Method for measuring liver magnetic resonance crosswise relaxation rate R2* parameter
A technology of transverse relaxation rate and measurement method, which is applied in the field of magnetic resonance transverse relaxation parameter R2* measurement, can solve the problems of poor repeatability, inaccuracy, and large difference in operation, and improve accuracy, reduce noise, and repeatability Good results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
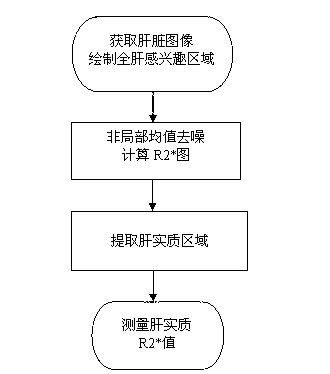
[0038] A method for measuring a liver magnetic resonance transverse relaxation rate R2* parameter, comprising the following steps in sequence:
[0039] (1) Using a multi-echo gradient echo sequence to obtain a magnetic resonance liver image, and drawing the region of interest of the whole liver on the obtained magnetic resonance liver image. The area of interest in the whole liver can be drawn manually, or automatically drawn by program control, or first automatically drawn by the program and then fine-tuned by manual drawing to improve the accuracy.
[0040] (2) Using the non-local mean filtering method to denoise the obtained magnetic resonance liver image and calculate the R2* map of the whole liver;
[0041]Specifically, the non-local mean filter method is used to denoise the magnetic resonance liver image to obtain the denoised magnetic resonance liver image; and then obtain the gray level of each pixel in the region of interest of the whole liver of the denoised magnet...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A method for measuring a liver magnetic resonance transverse relaxation rate R2* parameter comprises the following steps in sequence.
[0052] (1) Using a multi-echo gradient echo sequence to obtain a magnetic resonance liver image, and drawing the region of interest of the whole liver on the obtained magnetic resonance liver image.
[0053] The magnetic resonance liver image obtained by the multi-echo gradient echo sequence method has the characteristics of strong applicability, easy operation, low cost, and fast acquisition speed.
[0054] It should be noted that the method of obtaining the magnetic resonance liver image is not limited to the multi-echo gradient echo sequence method in this embodiment, and methods such as acquiring multiple times of a single echo can also be used.
[0055] (2) The non-local mean filtering method is used to denoise the obtained magnetic resonance liver image. Specifically, the following parameters are used in the non-local filtering me...
Embodiment 3
[0069] A method for measuring a liver magnetic resonance transverse relaxation rate R2* parameter takes human liver as a measurement object, and specifically includes the following steps.
[0070] Step 1: Acquire 12-echo liver magnetic resonance images, and the imaging parameters are set as follows: the echo time is respectively selected as 0.93, 2.27, 3.61, 4.95, 6.29, 7.63, 8.97, 10.4, 11.8, 13.2, 14.6 and 16 ms, and the repetition time is is 200 ms, the slice thickness is 10 mm, the matrix size is 64×128, and the flip angle is 20 o .
[0071] Step 2: On one of the echo liver magnetic resonance images, take a ROI of an appropriate size (such as 40 pixels) in the black background area, and use the following formula ( ), calculate the standard deviation of the background noise.
[0072]
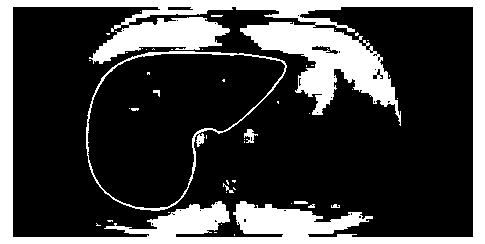
[0073] Step 3. Manually draw the ROI of the whole liver along the edge of the liver image, such as image 3 shown. It should be noted that the method of drawing the region of interest...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com