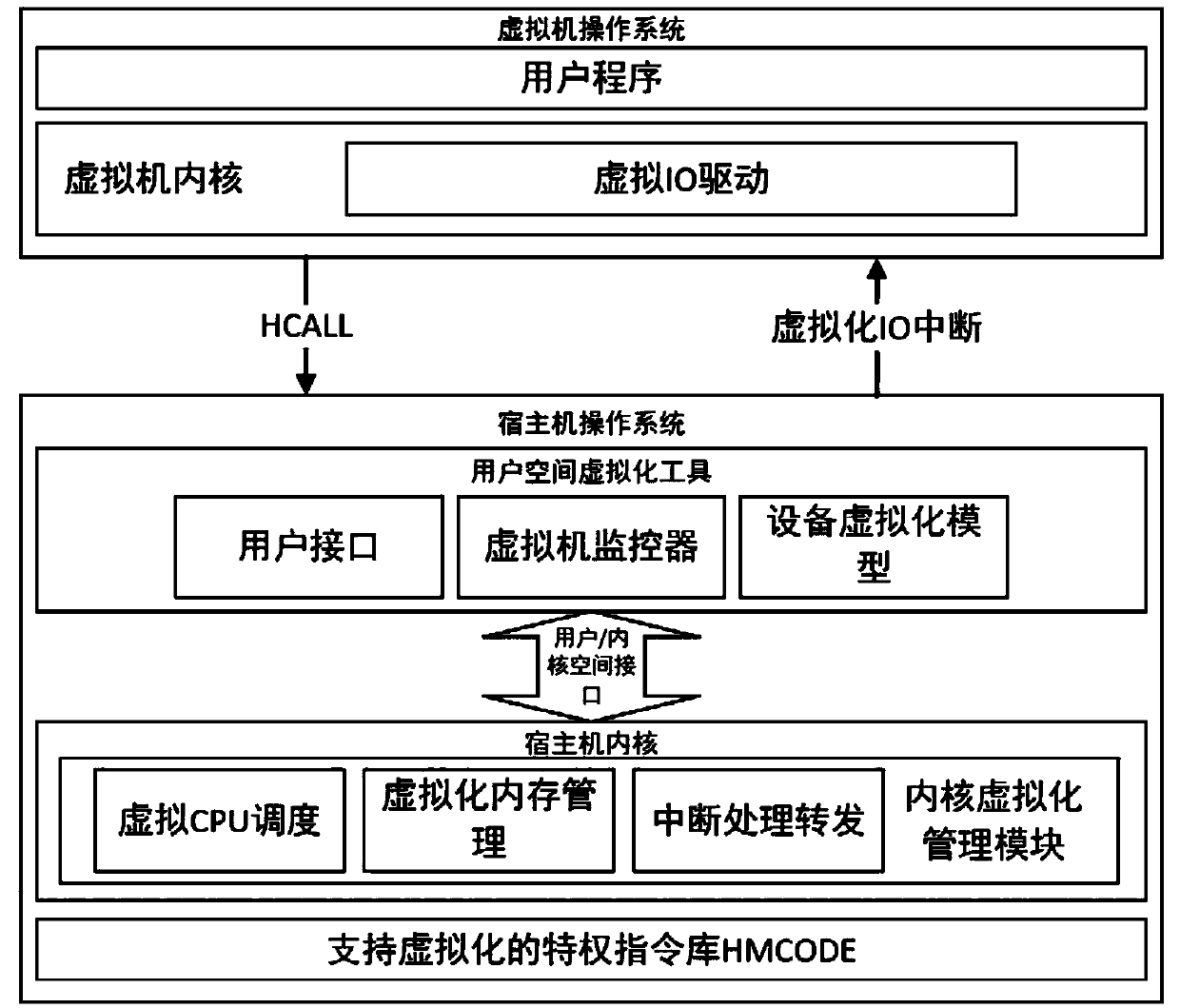
The invention provides a method and a system for building a virtual mechanism based on a processor. In a user space virtual machine management program, a configuration command is input to create and start a virtual machine. The user interface receives and parses configuration commands and accesses the kernel module interface. Creating device files in the physical machine file system as kernel module interfaces for user space hypervisor to access the physical machine kernel; The virtual management of the physical machine kernel responds to the user space hypervisor access, initializes the datastructure of the virtual machine instance, fills the virtual CPU state data, saves the current CPU running state of the physical machine, and accesses the HMCode specific call to switch to the virtualmachine running state. Lightweight virtual machine based on domestic Shenwei processor platform is built to realize virtual machine creation, start, pause, stop and other key input and output devicevirtualization functions, including virtualized storage access, virtualized display device and virtual network card.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Storage device, file storage device, and computer system
InactiveUS20070041234A1Improve data transfer performanceIncrease speedDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
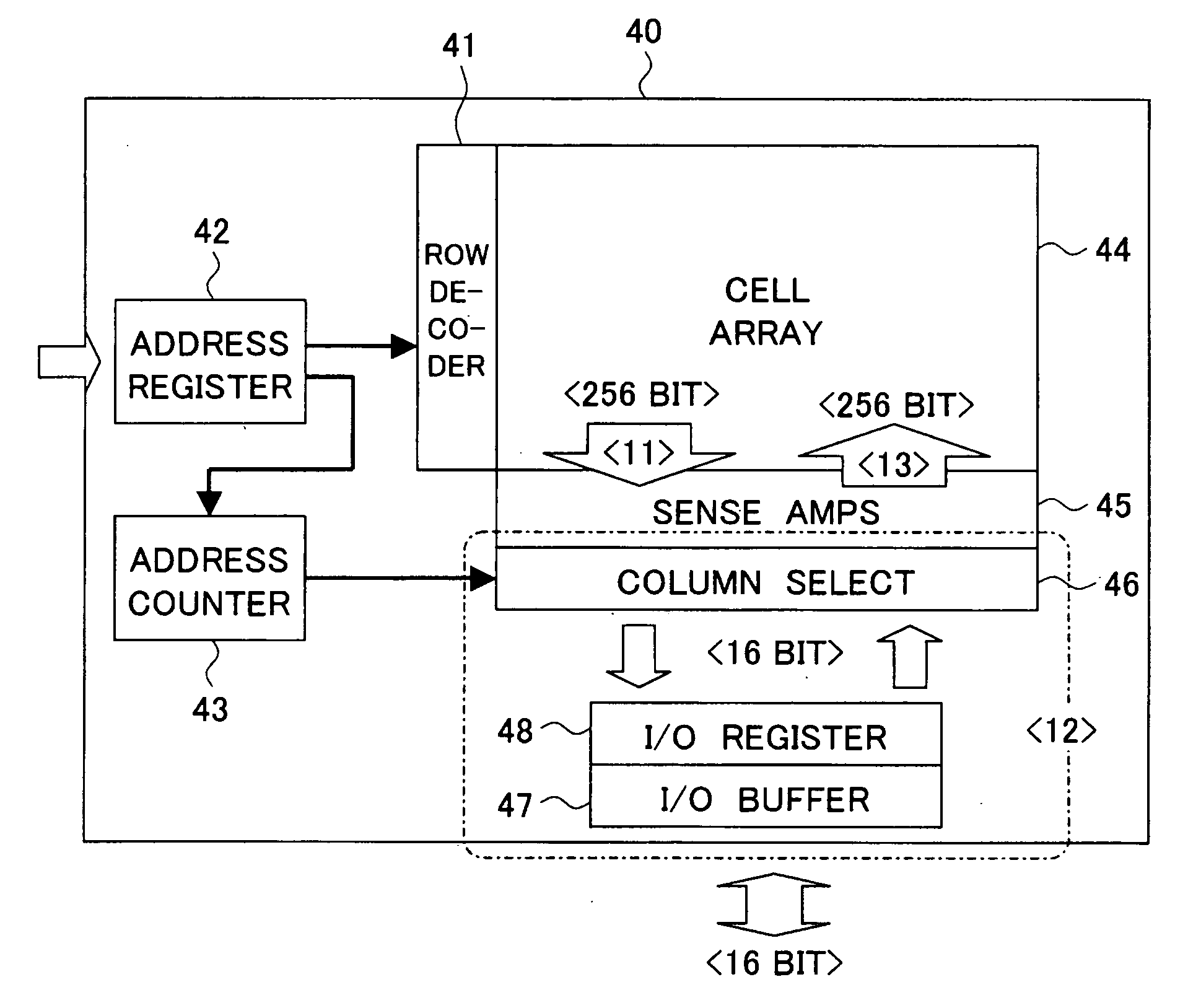
A storage device including a ferroelectric memory cell array including a plurality of memory cells; sense amplifiers connected to the bit lines and selected by a column address; an internal counter able to generate the column address; and a control part controlling data access, wherein the control part accesses data by a first processing of reading out a plurality of words of data from memory cells of a word line and a plate line selected according to a row address and storing it in the sense amplifiers, a second processing of selecting sense amplifiers from the column address and inputting / outputting data with the outside, and a third processing of writing back the data of the sense amplifiers into the memory cells, data being continuously input or output and transferred by repeatedly executing the second processsing using the column address generated in the internal counter for a group of words read out to the sense amplifiers at the first processing,and a file storage device and a computer system utilizing such a ferroelectric memory.
Owner:SONY CORP
Methods and systems for imaging device metadata management
InactiveUS7684074B2Multiple digital computer combinationsInternal/peripheral component protectionMetadata managementData management
Embodiments of the present invention comprise systems, methods and devices for imaging device file metadata management.
Owner:SHARP KK
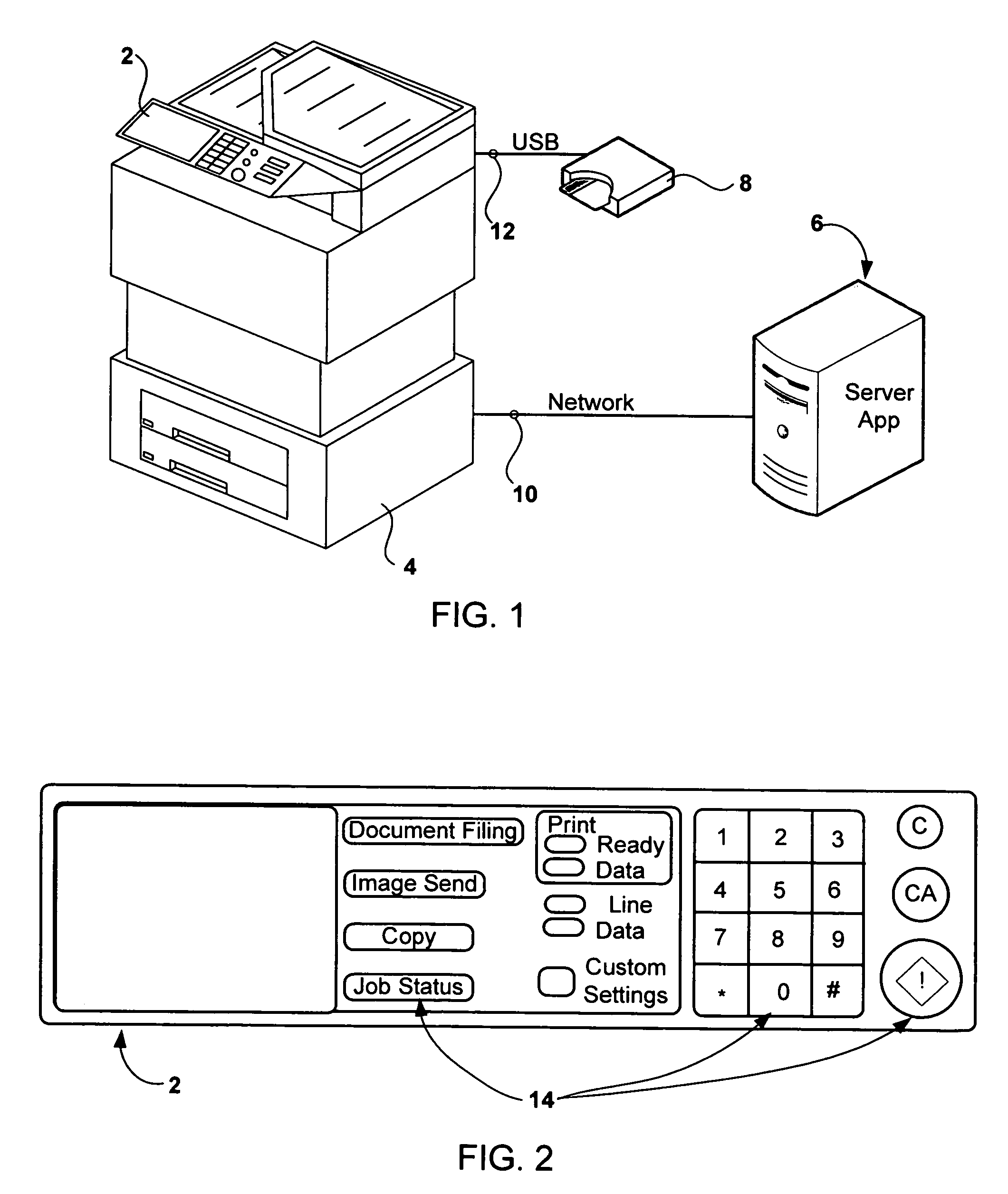
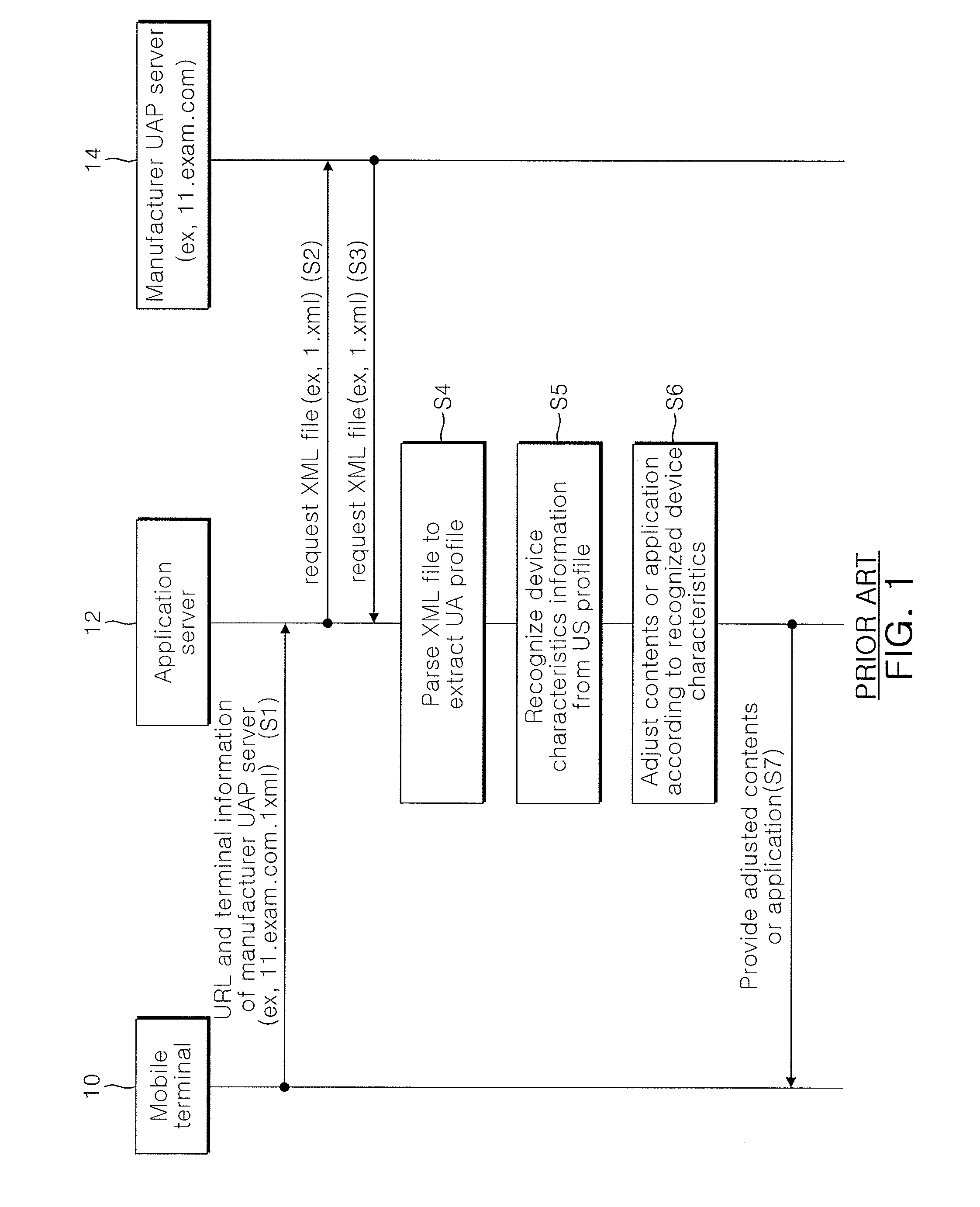
System and method for providing device file using device identifier
ActiveUS20100161804A1Improve efficiencyImprove utilizationDigital computer detailsPayment architectureApplication serverStructure of Management Information
A system and method for providing a device profile using a device identifier are disclosed. The system for providing a device profile using a device identifier includes: a mobile terminal that provides a device identifier having information regarding a hierarchical structure of a server and a model name; a plurality of servers that analyze the device identifier to recognize the lowermost server when the device identifier is queried, acquire a device profile corresponding to the device identifier through the lowermost server, and provide the acquired device profile; and an application server that connects to one of the plurality of servers, queries the device identifier, and is provided with a device profile corresponding to the device identifier. Device description of various mobile terminals can be more effectively managed and used in a mobile environment.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Storage system and a method for dissolving fault of a storage system
InactiveUS7702962B2Avoid performanceQuick selectionInput/output to record carriersAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputer scienceDevice file
The present invention detects the occurrence of a bottleneck on the basis of the states of respective elements of the storage system and presents a measure for eliminating the bottleneck before actually changing the constitution of the storage system. The host element N1 is connected to the element N10 in the storage device via the elements N3, N6 and N8 (S1). Element N1 is a device file or the like, for example. Element N10 is a logical volume or the like, for example. When a bottleneck occurs in the intermediate element N8 (S2), the bottleneck is detected (S4) on the basis of collected information on the respective elements of the storage system (S3). A measure that is effective in eliminating the bottleneck is then reviewed and selected (S5, S6). This measure manipulates any of the elements N1 and N2 or N9 and N10 located at the two ends of the path.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com